Page 1

CLI Manual
Product Model :
Layer 2 Managed Stackable Fast Ethernet Switch
Release 5.1
TM
DES-3500 Series
Page 2

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION ......................................................................................................................... 1
USING THE CONSOLE CLI ........................................................................................................ 3
COMMAND SYNTAX .................................................................................................................. 7
BASIC SWITCH COMMANDS .................................................................................................... 9
MODIFY BANNER AND PROMPT COMMANDS ..................................................................... 21
SWITCH PORT COMMANDS ................................................................................................... 25
PORT SECURITY COMMANDS ............................................................................................... 28
NETWORK MANAGEMENT (SNMP) COMMANDS ................................................................. 32
SWITCH UTILITY COMMANDS ................................................................................................ 54
NETWORK MONITORING COMMANDS .................................................................................. 62
MULTIPLE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (MSTP) COMMANDS .......................................... 76
FORWARDING DATABASE COMMANDS ............................................................................... 89
TRAFFIC CONTROL COMMANDS .......................................................................................... 97
QOS COMMANDS .................................................................................................................. 102
PORT MIRRORING COMMANDS ........................................................................................... 109
VLAN COMMANDS ................................................................................................................. 112
ASYMMETRIC VLAN COMMANDS ........................................................................................ 119
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS ...................................................................................... 121
IP-MAC BINDING .................................................................................................................... 126
LIMITED IP MULTICAST ADDRESS ...................................................................................... 142
Page 3

BASIC IP COMMANDS ........................................................................................................... 146
IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS ............................................................................................. 149
DHCP RELAY .......................................................................................................................... 159
802.1X COMMANDS (INCLUDING GUEST VLANS)............................................................. 171
ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS ..................................................................... 184
SAFEGUARD ENGINE COMMANDS ..................................................................................... 203
FILTER COMMANDS (DHCP/NETBIOS) ................................................................................ 205
LOOPBACK DETECTION COMMANDS ................................................................................ 210
TRAFFIC SEGMENTATION COMMANDS ............................................................................. 213
TIME AND SNTP COMMANDS ............................................................................................... 215
ARP COMMANDS ................................................................................................................... 221
ROUTING TABLE COMMANDS ............................................................................................. 225
MAC NOTIFICATION COMMANDS ........................................................................................ 227
ACCESS AUTHENTICATION CONTROL COMMANDS ........................................................ 231
SSH COMMANDS ................................................................................................................... 254
SSL COMMANDS ................................................................................................................... 261
D-LINK SINGLE IP MANAGEMENT COMMANDS ................................................................. 268
COMMAND HISTORY LIST .................................................................................................... 278
LLDP COMMANDS ................................................................................................................. 281
CPU FILTERING COMMANDS ............................................................................................... 303
CABLE DIAGNOSTICS COMMANDS .................................................................................... 305
DHCP LOCAL RELAY COMMANDS ...................................................................................... 306
Page 4

GRATUITOUS ARP COMMANDS .......................................................................................... 309
ARP SPOOFING PREVENTION COMMANDS ....................................................................... 313
TECHNICAL SUPPORT COMMANDS.................................................................................... 315
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................................. 317
Page 5

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
1
INTRODUCTION
The Switch can be managed through the Switch’s serial port, Telnet, or the Web-based management agent. The Command Line
Interface (CLI) can be used to configure and manage the Switch via the serial port or Telnet interfaces.
This manual provides a reference for all of the commands contained in the CLI. Configuration and management of the Switch via
the Web-based management agent is discussed in the Manual.
The DES-3500 Layer 2 stackable Fast Ethernet switches are members of the D-Link xStack family. Ranging from 10/100Mbps
edge switches to core gigabit switches, the xStack switch family has been future-proof designed to provide a stacking architecture
with fault tolerance, flexibility, port density, robust security and maximum throughput with a user-friendly management interface
for the networking professional.
This manual provides a reference for all of the commands contained in the CLI for members of the xStack DES-3500 series,
including the DES-3526, DES-3526DC, and the DES-3550. Examples present in this manual may refer to any member of the
xStack DES-3500 series and may show different port counts, but are universal to this series of switches, unless otherwise stated.
Configuration and management of the Switch via the Web-based management agent is discussed in the User’s Guide.
Accessing the Switch via the Serial Port
The Switch’s serial port’s default settings are as follows:
• 9600 baud
• no parity
• 8 data bits
• 1 stop bit
A computer running a terminal emulation program capable of emulating a VT-100 terminal and a serial port configured as above
is then connected to the Switch’s serial port via an RS-232 DB-9 cable.
With the serial port properly connected to a management computer, the following screen should be visible. If this screen does not
appear, try pressing Ctrl+r to refresh the console screen.
DES-3526 Fast Ethernet Switch Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 5.01-B47
Copyright(C) 2008 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
username:
Figure 1-1. Initial CLI screen
There is no initial username or password. Just press the Enter key twice to display the CLI input cursor − DES-3526:admin#.
This is the command line where all commands are input.
1
Page 6
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
MAC
Setting the Switch’s IP Address
Each Switch must be assigned its own IP Address, which is used for communication with an SNMP network manager or other
TCP/IP application (for example BOOTP, TFTP). The Switch’s default IP address is 10.90.90.90. Users can change the default
Switch IP address to meet the specification of your networking address scheme.
The Switch is also assigned a unique MAC address by the factory. This MAC address cannot be changed, and can be found on the
initial boot console screen – shown below.
Boot Procedure 3.00.008
-------------------------------------------------------------
Power On Self Test.................................100%
Address : 00-15-E9-41-5A-B9
H/W Version : 0A3G
Please wait, loading V5.01-B47 Runtime image........15%
Figure 1-2. Boot Screen
The Switch’s MAC address can also be found in the Web management program on the Switch Information (Basic Settings)
window on the Configuration menu.
The IP address for the Switch must be set before it can be managed with the Web-based manager. The Switch IP address can be
automatically set using BOOTP or DHCP protocols, in which case the actual address assigned to the Switch must be known.
The IP address may be set using the Command Line Interface (CLI) over the console serial port as follows:
1. Starting at the command line prompt, enter the commands config ipif System ipaddress
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy. Where the x’s represent the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface named
System and the y’s represent the corresponding subnet mask.
2. Alternatively, users can enter config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z. Where the x’s represent the IP address to
be assigned to the IP interface named System and the z represents the corresponding number of subnets in CIDR
notation.
The IP interface named System on the Switch can be assigned an IP address and subnet mask which can then be used to connect a
management station to the Switch’s Telnet or Web-based management agent.
DES-3526:admin#config ipif System ipaddress 10.73.21.51/8
Command: config ipif System ipaddress 10.73.21.51/8
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
Figure 1-3. Assigning an IP Address
In the above example, the Switch was assigned an IP address of 10.41.44.254 with a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0. The system
message Success indicates that the command was executed successfully. The Switch can now be configured and managed via
Telnet, SNMP MIB browser and the CLI or via the Web-based management agent using the above IP address to connect to the
Switch.
2
Page 7

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
2
USING THE CONSOLE CLI
The DES-3500 Series supports a console management interface that allows the user to connect to the Switch’s management agent
via a serial port and a terminal or a computer running a terminal emulation program. The console can also be used over the
network using the TCP/IP Telnet protocol. The console program can be used to configure the Switch to use an SNMP-based
network management software over the network.
This chapter describes how to use the console interface to access the Switch, change its settings, and monitor its operation.
Note: Switch configuration settings are saved to non-volatile RAM using the save command. The current
configuration will then be retained in the Switch’s NV-RAM, and reloaded when the Switch is rebooted. If
the Switch is rebooted without using the save command, the last configuration saved to NV-RAM will be
loaded.
Connecting to the Switch
The console interface is used by connecting the Switch to a VT100-compatible terminal or a computer running an ordinary
terminal emulator program (e.g., the HyperTerminal program included with the Windows operating system) using an RS-232C
serial cable. Your terminal parameters will need to be set to:
• VT-100 compatible
• 9600 baud
• 8 data bits
• No parity
• One stop bit
• No flow control
Users can also access the same functions over a Telnet interface. Once users have set an IP address for your Switch, users can use
a Telnet program (in VT-100 compatible terminal mode) to access and control the Switch. All of the screens are identical, whether
accessed from the console port or from a Telnet interface.
After the Switch reboots and users have logged in, the console looks like this:
DES-3526 Fast Ethernet Switch Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 5.01-B47
Copyright(C) 2008 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
username:
Figure 2-1. Initial Console Screen after logging in
Commands are entered at the command prompt, DES-3526:admin#.
There are a number of helpful features included in the CLI. Entering the ? command will display a list of all of the top-level
commands.
3
Page 8
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Next possible completions:
<username>
Next possible completions:
<username>
Next possible completions:
..
?
cable_diag ports
clear
clear address_binding dhcp_snoop binding_entry ports
clear arptable
clear counters
clear fdb
clear log
clear port_security_entry port
config 802.1p default_priority
config 802.1p user_priority
config 802.1x auth_mode
config 802.1x auth_parameter ports
config 802.1x auth_protocol
config 802.1x capability ports
config 802.1x guest_vlan ports
config 802.1x init
config 802.1x reauth
config access_profile profile_id
config account
config address_binding dhcp_snoop max entry ports
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
Figure 2-2. The ? Command
When users enter a command without its required parameters, the CLI will prompt users with a Next possible completions:
message.
DES-3526:admin#config account
Command: config account
DES-3526:admin#
Figure 2-3. Example Command Parameter Help
In this case, the command config account was entered with the parameter <username>. The CLI will then prompt users to enter
the <username> with the message, Next possible completions:. Every command in the CLI has this feature, and complex
commands have several layers of parameter prompting.
In addition, after typing any given command plus one space, users can see all of the next possible sub-commands, in sequential
order, by repeatedly pressing the Tab key.
To re-enter the previous command at the command prompt, press the up arrow cursor key. The previous command will appear at
the command prompt.
DES-3526:admin#config account
Command: config account
DES-3526:admin#config account
Command: config account
4
Page 9

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
<u
Available commands:
sername>
DES-3526:admin#
Figure 2-4. Using the Up Arrow to Re-enter a Command
In the above example, the command config account was entered without the required parameter <username>, the CLI returned
the Next possible completions: <username> prompt. The up arrow cursor control key was pressed to re-enter the previous
command (config account) at the command prompt. Now the appropriate username can be entered and the config account
command re-executed.
All commands in the CLI function in this way. In addition, the syntax of the help prompts are the same as presented in this manual
− angle brackets < > indicate a numerical value or character string, braces { } indicate optional parameters or a choice of
parameters, and brackets [ ] indicate required parameters.
If a command is entered that is unrecognized by the CLI, the top-level commands will be displayed under the Available
commands: prompt.
DES-3526:admin#the
.. ? cable_diag clear
config create delete dir
disable download drv enable
login logout ping reboot
reconfig reset save show
telnet upload
DES-3526:admin#
Figure 2-5. The Next Available Commands Prompt
The top-level commands consist of commands such as show or config. Most of these commands require one or more parameters
to narrow the top-level command. This is equivalent to show what? or config what? Where the what? is the next parameter.
For example, if users enter the show command with no additional parameters, the CLI will then display all of the possible next
parameters.
5
Page 10

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Next
packet port_security ports radius
DES-3526:admin#show
Command: show
possible completions:
802.1p 802.1x access_profile account
address_binding arp_spoofing_prevention arpentry
asymmetric_vlan authen authen_enable authen_login
authen_policy autoconfig bandwidth_control command_history
config cpu cpu_filter
cpu_interface_filtering current_config dhcp_local_relay
dhcp_relay error fdb filter
firmware flow_meter gratuitous_arp greeting_message
gvrp igmp_snooping ipif iproute
lacp_port limited_multicast_addr link_aggregation
lldp log loopdetect mac_notification
mirror multicast multicast_fdb multicast_range
router_ports safeguard_engine scheduling serial_port
session sim snmp sntp
ssh ssl stp switch
syslog system_severity tech_support terminal_line
time time_range traffic
traffic_segmentation trusted_host utilization
vlan
DES-3526:admin#
Figure 2-6. Next possible completions: Show Command
In the above example, all of the possible next parameters for the show command are displayed. At the next command prompt, the
up arrow was used to re-enter the show command, followed by the account parameter. The CLI then displays the user accounts
configured on the Switch.
6
Page 11
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
3
COMMAND SYNTAX
The following symbols are used to describe how command entries are made and values and arguments are specified in this
manual. The online help contained in the CLI and available through the console interface uses the same syntax.
Note: All commands are case-sensitive. Be sure to disable Caps Lock or
any other unwanted function that changes text case.
<angle brackets>
Purpose Encloses a variable or value that must be specified.
Syntax
Description In the above syntax example, users must supply an IP interface
Example
Command
config ipif <ipif_name 12> [{ipaddress <network_address> |
vlan <vlan_name 32> | state [enable | disable}] | bootp | dhcp]
name in the <ipif_name 12> space, a VLAN name in the
<vlan_name 32> space, and the network address in the
<network_address> space. Do not type the angle brackets.
config ipif Engineering ipaddress 10.24.22.5/255.0.0.0 vlan
Design state enable
[square brackets]
Purpose Encloses a required value or set of required arguments. One value
or argument can be specified.
Syntax
Description
Example
Command
create account [admin | operator | user] <username 15>
In the above syntax example, users must specify either an admin or
a user level account to be created. Do not type the square brackets.
create account admin Darren
| vertical bar
Purpose Separates two or more mutually exclusive items in a list, one of
which must be entered.
Syntax
Description
Example
Command
create account [admin | operator | user] <username 15>
In the above syntax example, users must specify either admin, or
user. Do not type the backslash.
create account admin Darren
{braces}
Purpose Encloses an optional value or set of optional arguments.
Syntax
Description In the above syntax example, users have the option to specify
reset {[config | system]} force_agree
config or system. It is not necessary to specify either optional value,
7
Page 12
{braces}
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
however the effect of the system reset is dependent on which, if any,
value is specified. Therefore, with this example there are three
possible outcomes of performing a system reset. See the following
chapter, Basic Commands for more details about the reset
command.
Example
command
reset config
Line Editing Key Usage
Delete Deletes the character under the cursor and then shifts the
remaining characters in the line to the left.
Backspace Deletes the character to the left of the cursor and then shifts the
remaining characters in the line to the left.
Insert or Ctrl+R Toggle on and off. When toggled on, inserts text and shifts previous
text to the right.
Left Arrow Moves the cursor to the left.
Right Arrow Moves the cursor to the right.
Up Arrow Repeats the previously entered command. Each time the up arrow
is pressed, the command previous to that displayed appears. This
way it is possible to review the command history for the current
session. Use the down arrow to progress sequentially forward
through the command history list.
Down Arrow The down arrow will display the next command in the command
history entered in the current session. This displays each command
sequentially as it was entered. Use the up arrow to review previous
commands.
Tab Shifts the cursor to the next field to the left.
Ctrl+k Erases a line in the Command Line interface from the position of
the cursor to the end of the line.
Multiple Page Display Control Keys
Space Displays the next page.
CTRL+c Stops the display of remaining pages when multiple pages are to be
displayed.
ESC Stops the display of remaining pages when multiple pages are to be
displayed.
n Displays the next page.
p Displays the previous page.
q Stops the display of remaining pages when multiple pages are to be
displayed.
r Refreshes the pages currently displayed.
a Displays the remaining pages without pausing between pages.
Enter Displays the next line or table entry.
8
Page 13
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
4
BASIC SWITCH COMMANDS
The basic switch commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in the
following table.
Command Parameters
enable password encryption
disable password encryption
create account [admin | operator | user] <username 15>
config account <username 15>>
show account
delete account [<username 15> | <username 15> force_agree]
show session
show switch
show serial_port
config serial_port {baud_rate [9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 115200] auto_logout [never | 2_minutes |
5_minutes | 10_minutes | 15_minutes]}
enable clipaging
disable clipaging
enable telnet <tcp_port_number 1-65535>
disable telnet
telnet <ipaddr> {tcp_port <value 0-65535>}
enable web <tcp_port_number 1-65535>
disable web
{encrypt [plain_text| sha_1] <password>}
{encrypt [plain_text| sha_1] <password>}
save
reboot
reboot force_agree
reset {[config | system]}
reset {[config force_agree | system force_agree]}
reset { system exclude [vlan | system] }
login
logout
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections.
enable/disable password encryption
Purpose
Syntax enable password encryption
Description
Used to enable or disable password encryption on user accounts
disable password encryption
The user account configuration information will be stored in the
configuration file, and can be applied to the system. If password
9
Page 14
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
enable/disable password encryption
encryption is enabled, the password will be in an encrypted form.
When password encryption is disabled, the user can specify the
password in plain text form, which means the password will be in
plain text form. However, if the user specifies the password in
encrypted form, or if the password has been converted to encrypted
form by the last enabled password encryption command, the
password will remain in the encrypted form. It can not be reverted to
the plaintext.
Example usage:
To enable/disable password encryption on the Switch.
Parameters
Restrictions
DES-3526:admin# enable password encryption
Command: enable password encryption
Success
DES-3526:admin#
None
You must have Operator-level privileges.
create account
Purpose
Syntax create [admin | operator | user] <username 15>>
Description
Used to create user accounts.
[plain_text| sha_1] <password>}
The create account command is used to create user accounts that
consist of a username of 1 to 15 characters and a password of 0 to
15 characters. Up to 8 user accounts can be created.
{encrypt
Example usage:
To create an administrator-level user account with the username “dlink”.
Parameters
Restrictions
[admin | operator | user] <username 15>
plain_text - Select to specify the password in plain text form.
sha_1 - Select to specify the password in the SHA-I enacrpted form.
Password - The password for the user account.
The length for of password in plain-text form and in encrypted form
are different. For the plain-text form, passwords must have a
minimum of 0 character and can have a maximum of 15 characters.
For the encrypted form password, the length is fixed to 35 bytes
long.
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Usernames can be between 1 and 15 characters.
Passwords can be between 0 and 15 characters.
DES-3526:admin#create account admin dlink
Command: create account admin dlink
Enter a case-sensitive new password:****
Enter the new password again for
confirmation:****
10
Page 15
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
NOTICE: In case of lost passwords or password corruption, please refer to the
D-Link website and the White Paper entitled “Password Recovery Procedure”,
which will guide you through the steps necessary to resolve this issue.
config account
Example usage:
To configure the user password of “dlink” account:
Purpose
Syntax config account <username>
Description The config account command configures a user account that has
Parameters <username>
Restrictions
Used to configure user accounts
{encrypt [plain_text| sha_1]
<password>}
been created using the create account command.
plain_text - Select to specify the password in plain text form.
sha_1 - Select to specify the password in the SHA-I enacrpted
form.
Password - The password for the user account.
The length for of password in plain-text form and in encrypted form
are different. For the plain-text form, passwords must have a
minimum of 0 character and can have a maximum of 15
characters. For the encrypted form password, the length is fixed to
35 bytes long.
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Usernames can be between 1 and 15 characters.
Passwords can be between 0 and 15 characters.
Example usage:
DES-3526:admin#config account dlink
Command: config account dlink
Enter a old password:****
Enter a case-sensitive new password:****
Enter the new password again for
confirmation:****
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show account
Purpose Used to display user accounts.
Syntax
Description Displays all user accounts created on the Switch. Up to 8 user
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
show account
accounts can exist at one time.
11
Page 16
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
To display the accounts that have been created:
DES-3526:admin#show account
Command: show account
Current Accounts:
Username Access Level
--------------- -----------dlink Admin
Total Entries: 1
DES-3526:admin#
delete account
Purpose Used to delete user accounts.
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To delete the user account “System”:
To enforce the user account “System” is deleted:
delete account [ <username> | <username> force_agree ]
The delete account command deletes a user account that has
been created using the create account command.
DES-3526:admin#delete account System
Command: delete account System
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin#delete account System
force_agree
Command: delete account System
force_agree
The last administrator account will be
deleted!
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show session
Purpose Used to display a list of currently logged-in users.
Syntax
Description This command displays a list of all the users that are logged-in at
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
show session
the time the command is issued.
12
Page 17

Example usage:
To display the way that the users logged in:
DES-3526:admin#show session
Command: show session
ID Login Time Live Time From Level Name
-- ------------------ -------- --------- ------ -----
*8 00000 days 00:00:37 03:36:27 Serial Port 4 Anonymous
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
show switch
Purpose Used to display general information about the Switch.
Example usage:
To display the Switch’s information:
Syntax
Description This command displays information about the Switch.
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
DES-3526:admin#show switch
Command: show switch
Device Type : DES-3526 Fast Ethernet
Switch
Combo Port : 1000Base-T + 1000Base-T
MAC Address : 00-01-02-03-04-00
IP Address : 10.41.44.22 (Manual)
VLAN Name : default
Subnet Mask : 255.0.0.0
Default Gateway : 0.0.0.0
Boot PROM Version : Build 3.00.005
Firmware Version : Build 5.01-B47
Hardware Version : 0A1
Device S/N :
Power Status : Main – Normal, Redundant –
Not Present
System Name : DES-3526
System Location : 7th_flr_east_cabinet
System Contact : Julius_Erving_212-555-6666
Spanning Tree : Disabled
GVRP : Disabled
IGMP Snooping : Disabled
TELNET : Enabled (TCP 23)
WEB : Enabled (TCP 80)
RMON : Enabled
Asymmetric VLAN : Disabled
DES-3526:admin#
show switch
show serial_port
Purpose Used to display the current serial port settings.
Syntax
show serial_port
13
Page 18
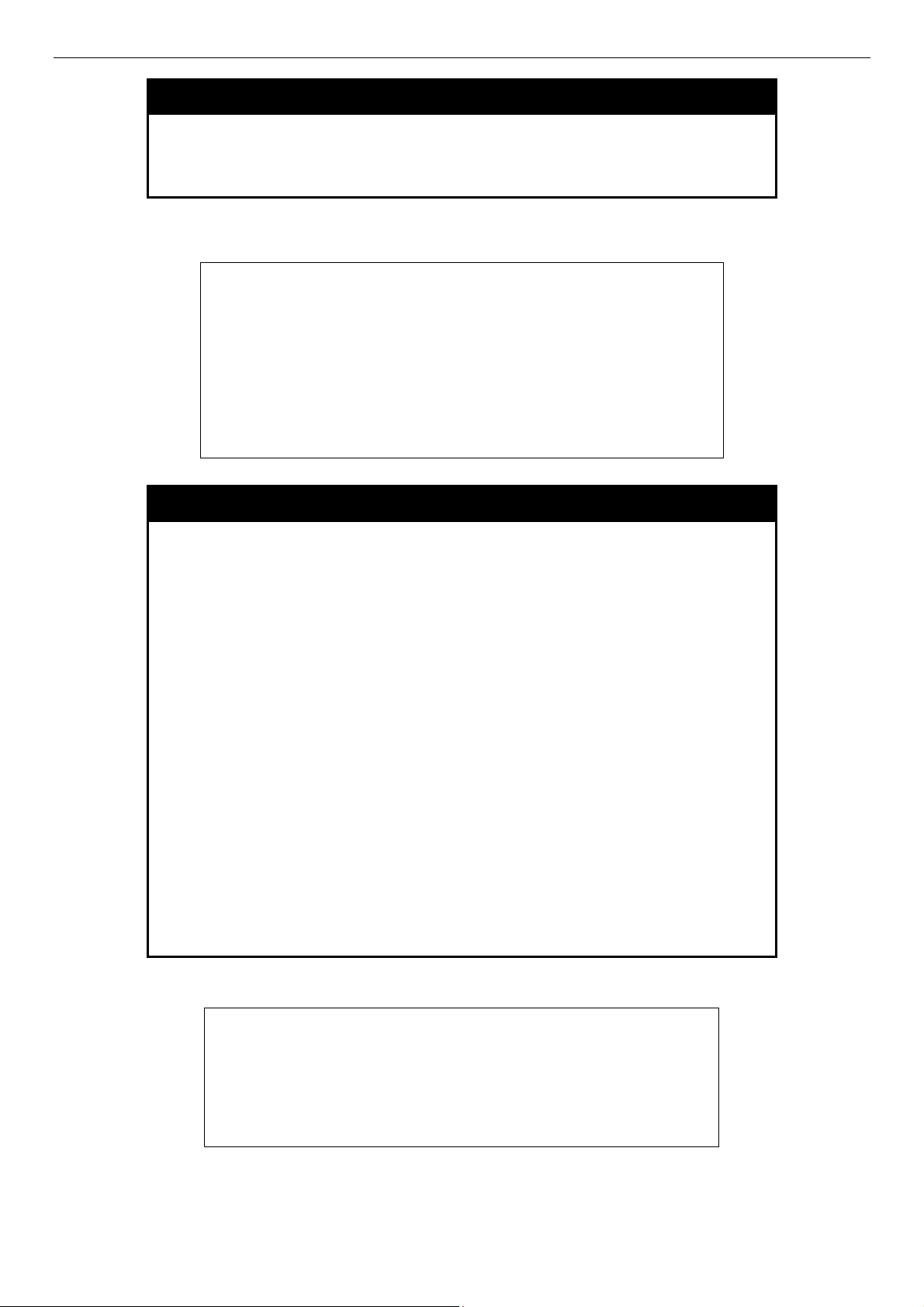
Example usage:
To display the serial port setting:
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
show serial_port
Description This command displays the current serial port settings.
Parameters None.
Restrictions None
DES-3526:admin#show serial_port
Command: show serial_port
Baud Rate : 9600
Data Bits : 8
Parity Bits : None
Stop Bits : 1
Auto-Logout : 10 mins
DES-3526:admin#
config serial_port
Purpose Used to configure the serial port.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
Restrictions
config serial_port {baud_rate [9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 115200] |
auto_logout [never | 2_minutes | 5_minutes | 10_minutes |
15_minutes]}
This command is used to configure the serial port’s baud rate and auto
logout settings.
baud_rate [9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 115200]− The serial bit rate that will be
used to communicate with the management host. There are four options:
9600, 19200, 38400, 115200.
never − No time limit on the length of time the console can be open with
no user input.
2_minutes − The console will log out the current user if there is no user
input for 2 minutes.
5_minutes − The console will log out the current user if there is no user
input for 5 minutes.
10_minutes − The console will log out the current user if there is no user
input for 10 minutes.
15_minutes − The console will log out the current user if there is no user
input for 15 minutes.
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To configure baud rate:
DES-3526:admin#config serial_port baud_rate 115200
Command: config serial_port baud_rate 115200
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
14
Page 19
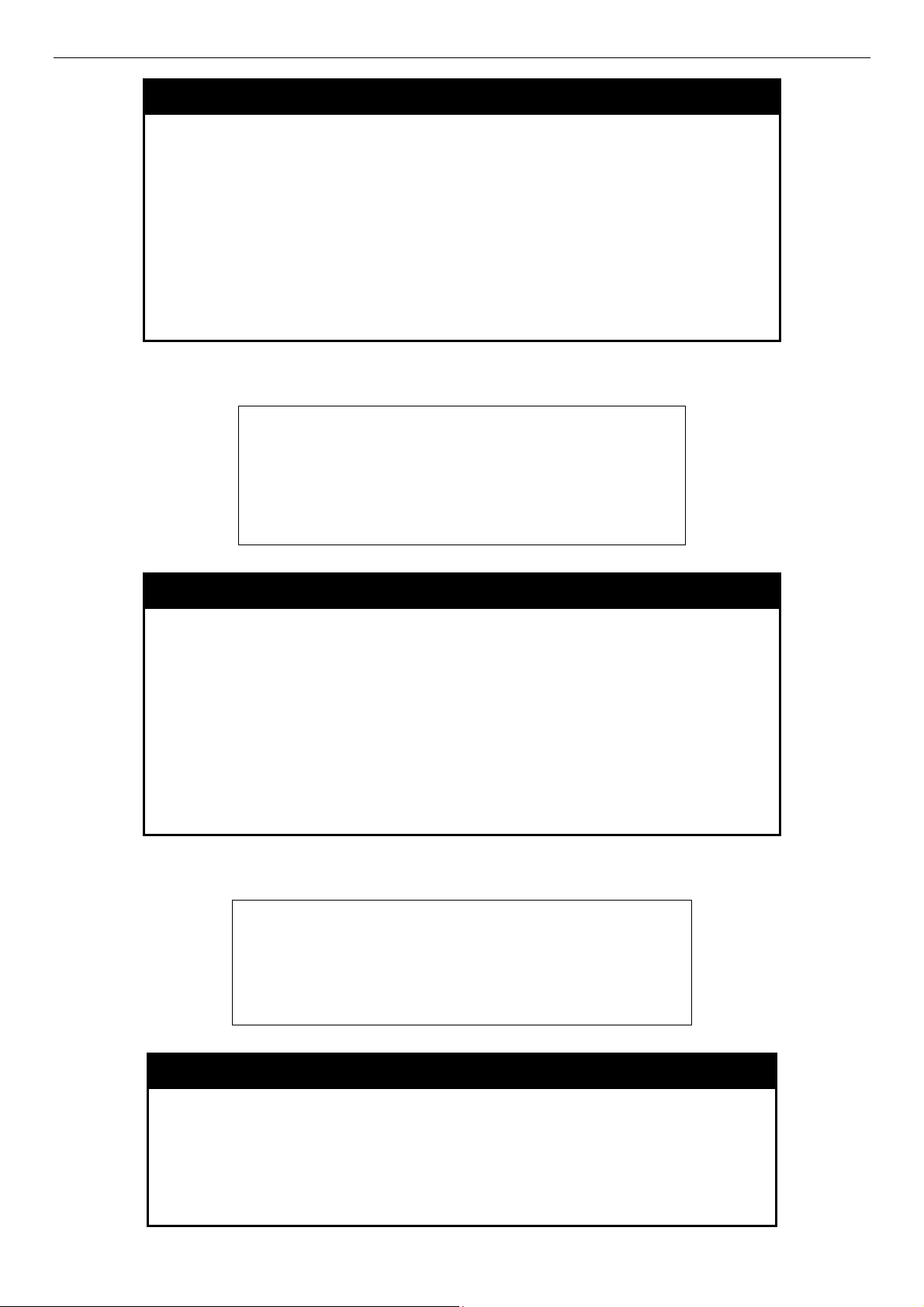
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
enable clipaging
Purpose Used to pause the scrolling of the console screen when a command
displays more than one page.
Example usage:
To enable pausing of the screen display when the show command output reaches the end of the page:
Syntax
Description This command is used when issuing a command which causes the
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#enable clipaging
Command: enable clipaging
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
enable clipaging
console screen to rapidly scroll through several pages. This
command will cause the console to pause at the end of each page.
The default setting is enabled.
command.
disable clipaging
Purpose Used to disable the pausing of the console screen scrolling at the
end of each page when a command displays more than one screen
of information.
Example usage:
To disable pausing of the screen display when show command output reaches the end of the page:
Syntax
Description This command is used to disable the pausing of the console screen
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#disable clipaging
Command: disable clipaging
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
disable clipaging
at the end of each page when a command would display more than
one screen of information.
command.
enable telnet
Purpose Used to enable communication with and management of the Switch
using the Telnet protocol.
Syntax
Description This command is used to enable the Telnet protocol on the Switch.
enable telnet <tcp_port_number 1-65535>
The user can specify the TCP or UDP port number the Switch will
use to listen for Telnet requests.
15
Page 20
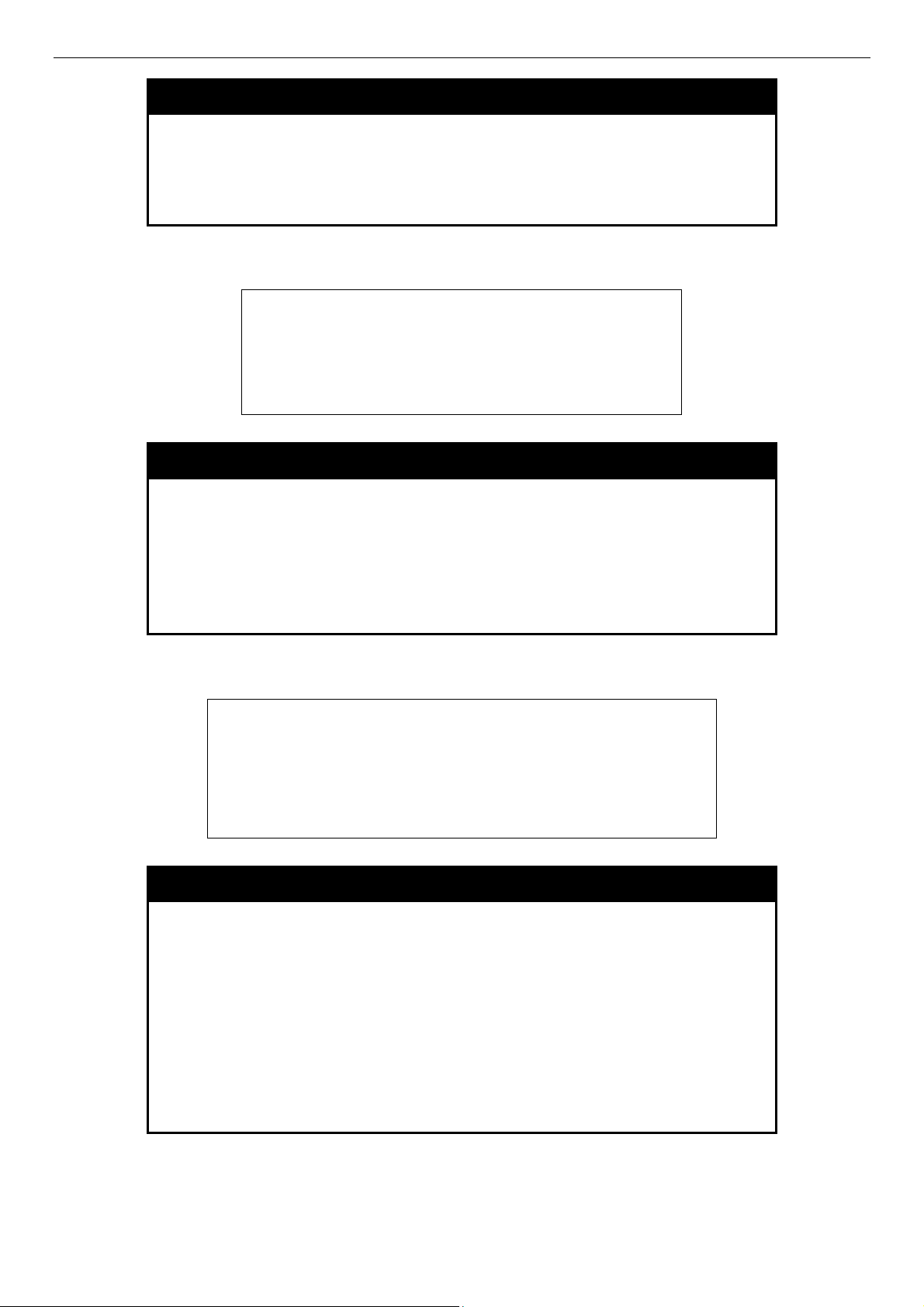
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
enable telnet
Example usage:
To enable Telnet and configure port number:
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#enable telnet 23
Command: enable telnet 23
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
<tcp_port_number 1-65535> − The TCP port number. TCP ports
are numbered between 1 and 65535. The “well-known” TCP port for
the Telnet protocol is 23.
command.
disable telnet
Purpose Used to disable the Telnet protocol on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command is used to disable the Telnet protocol on the Switch.
Parameters None.
disable telnet
Example usage:
To disable the Telnet protocol on the Switch:
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
command.
DES-3526:admin#disable telnet
Command: disable telnet
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
telnet
Purpose Used to Telnet another device on the network.
Syntax
Description This command is used to connect to another device’s management
Parameters
telnet <ipaddr> {tcp_port <value 0-65535>}
through Telnet.
<ipaddr> - Enter the IP address of the device to connect through,
using Telnet.
tcp_port <value 0-65535> - Enter the TCP port number used to
connect through. The common TCP port number for telnet is 23.
Example usage:
To connect to a device through telnet with a IP address of 10.53.13.99:
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
command.
16
Page 21

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#telnet 10.53.13.99 tcp_port 23
Command: telnet 10.53.13.99 tcp_port 23
enable web
Purpose Used to enable the HTTP-based management software on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command is used to enable the Web-based management software
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To enable HTTP and configure port number:
enable web <tcp_port_number 1-65535>
on the Switch. The user can specify the TCP port number the Switch will
use to listen for Telnet requests.
<tcp_port_number 1-65535> − The TCP port number. TCP ports are
numbered between 1 and 65535. The “well-known” port for the Webbased management software is 80.
DES-3526:admin#enable web 80
Command: enable web 80
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
disable web
Example usage:
To disable HTTP:
Purpose Used to disable the HTTP-based management software on the
Switch.
Syntax
Description This command disables the Web-based management software on
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#disable web
Command: disable web
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
disable web
the Switch.
command.
17
Page 22
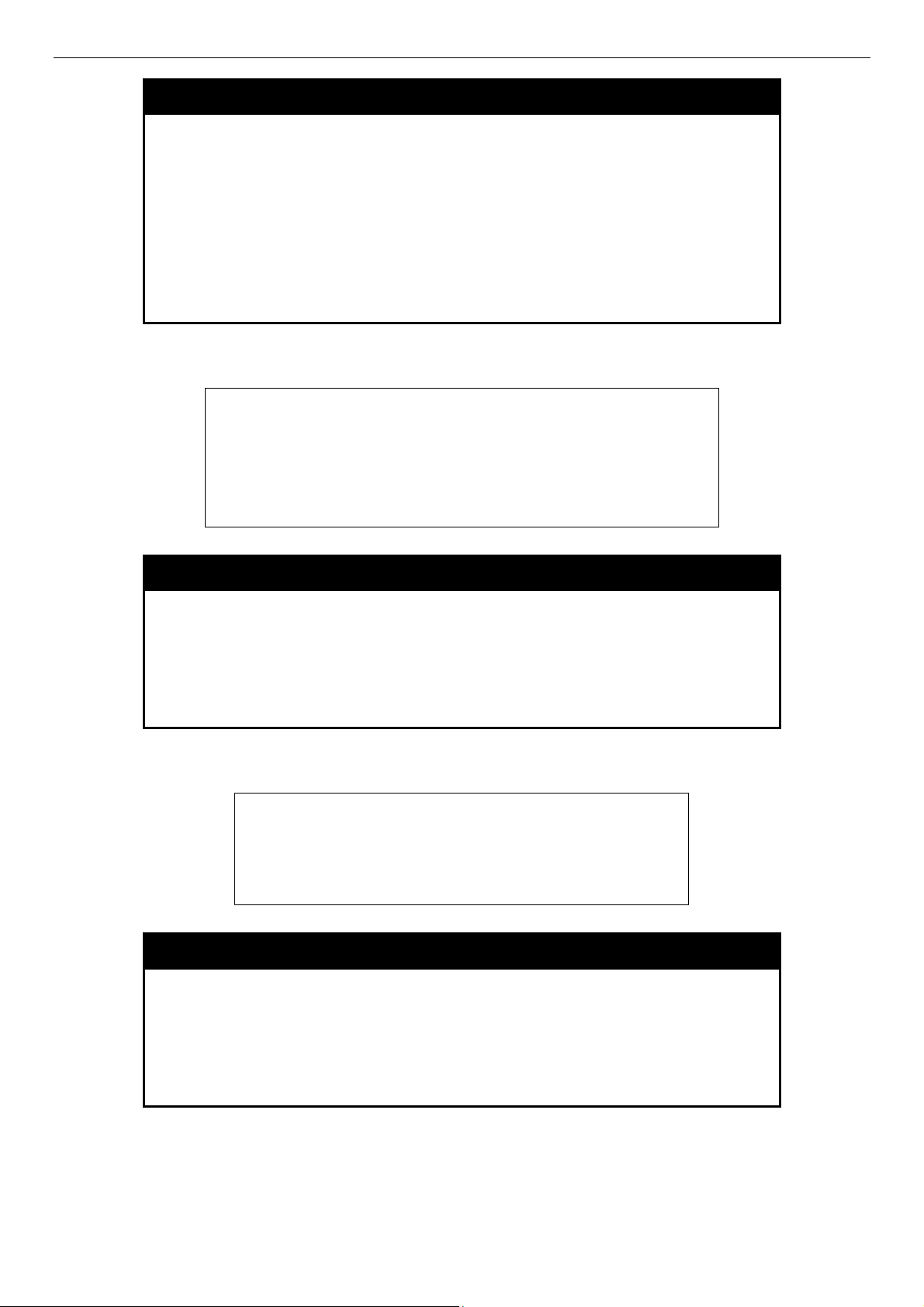
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
save
Purpose Used to save changes in the Switch’s configuration to non-volatile
RAM.
Example usage:
To save the Switch’s current configuration to non-volatile RAM:
Syntax
Description This command is used to enter the current switch configuration into
Parameters None
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#save
Command: save
Saving all configurations to NV-RAM... Done.
DES-3526:admin#
save
non-volatile RAM. The saved switch configuration will be loaded into
the Switch’s memory each time the Switch is restarted.
command.
reboot
Purpose Used to restart the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command is used to restart the Switch.
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To restart the Switch:
DES-3526:admin#reboot
Command: reboot
Are users sure want to proceed with the system
reboot? (y|n)
Please wait, the switch is rebooting...
reboot force_agree
Purpose Used to enforce the Switch to restart.
Syntax
Description This command is used to enforce the Switch to restart.
Parameters None.
reboot
reboot force_agree
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To enforce the Switch to restart:
18
Page 23
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#reboot force_agree
Command: reboot force_agree
Are users sure want to proceed with the system
reboot? (y|n)
Please wait, the switch is rebooting...
reset
Purpose Used to reset the Switch to the factory default settings.
Example usage:
Syntax
Description This command is used to restore the Switch’s configuration to the
Parameters
Restrictions Only administrator-level users can issue this command.
reset {[config | system {exclude [vlan|system_ip]}] }
{ force_agree}
default settings assigned from the factory.
config − If the keyword ‘config’ is specified, all of the factory default
settings are restored on the Switch including the IP address, user
accounts, and the switch history log. The Switch will not save or
reboot.
system − If the keyword ‘system’ is specified all of the factory default
settings are restored on the Switch. The Switch will save and reboot
after the settings are changed to default. Rebooting will clear all
entries in the Forwarding Data Base.
exclude –You can specify to exclude reset of VLAN or system IP
setting .
force_agree- When force_agree is specified, the reset command will
be executed immediatedly without further confirmation.
If no parameter is specified, the Switch’s current IP address, user
accounts, and the switch history log are not changed. All other
parameters are restored to the factory default settings. The Switch
will not save or reboot.
To restore all of the Switch’s parameters to their default values:
DES-3526:admin#reset config
Command: reset config
Are users sure to proceed with system reset?(y/n)
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
login
Purpose Used to log in a user to the Switch’s console.
Syntax
Description This command is used to initiate the login procedure. The user will be
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To initiate the login procedure:
login
prompted for a Username and Password.
19
Page 24

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#login
Command: login
UserName:
logout
Purpose Used to log out a user from the Switch’s console.
Example usage:
To terminate the current user’s console session:
Syntax
Description This command terminates the current user’s session on the Switch’s
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
DES-3526:admin#logout
logout
console.
20
Page 25
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
5
MODIFY BANNER AND PROMPT COMMANDS
Administrator level users can modify the login banner (greeting message) and command prompt by using the commands described
below.
Command Parameters
config command_ prompt [<string 16> | username | default]
config greeting_message {default}
show greeting_message
enable greeting_message
disable greeting_message
The Modify Banner and Prompt commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate
parameters) in the following table.
config command prompt
Purpose Used to configure the command prompt.
Syntax
Description Administrator level users can use this command to change the
Parameters
Restrictions Only administrator-level users can issue this command. Other
Example usage:
To modify the command prompt to “AtYourService”:
DES-3526:admin#config command_prompt AtYourService
Command: config command_prompt AtYourService
Success.
AtYourService:admin#
config command_prompt [<string 16> | username | default]
command prompt.
string 16 - The command prompt can be changed by entering a
new name of no more that 16 characters.
username - The command prompt will be changed to the login
username.
default – The command prompt will reset to factory default
command prompt.
restrictions include:
• If the “reset/reset config” command is executed, the
modified command prompt will remain modified. However,
the “reset system” command will reset the command
prompt to the original factory banner.
21
Page 26
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
config greeting _message
Purpose Used to configure the login banner (greeting message).
Syntax
Description Users can use this command to modify the login banner (greeting
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
config greeting _message {default}
message).
default – If the user enters default to the modify banner command, then
the banner will be reset to the original factory banner.
To open the Banner Editor, click enter after typing the config
greeting_message command. Type the information to be displayed on
the banner by using the commands described on the Banner Editor:
Quit without save: Ctrl+C
Save and quit: Ctrl+W
Move cursor: Left/Right/Up/Down
Delete line: Ctrl+D
Erase all setting: Ctrl+X
Reload original setting: Ctrl+L
Other restrictions include:
• If the “reset/reset config” command is executed, the modified
banner will remain modified. However, the “reset system”
command will reset the modified banner to the original factory
banner.
• The capacity of the banner is 6*80. 6 Lines and 80 characters per
line.
• Ctrl+W will only save the modified banner in the DRAM. Users
need to type the “save” command to save it into FLASH.
• Only valid in threshold level.
Example usage:
To modify the banner to read “Good evening Mr. Bond.”:
DES-3526:admin# config greeting_message
Command: config greeting_message
Greeting Messages Editor
================================================================================
DES-3526 Fast Ethernet Switch
Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 5.01-B47
Copyright(C) 2004-2007 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
================================================================================
<Function Key> <Control Key>
Ctrl+C Quit without save left/right/
Ctrl+W Save and quit up/down Move cursor
Ctrl+D Delete line
Ctrl+X Erase all setting
Ctrl+L Reload original setting
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
22
Page 27
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
show greeting_message
Purpose Used to view the currently configured greeting message
configured on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command is used to view the currently configured greeting
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To view the currently configured greeting message:
DES-3526:admin#show greeting_message
Command: show greeting_message
=========================================================================
Copyright(C) 2004-2005 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
=========================================================================
DES-3526:admin#
show greeting_message
message on the Switch.
DES-3526 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 5.01.B41
enable greeting_message
Purpose Used to enable viewing of the currently configured greeting
message configured on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command is used to enable viewing the currently configured
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To enable viewing of the currently configured greeting message:
DES-3526:admin#enable greeting_message
Command: enable greeting_message
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
enable greeting_message
greeting message on the Switch.
disable greeting_message
Purpose Used to disable viewing of the currently configured greeting
message configured on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command is used to disable viewing the currently
Parameters None.
disable greeting_message
configured greeting message on the Switch.
23
Page 28
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
disable greeting_message
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To disable viewing of the currently configured greeting message:
DES-3526:admin#disable greeting_message
Command: disable greeting_message
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
24
Page 29
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
6
SWITCH PORT COMMANDS
The switch port commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in the
following table.
Command Parameters
config ports [<portlist | all>] { medium_type [copper|fiber ] | speed [auto | 10_half | 10_full |100_half |
100_full | 1000_full]} | flow_control [enable | disable] | learning [enable | disable] | state
[enable | disable] | trap [enable | disable] | description <desc 32> | mdix [auto |normal
|cross]}
show ports [<portlist>] {description | err_disabled]}}
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections.
config ports
Purpose Used to configure the Switch’s Ethernet port settings.
Syntax
Description This command allows for the configuration of the Switch’s Ethernet ports. Only the ports
Parameters
config ports [<portlist | all>] { medium_type [copper|fiber] | speed [auto | 10_half |
10_full |100_half | 100_full | 1000_full]} | flow_control [enable | disable] | learning
[enable | disable] | state [enable | disable] | trap [enable | disable] | description
<desc 32> | mdix [auto |normal |cross] }
listed in the <portlist> will be affected.
all − Configure all ports on the Switch.
<portlist> − Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
medium_type [copper | fiber] – Allows the user to adjust the medium type of ports.
speed – Allows the user to adjust the speed for a port or range of ports. The user has a
choice of the following:
• auto − Enables auto-negotiation for the specified range of ports.
• [10 | 100 | 1000] − Configures the speed in Mbps for the specified range of
ports. Gigabit ports are statically set to 1000 and cannot be set to slower
speeds.
• [half | full] − Configures the specified range of ports as either full-duplex or halfduplex.
flow_control [enable | disable] – Enable or disable flow control for the specified ports.
learning [enable | disable] − Enables or disables the MAC address learning on the
specified range of ports.
state [enable | disable] − Enables or disables the specified range of ports.
trap [enable | disable] − Enables or disables trap support on the switch.
description <desc 32> - Enter an alphanumeric string of no more than 32 characters to
describe a selected port interface.
mdix [auto | normal | cross] - MDIX mode can be specified as auto, normal, or cross.
If set to normal state, the port in MDIX mode, can be connected to PC NIC using a
straight cable. If set to cross state, the port in mdi mode, can be connected to a port (in
mdix mode) on another switch through a straight cable.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To configure the speed of port 3 to be 10 Mbps, full duplex, with learning and state enabled:
DES-3526:admin#config ports 1-3 speed 10_full learning
enable state enable
25
Page 30
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Command: config ports 1-3 speed 10_full learning enable
state enable
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show ports
Purpose Used to display the current configuration of a range of ports.
Syntax
Description This command is used to display the current configuration of a
Parameters
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To display the configuration of all ports on a standalone switch:
DES-3526:admin#show ports
Command: show ports
Port State/ Settings Connection Address Trap
MDIX Speed/Duplex/FlowCtrl Speed/Duplex/FlowCtrl Learning State
----- ---------- --------------------- --------------------- -------- -------1 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
2 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
3 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
4 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
5 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
6 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
7 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
8 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
9 Enabled Auto/Disabled 100M/Full/None Enabled Enabled
Auto
10 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
show ports [<portlist>] {description | err_disabled}
range of ports.
<portlist> − Specifies a port or range of ports to be displayed.
{description} – Adding this parameter to the show ports command
indicates that a previously entered port description will be included
in the display.
{err_disabled} – Use this to list disabled ports including connection
status and reason for being disabled.
26
Page 31

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Example usage:
To display the configuration of all ports on a standalone switch, with description:
DES-3526:admin#show ports description
Command: show ports description
Port State/ Settings Connection Address Trap
MDIX Speed/Duplex/FlowCtrl Speed/Duplex/FlowCtrl Learning State
----- ---------- --------------------- --------------------- -------- -------1 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
Description:
2 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
Description:
3 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
Description:
4 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
Description:
5 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
Description:
6 Enabled Auto/Disabled Link Down Enabled Enabled
Auto
Description:
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
Example usage:
To display disabled ports including connection status and reason for being disabled on a standalone switch:
DES-3526:admin#show ports err_disabled
Command: show ports err_disabled
Port Port Connection status Reason
State
---- -------- --------------------- --------------
27
Page 32

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
7
PORT SECURITY COMMANDS
The Switch’s port security commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in
the following table.
Command Parameters
config port_security ports [<portlist> | all] {admin_state [enable| disable] | max_learning_addr
<max_lock_no 0-64> | lock_address_mode [Permanent |
DeleteOnTimeout | DeleteOnReset]}
delete port_security entry vlan_name <vlan_name 32> mac_address <macaddr> port <port>
clear port_security_entry port <portlist>
show port_security {ports <portlist>}
enable port_security
trap_log
disable port_security
trap_log
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections.
config port_security ports
Purpose Used to configure port security settings.
Syntax
Description This command allows for the configuration of the port security feature.
Parameters
config port_security ports [<portlist> | all ] {admin_state [enable|
disable] | max_learning_addr <max_lock_no 0-64> |
lock_address_mode [Permanent | DeleteOnTimeout |
DeleteOnReset]}
Only the ports listed in the <portlist> are affected.
portlist − Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
all − Configure port security for all ports on the Switch.
admin_state [enable | disable] – Enable or disable port security for the
listed ports.
max_learning_addr <max_lock_no 0-64> - Use this to limit the number of
MAC addresses dynamically listed in the FDB for the ports.
lock_address_mode [Permanent | DeleteOnTimout | DeleteOnReset] –
Indicates the method of locking addresses. The user has three choices:
Permanent – The locked addresses will not age out after the
aging timer expires.
DeleteOnTimeout – The locked addresses will age out after the
aging timer expires.
DeleteOnReset – The locked addresses will not age out until the
Switch has been reset.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
28
Page 33

Example usage:
5 admin_state
To configure the port security:
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#config port_security ports 1-5
admin_state enable max_learning_addr 5
lock_address_mode DeleteOnReset
Command: config port_security ports 1enable max_learning_addr 5 lock_address_mode
DeleteOnReset
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
delete port_security_entry
Purpose Used to delete a port security entry by MAC address, port number
and VLAN ID.
Syntax
Description This command is used to delete a single, previously learned port
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To delete a port security entry:
DES-3526:admin#delete port_security_entry vlan_name
default mac_address 00-01-30-10-2C-C7 port 6
Command: delete port_security_entry vlan_name
default mac_address 00-01-30-10-2C-C7 port 6
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
delete port_security_entry vlan name <vlan_name 32>
mac_address <macaddr> port <port>
security entry by port, VLAN name, and MAC address.
vlan name <vlan_name 32> - Enter the corresponding VLAN name
of the port to delete.
mac_address <macaddr> - Enter the corresponding MAC address,
previously learned by the port, to delete.
port <port> - Enter the port number which has learned the
previously entered MAC address.
command.
29
Page 34

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
clear port_security_entry
Purpose Used to clear MAC address entries learned from a specified port for
the port security function.
Syntax
Description This command is used to clear MAC address entries which were
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To clear a port security entry by port:
DES-3526:admin# clear port_security_entry port 6
Command: clear port_security_entry port 6
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
clear port_security_entry ports <portlist>
learned by the Switch by a specified port. This command only relates
to the port security function.
<portlist> − Specifies a port or port range to clear.
command.
show port_security
Purpose Used to display the current port security configuration.
Syntax
show port_security {ports <portlist>}
Example usage:
To display the port security configuration:
Description This command is used to display port security information of the
Switch’s ports. The information displayed includes port security,
admin state, maximum number of learning address and lock mode.
Parameters
Restrictions None.
DES-3526:admin#show port_security ports 1-5
Command: show port_security ports 1-5
Port_security Trap/Log : Disabled
Port Admin State Max. Learning Addr. Lock Address Mode
---- ----------- ------------------- ----------------1 Disabled 1 DeleteOnReset
2 Disabled 1 DeleteOnReset
3 Disabled 1 DeleteOnReset
4 Disabled 1 DeleteOnReset
5 Disabled 1 DeleteOnReset
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
<portlist> − Specifies a port or range of ports to be viewed.
30
Page 35

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
enable port_security trap_log
Purpose Used to enable the trap log for port security.
Example usage:
To enable the port security trap log setting:
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
enable port_security trap_log
This command, along with the disable port_security trap_log, will
enable and disable the sending of log messages to the Switch’s log
and SNMP agent when the port security of the Switch has been
triggered.
DES-3526:admin#enable port_security
trap_log
Command: enable port_security
trap_log
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
disable port_security trap_log
Example usage:
To enable the port security trap log setting:
Purpose Used to disable the trap log for port security.
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
disable port_security trap_log
This command, along with the enable port_security trap_log, will
enable and disable the sending of log messages to the Switch’s log
and SNMP agent when the port security of the Switch has been
triggered.
DES-3526:admin#enable port_security
trap_log
Command: enable port_security trap_log
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
31
Page 36

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
8
NETWORK MANAGEMENT (SNMP) COMMANDS
The DES-3500 Switch series supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) versions 1, 2c, and 3. Users can specify
which version of the SNMP users want to use to monitor and control the Switch. The three versions of SNMP vary in the level of
security provided between the management station and the network device. The following table lists the security features of the
three SNMP versions:
SNMP
Version
v1 Community String
v2c Community String
v3 Username
v3 MD5 or SHA Authentication is based on the HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA
v3 MD5 DES or SHA DES Authentication is based on the HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA
The network management commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in
the following table.
Authentication
Method
Description
Community String is used for authentication − NoAuthNoPriv
Community String is used for authentication − NoAuthNoPriv
Username is used for authentication − NoAuthNoPriv, AuthNoPriv
or AuthPriv
algorithms − AuthNoPriv
algorithms − AuthPriv.
DES 56-bit encryption is added based on the CBC-DES (DES-56)
standard
Command Parameters
create snmp user <snmp_username 32> <groupname 32> {encrypted
[by_password auth [md5 <auth_password 8-16 > | sha
<auth_password 8-20>] priv [none | des <priv_password 8-16>]
| by_key auth [md5 <auth_key 32-32> | sha <auth_key 40-40>]
priv [none | des <priv_key 32-32>]]}
delete snmp user <snmp_username 32>
show snmp user
create snmp view <view_name 32> <oid> view_type [included | excluded]
delete snmp view <view_name 32> [all | oid]
show snmp view <view_name 32>
create snmp community <community_string 32> view <view_name 32> [read_only |
read_write]
delete snmp community <community_string 32>
show snmp community <community_string 32>
config snmp engineID <snmp_engineID>
show snmp engineID
create snmp group <groupname 32> {v1 | v2c | v3 [noauth_nopriv | auth_nopriv |
auth_priv]} {read_view <view_name 32> | write_view
<view_name 32> | notify_view <view_name 32>}
delete snmp group <groupname 32>
show snmp groups
create snmp host <ipaddr> {v1 | v2c | v3 [noauth_nopriv | auth_nopriv | auth_priv]}
32
Page 37

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Command Parameters
<auth_string 32>
delete snmp host <ipaddr>
show snmp host <ipaddr>
create trusted_host <ipaddr>| network<network_address> {snmp | telnet | ssh | http
| https}
config trusted_host [<ipaddr> | network <network_address>] [add|delete] {snmp |
telnet | ssh | http | https}
delete trusted_host [all | ipaddr<ipaddr>| network<network_address>]
show trusted_host
enable snmp traps
enable snmp authenticate traps
show snmp traps
disable snmp traps
disable snmp authenticate traps
config snmp system_contact <sw_contact>
config snmp system_location <sw_location>
config snmp system_name <sw_name>
enable rmon
disable rmon
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections.
create snmp user
Purpose Used to create a new SNMP user and adds the user to an SNMP group that is also
created by this command.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
create snmp user <snmp_username 32> <groupname 32> {encrypted
[by_password auth [md5 <auth_password 8-16> | sha <auth_password 8-20>]
priv [none | des <priv_password 8-16>] | by_key auth [md5 <auth_key 32-32> |
sha <auth_key 40-40>] priv [none | des <priv_key 32-32> ]]}
The create snmp user command creates a new SNMP user and adds the user to
an SNMP group that is also created by this command. SNMP ensures:
Message integrity − Ensures that packets have not been tampered with during
transit.
Authentication − Determines if an SNMP message is from a valid source.
Encryption − Scrambles the contents of messages to prevent it from being viewed
by an unauthorized source.
<snmp_username 32> − An alphanumeric name of up to 32 characters that will
identify the new SNMP user.
<groupname 32> − An alphanumeric name of up to 32 characters that will identify
the SNMP group the new SNMP user will be associated with.
encrypted – Allows the user to choose a type of authorization for authentication
using SNMP. The user may choose:
by_password – Requires the SNMP user to enter a password for authentication
and privacy. The password is defined by specifying the auth_password below.
This method is recommended.
by_key – Requires the SNMP user to enter a encryption key for authentication and
33
Page 38
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
create snmp user dlink default encrypted by_password
create snmp user
auth - The user may also choose the type of authentication algorithms used to
authenticate the snmp user. The choices are:
md5 − Specifies that the HMAC-MD5-96 authentication level will be used. md5
sha − Specifies that the HMAC-SHA-96 authentication level will be used.
priv – Adding the priv (privacy) parameter will allow for encryption in addition to the
authentication algorithm for higher security. The user may choose:
des – Adding this parameter will allow for a 56-bit encryption to be added using the
none – Adding this parameter will add no encryption.
privacy. The key is defined by specifying the key in hex form below. This
method is not recommended.
may be utilized by entering one of the following:
• <auth password 8-16> - An alphanumeric sting of between 8 and
16 characters that will be used to authorize the agent to receive
packets for the host.
• <auth_key 32-32> - Enter an alphanumeric sting of exactly 32
characters, in hex form, to define the key that will be used to
authorize the agent to receive packets for the host.
• <auth password 8-20> - An alphanumeric sting of between 8 and
20 characters that will be used to authorize the agent to receive
packets for the host.
• <auth_key 40-40> - Enter an alphanumeric sting of exactly 40
characters, in hex form, to define the key that will be used to
authorize the agent to receive packets for the host.
DES-56 standard using:
• <priv_password 8-16> - An alphanumeric string of between 8 and
16 characters that will be used to encrypt the contents of messages
the host sends to the agent.
• <priv_key 32-32> - Enter an alphanumeric key string of exactly 32
characters, in hex form, that will be used to encrypt the contents of
messages the host sends to the agent.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To create an SNMP user on the Switch:
DES-3526:admin#
auth md5 canadian priv none
Command: create snmp user dlink default encrypted by_password auth
md5 canadian priv none
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
delete snmp user
Purpose Used to remove an SNMP user from an SNMP group and also to
delete the associated SNMP group.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
delete snmp user <snmp_username 32>
The delete snmp user command removes an SNMP user from its
SNMP group and then deletes the associated SNMP group.
<snmp_username 32> − An alphanumeric string of up to 32
characters that identifies the SNMP user that will be deleted.
34
Page 39

Example usage:
`To delete a previously entered SNMP user on the Switch:
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
delete snmp user
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
command.
DES-3526: DES-3526:admin#delete snmp user dlink
Command: delete snmp user dlink
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show snmp user
Purpose Used to display information about each SNMP username in the
SNMP group username table.
Example usage:
To display the SNMP users currently configured on the Switch:
DES-3526:admin#show snmp user
Command: show snmp user
Username Group Name SNMP Version Auth-Protocol PrivProtocol
--------- ----------- ------------ -------------- -----------initial initial V3 None None
Total Entries: 1
DES-3526:admin#
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
show snmp user
The show snmp user command displays information about each
SNMP username in the SNMP group username table.
35
Page 40

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
create snmp view
Purpose Used to assign views to community strings to limit which MIB objects
and SNMP manager can access.
Syntax create snmp view <view_name 32> <oid> view_type [included |
excluded]
Description The create snmp view command assigns views to community
strings to limit which MIB objects an SNMP manager can access.
Parameters <view_name 32> − An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters
that identifies the SNMP view that will be created.
<oid> − The object ID that identifies an object tree (MIB tree) that will
be included or excluded from access by an SNMP manager.
view type – Sets the view type to be:
• included − Include this object in the list of objects that an
SNMP manager can access.
• excluded − Exclude this object from the list of objects that
an SNMP manager can access.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
command.
Example usage:
To create an SNMP view:
DES-3526:admin#create snmp view dlinkview 1.3.6
view_type included
Command: create snmp view dlinkview 1.3.6 view_type
included
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
delete snmp view
Purpose Used to remove an SNMP view entry previously created on the
Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
delete snmp view <view_name 32> [all | <oid>]
The delete snmp view command is used to remove an SNMP view
previously created on the Switch.
<view_name 32> − An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that
identifies the SNMP view to be deleted.
all − Specifies that all of the SNMP views on the Switch will be
deleted.
<oid> − The object ID that identifies an object tree (MIB tree) that will
be deleted from the Switch.
Example usage:
To delete a previously configured SNMP view from the Switch:
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
DES-3526:admin#delete snmp view dlinkview all
Command: delete snmp view dlinkview all
36
Page 41

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show snmp view
Purpose Used to display an SNMP view previously created on the Switch.
Example usage:
To display SNMP view configuration:
Syntax
Description
Parameters
Restrictions None.
show snmp view {<view_name 32>}
The show snmp view command displays an SNMP view
previously created on the Switch.
<view_name 32> − An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters
that identifies the SNMP view that will be displayed.
37
Page 42

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#show snmp view
Command: show snmp view
Vacm View Table Settings
View Name : restricted
Subtree : 1.3.6.1.2.1.1
View Type : Included
View Mask :
View Name : restricted
Subtree : 1.3.6.1.2.1.11
View Type : Included
View Mask :
View Name : restricted
Subtree : 1.3.6.1.6.3.10.2.1
View Type : Included
View Mask :
View Name : restricted
Subtree : 1.3.6.1.6.3.11.2.1
View Type : Included
View Mask :
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
create snmp community
Purpose Used to create an SNMP community string to define the relationship
between the SNMP manager and an agent. The community string acts like
a password to permit access to the agent on the Switch. One or more of the
following characteristics can be associated with the community string:
An Access List of IP addresses of SNMP managers that are permitted to
use the community string to gain access to the Switch’s SNMP agent.
An MIB view that defines the subset of all MIB objects that will be
accessible to the SNMP community.
read_write or read_only level permission for the MIB objects accessible to
the SNMP community.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
create snmp community <community_string 32> view <view_name 32>
[read_only | read_write]
The create snmp community command is used to create an SNMP
community string and to assign access-limiting characteristics to this
community string.
<community_string 32> − An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that
is used to identify members of an SNMP community. This string is used like
a password to give remote SNMP managers access to MIB objects in the
Switch’s SNMP agent.
view <view_name 32> − An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that
is used to identify the group of MIB objects that a remote SNMP manager is
allowed to access on the Switch.
read_only − Specifies that SNMP community members using the community
string created with this command can only read the contents of the MIBs on
38
Page 43

create snmp community
create snmp community dlink view ReadView
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To create the SNMP community string “dlink:”
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
the Switch.
read_write − Specifies that SNMP community members using the
community string created with this command can read from and write to the
contents of the MIBs on the Switch.
DES-3526:admin#
read_write
Command: create snmp community dlink view ReadView
read_write
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
Example usage:
To delete the SNMP community string “dlink:”
delete snmp community
Purpose Used to remove a specific SNMP community string from the Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#delete snmp community dlink
Command: delete snmp community dlink
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
delete snmp community <community_string 32>
The delete snmp community command is used to remove a
previously defined SNMP community string from the Switch.
<community_string 32> − An alphanumeric string of up to 32
characters that is used to identify members of an SNMP community.
This string is used like a password to give remote SNMP managers
access to MIB objects in the Switch’s SNMP agent.
command.
show snmp community
Purpose Used to display SNMP community strings configured on the Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
show snmp community {<community_string 32>}
The show snmp community command is used to display SNMP
community strings that are configured on the Switch.
<community_string 32> − An alphanumeric string of up to 32
characters that is used to identify members of an SNMP community.
This string is used like a password to give remote SNMP managers
access to MIB objects in the Switch’s SNMP agent.
39
Page 44

Example usage:
To display the currently entered SNMP community strings:
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
show snmp community
Restrictions None.
DES-3526:admin#show snmp community
Command: show snmp community
SNMP Community Table
Community Name View Name Access Right
--------------- ------------- ------------dlink ReadView read_write
private CommunityView read_write
public CommunityView read_only
Total Entries: 3
DES-3526:admin#
Example usage:
To give the SNMP agent on the Switch the name “0035636666”
config snmp engineID
Purpose Used to configure a name for the SNMP engine on the Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#config snmp 0035636666
Command: config snmp engineID 0035636666
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config snmp engineID <snmp_engineID>
The config snmp engineID command configures a name for the
SNMP engine on the Switch.
<snmp_engineID> − An alphanumeric string that will be used to
identify the SNMP engine on the Switch.
command.
show snmp engineID
Example usage:
To display the current name of the SNMP engine on the Switch:
Purpose Used to display the identification of the SNMP engine on the Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
show snmp engineID
The show snmp engineID command displays the identification of
the SNMP engine on the Switch.
40
Page 45

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#show snmp engineID
Command: show snmp engineID
SNMP Engine ID : 0035636666
DES-3526:admin#
create snmp group
Purpose
Syntax create snmp group <groupname 32> [v1 | v2c | v3 [noauth_nopriv
Description The create snmp group command creates a new SNMP group, or a
Parameters
Used to create a new SNMP group, or a table that maps SNMP users
to SNMP views.
| auth_nopriv | auth_priv]] {read_view <view_name 32> |
write_view <view_name 32> | notify_view <view_name 32>}
table that maps SNMP users to SNMP views.
<groupname 32> − An alphanumeric name of up to 32 characters that
will identify the SNMP group the new SNMP user will be associated
with.
v1 – Specifies that SNMP version 1 will be used. The Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP), version 1, is a network management
protocol that provides a means to monitor and control network
devices.
v2c – Specifies that SNMP version 2c will be used. The SNMP v2c
supports both centralized and distributed network management
strategies. It includes improvements in the Structure of Management
Information (SMI) and adds some security features.
v3 – Specifies that the SNMP version 3 will be used. SNMP v3
provides secure access to devices through a combination of
authentication and encrypting packets over the network. SNMP v3
adds:
• Message integrity − Ensures that packets have
not been tampered with during transit.
• Authentication − Determines if an SNMP
message is from a valid source.
• Encryption − Scrambles the contents of
messages to prevent it being viewed by an
unauthorized source.
noauth_nopriv − Specifies that there will be no authorization and no
encryption of packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP
manager.
auth_nopriv − Specifies that authorization will be required, but there
will be no encryption of packets sent between the Switch and a
remote SNMP manager.
auth_priv − Specifies that authorization will be required, and that
packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP manger will be
encrypted.
read_view – Specifies that the SNMP group being created can
request SNMP messages.
write_view – Specifies that the SNMP group being created has write
privileges.
notify_view − Specifies that the SNMP group being created can
receive SNMP trap messages generated by the Switch’s SNMP
agent.
<view_name 32> − An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters
that is used to identify the group of MIB objects that a remote
41
Page 46

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
create snmp group
SNMP manager is allowed to access on the Switch.
Example usage:
To create an SNMP group named “sg1:”
Restrictions
DES-3526:admin#create snmp group sg1 v3 noauth_nopriv
read_view v1 write_view v1 notify_view v1
Command: create snmp group sg1 v3 noauth_nopriv read_view
v1 write_view v1 notify_view v1
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
delete snmp group
Purpose
Syntax delete snmp group <groupname 32>
Description The delete snmp group command is used to remove an SNMP
Parameters
Used to remove an SNMP group from the Switch.
group from the Switch.
<groupname 32> − An alphanumeric name of up to 32 characters that
will identify the SNMP group the new SNMP user will be associated
with.
Example usage:
To delete the SNMP group named “sg1”.
show snmp groups
Purpose
Syntax show snmp groups
Description The show snmp groups command displays the group-names of SNMP
Parameters
Restrictions
DES-3526:admin#delete snmp group sg1
Command: delete snmp group sg1
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Used to display the group-names of SNMP groups currently configured on
the Switch. The security model, level, and status of each group are also
displayed.
groups currently configured on the Switch. The security model, level, and
status of each group are also displayed.
None.
Restrictions
Example usage:
To display the currently configured SNMP groups on the Switch:
None.
42
Page 47

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#show snmp groups
Command: show snmp groups
Vacm Access Table Settings
Group Name : Group3
ReadView Name : ReadView
WriteView Name : WriteView
Notify View Name : NotifyView
Security Model : SNMPv3
Security Level : NoAuthNoPriv
Group Name : Group4
ReadView Name : ReadView
WriteView Name : WriteView
Notify View Name : NotifyView
Security Model : SNMPv3
Security Level : authNoPriv
Group Name : Group5
ReadView Name : ReadView
WriteView Name : WriteView
Notify View Name : NotifyView
Security Model : SNMPv3
Security Level : authNoPriv
Group Name : initial
ReadView Name : restricted
WriteView Name :
Notify View Name : restricted
Security Model : SNMPv3
Security Level : NoAuthNoPriv
Group Name : ReadGroup
ReadView Name : CommunityView
WriteView Name :
Notify View Name : CommunityView
Security Model : SNMPv1
Security Level : NoAuthNoPriv
Total Entries: 5
DES-3526:admin#
create snmp host
Purpose Used to create a recipient of SNMP traps generated by the Switch’s
SNMP agent.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
create snmp host <ipaddr> [v1 | v2c | v3 [noauth_nopriv |
auth_nopriv | auth_priv] <auth_string 32>]
The create snmp host command creates a recipient of SNMP traps
generated by the Switch’s SNMP agent.
<ipaddr> − The IP address of the remote management station that will
serve as the SNMP host for the Switch.
v1 – Specifies that SNMP version 1 will be used. The Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP), version 1, is a network management
protocol that provides a means to monitor and control network devices.
v2c – Specifies that SNMP version 2c will be used. The SNMP v2c
supports both centralized and distributed network management
strategies. It includes improvements in the Structure of Management
Information (SMI) and adds some security features.
43
Page 48

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
create snmp host
v3 – Specifies that the SNMP version 3 will be used. SNMP v3
provides secure access to devices through a combination of
authentication and encrypting packets over the network. SNMP v3
adds:
noauth_nopriv − Specifies that there will be no authorization and no
encryption of packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP
manager.
auth_nopriv − Specifies that authorization will be required, but there
will be no encryption of packets sent between the Switch and a remote
SNMP manager.
auth_priv − Specifies that authorization will be required, and that
packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP manger will be
encrypted.
<auth_sting 32> − An alphanumeric string used to authorize a
• Message integrity − ensures that packets have not been
tampered with during transit.
• Authentication − determines if an SNMP message is from a
valid source.
• Encryption − scrambles the contents of messages to prevent
it being viewed by an unauthorized source.
remote SNMP manager to access the Switch’s SNMP agent.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To create an SNMP host to receive SNMP messages:
DES-3526:admin#create snmp host 10.48.74.100 v3
auth_priv public
Command: create snmp host 10.48.74.100 v3 auth_priv
public
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
delete snmp host
Purpose Used to remove a recipient of SNMP traps generated by the Switch’s
SNMP agent.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
delete snmp host <ipaddr>
The delete snmp host command deletes a recipient of SNMP traps
generated by the Switch’s SNMP agent.
<ipaddr> − The IP address of a remote SNMP manager that will
receive SNMP traps generated by the Switch’s SNMP agent.
Example usage:
To delete an SNMP host entry:
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
44
Page 49

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
e/SNMPv3 User Name
DES-3526:admin#delete snmp host 10.48.74.100
Command: delete snmp host 10.48.74.100
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show snmp host
Purpose Used to display the recipient of SNMP traps generated by the
Switch’s SNMP agent.
Example usage:
To display the currently configured SNMP hosts on the Switch:
Syntax
Description
Parameters
Restrictions None.
DES-3526:admin#show snmp host
Command: show snmp host
SNMP Host Table
Host IP Address SNMP Version Community Nam
--------------- ------------ ------------------- ---------
10.48.76.23 V2c private
10.48.74.100 V3 authpriv public
Total Entries: 2
DES-3526:admin#
show snmp host {<ipaddr>}
The show snmp host command is used to display the IP addresses
and configuration information of remote SNMP managers that are
designated as recipients of SNMP traps that are generated by the
Switch’s SNMP agent.
<ipaddr> − The IP address of a remote SNMP manager that will
receive SNMP traps generated by the Switch’s SNMP agent.
create trusted_host
Purpose Used to create the trusted host.
Syntax
Description The create trusted host command creates the trusted host. The
Parameters
create trusted_host <ipaddr> {snmp | telnet | ssh | http | https}
switch allows you to specify IP addresses that are allowed to manage
the switch via in-band SNMP ,TELNET ,SSH, HTTP or HTTPs based
management software. These IP addresses must be members of the
Management VLAN. If no IP addresses are specified, then there is
nothing to prevent any IP address from accessing the switch,
provided the user knows the Username and Password.
When the access interface is not specified, the trusted host will be
created for all interfaces.
<ipaddr> − The IP address of the trusted host to be created.
snmp - Specifies trusted host for SNMP.
telnet - Specifies trusted host for TELENT.
ssh - Specifies trusted host for SSH
http - Specifies trusted host for HTTP.
45
Page 50

Example usage:
To create the trusted host:
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
create trusted_host
https - Specifies trusted host for HTTPs.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
DES-3526:admin# create trusted_host
10.48.74.121
Command: create trusted_host 10.48.74.121
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config trusted_host
Purpose Used to configure the access interfaces for the trusted host .
Example usage:
To create the trusted host network.
Syntax
Description The config trusted_host command is used to configure the access
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
DES-3526: config trusted_host 10.48.74.121 add
ssh telnet
Command: config trusted_host 10.48.74.121 add
ssh telnet
Success.
config trusted_host [<ipaddr> | network <network_address>]
[add|delete] {snmp | telnet | ssh | http | https}
interfaces for the trusted host .
ipaddr - The IP address of the trusted host.
network - The network address of the trusted network. The form of
network address is xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/y.
add - Add interfaces for that trusted host.
delete - Delete interfaces for that trusted host.
snmp - Specifies trusted host for SNMP.
telnet - Specifies trusted host for TELENT.
ssh - Specifies trusted host for SSH.
http - Specifies trusted host for HTTP.
https - Specifies trusted host for HTTPs.
create trusted_host network
Purpose Used to create the trusted host.
Syntax
Description The create trusted host network command creates the trusted host
create trusted_host network <network_address> {snmp | telnet |
ssh | http | https}
network. The switch allows you to specify IP addresses that are
allowed to manage the switch via in-band SNMP ,TELNET ,SSH,
HTTP or HTTPs based management software. These IP addresses
must be members of the Management VLAN. If no IP addresses are
46
Page 51

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
create trusted_host network
specified, then there is nothing to prevent any IP address from
accessing the switch, provided the user knows the Username and
Password.
When the access interface is not specified, the trusted host will be
created for all interfaces.
Example usage:
To create the trusted host network.
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
DES-3526:admin#create trusted_host network
10.62.32.1/16
Command: create trusted_host network
10.62.32.1/16
Success.
<network_address> − IP address and netmask of the trusted host to
be created.
snmp - Specifies trusted host for SNMP.
telnet - Specifies trusted host for TELENT.
ssh - Specifies trusted host for SSH
http - Specifies trusted host for HTTP.
https - Specifies trusted host for HTTPs.
show trusted_host
Purpose Used to display a list of trusted hosts entered on the Switch using
the create trusted_host command above.
Example Usage:
To display the list of trust hosts:
DES-3526: admin#show trusted_host
Command: show trusted_host
Management Stations
IP Address/Netmask Protocol Type
------------------ ------------------------------
Total Entries: 0
DES-3526:admin#
Syntax
Description This command is used to display a list of trusted hosts entered on
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
show trusted_host
the Switch using the create trusted_host command above.
47
Page 52

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
delete trusted_host ipaddr
Example usage:
To delete a trusted host with an IP address 10.62.32.1:
Purpose
Syntax
Description This command is used to delete a trusted host entry made using the
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#delete trusted_host ipaddr 10.62.32.1
Command: delete trusted_host ipaddr 10.62.32.1
Success.
Used to delete a trusted host entry made using the create
trusted_host command above.
delete trusted host ipaddr<ipaddr>
create trusted_host command above.
<ipaddr> − The IP address of the trusted host.
command.
delete trusted_host network
Purpose
Used to delete a trusted host entry made using the create
trusted_host network command above.
Example usage:
To delete a trusted host network IP address 10.62.31.1/16:
Syntax
Description This command is used to delete a trusted host entry made using the
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#delete trusted_host network 10.62.32.1/16
Command: delete trusted_host network 10.62.32.1/16
Success.
delete trusted _host network <network_address>
create trusted_host network command above.
<network_address> − IP address and netmask of the trusted host
network.
command.
delete trusted_host all
Purpose
Used to delete all trusted host entries made using the create
trusted_host ipaddr and create trusted_host network commands
above.
Syntax
Description This command is used to delete all trusted host entries made using
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
delete trusted _host all
the create trusted_host ipaddr and create trusted_host network
commands above.
command.
48
Page 53

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
To delete all trusted host entries:
DES-3526: admin#delete trusted_host all
Command: delete trusted_host all
Success.
enable snmp traps
Purpose Used to enable SNMP trap support.
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To enable SNMP trap support on the Switch:
DES-3526:admin#enable snmp traps
Command: enable snmp traps
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
enable snmp traps
The enable snmp traps command is used to enable SNMP trap
support on the Switch.
command.
enable snmp authenticate traps
Purpose Used to enable SNMP authentication trap support.
Syntax
enable snmp authenticate traps
Example Usage:
To turn on SNMP authentication trap support:
Description This command is used to enable SNMP authentication trap support
on the Switch.
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
command.
DES-3526:admin#enable snmp authenticate traps
Command: enable snmp authenticate traps
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show snmp traps
Purpose Used to show SNMP trap support on the Switch .
Syntax
show snmp traps
49
Page 54

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
show snmp traps
Description This command is used to view the SNMP trap support status
currently configured on the Switch.
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To view the current SNMP trap support:
DES-3526:admin#show snmp traps
Command: show snmp traps
SNMP Traps : Enabled
Authenticate Traps : Enabled
DES-3526:admin#
disable snmp traps
Example usage:
To prevent SNMP traps from being sent from the Switch:
Purpose Used to disable SNMP trap support on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command is used to disable SNMP trap support on the Switch.
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#disable snmp traps
Command: disable snmp traps
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
disable snmp traps
command.
disable snmp authenticate traps
Purpose Used to disable SNMP authentication trap support.
Syntax
disable snmp authenticate traps
Example usage:
To disable the SNMP authentication trap support:
Description This command is used to disable SNMP authentication support on
the Switch.
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
command.
50
Page 55

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#disable snmp authenticate
traps
Command: disable snmp authenticate traps
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config snmp system_contact
Purpose Used to enter the name of a contact person who is responsible for
the Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
config snmp system_contact{<sw_contact>}
The config snmp system_contact command is used to enter the
name and/or other information to identify a contact person who is
responsible for the Switch. A maximum of 255 character can be
used.
<sw_contact> - A maximum of 255 characters is allowed. A NULL
string is accepted if there is no contact.
command.
Example usage:
To configure the Switch contact to “MIS Department II”:
DES-3526:admin#config snmp system_contact MIS
Department II
Command: config snmp system_contact MIS Department
II
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config snmp system_location
Purpose Used to enter a description of the location of the Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
config snmp system_location {<sw_location>}
The config snmp system_location command is used to enter a
description of the location of the Switch. A maximum of 255
characters can be used.
<sw_location> - A maximum of 255 characters is allowed. A NULL
string is accepted if there is no location desired.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To configure the Switch location for “
HQ 5 F
”:
51
Page 56

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#config snmp system_location HQ
5F
Command: config snmp system_location HQ 5F
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config snmp system_name
Purpose Used to configure the name for the Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To configure the Switch name for “DES-3526 Switch”:
DES-3526:admin#config snmp system_name DES-3526
Switch
Command: config snmp system_name DES-3526 Switch
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config snmp system_name {<sw_name>}
The config snmp system_name command configures the name of
the Switch.
<sw_name> - A maximum of 255 characters is allowed. A NULL
string is accepted if no name is desired.
command.
enable rmon
Purpose Used to enable RMON on the Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To enable RMON:
DES-3526:admin#enable rmon
Command: enable rmon
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
enable rmon
This command is used, in conjunction with the disable rmon
command below, to enable and disable remote monitoring (RMON)
on the Switch.
command.
52
Page 57

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
disable rmon
Purpose Used to disable RMON on the Switch.
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To disable RMON:
DES-3526:admin#disable rmon
Command: disable rmon
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
disable rmon
This command is used, in conjunction with the enable rmon
command above, to enable and disable remote monitoring (RMON)
on the Switch.
53
Page 58

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
9
SWITCH UTILITY COMMANDS
The switch utility commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in the
following table.
Command Parameters
download [firmware_fromTFTP <ipaddr> <path_filename 64> {image_id
<int 1-2>} | cfg_fromTFTP <ipaddr> <path_filename 64>
{increment}]
config firmware image_id <value 1-n> [delete | boot_up]
show firmware_information
show config [current_config | config_in_nvram]
upload [cfg_toTFTP | log_toTFTP] <ipaddr> <path_filename 64>
enable autoconfig
disable autoconfig
show autoconfig
ping <ipaddr> {times <value 1-255>} {timeout <sec 1-99>}
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections.
download
Purpose Used to download and install new firmware or a Switch
configuration file from a TFTP server.
Syntax
Description This command is used to download a new firmware or a Switch
Parameters
download [firmware_fromTFTP <ipaddr> <path_filename 64>
{image_id <int 1-2>} | configuration <ipaddr> <path_filename
64> {increment}]
configuration file from a TFTP server.
firmware_fromTFTP − Download and install new firmware on the
Switch from a TFTP server.
cfg_fromTFTP − Download a switch configuration file from a TFTP
server.
<ipaddr> − The IP address of the TFTP server.
<path_filename> − The DOS path and filename of the firmware or
switch configuration file on the TFTP server. For example,
C:\3226S.had.
image_id <int 1-2> - Specify the working section ID. The Switch can
hold two firmware versions for the user to select from, which are
specified by section ID.
increment − Allows the download of a partial switch configuration
file. This allows a file to be downloaded that will change only the
switch parameters explicitly stated in the configuration file. All other
switch parameters will remain unchanged.
Restrictions The TFTP server must be on the same IP subnet as the Switch.
Only administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To download a configuration file:
54
Page 59

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#download cfg_fromTFTP 10.48.74.121 c:\cfg\setting.txt
Command: download cfg_fromTFTP 10.48.74.121 c:\cfg\setting.txt
Connecting to server................... Done.
Download configuration................. Done.
DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin##
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------DES-3526:admin## DES-3526 Configuration
DES-3526:admin##
DES-3526:admin## Firmware: Build 5.01-B47
DES-3526:admin## Copyright(C) 2000-2004 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
DES-3526:admin##-------------------------------------------------------------------DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin## BASIC
DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin#config serial_port baud_rate 9600 auto_logout 10_minutes
Command: config serial_port baud_rate 9600 auto_logout 10_minutes
The download configuration command will initiate the loading of the various settings in the order listed in the configuration file.
When the file has been successfully loaded the message “End of configuration file for DES-3526” appears followed by the
command prompt.
DES-3526:admin#disable authen_policy
Command: disable authen_policy
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin##--------------------------------------------------DES-3526:admin## End of configuration file for DES-3526
DES-3526:admin##--------------------------------------------------DES-3526:admin#
config firmware image_id
Purpose Used to configure the firmware section as a boot up section, or to
delete the firmware section
Syntax
Description This command is used to configure the firmware section. The user
config firmware image_id <value 1-n> [delete | boot_up]
may choose to remove the firmware section or use it as a boot up
section.
Parameters
image_id – Specifies the working section. The Switch can hold two
firmware versions for the user to select from, which are specified by
image ID.
delete – Entering this parameter will delete the specified firmware
section.
boot_up – Entering this parameter will specify the firmware image ID
as a boot up section.
55
Page 60

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
config firmware image_id
Restrictions Only administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To configure firmware section 1 as a boot up section:
DES-3526:admin# config firmware section_id 1 boot_up
Command: config firmware section_id 1 boot_up
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show firmware information
Purpose Used to display the firmware section information.
Syntax
Description This command is used to display the firmware section information.
Parameters None.
Restrictions None
Example usage:
To display the current firmware information on the Switch:
DES-3526:admin#show firmware information
Command: show firmware information
ID Version Size(B) Update Time From User
-- -------- ------- ------------------- ------------------ -------------- 1 4.01-B09 2711821 00000 days 00:00:00 Serial Port (PROM) Unknown
*2 5.01-B47 3281614 00000 days 00:12:34 10.73.21.1 RG
'*' means boot up section
(T) means firmware update through TELNET
(S) means firmware update through SNMP
(W) means firmware update through WEB
(SIM) means firmware update through Single IP Management
Free space: 2097152 bytes
DES-3526:admin#
show firmware information
show config
Purpose Used to display the current or saved version of the configuration settings of the
switch.
Syntax
Description Use this command to display all the configuration settings that are saved to NV
show config [current_config | config_in_nvram]
RAM or display the configuration settings as they are currently configured. Use the
keyboard to list settings one line at a time (Enter), one page at a time (Space) or
view all (a).
The configuration settings are listed by category in the following order:
56
Page 61

show config
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
1. Basic (serial port, Telnet and
2. storm control
3. IP group management
4. syslog
5. QoS
6. port mirroring
7. traffic segmentation
8. port
9. port lock
10. 8021x
11. SNMPv3
12. management (SNMP traps
Parameters
Restrictions None.
current_config – Entering this parameter will display configurations entered without
being saved to NVRAM.
config_in_NVRAM - Entering this parameter will display configurations entered and
saved to NVRAM.
web management status)
RMON)
13. vlan
14. FDB (forwarding data base)
15. MAC address table notification
16. STP
17. SSH
18. SSL
19. ACL
20. SNTP
21. IP route
22. LACP
23. ARP
24. IP
25. IGMP snooping
26. access authentication control
(TACACS etc.)
Example usage:
To view the current configuration settings:
DES-3526:admin#show config current_config
Command: show config current_config
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# DES-3526 Configuration
#
# Firmware: Build 5.01-B47
# Copyright(C) 2000-2004 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# BASIC
config serial_port baud_rate 9600 auto_logout 10_minutes
enable telnet 23
enable web 80
# STORM
config traffic control 1-5 broadcast disable multicast disable unicast disable thres
hold 128
# GM
config sim candidate
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
57
Page 62

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
upload
Purpose Used to upload the current switch settings or the switch history log
to a TFTP.
Syntax
Description This command is used to upload either the Switch’s current settings
Parameters
Restrictions The TFTP server must be on the same IP subnet as the Switch.
Example usage:
To upload a configuration file:
DES-3526:admin#upload cfg_toTFTP 10.48.74.121
c:\cfg\log.txt
Command: upload cfg_toTFTP 10.48.74.121 c:\cfg\log.txt
Connecting to server................... Done.
Upload configuration...................Done.
DES-3526:admin#
upload [cfg_toTFTP | log_toTFTP] <ipaddr> <path_filename
64>
or the Switch’s history log to a TFTP server.
cfg_toTFTP − Specifies that the Switch’s current settings will be
uploaded to the TFTP server.
log_toTFTP − Specifies that the switch history log will be uploaded
to the TFTP server.
<ipaddr> − The IP address of the TFTP server. The TFTP server
must be on the same IP subnet as the Switch.
<path_filename 64> − Specifies the location of the Switch
configuration file on the TFTP server. This file will be replaced by
the uploaded file from the Switch.
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
command.
enable autoconfig
Purpose Used to activate the autoconfiguration function for the Switch. This will load a
previously saved configuration file for current use.
Syntax
Description When autoconfig is enabled on the Switch, the DHCP reply will contain a
Parameters None.
Restrictions When autoconfig is enabled, the Switch becomes a DHCP client automatically
enable autoconfig
configuration file and path name. It will then request the file from the TFTP server
specified in the reply. When autoconfig is enabled, the ipif settings will
automatically become DHCP client.
(same as: config ipif System dhcp). The DHCP server must have the TFTP
server IP address and configuration file name, and be configured to deliver this
information in the data field of the DHCP reply packet. The TFTP server must be
running and have the requested configuration file in its base directory when the
request is received from the Switch. Consult the DHCP server and TFTP server
software instructions for information on loading a configuration file.
If the Switch is unable to complete the autoconfiguration process the previously
saved local configuration file present in Switch memory will be loaded.
58
Page 63

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
NOTE: Dual-purpose (DHCP/TFTP) server utility software may require entry of the
configuration file name and path within the user interface. Alternatively, the DHCP software
may require creating a separate ext file with the configuration file name and path in a specific
directory on the server. Consult the documentation for the DCHP server software if users are
unsure.
Example usage:
To enable autoconfiguration on the Switch:
DES-3526:admin#enable autoconfig
Command: enable autoconfig
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
When autoconfig is enabled and the Switch is rebooted, the normal login screen will appear for a few moments while the
autoconfig request (i.e. download configuration) is initiated. The console will then display the configuration parameters as they
are loaded from the configuration file specified in the DHCP or TFTP server. This is exactly the same as using a download
configuration command. After the entire Switch configuration is loaded, the Switch will automatically “logout” the server. The
configuration settings will be saved automatically and become the active configuration.
Upon booting up the autoconfig process is initiated, the console screen will appear similar to the example below. The
configuration settings will be loaded in normal order.
DES-3526 Fast Ethernet Switch Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 5.01-B47
Copyright(C) 2000-2004 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin#download configuration 10.41.44.44
c:\cfg\setting.txt
Command: download configuration 10.41.44.44 c:\cfg\setting.txt
Connecting to server................... Done.
Download configuration................. Done.
The very end of the autoconfig process including the logout appears like this:
DES-3526:admin#disable authen_policy
Command: disable authen_policy
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin##------------------------------------------------DES-3526:admin## End of configuration file for DES-3526
DES-3526:admin#
**********
* Logout *
**********
59
Page 64

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
NOTE: With autoconfig enabled, the Switch ipif settings now define the Switch as a
DHCP client. Use the show switch command to display the new IP settings status.
disable autoconfig
Purpose Use this to deactivate autoconfiguration from DHCP.
Syntax
Description This instructs the Switch not to accept autoconfiguration instruction from the
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To stop the autoconfiguration function:
DES-3526:admin#disable autoconfig
Command: disable autoconfig
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
disable autoconfig
DHCP server. This does not change the IP settings of the Switch. The ipif
settings will continue as DHCP client until changed with the config ipif
command.
show autoconfig
Purpose Used to display the current autoconfig status of the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command will list the current status of the autoconfiguration
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To upload a:
show autoconfig
function.
DES-3526:admin#show autoconfig
Command: show autoconfig
Autoconfig disabled.
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
60
Page 65

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
ping
Purpose Used to test the connectivity between network devices.
Example usage:
To ping the IP address 10.48.74.121 four times:
Syntax
Description The ping command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
Parameters
Restrictions None.
DES-3526:admin#ping 10.48.74.121 times 4
Command: ping 10.48.74.121
Reply from 10.48.74.121, time<10ms
Reply from 10.48.74.121, time<10ms
Reply from 10.48.74.121, time<10ms
Reply from 10.48.74.121, time<10ms
Ping statistics for 10.48.74.121
Packets: Sent =4, Received =4, Lost =0
DES-3526:admin#
ping <ipaddr> {times <value 1-255>} {timeout <sec 1-99>}
echo messages to a remote IP address. The remote IP address will
then “echo” or return the message. This is used to confirm
connectivity between the Switch and the remote device.
<ipaddr> - Specifies the IP address of the host.
times <value 1-255> - The number of individual ICMP echo
messages to be sent. A value of 0 will send an infinite ICMP echo
messages. The maximum value is 255. The default is 0.
timeout <sec 1-99> - Defines the time-out period while waiting for a
response from the remote device. A value of 1 to 99 seconds can be
specified. The default is 1 second
61
Page 66

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
10
NETWORK MONITORING COMMANDS
The network monitoring commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in the
following table.
Command Parameters
show packet ports <portlist>
show error ports <portlist>
show utilization [cpu | ports {<portlist>}]
clear counters ports <portlist>
clear log
show log index <value>
enable syslog
disable syslog
show syslog
create syslog host <index 1-4> ipaddress <ipaddr> {severity [informational | warning |
all] | facility [local0 | local1 | local2 | local3 | local4 | local5 | local6 |
local7] | udp_port <udp_port_number>| state [enable | disable]
config syslog host [all | <index 1-4>] {severity [informational | warning | all] | facility
[local0 | local1 | local2 | local3 | local4 | local5 | local6 | local7] |
udp_port <udp_port_number> | ipaddress <ipaddr> | state [enable
| disable]}
delete syslog host [<index 1-4> | all]
show syslog host <index 1-4>
config system_severity [trap | log | all] [critical | warning | information]
show system_severity
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections.
show packet ports
Purpose Used to display statistics about the packets sent and received by the
Switch.
Syntax
Description This command is used to display statistics about packets sent and
show packet ports <portlist>
received by ports specified in the <portlist>.
Example usage:
To display the packets analysis for port 7 of module 2:
Parameters
Restrictions None.
<portlist> − Specifies a port or range of ports to be displayed.
62
Page 67

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#show packet port 2
Command: show packet port 2
Port number : 2
Frame Size Frame Counts Frame/sec Frame Type Total Total/sec
----------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ------ --------64 3275 10 RX Bytes 408973 1657
65-127 755 10 RX Frames 395 19
128-255 316 1
256-511 145 0 TX Bytes 7918 178
512-1023 15 0 TX Frames 111 2
1024-1518 0 0
Unicast RX 152 1
Multicast RX 557 2
Broadcast RX 3686 16
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
show error ports
Example usage:
To display the errors of the port 3 of module 1:
Purpose Used to display the error statistics for a range of ports.
Syntax
Description This command will display all of the packet error statistics collected
Parameters
Restrictions None.
DES-3526:admin#show error ports 3
Command: show error ports 3
Port number : 1
RX Frames
TX Frames
---------------
---------------CRC Error 19 Excessive Deferral 0
Undersize 0 CRC Error 0
Oversize 0 Late Collision 0
Fragment 0 Excessive Collision 0
Jabber 11 Single Collision 0
Drop Pkts 20837 Collision 0
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next
show error ports <portlist>
and logged by the Switch for a given port list.
<portlist> − Specifies a port or range of ports to be displayed.
63
Page 68

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
show utilization
Purpose Used to display real-time port and CPU utilization statistics.
Syntax
Description This command will display the real-time port and CPU utilization
Parameters
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To display the port utilization statistics:
DES-3526:admin#show utilization ports
Command: show utilization ports
Port TX/sec RX/sec Util Port TX/sec RX/sec Util
------ ------ ------- ---- ------ -------- ------- ---1 0 0 0 22 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 23 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 24 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 25 0 26 1
5 0 0 0 26 0 0 0
6 0 0 0
7 0 0 0
8 0 0 0
9 0 0 0
10 0 0 0
11 0 0 0
12 0 0 0
13 0 0 0
14 0 0 0
15 0 0 0
16 0 0 0
17 0 0 0
18 0 0 0
19 0 0 0
20 0 0 0
21 0 0 0
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next
show utilization [cpu | ports {<portlist>}]
statistics for the Switch.
cpu – Entering this parameter will display the current cpu utilization
and CPU memory usage of the Switch.
ports - Entering this parameter will display the current port
utilization of the Switch.
<portlist> - Specifies a port or range of ports to be
displayed.
To display the current CPU utilization:
DES-3526:admin# CPU utilization :
------------------------------------------------------------------------------Five seconds - 2% One minute - 16% Five minutes - 1%
CPU Memory Usage: 59%
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
64
Page 69

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
clear counters
Purpose Used to clear the Switch’s statistics counters.
Example usage:
To clear the counters:
Syntax
Description This command will clear the counters used by the Switch to compile
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#clear counters ports 2-9
Command: clear counters ports 2-9
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
clear counters {ports <portlist>}
statistics.
<portlist> − Specifies a port or range of ports to be displayed.
command.
clear log
Purpose Used to clear the Switch’s history log.
Syntax
clear log
Example usage:
To clear the log information:
Description This command will clear the Switch’s history log.
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
command.
DES-3526:admin#clear log
Command: clear log
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show log
Purpose Used to display the switch history log.
Syntax
Description This command will display the contents of the Switch’s history log.
show log {index <value>}
Example usage:
Parameters
Restrictions None.
index <value> − This command will display the history log,
beginning at 1 and ending at the value specified by the user in the
<value> field.
If no parameter is specified, all history log entries will be displayed.
65
Page 70

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
5 00000 days 00:00:47 Firmware upgraded to SLAVE unsuccessfully!
To display the switch history log:
DES-3526:admin#show log index 5
Command: show log index 5
DES-3526:admin#show log index 5
Command: show log index 5
Index Time Log Text
----- ------------------- -------------------------------------------
(Username: Anonymous, IP: 0.0.0.0, MAC: 00-00-00-00-00-00)
4 00000 days 00:00:46 Log message upload was unsuccessful!
(Username, IP: 0.0.0.0, MAC: 00-00-00-00-00-00)
3 00000 days 00:00:46 BPDU Loop Back on port 0
2 00000 days 00:00:46 System warm start
1 00000 days 01:08:12 Configuration and log saved to flash by
console (Username: Anonymous)
DES-3526:admin#
NOTE: For detailed information regarding Log entries that will appear in
this window, please refer to Appendix C at the back of the xStack DES-
3500 Series Layer 2 Stackable Fast Ethernet Managed Switch User
Manual.
Example usage:
To the syslog function on the Switch:
enable syslog
Purpose Used to enable the system log to be sent to a remote host.
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#enable syslog
Command: enable syslog
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
enable syslog
The enable syslog command enables the system log to be sent to
a remote host.
command.
66
Page 71

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
disable syslog
Purpose Used to enable the system log to be sent to a remote host.
Example usage:
To disable the syslog function on the Switch:
show syslog
Purpose Used to display the syslog protocol status as enabled or disabled.
Syntax
Description
Syntax
Description
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
DES-3526:admin#disable syslog
Command: disable syslog
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
disable syslog
The disable syslog command enables the system log to be sent to a
remote host.
show syslog
The show syslog command displays the syslog status as enabled or
disabled.
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To display the current status of the syslog function:
DES-3526:admin#show syslog
Command: show syslog
Syslog Global State: Enabled
DES-3526:admin#
create syslog host
Purpose Used to create a new syslog host.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
create syslog host <index 1-4> ipaddress <ipaddr> {severity [informational | warning |
all] | facility [local0 | local1 | local2 | local3 | local4 | local5 | local6 | local7] | udp_port
<udp_port_number> | state [enable | disable]
The create syslog host command is used to create a new syslog host.
<index 1-4> − Specifies that the command will be applied to an index of hosts. There are
four available indexes, numbered 1 through 4.
ipaddress <ipaddr> − Specifies the IP address of the remote host where syslog messages
will be sent.
severity − Severity level indicator. These are described in the following:
Bold font indicates that the corresponding severity level is currently supported on the
Switch.
67
Page 72

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
create syslog host
Numerical Severity
Code
0 Emergency: system is unusable
1 Alert: action must be taken immediately
2 Critical: critical conditions
3 Error: error conditions
4 Warning: warning conditions
5 Notice: normal but significant condition
6 Informational: informational messages
7 Debug: debug-level messages
Numerical Facility
Code
68
Page 73

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
create syslog host
0 kernel messages
1 user-level messages
2 mail system
3 system daemons
4 security/authorization messages
5 messages generated internally by syslog
6 line printer subsystem
7 network news subsystem
8 UUCP subsystem
9 clock daemon
10 security/authorization messages
11 FTP daemon
12 NTP subsystem
13 log audit
14 log alert
15 clock daemon
16 local use 0 (local0)
17 local use 1 (local1)
18 local use 2 (local2)
19 local use 3 (local3)
20 local use 4 (local4)
21 local use 5 (local5)
22 local use 6 (local6)
23 local use 7 (local7)
local0 − Specifies that local use 0 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 16 from the list above.
local1 − Specifies that local use 1 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 17 from the list above.
local2 − Specifies that local use 2 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 18 from the list above.
local3 − Specifies that local use 3 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 19 from the list above.
local4 − Specifies that local use 4 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 20 from the list above.
local5 − Specifies that local use 5 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 21 from the list above.
local6 − Specifies that local use 6 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 22 from the list above.
local7 − Specifies that local use 7 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 23 from the list above.
udp_port <udp_port_number> − Specifies the UDP port number that the syslog protocol will
use to send messages to the remote host.
state [enable | disable] − Allows the sending of syslog messages to the remote host,
specified above, to be enabled and disabled.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To create syslog host:
DES-3526:admin#create syslog host 1 severity all
facility local0
Command: create syslog host 1 severity all facility
local0
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
69
Page 74

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
config syslog host
Purpose Used to configure the syslog protocol to send system log data to a remote host.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
config syslog host [all | <index 1-4>] {severity [informational | warning | all] | facility
[local0 | local1 | local2 | local3 | local4 | local5 | local6 | local7] | udp_port
<udp_port_number> | ipaddress <ipaddr> | state [enable | disable]
The config syslog host command is used to configure the syslog protocol to send system
log information to a remote host.
<index 1-4> − Specifies that the command will be applied to an index of hosts. There are
four available indexes, numbered 1 through 4.
ipaddress <ipaddr> − Specifies the IP address of the remote host where syslog messages
will be sent.
severity − Severity level indicator. These are described in the following:
Bold font indicates that the corresponding severity level is currently supported on the
Switch.
Numerical Severity
Code
0 Emergency: system is unusable
1 Alert: action must be taken immediately
2 Critical: critical conditions
3 Error: error conditions
4 Warning: warning conditions
5 Notice: normal but significant condition
6 Informational: informational messages
7 Debug: debug-level messages
informational − Specifies that informational messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 6 from the list above.
warning − Specifies that warning messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 4 from the list above.
all − Specifies that all of the currently supported syslog messages that are generated by the
Switch will be sent to the remote host.
facility − Some of the operating system daemons and processes have been assigned
Facility values. Processes and daemons that have not been explicitly assigned a Facility
may use any of the "local use" facilities or they may use the "user-level" Facility. Those
Facilities that have been designated are shown in the following: Bold font indicates the
facility values the Switch currently supports.
70
Page 75

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Parameters
Numerical Facility
Code
0 kernel messages
1 user-level messages
2 mail system
3 system daemons
4 security/authorization messages
5 messages generated internally by syslog
6 line printer subsystem
7 network news subsystem
8 UUCP subsystem
9 clock daemon
10 security/authorization messages
11 FTP daemon
12 NTP subsystem
13 log audit
14 log alert
15 clock daemon
16 local use 0 (local0)
17 local use 1 (local1)
18 local use 2 (local2)
19 local use 3 (local3)
20 local use 4 (local4)
21 local use 5 (local5)
22 local use 6 (local6)
23 local use 7 (local7)
Parameters
local0 − Specifies that local use 0 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 16 from the list above.
local1 − Specifies that local use 1 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 17 from the list above.
local2 − Specifies that local use 2 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 18 from the list above.
local3 − Specifies that local use 3 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 19 from the list above.
local4 − Specifies that local use 4 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 20 from the list above.
local5 − Specifies that local use 5 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 21 from the list above.
local6 − Specifies that local use 6 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 22 from the list above.
local7 − Specifies that local use 7 messages will be sent to the remote host. This
corresponds to number 23 from the list above.
udp_port <udp_port_number> − Specifies the UDP port number that the syslog protocol will
use to send messages to the remote host.
state [enable | disable] − Allows the sending of syslog messages to the remote host,
specified above, to be enabled and disabled.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To configure a syslog host:
71
Page 76

Example usage:
To configure a syslog host for all hosts:
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#config syslog host 1 severity all
facility local0
Command: config syslog host all severity all facility
local0
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
DES-3526:admin#config syslog host all severity all
facility local0
Command: config syslog host all severity all facility
local0
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
delete syslog host
Purpose Used to remove a syslog host that has been previously configured, from the
Syntax
Description
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To delete a previously configured syslog host:
Switch.
delete syslog host [<index 1-4> | all]
The delete syslog host command is used to remove a syslog host that has
been previously configured from the Switch.
<index 1-4> − Specifies that the command will be applied to an index of hosts.
There are four available indexes, numbered 1 through 4.
all − Specifies that the command will be applied to all hosts.
DES-3526:admin#delete syslog host 4
Command: delete syslog host 4
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
72
Page 77

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
show syslog host
Purpose Used to display the syslog hosts currently configured on the Switch.
Example usage:
To show Syslog host information:
DES-3526:admin#show syslog host
Command: show syslog host
Syslog Global State: Disabled
Host Id Host IP Address Severity Facility UDP port Status
------- --------------- ------------ -------- -------- -------1 10.1.1.2 All Local0 514 Disabled
2 10.40.2.3 All Local0 514 Disabled
3 10.21.13.1 All Local0 514 Disabled
Total Entries : 3
DES-3526:admin#
Syntax
Description
Parameters
Restrictions None.
show syslog host {<index 1-4>}
The show syslog host command is used to display the syslog
hosts that are currently configured on the Switch.
<index 1-4> − Specifies that the command will be applied to an
index of hosts. There are four available indexes, numbered 1
through 4.
73
Page 78

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
config system_severity
Purpose To configure system_severity level of an alert required for log entry or trap
message.
Syntax
config system_severity [trap | log | all] [critical | warning | information]
Description This command is used to configure the system_severity levels on the
Switch. When an event occurs on the Switch, a message will be sent to the
SNMP agent (trap), the Switch’s log or both. Events occurring on the Switch
are separated into three main categories, these categories are NOT
precisely the same as the parameters of the same name (see below).
•
Information – Events classified as information are basic events
occurring on the Switch that are not deemed as problematic, such as
enabling or disabling various functions on the Switch.
•
Warning - Events classified as warning are problematic events that
are not critical to the overall function of the Switch but do require
attention, such as unsuccessful downloads or uploads and failed
logins.
•
Critical – Events classified as critical are fatal exceptions occurring on
the Switch, such as hardware failures or spoofing attacks.
Parameters Choose one of the following to identify where severity messages are to be
sent.
•
trap – Entering this parameter will define which events occurring on
the Switch will be sent to a SNMP agent for analysis.
•
log – Entering this parameter will define which events occurring on the
Switch will be sent to the Switch’s log for analysis.
•
all – Entering this parameter will define which events occurring on the
Switch will be sent to a SNMP agent and the Switch’s log for analysis.
Choose one of the following to identify what level of severity warnings are to
be sent to the destination entered above.
critical – Entering this parameter along with the proper destination, stated
above, will instruct the Switch to send only critical events to the
Switch’s log or SNMP agent.
warning – Entering this parameter along with the proper destination, stated
above, will instruct the Switch to send critical and warning events to
the Switch’s log or SNMP agent.
information – Entering this parameter along with the proper destination,
stated above, will instruct the switch to send informational, warning
and critical events to the Switch’s log or SNMP agent.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To configure the system severity settings for critical traps only:
DES-3526:admin#config system_severity trap critical
Command: config system_severity trap critical
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
74
Page 79

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
show system_severity
Purpose To display system_severity level of an alert required for log entry or trap
message.
Syntax
Description This command is used to display system_severity level of an alert required
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To display the system severity settings for critical traps only:
show system_severity
for log entry or trap message.
DES-3526:admin#show system_severity
Command: show system_severity
System Severity
-------------------Log : information
Trap : information
DES-3526:admin#
75
Page 80
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
11
MULTIPLE SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL (MSTP) COMMANDS
This Switch supports three versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol; 802.1d STP, 802.1w Rapid STP and 802.1s MSTP. Multiple
Spanning Tree Protocol, or MSTP, is a standard defined by the IEEE community that allows multiple VLANs to be mapped to a
single spanning tree instance, which will provide multiple pathways across the network. Therefore, these MSTP configurations
will balance the traffic load, preventing wide scale disruptions when a single spanning tree instance fails. This will allow for faster
convergences of new topologies for the failed instance. Frames designated for these VLANs will be processed quickly and
completely throughout interconnected bridges utilizing either of the three spanning tree protocols (STP, RSTP or MSTP). This
protocol will also tag BDPU packets so receiving devices can distinguish spanning tree instances, spanning tree regions and the
VLANs associated with them. These instances will be classified by an instance_id. MSTP will connect multiple spanning trees
with a Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST). The CIST will automatically determine each MSTP region, its maximum
possible extent and will appear as one virtual bridge that runs a single spanning tree. Consequentially, frames assigned to different
VLANs will follow different data routes within administratively established regions on the network, continuing to allow simple
and full processing of frames, regardless of administrative errors in defining VLANs and their respective spanning trees. Each
switch utilizing the MSTP on a network will have a single MSTP configuration that will have the following three attributes:
a) A configuration name defined by an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters (defined in the config stp mst_config_id
command as name <string>).
b) A configuration revision number (named here as a revision_level) and;
c) A 4096 element table (defined here as a vid_range) which will associate each of the possible 4096 VLANs supported by
the Switch for a given instance.
To utilize the MSTP function on the Switch, three steps need to be taken:
a) The Switch must be set to the MSTP setting (config stp version)
b) The correct spanning tree priority for the MSTP instance must be entered (config stp priority).
c) VLANs that will be shared must be added to the MSTP Instance ID (config stp instance_id).
The Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate
parameters) in the following table.
Command Parameters
enable stp
disable stp
config stp version [mstp | rstp | stp]
config stp {maxage <value 6-40> | maxhops <value 6-40> | hellotime <value 1-2> |
forwarddelay <value 4-30>| txholdcount <value 1-10> | fbpdu [enable | disable]}
config stp ports <portlist> {externalCost [auto | <value 1-200000000>] | hellotime <value 1-2> |
migrate [yes | no] | edge [true | false | auto] | restricted_tcn [true | false] |
restricted_role [true | false] | p2p [true | false | auto] | state [enable | disable] |
fbpdu [enable |disable | hw_filtering] | recover_hw_filtering }
create stp instance_id <value 1-4>
config stp instance _id <value 1-4> [add_vlan | remove_vlan] <vidlist>
delete stp instance_id <value 1-4>
config stp priority <value 0-61440> instance_id <value 0-4>
config stp
mst_config_id
config stp mst_ports <portlist> instance_id <value 0-4> {internalCost [auto | value 1-200000000] |
{revision_level <int 0-65535> | name <string>}
priority <value 0-240>}
show stp
show stp ports {<portlist>}
76
Page 81

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Command Parameters
show stp instance {<value 0-4>}
show stp mst_config id
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections.
enable stp
Purpose Used to globally enable STP on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command allows the Spanning Tree Protocol to be globally
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To enable STP, globally, on the Switch:
disable stp
Purpose Used to globally disable STP on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command allows the Spanning Tree Protocol to be globally
enable stp
enabled on the Switch.
command.
DES-3526:admin#enable stp
Command: enable stp
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
disable stp
disabled on the Switch.
Parameters None.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To disable STP on the Switch:
config stp version
Purpose Used to globally set the version of STP on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command allows the user to choose the version of the spanning tree
Parameters
command.
DES-3526:admin#disable stp
Command: disable stp
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config stp version [mstp | rstp | stp]
to be implemented on the Switch.
mstp – Selecting this parameter will set the Multiple Spanning Tree
77
Page 82

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
config stp version
Protocol (MSTP) globally on the Switch.
rstp - Selecting this parameter will set the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
(RSTP) globally on the Switch.
stp - Selecting this parameter will set the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
globally on the Switch.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To set the Switch globally for the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP):
DES-3526:admin#config stp version mstp
Command: config stp version mstp
STP settings will return to default.
Are you sure to change the STP version?(y/n)
DES-3526:admin#
config stp
Purpose Used to setup STP, RSTP and MSTP on the Switch.
Syntax
Description This command is used to setup the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) for the
Parameters
config stp {maxage <value 6-40> | maxhops <value 6-40> | hellotime
<value 1-2> | forwarddelay <value 4-30>| txholdcount <value 1-10> |
fbpdu [enable | disable]}
entire Switch. All commands here will be implemented for the STP
version that is currently set on the Switch.
maxage <value 6-40> − This value may be set to ensure that old
information does not endlessly circulate through redundant paths in the
network, preventing the effective propagation of the new information. Set
by the Root Bridge, this value will aid in determining that the Switch has
spanning tree configuration values consistent with other devices on the
bridged LAN. If the value ages out and a BPDU has still not been
received from the Root Bridge, the Switch will start sending its own BPDU
to all other switches for permission to become the Root Bridge. If it turns
out that your switch has the lowest Bridge Identifier, it will become the
Root Bridge. The user may choose a time between 6 and 40 seconds.
The default value is 20.
maxhops <value 6-40> - The number of hops between devices in a
spanning tree region before the BPDU (bridge protocol data unit) packet
sent by the Switch will be discarded. Each switch on the hop count will
reduce the hop count by one until the value reaches zero. The Switch will
then discard the BDPU packet and the information held for the port will
age out. The user may set a hop count from 1 to 20. The default is 20.
hellotime <value 1-2> − The user may set the time interval between
transmission of configuration messages by the root device, thus stating
that the Switch is still functioning. A time between 1 and 2 seconds may
be chosen, with a default setting of 2 seconds.
NOTE:
and therefore, the hellotime must be set using the
configure stp ports command for switches utilizing the
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol.
In MSTP, the spanning tree is configured by port
forwarddelay <value 4-30> − The maximum amount of time (in seconds)
that the root device will wait before changing states. The user may
choose a time between 4 and 30 seconds. The default is 15 seconds.
78
Page 83

config stp
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To configure STP with maxage 18 and maxhops of 15:
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
txholdcount <1-10> - The maximum number of BPDU Hello packets
transmitted per interval. Default value = 6.
fbpdu [enable | disable] − Allows the forwarding of STP BPDU packets
from other network devices when STP is disabled on the Switch. The
default is enable.
DES-3526:admin#config stp maxage 18 maxhops 15
Command: config stp maxage 18 maxhops 15
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
79
Page 84

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
config stp ports
Purpose Used to setup STP on the port level.
Syntax
Description This command is used to create and configure STP for a group of ports.
Parameters
config stp ports <portlist> {externalCost [auto | <value 1-200000000>] |
hellotime <value 1-2> | migrate [yes | no] | edge [true | false | auto] |
restricted_tcn [true | false] | restricted_role [true | false] | p2p [true | false |
auto] | state [enable | disable] | fbpdu [enable |disable | hw_filter] |
recover_hw_filter}}
<portlist> − Specifies a range of ports to be configured.
externalCost − This defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding
packets to the specified port list. Port cost can be set automatically or as a metric
value. The default value is auto.
auto – Setting this parameter for the external cost will automatically set the speed
for forwarding packets to the specified port(s) in the list for optimal efficiency.
Default port cost: 100Mbps port = 200000. Gigabit port = 20000.
<value 1-200000000> - Define a value between 1 and 200000000 to determine
the external cost. The lower the number, the greater the probability the port
will be chosen to forward packets.
hellotime <value 1-2> − The time interval between transmission of configuration
messages by the designated port, to other devices on the bridged LAN, thus
stating that the Switch is still functioning. The user may choose a time between 1
and 2 seconds. The default is 2 seconds.
migrate [yes | no] – Setting this parameter as “yes” will set the ports to send out
BDPU packets to other bridges, requesting information on their STP setting If the
Switch is configured for RSTP, the port will be capable to migrate from 802.1d STP
to 802.1w RSTP. If the Switch is configured for MSTP, the port is capable of
migrating from 802.1d STP to 802.1s MSTP. RSTP and MSTP can coexist with
standard STP, however the benefits of RSTP and MSTP are not realized on a port
where an 802.1d network connects to an 802.1w or 802.1s enabled network.
Migration should be set as yes on ports connected to network stations or segments
that are capable of being upgraded to 802.1w RSTP or 802.1s MSTP on all or
some portion of the segment.
edge [true | false | auto] – true designates the port as an edge port. Edge ports
cannot create loops, however an edge port can lose edge port status if a topology
change creates a potential for a loop. An edge port normally should not receive
BPDU packets. If a BPDU packet is received it automatically loses edge port
status. false indicates that the port does not have edge port status.
restricted_role [true | false] – If true causes the Port not to be selected as Root Port
for the CIST or any MSTI, even it has the best spanning tree priority vector. Such a
Port will be selected as an Alternate Port after the Root Port has been selected.
This parameter should be false by default. If set, it can cause lack of spanning tree
connectivity. It is set by a network administrator to prevent bridges external to a
core region of the network influencing the spanning tree active topology, possibly
because those bridges are not under the full control of the administrator.
restricted_tcn [true | false] – If true causes the Port not to propagate received
topology change notifications and topology changes to other Ports. This parameter
should be false by default. If set it can cause temporary loss of connectivity after
changes in a spanning trees active topology as a result of persistent incorrectly
learned station location information. It is set by a network administrator to prevent
bridges external to a core region of the network, causing address flushing in that
region, possibly because those bridges are not under the full control of the
administrator or MAC_Operational for the attached LANs transitions frequently.
p2p [true | false | auto] – true indicates a point-to-point (P2P) shared link. P2P
ports are similar to edge ports however they are restricted in that a P2P port must
operate in full-duplex. Like edge ports, P2P ports transition to a forwarding state
rapidly thus benefiting from RSTP. A p2p value of false indicates that the port
cannot have p2p status. Auto allows the port to have p2p status whenever possible
and operate as if the p2p status were true. If the port cannot maintain this status
80
Page 85

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
(for example if the port is forced to half-duplex operation) the p2p status changes
to operate as if the p2p value were false. The default setting for this parameter is
auto.
state [enable | disable] − Allows STP to be enabled or disabled for the ports
specified in the port list. The default is enable.
fbpdu [enable | disable | hw_filtering] − When enabled, this allows the forwarding of
STP BPDU packets from other network devices when STP is disabled in the
specified ports. If users want to enable Forwarding BPDU on a per port basis, the
following settings must first be in effect: 1. STP must be globally disabled and 2.
Forwarding BPDU must be globally enabled. To globally disable STP, use the
disable stp command, to globally enable fbpdu, use the config stp command.
The default is disable.
When the state is set to hw_filtering, if STP BPDU is received by this port, the port
will be changed to BPDU hardware filtering mode such that all layer 2 control
packets will be dropped by hardware. The default is disable.
recover_hw_filtering − When a port is in BPDU hardware filtering mode, it can be
recovered by this option.
NOTE:
The following MAC addresses are layer 2 control packets:
01:80:C2:00:00:00 to 01:80:C2:00:00:10 and 01:80:C2:00:00:20 to
01:80:C2:00:00:2F.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To configure STP with path cost 19, hellotime set to 5 seconds, migration enable, and state enable for ports 1-5 of
module 1.
create stp instance_id
Purpose Used to create a STP instance ID for MSTP.
Syntax
Description This command allows the user to create a STP instance ID for the
DES-3526:admin#config stp ports 1-5 externalCost 19 hellotime 1
migrate yes state enable
Command: config stp ports 1-5 externalCost 19 hellotime 1 migrate
yes state enable
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
create stp instance_id <value 1-4>
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol. There are 5 STP instances on
the Switch (one internal CIST, unchangeable) and the user may
create up to 4 instance IDs for the Switch.
Parameters
<value 1-4> - Enter a value between 1 and 4 to identify the
Spanning Tree instance on the Switch.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
command.
Example usage:
To create a spanning tree instance 2:
DES-3526:admin#create stp instance_id 2
Command: create stp instance_id 2
Success.
81
Page 86

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#
config stp instance_id
Purpose Used to add or delete an STP instance ID.
Syntax
config stp instance_id <value 1-4> [add_vlan | remove_vlan]
<vidlist>
Description This command is used to map VIDs (VLAN IDs) to previously configured
STP instances on the Switch by creating an instance_id. A STP
instance may have multiple members with the same MSTP
configuration. There is no limit to the number of STP regions in a
network but each region only supports a maximum of 5 spanning tree
instances (one unchangeable default entry). VIDs can belong to only
one spanning tree instance at a time.
NOTE:
Switches in the same spanning tree region
having the same STP instance_id must be mapped
identically, and have the same configuration
Parameters
revision_level number and the same name.
<value 1-4> - Enter a number between 1 and 4 to define the
instance_id. The Switch supports 5 STP regions with one unchangeable
default instance ID set as 0.
add_vlan – Along with the vid_range <vidlist> parameter, this command
will add VIDs to the previously configured STP instance_id.
remove_vlan - Along with the vid_range <vidlist> parameter, this
command will remove VIDs to the previously configured STP
instance_id.
<vidlist> - Specify the VID range from configured VLANs set on the
Switch. Supported VIDs on the Switch range from ID number 1 to 4094.
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To configure instance ID 2 to add VID 10:
DES-3526:admin#config stp instance_id 2 add_vlan 10
Command : config stp instance_id 2 add_vlan 10
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
Example usage:
To remove VID 10 from instance ID 2:
DES-3526:admin#config stp instance_id 2 remove_vlan 10
Command : config stp instance_id 2 remove_vlan 10
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
delete stp instance_id
Purpose Used to delete a STP instance ID from the Switch.
Syntax
delete stp instance_id <value 1-4>
82
Page 87

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
delete stp instance_id
Description This command allows the user to delete a previously configured
STP instance ID from the Switch.
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To delete STP instance ID 2 from the Switch.
DES-3526:admin#delete stp instance_id 2
Command: delete stp instance_id 2
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
<value 1-4> Enter a value between 1 and 4 to identify the
Spanning Tree instance on the Switch.
command.
config stp priority
Purpose Used to update the STP instance configuration
Syntax
Description This command is used to update the STP instance configuration
config stp priority <value 0-61440> instance_id <value 0-4>
settings on the Switch. The MSTP will utilize the priority in selecting
the root bridge, root port and designated port. Assigning higher
priorities to STP regions will instruct the Switch to give precedence to
the selected instance_id for forwarding packets. The lower the
priority value set, the higher the priority.
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To set the priority value for instance_id 2 as 4096.
DES-3526:admin#config stp priority 4096 instance_id 2
Command : config stp priority 4096 instance_id 2
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
priority <value 0-61440> - Select a value between 0 and 61440 to
specify the priority for a specified instance ID for forwarding packets.
The lower the value, the higher the priority. This entry must be
divisible by 4094.
instance_id <value 0-4> - Enter the value corresponding to the
previously configured instance ID of which the user wishes to set the
priority value. An instance id of 0 denotes the default instance_id
(CIST) internally set on the Switch.
command.
config stp mst_config_id
Purpose Used to update the MSTP configuration identification.
Syntax
config stp mst_config_id {revision_level <int 0-65535> | name
<string 32>}
83
Page 88

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
config stp mst_config_id
Description This command will uniquely identify the MSTP configuration
currently configured on the Switch. Information entered here will
be attached to BPDU packets as an identifier for the MSTP region
to which it belongs. Switches having the same revision_level and
name will be considered as part of the same MSTP region.
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To configure the MSTP region of the Switch with revision_level 10 and the name “Trinity”:
DES-3526:admin#config stp mst_config_id revision_level 10
name Trinity
Command : config stp mst_config_id revision_level 10 name
Trinity
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
revision_level <int 0-65535>– Enter a number between 0 and
65535 to identify the MSTP region. This value, along with the
name will identify the MSTP region configured on the Switch. The
default setting is 0.
name <string> - Enter an alphanumeric string of up to 32
characters to uniquely identify the MSTP region on the Switch.
This name, along with the revision_level value will identify the
MSTP region configured on the Switch. If no name is entered, the
default name will be the MAC address of the device.
command.
config stp mst_ports
Purpose Used to update the port configuration for a MSTP instance.
Syntax
Description
Parameters
config stp mst_ports <portlist> instance_id <value 0-4>
{internalCost [auto | <value 1-20000000>] priority <value 0-240>
This command will update the port configuration for a STP instance_id.
If a loop occurs, the MSTP function will use the port priority to select an
interface to put into the forwarding state. Set a higher priority value for
interfaces to be selected for forwarding first. In instances where the
priority value is identical, the MSTP function will implement the lowest
MAC address into the forwarding state and other interfaces will be
blocked. Remember that lower priority values mean higher priorities for
forwarding packets.
<portlist> - Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
instance_id <value 0-4> - Enter a numerical value between 0 and 4 to
identify the instance_id previously configured on the Switch. An entry of
0 will denote the CIST (Common and Internal Spanning Tree.
internalCost – This parameter is set to represent the relative cost of
forwarding packets to specified ports when an interface is selected
within a STP instance. The default setting is auto. There are two
options:
auto – Selecting this parameter for the internalCost will set quickest
route automatically and optimally for an interface. The default
value is derived from the media speed of the interface.
value 1-2000000 – Selecting this parameter with a value in the range
of 1-2000000 will set the quickest route when a loop occurs. A
lower internalCost represents a quicker transmission.
84
Page 89

config stp mst_ports
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example usage:
To designate ports 1 through 5, with instance id 2, to have an auto internalCost and a priority of 16:
DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
priority <value 0-240> - Enter a value between 0 and 240 to set the
priority for the port interface. A higher priority will designate the
interface to forward packets first. A lower number denotes a higher
priority.
DES-3526:admin#config stp mst_config_id ports 1-5
instance_id 2 internalCost auto priority 16
Command : config stp mst_config_id ports 1-5 instance_id
2 internalCost auto priority 16
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
show stp
Example usage:
To display the status of STP on the Switch:
Status 1: STP enabled with STP compatible version
Status 2 : STP enabled for RSTP
Purpose Used to display the Switch’s current STP configuration.
Syntax
Description This command displays the Switch’s current STP configuration.
Parameters None
Restrictions None.
DES-3526:admin#show stp
Command: show stp
STP Status : Enabled
STP Version : STP Compatible
Max Age : 20
Hello Time : 2
Forward Delay : 15
Max Age : 20
TX Hold Count : 3
Forwarding BPDU : Enabled
DES-3526:admin#
show stp
DES-3526:admin#show stp
Command: show stp
STP Status : Enabled
STP Version : RSTP
Max Age : 20
Hello Time : 2
Forward Delay : 15
Max Age : 20
TX Hold Count : 3
Forwarding BPDU : Enabled
DES-3526:admin#
85
Page 90

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
Status 3 : STP enabled for MSTP
DES-3526:admin#show stp
Command: show stp
STP Status : Enabled
STP Version : MSTP
Max Age : 20
Forward Delay : 15
Max Age : 20
TX Hold Count : 3
Forwarding BPDU : Enabled
DES-3526:admin#
show stp ports
Purpose Used to display the Switch’s current STP ports configuration.
Syntax
Description This command displays the STP ports settings for a specified port or
Parameters
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To show STP ports information for port 5 (STP enabled on Switch):
DES-3526:admin#show stp ports
Command: show stp ports
MSTP Port Information
---------------------Port Index : 5 , Hello Time: 2 /2 , Port STP enabled
Restricted role : False, Restricted TCN : False
External PathCost : Auto/200000 , Edge Port : No /No , P2P : Auto /Yes
Port Forward BPDU disabled
BPDU Type : RSTP
Msti Designated Bridge Internal PathCost Prio Status Role
----- ------------------ ----------------- ---- ---------- ---------0 8000/0050BA7120D6 200000 128 Forwarding Root
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
show stp ports <portlist>
group of ports (one port at a time).
<portlist> − Specifies a port or range of ports to be viewed. Information
for a single port is displayed. If no ports are specified the STP
information for port 1 will be displayed. Users may use the Space bar,
p and n keys to view information for the remaining ports.
show stp instance_id
Purpose Used to display the Switch’s STP instance configuration
Syntax
Description This command displays the Switch’s current STP Instance
Parameters
show stp instance_id <value 0-4>
Settings and the STP Instance Operational Status.
<value 0-4> - Enter a value defining the previously configured
instance_id on the Switch. An entry of 0 will display the STP
86
Page 91

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
show stp instance_id
configuration for the CIST internally set on the Switch.
Restrictions None
Example usage:
To display the STP instance configuration for instance 0 (the internal CIST) on the Switch:
DES-3526:admin#show stp instance 0
Command: show stp instance 0
STP Instance Settings
-------------------------- Instance Type : CIST
Instance Status : Enabled
Instance Priority : 32768(bridge priority : 32768, sys ID ext : 0 )
STP Instance Operational Status
------------------------------- Designated Root Bridge : 32766/00-90-27-39-78-E2
External Root Cost : 200012
Regional Root Bridge : 32768/00-53-13-1A-33-24
Internal Root Cost : 0
Designated Bridge : 32768/00-50-BA-71-20-D6
Root Port : 1
Max Age : 20
Forward Delay : 15
Last Topology Change : 856
Topology Changes Count : 2987
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
show stp mst_config_id
Purpose Used to display the MSTP configuration identification.
Syntax
Description This command displays the Switch’s current MSTP configuration
Parameters None.
Restrictions None.
Example usage:
To show the MSTP configuration identification currently set on the Switch:
show stp mst_config_id
identification.
DES-3526:admin#show stp mst_config_id
Command: show stp mst_config_id
Current MST Configuration Identification
----------------------------------------------------------
Configuration Name : [00:53:13:1A:33:24] Revision Level :0
MSTI ID Vid list
------- ----------CIST 2-4094
1 1
DES-3526:admin#
87
Page 92

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
88
Page 93

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
12
FORWARDING DATABASE COMMANDS
The layer 2 forwarding database commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate
parameters) in the following table.
Command Parameters
create fdb <vlan_name 32> <macaddr> port <port>
create multicast_fdb <vlan_name 32> <macaddr>
config multicast_fdb <vlan_name 32> <macaddr> [add | delete] <portlist>
config fdb aging_time <sec 10-1000000>
delete fdb <vlan_name 32> <macaddr>
clear fdb [vlan <vlan_name 32> | port <port> | all]
show multicast_fdb {vlan <vlan_name 32> | mac_address <macaddr>}
show fdb show fdb { port <port> | [vlan <vlan_name 32> | vid <vlanid 1-4094>] |
mac_address <macaddr> | static | aging_time }
config multicast
port_filtering_mode
show multicast
port_filtering_mode
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections.
[<portlist> | all] [forward_all_groups | forward_unregistered_groups |
filter_unregistered_groups]
{<portlist>}
create fdb
Purpose Used to create a static entry to the unicast MAC address forwarding
table (database).
Syntax
Description This command will make an entry into the Switch’s unicast MAC
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
create fdb <vlan_name 32> <macaddr> port <port>
address forwarding database.
<vlan_name 32> − The name of the VLAN on which the MAC
address resides.
<macaddr> − The MAC address that will be added to the forwarding
table.
port <port> − The port number corresponding to the MAC destination
address. The Switch will always forward traffic to the specified
device through this port.
command.
Example usage:
To create a unicast MAC FDB entry:
89
Page 94

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
02
DES-3526:admin#create fdb default 00-00-00-00-01port 5
Command: create fdb default 00-00-00-00-01-02 port
5
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
create multicast_fdb
Purpose Used to create a static entry to the multicast MAC address
forwarding table (database)
Example usage:
To create multicast MAC forwarding:
Syntax
Description This command will make an entry into the Switch’s multicast MAC
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#create multicast_fdb default 01-0000-00-00-01
Command: create multicast_fdb default 01-00-00-0000-01
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
create multicast_fdb <vlan_name 32> <macaddr>
address forwarding database.
<vlan_name 32> − The name of the VLAN on which the MAC
address resides.
<macaddr> − The MAC address that will be added to the forwarding
table.
command.
90
Page 95

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
config multicast_fdb
Purpose Used to configure the Switch’s multicast MAC address forwarding
database.
Example usage:
To add multicast MAC forwarding:
Syntax
Description This command configures the multicast MAC address forwarding
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#config multicast_fdb default 01-00-00-0000-01 add 1-5
Command: config multicast_fdb default 01-00-00-00-00-01
add 1-5
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config multicast_fdb <vlan_name 32> <macaddr> [add | delete]
<portlist>
table.
<vlan_name 32> − The name of the VLAN on which the MAC
address resides.
<macaddr> − The MAC address that will be added to the multicast
forwarding table.
[add | delete] − add will add ports to the forwarding table. delete will
remove ports from the multicast forwarding table.
<portlist> − Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
command.
91
Page 96

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
config fdb aging_time
Purpose Used to set the aging time of the forwarding database.
Example usage:
To set the fdb aging time:
Syntax
Description The aging time affects the learning process of the Switch. Dynamic
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#config fdb aging_time 300
Command: config fdb aging_time 300
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config fdb aging_time <sec 10-1000000>
forwarding table entries, which are made up of the source MAC
addresses and their associated port numbers, are deleted from the
table if they are not accessed within the aging time. The aging time
can be from 10 to 1000000 seconds with a default value of 300
seconds. A very long aging time can result in dynamic forwarding
table entries that are out-of-date or no longer exist. This may cause
incorrect packet forwarding decisions by the Switch. If the aging time
is too short however, many entries may be aged out too soon. This
will result in a high percentage of received packets whose source
addresses cannot be found in the forwarding table, in which case the
Switch will broadcast the packet to all ports, negating many of the
benefits of having a switch.
<sec 10-1000000> − The aging time for the MAC address forwarding
database value. The value in seconds may be between 10 and
1000000 seconds.
command.
Example usage:
To delete a permanent FDB entry:
delete fdb
Purpose Used to delete an entry to the Switch’s forwarding database.
Syntax
Description This command is used to delete a previous entry to the Switch’s
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#delete fdb default 00-00-00-00-01-02
Command: delete fdb default 00-00-00-00-01-02
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
delete fdb <vlan_name 32> <macaddr>
MAC address forwarding database.
<vlan_name 32> − The name of the VLAN on which the MAC
address resides.
<macaddr> − The MAC address that will be added to the forwarding
table.
command.
92
Page 97

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
To delete a multicast FDB entry:
DES-3526:admin#delete fdb default 01-00-00-00-01-02
Command: delete fdb default 01-00-00-00-01-02
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
clear fdb
Purpose Used to clear the Switch’s forwarding database of all dynamically
learned MAC addresses.
Example usage:
To clear all FDB dynamic entries:
Syntax
Description This command is used to clear dynamically learned entries to the
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
DES-3526:admin#clear fdb all
Command: clear fdb all
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
clear fdb [vlan <vlan_name 32> | port <port> | all]
Switch’s forwarding database.
<vlan_name 32> − The name of the VLAN on which the MAC
address resides.
port <port> − The port number corresponding to the MAC
destination address. The Switch will always forward traffic to the
specified device through this port.
all − Clears all dynamic entries to the Switch’s forwarding database.
command.
Example usage:
To display multicast MAC address table:
show multicast_fdb
Purpose Used to display the contents of the Switch’s multicast forwarding
database.
Syntax
Description This command is used to display the current contents of the
Parameters
Restrictions None.
show mulitcast_fdb [vlan <vlan_name 32> | mac_address
<macaddr>]
Switch’s multicast MAC address forwarding database.
<vlan_name 32> − The name of the VLAN on which the MAC
address resides.
<macaddr> − The MAC address that is present in the forwarding
database table.
93
Page 98

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#show multicast_fdb vlan default
Command: show multicast_fdb vlan default
VLAN Name : default
MAC Address : 01-00-5E-00-00-00
Egress Ports : 1-5
Mode : Static
Total Entries : 1
DES-3526:admin#
show fdb
Purpose Used to display the current unicast MAC address forwarding database.
Syntax
Description This command will display the current contents of the Switch’s
Parameters
Restrictions None.
show fdb { port <port> | [vlan <vlan_name 32> | vid <vlanid 14094>] | mac_address <macaddr> | static | aging_time }
forwarding database.
port <port> − The port number corresponding to the MAC destination
address. The Switch will always forward traffic to the specified device
through this port.
<vlan_name 32> − The name of the VLAN on which the MAC address
resides.
< vid > - Displays the entries for the VLANs indicated by vid list.
<macaddr> − The MAC address that is present in the forwarding
database table.
static − Displays the static MAC address entries.
aging_time − Displays the aging time for the MAC address forwarding
database.
Example usage:
To display unicast MAC address table:
DES-3526:admin#show fdb
Command: show fdb
Unicast MAC Address Ageing Time = 300
VID VLAN Name MAC Address Port Type
---- ---------- ----------------- ------ ----1 default 00-00-39-34-66-9A 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-51-43-70-00 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-5E-00-01-01 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-74-60-72-2D 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-81-05-00-80 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-81-05-02-00 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-81-48-70-01 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-E2-4F-57-03 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-E2-61-53-18 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-E2-6B-BC-F6 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-E2-7F-6B-53 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-E2-82-7D-90 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-00-F8-7C-1C-29 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-01-02-03-04-00 CPU Self
1 default 00-01-02-03-04-05 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-01-30-10-2C-C7 10 Dynamic
1 default 00-01-30-FA-5F-00 10 Dynamic
94
Page 99

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
1 default 00-02-3F-63-DD-68 10 Dynamic
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
config multicast port_filtering_mode
Purpose Used to configure the multicast packet filtering mode on a port per
port basis.
Syntax
Description This command will configure the multicast packet filtering mode for
Parameters
Restrictions Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this
Example usage:
To configure the multicast filtering mode to forward all groups on ports 1 through 4.
DES-3526:admin#config multicast port_filtering_mode 1-4
forward_all_groups
Command: config multicast port_filtering_mode 1-4
forward_all_groups
Success.
DES-3526:admin#
config multicast port_filtering_mode [<portlist> | all]
[forward_all_groups | forward_unregistered_groups |
filter_unregistered_groups]
specified ports on the Switch.
<portlist> - Specifies a port or range of ports to view.
[forward_all_groups | forward_unregistered_groups |
filter_unregistered_groups] – The user may set the filtering mode to
any of these three options
command.
Example usage:
To view the multicast port filtering mode for all ports:
show multicast port_filtering_mode
Purpose Used to show the multicast packet filtering mode on a port per port
basis.
Syntax
Description This command will display the current multicast packet filtering
Parameters
Restrictions None.
show multicast port_filtering_mode {<portlist>}
mode for specified ports on the Switch.
<portlist> - Specifies a port or range of ports to view.
95
Page 100

DES-3500 Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Switch CLI Reference Manual
DES-3526:admin#show multicast port_filtering_mode
Command: show multicast port_filtering_mode
Port Multicast Filter Mode
------ --------------------------1 forward_unregistered_groups
2 forward_unregistered_groups
3 forward_unregistered_groups
4 forward_unregistered_groups
5 forward_unregistered_groups
6 forward_unregistered_groups
7 forward_unregistered_groups
8 forward_unregistered_groups
9 forward_unregistered_groups
10 forward_unregistered_groups
11 forward_unregistered_groups
12 forward_unregistered_groups
13 forward_unregistered_groups
14 forward_unregistered_groups
15 forward_unregistered_groups
16 forward_unregistered_groups
17 forward_unregistered_groups
18 forward_unregistered_groups
19 forward_unregistered_groups
20 forward_unregistered_groups
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
96
 Loading...
Loading...