Page 1

MVI46-PDPMV1
SLC Platform
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
March 25, 2011
USER MANUAL
Page 2

Your Feedback Please
We always want you to feel that you made the right decision to use our products. If you have suggestions, comments,
compliments or complaints about our products, documentation, or support, please write or call us.
How to Contact Us
ProSoft Technology
5201 Truxtun Ave., 3rd Floor
Bakersfield, CA 93309
+1 (661) 716-5100
+1 (661) 716-5101 (Fax)
www.prosoft-technology.com
support@prosoft-technology.com
Copyright © 2011 ProSoft Technology, Inc., all rights reserved.
MVI46-PDPMV1 User Manual
March 25, 2011
ProSoft Technology ®, ProLinx ®, inRAx ®, ProTalk ®, and RadioLinx ® are Registered Trademarks of ProSoft
Technology, Inc. All other brand or product names are or may be trademarks of, and are used to identify products
and services of, their respective owners.
ProSoft Technology® Product Documentation
In an effort to conserve paper, ProSoft Technology no longer includes printed manuals with our product shipments.
User Manuals, Datasheets, Sample Ladder Files, and Configuration Files are provided on the enclosed CD-ROM in
Adobe® Acrobat Reader file format (.PDFs). These product documentation files may also be freely downloaded from
our web site: www.prosoft-technology.com
Page 3

Important Installation Instructions
Power, Input, and Output (I/O) wiring must be in accordance with Class I, Division 2 wiring methods, Article 501-4 (b)
of the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70 for installation in the U.S., or as specified in Section 18-1J2 of the Canadian
Electrical Code for installations in Canada, and in accordance with the authority having jurisdiction. The following
warnings must be heeded:
WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - SUBSTITUTION OF COMPONENTS MAY IMPAIR SUITABILITY FOR CLASS
I, DIV. 2;
WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - WHEN IN HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS, TURN OFF POWER BEFORE
REPLACING OR WIRING MODULES
WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - DO NOT DISCONNECT EQUIPMENT UNLESS POWER HAS BEEN
SWITCHED OFF OR THE AREA IS KNOWN TO BE NON-HAZARDOUS.
THIS DEVICE SHALL BE POWERED BY CLASS 2 OUTPUTS ONLY.
MVI (Multi Vendor Interface) Modules
WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - DO NOT DISCONNECT EQUIPMENT UNLESS POWER HAS BEEN
SWITCHED OFF OR THE AREA IS KNOWN TO BE NON-HAZARDOUS.
AVERTISSEMENT - RISQUE D'EXPLOSION - AVANT DE DÉCONNECTER L'ÉQUIPEMENT, COUPER LE
COURANT OU S'ASSURER QUE L'EMPLACEMENT EST DÉSIGNÉ NON DANGEREUX.
Warnings
North America Warnings
A Warning - Explosion Hazard - Substitution of components may impair suitability for Class I, Division 2.
B Warning - Explosion Hazard - When in Hazardous Locations, turn off power before replacing or rewiring
modules.
Warning - Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect equipment unless power has been switched off or the area is
known to be nonhazardous.
C Suitable for use in Class I, division 2 Groups A, B, C and D Hazardous Locations or Non-Hazardous Locations.
ATEX Warnings and Conditions of Safe Usage:
Power, Input, and Output (I/O) wiring must be in accordance with the authority having jurisdiction
A Warning - Explosion Hazard - When in hazardous locations, turn off power before replacing or wiring modules.
B Warning - Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect equipment unless power has been switched off or the area is
known to be non-hazardous.
C These products are intended to be mounted in an IP54 enclosure. The devices shall provide external means to
prevent the rated voltage being exceeded by transient disturbances of more than 40%. This device must be used
only with ATEX certified backplanes.
D DO NOT OPEN WHEN ENERGIZED.
Warning: This module is not hot-swappable! Always remove power from the rack before inserting or removing this
module, or damage may result to the module, the processor, or other connected devices.
Battery Life Advisory
The MVI46, MVI56, MVI56E, MVI69, and MVI71 modules use a rechargeable Lithium Vanadium Pentoxide battery to
backup the real-time clock and CMOS. The battery should last for the life of the module. The module must be
powered for approximately twenty hours before the battery becomes fully charged. After it is fully charged, the battery
provides backup power for the CMOS setup and the real-time clock for approximately 21 days. When the battery is
fully discharged, the module will revert to the default BIOS and clock settings.
Note: The battery is not user replaceable.
Page 4

Markings
Electrical Ratings
Backplane Current Load: 800 mA @ 5 Vdc
Operating Temperature: 0°C to 60°C (32°F to 140°F)
Storage Temperature: -40°C to 85°C (-40°F to 185°F)
Shock: 30 g operational, 50 g non-operational; Vibration: 5 g from 10 Hz to 150 Hz
Relative Humidity 5% to 95% (with no condensation)
All phase conductor sizes must be at least 1.3 mm(squared) and all earth ground conductors must be at least
4mm(squared).
Agency Approvals and Certifications
Agency Applicable Standards
CSA 61010
CB Safety CA/10533/CSA IEC 61010-1 Ed. 2
CB 243333-2056722 (2090408)
243333
Page 5

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Contents
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Contents
Your Feedback Please ........................................................................................................................ 2
How to Contact Us .............................................................................................................................. 2
ProSoft Technology® Product Documentation .................................................................................... 2
Important Installation Instructions ....................................................................................................... 3
MVI (Multi Vendor Interface) Modules ................................................................................................ 3
Warnings ............................................................................................................................................. 3
Battery Life Advisory ........................................................................................................................... 3
Markings .............................................................................................................................................. 4
Guide to the MVI46-PDPMV1 User Manual 9
1 Start Here 11
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.7.1
System Requirements ............................................................................................. 12
Package Contents ................................................................................................... 13
Installing ProSoft Configuration Builder Software ................................................... 14
Setting Jumpers ...................................................................................................... 15
Installing the Module in the Rack ............................................................................ 16
Connecting Your PC to the Processor .................................................................... 18
Downloading the Sample Program to the Processor .............................................. 19
Configuring the RSLinx Driver for the PC COM Port .............................................. 20
Connecting Your PC to the Module ......................................................................... 22
2 Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module 23
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.2.1
2.2.2
2.2.3
2.2.4
2.3.1
2.3.2
2.3.3
2.3.4
2.3.5
2.3.6
2.4.1
2.4.2
2.4.3
2.4.4
2.4.5
Setting Up the Project ............................................................................................. 24
Setting Module Parameters ..................................................................................... 26
Input Data Size ........................................................................................................ 27
Output Data Size ..................................................................................................... 27
Input Byte Swap ...................................................................................................... 28
Output Byte Swap ................................................................................................... 28
Configuring the PROFIBUS Master ........................................................................ 29
Installing the GSD Files ........................................................................................... 30
Configuring the PROFIBUS Slaves ......................................................................... 31
Calculating the Checksums ..................................................................................... 45
Printing the Processor Network Memory Map......................................................... 45
Downloading the Project to the Module Using a Serial COM Port .......................... 47
Backing Up the Project ............................................................................................ 48
Verifying Correct Operation ..................................................................................... 50
Checking the PROFIBUS LEDs on the MVI46-PDPMV1 ....................................... 50
Viewing the Online Status of the PROFIBUS Network ........................................... 51
Viewing the Fieldbus Data from the MVI46-PDPMV1’s Configuration/Debug Menu53
Viewing the Data Files in RSLogix 500 ................................................................... 56
Sending a Mailbox Message in RSLogix 500 ......................................................... 58
3 Ladder Logic 59
3.1
Adding the Module to an Existing Project ............................................................... 60
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 5 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 6

Contents MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
4 Mailbox Messaging 63
4.1
4.2
4.3
4.4
4.1.1
4.2.1
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5
4.2.6
4.2.7
4.2.8
4.2.9
4.2.10
4.2.11
4.4.1
4.4.2
4.4.3
4.4.4
Mailbox Message Queuing ..................................................................................... 64
Queue Timeouts ..................................................................................................... 64
Special Function Mailbox Messaging Commands .................................................. 65
Mailbox Message: Set Slave Mode ........................................................................ 66
Mailbox Message: Get Slave Diagnostics .............................................................. 69
Mailbox Message: Get Slave Configuration ........................................................... 72
Mailbox Message: Set Slave Address .................................................................... 73
Mailbox Message: Get Live List .............................................................................. 76
Mailbox Message: Acyclic Data Read: Class 1 ...................................................... 77
Mailbox Message: Acyclic Data Write: Class 1 ...................................................... 79
Mailbox Message: Alarm Indication ........................................................................ 81
Mailbox Message: Set Operating Mode ................................................................. 83
Mailbox Message: Start Slave ................................................................................ 85
Mailbox Message: Stop Slave ................................................................................ 87
Receiving Mailbox Message Responses from the Module ..................................... 89
Mailbox Messaging Error Codes............................................................................. 90
Acyclic Message Status Word ................................................................................ 90
Return Codes .......................................................................................................... 91
Error Codes ............................................................................................................. 92
DP-V1 Error Codes ................................................................................................. 93
5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting 95
5.1
5.2
5.3
5.4
5.5
5.6
5.4.1
5.5.1
5.5.2
5.5.3
5.6.1
5.6.2
5.6.3
5.6.4
5.6.5
5.6.6
Basic Troubleshooting Steps .................................................................................. 96
LED Status Indicators: Front of MVI46 Module ...................................................... 97
Module Faceplate Status Indicators ....................................................................... 98
PROFIBUS Master Indicators ................................................................................. 99
Examples .............................................................................................................. 100
Using ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) for Diagnostics ................................. 102
Using the Diagnostic Window in ProSoft Configuration Builder ........................... 102
Navigation ............................................................................................................. 104
Main Menu ............................................................................................................ 105
Standard PROFIBUS Slave Diagnostic Bytes ...................................................... 108
Byte 0 - Station Status 1 Bits ................................................................................ 108
Byte 1 - Station Status 2 Bits ................................................................................ 108
Byte 2 - Station Status 3 Bits ................................................................................ 109
Byte 3 - Master Address ....................................................................................... 109
Byte 4 - Ident Number High .................................................................................. 109
Byte 5 - Ident Number Low ................................................................................... 109
6 Reference 111
6.1
6.2
6.1.1
6.1.2
6.1.3
6.2.1
6.2.2
6.2.3
6.2.4
Product Specifications .......................................................................................... 112
General Specifications .......................................................................................... 112
Hardware Specifications ....................................................................................... 112
Functional Specifications ...................................................................................... 113
Functional Overview ............................................................................................. 114
About the PROFIBUS Protocol ............................................................................. 114
Backplane Data Transfer ...................................................................................... 115
PROFIBUS DP Architecture ................................................................................. 120
Communication Types .......................................................................................... 121
Page 6 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 7

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Contents
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
6.2.5
6.3
6.4
6.5
6.6
6.7
6.8
6.9
6.3.1
6.3.2
6.3.3
6.3.4
6.3.5
6.3.6
Master/Slave Communication Phases .................................................................. 121
PROFIBUS comDTM ............................................................................................ 122
ProSoft Technology Product Availability ............................................................... 122
Introduction to PROFIBUS comDTM .................................................................... 123
System Requirements ........................................................................................... 126
Installation ............................................................................................................. 127
Quick Start ............................................................................................................. 128
Verifying the comDTM Version and comDTM Install Version ............................... 135
Disabling the RSLinx Driver for the Com Port on the PC ...................................... 140
RS-232 Configuration/Debug Port ........................................................................ 142
DB9 to RJ45 Adaptor (Cable 14) .......................................................................... 143
PROFIBUS Master Port ........................................................................................ 144
Supported PROFIBUS Services ........................................................................... 145
Constructing a Bus Cable for PROFIBUS DP ....................................................... 146
7 Support, Service & Warranty 151
Contacting Technical Support ......................................................................................................... 151
7.1
7.2
7.1.1
7.1.2
7.1.3
7.2.1
7.2.2
7.2.3
7.2.4
7.2.5
7.2.6
7.2.7
7.2.8
7.2.9
7.2.10
Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions.............................. 153
Returning Any Product .......................................................................................... 153
Returning Units Under Warranty ........................................................................... 154
Returning Units Out of Warranty ........................................................................... 154
LIMITED WARRANTY ........................................................................................... 155
What Is Covered By This Warranty ....................................................................... 155
What Is Not Covered By This Warranty ................................................................ 156
Disclaimer Regarding High Risk Activities ............................................................ 156
Intellectual Property Indemnity .............................................................................. 157
Disclaimer of all Other Warranties ........................................................................ 157
Limitation of Remedies ** ...................................................................................... 158
Time Limit for Bringing Suit ................................................................................... 158
No Other Warranties ............................................................................................. 158
Allocation of Risks ................................................................................................. 158
Controlling Law and Severability ........................................................................... 158
Index 159
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 7 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 8

Contents MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Page 8 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 9

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Guide to the MVI46-PDPMV1 User Manual
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Guide to the MVI46-PDPMV1 User Manual
Function
Introduction
(Must Do)
Diagnostic and
Troubleshooting
Reference
Product Specifications
Support, Service, and
Warranty
Index
Section to Read Details
Start Here (page 11) This section introduces the customer to the
→
Diagnostics and
→
Troubleshooting
(page 95)
Reference (page
→
111)
Product
Specifications (page
112)
Support, Service
→
and Warranty (page
151)
Index
module. Included are: package contents,
system requirements, hardware installation, and
basic configuration.
This section describes Diagnostic and
Troubleshooting procedures.
These sections contain general references
associated with this product and its
Specifications..
This section contains Support, Service and
Warranty information.
Index of chapters.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 9 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 10

Guide to the MVI46-PDPMV1 User Manual MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Page 10 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 11

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Start Here
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
1 Start Here
In This Chapter
System Requirements ........................................................................... 12
Package Contents ................................................................................. 13
Installing ProSoft Configuration Builder Software .................................. 14
Setting Jumpers .................................................................................... 15
Installing the Module in the Rack ........................................................... 16
Connecting Your PC to the Processor ................................................... 18
Downloading the Sample Program to the Processor ............................. 19
Connecting Your PC to the Module ....................................................... 22
To get the most benefit from this User Manual, you should have the following
skills:
Rockwell Automation® RSLogix™ software: launch the program, configure
ladder logic, and transfer the ladder logic to the processor
Microsoft Windows: install and launch programs, execute menu commands,
navigate dialog boxes, and enter data
Hardware installation and wiring: install the module, and safely connect
PROFIBUS DPV1 and SLC devices to a power source and to the MVI46PDPMV1 module’s application port(s)
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 11 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 12

Start Here MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
1.1 System Requirements
The MVI46-PDPMV1 module requires the following minimum hardware and
software components:
Rockwell Automation SLC 5/02 M0/M1 capable processors (or newer), with
compatible power supply and one free slot in the rack, for the MVI46PDPMV1 module. The module requires 800mA of available power.
Rockwell Automation RSLogix 500 programming software.
Rockwell Automation RSLinx communication software
Pentium® II 500 MHz minimum. Pentium III 733 MHz (or better)
recommended
Supported operating systems:
o
Microsoft® Windows 98
o
Windows NT® (version 4 with SP4 or higher)
o
Windows 2000
o
Windows XP
32 Mbytes of RAM minimum, 64 Mbytes of RAM recommended
50 Mbytes of free hard disk space (or more based on application
requirements)
16-color VGA graphics adapter, 640 x 480 minimum resolution (256 Color
800 × 600 recommended)
CD-ROM drive
Page 12 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 13

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Start Here
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
1.2 Package Contents
The following components are included with your MVI46-PDPMV1 module, and
are all required for installation and configuration.
Important: Before beginning the installation, please verify that all of the following items are
present.
Qty. Part Name Part Number Part Description
1 MVI46-PDPMV1
Module
1 Cable Cable #15, RS232
1 Cable Cable #14, RJ45 to
If any of these components are missing, please contact ProSoft Technology
Support for replacement parts.
MVI46-PDPMV1 PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
For RS232 Connection to the CFG Port
Null Modem
For DB9 Connection to Module’s Port
DB9 Male Adapter
cable
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 13 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 14

Start Here MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
1.3 Installing ProSoft Configuration Builder Software
You must install the ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) software to configure
the module. You can always get the newest version of ProSoft Configuration
Builder from the ProSoft Technology website.
To install ProSoft Configuration Builder from the ProSoft Technology website
1 Open your web browser and navigate to http://www.prosoft-
technology.com/pcb
2 Click the D
Configuration Builder.
3 Choose S
4 Save the file to your Windows Desktop, so that you can find it easily when
you have finished downloading.
5 When the download is complete, locate and open the file, and then follow the
instructions on your screen to install the program.
If you do not have access to the Internet, you can install ProSoft Configuration
Builder from the ProSoft Solutions Product CD-ROM, included in the package
with your module.
To install ProSoft Configuration Builder from the Product CD-ROM
1 Insert the ProSoft Solutions Product CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive of your
PC. Wait for the startup screen to appear.
2 On the startup screen, click P
Windows Explorer file tree window.
3 Click to open the U
and files you will need to set up and configure your module.
4 Double-click the S
PCB_*.
software on your PC. The information represented by the "*" character in the
file name is the PCB version number and, therefore, subject to change as
new versions of PCB are released.
OWNLOAD HERE
AVE
or S
AVE FILE
TILITIES
ETUP CONFIGURATION TOOL
EXE
file and follow the instructions on your screen to install the
link to download the latest version of ProSoft
when prompted.
RODUCT DOCUMENTATION
folder. This folder contains all of the applications
folder, double-click the
. This action opens a
Note: Many of the configuration and maintenance procedures use files and other utilities on the
CD-ROM. You may wish to copy the files from the Utilities folder on the CD-ROM to a convenient
location on your hard drive.
Page 14 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 15
MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Start Here
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
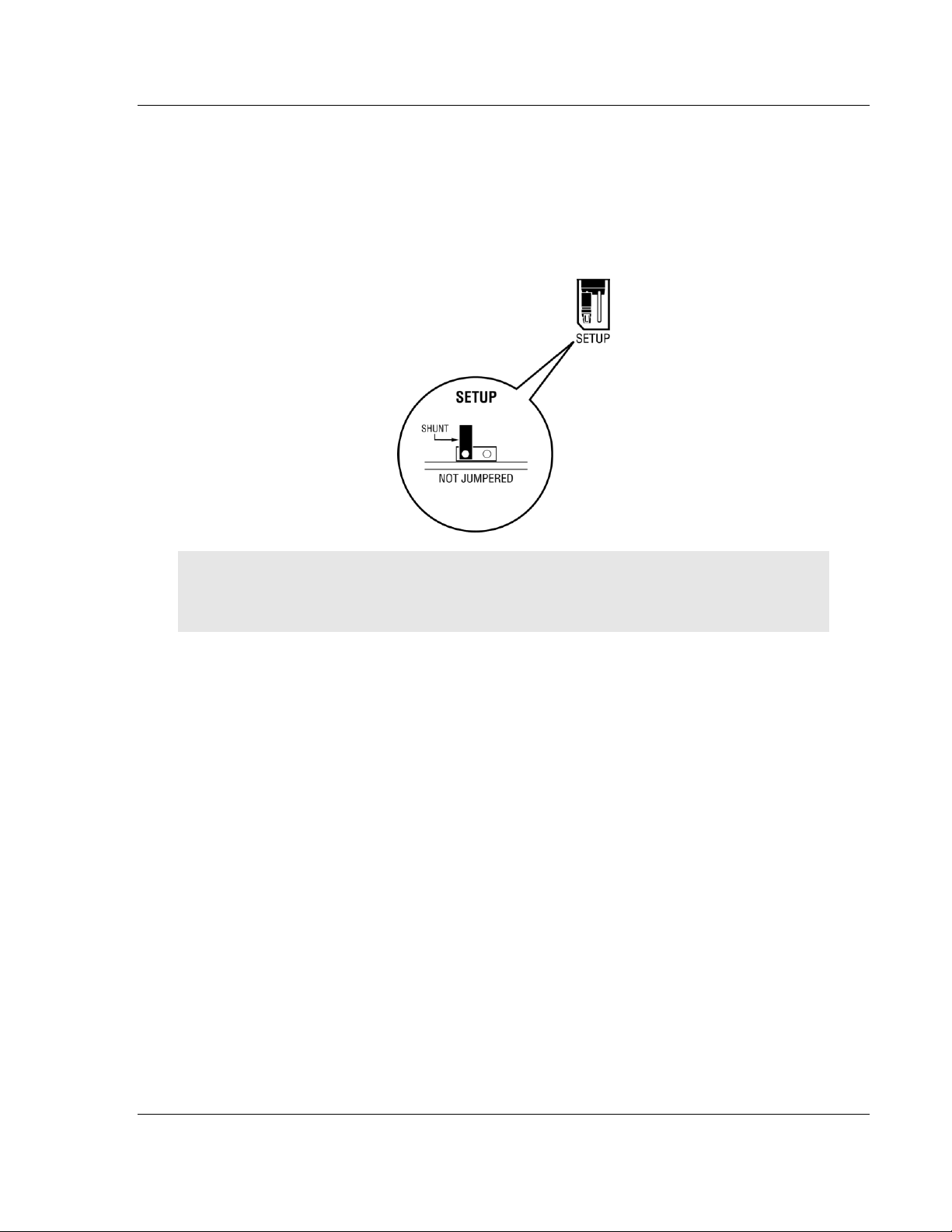
1.4 Setting Jumpers
The Setup Jumper acts as "write protection" for the module’s flash memory. In
"write protected" mode, the Setup pins are not connected, and the module’s
firmware cannot be overwritten. Do not jumper the Setup pins together unless
you are directed to do so by ProSoft Technical Support.
The following illustration shows the MVI46-PDPMV1 jumper configuration.
Note: If you are installing the module in a remote rack, you may prefer to leave the Setup pins
jumpered. That way, you can update the module’s firmware without requiring physical access to
the module.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 15 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 16
Start Here MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
1.5 Installing the Module in the Rack
If you have not already installed and configured your SLC processor and power
supply, please do so before installing the MVI46-PDPMV1 module. Refer to your
Rockwell Automation product documentation for installation instructions.
Warning: You must follow all safety instructions when installing this or any other electronic
devices. Failure to follow safety procedures could result in damage to hardware or data, or even
serious injury or death to personnel. Refer to the documentation for each device you plan to
connect to verify that suitable safety procedures are in place before installing or servicing the
device.
After you have checked the placement of the jumpers, insert MVI46-PDPMV1
into the SLC™ chassis. Use the same technique recommended by Rockwell
Automation to remove and install SLC™ modules.
Warning: This module is not hot-swappable! Always remove power from the rack before
inserting or removing this module, or damage may result to the module, the processor, or other
connected devices.
1 Turn power OFF.
2 Align the module with the top and bottom guides, and slide it into the rack
until the module is firmly against the backplane connector.
3 With a firm but steady push, snap the module into place.
Page 16 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 17

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Start Here
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4 Check that the holding clips on the top and bottom of the module are securely
in the locking holes of the rack.
5 Make a note of the slot location. You will need to identify the slot in which the
module is installed in order for the sample program to work correctly. Slot
numbers are identified on the green circuit board (backplane) of the SLC
rack.
6 Turn power ON.
Note: If you insert the module improperly, the system may stop working, or may behave
unpredictably.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 17 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 18
Start Here MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
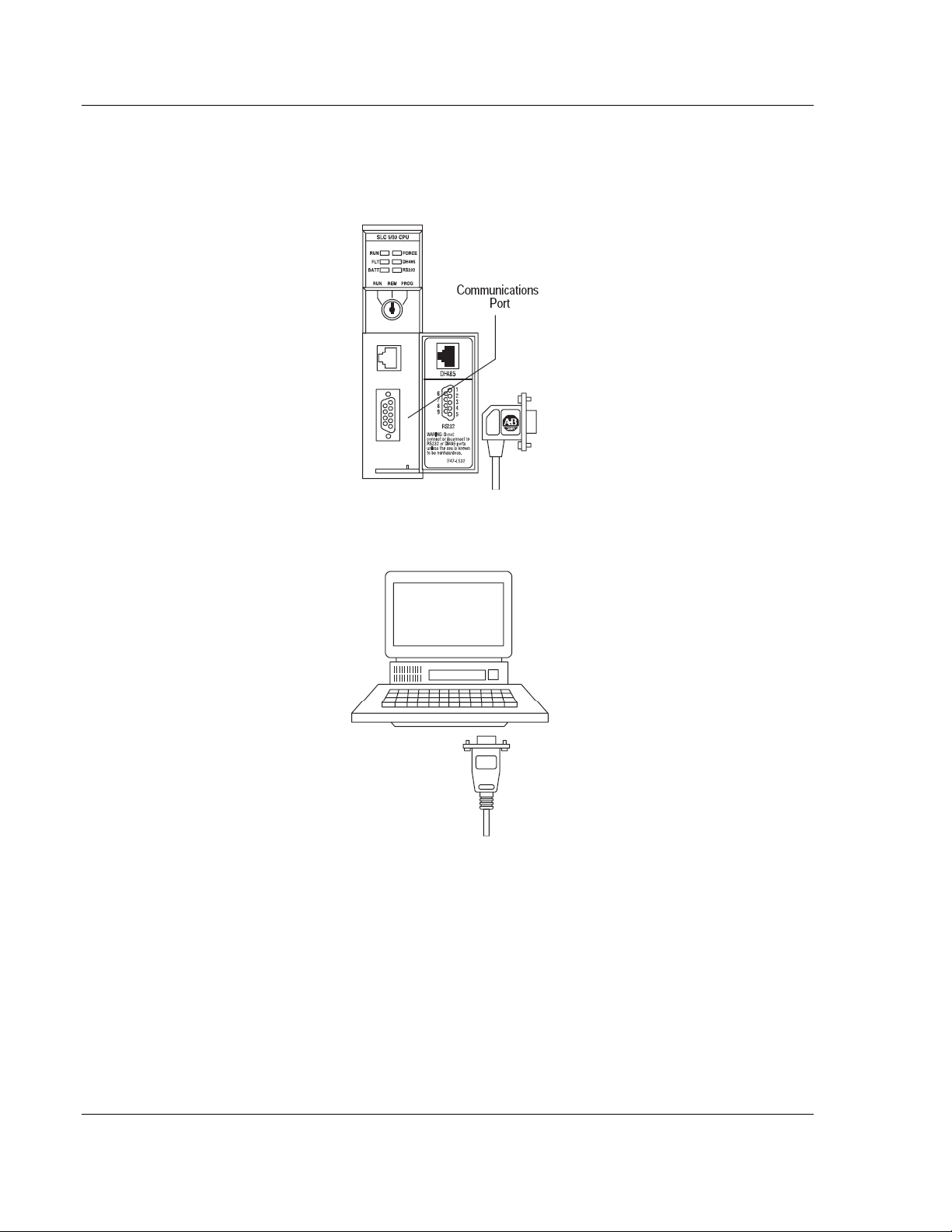
1.6 Connecting Your PC to the Processor
1 Connect the right-angle connector end of the cable to your controller at the
communications port.
2 Connect the straight connector end of the cable to the serial port on your
computer.
Page 18 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 19
MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Start Here
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
1.7 Downloading the Sample Program to the Processor
To download the sample program from RSLogix 500 to the SLC processor
Note: The key switch on the front of the SLC processor must be in the REM position.
1 If you are not already online to the processor, open the C
menu, and then choose D
with the processor.
OWNLOAD
. RSLogix will establish communication
OMMUNICATIONS
2 Click the D
OWNLOAD
button to transfer the sample program to the processor.
3 RSLogix will compile the program and transfer it to the processor. This
process may take a few minutes.
4 When the download is complete, RSLogix will open another confirmation
dialog box. Click YES to switch the processor from Program mode to Run
mode.
Note: If you receive an error message during these steps, refer to your RSLogix documentation to
interpret and correct the error.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 19 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 20
Start Here MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
1.7.1 Configuring the RSLinx Driver for the PC COM Port
If RSLogix is unable to establish communication with the processor, follow these
steps.
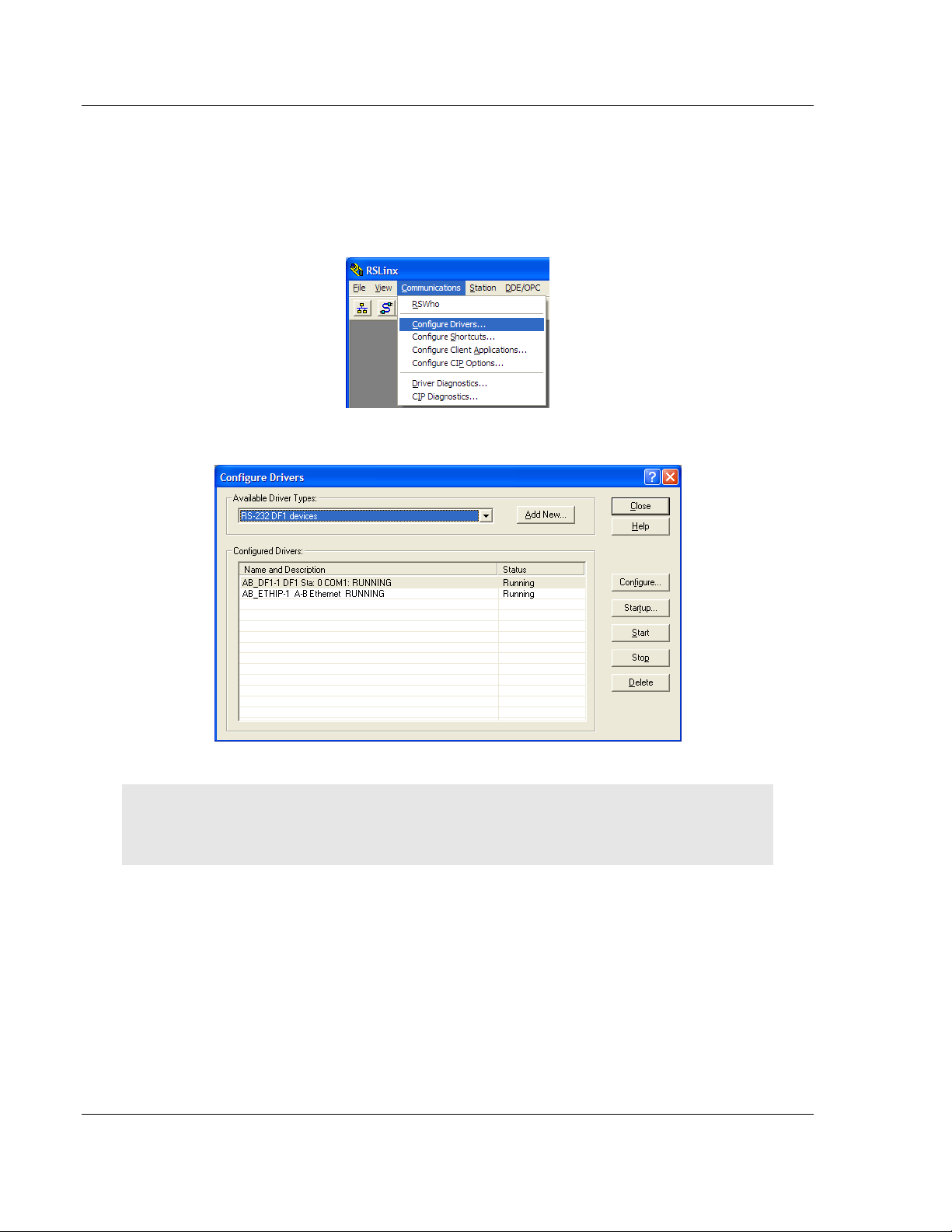
1 Open RSLinx.
2 Open the C
This action opens the Configure Drivers dialog box.
OMMUNICATIONS
menu, and choose C
ONFIGURE DRIVERS
.
Note: If the list of configured drivers is blank, you must first choose and configure a driver from the
Available Driver Types list. The recommended driver type to choose for serial communication with
the processor is RS-232 DF1 Devices.
Page 20 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 21
MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Start Here
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
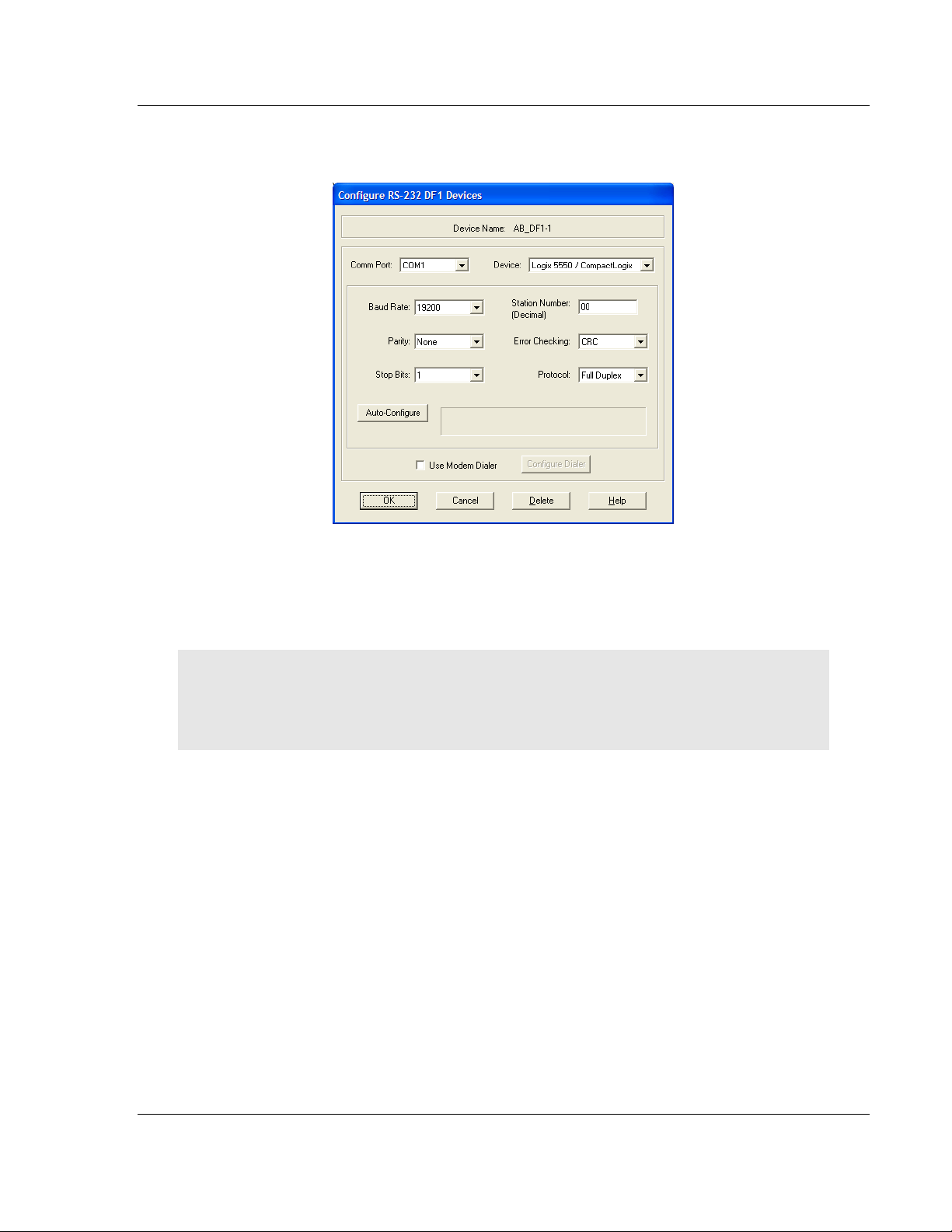
3 Click to select the driver, and then click C
ONFIGURE
. This action opens the
Configure RS-232 DF1 Devices dialog box.
4 Click the A
UTO-CONFIGURE
button. RSLinx will attempt to configure your
serial port to work with the selected driver.
5 When you see the message Auto Configuration Successful, click the OK
button to dismiss the dialog box.
Note: If the auto-configuration procedure fails, verify that the cables are connected correctly
between the processor and the serial port on your computer, and then try again. If you are still
unable to auto-configure the port, refer to your RSLinx documentation for further troubleshooting
steps.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 21 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 22

Start Here MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
1.8 Connecting Your PC to the Module
With the module securely mounted, connect your PC to the Configuration/Debug
port using the RJ45-DB-9 Serial Adapter Cable and the Null Modem Cable
included in the package with the MVI46-PDPMV1 module.
1 Connect the RJ45-DB-9 Serial Adapter Cable to the Null Modem Cable.
2 Insert the RJ45 cable connector from the RJ45-DB-9 cable into the
Configuration/Debug port of the module.
3 Attach the other end to the serial port on your PC.
Page 22 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 23

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
2 Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
In This Chapter
Setting Up the Project ........................................................................... 24
Setting Module Parameters ................................................................... 26
Configuring the PROFIBUS Master ....................................................... 29
Verifying Correct Operation ................................................................... 50
Because the task of configuring the PROFIBUS network can be challenging,
ProSoft Technology has provided a configuration tool called ProSoft
Configuration Builder (PCB) that will help you with the following tasks:
Creating a configuration project (page 24)
Setting module parameters (page 26)
Configuring the PROFIBUS network (page 29) (Master and slaves)
Downloading the project to the module (page 47)
The following topics of this chapter explain each task step-by-step.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 23 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 24
Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
2.1 Setting Up the Project
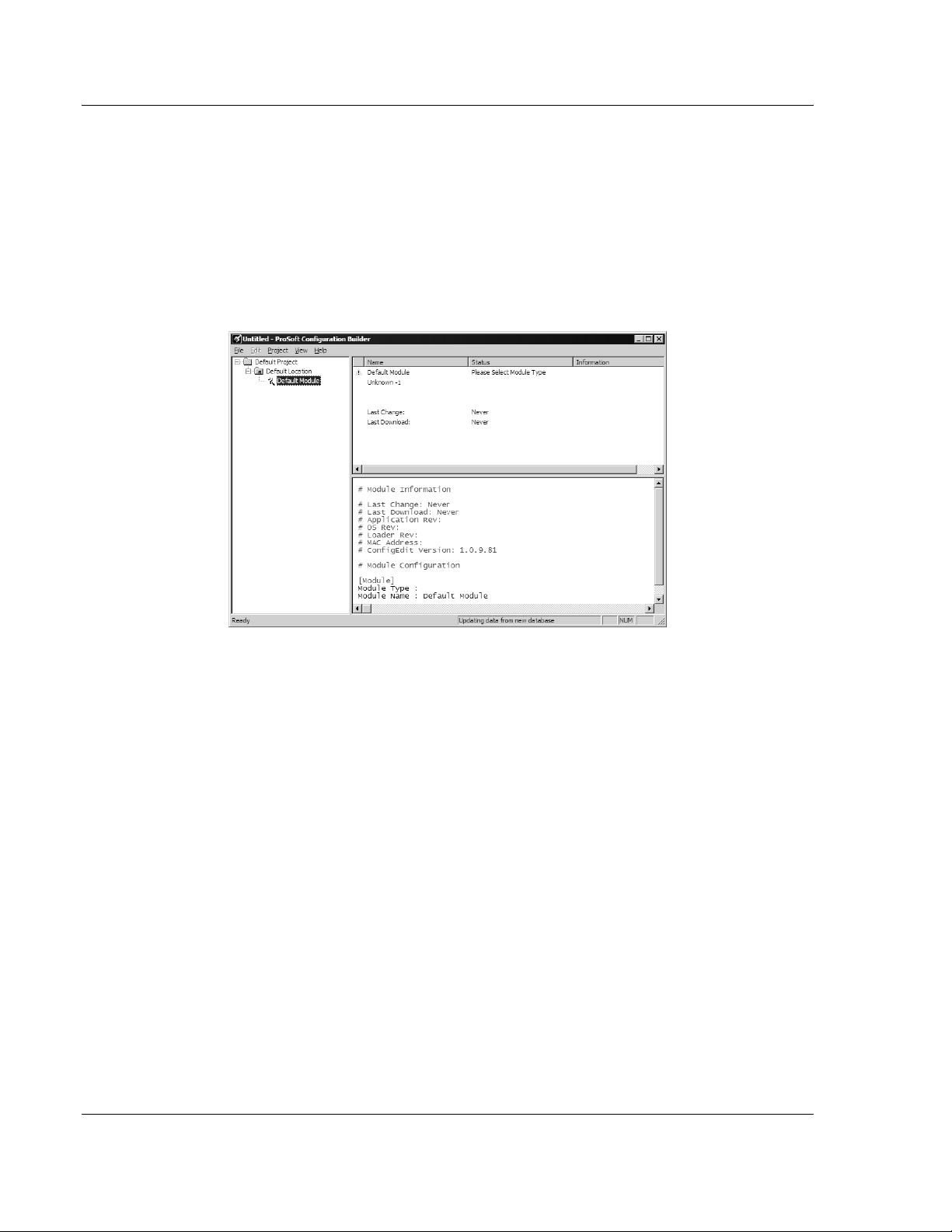
To begin, start ProSoft Configuration Builder. If you have used other Windows
configuration tools before, you will find the screen layout familiar. ProSoft
Configuration Builder’s window consists of a tree view on the left, and an
information pane and configuration pane on the right side of the window. When
you first start ProSoft Configuration Builder, the tree view consists of folders for
Default Project and Default Location, with a Default Module in the Default
Location folder. The following illustration shows the ProSoft Configuration Builder
window with a new project.
Your first task is to add the MVI46-PDPMV1 module to the project.
1 Use the mouse to select D
EFAULT MODULE
in the tree view, and then click the
right mouse button to open a shortcut menu.
Page 24 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 25
MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
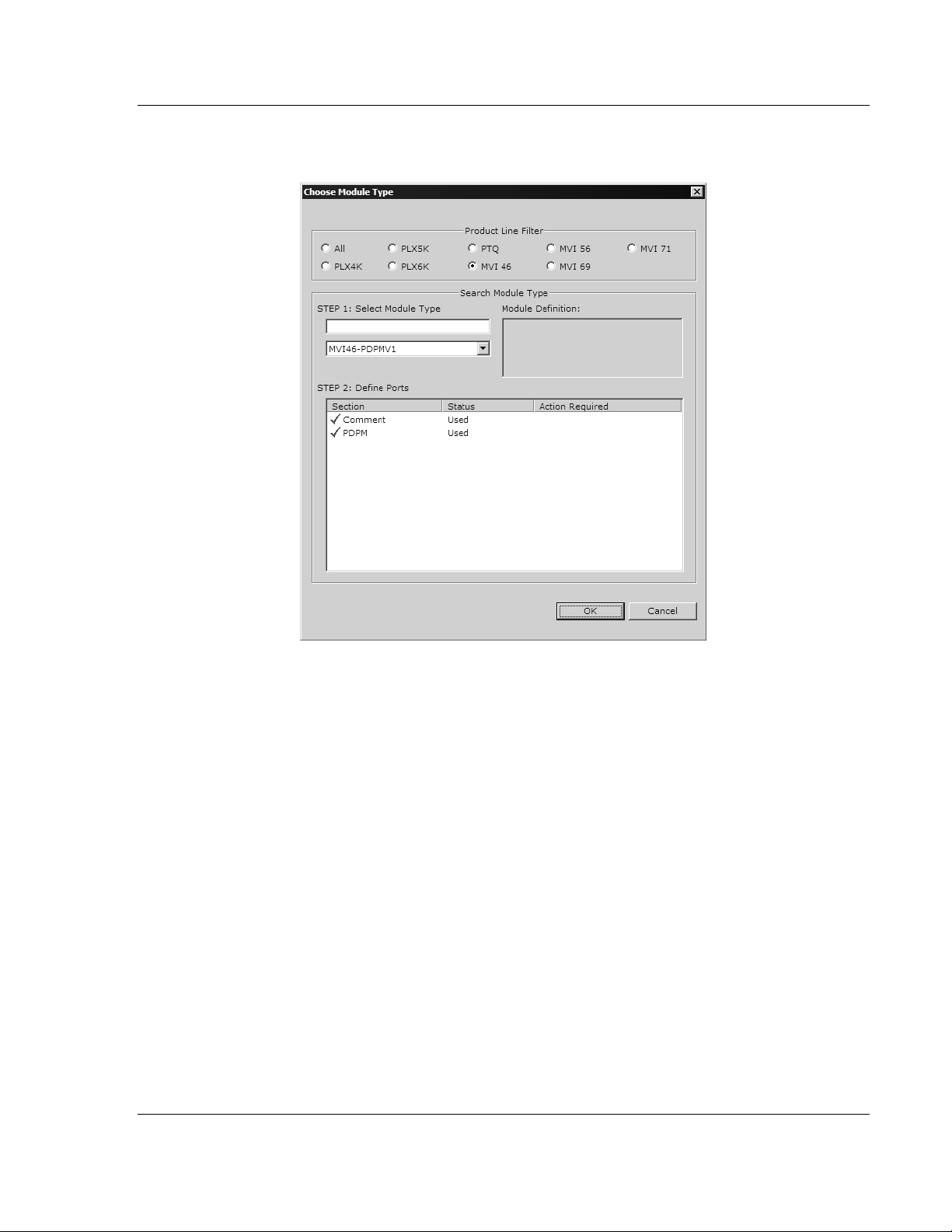
2 On the shortcut menu, select C
HOOSE MODULE TYPE
. This action opens the
Choose Module Type dialog box.
3 In the Product Line Filter area of the dialog box, select MVI46. In the Select
Module Type dropdown list, select MVI46-PDPMV1, and then click OK to
save your settings and return to the ProSoft Configuration Builder window.
The next task is to set the module parameters.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 25 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 26
Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
2.2 Setting Module Parameters
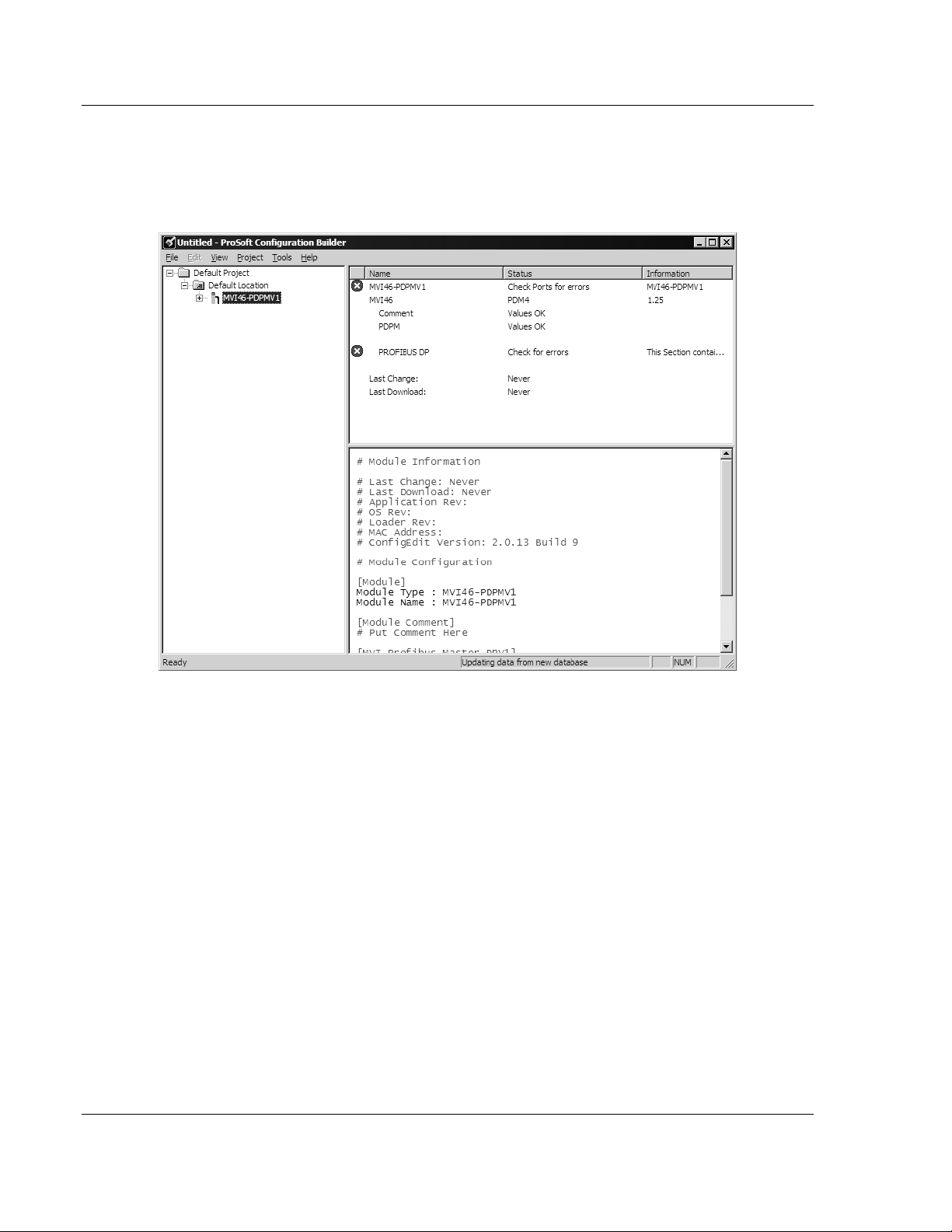
Notice that the contents of the information pane and the configuration pane
changed when you added the MVI46-PDPMV1 module to the project. The red
"X" icon indicates that the module’s configuration is incomplete.
In the following steps, you will provide the missing information to begin
configuring the module.
1 Click the plus sign [+] next to the module icon to expand the module tree, and
then expand the MVI PDPM-V1 tree.
2 Double-click the MVI P
ROFIBUS MASTER
DPV1 icon. This action opens the
Edit dialog box.
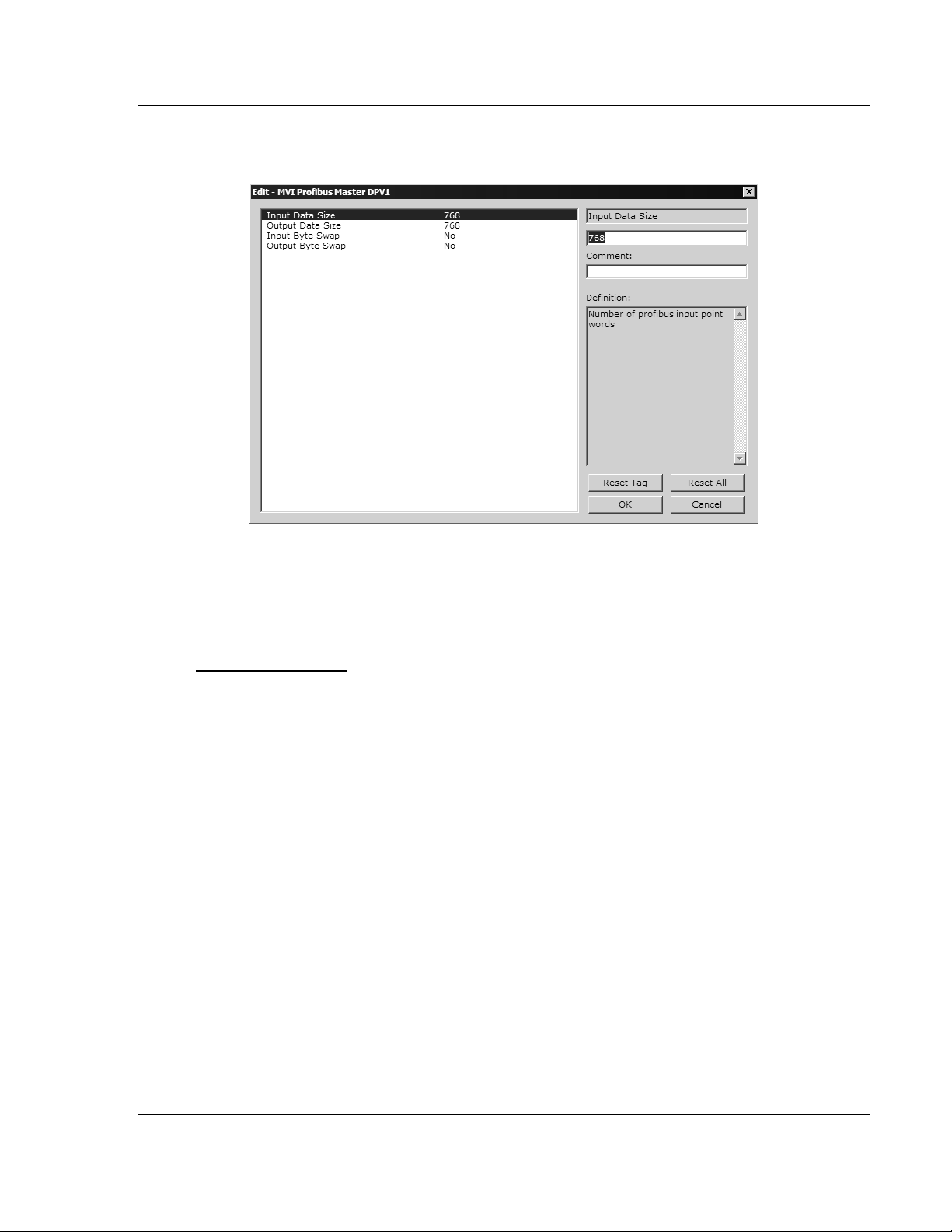
3 In the Edit dialog box, configure the values for Input Data Size and Output
Data Size (PROFIBUS input and output point words) to match the values
required by your application. To change a value, select the parameter to
modify in the left pane, and then type the new value in the edit field in the
right pane.
Page 26 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 27
MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
For the sample application, the Input Data Size and Output Data Size values
should both be 768.
4 Click OK to save your settings and return to the ProSoft Configuration Builder
window.
At this time, you may wish to rename the Default Project and Default Location
folders in the tree view.
To rename an object
1 Select the object, and then click the right mouse button to open a shortcut
menu. From the shortcut menu, choose R
ENAME
.
2 Type the name to assign to the object.
3 Click away from the object to save the new name.
2.2.1 Input Data Size
0 to 768
Number of words to transfer from the PROFIBUS input image to the controller.
2.2.2 Output Data Size
0 to 768
Number of words to transfer to the PROFIBUS output image from the controller.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 27 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 28

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
2.2.3 Input Byte Swap
YES or NO
This parameter determines if the bytes in the PROFIBUS Input Data area are
swapped before being stored in the module memory database. If the parameter
is set to NO, no swapping will be applied. If the parameter is set to YES, the order
of bytes in each word will be swapped before being stored in memory.
Example:
With Input Byte Swap set to NO, incoming order is unchanged - ABCDEF
With Input Byte Swap set to YES, each byte pair is swapped - BADCFE
2.2.4 Output Byte Swap
YES or NO
This parameter determines if the bytes in the PROFIBUS Output Data area are
swapped before being transmitted to slaves on the PROFIBUS network. If the
parameter is set to NO, no swapping will be applied. If the parameter is set to
YES, the order of bytes in each word will be swapped before being transmitted.
Example:
With Output Byte Swap set to NO, outgoing output order is unchanged -
ABCDEF
With Output Byte Swap set to YES, each output byte pair is swapped -
BADCFE
Page 28 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 29
MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
2.3 Configuring the PROFIBUS Master
In this task, you will configure the PROFIBUS Master, and then add PROFIBUS
slaves to the PROFIBUS network. When this step is complete, you will download
the configuration information to the MVI46 module. You will also export the I/O
maps for the processor.
1 In PCB tree view, click [+] to expand the MVI46-PDPMV1 tree, and then
double-click the PROFIBUS DP icon. This action opens the PDPMV1
PROFIBUS Master Setup dialog box.
2 In the PDPMV1 PROFIBUS Master Setup dialog box, click the C
PROFIBUS button. This action opens the ProSoft Configuration Builder for
PROFIBUS application.
3 Click [+] to expand the PROFIBUS Master tree.
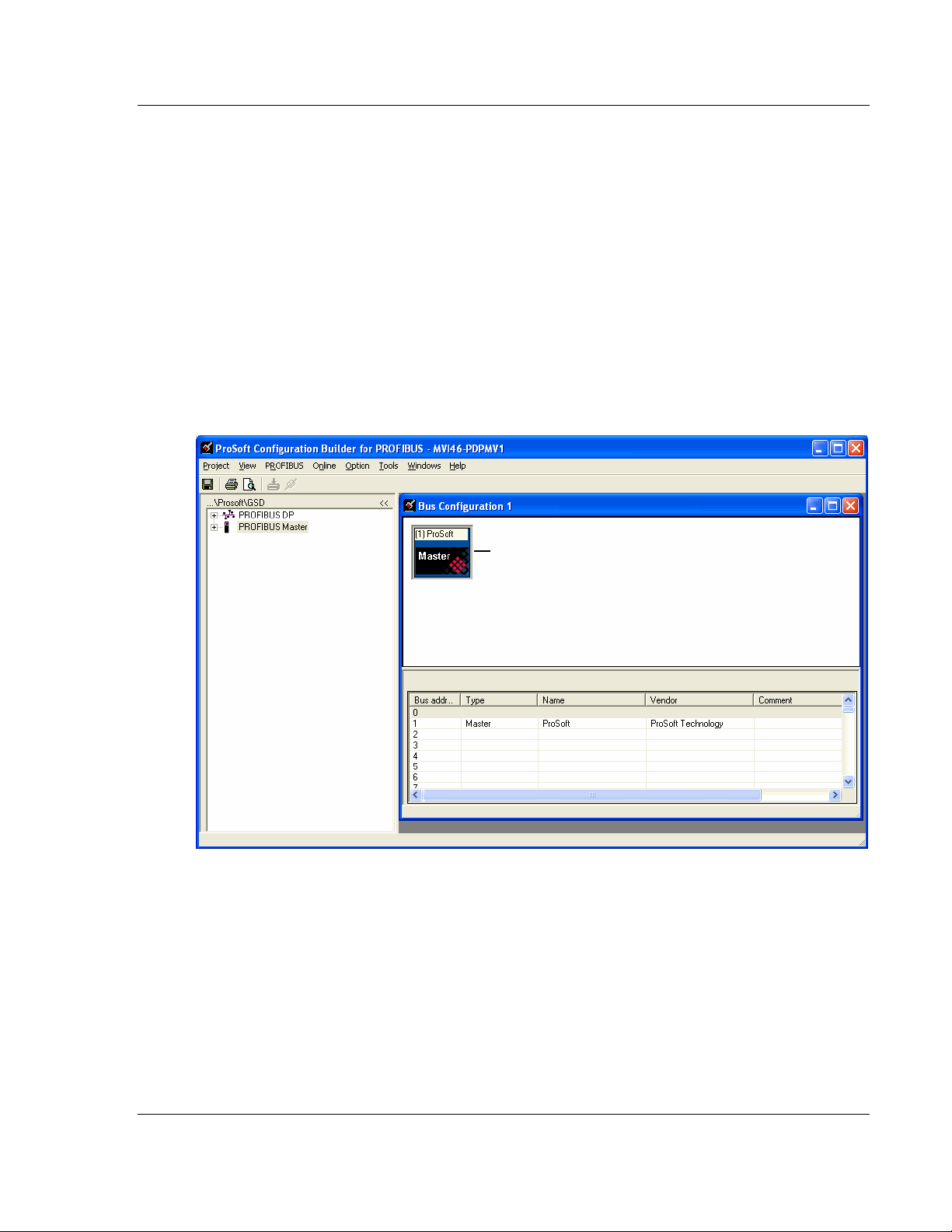
4 Drag the PROFIBUS Master icon into the Bus Configuration window. This is
automatically done by the software for new applications.
ONFIGURE
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 29 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 30
Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
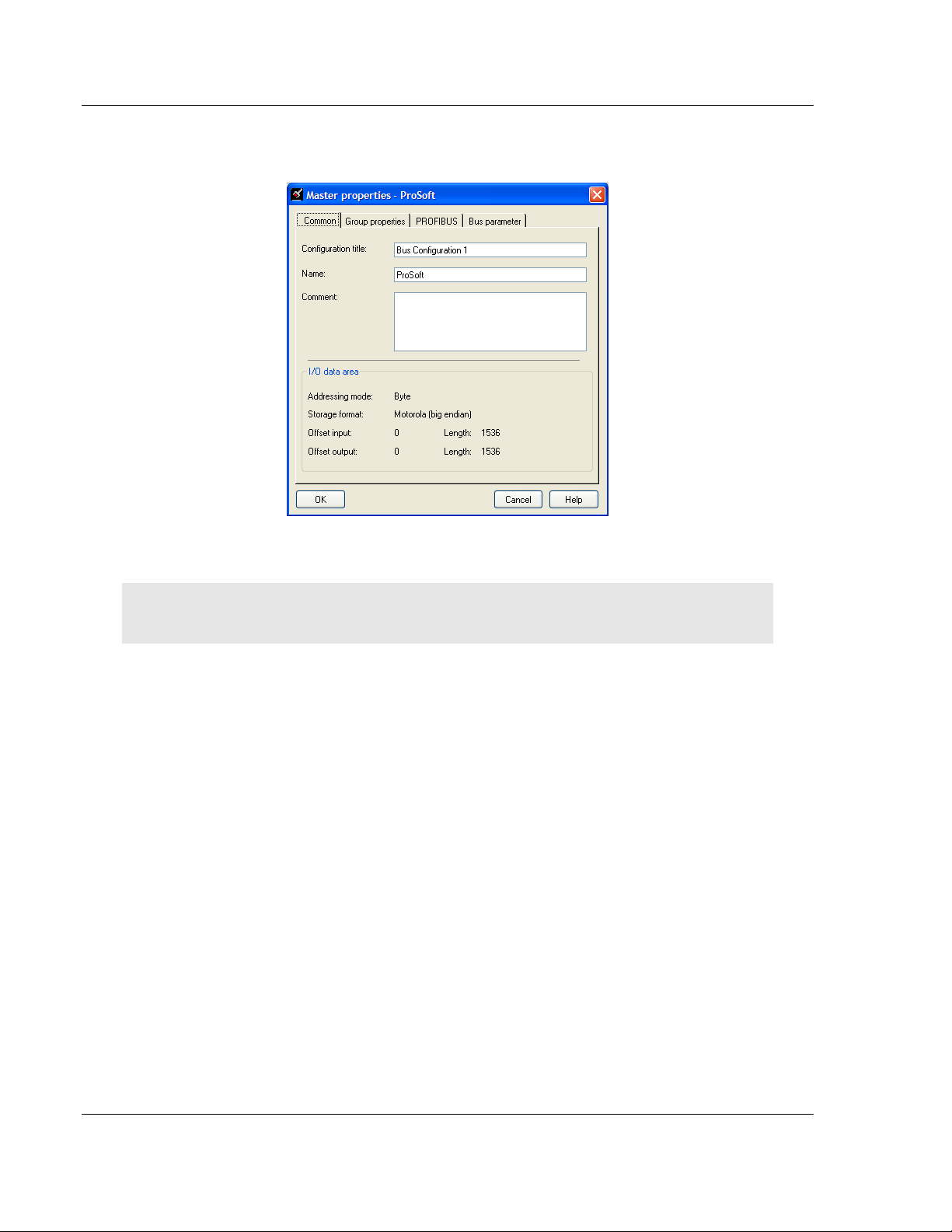
5 Double-click the PROFIBUS Master icon in the Bus Configuration window.
This action opens the Master Properties dialog box.
6 On the Common tab, name your PROFIBUS drop.
Note: The PROFIBUS tab contains the address setting and advanced configuration settings for the
Master. The default settings on this tab work best in most applications.
7 Click OK to save your changes and return to the Bus Configuration window.
2.3.1 Installing the GSD Files
ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) uses PROFIBUS slave device definition files
(GSD files) to obtain basic configuration information about the PROFIBUS slaves
you add to the network. The GSD configuration files identify the slave’s
capabilities so that the MVI46-PDPMV1 can communicate with it correctly. Slave
device manufacturers provide the GSD files for the equipment they make. Slave
device files sometimes come in various languages. When a manufacturer
provides slave device files in several languages, it is a common practice to use
the third letter of the file extension to indicate the language used in the file. For
instance:
o
.GSD is the most commonly used file extension and will usually be in
either English or German
o
.GSE will usually be in English
o
.GSS will usually be in Spanish
o
.GSF will usually be in French
o
other combinations may also be seen, as well as other languages using
the letters indicated above
Follow these steps to install the GSD file or files for your slave device or devices.
Page 30 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 31

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Tip: GSD configuration files for popular PROFIBUS slaves and ProSoft Technology solutions are
included with PCB. Before installing GSD files, browse the list of available slaves in the Tree View
window to see if GSD files for your slave are already installed.
GSD files are often both model number specific as well as model revision specific. Just because
you may have an older GSD file from a manufacturer for the particular make and model of your
slave device does not guarantee it will work for a newer revision of that device. Be sure you obtain
from the device manufacturer the correct GSD file or files for your PROFIBUS slave or slaves.
To install GSD files manually
1 In ProSoft Configuration Builder tree view, click [+] to expand the module
tree, and then double-click the PROFIBUS DP icon. This action opens the
PDPMV1 PROFIBUS Master Setup dialog box.
2 Click the C
ONFIGURE
PROFIBUS button. This action opens the ProSoft
Configuration Builder for PROFIBUS application.
3 Open the T
OOLS
menu, and then choose I
NSTALL NEW
GS*
FILE
. This action
opens a dialog box that allows you to browse for the location of the GSD
configuration files to install. (Depending on the device and language used in
the file, the actual extension may be ".GSD", ".GSE", ".GSS", or other
combinations; hence the generic reference to ".GS*" files, where "*" is a
wildcard that stands for any letter.)
4 Choose the file to install, and then click O
PEN
. If the file already exists in the
configuration file path, you will be prompted to overwrite the file.
5 You will be prompted to associate the GSD configuration file with a bitmap
image of the slave device. Use the F
ILE / OPEN
dialog box to browse for the
location of the image file to use. If you have no device-specific bitmap file,
you may C
the Bus Configuration window for this slave device.
ANCEL
the bitmap upload, and a generic device icon will be used in
2.3.2 Configuring the PROFIBUS Slaves
There are two essential steps to configuring a slave:
1 Add the slave in ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) as a device connected
to the PROFIBUS Master, specifying the slave address and any necessary
input and output configuration. Download the PROFIBUS Master
configuration to the MVI46-PDPMV1 module.
2 Configure the slave (using PCB or the configuration tool supplied by the
manufacturer, for some PROFIBUS slaves). Verify that the slave address
configured in the slave module matches the slave address configured in PCB.
Download the PROFIBUS Slave configuration to the slave module.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 31 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 32

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Scanning for Slaves Manually
In this part of the procedure, you will add and configure the PROFIBUS slaves. In
the following steps, you will add and configure a ProLinx PROFIBUS slave
module. The configuration information (.GSD file) for this module is provided on
the MVI46-PDPMV1 Solutions CD-ROM.
1 In ProSoft Configuration Builder for PROFIBUS, click the plus sign [+] to
expand the PROFIBUS DP tree.
2 Navigate to the folder containing the type of slave device to add, and then
click the plus sign [+] to expand the folder.
3 Drag the slave icon into the Bus Configuration window. The slave device
appears in the Bus Configuration window as a network location to the Master.
Page 32 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 33

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4 In the tree view, click the plus sign [+] to expand the slave device you added.
This action opens a list of device configuration values. The following
illustration shows the device configuration values for a ProLinx PROFIBUS
slave. The values for other devices may be different, so you should review
the specifications for the product you are installing in order to determine the
correct values to use.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 33 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 34

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
5 Drag the input and output parameters to the slot location grid below the Bus
Configuration window. This view displays the configuration data, order
number, and starting input and output addresses.
6 Double-click the slave icon to view the slave device properties.
Page 34 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 35

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
In particular, note the following settings:
o
Automatic PROFIBUS Address Assignment:
ProSoft Configuration Builder automatically assigns a PROFIBUS address
to each new slave. The address assignment begins at address 3, and is
incremented by 1 for each new slave added to the network. You can
change the address in the Common tab of the Slave Properties dialog
box.
o
Automatic Input/Output Address Assignment:
For each new slave added to the PROFIBUS network, ProSoft
Configuration Builder automatically converts the input/output byte
addresses to word input/output addresses for the State RAM in the
processor.
7 Repeat steps 2 through 6 for all slaves you intend to place on the network.
8 When you are finished adding slaves, open the Project menu and choose
E
XIT
to return to the Master Setup dialog box.
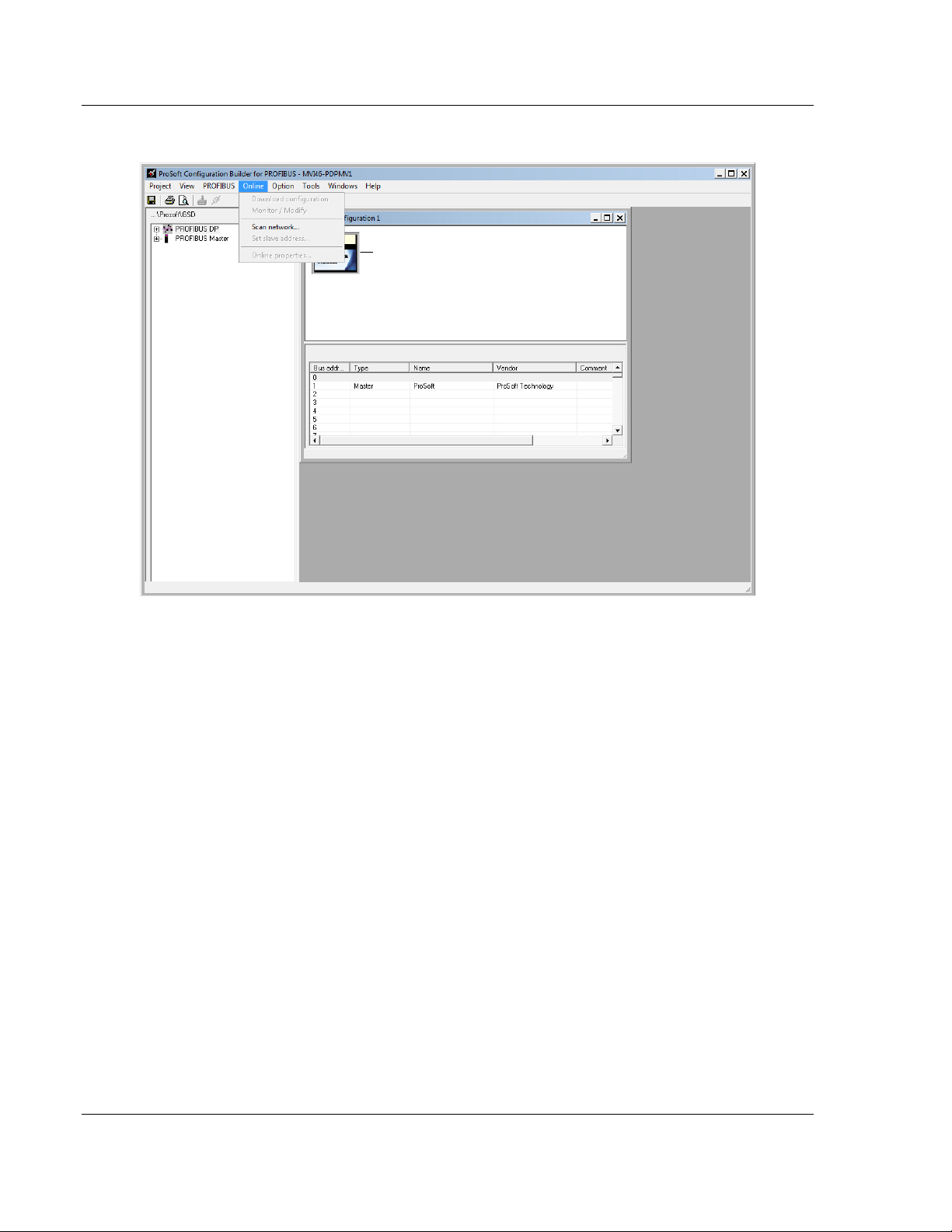
Using The Autoscan Feature
The concept of Automatic network scanning means that the user can instruct the
Bus Configuration window to automatically gather information about slaves that
are connected to the network. When the scan is completed the user can adopt
the detected slaves to the bus configuration and download to the Master.
This is a quick way to get a network up and running. However, one should be
aware that it is not guaranteed that any particular slave will enter data exchange
since the user parameter data might not match. This is especially obvious if no
associated GSD-file is found during the network scan, this means that no user
parameter data would be sent to the slave.
N
ETWORK SCAN
down menu for the M
is selectable from the Online menu as well as from the drop-
ASTER
icon.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 35 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 36
Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
When the download is completed, the PROFIBUS Master Configuration window
will initialize the Master to operate as a Class 2 Master only. In this mode it is
possible to initialize the Master even if the database does not contain any slaves.
After successful initialization, the PROFIBUS Master Configuration window will
issue the following mailboxes in order to gather information about the connected
slaves:
1 1. Send FB_APPL_GET_LIVE_LIST in order to detect connected slaves,
2 2. Send FB_APPL_GET_SLAVE_DIAG (external request) to all devices
identified as slaves according to the Live list.
3 3. Send FB_APPL_GET_SLAVE_CONFIG to all devices identified as slaves
according to the Live list.
Page 36 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 37

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
When the information is collected the PROFIBUS Master Configuration window
will find a matching GSD-file and extract information from it. Refer to the
flowchart below for this sequence:
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 37 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 38

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
GSD Selection Algorithm
If two or more matching GSD-files are found, the first one found should be
selected. The other compatible files should be stored so that the user can select
one of them instead. If the user selects another GSD-file, the PROFIBUS Master
Configuration window will run through the Module Selection Algorithm (described
below) again.
Module Selection Algorithm
The algorithm used to find modules in the GSD based on the Identifier byte(s) is
as follows:
Select the module that matches the largest number of Identifier bytes. If the GSD
contains two or more modules with the exact set of Identifier bytes, use the first
module found.
Example:
If a slave responds with identifier bytes: 0x11, 0x21, 0x31 and that the associated
GSD-file contains five modules: “A” = 0x11, “B” = 0x21, “C” = 0x31, “AB” = 0x11,
0x21 and “BC” = 0x21, 0x31. The PROFIBUS Master Configuration window will
then select modules "AB" and "C".
Note: If no matching module is found in the GSD, The PROFIBUS Master Configuration window
will display the identifier byte(s) instead.
Network scan window
The information extracted from the GSD-file(s) will be displayed in the Network
scan window.
Select
In this column all found slaves will be marked as selected by default, except for
slaves with the special address 126 (refer to the next section that describes the
Address column). Only selected slaves will be added to the PROFIBUS Master
Configuration when the A
DOPT SELECTED SLAVES
button is clicked.
Address
In this column the node address of the slaves will be displayed. Found slaves
should be listed in ascending order according to their node addresses.
Page 38 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 39

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Special address 126 -Set Slave address:
If a slave with node address 126 is detected during the network scan, the
PROFIBUS Master Configuration window will display the address in red color. It
will not be possible for the user to adopt the slave to the configuration since it is
not allowed to exchange data with devices having this address. The check box in
the Select column will be grayed out.
To be able to adopt a slave with address 126 the user must first assign a valid
address by clicking the icon next to the node address. By doing so the Set Slave
Address dialog box is started.
Note that the Old slave address is preset to a value of 126 that is not editable (grayed out).
If the Slave is in the configuration already then it will not affect the addressing.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 39 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 40

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Example:
After scanning, the network finds these other slaves: 2, 6, 25, and 40
Slaves 2, 6, and 25 are found, but are marked as in the bus configuration (the
mapping of the inputs and outputs will not be affected)
Slaves 40 is new and could be added and the input/output addressing will be
appended to the end as shown on the last screen.
Page 40 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 41

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
The PROFIBUS Master Configuration window will prevent the user from selecting
a New slave address that is already occupied by another device; this includes
detected Master stations as well. If the user selects an occupied address, a
message similar to the one shown here will open.
When an address has been successfully assigned, the PROFIBUS Master
Configuration window will update the Network scan window as shown here. The
node address will be updated to the one that the user selected in the Set Slave
dialog box.
Slave
In this column the name of the slave as stated in the assigned GSD-file will be
displayed. If no matching GSD-file is found the Ident number will be displayed in
red color in the drop-down list.
Module
This column shows the name of the module(s) as stated in the assigned GSDfile, which matches the Identifier byte(s) derived from the GetCfg mailbox
message. If no GSD-file or no matching module is found the Identifier byte(s) will
be displayed in red color. If the configuration for a slave is constructed of several
modules, the modules will be listed under each other.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 41 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 42

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
If there is more than one module in the GSD-file that matches the Identifer bytes,
the first matching module will be displayed in blue color in a drop-down list. The
drop-down list will contain all other matching modules so that the user can select
the desired one.
Note: Only modules that have the exact same Identifer bytes as the first matching module will be
displayed in the drop-down list.
GSD-file
This column shows the name of the GSD-file that matches the Ident number
derived from the SlaveDiag mailbox message. If there are more files with the
same Ident number in the device catalog, the first matching GSD-file will be
displayed in blue color in a drop-down list.
This could be the case if the device catalog contains two or more brand labeled
devices, or GSD-files for two or more languages (for example NICEDEV.GSD
and NICEDEV.GSE) exist.
Note: If the user selects another GSD-file, The PROFIBUS Master Configuration window will
update the modules for that slave accordingly.
Page 42 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 43

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
If no GSD-file is found the user will be able to copy the expected GSD to the
device catalog by clicking the icon next to the text No GSD found. This will start
the Install new GS*-file dialog box. When the file is installed, the PROFIBUS
Master Configuration window will verify that the installed file matches the slave
and update the modules for the slave accordingly.
Rescan
Pressing the Y
ES
button will trigger a new network scan. Before proceeding with
the scan a message similar to the one below will appear. If a new scan is
accepted, detected slaves found during the previous scan will be lost.
Note: The autoscan function cannot delete slaves in the current configuration, it can only change (if
slaves differs) or add. The slave must be manually removed from the bus configuration in order to
be able to add it again via the scan window.
Adopt selected slaves
Pressing this button will cause all selected slaves to be adopted to the
PROFIBUS Master Configuration window. Before carrying on with this action a
message similar to the one below will appear.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 43 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 44

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
If accepted, the network scan window will close and the PROFIBUS Master
Configuration window will be populated with the slaves that were found during
the network scan.
Note: Slave: is equal to the Ident number and that the Device path: and Order number/designation
fields are left empty.
Cancel and Help
If the C
ANCEL
button is pressed a message similar to the one below will appear.
If the H
ELP
button is pressed the online help will start.
Page 44 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 45

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
2.3.3 Calculating the Checksums
The checksum (CRC) values are calculated from the PROFIBUS configuration
data, and compare the contents of the configuration file in the module with the
value reported by the processor. The checksum (CRC) value allows the
processor to verify that the configuration file is valid, and has not changed since
the last time the configuration file was imported to the processor. Any change to
the contents of the configuration file in either location changes the unique
numeric CRC value for the file.
If the checksum values do not match, the APP STATUS light illuminates on the
module.
1 In the PDPMV1 PROFIBUS Master Setup dialog box, click the Calculate
Checksums button.
2 Make a note of the checksum values so that you can enter them later if
prompted.
2.3.4 Printing the Processor Network Memory Map
The Processor Memory Map dialog box uses the information about your
PROFIBUS Master and slaves to display the data types you configured. You will
need this information to determine the memory areas your application will use in
the SLC processor.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 45 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 46

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
To view or print the Processor Network Memory Map
1 In the Master Setup dialog box, click the S
HOW MEMORY MAP
button, near the
bottom of the window. This action opens the InRAx Data Type dialog box.
2 Notice that there are buttons in the "Display" area of the dialog box to show
inputs and outputs. These input and output maps correspond to the input and
output data you configured for the PROFIBUS slaves (page 31). Notice also
that there are check boxes to display slot numbers and PROFIBUS
addresses.
3 Click P
RINT
to print the input and output maps for reference. Note that you
must do this for both input and output maps.
4 When you have finished printing the processor memory maps, click OK to
close the dialog box. Click OK again to close the Master Setup dialog box.
5 Keep the printed memory maps available so you can refer to them when you
configure the sample ladder logic in RSLogix 500. The sample ladder logic
contains input and output arrays that must be cross-referenced with the
variables.
Page 46 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 47

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
2.3.5 Downloading the Project to the Module Using a Serial COM
Port
For the module to use the settings you configured, you must download (copy) the
updated Project file from your PC to the module.
To download the project file
1 In the tree view in ProSoft Configuration Builder, click once to select the
module.
2 Right-click the module icon to open a shortcut menu. From the shortcut
menu, choose D
PC for a valid com port (this may take a few seconds). When PCB has found
a valid COM port, the Download dialog box will open.
OWNLOAD FROM PC TO DEVICE
. The program will scan your
3 Choose the COM port to use from the dropdown list, and then click the
D
OWNLOAD
button.
The module will perform a platform check to read and load its new settings.
When the platform check is complete, the status bar in the Download dialog
box will display the message Module Running.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 47 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 48

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
2.3.6 Backing Up the Project
In this step, you will create a backup copy of your project and configuration files.
The backup procedure saves your data for reuse on another machine, or allows
you to restore your data in the event of a system failure.
To save your project and configuration files
1 In ProSoft Configuration Builder tree view, click [+] to expand the MVI46-
PDPMV1 tree, and then double-click the PROFIBUS DP icon. This action
opens the PDPMV1 PROFIBUS Master Setup dialog box.
2 In the PDPMV1 PROFIBUS Master Setup dialog box, click the E
M
ASTER CONFIG
button. This action saves the PROFIBUS network
configuration for your module in an XML file. The recommended location for
this file is your My Documents folder.
Tip: You can use the XML file created by ProSoft Configuration Builder in this step to simplify the
task of configuring additional PROFIBUS network modules. Because it saves the entire network
configuration, you can add modules quickly by modifying only the items that are unique for each
device, typically the slot number and I/O addresses. To use this saved configuration, open
Windows Explorer, navigate to the folder where you saved the Master Configuration XML file, and
then drag the file onto the new PROFIBUS DP icon in the ProSoft Configuration Builder tree view.
XPORT
3 In ProSoft Configuration Builder, open the F
ILE
menu, and then choose S
AVE
AS.
4 Name the project file, and click S
AVE
. The recommended location for this file
is your My Documents folder.
Note: All PCB project files and module-related files are automatically saved to C:\PCBExportfFiles.
A complete backup consists of the Project and Master Configuration files, plus
the GSD configuration files. The default location for the GSD files is
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\ProSoft\GSD (Windows
XP / 2000) or C:\My Documents\.
Page 48 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 49

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
PCB does this complete backup for you automatically. The default location for
these backup files is C:\PCBExportFiles. All the files associated with your PCB
configuration will be stored in a folder with the same name as the name you used
to save your PCB configuration (.ppf) file. When you exit PCB, you will be
prompted to overwrite your Export folder files.
If you have made changes to your configuration settings, you should click the
Y
ES
button every time you see this dialog box to have the backup files updated.
Having all the files for your PCB configuration stored in one folder makes it easier
to transfer the application from one system to the other or to send your files to
ProSoft Technical Support when you need assistance.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 49 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 50

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
2.4 Verifying Correct Operation
The final step is to verify that the MVI46-PDPMV1 module is communicating with
the PROFIBUS slave. Choose the method that best suits your connection and
proximity to the modules and the processor.
If you are able to view the module directly: Look at the PROFIBUS LEDs on
the MVI46-PDPMV1 (page 50)
If you are able to connect to the module using ProSoft Configuration Builder
and a serial cable: View the online status of the PROFIBUS network (page
51)
If you are able to connect to the module using ProSoft Configuration Builder
and a serial cable: View the Fieldbus Data from the MVI46-PDPMV1’s
Configuration/Debug menu (page 53)
If you are able to connect to the processor using RSLogix 500: View the Data
Files in RSLogix 500 (page 56)
If you are able to connect to the processor using RSLogix 500: Send a
Mailbox Message in RSLogix 500 (page 58)
2.4.1 Checking the PROFIBUS LEDs on the MVI46-PDPMV1
If all four PROFIBUS LEDs (page 99) are illuminated green, then the
PROFIBUS Master is communicating and exchanging data with all configured
PROFIBUS slaves.
If the COM STAT LED is green and flashing, the PROFIBUS Master is
communicating and exchanging data with at least one of the configured
slaves.
If the COM STAT LED is red, there is a communication or configuration error.
If the COM STAT LED is off, the PROFIBUS Master is not communicating
with any slaves. The most likely reason is that the slaves are not correctly
configured.
After restarting the MVI46-PDPMV1 Master and the PROFIBUS slave, look at
the PROFIBUS cable connection. If all the PROFIBUS LEDs on the MVI46PDPMV1 are illuminated green, then the Master is communicating
successfully with all slaves.
Page 50 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 51

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
2.4.2 Viewing the Online Status of the PROFIBUS Network
Note: For this procedure, you must connect a serial cable from the serial port on your PC to the
RJ45 to DB9M adaptor cable on the MVI46-PDPMV1 module.
1 In ProSoft Configuration Builder for PROFIBUS, open the O
then choose M
ONITOR/MODIFY
. ProSoft Configuration Builder will establish
communication with the MVI46-PDPMV1 module, and will indicate
communication status.
NLINE
menu, and
o
If the slave icon in the Bus Configuration window has a green border, then
the MVI46-PDPMV1 module is correctly communicating with the
PROFIBUS slave.
o
If the slave icon in the Bus Configuration window has a red border, then
the module is not communicating with the slave.
o
If the slave icon in the Bus Configuration window has a blue border, the
slave is communicating with the Master, but is generating diagnostic data.
To view diagnostic data for the slave, select the slave, and click the right
mouse button to open a shortcut menu. On the shortcut menu, choose
O
NLINE PROPERTIES
.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 51 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 52

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
2 In the Online Slave Properties dialog box, click the D
select (
CHECK) DETAILS FOR SLAVE DIAGNOSTIC
IAGNOSTIC
tab, and
. Slave diagnostic information
will appear in the Diagnostic window. Refer to the documentation for your
PROFIBUS slave to determine the meaning of the diagnostic data.
Page 52 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 53

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
2.4.3 Viewing the Fieldbus Data from the MVI46-PDPMV1’s
Configuration/Debug Menu
Note: For this procedure, you must connect a serial cable from the serial port on your PC to the
RJ45 to DB9M adaptor cable on the MVI46-PDPMV1 module.
1 In ProSoft Configuration Builder, select the MVI46-PDPMV1 module, then
click the right mouse button to open a shortcut menu.
2 On the shortcut menu, choose D
Diagnostics dialog box.
3 Press [?] to display the Main menu, and then press [2] to view Fieldbus data.
IAGNOSTICS
. This action opens the
4 Note the value in Operation State. If the Master and the slave are
communicating correctly, the operation state will be C0 (hex).
5 Note the values in SLAVE CFG LIST, TRANSFER LIST and SLAVE DIAG
LIST. If the Master and slave are communicating successfully, the values in
SLAVE CFG LIST will match the values in TRANSFER LIST.
Note: Each list is a hexadecimal representation of a bitmap of slave addresses on the PROFIBUS
network. In the illustration above, a value of 20h in the rightmost columns of both of the first two
lists means one slave at address 125 is configured and communicating with the Master. Notice that
the values in the leftmost columns of the first two lists do not match. This means that the slave at
address 1 is configured, but is not communicating with the Master. The slave at address 3,
however, is both configured and communicating with the Master. Below is an explanation on how
to read these bitmaps.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 53 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 54

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Each (XX XX) grouping represents one word containing 16 slave addresses.
In SLAVE CFG LIST in the example above
To find out which slave addresses in Word 1 are occupied by configured slaves,
expand Word 1's hexadecimal numbers into a bitmap.
Note: A zero (0) in the bitmap indicates an unoccupied slave address; one (1) indicates that the
slave address is occupied by a configured slave.
Page 54 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 55

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Here is the bitmap for Word 8:
So from the SLAVE CFG LIST, we can tell that there are configured slaves at
slave addresses 1, 3 and 125.
The TRANSFER LIST indicates which configured slaves are actually
communicating with the Master. Notice that Word 1 is different in the TRANSFER
LIST.
Here is the bitmap for Word 1 in the TRANSFER LIST:
In conclusion, there are configured slaves at addresses 1,3 and 125, but only the
slaves at addresses 3 and 125 are communicating with the Master.
Tip: This slave status data is also found in the M1 file, which is copied to the user-accessible N11
file by the sample ladder logic. You can use this data for process control. For more information, see
Backplane Data Transfer (page 115).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 55 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 56

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
2.4.4 Viewing the Data Files in RSLogix 500
Note: For this procedure, you must connect a serial cable from the serial port on your PC to the
DB9M connector on the SLC processor.
1 Open the sample ladder logic in RSLogix 500.
2 Open the C
3 In the Project Browser window, double-click N11 data file.
4 Verify that N11:20 is the last word of the slave configured list
OMMUNICATIONS
menu, and choose GO O
NLINE
.
The bit in N11:20/13 is set, indicating that slave 125 is configured.
5 Next, check the slave data exchange list at N11:28
The bit in N11:28/13 is set, indicating that slave 125 is exchanging data.
Page 56 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 57

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Tip: You can add ladder logic to perform an action based on the values of these tags, for example
to determine if a slave is misconfigured.
If the values of these tags show that the slave is configured, but is not
transferring data, the slave is not configured correctly. Refer to the
documentation provided with your PROFIBUS slave for troubleshooting
procedures.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 57 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 58

Configuring the MVI46-PDPMV1 Module MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
2.4.5 Sending a Mailbox Message in RSLogix 500
Note: For this procedure, you must connect a serial cable from the serial port on your PC to the
DB9M connector on the SLC processor.
1 Open the sample ladder logic in RSLogix 500.
2 Open the C
3 In the Project Browser window, double-click the B3 Data File.
4 Enter 1 (number one) in B3:0/4
OMMUNICATIONS
menu, and choose GO O
NLINE
.
5 Next, double-click on N51 and read the response to verify that the MVI46-
PDPMV1 responded to the GetLiveList message. The PROFIBUS Master
Address in this case =1. Notice that the value has changed from 4 (not
communicating) to 3 (Master).
For address [125] (the PROFIBUS Slave Address configured in the Slave
Configuration (page 31) procedure), notice that the value of N51:62 High byte
has changed from 4 (not communicating) to 0 (Slave OK).
Page 58 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 59

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Ladder Logic
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
3 Ladder Logic
In This Chapter
Adding the Module to an Existing Project .............................................. 60
Ladder logic is required for the MVI46-PDPMV1 module to work. Tasks that must
be handled by the ladder logic are module data transfer, special block handling,
and status data receipt. Additionally, a power-up handler may be needed to
handle the initialization of the module’s data and to clear any processor fault
conditions.
The sample ladder logic, on the inRAx CD-ROM, is extensively commented, to
provide information on the purpose and function of each rung. For most
applications, the sample ladder will work without modification.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 59 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 60

Ladder Logic MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
3.1 Adding the Module to an Existing Project
1 Add the MVI46-PDPMV1 module to the project. Double-click I/O
C
ONFIGURATION
2 This action opens the I/O Configuration dialog box. Select an empty slot in
the left pane, and then scroll to the bottom of the right pane.
in the Controller Organization window.
3 In the right pane, double-click O
action opens the "O
THER" TYPE IO CARD
THER -- REQUIRES
dialog box.
I/O C
ARD TYPE
ID. This
Page 60 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 61

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Ladder Logic
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4 The module's I/O card ID number is 12835. Enter that value in the ID number
field, and then click OK to dismiss the dialog box.
5 Observe that the module you selected is now in the list in the left pane of the
I/O Configuration dialog box.
6 Select and double-click the new module in the left pane. This action opens
the Advanced I/O Configuration dialog box. Fill in the dialog box with the
values shown in the following illustration.
Field Value
Scanned Input Words 2
Scanned Output Words 2
Interrupt Service Routine (ISR)# 0
M0 Length 1000
M1 Length 1000
G File Length 0
7 Click OK to save your configuration.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 61 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 62

Ladder Logic MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
8 Copy the ladder logic and data files from the sample program and paste them
into your existing program.
Important: Take care not to overwrite existing data files in your application with data files in the
sample application. Rename either the source or the destination data files, and then search and
replace references in the ladder for instances of any renamed files.
9 Save and download (page 19) the new application to the controller and place
the processor in RUN mode.
Page 62 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 63

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4 Mailbox Messaging
In This Chapter
Mailbox Message Queuing .................................................................... 64
Special Function Mailbox Messaging Commands ................................. 65
Receiving Mailbox Message Responses from the Module .................... 89
Mailbox Messaging Error Codes ........................................................... 90
The MVI46-PDPMV1 PROFIBUS DP Master uses a process called Mailbox
Messaging to exchange parameter data between the processor, Master, and
slave devices. This process provides a way to encapsulate and prioritize
commands and data sent between the PROFIBUS Master and slaves.
The PROFIBUS DP-V1 protocol specifies two types of data transmission
messages (telegrams): Cyclic Data Telegrams and Acyclic Data Telegrams.
Cyclic data communication is the exchange of normal slave input and output (I/O)
data and is handled automatically by the Master in a defined, recurring,
deterministic sequence based on the configuration you create in ProSoft
Configuration Builder (PCB).
Acyclic communication extends data communication beyond normal I/O data to
allow moving field device parameterization and calibration data over the bus
during runtime and to allow for extended diagnostics and alarm messages.
Acyclic data telegrams are transmitted in the gaps between cyclic data telegrams
and, therefore, have a lower priority and get less bandwidth than cyclic data.
Mailbox Messaging commands are incorporated into the sample ladder logic.
Mailbox messages and responses to mailbox messages are stored in mailbox
data types.
The following chapter discusses these features in more detail.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 63 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 64

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
4.1 Mailbox Message Queuing
The MVI46-PDPMV1 module operates asynchronously on the Mailbox Messages
and as such provides for the queuing of the messages as they are received. The
following queue sizes are used in the module.
Queue Type Queue Size Max Description
Output message from
processor
Input messages for processor 126
Alarm messages from slaves
for processor
126 Number of messages that the MVI46 module
500
4.1.1 Queue Timeouts
The MVI46-PDPMV1 module will only allow a message to stay in a queue for up
to 10 seconds. If the PROFIBUS Master (for output messages) or the processor
(for input and alarm messages) has not successfully received a message within
10 seconds, the module will clear the message out of the queue.
will queue by type of message. Note that
status of the queues can be monitored via the
Queue Message Count values.
Page 64 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 65

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4.2 Special Function Mailbox Messaging Commands
The MVI46-PDPMV1 module supports some extended PROFIBUS functions
using a mailbox data exchange mechanism.
The MVI46-PDPMV1 module supports the following special functions through
this mailbox messaging scheme:
Initiated from Processor
Message Description
Set Operation Mode Controls the operating state of the PROFIBUS Master
Set Slave Mode Sends special control command to one or several slaves
(Sync/Freeze)
Get Slave Diag Gets diagnostic information from a slave
Get Slave Config Gets slave configuration
Set Slave Address Sets node address of a slave (if supported by the slave)
Get Live List Gets information from all nodes on the network
MSAC1 Read DPV1 acyclic read (Class 1)
MSAC1 Write DPV1 acyclic write (Class 1)
Start Slave Starts slaves dynamically
Stop Slave Stops slaves dynamically
DPV1 Alarm Handling: Generated by Slave Devices
Message Description
Alarm Indications Spontaneous alarm indication from DPV1 slave. Structure of
data is slave-dependent
Alarm Confirmation This message is sent by the MVI46 module automatically as a
confirmation to the alarm indications.
The provided simplified ladder logic is required to implement these messaging
mailbox exchanges.
Sending a mailbox message to the MVI46-PDPMV1 module is a relatively simple
process, however, it is important to follow a certain sequence.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 65 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 66

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Mailbox Message Structure: To MVI46 module
Byte Offset Type Description
0 Message ID Processor logic or user set. The Message ID field is used
by the MVI46 module to detect a new message in the
PROFIBUS output data image.
When a non-zero value is detected, the message is
processed immediately. The sample ladder logic assigns
specific message IDs to different mailbox messages.
1 Message Info See individual commands for data values to be entered in
2 Command
3 Data Size
4 Frame Count
5 Frame Number
6 Offset High
7 Offset Low
8 Extended Word 1
9 Extended Word 2
10 Extended Word 3
11 Extended Word 4
12 Extended Word 5
13 Extended Word 6
14 Extended Word 7
15 Extended Word 8
- See individual
149
commands
each of these register locations.
4.2.1 Mailbox Message: Set Slave Mode
In addition to station-related user data transfer, which is executed automatically,
the Master can send control commands to a single slave, a group of slaves, or all
slaves simultaneously. These control commands are transmitted as multicast
commands. This permits use of sync and freeze modes for event-controlled
synchronization of the slaves.
The slaves begin sync mode when they receive a sync command from their
assigned Master. The outputs of all addressed slaves are then frozen in their
current state. During subsequent user data transmissions, the output data are
stored on the slaves, but the output states remain unchanged. The stored output
data are not sent to the outputs until the next sync command is received. Sync
mode is concluded with the unsync command.
Similarly, a freeze control command causes the addressed slaves to assume
freeze mode. In this operating mode, the states of the inputs are frozen until the
Master sends the next freeze command. Freeze mode is concluded with the
unfreeze command.
Page 66 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 67

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Note 1: It is only possible to send control commands when operating mode is either "CLEAR" or
"OPERATE".
Note 2: Not all slaves support this feature. Refer to the documentation for the actual slave for more
information.
Parameter Description
Command Initiator Application
Command Name SET SLAVE MODE
Command Number 0300h
Fragmented No
Extended Header Data Fault information may be returned in the header of the response.
Command and Response Layout: Set Slave Mode
Message ID
Message information
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1 Slave
Extended word 2 Control
Extended word 3
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
Command
(ID)
4002h
0003h
0000h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Group Select
Address
Command
-
-
-
-
-
Response
Slave
Address
Control
Command
Extended Fault Information
(ID)
0002h
0003h Set Slave Mode
0000h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Group Select
-
-
-
-
Fault Information
Message Information
Refer to Message Information (page 90).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 67 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 68

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Slave Address
Range 1 to 125; 127
If the request applies for only one slave, that slave address must be entered in
the range 1 to 125. If a slave group is to be addressed, slave address should be
127 (multicast address).
Group Select
Range 01h to FFh (Bit Coded)
This parameter determines which group to address. Refer to the following
example:
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Group 8 Group 7 Group 6 Group 5 Group 4 Group 3 Group 2 Group 1
Example:
To address Group 1, 2, and 4, the Group Select value should be D0h. If an
individual slave should be addressed, the correct group selection must also be
made, because the slave will ignore the message if it does not belong to the
requested group(s).
What group(s) a slave belongs to is determined during network configuration,
and is downloaded during initialization to each slave via the PROFIBUS telegram
Set_Prm.
Control Command
This parameter specifies the command to send:
Bit Explanation
0 (LSB) Reserved, set to zero
1 Reserved, set to zero
2 Unfreeze input data
3 Freeze input data
4 Unsynchronize output data
5 Synchronize output data
6 Reserved, set to zero
7 (MSB) Reserved, set to zero
Combinations of the bits (Unsync/Sync and Unfreeze/Freeze)
Bits 0 or 6 Bits 1 or 7 Explanation
0 0 No function
0 1 Function will be activated
1 0 Function will be inactive
1 1 Function will be inactive
Page 68 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 69

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Fault Information and Extended Fault Information
"Fault Information" Contents "Extended Fault Information" Contents
0100h Address out of range 0200h Group number 0 not
permitted
0A00h Failed to send Global
Control request
FE00h Command not
possible in Class 2
only mode
FF00h Module not initialized -
-
0A00h Incorrect operation mode (Clear/Operate Only)
0150h Invalid Freeze Group (Group is not initiated to be
Freeze Group)
0250h Invalid Sync Group (Group is not initiated to be
Sync Group)
0350h Incorrect Control Command
0450h No Sync -/ or Freeze groups enabled in Master
configuration
-
4.2.2 Mailbox Message: Get Slave Diagnostics
This command reads diagnostic data from a specified slave.
Note: The response data size depends on the actual slave implementation. Range 6 to 244.
Parameter Description
Command Initiator Application
Command Name GET SLAVE DIAGNOSTICS
Command Number 0400h
Fragmented No
Extended Header Data Fault information may be returned in the header of the response.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 69 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 70

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Command and Response Layout: Get Slave Diagnostics
Message ID
Message information
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1 Slave
Extended word 2
Extended word 3
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
Command
Address
(ID)
4002h
0004h
0000h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Type of
Request
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Response
Address
Status 1
Status 3
Extended Diagnostic Data Response data word 4
(ID)
0002h
0004h Get Slave Diagnostics
(Size of data)
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Slave
Extended Fault Info
Fault Information
Station
Station
Ident Number Response data word 3
Type of
Request
-
-
-
Station
Status 2
Station
Status 4
Response data word 1
Response data word 2
...
...
Response data word n
Message Information
Refer to Message Information (page 90).
Slave Address
Range 1 to 125; specifies the slave from which to read diagnostics.
Page 70 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 71

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Type of request
00h: Internal slave diagnostic request. Returns the diagnostic information stored
in the Master. Can only be requested for slaves configured by the Master.
Note: Not allowed when operating in "Class 2-Only" mode.
01h: External slave diagnostic request. Sends a diagnostic request on the
network to the specified slave. Can be requested for all slaves on the network.
Error code [1 ...4]
If "Return Code" equals 8030h ("Negative indication from lower layer"), status
values according to the DP-specification may be available in "Error Code 1".
Error Codes 2 to 4 are reserved.
Refer to Mailbox Messaging Error Codes (page 90).
Return Code
Refer to Mailbox Messaging Error Codes (page 90)
Fault Information
If "Invalid Other" is returned in the Message Information word in the header of the
response, information about the fault can be found here.
0100h: Address out of range.
0200h: Incorrect "Type of request"
0A00h: Failed to read diagnostic data from slave. Refer to Return Codes (page
91) for additional fault information.
0B00h: Remote station failure. Refer to Return Codes (page 91) for additional
fault information.
FE00h: Command not possible; module operates as a Class 2 Master only.
FF00h: Module offline (not initialized or no valid database).
Station Status [1 ... 3]
Refer to EN50170 Vol. 2 for more information.
Master Address
Address of the Master that parameterized the slave.
Ident Number
Unique ID assigned by the PROFIBUS User Organization.
Extended Diagnostic Data
Slave user-specific data. Refer to the documentation for the actual slave for more
information.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 71 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 72

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
4.2.3 Mailbox Message: Get Slave Configuration
This command reads the actual configuration (identifier bytes) of a specified
slave.
Note: The response data size depends on the actual slave implementation. Range 6 to 244.
Parameter Description
Command Initiator Application
Command Name GET SLAVE CONFIGURATION
Command Number 0500h
Fragmented No
Extended Header Data Fault information may be returned in the header of the response.
Command and Response Layout: Get Slave Configuration
Message ID
Acyclic Message Status
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1 Slave
Extended word 2
Extended word 3
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
Command Response
Word
Address
(ID)
4002h
0005h
0000h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Slave
Address
Error Code 1 Error Code 2
Error Code 3 Error Code 4
(ID)
0002h
0005h Get Slave Configuration
(Size of data) Number of identifier bytes
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Return Code
Fault Information
Identifier byte 1 Response data word 1
Identifier byte 2 Response data word 2
Identifier byte 3 Response data word 3
... ...
Identifier byte n Response data word n
(n)
-
-
-
Page 72 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 73

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Acyclic Message Status Word
Refer to Acyclic Message Status Word (page 90).
Slave Address
Range 1 to 125; specifies the slave from which to read the configuration.
Error Code [1 … 4]
If "Return Code" equals 3080h ("Negative indication from lower layer"), status
values according to the DP-specification may be available in "Error Code 1",
Error Codes 2 through 3 are reserved. Refer to Mailbox Messaging Error Codes
(page 90).
Return Code
Refer to Mailbox Messaging Error Codes (page 90).
Fault Information
If "Invalid other" is returned in the Acyclic Message Status Word in the header of
the response, information about the fault can be found here. Refer to Acyclic
Message Status Word (page 90).
0100h: Address out of range.
0A00h: Failed to execute request. Refer to Return Codes (page 91) for additional
information.
0B00h: Remote station failure. Refer to Return Codes (page 91) for additional
information.
FF00h: Module not initialized.
Identifier Bytes [1 … n]
Refer to EN50170 Vol. 2 for information on the structure of these bytes. In
addition, refer to the documentation provided with the slave device for more
information.
4.2.4 Mailbox Message: Set Slave Address
This command makes it possible to set the node address of a specified slave, if
the slave supports this feature.
Note: The message data size depends on the actual slave implementation. Range 0 to 240 bytes.
Parameter Description
Command Initiator Application
Command Name SET SLAVE ADDRESS
Command Number 0600h
Fragmented No
Extended Header Data Fault information may be returned in the header of the response.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 73 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 74

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Command and Response Layout: Set Slave Address
Message ID
Message information
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1 Current
Extended word 2
Extended word 3 No_add_
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
Message Data byte 1
Message Data byte 2
Message Data byte 3
...
Message Data byte "n"
Command
(ID)
4002h
0006h
(Size of data)
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Slave Addr.
Slave Ident Number
Chg
Slave Data 1
Slave Data 2
Slave Data 3
...
Slave Data n
New Slave
Address
-
-
-
-
Response
Current
Slave Addr.
- No_add_
Error Code 1 Error Code 2
Error Code 3 Error Code 4
(ID)
0002h
0006h Set Slave Address
(Size of data) No. of Slave Data bytes (n)
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
New Slave
Address
Slave Ident Number
Chg
-
Return Code
Fault Information
Slave Data 1
Slave Data 2
Slave Data 3
...
Slave Data n
Message Information
Refer to Message Information (page 90).
Current Slave Address
Range 1 to 125; specifies the current address of the slave.
New Slave Address
Range 1 to 125; specifies the new address of the slave.
Page 74 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 75

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Slave Ident Number
Ident number for the slave; which address should be altered.
No_add_Chg
This parameter specifies whether it is allowed to change the slave address again
later. If this is not allowed, it is only possible to change the address with this
function after initial reset. After the initial reset, the slave takes the default
address of 126.
00h: Change of address is still possible at a later stage.
01h-FFh: Change of address is only possible after the initial address (the default
address = 126).
Error Code [1 …4]
If "Return Code" equals 3080h ("Negative indication from lower layer"), status
values according to the DP-specification in available in "Error Code 1". Error
Codes 2 and 3 are reserved. Refer to Return Codes (page 91).
Return Code
Refer to Return Codes (page 91).
Fault Information
If "Invalid Other" is returned in the Message Information word in the header of the
response, information about the fault can be found here:
0100h: Current slave address out of range.
0200h: New slave address out of range.
0A00h: Failed to execute request.
0B00h: Remote station failure.
FF00h: Module not initialized.
Refer to Mailbox Messaging Error Codes (page 90).
Slave Data
With this parameter, it is possible to deliver user-specific data. The data is stored
in the slave if possible (EEPROM, FLASH, or other storage media).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 75 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 76

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
4.2.5 Mailbox Message: Get Live List
This command returns 127 bytes of information about the nodes on the network.
Every byte stands for one bus subscriber, and the position of the byte in the
response data assigns the address (0 to 126), the content assigns the Station
Type.
This command can be sent in all operation modes (STOP, CLEAR, and
OPERATE), however the module must be initialized properly.
Parameter Description
Command Initiator Application
Command Name GET LIVE LIST
Command Number 1800h
Fragmented No
Extended Header Data Fault information may be returned in the header of the response.
Command and Response Layout: Get Live List
Message ID
Message information
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1
Extended word 2
Extended word 3
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
Message Data byte 1
Message Data byte 2
Message Data byte 3
Message Data byte "n"
Command Response
(ID)
4002h
0018h
0000h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
...
(ID)
0002h
0018h Get Live List
0007h 127 Bytes of Data
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
-
-
-
-
-
Return Code
Fault Information
Station Type 0 Response Data Byte 1
Station Type 1 Response Data Byte 1
Station Type 2 Response Data Byte 1
... Response Data Byte 1
Station Type 126 Response Data Byte 1
Page 76 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 77

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Message Information
Refer to Message Information (page 90).
Station Type [0 … 126]
00h: Slave Station
01h: Master Station not yet ready for Token ring (station only physically at the
bus)
02h: Master Station ready to enter Token ring (there is not yet any Token
transmission)
03h: Master Station in Token Ring (Token transmission through the station)
04h: Station does not exist
Fault Information
If "Invalid Other" is returned in the Message Information word in the header of the
response, information about the fault can be found here. Refer to Message
Information (page 90).
0AH00: Failed to build Live List.
FF00h: Module offline (not initialized or no valid database)
4.2.6 Mailbox Message: Acyclic Data Read: Class 1
This command initiates a DPV1 Class 1 acyclic read request. Refer to EN50170
(DPV1) for more information.
Parameter Description
Command Initiator Application
Command Name MSAC1 READ
Command Number 2000h
Fragmented No
Extended Header Data Fault information may be returned in the header of the response.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 77 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 78
Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Command and Response Layout: Acyclic Read
Command
Message ID
Message information
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1 Slave Addr. Slot Number
Extended word 2 Index Length
Extended word 3
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
(ID)
4002h
0020h
0000h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
-
-
-
-
-
Response
Slave Addr. Slot Number
Error Code 1 Error Code 2
Extended Fault information
(ID)
0002h
0020h Acyclic Read
(Size of data) Number of data bytes (n)
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Index Length
-
-
Fault Information
Error
Decode
Data 1 Response Data byte 1
Data 2 Response Data byte 1
Data 3 Response Data byte 1
... ...
Data n Response Data byte 1
Message Information
Refer to Message Information (page 90).
Slave Address
Station address of the slave responder.
Slot Number and Slot Index
Used in the slave to address the desired data block.
Page 78 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 79

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Length
This parameter specifies the number of bytes of the data block to read. If the
server data block length is less than requested, the length of the response will be
the actual length of the data block. If the server data block is greater or equal, the
response will contain the same amount of data.
The slave may answer with an error response if data access is not allowed.
Data [1 … n]
Returned data.
Fault Information and Extended Fault Information
If "Invalid Other" is returned in the Message Information word in the header of the
response, information about the fault can be found here.
"Fault Information" "Extended Fault Information" Contents
0100h Address out of range 0A00h Failed to execute request Refer to Return Codes (page 91).
0B00h Remote station failure
1000h Remote station DPV1 failure Function_Number
1100h Length out of range (>240 bytes) 1200h Slave does not support DPV1 1300h Slave not active or not present in
configuration
FE00h Command not possible in "Class 2-
Only" mode
FF00h Module offline (not initialized or no
valid database)
-
-
-
Error Decode, Error Code 1 and Error Code 2
If "Fault Information" contains error code 1000h, more information according to
the DPV1 specification can be found here.
4.2.7 Mailbox Message: Acyclic Data Write: Class 1
This command initiates a DPV1 Class 1 acyclic write request. Refer to EN50170
(DPV1) for more information.
Parameter Description
Command Initiator Application
Command Name MSAC1 WRITE
Command Number 2100h
Fragmented No
Extended Header Data Fault information may be returned in the header of the response.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 79 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 80

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Command and Response Layout: Acyclic Write
Message ID
Acyclic Message Status
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1 Slave Addr. Slot Number
Command
Word
(Size of data)
(ID)
4002h
0021h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Response
Slave Addr. Slot Number
(ID)
0002h
0021h Acyclic Write
(Size of data) Number of data bytes (n)
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Extended word 2 Index Length
Extended word 3
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
Message Data byte 1
Message Data byte 2
Message Data byte 3
...
Message Data byte n
-
-
-
-
-
-
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
...
Data n
Index Length
Error Code 1 Error Code 2
Extended Fault information
Fault Information
Acyclic Message Status Word
Refer to Acyclic Message Status Word (page 90).
-
-
Error
Decode-
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
...
Data n
Slave Address
Station address of the slave responder.
Page 80 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 81

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Slot Number and Slot Index
Used in the slave to address the desired data block.
Length
This parameter specifies the number of bytes to write. If the destination data
block size is less than requested, the response will contain an error message. If
the data block length is greater than or equal to the requested length, the
response contains the number of bytes that have been written. The slave may
answer with an error response if data access is not allowed.
Data [1 … n]
Data that should be written.
Fault Information and Extended Fault Information
If "Invalid Other" is returned in the Acyclic Message Status Word in the header of
the response, information about the fault can be found here:
"Fault Information" "Extended Fault Information" Contents
0100h Address out of range 0A00h Failed to execute request Refer to Return Codes (page 91).
0B00h Remote station failure
1000h Remote station DPV1 failure Function_Number
1100h Length out of range (>240 bytes) 1200h Slave does not support DPV1 1300h Slave not active or not present in
configuration
FE00h Command not possible in "Class 2-
Only" mode
FF00h Module offline (not initialized or no
valid database)
-
-
-
Error Decode, Error Code 1, and Error Code 2
If "Fault Information" contains error code 1000h, more information according to
the DPV1 specification can be found here.
4.2.8 Mailbox Message: Alarm Indication
This message indicates to the application that a DPV1 slave has transferred an
alarm message to the Master. This mailbox message is sent spontaneously by
the module; the module itself initiates the mailbox communications.
Detailed information about the cause of the alarm is presented in extended words
1 to 3 and in the message data field (see below).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 81 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 82

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Command and Response Layout: Alarm Indication
Command
Message ID
Message information
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1 Slave
Address
Extended word 2 Seq Number Alarm Spec
Extended word 3 Alarm Type Ext Diag
(ID)
4002h
0022h
(request length)
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
Slot Number
Ack
Response
(ID)
0002h
0022h Alarm Indication
0000h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
-
-
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
Message Data byte 1
Message Data byte 2
Message Data byte 3
…
Message Data byte n
-
-
-
-
Fault Information
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
…
Data n
-
-
-
-
-
Slave Address
Station address of the slave that issued the alarm.
Slot Number
Used by the slave to indicate the source of the alarm. Range 0 to 254.
Seq Number
Unique identification number of the alarm. Range 0 to 31.
Page 82 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 83

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
Alarm Spec Ack
Provides additional information about the alarm, such as if an error appears or
disappears. Also indicates whether the slave needs additional knowledge from
the Master. For example: writing to a certain memory area with an Acyclic Write
request.
Alarm Type
Identifies the alarm type such as Process Alarm, Plug Alarm, and so on. Range 1
to 6, 32 to 126.
Extended Diagnostic Flag
FFh: Slave sends an alarm message with "Extended Diag flag" set
00h: Slave sends an alarm message with "Extended Diag flag" cleared
Data [1 … n]
Additional manufacturer-specific alarm information (Alarm - PDU)
Fault Information
If the Message Information word in the header of the message indicates "Invalid
Other", addition information is available in this register.
3E00h: Module has received an invalid alarm indication data structure from a
DPV1 slave ("Slave Address" contains the node address of the slave that issued
the erroneous indication).
Refer to the PNO document "Extensions to EN50170 (DPV)" for more
information on how to interpret these parameters.
4.2.9 Mailbox Message: Set Operating Mode
This command allows setting the operating mode of the module (STOP, CLEAR,
or OPERATE).
Parameter Description
Command Initiator Application
Command Name SET OPERATING MODE
Command Number 0200h
Fragmented No
Extended Header Data Fault information may be returned in the header of the response.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 83 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 84

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Command and Response Layout: Set Operating Mode
Command Response
Message ID
Message information
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1 Mode Conf. Req Mode Conf. Req
Extended word 2
Extended word 3
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
(ID)
4002h
0002h
0000h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(ID)
0002h
0002h Set Operation Mode
0000h
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
-
-
-
-
-
Fault Information
Mode
40h: STOP
80h: CLEAR
C0h: OPERATE
Conf. Req.
00h: Confirmation is not required
01h: Confirmation required. All confirmations are automatically sent by the
Master; the user is not required to send a confirmation message.
Fault Information
If "Invalid Other" is returned in the Message Information word in the header of the
response, information about the fault can be found here. Refer to Return Codes
(page 91) for more information.
0100h: Invalid operating mode
FF00h: Module not initialized
Page 84 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 85

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4.2.10 Mailbox Message: Start Slave
This mailbox message starts a selection of slaves that was previously removed
from the processing cycle by means of the mailbox message
FB_APPL_STOP_SLAVE.
This message is allowed in all Operation modes (STOP, CLEAR and
OPERATE).
Note: The message will be accepted even if one or several slaves are not part of the configuration
and can therefore obviously not be started. However, the application can find out about this
situation by evaluating the "Fault information" and "Message data words" of the response.
Command and Response Layout: Start Slave
Command Response
Message ID
Message information
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1
Extended word 2
Extended word 3
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
Message data word 1 Slave 0 Slave 1 Slave 0 Slave 1
Message data word 2 Slave 2 Slave 3 Slave 2 Slave 3
Message data word 3 to
62
Message data word 63 Slave 124 Slave 125 Slave 124 Slave 125
(ID)
4002h
000Bh
007Eh
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
... ... ... ..
Additional Fault Information
(ID)
0002h
000Bh Start Slave
007Eh
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
-
-
-
-
Fault Information
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 85 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 86

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Command:
Message data word 1-63
Byte-array stating which slave/slaves to start. Array index is equal to slave
address.
0: Do not affect slave
1: Start slave
2-255: Reserved
Response:
Message information (in response header)
"Invalid Data Size" is returned if Data size in the command header does not
equal 126.
If "Invalid Other" is returned, further information is to be found in Extended
word 8.
Additional Fault information (Extended word 7)
If Extended word 8 equals 0x000A -"Failed to execute request" additional info
can be found here.
Fault information (Extended word 8)
0x0001: Invalid setting in Message data word 1-63 of the command.
0x0002: At least one slave reports a warning. Refer to Message data word 1-
63.
0x000A: Failed to execute request. Additional fault information is to be found
in Extended word 7.
0x00FE: Command not possible, module operates as class 2 Master only.
0x00FF: Module not initialized (this command is only possible after
END_INIT).
Message data word 1-63
Byte-array stating the status of the slaves. Array index is equal to slave
address.
0: Slave unaffected
1: Slave started
2: Warning - Slave could not be started because it is not part of the
configuration
Page 86 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 87

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4.2.11 Mailbox Message: Stop Slave
This mailbox message stops a selection of slaves from the processing cycle.
This message is allowed in all Operation modes (STOP, CLEAR and
OPERATE).
Note: The message will be accepted even if one or several slaves are not part of the configuration
and can therefore obviously not be stopped. However, the application can find out about this
situation by evaluating the "Fault information" and "Message data words" of the response.
Command and Response Layout: Stop Slave
Message ID
Message information
Command
Data size
Frame count
Frame number
Offset high
Offset low
Extended word 1
Command
(ID)
4002h
000Ch
007Eh
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
Response
(ID)
0002h
000Ch Stop Slave
007Eh
0001h
0001h
0000h
0000h
-
Extended word 2
Extended word 3
Extended word 4
Extended word 5
Extended word 6
Extended word 7
Extended word 8
Message data word 1 Slave 0 Slave 1
Message data word 2 Slave 2 Slave 3
Message data word 3 to
62
Message data word 63 Slave 124 Slave 125
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
... ...
Additional Fault Information
Slave 0 Slave 1
Slave 2 Slave 3
Slave 124 Slave 125
-
-
-
-
-
Fault Information
... ...
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 87 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 88

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Command:
Message data word 1-63
Byte-array stating which slave/slaves to stop. Array index is equal to slave
address.
0: Do not affect slave
1: Stop slave
2-255: Reserved
Response:
Message information (in response header)
"Invalid Data Size" is returned if Data size in the command header does not
equal 126.
If "Invalid Other" is returned, further information is to be found in Extended
word 8.
Additional Fault information (Extended word 7)
If Extended word 8 equals 0x000A -"Failed to execute request" additional info
can be found here.
Fault information (Extended word 8)
0x0001: Invalid setting in Message data word 1-63 of the command.
0x0002: At least one slave reports a warning. Refer to Message data word 1-
63.
0x000A: Failed to execute request. Additional fault information is to be found
in Extended word 7.
0x00FE: Command not possible; module operates as class 2 Master only.
0x00FF: Module not initialized (this command is only possible after
END_INIT).
Message data word 1-63
Byte-array stating the status of the slaves. Array index is equal to slave
address.
0: Slave unaffected
1: Slave stopped
2: Warning - Slave could not be stopped because it is not part of the
configuration
3: Warning - Slave already stopped
Page 88 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 89

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4.3 Receiving Mailbox Message Responses from the Module
After a mailbox message has been sent, a response from the command, usually
containing the requested data or the status of the command, is returned from the
MVI46 module to the processor. The response is returned from the MVI46PDPMV1 via the M1 file.
Remembering the PROFIBUS Input Data Memory Map:
Byte Offset Name Description
0 to 72 Configuration, Status and Control data
73 Number of Messages in the In Mailbox Queue
74 Number of Messages in the Out Mailbox Queue
75 Number of Messages in the Alarm Queue
76 Last Out Mailbox Message ID processed from Output
Image
77 Current In Mailbox Control Index
78 Current Alarm Control Index
79 to 222 Incoming Mailbox Message data
223 to n PROFIBUS Input Data
The important section relevant to the Mailbox Messaging discussion is the
Incoming Mailbox Data section (Byte Offsets 79 to 222). Within this section of
data, the following structure exists:
Mailbox Message Structure: From MVI46 module
Byte Offset Type Description
79 Message ID Message ID value will match value used to generate the
outgoing mailbox message
80 Message Info See individual commands for data values to be entered in
81 Command
82 Data Size
83 Frame Count
84 Frame Number
85 Offset High
86 Offset Low
87 Extended Word 1
88 Extended Word 2
89 Extended Word 3
90 Extended Word 4
91 Extended Word 5
92 Extended Word 6
93 Extended Word 7
94 Extended Word 8
- See individual
222
commands
each of these register locations
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 89 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 90

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
4.4 Mailbox Messaging Error Codes
4.4.1 Acyclic Message Status Word
This register contains bit and code information about the mailbox message. The
register is divided into five areas according to the following illustration:
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Message Type ERR C/
Bit / Field Description Contents
ERR This bit indicates if the
received command contained
any errors.
C/R This bit specifies whether the
message is a command or a
response.
Error Code If the ERR bit is set, this field
contains additional information
about the error.
Message
Type
This field specifies the type of
the message.
0:
1:
0:
1:
0h:
1h:
2h:
3h:
4h:
5h:
6h:
8h:
9h:
Fh:
(All other values are reserved)
1h: Application Message
2h: PROFIBUS Specific Message
3h: Memory Message
5h: Reset Message
(All other values are reserved)
(reserved) Error Code
R
Message OK
Error (See also "Error Code" below)
Response Message
Command Message
Invalid Message ID
Invalid Message Type
Invalid Command
Invalid Data Size
Message header malformed (offset 008h)
Message header malformed (offset 00Ah)
Message header malformed (offset 00Ch to 00Dh)
Invalid Response
Flash Config Error
Invalid Other
Page 90 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 91

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4.4.2 Return Codes
Possible error codes in Message Data word "Return Code" (The Return Codes
can be byte swapped)
Return Code Name Meaning
8010h DPMC_ERR_V1C_CLOSED Internal DPMC instance no longer exists
8011h DPMC_ERR_V1C_STOPPED Internal DPMC instance has already been stopped
8012h DPMC_ERR_V1C_STARTED Internal DPMC instance has already been started
8013h DPMC_ERR_V1C_STATE_UNKNOWN Internal DPMC instance has entered an undefined
state
8021h DPMC_ERR_V1C_REQ_ACTIVE A request is already active
8022h DPMC_ERR_V1C_NOT_ALLOWED Internal DPMC module not initialized correctly
8023h DPMC_ERR_V1C_INVALID_PAR Invalid parameter in user request
8024h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MEM_ALLOC Internal memory allocation error
8025h DPMC_ERR_V1C_L2_REQ Unknown opcode in the confirmation
8026h DPMC_ERR_V1C_TIMEOUT Active request terminated with timeout
8028h DPMC_ERR_V1C_INVALID_LEN Invalid length in user request
8030h DPMC_ERR_V1C_REQ_NEG1 Negative indication from lower layer
8031h DPMC_ERR_V1C_REQ_RE Message frame format error in response
8042h DPMC_ERR_V1C_REQ_WITHDRAW Request was recalled
8043h DPMC_ERR_V1C_REQ_NOT_FOUND Associated request block not found
80C1h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_FE Format error in request frame
80C2h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_NI Function not implemented
80C3h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_AD Access denied
80C4h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_EA Area too large
80C5h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_LE Data block length too large
80C6h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_RE Format error in response frame
80C7h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_IP Invalid parameter
80C8h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_SC Sequence conflict
80C9h DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_SE Sequence error
80CAh DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_NE Area non-existent
80CBh DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_DI Data incomplete or incorrect
80CCh DPMC_ERR_V1C_MM_NC Master parameter set not compatible
Refer to Error Codes (page 92).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 91 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 92

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
4.4.3 Error Codes
If the return code indicates DPMC_ERR_V1C_REQ_NEG, the status values
according to the DP-standard may be available in Error Code 1. Refer to the
PROFIBUS DP specification for information on how to interpret these status
values.
Error Code Name Meaning
01h L2_STATUS_UE
02h L2_STATUS_RR
03h L2_STATUS_RS
0Ch L2_STATUS_RDL Refer to PROFIBUS DP specification
0Dh L2_STATUS_RDH
0Fh L2_STATUS_NA
Page 92 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 93

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Mailbox Messaging
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
4.4.4 DP-V1 Error Codes
Possible error codes in Message Data word "Return Code".
Return Code Name Meaning
0003h DPMC_ERR_M_MEM_ALLOC Internal memory allocation error
0004h DPMC_ERR_M_L2_REQ Unknown opcode in the configuration
0005h DPMC_ERR_M_INVALID_PAR Invalid parameter in user request
0007h DPMC_ERR_M_NOT_IN_DATA Slave is not in DataExchange (thus no DP-V1 request can
exist)
0012h DPMC_ERR_M_REQ_ACTIVE A request is already active
0018h DPMC_ERR_M_NOT_ALLOWED Internal DPMC module not initialized correctly
0021h DPMC_ERR_M_CLOSED Internal DPMC instance no longer exists
0022h DPMC_ERR_M_STOPPED Internal DPMC instance has already been stopped
0023h DPMC_ERR_M_STARTED Internal DPMC instance has already been started
0024h DPMC_ERR_M_STATE_UNKNOWN Internal DPMC instance has entered an undefined state
002Fh DPMC_ERR_M_SLAVE_NOT_FOUND Slave does not respond
0031h DPMC_ERR_M_TIMEOUT Active request terminated with timeout
0034h DPMC_ERR_M_INVALID_LEN Invalid length in user request
0035h DPMC_ERR_M_REQ_NEG Negative indication from lower layer
0036h DPMC_ERR_M_REQ_RE Message frame format error in response
0037h DPMC_ERR_M_REQ_WITHDRAW Request was recalled
0038h DPMC_ERR_M_REQ_NOT_FOUND Associated request block not found
0040h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_FE Format error in request frame
0041h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_NI Function not implemented
0042h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_AD Access denied
0043h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_EA Area too large
0044h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_LE Data block length too large
0045h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_RE Format error in response frame
0046h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_IP Invalid parameter
0047h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_SC Sequence conflict
0048h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_SE Sequence error
0049h DPMC_ERR_M_MM_NE Area non-existent
004Ah DPMC_ERR_M_MM_DI Data incomplete or incorrect
004Bh DPMC_ERR_M_MM_NC Master parameter set not compatible
004Ch DPMC_ERR_M_S7_XA
004Dh DPMC_ERR_M_S7_XR PROFIBUS error for DP-V1 (NRS-PDU received)
004Eh DPMC_ERR_M_S7_XW
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 93 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 94

Mailbox Messaging MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
Page 94 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 95

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
In This Chapter
Basic Troubleshooting Steps ................................................................. 96
LED Status Indicators: Front of MVI46 Module ..................................... 97
Module Faceplate Status Indicators ...................................................... 98
PROFIBUS Master Indicators ................................................................ 99
Using ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) for Diagnostics................. 102
Standard PROFIBUS Slave Diagnostic Bytes ..................................... 108
The module provides information on diagnostics and troubleshooting in the
following forms:
LED status indicators on the front of the module provide general information
on the module's status.
Status data contained in the module can be viewed through the
Configuration/Debug port, using the troubleshooting and diagnostic
capabilities of ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB).
Status data values can be transferred from the module to processor memory
and can be monitored there manually or by customer-created logic.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 95 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 96

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
5.1 Basic Troubleshooting Steps
1 Verify that the module is installed correctly, and is communicating with the
processor.
2 Install the most current version of ProSoft Configuration Builder.
3 Note the color and behavior of the LED Status Indicators (lights) on the front
panel. Refer to the chart in the following section for examples.
Page 96 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 97

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
5.2 LED Status Indicators: Front of MVI46 Module
The LEDs indicate the module’s operating status. The module has two sets of
LED status indicators:
MVI46 Module Status LEDs on the front of
the module near the top
PROFIBUS Master Status LEDs behind the
door on the front of the module.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 97 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 98

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
5.3 Module Faceplate Status Indicators
Indicator Color Status Indication
CFG Green ON Configuration/Debug Port is active
OFF Configuration/Debug Port is inactive
P1 Not Used
P2 Not Used
APP
STATUS
BP ACT Amber ON The LED is ON when the module is able to
BATT
OK Red/
Amber ON Configuration Error: This LED is illuminated when the
PROFIBUS and module CRC values do not match
between input/output blocks.
Verify that the values match the values generated with
the Calculate Checksums button in ProSoft
Configuration Builder. If they do not match, you must
manually change the values at the appropriate address
locations listed in the Input and Output block definitions
in this manual.
OFF Normal operation.
communicate over the backplane.
OFF The LED is OFF when the module is unable to
communicate with the processor. The processor is
either absent or not running.
Red OFF The battery voltage is OK and running.
ON The battery voltage is low or the battery is not present.
The battery LED will illuminate briefly upon the first
installation of the module or if the unit has not had
power for an extended period of time. This behavior is
normal; however, should the LED come ON in a
working installation, please contact ProSoft
Technology.
OF The card is not receiving any power and is not securely
Green
GREEN The module is operating normally.
RED The program has detected an error or is being
plugged into the rack.
configured. If the LED remains RED for over 10
seconds, the processor program may be incompatible
with the module. Check the module version and mode
(Legacy or Flex) to determine the correct sample
ladder logic. Remove the card from the rack and re-
insert the card to restart the module’s program.
Page 98 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
Page 99

MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
PROFIBUS DPV1 Master User Manual
5.4 PROFIBUS Master Indicators
LED State Description
TKN HLD GREEN The module has the token
DBASE
STAT
MSTR STAT GREEN Operating mode
COM STAT GREEN Data exchange with all configured slaves
ALL LEDs RED Fatal error
GREEN Database OK
GREEN-Flashing Clear mode
RED Stop mode
OFF Offline
GREEN-Flashing Database download in progress
GREEN 1 second/
RED 2 seconds
RED Invalid database
OFF No databases have been downloaded
GREEN-Flashing Data exchange with at least one of the configured slaves
RED Bus control error (possible bus short circuit or configuration
OFF No data exchange with any configured slave
OFF The module does not have the token
Module in Legacy mode while the Flex ladder is loaded to the
processor. Check processor program.
error)
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 99 of 160
March 25, 2011
Page 100

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI46-PDPMV1 ♦ SLC Platform
User Manual PROFIBUS DPV1 Master
5.4.1 Examples
The following table shows some of the possible status indicators:
Processor
Status
Normal
operation
MVI46PDPMV1
module does
not see the
processor
RUN (ON) ACTIVE (ON)
RUN (ON) or
STOP
MVI46PDPMV1
Module
Status
ACTIVE (OFF)
PROFIBUS Master
Status
PROFIBUS Master
Status LED Description
COM STAT
(GREEN/Solid or Flash):
Master is communicating
with slaves (GREEN) or at
least one (Blinking).
DBASE STAT (GREEN):
PROFIBUS has been
configured.
TKN HOLD (GREEN):
MVI is holding the
PROFIBUS token.
MSTR STAT (GREEN):
Master is in operate
mode.
COM STAT (OFF):
Master is not
communicating with
slaves.
DBASE STAT (GREEN):
PROFIBUS has been
configured.
TKN HOLD (OFF):
Master does not have the
token and is inactive
MSTR STAT (OFF):
Master is inactive
MVI
PROFIBUS
Master is
stopped
RUN or
STOP
ACTIVE
COM STAT (OFF):
Master is not
communicating with
configured slaves.
DBASE STAT (GREEN):
PROFIBUS has been
configured.
TKN HOLD (GREEN):
MVI is holding the
PROFIBUS token.
MSTR STAT (RED):
Master is in STOP mode.
Page 100 of 160 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
March 25, 2011
 Loading...
Loading...