Page 1

hp LaserJet
4100mfp 4101mfp
service
addendum
Page 2

Page 3

hp LaserJet 4100mfp series
service adden du m
Page 4

Copyright Information
© 2002 Hewlett-Packard
Company
All Rights Reserved.
Reproduction, adaptation, or
translation without prior written
permission is prohibited, except
as allowed under the copyright
laws.
Publication number
C9148-90909
Second edition, April 2002
Quick reference service PIN code: 04410002
Warranty
The information contained in this
document is subject to change
without notice.
Hewlett-Packard makes no
warranty of any kind with respect
to this information.
HEWLETT-PACKARD
SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS
THE IMPLIED WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE.
Hewlett-Packard shall not be
liable for any direct, indirect,
incidental, consequential, or
other damage alleged in
connection with the furnishing or
use of this information.
Trademark Credits
®
Adobe
, Acrobat®, PostScript™,
and the Acrobat logo are either
registered trademarks or
trademarks of Adobe Systems
Incorporated in the United States
and/or other countries/regions.
Microsoft
Windows
trademarks of Microsoft Corp.
Netscape™ is a U.S. trademark
of Netscape Communications
Corporation.
TrueType™ is a U.S. trademark
of Apple Computer, Inc.
ENERGY STAR
registered service mark of the
United States Environmental
Protection Agency.
®
,MS-DOS, and
®
are U.S. registered
®
is a U.S.
Hewlett-Packard Company
11311 Chinden Boulevard
Boise, Idaho 83714 U.S.A.
Page 5

Table of contents
List of figures
List of tables
1 Product Information
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Product configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
HP LaserJet 4100mfp (C9148A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
HP LaserJet 4101mfp (C9149A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Product features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Product speed and throughput . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Image quality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Paper handling. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Copying capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Expandable design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Product specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Media specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Special considerations for ADF documents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Supported media for the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Model and serial numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Product overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Front view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Back view. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
2 Service approach
Service approach . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Major assemblies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Contact HP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
World Wide Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
HP support assistant CD-ROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
HP authorized resellers and support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
HP service agreements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
3 Operation
Using the ADF unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
General guidelines for using the ADF unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Using the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
General guidelines for using the glass. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Using the control panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
C9148-90909 Table of contents 3
Page 6

Layout and operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Navigation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Walk-up copy display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Status bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Menus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Configure device, diagnostic, and service menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Menu map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
4 Maintenance
Cleaning the product . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
General guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Running the cleaning page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Cleaning the ADF delivery guide (clear mylar strip) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
User-replaceable parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Replacing user-replaceable parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Updating product firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Downloading a remote firmware update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Installing the update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
RFU installation messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Using HP Web JetAdmin (single update) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Using HP Web JetAdmin (multiple or unattended update) . . . . . . 42
Windows parallel connection (local printer) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Windows parallel connection (network printer) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Troubleshooting RFU installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
RFU installation error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Performing hard-drive disk initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Cold Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
NVRAM initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Performing automatic Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Performing manual calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Lead adjustment for the ADF. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Center adjustment for the ADF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Leading-edge adjustment for the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Side-edge adjustment for the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
5 Theory of operation
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Document transportation process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Document exposure system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Light-conversion process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
General descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Scan-unit components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
ADF components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Copy processor board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
CPB terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Typical scanning-process flow. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Copy processor board LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Scanner controller board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
ADF motor circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Optical-unit motor circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Scan-unit intake-fan motor circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
4 Table of contents C9148-90909
Page 7

Scanner controller board connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Intermediate PCB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Overcurrent and overvoltage protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Power-supply block diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Optical unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Inverter PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Scanning lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
CCD driver PCB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
ADF document-feed system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
ADF cover sensor (PS10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Document-detect sensor (PS2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Leading-edge sensor (PS1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
ADF motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Document pickup process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Document jams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Scan-unit intake fan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
6 Removal and replacement
Removal and replacement strategy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Required tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Before performing service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
After performing service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Common fasteners. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Parts removal order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
User-replaceable parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
ADF input tray . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
ADF pickup roller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
ADF separation roller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
ADF separation pad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
ADF unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Assemblies and covers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Control-panel door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Scan-unit right-side cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Copy processor board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Scan-unit left-side cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Intake fan filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Formatter cage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Scan unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Printing-unit top cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .91
Glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Scanning lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
Optical unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
ADF door open sensor (PS10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
Optical-unit drive gear/motor assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
Scan-unit power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
Inverter PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Scanner controller PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Intake fan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
C9148-90909 Table of contents 5
Page 8

7 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Preliminary operating checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Installation conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Media condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Unit condition. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Basic troubleshooting process flow. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Basic troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Power-on defects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Troubleshooting with the control panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Control-panel display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Event log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Print the event log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Interpret the event log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Display the event log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Control-panel messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Troubleshooting with the copy processor board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
User-level and service-level diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
ADF paper-path test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
To print a paper-path test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Diagnostic tests. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
To perform a diagnostic test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Service-level diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Service menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
To access the service menu (PIN code: 04410002) . . . . . . . . . . 127
Jam troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Jams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Clearing repeated ADF jams. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Creating a customer print job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Evaluate the information pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Configuration page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Configuration-page elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
JetDirect page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
JetDirect-page elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Supplies status page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Supplies-page elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Usage page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
File directory page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
File-directory-page elements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Image-formation troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Checking the print cartridge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
EconoMode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Image-defect tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Media troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Isolate a paper path . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Use the straightest paper path. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Isolate the source of the jam . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Determine where media jams occur . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Is the MFP is misfeeding or creating multifeed jams . . . . . . . . . . 140
Isolate a media brand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Isolate a media type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Wiring diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
6 Table of contents C9148-90909
Page 9

8 Parts and diagrams
Ordering parts, supplies and getting support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .144
Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Related documentation and software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .144
Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
Consumables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
Common hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
HP Laserjet 4100 differences. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .146
How to use the parts lists and diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Parts lists and diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .148
Alphabetical parts list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .162
Numerical parts list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .164
Index
C9148-90909 Table of contents 7
Page 10

8 Table of contents C9148-90909
Page 11

List of figures
Figure 1. Model and serial number label . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 2. Product parts (front view; right side) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 3. Optical-unit lock (front view; left side) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 4. Product parts (back view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 5. Major assemblies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 6. Using the ADF. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 7. Using the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 8. Control panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 9. Navigation buttons. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 10. Top-level control-panel menu display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 11. MFP menu map 1 of 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 12. MFP menu map 2 of 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 13. Open the delivery-guide cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 14. Remove the clear plastic sheet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 15. Replace the clear, plastic sheet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 16. Sample calibration target page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 17. Manual calibration registration lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 18. MFP block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 19. Scan-unit components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 20. ADF-unit components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Figure 21. Copy processor board components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 22. Copy processor board LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Figure 23. Scanner controller board connectors (shield off). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Figure 24. Power-supply block diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Figure 25. Optical unit block diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Figure 26. Scanning process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Figure 27. Signal conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 28. Document transport path. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Figure 29. Release the ADF input-tray hinge. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Figure 30. Remove the ADF input tray. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Figure 31. Release the roller shield . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Figure 32. Remove the roller shield . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Figure 33. Remove the ADF pickup roller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Figure 34. Remove the ADF separation roller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Figure 35. Remove the ADF separation pad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 36. Replace the ADF separation pad spring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 37. Disconnect the cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Figure 38. Remove the ADF unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Figure 39. Remove the print cartridge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Figure 40. Remove the control-panel wire-harness cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Figure 41. Disconnect the control-panel grounding strip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Figure 42. Release the control-panel door-support pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Figure 43. Remove the control-panel door. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Figure 44. Remove the product serial- and model-number panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Figure 45. Remove the right-side cover screw. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Figure 46. Remove the scan-unity right-side cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Figure 47. Disconnect the ADF cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Figure 48. Disconnect the high-speed copy connect cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Figure 49. Remove the left-side screw. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
C9148-90909 List of figures 9
Page 12

Figure 50. Gently pry the top edge of the left-side cover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Figure 51. Remove the scan-unit left-side cover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Figure 52. Remove the intake filter.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Figure 53. Remove the formatter-cage cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Figure 54. Slide the formatter cage toward the back of the product . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Figure 55. Disconnect the formatter high-speed copy connect cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Figure 56. Secure the optical unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Figure 57. Disconnect the CPB cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Figure 58. Disconnect the scan unit cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Figure 59. Remove the scan unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Figure 60. Remove the top-cover rear-mounting screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Figure 61. Remove the printing-unit top cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Figure 62. Remove the glass mounting screws. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Figure 63. Remove the glass. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Figure 64. Note the cable routing pattern . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Figure 65. Remove the scanning lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Figure 66. Scanning-lamp wire harness routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Figure 67. Release the optical unit ribbon cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Figure 68. Optical-unit ribbon-cable clip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Figure 69. Release the tension-spring bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Figure 70. Remove the optical unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Figure 71. Optical-unit drive-belt tension bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Figure 72. Optical-unit ribbon cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Figure 73. Remove the ADF door open sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Figure 74. Remove the optical-unit cover plate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Figure 75. Remove the optical-unit drive gear/motor assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Figure 76. Remove the power-supply shield . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Figure 77. Remove the power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Figure 78. Remove the inverter PCB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Figure 79. Unplug the connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Figure 80. Grasp the scanner controller PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Figure 81. Remove the scanner controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Figure 82. Remove the fan mounting screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Figure 83. Remove the intake fan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Figure 84. Correctly orient the intake fan and bracket. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Figure 85. Basic troubleshooting flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Figure 86. Sample MFP event-log page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Figure 87. Control-panel display of the event log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Figure 88. Copy processor board LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Figure 89. Sample configuration page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Figure 90. Sample JetDirect page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Figure 91. Sample supplies status page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Figure 92. Sample usage page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Figure 93. Sample file-directory page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Figure 94. Wiring diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Figure 95. Covers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Figure 96. Top-cover assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Figure 97. Scan unit (1 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Figure 98. Scan unit (2 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Figure 99. Glass, formatter,CPB, and cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Figure 100. ADF unit (1 of 2). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Figure 101. ADF unit (2 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
10 List of figures C9148-90909
Page 13

List of tables
Table 1. Physical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 2. Performance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 3. ADF/flatbed-unit acoustical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 4. Skew specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 5. Supported paper sizes and weights for the ADF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 6. General cleaning guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 7. User-replaceable parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 8. Print-unit maintenance kit parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 9. Copy processor board LEDs (initialization sequence) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 10. Scanner controller board connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 11. Low-voltage components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Table 12. Common fasteners found in the MFP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Table 13. Parts-removal tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Table 14. Primary steps for troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Table 15. Basic troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Table 16. Power malfunctions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Table 17. Firmware-update event-log errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Table 18. Control-panel error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Table 19. Troubleshooting copy processor board LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Table 20. Service menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Table 21. General ADF jam troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Table 22. Image-quality checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Table 23. Image defects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Table 24. Technical support websites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Table 25. Accessories and supplies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Table 26. Consumables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Table 27. Screws used in the ADF unit and scan unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Table 28. HP LaserJet 4100 differences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Table 29. Covers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Table 30. Top-cover assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Table 31. Scan unit (1 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Table 32. Scan unit (2 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Table 33. Glass, formatter, CPB, and cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Table 34. ADF unit (1 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Table 35. ADF unit (2 of 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Table 36. Alphabetical parts list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Table 37. Numerical parts list. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
C9148-90909 List of tables 11
Page 14

12 List of tables C9148-90909
Page 15

1 Product Information
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Product configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
HP LaserJet 4100mfp (C9148A). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
HP LaserJet 4101mfp (C9149A). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Product features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Product speed and throughput . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Image quality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Paper handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Copying capability. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Expandable design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Product specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Media specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Special considerations for ADF documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Supported media for the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Model and serial numbers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Product overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Front view. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Back view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
C9148-90909 1 Product Information 13
Page 16
Introduction
With the HP LaserJet 4100 series multifunction printer (MFP), a workgroup can print, make
copies, and send digital documents using a single device. Multiple functions can occur
simultaneously in the MFP.
This service manual is an addendum to the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer service manual.
The HP LaserJet 4100mfp can be upgraded to the HP LaserJet 4101mfp by ordering the
following parts:
• one additional 500-sheet media input tray (C8055A)
• duplex printing accessory (for automatic two-sided printing (C8054A)
• digital sending software (C7140A)
Note The terminology used in this manual contains minor differences from the HP LaserJet 4100 series
printer service manual. These differences reflect changes made since the publication of the HP
LaserJet 4100 series printer service manual.
Product configurations
The HP LaserJet 4100mfp series is available in two configurations.
HP LaserJet 4100mfp (C9148A)
● 64 MB RAM; 5 GB (or larger) hard disk for RIP ONCE, transmit and scan once; job retention;
and font, form, and signature storage
● HP Jetdirect 10/100 Base-TX print server card for network connection
● 100-sheet media input tray
● 500-sheet media input tray
● automatic document feeder (ADF) with 30-sheet capacity
● embedded scan to e-mail
HP LaserJet 4101mfp (C9149A)
● all of the features of the HP LaserJet 4100mfp listed above
● one additional 500-sheet media input tray
● a duplex printing accessory (for automatic two-sided printing)
● HP digital-sending service software version 3.0 (or later)
• full send-to-e-mail capability
• SMTP mail service support
• Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) compatibility
Note The HP LaserJet 4101mfp is available only in the United States and Canada.
14 Product Information C9148-90909
Page 17

Product features
Product speed and throughput
● copying of letter-size media at 25 pages per minute (ppm) or A4-size media at 24 ppm
● monochrome scanning of letter-size originals at 25 ppm or A4-size originals at 24 ppm, and
color scanning at 8 ppm
● instant-on fuser
● scan-once copying
● RIP ONCE copy capability
● scan-ahead capability to start copying or sending while the printer is busy
● monthly duty cycle of 150,000 pages
Image quality
● FastRes 1200: 1200 dots per inch (dpi) print quality for fast, high-quality printing of business
text and graphics
● copying and scanning at a resolution of 600 pixels per inch (ppi)
● up to 256 levels of gray for smooth, photo-like images
● HP print cartridge for crisp, sharp output
Paper handling
● HP LaserJet 4100mfp: the 100-page and 500-page input trays are standard
● HP LaserJet 4101mfp: the 100-page and two 500-page input trays are standard
● capable of copying on a wide range of media sizes, types, and weights
● expandable to hold up to 1600 sheets of media
● standard 250-sheet face-down output
● duplexing (standard on the HP LaserJet 4101mfp)
● glass, which can accommodate media sizes up to letter/A4 size
● ADF with 30-page capacity to handle media sizes up to legal size
Copying capability
● easy-to-use copy functionality
● document collation
● multiple copies
● multiple pages per sheet (n-up)
● document reduction and enlargement
• ADF: 25 percent to 200 percent in one-percent increments (in ten-percent increments
when the
• Flatbed glass: 25 percent to 400 percent in one-percent increments (in ten-percent
increments when the
● automatic page-to-page enlargement or reduction
● image-quality improvement through background removal, best-quality mode, and contrast
adjustment
REDUCE or ENLARGE button is held down)
REDUCE or ENLARGE button is held down)
C9148-90909 1 Product Information 15
Page 18

Expandable design
● stackable 500-sheet trays (up to two additional trays can be added to the HP LaserJet
4100mfp, and one additional tray can be added to the HP LaserJet 4101mfp)
● duplex printing accessory (standard with the HP LaserJet 4101mfp)
● HP Fast InfraRed printing adapter (FIR port)
● digital-sending service software (standard with the HP LaserJet 4101mfp)
● expandable memory through installation of additional dual inline memory modules (DIMMs)
Product specifications
Table 1. Physical specifications
4100mfp (print unit, scan unit, and ADF unit)
Height 637 mm (25.1 inches)
Depth 520.7 mm (20.5 inches)
Width 805 mm (31.7 inches)
Weight 26 kg (56.5 pounds)
Scan unit only
Height 140 mm (5.6 inches)
Depth 540 mm (21.6 inches)
Width 415 mm (16.6 inches)
Weight approximately 5 kg (11.1 pounds)
ADF unit only
Height 152 mm (6.1 inches)
Depth 344 mm (13.8 inches)
Width 415 mm (16.6 inches)
Weight approximately 3 kg (6.4 pounds)
Table 2. Performance
Category Specification
Scanning speed (ADF mode) 139 mm/second (5.6 inches/second)
Scanning speed (flatbed mode) 69 mm/second (2.8 inches/second)
Copy speed 25 ppm (letter)
24 ppm (A4)
Copy resolution 600 by 600 ppi optical
Digital send resolution 600 by 600 ppi optical
16 Product Information C9148-90909
Page 19

Table 3. ADF/flatbed-unit acoustical specifications
Category Specification
Sound Po wer Level, L
(1 bel = 10 decibels)
WAd
● Scanning: 6.7 dB (A)
● Standby: 5.2 dB (A)
Note Testing per International Standard Organization (ISO) 9296.
Note “Operating” means that the product is copying and printing continuously at 25 ppm. Values are
subject to change. See http://www.hp.com/lj4100mfp for current information.
Table 4. Skew specifications
Print unit
Tolerance Cut paper Envelope
Skew 1.5 mm (.03 inch) over 260 mm (10.24
inches) length---simplex
1.50 mm (.03 inch) over 260 mm (10.24
inches) length---duplex
First line
leading edge
Left margin 5.0 mm (.20 inch) +/- 1.5 mm (.06 inch) 15mm (.59 inch) +/- 4.5 mm (.18 inch)
Text stretching 1 percent for cut sheet---simplex
6.0 mm (.24 inch) +/- 2mm (.08 inch) 15mm (.59 inch) +/- 4.5 mm (.18 inch)
1 percent for cut sheet---duplex
6.0mm (.24 inch) over 220mm
(8.66 inches) length
None
Scan unit
Tolerance ADF Glass
Skew <= 1 percent <= 1 percent
Leading edge +/- 2 mm (.08 inch) +/- 1 mm (.04 inch)
Left margin +/- 1 mm (.04 inch) +/- 1 mm (.04 inch)
Parallel (vertical
and horizontal)
Image length and
width
+/- 0.6 percent +/- 0.6 percent
+/- 1.2 percent +/- 1 percent
C9148-90909 1 Product Information 17
Page 20
Media specifications
Note This section refers to the MFP only. See the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer service manual for
printing specifications, or see the Print Media Guide for the HP LaserJet printer family
requirements.
Table 5. Supported paper sizes and weights for the ADF
Size Dimensions Weight
Letter 216 by 279 mm
(8.5 by 11 inches)
A4 210 by 297 mm
(8.3 by 11.7 inches)
Legal 216 by 356 mm
(8.5 by 14 inches)
50 to 105 g/m
(13 to 28 lb)
2
for general
Custom sizes Minimum:
148.5 by 210 mm
(5.9 by 8.3 inches
Maximum:
215.9 by 355.6 mm
(8.5 to 14 inches)
60 to135 g/m2
(16 to 36 lb)
Special considerations for ADF documents
● Documents must be free of tears or perforations.
● Documents must be square or rectangular and in good condition (not fragile or worn).
● Documents must be free of glue, correction fluid, or wet ink.
● Remove sticky notes, tape flags, staples, and paper clips.
● Multipart forms cannot be used in the ADF.
Supported media for the glass
The glass can accommodate the following types of media:
● letter- or A4-size and smaller originals, books, manuals, receipts, and similar documents
● irregular and worn documents, stapled documents, and photographs
● multiple-page letter-size documents
18 Product Information C9148-90909
Page 21
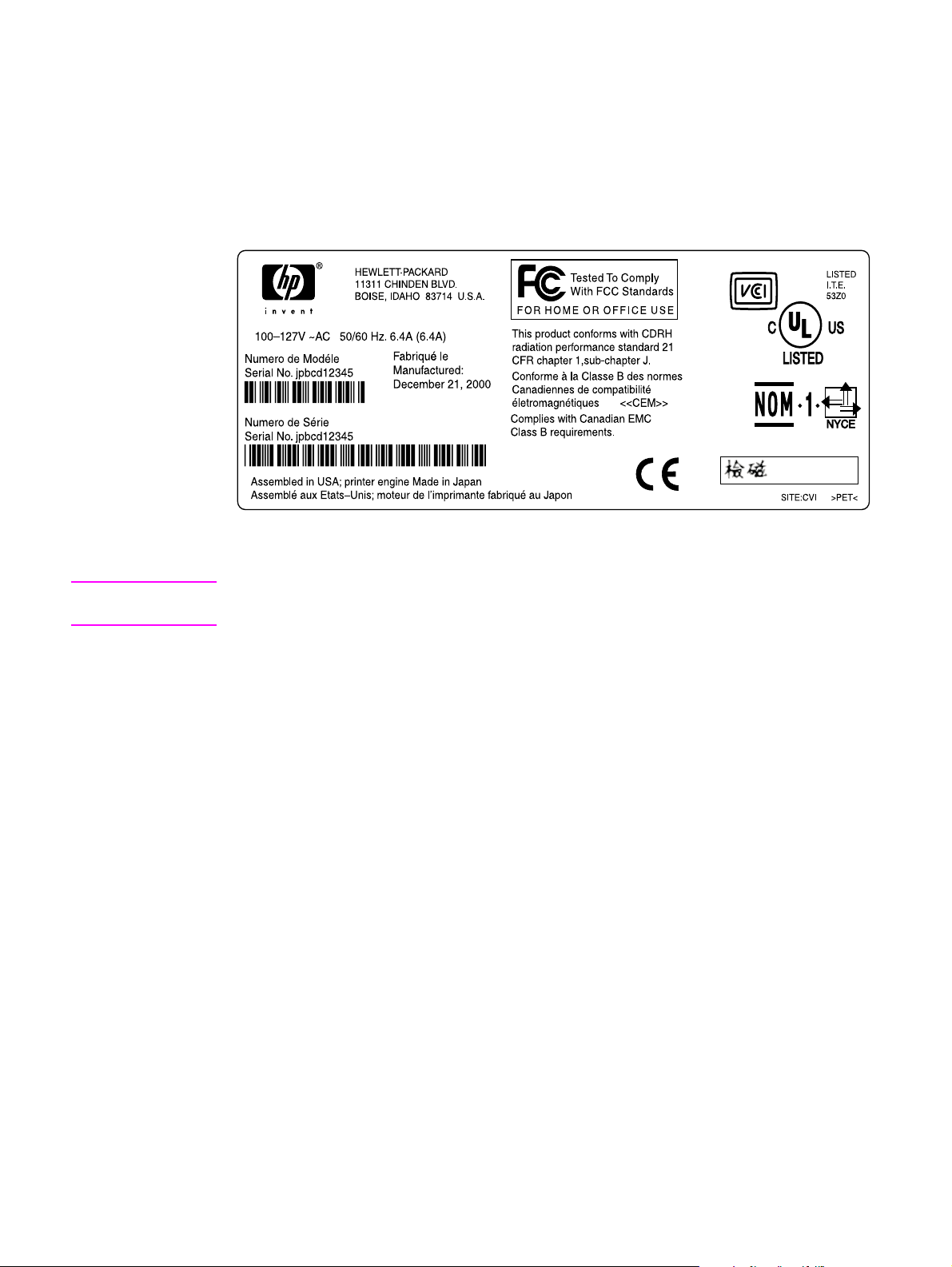
Model and serial numbers
The model number and serial number are listed on an identification label located underneath the
control panel door.
The serial number contains information about the country/region of origin, product revision level,
production code, and production number of the product.The label also contains power rating and
regulatory information.
Figure 1. Model and serial number label
Note If the control panel fails, the model and serial number label panel must be removed (see “Control-
panel door” on page 79) and installed on the replacement control panel.
C9148-90909 1 Product Information 19
Page 22
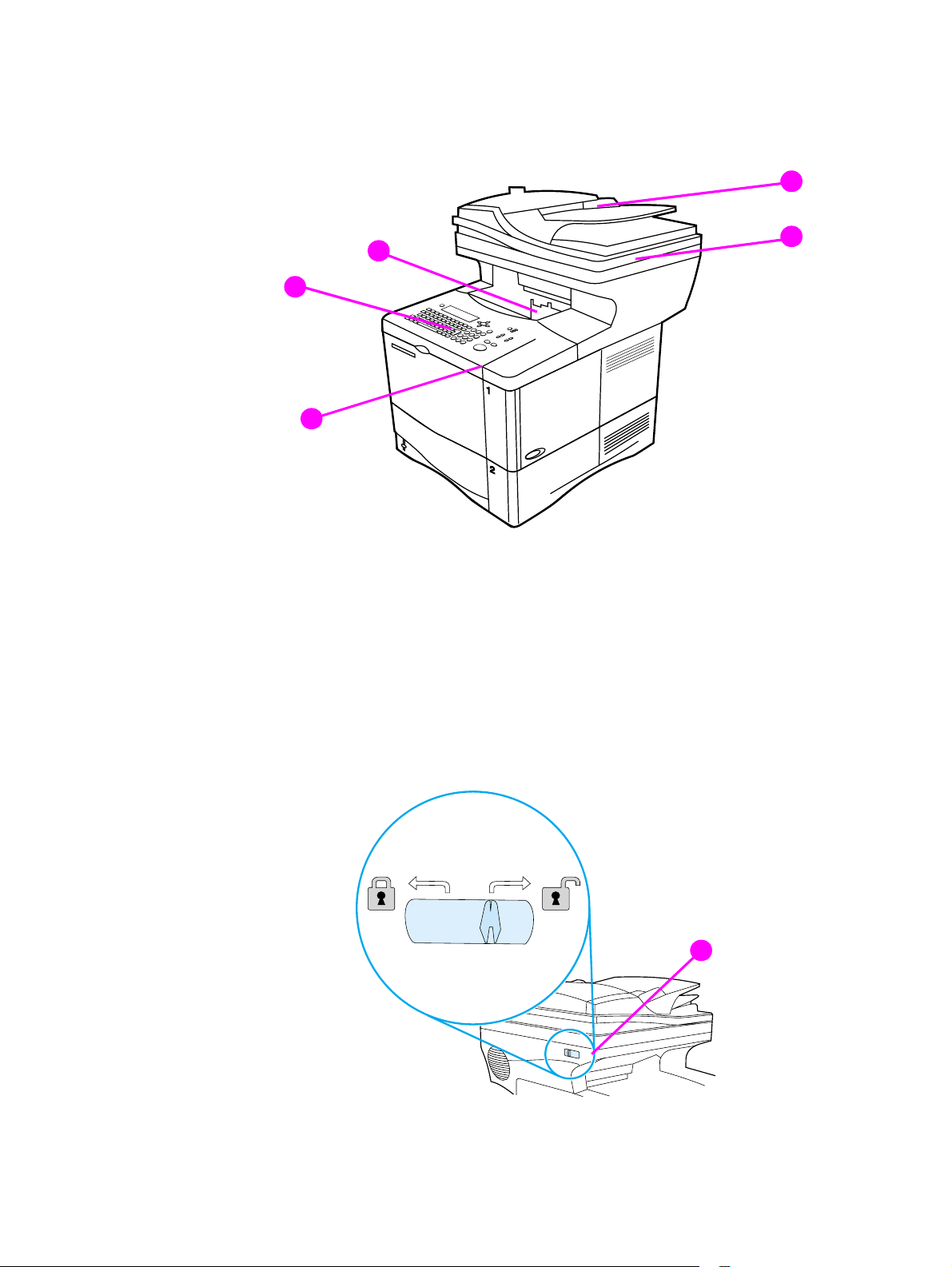
Product overview
Front view
1
5
4
3
Figure 2. Product parts (front view; right side)
1 automatic document feeder (ADF) input (with sliding media guides)
2 ADF cover (lifts for access to the glass)
3 control-panel door (provides access to the print cartridge; serial and model numbers are
located on a panel underneath the door)
2
4 control panel
5 output bin (for printed output and copies)
Figure 3. Optical-unit lock (front view; left side)
6
6 optical-unit lock
20 Product Information C9148-90909
Page 23
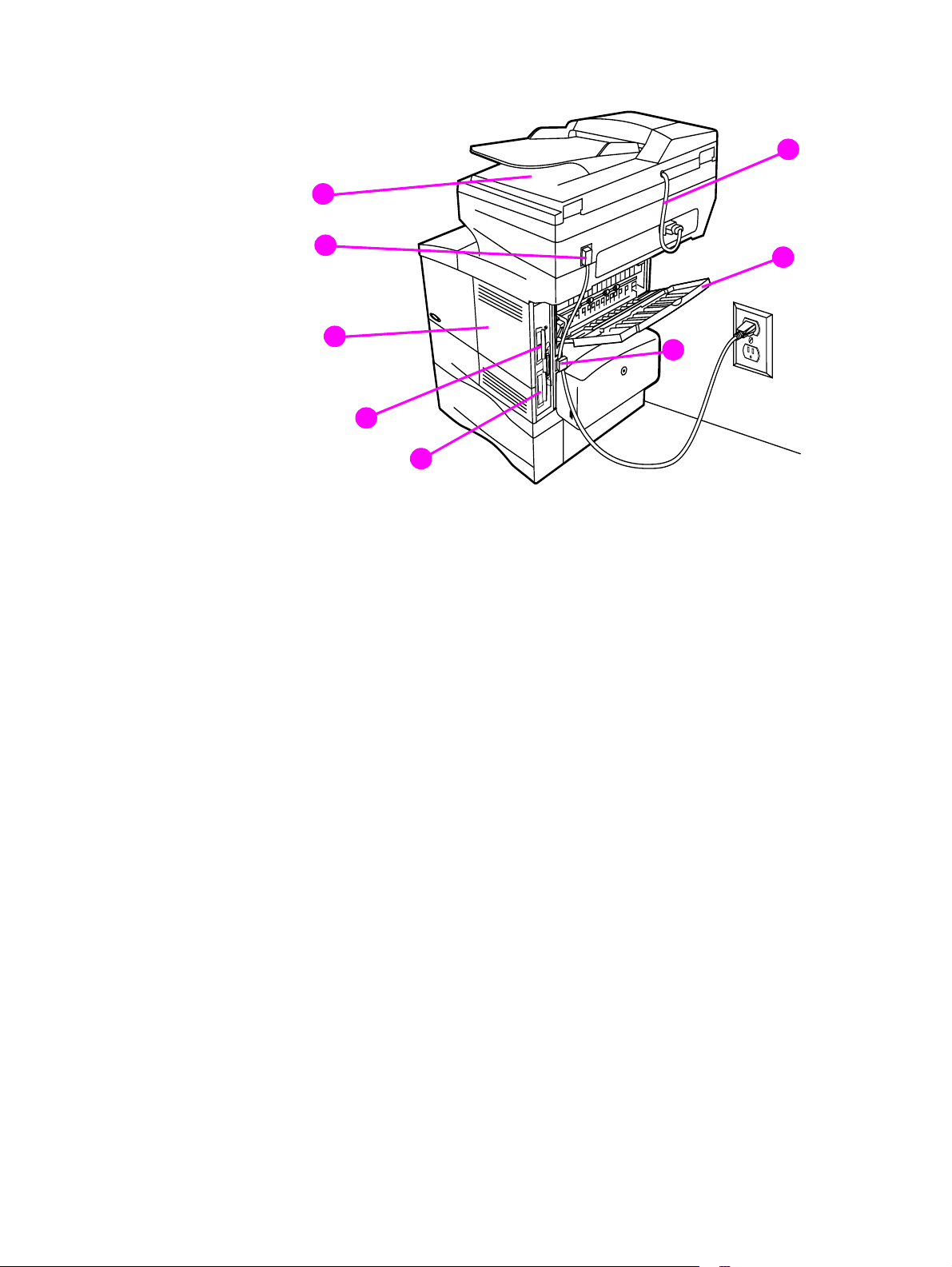
Back view
1
8
7
6
5
Figure 4. Product parts (back view)
1 ADF connector cable
2 straight-through output door
3 power connection (from power source to print unit)
4 hard disk
5 HP JetDirect card
6 memory access door (more than one DIMM can be installed)
2
3
4
7 power jumper cable (from print unit to scan unit)
8 ADF output bin
C9148-90909 1 Product Information 21
Page 24

22 Product Information C9148-90909
Page 25

2 Service approach
Service approach . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Major assemblies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Contact HP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Contact HP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
World Wide Web. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
HP support assistant CD-ROM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
HP authorized resellers and support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
HP service agreements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
2 Service approach 23
Page 26
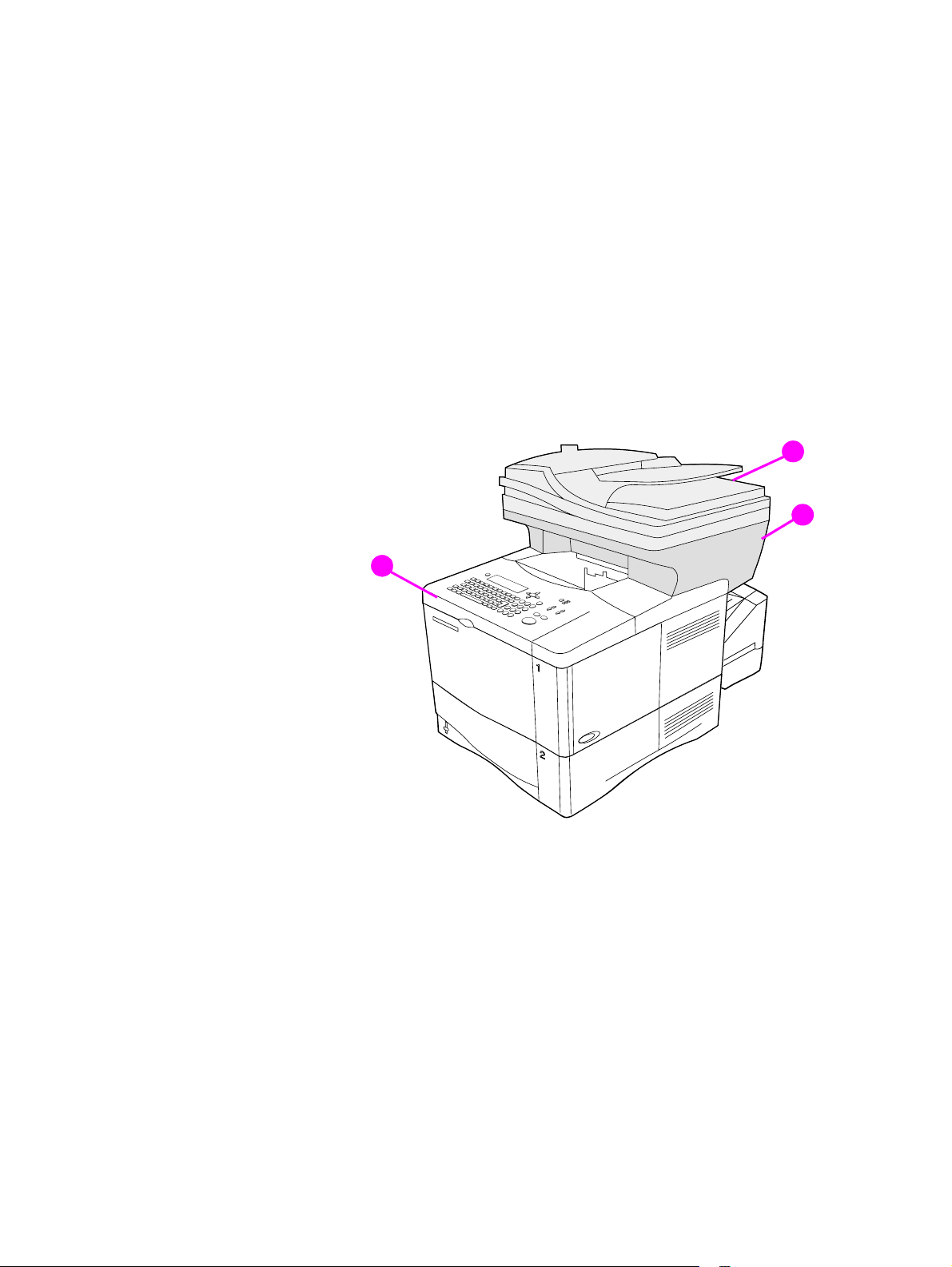
Service approach
Repair of the printer normally begins with a three-step process:
1 Isolate the problem to the major system (the host computer, the network and/or server, or
MFP major assemblies).
2 Determine whether the problem is located in one of the paper-handling devices or in the
product engine.
3 Troubleshoot the problem using the procedures in the troubleshooting chapter of this
manual. See “Troubleshooting” on page 109.
Major assemblies
When a faulty part is identified, repair is usually accomplished by assembly-level
replacement of field replaceable units (FRUs). Some mechanical assemblies can be
repaired at the subassembly level. Hewlett-Packard does not support replacement of
components on the printed circuit boards (PCBs).
1
2
Figure 5. Major assemblies
1 automatic document feed (ADF) unit
2 scan unit
3 print unit
3
24 Servic e appr o ach C9148-90909
Page 27

Contact HP
World Wide Web
Printer drivers, updated HP printer software, and product and support information can be
obtained from the following websites:
● U.S., http://www.hp.com/support/lj4100
● Europe, http://www.hp.com/support/lj4100
● China, ftp://www.hp.com.cn/support/lj4100
● Japan, ftp://www.jpn.hp.com/support/lj4100
● Korea, http://www.hp.co.kr/support/lj4100
● Taiwan, http://www.hp.com.tw/support/lj4100,
or the local driver website, http://www.dds.com.tw
HP support assistant CD-ROM
This support tool offers a comprehensive online information system designed to provide
technical and product information about Hewlett-Packard products. T o subscribe to this quarterly
service in the U.S. or Canada, call (1) (800) 457-1762. In Hong Kong, Indonesia, Malaysia, or
Singapore, call Mentor Media at (65) 740-4477.
HP authorized resellers and support
To locate HP authorized resellers and support, call (1) (800) 243-9816 in the U.S. or
(1) (800) 387-3867 in Canada
HP service agreements
Call (1) (800) 743-8305 in the U.S. or (1) (800) 268-1221 in Canada.
C9148-90909 2 Service approach 25
Page 28

26 Servic e appr o ach C9148-90909
Page 29

3 Operation
Using the ADF unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
General guidelines for using the ADF unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Using the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
General guidelines for using the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Using the control panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Layout and operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Navigation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Walk-up copy display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Status bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Menus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Configure device, diagnostic, and service menus . . . . . . . . . . 32
Menu map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3 Operation 27
Page 30
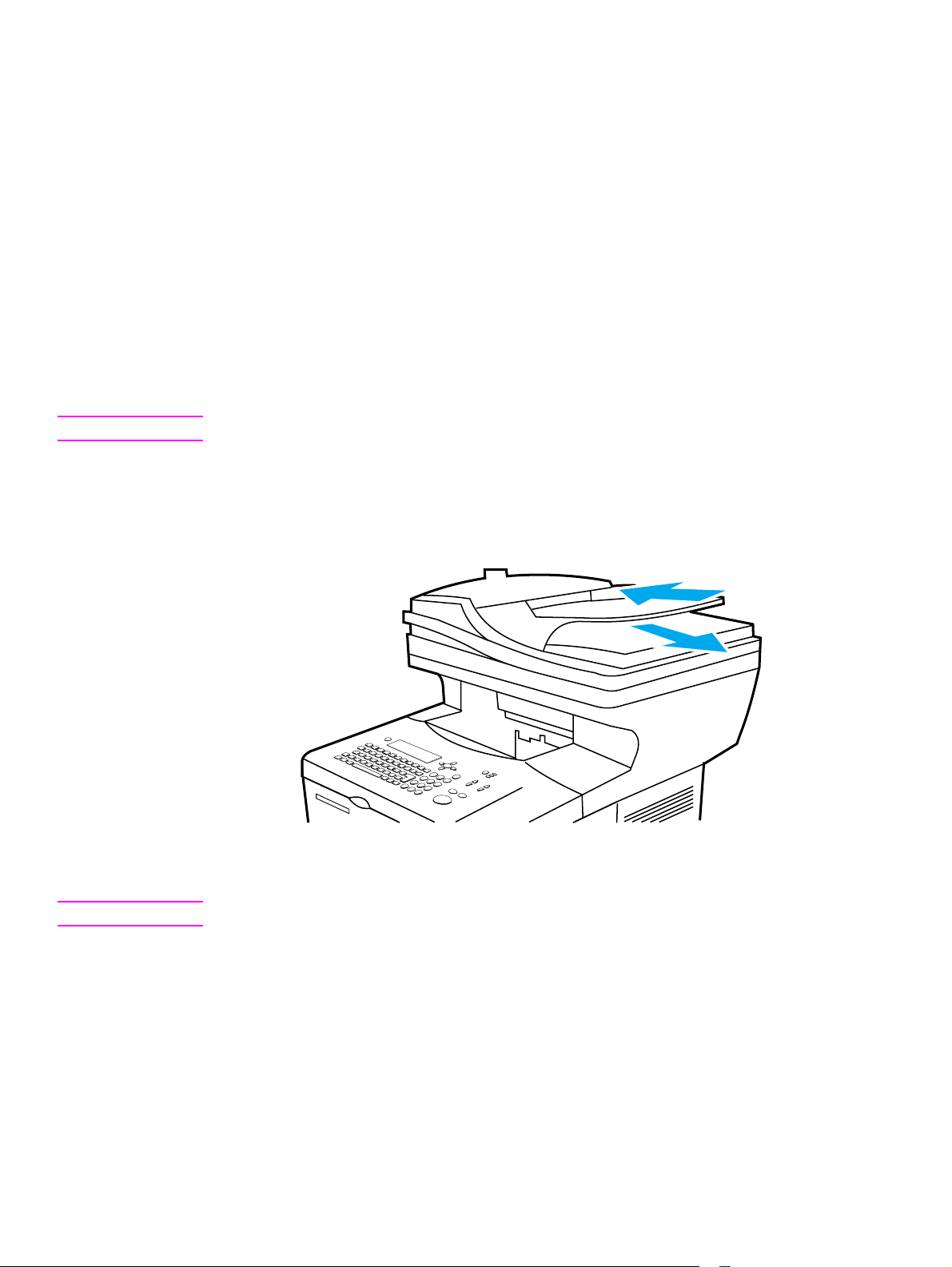
Using the ADF unit
The automatic document feeder (ADF) is a fast, convenient way to feed multiple-page originals
for copying or digital-sending. You can load the ADF with as many as 30 sheets of paper. The
ADF accepts documents that meet the following specifications:
● single-sided or double-sided originals
● documents on standard letter-size, A4-size, and legal-size paper
● documents ranging in size from 148.5 by 210.0 mm (5.9 by 8.3 inches) to 215.9 by
355.6 mm (8.5 by 14.0 inches)
● documents ranging in weight from 50 to 105 g/m
● documents that are free of tears or perforations
● documents that are square or rectangular and in good condition (not fragile or worn)
● documents that are free of glue, correction fluid, wet ink, sticky notes, tape flags, staples, or
paper clips
CAUTION Do not use multipart forms.
The ADF transports the original document through the ADF paper path. Copies made using the
ADF are delivered to the output bin beneath the scan unit.
General guidelines for using the ADF unit
2
(16 to 28lb)
Figure 6. Using the ADF
Note The source documents must be placed in the ADF input with the side you intend to copy facing up.
1 Before placing documents in the ADF, prepare the documents by doing the following:
• flatten curls or wrinkles
• remove staples, paper clips, sticky notes, and similar materials
2 Place documents in the ADF input tray.
3 On the control panel, select the sending or copying options you want to use. See the “Walk-
up copying” and “Sending to e-mail ” sections in the use guide for information about these
functions.
4 After making your selections, press
START. Copies are sent to the output bin beneath the
scan unit.
5 When the scan is complete, remove the original document from the ADF output.
28 Operation C9148-90909
Page 31

Using the glass
You can also use the digital-sending and copying features by using the glass, located below the
ADF. The glass can accommodate letter- or A4-size and smaller originals, books, manuals,
receipts, and similar documents. Irregular and worn documents, stapled documents, and
photographs can also be easily sent or copied using the flatbed.
General guidelines for using the glass
Figure 7. Using the glass
1 Open the ADF cover and place the original document face-down on the glass. Lower the
cover.
2 On the control panel, select the sending or copying options you want to use. See the “Walk-
up copying” and “Sending to e-mail” sections in the use guide for information about these
functions.
3 After making the selections, press
flatbed.
4 When the scan is complete, remove the original document from the glass.
START. Copies are sent to the output bin beneath the
C9148-90909 3 Operation 29
Page 32

Using the control panel
Layout and operation
1
Figure 8. Control panel
1 ? (Help): provides Help files that contain information about the control-panel display when
problems occur.
2 Control-panel display.
3 Navigation buttons: four arrow buttons that are used to move among elements on the
control-panel display. Use the central
menu.
2
3 4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
SELECT ( ) button to choose an element or enter a
12
4 C (Clear): resets the copy count or other numeric entries.
5
MENU: use to choose device configuration menus on the control panel.
6 Status lights: Ready light, Data light, and Attention light.
7 Light and dark buttons: use to increase or decrease the brightness of the copy image
8
REDUCE and ENLARGE buttons: use to scale the copy size.
9
RESET: returns all current job settings to their default values.
10
STOP: cancels a copy job, digital send job, or print job.
11
START: begins or resumes a job.
12 Numeric keypad and keyboard: the keypad is used to type numerical values. The keyboard is
used for digital-sending features and for typing other data.
Hint If the MFP is put into a paused mode (see “Menu map” on page 33), the control panel displays
the message Paused at the top of the display. To return the MFP to the ready mode, press
MENU
and then use the navigation buttons (callout 3) to highlight RESUME on the control-panel display.
Press the
SELECT ( ) button. The message displayed on the control panel changes from Paused
to Ready.
The MFP paused mode is not the same as PowerSave mode. When the MFP is in PowerSave
mode, the control-panel displays the message P
OWERSave On at the top of the display. When in
PowerSa ve mode, pressing any key or button on the control panel will return the MFP to the ready
state.
30 Operation C9148-90909
Page 33

Navigation
By pressing the arrow navigation buttons, you can shift focus between objects on the controlpanel display to describe the document to be handled and the actions to be performed. A bold
border around a graphic object or a reverse video effect in a text list indicates the current focus.
Use the central
SELECT ( ) button to select menus.
Figure 9. Navigation buttons
Walk-up copy display
Use the walk-up copy display menu on the control-panel display to describe the original
document and to specify the actions to be taken and their parameters. The primary walk-up copy
display menu choices are:
● Describe Original
● Copy Settings
● Send Options
After power is turned on the MFP initializes and the top-level menu display appears when the
MFP is ready to process jobs.
Select
Move left
Move up
Move right
Move down
Figure 10. Top-level control-panel menu display
The Describe Original menu is used for both digital-sending and copying. The other menus are
addressed in the “Walk-up copying” and “Sending to e-mail” sections in the use guide.
Status bar
The status bar is the uppermost line of available text on the control-panel display.
● The status line shows both product-status messages and user prompts. When the product is
idle, this line displays Ready To Copy, Accepting Copy Jobs, or Ready. During scanning, the
line might read Scanning Page x. During copying, you might see Data Recieved
Processing Job. Error messages are not communicated on the status line, but they appear
in a text box overlay that blocks normal display views until the message is cleared.
● The copy count shows the number of copies selected. This selection is made using the
keypad. Acceptable values are from 1 to 99.
C9148-90909 3 Operation 31
Page 34

Menus
The HP LaserJet 4100mfp series uses a system of control-panel menus to set job parameters,
set system defaults, and manage product performance and features. Menu options are reached
by pressing the
the list to locate the option you want to use. The following menus are available.
● Pause/Resume (see Hint on page 30)
● Retrieve job
● Information
● Paper handling
● Configure device
● Diagnostic
● Service (PIN code: 04410002)
For more information about menus, see “Control panel and control panel menus” in the use
guide.
Configure device, diagnostic, and service menus
The configure device menu is used to establish the product’s default settings. The selected
defaults can be locked by the system administrator. You can override the default settings at the
control panel for the current job only. It might be necessary to reset these options to factory
defaults when troubleshooting the MFP unit.
MENU button on the right side of the control-panel display and scrolling through
The diagnostic menu is used to calibrate and test MFP components. The diagnostic menu can
also be used to print or view an event log. An event log records the number and type of errors the
product has experienced.
The service menu is used by HP-authorized service representatives only and is protected by an
eight-digit personal identification number (PIN). See “Service menu” on page 127. The service
menu can be used to verify the serial number of the MFP unit.
32 Operation C9148-90909
Page 35

Menu map
The menu map is a graphical representation of the MFP menus. Press the MENU button on the
control panel to gain access to the main menu display . For more information about navigating the
menus, see “Navigation” on page 31.
Note Default settings shown in bold.
Figure 11. MFP menu map 1 of 2
C9148-90909 3 Operation 33
Page 36

Menu map, continued
Figure 12. MFP menu map 2 of 2
34 Operation C9148-90909
Page 37

4 Maintenance
Cleaning the product. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
General guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Running the cleaning page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Cleaning the ADF delivery guide (clear mylar strip) . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
User-replaceable parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Replacing user-replaceable parts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Updating product firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Downloading a remote firmware update. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Installing the update. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
RFU installation messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Using HP Web JetAdmin (single update). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Using HP Web JetAdmin (multiple or unattended update). . . . 42
Windows parallel connection (local printer) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Windows parallel connection (network printer) . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Troubleshooting RFU installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
RFU installation error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Performing hard-drive disk initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
NVRAM initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Performing automatic Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Performing manual calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Lead adjustment for the ADF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Center adjustment for the ADF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Leading-edge adjustment for the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Side-edge adjustment for the glass . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
C9148-90909 4 Maintenance 35
Page 38

Cleaning the product
General guidelines
Perf orm the following cleaning procedures when you change the print cartridge or when printquality problems occur. To minimize problems, keep the product free from dust and debris.
WARNING! T urn the main power-switch off and unplug the MFP power cord before you disconnect any cables
or accessories, and before you perform preventative maintenance or cleaning. Failure to follow
this warning can result in serious product damage or personal injury.
CAUTION While cleaning the product, do not to touch the transfer roller (the black rubber roller located
underneath the print cartridge). Skin oils on the roller can affect print quality.
Table 6. General cleaning guidelines
Part Cleaning interval Cloth Solvent
Covers Clean when visibly dirty . Soft, tight weave; lint-free. Water (ad d a mild dete rgent if
desired). See caution below.
Control panel Clean when dusty or when
fingerprints build up.
ADF rollers Clean if the user is experiencing
misfeeds, or multipage feeds, or if
documents are skewing when
traveling through the ADF.
Glass Clean when visibly dirty or if the
user is experiencin g poor co py
quality such as blurriness or
streaking.
Whiteboard cover (white vinyl
backing located on the bottom
of the ADF cover)
Clear mylar sheet (ADF
delivery guide)
Clean when visibly dirty. Soft, tight weave; lint-free. Ammonia-based cleaner or
Clean when visibly dirty or if the
user is experiencin g poor co py
quality such as blurriness or
streaking.
Soft, tight weave; lint-free. Water. See caution below.
Soft, tight weave; lint-free. Water. See caution below.
Soft, tight weave; lint-free. Ammonia-based cleaner or
water. See caution below.
water. See caution below.
Soft, tight weave; lint-free. Water. See caution below.
CAUTION T o prevent damage, do not pour or spray cleaning solvents directly onto MFP components. Spray
water or cleaning solvent onto a cloth and wipe down components that need cleaning. Because
some MFP components should never be exposed to ammonia fumes, use ammonia-based
cleaners sparingly and only where indicated.
36 Maintenance C9148-90909
Page 39

Running the cleaning page
Run the cleaning page to keep the fuser free of toner and paper particles. Accumulation of toner
and particles can cause specks to appear on the front-side or back-side of your jobs. It is
recommended that you either use the cleaning page every time you replace the print cartridge or
that you establish an automatic cleaning schedule.
You can run a cleaning page in two ways:
● automatically at an interval that you establish
● manually as needed from the control panel
For information about these procedures, see the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer service
manual.
1 Access the Configure Device menu. See “Menus” on page 32.
2 Select Print Quality.
3 Select Create Cleaning Page and follo w the instruction on the page.
Cleaning the ADF delivery guide (clear mylar strip)
1 Raise the ADF unit.
2 Open the delivery-guide cover by pressing in the small plastic handles on either side of the
delivery guide.
Figure 13. Open the delivery-guide cover
3 Remove the clear, plastic sheet (callout 1).
C9148-90909 4 Maintenance 37
Page 40

Figure 14. Remove the clear plastic sheet
4 Use a clean, soft, dry cloth to wipe the surface of the clear plastic sheet (do not use an
ammonia based cleaner.
5 Reinstall the clear, plastic sheet by sliding its leading edge under the gray ribbed guide
(callout 2), which is located under the white padded sheet.
6 Align the holes in the sheet with the small plastic spindles (callout 3) in the delivery guide.
Press the clear, plastic sheet down onto the spindles.
1
3
2
Figure 15. Replace the clear, plastic sheet
Note Make sure that the free end of the clear, plastic sheet (part number RB2-8793-000CN) is tucked
behind the gray ribbed guide and the white padded sheet.
7 Close the delivery-guide cover. The cover is properly closed when you hear the delivery-
guide cover plastic handles click into place.
8 Wipe the outside surface of the delivery guide with the cloth.
38 Maintenance C9148-90909
Page 41

User-replaceable parts
Replacing user-replaceable parts
To ensure that the product maintains optimal performance, replace certain parts when the
Perform Printer Maintenance message appears on the product control-panel display.
The maintenance message appears every 200,000 pages (default setting). To check the number
of pages the product has printed, either print a configuration page or a supplies status page. See
“Evaluate the information pages” on page 130.
Hint To order a print-unit maintenance kit, see the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer service manual.
Note Unless they are damaged, the ADF pickup roller, separation roller, and separation pad should not
need to be replaced.
Table 7. User-replaceable parts
MFP Item Procedure Interval
ADF unit See “ADF unit” on page 78. User replaceable. As
required.
ADF input tray See “ADF input tray” on page 73. User replaceable. As
required.
ADF delivery guide
(clear mylar strip)
ADF pickup roller See “ADF pickup roller” on page 74. User replaceable. As
ADF separation roller See “ADF separation roller” on page 76. User replaceable. As
ADF separation pad See “ADF separation pad” on page 77. User replaceable. As
ADF separation assembly
compression spring
ADF pick/feed cover See “ADF separation pad” on page 77
ADF delivery guide holde r (cle ar
mylar sheet holder)
See the removal step in “Cleaning the
ADF delive ry guide (cl ear mylar strip)” on
page 37.
See “ADF separation pad” on page 77
and “ADF unit (2 of 2)” on page 160.
and “ADF unit (2 of 2)” on page 160.
See the step in “Cleaning the ADF
delivery guide (clear mylar strip)” on
page 37 and “ADF unit (1 of 2)” on
page 158.
User replaceable. As
required.
required.
required.
required.
User replaceable. As
required.
User replaceable. As
required.
User replaceable. As
required.
ADF face-up bin handle See “Covers” on page 148. User replaceable. As
required.
5GB hard disk drive To locate the hard drive, see “Back view”
on page 21.
User replaceable. As
required.
C9148-90909 4 Maintenance 39
Page 42

Table 7. User-replaceable parts (continued )
MFP Item Procedure Interval
HP JetDirect network card To locate the HP JetDirect network card,
see “Back view” on page 21.
Memory DIMM To locate the memory DIMM, see “Copy
processor board” on page 57.
Firmware DIMM To locate the memory DIMM, see “Copy
processor board” on page 57.
Power jumper cable To locate the power jumper cable, see
“Back view” on page 21.
Print cartridge See the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer
service manual.
User replaceable. As
required.
User replaceable. As
required.
User replaceable. As
required.
User replaceable. As
required.
About ev ery 10,000 pages
for print cartridge part
number C8061X.
About ev ery 6000 pages f or
print cartridge part number
C8061A.
Table 8. Print-unit maintenance kit parts
MFP Item Procedure Interval
Print-unit transfer roller See the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer
service manual.
Print-unit feed rollers See the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer
service manual.
Print-unit separation pad See the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer
service manual.
Print-unit fuser See the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer
service manual.
User replaceable. See
“Expected life of
components” in the
HP LaserJet 4100 series
printer service manual.
User replaceable. See
“Expected life of
components” in the
HP LaserJet 4100 series
printer service manual.
User replaceable. See
“Expected life of
components” in the
HP LaserJet 4100 series
printer service manual.
User replaceable. See
“Expected life of
components” in the
HP LaserJet 4100 series
printer service manual.
40 Maintenance C9148-90909
Page 43

Updating product firmware
Downloading a remote firmware update
The HP LaserJet 4100mfp product supports remote firmware updates (RFUs). The update is
downloaded from the website http://www.hp.com/go/lj4100_firmware (downloading a firmware
update is similar to downloading printing-system software and printer drivers).
This website also features an “E-mail me when new software is available” link. This feature
notifies you by e-mail when a new firmware update version is available for the MFP. If you used
HP WebReg to register your product, you are automatically sent an e-mail notification when a
new firmware update version is available for the MFP.
Hint The RFU file on the website is a self-extracting .EXE file. Detailed instructions about how to
download the RFU file can be found at the website http://www.hp.com/go/lj4100_firmware.
The RFU process consists of three steps:
● Determine the version of firmware currently installed (print a configuration page; see
“Configuration page” on page 130). Look for the version information in the device information
section of the configuration page.
● Go to the website http://www.hp.com/go/lj4100_firmware website and download the update.
● Install the update.
Note For more information about remote firmware updates, contact your HP Customer Care Center
and ask for a software technical reference sheet (see “Support” on page 144).
Installing the update
CAUTION If a firmware update involves a change in the format on nonvolatile random-access memory
(NVRAM), any user-set settings (for example, configure device settings) revert to default settings.
Before installing an updated version of the firmware, print any information pages required to reset
user defined settings. See “Evaluate the information pages” on page 130.
Note To install a firmware update on a computer using the UNIX operating system, use any method
that delivers the .RFU file to the printer. For example, $cp/home/yourmachine/FILENAME/dev/
parallel where /home/yourmachine/FILENAME with substitutions for the locations that contain the
location of the .RFU file.
RFU installation messages
During normal RFU installation the following three messages appear on the control-panel
display.
● Recieving Upgrade
• This message appears from the time the printer recognizes the beginning of a .RFU file
being sent until the time the printer verifies the validity and integrity of the .RFU file.
● Performing Upgrading For Help Press?
• This message appears while the printer is reprogramming the DIMM with the .RFU file
information.
● Wait For Printer To Reinitialize
• This message appears from the time the printer finishes reprogramming the DIMM until
the printer re-initializes.
C9148-90909 4 Maintenance 41
Page 44

Using HP Web JetAdmin (single update)
Note This procedure requires Web JetAdmin version 6.1 or later. Download the update from the website
http://www.hp .com/go/lj4100_firmware and follow the steps below to update a single MFP product.
1 Start the HP Web JetAdmin program.
2 Enter the Internet protocol (IP) address or IP hostname of the printer in the
FIND FIELD, and click GO. The printer Status window appears.
3 Click the right arrow on the toolbar to display the
4 When prompted for the type of update, click
5 Under
UPLOAD NEW FIRMWARE IMAGE: click BROWSE to locate the .RFU file you downloaded
UPDATE button. Click the UPDATE button.
UPDATE PRINTERS, and then click CONTINUE.
QUICK DEVICE
from the website http://www.hp.com/go/lj4100_firmware.
6 Click
UPLOAD to move the .RFU file from your hard drive to the HP Web JetAdmin server.
Refresh the browser.
7 Select the .RFU file from the
8 Click
UPDATE FIRMWARE. HP Web JetAdmin sends the selected.RFU file to the printer.
SELECT NEW FIRMWARE VERSION: drop-down menu.
Using HP Web JetAdmin (multiple or unattended update)
Note This procedure requires Web JetAdmin version 6.1 or later. Download the update from the website
http://www.hp.com/go/lj4100_firmware and follow the steps below to update multiple MFP
products or perform an unattended installation.
1 Start the HP Web JetAdmin program.
2 Create a device group. One way to do this is:
• Click
• Click
• In the 3.
• Click
DEVICES on the 1. CHOOSE: drop-down menu.
DEVICE MODEL from the 2. FILTER: drop-down menu.
CRITERIA (OPTIONAL): field, type your MFP model number (for example, 4100)
GO.
3 In the
DEVICE LIST, select the printers you want to include in the group and click CREATE
GROUP.
4 When prompted, type a name for the new device group, and then click
5 Click
6 When prompted for the type of update, click
7 From the list of HP printers, select the printers to be updated or click
8 Click
UPDATE.
UPDATE PRINTERS, and then click CONTINUE.
SELECT ALL.
UPDATE FIRMWARE. HP Web JetAdmin sends the selected .RFU file to the selected
printers.
OK.
42 Maintenance C9148-90909
Page 45

Windows parallel connection (local printer)
Note Download the update from the website http://www.hp.com/go/lj4100_firmware and follow the
steps below to update the firmware on a non-shared local printer.
Hint The LaserJet 4100mfp series uses a type-B parallel cable to connect to a computer’s LPT1 port.
1 Open a MS-DOS command window.
2 Type copy /b path\filename portname at the comma nd prompt.
• pa th is the location the .RFU file was downloaded to
• filename is the name of the .RFU file downloaded from the website
• portname is the appropriate printer port (for example, LPT1)
3 Press the computer ENTER key. The .RFU file is sent to the printer.
Windows parallel connection (network printer)
Note Download the update from the website http://www.hp.com/go/lj4100_firmware and follow the
steps below to update the firmware on a network printer.
1 Open a MS-DOS command window.
2 Type copy /b path\filename\sharename\printername at the command prompt.
• pa th is the location the .RFU file was downloaded to
• filename is the name of the .RFU file downloaded from the website
• sharename is the name of the computer from which the printer is shared (host computer)
• printername is the printer share name
3 Press the computer’s ENTER key. The .RFU file is sent to the printer.
C9148-90909 4 Maintenance 43
Page 46

Troubleshooting RFU installation
RFU installation error messages
The following messages can appear on the control-panel display if the installation is interrupted
for some reason. Turn the MFP power off, and then back on again. Attempt the RFU installation
again.
Hint If the update is not successful but an error message does not appear on the control-panel display
check the event log for RFU error codes. See “Firmware-update event-log errors” on page 119.
● Job Canceled From Printer Control Panel
• No update occurred. Turn the MFP power off, and then back on again. Attempt the RFU
installation again.
● Break In I/o Stream During Send (for example the parallel cable was removed)
• No update occurred. Turn the MFP power off, and then back on again. Attempt the RFU
installation again.
● Power Cycle Occurred During Recieving Upgrade
• No update occurred. Turn the MFP power off, and then back on again. Attempt the RFU
installation again.
● Power Cycle Occurred During Upgrading Printer
• No update occurred. Turn the MFP power off, and then back on again. Attempt the RFU
installation again.
● Power Cycle Occurred During Wait For Printer To Reinitialize
• Update was completed (no action required).
● .RFU File Is Corrupt
• The printer recognizes that the RFU file is damaged (corrupted) and rejects the update.
Download a new RFU file from the website http://www.hp.com/go/lj4100_firmware. Turn
the MFP power off, and then back on again. Attempt the RFU installation again.
● Wrong Printer Model Contained In The .RFU File
• The printer recognizes that the RFU file is not correct for installation to the intended MFP
product and rejects the update. Download the correct RFU file from the website http://
www.hp.com/go/lj4100_firmware. Turn the MFP power off, and then back on again.
Attempt the RFU installation again.
● Update Was Interrupted
• See the information about the job canceled, break in I/O, and power cycle error messages
in this section.
● Flash Hardware Failure Occurred
• The flash DIMM has failed. Replace the flash DIMM on the formatter.
Hint The HP LaserJet 4100mfp product contains a backup copy of the latest version of firmware on
the flash DIMM. If a RFU update fails, the MFP uses this backup copy of the firmware to restart.
Then attempt to install the update again. When the MFP starts using the backup copy of the
firmware, some mfp capabilities are not functional (for example, copying or digital sending). A
successful update must be accomplished to fully restore MFP functions.
44 Maintenance C9148-90909
Page 47

Performing hard-drive disk initialization
Before performing hard-drive initialization, print the following MFP information pages. Use these
pages to reset any menu settings that the user has changed from factory defaults.
• Configuration page (see “Evaluate the information pages” on page 130).
• File directory page (see “Evaluate the information pages” on page 130).
1 Turn the product power off.
2 Press and hold down the
the
START button until the printer initializes and the three control panel LEDs illuminate
continuously. Release the
3 Press and release the
START button. Turn the product power on. Continue to hold down
START button.
LEFT navigation button. The message INITIALIZE DISKS appears on
the control-panel display.
4 Press and release the
SELECT ( ) button. Two rows of asterisks appear on the control-panel
display.
5 When the astericks disappear and the message READY appears on the control panel display,
the mfp can process jobs.
Cold Reset
A cold reset clears all data from the printer memory and sets may of the defaults back to the
factory setting s.
Before performing hard-drive initialization, print the following MFP information pages. Use these
pages to reset any menu settings that the user has changed from factory defaults.
• Configuration page (see “Evaluate the information pages” on page 130).
• File directory page (see “Evaluate the information pages” on page 130).
1 Turn the product off.
2 Press and hold down the
SELECT ( ) button.
3 Turn the product on.
4 Continue to hold down the
the
SELECT ( ) button.
5 Press the
UP navigation button twice. The message COLD RESET will appear on the control
SELECT ( ) button until all three LEDs are illuminated. Release
panel display.
6 Press the
SELECT ( ) button once. The message STARTS will appear on the control panel
display.
7 When the cold reset is complete, the MFP will restart.
C9148-90909 4 Maintenance 45
Page 48

NVRAM initialization
NVRAM initialization should be performed immediately after replacing the formatter board. Not
initializing NVRAM might result in print quality defects.
CAUTION Initializing NVRAM erases several memory settings (for example, page count, printer serial
number, and the event log). This information is permanently lost.
Before performing NVRAM initialization print the following MFP information page. Use this page
to reset any menu settings that the user has changed from factory defaults.
• Configuration page (see “Evaluate the information pages” on page 130).
1 Turn the product power off.
2 Press and hold down the
DOWN navigation button. Continue to hold the DOWN button down
until the printer initializes and the three control panel LEDs illuminate continuously. Release
the
DOWN button.
3 Press and release the
4 Press and hold down the
5 Press and release the
UP navigation button.
START button.
UP navigation button. Release the START button. The message SKIP
DISK LOAD appears on the control panel display.
6 Press the
DOWN navigation button until the message NVRAM INIT appears on the control
panel display.
7 Press the
SELECT ( ) button. The NVRAM initialization process will begin.
8 When completed, the printer will initialize and the message READY will appear on the control
panel display. The MFP is ready to process jobs.
46 Maintenance C9148-90909
Page 49

Calibration
Performing automatic Calibration
The MFP can be automatically calibrated to register scanned images correctly. When CALIBRATE
SCANNER is selected from the diagnostic menu, the MFP prints a calibration target page.
Messages appear on the control panel with instructions about automatically calibrating the MFP.
1 Press the
2 Select DIAGNOSTICS.
3 Select CALIBRATE SCANNER.
4 Select CALIBRATE.
5 The message To Print Target Page On Paper Size: Letter. Press Start. To Quit,
Press Stop appears on the control-panel display. Press the
calibration target page. While this page is printing, the message Target Page Printing To
Quit, Press Stop appears on the control-panel display.
Note The paper size displayed in the message is the cold-reset paper size (either letter or A4).
6 When the message Load Target Page Face Up In Adf Clear Flatbed And Press Start
To Quit, Press Stop appears, place the target page in the ADF and press the
button.
7 The target page is moved through the ADF paper path and automatic calibration begins. The
message calibration running do not raise cover appears on the control-panel display.
8 When calibration is over, the MFP returns to the ready mode (the message READY appears
on the control-panel display) and can process print and scan jobs.
MENU button.
START button to print the
START
Figure 16. Sample calibration target page
C9148-90909 4 Maintenance 47
Page 50

Performing manual calibration
Manual calibration provides precise control of image placement. Vertical and horizontal image
registry for both the ADF and the glass can be set individually. For example, changing the
leading-edge adjustment for the ADF does not effect the leading-edge adjustment of the glass.
Note Manual calibration increment values are in pixels (600 pixels-per-inch). All values are positive
numbers. The center adjustment value 2670 represents an imaginary center line through the ADF .
It may not be exactly centered due to mechanical tolerances between MFP units
Hint Before attempting to manually calibrate the MFP, first try the automatically calibrating procedure
(see “Performing automatic Calib ration” on page 47).
ADF lead adjustment
255
ADF center adjustment
2470
ADF
Control panel
Glass leading-edge adjustment
0
2870
ADF
Control panel
255
0,0
255
Glass left edge adjustment
Figure 17. Manual calibration registration lines
Lead adjustment for the ADF
Hint It might be helpful to reset the product settings to factory defaults before attempting manual
calibration. Be sure to print a configuration page before doing a setting reset so that any userdefined settings can be restored (see “Configuration page” on page 130).
1 Press the
MENU button.
2 Select DIAGNOSTICS.
3 Select CALIBRATE SCANNER.
4 Select LEAD ADJUSTMENT.
5 The message Lead Adjustment ### Range 0-255 appears on the control-panel display . Use
the numeric keypad to type a value for the leading-edge adjustment.
Hint Entering a lower value than current setting moves the image away from the leading edge (toward
the bottom of the page). Entering a higher value than the current setting moves the image toward
the leading edge (toward the top of the page).
6 Press the
SELECT ( ) button to save the setting.
7 Use the ADF to scan a source document (use the calibration target page if you have already
automatically calibrated the MFP). Verify that the leading edge is correctly positioned on the
output copy.
48 Maintenance C9148-90909
Page 51

Center adjustment for the ADF
Hint It might be helpful to reset the product settings to factory defaults before attempting manual
calibration. Be sure to print a configuration page before doing a setting reset so that any userdefined settings can be restored (see “Configuration page” on page 130).
1 Press the
MENU button.
2 Select DIAGNOSTICS.
3 Select CALIBRATE SCANNER.
4 Select CENTER ADJUSTMENT.
5 The message Center Adjustment #### RANGE 2470-2870 appears on the control-panel
display. Use the numeric keypad to type a value for the center adjustment.
Hint Entering a lower value than current setting moves the image away from the left edge (toward the
right side of the page). Entering a higher value than the current setting moves the image toward
the left edge of the page.
6 Press the
SELECT ( ) button to save the setting.
7 Use the ADF to scan a source document (use the calibration target page if you have already
automatically calibrated the MFP). Verify that the image is correctly positioned on the output
copy.
Leading-edge adjustment for the glass
Hint It might be helpful to reset the product settings to factory defaults before attempting manual
calibration. Be sure to print a configuration page before doing a setting reset so that any userdefined settings can be restored (see “Configuration page” on page 130).
1 Press the
MENU button.
2 Select DIAGNOSTICS.
3 Select CALIBRATE SCANNER.
4 Select LEAD ADJUSTMENT GLASS.
5 The message Leading Edge Glass ### Range 0-255 appears on the control-panel display.
Use the numeric keypad to type a value for the leading-edge adjustment.
Hint Entering a lower value than current setting moves the image away from the leading edge of the
page (towards the bottom of the page). Entering a higher value than the current setting moves
the image toward the leading edge (toward the top of the page).
6 Press the
SELECT ( ) button to save the setting.
7 Use the glass to scan a source document (use the calibration target page if you have already
automatically calibrated the MFP). Verify that the image is correctly positioned on the output
copy.
C9148-90909 4 Maintenance 49
Page 52

Side-edge adjustment for the glass
Hint It might be helpful to reset the product settings to factory defaults before attempting manual
calibration. Be sure to print a configuration page before doing a setting reset so that any userdefined settings can be restored (see “Configuration page” on page 130).
1 Press the
MENU button.
2 Select DIAGNOSTICS.
3 Select CALIBRATE SCANNER.
4 Select SIDE EDGE ADJUSTMENT GLASS.
5 The message Side Edge Glass ### Range 0-255 appears on the control-panel display. Use
the numeric keypad to type a value for the side-edge adjustment.
Hint Entering a lower value than current setting moves the image away from the left edge (toward the
right side of the page). Entering a higher value than the current setting moves the image toward
the left edge of the page.
6 Press the
SELECT ( ) button to save the setting.
7 Use the glass to scan a source document (use the calibration target page if you have already
automatically calibrated the MFP). Verify that the image is correctly positioned on the output
copy
50 Maintenance C9148-90909
Page 53

5 Theory of operation
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Document transportation process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Document exposure system. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Light-conversion process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
General descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Scan-unit components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
ADF components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Copy processor board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
CPB terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Typical scanning-process flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Copy processor board LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Scanner controller board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
ADF motor circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Optical-unit motor circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Scan-unit intake-fan motor circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Scanner controller board connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Intermediate PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Overcurrent and overvoltage protection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Power-supply block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Optical unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Inverter PCB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Scanning lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
CCD driver PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
ADF document-feed system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
ADF cover sensor (PS10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Document-detect sensor (PS2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Leading-edge sensor (PS1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
ADF motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Document pickup process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Document jams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Scan-unit intake fan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
C9148-90909 5 Theory of operation 51
Page 54

Introduction
Overview
This chapter presents an overview of the relationships between major components in the MFP. It
also provides a general description of the following:
● mechanical systems (for example, the flatbed inta ke fan)
● electronic circuits (for example, the scanner controller circuit)
● sensors (for example, the document-detect sensor)
Scanning a document consists of three main processes. First, the document is transported
through the ADF or manually placed on the glass. Second, the document is illuminated and the
light is captured (the document-exposure process). Third, the captured light is converted to a
digital signal and sent to the base printer for output (image processing).
When the copy processor board (CPB) receives a scan command from the control panel, it
sends the command to the scanner controller board, which initiates and controls the scanning
process.
These main components are used in the scanning process.
● scanner controller board (controls the scanning process and communication with the CPB)
● automatic document feeder (ADF) (transports the source document)
● optical unit (holds the scanning lamp and charged couple device [CCD])
● scanning lamp (exposes the document)
● charged-couple device (CCD) driver PCB (converts reflected light to digital RGB signals for
final out put)
Document transportation process
The ADF receives a signal from the scanner control PCB and begins to transport the document.
A sensor in the ADF detects the document in the input tray. The ADF picks up the document.
Then, the document travels through the ADF toward the flatbed. A second sensor in the ADF
confirms that the document was successfully transported through the ADF. After the scanning
process the document is transported to the ADF output.
Document exposure system
● The source document is loaded through the ADF.
After receiving the scan command from the copy processor board, the scanner controller
board sends a signal to the scanning lamp in the optical unit. The lamp illuminates the
document as the ADF passes the document past the optical unit (the optical unit does not
move). A calibration strip mounted under the glass allows automatic document registration
during the exposer process. The light is reflected from the scanning plate and is sent (by way
of three mirrors and a lens) to the CCD driver PCB for image processing. The source
document is deposited in the ADF output.
● The source document is manually placed on the glass.
After receiving the scan command from the copy processor board, the scanner controller
sends a signal to the scanning lamp. The lamp illuminates the document as the optical-unit
motor moves the optical unit down the length of the document. The light is reflected from the
scanning plate and is sent (by way of three mirrors and a lens) to the CCD driver PCB for
image processing. When the scanning process is complete, the optical unit returns to its
home position.
52 Theory of operation C9148-90909
Page 55

Light-conversion process
When the charged couple device receives the reflected light, it photo-electrically converts the
light to three analog signals (red-green-blue, or RGB). These three signals pass through an
analog-to-digital converter, and the resulting digital signals are sent to the scanner controller
board. The scanner controller board sends the digital signals to the copy processor board, which
initiates output through the base printer.
Note If the source document is manually placed on the glass, the scanning process is the same, except
for document transportation.
C9148-90909 5 Theory of operation 53
Page 56

General descriptions
This section describes the individual MFP components and their roles in the scanning process.
Figure
18 illustrates the relationship between the MFP components. Figure 19 illustrates the
flatbed-assembly component locations. Figure 20 illustrates the ADF-unit component locations.
The following components are identified:
● scanner controller board
• CPU
• fan-motor drive circuit
• ADF drive motor circuit
• optical-unit motor circuit
• optical-unit home-position
sensor (PI1201)
● optical unit
• scanner motor
• inverter PCB
● power supply
● flatbed intake fan
● intermediate PCB
● ADF cover-open sensor
(PS10)
● ADF unit
• document-detect sensor
(PS2)
• document leading-edge
sensor (PS1)
• ADF drive motor
• scanning lamp
• pickup solenoid
• CCD driver PCB
The block diagram below illustrates the relationship among the MFP components.
Figure 18. MFP block diagram
54 Theory of operation C9148-90909
Page 57

Scan-unit components
1
1
2 3
2 3
4
4
5
5
Figure 19. Scan-unit components
1 intake fan
2 inverter control PCB
3 ADF door-open sensor
(PS10)
4 optical-unit drive-belt
5 optical-unit motor (under the
shield)
6 power supply (under the
shield)
7 control-panel connector
8 scanner controller board
(under the shield)
91011
91011
9 optical-unit assembly
(includes the CCD driver
PCB)
10 scanner lamp
11 optical-unit lock
8
8
7 6
7 6
C9148-90909 5 Theory of operation 55
Page 58

ADF components
2
2
1
1
8
8
8
9
7
7
3
3
4
4
Figure 20. ADF - u nit components
1 ADF separation roller
2 ADF pickup roller
3 ADF pickup solenoid (SL1)
4 ADF drive motor
5 ADF-to-scanner controller
connector
6 document-detect sensor
flag(PS2)
7 leading-edge sensor (inside
the ADF; PS1)
6
6
5
5
8 ADF separation pad
9 ADF sliding media guides
56 Theory of operation C9148-90909
Page 59

Copy processor board
This section describes the operation of the copy processor board (CPB) during normal operation
of the MFP. This description is more detailed than the CPB troubleshooting chapter in this
manual.
The CPB is the link between the formatter in the print unit and the scanner controller board in the
scan unit. Control signals from the formatter are sent to the CPB. The CPB then sends these
control signals to the scanner controller board. After the scanner controller board completes the
scanning process, the scanned data is sent to the copy processor board. The copy processor
board processes the image and sends the image data to the formatter.
CPB terminology
● ASIC (application specific integrated circuit): is the system controller that provides the
peripheral component interconnect (PCI), DIMM, and processor interface. The ASIC
performs monochrome data compression.
● Firmware code DIMM (dual inline memory module): contains the firmware that controls the
system.
● Digital signal processor (DSP): runs the image processing algorithms.
● FPGA (field programmable gate array): provides an interface to the scanner, SRAM, DSP,
and PCI bridge and provides front-end image processing.
● IEEE 1394 phy. (physical layer): provides an interface from the CPB to the formatter (high-
speed copy connect cable)
● IEEE 1394 protocol chip: connects the PCI bus to the IEEE 1394 phy.
● MIPS (millions of instructions per second) processor: is the system processor that runs the
firmware.
● PCI (peripheral component interconnect) bridge: connects the PCI bus to the FPGA.
● RAM (random access memory) DIMM: provides main system memory and temporary
storage for image data and firmware variables.
● RAM for DSP: provides temporary storage for image processing in the DSP.
● SRAM (static RAM): is the memory used for aligning the image data from the scanner.
MIPS
processor
ASIC
16-MB
DIMM
Firmware
code
DIMM
IEEE 1394 phy.
SRAM FPGA DSP RAM
Figure 21. Copy processor board components
IEEE 1394 protocol chip
PCI
bridge
DSP
Hard
code for
FPGA
C9148-90909 5 Theory of operation 57
Page 60

The CPB controls the following scanning-process control signals:
● ADF unit and scan unit operation
• directs the scanner controller board about when to scan
• directs the scanner controller board about how to scan
• directs the scanner controller board about when to activate motors
• directs the scanner about when to turn the scanning lamp on and off
● Image processing
• color alignment
• resolution conversion
• image sharpening
• moire removal
• image scaling
• shifting of data strips (reconstructing separately processed image data before CPB
communication to the formatter)
• RGB conversion for CPB communication
• CPB communication over the high-speed copy connect cable to the formatter in one of the
following formats:
• Hardware Ready Bits (HRB) (fastpath) communication with the hard disk on the formatter
• PCL-XL (N-up, rotation, book mode) communication with the hard disk on the formatter
• JPEG compression (when sending data digitally) communication with the hard disk on the formatter
• data compression before sending to the formatter over the high-speed copy connect cable
Typical scanning-process flow
1 The original document is placed on the glass or in the ADF.
2 The user selects job preferences by using the control-panel buttons and keys. The user
presses the
3 Some job preferences are held and then processed later (for example, N-up) by the
formatter. Others are sent to the CPB.
4 The CPB sends control signals to the scanner controller board. The document is scanned.
5 The scanner controller board sends scanned-image data back to the CPB.
6 The CPB processes the image.
7 The CPB sends the image data to the formatter.
8 The formatter further processes the image data (if required).
9 The image data is then either printed or sent digitally, depending on what the user specified
at the beginning of the process.
START button. Job preferences are sent to the formatter.
58 Theory of operation C9148-90909
Page 61

Copy processor board LEDs
The CPB has four light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that can be viewed when you face the back of the
MFP (callout 1). These LEDs illuminate in specific patterns depending on the CPB status during
initialization (initialization occurs when power to the MFP is turned on). After initialization, the
LEDs can be used to troubleshoot the CPB (see “T r oubleshooting with the copy processor board”
on page 124).The table in this section describes the LED pattern sequences during the first and
second stage of CPB initialization.
Hint The LEDs can be difficult to see through the holes provided in the CPB faceplate (callout 1) in a
high-light environment. It might be necessary to turn off some lights or remove the faceplate to
see the LEDs.
The LED patterns an HP LaserJet 4100/4101mfp displays are the opposite of those on the
HP LaserJet 9000mfp because of how the CPBs are mounted. The CPB is mounted upside down
in the HP LaserJet 9000mfp.
Figure 22. Copy processor board LEDs
Table 9. Copy processor board LEDs (initialization sequence)
LED pattern CPB status
First stage of CPB initialization
ON* ON* ON ON
*LEDs might flash
before coming to a solid
illuminated state
● CPB flash DIMM detected
● CPB RAM DIMM detected
● CPB processor is working
● CPB has commun ic ation wi th the ASIC
11
Note If CPB initialization stops and the LEDs stay in the continuously illuminated
state, a CPB failure has occurred (for example, a memory DIMM is not
present or fully seated). T o troubleshoot a CPB failure, see “Troubleshooting
with the copy processor board” on page 124.
C9148-90909 5 Theory of operation 59
Page 62

Table 9. Copy processor board LEDs (initialization sequence)
LED pattern CPB status
ON ON OFF ON ● Communication is established between the MIPS processor and the PCI
bridge.
OFF ON OFF ON
OFF OFF OFF ON
OFF OFF OFF OFF
● Communication is established between the MIPS processor and the FPGA.
● The FPGA SRAM is checked.
● Communication is established between the MIPS processor, the DSP, and
the DSP RAM.
Second stage of CPB initialization
LED pattern CPB status
OFF OFF OFF ON ● The rightmost LED illuminates and stays on when the conne ction to the SSA
(the portion of the firmware tat runs in the print engines RAM) is established.
OFF OFF ON ON
● The LED second from the right illuminates when communication occurs
between the CPB and the scan engine.
ON* OFF ON ON
*Flashing after a one to
two second solid
● The leftmost LED illuminates to indica te the C PB has boot ed prope rly. When
this LED begins to flash (referred to as the CPB heartbeat), the CPB is
functioning normally and the MFP is ready to process jobs.
illumination state
Hint The CPB remains in this state even when the MFP is in PowerSave mode.
60 Theory of operation C9148-90909
Page 63

Scanner co n t roller bo a rd
The scanner controller board controls the operation of flatbed and ADF components used in the
following scanning processes: document transportation, document exposure, and imaging.
When the copy processor board sends the scan commands to the scanner controller board, the
scanner controller board sends signals to the motors, solenoids, scanning lamp, and CCD driver
PCB.
The scanner controller board controls the operation of the following components:
● ADF document transportation
• ADF sensors (door-open, document-detect, and leading-edge sensors)
• ADF solenoid
• ADF drive motor
● document exposure
• optical-unit home-position sensor
• scanning lamp
• scanning motor
● imaging process
• CCD driver PCB (converts reflected light to a digital RGB signal)
• copy processor com munic atio n
● flatbed intake fan (off in PowerSave mode, half-speed when idle; full-speed when scanning)
ADF motor circuit
The ADF motor circuit controls the operation of the ADF motor. The ADF motor is a +24 vdc
stepping motor. It rotates in a counterclockwise direction. The ADF motor is not fault-protected.
Note When a fault-protected motor circuit fails, an error message appears on the control panel. The
ADF motor circuit is not fault protected. No error message appears on the control-panel display
if this circuit fails.
Optical-unit motor circuit
The optical unit motor circuit controls the optical unit motor and the movement of the unit. The
optical unit motor is a +24 vdc stepping motor. It rotates in both a clockwise and
counterclockwise direction. If the optical unit motor fails, the message 30.1.17 SCAN FAILURE
appears on the control-panel display.
Scan-unit intake-fan motor circuit
The fan motor circuit controls the fan speed. The fan is off in PowerSave mode, it rotates at halfspeed when the product is idle, and at full-speed during the scanning process, when a document
is detected in the ADF, or when a control-panel button or key is pushed. If the fan motor fails, the
message 30.01.06 Scan Failure appears on the control panel-display.
C9148-90909 5 Theory of operation 61
Page 64

Scanner controller board connectors
J 1209
J1208
J1207
J1206
J1205
Figure 23. Scanner controller board connectors (shield off)
J1210
PI1201
Scanner controller
with the shield on
J1201
J1202
J1203
Table 10. Scanner controller board connectors
Connector Description Remarks
J1201 Power-supply connector 10-pin connector. To gain access to this connector,
J1202 Inverter PCB connector 5-pin connector. To gain access to this connector,
J1203 Flatbed intake fan 3-pin connector. To gain access to this connector,
J1205 ADF connector 15-pin connector. Verify that the connector’s locking
J1206 ADF door-open sensor (PS10) 3-pin connector. To gain access to this connector,
J1207 Optical-unit drive motor 4-pin connector. To gain access to this connector,
J1208 CCD connector Flat ribbon cable. To gain access to this cable, remove
J1209 Intermediate PCB This connector connects the copy processor board to the
J1210 Control panel 5-pin connector. To gain access to this connector,
PI1201 Optical-unit home-position sensor (PI1201) This sensor is soldered to the scanner controller board.
remove the glass. See “Glass” on page 92.
remove the glass. See “Glass” on page 92.
remove the glass. See “Glass” on page 92.
thumb screws are tight. This connector can be removed
accessed without removing any other MFP components.
remove the glass. See “Glass” on page 92.
remove the glass. See “Glass” on page 92.
the glass. See “Glass” on page 92.
scanner controller board. It cannot be disconnected
independently of removing the scanner controller board.
remove the glass. See “Glass” on page 92.
To gain access to this sensor, remove the glass. See
“Glass” on page 92.
62 Theory of operation C9148-90909
Page 65

Intermediate PCB
The intermediate PCB connects the copy processor board and the ADF to the scanner controller
board.
Po wer supply
The power supply converts ac power from the source inlet (power cord) to low-voltage dc power.
Low-voltage power is supplied to various flatbed and ADF components. Low-voltage power from
the power supply consists of +3.3 vdc, +5 vdc, +12 vdc, and +24 vdc voltages.
Table 11. Low-voltage components
Voltage Components
+3.3 vdc ● scanner controller board
● scanner controller-to-engine co ntrol le r conne ct or
● scanner controller-to-copy processor board intermediate PCB
● CCD drive circuit
● document-detect sensor
● leading-edge sensor
● optical unit home-position sensor
+5 vdc
+12 vdc
+24 vdc
● scanner controller board
● scanner controller-to-video control ler connector
● CCD drive circuit
● scanner controller board
● CCD drive circuit
● scanner controller board
● document-pickup solenoid
● ADF motor
● optical-unit motor
● flatbed intake fan
● inverter circuit
Overcurrent and overvoltage protection
The power supply uses overcurrent and overvoltage protection. If a short-circuit on the load side
(flatbed and ADF component side) causes an excessive current or voltage draw, the overcurrent
or overvoltage protection function interrupts the power-supply output. If this happens, turn the
printer off, and then identify and repair the malfunctioning component.
Note The power supply must remain off for at least two minutes for the overcurrent and overvoltage
functions to reset.
A fuse (power supply PCB F101) protects against overcurrent coming from the ac source inlet
(power cord).
C9148-90909 5 Theory of operation 63
Page 66

Power-supply block diagram
Figure 24. Power-supply block diagram
64 Theory of operation C9148-90909
Page 67

Optical unit
The optical unit consists of the optical unit chassis, the scanning lamp, the CCD driver PCB, and
the optical-unit motor. When the power is turned on, the scanner controller board activates the
optical-unit motor, and the unit begins to move along the rails. When the optical-unit home
sensor flag (located on the bottom of the unit) aligns with the home-position sensor (located on
the scanner controller board; PI1201), the unit stops in the home position.
Figure 25. Optical unit block diagram
The scanner controller board illuminates the flatbed lamp after receiving the scan command from
the copy processor board. As the document is exposed to the illumination of the scanning lamp,
the reflected light from the glass is sent by way of three scanning mirrors and a lens to the CCD
driver PCB for image processing. When the scanning process is complete, the optical unit
returns to the home position.
Figure 26. Scanning process
C9148-90909 5 Theory of operation 65
Page 68

Inverter PCB
The inverter PCB provides the current and voltage phase the scanning lamp requires.
Scanning lamp
The scanning lamp illuminates the source document, which causes reflected light from the glass
to be directed to the CCD driver PCB for document imaging.
CCD driver PCB
When the CCD driver receives the reflected light from the exposure process, it photo-electrically
converts the light into three analog signals (RGB). These three signals pass through an analogto-digital converter, and the resulting digital signals are sent to the scanner controller PCB. The
scanner controller sends the digital signals to the copy processor board for output by the base
printer, which initiates output through the base printer.
Figure 27. Signal conversion
66 Theory of operation C9148-90909
Page 69

ADF document-feed system
Overview
The ADF document-feed system detects the presence of a source document in the document
tray, picks up the document and transports it through the ADF paper path, and then delivers the
source document to the ADF output.
● The ADF motor rotates counterclockwise, which rotates the feed and delivery rollers. The
document pickup solenoid is activated, causing the pickup and separation rollers to rotate. If
more than one source document is in the ADF input tray, the separation roller and separation
pad clear the multiple-sheet feed, and then the first document is sent into the flatbed
scanning path.
● The leading-edge sensor detects the source document in the paper path and then the
scanning lamp illuminates.
● The source document is passed through the flatbed scanning path and the image
processing operation (controlled by the CCD driver) begins.
● The delivery roller transfers the source document to the ADF output. If more source
documents are in the input tray, the process repeats.
Figure 28. Document transport path
Hint To locate these components on the ADF, see “ADF components” on page 56.
C9148-90909 5 Theory of operation 67
Page 70

ADF cover sensor (PS10)
The ADF door-open sensor (PS10) detects ADF door status (open or closed). If the ADF door is
opened, a FLATBED COVER OPEN message appears on the control-panel display. If the ADF door
is opened during the document transport process, the ADF drive-motor stops and a door-open
message appears on the control panel.
Document-detect sensor (PS2)
The document-detect sensor (PS2) detects the presence of documents when they are placed
into the ADF document input tray.
Leading-edge sensor (PS1)
When a document enters the document transport path, it must pass the leading-edge sensor
(PS1) within a specified amount of time. If it does not, a paper-jam message appears on the
control-panel display.
ADF motor
The ADF motor is controlled by the scanner controller board. When the scanner controller
receives the scan command, the ADF motor rotates counterclockwise, which starts rotation of
the feed and delivery rollers.
Document pickup process
When the document pickup solenoid is activated, the pickup and separations rollers begin to
rotate. If more than one source document is in the pickup tray, the separation roller and
separation pad clear the multiple feed, and then the first document is sent toward the flatbed.
Document jams
The scanner controller board detects a jam by verifying that each document passes the leadingedge sensor in a specified amount of time. If a document does not pass by the sensor in time,
the scanning operation stops. A document-jam message appears on the control-panel display,
and the user must clear the jam. The scanner controller board can detect two types of jams:
● Document-delay jam: If the leading-edge sensor does not detect the leading edge of the
document after the document pickup solenoid is activated, the scanner controller initiates a
document-delay jam signal.
● Document-stationary jam: If the leading-edge sensor does not detect the trailing edge of
the document after it detects that the leading edge has passed, the scanner controller board
initiates a document-stationary jam signal.
Scan-unit intake fan
The intake fan draws fresh air into the flatbed assembly. It is controlled by the fan-drive circuit,
which is located on the scanner controller board. The fan is off in PowerSave mode, it rotates at
half-speed when the product is idle, and at full-speed during the scanning process. The intake
fan motor is fault-protected. If the fan motor fails, the message 30.01.06 Scan Failure appears
on the control-panel display.
CAUTION The fan must be replaced so that it draws air into the flatbed. Failure to correctly position the fan
can result in damage to MFP components. Verify that the airflow arrow (located under the drivebelt tension bracket) embossed on the fan housing points into the flatbed. See, “Correctly orient
the intake fan and bracket” on page 107.
68 Theory of operation C9148-90909
Page 71

6 Removal and replacement
Removal and replacement strategy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Required tools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Before performing service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
After performing service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Common fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Parts removal order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
User-replaceable parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
ADF input tray. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
ADF pickup roller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
ADF separation roller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
ADF separation pad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
ADF unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Assemblies and covers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Control-panel door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Scan-unit right-side cover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Copy processor board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Scan-unit left-side cover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Intake fan filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Formatter cage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Scan unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Printing-unit top cover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Glass. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Scanning lamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Optical unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
ADF door open sensor (PS10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Optical-unit drive gear/motor assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Scan-unit power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Inverter PCB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Scanner controller PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Intake fan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 69
Page 72

Removal and replacement strategy
This chapter documents the removal and replacement of field replaceable units (FRUs) only.
Reinstallation is generally the reverse of removal. Occasionally, notes are included to provide
directions for difficult or critical replacement procedures.
WARNING! Unplug the power cord from the power outlet (at the wall receptacle) before attempting to service
the product. If this warning is not followed, severe injury can result. Certain functional checks
during troubleshooting must be performed with power supplied to the product. However , the power
supply should be disconnected during removal.
The power cord must be unplugged from the wall receptacle. Unplugging the cord from the back
of the print unit does not prevent AC power from going to the scan unit. See “Back view” on
page 21.
CAUTION The product contains components that are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Always
perform service work at an ESD-protected workstation. If an ESD-protected workstation is not
available, discharge body static by grasping the print engine chassis before touching an ESD
sensitive component. Ground the print engine chassis before servicing the product.
Required tools
● #2 Phillips screwdriver with magnetic tip
● small flatblade screwdriver
● needle-nose pliers
● ESD mat (if available)
● penlight (optional)
CAUTION A PoziDriv screwdriver will damage screw heads on the product. Use a #2 Phillips screwdriver.
Hint To install a self-tapping screw, first turn it counterclockwise to align it with the existing thread
pattern, then carefully turn it clockwise to tighten. Do not overtighten.
Before performing service
● If possible, print a configuration page. See “Configuration page” on page 130.
● Remove all media from the product.
● Unplug the power cord from the wall receptacle. Unplugging the cord from the back of the
print unit does not prevent AC power from going to the scan unit.
● Place the product on an ESD mat, if available. If an ESD-protected workstation is not
available, discharge body static and ground the print engine chassis before servicing the
product.
● Remove the print cartridge. See “Checking the print cartridge” on page 137.
After performing service
● Replace the print cartridge.
● Reconnect all cables to the product.
● Replace all accessories and reload the media.
● Verify that the latest firmware is installed on the product. See “Configuration page” on
page 130.
● Restore customer configuration settings.
70 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 73

Common fasteners
Table 12. Common fasteners found in the MFP
Illustration and description
Black self-tapping Phillips-head screw
Silver self-tapping Phillips-head screw
Machine screw with serrated washer
Short Phillips-head screw with small shoulder
Long Phillips-head screw with large shoulder
Phillips-head machine screw with loose washer
Hint To order replacement screws,
see table 27 on page 146.
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 71
Page 74

Parts removal order
Use the following diagram to determine the order in which parts must be removed (scan unit and
ADF units only).
Table 13. Parts-removal tree
ADF input tray
ADF pickup roller
ADF separation roller
ADF separation pad
Control panel door
ADF unit
Glass
Door interlock (PS10)
Inverter PCB
Scanning lamp
scan-unit right-side cover Optical unit
Copy processor board Optical-unit drive gear/motor
scan-unit left-side cover Intake fan scan-unit power
supply
Intake fan filter Copy processor board
Formatter cage Scanner controller
scan unit
Printing-unit top cover
Note The copy processor board is intentionally listed twice.
72 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 75

User-replaceable parts
ADF input tray
1 Open the ADF cover. Gently pry the input-tray hinge pin (located towards the front of the
MFP; callout 1) out of its pivot hole.
CAUTION The hinge pin can easily be snapped off of the input tray if too much pressure is applied.
11
Figure 29. Release the ADF input-tray hinge
2 When the hinge pin clears the pivot hole, rotate the input tray away from the MFP (as
indicated by the arrow) and slide the other hinge pin out of its pivot hole. Remove the tray.
2
1
Figure 30. Remove the ADF input tray
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 73
Page 76

ADF pickup roller
1 Open the ADF cover (callout 1).
2 Pull the plastic tab (callout 2) to release the lower edge of the roller shield.
1221
Figure 31. Release the roller shield
3 Release the roller shield from the two small pins (callout 3), and remove it from the product.
33
Figure 32. Remove the roller shield
74 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 77

4 Slide the roller toward the gear end. Gently pry the roller-shaft locking tab (callout 4) away
from the roller. Remove the ADF pickup roller.
34
Figure 33. Remove the ADF pickup roller
Hint When replacing the roller, verify that the roller gear and drive gear are properly meshed.
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 75
Page 78

ADF separation roller
1 Open the ADF cover, and remove the roller shield. See “ADF pickup roller” on page 74.
2 Slide the roller toward the gear end. Gently pry the roller-shaft locking tab (callout 1) away
from the roller. Remove the ADF separation roller.
41
Figure 34. Remove the ADF separation roller
Hint When replacing the roller, verify that the roller gear and drive gear are properly meshed.
76 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 79

ADF separation pad
1 Open the ADF cover.
2 Press and release two separation locking tabs (callout 1; shown already released).
3 Rotate the separation pad until it is perpendicular to the product.
4 Release the separation-pad arms (callout 2) by gently pressing them toward the ADF cover.
1
212
Figure 35. Remove the ADF separation pad
Note When replacing the separation pad, verify that the spring is firmly seated on its pedestal (callout 3).
33
Figure 36. Replace the ADF separation pad spring
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 77
Page 80

ADF unit
1 Disconnect the ADF cable (callout 1).
11
Figure 37. Disconnect the cable
2 Open the ADF unit, and lift it straight up and off of the scan unit.
Figure 38. Remove the ADF unit
78 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 81

Assemblies and covers
Control-panel door
1 Open the control-panel door, and remove the print cartridge. Cover the print cartridge to
keep it out of direct light; see the HP LaserJet 4100 series printer service manual for printcartridge information.
Figure 39. Remove the print cartridge
2 Press the two tabs (callout 1) on the inside of the print-cartridge lever to release it.
3 Remove one screw (callout 2).
4 Remove the wire-harness plastic cover (callout 3).
3
3
2
2
1
1
Figure 40. Remove the control-panel wire-harness cover
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 79
Page 82

5 Remove one screw (callout 4), and disconnect the top edge of the grounding strip.
44
Figure 41. Disconnect the control-panel grounding strip
6 Disconnect the control-panel-cable connector (callout 5).
7 Separate the door-support pins (callout 6) to release them.
565
6
Figure 42. Release the control-panel door-support pins
80 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 83

8 Flex the left arm (callout 7) to the right (inward), and move the control-panel door toward the
right side of the product until the arm releases. Slide the control-panel door toward the left,
and remove it from the product.
77
Figure 43. Remove the control-panel door
Note Step 9 is essential. The MFP must retain the original serial- and model-number label panel.
WARNING! The control panel in figure 44 is shown installed in the open position so that the label panel screws
can be easily seen. Remove the control panel and lay it on a flat surface before
removing the label panel to keep from dropping the mounting screws into the print unit.
9 Remove seven screws (callout 8), and remove the panel. Reinstall the label panel on the
replacement control-panel door.
88
Figure 44. Remove the product serial- and model-number panel
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 81
Page 84

Scan-unit right-side cover
Note If a duplex accessory is installed, remove it to access the right-side cover mounting screw.
1 Remove one screw (callout 1) from the plastic tab on the scan-unit right-side cover.
Figure 45. Remove the right-side cover screw
2 Grasp the plastic tab and pull the cover downward and away from the right side of the
product. Lift the cover up to release it, and then remove it from the product.
77
Figure 46. Remove the scan-unity right-side cover
82 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 85

Copy processor board
1 Remove the scan-unit right-side cover. See “Scan-unit right-side cover” on page 82.
2 Unplug the ADF connector cable (callout 1) and remove two screws (callout 2).
121
2
Figure 47. Disconnect the ADF cables
CAUTION Sliding the CPB out without unplugging the high-speed copy connect cable (callout 3) will damage
the cable connector.
3 Slide the copy processor board (CPB) out of the product approximately 2.5 mm (1 inch), and
disconnect the high-speed copy connect cable (callout 3).
13
Figure 48. Disconnect the high-speed copy connect cable
4 Remove the CPB from the product.
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 83
Page 86

Scan-unit left-side cover
Note If a duplex accessory is installed, remove it to access the right-side cover mounting screw.
1 Remove one screw (callout 1) from the scan-unit left-side cover.
11
Figure 49. Remove the left-side screw
2 Gently pry the rounded top edge of the cover (callout 2) with a flatblade screwdriver until you
can grasp it.
12
Figure 50. Gently pry the top edge of the left-side cover
84 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 87

3 Pull the cover downward and away from the left side of the product. Lift the cover up to
release it, and then remove it from the product.
Figure 51. Remove the scan-unit left-side cover
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 85
Page 88

Intake fan filter
1 Remove the scan-unit left-side cover. See “Scan-unit left-side cover” on page 84.
2 Remove the intake filter (callout 1).
11
Figure 52. Remove the intake filter.
86 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 89

Formatter cage
1 Grasp the back edge (callout 1) of the formatter-cage cover.
2 Pull the cover toward the back of the product, and remove it.
11
Figure 53. Remove the formatter-cage cover
3 Remove two screws (callout 2).
4 Slide the formatter cage toward the back of the product approximately 2.5 mm (1 inch), and
locate the formatter end of the high-speed copy connect cable connector (callout 3).
2
323
Figure 54. Slide the formatter cage toward the back of the product
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 87
Page 90

5 Twist the formatter away from the right side of the product, and unplug the high-speed copy
connect cable (callout 4).
6 Remove the formatter cage.
44
Figure 55. Disconnect the formatter high-speed copy connect cable
Note When replacing the formatter cage, align the back of the formatter cage with two large guide pins
and then slide it forward
88 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 91

Scan unit
1 Remove the following covers and assemblies:
• ADF unit. See “ADF unit” on page 78.
• scan-unit right-side and left-side covers. See “Scan-unit right-side cover” on page 82
through “Scan-unit left-side cover” on page 84.
• formatter cage. See “Formatter cage” on page 87.
2 Secure the optical unit by sliding the lock to the closed position.
Figure 56. Secure the optical unit
3 Remove two screws from the CPB and slide the CPB out of the product approximately
2.5 mm (1 inch). It is not necessary to remove the CPB from the scan unit.
4 Disconnect the CPB cable (callout 1).
41
Figure 57. Disconnect the CPB cable
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 89
Page 92

5 Disconnect the scan unit cable (callout 2) under the glass.
Figure 58. Disconnect the scan unit cable
22
6 Face the front of the product, and remove two screws (callout 3).
7 Slide the scan unit toward the back of the product, and remove it.
33
Figure 59. Remove the scan unit
90 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 93

Printing-unit top cover
1 Remove the scan unit. See “Scan unit” on page 89.
2 Open the rear output door.
3 Remove two screws (callout 1) from the back of the product.
11
Figure 60. Remove the top-cover rear-mounting screws
4 Face the front of the product, and open the control-panel door.
5 Remove four screws (callout 2).
6 Lift the top cover off of the product.
22
Figure 61. Remove the printing-unit top cover
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 91
Page 94

Glass
Note It is not necessary to remove the scan unit from the print unit (as shown) to remove the glass.
1 Remove the ADF assembly. See “ADF unit” on page 78.
2 Remove three s crews (callout 1).
11
Figure 62. Remove the glass mounting screws
CAUTION Use caution, the thin plastic tab holders (callout 2) can bend or break. Avoid touching the glass.
Fingerprints and skin oils can cause poor print quality.
3 Move the glass toward the front of the product until the three plastic tabs (callout 2) release.
Lift the glass straight up, and remove it from the product.
4 After replacing the glass, calibrate the ADF/scan unit. See “Performing automatic
Calibration” on page 47.
22
Figure 63. Remove the glass
92 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 95

Scanning lamp
1 Remove the glass. See “Glass” on page 92.
CAUTION Do not touch the lamp, because skin oils can create hot spots. Do not touch the mirror, because
fingerprints will affect print quality.
2 Note the cable routing pattern, and examine the pink cable where it rests over the cable
guide. Verify that the cable has a small black mark (callout 1). If not, make the mark yourself.
Note When replacing the scanning lamp, transfer the black mark onto the replacement bulb cable.
Position the cable with this mark centered in the cable guide (callout 1). This ensures that the
cable has sufficient length to allow the optical unit to move to its home position. Lay the cable flat
in the cable trough. Verify that it is not twisted.
3 Disconnect the lamp connector (callout 2).
Note A torroid may be installed on the scanning lamp cable. If a torroid is installed, remove its single
mounting screw before going on to the next step.
122
Figure 64. Note the cable routing pattern
1
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 93
Page 96

4 Remove the cable from the cable guides and trough (callout 4).
5 Hold the black end (callout 5), and slide the lamp toward the back of the product (in the
direction of the arrow).
545
4
Figure 65. Remove the scanning lamp
CAUTION When installing the scanning lamp, the wire harness must be properly routed under the harness
clips and flat through the harness trough to avoid interference with the optical unit as it moves in
the scan unit.
1
Figure 66. Scanning-lamp wire harness routing
Reinstall Note Anytime the glass is removed and replaced, calibrate the ADF/scan unit. See “Calibration” on
page 47.
94 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 97

Optical unit
1 Remove the following assemblies:
• glass. See “Glass” on page 92
• scanning lamp. See “Scanning lamp” on page 93.
CAUTION Do not touch the mirror, because fingerprints will affect print quality.
CAUTION It is important to note the routing and placement of the optical-unit ribbon cable before removing
it. Incorrect routing or placement when the cable is re-installed might cause damage to the cable
or the optical unit. See figure 72 on page 97.
2 Open the cable clip (callout 1) and disconnect the scanner-carriage ribbon cable from the
scanner controller PCB.
.
11
Figure 67. Release the optical unit ribbon cable
Hint Unsnap the clip arm from its hinge end (see figure 68) and remove it to prevent losing the clip
arm during servicing. T ake note of how the clip is hinged and how it is fastened before removing it.
Hinge end Clip end
Figure 68. Optical-unit ribbon-cable clip
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 95
Page 98

3 Center the optical unit in the scan unit to allow access to the optical-unit drive-belt tension
bracket (callout 2).
4 Loosen, but do not remove, the tension-spring bracket screw (callout 3) and swivel the
bracket to release the tension on the drive-belt (callout 4). Slip both ends of the drive-belt off
the drive and tension gears.
3
3
2
2
4
4
Figure 69. Release the tension-spring bracket
5 Lift the round rail up to remove it from two holders (callout 5), and remove the optical unit
from the scan unit.
55
Figure 70. Remove the optical unit
96 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
Page 99

Reinstall Note Anytime the glass is removed and replaced, calibr ate the ADF/scan u nit. See “Calibration” on
page 47.
Reinstall Note With the optical unit installed, place the optical-unit drive-belt onto the drive and tension gears.
Verify that the drive-belt teeth face inward and are engaged with the gear teeth.
Position the bracket with the locator pins in the provided holes on the bracket, and tighten the
screw until it holds the bracket in place but still allows the bracket to move.
Verify that the bracket is correctly positioned on the locator pins, and fully tighten the screw.
Figure 71. Optical-unit drive-belt tension bracket
Figure 72. Optical-unit ribbon cable
CAUTION The optic al-unit rib bon cable must be looped behind the optical head and secured with the ribbon-
cable clip. Failure to correctly route or secure the ribbon cable might result in damage to the cable
or the optical unit.
C9148-90909 6 Removal and replacement 97
Page 100

ADF door open sensor (PS10)
1 Remove the glass. See “Glass” on page 92.
2 Unplug one connector (callout 1).
3 Remove one screw (callout 2).
4 Lift the ADF door sensor up, and remove it from the product.
121
2
Figure 73. Remove the ADF door open sensor
Reinstall Note When replacing the glass, verify that the sensor switch pin freely moves in the hole through the
glass mounting frame.
Anytime the glass is removed and replaced, calibrate the ADF/scan unit. See “Calibration” on
page 47.
98 Removal and replacement C9148-90909
 Loading...
Loading...