Page 1

Instruction Bulletin
Replaces 63230-216-207/A2 dated January 2002
63230-216-207/A3
POWERLOGIC® Power Server
PWRSRV710 and PWRSRV750 Models
Setup Guide
Retain for future use.
9/2002
Page 2
NOTICE
Read these instructions carefully and look at the equipment to become
familiar with the device before trying to install, operate, or maintain it. The
following special messages may appear throughout this bulletin or on the
equipment to warn of potential hazards or to call attenti on to information tha t
clarifies or simplifies a procedure.
The addition of either symbol to a “Danger” or “Warning” safety label
indicates that an electrical hazard exists which will result in personal injury if
the instr uctions are not followed.
This is the safety alert symbol. It is used to alert you to potential personal
injury hazards. Obey all safety messages that follow this symbol to avoid
possible injury or death.
DANGER
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, can result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
PLEASE NOTE
CLASS A FCC STATEMENT
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, can result in minor or moderate injury.
CAUTION
CAUTION, used without the safety alert symbol, indicates a potentially
hazardous situation w hi ch , if n ot a vo ide d, can result in property damage.
NOTE: Provides additional information to clarify or simplify a procedure.
Electrical equipmen t should be i nstalled, opera ted, serviced, and maintained
only by qualifie d p ers on nel . Th is document is not in ten ded as an instructio n
manual for untrained person s. No resp onsibility is assume d by Square D for
any consequences arising out of the use of this manual.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device , pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limi ts are
designated to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and u sed in acco rdance with the instruct ion manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communic ations. Operation of this equipment in
a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the
user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Page 3

63230-216-207/A3 Contents
9/2002
CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1—INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
CHAPTER 2—SAFETY PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
CHAPTER 3—INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
CHAPTER 4—CONNECTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Connections Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Control Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Fusing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
RS-232 Serial Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
COM 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
COM 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
RS-485 Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Biasing and Termination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Connecting 4-Wire Devices as 2-Wire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Communications Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
CHAPTER 5—SETUP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Summary of Setup Steps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Configuring the Power Server Communication Connection . . . . . . . . . . .17
Using a Null Modem Serial Cable to Configure the Power Server . . 17
Connecting to the PowerServer with NetMeeting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Starting NetMeeting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Configuring the PowerServer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Setting the Date/Time and Time Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 5
Changing the Mode from Run to Setup Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Configuring Your POWERLOGIC System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Changing the Mode from Setup to Run Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
APPENDIX A—SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
APPENDIX B—CHANGING YOUR PASSWORD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
APPENDIX C—USING A CROSSOVER CABLE TO CONFIGURE THE
POWER SERVER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
APPENDIX D—INTEGRATING THE POWER SERVER INTO SMS . . . . 39
APPENDIX E—UPLOADING AND DELETING FILES ON THE
POWER SERVER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
About the Software Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Uploading Files to the Power Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Deleting Files on the Power Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 5
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
i
Page 4

Contents 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
APPENDIX F—CONNECTING THIRD PARTY DEVICES TO THE
POWER SERVER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
APPENDIX G—POWERLOGIC SYSTEM DISPLAY (SD700)
INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Product Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Installation and Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Connecting to the Power Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Calibrating the Touch Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Care and Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
APPENDIX H—DATABASE BACKUP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Backing Up the Database on the Power Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Checking the Database Backup Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Backing Up the Power Server Database onto a Separate PC . . . . . . . . .59
Restoring the Database on the Power Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
INDEX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
ii
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 5

63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 1—Introduction
9/2002 Overview
CHAPTER 1—INTRODUCTION
OVERVIEW The Power Server is a self-contained device that can be used to transfer
power system informati on through a web browser an d an Ethernet local area
network (LAN) or a wide area network (WAN). It is designed specifically for
industrial and commercial applications, making it possible to view system
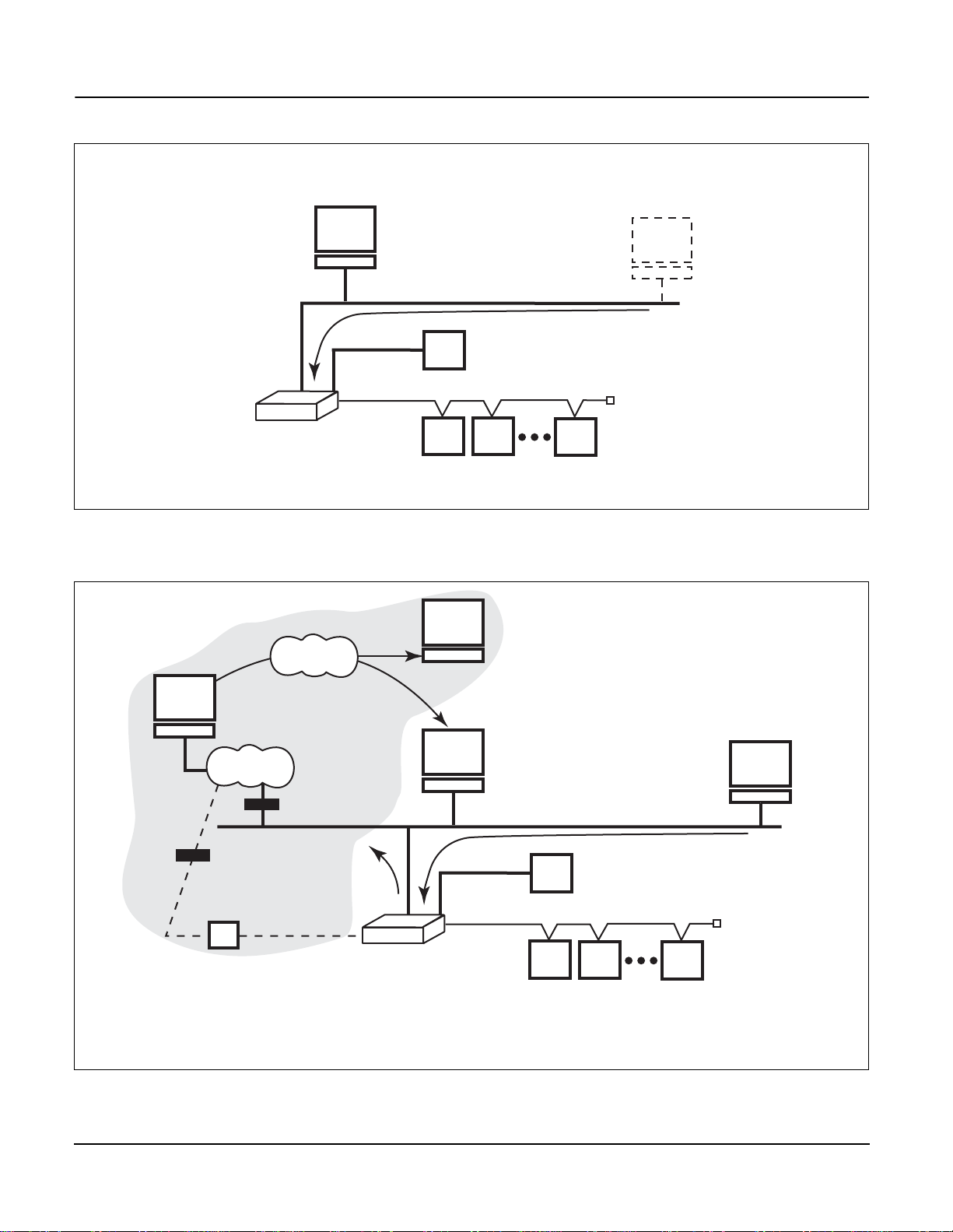
information from a standard web browser. Figure 1–2 on page 2 illustrates
this application. An optional touc h screen displ ay (Square D part n o. SD700)
is also available for viewing the Power Server locally.
Using an embedded POW ERLOGIC System Setup applicatio n, the Power
Server also provides setup capabilities for system components. The
Power Server can be used to create communications connections and
configure device settings for devices connected to a serial daisy chain, as
well as other Modbus/Jbus devices located on the Ethernet network.
Two models are available. PWRSRV710 is the basic model. The other
model, the PWRSRV750, has the s tan dard f eatures of the PWRSRV710 as
well as enhanced capabilities. These enhanced capabilities include
graphical diagram views, active alarm and alarm log views, and historical
data and waveform report views.
When integrated into a system using System Manager™ Software (SMS),
the Power Server can also serve as an Ethernet gateway for the local
system. As illustrated in Figure 1–3 on page 2, the Power Server provides
Ethernet routing from the SMS ap plica tion to the de vices on the seri al daisy
chain.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
30703000
Figure 1–1: Power Server
1
Page 6
Chapter 1—Introduction 63230-216-207/A3
Overview 9/2002
Initial setup
via
NetMeeting
Web browser
Device setup for the
POWERLOGIC System
Optional
touch screen
Mixed-mode daisy chain
Power Server used as a
component of the
POWERLOGIC System
30703059
Figure 1–2: The Power Server used as a standalone system monitoring device
POWERLOGIC Enterprise System
Internet
View reports via
Internet browser
Web browser
Optional
touch screen
Mixed-mode daisy chain
Firewall
POWERLOGIC
Enterprise System
Internet
via Ethernet
via
Modem
Firewall
PUSH application
sending data to
enterprise
Power Server used as
a gateway
PC with
System Manager
Software (SMS)
30703054
NOTE: The shaded area depicts a POWERLOGIC Enterprise System. Contact
POWERLOGIC Engineerin g Serv ic es for i nfor ma tion on this type of applicat ion .
Figure 1–3: The Power Server used as a gateway device with SMS and a web server
2
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 7
63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 2—Safety Precautions
9/2002
CHAPTER 2—SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
DANGER
HAZARD OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, BURN, OR EXPLOSION
• Only qual ified workers should insta ll th is equipment. Such work shoul d
be performed only after reading this entire set of instructions.
• NEVER work alone.
• Turn off al l powe r suppl ying t his equ ipme nt before worki ng on or inside .
• Always use a properly rated voltage sensing device to confirm that all
power is off.
• Before performing visual inspections, tests, or maintenance on this
equipment, disconnect all sources of electric power. Assume that all
circuits are live until they have been completely de-energized, tested,
and tagged. Pay particula r attenti on to t he desi gn of the power system .
Consider all sources of power, including the possibility of backfeeding.
• Beware of potential hazards, wear personal protective equipment,
carefully inspect the work area for tools and objec ts that may have been
left inside the equipment.
• Use caution while removing or installing panels so that they do not
extend into the energized bus; avoid handling the panels, which could
cause personal injury.
• The successful operation of this equipment depends upon proper
handling, installation, and operation. Neglecting fundamental
installation requ irements may l ead to perso nal injury as well as dam age
to electrical equipment or other property.
• Before performing Dielectric (Hi-Pot) or Megger testing on any
equipment in which the Power Server is installed, disconnect all input
and output wires to it. High voltage testing may damage electronic
components contained in the Power Server.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious
injury.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
3
Page 8

Chapter 2—Safety Precautions 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
4
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 9
63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 3—Installation
9/2002 Dimensions
CHAPTER 3—INSTALLATION
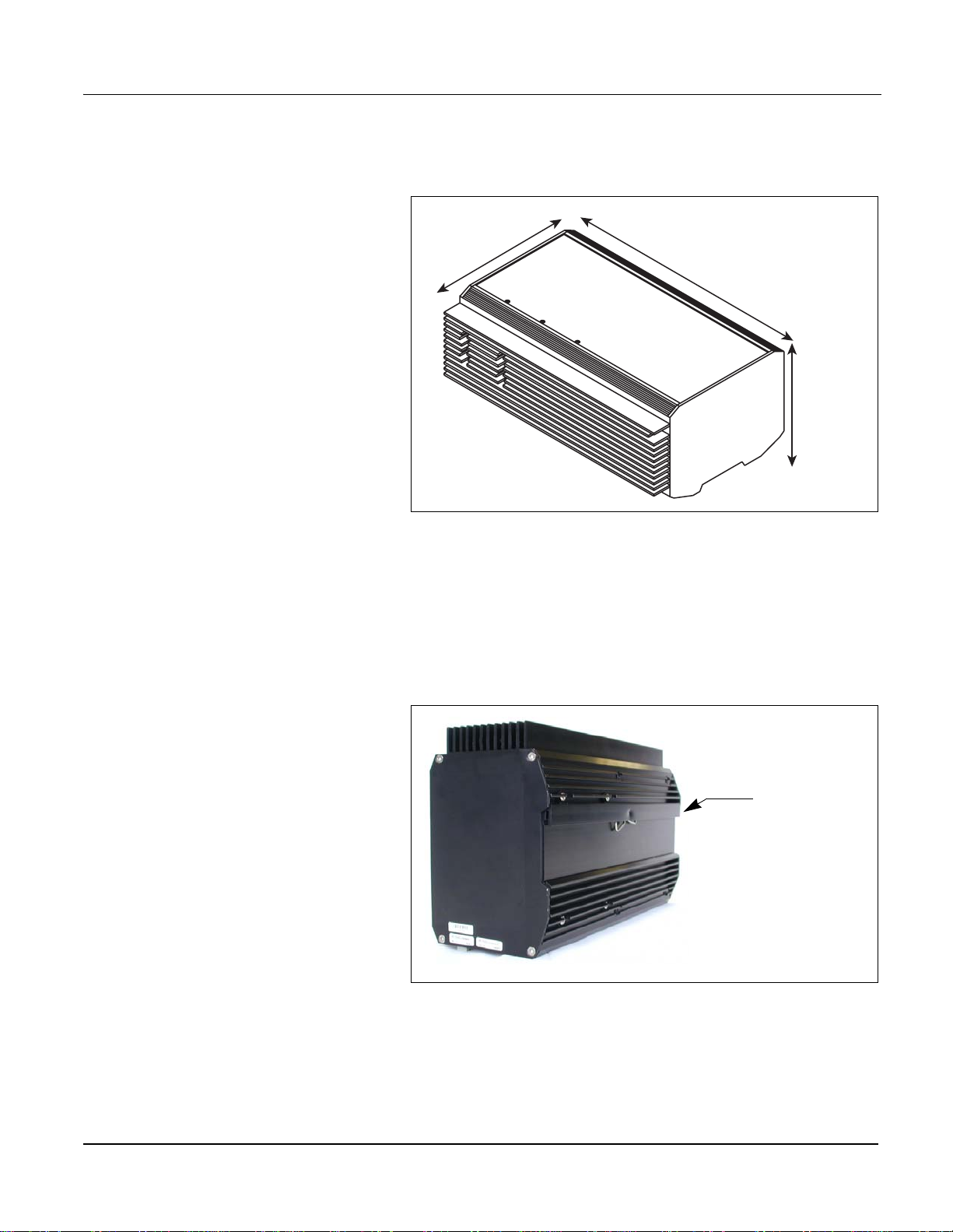
DIMENSIONS
5.63 in
143 mm
8.98 in
228 mm
3.62 in
92 mm
Figure 3–1: Power Server dimensi onal drawing
MOUNTING The Power Server is designed to be mounted directly on a 1.38 in (35 mm)
DIN rail. The unit has a snap-on DIN rail connector on the back (see
Figure 3–2). No tools are required. Mount the Power Server in a clean, dry,
well ventilated are a. Allow 15.75 in (400 m m) on the DIN rail fo r mounting the
Power Server and power supply. Also, allow 3 in (76 mm) clearance above
the Power Server for heat ventilation.
30703001
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Rear view DIN rail
connector location
30703002
Figure 3–2: Power Server rear view showing DIN rail connection
5
Page 10

Chapter 3—Installation 63230-216-207/A3
Mounting 9/2002
Mount the Power Server and Power Supply only in a horizontal position as
shown in Figure 3–3.
Figure 3–3: Proper orientation of Power Server and power supply
30703003
DANGER
HAZARD OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, BURN, OR EXPLOSION
• Turn of f all pow er supp lying thi s equip ment and the equip ment in which
it is installed before working on this equipment.
• Always use a properly rated voltage sensing device to confirm that
power is off.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious
injury.
To mount the Power Server on a DIN rail, follow these steps:
1. Turn off power to the Po wer Server and any equip ment i nto whic h it is to
be installed and verify that power is off.
2. Ensure that the DIN rail is attached horizontally to a surface with a
minimum thickness of 0.078 in (2 mm) for stability.
3. Place the Power Server o n the DIN rail with the upper slot first. Then push
against the lower edge to snap it on the rail.
6
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 11
63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 3—Installation
9/2002 Mounting
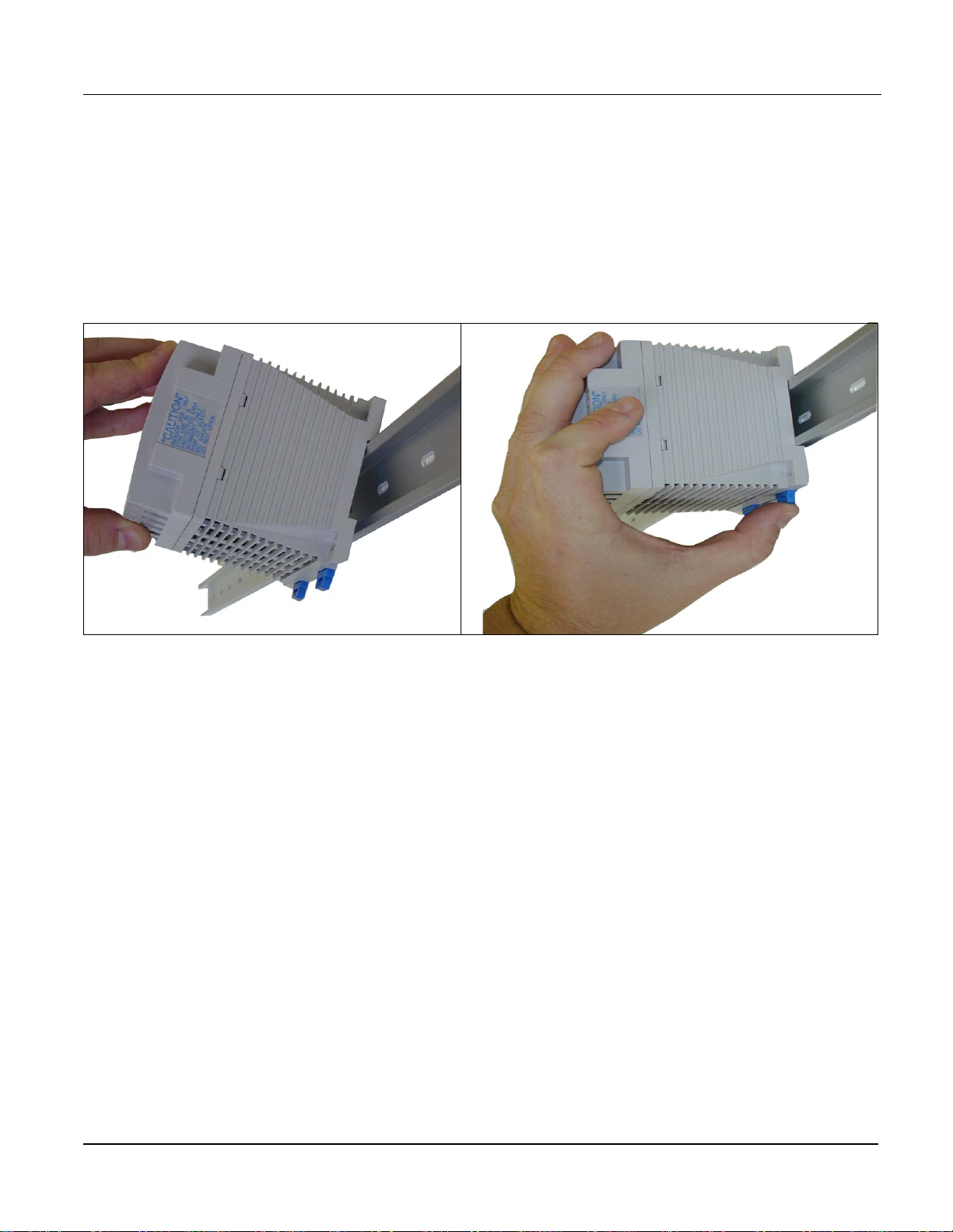
To mount the Power Supply (Square D part no. PS080), refer to Figure 3–4
and follow these steps:
1. Align the mounting groove on the power supply with the DIN rail.
2. Press the blue button to pull back the tabs.
3. Snap the power supply onto the DIN rail and release the blue button to
secure the unit onto the DIN rail.
NOTE: Refer to Appendix A—Specifications on page 29 for PS080
specifications.
30703005
Figure 3–4: Power Supply (PS080) mounting
30703004
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
7
Page 12

Chapter 3—Installation 63230-216-207/A3
Mounting 9/2002
8
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 13

63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 4—Connections
9/2002 Connections Summary
CHAPTER 4—CONNECTIONS
CONNECTIONS SUMMARY The Power Server connections are described in this chapter. Table 4–1
briefly descr ibes each conn ection.
Table 4–1: Connections description
Connection Description
UTP Port
Control Power Three-pin connector for 24 Vdc connection.
COM 1 RS-232 RS-232 serial port for configuring network settings using a PC.
COM 2 RS-232 Touchscreen serial cable port.
COM 3 RS-485
COM 4 RS-485
VGA output Connect to touchscreen.
Ethernet connection. Standard RJ-45 port for connection of
unshielded twisted-pair (10/100 BaseT) Ethernet cable. Category
5 recommended.
RS-485 comm ports for connecting POWERLOGIC or Modbus/
JBUS devices to the Power Server.
COM 1
RS-232 serial port
Setup connection
RS-232 RS-232
COM 2
RS-232 Touchs creen serial
connection
Figure 4–1: Power Server conn ect ions
COM 3
RS-485 port
UTP Port
RS-485RS-485
COM 4
RS-485 port
VGA output to
Touchscreen
monitor
Control Power
30703006
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
9
Page 14

Chapter 4—Connections 63230-216-207/A3
Control Power 9/2002
CONTROL POWER The Power Server accepts 24 Vdc control power with maximum power
consumption of 28 watts. A 50-watt power supply is recommended for this
application (order Square D part no. PS080).
NOTE: Check for proper polarity before applying power to the unit.
Fusing We recommend using one 2 A fast-blow fuse as shown in Figure4–2 and
Figure 4–3 on page 11.
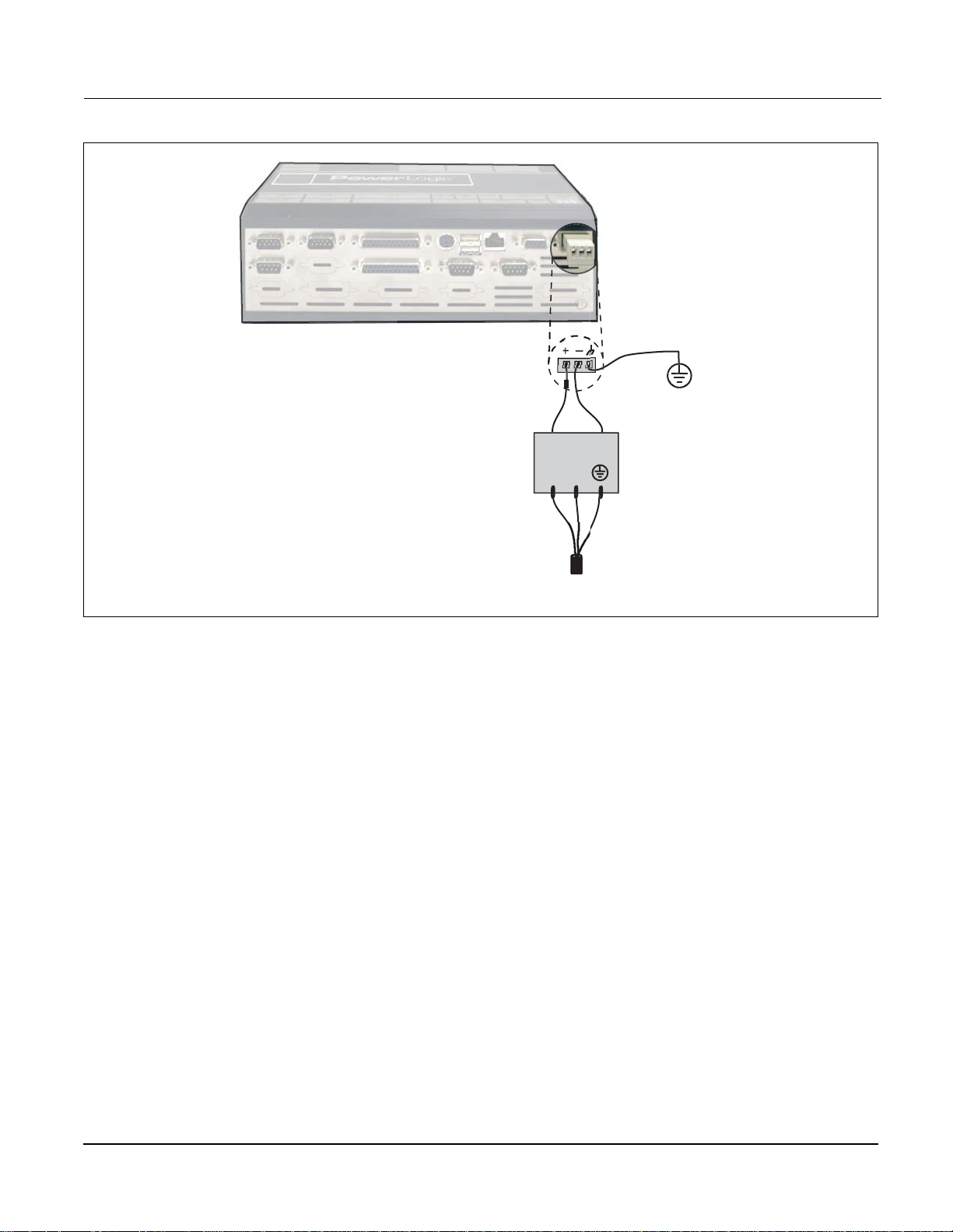
Grounding The Power Server is connected to ground via the co ntrol power ground
connection. Figure 4–2 depicts the recommended groundin g method for the
Power Server when used with po w er sup pl y PS 080 . If gro und ing th e Po wer
Server to local equipment, refer to Figure 4–3 on page 11.
NOTE: The control power source must be properly grounded.
Power Server
+
–
2 A Fast-Blow Fuse
recommended
24 Vdc
–
Power Supply
(PS080)
+
LN
100–240 Vac
Source
Figure 4–2: Power Server grounding to power supply PS080
30703007
10
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 15
63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 4—Connections
9/2002 Control Power
Power Server
+
–
2 A Fast-Blow Fuse
recommended
To local
equipment ground
24 Vdc
–
Power Supply
(PS080)
+
LN
100–240 Vac
Source
Figure 4–3: Power Server grounding to local equipme nt
30703010
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
11
Page 16

Chapter 4—Connections 63230-216-207/A3
RS-232 Serial Ports 9/2002
RS-232 SERIAL PORTS The Power Server has two RS-232 serial communications ports.
30703006
COM 1
Figure 4–4: COM 1 and COM 2 ports
COM 1 COM 1 is the port used for co nfiguring the Powe r Server. When you attach a
laptop or PC to this port, you can follow the instructions in this bulletin to
configure the network settings of the PowerServer. See “Configuring the
Power Server Communication Connection” on page 17 for complete
instructions.
COM 2
COM 2 COM 2 is the serial port used if you are using the optional touch screen
display (SD700).
12
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 17
63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 4—Connections
9/2002 RS-485 Ports
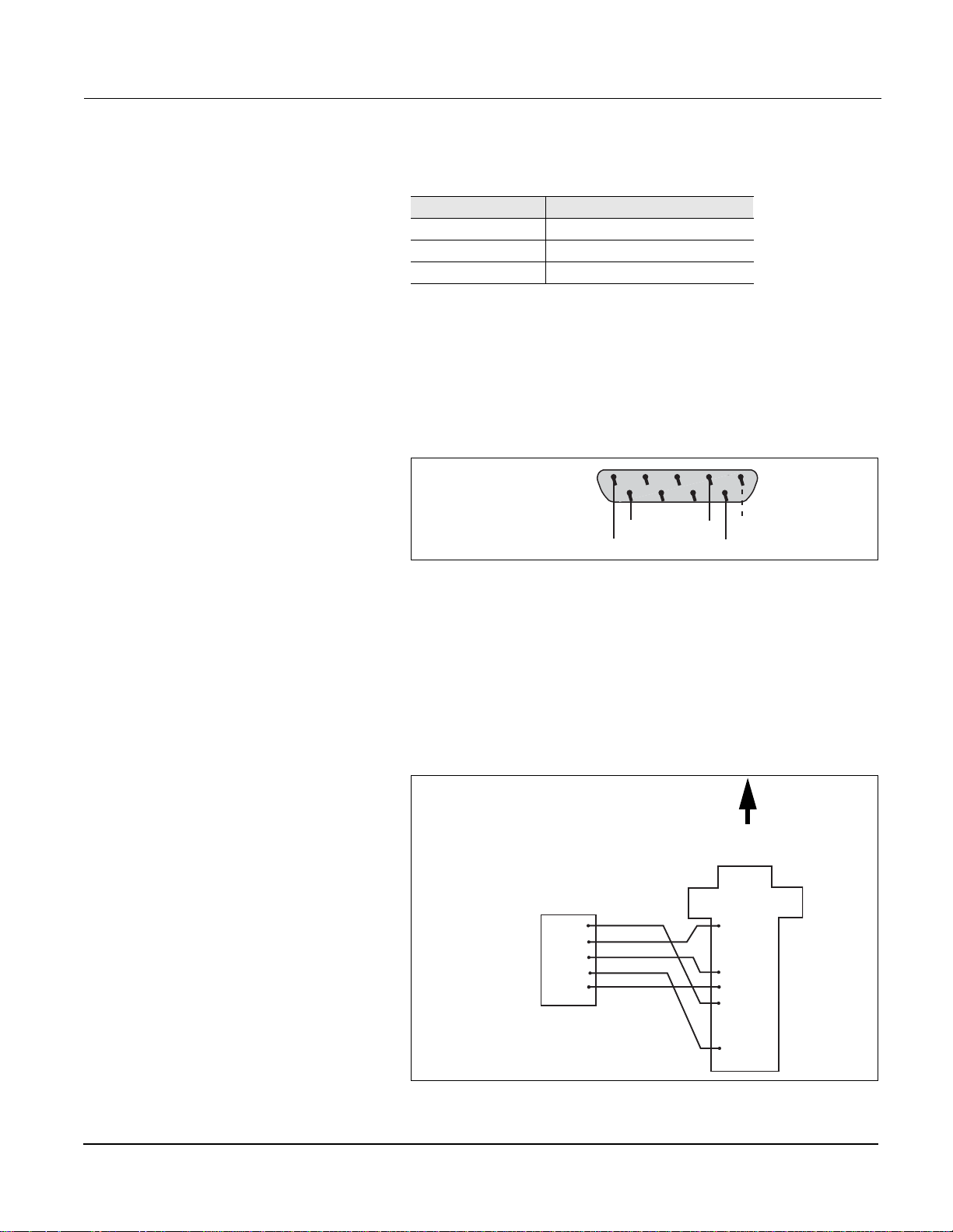
RS-485 PORTS Table 4–2 shows the default values for each of the RS-485 ports.
Table 4–2: Default Values for RS-485 Ports
Value Default Setting COM 3 and COM 4
Type 4-wire
Baud Rate Speed 19200
Parity Even
NOTE: On a 4-wire mixed mode (POWERLOGIC and Modbus) daisychain,
device address 1 c annot be a POW ERLOGIC or SY/MAX d evice and de vice
address 16 cannot be a Modbus device.
Each RS-485 port is a male DB-9 connector with the pin-out arrangement
shown in Figure 4–5.
2345
Male DB-9 of
Power Server
1
67 8
9
SHIELD
Tx+
Tx–
Rx+
Rx–
Figure 4–5: Male DB-9 connector (master port)
Two D B9-t o-te r mi nal bl ock ad ap ters (fem al e) [Sq ua re D part no. DB9F2TB]
are included with the Power Serv er . To connect the dais y chain of d evices to
the RS-485 port, att ach an adapt er to a Belden 8 723 or equiva lent cable a nd
plug the adapter into the COM 3 or COM 4 port on the Power Server. Wire
the cable and adapter as shown in Figure4–6.
NOTE: Because of pin out configurations, it is necessary to make these
connections as described. Square D cable CAB-107 is not compatible with
this application.
DB9F2TB to
Power Server
1 Tx –
2
3
4 Rx +
5 Shield
6 Tx +
7
8
9 Rx –
(IN+)
(IN–)
(OUT+)
(OUT–)
(Shld)
4-Wire
typical standard
POWERLOGIC
slave device
Rx +
Rx –
Tx +
Tx –
Shield
Green
White
Red
Black
30703009
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Figure 4–6: Typical POWERLOGIC standard device connection to
Power Server
13
Page 18
Chapter 4—Connections 63230-216-207/A3
Connecting 4-Wire Devices as 2-Wire 9/2002
Biasing and Termination Each RS-485 port has built-in communications signal biasing and
termination circuitry. Thus, a multipoint communications adapter is not
needed. However, an end-of-line terminator (Square D part no. MCT-485 o r
MCTAS-485) is required on the last device of each daisy chain. Refer to the
instruction bulletin for the last device on the daisy chain.
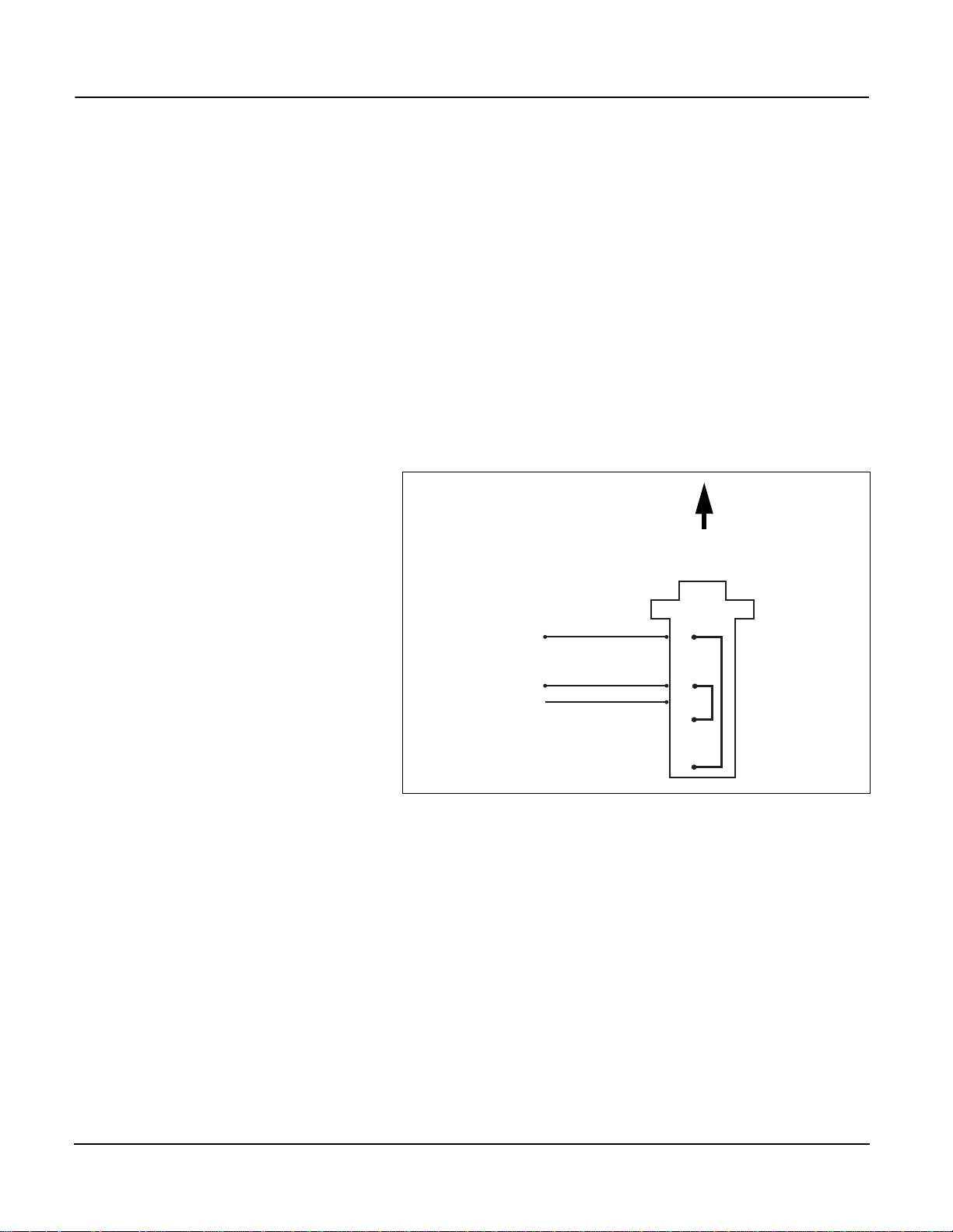
CONNECTING 4-WIRE DEVICES
AS 2-WIRE
Two DB 9-to-terminal block adapters (female) [Square D pa rt no . D B9F 2TB]
are included with the Power Server. Use an adapter to connect a 4-wire
device as 2-wire to the Power Server . Re fer to Figu re 4–7 and follow these
steps:
1. On the DB9F2TB adapter, jumper the Rx+ and Tx+ terminals together,
and jumper the Rx– and Tx– terminals together.
2. Connect the Rx+/Tx+ terminals to the L+ line.
3. Connect the Rx–/Tx– terminals to the L– line.
4. Plug the DB9F2TB adapter into the RS-485 port on the Power Server.
DB9F2TB to
Power Server
Typical 2-wire
POWERLOGIC device
L –
L +
Shield
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Tx –
Rx +
Shield
Tx +
Rx –
30703011
14
Figure 4–7: T ypic al 2-wire POWE RLOGIC dev ice conne ction to Power
Server
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 19
63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 4—Connections
9/2002 Communications Wiring
COMMUNICATIONS WIRING The maximum number of devices supported on a single daisy chain is
determined based on bau d rate, th e leng th of the dais y chai n, and the typ es
of RS-485 devices (2-wire/4-wire) on the daisy chain. The RS-485 interface
supports daisy chains as specified in Table 4–3 and Table 4–4.
Table 4–3: Daisy Chain Maximum Distances 4-Wire
Baud Rate
1200 10,000 ft (3,048 m) 10,000 ft (3,048 m)
2400 10,000 ft (3,048 m) 5,000 ft (1,524 m)
4800 10,000 ft (3,048 m) 5,000 ft (1,524 m)
9600 10,000 ft (3,048 m) 4,000 ft (1,219 m)
19200 5,000 ft (1,524 m) 2,500 ft (762 m)
38400 4,000 ft (1,219 m) 1,500 ft (457 m)
1–16 Devices 17–32 Devices
Maximum Distances*
* Due to the volume of RS-485 devices in the field, this table is only to be used as a guide and
was tabulated based on POWERLOGIC 4-wire devices and POWERLOGIC 4-wire devices
that support 2-wire connections.
Table 4–4: Daisy Chain Maximum Distances 2-Wire
Baud Rate
1200 10,000 ft (3,048 m) 10,000 ft (3,048 m)
2400 10,000 ft (3,048 m) 5,000 ft (1,524 m)
4800 9,000 ft (2,743
9600 6,000 ft (1,829 m) 4,000 ft (1,219 m)
19200 3,000 ft (915 m) 2,500 ft (762 m)
38400 2,000 ft (610 m) 1,500 ft (457 m)
1–8 Devices 9–16 Devices
Maximum Distances*
m) 5,000 ft (1,524 m)
* Due to the volume of RS-485 devices in the field, this table is only to be used as a guide and
was tabulated based on POWERLOGIC 4-wire devices and POWERLOGIC 4-wire devices
that support 2-wire connections.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
15
Page 20

Chapter 4—Connections 63230-216-207/A3
Communications Wiring 9/2002
16
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 21

63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 5—Setup
9/2002 Summary of Setup Steps
CHAPTER 5—SETUP
SUMMARY OF SETUP STEPS This chapter desc ribes the st eps fo r setting up the Powe r Serve r. To do this ,
you perform these main tasks:
1. Configure the Power Server c ommunication connecti on using your laptop
or PC.
2. Configure the PowerLogic System application using NetMeeting.
CONFIGURING THE POWER SERVER COMMUNICATION CONNECTION
Using a Null Modem Serial Cable to Configure
the Power Server
To set up the Power Server communication connection, you will need to
obtain a unique static IP addre ss, subnet mask, and router IP address from
your network administrator.
Two methods of configuration are possible:
• Use a null modem serial cable and HyperTerminal. See Using a Null
Modem Serial Cable to Configure the Power Server in the section that
follows. This method is recommended.
• Use an Ethernet cross-over cable and NetMeeting. This method is
described in Appendix C—Usin g a Crossove r Cable to Configure the
Power Server on page 33.
1. Connect and apply power to the Power Server. Allow ap prox im ate ly fiv e
minutes for the Power Server to complete the boot process.
2. Connect the null modem cabl e fr om the s erial p ort on your PC to CO M 1
of the Power Server.
Connect to COM1
COM 1
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
30703006
Null modem cable
(Square D part no. EGWNMC)
Figure 5–1: Null modem connection for Power Server configuration
3. From your PC, open the HyperTerminal accessory. From the Windows
Explorer taskbar, click Start > Programs > Accessories >
Communications > HyperTerminal.
NOTE: This path is typical for W indows 2000 and Windows XP. The path
may differ for other platforms.
30703012
17
Page 22

Chapter 5—Setup 63230-216-207/A3
Configuring the Power Serve r Com mu nic a t ion Connection 9/2002
4. Enter a name for your setup connection and select OK.
5. Define your connect ion . From the dropdown m enu , s ele ct the C OM p ort
on the PC that you are using to connect to the Power Server.
6. Click OK.
The COM port Properties dialog displays.
30703013
7. Set the serial port settings as shown above and click OK when finished.
The HyperTerminal entry screen displays.
Enter: Pwr_Srv
8. At the HyperTerminal login prompt, enter the
User Name: PowerServerAdmin
Leave the Domain name blank.
For Password (case-sensitive), enter: Pwr_Srv
18
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 23

63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 5—Setup
9/2002 Configuring the Power Server Communication Connection
9. At the C:\ > prompt, enter: nwsetup
The PowerLogic Network Setup Application displays in HyperTerminal.
30703014
NOTE: Even if the Power Server will not be used in a networked
environment, you must run the Network Setup application at le ast once
and then type 5 to quit.
10.Set all of the network setup options as described in Table 1.
NOTE: To change any of the options, enter the option number at the
Enter Option prompt and press Enter.
11. Follow the onscreen instructions to change the value.
Table 1: Power Server Setup—HyperTerminal Options
Option Description
The computer name defaults to the MAC Address. We
recommend that you leave the default computer name. If
Computer Name
IP Address 1
Subnet Mask 1
IP Address 2
Subnet Mask 2
(optional)
Router Address
MAC Address Unique media access control number (cannot be changed).
you must change the name, it must be a unique alphanumeric name, limited to 15 characters, no spaces or
special characters.
Use IP Address 1 as the primary address to access all the
capabilities of the Power Server.
Subnet Mask 1 is assigned to IP Address 1.
IP Address 2 and Subnet Mask 2 are optional. They should
only be used if slave Modbus/Jbus and PowerLogic devices
need to have the same address on both COM 3 and COM 4.
Address of your company’s Ethernet LAN router, if
applicable.
12.After changing the options verify that all settings are correct.
13.At the Enter Option prompt, type 5 to quit.
The Power Server reboots automatically.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
NOTE: It can take approximately five minutes to reboot. If errors occur,
review all configuration settings before exiting HyperTerminal.
14.Exit HyperTerminal.
19
Page 24

Chapter 5—Setup 63230-216-207/A3
Connecting to the Power Server with NetMeeting 9/2002
Now you are ready to configure the POWERLOGIC System applications
as described in the next section, Connecting to the Power Server with
NetMeeting.
CONNECTING TO THE POWER SERVER
WITH NETMEETING
T o perform this procedure, y ou can either conn ect remotely from a networked
PC as illustrated in Figure 5–2, or you can connect directly from your PC to
the Power Server usin g a crossove r cable (not supplied). See Appendix C—
Using a Crossover Cable to Configure th e Power Serve r on page 33 for
details on crossover cable connections.
After connecting the cables, you will use NetMeeting to take control of the
Power Server from your PC so that you can configure the POWERLOGIC
System application. NetMeeting is provided with the FULL installation of
Internet Explorer 5.5 and with the Windows 2000 operating system. If
needed, NetMeeting can be downloaded from the Microsoft.com website.
NOTE: For Windows XP users, Windows XP does not provide any shortcut
to NetMeeting. You can access it by searching for the file “conf.exe” or
launch it by typing conf.exe in the Run dialog.
Remote Connection
Ethernet
UTP Ethernet Port
Remote PC with
Netmeeting
Local Connection
UTP Ethernet Port
Crossover
Cable
Power Server
Figure 5–2: Power Sever remote or local connections for setup
30703015
20
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 25

63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 5—Setup
9/2002 Connecting to the Power Server with NetMeeting
Starting NetMeeting 1. From your PC, launch NetMeetin g. Click Start > Programs > Ac cessories
> Communications > Netmeeting (Windows 2000 path).
2. To connect to the Power Server us in g N e tme eti ng, cl ic k Tools > Opt ion s
> Security and check “I prefer to make secure outgoing calls” and click
OK.
30703016
Y o u shou ld only have to d o this onc e. NetMeet ing sto res thi s pr eferenc e.
Netmeeting displays the Not in a Call dialog.
Assigned IP Address from
Table 1 on page 19.
Place a Call button
30703017
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
21
Page 26

Chapter 5—Setup 63230-216-207/A3
Connecting to the Power Server with NetMeeting 9/2002
3. Call the Power Server. Enter the IP address in NetMeeting and click the
“Place a Call” button.
Use IP address 1 that you entered in nwsetup on page 19.
The Remote Desktop Sharing dialog displays.
30703018
4. For User, enter: PowerServerAdmin
For Password (case-sensitive), enter: Pwr_Srv
Leave domain blank and click OK.
You are now controlling the Power Server desktop and are ready to
configure the POWERLOGIC system as described in the next section,
“Configuring the Power Server” on page 23.
NOTE: We recommen d that y ou change your p assword after c ompleting
setup. See Appendix B—Changing Your Password on page 31 for
instructions.
22
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 27

63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 5—Setup
9/2002 Configuring the Power Server
CONFIGURING THE POWER SERVER 1. Use NetMeeting to access the Power Server.
The Power Server splash screen displays.
NOTE: During the startup process , the Power Server displays the splas h
screen with a DO NOT TOUCH Ø symbol. Wait until this symbol no
longer displays before proceeding with the configuration.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
23
Page 28

Chapter 5—Setup 63230-216-207/A3
Configuring the Power Server 9/2002
2. Press Ctrl-W to display the Power Server desktop.
The Power Server desktop displays. Verify that all the taskbar icons
display as shown in Figure 5–3.
Power Server icon
Powerlog ic Server
icon
Taskbar icons
NOTE: Icons may be arranged di fferently than they are shown in this
illustration.
Figure 5–3: Power Server Desktop
To configure the Power Server you:
1. Set the time zone and daylight savings time preference.
2. Place the Power Server in se tup mode.
3. Configure your
POWERLOGIC system.
4. Return the Power Server to run mode.
Each of these procedur es is describ ed in this section. You can also create
quick tables, diagrams, and reports for the Power Server Model
PWRSRV750. Refer to the Power Server user’s guide 63230-216-207 for
details.
24
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 29

63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 5—Setup
9/2002 Configuring the Power Server
Setting the Date/Time and Time Zone
To update the date/time and time zone settings follow these steps:
1. In the taskbar, double click the time display.
The Date/Time Properties dialog displays.
2. Click the Time Zone tab to display it.
3070302230703021
3. Select your time zone from the pull down list, select your preference for
daylight savings, and click Apply.
4. Click the Date & Time tab to display it.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
25
Page 30

Chapter 5—Setup 63230-216-207/A3
Configuring the Power Server 9/2002
5. Set the new date and time, then click Apply.
6. Click OK to exit and save the changes.
7. Set the Power Server to setup mode as described in the following
section, Changing the Mode from Run to Setup Mode.
CAUTION
HAZARD OF SYSTEM MALFUNCTION
After configuring your Power Server, if you have to adjust the Power
Server Time Zone and Date/Time, make sure you restart your Power
Server and then manually run any scheduled task configured in Reports or
in the Powerlogic System setup applications.
Failure to do so will result in al arms, reports, diagram s and database
management malfunction.
Changing the Mode from Run to Setup Mode The Power Server has two modes of operation, Run and Setup.
• Run mode is a view-only setting
• Setup mode lets you configure the
POWERLOGIC system
During operation, the Powe r Server should be left in run m ode. The green PS
icon indicates that the uni t is operating in run mode. It changes to the red PS
icon when it is in setup mode. Before making any changes anytime to the
Power Server, you must set the Power Server to setup mode. To do this,
follow these steps:
1. Click the green PS Power Server icon on the taskbar .
2. Click the Setup Mode button to change to setup mode.
After changing to setup mode, your NetMe etin g ses si on will be
disconnected while the Pow er Server restarts automatica lly . This process
may take up to two minutes.
3. Reconnect to the Power Serve r with NetMeeting. T he Power Server icon
displays red indicating it is in setup mode.
26
NOTE: If you leave the Power Serv er in Setup mode for more than 12
hours, it will automatically reboot in run mode.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 31

63230-216-207/A3 Chapter 5—Setup
9/2002 Configuring the Power Server
Configuring Your POWERLOGIC System While in setup mode, you can add devices to the POWERLOGIC System.
Serial connections for COM 3 and COM 4 of the Power Server are already
defined in the system. Do not delete these settings or define a new
communica tion connection for COM 3 or COM 4 ports.
To add devices to the Power Server, follow these steps.
1. Double click the PowerLog ic Server icon on the desktop to launch
the application.
2. For user ID, enter: master
3. For password, enter: master, then click OK.
4. Double click the Pow erLogic System Setu p icon on the desktop to
launch the application.
5. For user ID, enter: master
6. For password, enter: master, then click OK once the
System Setup is started.
7. Select File > Offline to place the POWERLOGIC System offline.
8. Configure the system by defining the communication connections and
adding devices. To do this, select Setup > Communications and then
Setup > Devices/Routing.
POWERLOGIC
NOTE: If you need help config uri ng th e Pow erL ogi c s ystem , refe r to the
online help file “Quick Starts” listed in the help contents. From the
PowerLogic System Setup utility, click Help > SMS-3000 Help > Quick
Starts > Quick Start: Serial Device Setup.
9. Depending on the typ e of Power Server you have an d functions requi red,
perform setup procedures as needed for:
•Alarms
• Reports
• Waveforms
• Diagrams
Refer to the Power Server user’s guide 63230-216-217 for details.
10.After configuring the system, place the
online by selecting File > Online > System.
The Power Server has only one system, which is always open for editing.
It should always be left online except during configuration.
POWERLOGIC system back
CAUTION
POSSIBLE LOSS OF COMMUNICATIONS
Ensure that your POWERLOGIC system is online before exiting
POWERLOGIC System Setup.
Failure to do so will result in communication errors.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
11. Close the
12.Set the Power Server to run mode.
Refer to “Changing the Mode from Setup to Run Mode” on page 28.
POWERLOGIC System setup application.
27
Page 32

Chapter 5—Setup 63230-216-207/A3
Configuring the Power Server 9/2002
Changing the Mode from Setup to Run Mode To change from setup mode to run mode, do the following:
1. Return the Power Server back to run mode: click the red Power Server
icon on the taskbar at the bottom right-hand portion of the screen.
The Embedded Switch dialog displays.
2. Click the Run Mode button.
The Power Server will reboot in run mode for normal operations. This
operation may take up to five minutes depending on the number and
types of devices in your
POWERLOGIC system.
3. From your PC desktop, close NetMeeting.
28
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 33

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix A—Specificati ons
9/2002
APPENDIX A—SPECIFICATIONS
Table A–1: Power Server Specifications
Type Description
CONTROL POWER INPUT SPECIFICATIONS
Operating Input Range 24 Vdc (± 10%) [sourced by Class 2 rated supply]
Burden, max. 28 W
ENVIRONMENTAL
Ambient Operating Temperature
Ambient Storage T emperature –20°C to 70°C
Sealing IP30: Sealed against particles > 2.5 mm
Altitude (maximum) 15,000 ft. (4.5 km)
PHYSICAL SP ECIFICATIONS
Housing Dimensions
Weight Approximately 4.35 lbs (2kg) for complete system
Isolation
REGULATORY/STANDARDS COMPLIANCE
EMC
SAFETY
0 to 50°C (< 95% relative humidity, noncondensing)
8.98 in long x 3.62 in high x 5.63 in deep
(228 mm long x 143 mm high x 92 mm deep)
COM 3 / COM 4:Opto-galvanic, 500 Vac
100BaseTX: Galvanic, 500 Vac rms
CE marked to the immunity to interference
(EN 50082-2) and emissions directive
(EN 50081-2) for industrial environments
Fast Transients—EN 50082-2 criteria B
compliance
UL Recognized, cUL Recognized
CE
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Table A–2: PS080 Specifications
Type Description
Output capacity 50 W
Input voltage (single phase,
2-wire)
Output voltage 24 Vdc
Output current (max) 2.1 A
Housing dimensions
Ambient operating temperature
Ambient storage temperature -30°C to 85°C
Regulatory approvals UL, cUL, CE, TUV
100–240 Vac, 50/60 Hz
110–340 Vdc
3.54 in long x 3.74 in high x 2.95 in deep
(90 mm long x 95 mm high x 75 mm deep)
-10°C to 60°C (20–90% relative humidity
non-condensing)
29
Page 34

Appendix A—Specificat ions 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
30
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 35

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix B—Changing Your Password
9/2002
APPENDIX B—CHANGING Y O UR PASSWORD
We recommend that you change your password a fter completing s etup of the
Power Server. To do this, follow these steps:
1. From the taskbar of your laptop or PC, launch NetMeeting and connect
to the Power Server.
See “Starting NetMeeting” on page 21 for instructions.
If the Power Server is up a nd runn ing, pre ss Ctrl-W on your keyboard to
switch to the Power Server desktop
2. Place the Power Server in setup mode.
See “Changing the Mode from Run to Setup Mode” on page 26 for
instructions.
3. From the taskbar, launch User Manager. Click Start > Programs >
Administrative Tools > User Manager.
The User Manager screen displays.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
30703048
4. Click the PowerServerAdmin line.
5. From the User pull-down menu, click Rename.
The Rename dialog displays.
30703049
6. In the Change To box, type the new administrator user name and click
OK.
31
Page 36

Appendix B—Changing Your Password 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
7. Double click the Powe r Server adminis trator li ne for th e n ame crea ted in
the previous step.
The User Properties dialog displays.
30703050
8. Type the new password in the Password and Confirm Password boxes
and click OK.
9. Close the User Manager.
10.Return the Power Server to run mode.
See “Changing the Mode from Setup to Run Mode” on page 28 for
instructions. The new password will take effect immediately.
NOTE: Use the new User name an d pass word whe never y ou log i n with
NetMeeting or connect with a null modem cable to change the network
settings.
32
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 37

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix C—Using a Crossover Cable to Configure the Power Server
9/2002
APPENDIX C—USING A CROSSOVER CABLE TO CONFIGURE THE POWER SERVER
If you choose to use a cross- over cable to configu re the Power Server , follow
these steps:
1. Connect the cross-over cable from the Ethernet UTP port on the Power
Server to your PC as illustrated in Figure C–1.
Ethernet
UTP port
30703006
Cross-over cable
Figure C–1: Cross-over connection for Power Server configuration
2. Connect the power supply and ground if you have not already done so.
For instructions, refer to the section “Control Power” on page 10.
3. From your PC’s taskbar, cl ick Start > Settings > Network and Dial-up
Connections.
The Network and Dial-up Connections screen displays.
NOTE: An example using Microsoft Windows
®
2000 is shown in the
following steps. For help with other system s, contact your network
administrator.
4. From the Network a nd D i al- up C o nne cti ons screen, click the Local Area
connection icon.
The Local Area Connection Status dialog box displays.
30703012
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
33
Page 38

Appendix C—Using a Crossover Cable to Configure the Power Server 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
5. From the Local Area Connection Status dialog box, click Properties.
The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box displays.
6. From the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, select Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box displays.
34
7. From the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, select “Use
the following IP address.”
8. Enter the IP address (10.10.10.11) and subnet mask (255.255.255.0).
9. Click OK and reboot your PC.
10.From your PC, start NetMeeting . Click Start > Programs > Acces sories >
Communications > Netmeeting (Windows 2000 path).
NOTE: For Windows XP users, Windows XP does not provide any
shortcut to NetMeeting. You can access it by searching for the file
“conf.exe” or launch it by typing conf.exe in the Run dialog.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 39

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix C—Using a Crossover Cable to Configure the Power Server
9/2002
1 1 .To connect to the Power Server using Ne tme eti ng, click Too ls > O pt ion s
> Security and check “I prefer to make secure outgoing calls.”
30703016
Y o u shou ld only have to d o this onc e. NetMeet ing sto res thi s pr eferenc e.
Netmeeting displays the Not in a Call dialog.
Assigned IP Address
30703017
Place a Call button
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
35
Page 40

Appendix C—Using a Crossover Cable to Configure the Power Server 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
12.Call the Power Server. Enter the IP address in NetMeeting and click the
“Place a Call” button. For this initial configuration, use IP address:
10.10.10.10
30703057
The Remote Desktop Sharing dialog displays.
13.For User, enter: PowerServerAdmin
For Password (case-sensitive), enter: Pwr_Srv
Leave domain blank.
30703018
36
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 41

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix C—Using a Crossover Cable to Configure the Power Server
9/2002
14.After you have connected to the Power Server via NetMeeting, press
Ctrl-W on your keyboard to switch to the Power Server desktop.
15.Double click the Network Setup icon on the Power Server
desktop.
NOTE: Even if the Power Server will not be used in a networked
environment, you must run the Network Setup application at le ast once
and then type 5 to quit.
16.Set all of the network setup options as described in Table C–1 on page
37.
NOTE: T o change any of the options, typ e the option numb er at the Enter
Option prompt and press Enter.
17.Follow the onscreen instructions to change the value.
Table C–1: Power Server Setup—HyperTerminal Options
Option Description
The computer name defaults to the MAC Address. We
recommend that you leave the default computer name. If
Computer Name
IP Address 1
Subnet Mask 1
IP Address 2
Subnet Mask 2
(optional)
Router Address
MAC Address Unique media access control number (cannot be changed).
you must change the name, it must be a unique alphanumeric name, limited to 15 characters, no spaces or
special characters.
Use IP Address 1 as the primary address to access all the
capabilities of the Power Server.
Subnet Mask 1 is assigned to IP Address 1.
IP Address 2 and Subnet Mask 2 are optional. They should
only be used if slave Modbus/Jbus and POWERLOGIC
devices need to have the same address on both COM 3 and
COM 4.
Address of your company’s Ethernet LAN router, if
applicable.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
37
Page 42

Appendix C—Using a Crossover Cable to Configure the Power Server 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
18.After changing the options, verify that all settings are correct.
19.At the Enter Option prompt, type 5 to quit.
The Power Server reboots automatically. During the reboot, your
NetMeeting session is closed automatically.
Now you are ready to configure the PowerLogic System applications as
described in the se ction, “Connecting to the Po wer Server with NetMeeting”
on page 20.
38
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 43

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix D—Integrating the Power Server into SMS
9/2002
APPENDIX D—INTEGRATING THE POWER SERVER INTO SMS
This appendix provides instructions for using System Manager Software
(SMS) to set up a PC i nterface to comm unicate through the Power Server a s
a gateway to the Power Server’s attached serial slave devices.
To communicate with SMS through the Power Server, follow these steps:
1. Launch SMS.
2. Open an existing system or create a new system.
3. Add a communication connection.
• For the communications connection name, type in a unique name for
your Power Server connection .
• For the communications driver, select “MODBUS/TCP driver.”
4. Enter the Power Server IP address in the communication connection
(MODBUS/TCP).
5. After defining the communications connection, add the serial daisychained devices us ing the previously defined Power Server
communication connection.
For more details, refer to the SMS Help option in SMS by going to SMS >
Quick Start > Quick start MODBUS/TCP device setup.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
39
Page 44

Appendix D—Integrating the Power Server into SMS 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
40
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 45

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix E—Uploading And Deleting Files On the Power Server 9/2002 About the Software Warranty
APPENDIX E—UPLOADING AND DELETING FILES ON THE POWER SERVER
ABOUT THE SOFTWARE WARRANTY The Power Serv er products are inte nded for use with POWERLOGIC System
software only . Install ation of any nonvoid the warranty for this product. Contact your local Schneider Elec tric
Technical Support center or your local Schneider representative for details
and information regardin g
POWERLOGIC compatible software.
POWERLOGIC compatible s oftware will
UPLOADING FILES TO THE
POWER SERVER
You can upload PDFs or custom web pa ge s (h tm l) o f re fere nce m ate rial s to
the Power Server. They can then be viewed through the Power Server
browser. To upload files to the Power Server, follow these steps:
1. Start N etMeeting and connect to the Power Server.
See “Starting NetMeeting” on page 21.
2. Once connected, press Ctrl-W to display the Power Server desktop.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Click the Minimize button to minimize the
NetMeeting Target’s desktop.
41
Page 46

Appendix E—Uploading And Deleting Files On the Power Server 63230-216-207/A3
Uploading Files to the Power Server 9/2002
3. Click the Minimize button in the top right corner to minimize the
NetMeeting Target’s desktop. Click OK if “Meeting Properties” or “The
directory server could not be found” dialogs display. Then, click the
Transfer Files icon on the NetMeeting connection dialog.
4. Wait for the Add Files icon to become enabled, then click it.
42
5. In the Select Files to Send dialog, select files to upload to the Power
Server and click Add.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 47

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix E—Uploading And Deleting Files On the Power Server
9/2002 Uploading Files to the Power Server
6. Click the Send All icon.
7. Restore the Target’s desktop window and then close all the Transfer
complete dialogs that display ed duri ng the transfer.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
43
Page 48

Appendix E—Uploading And Deleting Files On the Power Server 63230-216-207/A3
Uploading Files to the Power Server 9/2002
8. Double click the Apply Transferred Files icon on the Target’s desktop.
The following screen displays.
9. Press any key. The following screen displays.
10.Press any key.
1 1. Double-click the Power Serv er browser icon to display the Power
Server browser.
12.Minimize the Target’s desktop screen.
13.End the call and exit NetMeeting.
44
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 49

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix E—Uploading And Deleting Files On the Power Server
9/2002 Deleting Files on the Power S erver
DELETING FILES ON THE
POWER SERVER
To delete uploaded files, do the following:
1. Start N etMeeting and connect to the Power Server.
See “Starting NetMeeting” on page 21.
2. Once connected, press Ctrl-W to display the Power Server desktop.
3. Open the Access Transferred Files folder by doub le click ing the desk top
icon.
4. Select files to be deleted.
5. Click File > Delete.
6. Click Yes.
7. Close the Power Server\Maintenance window.
8. Double-click the Power Server browser icon to display the
Power Server browser.
9. Minimize the Target’s desktop screen.
10.End the call and exit NetMeeting.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
45
Page 50

Appendix E—Uploading And Deleting Files On the Power Server 63230-216-207/A3
Deleting Files on the Power Server 9/2002
46
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 51

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix F—Connecting Third Party Devices to the Power Server
9/2002
APPENDIX F—CONNECTING THIRD PARTY DEVICES TO THE POWER SERVER
You can connect third party devices to the Power Server using a custom
install application. Contact your field sales representative to determine the
availability of the custom install application for a particular device.
If you have retai ned the custom fi les, follow thes e steps to inst all the files a nd
connect to the device.
1. Start N etMeeting.
Refer to“Starting NetMeeting” on page 21 and connect to the Power
Server.
2. In the Target’s deskto p window , press Ctrl-W to display the Power Server
desktop.
3. Display NetMeeting again by clicking the NetMeeting icon on your PC’s
taskbar.
4. Click OK to close the Meeting Properties window.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
47
Page 52

Appendix F—Connecting Third Party Devices to the Power Server 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
5. Click the Transfer Files icon.
6. Click Add Files.
7. Select all the files for the custom install application and click Add.
48
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 53

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix F—Connecting Third Party Devices to the Power Server
9/2002
8. Click Send All.
9. When all files have transferred, close the File Transfer dialog.
10.Click the “Target’s Desktop” window.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
49
Page 54

Appendix F—Connecting Third Party Devices to the Power Server 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
11. Click the Power Server icon on the bottom right of your taskbar.
Power Server icon
The Power Server Embedded Switch dialog displays.
12.Click the Setup Mode button to change to setup mode.
After changing to setup mode, your NetMe etin g ses si on will be
disconnected while the Pow er Server restarts automatica lly . This process
may take up to two minutes.
13.Reconnect to the Power Server with NetMeeting.
14.Press Ctrl-W to display the Power Server desktop.
The Power Server icon displays red indicating it is in setup mode.
NOTE: Some third party device installations may be configured to
execute automatically with no interaction on your part. Check with your
field sales representative to see if this is the case. If so, skip to step 23.
50
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 55

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix F—Connecting Third Party Devices to the Power Server
9/2002
15.Double-click the My Computer icon on the Power Server desktop and
open the C:\Netmeeting Received Files folder.
16.Double-click Setup.exe.
17.Follow the onscreen instructions in the wizard.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
51
Page 56

Appendix F—Connecting Third Party Devices to the Power Server 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
18.Upon completion of the instal l wizard, select “N o. I will start my com puter
later.”
19.Click Finish.
20.Select all the files in the “C:\N etMeeting Received Files” folder and delete
them.
21.Close the My Computer window.
22.Delete the files in your rec yc le b in by righ t-c lic ki ng th e de sk top ico n and
selecting “Empty Recycle Bin.”
NOTE: If you want to configure your
POWERLOGIC system with the third
party device you just added, do not switch back to run mode. Instead
simply click the Restart button, configure your system, then proceed to
step 23.
23.After configuring your POWERLOGIC system with the new device type,
Click the Run Mode button on the Power Server Embedded Switch
window to restart the Power Server back in run mode.
52
24.Close NetMeeting.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 57

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix G—POWERLOGIC System Display (SD700) Installation
9/2002 Product Description
APPENDIX G—POWERLOGIC SYSTEM DISPLAY (SD700) INSTALLATION
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION The System Display is a full-color, panel-mount touch screen display
designed to be mounted on power equipment. The system display lets you
view the Power Server screens locally at the equipment. Water and dust
protection to NEMA 4 and 12 stand ards allow the sys tem displa y to be used
in a wide variety of industrial and commercial applications. A bright LCD
display with 800 X 600 pix el resolu tion and a wide vie wing an gle ensu re that
data is visible in a broad r ange of lighting conditions. For complete
specifications, see the user’s guide sh ipp ed wi th the display.
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION Refer to the user’s guide shipped with the display for information on:
• Installing the display
• Connecting control power
• Auto-adjusting the touchscreen
• Understanding the front panel LED indicators
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
DANGER
HAZARD OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, BURN, OR EXPLOSION
• This equipment must be installed and serviced only by qualified
personnel.
• Turn off all power supplying this equipment and the equipment it is
mounted in before working on or inside equipment.
• Always use a properly rated vo ltage sensing de vice to confirm th at power
is off.
• Replace all device doors and covers before turning on power to this
equipment.
Failure to observe these instructions will result in death or serious
injury.
CONNECTING TO THE POWER SERVER To connect the touch screen display to the Power Server, do the following:
1. Turn of f all powe r supplyin g the elect rical equip ment in w hich the displ ay
and power server are installed, and confirm that power is off using a
properly rated voltage sensing device.
2. Locate the serial ca ble supplied wit h the system di splay . The serial ca ble
has a male nine-pin connector on one end and a female nine-pin
connector on the other end.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
53
Page 58

Appendix G—POWERLOGIC System Display (SD700) Installation 63230-216-207/A3
Calibrating the Touch Screen 9/2002
3. Connect the female end of the serial cable to the COM 2 serial port on
the Power Server (see FigureG–2). Tighten the captive screws on the
cable connector.
4. Connect the male end of the serial cable to the Touch Screen Serial
Output port on the system display. Tighten the captive screws on the
cable connector.
5. Locate the video cable supplied with the system display.
6. Connect one end of the video ca ble to the female V ideo input port on the
side of the system display. Tighten the captive screws on the cable
connector.
7. Connect the other end of the video cable to the VGA output port on the
Power Server (see FigureG–2). Tighten the capti ve screws o n the cab le
connector.
COM 2 serial port — connect to
the touch screen output port on
the system display.
COM2
VGA output port — connect
to the VIDEO input port on
the system display.
Figure G–2: Power Server connectors
CALIBRATING THE TOUCH SCREEN The first time you power up the system display, you should calibrate the
touch screen.
To calibrate the touch screen, do the following:
1. Ensure that the Power Server is running and that the Power Server
interface is visible on the monitor.
2. Touch the Maintenance tab.
3. On the Maintenance tab, touch the Calibration button.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions.
5. When calibration is complete, touch the screen in several places and
ensure that the pointer arrow accurately fol lows your touc h. If it does not,
repeat the calibration procedure.
CARE AND CLEANING Occasionally clean the display panel with a soft cloth dampened with glass
cleaner. Spray cleaner on the cloth. Do not spray cleaner directly on the
touchscreen. Keep turning a fresh side of the cloth towar d the screen surface
to avoid scratching it with accumulated grit. Allow the screen to air dry.
NOTE: Never use ammonia-based cleaners to clean the touchscreen. Do
not use paper products to cl ean the sc reen as th ey may scra tch the su rface.
54
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 59

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix G—POWERLOGIC System Display (SD700) Installation
9/2002 Specifications
SPECIFICATIONS
Table G–1: Specifications
Display
Type Active matrix color thin film transistor (TFT) LCD
Nominal Display Area
Diagonal 12.1 in (308 mm)
Resolution 800 x 600 pixels
Electrical
Input voltage 100-240 Vac, 50–70 Hz, 0.5 A
SD700 DC option: 24 Vdc (± 10%) [sourced by
Class 2 rated supply], 1.5 A, 36 W
Environmental
Panel mount rating NEMA 4 and 12
Operating
temperature
Agency Approvals
FCC Class A; UL and cUL Recognize d; CE Marke d
0° C to 50° C
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
55
Page 60

Appendix G—POWERLOGIC System Display (SD700) Installation 63230-216-207/A3
Specifications 9/2002
56
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 61

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix H—Database Backup
9/2002 Backing Up the Database on the Power Server
APPENDIX H—DATABASE BACKUP
The Power Server contains four SQL databases: master, msdb,
SMS-System and SMS-History. By default, the Power Server automatically
backs up these databases every month. Although the master and msdb
databases are SQL system databases and they do not get updated
frequently, the System and History databases hold all the Power Server
configuration and data. Therefore, y ou may need to b ack up those data bases
manually (for exam ple, after the Power Server s etup), retriev e them from th e
Power Server, and save them on a separate PC. The following sections
cover procedures for these backups.
BACKING UP THE DATABASE ON THE POWER SERVER
The Power Server allows you to manually back up the system and history
databases. To do so, follow these steps:
1. Type http://Power Server IP/PowerServer/jobs/default.asp in Internet
Explorer using the IP address of the Power Serve r for “Power Serve r IP.”
The Enter Network Password dialog displays.
2. For User, enter: PowerServerAdmin
For Password (case-sensitive), enter: Pwr_Srv
The Power Server Database Maintenance page displays.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
3. From the Backup Jobs dropdown li st, select SMS System or SMS His tory
and click Execute.
57
Page 62

Appendix H—Database Backup 63230-216-207/A3
Backing Up the Database on the Power Server 9/2002
The web page displays “J ob command sent” and the Power Server starts
backing up the database on the Power Server.
Checking the Database Back up Status To check the status of the database backup, follow these steps:
1. Type http://Power Server IP/ to browse the main Power Server user
interface (using the IP address of the Power Server for “Power Server
IP”).
2. Click the Maintenance tab.
The Maintenance page displays.
3. Click the Diagnostics button .
The Diagnostics page displays.
4. Select Database Statistics from the list on the left side of the page.
The Power Server Database Statistics page displays.
“Executing” displays in the Status column while the database backup is
in progress.
Once the database is backed up, the Status column will display “IDLE”
with an updated date/time stamp.
NOTE: The Database Statistics page does not refresh automatically. To
refresh the page, click Database Statistics in the list again.
58
“Executing” displays in
the Status column while
the database backup is
in progress.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 63

63230-216-207/A3 Appendix H—Database Backup
9/2002 Backing Up the Power Server Database onto a Separate PC
BACKING UP THE POWER SERVER DATABASE ONTO A SEPARATE PC
In addition to backing up the database on the Pow er Server , we recommend
saving your backup s onto a sepa rate PC on a regular basis . To do so, follow
these steps:
1. Type ftp://Po wer Server IP/SQL in Internet Explorer usin g the IP address
of the Power Server for “Power Server IP.”
The Enter Network Password dialog displays.
2. For User, enter: PowerServerAdmin
For Password (case-sensitive), enter: Pwr_Srv
The SQL folder displays.
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
3. Select all files and right-click > Copy to Folder.
59
Page 64

Appendix H—Database Backup 63230-216-207/A3
Restoring the Database on the Power Server 9/2002
4. Select the destination folder to backup the database files.
RESTORING THE DATABASE ON THE POWER SERVER
If you need to restore the databa se on your Power Server , co ntact your local
Schneider Electric representative for instructions.
60
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 65

63230-216-207/A3 Index
9/2002
INDEX
Numerics
2-wire
connections,
max devices on daisy chain, 15
4-wire
connecting as 2-wire,
max devices on daisy chain, 15
RS-485 connections, 13
14
14
A
altitude sp ecification, 29
B
baud rate setting, 13
biasing, 14
C
calibrating the touch screen, 54
changing passwords, 31–33
changing the POWERLOGIC system mode, 26
COM 1, 12
COM 2, 12
communications
connections,
end-of-line terminator, 14
multipoint communications adapter, 14
ports described, 9
wiring, 15
with SMS, 39
compliance to standards, 29
configuring
power server communi cation connection,
17
33
the POWERLOGIC system, 23
configuring the POWERLOGIC System, 27
configuring the POWERLOGIC system, 27
connections
4-wire devices as 2-wire,
comms to power server, 17
for initia l setup, 17, 33
local or remote for setup, 20
overview, 9
system display, 53
third party devices, 47
control power, 9
described, 10
grounding, 10
input specifications, 29
crossover cable
for setup,
to configure the Power Server, 33
custom install application, 47
20
14
D
daisy chain
maximum devices,
mixed mode, 13
termination, 14
15
17,
date/time setup, 24
DB-9 connector, 13
deleting files, 45
devices
connecting third party,
number supported, 15
dimensions, 5
DIN rail mounting, 5
display, 53
47
E
environmental
specifications,
29
F
fusing
recommendations,
10
G
grounding, 10
H
HyperTerminal connection setup, 17–38
I
icons on the power server desk top , 24
installation
power server,
IP Address setup, 19, 37
5
L
local connections for setup, 20
local equipment grounding, 11
M
MCT terminator, 14
mixed-mode daisy chains, 13
mode
changing from run to setup,
changing from setup to run, 28
mounting
DIN rail,
power server, 5
multipoint communications adapter, 14
5
26
N
NetMeeting
changing the power server pass word,
connecting third party device types, 47
date/time/zone setup, 25
starting NetMeeting, 21
Windows XP users, 20, 34
null modem ca ble
configuration,
17
O
online
31
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
61
Page 66

Index 63230-216-207/A3
9/2002
placing POWERLOGIC system online, 27
P
parity setting, 13
password
changing the power server password,
for NetMeeting, 22, 36
physical specifications , 29
pin out
POWERLOGIC standard,
RS-485 DB-9 connector, 13
place a call in NetMeeting, 22
power server
applications,
communication connection, 17
connections described, 9
control power connections, 10
desk top icons, 24
desktop, 24
dimensional drawing, 5
grounding, 10
installation, 5
overview, 1
RS-232 serial connections, 12
RS-485 connections, 13
setup, 17
power supply
fusing,
grounding, 10
mounting, 6
POWERLOGIC sy stem
configuring in setup mode,
PS080
power supply,
specifications, 29
2
10
10
13
26
31
setup mode, 26
software warranty, 41
specifications, 29
power server, 29
PS080 power supply, 29
standard device connection, 13
standards compl ia nce , 29
system display, 53
care and cleaning, 54
specifications, 55
touch screen calibration, 54
T
temperature specifications, 29
termination, 14
third party device types, 47
time zone setup, 24
touch screen display, 1, 53
U
uploaded files
deleting,
uploading files, 41
custom web pages (htm l), 41
PDFs, 41
user manager screen, 31
UTP port, 9
45
62
R
regulatory standards comp liance, 29
remote
connections to power server,
desktop sharing, 22, 36
RS-232 serial ports, 12
RS-485 port
biasing,
described, 13
termination, 14
run mode, 26
14
20
S
safety
general safety precautions,
standards, 29
SD700, 1, 53
security
for NetMeeting,
setup
of the IP address,
of the power server, 17
21, 35
19, 37
3
© 2002 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 67

Page 68

POWERLOGIC® Power Server Setup Guide
Schneider Electric Technical Support Contacts / Schneider Electric contactos de soporte técnico
/ Schneider Electric contacts pour l’assistance technique
For technical support and additional information, cont act your local sales office or a n of fice listed below. /
Para obtener soporte téc nico e i nformaci ón adiciona l, póng ase en cont acto con su ofici na local de venta s
o con una de las oficinas que aparecen a continuación./
Pour obtenir de l’assistance technique et des informations supplémentaires, contac tez votre bureau de
vente local ou l’un des bureaux listés ci-dessous.
Argentina / Argentine
Viamonte 2850
1678 CASEROS
Provincia de BUENOS AIRES
tel - (54-11) 4716 8888
fax - (54-11) 4716 8888
Australia / Aust ra l ie
77 Ricketts Road
Mount Waverley
VIC 3149
Australia
tel - (03) 9558 9876
fax - (03) 9558 8091
Brazil / Brasil / Brésil
Av. Da Saudade, s/n
CEP 13171-320
Sumare SP Brazil
tel - (19) 3873 97 44
fax - (19) 3873 94 94
Canada / Canadá
6675 Rexwood Road
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1V1
tel - 1-615-287-3400
fax - 1-615-287-3404
Central America /
Centroamér ic a / A mé r iq u e
Centrale
1.5 km al oeste de la Embajada
Americana
San José, Costa Rica C.A.
Apdo 4123-1000,
San José, Costa Rica, C.A.
tel - (506) 232-60-55
fax - (506) 232-04-26
China / Chine
Schneider (Beijing)
Medium Voltage Co., Ltd.
Rm 709
No. 3 Yong Chang North Road
BJ Economic Technological
Development Area
Beijing 100176
P.R.C.
tel - (010) 6788 5557
fax - (010) 6788 0531
Colombia / Colombie
Schneider Electric de Colombia
CII 45A No. 102 - 48 Bogotá D.C.
tel - +57 (1) 426 97 00
fax - +57 (1) 426 97 40
Ecuador / Equateur
PO Box 17-11-6466 CCI
Av. Shyris y Rio Coca Esq.
Edif. Eurocentro, 2do Piso 17-11
6466 QUITO
tel - (593) 2 25 03 23
fax - (593) 2 43 49 40
France / Francia
PCR Usine M4
22 Rue du Vieux Chêne Meylan
38050 Grenoble
Cedex 9
tel - 04 76 60 62 35
fax - 04 76 39 40 72
Indonesia / Indonésie
Ventura Buildin g 7th Floor
Jl. R.A. Kartini Kav. 26
Cilandak, Jakarta 12430
tel - (62-21) 750 4406
fax - (62-21) 750 4415
Malaysia / Malasia / Malaisie
Schneider Malaysia Sdn Bhd
11, Jalan U1/19
Seksyen U1,
Hicom Glenmarie Industrial Park
40150 Shah Alam
Malaysia
tel - 603 78836 333
fax - 603 78836 188
Mexico / México / Mexique
Calz. Rojo Gomez 1121
Col. Guadalupe del Moral
Mexico 09300
tel - 58 04 55 44
fax - 56 86 27 10
Peru / Péru
Schneider Electric Peru S.A.
Sede Central
Los Telares 231 - Urb. Vulcan o -
Ate
Lima 3 - Peru
tel - (511) 348-4411
fax - (511) 348-0523
Philippines / Filipinas
1314 Batangas Street
Makati City 1234
METRO-MANILA
tel - (63 2) 844 84 18
fax - (63 2) 816 00 63
Bulletin No. 63230-216-207/A3 9/2002
Class 3070
Singapore / Singapur
10 Ang Mo Kio Street 65
#02-17/20
Tech Point
SINGAPOR E 56 9 05 9
tel - 484 7877
fax - 484 7800
Spain / España / Espagne
Schneider Electric Españ a
Pl. Dr. Letamendi, 5-7
08007 BARCELONA
tel - 93.484.31.00
fax - 47.657.77.32
Taiwan
Suite 11-2, Presidential Fin ancial
Plaza
11th Floor,
51 Keelung Road, Sec.2
TAIPEI 110
tel - 886-2-2733-1464
fax - 886-2-2 7 33-6410
Thailand / Tailandia / Thaïlande
Schneider (Thailand) Limited
Sales & Support Department
20th Floor, Richmond Bldg.
Klongton, Klongtoey, Bangkok
10110
tel - +66 (2) 324-6000
direct - +66 (2) 204-9842
fax - +66 (2) 204-9817
United Kingdom / Reino Unido /
Royaume-Uni
Schneider Electric Ltd.
PowerLogic Systems
Cheney Manor
SWINDON
Wiltshire SN2 2QG
tel - 44 (0) 1793 500 482
fax - 44 (0) 1793 500 428
United States / EE.UU /
Etats-Unis
295 Tech Park Drive, Suite 100
LaVergne, TN 37086
tel - 1-615-287-3400
fax - 1-615-287-3404
Venezuela
Schneider Electric Venezuela S.A.
Calle 6 con carrera 3
Zona Industrial II Comdibar
Barquisimeto - Edo. Lara
tel - 051-69.24.22 Ext. 242
fax - 051-69.11.62
 Loading...
Loading...