Actron CP9135 Instructions Manual

OBD II
CP9135
AutoScanner
™
Performs diagnostics on OBD II
compliant vehicles 1994 and
newer
Instructions in English, Spanish, and French
Instrucciones en Inglés, Español, y Francés
Instructions en Anglais, Espagnol, et les Français
15825 Industrial Parkway
Cleveland Ohio 44135 USA (EUA)
Voltage: 16V
Tension de 16V
Tension: 16V
FULL ONE (1) YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY
Actron Manufacturing Company (“Actron”) warrants to the original purchaser that
product will be free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of
this
(1) year from the date of original purchase. Any unit that fails within this period
one
be replaced or repaired at Actron’s discretion without charge. If you need to
will
product, please follow the instructions below. This warranty does not apply
return
damages (intentional or accidental), alterations or improper or unreasonable
to
use.
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY
ACTRON DISCLAIMS ALL EXPRESS WARRANTIES EXCEPT THOSE THAT
APPEAR
MERCHANTABILITY OF THE GOODS OR FITNESS OF THE GOODS FOR
OF
ANY
WARRANTY
PRODUCT
LIMITED
LONG
A SPECIFIC BUYER.)
TO
IN NO CASE SHALL ACTRON BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES BASED UPON ANY LEGAL THEORY INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, DAMAGES FOR LOST PROFITS AND/OR INJURY TO
PROPERTY.
OF INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THIS LIMITATION OR
EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO A SPECIFIC BUYER. THIS WARRANTY GIVES
YOU
WHICH VARY FROM STATE TO STATE.
ABOVE. FURTHER, ACTRON DISCLAIMS ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY
PURPOSE. (TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, ANY IMPLIED
OF MERCHANTABILITY OR OF FITNESS APPLICABLE TO ANY
IS SUBJECT TO ALL THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THIS
WARRANTY. SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS ON HOW
AN IMPLIED WARRANTY LASTS, SO THIS LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY
LIMITATION OF REMEDIES
SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION
SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS, AND YOU MAY ALSO HAVE OTHER RIGHTS
information, illustrations and specifications contained in this manual are based
All
on the latest information available from industry sources at the time of publication.
No warranty (expressed or implied) can be made for its accuracy or completeness,
nor is any responsibility assumed by Actron or anyone connected with it for loss or
damages suffered through reliance on any information contained in this manual or
misuse of accompanying product. Actron reserves the right to make changes at any
time to this manual or accompanying product without obligation to notify any person
or organization of such changes.
TO USE YOUR WARRANTY
If you need to return the unit, please follow this procedure:
Actron Te ch Support at 1-(800)228-7667. Our Technical Service Representatives
1. Call
trained to assist you.
are
2. Proof
3. In
4. If
5. Print
6. You will be responsible for shipping charges in the event that your repair is not
of purchase is required for all warranty claims. For this reason we ask that you
your sales receipt.
retain
the event that product needs to be returned, you will be given a Return Material
Authorization
number.
possible, return the product in its original package with cables and accessories.
the RMA number and your return address on the outside of the package and
to the address provided by your Customer Service representative.
send
covered
by warranty.
OUT OF WARRANTY REPAIR
If you need product repaired after your warranty has expired, please call Te ch Support at
(800) 228-7667.
You will be advised of the cost of repair and any freight charges.
Table of Contents
Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . SF-1
Section 1 - Quick Start
1.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.2 Quick Start. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Section 2 - Tool Basics
2.1 Tool Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 2-1
2.1.1 Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
2.1.2 OBD II (J1962) Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
2.1.3 Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
2.2 Lists and Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 2-2
2.3 Diagnostic Link Connector and Location . . . . . . . . .. 2-3
2.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 2-3
2.5 This Manual. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 2-4
2.6 Vehicle Service Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 2-5
Section 3 - Using the Tool
3.1 AutoScanner Connection and Power-Up . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2 Read Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.3 Erase Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 3-3
3.4 MIL Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 3-5
3.5 I/M Monitors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 3-5
3.6 Tool Setup/Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.6.1 Changing Display Contrast. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
3.6.2 Display Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 3-7
3.6.3 Keypad Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
3.6.4 Memory Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 3-8
3.6.5 Software Identification (SW ID) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Section 4 - Troubleshooting
4.1 Vehicle Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.2 AutoScanner Does Not Power Up: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.3 Link Errors or Erroneous Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 4-3
4.4 Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Appendix A - Glossary
Appendix B - About OBD II

Y
U
T
ONS
I
T
FE
A
S
A
C
E
R
P
To prevent accidents that could possibly result in serious
injury and/or damage to vehicles and/or test equipment,
carefully follow all safety rules and test procedures when
working on vehicles.
Always wear ANSI approved eye protection.
Always operate the vehicle in a well-ventilated area. Do
n
ot breath exhaust gases — they are very hazardous.
Always keep yourself, tools and test e
all moving or hot engine parts.
Always make sure the vehicle is in Park (
transmission) or Neutral (manual transmission).
Ensure the parking brake is firmly set.
Block the drive wheels.
Never leave vehicle unattended while testing.
Never lay tools on vehicle battery. You may short the
terminals together causing harm to yourself, the tools or
quipment away from
automatic
SF-1
e battery.
th
Always use caution when working around the ignition coil,
distributor cap, ignition wires, a
components can produce High Voltage while the engine
is running.
Battery electrolyte is sulfuric-acid and is extremely caustic.
If contacted, rinse with water or neutralize with a mild base
i.e. baking soda). If contacted in eyes, flush with water
(
and call a physician immediately.
Never smoke or have open flames near vehicle. Vapors
from gasoline and the battery during charge are highly
mable and explosive.
flam
Never use the AutoScanner
exposed to any moisture. Internal shorts could cause fire
and damage to the tool.
nd spark plugs. These
TM
if internal circuitry has been
Always keep a fire exting
gasoline/electrical/chemical fires readily available.
• Whe
• Always turn ignition key OFF when connecting or disconnecting
• Some vehicles are equipped with safety air bags. You MUST follow
n performing road tests, never operate the tool while driving
the vehicle. Always have one person drive the vehicle and an
assistant operate the AutoScanner
electrical components, unless otherwise instructed.
vehicle service manual cautions when working around the air bag
components or wiring. If the cautions are not followed, the air bag
may open up unexpectedly, resulting in personal injury. Note that
the air bag can still open up several minutes after the ignition key is
off (or even if the vehicle’s battery is disconnected) because of a
special energy reserve module.
uisher suitable for
TM
.
• Always follow vehicle manufacturer’s warnings, cautions and
service procedures.
SF-2

1
n
o
ti
ec
S
t
r
a
t
S
uic
Q
1.1 Introduction
Congratulations!
You've purchased an automotive scanner that can unlock the fault
code information stored in the on-board computer(s) of your car or
light truck. This information gives you the power to identify and repair
problems that may arise with the operation of your vehicle's engine.
Cars and trucks cannot completely diagnose their problems, and no
scanner available can tell you with pinpoint accuracy what is wrong
with the vehicle.
Once you have retrieved the diagnostic information from the computer,
you have taken the first step in finding and fixing the problem. Now it
is time to continue with the rest of the diagnostic process.
k
Important points to remember:
• Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) warn us of a symptom or
problem with a particular engine system, not a specific part.
• The computer can only report DTCs based on what its sensors
are telling it.
• Sometimes, sensors appear to be bad when in fact, they are not.
- A poor connection, broken wire or short circuit may be preventing
the sensor signal from reaching the computer.
- A malfunction in one system may cause a sensor in another
syste
• We recommend the use of a vehicle specific service manual to
assist you with the diagnostic process.
• Some of the vehicle computer's sensors and actuators can be
pretty expensive; it is best to make sure they are defective prior
to replacing them!
m to report a value that is too high or too low.
1-1
Quick Start
The next step in the diagnostic process is to test systems and parts
that are suspected to be defective. This testing process may include:
• Sensors
• Fuel injection system
Even when working on modern, computer-controlled vehicles there is
no substitute for good old-fashioned troubleshooting.
Once you have isolated and repaired the failed problem(s), you can
use your AutoScanner to clear the codes from the computer's memory.
This will also turn off your Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL), or Check
Engine Light, and may reset all Inspection/Maintenance (I/M) monitor
statuses to “Not Ready”.
The following Quick Start section will help you begin to use your OBD II
AutoScanner right away. Subsequent sections of this manual contain
more detailed information to help you get the most out of your scanner.
If you have questions not covered in the manual, please call our
Technical Support line at 1-800-228-7667 (8:00 - 6:00 EST Monday Friday), or send an email to tech_support@actron.com.
• Ignition system
• Vacuum & Pressure systems
1.2 Quick Start
Connect the OBD II AutoScanner to the vehicle’s Data Link Connector
(DLC) which is normally located under the dash on the driver’s side.
Once the connection is made, the tool will turn on, boot, and then
display the Main Menu. If the display is hard to read, adjust the contrast
using the Tool Setup/Test function.
All AutoScanner functions can be performed with the Key On-Engine
Off (KOEO). The ERASE function cannot be done with the Key
On-Engine Running (KOER).
To retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTCs), press the READ key on the
AutoScanner. This function can be
performed with the KOEO or KOER.
If DTCs are present, they will appear on the display. Use the ▲ or ▼
keys to view the codes. The definition will continuously scroll to the left if
it is longer than the display (20 characters). To freeze the scrolling message,
press and hold the ENTER key. When done, press the BACK key to return
to the Main Menu.
Main Menu
1)Read Codes ]
CAUTION! Avoid Cooling Fan! It May Turn On During Test.
!
Quick Start
1-2

To erase DTCs, press the ERASE
key on the AutoScanner. This
function must be performed with the
KOEO - Do not START engine.
Note: In addition to clearing DTCs, the Erase Codes function may
reset the status of the I/M System Monitors to “Not Ready.”
!
If DTCs are found, the tool will display the quantity and ask the user
“Erase Codes? (Y/N).” Pressing the NO key will display the message
“Cancelled, Erase Not Performed.” Pressing the YES key will display
a scrolling message on the bottom line. Press the BACK key to return
to the Main Menu.
“Hard” codes are codes that can be removed only by repairing
!
The MIL Status function displays the status of the computer module
that commanded the MIL to turn on. If the MIL Status is ON and the
MIL is not illuminated with the engine running, then a problem exists
in the MIL circuit.
the faults that they cause; therefore, hard codes will remain in
the computer’s memory until the condition is repaired.
Main Menu
2)Erase Codes
Select the MIL Status function and
press the ENTER key. The MIL
Status of the computer will display
on the AutoScanner. Press the
BACK key to return to the Main
Menu.
The I/M (Inspection and Maintenance) Monitors function displays the
state of the vehicle’s OBD II Monitors. Monitors test the operation of
emission related systems or components and detect out-of-range
values. The vehicle may have to be operated under certain driving
conditions to initiate a monitor.
Select I/M Monitors from the Main
Menu and press the ENTER key.
Use the
the list. Note the Monitors present
and their status. When done, press
the BACK key to return to the Main Menu
▲ or ▼ keys to scroll through
Main Menu
3)MIL Status
Main Menu
4)I/M Monitors
.
Detailed instructions are provided in Section 3 and OBD II background
information is provided in Appendix B.
Quick Start
1-3

s
c
ic
s
.
BOBD II connector &
cable with strain-relief.
CTwo-line LCD display.
DREAD key - performs
the Read Codes
function.
EERASE key - performs
the Erase Codes
function.
FV YES key - to scroll
up and answer YES.
GW NO key - to scroll
down and answer NO.
HBACK key - go to the
previous screen or
level.
IENTER key- selects
displayed items.
2
n
o
ti
ec
S
a
B
l
To
2.1 Tool Features
The
OBD II AutoScanner
service industry to help diagnose vehicles and assist in troubleshooting
procedures. The AutoScanner will perform OBD II functions on
compliant vehicles 1994 and newer. No batteries are needed; power is
provided from the vehicle’s data link connector (DLC)
o
was developed by experts in the automotive
B
D
E
Too l Basi cs
H
F
G
I
2-1
2.1.1
The AutoScanner uses a two-line liquid crystal display (LCD). The top
line contains 10 characters to show function headings, numbers and
user prompts. The bottom line contains 20 characters to display
selections and code information. Messages longer than the lines will
scroll continuously across the display from right to left. Display
contrast adjustment is accessed from the Tool Setup/Test menu.
Display
2.1.2
Connects the AutoScanner to the vehicle for power and
communication. The AutoScanner will automatically communicate
with the vehicle using a protocol built into the software
After initiating a function, the
AutoScanner will link with the
vehicle.
2.1.3
Do not use solvents such as alcohol to clean the keypad or display.
Use a mild nonabrasive detergent and a soft cotton cloth. Do not soak
the keypad as water might find its way inside the tool.
2.2
The AutoScanner is designed for ease
in navigation and operation. All menu
and lists operate the same way. Five
functions are selectable by the user. The
Read Codes
can be run using the keys identified in
Section 2.1-Tool Features
Lists and Menus
OBD II (J1962) Connector
Linking
* Please Wait *
Cleaning
and
Erase Codes
function
.
1)Read Codes
2)Erase Codes
3)MIL Status
4)I/M Monitors
5)Tool Setup/Test
1)Adjust Contrast
2)Display Test
3)Keypad Test
4)Memory Test
5)SW ID
▲
Use the
ENTER
item. An arrow icon will be displayed
on the right of the bottom line to
indicate the scrolling direction
available; up (
To return to previous screens, press the
or ▼ keys to scroll and the
key to select the function or
\
), down (]) or both ().
Tool Basics
2-2
Main Menu
1)Read Codes ]
BACK
key.
The AutoScanner may ask a question which requires a YES or NO
response from the user. Press either the
condition arises.
YES
key or
NO
key when the
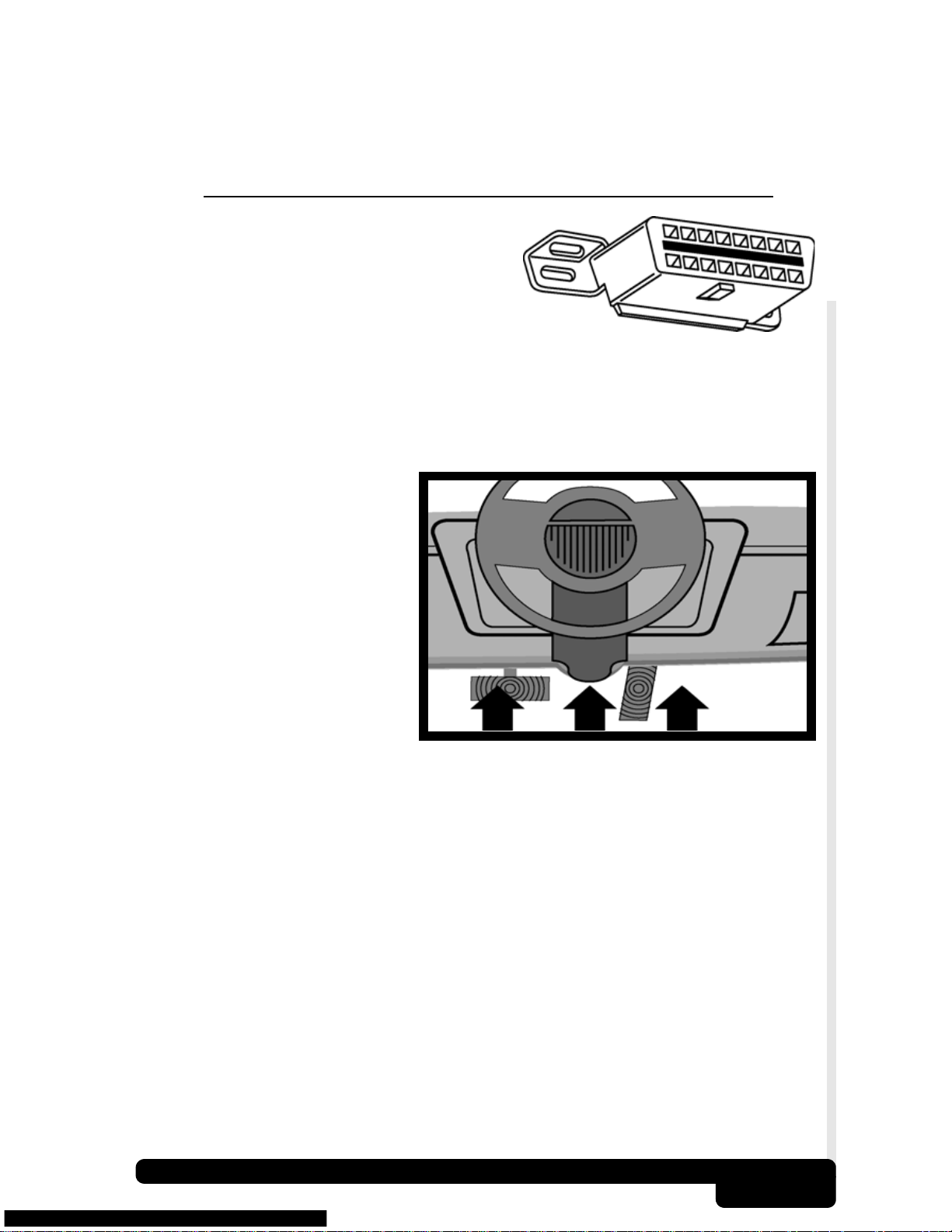
2.3
The AutoScanner communicates with
the vehicle’s computer modules via a
Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC).
OBD II regulations define the physical
and electrical specification for the DLC. Certain
pins in the connector are dedicated for power and
ground. The DLC is also referred to as a J1962 connector. The term J1962
is taken from a physical and electrical specification number assigned by
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers). The standard ensures that all
vehicles with OBD II systems use the same connector.
The J1962 specification
defines the location of the
DLC in the vehicle. The DLC
should be located under the
dashboard on the driver side
of the vehicle. If the DLC is
not located under the
dashboard as stated, a
decal describing its location
should be attached to the
dashboard in the area the
DLC should have been
located.
Diagnostic Link Connector and Location
Too l Basi cs
2-3
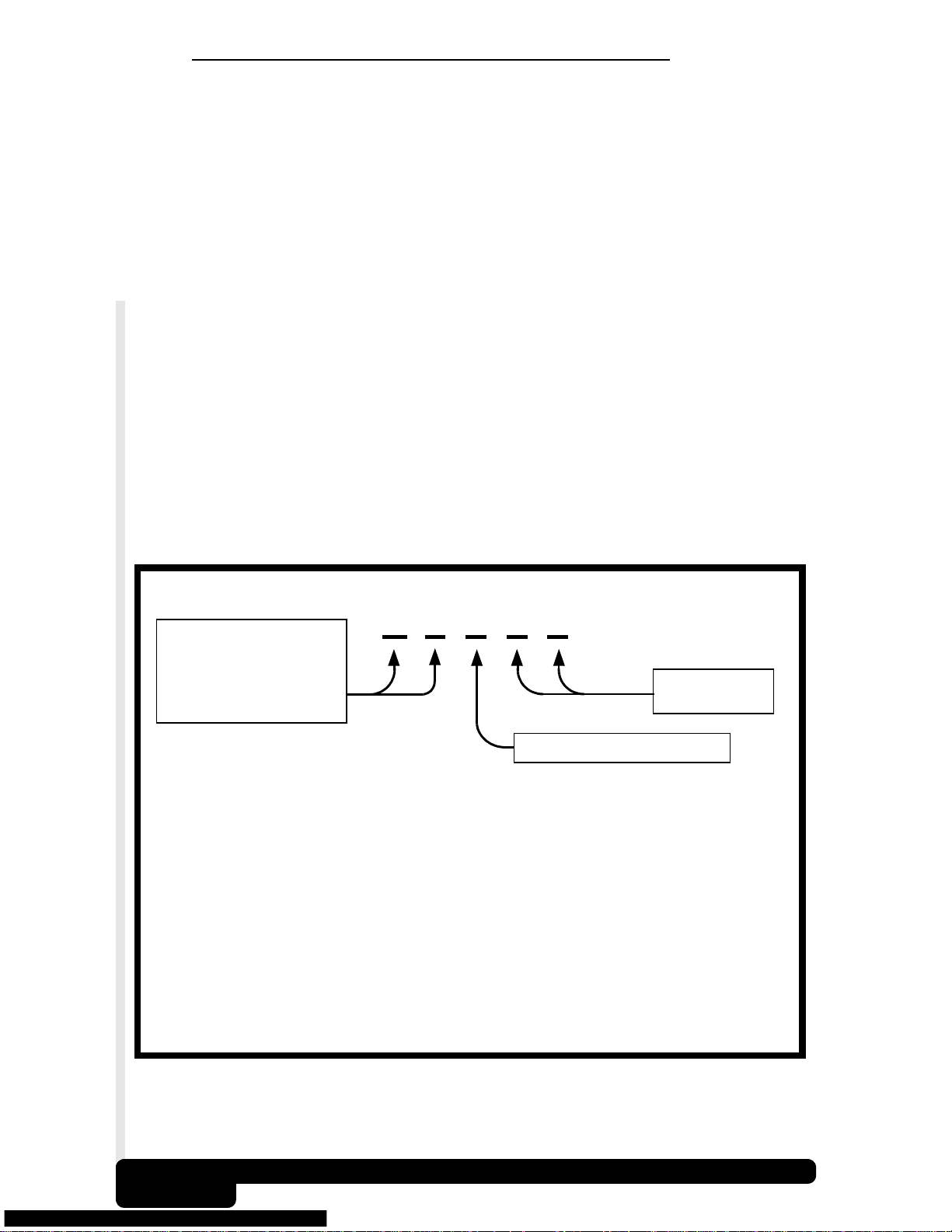
2.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) consist of a three-digit code preceded
by an alphanumeric designator. When the on-board computer recognizes
and identifies a problem, a DTC for that fault is stored in memory. These
codes are intended to help the user determine the root cause of a problem.
The format and type of DTCs is summarized on the next page.
J2012 is a standard for all DTCs established by the Society of Automotive
Engineers (SAE). Codes and the definitions assigned by this specification
are known as Generic (or Global) OBD II codes. OBD II requires
compliance of this standard, and has made it a standard for all cars, light
trucks, APVs, MPVs, and SUVs sold in the U.S. from Model Year 1996
and newer. Codes not reserved by the SAE are reserved for the
manufacturer and referred as Manufacturer Specific.
Periodically, new DTCs are developed and approved by the SAE. Upon
approval of the new codes, the AutoScanner’s software will be updated.
There is no established time period that updates are made to the database.
For more information regarding DTC updates, please call our Technical
Support line at
send an email to
1-800-228-7667
(8:00 - 6:00 EST Monday - Friday), or
tech_support@actron.com.
SAE J2012 OBD II DTC Recommended Standard
Bx - Body
Cx - Chassis
- Powertrain
Px
Ux - Network Comm.
x = 0, 1, 2 or 3
Example:
P0101 –Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit
Powertrain Codes
P0xxx
P1xxx
P2xxx
P30xx-P33xx
P34xx-P39xx
Chassis
C0xxx
C1xxx
C2xxx
C3xxx
Range/Performance Problem
- Generic (SAE)
- Manufacturer Specific
- Generic (SAE)
- Manufacturer Specific
- Generic (SAE)
Codes
- Generic (SAE)
- Manufacturer Specific
- Manufacturer Specific
- Generic (SAE)
P 0 1 0 1
Vehicle Specific System
Body
Codes
B0xxx
B1xxx
B2xxx
B3xxx
Network
U0xxx
U1xxx
U2xxx
U3xxx
- Generic (SAE)
- Manufacturer Specific
- Manufacturer Specific
- Generic (SAE)
Communication Codes
- Generic (SAE)
- Manufacturer Specific
- Manufacturer Specific
- Generic (SAE)
Specific Fault
Designation
2-4
Tool Basics
 Loading...
Loading...