Page 1

FANUC Series 0+-MODEL F
CONNECTION MANUAL (HARDWARE)
B-64603EN/01
Page 2

• No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form.
• All specifications and designs are subject to change without notice.
The products in this manual are controlled based on Japan’s “Foreign Exchange and
Foreign Trade Law”. The export from Japan is subject to an export license by the
government of Japan. Furthermore, the product may also be controlled by re-export
regulations of the United States government.
Should you wish to export or re-export these products, please contact FANUC for advice.
The products in this manual are manufactured under strict quality control. However, when
using any of the products in a facility in which a serious accident or loss is predicted due to
a failure of the product, install a safety device.
In this manual we have tried as much as possible to describe all the various matters.
However, we cannot describe all the matters which must not be done, or which cannot be
done, because there are so many possibilities.
Therefore, matters which are not especially described as possible in this manual should be
regarded as ”impossible”.
This manual contains the program names or device names of other companies, some of
which are registered trademarks of respective owners. However, these names are not
followed by ® or ™ in the main body.
Page 3
B-64603EN/01 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Described below are the safety precautions regarding the control units and those peripheral units
explained herein. The safety precautions must be observed in order to use these units safely.
Because exchanging, as well as performing daily maintenance operations on, the control units and those
peripheral units explained herein may incur diverse dangers, you cannot be involved in such work unless
you have been sufficiently trained for safety.
Some safety precautions may not apply to your control units or peripheral units explained herein because
the units have no corresponding function. If this is the case, skip reading those precautions.
As for safety precautions regarding machine tools, refer to the respective machine manuals provided by
the machine tool builders.
Before starting to operate machines for check purposes, be sure to read the manuals provided by the
machine tool builders and FANUC and sufficiently understand their descriptions.
Contents
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE.........................................................................s-1
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS REGARDING MOUNTING, WIRING, AND EXCHANGING..........s-2
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS REGARDING DESIGNING.................................................................s-4
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, AND NOTES REGARDING DAILY MAINTENANCE............................s-5
NOTE REGARDING KOREAN KC MARK ..........................................................................................s-5
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
This manual includes safety precautions for protecting the user and preventing damage to the machine.
Precautions are classified into Warning and Caution according to their bearing on safety. Also,
supplementary information is described as a Note. Read the Warning, Caution, and Note thoroughly
before attempting to use the machine.
WARNING
Applied when there is a danger of the user being injured or when there is a
danger of both the user being injured and the equipment being damaged if the
approved procedure is not observed.
CAUTION
Applied when there is a danger of the equipment being damaged, if the
approved procedure is not observed.
NOTE
The Note is used to indicate supplementary information other than Warning and
Caution.
• Read this manual carefully, and store it in a safe place.
s-1
Page 4
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS B-64603EN/01
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS REGARDING MOUNTING, WIRING, AND EXCHANGING
WARNING
1 Before starting mounting, wiring, and exchanging, be sure to shut off externally
supplied power. Otherwise, electrical shocks, breakdown, and blowout may
occur.
If a control unit is turned off but other units are not, it is likely that power may be
supplied to servo units, resulting in the units being damaged and workers getting
an electrical shock when the units are exchanged.
2 Voltage lingers in servo and spindle amplifiers for a while even after power has
been turned off, resulting in workers possibly getting an electrical shock when
the workers touch them. Before starting to exchange these amplifiers, wait for 20
minutes after power has been turned off.
3 Be sure to ground your control units and peripheral units in accordance with your
national grounding standards (protective grounding class C or stricter).
Otherwise, electrical shocks, breakdown, and blowout may occur.
4 In order to prevent damage that may be caused by static electricity, wear a
grounding wrist strap or take a similar protective measure before starting to
touch a printed-circuit board or unit or attach a cable.
Static electricity from human bodies can damage electrical circuits.
5 In unit replacement, specify the same settings and parameters in the newly
installed unit as those for the one removed. (For details, refer to the respective
manuals for the units.)
Operating the newly installed unit with incorrect settings or parameters will cause
the machine to behave unexpectedly, possibly leading to a damaged workpiece
or machine or injury.
6 If you notice an apparent hardware fault, such as abnormal noise, abnormal
odor, smoke, ignition, or abnormal heat, in the hardware while power is being
supplied to it, shut it off at once. These faults can cause fire, breakdown,
blowout, and malfunction.
7 The radiating fins of control units, servo amplifiers, spindle amplifiers, and other
devices can remain very hot for a while after power has been turned off, making
you get burned if you touch them. Before starting to work on them, wait and
make sure they are cool.
8 When exchanging heavy stuff, you should do so together with two or more
people.
If you try to exchange heavy stuff all by yourself, you may drop it and get hurt.
9 Wiring work in the control units and peripheral units must be done only after they
have been installed. Otherwise, electrical shocks can occur.
10 Be careful not to damage cables. Otherwise, electrical shocks can occur.
11 When working, wear suitable clothes with safety taken into account. Otherwise,
injury and electrical shocks can occur.
12 Do not work with your hands wet. Otherwise, electrical shocks and damage to
electrical circuits can occur.
s-2
Page 5
B-64603EN/01 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION
Failing to observe any caution stated below can lead to fire, breakdown, blowout,
and malfunction.
1 Do not attach the units directly to any flammable object or install the units near
any flammable object.
2 Do not allow any foreign matter (such as a screw, metal chip, or coolant) to get
in the units.
3 Handle the units and printed-circuit boards gently because they are precision
devices. Be careful not to drop them or give a high impact to them.
4 Lay signal wires away from power wires as stated in this manual.
5 When fastening each unit or wire, be sure to observe the screw tightening torque
specified for them. If screws are tightened too weakly or too strongly, it is likely
that the unit may drop, break, or malfunction, or the wire may be short-circuited.
Do not forget to tighten all necessary screw.
6 Do not block any cooling fan air inlet or outlet. For units having no cooling fan,
allow space for natural convection cooling above and below them.
7 Be careful not to make an incorrect wiring or connection. Be sure to attach wires
and cables to their respective corresponding terminals and connectors.
8 Confirm equipment’s electrical rating stated herein. Do not apply any unspecified
voltage to the equipment.
9 Do not confuse voltage polarity. Carefully confirm the arrangement of connector
pins.
10 When making a cable assembly, press-mount, crimp, or solder the wires, using
the tool specified by the cable manufacturer.
11 Use printed-circuit boards and peripheral units that match your control unit.
12 When mounting the units, pay attention to their mass.
13 When detaching a cable from a unit, hold the connector rather than the cable.
When attaching a cable, be sure to fit its connector to the connector pins
securely. For connectors having a lock mechanism, be sure to lock them
securely.
14 As for the shielding wires of the cables specified herein, securely ground them,
using, for example, cable clamps.
15 Always use wires whose length, diameter, heat resistance, and flex resistance
match their use.
s-3
Page 6
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS B-64603EN/01
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS REGARDING DESIGNING
WARNING
1 When designing, be sure to observe all rules stated in this document and any
related manuals. Otherwise, it is likely that failure and malfunction may occur.
2 Failures in the control units and I/O units as well as input power abnormality and
communication failures can hamper the normal operation of these I/O units.
Design each I/O unit in such a way that the machine can operate safely, for
example, by providing an external safety circuit to the I/O unit so that no accident
will occur even if the I/O unit fails to operate normally.
The DO function of each I/O unit has been designed in such a way that, if a
system alarm is issued in the control unit that controls the I/O unit or the power
of the control unit or the I/O unit is turned off, the DO function of all the I/O units
is turned off. However, it is not guaranteed that the DO function is surely turned
off. So, it is requested that, if a signal regarding safety is involved, a safety circuit
external to each I/O unit must be configured. Using the dual check safety
function makes it possible to detect a single fault in a portion related to safety.
For details of the dual check safety function, refer to the FANUC Series
30i/31i/32i-MODEL B Dual Check Safety Connection Manual (B-64483EN-2).
3 Install each control unit, display unit, MDI unit, and machine operator panel in
such a place that neither cutting chip nor coolant will spatter to them. Otherwise,
damage or malfunction may occur.
4 Coolants containing sulfur or chlorine at a high activation level, oil-free coolants
called synthetic, and water-soluble coolants at a high alkali level, in particular,
can largely affect the CNC and peripheral units. Please note that, even if
consideration is taken to protect them from direct exposure to these coolants,
the following trouble is likely to occur.
Coolants containing sulfur or chlorine at a high activation level
•
Some coolants containing sulfur or chlorine are at an extremely high activity
level. If such a coolant adheres to the CNC or peripheral units, it reacts
chemically with a material, such as resin, of equipment, possibly leading to
corrosion or deterioration. If it gets in the CNC or peripheral units, it corrodes
metals, such as copper and silver, used as component materials, possibly
leading to a defective component.
Synthetic-type coolants having a high permeability
•
Some synthetic-type coolants whose lubricating component is, for example,
PAG (polyalkylene glycol) have an extremely high permeability. If such a
coolant is used even in equipment having a high closeness, it can readily flow
into the CNC or peripheral units through, for example, gaskets. It is likely that,
if the coolant gets in the CNC or a peripheral unit, it may deteriorate the
insulation and damage the components.
Water-soluble coolants at a high alkali level
•
Some coolants whose pH is increased using alkanolamine are so strong
alkali that its standard dilution will lead to pH10 or higher. If such a coolant
spatters over the surface of the CNC or peripheral unit, it reacts chemically
with a material, such as resin, possibly leading to corrosion or deterioration.
s-4
Page 7
B-64603EN/01 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, AND NOTES REGARDING DAILY MAINTENANCE
WARNING
Battery replacement
Do not replace batteries unless you have been well informed of maintenance
work and safety.
When opening the cabinet and replacing batteries, be careful not to touch any
high-voltage circuit (marked with
and covered with an electric shock
prevention cover).
When the electric shock prevention cover has been removed, you will get an
electric shock if you touch any high-voltage circuit.
WARNING
Fuse replacement
Before replacing a blown fuse, it is necessary to remove the cause of the blown
fuse.
So, do not replace fuses unless you have been well informed of maintenance
work and safety.
When opening the cabinet and replacing fuses, be careful not to touch any
high-voltage circuit (marked with
and covered with an electric shock
prevention cover).
When the electric shock prevention cover has been removed, you will get an
electric shock if you touch any high-voltage circuit.
CAUTION
Handle the batteries gently. Do not drop them or give a strong impact to them.
NOTE
Each control unit uses batteries, because it must hold data, such as programs,
offset values, and parameters even when AC power for it is off.
Back up the data (programs, offset values, and parameters) regularly.
If the battery voltage becomes low, a low battery voltage alarm is displayed on
the machine operator’s panel or screen.
Once the battery voltage alarm has been displayed, replace the batteries within
one week. Otherwise, the memory contents may be lost.
For the battery replacement procedure, see Section 4.4, “Batteries”. Recollect or
discard old batteries in the way your local autonomous community specifies.
NOTE REGARDING KOREAN KC MARK
NOTE
This equipment is industrial (Class A) electromagnetic wave suitability equipment
and seller or user should take notice of it, and this equipment is to be used in the
places except for home.
이 기기는 업무용(A급) 전자파적합기기로서 판 매자 또는 사용자는 이 점을 주의하시기 바라며
가정외의 지역에서 사용하는 것을 목적으로 합니다
s-5
.
,
Page 8

Page 9
B-64603EN/01 PREFACE
PREFACE
This manual describes the information, that is, electrical and structural specifications, needed in
connecting machine tools to the control and peripheral units stated below. The manual covers the range
shown on the total connection diagrams mentioned in Chapter 2. The manual briefly describes the units
that are used in common with the FANUC control units, such as FANUC I/O units, FANUC PANEL
and servo motors. It also gives supplementary information for use of these units with the control units.
For detailed specifications, refer to the manuals of these components.
For options not covered in this manual, also refer to the manuals of these components.
Applicable models
The models covered by this manual, and their abbreviations are :
Model name Abbreviation
FANUC Series 0i– TF 0i–TF
FANUC Series 0i– MF 0i–MF
FANUC Series 0i– PF
0i–F
0i–PF
Series 0i
Organization of this manuals
This manual consists of chapters 1 to 12 and appendixes at the end of the book.
Chapter and title Contents
Chapter 1
CONFIGURATION
Chapter 2
TOTAL CONNECTION DAIGRAMS
Chapter 3
INSTALLATION
Chapter 4
POWER SUPPLAY CONNECTION
Chapter 5
CONNECTION TO CNC
PERIOHERALS
Chapter 6
SERVO AND SPINDLE
INTERFACES
Chapter 7
CONNECTION TO FANUC I/O Link
i
Chapter 8
UNITS CONNECTED TO FANUC
I/O Link i
Chapter 9
STOP AND EMERGENCY STOP
Chapter 10
CONNECTION TO OTHER
NETWORKS
Chapter 11
CONNECTION WITH THE FANUC
PANEL i AND COMMERCIAL
PERSONAL COMPUTERS
Chapter 12
PANEL i
Provides general information related to the connection, as well as an
introduction to detailed information.
Describes how to connect peripheral units.
Describes the installation requirements for using.
Describes how to make connections related to the power supply.
Describes how to connect the peripheral devices.
Describes how to connect the 30i–B series to servo or spindle amplifiers.
Also explains how to connect separate detector interface units.
Describes how to connect machine interface I/O units using the FANUC I/O
Link i.
Describes major units that correspond to the FANUC I/O Link i.
Describes how to handle the emergency stop signal.
A lot of important information regarding safety is included. Be sure to read It.
Describes how to connect to networks.
Describes how to connect to the FANUC PANEL i or a commercial personal
computer, using the high-speed serial bus (HSSB) or Ethernet.
Describes how to connect a PANEL i.
i,
p-1
Page 10
PREFACE B-64603EN/01
Chapter and title Contents
APPENDIX A) OUTLINE DRAWINGS OF UNITS AND CONNECTORS
B) 20-PIN INTERFACE CONNECTORS AND CABLES
C) CONNECTION CABLE (SUPPLIED FROM US)
D) OPTICAL FIBER CABLE
E) MEMORY CARD INTERFACE
Related manuals of 0i-F
The following table lists the manuals related to 0i-F. This manual is indicated by an asterisk(*).
Table 1 Related manuals
Manual name Specification number
DESCRIPTIONS B-64602EN
CONNECTION MANUAL (HARDWARE) B-64603EN *
CONNECTION MANUAL (FUNCTION) B-64603EN-1
OPERATOR’S MANUAL (Common to Lathe System/Machining Center System) B-64604EN
OPERATOR’S MANUAL (For Lathe System) B-64604EN-1
OPERATOR’S MANUAL (For Machining Center System) B-64604EN-2
MAINTENANCE MANUAL B-64605EN
PARAMETER MANUAL B-64610EN
0i-PF CONNECTION MANUAL (FUNCTION)
0i-PF OPERATOR’S MANUAL
0i-PF PARAMETER MANUAL
Programming
Macro Executor PROGRAMMING MANUAL B-63943EN-2
Macro Compiler PROGRAMMING MANUAL B-66263EN
C Language Executor PROGRAMMING MANUAL B-63943EN-3
PMC
PMC PROGRAMMING MANUAL B-64513EN
Network
PROFIBUS-DP Board CONNECTION MANUAL B-63993EN
Fast Ethernet / Fast Data Server OPERATOR’S MANUAL B-64014EN
DeviceNet Board CONNECTION MANUAL B-64043EN
FL-net Board CONNECTION MANUAL B-64163EN
CC-Link Board CONNECTION MANUAL B-64463EN
Industrial Ethernet CONNECTION MANUAL B-64013EN
Operation guidance function
MANUAL GUIDE i
(Common to Lathe System/Machining Center System) OPERATOR’S MANUAL
MANUAL GUIDE i (For Machining Center System) OPERATOR’S MANUAL
MANUAL GUIDE i (Set-up Guidance Functions) OPERATOR’S MANUAL
Dual Check Safety
Dual Check Safety CONNECTION MANUAL B-64483EN-2
B-64623EN
B-64624EN
B-64630EN
B-63874EN
B-63874EN-2
B-63874EN-1
p-2
Page 11
B-64603EN/01 PREFACE
Related manuals of SERVO MOTOR αis/αi/βis/βi series
The following table lists the manuals related to SERVO MOTOR αis/αi/βis/βi series
Manual name Specification number
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR αi series DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR αi series DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR βi series DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR βi series DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC SERVO AMPLIFIER αi series DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC SERVO AMPLIFIER βi series DESCRIPTIONS
FANUC SERVO MOTOR αis series
FANUC SERVO MOTOR αi series
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR αi series
FANUC SERVO AMPLIFIER αi series
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
FANUC SERVO MOTOR βis series
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR βi series
FANUC SERVO AMPLIFIER βi series
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR αi series
FANUC AC SERVO MOTOR βi series
FANUC LINEAR MOTOR LiS series
FANUC SYNCHRONOUS BUILT-IN SERVO MOTOR DiS series
PARAMETER MANUAL
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR αi series
FANUC AC SPINDLE MOTOR βi series
BUILT-IN SPINDLE MOTOR Bi series
PARAMETER MANUAL
B-65262EN
B-65272EN
B-65302EN
B-65312EN
B-65282EN
B-65322EN
B-65285EN
B-65325EN
B-65270EN
B-65280EN
Related manuals of FANUC PANEL i
The following table lists the manuals related to FANUC PANEL i.
Manual name Specification number
FANUC PANEL i CONNECTION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
B-64223EN
Related manuals of FANUC I/O Unit
The following table lists the manuals related to FANUC I/O Unit.
Manual name Specification number
FANUC I/O Unit-MODEL A CONNECTION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL B-61813E
FANUC I/O Unit-MODEL B CONNECTION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL B-62163E
Handy Machine Operator’s Panel CONNECTION MANUAL B-63753EN
Training
• FANUC runs FANUC Training Center to train those who will be involved in the connection,
maintenance, and operation of FANUC products. It is recommended to attend the class so you will
be able to use the products effectively.
Visit the following web site for detailed descriptions of its curriculum.
http://www.fanuc.co.jp/
p-3
Page 12

Page 13

B-64603EN/01 TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS............................................................................s-1
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE.............................................s-1
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS REGARDING MOUNTING, WIRING, AND
EXCHANGING............................................................................................s-2
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS REGARDING DESIGNING.....................................s-4
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, AND NOTES REGARDING DAILY MAINTENANCE ....s-5
NOTE REGARDING KOREAN KC MARK ..............................................................s-5
PREFACE....................................................................................................p-1
1 CONFIGURATION ..................................................................................1
1.1 CONTROL UNIT CONFIGURATION AND COMPONENT NAMES..............1
1.1.1 Configurations of LCD-mounted Type Control Units .............................................1
1.1.2 Configurations of Optional Boards ..........................................................................5
1.2 HARDWARE OVERVIEW..............................................................................6
1.2.1 LCD-mounted Type Control Unit Overview ...........................................................6
2 TOTAL CONNECTION DIAGRAMS.......................................................7
3 INSTALLATION ....................................................................................10
3.1 ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS OUTSIDE THE CABINET...............10
3.1.1 Environmental Conditions outside the Cabinet......................................................10
3.1.2 Installation Conditions of the Control Unit............................................................10
3.2 CAUTIONS REGARDING THE INSTALLATION DESIGN OF MACHINE
TOOL POWER MAGNETICS CABINETS ...................................................11
3.3 THERMAL DESIGN OF THE MACHINE TOOL MAGNETIC CABINET......14
3.3.1 Temperature Rise within the Machine Tool Magnetic Cabinet..............................14
3.3.2 Heat Output of Each Unit.......................................................................................14
3.3.3 Thermal Design of Operator's Panel.......................................................................15
3.4 COUNTERMEASURES AGAINST NOISE AND GROUNDING ..................16
3.4.1 Grounding as Noise Suppression Measures ...........................................................17
3.4.1.1 Grounding methods ...........................................................................................17
3.4.1.2 Cabinet............................................................................................................... 18
3.4.2 Protective Ground (Grounding for Protection against Indirect Contact) ...............21
3.4.3 Connecting the Ground Terminal of the Control Unit ...........................................22
3.4.4 Separating Signal Lines..........................................................................................23
3.4.5 Noise Suppressor....................................................................................................25
3.4.6 Cable Clamp and Shield Processing.......................................................................26
3.4.7 Lightning Surge Absorber Installation...................................................................28
3.5 INSTALLING THE CONTROL UNIT............................................................30
3.5.1 Installing the LCD-mounted Type Control Unit....................................................30
3.6 TIGHTENING TORQUE FOR FASTENING UNITS AND GROUND
TERMINALS................................................................................................31
3.7 DUSTPROOF MEASURES FOR CABINETS AND PENDANT BOXES......31
3.8 LCD PROTECTION COVER .......................................................................34
3.9 ATTACHING SCREW CAPS.......................................................................34
3.10 INSTALLATION CONDITION FOR UL RECOGNITION..............................35
c-1
Page 14

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-64603EN/01
4 POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION.........................................................36
4.1 24 VDC POWER (INSULATION AC/DC CONVERTOR).............................36
4.1.1 Connecting 24 VDC Power....................................................................................36
4.1.2 24 VDC Power Supply Specification.....................................................................38
4.1.3 Power Capacity of 24 VDC Power Supplies..........................................................40
4.2 TURNING ON AND OFF THE POWER TO THE CONTROL UNIT.............41
4.2.1 Power-on Sequence................................................................................................41
4.2.2 Power-off Sequence ...............................................................................................42
4.3 CABLE FOR POWER SUPPLY TO CONTROL UNIT.................................44
4.4 BATTERIES.................................................................................................44
4.4.1 Battery for Memory Backup in the Control Unit (3 VDC) ....................................44
4.4.1.1 Replacing the lithium battery............................................................................. 45
4.4.1.2 Replacing commercially available alkaline dry cells (size D)...........................46
4.4.2 Battery for Separate Absolute Pulsecoders (6VDC) ..............................................48
4.4.3 Battery for Absolute Pulse Coder Built into the Motor (6VDC)............................49
5 CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS .............................................50
5.1 CONNECTION BETWEEN THE LCD-MOUNTED TYPE CONTROL UNIT
AND MDI UNIT............................................................................................50
5.1.1 Overview................................................................................................................50
5.1.2 Connection with the MDI Unit...............................................................................51
5.1.3 Key Layout of MDI Unit........................................................................................53
5.1.4 Keyboard Cover .....................................................................................................55
5.2 CONNECTION WITH INPUT/OUTPUT DEVICES ......................................56
5.2.1 Overview................................................................................................................56
5.2.2 Connecting I/O Devices .........................................................................................56
5.2.3 RS232-C Serial Port...............................................................................................57
5.2.4 RS232-C Interface Specification............................................................................59
5.3 CONNECTING THE HIGH-SPEED SKIP (HDI)...........................................66
5.3.1 Connecting the High-speed Skip (HDI).................................................................66
5.3.2 Input Signal Rules for the High-speed Skip (HDI) ................................................67
5.4 LINKING THE ETHERNET INTERFACE.....................................................68
5.4.1 Connection to the Ethernet Interface......................................................................68
5.4.2 Specification of Twisted-Pair Cable.......................................................................70
5.4.3 Network Installation...............................................................................................72
5.4.4 Ethernet Connector Panel.......................................................................................73
5.5 USB PORT ..................................................................................................77
6 SERVO AND SPINDLE INTERFACES.................................................79
6.1 OVERVIEW .................................................................................................79
6.2 Interface to the Amplifiers............................................................................80
6.2.1 Number of Units That Can Be Connected..............................................................81
6.3 SEPARATE DETECTOR INTERFACE........................................................82
6.3.1 Overview................................................................................................................82
6.3.2 Connection Diagram...............................................................................................83
6.3.3 Separate Detector Interface Unit Specification ......................................................84
6.3.4 Connection of Power Supply..................................................................................84
6.3.5 Separate Detector Interface (Digital Input)............................................................86
6.3.5.1 FANUC serial interface..................................................................................... 86
6.3.5.2 Parallel interface................................................................................................ 87
6.3.5.3 Input Signal Requirements (Parallel interface).................................................. 88
6.3.6 Overview of the Analog Basic Unit .......................................................................90
c-2
Page 15

B-64603EN/01 TABLE OF CONTENTS
6.3.7 Connection Diagrams of an Analog Basic Unit .....................................................91
6.3.8 Separate Detector Interface (Analog Input)............................................................93
6.3.8.1 Analog 1Vp-p Interface..................................................................................... 93
6.3.8.2 Input signal requirements (analog 1Vp-p interface)..........................................94
6.3.8.3 Method for checking the encoder signals.......................................................... 95
6.3.9 Connection of Battery for Absolute Position Detector........................................... 96
6.3.10 Connection Between the Basic Unit and Additional Unit......................................98
6.3.11 Connector Locations...............................................................................................98
6.3.12 Installation............................................................................................................100
6.3.13 Notes on Installing a Separate Detector Interface Unit........................................101
7 CONNECTION TO FANUC I/O Link i.................................................103
7.1 OVERVIEW ...............................................................................................103
7.2 CONNECTION...........................................................................................104
7.2.1 Connection of I/O Link i by Electric Cable..........................................................105
7.2.2 Connection of FANUC I/O Link i by Optical Fiber Cable ..................................106
7.2.3 Connection When Multiple Channels of the I/O Link i is Used ..........................108
7.3 ASSIGNMENT FOR I/O UNITS.................................................................112
7.3.1 Assignment of Signals..........................................................................................112
7.3.2 Fixed Signals........................................................................................................112
7.3.3 Status Alarm.........................................................................................................113
7.4 MANUAL PULSE GENERATOR ...............................................................114
7.4.1 Manual Pulse Generator Connection....................................................................114
7.4.2 Cable Length for Manual Pulse Generator...........................................................115
7.4.3 Manual Pulse Generator Signal Specifications ....................................................115
7.5 POWER SUPPLY......................................................................................116
8 UNITS CONNECTED TO FANUC I/O Link i ......................................117
8.1 GENERAL UNITS......................................................................................117
8.2 CONNECTION OF I/O MODULE FOR CONNECTOR PANEL .................121
8.2.1 Configuration .......................................................................................................121
8.2.2 Connection Diagram.............................................................................................122
8.2.3 Module Specifications..........................................................................................123
8.2.4 Connection of the Basic Module, and Extension Modules A and B....................125
8.2.4.1 Connector pin arrangement..............................................................................125
8.2.4.2 DI (Input Signal) Connection ..........................................................................126
8.2.4.3 DO (Output Signal) Connection...................................................................... 128
8.2.4.4 DI/DO Signal Specifications ........................................................................... 129
8.2.5 Connection of Extension Module C (2A Output Module)...................................131
8.2.5.1 Connector pin arrangement..............................................................................131
8.2.5.2 2A Output Signal Connection.......................................................................... 132
8.2.5.3 2A output signal specifications........................................................................ 133
8.2.6 Connection of Extension Module D (Analog Input Module)...............................133
8.2.6.1 Analog Input Connector Pin Allocation ..........................................................133
8.2.6.2 Analog Input Signal Connections....................................................................134
8.2.6.3 Analog Input Signal Specifications .................................................................135
8.2.6.4 Channel selection and A/D conversion data....................................................135
8.2.7 Manual Pulse Generator Connection....................................................................138
8.2.8 Connection of Basic and Extension Modules.......................................................138
8.2.9 Module Installation...............................................................................................139
8.2.10 Other Notes...........................................................................................................144
8.2.11 Rotary Switch Setting...........................................................................................146
8.2.12 Connection of the Grounding Terminal of the Module........................................148
8.2.13 Terminal Conversion Adapter..............................................................................149
c-3
Page 16

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-64603EN/01
8.2.13.1 Connection diagram......................................................................................... 150
8.2.13.2 Component names ........................................................................................... 151
8.2.13.3 External view and dimensions......................................................................... 154
8.2.13.4 Installation .......................................................................................................155
8.2.13.5 Cable connection to the terminal block ........................................................... 156
8.2.13.6 Connection.......................................................................................................158
8.3 CONNECTION OF I/O MODULE FOR OPERATOR'S PANEL (FOR
MATRIX INPUT)........................................................................................163
8.3.1 Overall Connection Diagram................................................................................163
8.3.2 Power Connection ................................................................................................164
8.3.3 DI/DO Connector Pin Arrangement.....................................................................165
8.3.4 DI (General-purpose Input Signal) Connection ...................................................166
8.3.5 DI (Matrix Input Signal) Connection...................................................................168
8.3.6 DO (Output Signal) Connection...........................................................................169
8.3.7 Manual Pulse Generator Connection....................................................................172
8.3.8 External View.......................................................................................................173
8.3.9 Specifications .......................................................................................................174
8.3.10 Other Notes...........................................................................................................176
8.3.11 Connection of the Grounding Terminal of the Module........................................178
8.4 CONNECTION OF I/O MODULE FOR OPERATOR'S PANEL AND I/O
MODULE FOR POWER MAGNETICS CABINET......................................179
8.4.1 Overall Connection Diagram................................................................................179
8.4.2 Power Connection ................................................................................................180
8.4.3 DI/DO Connector Pin Arrangement.....................................................................181
8.4.4 DI (General-purpose Input Signal) Connection ...................................................182
8.4.5 DO (Output Signal) Connection...........................................................................186
8.4.6 Manual Pulse Generator Connection....................................................................187
8.4.7 External View.......................................................................................................188
8.4.8 Specifications .......................................................................................................189
8.4.9 Other Notes...........................................................................................................191
8.4.10 Connection of the Grounding Terminal of the Module........................................193
8.5 CONNECTION OF I/O MODULE TYPE-2 FOR CONNECTOR PANEL....194
8.5.1 Configuration .......................................................................................................194
8.5.2 Connector Layout Diagram..................................................................................195
8.5.3 Connection Diagram.............................................................................................196
8.5.4 Module Specifications..........................................................................................197
8.5.5 DI/DO Connector Pin Assignment.......................................................................198
8.5.6 DI (Input Signal) Connection...............................................................................199
8.5.7 DO (Output Signal) Connection...........................................................................206
8.5.8 DI/DO Signal Specifications................................................................................210
8.5.9 Power Supply Connection....................................................................................211
8.5.10 Manual Pulse Generator Connection....................................................................211
8.5.11 Connection between Modules..............................................................................211
8.5.12 Unit Dimensions...................................................................................................213
8.5.13 Mounting the Module...........................................................................................214
8.5.14 Connector Panel Printed Circuit Board................................................................215
8.5.15 Other Notes...........................................................................................................218
8.5.16 Connection of the Grounding Terminal of the Module........................................220
8.6 CONNECTION OF TERMINAL TYPE I/O MODULE.................................221
8.6.1 Overview..............................................................................................................221
8.6.2 Module Specifications..........................................................................................222
8.6.2.1 Types of modules.............................................................................................222
8.6.2.2 Installation conditions...................................................................................... 223
8.6.2.3 I/O signal specifications .................................................................................. 223
c-4
Page 17

B-64603EN/01 TABLE OF CONTENTS
8.6.2.4 Power supply rating......................................................................................... 226
8.6.2.5 Heat dissipation ............................................................................................... 226
8.6.2.6 Weight ............................................................................................................. 226
8.6.2.7 Applicable wire................................................................................................227
8.6.3 External View and Dimensions............................................................................228
8.6.3.1 Dimensions (common to the modules)............................................................ 228
8.6.3.2 Dimensions in a maximum configuration (one basic module + three
extension modules).......................................................................................... 228
8.6.3.3 Component names ........................................................................................... 229
8.6.4 Installation............................................................................................................232
8.6.5 Connection ...........................................................................................................234
8.6.5.1 Overall connection diagram............................................................................. 234
8.6.5.2 Power connection ............................................................................................ 235
8.6.5.3 Signal assignment on terminal blocks..............................................................236
8.6.5.4 DI/DO connection............................................................................................239
8.6.5.5 Manual pulse generator connection................................................................. 246
8.6.5.6 Inter-module connection..................................................................................246
8.6.5.7 Cable connection to a terminal block .............................................................. 247
8.6.5.8 Detaching a terminal block..............................................................................248
8.6.5.9 Connection of the ground terminal.................................................................. 249
8.6.6 Settings.................................................................................................................250
8.6.6.1 Address map....................................................................................................250
8.6.6.2 Channel selection and A/D conversion data for extension module D.............251
8.6.6.3 Channel selection and D/A conversion data for extension module E.............. 253
DO alarm detection........................................................................................................... 254
8.6.6.4 Setting the rotary switch.................................................................................. 256
8.6.7 Others ...................................................................................................................257
8.6.7.1 Method of common pin expansion..................................................................257
8.6.7.2 Parallel DO (output signal) connection ........................................................... 259
8.7 I/O Link CONNECTION UNIT....................................................................260
8.7.1 Overview..............................................................................................................260
8.7.2 Specification.........................................................................................................261
8.7.3 Installation............................................................................................................263
8.7.4 Connection ...........................................................................................................266
8.7.4.1 I/O Link connection.........................................................................................266
8.7.4.2 Power connection ............................................................................................ 267
8.8 CONNECTION TO MACHINE OPERATOR'S PANEL ..............................268
8.8.1 Overview..............................................................................................................268
8.8.2 Total Connection Diagram...................................................................................271
8.8.3 DI/DO Address Map ............................................................................................274
8.8.4 Each Connections.................................................................................................276
8.8.4.1 Pin assignment.................................................................................................276
8.8.4.2 Power supply connection.................................................................................280
8.8.4.3 I/O Link i connection....................................................................................... 281
8.8.4.4 Using the channel 2 of I/O Link i .................................................................... 281
8.8.4.5 Emergency stop signal connection .................................................................. 284
8.8.4.6 Power ON/OFF control signal connection.......................................................285
8.8.4.7 General-purpose DI signal connection ............................................................ 287
8.8.4.8 General-purpose DO signal connection...........................................................293
8.8.5 Manual Pulse Generator.......................................................................................295
8.8.5.1 Manual pulse generator connection................................................................. 295
8.8.5.2 Pendant type manual pulse generator connection............................................295
8.8.6 Connector (on the cable side) specifications........................................................297
8.8.7 DI/DO Addresses for the Keyboard .....................................................................297
8.8.8 Code Output for the Rotary Switch......................................................................299
8.8.9 Outline..................................................................................................................300
c-5
Page 18

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-64603EN/01
8.8.9.1 Outline of main panel ......................................................................................300
8.8.9.2 Outline of Safety machine operator’s panel.....................................................301
8.8.9.3 Outline of Safety machine operator’s panel type B.........................................302
8.8.9.4 Outline of sub panel AA..................................................................................303
8.8.9.5 Outline of sub panel D.....................................................................................304
8.8.9.6 Connector locations of main panel ..................................................................305
8.8.9.7 Connector locations of safety machine operator’s panel................................. 305
8.8.9.8 Connector locations of safety machine operator’s panel type B......................306
8.8.10 Specifications of the Machine Operator’s Panel..................................................306
8.8.10.1 Installation conditions...................................................................................... 306
8.8.10.2 Order specification...........................................................................................306
8.8.10.3 Main panel specification..................................................................................307
8.8.10.4 Safety machine operator’s panel and safety machine operator’s panel type B
specification.....................................................................................................307
8.8.10.5 Sub panel AA, D specification ........................................................................ 308
8.8.10.6 Power supply specification.............................................................................. 308
8.8.10.7 Heat output ...................................................................................................... 308
8.8.10.8 General-purpose DI signal definition .............................................................. 308
8.8.10.9 General-purpose DO signal definition.............................................................309
8.8.11 Keyboard..............................................................................................................309
8.8.11.1 Meaning of key symbols.................................................................................. 309
8.8.11.2 Detachable key top on the main panel............................................................. 311
8.8.11.3 Keyboard cover................................................................................................311
8.8.12 DO (Output Signal) Error Detection .................................................................... 312
8.9 CONNECTION OF OPERATOR'S PANEL CONNECTION UNIT
(SOURCE DO)...........................................................................................314
8.9.1 Overall Connection Diagram................................................................................314
8.9.2 Power Connection ................................................................................................314
8.9.3 DI/DO Connector Pin Arrangement.....................................................................315
8.9.4 DI (Input Signal) Connection...............................................................................316
8.9.5 DO (Output Signal) Connection...........................................................................323
8.9.6 External View.......................................................................................................327
8.9.7 Specifications .......................................................................................................327
8.9.8 Other Notes...........................................................................................................329
8.10 CONNECTION OF SAFETY IO UNIT........................................................331
8.10.1 Overview..............................................................................................................331
8.10.2 Total connection diagram.....................................................................................331
8.10.3 Power supply connection......................................................................................332
8.10.4 I/O Link i Connection...........................................................................................332
8.10.5 DI/DO Address.....................................................................................................333
8.10.6 Pin assignment of DI/DO.....................................................................................334
8.10.7 DI/DO connection ................................................................................................335
8.10.8 Outline of Safety IO Unit.....................................................................................343
8.10.9 Connector locations of Safety IO Unit.................................................................344
8.10.10 Color labels for connectors of Safety IO Unit......................................................345
8.10.11 Connector specification of Safety IO Unit...........................................................346
8.10.12 Specifications of Safety IO Unit...........................................................................346
8.10.13 DO (Output Signal) Error Detection....................................................................348
8.11 CONNECTION OF I/O MODULE FOR OPERATOR’S PANEL
SUPPORTING SAFETY FUNCTION.........................................................349
8.11.1 Overview..............................................................................................................349
8.11.2 Connection Diagram.............................................................................................349
8.11.3 Power Connection ................................................................................................350
8.11.4 DI/DO Address Map ............................................................................................351
8.11.5 DI/DO Connector Pin Arrangement.....................................................................353
c-6
Page 19

B-64603EN/01 TABLE OF CONTENTS
8.11.6 DI(General-purpose Input Signal)Connection................................................355
8.11.7 DO (Output Signal) Connection...........................................................................358
8.11.8 Manual pulse generator Connection.....................................................................359
8.11.9 External View.......................................................................................................360
8.11.10 Specifications .......................................................................................................361
8.11.11 DO (output signal) Error Detection......................................................................362
8.12 I/O UNIT FOR POWER MAGNETICS CABINET.......................................363
8.12.1 Overall Connection Diagram................................................................................363
8.12.2 Power Connection ................................................................................................364
8.12.3 DI/DO Connector Pin Arrangement.....................................................................365
8.12.4 DI(General-purpose Input Signal)Connection .....................................................366
8.12.5 DO(Output Signal) Connection............................................................................373
8.12.6 Manual Pulse Generator Connection....................................................................377
8.12.7 External View.......................................................................................................377
8.12.8 GND Cable Connection........................................................................................378
8.12.9 Specifications .......................................................................................................379
8.12.10 Other Notes...........................................................................................................381
9 STOP AND EMERGENCY STOP .......................................................383
9.1 STOP MODES...........................................................................................383
9.2 SHUTTING OFF THE MOTOR POWER...................................................383
9.3 STOPPING THE SPINDLE MOTOR .........................................................384
9.4 STOPPING THE SERVO MOTOR............................................................384
9.5 EMERGENCY STOP SIGNAL...................................................................385
9.6 CAUTIONS ABOUT MULTI-PATH CONTROL..........................................389
10 CONNECTION TO OTHER NETWORKS ...........................................390
11 CONNECTION WITH FANUC PANEL i AND COMMERCIAL
PERSONAL COMPUTERS.................................................................391
11.1 OVERVIEW ...............................................................................................391
11.2 CAUTIONS................................................................................................391
11.3 CONNECTION USING THE HIGH-SPEED SERIAL BUS (HSSB)............391
11.3.1 Overview..............................................................................................................391
11.3.2 Connection Diagram.............................................................................................392
11.3.3 Specifications of a Commercial PC......................................................................392
11.3.4 Installation Environment......................................................................................393
11.3.5 Handling Precautions ...........................................................................................393
11.3.6 Procedure for Installing Personal Computer Interface Boards.............................393
11.3.7 Cable Connection .................................................................................................394
11.4 CONNECTION USING Ethernet................................................................395
11.4.1 Overview..............................................................................................................395
11.4.2 Connection Diagram.............................................................................................395
12 PANEL i ..............................................................................................396
APPENDIX
A OUTLINE DRAWINGS OF UNITS AND CONNECTORS...................399
B 20-PIN INTERFACE CONNECTORS AND CABLES.........................432
B.1 BOARD-MOUNTED CONNECTORS........................................................432
c-7
Page 20

TABLE OF CONTENTS B-64603EN/01
B.1.1 Vertical-type Connectors......................................................................................432
B.1.2 Straight and Right-angled Connectors (for Spring and Screw-fixing Connector
Housings) .............................................................................................................432
B.2 CABLE CONNECTORS ............................................................................433
B.2.1 Strand Wire Press-mount Connector....................................................................433
B.2.2 Soldering Type Connector....................................................................................434
B.3 RECOMMENDED CONNECTORS, APPLICABLE HOUSINGS, AND
CABLES ....................................................................................................435
B.3.1 Recommended Connectors...................................................................................436
B.3.2 Applicable Cables.................................................................................................436
C CONNECTION CABLE (SUPPLIED FROM US).................................443
D OPTICAL FIBER CABLE....................................................................446
E MEMORY CARD INTERFACE............................................................456
F HOW TO ATTACH THE KEYBOARD COVER...................................458
c-8
Page 21

B-64603EN/01 1.CONFIGURATION
1 CONFIGURATION
1.1 CONTROL UNIT CONFIGURATION AND COMPONENT
NAMES
The LCD-mounted type is one having both control and indicator sections in it. Each unit has different
composition. Described below is the configuration of type. This manual focuses on how to attach the
connectors shown in the configuration diagrams to device.
1.1.1 Configurations of LCD-mounted Type Control Units
LCD-mounted type control units
Basic
unit
Basic unit
A
Basic unit
G
CAUTION
The touch panel is a device designed to be operated by touching directly its
screen. Touch panel is possible to be operated with the gloves or bare hand. It is
possible to get a better operating feeling when using a FANUC-supplied
exclusive touch panel pen (A02B-0236-K111).
Please be careful not to press too strongly when operating with a finger. There is
a risk that internal circuit of the touch panel fails or the glass cracks.
If you press the screen with the pointed pen or sharp tool like a driver, it may
cause failure or the surface of the display may be scratched. Be sure to keep
away from such improper use.
CAUTION
Do not poke the surface of the display with a sharp tool like a driver, or hit
strongly with a something hard like a grip of driver. It may cause failure or the
surface of the display may be scratched.
Screen
size
8.4"
10.4"
15"
Touch
panel
Without
With
Without
With
Without
With
(horizontal)
(vertical)
(horizontal)
(vertical)
Separate
(horizontal/ver
Separate
(horizontal/
vertical)
MDI
With
With
With
With
tical)
Number of
option slots
Without
2
Without
2
Without
2
Without
2
Without
2
Without
2
Without
2
Without
2
Number of
horizontal soft keys
5+2 without
10+2 (8+1)or Without
10+2 8+1
Number of vertical
soft keys
- 1 -
Page 22
1.CONFIGURATION B-64603EN/01
NOTE
The indicators having a touch panel has a protection sheet attached to its front
surface. Explanations about how to replace the protection sheet, refer to the
FANUC Series 0i-MODEL F Maintenance Manual (B-64605EN).
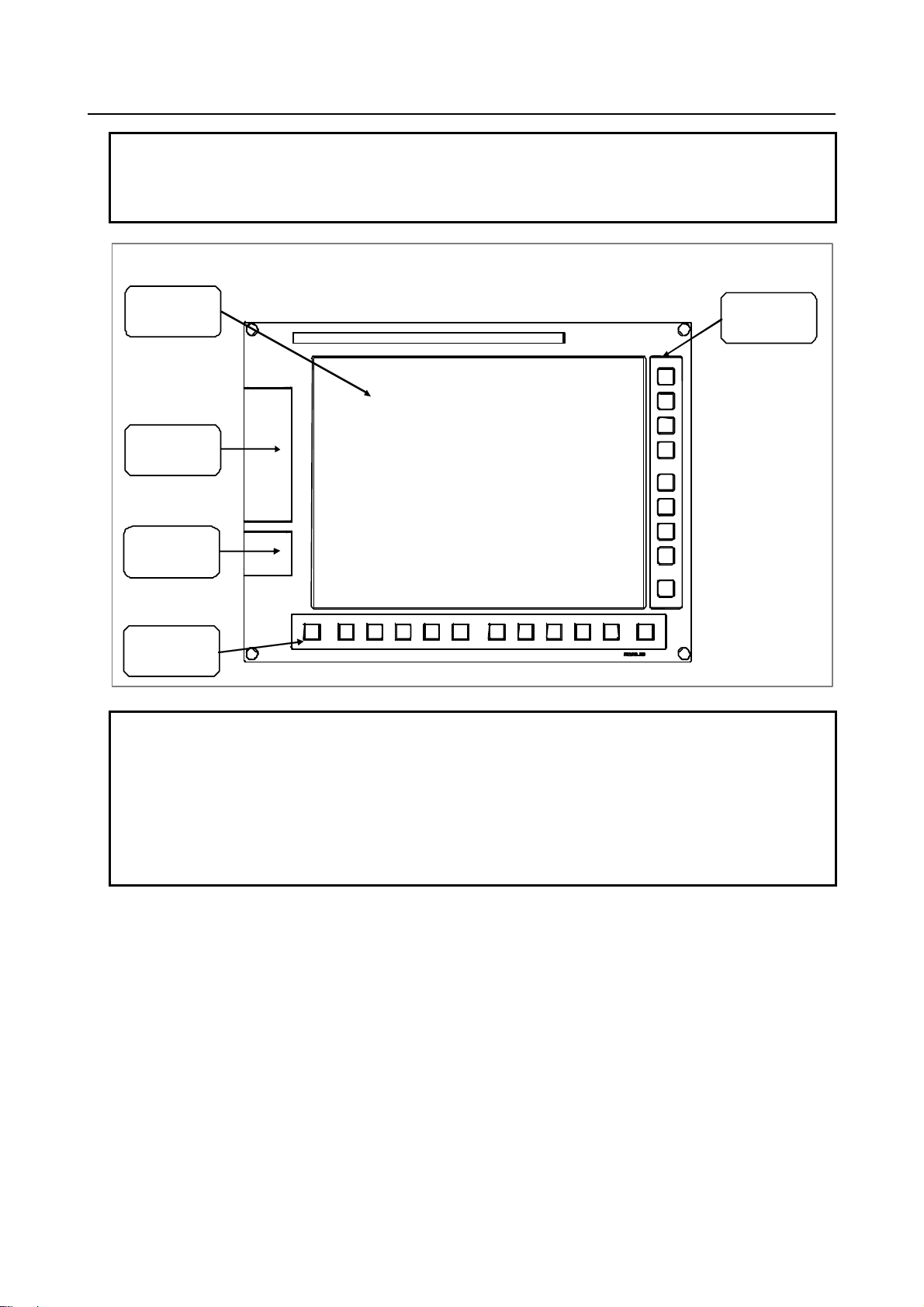
10.4” LC D unit (f ront view)
Liquid-crystal
display
Mem ory card
interface
USB port
Horiz ont a l s oft
keys
Vertical soft
keys
NOTE
1 This figure shows the 10.4” LCD-mounted control unit as viewed from the front.
The basic configuration of the other control unit models is the same, as viewed
from the front.
2 The LCD (liquid-crystal display) has been fabricated using an extreme precision
technology. However, some of their pixels may fail to light or stay constantly
lighting because of their characteristics. Please be forewarned that these
phenomena are not faults.
- 2 -
Page 23
B-64603EN/01 1.CONFIGURATION
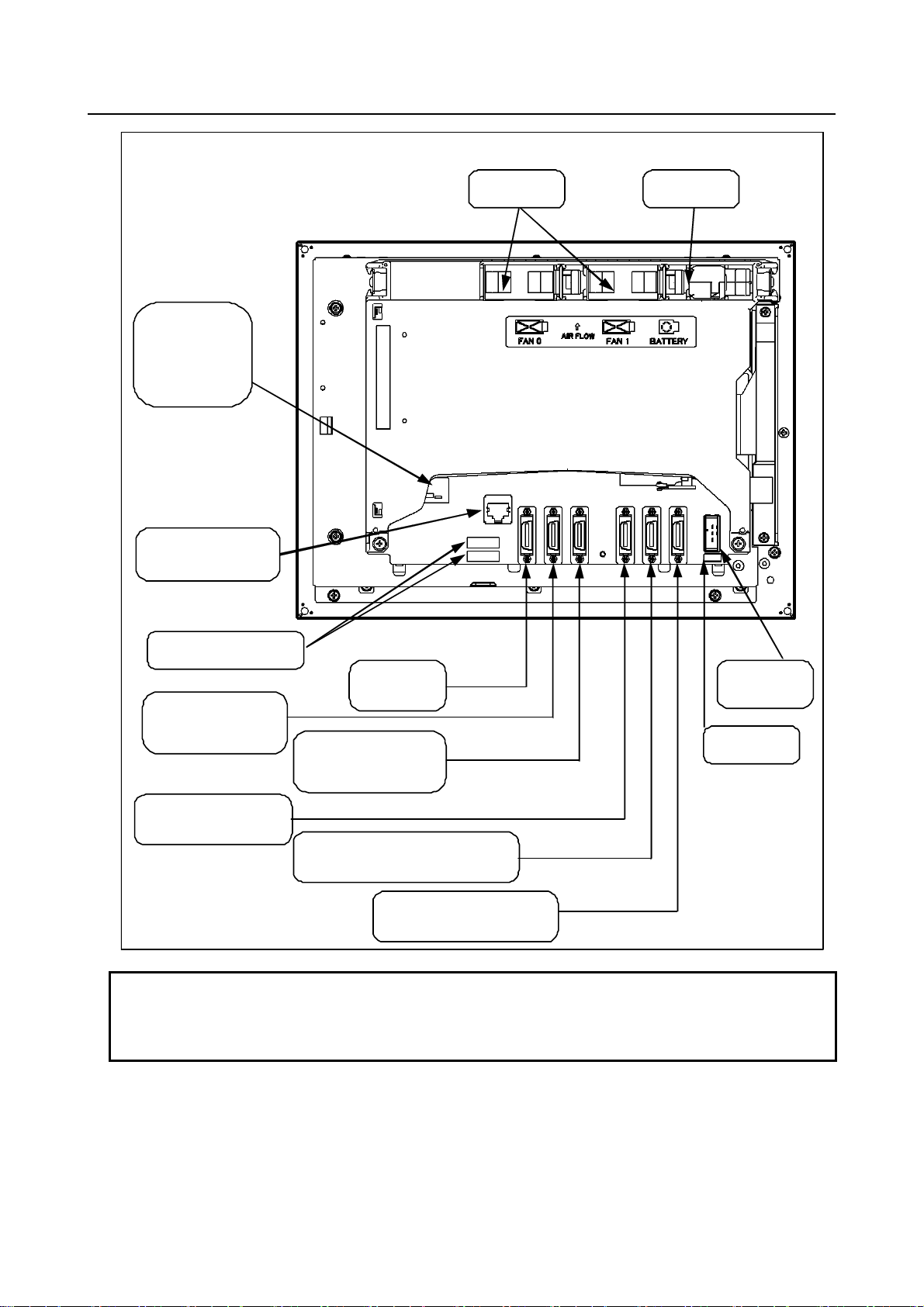
r
Basic unit A (rear view)
FSSB interface
connector
[COP10A]
Etherne t connec t or
(Embedded Ethernet )
[CD38A]
Fan unit
Battery
Soft key connect ors
Power supply
connector
[CP1 ]
Fuse
I/O devic e inter face
connector (RS-232C)
[JD36A]
High-speed skip
connector
[JA40]
MDI c onnect or
[JA2]
I/O dev i ce inte r face
connector (RS-232C)
[JD36B]
I/ O Link i or I/O Link connector
[JD51A]
Posit ion co der connec to
[JA41]
NOTE
1 This figure shows an LCD-mounted control unit having no option slot as viewed
from the rear.
2 The numbers in brackets [] in the figures are connector numbers.
- 3 -
Page 24
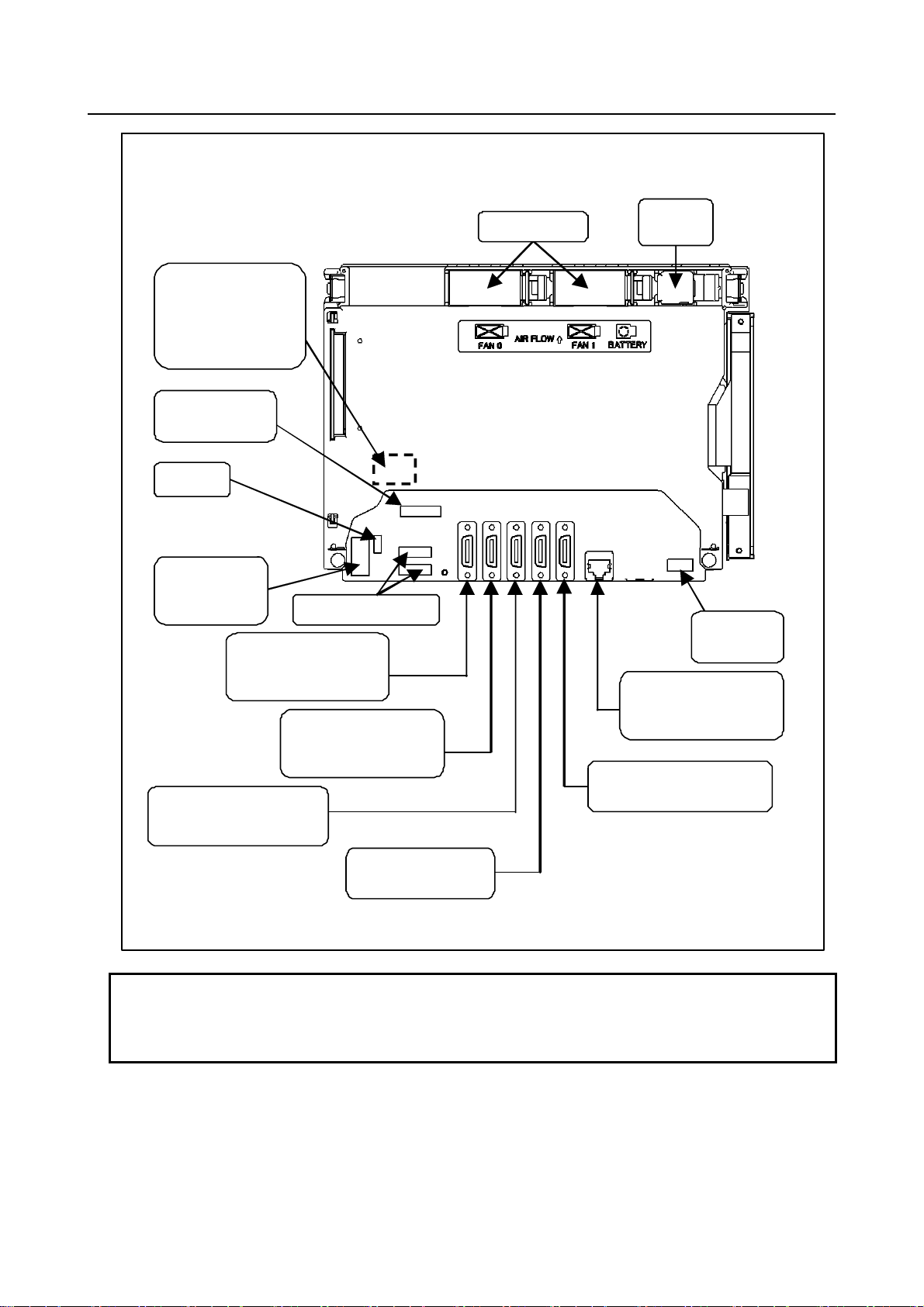
1.CONFIGURATION B-64603EN/01
Basic unit G (rear view)
FSSB interface
connector
[COP10A-1]
MDI connector
[CA55]
Fuse
Power supply
connector
[CPD16A]
I/O devic e interface
connec t or (RS-232C )
[JD56A]
High-s peed s ki p conn ector
[JA40]
Soft key connect ors
I/O device interface
connec t or (R S-232C )
[JD36A]
Fan unit
Battery
USB port
[CD41P]
Ethernet connector
(Embedded Ethernet )
[CD38S]
Po sition c oder connec t or
[JA41]
I/O Link i connector
[JD51A]
NOTE
1 This figure shows an LCD-mounted control unit having no option slot as viewed
from the rear.
2 The numbers in brackets [] in the figures are connector numbers.
- 4 -
Page 25
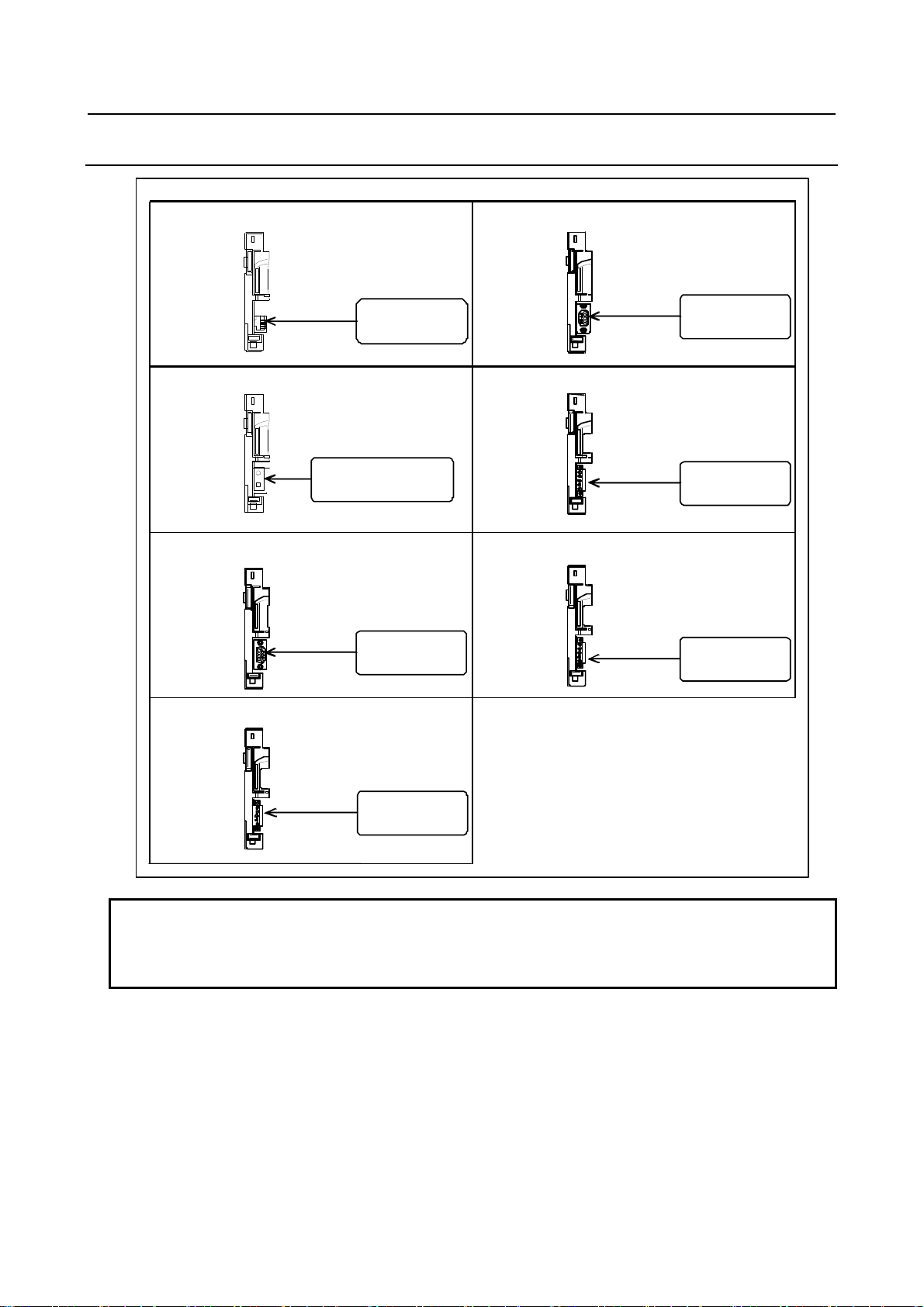
B-64603EN/01 1.CONFIGURATION
1.1.2 Configurations of Optional Boards
F ast Ethe rne t boar d
PROF I B US -DP sl ave b oa rd
HSSB interface board
For HSSB interface
[COP21N]
PROFIBUS-DP master b oard
CC-Li n k remote device stati on boar d
For Ethernet
[CD38R]
For Profibus
[CN1]
For Profibus
[CN2 ]
Devi ceN et master board
For DeviceNet
[TB L]
Devi ceN et sl ave b oa rd
For DeviceNet
[TBL]
For CC-Link
[CT1 ]
NOTE
The numbers in brackets [] in the figures are connector numbers.
The Fast Ethernet board may be used also as data server or FL-net functions,
depending on the settings of parameters.
- 5 -
Page 26
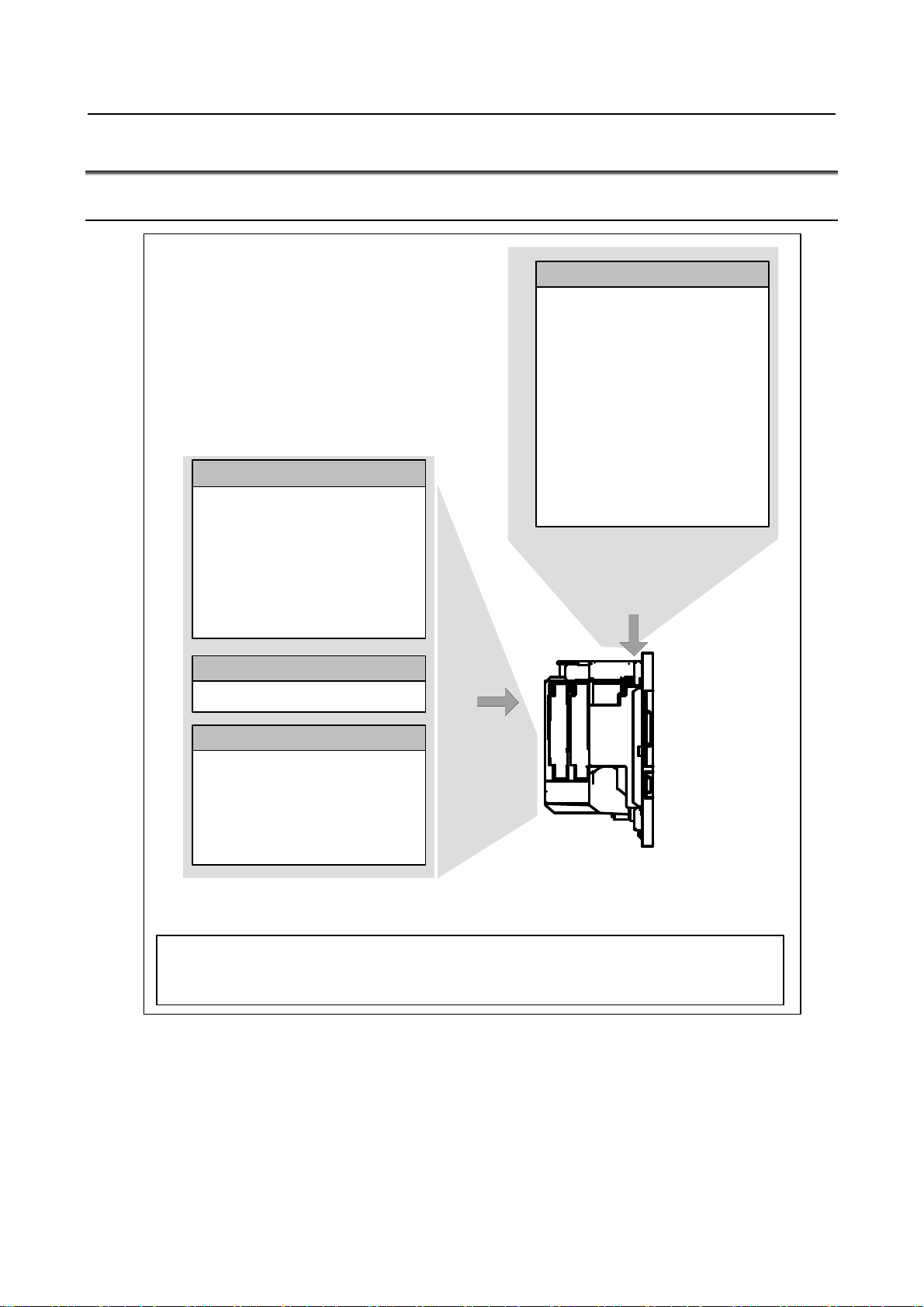
1.CONFIGURATION B-64603EN/01
1.2 HARDWARE OVERVIEW
1.2.1 LCD-mounted Type Control Unit Overview
Main board
- C PU for co ntrollin g CNC
- Power supply
- Ax is contro l functio n
- MDI I/F
- I/O Link i con trol function
- Analog output
- Position coder
- PM C cont rol functi on
- High-speed skip (HDI)
Fast E thernet board
Fas t Ethernet fu nction
Data server function
FL-net function
EtherNet/IP
master/slave function
PROFINET
master/slave function
Modbus/T CP func tion
- RS-232C I/ F
- Me mory card I/F
- USB I/ F
- Ethernet funct ion
B asic system
HSSB interface board
High-speed serial bus interface
Various ty pes of network b oard s
PROFIBUS-DP master board
PROFIBUS-DP s lave board
Devi ceNet maste r board
DeviceNet slave board
CC-Link remote device station boar d
Note
1 On a unit with optional slots , as many optional boards as the slots can be m ounted.
note2
Options
Unit without opti onal slots
or
Unit hav ing two optiona l slots
- 6 -
Page 27
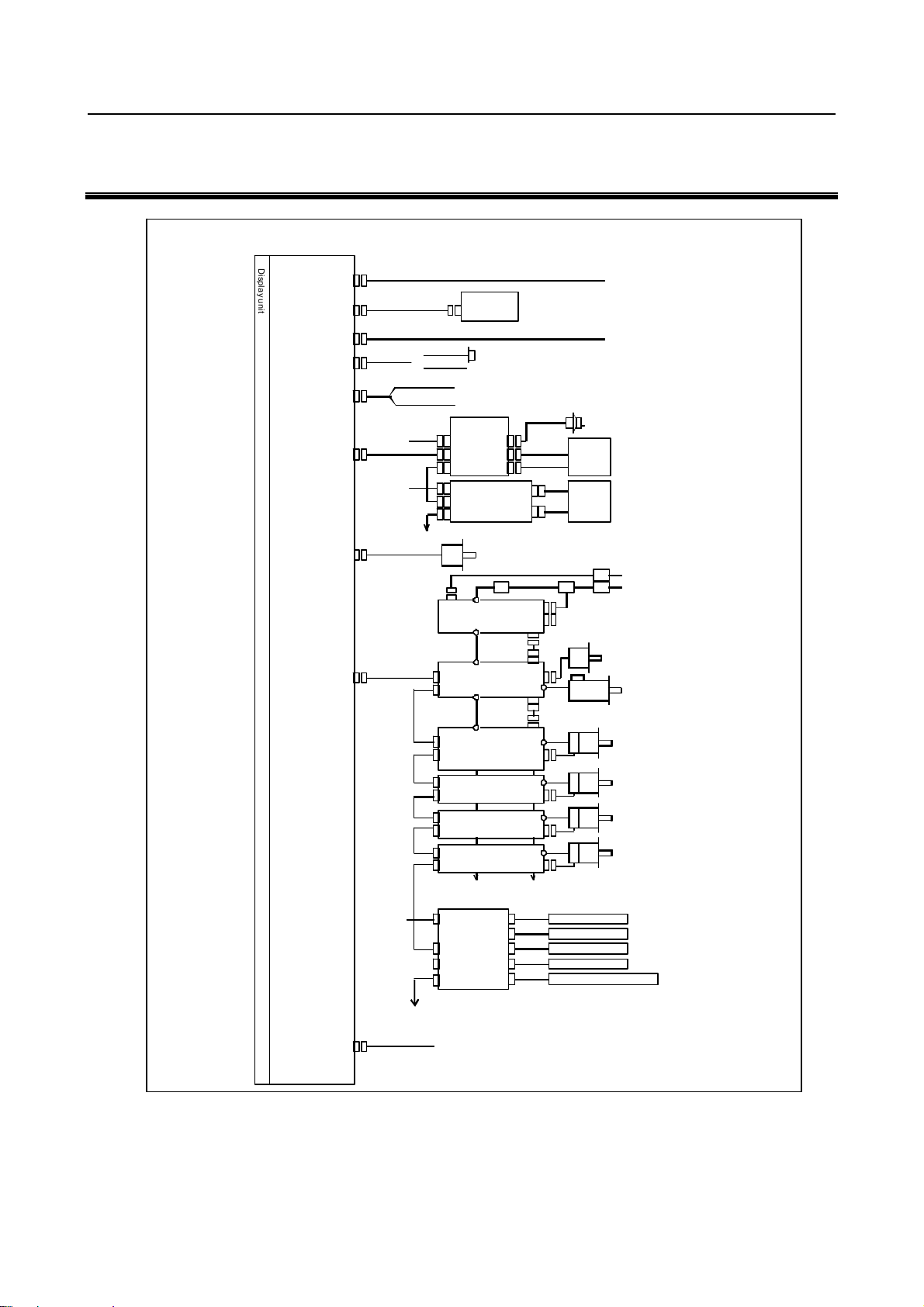
B-64603EN/01 2.TOTAL CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
A
y
A
A
JA4A
scale, axis
p
y
A
2 TOTAL CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
10.4”LCD unit and 8.4”LCD/MDI unit
D
Main board
i
s
24V-IN(CP1)
l
a
u
n
i
t
MDI(JA2)
MDI unit
CK27
24 VDC power supply
R232C-1(JD36A)
R232C-2(JD36B)
A-OUT&HDI(JA40)
I/O Link i
(JD51A)
P0S(JA41)
FSSB(COP10A)
{
DC24V
DC24V
((In this figure, a 1-axisamplifier is used.)
DC24V JF101
RS-232C I/Odevice
To uch panel
nalog output for tool drives
High-speed skip input
Distributed
I/O board
CPD1
A3
D1B
D1A
Distributed
CPD1
I/O board
JD1B
I/O unit, etc
JD1A
Position coder
COP10B
COP10A
COP10B
COP10A
COP10B
COP10A
COP10B
COP10A
Separate detector interface unit 1
CP11A
JF102
COP10B
JF103
JF104
COP10A
CNF1
RS-232C I/O device
Manual pulse generator
Operator's
panel
Power
magnetics
cabinet
Circuit breaker
C reac to r
MCC
αi PS
αi SP
αi SV
αiSV
αi SV
αi SV
Position coder
Serial spindle motor
Linear
Linear scale, axis 2
Linear scale, axis 3
Linear scale, axis 4
bsolute scale batt er
(Required only when an absolute scale is used)
DC24V
Circuit breaker
Servo mo tor
Servo mo tor
Servo mo tor
Servo mo tor
1
C200V
ETHERNET(CD38A)
To separate detector interface unit 2
Ethernet
- 7 -
Page 28
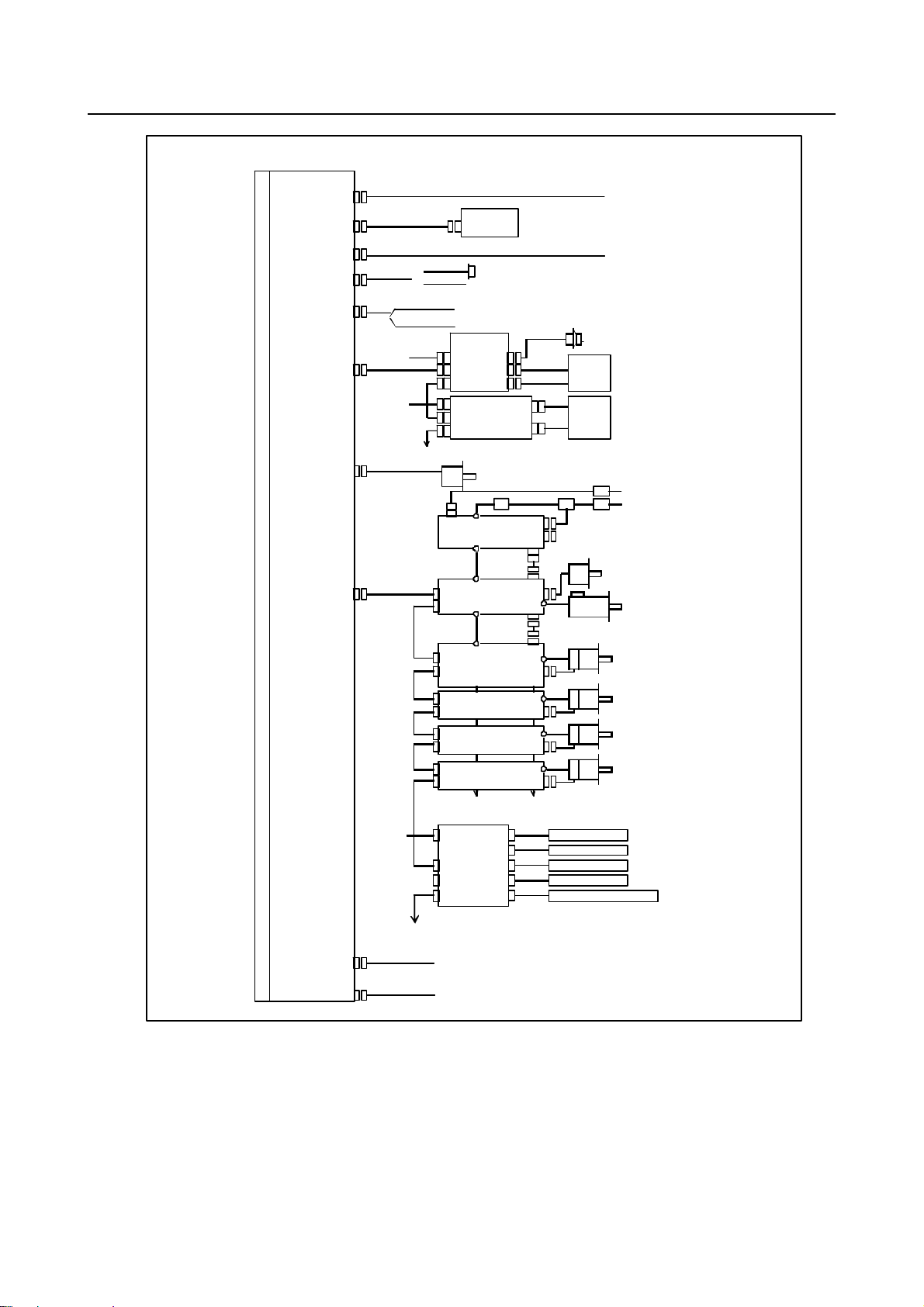
2.TOTAL CONNECTION DIAGRAMS B-64603EN/01
A
A
A
A
ear scale, axis
p
y
A
)
y
15”LCD uni t
Dis
Main board
la
unit
24V-IN(CPD16A
MDI(CA55)
MDI unit
24VDC power supply
R232C-1(JD56A)
R232C-2(JD36A)
A-OUT&HDI(JA40)
(JD51A)
I/O Link i
POS(JA41)
FSSB(COP10A)
RS-232C I/O device
{
DC24V
DC24V
(In this figure, a 1-axisamplifier is used.)
DC24V
RS-232C I/O device
Touch panel
nalog output for tool drives
High-speed skip input
Distributed
I//O board
CPD1
A3
D1B
D1A
Distribute
CPD1
JD1B
JD1A
COP10B
COP10A
COP10B
COP10A
COP10B
COP10A
COP10B
COP10A
Separate detector interface unit 1
CP11A
COP10B
COP10A
CNF1
I/O board
I/O unit, etc
Position coder
C reac to r
αi PS
αi SP
αi SV
αiSV
αi SV
αi SV
JF101
JF102
JF103
JF104
JA4
Lin
Linear scale, axis 2
Linear scale, axis 3
Linear sc al e , axi s 4
(Required only when an absolute scale is used)
Manual pulse generator
Operator’s
panel
Power
magnetics
cabinet
Circuit breaker
MCC
Circuit breaker
Position coder
Serial spindle motor
Servo mo tor
Servo mo tor
Servo mo tor
Servo mo tor
1
bsolute scale batt ery
DC24V
C200V
ETHERNET(CD38S)
USB(CD41P
To separate detector interface unit 2
Ethernet (Embedded Ethernet)
USB memor
- 8 -
Page 29
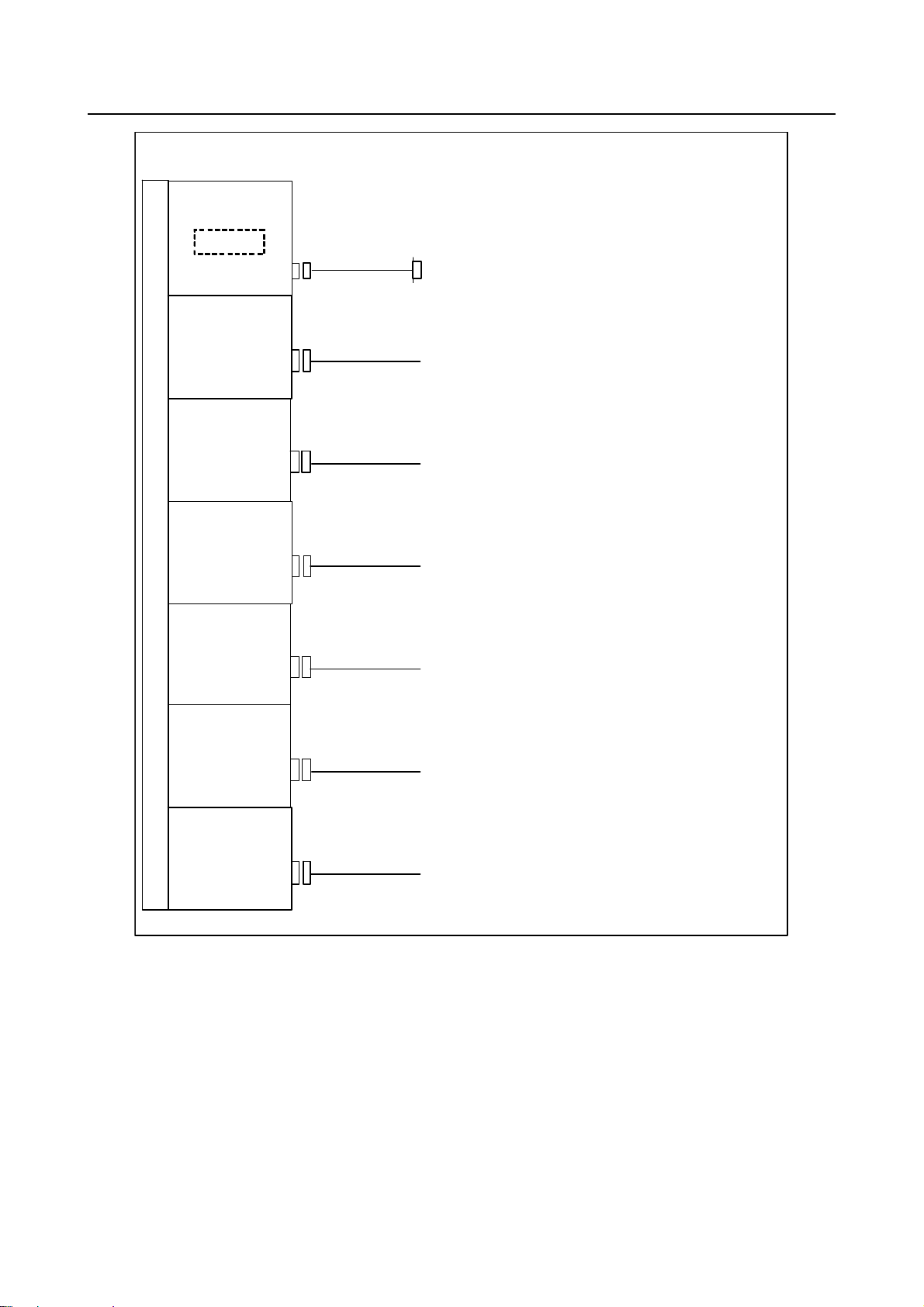
B-64603EN/01 2.TOTAL CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
When optional boards are provided
Optional slot
Fast Ethernet board
Memory c ard
ETHERNET(CD38R)
HSSB interface board
HSSB(COP21A)
PROFIBUS-DP
m aste r boar d
PROFI(CN1)
PROFIBUS-DP
slave board
PROFI(CN2)
DeviceNet
m aste r boar d
DVNET(TBL)
Use a compact flash card purchased from FANUC
E ther net or FL-net ,and so on
PANEL i
or Per sonal Computer
Other cont rol unit
or PROFIBUS device
Other cont rol unit
or PROFIBUS device
Other cont rol unit
or Devi ceNet device
DeviceNet
slave board
DVNET(TBL)
CC-Link remote
device sta tio n board
CCLNK(CT1)
Other cont rol unit
or Devi ceNet device
CC-Lin k devic e
- 9 -
Page 30
3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
3 INSTALLATION
3.1 ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS OUTSIDE THE
CABINET
3.1.1 Environmental Conditions outside the Cabinet
The control unit and the peripheral units have been designed on the assumption that they are housed in
closed cabinets. In this manual "cabinet" refers to the following:
• Cabinet manufactured by the machine tool builder for housing the control unit or peripheral units;
• Operation pendant, manufactured by the machine tool builder, for housing the MDI unit, or
operator's panel.
• Equivalent to the above.
The following table lists the environmental conditions required in installing these cabinets. Section 3.3 of
this connection manual explains the design conditions regarding installation of cabinets that will meet the
environmental conditions.
Ambient
temperature of
the cabinet
Humidity
Vibration
Meters above
sea level
Environment
Operating 0°C to 45°C
Nonoperating (including storage
and transportation)
Temperature change 0.3°C/minute or less
Normal 75%RH or less, no condensation
Short period (less than 1 month) 95%RH or less, no condensation
Operating 4.9m/s2 (0.5G) or less
Nonoperating (including storage
and transportation)
Operating Up to 1000 m
Nonoperating (including storage
and transportation)
Normal machine shop environment
(The environment must be considered if the cabinets are in a
location where the density of dust, coolant, organic solvent,
and/or corrosive gas is relatively high.)
-20°C to 60°C
2
9.8m/s
(1.0G) or less
(see Note 1 in the Subsec. 3.1.2.)
Up to 12000 m
3.1.2 Installation Conditions of the Control Unit
Condition LCD-mounted type control unit and display unit
Operating 0°C to 58°C
Ambient
temperature
Humidity
Nonoperating (including storage
and transportation)
Temperature change 0.3°C/minute or less
Normal 75%RH or less, no condensation
Short period (less than 1 month) 95%RH or less, no condensation
- 10 -
-20°C to 60°C
Page 31

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
Condition LCD-mounted type control unit and display unit
4.9m/s2 (0.5G) or less
FANUC’s evaluation test was conducted under the following
conditions complying with IEC 60068-2-6.
10 to 58Hz: 0.075mm (amplitude)
58 to 500Hz: 9.8m/s
Direction of vibration: Each of the X, Y, and Z directions
Number of sweep cycles: 10
Coolant, lubricant, or cutting chips shall not be sprinkled
directly over the CNC or servo unit. No corrosive gas shall be
allowed.
2
(1.0G)
2
9.8m/s
(1.0G) or less
Up to 12000m
(Note 1)
Vibration
Meters above
sea level
Environment
Operating
Nonoperating (including storage
and transportation)
Operating Up to 1000m
Nonoperating (including storage
and transportation)
NOTE
1 If the control unit is installed 1000 m or higher above sea level, the allowable
upper ambient temperature of the control unit in the cabinet is changed as
follows. Assume that the allowable upper ambient temperature of the control unit
in the cabinet installed 1000 m or higher above sea level decreases by 1.0°C for
every 100 m rise in altitude.
Example)
When a control unit whose required operating ambient temperature range is
0°C to 55°C is installed 1750 m above sea level:
55°C-(1750m-1000m)/100m × 1.0°C = 47.5°C
Therefore, the allowable ambient temperature range is from 0°C to 47.5°C.
2 When using a unit having additional installation conditions, be sure to meet also
these conditions.
3.2 CAUTIONS REGARDING THE INSTALLATION DESIGN OF
MACHINE TOOL POWER MAGNETICS CABINETS
When a cabinet is designed, it must satisfy the environmental conditions described in Section 3.1. In
addition, the magnetic interference on the screen, noise resistance, and maintenance requirements must be
considered. When mounting FANUC-supplied units, such as displays and operator’s panels, use packing
and fasten the mounting screws with the specified tightening torque. When designing magnetics cabinets,
pay due consideration to each item stated in the following “CAUTION”.
CAUTION
1 The cabinet must be fully closed. The cabinet must be designed to prevent the
entry of airborne dust, coolant, and organic solvent.
2 The cabinet must be designed so that the permissible temperature of each unit
is not exceeded. (See Section 3.3.)
3 A closed cabinet must be equipped with a fan to circulate the air within. (This is
not necessary for a unit with fan.) The fan must be adjusted so that the air
moves at 0.5 m/sec along the surface of each installed unit.
However, do not blow air from the fan directly to the unit, because doing so can
readily make dust attach the portion where the air flow hits, leading to possible
trouble. (This is not necessary for a unit with fan.)
- 11 -
Page 32

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
CAUTION
4 For the air to move easily, a clearance of 100 mm is required between each unit
and the wall of the cabinet.
5 Each FANUC-supplied unit, such as a display or operator’s panel, has been
designed on the assumption that they will be mounted using packing and with
the specified screw tightening torque. Failing to mount them as specified can
lead to unit damage and/or malfunction. Be sure to use packing and observe the
specified screw tightening torque. (See Sections 3.6 and 3.7.)
6 Failing to use packing or to provide complete sealing, or using any packing not
resistant to coolant in use will allow dust, coolant, and organic solvent to get in
the cabinet, leading to possible equipment trouble. Be sure to use an appropriate
packing and a secure sealing.
In addition, use an appropriate packing and a secure sealing for the cable outlets
and doors of the machine builder-provided units, such as displays, operator’s
panels, and cabinet pendant boxes. (See Section 3.7.)
7 The LCD must not be installed in such a place that coolant would directly fall
onto the unit. Be sure to attach a protection cover to the LCD if it will be used in
an environment where it is anticipated that coolant may come into contact with it,
for example, an environment with a relatively dense oil mist.
8 Noise must be minimized. As the machine and the control unit are reduced in
size, the parts that generate noise may be placed near noise-sensitive parts in
the magnetics cabinet.
The control unit is built to protect it from external noise. Cabinet design to
minimize noise generation and to prevent it from being transmitted to the control
unit is necessary. (See Section 3.4.)
9 When placing units in the cabinet, also consider ease of maintenance. The units
should be placed so that they can be checked and replaced easily when
maintenance is performed.
10 The hard disk drive and floppy disk drive must not be installed near the source of
a strong magnetic field.
11 The installation conditions of the I/O unit and connector panel I/O module must
be satisfied. In order to secure ventilation in the equipment, mount the I/O unit
and connector panel I/O module in the specified orientation. Clearances of 100
mm or more both above and below the I/O unit are required for wiring and
ventilation.
Equipment radiating too much heat must not be put below the I/O unit and
connector panel I/O module.
Top
I/O base unit
(No screws or protrusions shall extend from the
bottom of this unit.)
Bottom
- 12 -
Page 33

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
CAUTION
By a machine tool of a machine door adjacent to operator's panel, large shock
will be applied to the operator's panel every time of opening or closing the door.
CNC control unit and I/O unit on the operator's panel are deteriorated by
repeated large shock for a prolonged period every time opening and closing of
the door. So, attach a packing rubber or damper on the door to prevent damage
by direct large shock. Use the rubber for measures of the door and high
tolerance to a cutting fluid. Also, use the rubber even if repetition shock is
applied, form does not change and vibration absorption effect does not
deteriorate. When the rubber deteriorates, describe exchange method of the
rubber, make the structure which can be exchanged by an end user.
Describe the exchange method to manual of a machine tool.
Operator’s panel
Machine
door
A machine tool of the door and the operator’s panel are contiguous,
please attach the rubber or a damper for the measures of shock when
opening and closing the door.
- 13 -
Page 34

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
3.3 THERMAL DESIGN OF THE MACHINE TOOL MAGNETIC
CABINET
The internal air temperature of the cabinet increases when the units and parts installed in the cabinet
generate heat. Since the generated heat is radiated from the surface of the cabinet, the temperature of the
air in the cabinet and the outside air balance at certain heat levels. If the amount of heat generated is
constant, the larger the surface area of the cabinet, the less the internal temperature rises. The thermal
design of the cabinet refers to calculating the heat generated in the cabinet, evaluating the surface area of
the cabinet, and enlarging that surface area by installing heat exchangers in the cabinet, if necessary.
Such a design method is described in the following subsections.
3.3.1 Temperature Rise within the Machine Tool Magnetic Cabinet
The cooling capacity of a cabinet made of sheet metal is generally 6 W/°C per 1m2 surface area, that is,
when the 6W heat source is contained in a cabinet having a surface area of 1 m
2
, the temperature of the air
in the cabinet rises by 1°C. In this case the surface area of the cabinet refers to the area useful in cooling,
that is, the area obtained by subtracting the area of the cabinet touching the floor from the total surface
area of the cabinet. There are two preconditions : The air in the cabinet must be circuited by the fun, and
the temperature of the air in the cabinet must be almost constant. For example, the operator’s panel
cabinet may contain an LCD-mounted type control unit. To keep the temperature in the cabinet at 58°C or
below when the ambient temperature is 45°C, the equation below must be satisfied.
Internal heat loss P [W] ≤
2
6[W/m
⋅°C] × surface area S[m2] × 13[°C] of rise in temperature
(A cooling capacity of 6 W/°C assumes the cabinet is so large that agitation with the fan motor does not
make the temperature distribution uniform. For a small cabinet like the operator's panel, a cooling
capacity of 8 W/°C, indicated in Subsection 3.3.3, may be used.)
2
For example, a cabinet having a surface area of 4m
has a cooling capacity of 24W/°C. To limit the
internal temperature increase to 13°C under these conditions, the internal heat must not exceed 312W. If
the actual internal heat is 360W, however, the temperature in the cabinet rises by 15°C. When this
happens, the cooling capacity of the cabinet must be improved using the heat exchanger.
3.3.2 Heat Output of Each Unit
Table 3.3.2 Heat output
Unit Heat output Remarks
LCD-mounted type
control unit
15”LCD unit
Optional board
MDI units 0W
Fast Ethernet board
(when used as data server functions)
HSSB interface board 4W
PROFIBUS-DP master board 5W
PROFIBUS-DP slave board 2W
DeviceNet master board 3W
DeviceNet slave board 3.5W
CC-Link remote device station board 3W
Option 0 slot 8.4”LCD unit
Option 2 slots
Option 0 slot 10.4”LCD unit
Option 2 slots
Option 0 slot
Option 2 slots
32W Note 1)
32W Note 1)
37W Note 1)
3W
(3.3W)
- 14 -
Page 35

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
NOTE
1 The values listed above do not include any heat output of the option boards. To
obtain the total heat output of the control unit, add the heat output from the any
option boards.
2 See Chapter 6 for the heat output of the separate detector interface unit.
3 See Chapter 8 for the heat output of each I/O unit.
4 Refer to the PANEL i Connection and Maintenance Manual (B-64223EN) for the
heat output of the PANEL i.
3.3.3 Thermal Design of Operator's Panel
With a small cabinet like the operator's panel, the heat dissipating capacity of the cabinet is as shown
below, assuming that there is sufficient mixing of the air inside the cabinet.
Coated metal surfaces: 8 W/m
Plastic surfaces: 3.7 W/m
An example of the thermal design for the cabinet shown in Fig. 3.3.3 is shown below.
2
°C
2
°C
Fig. 3.3.3
Assume the following.
Thermal exchange rates
2
Coated metal surfaces : 8 W/m
Plastic surfaces : 3.7 W/m
⋅°C
2
⋅°C
Allowable temperature rise : 13°C higher than the exterior temperature
Also, assume the following.
Dimensions of pendant type cabinet shown in Fig. 3.3.3: 560(W) × 470(H) × 150(D) mm
- 15 -
Page 36

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
Surface area of metallic sections : 0.5722 m2
Surface area of plastic sections : 0.2632 m
2
In this case, the allowable total heat dissipation for the cabinet is:
8 × 0.5722 × 13 + 3.7 × 0.2632 × 13 = 72 W.
In consequence, it can be concluded that the units shown in Table 3.3.3 on the next page can be installed
in this cabinet.
Table 3.3.3
LCD-mounted type control unit (with 10.4”LCD unit) 32W
Standard machine operator's panel 15W
120-mm square fan motor for air mixing 8W
Total heat dissipation of the above
55W
(Note)
NOTE
The 15 W quoted for the standard machine operator's panel represents an
example heat output value when half of all the input signals are turned on. This
value varies, depending on the mechanical configuration.
3.4 COUNTERMEASURES AGAINST NOISE AND
GROUNDING
In general, noise can occur because of electrostatic coupling, electromagnetic induction, and ground loop
and get in a control unit.
On the control unit side, due consideration is paid to a protective measure for external noise. However, it
is hard to measure the magnitude and frequency of noise quantitatively and there are lots of uncertainties
with noise. So, it is important to take measures for minimizing noise occurrence and keeping any noise
from entering the control unit in order to enhance stability in CNC-based machine tool system operation.
Grounding the power magnetics cabinet and devices is very important to prevent an electric shock and
suppress a noise influence. The CNC system uses the following three types of grounding:
(1) Signal grounding
This type of grounding is used to supply a reference potential (0 V) for the electrical signal system.
(2) Frame grounding
This type of grounding is used for safety reasons as well as to suppress external and internal noise.
For example, grounding is provided for the device frames, panels, and shielding on the interface
cables connecting the devices.
(3) System grounding (PE)
This type of grounding is used to connect frame grounds, which are provided for the individual
devices or between the units, to the ground as a system at a single point.
When designing the power magnetics cabinet, guard against noise in the machine as described in the
following section.
- 16 -
Page 37

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
α
α
α
(
)
3.4.1 Grounding as Noise Suppression Measures
3.4.1.1 Grounding methods
Typically, noise that becomes a problem is high–frequency noise. To suppress high–frequency noise, it is
important that the devices are grounded at low impedance
(NOTE)
.
The grounding schemes for this purpose are described below.
NOTE
Impedance includes a resistance component that converts electric current to
heat as well as a component called “reactance”, and indicates a characteristic of
resistance to the flow of alternating current at a certain frequency.
(1) Multipoint grounding scheme
In this grounding scheme, when grounded at sufficiently low impedance, the cabinet metal plates are used
as ground plates, to which grounding is provided in the vicinity of each device.
This scheme has a great effect of suppressing high–frequency noise because it enables grounding to the
low–impedance metal plates of the cabinet in the shortest distance. However, the noise suppression effect
depends on the cabinet structure because the cabinet metal plates are used as ground plates.
See Subsection 3.4.1.2 for the cabinet. Fig. 3.4.1.1 (a) is a schematic wiring diagram.
i
Cabinet
PS
i
SV
Ground bar for
shield clamp
JF*
i
SP
(Lower-impedance metal plates)
(Lower-impedance metal plates)
Pendant box
Control unit
Connect the unit
to a metal plate
close to it.
However, keep
signal grounding
points at least
10 cm away
from power wire
grounding
points.
PE terminal (for connecting external
protective conductor)
Do not coat mating surfaces.
Grounding electrode or main
grounding terminal
24 V output power
AC input
Connection at
low impedance
Signal line
Power line
Separate the signal line
and power line when
routing them.
Frame grounding
System grounding (PE)
Machine
operator’s panel
Machine side
Motor
Fig. 3.4.1.1 (a) Schematic diagram for multipoint grounding scheme
When the multipoint grounding scheme is adopted, the units can be grounded at low impedance, and
ground wires (wires from the unit’s ground terminal to a grounding plate) can be shortened, so that wiring
may be simplified. So, FANUC recommends the multipoint grounding scheme.
- 17 -
Page 38

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
α
α
A
α
CAUTION
If it is impossible to configure cabinet metal plates with a low impedance, it is
likely that noise may effect grounding circuits shared by power wires and signal
wires.
(2) Single–point grounding scheme
In this grounding scheme, grounding separation is achieved between the signal system and power system,
and grounding is provided at a single point to suppress the noise influence of the power system on the
signal system.
This scheme tends to need longer connection wires for grounding the devices. To produce a sufficient
effect of suppressing high–frequency noise, it is therefore necessary to use larger–diameter wires or use
two or more wires for each connection. Fig. 3.4.1.1 (b) is a schematic wiring diagram.
chieve grounding
separation between
the signal system
and power system.
Grounding electrode or
main grounding terminal
Cabinet
i
PS
i
i
SP
SV
JF*
Power system ground
bar
24 V output power
AC input
Signal system
ground bar
PE terminal (for connecting
external protective conductor)
Ground bar for
shield clamp
Signal system ground bar
Signal line
Power line
Separate the signal line
and power line when
routing them.
Frame grounding
System grounding (PE)
Pendant box
Control unit
operator’s panel
Machine
Machine side
Motor
Fig. 3.4.1.1 (b) Schematic diagram for multipoint grounding scheme
3.4.1.2 Cabinet
A cabinet is an important element in improving noise immunity and suppressing radiated noise. One of
the causes of problems related to noise immunity and radiated noise is faulty electrical continuity between
the metal plates that make up the cabinet. Typically, noise that becomes a problem is high–frequency
noise, against which measures must be taken in the cabinet design.
- 18 -
Page 39

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
(1) Basic cabinet structure
A cabinet should basically be made of metal.
To improve noise immunity, there must be low–impedance electrical continuity between the metal plates
that make up the cabinet, which are the side plates, top plate, and bottom plate, and a welding–type
cabinet structure is recommended.
As for a cabinet welding method, bead welding is more suitable than spot welding for providing
low–impedance electrical continuity between the metal plates.
For an assembly–type cabinet structure, provide electrical continuity by bringing the metal plates into
direct contact with each other, without applying a coating to their joint surface areas.
In a structure that has the metal plates connected only with wires because of structural constraints,
low–impedance connections are more difficult to make than in a structure in which welding is made or
the metal plates are brought into direct contact with each other. It is necessary to maintain sufficient
levels of items such as the cross–sectional area of a wire to use, continuity of connections, and contact
areas.
Bead welding
Fig. 3.4.1.2 (a) Cabinet structure
Bring the metal plates into direct contact with each
other, without applying a coating to their joint areas.
NOTE
Explained above is how to provide cabinets with low-impedance electrical
continuity so as to increase noise immunity and to suppress noise radiation. See
Subsection 3.4.2 for conditions required to configure protective grounding
circuits.
(2) Mounting units on the cabinet
The shortest possible lengths of unit ground wires (wires from the unit’s ground terminal to a grounding
plate) should be used to make connections. A ground wire with a small conductor diameter causes
impedance to high-frequency noise to become particularly higher, leading to an insufficient grounding
effect. For the location of the ground terminal of each unit, refer to the manual relevant to the unit. The
following shows the recommended method by which the metal plate with the unit mounted is installed on
the cabinet. Care should be taken so that the cabinet and metal plate are connected to each other on their
broad areas with no coating. It is not recommended that electrical continuity be provided only by screws,
because impedance to high frequency cannot be sufficiently low.
- 19 -
Page 40

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
<Good example>
Coating
mask
Coating
Metal plate
Cabinet
Screw
Shortest connection
with thick ground wire
Cabinet
Metal
plate
Unit
Continuity on areas
with no coating
<Bad example>
Cabinet
Metal
plate
Unit
Continuity only by screw
in a coated area
Fig. 3.4.1.2 (b) Installing a unit in a cabinet
Thin ground wire, long
ground wire
- 20 -
Page 41

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
3.4.2 Protective Ground (Grounding for Protection against Indirect
Contact)
Protection against indirect contract is intended to prevent the risk that may occur in a conductive portion
which is not charged with electricity (applied with voltage) during normal operation but may be charged
with electricity if insulation is accidentally destroyed. It must be implemented by:
- measures to prevent the occurrence of a touch voltage, or
- automatic disconnection of the supply before the time of contact with a touch voltage can become
hazardous
As for protective grounding in “automatic disconnection of the supply before the time of contact with a
touch voltage can become hazardous”, follow any standards the machine tool is supposed to meet. Some
standard examples follow:
Regarding protective grounding
IEC 60364-4-41:2005 and JIS C 60364-4-41:2010 (Low-voltage electrical installations - Part 4-41:
Protection for safety - Protection against electric shock) 411
Regarding the minimum cross-sectional area of protective conductors
IEC 60204-1:2005/A1:2008 and JIS B 9960-1:2008/A1:2011 (Safety of Machinery – Electrical
Equipment of Machines – Part 1: General Requirements) 8.2.2
NFPA 79:2012 (Electrical Standard for Industrial Machinery) 8.2.2 Equipment Grounding
(Protective) Conductors and Bonding Jumpers
NFPA 79:2012 (Electrical Standard for Industrial Machinery) 18.2 Continuity of the Equipment
Grounding (Protective Bonding) Circuit
Regarding the cross-sectional area of a protective conductor shared by multiple circuits
IEC 60364-5-54:2011 and JIS C 60364-5-54:2006 (Electrical installations of buildings – Part 5-54:
Selection and erection of electrical equipment – Earthing arrangements, protective conductors and
protective bonding conductors) 543.1.4
Regarding use of enclosures (cabinets) or frames as protective conductors
IEC 60204-1:2005/A1:2008 and JIS B 9960-1:2008/A1:2011 (Safety of Machinery – Electrical
Equipment of Machines – Part 1: General Requirements) 8.2.3
IEC 60364-5-54:2011 and JIS C 60364-5-54:2006 (Electrical installations of buildings – Part 5-54:
Selection and erection of electrical equipment – Earthing arrangements, protective conductors and
protective bonding conductors) 543.2.2, 543.2.3;
NFPA 79:2012 (Electrical Standard for Industrial Machinery) 12.2.1 Conductor Material
- 21 -
Page 42

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
0
3.4.3 Connecting the Ground Terminal of the Control Unit
Continuity between the control unit’s and a 0 V terminals
CAUTION
In each control unit, the 0 V and ground terminals are electrically connected to
each other. So, do not connect any external unit’s 0 V connected to the control
unit’s 0 V to any other line’s grounding electrode that can have an electrical
potential different from that of the grounding electrode connected to the control
unit.
Machine
Control unit
Control
signal
0V
I/O module
DOCOM
Out put
signal
V
Machine-side main grou nd term inal (m ain g roun d bu s)
Power mag netics cabinet
+24V
24 VDC
output
power
Relay
0V
Other ground terminal
Grounding electrode
Fig. 3.4.3 (a) Undesired example of using other ground terminal
Other grounding electrode
- 22 -
Page 43

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
Connecting the ground terminal of an LCD-mounted type control unit
Connect the 0 V line in the control unit to the cabinet’s metal plate or signal system ground bar nearby via
the protective ground terminal (see below).
Signal syst em ground bar
Rear view
Single-point gr ounding
Protec tive
ground terminal
(M4 stu d)
Electric wire
(2 mm
thicker)
Protec tive ground
tap o n cabinet’s
metal plate
Multiple-point gr ounding
2
Side view
or
Fig. 3.4.3 (b) Ground terminal connection
3.4.4 Separating Signal Lines
The cables used for the CNC machine tool are classified as listed in the following table. Process the
cables in each group as described in the action column.
Table 3.4.4 Cable grouping
Group Signal line Action
A
Primary AC power line
Secondary AC power line
AC/DC power lines (containing the power lines
for the servo and spindle motors)
AC/DC solenoid
Bind the cables in group A separately
groups B and C, or cover group A with an
electromagnetic shield
(Note 2)
.
See Subsection 3.4.5 and connect spark killers or
diodes with the solenoid and relay.
AC/DC relay
- 23 -
(Note 1)
from
Page 44

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
A
Group Signal line Action
B
DC solenoid (24 VDC)
DC relay (24 VDC)
DI/DO cable between the I/O unit and power
magnetics cabinet
DI/DO cable between the I/O unit and machine
24 VDC input power cables connected to the
Connect diodes with the DC solenoid and relay.
Bind the cables in group B separately from group A,
or cover group B with an electromagnetic shield.
Separate group B as far from group C as possible.
It is desirable to apply shield processing described
in Subsection 3.4.6.
control unit and its peripherals
C
I/O Link i cable
Cable for the position coder
Cable for the manual pulse generator
Cable for the MDI
(Note 3)
RS–232C interface cable
Bind the cables in group C separately from group A,
or cover group C with an electromagnetic shield.
Separate group C as far from group B as possible.
Be sure to perform shield processing as described in
Subsection 3.4.6.
Cable for the battery
Cable for the Ethernet
Other cables for which shield processing is
specified
NOTE
1 Binding the cables in one group separately from another means that the groups
are placed 10 cm or more apart from one another.
2 Covering a group with an electromagnetic shield means that shielding is
provided between groups with grounded steel plates.
3 The shield is not required when the cable for the MDI is no more than 50 cm in
length.
Cabinet
Pendant box
To motor
and the like
24VDC
power
supply
Spindle
amp lifier
Servo
amp lifier
I/O
Unit
Cable of group A Cable of group B, C
Fig. 3.4.4 Cable layout example
Section of duct
Group A
Duct
Sh ielding
plate
Group B, C
Shielding plate
Control
unit
Unit
receiv ing
C
voltage
- 24 -
Page 45

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
3
3.4.5 Noise Suppressor
Actuators, such as solenoids and relays, used in power magnetics cabinets need a noise suppressor.
Because an actuator, which converts electrical energy to mechanical action, is an inductive load, it
resonates with the parasitic capacitance in a circuit containing it, when it works on and off, thus
generating intermittent arcs accompanied by abrupt voltage rises and falls at its contacts, hence
electromagnetic waves interfering with electronics circuits. As a remediation measure, treat the inductive
load as described below.
1) While referencing the processing for cable groups A and B described in Subsection 3.4.4,
“Separating Signal Lines”, apply a CR snubber circuit and a diode, respectively, to an inductive load
in an AC circuit and that in a DC circuit.
2) When selecting a CR snubber or diode, observe the following cautions.
Cautions for selecting and using a CR snubber
• Use a CR snubber in an AC circuit.
A varistor, voltage clamping element, can limit the peak of an oscillating voltage waveform but
cannot relax an abrupt voltage transition . For this reason, we recommend using a CR snubber rather
than the varistor.
• Determine the rating of the resistor and capacitor in the CR snubber according to the steady-state
current I (A) and DC resistance RL (Ω) of the inductive load as follows:
)(RLRΩ≅
1) CR snubber resistance:
2
2) CR snubber capacitance:
I
10
• Place the CR snubber close to the inductive load to minimize its wiring.
2
I
C
(μF)
≤≤
20
Inductive load (such as relay)
CR snubber
M
General-purpose induction motor
Fig. 3.4.5 (a) Example of applying a CR snubber
Cautions for selecting and using a diode
• A diode (freewheeling diode) can be used as a noise suppressor for a DC driver circuit.
• Determine the ratings of the diode according to the drive voltage and current for the inductive load
(such as a solenoid coil, relay, or motor) as follows:
1) Voltage rating: Approximately twice the voltage applied to the inductive load
2) Current rating: Approximately twice the steady-state current flowing through the inductive load
• Place the diode close to the inductive load in order to minimize its wiring.
- 25 -
Page 46

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
+
Diode
図3.4.5 (b) Example of applying a diode
Inductive load (such as a relay)
3.4.6 Cable Clamp and Shield Processing
Some cables that are drawn into the control unit, servo amplifier, or spindle amplifier need shielding
(basically, every signal line needs shielding). Clamp all these cables in the way shown below. This type
of clamping works for both cable supporting and shielding. Be sure to make clamping because it is quite
important to make system operation stable. Clamping shield correctly can suppress effect from external
noise.
Partially peel the sheath off a cable and expose the shield, and press the exposed portion against the
ground bar with the clamp. Care should be taken so that the ground bar and shield have a surface contact
in a larger area. (See the figure below.)
The machine builder is requested to prepare the ground bar for cable clamping and place it as shown
below.
When the multipoint grounding scheme is used, care should be taken so that the ground bar for the shield
clamp and cabinet are connected at low impedance by, for example, preventing the cabinet side contact
surface from being coated.
When using an in-line connector or the like to split a cable, it is necessary to connect the shield of one
portion of the cable and that of the other portion and to keep the total impedance of the two cable portions
from becoming high. Even if the connector is placed at the inlet of the cabinet, it is also necessary to use
the shield for the intra-cabinet portion of the cable all the way to the other end of the cable.
Ground bar for shield clamp
Cable
Metal fittings
for clamp
40 mm to 80 mm
Fig. 3.4.6 (a) Cable clamp (1)
- 26 -
Page 47

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
NOTE
1 Select a cable with a proper length.
2 If the cable is too long, the noise immunity may be reduced or noise may be
caused on other cables. In addition, when the excess length is coiled, the
inductance is increased and a high voltage is induced during turning on or off of
signals. This may cause a failure or a malfunction due to noise.
3 Bundle and clamp the shields of cables that lead into the control unit or amplifier
at a point, respectively, close to the unit or amplifier.
Control unit
Metal fittings for clamp
Shield
Fig. 3.4.6 (b) Cable clamp (2)
Prepare a ground bar for cable clamping shown below.
Cabinet
Ground bar for shield clamp
Ground terminal
(grounded)
Hole for securing metal
fitting clamp
Mount screw hole
Fig. 3.4.6 (c) Ground bar for shield clamp (outline drawing)
- 27 -
Page 48

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
The ground bar for cable clamping must be made of a steel plate at least 2 mm thick and plated with
nickel.
12
8
Ground bar for shield clamp
20
Fig. 3.4.6 (d) Ground bar for shield clamp (hole arrangement and dimension drawing)
Reference)
6
Fig. 3.4.6 (e) Clamping metal fixture (outline drawing)
Max. 60
Ordering specification for metal fittings for clamp
A02B-0303-K001 (8 pieces)
(Unit: mm)
28
17
(Unit: mm)
3.4.7 Lightning Surge Absorber Installation
It is recommended to install a surge absorber between input power lines and between input power lines
and the ground in order to protect equipment from thunderbolt-caused voltage surges. However, installing
a surge absorber does not always ensure protection from lightning surges.
For recommended lightning surge absorbers, refer to your respective servo amplifier descriptions.
Installation procedure
The surge-absorbing elements used for measures against surges due to lightening must be installed in the
input power unit as shown in the figure below. The figure below shows an example in which an
insulating transformer, shown by dotted lines, is not installed. If an insulating transformer is installed,
surge-absorbing element 2 (between line and ground) is not required.
- 28 -
Page 49

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
A
(
)
(
)
A
b
(
)
input
Circuit
breaker
MCCB
R
C
S
T
PE
Circuit
breaker
(MCCB)
Insulating
transformer
Circuit
breaker
5A,MCCB
a
Circuit
breaker
MCCB
Magnetic
contactor
To other electric parts on the machine
To control power input for control unit
24 VDC power and control power
supply input of Power Supply for
servo amplifier
C
reactor
To main circuit
power input of
Power Supply for
servo amplifier
Surge-absorbing element 1
(between lines)
Surge-absorbing element 2
(between line and ground)
Fig. 3.4.7 Example of installing lightning surge absorbers on 200 VAC lines
CAUTION
1 For a better surge absorbing effect, the wiring shown by heavy line must be as
short as possible.
Wire size : Cross-sectional area at least 2 mm2 large
Wire length: The sum of the length (a) of the wire for the connection of
surge-absorbing element 1 and that (b) of surge-absorbing element
2 must be 2 m or less.
2 If conducting dielectric strength tests by applying overvoltages (1000 VAC and
1500 VAC) to the power line, remove surge-absorbing element 2. Otherwise, the
overvoltages would activate the element.
3 The circuit breaker (5A) is a short circuit protection of lines if the surge-absorbing
elements result in short circuit breakdown due to the absorption of an excessive
amount of energy.
NOTE
The circuit breaker (5A) can be used also for other electric parts on the machine
because no current flows through surge-absorbing elements 1 and 2 in the
normal state. The “other electric parts on the machine” can be the control power
supply of Power Supply for servo unit and the power supply for the fan motor for
a spindle motor.
- 29 -
Page 50

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
A
AAA
A
A
3.5 INSTALLING THE CONTROL UNIT
CAUTION
The control unit has a built-in fan motor. Failing to secure a space sufficient to
maintain a satisfactory air flow in the control unit can lead to abnormal heat
generation and faults.
3.5.1 Installing the LCD-mounted Type Control Unit
Air enters the control unit through the bottom and is drawn through the fan motor which is located on the
top of the control unit.
Space
should be provided whenever possible. When space
placed in the immediate vicinity which could obstruct the air flow.
, shown in Fig. 3.5.1, must be provided to ensure unrestricted air flow. Also, space B
B
cannot be provided, ensure that nothing is
IR FL OW
50mm
IR FLOW
Rear view
50mm
B B B
Fig. 3.5.1
Unit: mm
- 30 -
Page 51

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
3.6 TIGHTENING TORQUE FOR FASTENING UNITS AND
GROUND TERMINALS
The following table lists the tightening torque for screws and nuts used to fasten the units (except those
having molded mounting parts) explained herein and ground terminals in the units.
Screw and nut diameter Tightening torque
M3 0.8 to 1.0 N⋅m
M4 1.6 to 2.0 N⋅m
The following table lists the tightening torque for screws and nuts used to fasten those units having
molded mounting parts, such as separate detector interface units.
Screw and nut diameter Tightening torque
M4 1.1 to 1.5 N⋅m
M5 2.4 to 2.8 N⋅m
CAUTION
Be sure to observe the rules listed above when tightening screws. If screws are
tightened too weakly or too strongly, it is likely that the unit may drop, break, or
malfunction.
For units having a touch panel in particular, be sure to observe the above rules.
Failing to observe them can cause the touch panel to malfunction.
NOTE
For units having different installation conditions specified herein, observe them
first.
3.7 DUSTPROOF MEASURES FOR CABINETS AND
PENDANT BOXES
When designing and manufacturing cabinets or pendant boxes for housing displays and operator’s panels,
they are requested to observe the following cautions to make their structures resistant to intrusion of dust,
cutting chips, coolant, organic solvent, and oil mist because these cabinets and pendant boxes are
susceptible to them.
1) The cabinet and pendant box must be of a hermetically sealed structure.
2) Apply packing to the panel mounting surface to which a display and operator's panel are to be
mounted.
3) Make sure that the door packing of the cabinet and pendant box is sealed firmly.
4) For a cabinet or pendant box with a rear cover, apply packing to the mounting surface.
5) Make sure that the cable entrance is sealed with packing, connectors for conduits, etc.
6) Make sure that all other openings are blocked, if any.
7) Pay due consideration to keep the display and operator’s panel from direct exposure to cutting chips
and coolant; do not let any coolant come into contact with them.
8) Coolant can readily form puddles on the cabinet and pendant box and may drop on the panel surface
of the display and operator’s panel. Use such a structure that can prevent coolant from forming
puddles on the display and operator’s panel or dropping on the panel surface.
- 31 -
Page 52

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
WARNING
Coolants containing sulfur or chlorine at a high activation level, oil-free coolants
called synthetic, and water-soluble coolants at a high alkali level, in particular,
can largely affect the CNC and peripheral units. Please note that, even if
consideration is taken to protect them from direct exposure to these coolants,
the following trouble is likely to occur.
- Coolants containing sulfur or chlorine at a high activation level
Some coolants containing sulfur or chlorine are at an extremely high activity
level. If such a coolant adheres to the CNC or peripheral units, it reacts
chemically with a material, such as resin, of equipment, possibly leading to
corrosion or deterioration. If it gets in the CNC or a peripheral unit, it corrodes
metals, such as copper and silver, used as component materials, possibly
leading to a defective component.
- Synthetic-type coolants having a high permeability
Some synthetic-type coolants whose lubricating component is, for example,
PAG (polyalkylene glycol) have an extremely high permeability. If such a
coolant is used even in equipment having a high closeness, it can readily flow
into the equipment through, for example, gaskets, or packing. It is likely that,
if the coolant gets in the CNC or a peripheral unit, it may deteriorate the
insulation and damage the components.
- Water-soluble coolants at a high alkali level
Some coolants whose pH is increased using alkanolamine are so strong
alkali that its standard dilution will lead to pH10 or higher. If such a coolant
spatters over the surface of the CNC or peripheral unit, it reacts chemically
with a material, such as resin, possibly leading to corrosion or deterioration.
When making screw holes in packing, be careful not to cut to the edge of the packing. Any extra cut can
let coolant get in the cabinet through the screw hole, causing trouble.
- 32 -
Page 53

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
A
Packing
Screw hole
*) When making screw hole s in packing, be careful not to cut to the edge of the packing.
ny extra cut can let coolant
get in the cabinet through the
Packing
Screw hole
screw hole.
Packing for LCD units, MDI units, and machine operator’s panels
Observe the following rough standards for the thickness and hardness of packing used with LCD units
(included LCD-mounted control units or display units), MDI units, and machine operator’s panels.
Thickness : 1.4mm(including double-stick tape)
Hardness : 8(Asker C)
The following models of packing can be purchased from FANUC. These models are electrically
conductive. When they are used to mount a unit on a cabinet or pendant box, they leave no electrical gap
between the unit and cabinet or pendant box, being effective in electromagnetic wave shielding and EMC
measures.
Ordering information Use
A02B-0319-K150 For 8.4” LCD/MDI (horizontal)
A02B-0319-K151 For 8.4” LCD/MDI (vertical)
A02B-0323-K302 For standard MDI unit (ONG) (200x260mm)
A02B-0323-K301 For 10.4” LCD unit, for standard MDI unit (ONG vertical type) (220x290mm)
A02B-0323-K304 For 15” LCD unit
A02B-0323-K310 For standard MDI unit (ONG vertical type) (220x230mm)
A02B-0323-K313 For small MDI unit (ONG) (200x140mm)
A02B-0323-K314 For standard MDI unit (QWERTY) (160x290mm)
A02B-0323-K315 For standard MDI unit (QWERTY type B) (145x400mm)
A02B-0323-K320 For main panel of standard machine operator’s panel or safety machine
operator’s panel (140x290mm)
A02B-0323-K321 For safety machine operator’s panel type B
CAUTION
1 We have evaluated the above models of packing for many different coolants.
However, we do not necessarily guarantee that they are resistant to all coolants.
They are not resistant to, for example, coolants containing sulfur or chlorine at a
high activation level and water-soluble coolants at a high alkali level.
2 When attaching these models of packing, observe the cautions provided
together with them.
When using packing to install a LCD unit, MDI unit, or machine operator’s panel in a cabinet or pendant
box, be careful not to pinch the packing between the mounting surface of the cabinet or pendant box and
the brim of the unit being installed.
- 33 -
Page 54

3.INSTALLATION B-64603EN/01
When attaching packi ng,
be careful not to pinch it.
LCD unit, MDI unit,
standard machine operator’s
panel
Cabinet, pendant box
Packing
3.8 LCD PROTECTION COVER
FANUC offers LCD-mounted control units and display units having a protection cover for the LCD
screen and soft keys on their front surface. The protection cover can be purchased also on an unbundling
basis.
CAUTION
Do not install the LCD-mounted control unit and the display unit in such a place
that coolant would directly fall onto the unit. Be sure to attach a protection cover
to the LCD-mounted control unit and the display unit if they will be used in an
environment where it is anticipated that coolant may scatter over them, for
example, an environment with a relatively dense oil mist.
3.9 ATTACHING SCREW CAPS
After mounting any of the LCD-mounted control unit, display unit, MDI unit, and machine operator’s
panel main panel, which are supposed to be mounted on the front of a cabinet or pendant box using M3
screws, attach screw caps to the screw mounting hole at every corner.
CAUTION
When attaching screw caps, pay due attention to the dent in them and be careful
not leave any gap. Otherwise, coolant may get in the equipment, causing
trouble.
Dent
- 34 -
Page 55

B-64603EN/01 3.INSTALLATION
3.10 INSTALLATION CONDITION FOR UL RECOGNITION
1. Outline
For UL recognition of the product, installed after due considerations on UL requirements.
2. Notes on the installation conditions for UL recognition
• Set up the LCD-mounted type control unit, display unit and MDI unit on a flat surface of a
Type 1 Enclosure
(*1. Type 1 Enclosure is defined in standard UL 50 as follows.
TYPE 1 - Enclosures constructed for indoor use to provide a degree of protection to
personnel against incidental contact with the enclosed equipment and to provide a degree
of protection against falling dirt.)
• Use CNC, Display and MDI unit in Pollution degree 2
except for part exposed on the outside of enclosure.
(*2. Pollution degree is a classification according to the amount of pollution and condensation
present in the environment.
"Pollution Degree 2" is defined in the standard UL 508 as follows.
Normally, only nonconductive pollution occurs; however, temporary conductivity caused
by condensation may be expected.)
• Maximum surrounding air temperature rating: +60°C
(*3. This temperature rating is a condition of UL evaluation for recognition. However, for
long-term reliability, the cabinet should be actually designed in accordance with the
maximum operating surrounding air temperature that described in the subsection 3.1.2 in
the connection manual (B-64603EN).)
• Power supply unit for this unit must have an isolating device and the DC 24 Volt output must
be isolated from AC mains supply.
(This isolation can be achieved with the use of the isolating DC power supply unit that
complies with UL standard.)
DC 24 Volt power cable needs to be used with 14AWG or 16AWG size conductors.
*1
.
*2
environment or cleaner environment,
*3
- 35 -
Page 56

4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION B-64603EN/01
A
A
pply
4 POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION
4.1 24 VDC POWER (INSULATION AC/DC CONVERTOR)
4.1.1 Connecting 24 VDC Power
Prepare a 24 VDC power supply (insulation AC/DC converter) and supply power to the 24 VDC input of
the control unit and peripheral units, such as I/O units.
It is recommended to provide an ON/OFF circuit external to the 24 VDC power supply as shown in Fig.
4.1.1(a) so that it can turn on and off the AC input to the 24 VDC power supply.
It is also recommended to use a separate 24 VDC power supply for any unit whose load fluctuates largely
or which may generate noise, in order to minimize effect of noise and voltage variation to the control unit
or peripheral unit.
C input
Main circuit
breaker
Magnetic
contactor
C line
filter
Power supply
3-phase
200VAC for
power line
SV
Control unit
24 VDC
input for
control
ON/OFF
circuit
Fig. 4.1.1 (a) Example of recommended 24 VDC power supply connection
24VDC power
supply
24VDC power
supply
24VDC power
su
24VDC
input
Peripheral unit such
as an I/O unit
Device with large
noise or load
fluctuations
- 36 -
Page 57

B-64603EN/01 4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION
A
A
CAUTION
When the ON/OFF circuit is provided on the DC side of a 24 VDC power supply,
on-time rush current imposes an extremely heavy burden on the relay contact in
the ON/OFF circuit compared with the time when the ON/OFF circuit is provided
on the AC side. So, it is necessary to select a relay that is highly resistant to rush
current. In general, a relay having a high current rating and being large in size
should be selected.
In the connection shown in Fig. 4.1.1(b), for example, use a separate 24 VDC
power supply if voltage variation due to abrupt changes in the load or rush
current may transiently exceed the rated input voltage range (24 VDC ±10%) for
the control unit or peripheral unit.
Example 1
C input
Example 2
C input
Fig. 4.1.1 (b) Example of connection with h igh transient voltage variation
24VDC power supply
24VDC power supply
Control unit or
peripheral unit
Unit with
high load
fluctuation
Control unit or
peripheral unit
Unit with high
rush current
NOTE
Try as much as possible to avoid the configuration shown in Fig. 4.1.1(b) even
when load fluctuation and rush current are low.
In a configuration where two or more units are connected to the same 24 VDC
power supply, the control unit will not be able to start, thus failing to issue an
alarm, if the power supply fails to operate because of a fault in a unit other than
the control unit. For this reason, it is likely that it may take time to locate the fault.
If the 24 VDC power supply for the control unit and peripheral units must be
connected also to another unit because of a limited space in the power
magnetics cabinet, insert a noise filter, example: ZGB2203-01U manufactured by
TDK, before the 24 VDC input for the control unit and peripheral units in order to
prevent noise from the 24 VDC power supply from entering the control unit and
peripheral units after paying due consideration to the voltage variation resulting
from load fluctuation or rush current. In case of using a noise filter, enough
inspect workings of the control unit and peripheral units, because there may be
influenced of another noise by the noise filter.
- 37 -
Page 58

4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION B-64603EN/01
4.1.2 24 VDC Power Supply Specification
Specifications of recommended 24 VDC power supply:
Output voltage: +24V±10% (21.6V to 26.4V)
(In the 24 VDC input for the control unit and peripheral units, ripple voltage and noise are contained. See
Fig. 4.1.2.)
Output current:
The continuous load current of the 24 VDC power supply is higher than or equal to the current used
by the control unit and peripheral units that are connected to the power supply.
(At the maximum temperature inside the power magnetics cabinet in which the power supply is
located. See Subsection 4.1.3.)
Load fluctuations (including rush current):
The output voltage must not go out of the above range due to load fluctuations by external DO and
other factors.
Instantaneous input interruption retention time: 10 ms or more (for -100%), 20 ms or more (for -50%)
Safety standard
UL 60950-1, CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-1, EN60950-1 approved
Noise voltage at terminal/electrical field intensity of noise
EN55011/EN55022-B, FCC-B, VCCI-B compliant
NOTE
Safety standard and Noise voltage at terminal/electrical field intensity of noise
are recommended for selecting the 24 VDC power supply on the market.
However, the required standards may be different from above standards by the
machine, an importing country, revision of the standard, or etc, prepare the 24
VDC power supply that is conformed to required standards.
- 38 -
Page 59

B-64603EN/01 4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION
A
A
A
Timing chart
C input
voltage
Output
voltage
Output
current
In the 24 VDC input for
the control unit and
peripheral units, noise
and ripple voltage must
fall within this range.
Instantaneous
interruption (-100%)
10mS
26.4V
21.6V
0A
Example of ripple voltage and n oise due t o swit ching power supply
26.4V
Instantaneous
interruption (-50% )
20mS
brupt load change
Noise
Ripple voltage
Noise
21.6V
Fig. 4.1.2 (a) Timing chart
CAUTION
Do not use any power supply circuit, consisting of a capacitor and rectifier circuit,
like one shown in Fig. 4.1.2 (b), because it cannot maintain a voltage of 24 VDC
(the voltage falls to 21.6 V or below in each 24 VDC input for the control unit and
peripheral units) due to instantaneous interruption or voltage variation in the AC
input. Instead, use a voltage regulator.
C input
(*) The rectifier circuit here refers to a diode-based full-wave rectifier circuit or the like.
Fig. 4.1.2 (b) Example of a power supply circuit that cannot maintain 24 VDC
Rectifier
circuit
(*)
Control unit
and other units
- 39 -
Page 60

4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION B-64603EN/01
4.1.3 Power Capacity of 24 VDC Power Supplies
The 24 VDC power supply for the control unit and peripheral units must have the power capacity that can
supply current required by them.
Calculate the power capacity required of each 24 VDC power supply according to what control unit and
options are connected to the power supply while referencing Table 4.1.3.
Table 4.1.3 Power capacity
Unit Power capacity Remarks
LCD-mounted type
control unit
Option board
MDI units 0A
8.4”LCD/MDI unit
15”LCD unit
Fast Ethernet board 0.1A
HSSB interface board 0.2A
PROFIBUS-DP master board 0.2A
PROFIBUS-DP slave board 0.1A
DeviceNet master board 0.1A
DeviceNet slave board 0.1A
CC-Link remote device station board 0.1A
Option 0 slot
Option 2 slots
Option 0 slot 10.4”LCD unit
Option 2 slots
Option 0 slot
Option 2 slots
NOTE
1 Each power capacity listed above does not include that of option boards.
2 When connecting the RS-232C device which will draw power from the control
unit, add the power capacity that the device requires to the listed power capacity.
3 Limit the total power consumption of memory cards and USB memories to within
2 W.
4 See Chapter 6 for the power capacity of the separate detector interface unit.
5 See Chapter 8 for the power capacity of I/O units.
6 Refer to the PANEL i Connection and Maintenance Manual (B-64223EN) for the
power capacity of the PANEL i.
7 Selecting 24 VDC power supplies impose restrictions besides their power
capacity. Be sure to read also Subsection 4.1.2.
WARNING
If the machine tool of interest has a vertical axis, it is necessary to select a 24
VDC power supply that can hold its output of 24 VDC for a prolonged time even
after the AC input has been interrupted (including power failure and
instantaneous power interruption) in order to keep a possible fall along the
vertical axis within an acceptable range. The control unit deenergizes servo
circuits if its 24 VDC input falls to 21.6 V or below. For this reason, failing to
maintain the 24 VDC input to the control unit for a satisfactory period after the
AC input has been interrupted may lead to a larger amount of fall along the
vertical axis, depending on a peripheral circuit in use, because the servo for the
vertical axis is deenergized before the peripheral circuit detects an AC input
interruption and activates the brake. In general, selecting a 24 VDC power
supply having a power capacity with a wide margin would prolong the hold time
of the 24 VDC output after an AC input interruption.
- 40 -
1.4A Note 1)
1.4A Note 1)
2.0A Note 1)
Page 61

B-64603EN/01 4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION
4.2 TURNING ON AND OFF THE POWER TO THE CONTROL
UNIT
4.2.1 Power-on Sequence
Turn on the power to all the units at the same time, or in the following sequence:
1 Power to the overall machine (AC input)
2 Servo amplifier control power supply (24VDC)
3 Power to the slave I/O units connected via the I/O Link i, the separate detector interface unit, and power to the
control unit (24 VDC), power to the separate detector (scale)
The expression “the same time” here means that the power to the units mentioned in Steps 1 and 2 above
has been turned on at least within 500 ms after the 24 VDC power supply for the control unit mentioned
in Step 3 above has been turned on. The power to each unit mentioned in Step 3 must have been turned on
within a period between 200 ms before the 24 VDC power supply for the control unit is turned on and
500 ms after that time.
Power to the overall machine
Servo amplifier control power
supply
Power to the control unit
ON
OFF
ON
t1
Power to peripheral units
(including Power Mate i)
OFF
ON
OFF
Fig. 4.2.1
t2
t3
t1:-500ms It is meant that the power to the overall machine and the servo amplifier control
power are turned on at least within 500 ms after the control unit power has been
turned on.
t2: 200ms It is meant that the power to peripheral units (including Power Mate i) is turned on
not earlier than 200 ms before the control unit power is turned on.
t3:-500ms It is meant that the power to peripheral units (including Power Mate i) is turned on
not earlier than 500 ms before the control unit power is turned on.
NOTE
Leave each of the memory backup battery (3 VDC) and separate absolute pulse
coder battery (6 VDC) connected regardless of whether the control unit power is
on or off. Removing these batteries with the control unit power turned off can
corrupt parameters and programs in the control unit as well as position data in
the pulse coder.
See Subsection 4.4.1 for explanations about how to replace the memory backup
battery.
See Subsection 4.4.2 for explanations about how to replace the separate
absolute pulse coder battery.
- 41 -
Page 62

4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION B-64603EN/01
4.2.2 Power-off Sequence
Turn off the power to all the units at the same time, or in the following sequence:
1 Power to the slave I/O units connected via the I/O Link i, the separate detector interface unit, and power to the
control unit (24 VDC)
2 Servo amplifier control power supply (24 VDC), power to the separate detector (scale)
3 Power to the overall machine (AC input)
The expression “the same time” here means that there is no problem even if the power to the units
mentioned in Steps 5 and 6 above is turned off not earlier than 500 ms before the power to the control
unit mentioned in Step 4 above is turned off. If the power to the units mentioned in Steps 5 and 6 is
turned off earlier, alarm information is left in the control unit. In addition, the power to each peripheral
unit mentioned in Step 4 above must be turned off not earlier than 500 ms before the power to the control
unit is turned off. Otherwise, alarm information is left in the control unit.
Power to peripheral units
(including Power Mate i)
ON
OFF
t4
Power to the control unit
Servo amplifier control power supply
Power to the overall machine
ON
OFF
t4
ON
OFF
Fig. 4.2.2
t4:500ms It is meant that the power of interest is turned off not earlier than 500 ms before the
power to the control unit is turned off.
CAUTION
The power to the control unit cannot be turned on or off with peripheral units
supplied with power.
Before turning off the power to the control unit, be sure to turn off the power to
the units (such as slave I/O units connected via the I/O Link i, the I/O Link i, I/O
Link i -equipped
i
series servo amplifier, Power Mate i, separate detector I/F
β
units, servo amplifier control power, and separate detectors (scale)) connected to
the control unit.
- 42 -
Page 63

B-64603EN/01 4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION
WARNING
It is impossible for the control side to control motors if the power supply is off or
there is no AC input (including power failure). It is necessary for the machine
side to perform any necessary processing.
If the control unit is used to control a vertical axis, for example, provide the motor
with a brake mechanism to prevent a fall along the vertical axis. The brake
should be controlled in such a way that the motor is clamped when the servo has
not be started or when the motor is not supposed to rotate and unclamped only
when it is supposed to rotate. It is common practice to clamp servo motors when
the servo axes cannot be controlled because of the power supply being off or of
a power failure. Even with this common practice, a fall may occur along a
controlled axis before the relay works. So, it is necessary to examine whether
the fall distance poses any problem.
Power-off: Before turning off the control unit power, be sure to apply the
brake to clamp the motor.
Power failure: On detecting a power failure, apply the brake quickly.
Turning off the control unit power results in the servo being
deenergized. So, select a 24 VDC power supply that can maintain
its 24 VDC output for a prolonged time after an AC input
interruption.
- 43 -
Page 64

4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION B-64603EN/01
4.3 CABLE FOR POWER SUPPLY TO CONTROL UNIT
Supply the power to the control unit from a 24 VDC power supply.
Control unit
CPD16A or CPD19A
1
+24V
2
0V
3
GND
Cable
CPD16A or CPD19A
Tyco Electronics
1-178288-3 (housing)
1-175218-5 (contact)
Use terminals that match
24 VDC power.
24VDC power supply
24VDC stabilized power
24VDC ±10%
24VDC power
supply
+24V (1)
0V (2)
Recommended cable: A02B-0124-K830(5m)
(Crimp terminal of size M3 is available on the
24VDC power supply side)
+24V
0V
FG
Interconnect 0V and FG, and
ground them.
4.4 BATTERIES
A system using this control unit uses batteries in the places listed below. Refer to the FANUC PANEL i
Connection and Maintenance Manual (B-64223EN) for explanations about the batteries used for the
PANEL i. Used batteries must be discarded according to appropriate local ordinances or rules. When
discarding batteries, insulate them by using tape and so forth to prevent the battery terminals from
short-circuiting.
Use Component connected to battery
Memory backup in the control unit Control unit
Preservation of the current position indicated by the separate absolute
pulse coder
Preservation of the current position indicated by the absolute pulse
coder built into the motor
Separate detector interface unit
Servo amplifier
4.4.1 Battery for Memory Backup in the Control Unit (3 VDC)
Offset data, and system parameters are stored in SRAM in the control unit. The SRAM power is backed
up with the memory backup batteries held in the control unit.
When the voltage of the battery becomes low, alarm message "BAT" blinks on the LCD screen and the
battery alarm signal is output to the PMC. Upon the alarm, replace the battery as soon as possible. The
rough standard for the replacement limit is one week. However, how long the battery lasts after the alarm
varies, depending on the system configuration of interest.
If the voltage of the battery becomes any lower, memory can no longer be backed up. Turning on the
power to the control unit in this state causes system alarm to occur because the contents of memory are
lost. Clear the entire memory and reenter data after replacing the battery.
FANUC thus recommends that the battery be replaced periodically, once a year, regardless of whether a
battery alarm is issued.
The following two kinds of batteries can be used.
• Lithium battery built into the CNC control unit.
• Alkaline dry cell (size D) inserted in an external battery case attached to the control unit.
- 44 -
Page 65

B-64603EN/01 4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION
p
NOTE
Before shipped from FANUC, the control unit is equipped with a lithium battery
set as default. With this lithium battery, memory contents can be preserved for
one year.
4.4.1.1 Replacing the lithium battery
For LCD-mounted type control unit
Prepare a new lithium battery (ordering code: A02B-0323-K102).
(1) Turn on the power to the machine (control unit). After about 30 seconds, turn off the power.
(2) Take out the lithium battery from the rear of the control unit (by holding the latch of the lithium
battery and pulling it up while unlatching the claw held in the case).
Extract the unit while holding this
ortion.
(3) Insert a new lithium battery, prepared in advance, into the battery case (by pushing it in until the
claw of the lithium battery fits in the case). Make sure that the claw is latched securely.
Push the unit in until the
claw is latched into the
case.
WARNING
It is likely that the lithium battery may explode unless it is replaced correctly.
Do not use any battery other than the specified one (A02B-0323-K102).
- 45 -
Page 66

4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION B-64603EN/01
CAUTION
Steps (1) to (3) should be completed within 30 minutes.
Do not leave the control unit without a battery for any longer than the specified
period. Otherwise, the contents of SRAM may be lost.
Before starting battery replacement, save the SRAM contents in a batch. They
can be restored easily even if they are lost.
Refer to the Maintenance Manual (B-64605EN) for explanations about how to
save and restore SRAM contents in a batch.
NOTE
Discard used batteries as “industrial waste” according to the rules and
ordinances of the country where the machine is installed and of the local
government that has jurisdiction over the location of the machine. When
discarding them, insulate the battery terminals with tape or the like to protect
them from short-circuiting.
4.4.1.2 Replacing commercially available alkaline dry cells (size D)
In place of the built-in lithium battery in the control unit, commercially available alkaline dry cells (size
D) can be used by installing a battery case outside the control unit and inserting the dry cells in the case.
How to connect the battery case to the control unit
For the LCD-mounted type control unit, connect the battery cable (A02B-0323-K103) to the battery case
(A02B-0236-C282). For the stand-alone type control unit, use the battery case (A02B-0236-C281), which
comes with the battery cable attached.
Example of connecting the battery case to the control unit (LCD-mounted type)
NOTE
1 The battery cable is engaged with its connector using a simple lock mechanism.
Fasten the cable at a length of 500 mm or smaller measured from the connector
with some slack so that the connector will not be disengaged due to the weight
or tension of the cable.
2 Keep the battery cable away from any possible noise source, such as power
wires.
- 46 -
Page 67

B-64603EN/01 4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION
o
Battery cable for LCD-mounted type control unit
LCD-mounted type control unit
Battery
1 2
B +
A -
cable
+ (B 1 )
- (A 1 )
Shield
Gr oun d pl at e
mmen ded cable: A02B-0323-K103(14 m)
Rec
Conne c t or ki t ( CNC s ide): A 02B -0323-K107
Terminal(B attery case side ): M4 terminal
Recommended wire: #2 2A WG 2wires, with s hie ld, outs ide diameter:5mm or less
( CNC s ide cases, hou s ings an d contact s * for 10 ca ble s )
* contact is 1-206933 7-1 (TE connectivity)
Battery case
(M4 t er min al s )
Batte ry ca se
+
-
Battery cable for LCD-mounted type control unit
NOTE
1 In case of assemble this cable, please keep loosening the cable length in the case
and clamp with nylon band etc. as bellow figure in order to prevent tension to the
contacts directly.
2 Special tool provided by
connector manufacture is
required to assemble this cable.
Housing
Contact
Clamp with
Nylon
band .
Keep loosening.
Internal figure of CNC side connector
Case
Replacing the alkaline dry cells (size D)
(1) Prepare two new alkaline dry cells (size D).
(2) Turn on the power to the machine (control unit).
(3) Remove the battery case cover.
(4) Replace the batteries, paying careful attention to their orientation.
(5) Replace the battery case cover.
CAUTION
To replace the battery when the power is off, follow the same procedure as that
for the replacement of a lithium battery, described above.
Pay attention to the battery polarity. If a battery is installed with incorrect polarity,
the battery may overheat, blow out, or catch fire
- 47 -
Page 68

4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION B-64603EN/01
×
2
Cover
Connection
terminal on the rear
Battery case
Dry cell
Mounting hole
× 4
4.4.2 Battery for Separate Absolute Pulsecoders (6VDC)
• The absolute Pulsecoder uses a battery because it must hold data on absolute positions. When the
voltage of the batteries for absolute Pulsecoders becomes low, alarm 307 or 306 occurs, with the
following indication in the CNC state display at the bottom of the CNC screen.
Alarm 308 (alarm 2 indicating the voltage of the battery becomes low) :
The indication "APC" blinks in reversed display.
Alarm 307 (alarm indicating the voltage of the battery becomes low) :
The indication "APC" blinks in reversed display.
Alarm 306 (battery zero alarm) :
The indication "ALM" blinks in reversed display.
• When alarm 307 (alarm indicating the voltage of the battery becomes low) occurs, replace the
battery as soon as possible. In general, the battery should be replaced within one or two weeks,
however, this depends on the number of Pulsecoders used.
• When alarm 306 (battery zero alarm) occurs, Pulsecoders are reset to the initial state, in which
absolute positions are not held. Alarm 300 (reference position return request alarm) also occurs,
indicating that reference position return is required.
• In general, replace the batteries periodically within the service life listed below.
- A06B-6050-K061 or D-size alkaline dry cells (LR20) : Two years (for each six-axis
configuration)
- A06B-6073-K001 : Two years (for each three-axis configuration)
- A06B-6114-K504 : One year (for each three-axis configuration)
NOTE
The above values indicate the estimated service life of batteries used with
FANUC absolute Pulsecoders. The actual battery service life depends on the
machine configuration based on, for example, detector types. For details,
contact the machine tool builder.
Replacing batteries
To prevent absolute position information in absolute Pulsecoders from being lost, turn on the machine
power before replacing the battery. The replacement procedure is described below.
<1> Ensure that the power to the servo amplifier is turned on.
<2> Ensure that the machine is in the emergency stop state (the motor is inactive).
<3> Ensure that the DC link charge LED of the servo amplifier is off.
<4> Detach the old batteries and attach new ones.
- 48 -
Page 69

B-64603EN/01 4.POWER SUPPLY CONNECTION
A
WARNING
The absolute Pulsecoder of each of the
•
series servo motors (
i
S0.4 to
β
i
S22) has a built-in backup capacitor.
β
i
/
S series servo motors and the
α
α
i
S
β
i
Therefore, even when the power to the servo amplifier is off and the batteries
are replaced, reference position return is not required if the replacement
completes within less than 10 minutes. Turn the power on and replace the
batteries if the replacement will take 10 minutes or more.
To prevent electric shock, be careful not to touch metal parts in the power
•
magnetics cabinet when replacing the batteries.
Because the servo amplifier uses a large-capacitance electrolytic capacitor
•
internally, the servo amplifier remains charged for a while even after the power is
turned off. Before touching the servo amplifier for maintenance or other
purposes, ensure your safety by measuring the residual voltage in the DC link
with a tester and confirming that the charge indication LED (red) is off.
Be sure to replace the batteries with specified ones. Pay attention to the battery
•
polarity. If a wrong type of battery is used or a battery is installed with incorrect
polarity, the battery may overheat, blow out, or catch fire, or the absolute
position information in the absolute Pulsecoders may be lost.
Ensure that the battery connector is inserted in the correct position.
•
How to insert batteries into the battery case
Use the following procedure to replace the batteries in the battery case.
<1> Loosen the screws on the battery case and detach the cover.
<2> Replace the batteries in the case (pay attention to the polarity).
<3> Attach the cover to the battery case.
Battery case (with a cover)
06B-6050-K060
Batteries
Four A06B-6050-K061 batteries or
D-size alkaline dry cells
CAUTION
Four D-size alkaline dry cells (LR20) that are commercially available can be
•
used as batteries. A set of four A06B-6050-K061 batteries is optionally available
from FANUC.
Replace all the four batteries with new ones. If old and new batteries are mixed,
•
the absolute position information in the absolute Pulsecoders may be lost.
When connecting batteries, pay due attention to their polarity. If they are
•
connected in reverse polarity, it is likely that they may get hot, explode, or catch
fire. In addition, it is also likely that information on absolute positions may be lost
from the absolute Pulsecoder.
4.4.3 Battery for Absolute Pulse Coder Built into the Motor (6VDC)
The battery for the absolute pulse coder built into the motor is installed in the servo amplifier.
Explanations about how to connect and replace the battery, refer to the maintenance manual for the servo
amplifier in use.
- 49 -
Page 70

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
t
5 CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
5.1 CONNECTION BETWEEN THE LCD-MOUNTED TYPE
CONTROL UNIT AND MDI UNIT
5.1.1 Overview
A MDI is embedded in 8.4” LCD/MDI unit of Basic unit A, therefore it is not necessary to connect the
MDI cable by a machine maker.
Connection of the MDI cable of a control unit without the MDI is described below.
LCD-mounted type control uni
For basic unit A (10.4”LCD)
JA2
CK27
MDI cable
MDI unit
- 50 -
Page 71

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
A
5.1.2 Connection with the MDI Unit
・For basic unit A (10.4”LCD)
Control unit
JA2
FI80-20P
Honda tsushin Kogyo Co., Ltd.
(including housing s)
PCR-E20FA-E20SPF1A+(press-mount
type) or
PCR-E20FS-E20S PF1A+(soldering
type)
R e c om m e n de d MDI un it
connector
PCR-E20FA (Honda Tsushi n Kogyo)
FI30-20S(Hirose Electric)
FCN-24 7J020-G/E(FUJITSU COMPONENT)
52622-2011(Molex)
JA2
MDI uni t
CK27
SHIELD
GROUNDING PLATE
Rec ommended cable specification
Recommended wire specif ication
02B-0319-K813(45cm)
(#28AWG X 10 pair s, Maximum cable length : 20m)
NOTE
Clamp the cable so that excessive force is not applied due to vibration. However,
shielding and clamping are not required for a cable of up to 50 cm.
- 51 -
Page 72

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
A
A
・For basic unit G (15.4”LCD)
Control unit
CK27
Recommended MDI unit
connector
PCR-E20FA(Honda T s ushin Kogyo)
FI30-20S(Hirose Electric)
FCN-247J020-G/E(FUJITSU
COMPONENT)
52622-2011(Molex)
CK27
02B-0236-K813(45cm)
02B-0236-K814(1.5m)
, Maximum cable length : 20m)
NOTE
For MDI cable connector mating on the CA55 side, a simple lock mechanism is
employed. Ensure that a load greater than 1 kg is not applied to the connectors.
Moreover, clamp the cable so that excessive force is not applied due to
vibration. However, shielding and clamping are not required for a cable of up to
50 cm.
- 52 -
Page 73

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
A
A
A
A
5.1.3 Key Layout of MDI Unit
For Lathe (T series)
- Standard MDI unit (ONG keys)
Case shift key
Shift key
UX key
CTRL key
LT key
TAB key
Reset key Help key
ddress/numeric keys
Edit keys
Cancel (CAN) key
Input key
Page change keys
- Small MDI unit (ONG keys)
Function keys
Page change keys
Cursor keys Function keys
ddress keys/Numer ic keys
Cancel (CAN) key
Input key
Shift key
Help key
Reset key
Edit keys
Cursor keys
- 53 -
Page 74

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
A
AUX
A
A
For Machining center (M series)
- Standard MDI unit (ONG keys)
Case shift key
Shift key
key
CTRL key
LT key
TAB key
Reset key Help key
ddress/numeric keys
Edit keys
Cancel (CAN) key
Input key
Page change keys
- Small MDI unit (ONG keys)
Function keys
Page change keys
Cursor keys Function keys
ddress/numeric keys
Cancel (CAN) key
Input key
Shift key
Help key
Reset key
Edit keys
Cursor keys
- 54 -
Page 75

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
A
A
A
Common to lathe system / machining center system
- Standard MDI unit (QWERTY keys)
Help key
Reset key
Function keys
Address keys
Case shift key
AUX key
CTRL key
ALT key
TAB key
Page change keys
Cursor keys
- Standard MDI unit (QWERTY type B keys)
Help key
Function keys
Case shift key
ddress keys
Reset key
Edit keys
Cancel (CAN) key
Edit keys
Numeric keys
Shift key
Input key
Numeric keys
LT key
UX key
Shift key
Cursor keys
Page change keys
Input key
Cancel (CAN) key
CTRL key
TAB key
5.1.4 Keyboard Cover
Use the keyboard cover when using the system under environments with higher degree of dust or coolant.
Refer Appendix F about how to setting.
WARNING
Use the keyboard cover, when it may become impossible to operate key switch
because the dust, cutting chips, etc. get in the crevice between keyboards.
- 55 -
Page 76

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
5.2 CONNECTION WITH INPUT/OUTPUT DEVICES
5.2.1 Overview
An input/output device is used to enter information such as control unit programs and parameters from an
external device to the control unit, or to output information from the control unit to an external device.
The input/output devices usable with this control unit include Handy File.
The interface of the input/output devices electrically conforms to RS232-C, so that a connection can be
made with a device that has an RS232-C interface.
The tables below indicate the serial ports of this control unit.
Port name Interface location
1CH (JD36A) Main control unit
2CH (JD36B) Main control unit Note
The serial ports of the 15” LCD LCD-mounted type control unit are as listed in the table below, however.
Port name Interface location
1CH (JD56A) Main control unit
2CH (JD36A) Main control unit Note
NOTE
When a touch panel is used, this serial port is used for touch panel
communication on the control unit side, so that this port cannot be used as a
general-purpose port.
5.2.2 Connecting I/O Devices
R232C-1
JD36A
Thi s fig u re sh o ws an
example of connection
for the LCD-m ount ed
ty pe co n tro l uni t.
R232C-2
JD36B
Punch pan el
External I/O device
- 56 -
Page 77

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
R
NOTE
This interface is the RS232-C interface on the control unit side.
For these devices, the RS232-C interface on the control unit is used for the
following cases:
Ladder monitoring, storing, or loading using FANUC LADDER III
•
DNC operation via RS232-C, external I/O device control
•
Input/output of parameters and programs by using the control unit screen
•
display function
5.2.3 RS232-C Serial Port
Contro l u nit
JD 5 6 A, JD3 6A
FI80-20P, DF1R020WB1
RD
10
1
0V
2
DR
3
0V
4
CS
5
0V
6
CD
7
0V
8
(*)
9
+24V
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
0
SD
0V
ER
0V
RS
0V
(*)
(+5V) (*)
+24V
(+5V) (*)
>„
„ <
Rel a y co nne ctor
(DBM-25S)
1
FG
SD
2
RD
3
RS
4
CS
5
D
6
SG
7
8
CD
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
ER
+24V
NOTE
1 Do not connect anything to those pins for which signal names are not indicated.
2 Pins 18 and 20 (+5V) are provided for touch channel connection.
- 57 -
Page 78

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
(FUJITSU COMPONENT)
For LCD-mounted type
For stand-alone type
NOTE
1 Do not connect anything to those pins for which signal names are not indicated.
- 58 -
Page 79

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
A
5.2.4 RS232-C Interface Specification
RS232-C Interface signals
Generally signals as follows are used in RS232-C interface.
Control unit
Output
SD (Send data)
Input
RD (Receive data)
RS (Request to Send)
When CS is not used short CS
and RS.
CS (Enable to send)
ER (Ready)
DR (Data set ready)
CD (Check data)
SG (Signal ground)
FG (Frame ground)
Fig. 5.3.4 RS232-C interface
Signal description of RS232-C interface
Signal I/O Description
SD Output Sending data
RD Input Receiving data
Start bit
Stop bits
When DR is not used
short DR and ER.
lways short ER and
CD.
(When ISO code 0 is sent)
RS Output Sending
request
CS Input Sending
permitted
This signal is set to on when control unit starts sending data and is turned
off when transmission ends.
When both this signal and the DR signal are set, the control unit can send
data. If I/O device processing is delayed by a punching operation, etc.,
control unit data sending can be stopped by turning off this signal after
sending two characters, including the data being sent currently. If this signal
will not be used, make sure to strap this signal circuit to the RS signal
circuit.
DR Input Data set ready When I/O device is ready to operate, this signal is set. This signal should
usually be connected to the signal indicating I/O device power supply being
on. (ER signal
(Note)
of I/O device). See Note below.
The control unit transfers data when this signal is set. If the signals turned
off during data transfer, alarm 086 is issued. If the DR signal will not be
used, make sure to strap this signal circuit to the ER signal circuit.
ER Output Control unit
ready to
This signal is set when the control unit is ready to operate. External device
should regard the SD signal as being significant when the ER signal is set.
operation
CD Input Signal
Condition
Since this signal is not used in connections with I/O device, the signal circuit
must be strapped, inside the connecting cable, to the ER signal circuit.
SG Signal grounding
FG Frame grounding
- 59 -
Page 80

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
NOTE
Signal on/off state is defined as follows;
-3V or lower +3V or higher
Function OFF ON
Signal Condition Marking Spacing
Transmission Method of RS232-C interface
- Start-stop
Generally, two transmission methods are available at the serial interface. This control unit uses the
start-stop method.
NOTE
Start-stop method:
With this method, start and stop signals are output before and after each data
bit.
One character in start-stop
b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 b8
Start bit Data bit
(8 bits including one parity bit)
Stop bits
(2 bits)
- Codes
Transmission codes are as follows:
(1) EIA code and Control codes DC1 to DC4.
(2) ISO code and Control codes DC1 to DC4
The connected I/O device must be able to recognize the following control codes, sent from control
unit.
Control code 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
DC1 Tape reader start
DC2 Tape punch designation
DC3 Tape reader stop
DC4 Tape punch release
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○ ○
○
NOTE
The listed control codes are used for both EIA and ISO.
In this interface, control codes DC1 to DC4 are used.
(a) Control unit can control I/O device by issuing codes DC1 to DC4.
(b) If processing is delayed at the I/O device (when the control unit outputs data)
(i) External device can temporarily stop control unit data output by using the control unit's
CS signal. Data output stops within two characters including a currently transmitting
character when CS OFF signal is input to control unit. When CS signal is turned on again,
data transmission start.
(ii) If control code DC3 is input to control unit, control unit stops data output within ten
characters. When control code DC1 is input to control unit, control unit starts sending data
again.
○
- 60 -
Page 81

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
(c) When the external device is equipped with an ISO/EIA converter, the external device must
satisfy the specification shown in Table 5.3.4.
Table 5.3.4
ISO code EIA code Remarks
Character 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Character 87654 321
0 ○ ○ ● 0 ○ ● Number 0
1 ○ ○ ○ ● ○ 1 ● ○ Number 1
2 ○ ○ ○ ● ○ 2 ● ○ Number 2
3 ○ ○ ● ○ ○ 3 ○ ● ○○ Number 3
4 ○ ○ ○ ● ○ 4 ●○ Number 4
5 ○ ○ ● ○ ○ 5 ○ ●○ ○ Number 5
6 ○ ○ ● ○ ○ 6 ○ ●○○ Number 6
7 ○ ○ ○ ● ○ ○ ○ 7 ●○○○ Number 7
8 ○ ○ ○ ○ ● 8 ○● Number 8
9 ○ ○ ○ ● ○ 9 ○○● ○ Number 9
A ○ ● ○ a ○○ ● ○ Address A
B ○ ● ○ b ○○ ● ○ ? Address B
C ○ ○ ● ○ ○ c ○○○ ● ○○ Address C
D ○ ● ○ d ○○ ●○ ? Address D
E ○ ○ ● ○ ○ e ○○○ ●○ ○ ? Address E
F ○ ○ ● ○ ○ f ○○○ ●○○ Address F
G ○ ● ○ ○ ○ g ○○○ ●○○○ Address G
H ○ ○● h ○○ ○● Address H
I ○ ○ ○● ○ i ○○○○● ○ Address I
J ○ ○ ○● ○ j ○ ○ ● ○○ ? Address J
K ○ ○● ○ ○ k ○ ○ ● ○ Address K
L ○ ○ ○● ○ l ○ ● ○○ ? Address L
M ○ ○● ○ ○ m ○ ○ ●○ Address M
N ○ ○● ○ ○ n ○ ●○ ○ Address N
O ○ ○ ○● ○ ○ ○ o ○ ●○○ Address O
P ○ ○ ● p ○ ○ ●○○○ Address P
Q ○ ○ ○ ● ○ q ○ ○○● Address Q
R ○ ○ ○ ● ○ r ○ ○● ○ Address R
S ○ ○ ● ○ ○ s ○○ ● ○ Address S
T ○ ○ ○ ● ○ t ○ ● ○○ Address T
U ○ ○ ● ○ ○ u ○○ ●○ Address U
V ○ ○ ● ○ ○ v ○ ●○ ○ ? Address V
W ○ ○ ○ ● ○ ○ ○ w ○ ●○○ Address W
X ○ ○ ○ ○ ● x ○○ ●○○○ Address X
Y ○ ○ ○ ● ○ y ○○○● ? Address Y
Z ○ ○ ○ ● ○ z ○ ○● ○ Address Z
DEL ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ● ○ ○ ○ Del ○○○○●○○○ *
NUL ● Blank ● *
BS ○ ○● BS ○ ○● ○ *
HT ○● ○ Tab ○○○●○○ *
LF or NL ○● ○ CR or
CR ○ ○● ○ ○ *
SP ○ ○ ● SP ○ ● *
% ○ ○ ● ○ ○ ER ○● ○○
( ○ ○● ( 2-4-5 ) ○○● ○
) ○ ○ ○● ○ ( 2-4-7 ) ○ ○● ○
+ ○ ○● ○ ○ + ○○○ ● *
- ○ ○● ○ ○ - ○ ●
: ○ ○ ○ ● ○
/ ○ ○ ○● ○ ○ ○ / ○○ ● ○
. ○ ○● ○ ○ . ○○ ○● ○○
# ○ ○ ● ○ ○
$ ○ ● ○
& ○ ○ ● ○ ○ & ○●○○ *
▽ ○ ● ○ ○ ○ *
* ○ ○ ○● ○ *
, ○ ○ ○● ○ , ○○○● ○○ *
; ○ ○ ○ ○ ● ○ ○ *
< ○ ○ ○ ● ○ *
= ○ ○ ○ ○ ● ○ ○ *
> ○ ○ ○ ○ ● ○ ○ *
? ○ ○ ○ ● ○ ○ ○ *
@ ○ ○ ● *
” ○ ○ *
EOB
○ ●
- 61 -
Page 82

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
NOTE
1 When the external device is equipped with an ISO/EIA converter, the following
items must be noted in Table 5.3.4.
Control out (Comment field start)
Control in (Comment field end)
EIA code (....................)) o .. ..................
Condition 1
ISO code (.....................) : ....................
CR
Condition 2
LF
Condition 3Condition 1
Condition1 Left parenthesis "("of the ISO code punches holes at bits 2, 4 and 5
when used in the EIA code.
Right parenthesis ")"of the ISO code punches holes at bits 2, 4 and
7 when used in the EIA code.
Condition2 EIA code
CR
is LF in ISO code.
Condition3 EIA code O is : in ISO code.
2 Control codes DC1 to DC4 are transmission codes output from the control unit.
So they need not to be punched on the control unit tape.
(3) Transmission rate (Baud rate)
The transmission rate (Baud rate) is the number of bits transferred per second.
The following baud rates are available depending on the system parameter.
50, 100, 110, 150, 200, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600
[Example] Baud rate : 110
When using one start bit and two stop bits (totaling 11 bits per character):
Transmission characters/second= 110/11 =10 characters/second (Max.)
(4) Cable length
The cable length depends on the external device type. Consult with the device manufacturers for
actual connecting cable lengths.
Cable length is as follows by the specification of control unit.
RS232-C Baud rate 4800 or less: Up to 100 m
Baud rate 9600 or less: Up to 50 m
Time chart when the control unit receives data (Read into memory)
(1) Control unit outputs DC1.
(2) The I/O device starts sending data upon receiving DC1.
(3) Control unit sends DC3 when control unit processing is delayed.
(4) The I/O device stops sending data to control unit after receiving DC3.
The device may send up to 10 characters after receiving DC3. If it sends more than 10 characters,
alarm 087 will occur.
(5) Control unit reissues DC1 upon completing delayed processing.
(6) The I/O device restarts data output upon receiving the DC1 code (the data must be the next data to
the preceding.)
(7) Control unit sends DC3 upon completing data read.
(8) The I/O device stops sending data.
- 62 -
Page 83

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
ER
(output)
RS (output)
SD (output)
RD (input)
DR (input)
CS (input)
10ms or longer
DC1 DC3 DC1
ER code
Up to 10 characters
1ms or longer
100ms or longer
DC3
Time chart when the control unit send data (Punch out)
(1) Control unit output DC2.
(2) Control unit outputs punch data in succession.
(3) When data processing is delayed at the I/O device.
(a) Data output stops within two characters including a currently transmitting character when CS
signal is turned off.
When CS signal is turned on again, data transmission starts. (See Fig. 5.3.4 (b))
(b) If control code DC3 is input to control unit, control unit stops data output within ten characters.
When control code DC1 is input to control unit, control unit starts sending data again. (See Fig.
5.3.4 (c))
(4) The control unit starts sending the next data if the CS signal is turned on after the I/O device
completes data processing.
(5) The control unit issues DC4 upon completing data output.
10ms or longer 100ms or longer
ER (output)
RS (output)
SD (output)
RD (input)
CS (input)
DC4 DC2
1ms or longer Within 2 characters
Fig. 5.3.4 (b)
- 63 -
Page 84

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
10ms or longer 100ms or longer
ER (output)
RS (output)
SD (output)
DC3 DC1
RD (input)
Within 2 characters
DR (input)
CS (input)
1ms or longer
DC4 DC2
Fig. 5.3.4 (c)
Connection between RS232-C interface and external device
Control unit side
SD
RD
RS
I/O device side
SD
RD
RS
CS
ER
DR
CD
SG
FG
CS
ER
DR
CD
SG
FG
- 64 -
Page 85

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
● Use the connection shown in the figure below when the ER and DR signals are not used for
handshaking.
Control unit
side
SD
RD
RS
CS
ER
DR
CD
SG
FG
SD
RD
RS
CS
ER
DR
CD
SG
FG
I/O device side
The cable for connecting the I/O device to the control unit should be connected as shown in the below
diagram.
Serial interface
SD
RD
RS
CS
SG
ER
DR
Cable : twist 10 pairs × 0.18mm2, with shield
- 65 -
Page 86

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
5.3 CONNECTING THE HIGH-SPEED SKIP (HDI)
5.3.1 Connecting the High-speed Skip (HDI)
Cont rol un it
JA40
FI80-20P, DF1R020WB1
1
DI0
11 HDI1
2 0V
3
4 0V
5 0V
6 < >
7
8
9 19 < >
10 0V 20
NOTE
1 No connections must be made to the pins with angle brackets (<>) because they
are reserved for expansions.
DI2
< >
< >
< >
12 0V
13 HDI3
14 0V
15 < >
16 0V
17
< >
< >
18
< >
- 66 -
Page 87

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
3
Cable connections
JA40
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
0V
1
2
11
12
3
4
13
14
6
10
5
or
15
16
17
18
19
20
7
8
9
10
Shield
HDI0
HDI1
HDI2
HDI
Ground plat e
Recommended cable–side connectors
P C R- E2 0F A (H on d a Ts us h i n K ogy o )
FI 30- 2 0S (Hi ro s e El ec tr i c )
FCN -247J020-G/E ( FU JITSU COM PONENT)
52622-2011 (Mole x Japan)
5.3.2 Input Signal Rules for the High-speed Skip (HDI)
Circuit configuration
Control unit
DRIVER
SHIELD
Absolute maximum rating
Input voltage range Vin: -3.6V to +13.6V
IiL/IiH
FILTER
VH/VL
RECEIVER
- 67 -
Page 88

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
Input characteristics
Unit Symbol Specification Unit Remarks
High level input voltage VH 3.6 to 11.6 V
Low level input voltage VL 0 to 1.0 V
High level input current IiH
Low level input current IiL -8.0 (max) mA Vin=0V
Input signal pulse duration 20 (min) μs
Input signal delay or variations 0.02 (max) ms
2 (max) mA Vin=5V
11 (max) mA Vin=10V
NOTE
1 The plus (+) sign of IiH/IiL represents the direction of flow into the receiver. The
minus (-) sign of IiH/IiL represents the direction of flow out of the receiver.
2 The high-speed skip signal is assumed to be 1 when the input voltage is at the
low level and 0 when it is at the high level.
3 The input level for the control unit receiver is high when the circuit is open. So,
the input level for the external driver must be low.
5.4 LINKING THE ETHERNET INTERFACE
CAUTION
Before attaching or removing cables, power off the control unit main unit, and
confirm that the power is off.
Ask the respective manufacturers for explanations about how to build a network
and about conditions for using units (such as a media converter, hub,
transceiver, and cable) other than the control unit. When installing network
cables, exercise sufficient caution so that the network will not be affected by any
noise source. Electrically separate the network wiring sufficiently from noise
sources like motors and their power lines. Also, ground each unit as required. If
the grounding impedance is high, it may cause trouble in communication. Once
the equipment is installed, conduct communication tests to verify normal
operation before starting actual use of the equipment.
FANUC is not liable to any damage related to trouble arising from any unit other
than the control unit.
5.4.1 Connection to the Ethernet Interface
A hub (line concentrator) is used to connect the control unit to a system. A typical example of connection
is shown below. For the connection of the control unit with the FANUC PANEL i and a commercially
available personal computer using Ethernet, see also Chapter 11.
- 68 -
Page 89

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
Control unit
Max. 100m
Twisted-pair cable
HUB
(line concentrator)
NOTE
1 To connect the control unit to the 10BASE-T Ethernet interface, use a hub which
satisfies the following conditions:
- Supports 100BASE-TX.
- Has an auto-negotiation function.
- Supports store-and-forward switching.
2 The cable can be up to 100 m long (for the FANUC- recommended cable for
movable sections, up to 50 m). Do not make the cable longer than necessary.
3 An Ethernet cable needs clamping to make system operation stable. For details
of clamping, see Subsection 3.4.6, “Cable Clamp and Shield Processing”. The
clamp for grounding the shield of the cable can also fix the cable.
Control unit
Ethernet cable
Clamp
Grounding plate
4 Some of the units (hub, transceiver, etc.) required to build a network are not
dust-proof. They should be enclosed in a dust-proof cabinet. Using them in an
atmosphere with dust or oil mist may lead to a communication error or failure.
Pin arrangement of the Ethernet connector (CD38A, CD38S)
CD38A, CD38S
Pin No. Signal name Description
1 TX+ Transmit +
2 TX- Transmit 3 RX+ Receive +
4 Not used
5 Not used
- 69 -
Page 90

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
2
5
7
8
2
5
7
8TX+
-
-
2
3
Pin No. Signal name Description
6 RX- Receive 7 Not used
8 Not used
5.4.2 Specification of Twisted-Pair Cable
Cable connection
The connectors of a cable for connecting between the Ethernet interface (CD38A, CD38S) and the hub
have the pin arrangement shown below.
CD38A,CD38S
HUB
1TX+
TX-
3RX+
4
6RX-
CD38A, CD38S
TX
RX+
RX
RJ-45
mo dular jack
Max. 1 00m
1
2
3
6
1TX+
TX-
3RX+
4
6RX-
HUB
1
TX+
TX-
RX+
6
RX-
Shield
NOTE
The cable can be up to 100 m long (for the FANUC- recommended cable for
movable sections, up to 50 m). Do not make the cable longer than necessary.
Cable Wires
Many cables without a shield (UTP cables) are commercially available as twisted pair cables conforming
to 10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX. To improve noise immunity in factory automation environments,
however, be sure to use twisted pair cables (STP cables) with a common shield in category 5.
Recommended cable wire (for fixed parts)
Manufacturer Specification Remark
Nissei Electric Co., Ltd. F-4PWMWM F Single-wire cable
- 70 -
Page 91

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
NOTE
No cable recommended for use in fixed sections shall be used in movable
sections.
For movable sections, be sure to use the recommended cables for movable
sections listed below.
Recommended cable wire (for movable sections)
Manufacturer Specification Remark
Oki Electric Cable Co., Ltd. AWG26 4P TPMC-C5-F (SB)
SHINKO ELECTRIC
INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.
FNC-118
Dedicated to FANUC products, with no
connector
Specification
• Ordering specifications : A66L-0001-0453
• Electrical characteristic : Complying with EIA/TIA 568A categories 3 and 5
• Structure : Common-shield braided cable with drain wire
The conductors of the cable are AWG26 annealed-copper strand wire, with a
sheath 0.8 mm thick and an outer diameter of 6.7 ± 0.3 mm
• Fire resistance : UL1581 VW-1
• Oil resistance : As per FANUC's internal standard (Equivalent to conventional oil-resistant
electrical cable)
• Flex resistance : Million or more bending cycles with a bending radius of 50 mm (U-shaped
bend test)
• UL style No. : AWM20276(80℃/30V/VW-1)
NOTE
When using this cable, keep the length between the control unit and hub within
50 m because of its attenuation performance. Be sure to use the
TM21CP-88P(03) connector manufactured by Hirose Electric Co., Ltd.
About cable assemblies
Oki Electric Cable Co., Ltd. can offer a cable assembly that uses the TM21CP-88P(03) connector made
by Hirose Electric Co., Ltd. To get this cable assembly, negotiate directly with the manufacturer on its
specifications (cable length, shipping test, package, etc.).
Connector specification
An 8-pin modular connector called the RJ-45 is used with a twisted-pair cable for Ethernet interfaces. Use
the connector listed below or equivalent.
Manufacturer’s
model number
Connector used with cable AWG26 4P TPMC-C5-F(SB) TM21CP-88P(03) Hirose Electric
Manufacturer Remark
(Note)
Co., Ltd.
- 71 -
Page 92

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
[
NOTE
About TM21CP-88P(03)
Ordering specifications: A63L-0001-0823#P
Complying with EIA/TIA 568A categories 3 and 5
Ask Hirose Electric Co., Ltd. for explanations about how to attach the connector
to a cable. (Hirose Electric Co., Ltd. offers the TM21CP-88P(03) Wiring
Procedure Specification (Engineering Specification No. ATAD-E2367) to explain
the related technical information.)
5.4.3 Network Installation
Even when the machine satisfies its grounding requirements, noise from the machine may get on
communication lines depending on the way the machine is installed and its environment, resulting in a
communication error. Separating and isolating the Ethernet backbone cable and PC from the machine can
prevent noise from getting on the communication lines.
An example of connection is shown below.
E xample of co nnect i on]
Note 1
HUB
PC and backbone c able side
Elec tri cal separation by
connection with
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX
Machine system side
Machine Machine Machine
Note 1 Note 1 N ote 1
STP cable
STP cable
Po wer supply
f or the HUB
NOTE
1 Ground the PC and backbone cable separately from the machine system.
If this is impossible because there is only one grounding point, use separate
grounding wires for the PC/backbone cable and the machine system up to the
grounding point.
The grounding resistance must not be higher than 100 Ω (class 3 grounding).
The grounding wire must not be thinner than the AC power line conductor, and
its cross-sectional area must not smaller than 5.5 mm
2
.
2 In some cases, the aforementioned isolation/separation method based on
10BASE-T/ 100BASE-TX cannot assure normal communication because of
influence by noise. In such worst environments, use optical fiber media to
completely isolate the machine from the PC.
- 72 -
Page 93

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
r
r
V
p
y
5.4.4 Ethernet Connector Panel
Ethernet Connector Panel enables user to connect/disconnect Ethernet cable at the front panel of the
cabinet with ease.
Specification
Name Specification
A02B-0303-C194 with 1m cable
Ethernet Connector Panel
Ethernet Cable for Connector Panel
Component
A02B-0303-C195 with 2m cable
A02B-0303-C196 with 5m cable
A02B-0303-K820 cross cable 1.5m
A02B-0303-K821 cross cable 5m
A02B-0303-K822 straight cable 1.5m
A02B-0303-K823 straight cable 5m
Ethernet Connector Panel
CPD20
Connector for DC24
ower suppl
FG
Connect to cabinet
(Crimp terminal M4)
Connect to the
PC or HUB
CD51
Connector fo
Ethernet Cable fo
Connector Panel
Ethernet Cable for Connect or Panel
CD51
Connect to the Ethernet
Connector Panel
CD38
Connect to CNC
- 73 -
Page 94

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
A
Connection of Ethernet Connector Panel
CNC
CD38x
1 TPTX+
2 TPTX-
3 TPRX+
4
5
6 TPRX-
7
8
CD38
ttached cable
24V input (*1)
FG
Ethernet Connector Panel
CPD20
1 (+24V)
2(0V)
3
CD51
1TPTX+
2TPTX-
3(0V)
4 (+24V)
5TPRX+
6TPRX-
7 (+24V)
8(0V)
(*1)When DC24V is used at CD51, CPD20 connect to DC24V power supply. Do not connect when
it is unnecessary.
Cable connection
CD38
(RJ-45)
TPTX
TPTX
TPRX
TPRX
1
+
2
-
3
+
6
-
4
5
7
Grounding plate
8
SHIELD
CPD20
(+24V)
(0V)
CD51
1
TPTX+
2
5
6
3
4
7
8
FG
1
2
TPTX
TPRX
TPRX
(0V)
(+24V)
(+24V)
(0V)
-
+
-
3
- 74 -
Page 95

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
Connection of Ethernet Cable for Connector Panel
Ethernet Connector Panel
CD51
1 TPTX+
2 TPTX-
3 (0V)
4 (+24V)
5 TPRX+
6 TPRX-
7 (+24V)
8 (0V)
CD51
Peripherals side
connector
PC or HUB (line
concentrator)
Cable connection
[Cross cable]
CD51
TPTX+
TPTX-
TPRX+
TPRX-
(+24V)
(+24V)
Connector
Frame
[Straight cable]
CD51
TPTX+
TPTX-
TPRX+
TPRX-
(+24V)
(+24V)
Connector
Frame
(0V)
(0V)
(0V)
(0V)
Peripherals
side connector
1
2
5
6
3
4
7
8
SHIELD
1
2
5
6
3
4
7
8
SHEILD
3
TPRX+
6
TPRX-
1
TPTX+
2
TPTX-
4
5
7
8
Connector
Frame
Peripherals
side connector
1
TPTX+
2
TPTX-
3
TPRX+
6
TPRX-
4
5
7
8
Connector
Frame
- Recommended cable side connector
CD51 side: JB5DT08YN121 (Japan Aviation Electronics)
Peripheral side: TMP21P-88P (Hirose Electric)
- Recommended cable conductor : A66L-0001-0453
- 75 -
Page 96

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
- Maximum cable length: 40m (in case of recommended cable)
Do not make the cable longer than necessary.
- Recommended cable specification
[Cross cable]
A02B-0303-K820 (Cable length: 1.5m)
A02B-0303-K821 (Cable length: 5m)
[Straight cable]
A02B-0303-K822 (Cable length: 1.5m)
A02B-0303-K823 (Cable length: 5m)
NOTE
Technical information about connecting wires and the assembly of the connector
is prepared. Refer to this information.
- Japan Aviation Electronics: JB5DT08YN121 Operator’s Manual (No.
JAHL-50007)
- Hirose Electric: TM21CP-88P(03) Wiring Procedure Specification
(Engineering Specification No.ATAD-E2367)
- 76 -
Page 97

B-64603EN/01 5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS
5.5 USB PORT
The LCD-mounted type control unit have a USB port for a USB memory. Via the USB port, data can be
input to the control unit and output from it.
Refer to the next paragraph for the USB port of basic unit G (15”LCD).
USB port (front)
NOTE
1 This USB port is dedicated to a USB memory. Do not connect other USB
devices to the port.
2 It is not guaranteed that every commercially available USB memory can operate
normally. For example, a USB memory with a security function does not operate.
Some commercially available USB memories may not be designed for the use in
an FA environment.
CAUTION
1 While the control unit is accessing the USB memory, do not turn the power to the
control unit off or remove the USB memory.
2 Close the cover of the USB port when no USB memory is inserted.
3 The maximum USB power supply (USB_5V) current is 500 mA in total.
- 77 -
Page 98

5.CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS B-64603EN/01
Basic unit G (15”LCD)
Basic unit G (15” LCD) has two USB ports for a USB memory.
Via the USB port, data can be input to the control unit and output from it.
NOTE
1 The connected USB cable must not become longer than 5m surely. When using
2 These USB ports are dedicated to a USB memory. Do not connect other USB
3 It is not guaranteed that every commercially available USB memory can operate
1 While the control unit is accessing the USB memory, do not turn the power to the
2 Close the cover of the USB port when no USB memory is inserted in front USB
3 The maximum USB power supply (USB_5V) current on the front and rear sides is
USB port
USB port (rear side)
USB_5V
1
USB -
2
USB +
3
USB_0V
4
1 2 3 4
USB device through the relay cable, confirm the operation enough in the
machine maker.
devices to the port.
normally. For example, a USB memory with a security function does not operate.
Some commercially available USB memories may not be designed for the use in
an FA environment.
CAUTION
control unit off or remove the USB memory.
port.
500mA in total.
- 78 -
Page 99

B-64603EN/01 6.SERVO AND SPINDLE INTERFACES
r
6 SERVO AND SPINDLE INTERFACES
6.1 OVERVIEW
Cont rol unit
COP10A
Optic al fibe r cab le
Power
supply
This figur e is an exa m ple of connecting to control unit a
LCD -m ount e d type.
Separate
de tect or int er f ace
unit
Sp indle am plif ier
Se rvo amplifie
- 79 -
Page 100

6.SERVO AND SPINDLE INTERFACES B-64603EN/01
This chapter describes how to connect the control unit to the servo amplifiers, spindle amplifiers, and
separate detector interface units.
The control unit is connected to servo amplifiers, spindle amplifiers, and separate detector interface units
via serial buses using optical fiber cables (called FSSBs below). A FSSB lines can be connected to the
control unit. For the FSSB lines, optical connectors are located on the main board.
Slave units to be connected to the control unit must support the 30i-B series. Slave units include servo
amplifiers, spindle amplifiers, and separate detector interface units.
6.2 Interface to the Amplifiers
Control unit
Main board
Slave unit
COP10A
Maximum allowable cable length
1) The total cable length on each line shall satisfy the follo wing
conditions.
2) Between the control unit and 1st slave unit:
- When A66L-6001-0026#~ is used: 50 m
- When A66L-6001-0049#~ is used: 100 m
3) Between slave units: 40 m
Note: Slave units include servo amplifiers, spindle amplifiers, and
separate detector interface units.
FSSB line 2)
Optical fiber cable
3)
3)
3)
<Total cable length on each line>
Control mode Maximum total cable length
HRV2 500m
HRV3 200m
<Optical fiber cable types>
Usage Cable drawing number Cable length
For internal
connection
02B-0236-K851 to -K856 and
-K860 to –K862
(A66L-6001-0023#~)
Length of 10 m or less
Servo amplifier
COP10B
COP10A
COP10B
COP10A
Spindle amplifier
COP10B
COP10A
Separate detector
interface unit
COP10B
COP10A
- 80 -
 Loading...
Loading...