Siemens SAB-C515A-4R24M, SAB-C515A-4RM, SAB-C515A-L24M, SAB-C515A-LM, SAF-C515A-4R24M Datasheet
...
Microcomputer Components
8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller
C515A
Data Sheet 10.97
C515A Data Sheet
Revision History: Current Version: 10.97
Previous Version: none
Page
(in previous
Version)
Page
(in current
Version)
Subjects (major changes since last revision)
Edition 10.97
Published by Siemens AG,
Bereich Halbleiter, MarketingKommunikation, Balanstraße 73,
81541 München
Siemens AG 1997.
©
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
As far as patents or other rights of third parties are concerned, liability is only assumed for components, not for applications, processes
and circuits implemented within components or assemblies.
The information describes the type of component and shall not be considered as assured characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to change design reserved.
For questions on technology, delivery and prices please contact the Semiconductor Group Offices in Germany or the Siemens Companies
and Representatives worldwide (see address list).
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the types in question please contact
your nearest Siemens Office, Semiconductor Group.
Siemens AG is an approved CECC manufacturer.
Packing
Please use the recycling operators known to you. We can also help you – get in touch with your nearest sales office. By agreement we
will take packing material back, if it is sorted. You must bear the costs of transport.
For packing material that is returned to us unsorted or which we are not obliged to accept, we shall have to invoice you for any costs incurred.
Components used in life-support devices or systems must be expressly authorized for such purpose!
Critical components
written approval of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG.
1 A critical component is a component used in a life-support device or system whose failure can reasonably be expected to cause the
failure of that life-support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness of that device or system.
2 Life support devices or systems are intended (a) to be implanted in the human body, or (b) to support and/or maintain and sustain hu-
man life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the user may be endangered.
1
of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG, may only be used in life-support devices or systems
2
with the express
8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller
Advance Information
Full upward compatibility with SAB 80C515A/83C515A-5
•
•
Up to 24 MHz external operating frequency
– 500 ns instruction cycle at 24 MHz operation
•
32K byte on-chip ROM (with optional ROM protection)
– alternatively up to 64K byte external program memory
•
Up to 64K byte external data memory
•
256 byte on-chip RAM
•
1K byte on-chip RAM (XRAM)
•
Six 8-bit parallel I/O ports
•
One input port for analog/digital input
•
Full duplex serial interface (USART)
– 4 operating modes, fixed or variable baud rates
•
Three 16-bit timer/counters
– Timer 0 / 1 (C501 compatible)
– Timer 2 for 16-bit reload, compare, or capture functions
C515A
(further features are on next page)
Oscillator
Watchdog
Power
Saving
Support Module
Modes
On-Chip Emulation
A / D Converter
Digital
Input
Watchdog
Timer
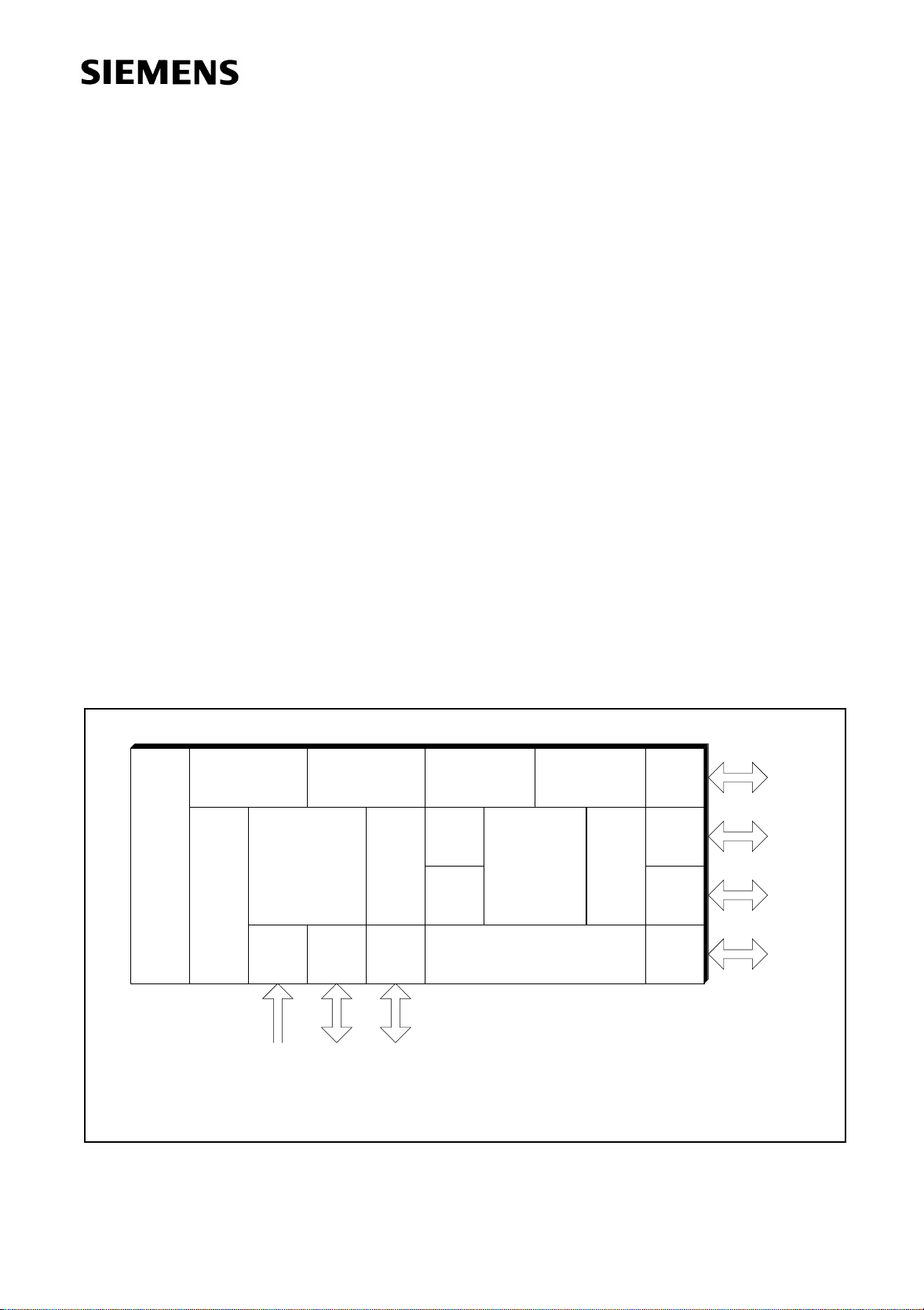
10-Bit
Port 5Port 6
I / O I / OAnalog /
T 2
Port 4
XRAM
1 K x 8
T 0
T 1
256 x 8
CPU
ROM
32 k x 8
RAM
USART
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
I / O
I / O
I / O
I / O
MCA03239
Figure 1
C515A Functional Units
Semiconductor Group 3 1997-10-01
Features (cont’d):
•
10-bit A/D converter
– 8 multiplexed analog inputs
– Built-in self calibration
•
16-bit watchdog timer
•
Power saving modes
– Slow down mode
– Idle mode (can be combined with slow down mode)
– Software power down mode with wake-up capability through INT0
– Hardware power down mode
•
12 interrupt sources (7 external, 5 internal) selectable at 4 priority levels
•
ALE switch-off capability
•
On-chip emulation support logic (Enhanced Hooks Technology
•
P-MQFP-80-1 package
•
Temperature Ranges: SAB-C515A
SAF-C515A
SAH-C515A
SAK-C515
T
= 0 to 70 ° C
A
T
= – 40 to 85 ° C
A
T
= – 40 to 85 ° C
A
T
= – 40 to 110 ° C (max. operating frequency: 18 MHz)
A
TM
C515A
pin
)
The C515A is an upward compatible version of the SAB 80C515A/83C515A-5 8-bit microcontroller
which additionally provides an improved 10-bit A/D converter, ALE switch-off capability, on-chip
emulation support, ROM protection, and enhanced power saving mode capabilities. With a
maximum external clock rate of 24 MHz it achieves a 500 ns instruction cycle time (1
The C515A is mounted in a P-MQFP-80 package.
Ordering Information
Type Ordering Code Package Description
(8-Bit CMOS microcontroller)
SAB-C515A-4RM Q67121-DXXXX P-MQFP-80-1 with mask programmable ROM (18 MHz)
SAF-C515A-4RM Q67121-DXXXX P-MQFP-80-1 with mask programmable ROM (18 MHz)
ext. temp. – 40 ° C to 85 ° C
SAB-C515A-4R24M Q67121-DXXXX P-MQFP-80-1 with mask programmable ROM (24 MHz)
SAF-C515A-4R24M Q67121-DXXXX P-MQFP-80-1 with mask programmable ROM (24 MHz)
ext. temp. – 40 ° C to 85 ° C
SAB-C515A-LM Q67121-C1068 P-MQFP-80-1 for external memory (18 MHz)
SAF-C515A-LM Q67121-C1069 P-MQFP-80-1 for external memory (18 MHz)
ext. temp. – 40 ° C to 85 ° C
SAB-C515A-L24M Q67121-C1070 P-MQFP-80-1 for external memory (24 MHz)
µ
s at 12 MHz).
SAF-C515A-L24M Q67127-C2020 P-MQFP-80-1 for external memory (24 MHz)
ext. temp. – 40 ° C to 85 ° C
Note: Versions for extended temperature ranges – 40 ° C to 110 ° C and – 40 ° C to 125 ° C
(SAH-C515A and SAK-C515A) are available on request. The ordering number of ROM
types (DXXXX extensions) is defined after program release (verification) of the customer.
Semiconductor Group 4 1997-10-01
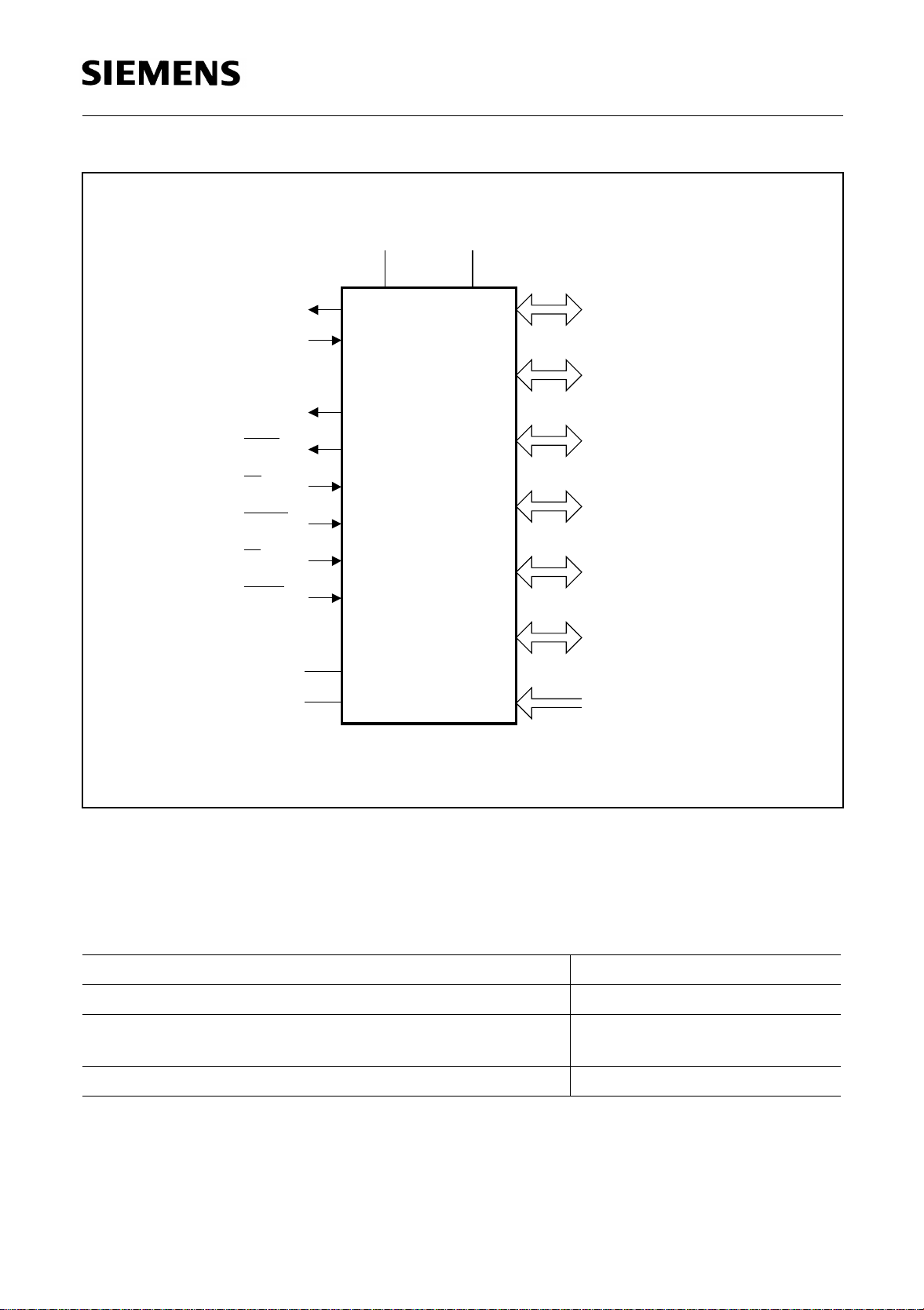
C515A
XTAL1
XTAL2
ALE
PSEN
EA
RESET
PE / SWD
HWPD
V
AREF
V
AGND
V
CC
C515A
V
SS
Port 0
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 1
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 2
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 3
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 4
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 5
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 6
8-Bit Analog /
Digital Input
MCL03240
Figure 2
Logic Symbol
Additional Literature
For further information about the C515A the following literature is available:
Title Ordering Number
C515A 8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller User’s Manual B158-H7051-X-X-7600
C500 Microcontroller Family
B158-H6987-X-X-7600
Architecture and Instruction Set User’s Manual
C500 Microcontroller Family - Pocket Guide B158-H6986-X-X-7600
Semiconductor Group 5 1997-10-01
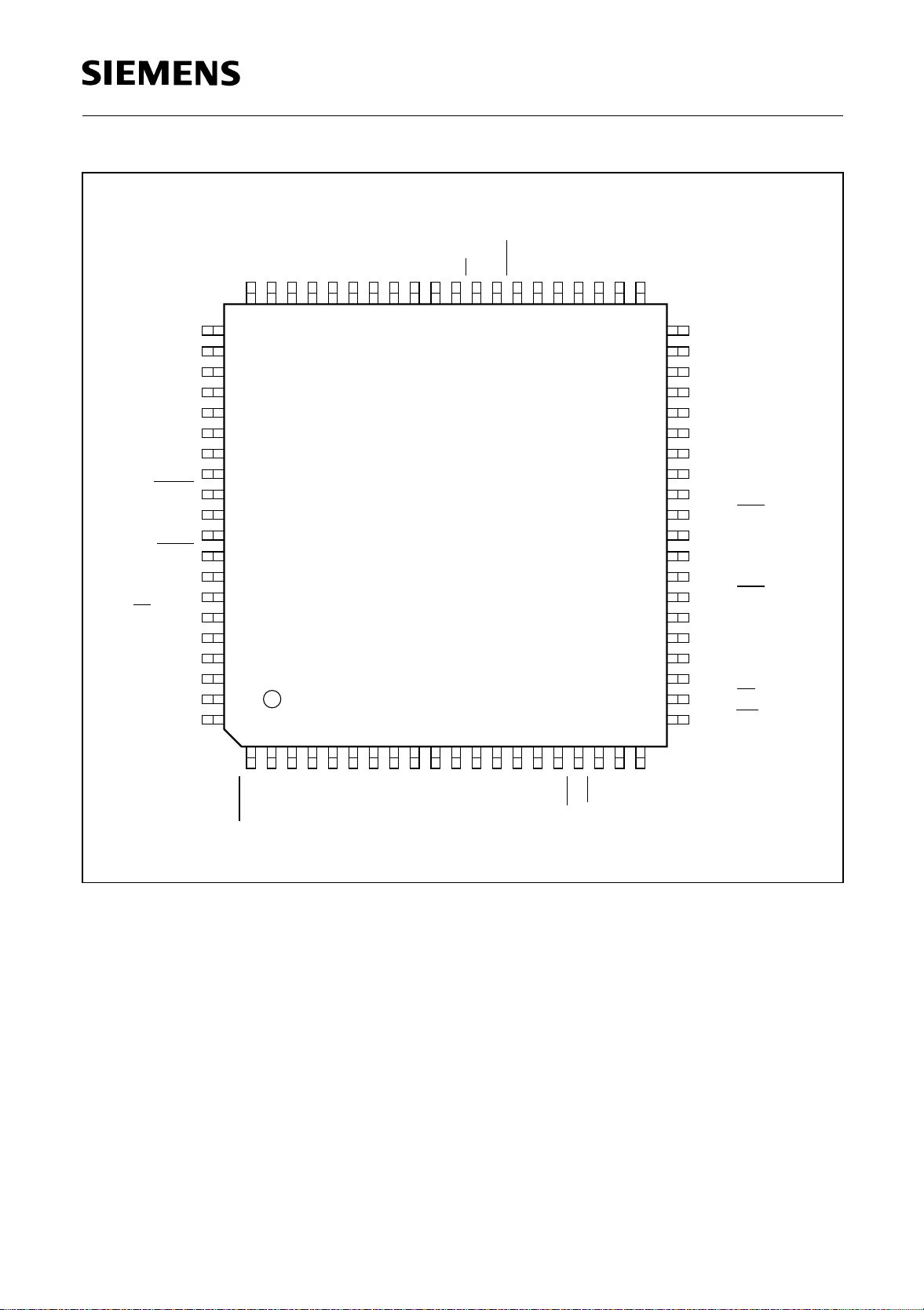
P5.7
P0.7 / AD7
P0.6 / AD6
P0.5 / AD5
P0.4 / AD4
P0.3 / AD3
P0.2 / AD2
P0.0 / AD0
P0.1 / AD1
N.C.
N.C.
EA
ALE
PSEN
N.C.
P2.7 / A15
P2.6 / A14
P2.4 / A12
P2.5 / A13
P2.3 / A11
C515A
P5.6
P5.5
P5.4
P5.3
P5.2
P5.1
P5.0
N.C.
HWPD
N.C.
N.C.
P4.0 / ADST
P4.1
P4.2
PE / SWD
P4.3
P4.4
P4.5
P4.6
P4.7
42434445464748495459 58 5657 55 5253 51
4150
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
60
C515A
80 21
23456789 1311 12 14 15 16 17 18 19
20101
P2.2 / A10
P2.1 / A9
P2.0 / A8
XTAL1
XTAL2
V
SS
V
SS
V
CC
V
CC
P1.0 / INT3 / CC0
P1.1 / INT4 / CC1
P1.2 / INT5 / CC2
P1.3 / INT6 / CC3
P1.4 / INT2
P1.5 / T2EX
P1.6 / CLKOUT
P1.7 / T2
N.C.
P3.7 / RD
P3.6 / WR
N.C.
AREFVAGND
V
RESET
P6.1 / AIN1
P6.2 / AIN2
P6.4 / AIN4
P6.3 / AIN3
P6.0 / AIN0
P6.5 / AIN5
P6.6 / AIN6
P6.7 / AIN7
Figure 3
Pin Configuration P-MQFP-80 Package (top view)
N.C.
N.C.
P3.1 / TxD
P3.0 / RxD
P3.3 / INT1
P3.2 / INT0
P3.5 / T1
P3.4 / T0
MCP03241
Semiconductor Group 6 1997-10-01

Table 1
Pin Definitions and Functions
C515A
Symbol Pin Number
(P-MQFP-80)
P4.0-P4.7 72-74,
76-80
72
PE
/SWD 75 I
I/O*) Function
I/O Port 4
is an 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup resistors. Port 4 pins that have 1’s written to them are
pulled high by the internal pull-up resistors, and in that
state can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 4 pins being
externally pulled low will source current ( I
characteristics) because of the internal pull-up resistors.
P4 also contains the external A/D converter control pin.
The output latch corresponding to a secondary function
must be programmed to a one (1) for that function to
operate. The secondary function is assigned to port 6 as
follows:
P4.0 / ADST
Power Saving Mode
A low level on this pin allows the software to enter the
power down, idle, and slow down mode. In case the low
level is also seen during reset, the watchdog timer
function is off on default.
Use of the software controlled power saving modes is
blocked when this pin is held on high level. A high level
during reset performs an automatic start of the
watchdog timer immediately after reset.
When left unconnected this pin is pulled high by a weak
internal pull-up resistor.
Note: If PE
watchdog is disabled (testmode)!
external A/D converter start pin
Enable
/SWD is low and V
, in the DC
IL
/ Start Watchdog Timer
is low the oscillator
AREF
RESET
1I
RESET
A low level on this pin for the duration of two machine
cycles while the oscillator is running resets the C515A.
A small internal pullup resistor permits power-on reset
VAREF 3 –
VAGND 4 –
P6.0-P6.7 12-5 I
using only a capacitor connected to V
Reference Voltage for the A/D converter
Reference Ground for the A/D converter
Port 6
SS
.
is an 8-bit unidirectional input port to the A/D converter.
Port pins can be used for digital input, if voltage levels
simultaneously meet the specifications for high/low input
voltages and for the eight multiplexed analog inputs.
*) I = Input
O = Output
Semiconductor Group 7 1997-10-01
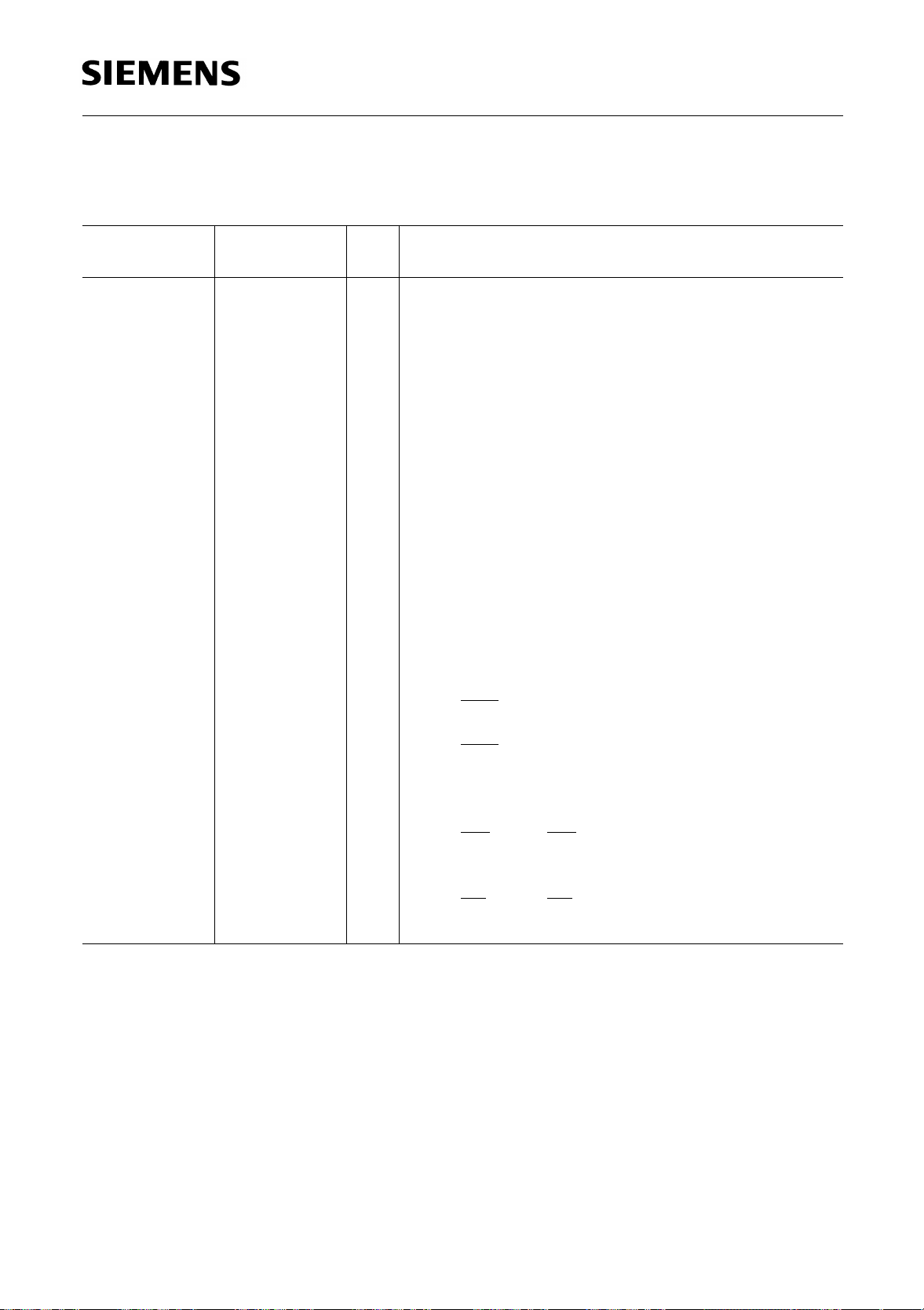
Table 1
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
C515A
Symbol Pin Number
(P-MQFP-80)
P3.0-P3.7 15-22
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
I/O*) Function
I/O Port 3
is an 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup
resistors. Port 3 pins that have 1's written to them are
pulled high by the internal pullup resistors, and in that
state can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 3 pins being
externally pulled low will source current (I IL, in the DC
characteristics) because of the internal pullup resistors.
Port 3 also contains the interrupt, timer, serial port and
external memory strobe pins that are used by various
options. The output latch corresponding to a secondary
function must be programmed to a one (1) for that
function to operate. The secondary functions are
assigned to the pins of port 3, as follows:
P3.0 / RxD Receiver data input (asynch.)
P3.1 / TxD Transmitter data output
P3.2 / INT0 External interrupt 0 input /
P3.3 / INT1 External interrupt 1 input /
P3.4 / T0 Timer 0 counter input
P3.5 / T1 Timer 1 counter input
P3.6 / WR
P3.7 / RD RD control output; enables
or data input/output (synch.)
of serial interface
(asynch.) or clock output
(synch.) of serial interface
timer 0 gate control input
timer 1 gate control input
WR control output; latches
the data byte from port 0 into
the external data memory
the external data memory
*) I = Input
O = Output
Semiconductor Group 8 1997-10-01
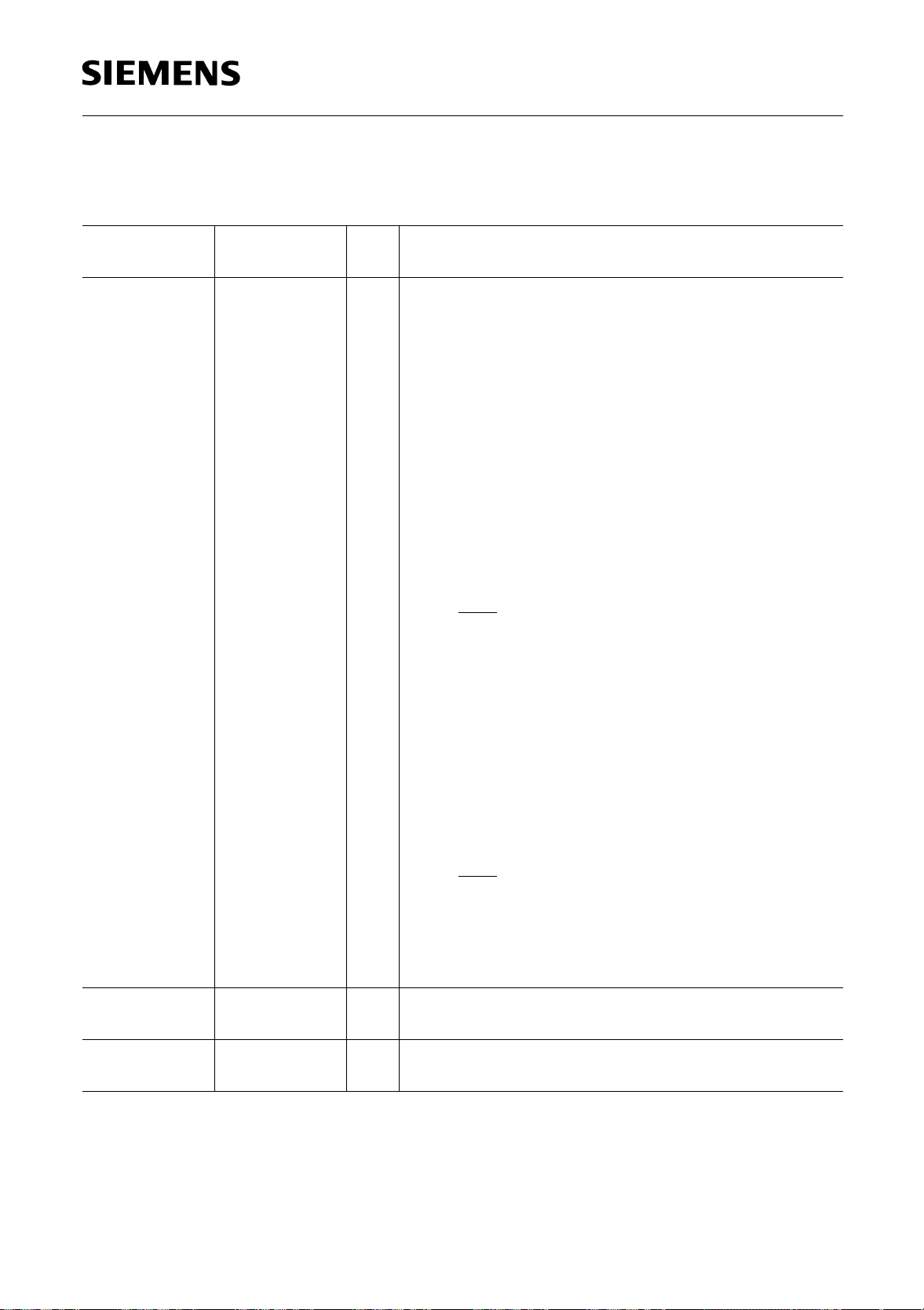
Table 1
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
C515A
Symbol Pin Number
(P-MQFP-80)
P1.0 - P1.7 31-24
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
I/O*) Function
I/O Port 1
is an 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup
resistors. Port 1 pins that have 1's written to them are
pulled high by the internal pullup resistors, and in that
state can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 1 pins being
externally pulled low will source current (I IL, in the DC
characteristics) because of the internal pullup resistors.
The port is used for the low-order address byte during
program verification. Port 1 also contains the interrupt,
timer, clock, capture and compare pins that are used by
various options. The output latch corresponding to a
secondary function must be programmed to a one (1) for
that function to operate (except when used for the
compare functions). The secondary functions are
assigned to the port 1 pins as follows:
P1.0 / INT3 / CC0 Interrupt 3 input /
P1.1 / INT4 / CC1 Interrupt 4 input /
P1.2 / INT5 / CC2 Interrupt 5 input /
P1.3 / INT6 / CC3 Interrupt 6 input /
P1.4 / INT2
P1.5 / T2EX Timer 2 external reload /
P1.6 / CLKOUT System clock output
P1.7 / T2 Counter 2 input
compare 0 output /
capture 0 input
compare 1 output /
capture 1 input
compare 2 output /
capture 2 input
compare 3 output /
capture 3 input
Interrupt 2 input
trigger input
V
CC
32, 33 – Supply Voltage
during normal, idle, and power down mode.
V
SS
34, 35 – Ground (0V)
during normal, idle, and power down operation.
*) I = Input
O = Output
Semiconductor Group 9 1997-10-01

Table 1
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
C515A
Symbol Pin Number
I/O*) Function
(P-MQFP-80)
XTAL2 36 – XTAL2
Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the
internal clock generator circuits. To drive the device
from an external clock source, XTAL2 should be driven,
while XTAL1 is left unconnected. Minimum and
maximum high and low times as well as rise/fall times
specified in the AC characteristics must be observed.
XTAL1 37 – XTAL1
Output of the inverting oscillator amplifier.
P2.0-P2.7 38-45 I/O Port 2
is an 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup
resistors. Port 2 pins that have 1's written to them are
pulled high by the internal pullup resistors, and in that
state can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 2 pins being
externally pulled low will source current (I
characteristics) because of the internal pullup resistors.
Port 2 emits the high-order address byte during fetches
from external program memory and during accesses to
external data memory that use 16-bit addresses
(MOVX @DPTR). In this application it uses strong
internal pullup resistors when issuing 1's. During
accesses to external data memory that use 8-bit
addresses (MOVX @Ri), port 2 issues the contents of
the P2 special function register.
, in the DC
IL
PSEN
47 O The Program Store Enable
output is a control signal that enables the external
program memory to the bus during external fetch
operations. It is activated every six oscillator periods,
except during external data memory accesses. The
signal remains high during internal program execution.
ALE 48 O The Address Latch Enable
output is used for latching the address into external
memory during normal operation. It is activated every
six oscillator periods, except during an external data
memory access. ALE can be switched off when the
program is executed internally.
*) I = Input
O = Output
Semiconductor Group 10 1997-10-01
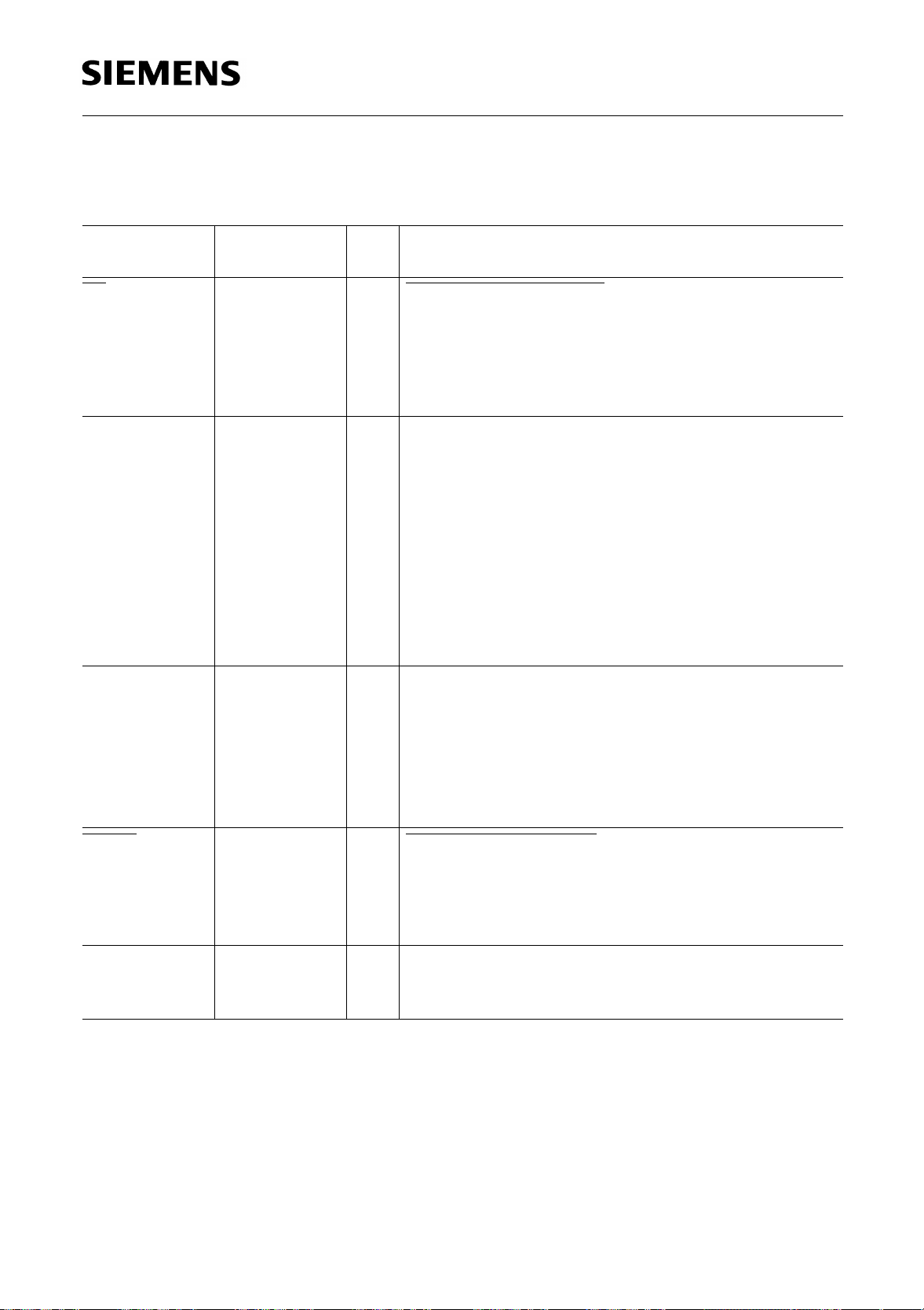
Table 1
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
C515A
Symbol Pin Number
I/O*) Function
(P-MQFP-80)
EA 49 I External Access Enable
When held high, the C515A executes instructions from
the internal ROM (C515A-4R) as long as the PC is less
than 8000H. When held low, the C515A fetches all
instructions from external program memory. For the
C515A-L this pin must be tied low.
P0.0-P0.7 52-59 I/O Port 0
is an 8-bit open-drain bidirectional I/O port. Port 0 pins
that have 1's written to them float, and in that state can
be used as high-impedance inputs.
Port 0 is also the multiplexed low-order address and
data bus during accesses to external program and data
memory. In this application it uses strong internal pullup
resistors when issuing 1's. Port 0 also outputs the code
bytes during program verification in the C515A-4R.
External pullup resistors are required during program
verification.
P5.0-P5.7 67-60 I/O Port 5
is an 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup
resistors. Port 5 pins that have 1's written to them are
pulled high by the internal pullup resistors, and in that
state can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 5 pins being
externally pulled low will source current (I IL, in the DC
characteristics) because of the internal pullup resistors.
HWPD
69 I Hardware Power Down
A low level on this pin for the duration of one machine
cycle while the oscillator is running resets the C515A. A
low level for a longer period will force the C515A into
Hardware Power Down Mode with the pins floating.
N.C. 2, 13, 14, 23,
46, 50, 51, 68,
70, 71
*) I = Input
O = Output
– Not connected
These pins of the P-MQFP-80 package need not be
connected.
Semiconductor Group 11 1997-10-01
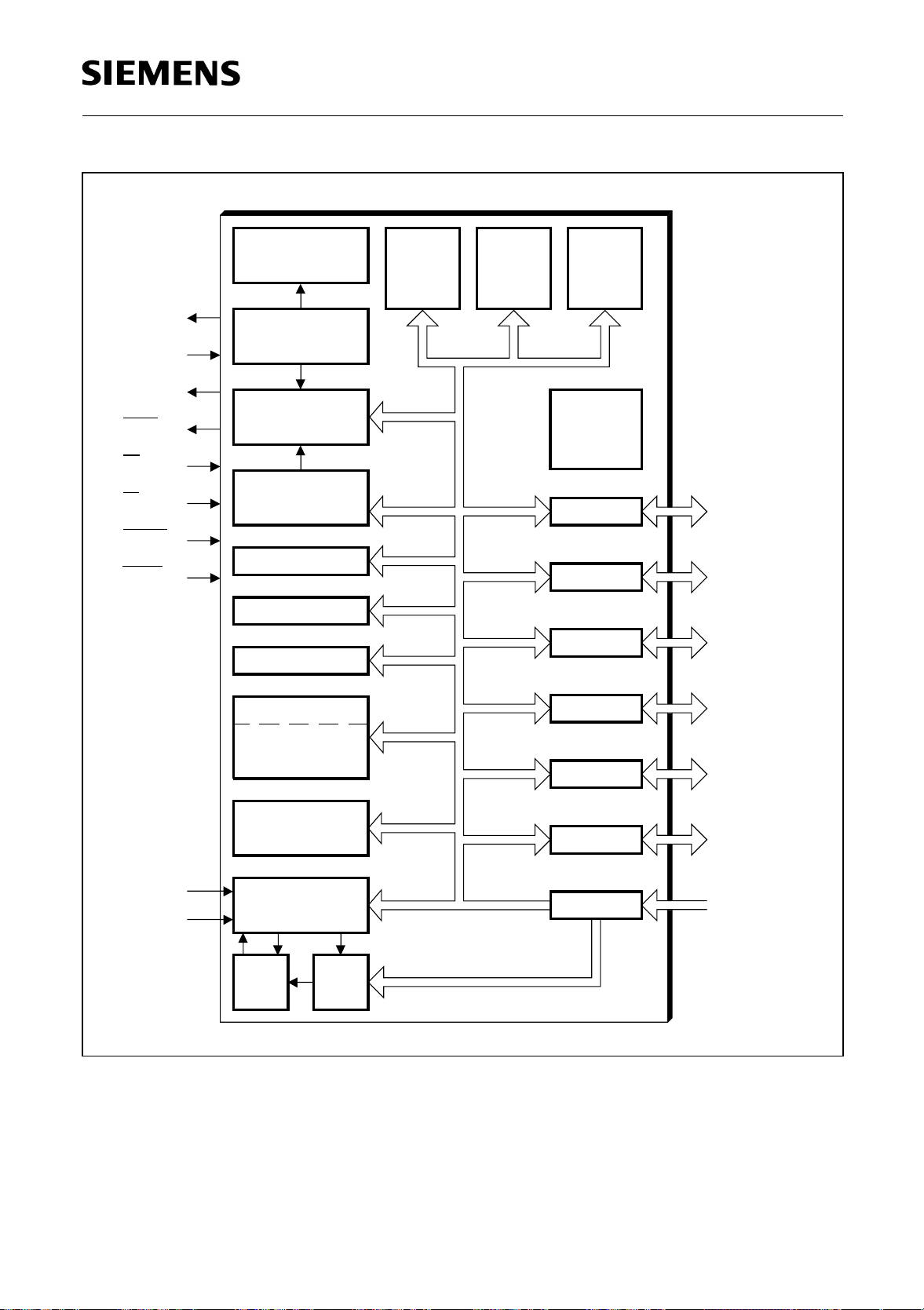
C515A
XTAl1
XTAL2
ALE
PSEN
EA
PE / SWD
RESET
HWPD
Oscillator
Watchdog
OSC & Timing
CPU
Programmable
Watchdog Timer
Timer 0
Timer 1
Timer 2
USART
Baud Rate
Generator
RAM XRAM
256 x 8
1 K x 8 32 K x 8
ROM
Emulation
Support
Logic
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
Port 0
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 1
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 2
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 3
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 4
8-Bit Digit. I / O
V
AREF
V
AGND
Interrupt
Unit
A/D Converter
10-Bit
S&H
Analog
MUX
Port 5
Port 6
C515A
Port 5
8-Bit Digit. I / O
Port 6
8-Bit Analog /
Digital Input
MCB03242
Figure 4
Block Diagram of the C515A
Semiconductor Group 12 1997-10-01

C515A
CPU
The C515A is efficient both as a controller and as an arithmetic processor. It has extensive facilities
for binary and BCD arithmetic and excels in its bit-handling capabilities. Efficient use of program
memory results from an instruction set consisting of 44 % one-byte, 41 % two-byte, and 15%
three-byte instructions. With a 18 MHz crystal, 58% of the instructions are executed in 666 ns
(24 MHz : 500 ns).
Special Function Register PSW (Address D0H) Reset Value : 00H
Bit No. MSB LSB
H
D7
CY AC
H
D6
H
D5
F0
H
D4
RS1 RS0 OV F1 PD0
Bit Function
CY Carry Flag
Used by arithmetic instruction.
AC Auxiliary Carry Flag
Used by instructions which execute BCD operations.
F0 General Purpose Flag
RS1
RS0
Register Bank select control bits
These bits are used to select one of the four register banks.
RS1 RS0 Function
0 0 Bank 0 selected, data address 00H-07
0 1 Bank 1 selected, data address 08H-0F
1 0 Bank 2 selected, data address 10H-17
1 1 Bank 3 selected, data address 18H-1F
H
D3
H
D2
H
D1
H
D0
H
PSW
H
H
H
H
OV Overflow Flag
Used by arithmetic instruction.
F1 General Purpose Flag
P Parity Flag
Set/cleared by hardware after each instruction to indicate an odd/even
number of “one” bits in the accumulator, i.e. even parity.
Semiconductor Group 13 1997-10-01

Memory Organization
The C515A CPU manipulates operands in the following five address spaces:
– up to 64 Kbyte of program memory (32K on-chip program memory for C515A-4R)
– up to 64 Kbyte of external data memory
– 256 bytes of internal data memory
– 1K bytes of internal XRAM data memory
– a 128 byte special function register area
Figure 5 illustrates the memory address spaces of the C515A.
Alternatively
C515A
Ext.
FFFF
H
Ext.
Data
Memory
Internal
XRAM
(1 KByte)
FBFF
H
FFFF
FC00
H
H
Indirect
8000
H
7FFF
H
Ext.
Addr.
Internal
RAM
Data
Memory
Int.
EA = 1)
Ext.
EA = 1)
Internal
RAM
0000
H
0000
H
"Code Space" "Data Space" "Internal Data Space"
Direct
Addr.
Special
Function
Regs.
7F
H
00
H
MCB03243
FF
80
H
H
Figure 5
C515A Memory Map
Semiconductor Group 14 1997-10-01

C515A
Reset and System Clock
The reset input is an active low input at pin RESET. Since the reset is synchronized internally, the
RESET pin must be held low for at least two machine cycles (24 oscillator periods) while the
oscillator is running. A pullup resistor is internally connected to VCC to allow a power-up reset with
an external capacitor only. An automatic reset can be obtained when VCC is applied by connecting
the RESET pin to VSS via a capacitor. Figure 6 shows the possible reset circuitries.
Figure 6
Reset Circuitries
Semiconductor Group 15 1997-10-01

C515A
Figure 7 shows the recommended oscillator circuitries for crystal and external clock operation.
Crystal Oscillator Mode Driving from External Source
C
3.5 - 24
MHz
C
Crystal Mode: C = 20 pF 10 pF
(Incl. Stray Capacitance)
Figure 7
Recommended Oscillator Circuitries
XTAL1
XTAL2
N.C.
External Oscillator
Signal
XTAL1
XTAL2
MCS03245
Semiconductor Group 16 1997-10-01

C515A
Enhanced Hooks Emulation Concept
The Enhanced Hooks Emulation Concept of the C500 microcontroller family is a new, innovative
way to control the execution of C500 MCUs and to gain extensive information on the internal
operation of the controllers. Emulation of on-chip ROM based programs is possible, too.
Each production chip has built-in logic for the support of the Enhanced Hooks Emulation Concept.
Therefore, no costly bond-out chips are necessary for emulation. This also ensure that emulation
and production chips are identical.
1)
The Enhanced Hooks Technology
together with an EH-IC to function similar to a bond-out chip. This simplifies the design and reduces
costs of an ICE-system. ICE-systems using an EH-IC and a compatible C500 are able to emulate
all operating modes of the different versions of the C500 microcontrollers. This includes emulation
of ROM, ROM with code rollover and ROMless modes of operation. It is also able to operate in
single step mode and to read the SFRs after a break.
TM
, which requires embedded logic in the C500 allows the C500
SYSCON
PCON
TCON
opt.
I/O Ports
C500
MCU
RESET
EA
ALE
PSEN
Port 0
Port 2
Port 1Port 3
Target System Interface
RPORT RPORT
ICE-System interface
to emulation hardware
RSYSCON
RPCON
RTCON
Enhanced Hooks
Interface Circuit
2
0
EH-IC
TEA TALE TPSEN
MCS03254
Figure 8
Basic C500 MCU Enhanced Hooks Concept Configuration
Port 0, port 2 and some of the control lines of the C500 based MCU are used by Enhanced Hooks
Emulation Concept to control the operation of the device during emulation and to transfer
informations about the program execution and data transfer between the external emulation
hardware (ICE-system) and the C500 MCU.
1 “Enhanced Hooks Technology” is a trademark and patent of Metalink Corporation licensed to Siemens.
Semiconductor Group 17 1997-10-01
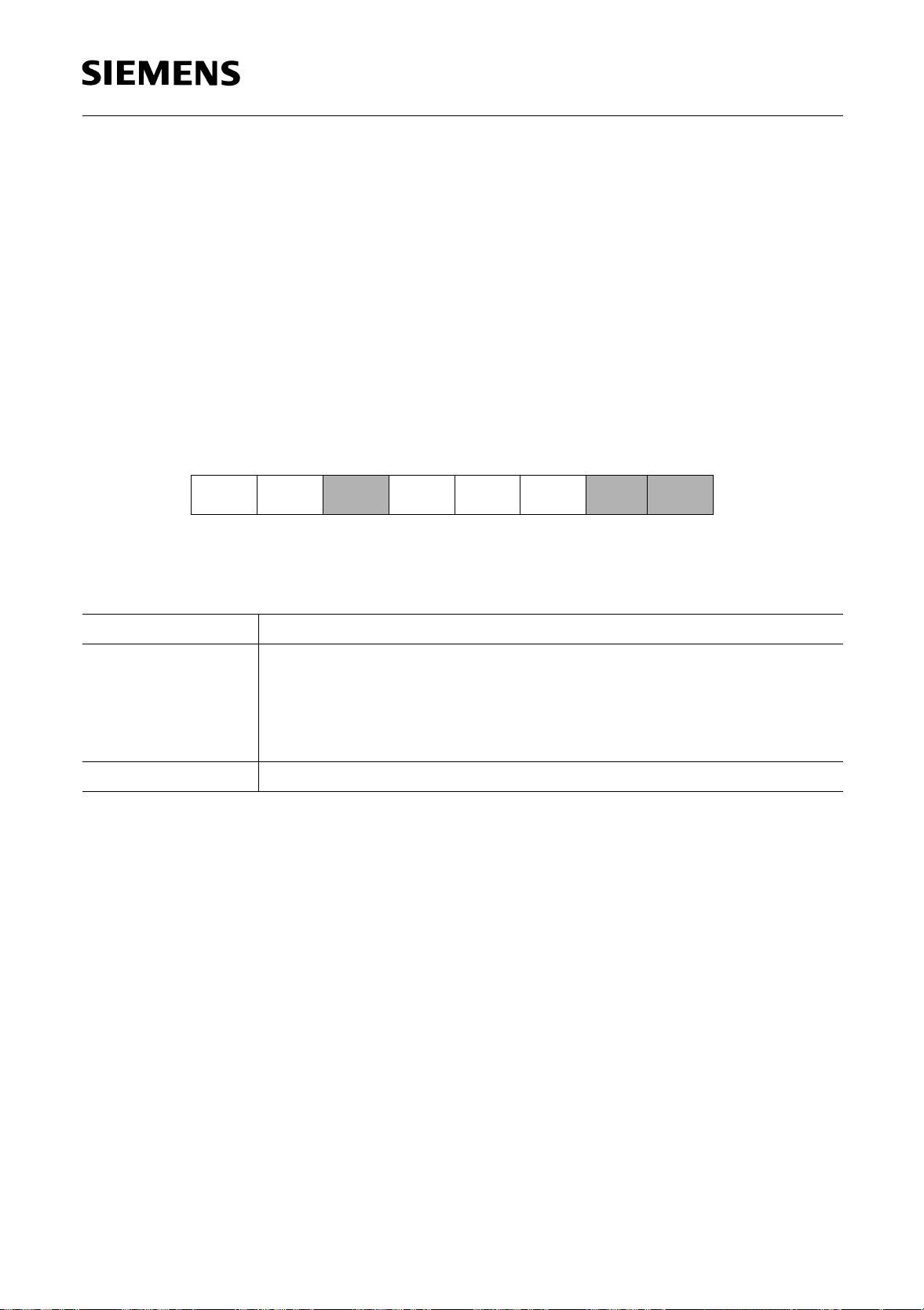
C515A
Special Function Registers
The registers, except the program counter and the four general purpose register banks, reside in
the special function register area. The special function register area consists of two portions: the
standard special function register area and the mapped special function register area. One special
function register of the C515A (PCON1) is located in the mapped special function register area. For
accessing this mapped special function register, bit RMAP in special function register SYSCON
must be set. All other special function registers are located in the standard special function register
area which is accessed when RMAP is cleared (“0“).
Special Function Register SYSCON (Address B1H) Reset Value : XX10XX01
Bit No. MSB LSB
76543210
B1
H
Bit Function
RMAP Special function register map bit
– Reserved bits for future use. Read by CPU returns undefined values.
As long as bit RMAP is set, the mapped special function register area (SFR PCON1) can be
accessed. This bit is not cleared by hardware automatically. Thus, when non-mapped/mapped
registers are to be accessed, the bit RMAP must be cleared/set respectively by software.
––
The functions of the shaded bits are not described in this section.
RMAP = 0: The access to the non-mapped (standard) special function
RMAP = 1: The access to the mapped special function register area (SFR
EALE RMAP –
register area is enabled.
PCON1) is enabled.
–
XMAP1
XMAP0
SYSCON
B
The 49 special function registers (SFRs) in the standard and mapped SFR area include pointers
and registers that provide an interface between the CPU and the other on-chip peripherals. All
SFRs with addresses where address bits 0-2 are 0 (e.g. 80H, 88H, 90H, 98H, …, F8H, FFH) are
bitaddressable. The SFRs of the C515A are listed in table 2 and table 3. In table 2 they are
organized in groups which refer to the functional blocks of the C515A. Table 3 illustrates the
contents of the SFRs in numeric order of their addresses.
Semiconductor Group 18 1997-10-01
 Loading...
Loading...