Cisco Systems 102068 User Manual

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
DGETTING STARTED GUIDE
Cisco Aironet 1430 Series Wireless Bridge
1About this Guide
2Safety Instructions
3Unpacking
4Overview
5Configuring the Bridge for the First Time
6Mounting the Bridge
7Troubleshooting
8Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information
9Bridge Specifications

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
Revised October 2008 P/N 78-18922-01
1 About this Guide
This Guide provides instructions on how to install and configure your Cisco Aironet 1430 Series Wireless Bridge (hereafter called the bridge). This guide also provides bridge alignment instructions and limited troubleshooting procedures.
The Cisco Aironet 1430 Series Wireless bridge is an updated replacement for the Cisco Aironet 1400 Series Wireless Bridge. The 1430 series is a 802.11a wireless bridge supporting point-to-point and point-to-multipoint applications operating in the 4.9-, 5.6-, and 5.8-GHz spectrum. The bridge delivers long-range, high capacity, and is easy to deploy. The bridge supports 40 MHz channelization in the 5.6- and 5.8-GHz bands to deliver data rates at or above 130 Mbps. The bridge also supports external and integrated antenna configurations for various deployment scenarios for enterprise and commercial customer applications.
The bridge is deployed as an autonomous point-to-point bridge, providing intelligent network services in a simple autonomous environment. Cisco’s wireless controller software (WCS) management provides centralized management and monitoring services for the bridge.
2 Safety Instructions
Translated versions of the following safety warnings are provided in the translated safety warnings document that is shipped with your bridge. The translated warnings are also in the Translated Safety Warnings for Cisco Aironet 1430 Series Wireless Bridges, which is available on your documentation CD and cisco.com.
Warning |
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. |
|
|
|
Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical |
|
|
circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. (To see |
|
|
translations of the warnings that appear in this publication, refer to the appendix |
|
|
“Translated Safety Warnings.”) |
|
|
Statement 1071 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service |
|
|
|
this equipment. |
|
|
Statement 1030 |
|
|
|
2

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
Warning |
Do not locate the antenna near overhead power lines or other electric light or power |
|
|
|
circuits, or where it can come into contact with such circuits. When installing the |
|
|
antenna, take extreme care not to come into contact with such circuits, because they |
|
|
may cause serious injury or death. For proper installation and grounding of the antenna, |
|
|
please refer to national and local codes (for example, U.S.:NFPA 70, National Electrical |
|
|
Code, Article 810, Canada: Canadian Electrical Code, Section 54). |
|
|
Statement 1052 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) |
|
|
|
protection. Ensure that the protective device is rated not greater than: |
|
|
120 VAC, 15A U.S. (240 VAC, 10A International) |
|
|
Statement 1005 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the |
|
|
|
equipment in the absence of a suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the |
|
|
appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain that |
|
|
suitable grounding is available. |
|
|
Statement 366 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
Read the installation instructions before connecting the system to the power source. |
|
|
|
Statement 1004 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning |
|
|
|
activity. |
|
|
Statement 1001 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
Do not operate your wireless network device near unshielded blasting caps or in an |
|
|
|
explosive environment unless the device has been modified to be especially qualified for |
|
|
such use. |
|
|
Statement 245B |
|
|
|
3

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
Warning |
In order to comply with radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, the antennas for this |
|
|
|
product should be positioned no less than 6.56 ft (2 m) from your body or nearby persons. |
|
|
Statement 332 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area |
|
|
|
can be accessed only through the use of a special tool, lock and key, or other means of |
|
|
security and is controlled by the authority responsible for the location. |
|
|
Statement 37 |
|
|
|
3 Unpacking
Figure 1 shows the typical contents of the shipping container. The contents of your shipping container may be different depending on what you ordered. Follow these steps to unpack the shipping container.
Step 1 Unpack and remove the bridge and the accessory kit from the shipping box.
Step 2 Return any packing material to the shipping container and save it for future use.
Step 3 Verify that you have received the items shown in Figure 1. If any item is missing or damaged, contact your Cisco representative or reseller for instructions.
4
THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
Figure 1 Shipping Box Contents
1 |
1430 series wireless bridge |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
6 |
Documentation CD |
|
|
|
|
5
THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
4 Overview
The following illustrations show the bridge connections and features.
Figure 2 Bridge Connections and Features
1 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
6

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
5 Configuring the Bridge for the First Time
This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your bridge for the first time. The contents of this chapter are similar to the instructions in the quick start guide that shipped with your bridge. You can configure all the settings described in this chapter using the command-line interface (CLI), but it might be simplest to browse to the bridge’s web-browser interface to complete the initial configuration and then use the CLI to enter additional settings for a more detailed configuration.
This chapter contains these sections:
•Before You Start, page 7
•Obtaining and Assigning an IP Address, page 8
•Connecting to the Bridge Locally, page 9
•Assigning Basic Settings, page 10
•What To Do Next, page 14
•Assigning an IP Address Using the CLI, page 15
•Using a Telnet Session to Access the CLI, page 15
Before You Start
Before you install the bridge, make sure you are using a computer connected to the same network as the bridge, and obtain the following information:
•From your network system administrator:
–A system name
–The case-sensitive wireless service set identifier (SSID) for your radio network
–If not connected to a DHCP server, a unique IP address for your bridge (such as 172.17.255.115)
–If the bridge is not on the same subnet as your PC, a default gateway address and subnet mask
–A Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) community name and the SNMP file attribute (if SNMP is in use)
Resetting the Bridge to Default Settings
If you need to start over during the initial setup process, follow these steps to reset the bridge to factory default settings using the power injector’s Mode button:
Step 1 Disconnect the power jack from the power injector.
7

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
Step 2 Press and hold the power injector’s MODE button while you reconnect the power jack.
Step 3 Hold the MODE button until the Status LED turns amber (approximately 1 to 3 seconds) and wait until the bridge boots up (Status LED turns green). All bridge settings return to factory defaults.
You can also use the web-browser interface to reset the bridge to defaults. Follow these steps to return to default settings using the web-browser interface:
Step 1 Open your Internet browser. You must use Microsoft Internet Explorer (version 5.x or later) or Netscape Navigator (version 4.x).
Step 2 Enter the bridge’s IP address in the browser address line and press Enter. An Enter Network Password window appears.
Step 3 Enter your username in the User Name field. The default username is Cisco.
Step 4 Enter the bridge password in the Password field and press Enter. The default password is Cisco. The Summary Status page appears.
Step 5 Click System Software and the System Software screen appears.
Step 6 Click System Configuration and the System Configuration screen appears.
Step 7 Click Default.
Note If the bridge is configured with a static IP address, the IP address is not changed.
Obtaining and Assigning an IP Address
To browse to the bridge’s Express Setup page, you must either obtain or assign the bridge’s IP address using one of the following methods:
•Use default address 10.0.0.1 when you connect to the bridge locally. For detailed instructions, see the “Connecting to the Bridge Locally” section on page 9.
•Use a DHCP server (if available) to automatically assign an IP address. You can find the DHCP-assigned IP address using one of the following methods:
–Provide your organization’s network administrator with your bridge’s Media Access Control (MAC) address. Your network administrator will query the DHCP server using the MAC address to identify the IP address. The bridge’s MAC address is on label attached to the bottom of the bridge.
8

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
Connecting to the Bridge Locally
If you need to configure the bridge locally (without connecting the bridge’s power injector to a wired LAN), you can connect a PC to the power injector’s Ethernet port using a Category 5 Ethernet cable. You can use a local connection to the Ethernet port much as you would use a serial port connection.
Note You do not need a special crossover cable to connect your PC to the bridge’s power injector; you can use either a straight-through cable or a crossover cable.
If the bridge is configured with default values and not connected to a DHCP server or cannot obtain an IP address, it defaults to IP address 10.0.0.1 and becomes a mini-DHCP server. In that capacity, the bridge provides up to twenty IP addresses between 10.0.0.11 and 10.0.0.30 to an Ethernet-capable PC connected to the power injector’s Ethernet port.
The mini-DHCP server feature is disabled automatically when you assign a static IP address to the bridge.
Caution When a bridge with default settings is connected on a wired LAN and does not receive an IP address from a DHCP server, the bridge provides an IP address to any DHCP requests it receives.
Follow these steps to connect to the bridge locally:
Step 1 Make sure that the PC you intend to use is configured to obtain an IP address automatically, or manually assign it an IP address from 10.0.0.31 to 10.0.0.40. Connect your PC to the power injector using a Category 5 Ethernet cable. You can use either a crossover cable or a straight-through cable.
Note When you connect your PC to the bridge’s power injector or reconnect your PC to the wired LAN, you might need to release and renew the IP address on the PC. On most PCs, you can perform a release and renew by rebooting your PC or by entering ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew commands in a command prompt window. Consult your PC operating instructions for detailed instructions.
Step 2 Power up the power injector.
Step 3 Follow the steps in the “Assigning Basic Settings” section on page 10. If you make a mistake and need to start over, follow the steps in the “Resetting the Bridge to Default Settings” section on page 7.
9

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
Step 4 After configuring the bridge, remove the Ethernet cable from your PC and connect the power injector to your wired LAN.
Assigning Basic Settings
After you determine or assign the bridge’s IP address, you can browse to the bridge’s Express Setup page and perform an initial configuration. Follow these steps:
Step 1 Open your Internet browser. You must use Microsoft Internet Explorer (version 5.x or later) or Netscape Navigator (version 4.x).
Step 2 Enter the bridge’s IP address in the browser address line and press Enter. An Enter Network Password screen appears.
Step 3 Press Tab to bypass the Username field and advance to the Password field.
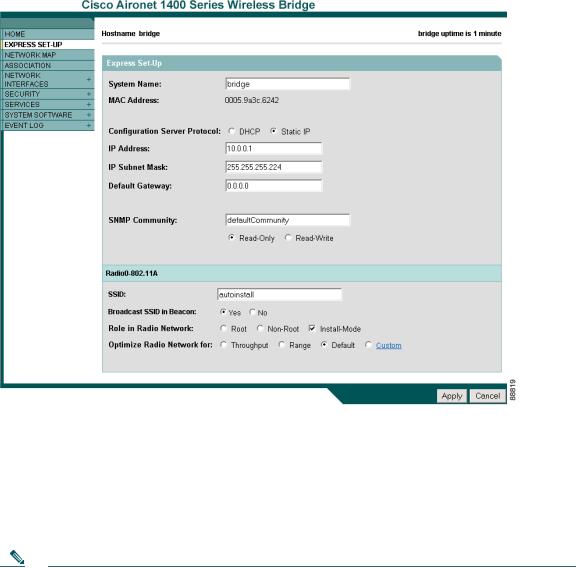
Step 4 Enter the case-sensitive password Cisco and press Enter. The Summary Status page appears. Figure 3 shows the Summary Status page.
Figure 3 Summary Status Page
Step 5 Click Express Setup. The Express Setup screen appears. Figure 4 shows the Express Setup page.
10
THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
Figure 4 Express Setup Page
Step 6 Enter the configuration settings you obtained from your system administrator. The configurable settings include:
•System Name—The system name, while not an essential setting, helps identify the bridge on your network. The system name appears in the titles of the management system pages.
•Configuration Server Protocol—Click on the button that matches the network’s method of IP address assignment.
•DHCP—IP addresses are automatically assigned by your network’s DHCP server.
Note |
• |
When DHCP is enabled, the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway fields |
|
|
indicate Negotiated by DHCP |
|
• |
Static IP—The bridge uses a static IP address that you enter in the IP address field. |
11

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
•IP Address—Use this setting to assign or change the bridge’s IP address. If DHCP is enabled for your network, leave this field blank.
Note If the bridge’s IP address changes while you are configuring the bridge using the web-browser interface or a Telnet session over the wired LAN, you lose your connection to the bridge. If you lose your connection, reconnect to the bridge using its new IP address. Follow the steps in the “Resetting the Bridge to Default Settings” section on page 7 if you need to start over.
•IP Subnet Mask—Enter the IP subnet mask provided by your network administrator so the IP address can be recognized on the LAN. If DHCP is enabled, leave this field blank.
•Default Gateway—Enter the default gateway IP address provided by your network administrator. If DHCP is enabled, leave this field blank.
•SNMP Community—If your network is using SNMP, enter the SNMP Community name provided by your network administrator and select the attributes of the SNMP data (also provided by your network administrator).
•Read-Only—indicates the bridge allows only SNMP read accesses. Using this option, an SNMP user cannot change bridge configuration settings.
•Read-Write—indicates the bridge allows SNMP read and write accesses. This setting allows an SNMP user to change the bridge configuration.
•Radio Service Set ID (SSID)—Enter the case-sensitive SSID (32 alphanumeric characters maximum) provided by your network administrator. The SSID is a unique identifier that remote bridges use to associate with your bridge.
•Broadcast SSID in Beacon—Use this setting to allow devices that do not specify an SSID to associate with the bridge.
–Yes—This is the default setting; it allows a remote bridge that does not specify an SSID to associate with the bridge.
–No—Remote bridges must specify an SSID to associate with the bridge. With No selected, the SSID used by the remote bridge must match exactly the bridge’s SSID.
•Role in Radio Network—Click on the check box and button that describes the role of the bridge on your network.
•Install Mode—Activates the bridge install and alignment mode. Specifies that the bridge automatically determines the network role. If the bridge is able to associate to another root bridge within 60 seconds, the bridge assumes a non-root bridge role. If the bridge is unable to associate with another root bridge within 60 seconds, the bridge assumes a root bridge role.
You can also pre-configure the bridge into root or non-root modes and avoid the 60 seconds automatic detection phase.
12

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
•Root—Specifies that the bridge connects directly to the main Ethernet LAN network and accepts associations from other bridges.
•Non-root—Specifies that the bridge connects to a remote LAN network and must associate with the root bridge using the wireless interface.
Note When initially powered up, the bridge is configured in Install mode with automatic detection activated.
•Optimize Radio Network for—Use this setting to select either preconfigured settings for the bridge radio or customized settings for the bridge radio.
–Throughput—Maximizes the data volume handled by the bridge but might reduce its range.
–Range—Maximizes the bridge’s range but might reduce throughput.
–Default—The bridge retains default radio settings that are designed to provide good range and throughput for most bridges.
–Custom—The bridge uses settings you enter on the Network Interfaces: Radio-802.11a Settings page. Clicking Custom takes you to the Network Interfaces: Radio-802.11a Settings page.
–Click Apply to save your settings. If you changed the IP address, you lose your connection to the bridge. Browse to the new IP address to reconnect to the bridge.
Note You can restore the bridge to its factory defaults by unplugging the power injector’s power jack and plugging it back in while holding down the Mode button for a few seconds, or until the Status LED turns amber.
Default Settings on the Express Setup Page
Table 1 lists the default settings for the settings on the Express Setup page.
Table 1 Default Settings on the Express Setup Page
Setting |
Default |
|
|
System Name |
Bridge |
|
|
Configuration Server Protocol |
DHCP |
|
|
13
|
THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL) |
|
Table 1 |
Default Settings on the Express Setup Page (continued) |
|
|
|
|
Setting |
|
Default |
|
|
|
IP Address |
|
Assigned by DHCP (default setting); if DHCP is disabled, the |
|
|
default setting is 10.0.0.1 |
|
|
|
IP Subnet Mask |
Assigned by DHCP (default setting); if DHCP is disabled, the |
|
|
|
default setting is 255.255.255.224 |
|
|
|
Default Gateway |
Assigned by DHCP (default setting); if DHCP is disabled, the |
|
|
|
default setting is 0.0.0.0 |
|
|
|
SNMP |
|
defaultCommunity |
|
|
|
|
|
Read Only |
|
|
|
SSID |
|
autoinstall1 |
Broadcast SSID in Beacon |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
Role in Radio Network |
Install |
|
|
|
|
Optimize Radio Network for |
Throughput |
|
|
|
|
1. During Install Mode, the SSID is autoinstall.
What To Do Next
After your bridge has basic settings, you need to complete your bridge’s configuration. You might need to adjust the output power level and other network and security settings.
Output Power Level
Your bridge’s output power level might require adjustment under the following conditions:
•When bridges are installed less than 328 ft (100 m) apart, you should reduce their output power to avoid overloading the bridge’s receivers.
To configure your bridge’s output power level, refer to the Power Levels and Channels for Cisco Aironet Access Points and Bridges.
14

THIRD FCC DRAFT (CISCO CONFIDENTIAL)
Protecting Your Wireless LAN
To prevent unauthorized access to your network, you must configure security settings. Because the bridge is a radio device, the bridge communicates beyond the physical boundaries of your building. Refer to the Cisco Aironet 1400 Series Wireless Bridge Software Configuration Guide to configure security features to protect your network from intruders:
•Unique SSIDs that are not broadcast in the bridge beacon
•WEP and additional WEP features, such as TKIP and broadcast key rotation
•Dynamic WEP and EAP authentication
Assigning an IP Address Using the CLI
When you connect the bridge to the wired LAN, the bridge links to the network using a bridge virtual interface (BVI) that it creates automatically. Instead of tracking separate IP addresses for the bridge’s Ethernet and radio ports, the network uses the BVI.
When you assign an IP address to the bridge using the CLI, you must assign the address to the BVI. Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to assign an IP address to the bridge’s BVI:
|
Command |
|
Purpose |
|
|
|
Step 1 |
|
|
|
|
||
configure terminal |
|
Enter global configuration mode. |
|
|||
Step 2 |
|
|
|
|
||
interface bvi1 |
|
Enter interface configuration mode for the BVI. |
|
|||
Step 3 |
|
|
|
|
||
ip address address |
|
Assign an IP address and address mask to the BVI. This step |
|
|||
|
mask |
|
automatically saves the running configuration to the startup |
|
||
|
|
|
configuration. |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note |
You lose your connection to the bridge when you |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
assign a new IP address to the BVI. If you need to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
continue configuring the bridge, use the new IP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
address to open another Telnet session to the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
bridge. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Using a Telnet Session to Access the CLI
Follow these steps to access the CLI using a Telnet session. These steps are for a PC running Microsoft Windows with a Telnet terminal application. Check your PC operating instructions for detailed instructions for your operating system.
15
 Loading...
Loading...