Mitsubishi Electronics Q173CPUN, Q172CPUN User Manual

 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS 
(Please read these instructions before using this equipment.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals introduced in this manual carefully and pay full attention to safety to handle the product correctly.
These precautions apply only to this product. Refer to the Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Users manual for a description of the Motion controller safety precautions.
In this manual, the safety instructions are ranked as "DANGER" and "CAUTION".

 DANGER
DANGER

 CAUTION
CAUTION
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in medium or slight personal injury or physical damage.
Depending on circumstances, procedures indicated by  CAUTION may also be linked to serious results.
CAUTION may also be linked to serious results.
In any case, it is important to follow the directions for usage.
Please save this manual to make it accessible when required and always forward it to the end user.
A - 1

For Safe Operations
1. Prevention of electric shocks
 DANGER
DANGER
 Never open the front case or terminal covers while the power is ON or the unit is running, as this may lead to electric shocks.
Never open the front case or terminal covers while the power is ON or the unit is running, as this may lead to electric shocks.
 Never run the unit with the front case or terminal cover removed. The high voltage terminal and charged sections will be exposed and may lead to electric shocks.
Never run the unit with the front case or terminal cover removed. The high voltage terminal and charged sections will be exposed and may lead to electric shocks.
 Never open the front case or terminal cover at times other than wiring work or periodic inspections even if the power is OFF. The insides of the Motion controller and servo amplifier are charged and may lead to electric shocks.
Never open the front case or terminal cover at times other than wiring work or periodic inspections even if the power is OFF. The insides of the Motion controller and servo amplifier are charged and may lead to electric shocks.
 Completely turn off the externally supplied power used in the system before mounting or removing the module, performing wiring work, or inspections. Failing to do so may lead to electric shocks.
Completely turn off the externally supplied power used in the system before mounting or removing the module, performing wiring work, or inspections. Failing to do so may lead to electric shocks.
 When performing wiring work or inspections, turn the power OFF, wait at least ten minutes, and then check the voltage with a tester, etc. Failing to do so may lead to electric shocks.
When performing wiring work or inspections, turn the power OFF, wait at least ten minutes, and then check the voltage with a tester, etc. Failing to do so may lead to electric shocks.
 Be sure to ground the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor. (Ground resistance : 100
Be sure to ground the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor. (Ground resistance : 100  or less) Do not ground commonly with other devices.
or less) Do not ground commonly with other devices.
 The wiring work and inspections must be done by a qualified technician.
The wiring work and inspections must be done by a qualified technician.
 Wire the units after installing the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor. Failing to do so may lead to electric shocks or damage.
Wire the units after installing the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor. Failing to do so may lead to electric shocks or damage.
 Never operate the switches with wet hands, as this may lead to electric shocks.
Never operate the switches with wet hands, as this may lead to electric shocks.
 Do not damage, apply excessive stress, place heavy things on or sandwich the cables, as this may lead to electric shocks.
Do not damage, apply excessive stress, place heavy things on or sandwich the cables, as this may lead to electric shocks.
 Do not touch the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor terminal blocks while the power is ON, as this may lead to electric shocks.
Do not touch the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor terminal blocks while the power is ON, as this may lead to electric shocks.
 Do not touch the built-in power supply, built-in grounding or signal wires of the Motion controller and servo amplifier, as this may lead to electric shocks.
Do not touch the built-in power supply, built-in grounding or signal wires of the Motion controller and servo amplifier, as this may lead to electric shocks.
2. For fire prevention
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Install the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor on incombustible. Installing them directly or close to combustibles will lead to fire.
Install the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor on incombustible. Installing them directly or close to combustibles will lead to fire.
 If a fault occurs in the Motion controller or servo amplifier, shut the power OFF at the servo amplifier’s power source. If a large current continues to flow, fire may occur.
If a fault occurs in the Motion controller or servo amplifier, shut the power OFF at the servo amplifier’s power source. If a large current continues to flow, fire may occur.
 When using a regenerative resistor, shut the power OFF with an error signal. The regenerative resistor may abnormally overheat due to a fault in the regenerative transistor, etc., and may lead to fire.
When using a regenerative resistor, shut the power OFF with an error signal. The regenerative resistor may abnormally overheat due to a fault in the regenerative transistor, etc., and may lead to fire.
 Always take heat measures such as flame proofing for the inside of the control panel where the servo amplifier or regenerative resistor is installed and for the wires used. Failing to do so may lead to fire.
Always take heat measures such as flame proofing for the inside of the control panel where the servo amplifier or regenerative resistor is installed and for the wires used. Failing to do so may lead to fire.
 Do not damage, apply excessive stress, place heavy things on or sandwich the cables, as this may lead to fire.
Do not damage, apply excessive stress, place heavy things on or sandwich the cables, as this may lead to fire.
A - 2
3. For injury prevention
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Do not apply a voltage other than that specified in the instruction manual on any terminal. Doing so may lead to destruction or damage.
Do not apply a voltage other than that specified in the instruction manual on any terminal. Doing so may lead to destruction or damage.
 Do not mistake the terminal connections, as this may lead to destruction or damage.
Do not mistake the terminal connections, as this may lead to destruction or damage.
 Do not mistake the polarity ( + / - ), as this may lead to destruction or damage.
Do not mistake the polarity ( + / - ), as this may lead to destruction or damage.
 Do not touch the heat radiating fins of controller or servo amplifier, regenerative resistor and servomotor, etc., while the power is ON and for a short time after the power is turned OFF. In this timing, these parts become very hot and may lead to burns.
Do not touch the heat radiating fins of controller or servo amplifier, regenerative resistor and servomotor, etc., while the power is ON and for a short time after the power is turned OFF. In this timing, these parts become very hot and may lead to burns.
 Always turn the power OFF before touching the servomotor shaft or coupled machines, as these parts may lead to injuries.
Always turn the power OFF before touching the servomotor shaft or coupled machines, as these parts may lead to injuries.
 Do not go near the machine during test operations or during operations such as teaching. Doing so may lead to injuries.
Do not go near the machine during test operations or during operations such as teaching. Doing so may lead to injuries.
4. Various precautions
Strictly observe the following precautions.
Mistaken handling of the unit may lead to faults, injuries or electric shocks.
(1) System structure
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Always install a leakage breaker on the Motion controller and servo amplifier power source.
Always install a leakage breaker on the Motion controller and servo amplifier power source.
 If installation of an electromagnetic contactor for power shut off during an error, etc., is specified in the instruction manual for the servo amplifier, etc., always install the electromagnetic contactor.
If installation of an electromagnetic contactor for power shut off during an error, etc., is specified in the instruction manual for the servo amplifier, etc., always install the electromagnetic contactor.
 Install the emergency stop circuit externally so that the operation can be stopped immediately and the power shut off.
Install the emergency stop circuit externally so that the operation can be stopped immediately and the power shut off.
 Use the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor with the correct combinations listed in the instruction manual. Other combinations may lead to fire or faults.
Use the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor with the correct combinations listed in the instruction manual. Other combinations may lead to fire or faults.
 Use the Motion controller, base unit and motion module with the correct combinations listed in the instruction manual. Other combinations may lead to faults.
Use the Motion controller, base unit and motion module with the correct combinations listed in the instruction manual. Other combinations may lead to faults.
 If safety standards (ex., robot safety rules, etc.,) apply to the system using the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor, make sure that the safety standards are satisfied.
If safety standards (ex., robot safety rules, etc.,) apply to the system using the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor, make sure that the safety standards are satisfied.
 Construct a safety circuit externally of the Motion controller or servo amplifier if the abnormal operation of the Motion controller or servo amplifier differ from the safety directive operation in the system.
Construct a safety circuit externally of the Motion controller or servo amplifier if the abnormal operation of the Motion controller or servo amplifier differ from the safety directive operation in the system.
 In systems where coasting of the servomotor will be a problem during the forced stop, emergency stop, servo OFF or power supply OFF, use dynamic brakes.
In systems where coasting of the servomotor will be a problem during the forced stop, emergency stop, servo OFF or power supply OFF, use dynamic brakes.
 Make sure that the system considers the coasting amount even when using dynamic brakes.
Make sure that the system considers the coasting amount even when using dynamic brakes.  In systems where perpendicular shaft dropping may be a problem during the forced stop,
In systems where perpendicular shaft dropping may be a problem during the forced stop,
emergency stop, servo OFF or power supply OFF, use both dynamic brakes and electromagnetic brakes.
A - 3

 CAUTION
CAUTION
 The dynamic brakes must be used only on errors that cause the forced stop, emergency stop, or servo OFF. These brakes must not be used for normal braking.
The dynamic brakes must be used only on errors that cause the forced stop, emergency stop, or servo OFF. These brakes must not be used for normal braking.
 The brakes (electromagnetic brakes) assembled into the servomotor are for holding applications, and must not be used for normal braking.
The brakes (electromagnetic brakes) assembled into the servomotor are for holding applications, and must not be used for normal braking.
 The system must have a mechanical allowance so that the machine itself can stop even if the stroke limits switch is passed through at the max. speed.
The system must have a mechanical allowance so that the machine itself can stop even if the stroke limits switch is passed through at the max. speed.
 Use wires and cables that have a wire diameter, heat resistance and bending resistance compatible with the system.
Use wires and cables that have a wire diameter, heat resistance and bending resistance compatible with the system.
 Use wires and cables within the length of the range described in the instruction manual.
Use wires and cables within the length of the range described in the instruction manual.
 The ratings and characteristics of the parts (other than Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor) used in a system must be compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor.
The ratings and characteristics of the parts (other than Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor) used in a system must be compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor.
 Install a cover on the shaft so that the rotary parts of the servomotor are not touched during operation.
Install a cover on the shaft so that the rotary parts of the servomotor are not touched during operation.
 There may be some cases where holding by the electromagnetic brakes is not possible due to the life or mechanical structure (when the ball screw and servomotor are connected with a timing belt, etc.). Install a stopping device to ensure safety on the machine side.
There may be some cases where holding by the electromagnetic brakes is not possible due to the life or mechanical structure (when the ball screw and servomotor are connected with a timing belt, etc.). Install a stopping device to ensure safety on the machine side.
(2) Parameter settings and programming
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Set the parameter values to those that are compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor model and the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
Set the parameter values to those that are compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor model and the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
 The regenerative resistor model and capacity parameters must be set to values that conform to the operation mode, servo amplifier and servo power supply module. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
The regenerative resistor model and capacity parameters must be set to values that conform to the operation mode, servo amplifier and servo power supply module. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
 Set the mechanical brake output and dynamic brake output validity parameters to values that are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
Set the mechanical brake output and dynamic brake output validity parameters to values that are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
 Set the stroke limit input validity parameter to a value that is compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the setting is incorrect.
Set the stroke limit input validity parameter to a value that is compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the setting is incorrect.
 Set the servomotor encoder type (increment, absolute position type, etc.) parameter to a value that is compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the setting is incorrect.
Set the servomotor encoder type (increment, absolute position type, etc.) parameter to a value that is compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the setting is incorrect.
 Set the servomotor capacity and type (standard, low-inertia, flat, etc.) parameter to values that are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
Set the servomotor capacity and type (standard, low-inertia, flat, etc.) parameter to values that are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
 Set the servo amplifier capacity and type parameters to values that are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
Set the servo amplifier capacity and type parameters to values that are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.  Use the program commands for the program with the conditions specified in the instruction manual.
Use the program commands for the program with the conditions specified in the instruction manual.
A - 4

 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Set the sequence function program capacity setting, device capacity, latch validity range, I/O assignment setting, and validity of continuous operation during error detection to values that are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
Set the sequence function program capacity setting, device capacity, latch validity range, I/O assignment setting, and validity of continuous operation during error detection to values that are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
 Some devices used in the program have fixed applications, so use these with the conditions specified in the instruction manual.
Some devices used in the program have fixed applications, so use these with the conditions specified in the instruction manual.
 The input devices and data registers assigned to the link will hold the data previous to when communication is terminated by an error, etc. Thus, an error correspondence interlock program specified in the instruction manual must be used.
The input devices and data registers assigned to the link will hold the data previous to when communication is terminated by an error, etc. Thus, an error correspondence interlock program specified in the instruction manual must be used.
 Use the interlock program specified in the intelligent function module's instruction manual for the program corresponding to the intelligent function module.
Use the interlock program specified in the intelligent function module's instruction manual for the program corresponding to the intelligent function module.
(3) Transportation and installation
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Transport the product with the correct method according to the mass.
Transport the product with the correct method according to the mass.
 Use the servomotor suspension bolts only for the transportation of the servomotor. Do not transport the servomotor with machine installed on it.
Use the servomotor suspension bolts only for the transportation of the servomotor. Do not transport the servomotor with machine installed on it.
 Do not stack products past the limit.
Do not stack products past the limit.
 When transporting the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the connected wires or cables.
When transporting the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the connected wires or cables.
 When transporting the servomotor, never hold the cables, shaft or detector.
When transporting the servomotor, never hold the cables, shaft or detector.
 When transporting the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the front case as it may fall off.
When transporting the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the front case as it may fall off.
 When transporting, installing or removing the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the edges.
When transporting, installing or removing the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the edges.
 Install the unit according to the instruction manual in a place where the mass can be withstood.
Install the unit according to the instruction manual in a place where the mass can be withstood.
 Do not get on or place heavy objects on the product.
Do not get on or place heavy objects on the product.
 Always observe the installation direction.
Always observe the installation direction.
 Keep the designated clearance between the Motion controller or servo amplifier and control panel inner surface or the Motion controller and servo amplifier, Motion controller or servo amplifier and other devices.
Keep the designated clearance between the Motion controller or servo amplifier and control panel inner surface or the Motion controller and servo amplifier, Motion controller or servo amplifier and other devices.
 Do not install or operate Motion controller, servo amplifiers or servomotors that are damaged or that have missing parts.
Do not install or operate Motion controller, servo amplifiers or servomotors that are damaged or that have missing parts.
 Do not block the intake/outtake ports of the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor with cooling fan.
Do not block the intake/outtake ports of the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor with cooling fan.
 Do not allow conductive matter such as screw or cutting chips or combustible matter such as oil enter the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor.
Do not allow conductive matter such as screw or cutting chips or combustible matter such as oil enter the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor.
 The Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor are precision machines, so do not drop or apply strong impacts on them.
The Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor are precision machines, so do not drop or apply strong impacts on them.
 Securely fix the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor to the machine according to the instruction manual. If the fixing is insufficient, these may come off during operation.
Securely fix the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor to the machine according to the instruction manual. If the fixing is insufficient, these may come off during operation.
A - 5

 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Always install the servomotor with reduction gears in the designated direction. Failing to do so may lead to oil leaks.
Always install the servomotor with reduction gears in the designated direction. Failing to do so may lead to oil leaks.
 Store and use the unit in the following environmental conditions.
Store and use the unit in the following environmental conditions.
Environment |
Conditions |
|
||
|
|
|
||
Motion controller/Servo amplifier |
|
Servomotor |
||
|
|
|||
Ambient |
According to each instruction manual. |
|
0°C to +40°C (With no freezing) |
|
temperature |
|
(32°F to +104°F) |
||
|
|
|||
Ambient humidity |
According to each instruction manual. |
|
80% RH or less |
|
|
(With no dew condensation) |
|||
|
|
|
||
Storage |
According to each instruction manual. |
|
-20°C to +65°C |
|
temperature |
|
(-4°F to +149°F) |
||
|
|
|||
Atmosphere |
Indoors (where not subject to direct sunlight). |
|||
No corrosive gases, flammable gases, oil mist or dust must exist |
||||
|
||||
Altitude |
1000m (3280.84ft.) or less above sea level |
|||
Vibration |
According to each instruction manual |
|||
 When coupling with the synchronous encoder or servomotor shaft end, do not apply impact such as by hitting with a hammer. Doing so may lead to detector damage.
When coupling with the synchronous encoder or servomotor shaft end, do not apply impact such as by hitting with a hammer. Doing so may lead to detector damage.
 Do not apply a load larger than the tolerable load onto the synchronous encoder and servomotor shaft. Doing so may lead to shaft breakage.
Do not apply a load larger than the tolerable load onto the synchronous encoder and servomotor shaft. Doing so may lead to shaft breakage.
 When not using the module for a long time, disconnect the power line from the Motion controller or servo amplifier.
When not using the module for a long time, disconnect the power line from the Motion controller or servo amplifier.
 Place the Motion controller and servo amplifier in static electricity preventing vinyl bags and store.
Place the Motion controller and servo amplifier in static electricity preventing vinyl bags and store.  When storing for a long time, please contact with our sales representative.
When storing for a long time, please contact with our sales representative.
Also, execute a trial operation.
A - 6
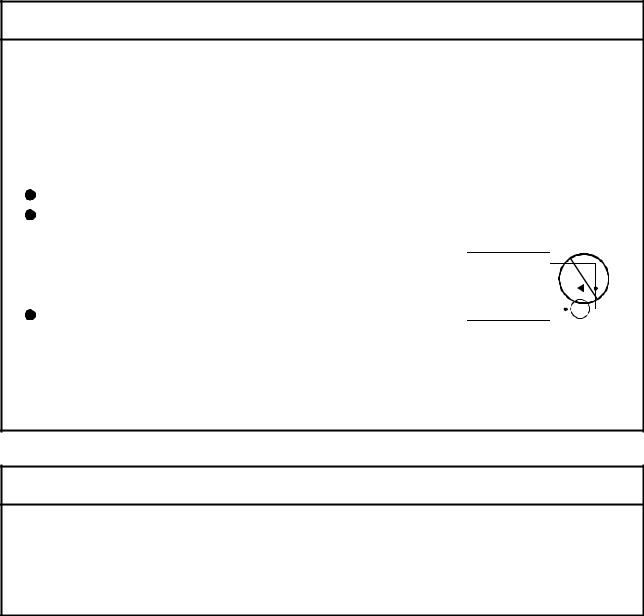
(4) Wiring
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Correctly and securely wire the wires. Reconfirm the connections for mistakes and the terminal screws for tightness after wiring. Failing to do so may lead to run away of the servomotor.
Correctly and securely wire the wires. Reconfirm the connections for mistakes and the terminal screws for tightness after wiring. Failing to do so may lead to run away of the servomotor.
 After wiring, install the protective covers such as the terminal covers to the original positions.
After wiring, install the protective covers such as the terminal covers to the original positions.
 Do not install a phase advancing capacitor, surge absorber or radio noise filter (option FR-BIF) on the output side of the servo amplifier.
Do not install a phase advancing capacitor, surge absorber or radio noise filter (option FR-BIF) on the output side of the servo amplifier.
 Correctly connect the output side (terminal U, V, W) and ground. Incorrect connections will lead the servomotor to operate abnormally.
Correctly connect the output side (terminal U, V, W) and ground. Incorrect connections will lead the servomotor to operate abnormally.
Do not connect a commercial power supply to the servomotor, as this may lead to trouble. |
||||
Do not mistake the direction of the surge absorbing diode |
|
|
|
|
installed on the DC relay for the control signal output of brake |
Servo amplifier |
|
|
|
signals, etc. Incorrect installation may lead to signals not being |
|
|
||
VIN |
|
|
||
output when trouble occurs or the protective functions not |
(24VDC) |
|
|
|
functioning. |
Control output |
|
|
|
RA |
||||
Do not connect or disconnect the connection cables between |
signal |
|||
|
|
|||
each unit, the encoder cable or PLC expansion cable while the power is ON.
 Securely tighten the cable connector fixing screws and fixing mechanisms. Insufficient fixing may lead to the cables combing off during operation.
Securely tighten the cable connector fixing screws and fixing mechanisms. Insufficient fixing may lead to the cables combing off during operation.
 Do not bundle the power line or cables.
Do not bundle the power line or cables.
(5) Trial operation and adjustment
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Confirm and adjust the program and each parameter before operation. Unpredictable movements may occur depending on the machine.
Confirm and adjust the program and each parameter before operation. Unpredictable movements may occur depending on the machine.
 Extreme adjustments and changes may lead to unstable operation, so never make them.
Extreme adjustments and changes may lead to unstable operation, so never make them.  When using the absolute position system function, on starting up, and when the Motion controller or absolute value motor has been replaced, always perform a home position return.
When using the absolute position system function, on starting up, and when the Motion controller or absolute value motor has been replaced, always perform a home position return.
A - 7
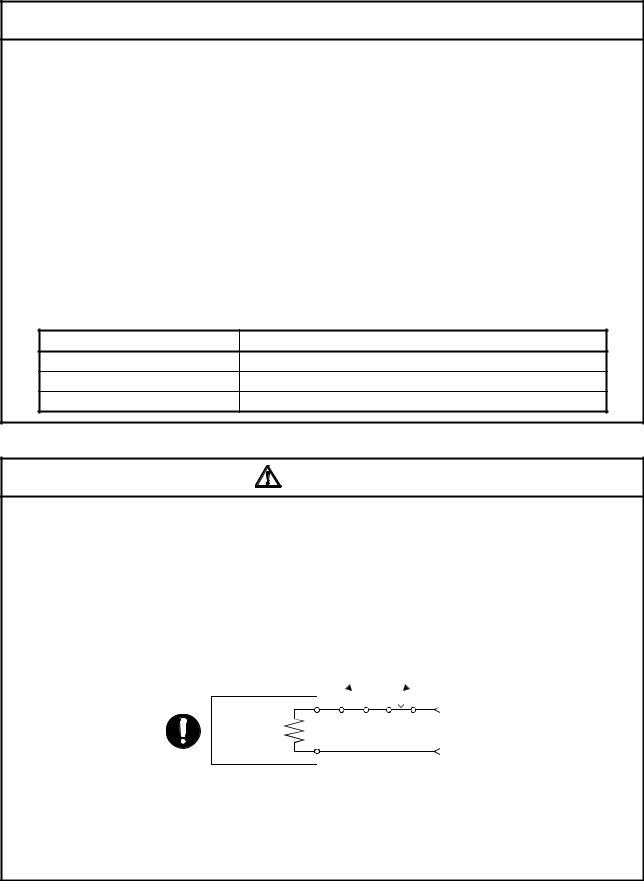
(6) Usage methods
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Immediately turn OFF the power if smoke, abnormal sounds or odors are emitted from the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor.
Immediately turn OFF the power if smoke, abnormal sounds or odors are emitted from the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor.
 Always execute a test operation before starting actual operations after the program or parameters have been changed or after maintenance and inspection.
Always execute a test operation before starting actual operations after the program or parameters have been changed or after maintenance and inspection.
 Do not attempt to disassemble and repair the units excluding a qualified technician whom our company recognized.
Do not attempt to disassemble and repair the units excluding a qualified technician whom our company recognized.
 Do not make any modifications to the unit.
Do not make any modifications to the unit.
 Keep the effect or electromagnetic obstacles to a minimum by installing a noise filter or by using wire shields, etc. Electromagnetic obstacles may affect the electronic devices used near the Motion controller or servo amplifier.
Keep the effect or electromagnetic obstacles to a minimum by installing a noise filter or by using wire shields, etc. Electromagnetic obstacles may affect the electronic devices used near the Motion controller or servo amplifier.
 When using the CE Mark-compliant equipment, refer to the "EMC Installation Guidelines" (data number IB(NA)-67339) for the Motion controllers and refer to the corresponding EMC guideline information for the servo amplifiers, inverters and other equipment.
When using the CE Mark-compliant equipment, refer to the "EMC Installation Guidelines" (data number IB(NA)-67339) for the Motion controllers and refer to the corresponding EMC guideline information for the servo amplifiers, inverters and other equipment.
 Use the units with the following conditions.
Use the units with the following conditions.
Item |
Conditions |
Input power |
According to each instruction manual. |
Input frequency |
According to each instruction manual. |
Tolerable momentary power failure |
According to each instruction manual. |
(7) Corrective actions for errors |
|
|
CAUTION |
 If an error occurs in the self diagnosis of the Motion controller or servo amplifier, confirm the check details according to the instruction manual, and restore the operation.
If an error occurs in the self diagnosis of the Motion controller or servo amplifier, confirm the check details according to the instruction manual, and restore the operation.
 If a dangerous state is predicted in case of a power failure or product failure, use a servomotor with electromagnetic brakes or install a brake mechanism externally.
If a dangerous state is predicted in case of a power failure or product failure, use a servomotor with electromagnetic brakes or install a brake mechanism externally.
 Use a double circuit construction so that the electromagnetic brake operation circuit can be operated by emergency stop signals set externally.
Use a double circuit construction so that the electromagnetic brake operation circuit can be operated by emergency stop signals set externally.
Shut off with servo ON signal OFF, alarm, electromagnetic brake signal.
Shut off with the emergency stop signal (EMG).
Servomotor |
EMG |
||||||
|
|
RA1 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electromagnetic |
|
|
24VDC |
||||
brakes |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||
 If an error occurs, remove the cause, secure the safety and then resume operation after alarm release.
If an error occurs, remove the cause, secure the safety and then resume operation after alarm release.
 The unit may suddenly resume operation after a power failure is restored, so do not go near the machine. (Design the machine so that personal safety can be ensured even if the machine restarts suddenly.)
The unit may suddenly resume operation after a power failure is restored, so do not go near the machine. (Design the machine so that personal safety can be ensured even if the machine restarts suddenly.)
A - 8

(8) Maintenance, inspection and part replacement
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 Perform the daily and periodic inspections according to the instruction manual.
Perform the daily and periodic inspections according to the instruction manual.
 Perform maintenance and inspection after backing up the program and parameters for the Motion controller and servo amplifier.
Perform maintenance and inspection after backing up the program and parameters for the Motion controller and servo amplifier.
 Do not place fingers or hands in the clearance when opening or closing any opening.
Do not place fingers or hands in the clearance when opening or closing any opening.
 Periodically replace consumable parts such as batteries according to the instruction manual.
Periodically replace consumable parts such as batteries according to the instruction manual.
 Do not touch the lead sections such as ICs or the connector contacts.
Do not touch the lead sections such as ICs or the connector contacts.
 Before touching the module, always touch grounded metal, etc. to discharge static electricity from human body. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
Before touching the module, always touch grounded metal, etc. to discharge static electricity from human body. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
 Do not directly touch the module's conductive parts and electronic components. Touching them could cause an operation failure or give damage to the module.
Do not directly touch the module's conductive parts and electronic components. Touching them could cause an operation failure or give damage to the module.
 Do not place the Motion controller or servo amplifier on metal that may cause a power leakage or wood, plastic or vinyl that may cause static electricity buildup.
Do not place the Motion controller or servo amplifier on metal that may cause a power leakage or wood, plastic or vinyl that may cause static electricity buildup.
 Do not perform a megger test (insulation resistance measurement) during inspection.
Do not perform a megger test (insulation resistance measurement) during inspection.
 When replacing the Motion controller or servo amplifier, always set the new module settings correctly.
When replacing the Motion controller or servo amplifier, always set the new module settings correctly.
 When the Motion controller or absolute value motor has been replaced, carry out a home position return operation using one of the following methods, otherwise position displacement could occur.
When the Motion controller or absolute value motor has been replaced, carry out a home position return operation using one of the following methods, otherwise position displacement could occur.
1)After writing the servo data to the Motion controller using programming software, switch on the power again, then perform a home position return operation.
2)Using the backup function of the programming software, load the data backed up before
replacement.
 After maintenance and inspections are completed, confirm that the position detection of the absolute position detector function is correct.
After maintenance and inspections are completed, confirm that the position detection of the absolute position detector function is correct.
 Do not drop or impact the battery installed to the module.
Do not drop or impact the battery installed to the module.
Doing so may damage the battery, causing battery liquid to leak in the battery. Do not use the dropped or impacted battery, but dispose of it.
 Do not short circuit, charge, overheat, incinerate or disassemble the batteries.
Do not short circuit, charge, overheat, incinerate or disassemble the batteries.
 The electrolytic capacitor will generate gas during a fault, so do not place your face near the Motion controller or servo amplifier.
The electrolytic capacitor will generate gas during a fault, so do not place your face near the Motion controller or servo amplifier.
 The electrolytic capacitor and fan will deteriorate. Periodically replace these to prevent secondary damage from faults. Replacements can be made by our sales representative.
The electrolytic capacitor and fan will deteriorate. Periodically replace these to prevent secondary damage from faults. Replacements can be made by our sales representative.
 Lock the control panel and prevent access to those who are not certified to handle or install electric equipment.
Lock the control panel and prevent access to those who are not certified to handle or install electric equipment.
 Do not burn or break a module and servo amplifier. Doing so may cause a toxic gas.
Do not burn or break a module and servo amplifier. Doing so may cause a toxic gas.
A - 9

(9) About processing of waste
When you discard Motion controller, servo amplifier, a battery (primary battery) and other option articles, please follow the law of each country (area).
 CAUTION
CAUTION
 This product is not designed or manufactured to be used in equipment or systems in situations that can affect or endanger human life.
This product is not designed or manufactured to be used in equipment or systems in situations that can affect or endanger human life.
 When considering this product for operation in special applications such as machinery or systems used in passenger transportation, medical, aerospace, atomic power, electric power, or submarine repeating applications, please contact your nearest Mitsubishi sales representative.
When considering this product for operation in special applications such as machinery or systems used in passenger transportation, medical, aerospace, atomic power, electric power, or submarine repeating applications, please contact your nearest Mitsubishi sales representative.  Although this product was manufactured under conditions of strict quality control, you are strongly advised to install safety devices to forestall serious accidents when it is used in facilities where a breakdown in the product is likely to cause a serious accident.
Although this product was manufactured under conditions of strict quality control, you are strongly advised to install safety devices to forestall serious accidents when it is used in facilities where a breakdown in the product is likely to cause a serious accident.
(10) General cautions
 All drawings provided in the instruction manual show the state with the covers and safety partitions removed to explain detailed sections. When operating the product, always return the covers and partitions to the designated positions, and operate according to the instruction manual.
All drawings provided in the instruction manual show the state with the covers and safety partitions removed to explain detailed sections. When operating the product, always return the covers and partitions to the designated positions, and operate according to the instruction manual.
A - 10

REVISIONS
|
|
The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover. |
Print Date |
Manual Number |
Revision |
Jun., 2002 |
IB(NA)-0300042-A |
First edition |
Feb., 2004 |
IB(NA)-0300042-B |
[Addition model] |
|
|
Q173CPUN-T/Q172CPUN-T, A31TU-D3K13/A31TU-DNK13, |
|
|
Q172EX-S1, Q173PX-S1, Q00CPU, Q01CPU, 64AD, Q68ADV, Q68ADI, |
|
|
Q62DA, Q64DA, Q68DAV, Q68DAI, Q170TUD3CBL3M, |
|
|
Q170TUDNCBL3M, Q170TUDNCBL03M-A, Q170TUTM, A31TUD3TM, |
|
|
FR-V5 0- , Software for SV43 |
|
|
[Addition function] |
|
|
For WindowsXP, Home position return function, ROM operation function, |
|
|
Online change function |
|
|
[Additional correction/partial correction] |
|
|
Safety precautions, About processing of waste, Startup slow of the |
|
|
Multiple CPU system, User file list, Error code list, etc. |
|
|
[partial correction] |
Mar., 2006 |
IB(NA)-0300042-C |
[Addition model] |
|
|
Q62P, Q172EX-S2, Q172EX-S3, Q170ENC |
|
|
[Addition function] |
|
|
Cam axis command signal, Smoothing clutch complete signal, Gain |
|
|
changing signal, Real mode axis information register, Motion SFC |
|
|
instruction "FMOV", Bit device setting by Motion SFC instruction, Security |
|
|
function |
|
|
[Additional correction/partial correction] |
|
|
Safety precautions, User file list, Error code list, Warranty, Manual model |
|
|
code (1CT781 1XB781), etc. |
Apr., 2010 |
IB(NA)-0300042-D |
[Additional correction/partial correction] |
|
|
Safety precautions, "1.6.1 I/O No. for I/O modules and intelligent function |
|
|
modules", Warranty |
|
|
|
Japanese Manual Version IB(NA)-0300023
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent licenses. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
© 2002 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
A - 11
INTRODUCTION |
|
Thank you for choosing the Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion Controller. |
|
Please read this manual carefully so that equipment is used to its optimum. |
|
CONTENTS |
|
Safety Precautions ......................................................................................................................................... |
A- 1 |
Revisions ........................................................................................................................................................ |
A-11 |
Contents ......................................................................................................................................................... |
A-12 |
About Manuals ............................................................................................................................................... |
A-18 |
|
|
1. OVERVIEW |
1- 1 to 1-96 |
1.1 Overview................................................................................................................................................... |
1- 1 |
1.2 Features ................................................................................................................................................... |
1- 3 |
1.2.1 Features of Motion CPU ................................................................................................................... |
1- 3 |
1.2.2 Basic specifications of Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)......................................................................... |
1- 6 |
1.2.3 Operation control/transition control specifications ........................................................................... |
1- 9 |
1.2.4 Differences between Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)and A173UHCPU/A172SHCPUN.................... |
1-13 |
1.2.5 Positioning dedicated devices/special relays/special registers ....................................................... |
1-15 |
1.3 Hardware Configuration........................................................................................................................... |
1-55 |
1.3.1 Motion system configuration ............................................................................................................. |
1-55 |
1.3.2 Q173CPU(N) System overall configuration...................................................................................... |
1-61 |
1.3.3 Q172CPU(N) System overall configuration...................................................................................... |
1-63 |
1.3.4 Software packages............................................................................................................................ |
1-65 |
1.3.5 Restrictions on motion systems........................................................................................................ |
1-69 |
1.4 Multiple CPU System ............................................................................................................................... |
1-71 |
1.4.1 Overview............................................................................................................................................ |
1-71 |
1.4.2 Installation of PLC CPU and Motion CPU ........................................................................................ |
1-72 |
1.4.3 Precautions for using Q series I/O modules and intelligent function modules................................ |
1-73 |
1.4.4 Modules subject to installation restrictions ....................................................................................... |
1-74 |
1.4.5 Processing time of the Multiple CPU system ................................................................................... |
1-75 |
1.4.6 How to reset the Multiple CPU system............................................................................................. |
1-76 |
1.4.7 Processing at a CPU DOWN error occurrence by a PLC CPU or Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N).... 1-77
1.5 System Settings ....................................................................................................................................... |
1-80 |
1.5.1 System data settings......................................................................................................................... |
1-80 |
1.5.2 Common system parameters ........................................................................................................... |
1-81 |
1.5.3 Individual parameters........................................................................................................................ |
1-87 |
1.6 Assignment of I/O No............................................................................................................................... |
1-92 |
1.6.1 I/O No. for I/O modules and intelligent function modules ................................................................ |
1-92 |
1.6.2 I/O No. of PLC CPU and Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)..................................................................... |
1-95 |
1.6.3 Setting I/O No.................................................................................................................................... |
1-96 |
|
|
2. STARTING UP THE MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM |
2- 1 to 2- 2 |
2.1 Startup Flow of the Multiple CPU System ............................................................................................... |
2- 1 |
A - 12
3. COMMUNICATION BETWEEN THE PLC CPU AND THE MOTION CPU IN |
|
|
|
|
||
THE MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM |
|
|
|
3- 1 to 3-26 |
||
3.1 Automatic Refresh Function of The Shared CPU Memory .................................................................... |
|
|
3- 1 |
|||
3.2 Control Instruction from the PLC CPU to The Motion CPU (Motion dedicated instructions) |
................ |
3-20 |
||||
3.3 Reading/Writing Device Data .................................................................................................................. |
|
|
|
3-21 |
||
3.4 Shared CPU Memory............................................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
3-22 |
||
|
|
|
|
|||
4. STRUCTURE OF THE MOTION CPU PROGRAM |
|
|
4- 1 to 4- 4 |
|||
4.1 Motion Control in SV13/SV22 Real Mode............................................................................................... |
|
|
|
4- 2 |
||
4.2 Motion Control in SV22 Virtual Mode ...................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
4- 3 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
5. MOTION DEDICATED PLC INSTRUCTION |
|
|
|
5- 1 to 5-48 |
||
5.1 Motion Dedicated PLC Instruction........................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
5- 1 |
||
5.1.1 Restriction item of the Motion dedicated PLC instruction ................................................................ |
|
|
5- |
1 |
||
5.2 Motion SFC Start Request from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU: |
|
|
|
|
||
|
S(P).SFCS (PLC instruction: |
) ............................................................................................ |
|
|
5- |
9 |
5.3 Servo Program Start Request from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU: |
|
|
|
|
||
|
S(P).SVST (PLC instruction: |
) ........................................................................................... |
|
|
5-12 |
|
5.4 Current Value Change Instruction from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU: |
|
|
|
|
||
|
S(P).CHGA (PLC instruction: |
) .......................................................................................... |
|
|
5-17 |
|
5.5 Speed Change Instruction from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU: |
|
|
|
|
||
|
S(P).CHGV (PLC instruction: |
) .......................................................................................... |
|
|
5-30 |
|
5.6 Torque Limit Value Change Request Instruction from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU: |
|
|
|
|||
|
S(P).CHGT (PLC instruction: S(P).CHGT )........................................................................................... |
|
|
5-34 |
||
5.7 Write from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU: S(P).DDWR (PLC instruction: |
|
) ............. |
5-38 |
|||
5.8 |
Read from The Devices of The Motion CPU: S(P).DDRD (PLC instruction: |
) ................. |
|
5-42 |
||
5.9 |
Interrupt Instruction to The Other CPU: S(P).GINT (PLC instruction: |
).............................. |
|
5-46 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
6. MOTION SFC PROGRAMS |
|
|
|
6- 1 to 6-28 |
||
6.1 |
Motion SFC Program Configuration ........................................................................................................ |
|
|
|
6- 1 |
|
6.2 |
Motion SFC Chart Symbol List ................................................................................................................ |
|
|
|
6- 2 |
|
6.3 |
Branch and Coupling Chart List............................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
6- 5 |
|
6.4 Motion SFC Program Name .................................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
6- 9 |
||
6.5 |
Steps......................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
6-10 |
|
6.5.1 Motion control step............................................................................................................................ |
|
|
|
6-10 |
||
6.5.2 Operation control step....................................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
6-11 |
||
6.5.3 Subroutine call/start step................................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
6-12 |
||
6.5.4 Clear step .......................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
6-14 |
||
6.6 |
Transitions ................................................................................................................................................ |
|
|
|
6-15 |
|
6.7 |
Jump, Pointer ........................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
6-17 |
|
6.8 END .......................................................................................................................................................... |
|
|
|
6-17 |
||
6.9 |
Branches, Couplings................................................................................................................................ |
|
|
|
6-18 |
|
6.9.1 Series transition................................................................................................................................. |
|
|
|
6-18 |
||
|
|
A - 13 |
|
|
|
|
6.9.2 Selective branch, selective coupling................................................................................................. |
6-19 |
||||||
6.9.3 Parallel branch, parallel coupling...................................................................................................... |
6-20 |
||||||
6.10 Y/N Transitions....................................................................................................................................... |
6-22 |
||||||
6.11 Motion SFC Comments ......................................................................................................................... |
6-26 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7. OPERATION CONTROL PROGRAMS |
7- 1 to 7-96 |
||||||
7.1 Operation Control Programs.................................................................................................................... |
7- 1 |
||||||
7.2 Device Descriptions ................................................................................................................................. |
7- |
7 |
|||||
7.3 Constant Descriptions.............................................................................................................................. |
7- |
9 |
|||||
7.4 Binary Operations .................................................................................................................................... |
7-10 |
||||||
7.4.1 Substitution : =................................................................................................................................... |
7-10 |
||||||
7.4.2 Addition : +......................................................................................................................................... |
7-12 |
||||||
7.4.3 Subtraction : |
|
.................................................................................................................................. |
|
|
7-13 |
||
|
|||||||
7.4.4 Multiplication : * ................................................................................................................................. |
7-15 |
||||||
7.4.5 Division : / .......................................................................................................................................... |
7-16 |
||||||
7.4.6 Remainder : %................................................................................................................................... |
7-17 |
||||||
7.5 Bit Operations........................................................................................................................................... |
7-18 |
||||||
7.5.1 Bit inversion(Complement) : ~ .......................................................................................................... |
7-18 |
||||||
7.5.2 Bit logical AND : & ............................................................................................................................. |
7-19 |
||||||
7.5.3 Bit logical OR : |................................................................................................................................. |
7-20 |
||||||
7.5.4 Bit exclusive logical OR : ^................................................................................................................ |
7-21 |
||||||
7.5.5 Bit right shift : >>................................................................................................................................ |
7-22 |
||||||
7.5.6 Bit left shift : <<.................................................................................................................................. |
7-23 |
||||||
7.5.7 Sign inversion(Complement of 2) : |
|
............................................................................................... |
7-24 |
||||
|
|||||||
7.6 Standard Functions.................................................................................................................................. |
7-25 |
||||||
7.6.1 Sine : SIN........................................................................................................................................... |
7-25 |
||||||
7.6.2 Cosine : COS..................................................................................................................................... |
7-26 |
||||||
7.6.3 Tangent : TAN ................................................................................................................................... |
7-27 |
||||||
7.6.4 Arcsine : ASIN ................................................................................................................................... |
7-28 |
||||||
7.6.5 Arccosine : ACOS ............................................................................................................................. |
7-29 |
||||||
7.6.6 Arctangent : ATAN ............................................................................................................................ |
7-30 |
||||||
7.6.7 Square root : SQRT .......................................................................................................................... |
7-31 |
||||||
7.6.8 Natural logarithm : LN ....................................................................................................................... |
7-32 |
||||||
7.6.9 Exponential operation : EXP............................................................................................................. |
7-33 |
||||||
7.6.10 Absolute value : ABS ...................................................................................................................... |
7-34 |
||||||
7.6.11 Round-off : RND.............................................................................................................................. |
7-35 |
||||||
7.6.12 Round-down : FIX ........................................................................................................................... |
7-36 |
||||||
7.6.13 Round-up : FUP .............................................................................................................................. |
7-37 |
||||||
7.6.14 BCD |
BIN conversion : BIN ......................................................................................................... |
7-38 |
|||||
7.6.15 BIN |
BCD conversion : BCD........................................................................................................ |
7-39 |
|||||
7.7 Type Conversions .................................................................................................................................... |
7-40 |
||||||
7.7.1 Signed 16-bit integer value conversion : SHORT ............................................................................ |
7-40 |
||||||
7.7.2 Unsigned 16-bit integer value conversion : USHORT ..................................................................... |
7-41 |
||||||
7.7.3 Signed 32-bit integer value conversion : LONG............................................................................... |
7-42 |
||||||
7.7.4 Unsigned 32-bit integer value conversion : ULONG........................................................................ |
7-43 |
||||||
7.7.5 Signed 64-bit floating-point value conversion : FLOAT ................................................................... |
7-44 |
||||||
7.7.6 Unsigned 64-bit floating-point value conversion : UFLOAT ............................................................ |
7-45 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
A - 14 |
|
|
7.8 Bit Device Statuses.................................................................................................................................. |
7-46 |
7.8.1 ON (Normally open contact) : (None)............................................................................................... |
7-46 |
7.8.2 OFF (Normally closed contact) : !..................................................................................................... |
7-47 |
7.9 Bit Device Controls................................................................................................................................... |
7-48 |
7.9.1 Device set : SET................................................................................................................................ |
7-48 |
7.9.2 Device reset : RST ............................................................................................................................ |
7-50 |
7.9.3 Device output : DOUT....................................................................................................................... |
7-52 |
7.9.4 Device input : DIN ............................................................................................................................. |
7-53 |
7.9.5 Bit device output : OUT.................................................................................................................... |
7-54 |
7.10 Logical Operations ................................................................................................................................. |
7-56 |
7.10.1 Logical acknowledgement : (None) ................................................................................................ |
7-56 |
7.10.2 Logical negation : ! .......................................................................................................................... |
7-57 |
7.10.3 Logical AND : * ................................................................................................................................ |
7-58 |
7.10.4 Logical OR : +.................................................................................................................................. |
7-59 |
7.11 Comparison Operations......................................................................................................................... |
7-60 |
7.11.1 Equal to : == .................................................................................................................................... |
7-60 |
7.11.2 Not equal to : !=............................................................................................................................... |
7-61 |
7.11.3 Less than : <.................................................................................................................................... |
7-62 |
7.11.4 Less than or equal to : <= ............................................................................................................... |
7-63 |
7.11.5 More than : > ................................................................................................................................... |
7-64 |
7.11.6 More than or equal to : >=............................................................................................................... |
7-65 |
7.12 Motion-Dedicated Functions(CHGV, CHGT) ........................................................................................ |
7-66 |
7.12.1 Speed change request : CHGV...................................................................................................... |
7-66 |
7.12.2 Torque limit value change request : CHGT.................................................................................... |
7-72 |
7.13 Other Instructions................................................................................................................................... |
7-74 |
7.13.1 Event task enable : EI ..................................................................................................................... |
7-74 |
7.13.2 Event task disable : DI .................................................................................................................... |
7-75 |
7.13.3 No operation : NOP......................................................................................................................... |
7-76 |
7.13.4 Block transfer : BMOV .................................................................................................................... |
7-77 |
7.13.5 Same data block transfer : FMOV .................................................................................................. |
7-80 |
7.13.6 Write device data to shared CPU memory of the self CPU : MULTW .......................................... |
7-82 |
7.13.7 Read device data from shared CPU memory of the other CPU: MULTR..................................... |
7-85 |
7.13.8 Write device data to intelligent function module/special function module : TO............................. |
7-88 |
7.13.9 Read device data from intelligent function module/special function module : FROM .................. |
7-91 |
7.13.10 Time to wait : TIME ....................................................................................................................... |
7-94 |
7.14 Comment Statement : //......................................................................................................................... |
7-96 |
|
|
8. TRANSITION PROGRAMS |
8- 1 to 8- 2 |
8.1 Transition Programs................................................................................................................................. |
8- 1 |
|
|
9. MOTION CONTROL PROGRAMS |
9- 1 to 9-22 |
9.1 Servo Instruction List................................................................................................................................ |
9- 1 |
9.2 Servomotor/Virtual Servomotor Shaft Current Value Change................................................................ |
9-14 |
9.3 Synchronous Encoder Shaft Current Value Change Control (SV22 Only)............................................ |
9-17 |
9.4 Cam Shaft Within-One-Revolution Current Value Change Control (SV22 Only) .................................. |
9-20 |
A - 15 |
|
9.5 Programming Instructions........................................................................................................................ |
9-22 |
||||
9.5.1 Cancel • start ..................................................................................................................................... |
9-22 |
||||
9.5.2 Indirect designation using motion devices........................................................................................ |
9-22 |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
10. MOTION DEVICES |
10- 1 to 10- 6 |
||||
10.1 |
Motion Registers (#0 to #8191) ............................................................................................................ |
10- 1 |
|||
10.2 |
Coasting Timer (FT).............................................................................................................................. |
10- 6 |
|||
|
|
|
|
||
11. MOTION SFC PARAMETER |
11- 1 to 11-20 |
||||
11.1 |
Task Definitions.................................................................................................................................... |
11- |
1 |
||
11.2 |
Number of Consecutive Transitions and Task Operation .................................................................. |
11- 2 |
|||
11.2.1 Number of consecutive transitions ............................................................................................... |
11- |
2 |
|||
11.2.2 Task operation............................................................................................................................... |
11- 3 |
||||
11.3 |
Execution Status of The Multiple Task................................................................................................ |
11- 7 |
|||
11.4 Task Parameters.................................................................................................................................. |
11- 8 |
||||
11.5 |
Program Parameters............................................................................................................................ |
11-10 |
|||
11.6 |
How to Start The Motion SFC Program .............................................................................................. |
11-16 |
|||
11.6.1 Automatic start .............................................................................................................................. |
11-16 |
||||
11.6.2 Start from the Motion SFC program ............................................................................................. |
11-16 |
||||
11.6.3 Start from PLC (PLC instruction |
|
) |
11-16 |
||
S(P).SFCS |
|||||
11.7 How to End The Motion SFC Program ............................................................................................... |
11-17 |
||||
11.8 |
How to Change from One Motion SFC Program to Another.............................................................. |
11-17 |
|||
11.9 How to Manage The Executing Program............................................................................................ |
11-17 |
||||
11.10 Operation Performed at CPU Power-Off or Reset.......................................................................... |
11-18 |
||||
11.11 Operation Performed when CPU is Switched from RUN/STOP ...................................................... |
11-18 |
||||
11.12 Operation Performed when PLC Ready flag (M2000) Turns OFF/ON............................................ |
11-19 |
||||
11.13 Operation at The Error Occurrence................................................................................................... |
11-20 |
||||
|
|
||||
12. USER FILES |
12- 1 to 12- 8 |
||||
12.1 |
Projects................................................................................................................................................. |
12- |
1 |
||
12.2 |
User File List ........................................................................................................................................ |
12- |
2 |
||
12.3 Online Change in The Motion SFC Program ...................................................................................... |
12- 3 |
||||
12.3.1 Operating method for The Online Change................................................................................... |
12- 4 |
||||
12.3.2 Transfer of program ...................................................................................................................... |
12- 7 |
||||
|
|
||||
13. LIMIT SWITCH OUTPUT FUNCTION |
13- 1 to 13- 8 |
||||
13.1 |
Operations............................................................................................................................................ |
13- 1 |
|||
13.2 |
Limit Output Setting Data..................................................................................................................... |
13- |
4 |
||
|
|
||||
14. ROM OPERATION FUNCTION |
14- 1 to 14-12 |
||||
14.1 |
About the ROM Operation Function.................................................................................................... |
14- 1 |
|||
14.2 |
Specifications of LED • Switch............................................................................................................. |
14- |
3 |
||
14.3 |
ROM Operation Function Details ........................................................................................................ |
14- 5 |
|||
14.4 |
Operating Procedure of "ROM writing" ............................................................................................... |
14-11 |
|||
|
|
A - 16 |
|
|
|
15. SECURITY FUNCTION |
15- 1 to 15- 6 |
|
15.1 |
Password Registration/change............................................................................................................ |
15- 1 |
15.2 |
Password Clearance............................................................................................................................ |
15- 3 |
15.3 |
Password Check .................................................................................................................................. |
15- 4 |
15.4 |
Password Save .................................................................................................................................... |
15- 5 |
15.5 |
Clear All ................................................................................................................................................ |
15- 6 |
|
|
|
16. COMMUNICATIONS VIA NETWORK |
16- 1 to 16-10 |
|
16.1 |
Specifications of The Communications via Network........................................................................... |
16- 2 |
16.2 |
Access Range of The Communications via Network ......................................................................... |
16- 3 |
16.2.1 Network configuration via the MELSECNET/10(H) or the Ethernet............................................ |
16- 3 |
|
16.2.2 Network configuration via the CC-Link ......................................................................................... |
16- 5 |
|
16.2.3 Network configuration via the RS422/485.................................................................................... |
16- 6 |
|
16.2.4 Network configuration which MELSECNET/10 (H), Ethernet, CC-Link, RS422/485 were mixed |
||
.................................................................................................................................................................. |
|
16- 7 |
|
|
|
17. MONITOR FUNCTION OF THE MAIN CYCLE |
17- 1 to 17- 2 |
|
18. SERVO PARAMETER READING FUNCTION |
18- 1 to 18- 2 |
|
18.1 |
About The Servo Parameter Read Request Devices......................................................................... |
18- 1 |
18.2 Operating Procedure of The Servo Parameter Reading Function..................................................... |
18- 2 |
|
|
|
|
19. ERROR CODE LISTS |
19- 1 to 19-18 |
|
19.1 |
Reading Procedure for Error Codes.................................................................................................... |
19- 1 |
19.2 |
Motion SFC Error Code List ................................................................................................................ |
19- 2 |
19.3 |
Motion SFC Parameter Errors............................................................................................................. |
19-11 |
19.4 |
Multiple CPU Error Codes ................................................................................................................... |
19-13 |
19.4.1 Self-diagnosis error code.............................................................................................................. |
19-13 |
|
19.4.2 Release of self-diagnosis error ..................................................................................................... |
19-18 |
|
|
|
|
APPENDICES |
APP- 1 to APP-32 |
|
APPENDIX 1 Processing Times............................................................................................................... |
APP- 1 |
|
APPENDIX 1.1 Processing time of operation control/Transition instruction ....................................... |
APP- 1 |
|
APPENDIX 2 Sample Program ................................................................................................................ |
APP- 9 |
|
APPENDIX 2.1 Program example to execute the Multiple CPU dedicated instruction continuously.APP- 9 APPENDIX 2.2 The program example to execute plural Multiple CPU instruction by the instructions of
one time........................................................................................................................ |
APP-11 |
APPENDIX 2.3 Motion control example by Motion SFC program....................................................... |
APP-13 |
APPENDIX 2.4 Continuation execution example at the subroutine re-start by the Motion SFC program
..................................................................................................................................... |
APP-24 |
APPENDIX 2.5 Continuation execution example after the stop by the Motion SFC program............ |
APP-28 |
A - 17 |
|

About Manuals
The following manuals are related to this product.
Referring to this list, please request the necessary manuals.
Related Manuals
(1) Motion controller
Manual Name |
Manual Number |
|
(Model Code) |
||
|
||
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller User's Manual |
|
|
This manual explains specifications of the Motion CPU modules, Q172LX Servo external signal interface |
|
|
module, Q172EX Serial absolute synchronous encoder interface module, Q173PX Manual pulse |
IB-0300040 |
|
generator interface module, Teaching units, Power supply modules, Servo amplifiers, SSCNET cables, |
(1XB780) |
|
|
||
synchronous encoder cables and others. |
|
|
(Optional) |
|
|
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual |
|
|
(REAL MODE) |
IB-0300043 |
|
This manual explains the servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list, error list and others. |
(1XB782) |
|
|
||
(Optional) |
|
|
|
|
|
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV22) Programming Manual |
|
|
(VIRTUAL MODE) |
|
|
This manual describes the dedicated instructions use to the synchronous control by virtual main shaft, |
IB-0300044 |
|
mechanical system program create mechanical module. |
(1XB783) |
|
|
||
This manual explains the servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list, error list and others. |
|
|
(Optional) |
|
|
|
|
|
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV43) Programming Manual |
|
|
This manual describes the dedicated instructions to execute the positioning control by Motion program of |
|
|
EIA language (G-code). |
IB-0300070 |
|
This manual explains the Multiple CPU system configuration, performance specifications, functions, |
(1CT784) |
|
programming, debugging, servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list error list and others. |
|
|
(Optional) |
|
|
|
|
A - 18
(2) PLC
Manual Name |
Manual Number |
|
(Model Code) |
||
|
||
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection) |
|
|
This manual explains the specifications of the QCPU modules, power supply modules, base units, |
SH-080483ENG |
|
extension cables, memory card battery, and the maintenance/inspection for the system, trouble shooting, |
||
(13JR73) |
||
error codes and others. |
||
|
||
(Optional) |
|
|
|
|
|
Qn(H)/QnPH/QnPRHCPUCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program |
|
|
Fundamentals) |
SH-080808ENG |
|
This manual explains the functions, programming methods and devices and others to create programs |
||
(13JZ28) |
||
with the QCPU. |
||
|
||
(Optional) |
|
|
|
|
|
QCPU User's Manual (Multiple CPU System) |
|
|
This manual explains Multiple CPU system overview, system configuration, I/O modules, communication |
SH-080485ENG |
|
between CPU modules and communication with the I/O modules or intelligent function modules. |
(13JR75) |
|
(Optional) |
|
|
|
|
|
QCPU Programming Manual (Common Instructions) |
|
|
This manual explains how to use the sequence instructions, basic instructions, application instructions and |
SH-080809ENG |
|
micro computer program. |
(13JW10) |
|
|
||
(Optional) |
|
|
QCPU (Q Mode)/QnACPU Programming Manual (PID Control Instructions) |
SH-080040 |
|
This manual explains the dedicated instructions used to exercise PID control. |
||
(13JF59) |
||
(Optional) |
|
|
QCPU (Q Mode)/QnACPU Programming Manual (SFC) |
|
|
This manual explains the system configuration, performance specifications, functions, programming, |
SH-080041 |
|
debugging, error codes and others of MELSAP3. |
(13JF60) |
|
|
||
(Optional) |
|
|
I/O Module Type Building Block User's Manual |
|
|
This manual explains the specifications of the I/O modules, connector, connector/terminal block |
SH-080042 |
|
conversion modules and others. |
(13JL99) |
|
|
||
(Optional) |
|
A - 19
MEMO
A - 20
1 OVERVIEW
1. OVERVIEW
1.1 Overview
1
This programming manual describes the Motion SFC program and Multiple CPU system of the operating system software packages "SW6RN-SV13Q ", "SW6RNSV22Q
", "SW6RNSV22Q " for Motion CPU module(Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)).
" for Motion CPU module(Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)).
In this manual, the following abbreviations are used.
Generic term/Abbreviation
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) or Motion CPU (module)
Q172LX/Q172EX/Q173PX or Motion module
MR-H-BN
MR-J2 -B
-B
AMP or Servo amplifier
QCPU, PLC CPU or PLC CPU module
Multiple CPU system or Motion system
CPUn
Programming software package
Operating system software
SV13
SV22
MT Developer
GX Developer
Manual pulse generator or MR-HDP01
Serial absolute synchronous encoder or MR-HENC/Q170ENC
SSCNET (Note-2)
Absolute position system
Cooling fan unit
Dividing unit
Battery unit
Description Q173CPUN/Q172CPUN/Q173CPUN-T/Q172CPUN-T/Q173CPU/Q172CPU Motion CPU module
Q172LX Servo external signals interface module/
Q172EX(-S1/-S2/-S3) Serial absolute synchronous encoder interface module(Note-1)/ Q173PX(-S1) Manual pulse generator interface module
Servo amplifier model MR-H BN
BN
Servo amplifier model MR-J2S- B/MR-J2M-B/MR-J2-
B/MR-J2M-B/MR-J2- B/MR-J2-03B5 General name for "Servo amplifier model MR-H
B/MR-J2-03B5 General name for "Servo amplifier model MR-H BN/MR-J2S-
BN/MR-J2S- B/MR-J2M-B/ MR-J2-
B/MR-J2M-B/ MR-J2- B/MR-J2-03B5, Vector inverter FREQROL-V500 series"
B/MR-J2-03B5, Vector inverter FREQROL-V500 series"
Qn(H)CPU
Abbreviation for "Multiple PLC system of the Q series"
Abbreviation for "CPU No.n (n= 1 to 4) of the CPU module for the Multiple CPU system"
General name for "MT Developer" and "GX Developer" General name for "SW  RN-SV
RN-SV Q
Q "
"
Operating system software for conveyor assembly use (Motion SFC) : SW6RN-SV13Q
Operating system software for automatic machinery use (Motion SFC) : SW6RN-SV22Q
Abbreviation for Integrated start-up support software package "MT Developer"
Abbreviation for MELSEC PLC programming software package "GX Developer (Version 6 or later)"
Abbreviation for "Manual pulse generator (MR-HDP01)"
Abbreviation for "Serial absolute synchronous encoder (MR-HENC/Q170ENC)"
High speed serial communication between Motion controller and servo amplifier General name for "System using the servomotor and servo amplifier for absolute position"
Cooling fan unit (Q170FAN)
Dividing unit (Q173DV)
Battery unit (Q170BAT)
1 - 1
1 OVERVIEW
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Generic term/Abbreviation |
Description |
|
|
A 0BD-PCF |
A10BD-PCF/A30BD-PCF SSC I/F board |
|
|
SSC I/F communication cable |
Abbreviation for "Cable for SSC I/F board/card" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Teaching Unit |
A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN Teaching unit(Note-3) |
|
|
or A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intelligent function module |
Abbreviation for "MELSECNET/H module/Ethernet module/CC-Link module/ |
|
|
Serial communication module" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vector inverter (FR-V500) |
Vector inverter FREQROL-V500 series |
|
(Note-1) |
: Q172EX can be used in SV22. |
(Note-2) |
: SSCNET: Servo System Controller NETwork |
(Note-3) |
: Teaching unit can be used in SV13. |
REMARK
For information about the each module, design method for program and parameter, refer to the following manuals relevant to each module.
|
Item |
Reference Manual |
|
Motion CPU module/Motion unit |
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) User’s Manual |
||
PLC CPU, peripheral devices for PLC program design, I/O |
Manual relevant to each module |
||
modules and intelligent function module |
|||
|
|||
Operation method for MT Developer |
Help of each software |
||
|
• Design method for positioning control |
|
|
SV13/SV22 |
program in the real mode |
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller |
|
• Design method for positioning control |
(SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (REAL MODE) |
||
|
|||
|
parameter |
|
|
SV22 |
• Design method for mechanical system |
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV22) |
|
(Virtual mode) |
program |
Programming Manual (VIRTUAL MODE) |
|
1 - 2

1 OVERVIEW
1.2 Features
The Motion CPU and Multiple CPU system have the following features.
1.2.1Features of Motion CPU
(1)Q series PLC Multiple CPU system
(a)The load of control processing for each CPU can be distributed by controlling the complicated servo control with the Motion CPU, and the machine control or information control with the PLC CPU, and flexible system configuration can be realized.
(b)The Motion CPU and PLC CPU are selected flexibly, and the Multiple CPU system up to 4 CPU modules can be realized.
The Motion CPU module for the number of axis to be used can be selected.
Q173CPU(N) |
: Up to 32 axes |
Q172CPU(N) |
: Up to 8 axes |
The PLC CPU module for the program capacity to be used can be selected. (One or more PLC CPU is necessary with the Multiple CPU system.)
Q00CPU |
: 8k steps |
Q01CPU |
: 14k steps |
Q02CPU, Q02HCPU |
: 28k steps |
Q06HCPU |
: 60k steps |
Q12HCPU |
: 124k steps |
Q25HCPU |
: 252k steps |
(c)The device data of other CPU can be used as the device data of self CPU because the Multiple CPU automatic refresh may do automatically data giving and receiving between each CPU of the Multiple CPU system.
(d)The device data access of the Motion CPU and the Motion SFC program start can be executed from PLC CPU by the Motion dedicated PLC instruction.
(2)Programming in the Motion SFC programs
(a)Since a program intelligible for anyone can be created in flow chart form by macking a sequence of machine operation correspond to each operation step, maintenance nature improves.
(b)Since transition conditions are judged with Motion CPU side and positioning starts, there is not dispersion in the response time influenced by PLC scan time.
1 - 3

1 OVERVIEW
(c)High speed and high response processing is realizable with the step processing method (only active steps) of Motion SFC.
(d)Not only positioning control but also numerical operations, device SET/RST, etc. can be processed with Motion CPU side, making via PLC CPU is unnecessary and a tact time can be shortened.
(e)By transition condition description peculiar to Motion SFC, the instructions to servo amplifier is possible at completion of starting condition.
(f)By transition condition description peculiar to Motion SFC, after starting, transition to next step is possible without waiting for positioning completion.
(g)Motion SFC program that responds and executes it at high speed for interrupt input from external source can be set.
(h)Motion SFC program executed in the fixed cycle (0.88ms, 1.77ms, 3.55ms, 7.11ms, 14.2ms) by synchronizing to the Motion operation cycle can be set.
(3)High speed operation processing
(a)The minimum operation cycle of the Motion CPU is made 0.88[ms] (so far, the ratio of 4 times), and it correspond with high frequency operation.
(b)High speed PLC control is possible by the Q series PLC CPU.
(For LD instruction)
Q02HCPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU, Q25HCPU Q02CPU
Q00CPU
Q01CPU
:0.034[µs]
:0.079[µs]
:0.16[µs]
:0.10[µs]
(4)Connection between the Motion controller and servo amplifier with high speed serial communication by SSCNET
High speed serial communication by SSCNET connect between the Motion controller and servo amplifier, and batch control the charge of servo parameter, servo monitor and test operation, etc.
It is also realised reduce the number of wires.
(5) The operating system software package for your application needs
By installing the operating system software for applications in the internal flash memory of the Motion CPU, the Motion controller suitable for the machine can be realized.
And, it also can correspond with the function improvement of the software package.
(a) Conveyor assembly use (SV13)
Offer liner interpolation, circular interpolation, helical interpolation, constantspeed control, speed control, fixed-pitch feed and etc. by the dedicated servo instruction. Ideal for use in conveyors and assembly machines.
1 - 4

1 OVERVIEW
(b) Automatic machinery use (SV22)
Provides synchronous control and offers electronic cam control by mechanical support language. Ideal for use in automatic machinery.
(c)Machine tool peripheral use (SV43)
Offer liner interpolation, circular interpolation, helical interpolation, constantspeed positioning and etc. by the EIA language (G-code). Ideal for use in machine tool peripheral.
1 - 5

1 OVERVIEW
1.2.2 Basic specifications of Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)
(1) Module specifications
Item |
Q173CPUN |
Q173CPUN-T |
Q173CPU |
Q172CPUN |
Q172CPUN-T |
Q172CPU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Teaching unit |
—— |
Usable |
—— |
—— |
Usable |
—— |
|
Internal current |
1.25 |
1.56 (Note) |
1.75 |
1.14 |
1.45 (Note) |
1.62 |
|
consumption(5VDC) [A] |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Mass [kg] |
0.23 |
0.24 |
0.22 |
0.22 |
0.23 |
0.21 |
|
Exterior dimensions |
98(3.86)(H) |
27.4(1.08)(W) |
118(4.65)(H) |
98(3.86)(H) |
27.4(1.08)(W) |
118(4.65)(H) |
|
27.4(1.08)(W) |
27.4(1.08)(W) |
||||||
[mm(inch)] |
114.3(4.50)(D) |
114.3(4.50)(D) |
|||||
89.3(3.52)(D) |
89.3(3.52)(D) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(Note) : Current consumption 0.26[A] of the teaching unit is included.
(2)SV13/SV22 Motion control specifications/performance specifications
(a) Motion control specifications
Item |
Q173CPUN(-T) |
|
Q173CPU |
|
Q172CPUN(-T) |
|
Q172CPU |
||
Number of control axes |
Up to 32 axes |
|
Up to 8 axes |
|
|||||
|
|
0.88ms/ 1 to 8 axes |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
SV13 |
1.77ms/ 9 to 16 axes |
|
0.88ms/1 to 8 axes |
|||||
Operation cycle |
|
3.55ms/17 to 32 axes |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
0.88ms/ 1 to |
4 axes |
|
|
|
|
|||
(default) |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
1.77ms/ 5 to 12 axes |
|
0.88ms/1 to 4 axes |
||||||
|
SV22 |
|
|||||||
|
3.55ms/13 to 24 axes |
|
1.77ms/5 to 8 axes |
||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
7.11ms/25 to 32 axes |
|
|
|
|
|||
Interpolation functions |
Linear interpolation (Up to 4 axes), Circular interpolation (2 axes), |
||||||||
|
|
Helical interpolation (3 axes) |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
PTP(Point to Point) control, Speed control, Speed-position control, Fixed-pitch feed, |
|||||||
Control modes |
Constant speed control, Position follow-up control, Speed switching control, |
||||||||
|
|
High-speed oscillation control, Synchronous control (SV22) |
|
||||||
Acceleration/ |
|
Automatic trapezoidal acceleration/deceleration, |
|
||||||
deceleration control |
|
|
S-curve acceleration/deceleration |
|
|||||
Compensation |
|
|
Backlash compensation, Electronic gear |
|
|||||
Programming language |
Motion SFC, Dedicated instruction, Mechanical support language (SV22) |
||||||||
Servo program capacity |
|
|
|
14k steps |
|
||||
Number of positioning |
|
|
|
3200 points |
|
||||
points |
|
(Positioning data can be designated indirectly) |
|
||||||
Programming tool |
|
|
|
IBM PC/AT |
|
||||
Peripheral I/F |
|
|
USB/RS-232/SSCNET |
|
|||||
Teaching operation |
Provided (Q173CPUN-T/Q172CPUN-T, SV13 use) |
|
|||||||
function |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Home position return |
Proximity dog type (2 types), Count type (3 types), Data set type (2 types), Dog cradle type, |
||||||||
Stopper type (2 types), Limit switch combined type |
|
||||||||
function |
|
||||||||
(Home position return re-try function provided, home position shift function provided) |
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||
JOG operation function |
|
|
|
Provided |
|
||||
1 - 6

1 OVERVIEW
Motion control specifications (continued)
Item |
Q173CPUN(-T) |
|
Q173CPU |
Q172CPUN(-T) |
|
Q172CPU |
|
Manual pulse generator |
|
|
Possible to connect 3 modules |
|
|||
operation function |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Synchronous encoder |
Possible to connect 12 modules |
Possible to connect 8 modules |
|||||
operation function |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
M-code function |
|
|
M-code output function provided |
|
|||
|
|
M-code completion wait function provided |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
Limit switch output |
|
|
Number of output points 32 points |
|
|||
function |
|
|
Watch data: Motion control data/Word device |
|
|||
|
|
Made compatible by setting battery to servo amplifier. |
|
||||
Absolute position system |
(Possible to select the absolute data method or incremental method for each axis) |
||||||
|
(Note) : When the vector inverter is used, only the increment method. |
||||||
Number of SSCNET I/F |
5CH (Note-1) |
2CH |
|
||||
Motion related interface |
Q172LX : 4 modules usable |
Q172LX : 1 module usable |
|||||
Q172EX : 6 modules usable |
Q172EX : 4 modules usable |
||||||
module |
|||||||
Q173PX : 4 modules usable (Note-2) |
Q173PX : 3 modules usable (Note-2) |
||||||
(Note-1) : Use the Dividing unit(Q173DV) or dividing cable(Q173J2B CBL
CBL M/Q173HB
M/Q173HB CBL
CBL M).
M).
(Note-2) : When using the incremental synchronous encoder (SV22 use), you can use avobe number of modules. When connecting the manual pulse generator, you can use only 1 module.
1 - 7

1 OVERVIEW
(b) Motion SFC Performance Specifications
|
Item |
|
|
|
|
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Code total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Motion SFC chart+ Operation control |
287k bytes |
|||||
Motion SFC program capacity |
+ Transition) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Text total |
|
|
|
|
224k bytes |
|
|
(Operation control + Transition) |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Number of Motion SFC programs |
256 (No.0 to 255) |
|||||
|
Motion SFC chart size/program |
Up to 64k bytes (Included Motion SFC chart comments) |
|||||
Motion SFC program |
Number of Motion SFC steps/program |
Up to 4094 steps |
|||||
Number of selective branches/branch |
255 |
||||||
|
|||||||
|
Number of parallel branches/branch |
255 |
|||||
|
Parallel branch nesting |
|
Up to 4 levels |
||||
|
Number of operation control programs |
4096 with F(Once execution type) and FS(Scan execution type) |
|||||
|
combined. (F/FS0 to F/FS4095) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Number of transition programs |
4096(G0 to G4095) |
|||||
Operation control program |
Code size/program |
|
Up to approx. 64k bytes (32766 steps) |
||||
(F/FS) |
Number of blocks(line)/program |
Up to 8192 blocks (in the case of 4 steps(min)/blocks) |
|||||
/ |
Number of characters/block (line) |
Up to 128 (comment included) |
|||||
Transition program |
Number of operand/block |
Up to 64 (operand: constants, word device, bit devices) |
|||||
(G) |
( ) nesting/block |
|
|
Up to 32 levels |
|||
|
Descriptive |
Operation control program |
Calculation expression/bit conditional expression |
||||
|
|
|
Calculation expression/bit conditional expression/ |
||||
|
expression |
Transition program |
|||||
|
comparison conditional expression |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Number of multi executed programs |
Up to 256 |
|||||
|
Number of multi active steps |
Up to 256 steps/all programs |
|||||
|
|
Normal task |
|
Executed in motion main cycle |
|||
|
|
Event task |
Fixed cycle |
Executed in fixed cycle |
|||
|
|
(0.88ms, 1.77ms, 3.55ms, 7.11ms, 14.2ms) |
|||||
Execute specification |
|
(Execution |
|
||||
Executed |
External |
Executed when input ON is set among interrupt module QI60 |
|||||
|
can be |
|
|||||
|
task |
masked.) |
interrupt |
(16 points). |
|||
|
|
PLC interrupt |
Executed with interrupt instruction (S(P).GINT) from PLC CPU. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
NMI task |
|
Executed when input ON is set among interrupt module QI60 |
|||
|
|
|
(16 points). |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Number of I/O points (X/Y) |
|
|
|
|
|
8192 points |
|
Number of real I/O points (PX/PY) |
|
|
|
|
256 points |
||
|
Internal relays |
(M) |
|
Total (M + L) : 8192 points |
|||
|
Latch relays |
|
(L) |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
Number of devices |
Link relays |
|
|
(B) |
|
8192 points |
|
Annunciators |
(F) |
|
2048 points |
||||
(Device In the Motion CPU |
|
||||||
Special relays |
(M) |
|
256 points |
||||
only) |
|
||||||
Data registers |
(D) |
|
8192 points |
||||
(Included the positioning |
|
||||||
Link registers |
(W) |
|
8192 points |
||||
dedicated device) |
|
||||||
Special registers |
(D) |
|
256 points |
||||
|
|
||||||
|
Motion registers |
(#) |
|
8192 points |
|||
|
Coasting timers |
(FT) |
|
1 point (888µs) |
|||
1 - 8
1 OVERVIEW
1.2.3 Operation control/transition control specifications
(1) Table of the operation control/transition control specifications
Item |
|
|
Specifications |
Remark |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Returns a numeric result. |
|
|
Calculation expression |
Expressions for calculating indirectly specified data using constants |
D100+1,SIN(D100), etc. |
|
|
|
|
and word devices. |
|
Expression |
|
Bit conditional |
Returns a true or false result. |
M0, !M0, M1*M0, |
|
expression |
Expression for judging ON or OFF of bit device. |
(M1+M2)*(!M3+M4), etc. |
|
|
Conditional |
|||
|
Comparison |
|
|
|
|
expression |
Expressions for comparing indirectly specified data and calculation |
D100==100 |
|
|
conditional |
|||
|
|
expressions using constants and word devices. |
D10<D102+D10, etc. |
|
|
|
expression |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The input X/output Y are |
|
|
Device |
Symbol |
Accessibility |
|
Usable tasks |
|
Description |
written with the actual input |
|
|
|
Read |
Write |
Normal |
Event |
NMI |
example |
PX/actual output PY. |
||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Input module |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It does the layput of the I/O |
|
|
non-loaded |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
X100 |
numbers of PX, PY by a set |
|
Input |
range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
up of as system. |
|
|
Input module |
PX |
|
|
|
|
|
PX180 |
(In the operation control |
|
|
loaded range |
|
|
|
|
|
program/transition program, |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Output module |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
automatically represented |
|
|
non-loaded |
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
Y100 |
as PX/PY according to the |
|
Output |
range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
system setting information.) |
|
|
Output module |
PY |
|
|
|
|
|
PY1E0 |
|
|
|
loaded range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal relay |
M |
|
|
|
|
|
M20 |
|
|
|
Latch relay |
L |
|
|
|
|
|
L1000 |
|
|
|
Link relay |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
B3FF |
|
|
|
Annunciator |
F |
|
|
|
|
|
F0 |
|
|
Bit devices |
Special relay |
M |
|
|
|
|
|
M9000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
: usable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
: unusable |
|
CAUTION
<Restrictions on write-enabled bit devices>
1)Write to device X is allowed only within the input module non-installed range.
2)Special relay has predetermined applications in the system.
Do not perform write to other than the user setting device. (Note) : SET/RST is disabled in the following device ranges.
SET/RST disable range |
Remark |
M2001 to M2032 |
Start accept device |
(Note) : DOUT output disabled in the following device ranges. DOUT output disable range Remark
Designation including
M2000 to M2127
M9000 to M9255
1 - 9
 Loading...
Loading...