Pitney Bowes 3200 User Guide

Multi-Protocol On-board
Multi-function Print Server
NETWORK USER’S GUIDE
3200
Please read this manual thoroughly before using this machine on your network. You can print or view this manual from the CD-ROM at any time, please keep the CD-ROM in a convenient place for quick and easy reference at all times.

Definitions of warnings, cautions, and notes
We use the following icon throughout this User’s Guide:
Notes tell you how you should respond to a situation that may arise or give tips about how the operation works with other features.
Trademarks
The Pitney Bowes logo is a registered trademark of Pitney Bowes Inc.
BRAdmin Professional is a trademark of Brother Industries, Ltd.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Apple, Macintosh, and LaserWriter are registered trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc.
HP, Hewlett-Packard, Jetdirect and PCL are registered trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company.
Microsoft, Windows and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
OpenLDAP is a registered trademark of the OpenLDAP Foundation.
All other terms, brand and product names mentioned in this User’s Guide are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective companies.
OpenLDAP Statements
This product includes software developed by the OpenLDAP Project.
Unless otherwise expressly stated herein, The OpenLDAP Public License Version 2.8 shall be applied to individual files.
Copyright 1998-2005 The OpenLDAP Foundation All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted only as authorized by the OpenLDAP Public License.
A copy of this license is available in the file LICENSE in the top-level directory of the distribution or, alternatively, at <http://www.OpenLDAP.org/license.html>.
Portions Copyright 1999 Lars Uffmann.
Portions Copyright 1998 A. Hartgers.
All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted only as authorized by the OpenLDAP Public License.
Portions Copyright ©1990, 1993-1996 Regents of the University of Michigan. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms are permitted provided that this notice is preserved and that due credit is given to the University of Michigan at Ann Arbor. The name of the University may not be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission. This software is provided ''as is'' without express or implied warranty.
i

Portions Copyright ©1999, 2000 Novell, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
THIS WORK IS SUBJECT TO U.S. AND INTERNATIONAL COPYRIGHT LAWS AND TREATIES. USE, MODIFICATION, AND REDISTRIBUTION OF THIS WORK IS SUBJECT TO VERSION 2.0.1 OF THE OPENLDAP PUBLIC LICENSE, A COPY OF WHICH IS AVAILABLE AT HTTP://WWW.OPENLDAP.ORG/LICENSE.HTML OR IN THE FILE "LICENSE" IN THE TOP-LEVEL DIRECTORY OF THE DISTRIBUTION. ANY USE OR EXPLOITATION OF THIS WORK OTHER THAN AS AUTHORIZED IN VERSION 2.0.1 OF THE OPENLDAP PUBLIC LICENSE, OR OTHER PRIOR WRITTEN CONSENT FROM NOVELL, COULD SUBJECT THE PERPETRATOR TO CRIMINAL AND CIVIL LIABILITY.
Portions Copyright ©The Internet Society (1997).
see RFC 2251 for full legal notices.
The OpenLDAP Public License Version 2.8, 17 August 2003
Redistribution and use of this software and associated documentation ("Software"), with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
1.Redistributions in source form must retain copyright statements and notices,
2.Redistributions in binary form must reproduce applicable copyright statements and notices, this list of conditions, and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution, and
3.Redistributions must contain a verbatim copy of this document.
The OpenLDAP Foundation may revise this license from time to time. Each revision is distinguished by a version number. You may use this Software under terms of this license revision or under the terms of any subsequent revision of the license.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE OPENLDAP FOUNDATION AND ITS CONTRIBUTORS ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE OPENLDAP FOUNDATION, ITS CONTRIBUTORS, OR THE AUTHOR(S) OR OWNER(S) OF THE SOFTWARE BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
The names of the authors and copyright holders must not be used in advertising or otherwise to promote the sale, use or other dealing in this Software without specific, written prior permission. Title to copyright in this Software shall at all times remain with copyright holders.
OpenLDAP is a registered trademark of the OpenLDAP Foundation. Copyright 1999-2003 The OpenLDAP Foundation, Redwood City,California, USA. All Rights Reserved.
Permission to copy and distribute verbatim copies of this document is granted.
ii

A number of files contained in OpenLDAP Software contain a statement:
USE, MODIFICATION, AND REDISTRIBUTION OF THIS WORK IS SUBJECT TO VERSION 2.0.1 OF THE OPENLDAP PUBLIC LICENSE, A COPY OF WHICH IS AVAILABLE AT HTTP://WWW.OPENLDAP.ORG/LICENSE.HTML OR IN THE FILE "LICENSE" IN THE TOP-LEVEL DIRECTORY OF THE DISTRIBUTION.
The following is a verbatim copy of version 2.0.1 of the OpenLDAP Public License referenced in the above statement.
The OpenLDAP Public License
Version 2.0.1, 21 December 1999
Copyright 1999, The OpenLDAP Foundation, Redwood City, California, USA. All Rights Reserved.
Redistribution and use of this software and associated documentation ("Software"), with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
1.Redistributions of source code must retain copyright statements and notices. Redistributions must also contain a copy of this document.
2.Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
3.The name "OpenLDAP" must not be used to endorse or promote products derived from this Software without prior written permission of the OpenLDAP Foundation. For written permission, please contact foundation@openldap.org.
4.Products derived from this Software may not be called "OpenLDAP" nor may "OpenLDAP" appear in their names without prior written permission of the OpenLDAP Foundation. OpenLDAP is a trademark of the OpenLDAP Foundation.
5.Due credit should be given to the OpenLDAP Project (http://www.openldap.org/).
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE OPENLDAP FOUNDATION AND CONTRIBUTORS ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE OPENLDAP FOUNDATION OR ITS CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
RFC 2251 Full Copyright Statement
Copyright ©The Internet Society (1997). All Rights Reserved.
This document and translations of it may be copied and furnished to others, and derivative works that comment on or otherwise explain it or assist in its implementation may be prepared, copied, published and distributed, in whole or in part, without restriction of any kind, provided that the above copyright notice and
iii

this paragraph are included on all such copies and derivative works. However, this document itself may not be modified in any way, such as by removing the copyright notice or references to the Internet Society or other
Internet organizations, except as needed for the purpose of developing Internet standards in which case the procedures for copyrights defined in the Internet Standards process must be followed, or as required to translate it into languages other than English.
The limited permissions granted above are perpetual and will not be revoked by the Internet Society or its successors or assigns.
This document and the information contained herein is provided on an "AS IS" basis and THE INTERNET SOCIETY AND THE INTERNET ENGINEERING TASK FORCE DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY THAT THE USE OF THE INFORMATION HEREIN WILL NOT INFRINGE ANY RIGHTS OR ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Compilation and publication notice
Under the supervision of Pitney Bowes Inc., this manual has been compiled and published, covering the latest product’s descriptions and specifications.
The contents of this manual and the specifications of this product are subject to change without notice.
Pitney Bowes reserves the right to make changes without notice in the specifications and materials contained herein and shall not be responsible for any damages (including consequential) caused by reliance on the materials presented, including but not limited to typographical and other errors relating to the publication.
©2006 Pitney Bowes Inc.
iv

Table of contents |
|
|
1 |
Introduction |
|
|
Overview................................................................................................................................................ |
1 |
|
Network function features...................................................................................................................... |
2 |
|
Network printing............................................................................................................................... |
2 |
|
Network scanning ............................................................................................................................ |
2 |
|
Network PC-FAX ............................................................................................................................. |
2 |
|
Fax to server.................................................................................................................................... |
2 |
|
Management utility .......................................................................................................................... |
2 |
|
BRAdmin Professional (for Windows®) ....................................................................................... |
2 |
|
BRAdmin Light (for Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater) ...................................................................... |
2 |
|
Remote Setup ............................................................................................................................. |
3 |
|
Types of Network Connections.............................................................................................................. |
3 |
|
Network Connection Example ......................................................................................................... |
3 |
|
Peer-to-Peer printing using TCP/IP............................................................................................. |
3 |
|
Network Shared Printing.............................................................................................................. |
4 |
|
Protocols................................................................................................................................................ |
5 |
|
TCP/IP Protocols ............................................................................................................................. |
5 |
|
DHCP/BOOTP/RARP.................................................................................................................. |
5 |
|
APIPA.......................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
|
DNS client.................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
|
LPR/LPD ..................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
|
Port 9100..................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
|
SMTP client ................................................................................................................................. |
6 |
|
IPP............................................................................................................................................... |
6 |
|
mDNS.......................................................................................................................................... |
6 |
|
TELNET....................................................................................................................................... |
6 |
|
SNMP .......................................................................................................................................... |
6 |
|
Web server (HTTP) ..................................................................................................................... |
6 |
|
FTP.............................................................................................................................................. |
6 |
|
LDAP ........................................................................................................................................... |
6 |
|
IPv6 ............................................................................................................................................. |
6 |
2 |
Configuring your network printer |
|
|
Overview................................................................................................................................................ |
7 |
|
IP addresses, subnet masks and gateways .......................................................................................... |
7 |
|
IP address ....................................................................................................................................... |
7 |
|
Subnet mask.................................................................................................................................... |
8 |
|
Gateway (and router)....................................................................................................................... |
8 |
|
Setting the IP address and subnet mask............................................................................................... |
9 |
|
Using the BRAdmin Professional utility and the TCP/IP protocol to |
|
|
configure your network printer (for Windows® only) ........................................................................ |
9 |
|
BRAdmin Professional utility ....................................................................................................... |
9 |
|
How to configure your machine using the BRAdmin Professional utility ..................................... |
9 |
|
Using the control panel to configure your machine for a network.................................................. |
10 |
|
Using other methods to configure your machine for a network ..................................................... |
10 |
|
Changing the print server settings....................................................................................................... |
10 |
|
Using the BRAdmin Professional utility to change the print server settings |
|
|
(for Windows® only) ....................................................................................................................... |
10 |
v

|
Using a HTTP (web browser) to change the print/scan settings ................................................... |
11 |
|
Using the Remote Setup to change the print server settings |
|
|
(for Windows® and Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater)..................................................................... |
12 |
|
Remote Setup for Windows® ..................................................................................................... |
12 |
|
Remote Setup for Macintosh® ................................................................................................... |
12 |
3 |
Control Panel Setup |
|
|
LAN Main Setup Menu......................................................................................................................... |
13 |
|
Setup TCP/IP................................................................................................................................. |
13 |
|
BOOT Method ........................................................................................................................... |
13 |
|
IP Address................................................................................................................................. |
15 |
|
Subnet Mask ............................................................................................................................. |
16 |
|
Gateway .................................................................................................................................... |
16 |
|
Node Name ............................................................................................................................... |
16 |
|
WINS Config.............................................................................................................................. |
17 |
|
WINS Server.............................................................................................................................. |
17 |
|
DNS Server ............................................................................................................................... |
18 |
|
APIPA........................................................................................................................................ |
18 |
|
IPv6 ........................................................................................................................................... |
19 |
|
Ethernet ......................................................................................................................................... |
19 |
|
Setup I-Fax.................................................................................................................................... |
20 |
|
SMTP Server address ............................................................................................................... |
20 |
|
POP3 Server address................................................................................................................ |
21 |
|
Mailbox Name............................................................................................................................ |
22 |
|
Mailbox Pwd .............................................................................................................................. |
22 |
|
Setup Mail RX................................................................................................................................ |
23 |
|
Auto Polling ............................................................................................................................... |
23 |
|
Poll Frequency........................................................................................................................... |
23 |
|
Header....................................................................................................................................... |
23 |
|
Del Error Mail............................................................................................................................. |
24 |
|
Notification................................................................................................................................. |
24 |
|
Setup Mail TX ................................................................................................................................ |
24 |
|
Sender Subject.......................................................................................................................... |
24 |
|
Size Limit................................................................................................................................... |
25 |
|
Notification................................................................................................................................. |
25 |
|
Setup Relay ................................................................................................................................... |
26 |
|
Rly Broadcast ............................................................................................................................ |
26 |
|
Relay Domain............................................................................................................................ |
26 |
|
Relay Report.............................................................................................................................. |
27 |
|
Scan to E-mail (E-mail server)....................................................................................................... |
27 |
|
Color File Type for Scan to E-mail (E-mail server) .................................................................... |
27 |
|
Black and White File Type for Scan to E-mail (E-mail server)................................................... |
27 |
|
Scan to FTP................................................................................................................................... |
28 |
|
Color File Type for Scan to FTP ................................................................................................ |
28 |
|
Black and White File Type for Scan to FTP............................................................................... |
28 |
|
Fax to Server ................................................................................................................................. |
29 |
|
Setting Fax to Server to On....................................................................................................... |
30 |
|
How to Operate ......................................................................................................................... |
30 |
|
Time Zone ..................................................................................................................................... |
31 |
|
Windows® Time Zone Setting.................................................................................................... |
31 |
|
Restoring the network settings to factory default........................................................................... |
31 |
|
Printing the Network Configuration List ......................................................................................... |
32 |
vi

4 |
Network printing from Windows® basic TCP/IP Peer-to-Peer printing |
|
|
Overview.............................................................................................................................................. |
33 |
|
For Windows® 98/Me/NT®/2000/XP users........................................................................................... |
33 |
|
Configuring the standard TCP/IP port ........................................................................................... |
33 |
|
Printer driver not yet installed .................................................................................................... |
33 |
|
Printer driver already installed ................................................................................................... |
34 |
|
For Windows NT® 4.0 users ................................................................................................................ |
35 |
|
Installing the TCP/IP protocol ........................................................................................................ |
35 |
|
Other sources of information ............................................................................................................... |
35 |
5 |
Internet printing for Windows® |
|
|
Overview.............................................................................................................................................. |
36 |
|
Quick Tips.................................................................................................................................. |
36 |
|
Pitney Bowes Internet Print General Information .......................................................................... |
36 |
|
Pitney Bowes Internet Print: Configuring the Pitney Bowes Print Server ...................................... |
37 |
|
Print Server Configuration Checklist.......................................................................................... |
37 |
|
Pitney Bowes Internet Print: Using the BRAdmin |
|
|
Professional utility to Configure the Print Server ........................................................................... |
38 |
|
Pitney Bowes Internet Print: Using a Web Browser to Configure the Print Server........................ |
39 |
|
Pitney Bowes Internet Print: Installing the BIP software on |
|
|
Windows® 98/Me/2000/XP and Windows NT® 4.0 ........................................................................ |
39 |
|
Setup from CD-ROM ................................................................................................................. |
39 |
|
Adding a Second Pitney Bowes Internet Port................................................................................ |
41 |
|
Windows® 2000/XP IPP printing.................................................................................................... |
42 |
|
Specifying a different URL............................................................................................................. |
44 |
|
Other sources of information ............................................................................................................... |
44 |
6 |
Network printing from a Macintosh® |
|
|
Overview.............................................................................................................................................. |
45 |
|
How to select the print server (TCP/IP) (Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater) ........................................ |
45 |
|
How to select the print server (TCP/IP) (Mac OS® 9.1 - 9.2)......................................................... |
47 |
|
Changing the print server settings....................................................................................................... |
49 |
|
Changing the configuration using a web browser.......................................................................... |
49 |
|
Changing the configuration using the Remote Setup .................................................................... |
49 |
|
Using the BRAdmin Light utility to change the print server settings |
|
|
(for Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater) ................................................................................................. |
49 |
|
Other sources of information ............................................................................................................... |
50 |
7 |
Web Based Management |
|
|
Overview.............................................................................................................................................. |
51 |
|
How to connect to your machine using a Browser ........................................................................ |
52 |
|
Password Information.................................................................................................................... |
52 |
|
Changing the Scan to FTP configuration using a Browser............................................................ |
52 |
|
Changing the LDAP configuration using a Browser ...................................................................... |
53 |
vii

8 |
LDAP Operation |
|
|
Overview.............................................................................................................................................. |
54 |
|
Changing the LDAP configuration using a Browser ...................................................................... |
54 |
|
LDAP operation using the control panel ........................................................................................ |
54 |
9 |
Internet FAX |
|
|
Overview.............................................................................................................................................. |
56 |
|
Getting Connected .................................................................................................................... |
56 |
|
Control Panel Key Functions ......................................................................................................... |
57 |
|
Sending an Internet Fax ................................................................................................................ |
57 |
|
Manually Entering Text.................................................................................................................. |
58 |
|
Receiving E-mail or Internet Fax ................................................................................................... |
58 |
|
Receiving an Internet Fax to a PC................................................................................................. |
59 |
|
Forwarding Received E-mail and Fax Messages .......................................................................... |
59 |
|
Relay Broadcasting ....................................................................................................................... |
59 |
|
Relay Broadcast from a machine .............................................................................................. |
60 |
|
Sending to multiple phone numbers:......................................................................................... |
60 |
|
Outlook 97/98/2000/2002/2003: ................................................................................................ |
61 |
|
TX Verification Mail........................................................................................................................ |
61 |
|
Setup Mail (TX).............................................................................................................................. |
62 |
|
Setup Mail (RX) ............................................................................................................................. |
62 |
|
Error mail ....................................................................................................................................... |
62 |
|
Important information on Internet Fax ........................................................................................... |
63 |
10 |
Troubleshooting |
|
|
Overview.............................................................................................................................................. |
64 |
|
General problems ................................................................................................................................ |
64 |
|
CD-ROM is inserted, but does not start automatically............................................................... |
64 |
|
How to reset the Pitney Bowes print server to factory default................................................... |
64 |
|
Network print software installation problems ....................................................................................... |
64 |
|
The Pitney Bowes print server is not found during setup of the network print |
|
|
software installation or from the printer driver of the Pitney Bowes machine in Windows®....... |
64 |
|
The Pitney Bowes print server is not found using |
|
|
the Simple Network Configuration capabilities of Mac OS® X................................................... |
64 |
|
Printing problems................................................................................................................................. |
67 |
|
Print job is not printed................................................................................................................ |
67 |
|
Error during printing................................................................................................................... |
68 |
|
Protocol-specific troubleshooting......................................................................................................... |
69 |
|
Windows® 2000/XP IPP troubleshooting....................................................................................... |
69 |
|
Want to use a different Port number other than 631. ................................................................ |
69 |
|
Get More Info option in Windows® 2000 not working ................................................................ |
69 |
|
Web browser troubleshooting (TCP/IP)......................................................................................... |
69 |
|
LDAP troubleshooting.................................................................................................................... |
69 |
viii

A Appendix A
Using services ..................................................................................................................................... |
70 |
Other ways to set the IP address (for advanced users and Administrators)........................................ |
70 |
Using DHCP to configure the IP address ...................................................................................... |
70 |
Using BOOTP to configure the IP address.................................................................................... |
71 |
Using RARP to configure the IP address ...................................................................................... |
71 |
Using APIPA to configure the IP address...................................................................................... |
72 |
Using ARP to configure the IP address ......................................................................................... |
72 |
Windows® systems .................................................................................................................... |
72 |
UNIX®/Linux systems ................................................................................................................ |
73 |
Using the TELNET console to configure the IP address ............................................................... |
73 |
Installation when using a Network Print Queue or Share (printer driver only)..................................... |
75 |
Multi-function Print Server specifications............................................................................................. |
76 |
Function Table and Default Factory Settings....................................................................................... |
77 |
Entering Text ....................................................................................................................................... |
79 |
I Index
ix

1 Introduction
Overview
The Pitney Bowes machine can be shared on a 10/100 MB wired Ethernet network using the internal network |
1 |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
print server. The print server supports various functions and methods of connection depending on the |
|
||||||||
operating system you are running on a network supporting TCP/IP. These functions include printing, |
|
||||||||
scanning, PC-FAX send, PC-FAX receive, Remote Setup and Status Monitor. The following chart shows |
|
||||||||
what network features and connections are supported by each operating system. |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating |
10/100 |
Printing |
Scanning |
PC-Fax |
PC-Fax |
Remote |
Status |
|
|
Systems |
BASE-TX |
|
|
Send* |
Receive* |
Setup* |
Monitor |
|
|
|
Wired |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethernet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(TCP/IP) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Windows® |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
98/98SE/Me/ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
|
2000/XP/XP |
|
|
|||||||
Professional x64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Edition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Windows NT® 4.0 |
√ |
√ |
|
√ |
|
|
√ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mac OS® X 10.2.4 |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
√ |
√ |
|
|
or greater |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mac OS® 9.1-9.2 |
√ |
√ |
|
√ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To use the Pitney Bowes machine through a network, you need to configure the print server, and set up the computers you use.
In this chapter, you will learn the basic concept of the network function, connection and protocols. In Chapter 2, you will read information on network configuration. In Chapter 3, you will learn how to configure the print server using the control panel. Chapter 4 through Chapter 6 describe how to configure your print server with your operating system:
Chapter 2: Configuring your network printer
Chapter 3: Control Panel Setup
Chapter 4: Network printing from Windows® basic TCP/IP Peer-to-Peer printing
Chapter 5: Internet printing for Windows®
Chapter 6: Network printing from a Macintosh®
1

Introduction
Network function features
Pitney Bowes machine has the following basic network functions.
1
Network printing
The print server provides printing services for Windows® 98/98SE/Me/NT®/2000/XP supporting the TCP/IP protocols and Macintosh® supporting TCP/IP (Mac OS® 9.1-9.2 / Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater for a wired network).
Network scanning
You can scan documents over the network to your computer or to a central server (See Chapter 4 for Windows® and Chapter 10 for Macintosh® of the Software User’s Guide on the CD-ROM).
Network PC-FAX
You can directly send and receive a PC file as a PC-FAX on your network (See Chapter 6 for Windows® and Chapter 7 for Macintosh® of the Software User’s Guide on the CD-ROM for complete description).
Fax to server
The Fax to Server feature allows the machine to scan documents and send them via a separate fax server. Unlike Internet Fax or I-Fax, the Fax to Server feature utilizes a server to send the documents as fax data over phone or T-1 lines.
Management utility
BRAdmin Professional (for Windows®)
The BRAdmin Professional utility provides powerful, easy to use configuration and management of fax and network settings.
BRAdmin Light (for Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater)
BRAdmin Light is a utility for viewing machine status and configuring network settings from a computer running Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater.
2

Introduction
Remote Setup
The Remote Setup software allows you to configure network settings from a Windows® or Macintosh® (Mac |
|
OS® X 10.2.4 or greater). (See Chapter 5 for Windows® and Chapter 11 for Macintosh® of the Software User’s |
|
Guide on the CD-ROM). |
1 |
|
Types of Network Connections
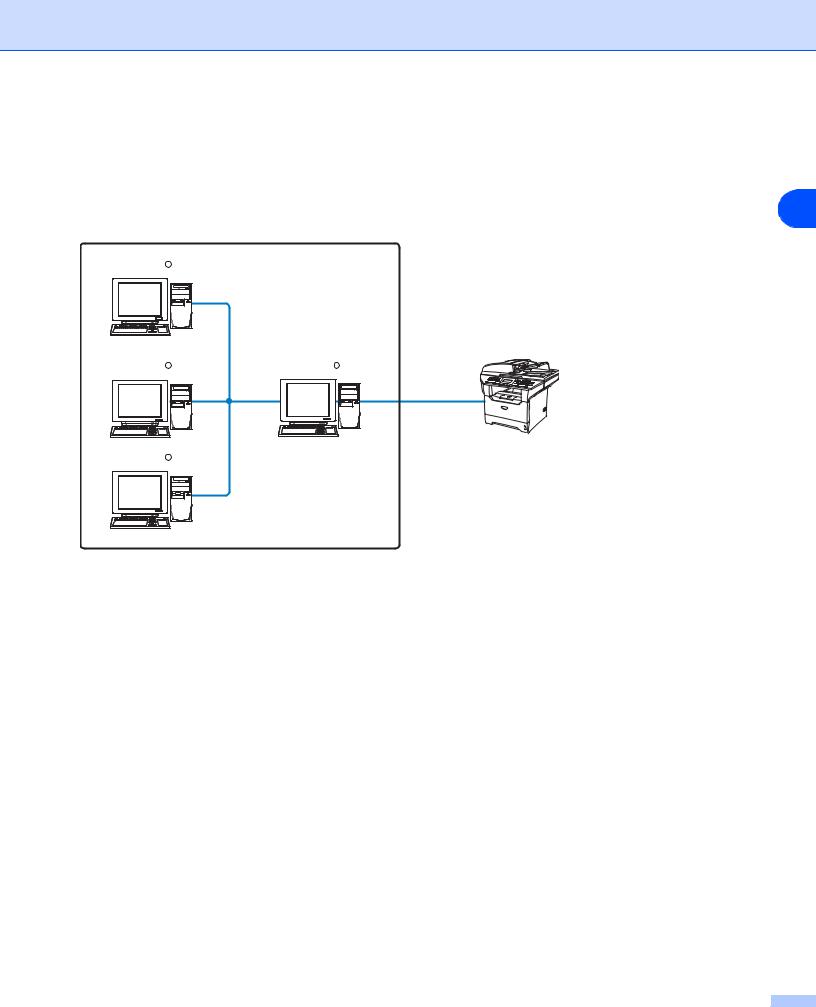
Generally speaking, there are two types of networks: A Peer-to-Peer network and a shared Network.
Network Connection Example
Peer-to-Peer printing using TCP/IP
In a Peer-to-Peer environment, each computer directly sends and receives data to each device. There is no central server controlling File access or Printer sharing.
WindowsR |
Windows R |
Windows R |
Network printer (your machine)
|
Switch or |
TCP/IP |
Router |
TCP/IP |
■In a smaller network of 2 or 3 computers, we recommend the Peer-to-Peer printing method as it is easier to configure than the Network Shared Printing method described on the following page. See Network Shared Printing on page 4.
■Each computer must use the TCP/IP Protocol.
■The Pitney Bowes machine needs an appropriate IP address configuration.
■If you are using a router, the Gateway address must be configured on the computers and the Pitney Bowes machine.
3
Introduction
Network Shared Printing
In a Network Shared environment, each computer sends data via a centrally controlled computer. This type of computer is often called a “Server” or a “Print Server”. Its job is to control the printing of all print jobs.
1
WindowsR
WindowsR |
WindowsR |
|
|
|
TCP/IP |
WindowsR |
Also known as |
Network printer (your machine) |
|
||
|
“Server” or “Print |
|
|
Server” |
|
Network Shared
■In a larger network, we recommend a Network Shared printing environment.
■The “Server” or the “Print Server” must use the TCP/IP Print Protocol.
■The Pitney Bowes machine needs an appropriate IP address configuration unless the machine is shared via the parallel port or USB port of the server.
4
Introduction
Protocols
TCP/IP Protocols
1
Protocols are the standardized sets of rules for transmitting data on a network. Protocols allow users to gain access to network-connected resources.
The print server used on this Pitney Bowes product supports the TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) protocols.
TCP/IP is the most popular set of protocols and can be used in almost all operating systems such as Windows®, Macintosh® and Linux.
The following TCP/IP protocols are available on this Pitney Bowes product.
DHCP/BOOTP/RARP
By using the DHCP/BOOTP/RARP protocols, the IP address can be automatically configured.
 Note
Note
To use the DHCP/BOOTP/RARP protocols, please contact your Network Administrator.
APIPA
If you do not assign an IP address manually (using the Multi-Function Suite Installation or BRAdmin software) or automatically (using a DHCP/BOOTP/RARP server), the Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) protocol will automatically assign an IP address from the range 169.254.1.0 to 169.254.254.255.
DNS client
The Pitney Bowes print server supports the Domain Name Service (DNS) client function. This function allows the print server to communicate with other devices by using its DNS name.
LPR/LPD
Commonly used printing protocol on a TCP/IP network.
Port 9100
Another commonly used printing protocol on a TCP/IP network.
5

Introduction
SMTP client
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) allows the Pitney Bowes machine to send and receive e-mails.
IPP |
1 |
|
The Internet Printing Protocol (IPP Version 1.0) allows you to print documents via the internet.
mDNS
mDNS allows the Pitney Bowes print server to automatically configure itself to work in a Mac OS® X Simple Network Configured system. (Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater).
TELNET
The Pitney Bowes print server supports TELNET server for command line configuration.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used to manage network devices including computers, routers and Pitney Bowes network ready machines.
Web server (HTTP)
The Pitney Bowes print server is equipped with a built in web server that allows you to monitor its status or change its configuration settings.
 Note
Note
We recommend Internet Explorer 6.0 (or higher) or Netscape Navigator 7.1 (or higher). If a different web browser is used, make sure it is compatible with HTTP 1.0 and HTTP 1.1.
FTP
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) allows the Pitney Bowes machine to scan black and white or color documents directly to an FTP server located locally on your network or on the internet.
LDAP
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) allows the Pitney Bowes machine to search for information such as fax numbers and E-mail addresses from an LDAP server.
IPv6
This machine is compatible with the IPv6, the next generation internet protocol.
6

2 Configuring your network printer
Overview
2
Before you can use your Pitney Bowes machine on your network, you need to install the Pitney Bowes software and also configure the appropriate TCP/IP network settings on the machine itself. To do this, we recommend that you use the automatic installer on the Pitney Bowes CD-ROM as this will guide you through the software and network installation.
If you do not wish to use the automatic installer, or you do not understand some of the terms used by the automatic installer, refer to the remainder of this chapter for more information.
 Note
Note
If you do not wish to, or are unable to use the automatic installer or any of Pitney Bowes’s software tools, you can also use the machine’s control panel to change network settings. For more information, see Control Panel Setup on page 13.
IP addresses, subnet masks and gateways
To use the machine in a networked TCP/IP environment, you need to configure its IP address and subnet mask. The IP address you assign to the print server must be on the same logical network as your host computers. If it is not, you must properly configure the subnet mask and the gateway address.
IP address
An IP address is a series of numbers that identifies each device connected to a network. An IP address consists of four numbers separated by dots. Each number is between 0 and 255.
Example: In a small network, you would normally change the final number.
192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2, 192.168.1.3
If you have a DHCP/BOOTP/RARP server in your network (typically a UNIX®/Linux or Windows® 2000/XP network) the print server will automatically obtain its IP address from the DHCP server.
 Note
Note
On smaller networks, the DHCP server may be the Router.
For more information on DHCP, BOOTP and RARP, see Using DHCP to configure the IP address on page 70, Using BOOTP to configure the IP address on page 71 and Using RARP to configure the IP address on page 71.
7
Configuring your network printer
If you do not have a DHCP/BOOTP/RARP server, the Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) protocol will automatically assign an IP address from the range 169.254.1.0 to 169.254.254.255. For more information on APIPA, see Using APIPA to configure the IP address on page 72.
If the APIPA protocol is disabled, the default IP address of a Pitney Bowes print server is 192.0.0.192.
However, you can easily change this IP address number to match with the IP address details of your network. 2 For information on how to change the IP address, see Setting the IP address and subnet mask on page 9.
Subnet mask
Subnet masks restrict network communication.
Example: PC1 can talk to PC2
PC1 IP Address:192.168.1.2
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
PC2 IP Address:192.168.1.3
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
 Note
Note
0 denotes that there is no limit to communication at this part of the address.
In the above example, we can communicate with anything that has an IP address that begins with 192.168.1.X
Gateway (and router)
A gateway is a network point that acts as an entrance to another network and sends data transmitted via the network to an exact destination. The router knows where to direct data that arrives at the gateway. If a destination is located at an external network, the router transmits data to the external network. If your network communicates with other networks, you may need to configure the Gateway IP address. If you do not know the Gateway IP address then contact your Network Administrator.
8

Configuring your network printer
Setting the IP address and subnet mask
Using the BRAdmin Professional utility and the TCP/IP protocol to configure |
|
your network printer (for Windows® only) |
2 |
|
BRAdmin Professional utility
The BRAdmin Professional utility is designed to allow you to manage your network connected Pitney Bowes machines in a TCP/IP environment.
How to configure your machine using the BRAdmin Professional utility
 Note
Note
•Please use the BRAdmin Professional utility that was supplied on the CD-ROM of your Pitney Bowes product. This utility is only available for Windows® users.
•If you are using Personal Firewall software (e.g. the Internet Connection Firewall available in Windows® XP), disable it. Once you are sure that you can print, re-start your Personal Firewall software.
•Node name: Node name appears in current BRAdmin Professional window. The default Node name is “BRN_xxxxxx” (“xxxxxx” is the last six digits of Ethernet address.).
•The default password for Pitney Bowes print servers is “access”.
1Start the BRAdmin Professional utility (from Windows® 98/98SE/Me, Windows NT® 4.0 and Windows® 2000/XP), by clicking Start / Programs / Administrator Utilities / BRAdmin Professional Utilities / BRAdmin Professional.
2Select TCP/IP in the left frame of the main BRAdmin window.
3Select Search Active Devices from the Devices menu. BRAdmin Professional will search for new devices automatically.
9

Configuring your network printer
 Note
Note
•If the print server is set to its factory default settings without using a DHCP/BOOTP/RARP server, the device will appear as an APIPA device in the BRAdmin Professional utility screen.
•You can find the node name and IP address by printing the Network Configuration List. See Printing
the Network Configuration List on page 32 for information on how to print the Network Configuration |
2 |
List on your print server. |
|
|
|
4 Double-click the unconfigured device.
5 Enter the IP address, Subnet Mask and Gateway (if needed) of your print server.
6 Click OK.
7 With the correctly programmed IP address, you will see the Pitney Bowes print server in the device list.
Using the control panel to configure your machine for a network
You can configure your machine for a network using the control panel LAN menu. See Control Panel Setup on page 13.
Using other methods to configure your machine for a network
You can configure your machine for a network using other methods. See Other ways to set the IP address (for advanced users and Administrators) on page 70.
Changing the print server settings
Using the BRAdmin Professional utility to change the print server settings (for Windows® only)
1 Start the BRAdmin Professional utility (from Windows® 95/98/Me, Windows NT® 4.0 and Windows® 2000/XP), by clicking Start / Programs /Administrator Utilities /BRAdmin Professional Utilities / BRAdmin Professional.
2
3
4
5
Select TCP/IP in the left frame of the main BRAdmin window.
Select the print server which you want to configure, in the right frame of the main BRAdmin window.
Select Configure Print Server from the Control menu.
Enter a password. The default Password is “access”.
10

Configuring your network printer
6 You can now change the print server settings.
Using a HTTP (web browser) to change the print/scan settings
A standard web browser (we recommend Microsoft Internet Explorer® version 6.0 or later, or Netscape |
2 |
Navigator® version 7.1 or later) can be used to change your print server settings using the HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol). To use a web browser, you must have assigned an IP address to the print server.
1 Type http://printer_ip_address/ into your browser. (Where printer_ip_address is the IP address or the print server name)
For example: http://192.168.1.2/ (if the printer’s IP address is 192.168.1.2.)
 Note
Note
If you have edited the hosts file on your computer or are using Domain Name System (DNS), you can also enter the DNS name of the print server. As the print server supports TCP/IP and NetBIOS names, you can also enter the NetBIOS name of the print server. The NetBIOS name can be seen in the Network Configuration List. See Printing the Network Configuration List on page 32 for information on how to print the Network Configuration List on your print server. The NetBIOS name assigned is the first 15 characters of the node name and by default it will appear as BRN_xxxxxx where xxxxxx is the last six digits of the Ethernet address.
2
3
4
5
6
Click Network Configuration.
Enter a user name and a password. The User Name is “admin” and the default Password is “access”.
Click OK.
Click Configure TCP/IP.
You can now change the printer server settings.
11

Configuring your network printer
Using the Remote Setup to change the print server settings (for Windows® and Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater)
Remote Setup for Windows® 2
The Remote Setup application allows you to configure network settings from a Windows® application. When you access this application, the settings on your machine will be downloaded automatically to your PC and displayed on your PC screen. If you change the settings, you can upload them directly to the machine.
1 Click the Start button, All Programs, Pitney Bowes, Multi-Function Suite 3200, Remote Setup, then 3200 LAN .
2
3
4
Enter a password. The default Password is “access”.
Click TCP/IP.
You can now change the print server settings.
Remote Setup for Macintosh®
The Remote Setup application allows you to configure many 3200 settings from a Macintosh® application. When you access this application, the settings on your machine will be downloaded automatically to your Macintosh® and displayed on your Macintosh® screen. If you change the settings, you can upload them directly to the machine.
1
2
3
4
5
Double click the Macintosh HD icon on your desktop, Library, Printers, Pitney Bowes, then Utilities.
Double click the Remote Setup icon.
Enter a password. The default Password is “access”.
Click TCP/IP.
You can now change the print server settings.
12

3 Control Panel Setup
LAN Main Setup Menu
3
The control panel LAN menu section can be used to configure network settings.
Press Menu, then press number 7 and then proceed to the menu selection you wish to configure.
Please note that the machine is supplied with Remote Setup applications for Windows® and Macintosh®, the BRAdmin Professional utility for Windows®, BRAdmin Light utility for Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater and HTTP protocol (web based management) for Windows® and Macintosh®, which also can be used to configure many aspects of the network. See Changing the print server settings on page 10 for Windows® and Changing the print server settings on page 49 for Macintosh®.
Setup TCP/IP
This menu has ten sections: Boot Method, IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, Node Name, WINS Config, WINS Server, DNS Server, APIPA and IPv6.
BOOT Method
1 Press Menu, 7, 1, 1.
2 Press ▲ or ▼ to select Auto, Static, RARP, BOOTP or DHCP.
3 Press OK.
4 Press Stop/Exit.
Auto mode
In this mode, the machine will scan the network for a DHCP server, if it can find one, and if the DHCP server is configured to allocate an IP address to the machine, then the IP address supplied by the DHCP server will be used. If no DHCP server is available, the machine will scan for a BOOTP server. If a BOOTP server is available, and it is configured correctly, the machine will take its IP address from the BOOTP server. If a BOOTP server is not available, the machine will scan for a RARP server. If a RARP server also does not answer, the machine will use an APIPA address, see Using APIPA to configure the IP address on page 72. This whole process can take 2 to 3 minutes so we recommend printing a Network Configuration List to confirm the network settings are set correctly.
Static mode
In this mode the machine’s IP address must be manually assigned. Once entered the IP address is locked to the assigned address.
13
Control Panel Setup
RARP mode
Pitney Bowes print server IP address can be configured using the Reverse ARP (RARP) facility on your host computer. This is done by editing the /etc/ethers file (if this file does not exist, you can create it) with an entry similar to the following:
00:80:77:31:01:07 |
BRN_310107 |
3 |
|
Where the first entry is the Ethernet address of the print server and the second entry is the name of the print server (the name must be the same as the one you put in the /etc/hosts file).
If the RARP daemon is not already running, start it (depending on the system the command can be rarpd, rarpd -a, in.rarpd -a or something else; type man rarpd or refer to your system documentation for additional information). To verify that the RARP daemon is running on a Berkeley UNIX-based system, type the following command:
ps -ax | grep -v grep | grep rarpd
For AT&T UNIX-based systems, type:
ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep rarpd
The Pitney Bowes print server will get the IP address from the RARP daemon when it is powered on.
BOOTP mode
BOOTP is an alternative to RARP. However, unlike RARP, it is able to configure the subnet mask and gateway. In order to use BOOTP to configure the IP address make sure that BOOTP is installed and running on your host computer (it should appear in the /etc/services file on your host as a real service; type man bootpd or refer to your system documentation for information). BOOTP is usually started up via the /etc/inetd.conf file, so you may need to enable it by removing the “#” in front of the bootp entry in that file. For example, a typical bootp entry in the /etc/inetd.conf file would be:
#bootp dgram udp wait /usr/etc/bootpd bootpd -i
 Note
Note
Depending on the system, this entry might be called “bootps” instead of “bootp”.
In order to enable BOOTP, simply use an editor to delete the “#” (if there is no “#”, then BOOTP is already enabled). Then edit the BOOTP configuration file (usually /etc/bootptab) and enter the name, network type (1 for Ethernet), Ethernet address and the IP address, subnet mask and gateway of the print server.
Unfortunately, the exact format for doing this is not standardized, so you will need to refer to your system documentation to determine how to enter this information (many UNIX® systems also have template examples in the bootptab file that you can use for reference). Some examples of typical /etc/bootptab entries include:
BRN_310107 1 00:80:77:31:01:07 192.189.207.3
and:
BRN_310107:ht=ethernet:ha=008077310107:\ ip=192.189.207.3:
14

Control Panel Setup
Certain BOOTP host software implementations will not respond to BOOTP requests if you have not included a download filename in the configuration file; if this is the case, simply create a null file on the host and specify the name of this file and its path in the configuration file.
As with RARP, the print server will load its IP address from the BOOTP server when the printer is powered on.
3
DHCP mode
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is one of several automated mechanisms for IP address allocation. If you have a DHCP server in your network (typically a UNIX®, Windows® 2000/XP network) the print server automatically obtains its IP address from DHCP server and register its name with any RFC 1001 and 1002-compliant dynamic name services.
 Note
Note
If you do not want your print server to be configured using DHCP, BOOTP or RARP, you must set the BOOT METHOD to static, this will prevent the print server from trying to obtain an IP address from any of these systems. To change the BOOT METHOD, use the control panel, Web browser or by using the BRAdmin application.
IP Address
This field displays the current IP address of the machine. If the BOOT Method is set to Static, enter the IP address that you wish to assign to the machine (check with your network manager for the IP address to use). If you have selected a method other than Static, the machine will attempt to determine its IP address using the DHCP, RARP or BOOTP protocols. The default IP address of your machine will probably be incompatible with the IP address numbering scheme of your network. We recommend that you contact your network manager for the correct IP address settings.
1 Press Menu, 7, 1, 2.
2
3
4
Select 1 to change. Enter the IP address.
Press OK.
Press Stop/Exit.
15

Control Panel Setup
Subnet Mask
This field displays the current subnet mask used by the machine. If you are not using DHCP or BOOTP to obtain the subnet mask, enter the desired subnet mask. Check with your network manager for the subnet mask to use.
1
2
3
4
3
Press Menu, 7, 1, 3.
Select 1 to change. Enter the Subnet Mask address.
Press OK.
Press Stop/Exit.
Gateway
This field displays the current gateway or router address used by the machine. If you are not using DHCP or BOOTP to obtain the gateway or router address, enter the address you wish to assign. If you do not have a gateway or router, leave this field blank. Check with your network manager if you are unsure.
1 Press Menu, 7, 1, 4.
2
3
4
Enter the Gateway address.
Press OK.
Press Stop/Exit.
Node Name
You can register the machine name on the Network. This name is often referred to as a NetBIOS name; and is the name that is registered by the WINS server on your network. Pitney Bowes recommends the name BRN_XXXXXX (where XXXXXX is the last six digits of the Ethernet address) (up to 15 characters).
1 Press Menu, 7, 1, 5.
2
3
4
Select 1 to change. Enter the Node Name.
Press OK.
Press Stop/Exit.
16

Control Panel Setup
WINS Config
This selection controls how the machine obtains the IP address of the WINS server.
1 Press Menu, 7, 1, 6.
3
2
3
4
Press ▲ or ▼ to select Auto or Static.
Press OK.
Press Stop/Exit.
Auto
Automatically uses a DHCP request to determine the IP addresses for the primary and secondary WINS servers. You must set the BOOT Method to Auto for this feature to work.
Static
Uses a specified IP address for the primary and secondary WINS servers.
WINS Server
1 Press Menu, 7, 1, 7.
2
3
4
5
6
Press ▲ or ▼ to select Primary or Secondary.
Press OK.
Enter the WINS Server address.
Press OK.
Press Stop/Exit.
Primary WINS Server IP Address
This field specifies the IP address of the primary WINS (Windows® Internet Naming Service) server.
Secondary WINS Server IP Address
This field specifies the IP address of the secondary WINS server. It is used as a backup to the Primary WINS server address. If the Primary server is unavailable, the machine still can register itself with a secondary server. If you have a primary WINS server, but no secondary WINS server, simply leave this field blank.
17

Control Panel Setup
DNS Server
1
2
3
4
5
6
Press Menu, 7, 1, 8.
Press ▲ or ▼ to select Primary or Secondary. |
3 |
|
Press OK.
Enter the DNS Server address.
Press OK.
Press Stop/Exit.
Primary DNS Server IP Address
This field specifies the IP address of the primary DNS (Domain Name Service) server.
Secondary DNS Server IP Address
This field specifies the IP address of the secondary DNS server. It is used as a backup to the Primary DNS server address. If the Primary server is unavailable, the machine will contact the Secondary DNS server.
APIPA
When enabled, the print server will automatically allocate a IP address in the range (169.254.1.0 - 169.254.254.255) when the print server cannot obtain an IP address through the BOOT Method you have set (Menu, 7, 1, 1 ). Selecting Off means the IP address doesn’t change, when the print server cannot obtain an IP address through the BOOT Method you have set.
1 Press Menu, 7, 1, 9.
2
3
4
Press ▲ or ▼ to select On or Off.
Press OK.
Press Stop/Exit.
18
 Loading...
Loading...