Hino j05d, j08e Service Manual

For DENSO Authorized
ECD Service Dealer Only
Diesel Injection Pump
SERVICE MANUAL
Common Rail System for HINO
J05D/J08E Type Engine
OPERATION
October, 2003
00400041E
-1
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|
1. Product Application ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
1 |
1.1 Application ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
1 |
1.2 System Components Parts Numbers --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
1 |
2. Outline ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
2 |
2.1 Features of System ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
2 |
[1] System Characteristics ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
2 |
[2] Comparison to the Conventional System ------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
3 |
2.2 Outline of System ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
4 |
[1] Composition -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
4 |
[2] Operation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
4 |
2.3 Fuel System and Control System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
5 |
[3] Fuel System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
5 |
[4] Control System ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
5 |
3. Construction and Operation--------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
6 |
3.1 Description of Main Components ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
6 |
[1] Supply Pump (HP3, HP4) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
6 |
[2] Description of Supply Pump Components ------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
13 |
[3] Rail -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
16 |
[4] Injector (G2 Type) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
17 |
[5] Engine ECU (Electronic Control Unit) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
22 |
3.2 Description of Control System Components ------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
22 |
[1] Engine Control System Diagram ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
22 |
[2] Sensor and Relays ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
23 |
3.3 Various Types of Controls ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
29 |
[1] Fuel Injection Rate Control ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
30 |
[2] Fuel Injection Quantity Control --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
31 |
[3] Fuel Injection Timing Control ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
35 |
3.4 Other Relevant Engine Control ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
36 |
[1] EGR Control -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
36 |
3.5 Engine ECU ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
37 |
[1] Diagnosis Codes -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
37 |
[2] ECU External Wiring Diagram --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
44 |
[3] ECU Connector Diagram ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
45 |
0
1. Product Application
1.1 Application
Vehicle Name |
Vehicle Model |
|
Engine Model |
|
Exhaust Volume |
|
|
Reference |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HINO145, HINO165, |
|
|
J05D |
|
|
4.73L |
|
|
|
|
|
HINO185 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales from |
|||
Medium Truck |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
HINO238, HINO268, |
|
|
J08E |
|
|
7.68L |
|
Early ’04 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
HINO308, HINO338 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.2 System Components Parts Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Part Name |
Vehicle |
|
DENSO Part |
|
CarManufacturer |
|
Reference |
||||
|
|
Name |
|
Number |
|
Part Number |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Supply Pump |
|
|
|
|
294050-0011 |
|
22730-1311A |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Injector |
|
|
|
|
095000-5281 |
|
23910-1360A |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Rail |
|
|
|
|
095440-0480 |
|
22760-1180A |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Engine ECU |
|
|
|
|
102758-3010 |
|
89560-6540A |
|
|
||
|
Medium Truck |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Accelerator Position Sensor |
198800-3160 |
|
78010-1200A |
|
|
||||||
|
|
HINO238, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coolant Temp. Sensor |
|
071560-0110 |
|
83420-1250A |
|
|
|||||
HINO268, |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Crankshaft Position Sensor |
|
029600-0570 |
|
89410-1280A |
|
|
|||||
HINO308, |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
HINO338 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cylinder Recognition Sensor |
|
949979-1360 |
|
89410-1590A |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Intake Air Pressure Sensor |
|
|
|
079800-5890 |
|
89390-1080A |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
EGR Valve |
|
|
|
|
135000-7091 |
|
17350-1220A |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Air Flow Meter |
|
|
|
|
197400-2000 |
|
22204-21010B |
|
For EGR |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Supply Pump |
|
|
|
|
294000-0251 |
|
22730-1321A |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Injector |
|
|
|
|
095000-5391 |
|
23910-1310A |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Rail |
|
|
|
|
095440-0530 |
|
22760-1220A |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Engine ECU |
|
|
|
|
102758-3010 |
|
89560-6540A |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Accelerator Position Sensor |
Medium Truck |
198800-3160 |
|
78010-1200A |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Coolant Temp. Sensor |
HINO145, |
|
071560-0110 |
|
83420-1250A |
|
|
||||
|
|
HINO165, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crankshaft Position Sensor |
|
029600-0570 |
|
89410-1280A |
|
|
|||||
HINO185 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cylinder Recognition Sensor |
|
949979-1360 |
|
89410-1590A |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Intake Air Pressure Sensor |
|
|
|
079800-5890 |
|
89390-1080A |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
EGR Valve |
|
|
|
|
135000-7071 |
|
17350-1210A |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Air Flow Meter |
|
|
|
|
197400-2000 |
|
22204-21010B |
|
For EGR |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
1

2. Outline
2.1 Features of System
The common rail system was developed primarily to cope with exhaust gas regulations for diesel engines, and aimed for 1. further improved fuel economy; 2. noise reduction; and 3. high power output.
[1] System Characteristics
The common rail system uses a type of accumulation chamber called a rail to store pressurized fuel, and injectors that contain electronically controlled solenoid valves to spray the pressurized fuel into the cylinders. Because the engine ECU controls the injection system (including the injection pressure, injection rate, and injection timing), the system is unaffected by the engine speed or load. This ensures a stable injection pressure at all times, particularly in the low engine speed range, and dramatically decreases the amount of black smoke ordinarily emitted by a diesel engine during start-up and acceleration. As a result, exhaust gas emissions are cleaner and reduced, and higher power output is achieved.
(1)Injection Pressure Control
a.Enables high-pressure injection, even in the low engine speed range.
b.Optimizes control to minimize particulate matter and NOx emissions.
(2)Injection Timing Control
a.Optimally controls the timing to suit driving conditions.
(3)Injection Rate Control
a.Pilot injection control sprays a small amount of fuel before the main injection.
|
Common Rail System |
|
||||||
|
Injection Pressure Control |
|
Injection Timing Control |
Injection Rate Control |
||||
|
Optimization, High Pressurization |
|
|
Optimization |
Rate |
Pilot Injection |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Rail System |
|
|
|
|
Common Rail System |
Injection |
Main |
Injection Pressure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Injection |
|
|
|
|
|
Injection Timing |
|
Crankshaft Angle |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Particulate |
|
NOx |
|
Injection Quantity Control |
|||
Conventional |
|
|
|
Cylinder Injection |
||||
|
Conventional |
|
Volume Correction |
|||||
Pump |
|
Pump |
Speed |
|
||||
|
|
|
||||||
Speed |
Injection |
Speed |
|
|||||
|
|
|
Pressure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QD0734E |
(4) EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) Control
a. By recirculating the exhaust gas into the intake side of the engine, the combustion temperature is reduced and NOx is decreased.
2

[2] Comparison to the Conventional System |
|
|
||
|
In-line, VE Pump |
|
Common Rail System |
|
|
High-pressure Pipe |
|
|
|
|
Momentary High Pressure |
|
Rail |
|
|
|
TWV |
||
|
|
|
||
|
Timer |
Nozzle |
Supply Pump |
|
|
Usually High Pressure |
|
||
|
Governor |
|
||
|
|
Delivery Valve |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
System |
In-line Pump |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feed Pump SCV (Suction Control Valve) |
|
|
|
|
Injector |
|
|
|
|
Fuel Tank |
|
|
VE Pump |
|
|
|
Injection Quantity Control |
Pump (Governor) |
|
Engine ECU, Injector (TWV)*1 |
|
Injection Timing Control |
Pump (Timer) |
|
Engine ECU, Injector (TWV)*1 |
|
Rising Pressure |
Pump |
|
Engine ECU, Supply Pump |
|
Distributor |
Pump |
|
Engine ECU, Rail |
|
Injection Pressure Control |
Dependent upon Speed and Injection Quantity |
Engine ECU, Supply Pump (SCV)*2 |
|
|
|
|
*1 TWV: Two Way Valve *2 SCV: Suction Control Valve |
QD2341E |
|
3

2.2 Outline of System [1] Composition
The common rail system consists primarily of a supply pump, rail, injectors, and engine ECU.
Fuel Temperature Sensor
Vehicle Speed 
Accelerator Opening
Intake Air Pressure
Intake Air Temperature  Engine ECU
Engine ECU
Coolant Temperature
Crankshaft Position 
Cylinder Recognition Sensor 
Intake Airflow Rate |
|
|
|
Rail |
Pressure |
Injector |
|
Limiter |
|||
|
|
||
Rail Pressure |
|
|
|
Sensor |
|
|
Fuel Temperature Sensor
Supply Pump |
SCV (Suction |
Fuel Tank |
|
Control Valve) |
|
|
|
Q000144E
[2] Operation
(1)Supply pump (HP3)
a.The supply pump draws fuel from the fuel tank, and pumps the high pressure fuel to the rail. The quantity of fuel discharged from the supply pump controls the pressure in the rail. The SCV (Suction Control Valve) in the supply pump effects this control in accordance with the command received from the ECU.
(2)Rail
a.The rail is mounted between the supply pump and the injector, and stores the highpressure fuel.
(3)Injector (G2 type)
a.This injector replaces the conventional injection nozzle, and achieves optimal injection by effecting control in accordance with signals from the ECU. Signals from the ECU determine the length of time and the timing in which current is applied to the injector. This in turn, determines the quantity, rate and timing of the fuel that is injected from the injector.
(4)Engine ECU
a.The engine ECU calculates data received from the sensors to comprehensively control the injection quantity, timing and pressure, as well as the EGR (exhaust gas recirculation).
4

2.3 Fuel System and Control System [1] Fuel System
This system comprises the route through which diesel fuel flows from the fuel tank to the supply pump, via the rail, and is injected through the injector, as well as the route through which the fuel returns to the tank via the overflow pipe.
[2] Control System
In this system, the engine ECU controls the fuel injection system in accordance with the signals received from various sensors. The components of this system can be broadly divided into the following three types: (1) Sensors; (2) ECU; and (3) Actuators.
(1)Sensors
a.Detect the engine and driving conditions, and convert them into electrical signals.
(2)Engine ECU
a.Performs calculations based on the electrical signals received from the sensors, and sends them to the actuators in order to achieve optimal conditions.
(3)Actuators
a.Operate in accordance with electrical signals received from the ECU. Injection system control is undertaken by electronically controlling the actuators. The injection quantity and timing are determined by controlling the length of time and the timing in which the current is applied to the TWV (Two-Way Valve) in the injector. The injection pressure is determined by controlling the SCV (Suction Control Valve) in the supply pump.
|
Sensor |
|
|
|
|
Actuator |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Engine Speed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crankshaft Position Sensor NE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Injector |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cylinder Recognition |
|
|
|
|
•Injection Quantity Control |
||
|
|
||||||||
|
Cylider Recognition Sensor G |
|
|
|
|
|
|
•Injection Timing Control |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Load |
Engine |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Accelerator Position Sensor |
ECU |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supply Pump (SCV) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rail Pressure Sensor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
•Injection Pressure Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EGR, Engine Warning Light |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Sensors and Switches |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q000282E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
5

3. Construction and Operation
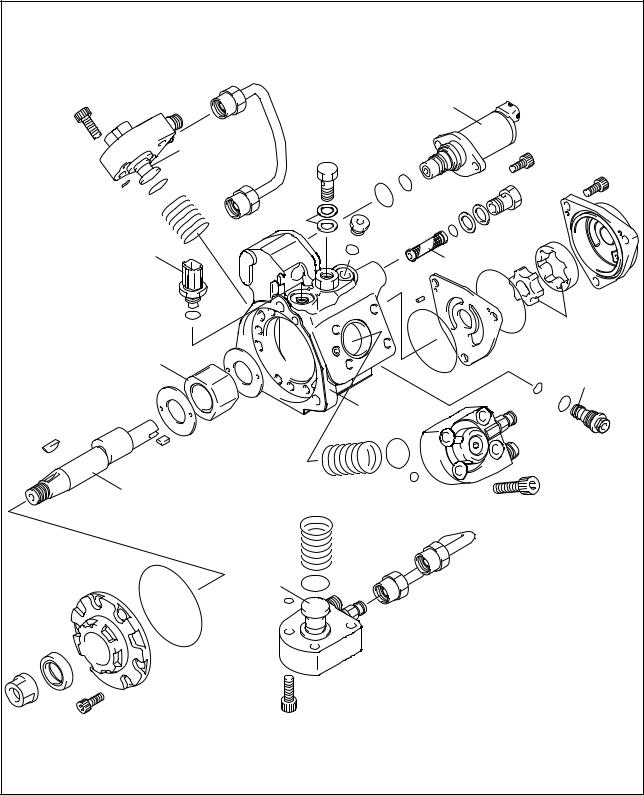
3.1 Description of Main Components [1] Supply Pump (HP3, HP4)
(1)Outline
a.The supply pump consists primarily of the pump body (cam shaft, ring cam, and plungers), SCV (Suction Control Valve), fuel temperature sensor, and feed pump.
b.The two plungers for HP3 or the three plungers for HP4 are positioned vertically on the outer ring cam for compactness.
c.The engine drives the supply pump at a ratio of 1:1. The supply pump has a built-in feed pump (trochoid type), and draws the fuel from the fuel tank, sending it to the plunger chamber.
d.The internal camshaft drives the two plungers, and they pressurize the fuel sent to the plunger chamber and send it to the rail. The quantity of fuel supplied to the rail is controlled by the SCV, using signals from the engine ECU. The SCV is a normally opened type (the intake valve opens during de-energization).
HP3
SCV
Fuel Temperature Sensor
Q000252E
HP4
Fuel Temperature Sensor
SCV
Q000253E
6

|
|
|
Intake Valve |
Intake Pressure |
|
Injector |
Rail |
Discharge Valve |
Feed Pressure |
||
|
|||||
|
|
|
High Pressure |
||
|
|
|
Plunger |
||
|
|
|
Return Pressure |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Return Spring |
|
|
Return |
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel Overflow |
|
SVC |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Regulating Valve |
|
|
|
|
Filter |
Feed Pump |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Camshaft |
|
Fuel Inlet |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Intake |
|
Fuel Tank |
|
|
|
Fuel Filter (with Priming Pump) |
|
|
|
|
|
QD0704E |
|
7

HP3 |
|
|
SCV |
|
Plunger |
|
Feed Pump |
Pump Body |
|
|
Fuel Temperature |
Ring Cam |
Sensor |
|
|
|
Regulating |
|
Valve |
Drive Shaft |
Filter |
|
|
|
Plunger |
|
Q000254E |
|
8 |
HP4 |
|
|
|
SCV |
|
Plunger |
|
|
Fuel Temperature |
Filter |
|
Sensor |
||
|
||
|
Feed Pump |
|
Ring Cam |
Regulating |
|
|
||
|
Valve |
|
|
Pump Body |
|
Drive Shaft |
|
|
|
Plunger |
|
|
Q000255E |
|
|
9 |

(2)Supply Pump Internal Fuel Flow
a. The fuel that is drawn from the fuel tank passes through the route in the supply pump as illustrated, and is fed into the rail.
Supply Pump Interior
Regulating Valve
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feed Pump |
|
|
SCV (Suction Control Valve) |
|
Pumping Portion (Plunger) |
|
Rail |
|
Overflow
Intake Valve
Fuel Tank
Q000283E
(3)Construction of Supply Pump (in case of HP3 pump)
a. The eccentric cam is attached to the cam shaft. The eccentric cam is connected to the ring cam.
Cam Shaft
Eccentric Cam |
Ring Cam |
|
QD0706E
b.As the cam shaft rotates, the eccentric cam rotates eccentrically, and the ring cam moves up and down while rotating.
Plunger
Eccentric Cam
 Ring Cam
Ring Cam
Cam Shaft
QD0727E
10

c.The plunger and the suction valve are attached to the ring cam. The feed pump is connected to the rear of the cam shaft.
Plunger A
Ring Cam
Feed Pump
Plunger B
QD0728E
11

(4)Operation of the Supply Pump
a. As shown in the illustration below (in case of HP3 pump), the rotation of the eccentric cam causes the ring cam to push Plunger A upwards. Due to the spring force, Plunger B is pulled in the opposite direction to Plunger A. As a result, Plunger B draws in fuel, while
Plunger A pumps it to the rail. In the case of the 4-cylinder engine used with the HP3 pump, each plunger pumps fuel in a reciprocal movement during the 360° cam rotation. Conversely, in the case of the 6-cylinder engine used with the HP4 pump, 3 plungers pump fuel in a reciprocal movement for each one rotation of the cam.
Suction Valve
Plunger A |
Delivery Valve
Eccentric Cam
Ring Cam
SCV
Plunger B
Plunger A: Complete Compression |
Plunger A: Begin Intake |
Plunger B: Complete Intake |
Plunger B: Begin Compression |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plunger A: Begin Compression |
|
Plunger A: Complete Intake |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Plunger B: Begin Intake |
|
Plunger B: Complete Compression |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QD0707E |
NOTE:
There are 3 plungers for the HP4.
12

[2] Description of Supply Pump Components
(1)Feed Pump
a. The trochoid type feed pump, which is integrated in the supply pump, draws fuel from the fuel tank and feeds it to the two plungers via the fuel filter and the SCV (Suction Control
Valve). The feed pump is driven by the drive shaft. With the rotation of the inner rotor, the feed pump draws fuel from its suction port and pumps it out through the discharge port. This is done in accordance with the space that increases and decreases with the movement of the outer and inner rotors.
Quantity Decrease |
Quantity Decrease (Fuel Discharge) |
Outer Rotor |
to Pump Chamber |
Inner Rotor
Intake Port
|
Discharge |
Quantity Increase |
Quantity Increase (Fuel Intake) |
|
Port |
||
|
|
||
from Fuel Tank |
|
|
|
|
|
QD0708E |
|
|
|
|
(2)SCV: Suction Control Valve (Normally open type)
a.A linear solenoid type valve has been adopted. The ECU controls the duty ratio (the duration in which current is applied to the SCV), in order to control the quantity of fuel that is supplied to the high-pressure plunger.
b.Because only the quantity of fuel that is required for achieving the target rail pressure is drawn in, the actuating load of the supply pump decreases.
c.When current flows to the SCV, variable electromotive force is created in accordance with the duty ratio, moving the armature to the left side. The armature moves the cylinder to the left side, changing the opening of the fuel passage and thus regulating the fuel quantity.
d.With the SCV OFF, the return spring contracts, completely opening the fuel passage and supplying fuel to the plungers. (Full quantity intake and full quantity discharge)
e.When the SCV is ON, the force of the return spring moves the cylinder to the right, closing the fuel passage (normally opened).
f.By turning the SCV ON/OFF, fuel is supplied in an amount corresponding to the actuation duty ratio, and fuel is discharged by the plungers.
Exterior View of SCV |
Cross-section of SCV |
SCV |
|
|
|
|
Return Spring |
|
|
|
Pump Body
Cylinder
Q000270E
13
 Loading...
Loading...