Page 1
precision electronic solutions
CODE SCANNER
FAVOR DE LEER INSTRUCTCTIVO ANTES DE USAR EL ARTICULO
Car Computer
Code Reader
Domestic Ford, Lincoln,
Mercury with EEC-IV or
MCU Engine Computer
Control Systems
Lector de Códigos
de Computadoras
de Automóvil
Ford, Lincoln, Mercury
nacionales de EE.UU. con
Systemas MCU y EEC-IV (para EUA)
Instrucciónes
en español - página 67
CP9015
Lecteur de code
d'ordinateur
automobile
Ford, Lincoln, Mercury
domestiques Étas-Unis
avec Systèmes MCU ou EEC-IV
Instructions en
français - page 133
AUDI O
ON
OFF
T
O
S
E
U
T
T
P
F
U
L
E
T
S
STO
T
M
Domestic Ford,
Lincoln & Mercury
¨
TEST
HOLD
Tensi
ón: 16V
Hecho en: China
Para Nombre, Domicilio y Telefono
del Importador: Ver Empaque
1
CP9015
Page 2

2
Page 3

CP9015
™
Congratulations on purchasing your
Actron Code Scanner for accessing
engine trouble-codes required for
repairing vehicles equipped with
computers. Y our Actron Code Scanner is
made by Actron, the largest and most
trusted name in automotive diagnostic
equipment for the home mechanic. Y ou
can have confidence this product
maintains the highest quality in
manufacturing, and will provide you
years of reliable service.
This instruction manual is divided into
several key sections. Y ou will find
detailed steps on using the Code
Scanner and important information about
trouble code meanings, how a computer
controls engine operation, and more!
Identifying the problem is the first step in
solving that problem. Y our Actron Code
Scanner can help you determine by
accessing the engine computer trouble
codes. Armed with that knowledge, you
can either refer to an appropriate service
manual or discuss your problem with a
knowledgeable service technician. In
either event you can save yourself a lot
of valuable time and money in auto
repair. And feel confident that your
vehicle’s problem has been fixed!
Actron offers a compete
line of high quality
automotive diagnostic and
repair equipment.
See your local Actron
dealer for other
Actron products.
CONTENTS
1 About Codes: Where do they
come from and what are they for? .. 3
2 Code Scanner Basics: When do
you use it and what does it do?....... 5
3 Connector Location: Connector
type identifies the computer system
in your vehicle: EEC-IV or MCU. .....7
4 Using the Code Scanner – EEC-IV
system: Complete description for
reading and using service codes ....8
5 Code Meanings – EEC-IV system:
Service Code Definitions for Ford
EEC-IV engines ............................20
6 Other Features – EEC-IV system:
Additional Code Scanner Diagnostic
Tests.............................................. 31
7 Using the Code Scanner – MCU
system: Includes engine off and
engine running tests...................... 37
8 Code Meanings – MCU system:
Service Code Definitions for Ford
MCU engines ................................ 47
9 Computer Basics: What does the
engine computer do?
Learn more about how your engine
computer operates and controls
vehicle functions............................ 49
10
Reference Glossary: Includes
component descriptions and term
definitions commonly used in
reference to engine computer
systems......................................... 55
Instrucciónes en español67
Instructions en français131
3
Page 4

General Safety Guidelines to follow
when working on vehicles
• Always wear approved eye protection.
• Always operate the vehicle in a well ventilated area.
Do not inhale exhaust gases – they are very poisonous!
• Always keep yourself, tools and test equipment away from all
moving or hot engine parts.
• Always make sure the vehicle is in park (Automatic transmission) or neutral (manual transmission) and that the parking
brake is firmly set. Block the drive wheels.
• Never leave vehicle unattended while running tests.
• Never lay tools on vehicle battery . You may short the terminals
together causing harm to yourself, the tools or the battery.
• Never smoke or have open flames near vehicle.
Vapors from gasoline and charging battery are highly flammable and explosive.
• Always keep a fire extinguisher suitable for gasoline/electrical/
chemical fires handy .
• Always turn ignition key OFF when connecting or disconnecting electrical components, unless otherwise instructed.
• Always follow vehicle manufacturer’s warnings, cautions and
service procedures.
CAUTION:
Some vehicles are equipped with safety air bags.
You must follow vehicle service manual cautions when working
around the air bag components or wiring. If the cautions are not
followed, the air bag may open up unexpectedly , resulting in
personal injury . Note that the air bag can still open up several
minutes after the ignition key is off (or even if the vehicle battery
is disconnected) because of a special energy reserve module.
4
Page 5

About Codes
Where do they come from and what are they for?
Engine computers can find
problems.
The computer system in today’s vehicles
does more than control engine operation
– it can help you find problems, too!
Special testing abilities are permanently
programmed into the computer by factory
engineers. These tests check the
components connected to the computer
which are used for (typically): fuel
delivery, idle speed control, spark timing
and emission systems. Mechanics have
used these tests for years. Now you can
do the same thing by using the Actron
Code Scanner tool!
Engine computers perform special
tests.
The engine computer runs the special
tests. The type of testing varies with
manufacturer, engine, model year etc.
There is no “universal” test that is the
same for all vehicles. The tests examine
INPUTS (electrical signals going IN to
the computer) and OUTPUTS (electrical
signals coming OUT of the computer.)
Input signals which have “wrong” values
or output circuits which don’t behave
correctly are noted by the test program
and the results are stored in the
computer’s memory. These tests are
important. The computer can not control
the engine properly if it has bad inputs or
outputs!
Code numbers give test results.
The test results are stored by using code
numbers, usually called “trouble codes”
or “service codes.” For example, a code
63 might mean “throttle position sensor
signal voltage is too low.” Code meanings
are listed in Sections 5 and 8. Specific
code definitions vary with manufacturer,
engine and model year, so you may want
to refer to a vehicle service manual for
additional information. These manuals
are available from the manufacturer,
other publishers or your local public
library. (See manual listing on page 4.)
Read Codes with the Code
Scanner.
Y ou obtain trouble codes from the
engine computer memory by using the
Actron Code Scanner tool. Refer to
section 4 or 7 for details. After you get
the trouble codes, you can either:
• Have your vehicle professionally
serviced. Trouble codes indicate
problems found by the computer.
or,
• Repair the vehicle yourself using
trouble codes to help pinpoint the
problem.
Trouble Codes and Diagnostics
help you fix the problem.
To find the problem cause yourself, you
need perform special test procedures
called “diagnostics”. These procedures
are in the vehicle service manual. There
are many possible causes for any
problem. For example, suppose you
turned on a wall switch in your home
and the ceiling light did not turn on. Is it
a bad bulb or light socket? Is the bulb
installed correctly? Are there problems
with the wiring or wall switch? Maybe
there is no power coming into the
house! As you can see, there are many
possible causes. The diagnostics written
for servicing a particular trouble code
take into account all the possibilities. If
you follow these procedures, you should
be able to find the problem causing the
code and fix it if you want to “do-ityourself.”
Actron makes it easy to fix
computer-controlled vehicles
Using the Actron Code Scanner to
obtain trouble codes is fast and easy.
5
Page 6

Trouble codes give you valuable
knowledge – whether you go for
professional vehicle servicing or “do-ityourself. ” Now that you know what
trouble codes are and where they come
from, you are well on your way to fixing
today’s computer controlled vehicles!
Vehicle Service Information
The following is a list of publishers who have manuals containing trouble code repair
procedures and related information. Some manuals may be available at auto parts
stores or your local public library. For others, you need to write for availability and
prices, specifying the make, style and model year of your vehicle.
Vehicle Service Manuals:
Chilton Book Co.
Chilton Way
Radnor, PA 19089
Haynes Publications
861 Lawrence Drive
Newbury Park, CA 91320
Cordura Publications
Mitchell Manuals, Inc.
P . O. Box 26260
San Diego, CA 92126
“Electronic Engine Controls”
“Fuel Injection and Feedback Carbure-
tors”
“Fuel Injection and Electronic Engine
Controls”
“Emissions Control Manual”
...or similar titles
Vehicle Service Manuals from Ford
Motor Company: (Ford, Lincoln,
Mercury)
Ford Publication Department
Helm Incorporated
P . O. Box 07150
Detroit, MI 48207
1985 & Newer: “Emission Diagnosis
Engine/Electronics”
1981-1984: “Engine/Emissions
Diagnosis”
6
Page 7
Scanner Basics
When Do You Use it and What Does it Do?
When to Use the Code Scanner
Use the Code Scanner:
• When you experience a driveability
problem with your vehicle.
• When the “Check Engine” light comes
on (if used on vehicle).
• For a routine system check – even on
vehicles with a “Check Engine” light.
3
AUDIO
ON
OFF
CP9015 – Ford, Lincoln & Mercury
T
S
E
T
F
L
E
S
ST0
Domestic 1981& Newer
2
O
U
T
P
U
T
®
TM
HOLD
1
What the Code Scanner Does
The Code Scanner makes the vehicle
computer run special tests to check out
various parts of the system. The Code
Scanner plugs into vehicle wiring which
connects directly into two engine
computer circuits. One circuit is called
Self-T est Input (STI). The Code Scanner
uses this wire to tell the computer to run
the tests. The other circuit is called SelfT est Output (STO).
The computer sends test results back to
the Code Scanner by using a pulse type
signal on this wire.
TEST
M
T
HOLD
AUDIO
ON
OFF
9015 - Ford, Lincoln & Mercury
Code Scanner Controls
1 HOLD/TEST switch
This switch connects to the computer’s
Self-Test Input (STI) circuit.
•
HOLD – The STI wire is unconnected.
(Normal position – no testing.)
• TEST – The STI wire is connected to
vehicle ground. (Computer starts
testing procedure.)
2 SELF-TEST OUTPUT light
This light is connected to the STO circuit
coming from the computer.
• Light OFF – The STO signal is “high”
(about 5 volts present).
• Light ON – The STO signal is “low”
(near zero volts).
A pulse type signal on the STO wire will
cause this light to blink. This is how the
computer sends test results to the Code
Scanner. See Section 4 or 7 for details.
Note: With the Code Scanner connected and ignition key OFF, the light
may be ON or OFF – depends upon
vehicle. This does not affect testing
performance.
3 AUDIO switch
•
Switch ON – A tone sounds whenever
the Self-Test Output light is lit.
• Switch OFF – Tone is always OFF.
This feature is useful when the STO light
can not be easily seen, such as when
performing the “wiggle” test described in
Section 6.
Note: With the Code Scanner connected, Audio switch ON and ignition key
OFF, the tone may be ON or OFF (no
matter what the light does) – depends
upon vehicle. This does not affect testing
performance.
7
Page 8
Code Scanner Power
A 9 volt transistor radio battery (NEDA
1604) is required to power the Code
Scanner. Either a regular or alkaline
battery may be used. The Code
Scanner has an automatic battery shutoff when not in use. There is no “power
off” switch because the unit uses no
power when the light is off and the tone
is quiet. The battery must be installed
before use.
Installing the Battery
Do the following:
1) Remove two screws from the bottom
side of the Code Scanner.
2) Separate the two halves of the Code
Scanner.
3) Insert battery:
4) Reassemble Code Scanner case
and replace screws.
Checking the Battery
Do the following:
1) Put the Hold/Test switch in TEST
position.
T
O
S
E
AUDIO
ON
OFF
CP9015 – Ford, Lincoln & Mercury
Domestic 1981& Newer
U
T
T
P
F
U
L
E
T
S
TEST
ST0
®
TM
HOLD
2) Put the Audio switch in ON position.
3) Use a coin to touch the two side-byside terminals on the bottom row (the
one with three terminals) of the Code
Scanner connector.
4) Both the STO light and the tone
should turn ON. Replace battery
when the light or tone gets weak.
8
Page 9
Connector Location
Where the Self-Test connector can be found.
Connector Types
The Code Scanner plugs into the
vehicle “Self-T est” connector which is
located in the engine compartment.
• The EEC-IV computer system (most
1984 & up vehicles) uses TWO test
connectors.
– A large six sided connector.
– A small single wire “pigtail”
connector.
Both of these connectors must be
plugged into the Code Scanner
before use.
• The MCU system (most 1981 – 1983
vehicles) uses ONE test connector.
– A large six sided connector,
identical to the one used with EEC-IV
systems. This connector must be
plugged into the Code Scanner
before use. The MCU system does
NOT use the small “pigtail” connector.
TEST
U
T
P
O
U
T
T
S
E
T
F
L
E
S
M
T
HOLD
AUDIO
ON
81 & Newer
, Lincoln & Mercury
Connector locations
Y ou can tell which computer system is in
your vehicle by noting which connector
type is installed!
The connectors are located in one of six
general areas.
• Near the fire wall (right or left side of
vehicle)
• Near the wheel well (right or left side
of vehicle)
• Near the front corner of the engine
compartment (right or left side of
vehicle)
The connectors are easy to miss – take
your time looking! They are usually gray ,
or other dark color, and located close to
a wiring harness. They may be capped
with a plastic cover or shroud labeled
“EEC TEST” or similar wording.
Other Test Connectors
Vehicles made after 1988 may have
additional computer controlled systems
installed, such as Anti-Lock Brakes
(ABS), active suspension and the like.
These systems use a test connector
identical to EEC-IV six sided one. These
systems do NOT use the extra “pigtail”
connector! The Code Scanner is
compatible with most of these systems –
refer to vehicle service manual for
system description and test methods.
9
Page 10

EEC-IV System
Using the Code Scanner (EEC-IV Systems).
Complete Description for Reading and Using Service Codes.
Do This First
This section shows you how to use the
Code Scanner for:
• Running tests of the engine computer
system. (Engine off, ignition timing
and engine running tests.)
• Reading service codes to pinpoint
problem causes.
Before using this section:
– Read Sections 1 and 2 to learn
about service codes and the Code
Scanner tool.
– Read Section 3 to find the location
of the Self-Test connector in your
vehicle. The connector type will tell
you whether you have an EEC-IV
system or an MCU system.
– Read this section (4) if you have an
EEC-IV system. Use Section 7 if you
have an MCU system.
Self-Test Summary
The Self-Test procedure (also called
“Quick Test”) involves engine off and
engine running tests. The entire
procedure is summarized in the chart.
Each part is fully explained on the
following pages.
IMPORTANT: All parts must be
performed as shown for accurate
testresults!
Part 1: Test Preparation.
• Safety First! Follow all safety rules.
• Perform Visual Inspection. This often
reveals the problem.
• Prepare Vehicle. Engine must be
thoroughly warmed-up.
Part 2: To Key On Engine Off (KOEO)
Self-Test.
• Get service codes to help pinpoint
problems.
Part 3: Check Engine Timing.
• Verify correct “base” timing (no
computer
control) before doing next part.
Part 4: Do Key On Engine Running
(KOER) Self-Test.
• Get more service codes to pinpoint
problems found during engine
operating conditions.
Part 5: Evaluate/Erase “Continuous
Memory” Codes
• Helps locate intermittent problems.
• Removes service codes stored in
computer memory.
10
Page 11
Self-Test Part 1: Test Preparation
1) Safety First!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission).
• Block the drive wheels.
• Make sure
ignition key
is in OFF
position.
2) Perform
Visual Inspection.
Doing a thorough visual and “handson” underhood inspection before
starting any diagnostic procedure is
essential!! Y ou can find the cause of
many drivability problems by just
looking, thereby saving yourself a lot
of time.
• Has the vehicle been serviced
recently?
Sometimes things get reconnected
in the wrong place, or not at all.
• Don’t take shortcuts. Inspect hoses
and wiring which may be difficult to
see because of location beneath air
cleaner housings, alternators and
similar components.
• Inspect the air cleaner and ductwork
for defects.
• Check sensors and actuators for
damage.
• Inspect all vacuum hoses for:
– Correct routing. Refer to vehicle
service manual, or Vehicle Emission
Control Information (VECI) decal
located in the engine compartment.
– Pinches and kinks.
– Splits, cuts or breaks.
HVAC/
ER
P
A.
CRUISE
EGR
VAC
REG
EGR
VAC
REG
FUEL
PRESS
REG
. ..
BRAKE BOOSTER
TO TRANS
MODE
FRONT
OF CAR
9RAC2LAB
• Inspect wiring for:
– Contact with sharp edges. (This
happens often.)
– Contact with
hot surfaces,
such as
exhaust
manifolds.
– Pinched,
burned or
chafed
insulation.
– Proper routing and connections.
• Check Electrical Connectors for:
– Corrosion on pins.
– Bent or damaged pins.
– Contacts not properly seated in
housing.
– Bad wire crimps to terminals.
Bent Pins Corrosion
Problems with connectors are common
in the engine control system. Inspect
carefully. Note that some connectors use
a special grease on the contacts to
prevent corrosion. Do not wipe off!
Obtain extra grease, if needed, from
your vehicle dealer. It is a special type
for this purpose.
3) Prepare Vehicle.
• Turn off all electrical equipment and
accessories in vehicle.
• Keep all vehicle doors closed during
testing.
• Make sure radiator coolant and
transmission fluid are at proper
levels.
• Start the engine and let it idle until
the upper radiator hose is hot and
pressurized and RPM has settled to
warm engine idle speed.
Check for leaks around hose
connections.
11
Page 12

• Turn ignition key to OFF position.
WARNING: Always operate vehicle
in a well ventilated area.
Do NOT inhale exhaust gases – they
are very poisonous!
4) Check Code Scanner Battery.
• Refer to Section 2.
5) Plug the Code Scanner into the
Vehicle Self-Test Connectors.
• Refer to Section 3, “Connector
Location”.
• Connect the Code Scanner to
BOTH test connectors: the small,
single wire connector and the larger
6-sided one.
Note: One Code Scanner pin plugs
into an unused position on large test
connector. This is normal. Also, large
test connector may have other
contacts not used by Code Scanner.
• The Code Scanner
will not harm
vehicle engine computer.
TEST
U
T
P
O
U
T
T
S
E
T
F
L
E
S
M
T
HOLD
AUDIO
ON
1981 & Newer
ord, Lincoln & Mercury
6) Have a Pencil
and Paper
Ready.
• This is for
writing down
all the codes.
7) Go to SELF-TEST PART 2: Key On
Engine Off (KOEO) Self-Test.
• Do Self-Test Part 2 even if engine
will not start, stalls or runs rough.
The service codes you get may
pinpoint the problem. If not, refer to
vehicle service manual for
troubleshooting charts related to
the vehicle symptom.
the
12
Page 13
Self-Test Part 2:
Domestic 1981& Newer
Key On Engine Off (KOEO) Self-Test.
IMPORTANT: You must complete all steps in Self-Test Part 1 before
proceeding to Part 2.
Verify good battery in Code Scanner
(Section 2).
1) Verify
Ignition
Key is in
OFF
Position.
T
O
S
E
2) Put Code
Scanner
HOLD/TEST
Switch in
AUDIO
CP9015 – Ford, Lincoln & Mercury
U
T
T
P
F
U
L
E
T
S
ON
OFF
TEST
ST0
®
TM
HOLD
HOLD
Position.
• Do the following also:
– For 4.9L only, depress clutch until
Step 5 (codes sent).
– For 7.3L diesel only , completely
depress throttle until Step 5 (codes
sent).
– For 2.3L turbo with octane switch,
put switch in premium position.
3) Turn Ignition Key to ON Position
but DO NOT START THE ENGINE.
4) Put Code Scanner HOLD/TEST
Switch in TEST Position.
• This starts the KOEO Self-Test.
• Testing takes anywhere from 10
seconds to one minute before codes
are sent.
• Y ou may hear clicking sounds in the
engine compartment as relays are
being tested.
WARNING: Stay away from
the radiator cooling fan! It
may turn on momentarily
during the test procedure. (On
certain vehicles with
electrically operated fans.)
5) Get Codes from the Flashing STO
Light.
NOTE: If the light does not flash, go
back and repeat SELF-TEST P A R T 2
starting with Step 1. If the light still
does not flash, you have a problem
which must be repaired before
proceeding. Refer to the vehicle
service manual “No Codes” troubleshooting chart.
• Pay no attention to the brief, rapid
blinks which occur before the regular
codes are sent.
• Count flashes to get service codes.
Code 12 looks like:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(FLASH = 1, FLASH FLASH = 2.
Put 1 and 2 together = code 12.)
Code 23 looks like:
❊❊
FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH FLASH
NOTE: Certain 1991 and newer vehicles
use 3 digit codes (refer to vehicle service
manual to determine whether your
system uses 2 or 3 digit codes).
These codes are sent as follows:
Code 123 looks like:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH (pause)
• Two groups of codes are sent at this
❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH
time. Each group is separated by a
PAUSE
❊❊
❊❊❊
PAUSE
❊❊❊
13
Page 14

single flash (called a “separator
code”)
• The first code group has KOEO
(Key On Engine Off) codes – for
problems which are present now.
Some service manuals call these
“hard” or “on demand” codes.
– The KOEO group will always
contain at least one code. This will
be a “system pass” code (11 or 111)
if no problems were seen.
– The KOEO code group is sent
twice (so you can double check your
code list).
• The second code group has
Continuous Memory codes – for
problems which occurred in the past
and have been “memorized” by the
computer. These problems
(sometimes called “intermittences”)
may or may not be present now.
– The Continuous Memory group
will always contain at least one
code. This will be a “system pass”
code (11 or 111) if no problems
were seen.
– The Continuous Memory code
group is sent twice (so you can
double check your code list).
• Code sequence example with
KOEO codes = 21 and 32,
Continuous Memory code =14:
PAUSE
❊❊
FLASH FLASH (pause) FLASH
(longer pause).
❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH
(longer pause).
❊❊
FLASH FLASH (pause) FLASH
(longer pause).
❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH
(very long pause)
SEPARA T OR CODE
❊
FLASH (“separator code”)
PAUSE
PAUSE
PAUSE
❊
❊❊
❊
❊❊
14
(very long pause)
PAUSE
❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH FLASH
❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH FLASH
❊❊❊❊
FLASH (pause)
(longer pause).
PAUSE
❊❊❊❊
FLASH (pause)
Page 15

• Write down codes in the order they are sent.
6) Turn Ignition Key to OFF Position.
At this point you can either:
• Have your vehicle professionally serviced. Codes indicate problems found by the
computer.
or,
• Repair the vehicle yourself using service codes to help pinpoint the problem.
Refer to Test Results Chart.
Key On Engine Off (KOEO) Test Results
KOEO SEPARATOR MEMORY
CODES CODES CODES ACTION TO T AKE:
11 1 11 System pass. No problem found by computer during
(or 111) (or 111) KOEO Self-Test. No codes stored in computer
Any 1 11 KOEO codes indicate system problems are present
Code(s) (or 111) now. Write down all codes. Make repairs based on
Any 1 Any KOEO and Continuous Memory codes indicate
Code(s) Code(s) system problems. Write down ALL codes. DO NOT
11 1 Any Code(s) Continuous Memory codes indicate system faults.
(or 111) not in Write down ALL codes but DO NOT repair these
CONTINUOUS MEMORY 15 1989 & older
CODE EXCEPTIONS 56, 66 1988-1989 5.0L SFI Mustang only
(REPAIR NOW) 45, 46, 48, 215, 216, 217, 232 and 238 vehicles with
DIS (Distributorless Ignition System) only.
CONTINUOUS
memory. Go to SELF-TEST PART 3: Check Engine
Note:
Timing.
rough, refer to vehicle service manual for
troubleshooting charts related to the symptom.
KOEO codes starting with the first code received.
Refer to vehicle service manual for code troubleshooting charts and repair procedures. Repeat
KOEO Self-T est after every repair. (Sometimes a
repair procedure will eliminate more than one code.)
Do not proceed to SELF-TEST PART 3 until a
KOEO pass code (11 or 111) is received.
repair Continuous Memory codes at this time! (But
keep them written down for later use in Self-Test
Step 5.) First make repairs based on KOEO codes
starting with the first code received. Refer to vehicle
service manual for code troubleshooting charts and
repair procedures. Repeat KOEO Self-T est after
every repair. (Sometimes a repair procedure will
eliminate more than one code.)
SELF-TEST PART 3 until a KOEO pass code (11 or
111) is received.
Exceptions List codes at this time! Keep them written down for later
use in Self-T est Step 5. Continue the Self-Test
procedure: go to SELF-TEST P ART 3.
EXCEPTIONS: Some Continuous Memory codes
must be repaired before going to Part 3. These are
listed below. Refer to vehicle service manual for
code troubleshooting charts and repair procedures.
Repeat KOEO Self-T est after every repair . Do not
proceed to SELF-TEST PART 3 until all code
exceptions are eliminated.
If engine will not start, stalls or runs
Do not proceed to
15
Page 16

Self-Test Part 3: Check Engine Timing.
OFF
AUDIO
ON
CP9015 – Ford, Lincoln & Mercury
Domestic 1981& Newer
TM
®
TEST
ST0
HOLD
S
E
L
F
T
E
S
T
O
U
T
P
U
T
HVAC/
ER
P
A.
CRUISE
EGR
VAC
REG
BRAKE BOOSTER
FUEL
TO TRANS
PRESS
MODE
REG
. ..
EGR
VAC
REG
FRONT
OF CAR
9RAC2LAB
(NOTE: 7.3L
Diesel This
Part does
not apply. Go
to Part 4.)
This portion of
the Self-Test procedure is where you
check both the “base” engine timing (no
computer adjustment ) and the ability of
the computer to control spark advance.
The correct value for base engine timing
is printed on the Vehicle Emission
Control Information (VECI) decal, located
in the engine compartment. (Base timing
is 10° BTDC if not specified on the VECI
decal.) A timing light is required for this
test. Connect it to vehicle according to
manufacturers directions. (For 2.3L dual
plug engines, use exhaust side plug.
Refer to ignition system section in vehicle
service manual for specific instructions.)
For 1991 & Older Vehicles:
(See page 15 for 1992 & newer
vehicles.)
1) Turn Ignition Key OFF.
• Wait 10 seconds before proceeding.
2) Put Code Scanner HOLD/TEST
Switch in HOLD Position.
WARNING: The next step involves
starting the engine. Observe safety
precautions.
• Always operate vehicle in a well
ventilated area. Do NOT inhale
exhaust gases – they are very
poisonous!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission).
• Block the drive wheels.
• Stay away from moving engine parts.
3) Start the Engine.
• If engine will not start, stalls or runs
rough, refer to vehicle service
manual for troubleshooting charts
related to the symptom.
4) Put Code
Scanner
HOLD/TEST
Switch in
TEST
Position.
• The computer is now performing an
Engine Running Self-Test, but do not
be concerned with the test or the
resulting codes at this time. It takes
several seconds before codes are
sent.
5) Wait For End of All Service Code
Signals.
• STO light on Code Scanner stops
blinking.
6) Check Ignition Timing.
• After the last code is sent, the
timing will remain fixed for 2
minutes (unless Self-Test is
deactivated by moving T est/Hold
switch to HOLD position).
• Ignition timing (only during this 2
minute period) should be 20
degrees more than the base timing
value (give or take 3 degrees).
EXAMPLE: If base timing is
specified at 10°, the measured
value in this step should be
10°+20°=30°±3°. That is, the timing
should be in the range of 27° to 33°
BTDC.
• If measured timing does not meet
this specification, refer to vehicle
service manual for procedures to
check base timing and computer
timing advance circuits.
• If measured timing is OK, proceed
to SELF-TEST P AR T 4: Key On
Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test.
7) Turn Ignition Key to OFF Position.
16
Page 17

For 1992 & Newer Vehicles:
(See page 14 for 1991 & older vehicles.)
1) Turn Ignition Key OFF.
• Wait 10 seconds before proceeding.
2) Turn off Electrical Loads.
• This includes radio, headlights,
blower fans, air conditioner, and the
like.
4) Start the
Engine.
• Only use the
ignition key to
start engine –
do not use a
remote starter.
• If engine will not start, stalls or runs
rough, refer to vehicle service
manual for troubleshooting charts
related to the symptom.
3) Disconnect the In-Line SPOUT or
SAW Connector. (Depends upon
ignition system: SPOUT= Spark
Output; SAW = Spark Advance
Word.)
• This disconnects the computer
advance timing signal from the
ignition system.
• The ignition system will now operate
at “base engine” timing.
• The connector is located close to the
ignition module.
• There are 3 different styles
illustrated, depending upon your
vehicle type.
WARNING: The next step involves
starting the engine. Observe safety
precautions.
• Always operate vehicle in a well
ventilated area. Do NOT inhale
exhaust gases – they are very
poisonous!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission).
• Block the drive wheels.
• Stay away from moving engine
parts.
5) Check Engine Timing.
• Base timing should be the same as
the VECI decal specification, give or
take 2°. Example: Specified timing is
10° BTDC. Measured timing should
be in the range of 8° to 12°BTDC.
— Distributor System: If base timing
not correct, adjust or repair as
necessary before proceeding.
Refer to ignition system section in
vehicle service manual for
instructions.
— Distributorless System: Base
timing is NOT adjustable. If timing
not correct, refer to ignition system
section in vehicle service manual for
possible causes. Repair as
necessary before proceeding.
6) Reconnect the In-Line SPOUT or
SAW Connector.
7) Check for Timing Advance (or RPM
Increase).
• Timing change (or RPM increase)
should occur as soon as connector
is reconnected.
• If O.K. proceed to SELF-TEST
PART 4.
• If not O.K. proceed to SELF-TEST
PAR T 4, but repair Engine Run
codes 213 or 218 immediately, if
received.
8) Turn Ignition Key to OFF Position.
17
Page 18

Self-Test Part 4: Key On Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test.
IMPORTANT: You must complete all steps in Self-Test Parts 1,2 and 3 before
proceeding to Part 4.
Verify good battery in Code Scanner (Section 2).
1) Verify Ignition Key is in OFF
Position.
2) Put Code Scanner HOLD/TEST
Switch in HOLD Position.
WARNING: The next step involves
starting the engine. Observe safety
precautions.
• Always operate vehicle in a well
ventilated area. Do NOT inhale
exhaust gases – they are very
poisonous!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission).
• Block the drive wheels.
• Stay away from moving engine
parts.
3) Start the Engine.
• If engine will not start, stalls or runs
rough, refer to vehicle service
manual for troubleshooting charts
related to the symptom.
4) Run the Engine to Warm the EGO
Sensor.
• The EGO (Exhaust Gas Oxygen)
sensor must be warmed-up to
operate for this test.
• Run engine at 2000 RPM for at
least 2 minutes.
7) Get Engine Identification (ID) Code
from the Flashing STO Light.
NOTE: If the light does not flash, go
back and repeat SELF-TEST P A R T 4
starting with Step 5. If the light still
does not flash, you have a problem
which must be repaired before
proceeding. Refer to the vehicle
service manual “No Codes” troubleshooting chart.
• An engine ID code is sent after a
few seconds to signal the beginning
of KOER Self-T est.
• Count flashes on the STO light.
– 4 cylinder: 2 Flashes.
– 6 cylinder: 3 Flashes.
– 8 cylinder: 4 Flashes.
– 7.3L Diesel: 5 Flashes.
IMPORTANT:
required at this time.
• Vehicles with PSPS (Power Steering
Pressure Switch): Turn steering
wheel one half turn and release
within 1 or 2 seconds AFTER
seeing engine ID code. (The
computer checks for switch action.)
• Vehicles with BOO (Brake On/Off
switch) when used by computer:
Press and release the brake pedal
AFTER seeing engine ID code. (The
computer checks for switch action.)
• Vehicles with OCS (Overdrive
Cancel Switch): Toggle the switch
on and off AFTER seeing engine ID
code. (The computer checks for
switch action.)
Some actions may be
5) Turn Engine OFF – Wait 10
Seconds – Restart Engine.
6) Put Code Scanner HOLD/TEST
Switch in TEST Position.
• This starts the KOER (Key On
Engine Running) Self-Test.
8) Perform WOT Action After
“Dynamic Response” Signal.
• The Dynamic Response signal is a
single flash on the STO light
occurring 6 to 20 seconds after the
engine ID code is sent.
DYNAMIC RESPONSE
❊
18
Page 19
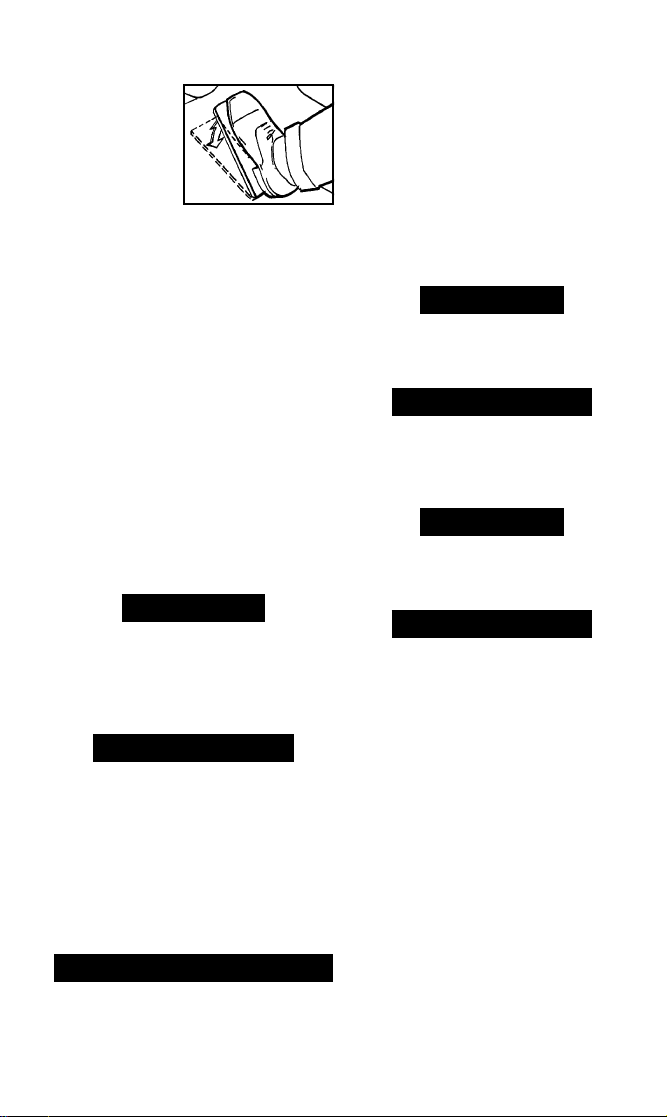
• Perform a brief Wide-Open-Throttle
(WOT) action right after the Dynamic
Response
signal.
(Completely
press and
release
throttle.)
• Some
vehicles do
not use this signal – no throttle
action is necessary.
9) Get Codes from the Flashing STO
Light.
• The KOER (Key On Engine
Running) codes are sent 4 to 15
seconds after the Dynamic
Response signal. There are no other
code groups or separator signals
sent.
• Pay no attention to the brief, rapid
blinks which occur before the regular
codes are sent.
• Count flashes to get service codes.
This is done the same way as in
Self-Test Part 2.
Code 12 looks like:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(FLASH = 1, FLASH FLASH = 2.
Put 1 and 2 together = code 12.)
Code 23 looks like:
❊❊
FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH FLASH
NOTE: Certain 1991 and newer vehicles
use 3 digit codes (refer to vehicle service
manual to determine whether your
system uses 2 or 3 digit codes).
These codes are sent as follows:
Code 123 looks like:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH (pause)
• The KOER (Key On Engine
❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH
PAUSE
❊❊
❊❊❊
PAUSE
❊❊❊
Running) codes are sent as a
group.
— The KOER group will always
contain at least one code. This will
be a “system pass” code (11 or 111)
if no problems are seen.
— The KOER code group is sent
twice (so you can double check your
code list).
• Code sequence example with
KOER codes = 21 and 32:
PAUSE
❊❊
FLASH FLASH (pause) FLASH
(longer pause).
❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH
(longer pause).
❊❊
FLASH FLASH (pause) FLASH
(longer pause).
❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
• Write down codes in the order they
are sent.
• Code definitions are listed in
Section 5, “Code Meanings (EEC-IV
system).”
10)
Turn Ignition Key to OFF Position.
Refer to KOER Test Results chart
following.
19
FLASH FLASH
PAUSE
PAUSE
PAUSE
❊
❊❊
❊
❊❊
Page 20

Key On Engine Running (KOER) Test Results
ENGINE RESPONSE RUNNING
ID CODE CODE CODE ACTION TO TAKE:
2,3,4 or 5 1 11 No problems found by computer during KOER Self-
2,3,4 or 5 1 Any Engine Running codes indicate system problems
(or 998) performed. The computer has spotted system
DYNAMIC ENGINE
•If Continuous Memory codes were obtained in
•If Continuous Memory codes were NOT obtained
•If Continuous Memory codes were NOT obtained in
Codes are present now. Write down all codes. Make repairs
98 Not sent Any Codes The Key On Engine Running Self-Test CANNOT be
(or 111) Test, however…
Self-Test Part 2, go to SELF-TEST PART 5:
Evaluate “Continuous Memory” codes.
in Self-Test Part 2, BUT other vehicle symptoms are
still present, refer to Diagnosis by Symptom
Troubleshooting Charts in vehicle service manual.
(The faults are probably not related to the computer
system.)
Self-Test Part 2 and NO other vehicle symptoms are
present, the Self-Test Diagnostic Procedure is
complete.
based on Engine Running codes starting with the
first code received. (
213 or 218 first, if received.) Refer to vehicle service
manual for code troubleshooting charts and repair
procedures. Repeat KOER Self-T est after every
repair. (Sometimes a repair procedure will eliminate
more than one code.)
problems which must be repaired before running
this test. Go to Part 2: Key On Engine Off (KOEO)
Self-Test and follow all steps.
Exception:
Take care of code
20
Page 21

Self-Test Part 5: Evaluate/Erase Continuous
Memory Codes.
Do this Part if “Continuous Memory”
codes (other than an 11 or 111 pass
code) were received during SELF-TEST
PAR T 2: Key On Engine Off (KOEO)
and, all other Parts of the Self-T est
procedure have been completed.
• Continuous Memory codes come
from faults which occurred in the past.
The problem may still be present, or it
may have gone away. Regardless, the
codes will remain in stored in
computer memory (for retrieval during
Self-Test Part 2) until:
• The codes are erased using the
procedure detailed later in this part.
or,
• Power is removed from the computer
for more than a few minutes. (NOTE:
The KAPWR circuit supplies vehicle
battery power to the computer
memory when the ignition key is off.)
or,
• The problem goes away and does not
reappear. After at least 40 engine
warm-up cycles (depends upon
vehicle) the code will automatically be
erased from computer memory if the
problem stays away during that time.
4) If any codes remain, refer to vehicle
service manual for Continuous
Memory code troubleshooting charts
and repair procedures.
5) Erase Continuous Memory codes
after all repairs have been made.
Erasing Continuous Memory
Codes
1) Verify Ignition Key is in OFF
Position.
2) Put Code Scanner HOLD/TEST
Switch in HOLD Position.
3) Turn Ignition Key to ON Position
but DO NOT START THE ENGINE.
4) Put Code Scanner HOLD/TEST
Switch in TEST Position.
• This starts the normal KOEO Self-
Test.
WARNING: Stay away from the
radiator cooling fan! It may turn on
momentarily. (On certain vehicles
with electrically operated fans.)
5) Wait for the STO Light to Start
Blinking (Codes are Being Sent).
What to Do:
1) Look at the list of Continuous
Memory codes obtained during SelfTest Part 2: Key On Engine Off
(KOEO).
2) Previous repairs may have eliminated
the causes of some (or all) of these
codes!
3) Disregard codes which are related to
repairs already made. For example, if
repairs were made to the Engine
Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
circuit as the result of a KOEO code,
then a Continuous Memory code 21
(ECT signal voltage too high) would
be disregarded.
6) Put Code Scanner HOLD/TEST
Switch in HOLD Position.
• The switch must be moved during
the time the STO light is blinking
(the time period when codes are
being sent).
7) The “Continuous Memory” Codes
are Now Erased.
8) Turn Ignition Key to OFF Position.
9) Disconnect Code Scanner.
21
Page 22

CODE MEANINGS
Code Definitions for FORD Engines with EEC-IV Computer System (Electronic
Engine Control system,
version IV)
Code definitions
are listed in this
section
• If more than one
definition is listed,
consult your vehicle
service manual to get
the specific meaning
for your vehicle.
• Code meanings can
vary with vehicle,
model year, engine
type, options and type
of test being performed.
• Many of the codes
listed may not apply to
your vehicle.
• Follow vehicle service
manual procedures to
find the cause of the
code. Always start with
the first code
displayed.
Remember:
1) Visual inspections are
important!
2) Problems with wiring
and connectors are
common, especially for
intermittent faults.
3) Mechanical problems
(vacuum leaks, binding
or sticking linkages,
etc.) can make a good
sensor look bad to the
computer.
4) Incorrect information
from a sensor may
cause the computer to
control the engine in
the wrong way. Faulty
engine operation might
even make the
computer show a
different good sensor
as being bad!
Three Digit Codes:
Certain 1991 and newer
vehicles use 3 digit codes
to report the results of the
system Self-Test
procedure. Refer to your
vehicle service manual to
determine if your system
uses 2 or 3 digit codes.
The listing of 3 digit code
meanings begins on
page 24.
11
System pass.
12
System cannot raise engine
speed above normal idle.
13
RPM out of specification
during normal idle
operation.
or,
D.C. motor does not follow
dashpot.
14
The Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) has
detected an intermittent loss
of Profile Ignition Pick-up
(PIP) signal during recent
operation.
15
Failure in Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) –
problems with Keep Alive
Memory.
16
RPM too low during Engine
Run Self-Test (lean fuel
test).
or,
Idle Speed Control (ISC)
RPM out of Self-Test
specification.
or,
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS)
fault – Ignition Diagnostic
Monitor (IDM) signal not
received.
or,
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(EGO) sensor – signal
voltage indicates “rich”
during Engine Run SelfTest (lean air/fuel
conditions).
17
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(EGO) sensor - signal
voltage indicates “rich”
during Engine Run SelfTest (lean air/fuel
conditions).
or,
RPM too low during Engine
Run Self-Test (rich fuel
test).
or,
Idle Speed Control (ISC)
RPM below Self-Test
specification.
18
Loss of TACH signal to
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA).
or,
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) fault –
primary circuit failure in coil
1,2,3 or 4.
or,
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS) fault
– failure in Spark Angle
Word (SAW) circuit.
19
Failure in Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) –
problems with internal
voltage regulator.
or,
RPM too low for EGR
check during Engine Run
Self-Test.
or,
Cylinder Identification (CID)
sensor input failure.
22
Page 23

21
Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor
signal voltage: out of range
(Key On Engine Off SelfTest), not at normal
operating temperature
(Engine Run Self-Test) or
loss of signal (during
normal engine operation).
or,
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS) fault
– problems with Crankshaft
Position Sensor (CPS)
circuit.
22
Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor or Barometric
Pressure (BP) sensor –
signal voltage out of
specification (engine off) or
not at normal vacuum levels
(engine running).
23
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor – signal voltage out
of Self-Test specification.
24
Air Charge Temperature
(ACT) sensor or Vane Air
Temperature (VAT) sensor –
signal voltage is out of
specification (engine off) or
not at normal levels (engine
running).
or,
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS) fault –
failure in coil 1 primary
circuit.
25
Knock Sensor (KS) signal
not detected during Engine
Run Self-Test (Dynamic
Response test).
26
Vane Air Flow (VAF) sensor
or Mass Air Flow (MAF)
sensor – signal voltage out
of Self-Test specifications.
or,
Transmission Oil
Temperature (TOT) sensor
– signal voltage is out of
Self-Test specification.
27
Vehicle Speed Sensor
(VSS) – signal voltage is
too low.
or,
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS) fault
– failure in coil 2 primary
circuit.
28
Vane Air Temperature
(VAT) sensor – signal
voltage out of Self-Test
specification.
or,
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS) fault
– failure in coil 3 primary
circuit.
or,
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) fault – Loss of
right side TACH signal.
29
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
– signal voltage is too low.
31
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor or Pressure
Feedback EGR (PFE)
sensor – signal voltage is
below minimum
specification.
or,
EGR Vacuum Regulator
(EVR) solenoid circuit
problems.
or,
EGR valve is not in its
normal closed position.
32
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor or Pressure
Feedback EGR (PFE)
sensor – signal voltage is
below closed limit or has
gone beyond set limits.
or,
Problems with EGR valve
controlling.
33
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor or Pressure
Feedback EGR (PFE)
sensor indicates EGR valve
is not opening.
or,
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor or Pressure
Feedback EGR (PFE)
sensor indicates EGR valve
not seated (closed) properly.
34
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor or Pressure
Feedback EGR (PFE)
sensor: signal voltage out of
Self-Test specification limits,
or,
signal voltage above closed
limit during normal engine run
operation,
or,
signal indicates insufficient
EGR flow.
35
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor or Pressure
Feedback EGR (PFE)
sensor: signal voltage above
Self-Test specification limits,
or,
23
signal voltage too high
during normal engine run
operation.
or,
RPM too low to perform
EGR test (Engine Run SelfTest).
38
Idle Tracking Switch (ITS)
circuit open.
39
Transaxle problem: lock-up
failed in torque convertor,
or,
convertor bypass clutch not
applying properly.
41
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(EGO) sensor: voltage
signal always “lean” (low
value) – does not switch.
42
Exhaust Gas Oxygen (EGO)
sensor: voltage signal
always “rich” (high value) –
does not switch.
43
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(EGO) sensor: voltage
signal “lean” (low value)
during wide-open -throttle
driving condition,
or,
sensor has cooled down
and may not have
responded properly during
Engine Run Self-Test.
44
Problems in Thermactor Air
Control system.
45
Thermactor air flow is
always upstream during
Engine Run Self-Test.
or,
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) or Electronic
Distributorless Ignition
System (EDIS) problems –
primary circuit failure in coil
1, 2, 3 or 4.
46
Thermactor Air System
unable to bypass air (vent
to atmosphere).
or,
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) or Electronic
Distributorless Ignition
System (EDIS) problems –
primary circuit failure in coil
2.
47
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(EGO) sensor signal
voltage indicates “rich”
during “lean” air/fuel
conditions.
or,
Page 24

Vane AIr Flow (VAF)
sensor – voltage signal is
too low.
or,
Transaxle problem – 4x4L
switch is closed.
48
Vane Air Flow (VAF)
sensor – voltage signal too
high.
or,
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) problems:
Coil 3 circuit failure,
or,
Loss of left side
TACH signal.
or,
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(EGO) sensor – signal
voltage indicates opposite
from fuel.
49
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS) –
Spark Advance Word
(SAW) signal error.
or,
Spark Output (SPOUT)
signal changed ignition
timing to 10° BTDC (Before
Top Dead Center).
or,
Transaxle problem: 1-2
shift error.
51
Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor
– signal voltage is too high.
52
Power Steering Pressure
Switch (PSPS) – circuit is
open or no changes
detected.
53
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor – signal voltage is
too high (as if indicating
wide-open-throttle
condition).
54
Air Charge Temperature
(ACT) sensor or Vane Air
Temperature (VAT) sensor
– signal voltage is too high.
55
Open connection in
Keypower circuit or
electrical charging voltage
too low.
56
Mass Air Flow (MAF)
sensor or Vane Air Flow
(VAF) sensor – voltage
signal too high.
or,
Electronic 4-Speed
Overdrive Automatic
Transaxle (E4OD):
Transmission Oil
Temperature (TOT) sensor
– signal voltage is too high.
57
Neutral Pressure Switch
(NPS) – open circuit failure,
or,
Circuit failed in Neutral
position.
or,
Octane adjust service pin
installed.
58
Vane Air Temperature (VAT)
sensor – signal voltage too
high (open connection in
circuit).
or,
Crank fuel delay service pin in
use – circuit connected to
ground.
or,
Idle Tracking Switch (ITS)
circuit failure – incorrect switch
signal indications during SelfTest.
59
Transaxle problem – failure
in 4/3 pressure switch
circuit (open connection).
or,
Low speed fuel pump circuit
failure.
or,
Idle speed adjust service
pin in use – circuit
connected to ground.
61
Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor
– signal voltage is too low.
or,
Indicates that the Idle
Tracking Switch is open (in
contact with the throttle
lever) with the Idle Speed
Control Motor fully
retracted.
62
Transaxle problem – 4/3 or
3/2 pressure switch circuit
failed closed,
or,
convertor clutch failure.
63
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor – signal voltage is
too low.
64
Air Charge Temperature
(ACT) sensor or Vane Air
Temperature (VAT) sensor
– signal voltage is too low.
65
Electrical charging system
problem occurred – voltage
too high (over 17.5 volts).
24
or,
Engine control system
never went into closed loop
fuel operation.
or,
Transaxle problem –
Overdrive Cancel Switch
(OCS) was not cycled
during Engine Run SelfTest.
66
Mass Air Flow (MAF)
sensor or Vane Air Flow
(VAF) sensor – voltage
signal too low.
or,
Transmission Oil
Temperature (TOT) sensor
– signal voltage is too low.
67
Improper signals are being
received from either the
Neutral Drive Switch (NDS),
Neutral Gear Switch (NGS),
Neutral Pressure Switch
(NPS), Clutch Switch (CS),
Manual Lever Position
(MLP) sensor or Air
Conditioner Clutch (ACC).
or,
Air Conditioner (A/C) on
during Self-Test.
68
Vane Air Temperature
(VAT) sensor – signal
voltage is too low.
or,
Transmission Temperature
Switch (TTS) – open circuit
failure.
or,
Idle Tracking Switch (ITS)
circuit failure – incorrect
switch signal indications
during Self-Test.
69
Transaxle problem – Open
circuit failures with 3/2
pressure switch or 3/4
pressure switch,
or,
3-4 switch error.
70
Problem with Electronic
Control Assembly (ECA) –
failure in Data
Communications Link
(DCL).
71
Problem with Electronic
Control Assembly (ECA) –
software reset detected.
or,
Problem with Message
Center Control Assembly
(MCCA) – failure in Data
Communications Link
(DCL).
Page 25

72
Insufficient manifold
vacuum change detected
during Dynamic Response
portion of Engine Run SelfTest.
or,
Problem with Message
Center Control Assembly
(MCCA) – failure in Data
Communications Link
(DCL).
or,
Power interrupt detected.
73
Insufficient throttle position
change detected during
Dynamic Response portion
of Engine Run Self-Test.
74
Brake ON/OFF (BOO)
switch action not detected
during Dynamic Response
portion
of Engine Run Self-Test.
75
Brake ON/OFF (BOO)
switch always closed
circuit.
76
Insufficient Vane Air Flow
(VAF) sensor change
detected during Dynamic
Response portion of Engine
Run Self-Test.
77
Operator error during
Dynamic Response portion
of Engine Run Self-Test.
78
Power interrupt detected.
or,
Flexible fuel sensor circuit
failure.
79
Air Conditioner (A/C) on
during Self-Test.
81
Thermactor Air Diverter
(TAD or AM-2) solenoid:
circuit failure.
or,
Electro-Drive Fan: circuit
failure.
or,
Intake Air Control (IAC)
valve: circuit failure.
or,
Boost solenoid – circuit
failure.
82
Thermactor Air Bypass
(TAB or AM-1) solenoid:
circuit failure.
or,
Electro-Drive Fan: circuit
failure.
or,
Supercharger Bypass
Solenoid (SBS): circuit
failure.
83
High Speed Electro-Drive
Fan (HEDF) – circuit failure.
or,
EGR Control (EGR-C)
solenoid–open circuit failure.
or,
Low speed fuel pump relay –
open circuit failure.
84
EGR Vacuum (EGR-V)
solenoid – circuit failure.
or,
EGR Vacuum Regulator
(EVR) solenoid–circuit failure.
or,
EGR Shut-Off (EGR S/O)
solenoid – circuit failure.
85
Cannister Purge (CANP)
solenoid – circuit failure.
or,
Transaxle problem – 3/4 shift
solenoid circuit failure.
or,
Electronic Control Assembly
(ECA) status – adaptive
“lean” limit reached in fuel
control program.
86
Transaxle problem – 3/4 shift
solenoid circuit failure.
or,
Electronic Control Assembly
(ECA) status – adaptive
“rich” limit reached in fuel
control program.
or,
Wide-open-throttle Air
conditioner Clutch (WAC)
solenoid – circuit failure.
87
Fuel Pump (FP) relay –
circuit failure.
88
Electro-Drive Fan (EDF)
relay – circuit failure.
or,
Converter Clutch Override
(CCO) solenoid – circuit
failure.
or,
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) problems –
loss of dual plug control.
or,
Throttle Kicker (TK) solenoid
– circuit failure.
89
Lock-Up Solenoid (LUS) –
circuit failure.
or,
Converter Clutch Override
(CCO) solenoid – circuit
failure.
or,
Exhaust Heat Control
(EHC) solenoid – circuit
failure.
91
Exhaust Gas Oxygen (EGO)
sensor – signal voltage
always indicates “lean”
either during Engine Run
Self-Test (“rich” air/fuel
conditions) or normal
engine operating
conditions.
or,
Transaxle problem – Shift
Solenoid 1 (SS1) circuit
failure.
92
Right side Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (EGO) sensor –
signal voltage always
indicates “rich” during
Engine Run Self-Test
(“lean” air/fuel conditions).
or,
Transaxle problem – Shift
Solenoid 2 (SS2) circuit
failure.
93
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor – signal voltage too
low during Self-Test (at
maximum extension of idle
speed control motor).
or,
Right side Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (EGO) sensor –
cool down occurred.
or,
Transaxle problem – Coast
Clutch Solenoid (CCS)
circuit failure.
94
Thermactor Air System –
problem on the right bank
(passenger side).
or,
Transaxle problem – Shift
Solenoid 1 (SS1) circuit
failure.
95
Thermactor Air System
problem – right (passenger)
side air flow always
upstream.
or,
Fuel Pump Monitor (FPM)
signal – indicates circuit
problem.
96
Thermactor Air System
problem – right (passenger)
side air flow will not bypass.
or,
Fuel Pump (FP) circuit
failure.
or,
High speed fuel pump relay
circuit failure.
25
Page 26

97
Right side Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (EGO) sensor –
signal voltage indicates
“rich” during “lean” air/fuel
conditions.
or,
Overdrive Cancel Indicator
Light (OCIL) – circuit
failure.
98
A system problem is present
causing the Electronic
Control Assembly (ECA) to
operate in Failure
Management and Effects
Mode (FMEM).
or,
Right side Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (EGO) sensor –
signal voltage indicates
“lean” during “rich” air/fuel
conditions.
or,
Electronic Pressure Control
(EPC) solenoid – circuit
failure.
99
The Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) has not
learned to control engine
idle speed (ignore code 12
or 13).
or,
Electronic Pressure Control
(EPC) solenoid – circuit
failure.
Three Digit Codes
Certain 1991 and newer
vehicles use 3 digit codes
to report the results of
the system Self-Test
procedure. Refer to your
vehicle service manual to
determine if your system
uses 2 or 3 digit codes.
• Code meanings can
vary with vehicle, model
year, engine type,
options and type of test
being performed.
• Many of the codes
listed may not apply to
your vehicle.
• Follow vehicle service
manual procedures to
find the cause of the
code. Always start with
the first code displayed.
Remember:
1) Visual inspections are
important!
2) Problems with wiring
and connectors are
common, especially for
intermittent faults.
3) Mechanical problems
(vacuum leaks, binding
or sticking linkages,
etc.) can make a good
sensor look bad to the
computer.
4) Incorrect information
from a sensor may
cause the computer to
control the engine in
the wrong way. Faulty
engine operation might
even make the
computer show a
different good sensor
as being bad!
111
System pass.
112
Air Charge Temperature
(ACT) sensor – signal
voltage is too low.
113
Air Charge Temperature
(ACT) sensor – signal
voltage is too high.
114
Air Charge Temperature
(ACT) sensor – signal
voltage is higher or lower
than expected.
116
Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor
– signal voltage is higher or
lower than expected.
117
Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor
– signal voltage is too low.
118
Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor
– signal voltage is too high.
121
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor– signal voltage is
higher or lower than
expected.
or,
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor– signal voltage
inconsistent with engine
intake air flow.
122
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor – signal voltage is
too low.
123
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor – signal voltage is
too high.
124
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor – signal voltage is
higher than expected.
125
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor – signal voltage is
lower than expected.
126
Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) or Barometric
Pressure (BP) – signal
values higher or lower than
expected.
128
Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor – vacuum
hose disconnected or
damaged.
129
Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor or Mass Air
Flow (MAF) sensor –
insufficient signal value
change during Dynamic
Response test (Engine Run
Self-Test).
26
Page 27

136
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal not switching
during Engine Run SelfTest. Indicates “lean” (Bank
#2).
137
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal not switching
during Engine Run SelfTest. Indicates “rich” (Bank
#2).
138
Cold Start Injector (CSI) –
insufficient flow during
Engine Run Self-Test.
139
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(EGO) sensor – no
switching detected (Bank
#2).
141
Fuel system indicates
“lean” with high flow
demand.
144
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(EGO) sensor – no
switching detected (Bank
#1).
157
Mass Air Flow (MAF)
sensor – signal voltage is
too low
158
Mass Air Flow (MAF)
sensor – signal voltage is
too high
159
Mass Air Flow (MAF)
sensor – signal voltage is
higher or lower than
expected.
165
“Downstream” Heated
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(HEGO) sensor – voltage
signal indicates “lean”
(Bank #1).
166
“Downstream” Heated
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(HEGO) sensor – voltage
signal indicates “rich”
(Bank #1).
167
Throttle Position (TP)
sensor – insufficient signal
voltage change during
Dynamic Response test
(Engine Run Self-Test).
168
“Downstream” Heated
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(HEGO) sensor – signal
voltage too high.
169
“Downstream” Heated
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
(HEGO) sensor – signal
voltage too low.
171
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal not switching
(Bank #1).
172
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal indicates
“lean” (Bank #1).
173
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal indicates
“rich” (Bank #1).
175
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal not switching
(Bank #2).
176
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal indicates
“lean” (Bank #2).
177
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal indicates
“rich” (Bank #2).
179
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal not
switching: indicates “rich”
during part throttle engine
operation (Bank #1).
181
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal not
switching: indicates “lean”
during part throttle engine
operation (Bank #1).
182
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) status –
adaptive “rich” limit reached
in fuel control program
(engine idle, Bank #1).
183
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) status –
adaptive “lean” limit
reached in fuel control
program (engine idle, Bank
#1).
184
Mass Air Flow (MAF)
sensor – signal voltage is
higher than expected.
27
185
Mass Air Flow (MAF)
sensor – signal voltage is
lower than expected.
186
Injector pulsewidth higher
than expected or Mass Air
Flow (MAF) sensor signal
voltage is lower than
expected.
187
Injector pulsewidth lower
than expected or Mass Air
Flow (MAF) sensor signal
voltage is higher than
expected.
188
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal not
switching: indicates “rich”
during part throttle engine
operation (Bank #2).
189
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen (HEGO) sensor –
voltage signal not
switching: indicates “lean”
during part throttle engine
operation (Bank #2).
191
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) status –
adaptive “rich” limit reached
in fuel control program
(engine idle, Bank #2).
192
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) status –
adaptive “lean” limit
reached in fuel control
program (engine idle, Bank
#2).
193
Flexible Fuel Sensor –
circuit failure.
211
Profile Ignition Pick-Up
(PIP) sensor – circuit
failure.
212
Loss of Ignition Diagnostic
Monitor (IDM) signal –
short
to ground in Spark Output
(SPOUT) circuit.
213
Spark Output (SPOUT)
circuit – open connection
failure.
214
Cylinder Identification (CID)
sensor – circuit failure.
215
Ignition system (distributorless) problem – Coil #1
primary side circuit failure.
Page 28

216
Ignition system (distributorless) problem – Coil #2
primary side circuit failure.
217
Ignition system (distributorless) problem – Coil #3
primary side circuit failure.
218
Ignition system (distributorless) problem – Loss of left
side Ignition Diagnostic
Monitor (IDM) signal.
219
Ignition system problem –
Spark Output (SPOUT)
signal open circuit (no
spark advance timing).
221
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) problem –
Spark timing error.
222
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) problem –
Loss of right side Ignition
Diagnostic Monitor (IDM)
signal.
223
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) problem –
Loss of Dual Plug Inhibit
(DPI) control.
224
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) problem –
Primary circuit failure in
Coil #1, 2, 3 or 4.
225
Knock Sensor (KS) signal
not detected during
Dynamic Response Test
(Engine Run Self-Test).
226
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS)
problem – Ignition
Diagnostic Monitor (IDM)
signal not received.
227
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS)
problem – Crankshaft
Position Sensor (CPS)
error.
232
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS)
problem – Coil #1, 2, 3 or 4
circuit failure.
233
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS)
problem – Spark Advance
Word (SAW) signal error.
238
Ignition system
(distributorless) problem –
Coil #4 primary side circuit
failure.
239
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS)
problem – Crankshaft
Position Sensor (CPS)
signal received with engine
off.
241
Ignition Diagnostic Monitor
(IDM) signal problem –
pulsewidth error between
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS) and
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA).
242
Distributorless Ignition
System (DIS) problem –
operating in failure mode.
243
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System (EDIS)
problem – Secondary
circuit failure in Coil #1, 2, 3
or 4.
244
Cylinder Identification (CID)
circuit failure during
Cylinder Balance Test.
311
Thermactor Air System
problem – no operation
during Engine Run SelfTest (Bank #1).
312
Thermactor Air System
problem – air flow
misdirected during Engine
Run Self-Test.
313
Thermactor Air System
problem – air flow not
bypassed (vented to
atmosphere) during Engine
Run Self-Test.
314
Thermactor Air System
inoperative during Engine
Run Self-Test (Bank #2
with dual oxygen sensors).
315
Thermactor Air System
problem – inadequate air
flow during cold start.
316
Thermactor Air System
problem – inadequate air
flow during hot engine low
RPM.
28
317
Thermactor Air System
problem – air flow not
bypassed (vented to
atmosphere) during Engine
Run Self-Test.
318
Engine Air Management
(EAM) System problem –
monitor circuit signal
voltage is high when
commanded off.
319
Engine Air Management
(EAM) System problem –
monitor circuit signal
voltage is low when
commanded on.
326
Pressure Feedback EGR
(PFE) sensor or EGR
Pressure Transducer (EPT)
– signal voltage lower than
expected.
327
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor, Pressure Feedback
EGR (PFE) sensor or EGR
Pressure Transducer (EPT)
– signal voltage too low.
328
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor – signal voltage
lower than expected
(closed valve position).
332
Insufficient EGR flow
detected.
334
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor – signal voltage
higher than expected
(closed valve position).
335
Pressure Feedback EGR
(PFE) sensor or EGR
Pressure Transducer (EPT)
– signal voltage higher or
lower than expected (Key
On Engine Off Self-Test).
336
Pressure Feedback EGR
(PFE) sensor or EGR
Pressure Transducer (EPT)
– signal voltage higher than
expected (exhaust pressure
high).
337
EGR Valve Position (EVP)
sensor, Pressure Feedback
EGR (PFE) sensor or EGR
Pressure Transducer (EPT)
– signal voltage too high.
338
Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor
– signal voltage lower than
expected.
Page 29

339
Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor
– signal voltage higher than
expected.
341
Octane Adjust service pin
in use.
381
Air Conditioner (A/C) clutch
is cycling frequently.
411
Cannot control RPM during
Engine Run Self-Test – low
RPM check.
412
Cannot control RPM during
Engine Run Self-Test –
high RPM check.
413
Idle Speed Control actuator
– operating at minimum
limit.
414
Idle Speed Control actuator
– operating at maximum
limit.
415
Idle Speed Control system
– minimum learning limit
reached.
416
Idle Speed Control system
– maximum learning limit
reached.
452
Vehicle Speed Sensor
(VSS) – signal too small.
461
RPM or Vehicle Speed
Sensor (VSS) limit reached.
NO REPAIR REQUIRED.
511
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) problem –
Read-Only Memory (ROM)
test failure.
512
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) problem –
Keep Alive Memory test
failure.
513
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) problem –
internal voltage test failure.
519
Power Steering Pressure
Switch (PSPS) – open
connection circuit failure.
521
Power Steering Pressure
Switch (PSPS) – circuit
switching not detected.
522
Vehicle transmission not in
PARK during Key On
Engine Off Self-Test.
524
Low Speed Fuel Pump –
open circuit failure between
battery and Electronic
Control Assembly (ECA).
525
Vehicle transmission in
gear or air conditioner on.
527
Neutral Position Switch
(NPS) open circuit failure or
Air Conditioner on during
Engine Off Self-Test.
528
Clutch Switch (CS) – circuit
failure.
529
Data Communication Link
(DCL) or Electronic Engine
Control (EEC) system –
circuit failure.
532
Cluster Control Assembly
(CCA) – circuit failure.
533
Electronic Instrument
Cluster (EIC) – circuit
failure in Data
Communication Link (DCL).
536
Brake On-Off (BOO) switch
– circuit failure or not
activated during Engine
Run Self-Test.
538
Insufficient RPM change
during Dynamic Response
Test (Engine Run SelfTest).
or,
Invalid cylinder balance test
– throttle position
movement.
or,
Invalid cylinder balance test
– cylinder identification
problems.
539
Air conditioner or defroster
on.
542
Fuel Pump (FP) circuit
open connection –
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) to motor
ground.
543
Fuel Pump (FP) circuit
open connection –
Electronic Control
Assembly (ECA) to battery.
551
Idle Air Control (IAC)
solenoid – circuit failure.
552
Thermactor Air Bypass
(TAB or AM-1) solenoid:
circuit failure.
553
Thermactor Air Diverter
(TAD or AM-2) solenoid:
circuit failure.
554
Fuel Pressure Regulator
Control (FPRC) – circuit
failure.
555
SBS circuit failure.
556
Fuel Pump (FP) relay –
primary circuit failure.
557
Low Speed Fuel Pump –
primary circuit failure.
558
EGR Valve Regulator
(EVR) solenoid – circuit
failure.
559
Air Conditioner Clutch
(ACC) relay – circuit failure.
561
Turbocharger Control
Solenoid (TCS) – output
circuit failure.
562
Auxiliary Electro-Drive Fan
(AEDF) – circuit failure.
563
High Speed Electro-Drive
Fan (HEDF) – circuit failure.
564
Electro-Drive Fan (EDF) –
circuit failure.
565
Cannister Purge (CANP)
solenoid – circuit failure.
566
3/4 Shift solenoid – circuit
failure.
569
Auxiliary Cannister Purge
(AUX-CANP) – circuit
failure.
571
EGR vacuum solenoid –
circuit failure.
572
EGR vent solenoid – circuit
failure.
573
Electro-Drive Fan (EDF) –
operation not detected
during Key On Engine Off
Self Test.
29
Page 30

574
High Speed Electro-Drive
Fan (HEDF) – operation
not detected during Key On
Engine Off Self-Test.
578
Variable Control Relay
Module (VCRM) – Air
Conditioner Pressure
sensor circuit shorted.
579
Variable Control Relay
Module (VCRM) –
insufficient Air Conditioner
Pressure change.
581
Variable Control Relay
Module (VCRM) –
excessive current flow in
fan circuit.
582
Variable Control Relay
Module (VCRM) – open
circuit failure in fan circuit.
583
Variable Control Relay
Module (VCRM) –
excessive current flow in
fuel pump circuit.
584
Variable Control Relay
Module (VCRM) – open
circuit failure in module
power ground circuit.
585
Variable Control Relay
Module (VCRM) –
excessive current flow in
Air Conditioner Clutch
circuit.
586
Variable Control Relay
Module (VCRM) – open
circuit failure in Air
Conditioner Clutch circuit.
587
Variable Control Relay
Module (VCRM) –
communication failure.
617
Transmission problem: 1-2
shift error.
618
Transmission problem: 2-3
shift error.
619
Transmission problem: 3-4
shift error.
621
Transmission problem –
Shift Solenoid 1 (SS1)
circuit failure.
622
Transmission problem –
Shift Solenoid 2 (SS2)
circuit failure.
624
Electronic Pressure Control
(EPC) solenoid – circuit
failure.
625
Electronic Pressure Control
(EPC) solenoid – circuit
driver problem in Electronic
Control Assembly (ECA).
626
Coast Clutch Solenoid
(CCS) – circuit failure.
627
Converter Clutch Solenoid
(CCC) – circuit failure.
628
Excessive converter clutch
slippage.
629
Converter Clutch Solenoid
(CCC), Converter Clutch
Override (CCO) solenoid,
Lock-Up Solenoid (LUS) or
MLUS – circuit failure.
631
Overdrive Cancel Indicator
Light (OCIL) – circuit
failure.
632
Overdrive Cancel Switch
(OCS) – no switch action
detected during Engine
Run Self-Test.
633
4x4L switch closed during
Key On Engine Off SelfTest.
634
Manual Lever Position
(MLP) sensor – signal
voltage higher or lower than
expected.
635
Transmission Temperature
Switch (TTS) – open circuit
failure.
636
Transmission Oil
Temperature (TOT) sensor
– signal voltage higher or
lower than expected.
637
Transmission Oil
Temperature (TOT) sensor
– signal voltage
too high.
638
Transmission Oil
Temperature (TOT) sensor
– signal voltage too low.
639
Turbine Speed Sensor
(TSS) – insufficient signal
level.
641
Shift Solenoid 3 (SS3) –
circuit failure.
643
Shift Solenoid #4 (SS4) –
circuit failure.
645
Transmission problem –
incorrect gear ratio
obtained for first gear.
646
Transmission problem –
incorrect gear ratio
obtained for second gear.
647
Transmission problem –
incorrect gear ratio
obtained for third gear.
648
Transmission problem –
incorrect gear ratio
obtained for fourth gear.
649
Electronic Pressure Control
(EPC) – signal higher or
lower than expected.
651
Electronic Pressure Control
(EPC) solenoid – circuit
failure.
652
Modulated Lock-Up
Solenoid (MLUS) – circuit
failure.
653
Transmission Control
Switch (TCS) – did not
switch during Key On
Engine Run Self-Test.
654
Manual Lever Position
(MLP) sensor – not
indicating PARK position
during Key On Engine Off
Self-Test.
655
Manual Lever Position
(MLP) sensor – not
indicating NEUTRAL
position during Key On
Engine Off Self Test.
656
Converter Clutch Control –
continuous slip error.
657
Excessively hot
transmission oil
temperature detected
during engine operation.
659
High vehicle speed
detected while shift lever
indicating PARK position.
30
Page 31

667
Manual Lever Position
(MLP) sensor – signal
voltage too low.
668
Manual Lever Position
(MLP) sensor – signal
voltage too high.
675
Manual Lever Position
(MLP) sensor – signal
voltage out of range.
676
Transmission problem –
mechanical failure in first
gear and reverse.
677
Transmission problem –
mechanical failure in first
gear and second gear.
678
Transmission problem –
third gear to second gear
downshift error.
679
Transmission problem –
second gear to first gear
downshift error.
691
4x4 low circuit failure.
811
Fuel injector Pump Lever
(FIPL) – signal voltage
higher or lower than
expected.
812
Fuel Injector Pump Lever
(FIPL) – signal voltage too
high.
813
Fuel Injector Pump Lever
(FIPL) – signal voltage too
low.
998
Engine control system
operating in Failure Mode
and Effects Management
(FMEM) programming
strategy.
31
Page 32

32
Page 33

OTHER FEATURES
Additional Code Scanner Diagnostic Features.
Part 1: Relay and Solenoid Test
Service manuals call this the “Output
State Check.” Y ou can turn on most of
the computer controlled relays and
solenoids except the fuel pump relay and
fuel injectors. This is helpful for checking
voltages, relay operation, etc. The
“output state check” is automatically
activated at the end of the normal Key
On Engine Off Self-Test procedure
(explained in Section 4).
Do the following:
1) Safety First!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission).
• Block the drive wheels.
2) Make Sure
Ignition Key
is in OFF
Position
3) Check Code
Scanner
Battery
• Refer to
Section 2.
4) Connect Code Scanner
• Refer to Section 3.
• Plug BOTH test connectors into the
Code Scanner!
TEST
U
T
P
O
U
T
T
S
E
T
F
L
E
S
M
T
HOLD
AUDIO
ON
81 & Newer
, Lincoln & Mercury
5) Put Hold/Test Switch in HOLD
Position
6) Turn Ignition
Key to ON
Position but DO
NOT START
ENGINE
7) Put Hold/Test
Switch in TEST
Position
• Computer is
now running
AUDIO
ON
OFF
CP9015 – Ford, Lincoln & Mercury
Domestic 1981& Newer
normal Key
On Engine Off Self-Test.
WARNING: Stay away from electric
motor driven radiator fan. It may
turn on during this procedure.
8) Wait For End of All Service Code
Signals
• STO light on Code Scanner stops
blinking.
9) “Output State Check” is Now
Activated
• Fully depress
and release the
throttle. At this
time most of the
computer
controlled relays
and solenoids
(except fuel pump and fuel injectors)
will be energized.
NOTE: The STO circuit is also
energized, so the STO light on the
Code Scanner will turn on too!
• Repeat the action of depressing and
releasing the throttle. This will deenergize the components (STO light
will turn off, also).
33
T
O
S
E
U
T
T
P
F
U
L
E
T
S
TEST
ST0
®
TM
HOLD
Page 34

• Throttle action may repeated as
often as desired to turn the
actuators on and off.
NOTE: If vehicle is equipped with
Integrated Vehicle Speed Control
(IVSC), disconnect vacuum supply
hose from the Speed Control Servo
(to release stored vacuum).
Otherwise, the Speed Control
Solenoids will energize the first
time the throttle is depressed
causing the servo to hold the
throttle wide open! Reconnect the
vacuum hose after testing.
10)Turn
Ignition
Key to
OFF
Position
11)Disconnect Code Scanner
34
Page 35

Part 2: Cylinder Balance Test
This test is only used on vehicles with
Sequential electronic Fuel Injection
(SFI) engines. (Where the injectors are
fired individually in the same sequence
as the spark plug firing sequence.) The
test turns each injector on and off and
checks for an RPM decrease. Codes
indicate cylinders which are weak or not
contributing due to problems such as
damaged injectors, spark plugs and
wiring. The test must be run at the end
of the normal Key On Engine Running
Self-T est procedure (explained in
Section 4) and may be repeated as
often as desired.
Warning: The following procedure
involves starting the engine.
Always operate vehicle in a well
ventilated area.
Exhaust gases are very poisonous!
1) Safety First!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission).
• Block the drive wheels.
2) Make Sure Ignition Key is in OFF
Position
3) Check Code Scanner Battery
• Refer to Section 2.
7) Start the Engine
• Stay away from moving parts.
8) Put Hold/Test Switch in TEST
Position
• Computer is now running normal
Key On Engine Running Self-T est.
9) Wait For End of All Service Code
Signals
• STO light on Code Scanner stops
blinking.
B egin the Cylinder Balance Test
10)
Lightly Press and Release Throttle
about 10 seconds after STO Light
stops blinking
• Do NOT press throttle all the way
down!
Exception:
throttle for 1986 only.
• Test time is less than 3 minutes.
• Do not move throttle until test is
over.
11)
Get Codes from Flashing STO
Light
• Count flashes to get codes.
NOTE: This test can give single
digit codes.
Code 3 looks like:
Do brief wide-open-
4) Connect Code Scanner
• Refer to Section 3.
• Plug BOTH test connectors into the
Code Scanner!
5) Put Hold/Test Switch in HOLD
Position
6) Have a Pencil and Paper Ready
• This is for writing down the codes.
❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH
Code 12 looks like:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(FLASH=1, FLASH FLASH=2.
Put 1 and 2 together = code 12.)
• Testing is complete
35
❊❊
Page 36

12)
Optional Retest - 1987 & Newer
• Lightly press and release throttle
within 2 minutes after the last code
is sent. This will repeat the entire
cylinder balance test.
• IMPORTANT: (Some 1987 and all
1988 & newer) Repeating the test
Example: All cylinders equal
can tell you how weak a bad
cylinder is. (The computer alters
inspection during retest.) Test
results will be different for a good,
weak or “dead” cylinder. See charts
below using cylinder #7 as an
example.
1st TEST 2nd TEST 3rd TEST
Code #9 (pass) Not necessary Not necessary
Example: Cylinder 7 is weak
1st TEST 2nd TEST 3rd TEST
Code #7 Code #9 (pass) Not necessary
Example: Cylinder 7 is very weak
1st TEST 2nd TEST 3rd TEST
Code #7 Code #7 Code #9 (pass)
Example: Cylinder 7 is extremely weak or dead
1st TEST 2nd TEST 3rd TEST
Code #7 Code #7 Code #7
Service Code Test Results
9 System PASS
1 #1 Cylinder / Injector problem
2 #2 Cylinder / Injector problem
3 #3 Cylinder / Injector problem
4 #4 Cylinder / Injector problem
5 #5 Cylinder / Injector problem
6 #6 Cylinder / Injector problem
7 #7 Cylinder / Injector problem
8 #8 Cylinder / Injector problem
77
Throttle was moved during test. Testing could not be
completed. Repeat test procedure starting from step 1.
13) Turn Ignition Key to Off Position
14) Disconnect Code Scanner
36
Page 37

Part 3: Wiggle Test
ury
(Sometimes called Continuous Monitor test.)
• This test can help locate intermittent
faults in SOME circuits (see chart on
page 36).
• When Wiggle test is activated, the
Code Scanner STO light and Audio
tone will turn on if a problem is
detected.
• The STO light and tone are only
energized as long as the fault is
present. If the problem goes away,
the light and tone will turn off.
• If the STO light and tone come on as
you wiggle a sensor, connector or
wiring, that’s where the problem is!
1) Safety First!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission).
• Block the drive wheels.
2) Make Sure
Ignition Key
is in OFF
Position
3) Check Code Scanner Battery
• Refer to Section 2.
4) Connect Code Scanner
• Refer to Section 3.
• Plug BOTH test connectors into the
Code Scanner!
8) Depending upon Vehicle Model
Year....
• 1986 & Older: “Wiggle Test” is now
activated! Go to Step 9.
• 1987 & Newer:
—Without pausing, move HOLD/
TEST switch to TEST then to
HOLD and then back to TEST .
—“Wiggle Test” is now activated!
Go to Step 9.
9) Perform “Wiggle Test” on
Suspected Circuit
• Lightly tap sensor.
• Wiggle sensor connector.
• Twist and shake wiring between
sensor and computer.
• If the above
actions recreate
TEST
an intermittent
fault, the STO
light will light
and a tone will
sound for as
long as the fault
AUDIO
ON
OFF
CP 9015 - Ford, Lincoln & Merc
is present. This
can help locate the area of an
intermittent problem!
NOTE: If a fault is recreated this way,
a service code will be stored in
computer memory. Be sure to erase
this code from memory after making
all repairs. Refer to Section 4 (SelfT est Part 5: Erasing “Continuous
Memory” codes).
M
T
HOLD
5) Put HOLD/TEST Switch in HOLD
Position
6) Put AUDIO Switch in ON Position
7) Turn Ignition Key to ON Position
but DO NOT START ENGINE
10) Move Switches:
• HOLD/TEST switch to HOLD.
• AUDIO switch to OFF.
11) Turn Ignition Key to Off Position
12) Disconnect Code Scanner
37
Page 38

Circuits Checked by Continuous Monitor
ACT..............1984 & up
BP ................1984 & up
ECT .............1984 & up
EGO.............1990 & up
EVP .............1984 & up
IDM ..............1990 & up
(DIS or dual plug DIS only)
ITS ...............1990 & up
MAF .............1990 & up
MAP .............1984 & up
PFE..............1986 & up
TP ...............1984 & up
VAF..............1985 & up
VAT ..............1984 & up
38
Page 39

MCU SYSTEM
Using the Code Scanner (MCU Systems)
Complete Description for Reading and Using Service Codes
Do This First
This section shows you how to use the
Code Scanner for:
• Running tests of the engine computer
system.
• Reading service codes to pinpoint
problem causes.
Before using this section:
—Read Sections 1 and 2 to learn about
service codes and the Code Scanner
tool.
—Read Section 3 to find the location of
the Self- Test connector in your
vehicle. The connector type will tell
you whether you have an MCU
system or an EEC-IV system.
—Read this section (7) if you have an
MCU system. Use Section 4 if you
have an EEC-IV system.
Self-Test Summary
The Self-Test procedure (also called
“Quick Test”) involves engine off and
engine running tests.
The entire procedure is summarized
below. Each part is fully explained on
the following pages. IMPORTANT: All
parts must be performed as shown for
accurate test results!
Self-Test Summary
Part 1: Test Preparation.
• Safety First! Follow all safety rules.
• Perform Visual Inspection. This often
reveals the problem.
• Prepare Vehicle. Check choke voltage
and warm-up engine.
Part 2: Do Key On Engine Off
(KOEO) Self-Test.
• Get service codes to help pinpoint
problems.
Part 3: Do Key On Engine
Running (KOER) Self-Test.
• Get more service codes to pinpoint
problems found during engine
operating conditions.
Self-Test Part 1:
Test Preparation
1) Safety First!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission).
• Block the drive wheels.
• Make sure ignition key is in OFF
position.
2) Perform Visual Inspection.
Doing a thorough visual and “handson” underhood inspection before
starting any diagnostic procedure is
essential!! Y ou can find the cause of
many drivability problems by just
looking, thereby saving yourself a lot
of time.
• Has the vehicle been serviced
39
Page 40

recently? Sometimes things get
reconnected in the wrong place, or
not at all.
• Don’t take shortcuts. Inspect hoses
and wiring which may be difficult to
see because of location beneath air
cleaner housings, alternators and
similar components.
• Inspect the air cleaner and ductwork
for defects.
• Check sensors and actuators for
damage.
• Inspect all vacuum hoses for:
– Correct routing. Refer to vehicle
service manual, or Vehicle Emission
Control
Information
(VECI) decal
located in the
engine
compartment.
ER
P
A.
EGR
VAC
REG
PRESS
. ..
EGR
VAC
REG
HVAC/
CRUISE
BRAKE BOOSTER
FUEL
TO TRANS
MODE
REG
FRONT
OF CAR
9RAC2LAB
– Pinches and kinks.
– Splits, cuts or breaks.
• Inspect wiring for:
– Contact
with sharp
edges. (This
happens
often.)
– Contact
with hot
surfaces, such as exhaust manifolds.
– Pinched, burned or chafed
insulation.
– Proper routing and connections.
• Check electrical connectors for:
– Corrosion on pins.
– Bent or damaged pins.
– Contacts not properly seated in
housing.
– Bad wire crimps to terminals.
Bent Pins Corrosion
Problems with connectors are
common in the engine control system.
Inspect carefully. Note that some
connectors use a special grease on
the contacts to prevent corrosion. Do
not wipe off! Obtain extra grease, if
needed, from your vehicle dealer. It is
a special type for this purpose. Repair
any problems found during the visual
inspection and retest the vehicle. If
the original symptom is still present,
continue the test. Go to Step 3,
“Prepare Vehicle.”
3) Prepare Vehicle.
• Turn off all electrical equipment and
accessories in vehicle.
• Keep all vehicle doors closed during
testing.
• Make sure radiator coolant and
transmission fluid are at proper
levels.
• If the air cleaner must be removed
(for example to measure the choke
voltage), leave all vacuum hoses
attached to the air cleaner housing.
• Start the engine and allow it to idle.
If the engine does not start, refer to
the “No Start” diagnostic procedure
in the vehicle service manual.
WARNING: Always operate vehicle
in a well ventilated area.
Do NOT inhale exhaust gases –
they are very poisonous! Stay away
from moving parts!
• Check for power at the choke while
the engine is running. Use a
voltmeter to measure the voltage
between the choke cap terminal and
engine ground.
— Battery Powered Choke: voltage
should be about 12 volts.
— Alternator Powered Choke:
voltage should be about 7.5 volts. If
any problems are found in the choke
power circuit, make necessary
repairs and re-do the Self-T est
process starting with Step 1.
Continue this procedure if no
problems are found.
• Allow the engine to idle until the
upper radiator hose is hot and
pressurized and RPM has settled to
warm engine idle speed. Check for
leaks around hose connections.
• Turn ignition key to OFF position.
40
Page 41

4) Plug the Code Scanner into the
Vehicle Self-Test Connector.
• Refer to Section 3, “Connector
Location”. (The Self-T est connector
is near the MCU computer module.)
Not used in
systems
TEST
U
T
P
O
U
T
T
S
E
T
F
L
E
S
TM
HOLD
AUDIO
ON
1981 & Newer
ord, Lincoln & Mercury
• Connect the Code Scanner to the 6-
sided test connector only. The Code
Scanner has a spot for a second
small connector, which is NOT
USED in MCU systems. Do not
connect anything to this unused
location.
• The Code Scanner will not harm the
vehicle engine computer.
5) Do Special Set-Up Procedures.
The engine types listed require
additional preparation before
continuing with the Self-Test.
In-Line 4 and 6 cylinder engines
with a canister control valve
MCU
V-6 and V-8 engines.
Remove PCV valve from breather cap
on valve cover. Be sure to replace PCV
valve after testing and servicing is
completed!
2.3L engines with the GK code.
Manifold Vacuum
Remove
cap
Anti-backfire
vacuum switch
Remove the cap from the anti-backfire
vacuum switch tee during testing. The
switch is located behind the MCU
module. Be sure to replace the cap after
testing and servicing is complete!
2.3L engines with an EGR vacuum load
control (wide open throttle) valve.
Remove hose from connection port B.
(This hose runs between the canister
control valve and the carbon canister.)
Do NOT plug the hose for the remainder
of the test procedure. Be sure to
reconnect the hose after testing and
servicing is completed!
Cover the atmospheric vent holes with a
piece of tape. Be sure to remove the
tape after testing and servicing is
completed!
41
Page 42

4.2L and 5.8L engines with a vacuum
delay valve.
There is a tee with a restrictor in the
Thermactor Vacuum control line. The
restrictor must be uncapped during the
test. Replace the cap after testing. Refer
to drawing for location of restrictor on
the TAD vacuum line (4.2L engines) or
the TAB vacuum line (5.8L engines).
6) Have a Pencil and Paper Ready.
• This is for writing down all the
codes.
7) Go to SELF-TEST PART 2: Key On
Engine Off (KOEO) Self-Test.
42
Page 43

Self-Test Part 2:
Key On Engine Off (KOEO) Self-Test.
IMPORTANT: You must complete all steps in Self-Test Part 1
before proceeding to Part 2.
1) Verify:
Ignition Key is in OFF Position and
Code Scanner is Connected.
2) Put Code Scanner HOLD/TEST
Switch in TEST Position.
• Optional: Turn the AUDIO switch ON to
hear “beeps” when the codes are sent.
3) Turn Ignition Key to ON Position but
DO NOT START THE ENGINE.
• This starts the KOEO Self-Test.
• Codes are sent after 5 seconds.
• Pay no attention to a brief blink which
may occur after ignition key is turned
to ON position.
4) Get Codes from the Flashing STO
Light.
Note: If the light does not flash, go
back and repeat SELF-TEST P A R T 2
starting with Step 1.
If the light still does not flash, you have
a problem which must be repaired
before proceeding. Refer to the vehicle
service manual “Self-Test Not
Functional” (or similar title) troubleshooting chart.
• Count flashes to get service codes.
(Each flash lasts 1/2 second.)
Code 12 looks like:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(FLASH = 1, FLASH FLASH = 2.
(Put 1 and 2 together = code 12.)
Code 23 looks like:
❊❊
FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH FLASH
PAUSE
❊❊
❊❊❊
• All codes are 2 digits long.
• The pause between each digit is 2
seconds.
• After all codes are sent, the whole
group is sent again just one more
time (so you can double check your
code list).
• The longer pause between each
code is 4 seconds.
Example of code 12 only:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(longer pause)
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
Example of code series 12 and 42:
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(longer pause)
❊❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH
(longer pause)
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(longer pause)
❊❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH
5) Turn Ignition Key to OFF Position.
At this point you can either:
43
PAUSE
PAUSE
PAUSE
PAUSE
PAUSE
❊❊
❊❊
❊❊
❊❊
❊❊
❊❊
Page 44

• Have your vehicle professionally
serviced. Codes indicate problems
found by the computer.
or,
• Repair the vehicle yourself using
service codes to help pinpoint the
problem. Refer to T est Results
Chart.
Key On Engine Off (KOEO) Test Results
KOEO
CODES ACTION TO TAKE:
11* System pass. No problem found by computer during KOEO Self-
(all except Test. Go to SELF-TEST PART 3: Key On Engine Running
high altitude) (KOER) Self-Test.
62* System pass. No problem found by computer during KOEO Self-
(high altitude V- 6 T est. Go to SELF-TEST PART 3: Key On Engine Running
or V-8 ONL Y) (KOER) Self-T est.
65* System pass. No problem found by computer during KOEO Self-
(high altitude T est. Go to SELF-TEST PART 3: Key On Engine Running
I-4 ONLY) (KOER) Self-Test.
Any Code(s) Codes indicate system problems are present now. Write down all
No Codes Y ou have a problem which must be repaired before proceeding.
Received Refer to the vehicle service manual “Self-Test Not Functional” (or
(STO light similar title) troubleshooting chart.
always
on or off)
codes. Refer to vehicle service manual for code troubleshooting
charts and repair procedures. Repeat PAR T 2: Key On Engine
Off (KOEO) Self-Test after every repair. Do not proceed to SELFTEST PART 3 until a system pass code is received.
*Note: “High Altitude” refers to vehicles with computer adjusted for operation at high
elevations such as in Denver, Colorado.
44
Page 45

Self-Test Part 3:
Key On Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test.
IMPORTANT: You must complete all steps in Self-Test Parts 1 and 2 before
proceeding to Part 3.
For Vehicles With I-4 & I-6 Engines:
(Refer to page 44 for V-6 & V -8
engines.)
1) Verify:
• Ignition Key is in OFF Position.
• Code Scanner is Connected.
• HOLD/TEST Switch is in TEST
Position.
WARNING: The next step involves
starting the engine.
Observe safety precautions.
• Always operate vehicle in a well
ventilated area.
Do NOT inhale exhaust gases –
they are very poisonous!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL (manual
transmission).
• Block the drive wheels.
• Stay away from moving engine
parts.
2) Start the Engine.
3) Increase and Hold Engine Speed at
3000 RPM Within 20 Seconds of
Start.
• Maintain engine speed at 3000
RPM until service codes are sent
(end of Step 5).
4) Get Engine Identification (ID) Code
from the Flashing STO Light.
• Maintain engine speed at 3000
RPM.
• An engine ID code is sent after a
few seconds to signal the beginning
of KOER Self-T est.
• Count flashes on the STO light.
(Ignore any flashes lasting longer
than 1 second.)
– 4 cylinder: 2 Flashes.
– 6 cylinder: 3 Flashes.
Note: If the light does not flash or
flashes the wrong number, go back
and repeat SELF-TEST P A R T 3
starting with Step 1. If the light still
does not flash correctly, you have a
problem which must be repaired
before proceeding. Refer to the
vehicle service manual “Self-Test Not
Functional” (or similar title) troubleshooting chart.
5) Get Service Codes From the
Flashing STO Light.
• Maintain engine speed at 3000
RPM until codes are sent, then
release throttle and return to idle
RPM.
• Count flashes on the STO light.
This is done the same way as in
Self-T est Part 2. (Ignore any flashes
lasting longer than 1 second.)
Code 12 looks like:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(FLASH = 1, FLASH FLASH = 2.
(Put 1 and 2 together = code 12.)
• All codes are 2 digits long.
• After all codes are sent, the whole
series is sent again just one more
time (so you can double check your
code list).
45
❊❊
Page 46

Example of code series 12 and 42:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(longer pause)
❊❊
• Block the drive wheels.
• Stay away from moving engine
parts.
2) Start the Engine.
❊❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
❊❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
6) Turn Ignition Key to OFF Position.
7) Remove Code Scanner.
PAUSE
FLASH FLASH
(longer pause)
PAUSE
❊❊
(longer pause)
PAUSE
FLASH FLASH
❊❊
❊❊
For Vehicles With V-6 & V-8
Engines:
(Refer to page 43 for I-4 and I-6
engines.)
1) Verify:
• Ignition Key is in OFF Position.
• Code Scanner is Connected.
• HOLD/TEST Switch is in TEST
Position.
WARNING: The next step involves
starting the engine. Observe
safety precautions.
• Always operate vehicle in a well
ventilated area.
Do NOT inhale exhaust gases –
they are very poisonous!
• Set the parking brake.
• Put shift lever in PARK (automatic
transmission) or NEUTRAL
(manual transmission).
3) Warm-Up Engine.
• Allow engine to idle until it reaches
normal operating temperature.
Then...
• Run engine at 2000 RPM for 2
minutes.
4) Turn Engine Off, Then Immediately
Restart Engine and Allow to Idle.
Note: Vehicles with Throttle Kicker
actuator – the Throttle Kicker will
extend (increasing RPM) and remain
so throughout the test.
5) Get Engine Identification (ID) Code
from the Flashing STO Light.
• An engine ID code is sent after a
few seconds to signal the beginning
of KOER Self-T est.
• Count flashes on the STO light.
(Ignore any flashes lasting longer
than 1 second.)
– 6 cylinder: 3 Flashes.
– 8 cylinder: 4 Flashes.
Note: If the light does not flash or
flashes the wrong number, go back and
repeat SELF-TEST P AR T 3 starting
with Step 1. If the light still does not
flash correctly , you have a problem
which must be repaired before
proceeding. Refer to the vehicle service
manual “Self-T est Not Functional” (or
similar title) troubleshooting chart.
6) Test Knock Sensor (if used on
vehicle).
• If vehicle does not use knock sensor,
skip this step and go to Step 7.
• Do the following immediately after
engine ID code is sent:
– Simulate spark knock by placing a
3/8 inch socket extension (or similar
tool) on manifold near base of knock
sensor.
46
Page 47

– T ap on
end of
extension
with a
light (4
oz.)
hammer for 15 seconds.
– DO NOT T AP SENSOR!
7) Get Service Codes From the
Flashing STO Light.
• Count flashes on the STO light. This
is done the same way as in Self-Test
Part 2. (Ignore any flashes lasting
longer than 1 second.)
Code 12 looks like:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(FLASH = 1, FLASH FLASH = 2.
(Put 1 and 2 together = code 12.)
• All codes are 2 digits long.
• After all codes are sent, the whole
group is sent again just one more
time (so you can double check your
code list).
❊❊
8) Turn Ignition Key to OFF Position.
9) Remove Code Scanner.
At this point you can either:
• Have your vehicle professionally
serviced. Codes indicate problems
found by the computer.
or,
• Repair the vehicle yourself using
service codes to help pinpoint the
problem. Refer to Test Results Chart.
Code definitions are listed in Section
8, “Code Meanings (MCU system).”
Example of code series 12 and 42:
PAUSE
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(longer pause)
❊❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH
(longer pause)
❊
FLASH (pause) FLASH FLASH
(longer pause)
❊❊❊❊
FLASH FLASH FLASH FLASH (pause)
FLASH FLASH
PAUSE
❊❊
PAUSE
❊❊
PAUSE
❊❊
❊❊
47
Page 48

Key On Engine Running (KOER) Test Results
KOER
CODES ACTION TO TAKE:
11* System pass. No problem found by computer during KOER Self-
(all except Test. The Self-Test Diagnostic Procedure is complete. If vehicle
high altitude) symptoms are still present, they are probably not related to the
62* System pass. No problem found by computer during KOER Self-
(high altitude V-6 Test. The Self-Test Diagnostic Procedure is complete. If vehicle
or V-8 ONLY) symptoms are still present, they are probably not related to the
65* System pass. No problem found by computer during KOER Self-
(high altitude T est. The Self-Test Diagnostic Procedure is complete. If vehicle
I-4 ONLY) symptoms are still present, they are probably not related to the
computer system.
computer system.
computer system.
Any Code(s) Codes indicate system problems are present now. Write down all
No Codes Y ou have a problem which must be repaired before proceeding.
Received Refer to the vehicle service manual “Self-Test Not Functional” (or
(STO light similar title) troubleshooting chart.
always
on or off)
codes. Refer to vehicle service manual for code troubleshooting
charts and repair procedures. Repeat PAR T 3: Key On Engine
Running (KOER) Self-T est after every repair .
*Note: “High Altitude” refers to vehicles with computer adjusted for operation at high
elevations such as in Denver, Colorado.
48
Page 49

CODE MEANINGS
Code Definitions for FORD Engines with MCU Computer System
(Microprocessor Control Unit)
Code definitions are
listed in this section
• Many of the codes
listed may not apply to
your vehicle.
• Use the definition that
applies to your engine
type: In-Line 4 or 6
cylinder (I-4, I-6) or V-6
or V-8.
• Follow vehicle service
manual procedures to
find the cause of the
code.
Remember:
1) Visual inspections are
important!
2) Problems with wiring
and connectors are
common, especially for
intermittent faults.
3) Mechanical problems
(vacuum leaks, binding
or sticking linkages,
etc.) can make a good
sensor look bad to the
computer.
11
“High Altitude” computer
adjusted for operation at
high elevations such as in
Denver, Colorado.
I-4 (All except High
Altitude): System pass.
I-4 (High Altitude only):
Altitude (ALT) circuit is
open.
I-6: System pass.
V-6 (All except High Altitude):
System pass.
V-6 (High Altitude only):
Altitude (ALT) circuit is
open.
V-8 (All except High Altitude):
System pass.
V-8 (High Altitude only):
Altitude (ALT) circuit is
open.
12
V-8: RPM out of
specification – Throttle
Kicker (TK) system.
25
V-8: Knock Sensor (KS)
signal not detected during
Key On Engine Run
(KOER) Self-Test.
33
All Engines: Key On
Engine Run (KOER) SelfTest not initiated.
41
All Engines: Exhaust
Gas Oxygen (EGO)
sensor: voltage signal
always “lean” (low value) –
does not switch.
42
All Engines: Exhaust
Gas Oxygen (EGO)
sensor: voltage signal
always “rich” (high value) –
does not switch.
44
All Engines: Exhaust
Gas Oxygen (EGO)
sensor: signal voltage
indicates “rich” (high value)
with Thermactor air
switched upstream to the
exhaust manifold (a “lean”
air/fuel condition).
45
All Engines: Thermactor
air flow is always upstream
(going to exhaust
manifold).
46
All Engines: Thermactor
Air System unable to
bypass air (vent to
atmosphere).
51
I-4: Low or Mid
Temperature Switch circuit
is open when engine is hot.
I-6: Low Temperature
Vacuum Switch circuit is
open when engine is hot.
V-6: Hi or Hi/Low Vacuum
Switch circuit is always
open.
V-8: Hi or Hi/Low Vacuum
Switch circuit is always
open.
52
I-4 (car): Idle Tracking
Switch (ITS) – voltage does
not change from closed to
open throttle. (Closed
throttle checked during Key
On Engine Off condition.
Open throttle checked
during Engine Running
conditions.)
I-4 (truck): Idle/Decel
Vacuum Switch circuit
always open.
I-6: Wide Open Throttle
(WOT) Vacuum Switch
circuit is always open.
53
I-4: Wide Open Throttle
(WOT) Vacuum Switch
circuit is always open.
I-6: CROWD Vacuum
Switch circuit is always
open.
V-6: Dual Temperature
Switch circuit is always
open.
V-8: Dual Temperature
Switch circuit is always
open.
54
V-6: Mid Temperature
Switch circuit is always
open.
V-8: Mid Temperature
Switch circuit is always
open.
55
I-4: Road Load Vacuum
Switch circuit is always
open.
49
Page 50

V-6: Mid Vacuum Switch
circuit is always open.
V-8: Mid Vacuum Switch
circuit is always open.
56
I-6: Closed Throttle
Vacuum Switch circuit is
always open.
61
V-6: Hi/Low Vacuum
Switch circuit is always
closed.
V-8: Hi/Low Vacuum
Switch circuit is always
closed.
62
Note: “High Altitude”
refers to vehicles with
computer adjusted for
operation at high elevations
such as in Denver,
Colorado.
I-4 (car): Idle Tracking
Switch (ITS) circuit is
closed at idle.
I-4 (truck): Idle/Decel
Vacuum Switch circuit is
always closed.
I-6: Wide Open Throttle
(WOT) Vacuum Switch
circuit is always closed.
V-6 (All except High Altitude):
Altitude (ALT) circuit is
open.
V-6 (High Altitude only):
System pass.
V-8 (All except High
Altitude): Altitude (ALT)
circuit is open.
V-8 (High Altitude only):
System pass.
63
I-4: Wide Open Throttle
(WOT) Vacuum Switch
circuit is always closed.
I-6: CROWD Vacuum
Switch circuit is always
closed.
65
Note: “High Altitude” refers
to vehicles with computer
adjusted for operation at
high elevations such as in
Denver, Colorado.
I-4 (All except High Altitude):
Altitude (ALT) circuit is
open.
I-4 (High Altitude only):
System pass.
V-6: Mid Vacuum Switch
circuit is always closed.
V-8: Mid Vacuum Switch
circuit is always closed.
66
I-6: Closed Throttle
Vacuum Switch circuit is
always closed.
50
Page 51

COMPUTER BASICS
What does the Engine Control Computer do?
EEC-IV and MCU
This section explains the EEC-IV engine
computer control system, the types of
sensors and how the computer controls
fuel delivery, idle speed, spark timing
and emission devices. The MCU system
is described later, but this entire section
must still be read for complete understanding.
The following is an introduction to
computer controlled engine systems.
Additional information may be found in
books dealing with this subject available
at your local library or auto parts store.
The more you know about the computer
system, the better and faster you can
troubleshoot and fix problems.
Why Computers?
Computer controls were installed in
vehicles to meet Federal Government
regulations for lower emissions and
better fuel economy. This all began in the
early 1980’s when purely mechanical
control systems just were not good
enough anymore. A computer could be
programmed to precisely control the
engine under various operating
conditions and eliminate some mechanical parts making the engine more
reliable.
What the computer controls
The main control areas of the computer
are:
• Fuel delivery
• Idle speed
• Spark advance timing
• Emission devices (EGR valve, carbon
cannister, etc.)
The changes made to the basic engine
to allow a computer to control these
tasks are the only differences between
an older engine and a computerized one.
A little later we will discuss just how the
computer handles these tasks.
What has NOT changed?
A computer controlled engine is basically
the same as earlier types. It is still an
internal combustion engine with pistons,
spark plugs, valves and cams. The
ignition, charging, starting, and exhaust
systems are almost the same, as well.
You test and repair these systems the
same way as before, using familiar tools.
The instruction manuals for these tools
show you how to perform the tests. Y our
compression gauge, vacuum pump,
dwell-tach meter, engine analyzer, timing
light, etc., are still valuable!
The Engine Computer Control
System
The computer module is the “heart” of
the system. It is sealed in a metal box
and linked to the rest of the system by a
wiring harness. The computer module is
located in the passenger compartment,
usually behind the dashboard or front
kick panels. This protects the electronics
from moisture, extreme temperatures
and excess vibration, which are common
in the engine compartment.
The computer is permanently programmed by factory engineers. The
program is a complex list of instructions
telling the computer how to control the
engine under various driving conditions.
To do its job, the computer needs to
know what is happening and then it
needs devices to control things.
Sensors give the computer
information
The computer can only work with
electrical signals The job of the sensor is
to take something the computer needs to
know, such as engine temperature, and
convert it to an electrical signal which the
computer can understand. Y ou can think
of sensors as “high tech” senders the
devices found in older vehicles for
gauges and dashboard message lights
51
Page 52

INPUT
SENSORS
ECA
BRAINS OF THE
COMPUTER
(oil pressure, fuel level, etc.)
Signals running into the computer
are referred to as “inputs.”
Sensors monitor such things as:
• Engine temperature
• Intake manifold vacuum
• Throttle position
• RPM
• Incoming air (temperature, amount)
• Exhaust gas oxygen content
• EGR Valve flow
Most engine computer systems will use
the sensor types listed above.
Additional sensors may be used
depending upon the engine, vehicle
type or other tasks the computer must
do. Note that information from one
sensor may be used by the computer
for many different tasks. For example,
engine temperature is something the
computer needs to know when
controlling fuel delivery, spark timing,
idle speed and emission systems. The
sensor information may be very
important for one engine control
function, but only used to “fine tune” a
second one.
OUTPUT
ACTUATORS
OFF (no voltage signal to the
computer). Switches connect to two
wires and tell the computer simple
things, such as whether or not the air
conditioner is running.
•
Signal Generator
their own signal to tell the
computer of some condition, such
as exhaust gas oxygen content,
camshaft position, or intake
manifold vacuum. They may have
one, two or three wires connected to
them.
– These create
The computer controls things
with Actuators
The computer can only send out
electrical signals (referred to as
“outputs”). Devices called actuators are
powered by the computer to control
things. Actuator types include:
•
Solenoids
a vacuum signal, bleed air, control fuel
flow, etc.
•
Relays
power devices on and off, such as
electric fuel pumps or electric cooling
fans.
•
Motors
to control idle speed.
– These are used to control
– These switch high amperage
– Small motors are often used
Other output signals
Not all of the computer outgoing signals
go to actuators. Sometimes information is
sent to electronic modules, such as
ignition or trip computer.
There are several types of
sensors
•
Thermistor
resistance changes with temperature.
It is used to measure temperatures of
coolant or incoming air. It has two
wires connected to it.
•
Potentiometer
position, such as throttle position or
EGR valve position. It connects to
three wires: one for power, one for
ground and one to carry the position
signal back to the computer.
•
Switches
(voltage signal to the computer) or
– This is a resistor whose
– This signals a
– These are either ON
How the computer controls
Fuel Delivery
Operation and emission performance
depend upon precise fuel control. Early
computer controlled vehicles used
electronically adjustable carburetors, but
fuel injectors were soon introduced.
The job of the computer is to provide the
optimum mixture of air and fuel (air/fuel
ratio) to the engine for best performance
under all operating conditions.
The computer needs to know:
• ...what the engine operating condition
52
Page 53

is. Sensors used: coolant temperature, throttle position, manifold
absolute pressure, mass air flow,
RPM.
• ...how much air is coming into the
engine. Sensors used: mass air flow
or a combination of manifold absolute
pressure, manifold air temperature,
RPM.
• ...how much fuel is being delivered. The
computer knows this by how long it
turns on the fuel injectors. (The
computer uses a “feedback control” or
“duty cycle” solenoid on electronic
controlled carburetors.)
• ...that everything is working the way it
should. Sensor used: exhaust gas
oxygen sensor.
Note: Not all engines use every sensor
listed above.
Cold engine warm-up condition
“Open Loop” operation
The coolant temperature sensor tells the
computer how warm the engine is.
Factory engineers know what the best
air/fuel mixture is for the engine at
various operating temperatures. (More
fuel is needed for a cold engine.) This
information is permanently programmed
into the computer. After the computer
knows the engine temperature, it
determines the amount of air coming in,
then it will look at its programming to find
out how much fuel to deliver and operate
the fuel injectors accordingly. (Engines
with feedback carburetors don’t do any
of this. They use a “Variable Voltage
Choke.” The computer controls the
amount of choke opening.)
This is an example of “Open Loop”
operation by the computer. The control
system performs an action (expecting a
certain result), but has no way of
verifying if the desired results were
achieved. In this case, the computer
pulses a fuel injector expecting a certain
amount of fuel to be delivered. (The
computer assumes everything in the fuel
system is operating as expected.) In
open loop operation, the computer has
no way of checking the actual amount of
fuel delivered. Thus, a faulty injector or
incorrect fuel pressure can change the
amount of fuel delivered and the
computer would not know it.
Hot engine cruise condition
“Closed Loop” operation
The computer watches the coolant
temperature and throttle position sensors
to tell when the engine is all warmed up
and cruising. As before, the computer
determines the amount of air coming into
the engine, then delivers the amount of
fuel that should provide the optimum air/
fuel mixture. The big difference is that
this time the computer uses the oxygen
sensor to check how well it’s doing and
readjust things, if needed, to make sure
the fuel delivery is correct.
This is an example of “Closed Loop”
operation. The control system performs
an action (expecting a certain result),
then checks the results and corrects its
actions (if necessary) until the desired
results are achieved.
The oxygen sensor only works when it is
very hot. Also, it can only monitor the
“hot engine” air/fuel mixture value and
send back a signal to the computer. The
sensor can not monitor the other air/fuel
mixture values used during engine
warm-up, so the computer must operate
“open loop” at that time.
Acceleration, Deceleration & Idle
Conditions
As long as the engine and oxygen
sensor are hot, the computer can
operate “closed loop” for best economy
and least emissions. During the drive
conditions listed above, the computer
may have to ignore the sensor and run
“open loop,” relying on internal programming for fuel delivery instructions. During
idle, for example, the oxygen sensor may
cool down and stop sending a signal. A
different situation can occur during wideopen-throttle acceleration. The computer
sometimes adds additional fuel (on
purpose) for temporary acceleration
power. The computer knows it is running
“rich” so it ignores the sensor signal until
the wide-open-throttle condition is over.
53
Page 54

How the computer controls Idle
Speed
Throttle position and RPM sensors tell
the computer when the vehicle is idling.
(Sometimes an idle position switch on the
throttle is used.) The computer merely
watches RPM and adjusts an idle speed
control device on the vehicle to maintain
the desired idle condition. Note that this
is another example of “closed loop”
operation. The computer performs an
action (activating an idle control device),
then watches the results of its action
(engine RPM) and readjusts as
necessary until the desired idle speed is
achieved.
There are two types of idle speed
control devices. The first is an adjustable throttle stop that can be positioned
by a computer controlled motor. The
second method allows the throttle to
close completely, then has a computer
controlled solenoid to pass air around
the closed throttle to set the idle speed.
Smaller engines can stumble or stall at
idle when the air conditioner compressor turns on or the power steering is
used. To prevent this, switches tell the
computer when these demands are
coming so it can increase the idle
accordingly.
A simple form of idle speed adjustment
using a “throttle kicker” actuator is used
on early EEC-IV V-8 engines. This
device is described later in the MCU
section.
How the computer controls
Spark Advance Timing
You set spark timing in a non-computer
engine by using a timing light and
adjusting the distributor at idle RPM.
During vehicle operation, timing is
changed by either engine vacuum
(vacuum advance function) or by engine
RPM (centrifugal advance function.)
These spark timing changes are done
mechanically inside the distributor.
Computer controlled vehicles using a
distributor still have you set spark timing
by using a timing light and adjusting the
distributor at idle RPM. The timing
changes which occur during vehicle
operation, however, are controlled
electronically. The computer looks at
sensors to determine vehicle speed,
engine load and temperature. (RPM,
throttle position, coolant temperature
and manifold pressure or mass air flow
sensors are used.) Then, the computer
adjusts timing according to factory
programmed instructions. Some vehicles
have a “knock” sensor. The computer
can “fine tune” the spark timing if this
sensor signals an engine knock
condition. A timing advance signal is
sent by the computer to an ignition
module which eventually creates the
spark.
Computer Controlled Emission
Systems
•
EGR Valve
exhaust gases re-enter the intake
manifold and mix with the incoming air/
fuel. The presence of exhaust gases
reduces combustion temperatures in
the cylinders and this reduces
poisonous NOx emissions. The
computer controls the flow of gases
through the EGR valve. The EGR
system is only used during warm
engine cruise conditions. A partially
open EGR valve at other times can
cause stalling.
•
Thermactor Air System
works with the catalytic convertor. The
computer takes outside air from an air
pump and directs it to the exhaust
manifold or catalytic convertor as
necessary for best emission
performance. Refer to “Thermactor Air
System” in Reference Glossary for
more explanation.
•
Fuel Evaporation Recovery System
A special canister collects vapors
evaporating from the fuel tank,
preventing them from escaping into
the atmosphere and causing pollution.
During warm engine cruise conditions,
the computer draws the trapped
vapors into the engine for burning.
(See “CANP” in Reference Glossary.)
– The EGR valve lets
– This system
Other computer functions
The computer controls other odd jobs
like handling “speed control” and
transmission torque convertor lock-up
and shifting functions. Detailed
explanations may be found in your
54
vehicle service manual.
–
Page 55

More information
The Reference Glossary describes the
various sensors and actuators used in
the EEC-IV and MCU systems. Y ou can
learn more by reading these definitions.
THE MCU SYSTEM
(Make sure you have read
everything in the beginning part of
this section before continuing!)
The MCU system is similar (but simpler)
than the EEC-IV version just described.
The MCU computer module is located in
the engine compartment. The MCU uses
sensors to monitor engine operation and
actuators to control things.
What MCU controls
The original MCU just controls fuel
delivery (Air/Fuel ratio) and the
Thermactor Air System. Features added
later included limited control of idle
speed, spark timing retard and fuel
evaporation canister. To do these tasks,
the MCU needs information about
engine temperature, throttle position,
tach signal and knock conditions.
How MCU measures Engine T emperature
• Some MCU systems use a single
electrical switch (“Low Temperature
Switch”). The switch is activated by
vacuum. The vacuum comes from a
“Ported Vacuum Switch” which is
temperature controlled. When engine
temperature reaches a certain value,
the Ported Vacuum Switch sends
vacuum to the Low Temperature
Switch, which toggles and sends a
signal to the MCU computer. The Low
T emperature and Ported Vacuum
switches may be separate units or
combined into one assembly.
• Other MCU systems use two
switches: Mid and Dual T emperature.
The Mid Temperature Switch is similar
to the Low Temperature Switch. The
Dual Temperature Switch sends a
signal when engine temperature is
either cold OR very hot.
How MCU measures Throttle Position
• Some MCU systems use an Idle
Tracking Switch. This is an electrical
switch mounted near the throttle
linkage on the carburetor. The switch
is open when the throttle is resting in
idle position. The switch closes as
soon as the throttle is moved off idle.
A Wide-Open-Throttle (WOT) Vacuum
Switch is also used. Weak manifold
vacuum due to WOT operation causes
the WOT V acuum Switch to send a
signal to the MCU computer.
• Other versions of MCU monitor
engine vacuum to sense idle (high
vacuum), cruise (moderate vacuum)
or WOT (low vacuum) conditions.
Vacuum operated electrical switches
are used. The switches toggle at
various vacuum levels and send
signals to the MCU computer. These
parts are sometimes called “Low”,
“Mid” and “High” vacuum switches (a
“Zone Vacuum Switch” assembly).
Other names are “Wide-OpenThrottle”, “Crowd” and “Closed
Throttle” vacuum switches.
Tach Signal information
The MCU system monitors this ignition
signal to measure engine RPM. A wire
connects the computer to the Tach
terminal on the ignition coil. The
computer watches RPM to insure
smooth operation when the air/fuel
mixture is changed.
Knock Sensor information
Some MCU systems have a Knock
Sensor which sends a pulse signal to the
computer when an engine knock
condition occurs.
How MCU controls Fuel Delivery
The MCU computer controls air/fuel
delivery using a “Feedback Carburetor”.
The choke and idle cam mechanisms
are similar to those on a conventional
carburetor.
• One version has the computer
controlling a fuel metering rod inside
the carburetor. The computer controls
55
Page 56

an electric motor (“Feedback
Carburetor Actuator”) to position this
rod.
• Another method uses a fuel metering
rod positioned by vacuum. The
computer controls vacuum to this rod
by using a “Vacuum Regulator
Solenoid”. The computer sends a
duty cycle signal (see definition in
Reference Glossary) to the solenoid
to vary vacuum.
• A third version has the computer
controlling air into the carburetor idle
and main system vacuum passages.
A “Feedback Control Solenoid” is
used to control air entry. A duty cycle
signal from the computer controls this
solenoid to vary air flow.
Hot engine cruise condition
“Closed Loop” operation
The computer uses the engine
temperature and throttle position
information to tell when the engine is all
warmed up and cruising. At this time the
computer will use the Exhaust Gas
Oxygen sensor to run the engine in a
“closed loop” mode for minimum
emissions and best fuel economy.
Cold start, Acceleration,
Deceleration and Idle
“Open Loop” operation
The computer runs the engine in an
“open loop” mode when sensor
information signals one of the driving
conditions listed above. The computer
relies on factory programmed instructions to determine the proper air/fuel
mixture to deliver.
MCU idle speed adjustment
The MCU system does not control idle
speed – a standard mechanical idle cam
mechanism is used. However, some
MCU systems have a vacuum operated
“Throttle Kicker” actuator. The computer
uses this device to push the throttle
linkage off idle position when additional
idle RPM is required. This happens
when sensors indicate a cold start or
engine overheat condition. The
computer energizes a “Throttle Kicker
Solenoid” to apply vacuum to the
actuator.
MCU spark retard
The MCU system does not control spark
timing – a standard distributor is used.
However, some MCU systems can send
a signal to retard timing if the knock
sensor indicates an engine knock
condition. The computer energizes a
“Spark Retard Solenoid” to bleed control
vacuum from the distributor advance to
retard the ignition timing.
MCU Controlled Emission Systems
•
Thermactor Air System
vehicles have this system which is
similar to the one discussed earlier in
this section. The MCU uses engine
temperature throttle position
information to determine proper
operation of the thermactor system.
•
Fuel Evaporation Recovery System
This system is similar to the one
discussed earlier in this section. It is
only used on some MCU vehicles.
The MCU uses engine temperature
and throttle position information to
determine proper operation of this
system.
– All MCU
–
56
Page 57

REFERENCE GLOSSARY
A/C
Air conditioner
ACC
Air Conditioner Clutch
signal. This tells the ECA
that either the A/C
compressor is running or
that A/C operation is being
requested (depends upon
vehicle).
ACT
Air Charge Temperature
sensor. This sensor is a
thermistor – a resistor
whose resistance
decreases with
temperature. It is threaded
into the intake manifold so
the ECA can determine the
temperature of the
incoming air. This is used
for fuel delivery
calculations.
Actuator
Devices which are powered
by the ECA to control
things. Actuator types
include relays, solenoids
and motors. Actuators allow
the ECA to control engine
operation.
A/F
Air/fuel.
AM-1
Air Management solenoid
#1. Also called TAB
solenoid. (See TAB for
explanation.)
AM-2
Air Management solenoid
#2. Also called TAD
solenoid.
(See TAD definition.)
AXOD
Automatic Transaxle with
Overdrive gear.
BOO
Brake On-Off switch signal.
Tells the ECA when the
brakes are being applied.
BP
Barometric Pressure
sensor. (See MAP
definition.)
CANP
Canister Purge solenoid.
This device controls the
flow of fuel vapors from the
canister to the intake
manifold. The canister
collects vapors evaporating
from the fuel tank,
preventing them from
escaping into the
atmosphere. During warm
engine cruise conditions,
the ECA energizes CANP
so the trapped vapors are
drawn into the engine and
burned.
CCC
Converter Clutch solenoid.
Located in certain
electronically controlled
transmissions. The ECA
uses this solenoid to
control the lock-up clutch in
the torque converter. The
ECA will engage or release
lock-up depending upon
engine operation.
CCS
Coast Clutch Solenoid.
Located in certain
electronically controlled
transmissions. The ECA
uses this solenoid to permit
engine braking during
deceleration when in third
gear (with gear shift lever in
Drive).
CCO
Converter Clutch Override
solenoid. Located inside
transmission having
mechanically controlled
lock-up torque converter.
The ECA uses this solenoid
to disable lock-up under
certain engine operating
conditions.
CFI
Central Fuel Injection. A
fuel injection system having
one (or two) injectors
mounted in a centrally
located throttle body, as
opposed to positioning the
injectors close to an intake
valve port.
57
CID
Cylinder Identification signal.
This is a frequency type
signal coming from a
camshaft mounted sensor.
The ECA uses this signal to
reference fuel injector
operation and synchronize
spark plug firing on
distributorless ignitions.
Closed Loop (C/L)
This is when a control
system performs an action
(expecting a certain result),
then checks the results and
corrects its actions (if
necessary) until the desired
results are achieved.
Example: The ECA pulses a
fuel injector expecting a
certain amount of fuel to be
delivered. In closed loop
operation, the ECA uses a
sensor to check the actual
amount of fuel delivered.
The ECA will correct the
injector pulse width as
necessary to obtain the
desired fuel delivery.
Continuity
An unbroken, continuous
circuit through which an
electric current can flow.
Coolant
Temperature
Switches
Used on MCU systems.
These are vacuum controlled
electrical switches which
signal various engine
operating temperatures to
the MCU module. A ported
vacuum switch is used along
with the temperature
switches. The normally
closed ported vacuum
switches open at a specific
temperature and allow
vacuum to pass. This
vacuum then causes the
temperature switches to
switch and send a signal to
the MCU module. Some
MCU systems use a single
Low Temperature Switch to
tell the MCU module when
the engine has warmed up.
Other MCU systems use two
switches: one for mid
temperature and a second
for high/low temperatures
(the switch will signal when
the temperature is either too
high or too low). The MCU
module uses temperature
Page 58

information when controlling
fuel delivery, Thermactor Air
System, spark retard,
throttle kicker and canister
purge.
CPS
Crankshaft Position
Sensor. This crankshaft
mounted sensor sends a
frequency signal to the
ECA. (See PIP signal
definition.) It is used to
reference fuel injector
operation and synchronize
spark plug firing on
distributorless ignitions.
CS
Clutch switch.
Cylinder
Balance Test
A diagnostic Self-Test only
used on Sequential
Electronic Fuel Injector
(SEFI) engines. The test
turns each injector on and
off to check if they are
closed or damaged.
DCL
Data Communication Link.
A two wire circuit used by
the ECA to exchange
information with other
computer controlled
modules.
Digital Signal
An electronic signal which
has only two (2) voltage
values: a “low” value (close
to zero) and a “high” value
(usually 5 volts or greater).
Sometimes the low voltage
condition is called “Off” and
the high voltage condition
is called “On”. Signals
which can have any
voltage value are called
“analog” signals.
DIS
Distributorless Ignition
System. In general use,
this refers to a system
which produces the ignition
spark without the use of a
distributor. Ford technical
manuals use DIS when
referring to a particular
distributorless ignition
system where the ECA
directly controls timing of
spark firing. (Compare to
EDIS definition.)
Driver
A transistor “switch” inside
the ECA used to apply
power to an external
device. This allows the
ECA to control relays,
solenoids and small
motors.
Duty Cycle
A term applied to frequency
signals – those which are
constantly switching
between a small voltage
value (close to zero) and a
larger value (usually 5 volts
or greater). Duty cycle is
the percentage of time the
signal has a large voltage
value. For example, if the
signal is “high” (large
voltage) half of the time
then the duty cycle is 50%.
If the signal is “high” only
one fourth of the time, then
the duty cycle is 25%. A
duty cycle of 0% means the
signal is always at a “low”
value and not changing. A
duty cycle of 100% means
the signal is always at a
“high” value and not
changing. The engine
control computer uses duty
cycle type signals when it
wants more than just “onoff” control of an actuator.
This is how it works: A 50%
duty cycle signal going to a
vacuum switching solenoid
means the solenoid will be
“on” (passing full vacuum)
half the time and “off”
(passing no vacuum) half
the time. The average
amount of vacuum passing
through the solenoid will be
one half of the full value
because the solenoid is
only “on” for one half of the
time. (The signal switches
at a rapid rate, such as ten
times a second.) Thus, the
computer can get a
vacuum controlled actuator
to move half way between
“no vacuum” position and
“full vacuum” position.
Other positions can be
achieved by changing the
duty cycle of the control
signal which in turn
changes the average
amount of control vacuum.
DVM
Digital Volt Meter. An instrument using a numeric readout to display measured
voltage values as opposed
to a moving needle on a
gauge face. Usually the
instrument has other measuring capabilities, such as
resistance and current, and
may be called a DMM
(Digital Multi-Meter). Most
DVM’s have 10 Megohm
input impedance. This means
the circuit under test will not
be electronically disturbed
when the DVM is connected
for a measurement.
Dynamic
Response
A user action expected by
the ECA during the course
of a diagnostic Self-Test.
Normally, this means
performing a brief wideopen-throttle action during
the Engine Running SelfTest. The ECA sends a
single voltage pulse through
the STO circuit (making a
blink on the Code Scanner
LED) signaling the user to
perform the Dynamic
Response action.
ECA
Electronic Control
Assembly. The “brains” of
the engine control system. It
is a computer housed in a
metal box with a number of
sensors and actuators
connected with a wiring
harness. Its job is to control
fuel delivery, idle speed,
spark advance timing and
emission systems. The ECA
receives information from
sensors, then energizes
various actuators to control
the engine. Sometimes
vehicles have additional
computers controlling other
functions. These include
anti-lock brake and active
suspension systems.
ECT
Engine Coolant Temperature
sensor. This sensor is a
thermistor – a resistor whose
resistance decreases with
increases in temperature.
The sensor is threaded into
the engine block and
contacts the engine coolant.
The ECA uses this signal for
control of fuel delivery, spark
advance, EGR flow and
other emission control
devices.
58
Page 59

EDF
Electro-Drive Fan relay.
The ECA energizes this
relay to apply power to the
Electro-Drive Fan (mounted
in front
of the radiator) for engine
cooling purposes. The fan
is only turned on when the
ECA determines cooling is
necessary.
EDIS
Electronic Distributorless
Ignition System. Ford
technical manuals use
EDIS when referring to a
particular distributorless
ignition system where a
separate module (EDIS
module) directly controls
spark firing and
synchronization. All the
ECA does is send a signal
requesting a particular
spark timing based on
engine operation. (Refer to
SAW definition.) The EDIS
module and associated
sensors take care of all
other aspects of ignition
system operation.
EEC-IV
Electronic Engine Control
system, version 4. The
name for Ford’s
computerized engine
control system used on
vehicles starting in 1983.
The system consists of a
control module (ECA)
containing a computer, and
several different sensors
and actuators. The system
controls fuel delivery, idle
speed, ignition timing and
various emission devices.
EFI
Electronic Fuel Injection. In
common usage, this term
applied to any system
where a computer controls
fuel delivery to an engine
by using fuel injectors. In
Ford vehicle usage, an EFI
system is one using one
injector for each cylinder.
The injectors are mounted
in the intake manifold. The
injectors are fired in groups
(“banks”). Usually all
injectors on one side of the
engine are fired together.
Injectors are fired
individually in SFI engines
(see SFI definition).
EGO
Exhaust Gas Oxygen
sensor. The EGO sensor is
threaded into the exhaust
manifold, directly into the
stream of the exhaust
gases. The ECA uses the
sensor to “fine tune” fuel
delivery. The sensor
generates a voltage of 0.6
to 1.1 volts when the
exhaust gas is rich (low
oxygen content). The
voltage changes to 0.4
volts or less when the
exhaust gas is lean (high
oxygen content). The
sensor only operates after
it reaches a temperature of
349°C (660°F).
EGR
Exhaust Gas Recirculation.
The EGR system
recirculates exhaust gases
back into the intake
manifold to reduce NOx
emissions. Various types of
systems are in use on
different vehicles. Usually
the ECA directly controls
EGR flow, but on some
vehicles it may just activate
a system controlled by nonelectronic means. Vacuum
controlled EGR valves are
normally closed. Applying
vacuum opens the valve.
EGR-C
EGR Control solenoid. Used
in certain EGR systems.
The ECA energizes this
actuator to apply vacuum
(and thus open) the EGR
valve. Used along with the
EGR-V solenoid.
EGR S/O
EGR valve Shut-Off
solenoid. Used in
mechanically operated
EGR systems where the
ECA does not control EGR
flow. The ECA can
completely stop flow by
energizing this solenoid, if
engine operating conditions
require this.
EGR-V
EGR Vent solenoid. Used
in certain EGR systems.
The ECA energizes this
actuator to vent vacuum
(and thus close) the EGR
valve. Used along with the
EGR-C solenoid.
59
EHC
Exhaust Heat Control
solenoid. The ECA
energizes this solenoid to
apply vacuum (and thus
activate) the EHC valve.
When activated, this valve
diverts hot gases from the
exhaust manifold to the
intake manifold heat riser
pad. Heat is transferred
from the exhaust gas to the
riser pad, which in turn
heats the incoming air. This
aids in fuel atomization for
better combustion efficiency
during engine warm-up.
EIC
Electronic Instrument
Cluster. A vehicle instrument
panel using electronic
displays (numbers or bar
graph type) in place of
standard gauges. Receives
information from the ECA by
using the Data
Communications Link (DCL).
EMI
Electromagnetic
Interference. Undesired
signals interfering with a
needed signal. For
example: static on a radio
brought about by lightning
flashes or closeness to
high voltage power lines.
EPC
Electronic Pressure Control
solenoid. Located in certain
electronically controlled
transmissions. Used by the
ECA to set hydraulic line
pressures inside the
transmission – for soft or
firm shifting (depending
upon vehicle acceleration).
EVP
EGR Valve Position sensor.
This sensor is mounted on
top of the EGR valve. It
monitors the position of the
EGR valve stem (that is,
how far the valve is open).
This signal allows the ECA
to calculate EGR flow at
any time.
EVR
EGR Vacuum Regulator
solenoid. This solenoid is
controlled by a duty cycle
signal from the ECA and is
used to vary the amount of
vacuum applied to the EGR
valve. The solenoid not
only controls the vacuum, it
also functions as a vent to
allow the EGR valve to
close. The ECA controls
the amount of EGR valve
opening by adjusting the
vacuum being applied.
(See Duty Cycle definition.)
Page 60

FBC
Feedback Carburetor. This
is used on early versions of
computer controlled
engines. It is a carburetor
which can have its air/fuel
delivery modified by an
electronic signal from the
ECA. Three versions are
used. See definitions for
FBCA, FCS and VRS.
FBCA
Feedback Carburetor
Actuator. Used on
feedback carburetors –
those where the engine
computer controls the air/
fuel ratio.
The FBCA is a stepper
motor (see Stepper Motor
definition). It controls a
metering assembly in the
carburetor which can vary
the amount of air entering
the main discharge area.
The computer uses FBCA
to vary this metered air and
control air/fuel mixtures
anywhere from “rich” to
“lean”.
FCS
Feedback Control Solenoid.
Used on feedback
carburetors – those where
the engine computer
controls the air/fuel ratio.
This solenoid receives a
duty cycle signal from the
computer. (See Duty Cycle
definition.) The solenoid
introduces fresh air from
the air cleaner into the idle
and main system vacuum
passages. A low duty cycle
signal reduces air passing
through the solenoid for
“rich” operation. A high duty
cycle signal increases air
passing through the
solenoid for “lean”
operation.
FMEM
Failure Management and
Effects Mode. The name
given to the way the ECA
operates when failures are
detected in sensor or actuator
circuits and normal operation
is no longer possible. The
ECA runs the engine the best
way it can until the vehicle
driver can get the problem
repaired. The effect on engine
performance can be slight or
severe.
Frequency
The frequency of an
electronic signal is a
measure of how often the
signal repeats a voltage
pattern in a one second
time span. For example:
suppose a signal starts at
zero volts, goes to five
volts then returns to zero
again. If this pattern
repeats itself 100 times in
one second, then the signal
frequency is 100 cycles per
second – or 100 Hertz.
Fuel Injector
An electronically controlled
flow valve. Fuel injectors
are connected to a
pressurized fuel supply.
(The pressure is created by
a fuel pump.) No flow
occurs when the injector is
off (not energized). When
the injector is powered, it
opens fully allowing the fuel
to flow. The ECA controls
fuel delivery by varying the
amount of time the injectors
are turned on.
FP
Fuel Pump relay. The ECA
energizes this relay to
apply power to the vehicle
fuel pump. For safety
reasons, the ECA removes
power from the fuel pump
when ignition signals are
not present.
FPM
Fuel Pump Monitor signal.
This is a wire between the
ECA and the fuel pump
motor power terminal. The
ECA uses this signal to
verify when voltage is at
the fuel pump (for
diagnosing fuel system
problems).
Ground
The return path for current
to flow back to its source.
(Usually the negative
battery terminal.) It is also
the reference point from
which voltage
measurements are made.
That is, it is the connection
place for the minus (-) test
lead from the voltmeter.
HEDF
High-speed Electro-Drive
Fan relay. The ECA
energizes this relay when it
determines extra engine
cooling (more than that
provided by EDF) is
necessary. Depending
upon the vehicle, the HEDF
relay will either speed-up
the same fan used by EDF,
or it will turn on a second
fan mounted in front of the
radiator.
HEGO
Heated Exhaust Gas
Oxygen sensor. An EGO
sensor (see EGO
definition) having a built-in
electric heating element.
The heater reduces sensor
warm-up time.
Hertz (Hz)
A term for frequency –
cycles per second.
IAC
Intake Air Control.
IDM
Ignition Diagnostic Monitor.
A wire between the ECA
and the switched side
(Tach terminal) of the
ignition coil. The ECA uses
this circuit to check for the
presence of ignition pulses.
Inputs
Electrical signals running
into the ECA. These
signals come from sensors,
switches or other electronic
modules. They give the
ECA information about
vehicle operation.
Integrated
Relay Control
Module (IRCM)
A single module containing
several relays and some
other circuitry. The ECA
uses these relays for
control of functions such as
fuel pump, air conditioner
clutch, electric cooling fan
and EEC-IV system power.
60
Page 61

ISC
Idle Speed Control. This
refers to a small electric
stepper motor mounted on
the throttle body and
controlled by the ECA. (See
Stepper Motor definition.)
The ISC motor moves a
spindle back and forth.
When the throttle is
released during idle, it rests
on this spindle. The ECA
can control idle speed by
adjusting this spindle
position. The ECA
determines the desired idle
speed by looking at coolant
temperature, engine load
and RPM. The Idle
Tracking Switch (see ITS
definition) is built-into the
tip of the spindle. The ISC
motor also performs
dashpot and anti-dieseling
functions.
ISC-BPA
Idle Speed Control By-Pass
Air valve. This is a solenoid
type actuator mounted on
the throttle body and
controlled by the ECA with
a duty cycle type signal.
(See Duty Cycle definition.)
It is used for idle speed
control. The valve operates
by regulating the amount of
incoming air bypassing the
closed throttle plate. When
the ECA increases control
signal duty cycle, more air
is bypassed through the
valve for faster idle speed.
The ECA determines the
desired idle speed by
looking at coolant
temperature, engine load
and RPM. The ISC-BPA
also performs dashpot and
anti-dieseling functions.
ITS
Idle Tracking Switch. This
is a mechanical switch
built-into the tip of the Idle
Speed Control motor
spindle. (See ISC
definition.) The ECA uses
this switch to identify
closed throttle condition.
The switch is open when
the throttle rests on it
(closed throttle position).
The MCU systems use a
similar acting ITS which is
mounted on the carburetor
near the throttle linkage.
IVSC
Integrated Vehicle Speed
Control. The name given to
the speed control function
when it is built-into the ECA
and not controlled by an
outside module.
KAPWR
Keep Alive Power. A power
connection running from
the ECA directly to the
vehicle battery. This power
is used energize the
“learning memory” circuits
inside the ECA – even
when the ignition key is off.
The memory stores
adjustment information the
ECA uses to compensate
for aging sensors, and the
like. The information is lost
when power is
disconnected, such as
when the vehicle battery is
removed for service, but
can be “relearned” by the
ECA during normal engine
operation.
Keypower
The circuit which provides
power to the engine control
system. Includes the
ignition key switch.
KS
Knock Sensor. The ECA
uses this device to detect
engine detonation
(knocking). When spark
knock occurs, the sensor
sends a pulsing signal. The
ECA than retards spark
advance until no detonation
is sensed. The sensor
contains a piezoelectric
element and is threaded
into the engine block.
Vibrating the element
generates the signal.
Special construction makes
the element only sensitive
to the engine vibrations
associated with knocking.
LED
Light Emitting Diode. A
semiconductor device
which acts like a miniature
light bulb. When a small
voltage is applied, the LED
glows. LED’s may be red,
orange or yellow or green.
They are often used as
indicators or in numeric
displays.
LUS
Lock-Up solenoid. Located
in automatic transaxle. The
ECA uses this solenoid to
control the lock-up clutch in
the torque converter. The
ECA
will engage or release lockup depending upon engine
operation.
61
MAF
Mass Air Flow sensor. This
sensor measures the
amount of air entering the
engine and sends a voltage
signal to the ECA. The
signal voltage increases
when the amount of
incoming air goes up. This
gives the ECA information
required for control of fuel
delivery, spark advance
and EGR flow.
MAP
Manifold Absolute Pressure
sensor. This sensor
measures manifold vacuum
and sends a frequency
signal to the ECA. This
gives the ECA information
on engine load for control
of fuel delivery, spark
advance and EGR flow.
MCCA
Message Center Control
Assembly. A dashboard
mounted electronic display
giving the driver trip
computer and vehicle
status information.
Exchanges information with
the ECA by using the Data
Communications Link
(DCL).
MCU
Microprocessor Control
Unit. A computerized
engine control module used
on many Ford vehicles
between 1980 and 1984.
The MCU system consists
of a computerized control
module (MCU), sensors
and actuators. The system
controls fuel delivery and
thermactor air flow. Later
versions of MCU also
controlled canister purge
(see CANP definition),
spark retard and idle
speed. The MCU system
was eventually replaced by
EEC-IV.
MLP
Manual Lever Position
sensor. Connected to gear
shift lever. Sends a voltage
signal to the ECA indicating
lever position (P, R, N, D, 2
or 1).
Mode
A type of operating
condition, such as “idle
mode” or “cruise mode.”
Page 62

NDS
Neutral Drive Switch. Used
on vehicles with automatic
transmissions. The ECA
uses this switch to
determine when the
transmission is in or out of
gear. The ECA can adjust
idle speed to compensate
for increased engine
loading due to engaged
transmission.
NGS
Neutral Gear Switch. Used
on vehicles with manual
transmissions. The ECA
uses this switch to
determine when the
transmission is in or out of
gear.
NPS
Neutral Pressure Switch.
Located in automatic
transaxle. The ECA uses
this switch to determine
when the transaxle is in or
out of gear.
OCS
Overdrive Cancel Switch.
Used by vehicle operator.
Signals ECA to prevent
shifting transmission into
overdrive (4th gear)
regardless of operating
conditions.
OCIL
Overdrive Cancel Indicator
Light. Located in
passenger compartment.
Light turns on when vehicle
operator uses Overdrive
Cancel Switch to disable
4th gear transmission
operation.
Open (circuit)
A break in the continuity of
a circuit such that no
electrical current can flow.
Open Loop (O/
L)
This is when a control
system performs an action
(expecting a certain result),
but has no way of verifying
if the desired results were
achieved. Example: The
ECA pulses a fuel injector
expecting a certain amount
of fuel to be delivered. (The
ECA assumes everything
in the fuel system is
operating as expected.) In
open loop operation, the
ECA has no way of
checking the actual amount
of fuel delivered. Thus, a
faulty injector or incorrect
fuel pressure can change
the amount of fuel delivered
and the ECA would not
know it.
Outputs
Electrical signals sent from
the ECA. These signals
may activate relays or
other actuators for control
purposes around the
vehicle. The signals can
also send information from
the ECA to other electronic
modules, such as ignition
or trip computer.
PFE
Pressure Feedback EGR
sensor. The ECA uses this
sensor to determine the
amount EGR flow. The task
is involved. In this EGR
system, a small opening
separates the exhaust
manifold from the EGR
valve input. All the gases
flowing through the EGR
valve must first pass
through this opening.
Scientific principles allow
the ECA to calculate EGR
flow providing it can
determine the pressure on
both sides of this opening
(that is, both the EGR valve
input side and the manifold
side). The PFE sensor
measures the pressure
seen at the EGR side. The
sensor sends a voltage
signal which increases as
pressure is increased. The
manifold side pressure must
be calculated by the ECA
based on RPM, exhaust
system characteristics and
other information. The ECA
can then finally calculate
EGR flow. Note that with
this system, the PFE signal
is NOT a direct measure of
EGR flow!
PIP
Profile Ignition Pick-Up
signal. It is a frequency
type, providing crankshaft
position and speed
information. The ECA uses
PIP as a reference to
create properly timed
ignition system and fuel
injector signals. The PIP
signal comes from a sensor
mounted in the distributor
(TFI-IV ignitions) or from a
separate crankshaft
mounted sensor
(Crankshaft Position
Sensor) used on
distributorless ignitions.
62
PSPS
Power Steering Pressure
Switch. This tells the ECA
when power steering is
being used. The ECA can
prevent stalling on a small,
idling engine by watching
this switch and increasing
idle speed if power steering
is being used.
Quick Test
Another name for Self-Test.
(See Self-Test definition.)
Relay
A mechanical device for
switching high current
circuits on and off. It is
electronically controlled by
a low current circuit.
Relays allows a low power
ECA signal to control a
high power device such as
an electric cooling fan.
ROM
Read-Only Memory. This is
inside the ECA. The ROM
contains permanent
programming information
the ECA needs to operate
a specific vehicle model.
Included are vehicle
weight, engine and
transmission type, axle
ratio and other specifics.
SAW
Spark Advance Word.
A signal used in some
Distributorless Ignition
Systems. Sent from the
ECA to the DIS ignition
module to control spark
advance timing. The SAW
signal is a series of voltage
pulses. The width of the
pulses is what tells the DIS
module what timing is
desired – wider pulses
mean less spark advance.
An extra-wide pulse puts
the DIS module
in a “repetitive spark” mode
where several sparks are
generated for every
cylinder firing (used on
some vehicles at idle for
lower emissions and
smoother performance).
Self-Test
Sometimes called “Quick
Test”. A series of tests
built-into the ECA which
help locate vehicle
problems.
The Code Scanner is used
to perform the tests and get
the results (in the form of
code numbers).
Page 63

Self-Test
Connector
The connector that the
Code Scanner plugs into
for testing purposes. The
connector is wired to the
ECA, and is located in the
engine compartment. Tests
are run and codes are read
with the Code Scanner
connected. Sometimes this
connector is called VIP
(Vehicle in Process).
Self-Test Input
(STI)
A wire between the ECA
and either the Self-Test
connector (MCU systems)
or a separate connector
(EEC-IV systems). The
wire is used to activate the
Self-Test procedures. The
Code Scanner connects
STI to vehicle ground when
the Test/Hold switch is in
the TEST position and
disconnects STI when the
Test/Hold switch is in the
HOLD position.
Self-Test
Output (STO)
A wire between the ECA
and the Self-Test
connector. Results of
vehicle diagnostic tests are
sent along this circuit by
using a voltage pulse
signal. The signal switches
between “High” (+5 volts)
and “Low” (close to zero
volts). The Code Scanner
light is OFF when STO is
“High” and ON when STO
is “Low”. Note: the light
may be on or off when the
ignition key is off – depends
upon vehicle. The flashes
represent code numbers
used to locate problems.
Sensor
Device which give the ECA
information. The ECA can
only work with electrical
signals. The job of the
sensor is to
take something the ECA
needs to know, such as
engine temperature, and
convert it to an electrical
signal which the ECA can
understand. The ECA uses
sensors to measure such
things as throttle position,
coolant temperature,
engine speed, incoming air,
etc.
SFI or SEFI
Sequential Fuel Injection or
Sequential Electronic Fuel
Injection. A fuel injection
system using one injector
for each cylinder. The
injectors are mounted in the
intake manifold. The
injectors are fired
individually in the same
sequence as the spark plug
firing sequence.
Short (circuit)
A fault condition: an
unwanted connection of
one electric circuit to
another causing a change
in the normal current flow
path.
Solenoid
A device to convert an
elec- trical current to
mechanical motion. It
consists of a coil of wire
with a movable metal rod in
the center. When power is
applied to the coil, the
resulting electromagnetism
moves the rod and
performs some mechanical
action. The ECA often uses
solenoids to switch vacuum
lines on and off. This allows
the ECA to control vacuum
operated devices such as
an EGR valve. Fuel
injectors are another type
of solenoid.
Spark Retard
Solenoid
Used on MCU systems
having a knock sensor. The
MCU module energizes this
solenoid during engine
knock conditions. The
solenoid bleeds vacuum
from the distributor
advance to retard spark
timing.
SPOUT
Spark Output signal from
the ECA. Sent to TFI-IV or
DIS ignition modules to fire
the ignition coil(s) and
create spark voltage.
SS1
Shift Solenoid #1. Located
in certain electronically
controlled transmissions
along with Shift Solenoid
#2. The ECA energizes
these solenoids (one or
both) to engage the desired
transmission gear.
Stepper Motor
A special type of electric
motor with a shaft that
rotates in small “steps”
instead of a continuous
motion. A certain sequence
of frequency type signals is
required to step the motor
shaft. A different signal
sequence will step the shaft
in the opposite direction.
No signals keeps the shaft
still in position. A constant
signal drive will
continuously rotate the
shaft. The shaft is usually
connected to a threaded
assembly which moves
back and forth to control
things such as throttle
position. The engine
computer sends the correct
signals to the motor for
control.
STI
Self-Test Input. (See SelfTest Input definition.)
STO
Self-Test Output. (See SelfTest Output definition.)
TAB
Thermactor Air Bypass
solenoid. (Sometimes
called AM-1.) The ECA
energizes this solenoid to
apply vacuum (and thus
activate) the TAB valve.
Normally, this valve allows
incoming air to pass into
the rest of the system.
When activated, the valve
takes the incoming air and
dumps it back into the
atmosphere. Refer to
Thermactor Air System
description for more details.
TAD
Thermactor Air Diverter
solenoid. (Sometimes
called AM-2.) The ECA
energizes this solenoid to
apply vacuum (and thus
activate) the TAD valve.
Normally, this valve directs
incoming air to the catalytic
converter. When activated,
the valve takes the
incoming air and and
directs it to the exhaust
manifold. Refer to
Thermactor Air System
description for more details.
TDC
Top Dead Center. When a
piston is at its uppermost
position in the cylinder –
maximum compression.
63
Page 64

TFI-IV
Thick Film Ignition system,
version 4. An ignition
system consisting of a
distributor, ignition coil and
TFI-IV module. The ECA
controls the spark advance
timing. A camshaft position
sensor in the distributor
sends a reference signal
(called PIP) to the ECA.
The ECA sends a spark
advance signal (called
SPOUT) to the TFI-IV
module which fires the
spark coil. The distributor
mechanically switches the
spark voltage to the various
plugs in the usual manner.
The ECA determines
optimum spark timing from
sensor information – engine
speed and RPM, throttle
position, coolant
temperature, engine load,
vehicle speed, gear lever
position and knock sensor
condition.
Thermactor Air
System
An emission control system
consisting of an air pump,
air flow control valves (TAB
& TAD) and a catalytic
converter. The converter
removes pollutants from the
exhaust stream. An air
pump brings outside air
(when needed) and sends
it either to the exhaust
manifold (“upstream”) or
directly into the converter
(“downstream”). The ECA
controls the air path for
best performance under
different engine operating
conditions. The air pump
always runs when the
engine runs. Usually the
incoming air is directed to
the converter. Air is kept
out during extended idling
(prevent converter
overheat) or during very
cold engine starting. Air
goes into the exhaust
manifold during normal
engine warm-up. This helps
burn hot, unused fuel
vapors in the exhaust
stream (reduces pollutants
– speeds exhaust warmup). The TAB and TAD
valves may be separate
units, or combined into one
assembly.
Thermistor
A resistor whose resistance
changes with temperature.
Thermistors are used as
sensors for vehicle coolant
and manifold air
temperature. The
resistance decreases as
temperature goes up.
THS 3/2 and
THS 4/3
Transmission Hydraulic
Switch. These are pressure
switches used in some
automatic transaxles. They
send gear information to
the ECA as follows: THS 3/
2 (only) signal means 2nd
gear. Both THS 3/2 and
THS 4/3 signals means 3rd
gear. THS 4/3 (only) signal
means 4th gear.
TK
Throttle Kicker solenoid.
The ECA uses this solenoid
to apply vacuum (and thus
activate) the throttle kicker
actuator. The actuator
increases the amount of
idle position throttle
opening by a fixed amount.
The
ECA activates TK when
operating conditions require
faster idle, such as when
the A/C compressor is on,
or during cold engine
start-up.
TOT
Transmission Oil
Temperature sensor. This
sensor is a thermistor – a
resistor whose resistance
decreases with temperature. It lies within the
transmission housing in
contact with the oil. The
ECA uses this sensor to
monitor transmission
operating temperature.
TP
Throttle Position sensor.
This is a rotary type
potentiometer connected to
the throttle shaft. It has a
voltage signal output which
increases as the the throttle
is opened. The ECA uses
this sensor to determine if
the engine is in idle, part
throttle or wide-openthrottle operation. Then the
ECA can properly control
systems such as idle
speed, spark advance, fuel
delivery and emission
controls.
TTS
Transmission Temperature
Switch. Sends a
temperature status signal
to the ECA.
Vacuum Switch
A vacuum operated
electrical switch. The
switching action occurs
when applied vacuum
reaches a certain level. The
switches may either be
normally closed or normally
open. These are used
mainly in the MCU engine
control system. The
switches send signals to
the MCU module.
VAF
Vane Air Flow sensor.
This sensor is a rotary type
potentiometer connected to
a moveable flap. It is
located inside the vane
meter assembly – a
housing between the air
cleaner and throttle body
through which all incoming
air passes. Flowing air
pushes against the flap.
The sensor sends a signal
based on the flap position.
The voltage signal
increases when the flap
moves because of
increased incoming air
flow. The ECA determines
the amount of incoming air
with this sensor. This
information is used for for
control of fuel delivery,
spark advance and EGR
flow.
VAT
Vane Air Temperature
sensor. This sensor is a
thermistor – a resistor
whose resistance
decreases with
temperature. It is located
inside the vane meter
assembly – a housing
between the air cleaner
and throttle body through
which all incoming air
passes. The ECA
measures incoming air
temperature with this
sensor. This information is
used for fuel delivery
calculations.
64
Page 65

VCRM
Variable Control Relay
Module. Contains
electronic switches to
control power to A/C clutch,
engine cooling fan, fuel
pump, etc. ECA controls
module. A 2-wire DCL
circuit carries ECA
instruction signals to a
computer circuit inside
VCRM. Power delivered by
VCRM can be adjusted so
that, for example, engine
fan can be slowly turned on
or run at various speeds.
VRS
(EEC-IV systems): Variable
Reluctance Sensor. A
sensor mounted on the
crankshaft which sends a
frequency type signal to the
ECA. The ECA uses VRS
to obtain information on
crankshaft position and
speed.(MCU systems):
Vacuum Regulator
Solenoid. Used with
feedback carburetors
having a vacuum controlled
fuel metering system.
(Feedback carburetors let
the engine computer
control air/fuel ratios.) The
MCU module sends a duty
cycle signal to VRS which
controls vacuum applied to
the fuel metering rod in the
carburetor. (See Duty
Cycle definition.) A low duty
cycle signal reduces
control vacuum for “rich”
operation.
A high duty cycle signal
increases control vacuum
for “lean” operation.
VSS
Vehicle Speed Sensor.
This sensor, mounted in
the transmission, sends a
frequency signal to the
ECA. The frequency
increases as the vehicle
moves faster to give the
ECA vehicle speed
information.
VVC
Voltage Variable Choke
actuator. Used on feedback
carburetors in MCU
systems. The MCU module
sends a duty cycle type
signal to this actuator in
order to control the amount
of choke opening. (See
Duty Cycle definition.)
WAC
Wide-open-throttle Air
conditioner Cut-off relay.
Used by the ECA to turn off
the A/C clutch and thus
reduce engine loading. This
is desirable during heavy
acceleration, engine cranking
or engine overheating
conditions.
WOT
Wide Open Throttle. The
vehicle operating condition
brought about when the
throttle is completely (or
nearly so) open. The ECA
typically delivers extra fuel to
the engine at this time for
acceleration purposes. The
ECA uses the Throttle
Position sensor to identify the
WOT condition.
WOT Vacuum
Switch
Wide Open Throttle
Vacuum Switch. Used on
MCU systems. The switch
is closed when applied
vacuum is weak, and open
when vacuum is strong. The
MCU module detects WOT
operation when the weak
manifold vacuum present
during WOT conditions
causes the vacuum switch to
close. The MCU module
provides extra fuel at this
time for acceleration
purposes.
Zone Vacuum
Switches
Used in some
Microprocessor Control Unit
(MCU) systems. These three
switches are used to detect
low, medium and high
vacuum levels in the intake
manifold. They send electrical
signals to the MCU module.
The MCU module can then
calculate throttle position and
engine load.
65
Page 66

ONE (1) YEAR LIMITED W ARRANTY
Actron Manufacturing Company (“Actron”) warrants to the original purchaser that this product will be free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one (1) year from
the date of original purchase. Any unit that fails within this period will be replaced or repaired
at Actron’s discretion without charge. If you need to return product, please follow the instructions below. This warranty does not apply to damages (intentional or accidental), alterations
or improper or unreasonable use.
ACTRON DISCLAIMS ALL EXPRESS WARRANTIES EXCEPT THOSE THAT APPEAR
ABOVE. FURTHER, ACTRON DISCLAIMS ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OF THE GOODS OR FITNESS OF THE GOODS FOR ANY PURPOSE. (T O THE
EXTENT ALLOWED BY LA W , ANY IMPLIED W ARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR OF
FITNESS APPLICABLE TO ANY PRODUCT IS SUBJECT TO ALL THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THIS LIMITED WARRANTY. SOME STA TES DO NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS
ON HOW LONG AN IMPLIED W ARRANTY LASTS, SO THIS LIMIT A TION MA Y NOT APPL Y
TO A SPECIFIC BUYER.)
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY
IN NO CASE SHALL ACTRON BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES BASED UPON ANY LEGAL THEORY INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, DAMAGES FOR LOST PROFITS AND/OR INJURY TO PROPERTY. SOME
STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THIS LIMIT ATION OR EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO A
SPECIFIC BUYER. THIS WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS, AND YOU
MAY ALSO HAVE OTHER RIGHTS WHICH VARY FROM STATE TO ST ATE.
TO USE YOUR W ARRANTY
If you need to return the unit, please follow this procedure:
1. Call Actron Tech Support at (800) 253-9880. Our Technical Service representatives are
trained to assist you.
2. Proof of purchase is required for all warranty claims. Please retain your sales receipt.
LIMITATION OF REMEDIES
3. In the event that product needs to be returned, you will be given a Return Material
Authorization number.
4. If possible, return the product in its original package with cables and accessories.
5. Print the RMA number and your return address on the outside of the package and send to
the address provided by your Customer Service representative.
6. Y ou will be responsible for shipping charges in the event that your repair is not covered by
warranty.
OUT OF WARRANTY REPAIR
If you need product repair after your warranty has expired, please call Tech Support at (800)
253-9880. You will be advised of the cost of repair and any freight charges.
All information, illustrations and specifications contained in this manual are based on the latest information
available from industry sources at the time of publication. No warranty (expressed or implied) can be made
for its accuracy or completeness, nor is any responsibility assumed by Actron or anyone connected with it for
loss or damages suffered through reliance on any information contained in this manual or misuse of
accompanying product. Actron reserves the right to make changes at any time to this manual or
accompanying product without obligation to notify any person or organization of such changes.
66
 Loading...
Loading...