Yaesu VX-7R Service Manual
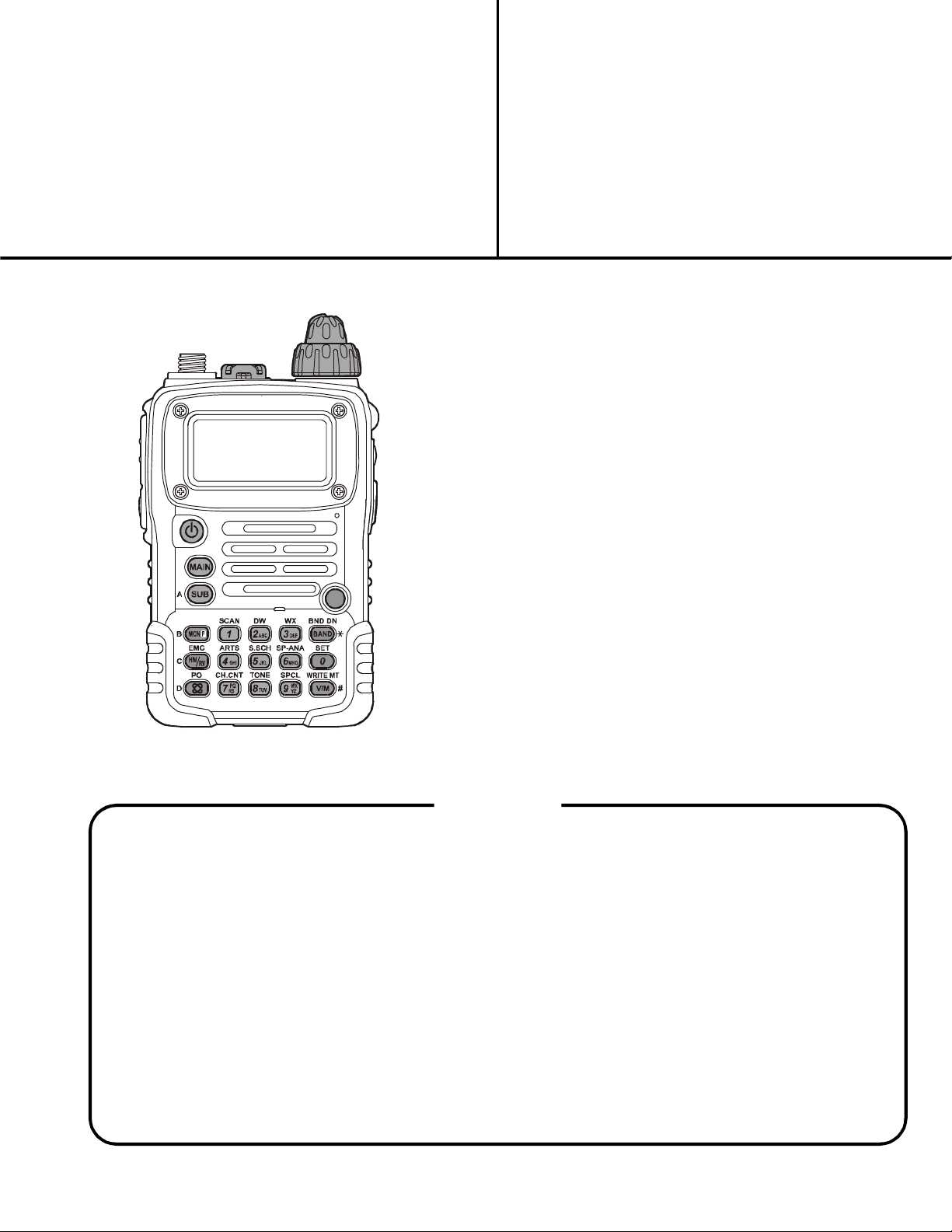
50/144/430 MHz Triple-Band
DW
Heavy Duty Submersible Transceiver
VX-7R
Technical Supplement
©2002 VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD. Printed in Japan.
EH009M90A
Introduction
the VX-7R 50/144/430 MHzTriple-Band Heavy Duty Submersible Transceiver.
chip components. Attempts by non-qualified persons to service this
equipment may result in permanent damage not covered by the warranty, and may be illegal in some countries.
this transceiver. Each side of the board is referred to by the type of the
majority of components installed on that side ("Side A" or "Side B"). In
most cases one side has only chip components, and the other has either
a mixture of both chip and leaded components (trimmers, coils, electrolytic capacitors, ICs, etc.), or leaded components only.
TEX STANDARD assumes no liability for damage that may occur as a
result of typographical or other errors that may be present. Your cooperation in pointing out any inconsistencies in the technical information
would be appreciated.
VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
4-8-8 Nakameguro, Meguro-Ku, Tokyo 153-8644, Japan
VERTEX STANDARD
US Headquarters
10900 Walker Street, Cypress, CA 90630, U.S.A.
International Division
8350 N.W. 52nd Terrace, Suite 201, Miami, FL 33166, U.S.A.
YAESU EUROPE B.V.
P.O. Box 75525, 1118 ZN Schiphol, The Netherlands
YAESU UK LTD.
Unit 12, Sun Valley Business Park, Winnall Close
Winchester, Hampshire, SO23 0LB, U.K.
VERTEX STANDARD HK LTD.
Unit 5, 20/F., Seaview Centre, 139-141 Hoi Bun Road,
Kwun Tong, Kowloon, Hong Kong
This manual provides the technical information necessary for servicing
Servicing this equipment requires expertise in handing surface-mount
Two PCB layout diagrams provided for each double-sided board in
While we believe the information in this manual to be correct, VER-
Contents
Specification ....................................................................................................................................2
Exploded View & Miscellaneous Parts........................................................................................4
Block Diagram .................................................................................................................................5
Interconnection Diagram ...............................................................................................................6
Circuit Description ........................................................................................................................7
Alignment ...................................................................................................................................... 11
Board Unit (Schematics, Layouts & Parts)
RF Unit ....................................................................................................................................................................19
AF Unit....................................................................................................................................................................33
CNTL Unit ..............................................................................................................................................................43
VCO Unit ................................................................................................................................................................53
1

Specifications
General
Frequency Ranges:
Channel Steps:
Frequency Stability:
Emission Type:
Antenna Impedance:
Supply Voltage:
Current Consumption:
Operating Temperature:
Case Size:
Weight:
Rx (MAIN):
0.5 - 1.8 MHz (BC Band)
1.8 - 30 MHz (SW Band)
30-59 MHz (50 MHz HAM: USA version)
30-76 MHz (50 MHz HAM: EXP version)
59-108 MHz (FM: USA version)
76-108 MHz (FM: EXP version)
108-137 MHz (Air Band)
137-174 MHz (144 MHz HAM)
174-222 MHz (VHF-TV)
222-225 MHz (220 MHz HAM: USA version)
225-420 MHz (ACT1: Action Band 1: USA version)
222-420 MHz (ACT1: Action Band 1: EXP version)
420-470 MHz (430 MHz HAM)
470-729 MHz (UHF-TV: USA version)
470-800 MHz (UHF-TV: EXP version)
800-999 MHz (ACT2: Action Band 2, cellular Blocked)
Rx (SUB):
50 - 54 MHz
137 - 174 MHz
420 - 470 MHz
Tx: 50 - 54 MHz (MAIN & SUB)
144 - 146 MHz or 144 - 148 MHz (MAIN & SUB)
222-225 MHz (MAIN, USA version)
430 - 440 MHz or 430 - 450 MHz (MAIN & SUB)
5/9/10/12.5/15/20/25/50/100 kHz
±5 ppm (+14°F to +122°F, –10°C to +50°C)
F2, F3, A3
50-ohm
Nominal: 7.4 V DC, Negative Ground
Operating: 10 - 16 V DC, Negative Ground (EXT DC jack)
150 mA (Mono Band Receive)
200 mA (Dual Band Receive)
55 mA (Mono Band Receive, Standby, Saver Off)
100 mA (Dual Band Receive, Standby, Saver Off)
25 mA (Mono Band Receive, Standby, Saver On "Save Ratio 1:5")
50 mA (Dual Band Receive, Standby, Saver On "Save Ratio 1:5")
400 µA (Auto Power Off)
1.6/1.3/1.0/0.7 A (50 MHz, Tx HI/L3/L2/L1)
1.71.4/1.1/0.8 A (144 MHz, Tx HI/L3/L2/L1)
0.6 A (220 MHz, Tx)
1.8/1.5/1.2/0.9/ A (430 MHz, Tx HI/L3/L2/L1)
–4°F to +140°F (–20°C to +60°C)
60 (W) x 90 (H) x 28 (D) mm (w/o knob & antenna)
250 g
2

Transmitter
RF Power Output:
Modulation Type:
Maximum Deviation:
Spurious Emission:
Microphone Impedance:
Receiver
Circuit Type:
Intermediate Frequencies:
Sensitivity:
Selectivity:
AF Output:
Specifications
5/2.5/1.0/0.5 W (50/144/430 MHz, FM)
0.3 W (220 MHz, FM)
1.0 W (50 MHz, FM)
FM: Variable Reactance
AM: Early Stage (Low Level)
±5/±2.5 kHz
At least 60 dB below (@ Tx 1W)
2 k-ohm
N-FM, AM: Double-Conversion Superheterodyne
W-FM: Triple-Conversion Superheterodyne
1st: 47.25 MHz (N-FM, AM)
45.8 MHz (W-FM)
2nd: 450 kHz (N-FM, AM)
10.7 MHz (W-FM)
3rd: 1 MHz (W-FM)
3.0 µV for 10 dB SINAD (0.5 - 30 MHz, AM)
0.5 µV for 12 dB SINAD (30 - 50 MHz, N-FM)
0.16 µV for 12 dB SINAD (50 - 54 MHz, N-FM)
15 kHz/35 kHz (-6 dB/-60 dB: N-FM, AM)
200 kHz/300 kHz (-6 dB/-20 dB: W-FM)
200 mW @ 8 ohm for 10 % THD (@ 7.4V DC)
400 mW @ 8 ohm for 10 % THD (@ 13.8V DC)
Specifications are subject to change without notice, and are guaranteed within amateur bands only.
3
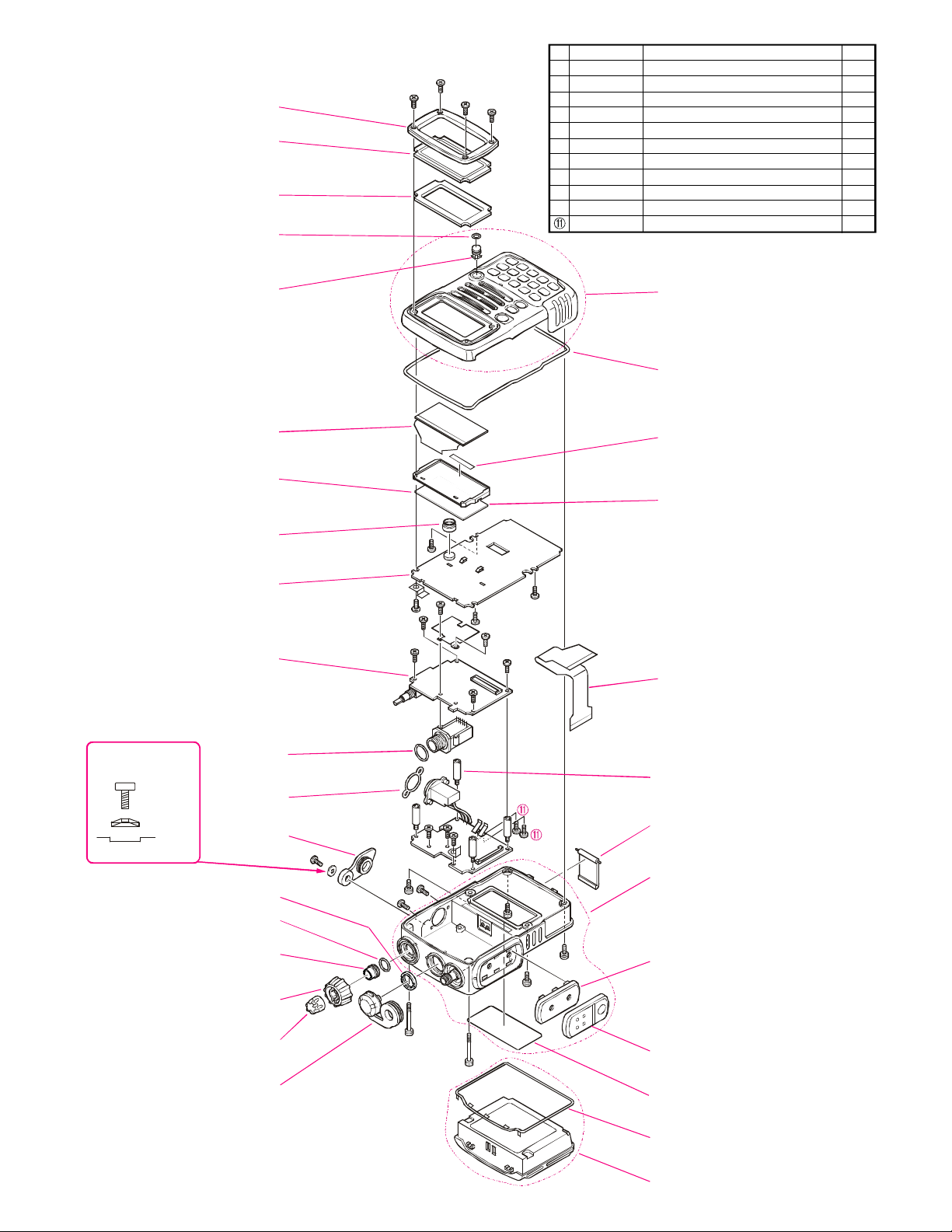
Exploded View & Miscellaneous Parts
Â
RA0417100
PANEL FRAME
RA03995000
WINDOW
RA03994000
DOUBLE FACE TAPE
RA0401600
O RING
RA0399800
LIGHT GUIDE (LED)
Q7000426
LCD MODULE
RA0399100
LIGHT GUIDE (LED)
RA0405600
MIC HOLDER RUBBER
Â
Â
Â
È
No.
VXSTD P/N DISCRIPTION QTY.
À U9900137
Á U9900138
 U07225120
à U9900136
Ä RA0304300
Å U00103002
Æ U00104002
Ç U9900140
È U44104002
É U9900141
U07125102
BINDING HEAD SCREW M2X21.7 (W/ O RING)
BINDING HEAD SCREW M2X5 (W/ O RING)
PAN HEAD SCREW M2X2.5SUS#1
SPECIAL SCREW M2X2.35
WASHER
PAN HEAD SCREW M2X3NI
PAN HEAD SCREW M2X4NI
TAPTITE SCREW M2X6SUS#3
TAPTITE SCREW M2X4NI
TAPTITE SCREW M1.7X5NI#3
TAPTITE SCREW M1.7X2.5SUS#1
CP7346002 (USA)
CP7346003 (EXPORT)
CP7346004 (GERMANY)
PANEL ASS’Y
with RUBBER KNOB, MIC SHEET,
SP SHEET, SP, PROTECTOR L,
PROTECTOR R
RA0400000
RUBBER PACKING
RA014250A
DOUBLE FACE TAPE (LCD)
RA0399900
REFLECTOR SHEET
2
4
4
1
1
1
6
2
4
2
2
There is a direction in
WASHER.
SCREW
WASHER
EXP CAP
RA0401200
ENCODER KNOB
CNTL-Unit
AF-Unit
RA0426800
O RING
RA0400900
O RING
RA0400500
EXT CAP
RA0292200
SPECIAL NUT
RA0426900
O RING
RA0087900
SPECIAL NUT
RA0401900
VOLUME KNOB
RA0400600
CAP(SP/MIC)
È
É
Æ
È
È
É
Æ
Æ
Æ
Æ
Æ
Å
Ã
Ä
Á
Ç
Ç
Á
Á
FR008330C
FPC CABLE
RA0400200
STUD (X4 pcs)
RA01403AA
LATCH NAIL
CP7342003
REAR CASE ASS’Y
with SMA CONNECTOR ASS’Y,
TERMINAL BOARD ASS’Y,
RUBBER KNOB (PTT),
RUBBER KNOB (PTT)
RA0399700
HOLDER (PTT)
Á
À
À
RA0400100
RUBBER KNOB (PTT)
RA0140100
MASK SHEET
RA0141600
RUBBER PACKING
FNB-80LI
4
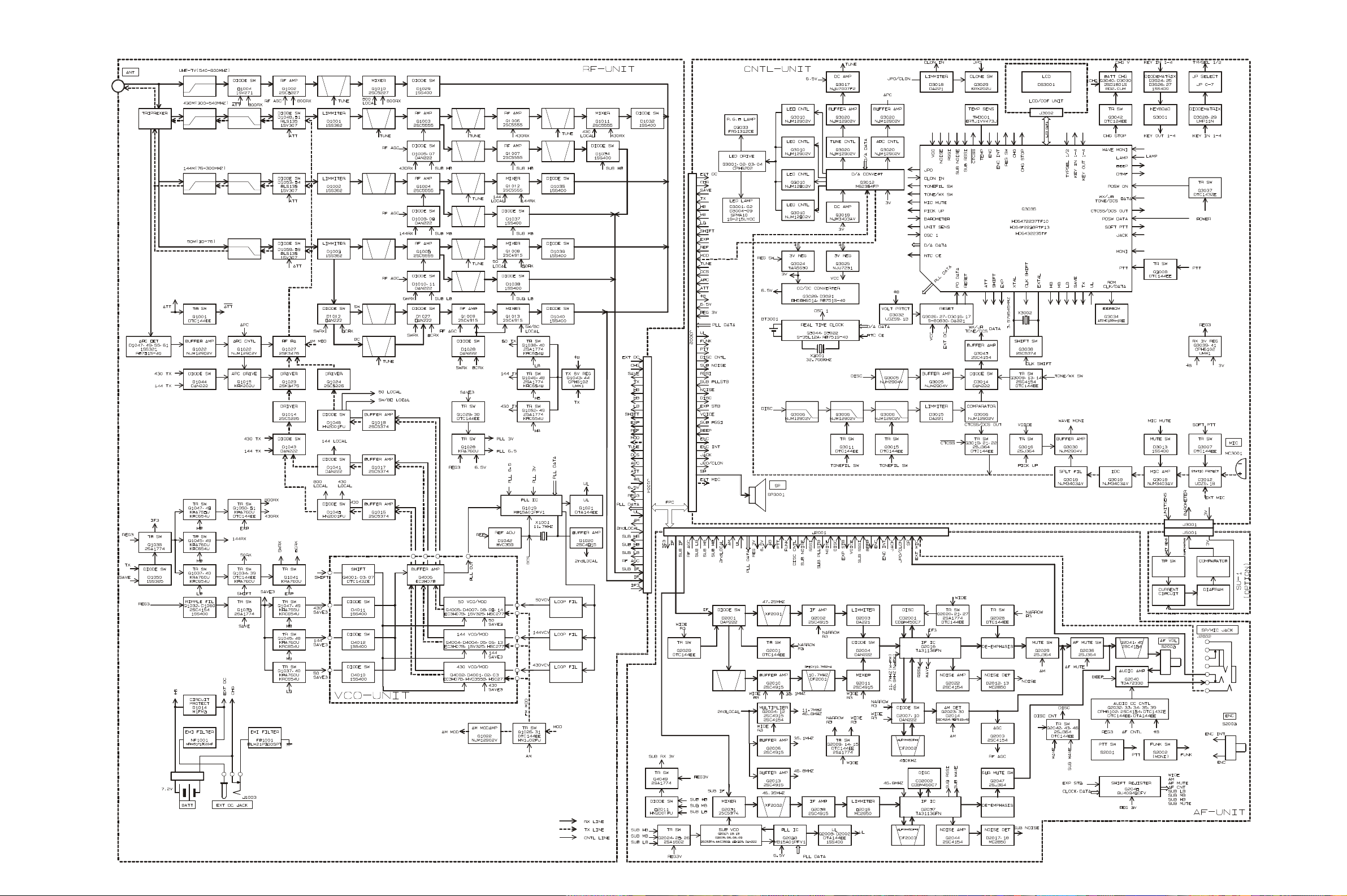
Block Diagram
5
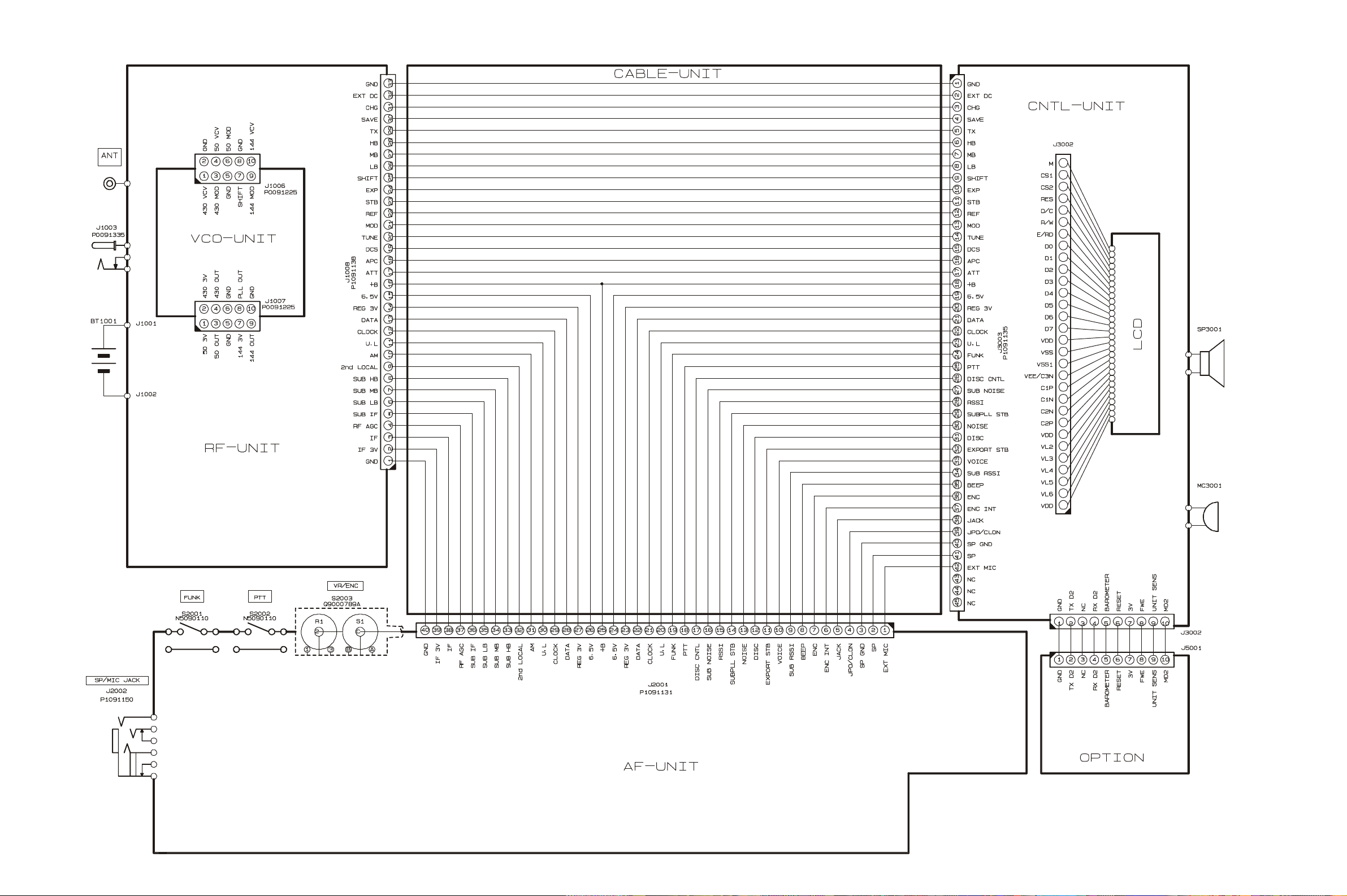
Interconnection Diagram
6

Circuit Description
The VX-7R consists of a RF-UNIT, a CNTL-UNIT and
an AF-UNIT. The RF-UNIT contains the receiver front
end, PLL IC, power and switching circuits, and the VCOUNIT for transmit and receive local signal oscillation.
The CNTL-UNIT contains the CPU, and audio ICs, and
the power circuitry for the LCD. The AF-UNIT contains
the IF, and audio ICs.
Receiver Signal Flow
The VX-7R includes five receiver front ends, each
optimized for a particular frequency range and mode
combination.
(1) Triplexer
Signals between 0.5 and 540 MHz received at the antenna terminal pass through a first low-pass filter composed of C1266, C1269, C1289, C1291, C1296, C1297,
L1059, L1060, L1067 and L1068.
Received 430-MHz signals, after passing through the
low-pass filter, are fed to the UHF T/R switch circuit composed of diode switch D1048 (RLS135), D1051 (1SV307).
Received 145-MHz signals, after passing through the
low-pass filter, are fed to the VHF T/R switch circuit composed of diode switch D1053 (RLS135), D1054 (1SV307).
Received 50-MHz signals, after passing through the
low-pass filter, are fed to the 50MHz T/R switch circuit
composed of diode switch D1058 (RLS135), D1059
(1SV307).
(2) 145-MHz Band and 76-300MHz Reception
Received signals between 76 and 300 MHz pass through
the Triplexer circuit, low-pass filter/high-pass filter circuit, VHF T/R switch circuit and protector diode D1002
(1SS362) before additional filtering by a band-pass filter prior to application to RF amplifier Q1004 (2SC5555).
The amplified RF signal is passed through a band-pass
filter to first mixer Q1012 (2SC5555). Meanwhile, VHF
output from the VCO-UNIT is amplified by Q1017
(2SC5374) and applied through diode T/R switch D1041
(DAN222) to mixer Q1012 as the first local signal.
The 47.25-MHz intermediate frequency product of the
mixer is delivered to the AF-UNIT.
The TUNE voltage from the CPU on the CNTL-UNIT
is amplified by DC amplifier Q3017 (NJU7007F2) and
applied to varactors D1020 and D1022 (HVC369B),
D1019, D1021, D1023, D1024, D1033 and D1036 (1SV325)
in the variable frequency band-pass filters. By changing
the electrostatic capacitance of the varactors, optimum
filter characteristics are provided for each specific operating frequency.
(3) 435-MHz Band and 222-540MHz Reception
Received signals between 222 and 540 MHz pass
through the Triplexer circuit, low-pass filter/high-pass
filter circuit, UHF T/R switch circuit and protector diode D1001 (1SS362) before additional filtering by a bandpass filter prior to application to RF amplifier Q1003
(2SC5555). The amplified RF signal is passed through a
band-pass filter, RF amplifier Q1006 (2SC5555) and
band-pass filter to first mixer Q1011 (2SC5555). Meanwhile, UHF output from the VCO-UNIT is amplified by
Q1016 (2SC5374) and applied through diode T/R switch
D1045 (HN2D01FU) to mixer Q1011 as the first local signal.
The 47.25-MHz intermediate frequency product of the
mixer is delivered to the AF-UNIT.
The TUNE voltage from the CPU on the CNTL-UNIT
is amplified by DC amplifier Q3017 and applied to varactors D1005, D1018, D1030 and D1031 (HVC358B) in
the variable frequency band-pass filters. By changing the
electrostatic capacitance of the varactors, optimum filter characteristics are provided for each specific operating frequency.
(4) 50-MHz-Band and 30-76 MHz Reception
Received signals between 30 and 76 MHz pass through
the Triplexer circuit, low-pass filter circuit, 50 MHz T/R
switch circuit and protector diode D1003 (1SS362) before additional filtering by a band-pass filter prior to
application to RF amplifier Q1005 (2SC5555). The amplified RF signal is passed through a band-pass filter to
first mixer Q1008 (2SC5555). Meanwhile, 50 MHz output from the VCO-UNIT is amplified by Q1018
(2SC5374) and applied through diode T/R switch D1046
(HN2D01FU) to mixer Q1008 as the first local signal.
The 47.25-MHz intermediate frequency product of the
mixer is delivered to the AF-UNIT.
The TUNE voltage from the CPU on the CNTL-UNIT
is amplified by DC amplifier Q3017 and applied to varactors D1025 and D1026 (1SV325) in the variable frequency band-pass filters. By changing the electrostatic capacitance of the varactors, optimum filter characteristics are
provided for each specific operating frequency.
7

Circuit Description
(5) 0.5 - 30 MHz Reception
Received signals between 0.5 and 30 MHz pass through
the Triplexer circuit, low-pass filter circuit, HF T/R switch
circuit and protector diode D1003 before additional filtering by a band-pass filter prior to application to RF
amplifier Q1009 (2SC4915-0). The amplified RF signal
is passed through a band-pass filter to first mixer Q1013
(2SC4915-0). Meanwhile, HF output from the VCOUNIT is amplified by Q1018 and applied through diode
T/R switch D1046 to mixer Q1013 as the first local signal.
The 47.25-MHz intermediate frequency product of the
mixer is delivered to the AF-UNIT.
The TUNE voltage from the CPU on the CNTL-UNIT
is amplified by DC amplifier Q3017 and applied to varactors D1013 (HVR100) in the variable frequency bandpass filters. By changing the electrostatic capacitance of
the varactors, optimum filter characteristics are provided for each specific operating frequency.
(6) 540 - 999 MHz Reception
Received signals between 540 and 999 MHz pass
through the high-pass filter circuit, T/R switch D1004
(1SV271) prior to application to RF amplifier Q1002
(2SC5277). The amplified RF signal is passed through a
band-pass filter to first mixer Q1010 (2SC5277). Meanwhile, UHF output from the VCO-UNIT is amplified by
Q1016 and applied through diode T/R switch D1045 to
mixer Q1010 as the first local signal.
The 47.25-MHz intermediate frequency product of the
mixer is delivered to the AF-UNIT.
The TUNE voltage from the CPU on the CNTL-UNIT
is amplified by DC amplifier Q3017 and applied to varactors D1015 and D1017 (HVC355B) in the variable frequency band-pass filters. By changing the electrostatic
capacitance of the varactors, optimum filter characteristics are provided for each specific operating frequency.
(7) 47.25-MHz First Intermediate Frequency
The 47.25-MHz first intermediate frequency from the
first mixers is delivered from the RF-UNIT to the AFUNIT through jacks J1008 and J2001. On the AF-UNIT,
the IF for AM and FM-narrow signals is passed through
NAR/WIDE switch D2001 (DAP222) and the 47.25-MHz
monolithic crystal filter (MCF) XF2001 to narrow IF amplifier Q2002 (2SC4915-0) for input to pin 16 of the Narrow IF IC Q2016 (TA31136FN), after amplitude limiting
by D2003 (DA221).
Meanwhile, a portion of the output of 11.7-MHz crys-
tal X1001 on the RF-UNIT is multiplied fourfold by Q2004
(2SC4915-0) and Q2012 (2SC4154E) to provide the 46.8MHz second local signal, applied to the Narrow IF IC.
Within the IC, this signal is mixed with the 47.25-MHz
first intermediate frequency signal to produce the 450
kHz second intermediate frequency.
This second IF is filtered by ceramic filter CF2002
(ALFYM450F=k) and amplified by the limiting amplifier within the Narrow IF IC before quadrature detection
by ceramic discriminator CD2001 (CDBM450C7).
Demodulated audio is passed from pin 9 of the Nar-
row IF IC through the "Mute" analog switch Q2029
(2SJ364) and squelch gate Q2036 (2SJ364) before de-emphasis at Q2028 (DTC144EE).
The resulting audio is amplified by AF amplifier Q2040
(TDA7233D) and fed through the MIC/EAR jack J2002
to internal speaker SP1001 or an external earphone.
(8) Squelch Control
Signal components in the neighborhood of 15 kHz contained in the discriminator output pass through an active band-pass filter composed of R2059, R2060, R2062,
C2076, C2078 and the operational amplifier between pins
7 and 8 within Narrow IF IC Q2016. They are then rectified by D2012 and D2013 (MC2850) to obtain a DC voltage corresponding to the level of noise. This voltage is
fed to pin 49 of CPU Q3035 (HD6472237TF10), which
compares the input voltage with a previously set threshold. When the input voltage drops below the threshold,
normally due to the presence of a carrier, the CPU turns
on squelch gate Q2036 and allows any demodulated audio to pass. At the same time, Q3001 and/or Q3003 and/
or Q3004 goes on, causing the BUSY/TX lamp D3033
(FRGB1312CE-10-TF) to light.
Transmitter Signal Flow
(1) 145-MHz-Band Transmit/Receive Switching
Closing PTT switch S2002 on the AF-UNIT pulls the
base of Q3008 (DTA144EE) low, causing the collector to
go high. This signal is fed to pin 33 (PTT) of CPU Q3035,
allowing the CPU to recognize that the PTT switch has
been pushed. When the CPU detects closure of the PTT
switch, pin 10 (TX) goes high. This control signal is delivered to the RF-UNIT, where it switches Q1044 (UMW1)
and Q1043 (CPH6102) to produce the TX control signal
that activates Q1046 (2SA1774). At the same time, PLL
division data is fed to PLL IC Q1019 (MB15A01PFV1)
from the CPU, to disable the receiver power saver. Also,
8

Circuit Description
it switches Q1048 (KRC654U) to disable the receiver circuits. This causes the "red" mode of BUSY/TX lamp D3033
to light.
(2) Modulation
Voice signal input from either built-in microphone
MC3001 (EM-140) on the CNTL-UNIT or external jack
J2002 on the AF-UNIT is pre-emphasized by C3012 and
R3031, and processed by microphone amplifier Q3018
(NJM3403AV), IDC (instantaneous deviation control) circuit Q1014 to prevent overmodulation, and fed through
active low-pass filter Q1014.
During CTCSS operation, the voice signal is mixed with
the TONE ENC subaudible tone signal from pin 43 of
the CPU and delivered to the RF-UNIT through jacks
J3003 and J1008. During DTMF operation, the DTMF
tones from pin 44 of the CPU are fed to the IDC stage.
(3) 145-MHz-Band Transmission
Modulating audio from the CNTL-UNIT passes
through deviation setting D/A converter Q3012 to the
VHF modulator portion of the VCO-UNIT mounted on
the RF-UNIT. This signal is applied to varactor D4005
(HSC277 ) in the tank circuit of VHF VCO Q4004
(EC3H07B), which oscillates at the desired VHF transmitting frequency. The modulated VCO signal is buffered by amplifier Q4006 (EC3H07B) and Q1017 and delivered through VHF T/R diode switch D1041 to the RFUNIT. The modulated low-level VHF transmit signal
from the VCO is passed through diode switch D1043
(DAN222) to amplifier Q1014 (2SC5226-5). The modulated VHF transmit signal from the VCO is amplified by
Q1023 (2SK3475) and RF power amplifier Q1027
(2SK3476) up to 0.05, 1.0, 2.5 or 5 Watts (depending on
the power source). The RF output passes through TX
diode switch D1053. RF output is passed by the T/R
switch and low-pass filter to suppress harmonics and
spurious products before output gets to the antenna at
the antenna terminal.
ered by amplifier Q4006 and Q1016 and delivered
through UHF T/R diode switch D1045 to the RF-UNIT.
The modulated low-level UHF transmit signal from the
VCO is passed through diode switch D1045 (HN2D01FU)
to amplifier Q1014. The modulated UHF transmit signal
from the VCO is amplified by Q1023 and RF power amplifier Q1027 up to 0.05, 1.0, 2.5 or 5 Watts (depending
on the power source). The RF output passes through TX
diode switch D1048. RF output is passed through the T/
R switch and low-pass filter to suppress harmonics and
spurious products before output gets to the antenna at
the antenna terminal.
(5) 50-MHz-Band Transmission
Modulating audio from the CNTL-UNIT passes
through deviation setting D/A converter Q3012 to the 50
MHz modulator portion of the VCO-UNIT mounted on
the RF-UNIT. This signal is applied to varactor D4009
(HSC277) in the tank circuit of 50 MHz VCO Q4005
(EC3H07B), which oscillates at the desired 50 MHz transmitting frequency. The modulated VCO signal is buffered by amplifier Q4006 and Q1018 and delivered
through 50 MHz T/R diode switch D1046 to the RF-UNIT.
The modulated low-level 50 MHz transmit signal from
the VCO is passed through diode switch D1046
(HN2D01FU) to amplifier Q1014. The modulated 50 MHz
transmit signal from the VCO is amplified by Q1023 and
RF power amplifier Q1027 up to 0.05, 1.0, 2.5 or 5 Watts
(depending on the power source). The RF output passes
through TX diode switch D1058. RF output is passed
through the T/R switch and low-pass filter to suppress
harmonics and spurious products before output gets to
the antenna at the antenna terminal.
(4) 435-MHz-Band Transmission
Modulating audio from the CNTL-UNIT passes
through deviation setting D/A converter Q3012 to the
UHF modulator portion of the VCO-UNIT mounted on
the RF-UNIT. This signal is applied to varactor D4002
(HSC277) in the tank circuit of UHF VCO Q4002
(EC3H07B), which oscillates at the desired UHF transmitting frequency. The modulated VCO signal is buff-
9

Circuit Description
PLL Frequency Synthesizer
PLL IC Q1019 on the RF-UNIT consists of a data shift
register, reference frequency divider, phase comparator,
charge pump, "intermittent operation" circuit, and band
selector switch. Serial PLL data from the CPU is converted into parallel data by the shift register in the PLL
IC and is latched into the comparative frequency divider and reference frequency divider to set a frequency
dividing ratio for each. An 11.7-MHz reference signal
produced by X1001 is fed to "REF" pin 1 of the PLL IC.
The internal reference frequency divider divides the 11.7MHz reference by 2,050 (or 1,640) to obtain a reference
frequency of 5 kHz (or 6.25 kHz), which is applied to the
phase comparator. Meanwhile, a sample of the output
of VHF VCO Q4004 or UHF VCO Q4002 or 50 MHz VCO
Q4005 on the VCO-UNIT, buffered by Q4006, is fed to
the PLL IC, where it is divided by the internal comparative frequency divider to produce a comparative frequency which also is applied to the phase comparator. The
phase comparator compares the phase between the reference frequency and comparative frequency to output
a pulse corresponding to the phase difference between
them. This pulse is fed to the charge pump, and the output from the charge pump passes through a loop filter
composed of L1044, R1089, C1175, and either R1090,
C1192, R1103 and C1195 for VHF, or R1086, C1189, R1102
and C1194 for UHF, or R1091, C1193, R1104 and C1196
for 50 MHz, which convert the pulse into a corresponding smoothed varactor control voltage (VCV). The VCV
is applied to varactors D4004 and D4013 (1SV325) in the
VHF VCO tank circuit, or to varactor D4001 (HVC355B)
in the UHF VCO tank circuit, or to varactors D4007 and
D4008 (1SV325) in the 50 MHz VCO, to eliminate any
phase difference between the reference frequency and
comparative frequency, thus locking the VCO oscillation
frequency to the reference crystal. The VCO frequency
is determined by the frequency-dividing ratio sent from
the CPU to the PLL IC. During receiver power save operation, the PLL circuit operates intermittently to reduce
current consumption, for which the "intermittent operation" control circuit reduces the lock-up time.
10
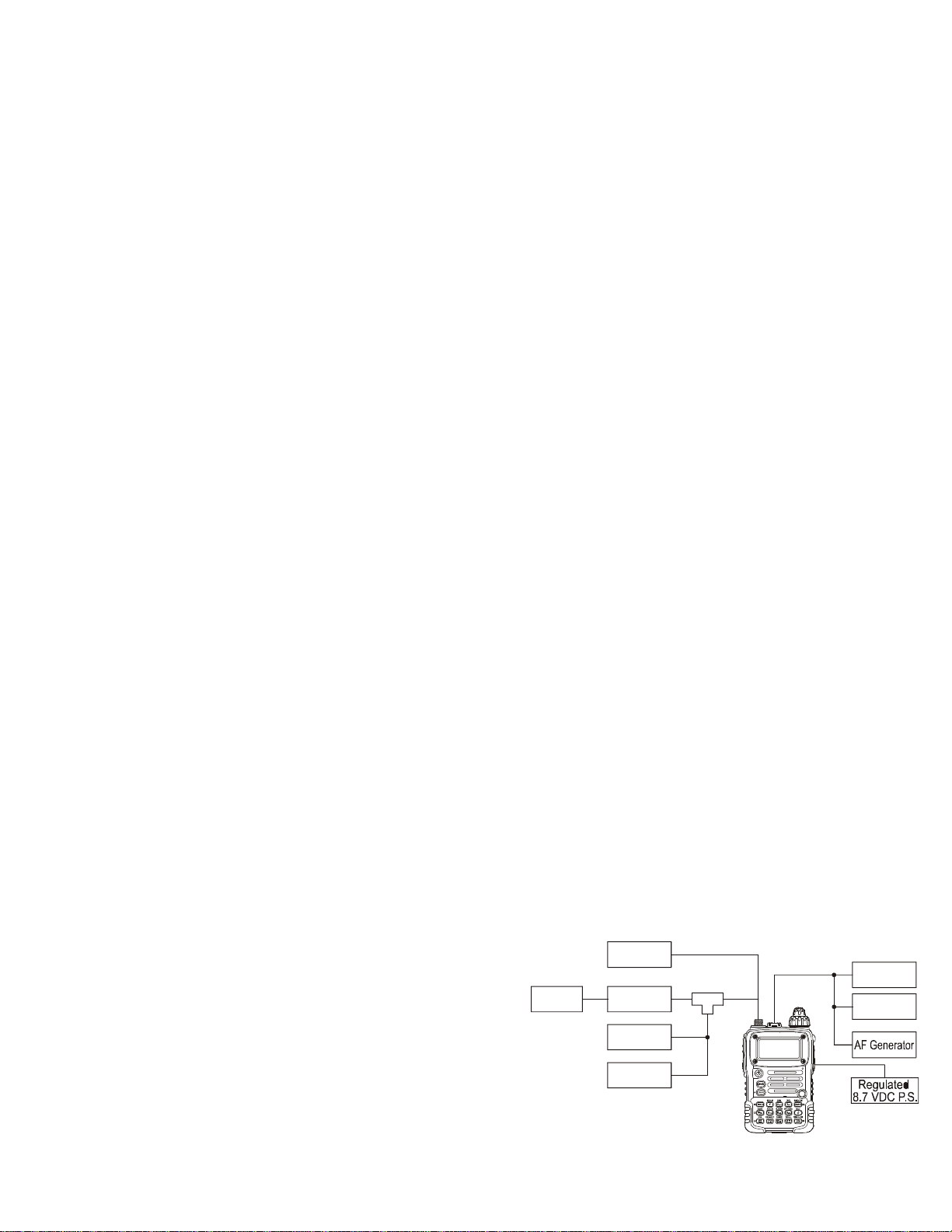
Alignment
Meter
SINAD
AF Load
DW
Introduction and Precautions
The VX-7R has been carefully aligned at the factory for
the specified performance across the specified amateur
bands. Realignment should therefore not be necessary
except in the event of a component failure. All component replacement and service should be performed only
by an authorized VERTEX STANDARD representative,
or the warranty policy may be voided.
The following procedures cover the sometimes critical
and tedious adjustments that are not normally required
once the transceiver has left the factory. However, if damage occurs and some parts are replaced, realignment may
be required. If a sudden problem occurs during normal
operation, it is likely due to component failure; realignment should not be done until after the faulty component has been replaced.
We recommend that servicing be performed only by
authorized VERTEX STANDARD service technicians,
who are experienced with the circuitry and fully
equipped for repair and alignment. Therefore, if a fault
is suspected, contact the dealer from whom the transceiver was purchased for instructions regarding repair.
Authorized VERTEX STANDARD service technicians
realign all circuits and make complete performance
checks to ensure compliance with factory specifications
after replacing any faulty components.
Those who do undertake any of the following alignments are cautioned to proceed at their own risk. Problems caused by unauthorized attempts at realignment
are not covered by the warranty policy. Also, VERTEX
STANDARD must reserve the right to change circuits
and alignment procedures in the interest of improved
performance, without notifying owners.
Under no circumstances should any alignment be attempted unless the normal function and operation of the
transceiver are clearly understood, the cause of the malfunction has been clearly pinpointed and any faulty components replaced, and the need for realignment determined to be absolutely necessary.
Required Test Equipment
m RF Signal Generator with calibrated output level at 500 MHz
m Deviation Meter (linear detector)
m In-line Wattmeter with 5% accuracy at 500 MHz
m 50-ohm, 10-W RF Dummy Load
m 8-ohm AF Dummy Load
m Regulated DC Power Supply adjustable from 3 to 15 V DC,
3A
m Frequency Counter: 0.2-ppm accuracy at 500 MHz
m AF Signal Generator
m AC Voltmeter
m DC Voltmeter: high impedance
m UHF Sampling Coupler
m SINAD Meter
Alignment Preparation & Precautions
A 10-W RF dummy load and in-line wattmeter must
be connected to the main antenna jack in all procedures
that call for transmission, alignment is not possible with
an antenna. After completing one step, read the next step
to see if the same test equipment is required. If not, remove the test equipment (except dummy load and wattmeter, if connected) before proceeding.
Correct alignment requires that the ambient temperature be the same as that of the transceiver and test equipment, and that this temperature be held constant between
68~86°F (20~30°C). When the transceiver is brought into
the shop from hot or cold air, it should be allowed some
time to come to room temperature before alignment.
Whenever possible, alignments should be made with oscillator shields and circuit boards firmly affixed in place.
Also, the test equipment must be thoroughly warmed
up before beginning.
Note: Signal levels in dB referred to in the alignment proce-
dure are based on 0 dBµ=0.5 µV (closed circuit).
RF Signal
50-ohm
RF Load
Generator
In-Line
Wattmeter
Sampling
Coupler
8-ohm
Deviation
Meter
Frequency
Counter
Alignment Setup
11

Alignment
Test Setup
Set up the test equipment as shown below for transceiver alignment, and apply 8.7 V DC power to the transceiver. Refer to the drawings for Alignment Points.
Internal System Alignment Routine
This uses a programmed routine in the transceiver
which simplifies many previously complex discrete component settings and adjustments with digitally-controlled
settings via front panel buttons and LCD indications.
To begin, set the transceiver to the center of the 50 MHz,
144 MHz, 222 MHz and 430 MHz bands. Next, select the
430 MHz band, then turn the transceiver off.
Now, press and hold in the MON/F, and 0 buttons
(at the same time) while powering the radio on again.
The display will show the first setting. Thereafter, the
frequencies used during alignment will automatically be
set without action by the technician.
In the alignment process, each adjustment is selected
by rotating the DIAL. Alignment is performed by:
m Pressing the V/M button;
m Injecting a signal of the required frequency and lev-
el; then
m Pressing the V/M button after a level setting or ad-
justment is made. This second pressing of the MON/
F button stores the entry.
To exit the alignment routine, press the HM/RV button. After performing the system alignment in its entirety, individual settings can be returned to and adjusted
should the need arise.
As each transceiver is individually optimized at the
factory, the precise settings for the transceiver on your
bench may be slightly different.
Main Band Alignment
PLL Reference Frequency (PLL REF)
Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the
counter frequency to 440.000 (±300 Hz) by rotating the
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
430 MHz band Alignment
Squelch Hysteresis Adjustment (HIS SQL)
m Rotate the DIAL for minimum squelch hysteresis. Press
the V/M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
12
Squelch Preset Threshold (THLD SQL) [86]
m Inject a –15.0 dBµ RF signal (1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz
deviation), then press the V/M button, then press the
MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button, then rotate
the DIAL to select the next setting.
Squelch Preset Tight (TIGH SQL)
m Adjust the generator level to –4.0 dBµ, then press the
V/M button, then press the MON/F button twice. Press
the V/M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
S-Meter S-1 Adjustment (S1 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to –7.0 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
S-Meter Full-Scale Adjustment (S9 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to +20 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
Wide-FM S-Meter S-1 Adjustment (S1 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to 0 dBµ (1 kHz tone @ ±20
kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then press
the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button, then
rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
Wide-FM S-Meter Full-Scale Adjustment (S9 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to +20 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±20 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
The alignment frequency will now be automatically set
to 430.000 MHz.
High TX Power Adjustment (HI POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 5.0 W
(±0.3 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
L3 Tx Power Adjustment (L3 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 2.5 W
(±0.2 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
L2 Tx Power Adjustment (L2 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 1.0 W
(±0.1 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.

Alignment
L1 Tx Power Adjustment (L1 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 50 mW
(+50/-30 mW) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M
button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
TX Deviation Adjustment (MAX DEV)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 50 mV (rms) to
the MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and
adjust the deviation for 4.5 kHz (±0.2 kHz) (USA Version: 4.2 kHz (±0.2 kHz)) by rotating the DIAL, then
press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 67.0)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (+0.05/-0.1 kHz) by rotating the
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to
select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 183.5)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 254.1)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
DCS Tx Deviation Adjustment (DCS DEV)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.6 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
Press the MON/F to activate the TX Power and Devia-
tion alignment routine.
The alignment frequency will automatically be set to
440.000 MHz (USA Version: 450.000 MHz).
High TX Power Adjustment (HI POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 5.0 W
(±0.3 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
High TX Power Adjustment (L3 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 2.5 W
(±0.2 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
High TX Power Adjustment (L2 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 1.0 W
(±0.1 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
High TX Power Adjustment (L1 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 50 mW
(+50/-30 mW) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M
button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
TX Deviation Adjustment (MAX DEV)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 50mV (rms) to the
MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the deviation for 4.5 kHz (±0.2 kHz) (USA Version:
4.2 kHz (±0.2 kHz)) by rotating the DIAL, then press the
V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 67.0)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (+0.05/-0.1 kHz) by rotating the
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to
select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 183.5)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 254.1)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
DCS Tx Deviation Adjustment (DCS DEV)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.6 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
Press the BAND button to activate the 50 MHz band
internal alignment routine.
The alignment frequency will automatically be set to
52.100 MHz.
50 MHz Band Alignment
Squelch Hysteresis Adjustment (HIS SQL)
m Rotate the DIAL for minimum squelch hysteresis. Press
the V/M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
13

Alignment
Squelch Preset Threshold (THLD SQL)
m Inject a –15.0 dBµ RF signal (1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz
deviation), then press the V/M button, then press the
MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button, then rotate
the DIAL to select the next setting.
Squelch Preset Tight (TIGH SQL)
m Adjust the generator level to –4.0 dBµ, then press the V/M
button, then press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/
M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
S-Meter S-1 Adjustment (S1 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to –7.0 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
S-Meter Full-Scale Adjustment (S9 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to +19 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
Wide-FM S-Meter S-1 Adjustment (S1 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to 0 dBµ (1 kHz tone @ ±20
kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then press
the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button, then
rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
Wide-FM S-Meter Full-Scale Adjustment (S9 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to +20 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±20 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
The alignment frequency will now be automatically set
to 50.000 MHz.
L1 Tx Power Adjustment (L1 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 50 mW
(+50/-30 mW) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M
button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
TX Deviation Adjustment (MAX DEV)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 50mV (rms) to the
MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the deviation for4.5 kHz (±0.2 kHz) (USA Version:
(4.2 ±0.2 kHz)) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M
button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
AM Modulation (AM MOD)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 100 mV (rms) to
the MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and
adjust the modulation for 60% (±10%) by rotating the
DIAL, then press and hold in the MON/F button for
one second.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 67.0)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (+0.05/-0.1 kHz) by rotating the
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to
select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 183.5)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 254.1)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
High TX Power Adjustment (HI POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 5.0 W
(±0.3 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
L3 Tx Power Adjustment (L3 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 2.5 W
(±0.2 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
L2 Tx Power Adjustment (L2 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 1.0 W
(±0.1 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
14
DCS Tx Deviation Adjustment (DCS DEV)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.6 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
Press the MON/F button to activate the TX Power and
Deviation alignment routine.
The alignment frequency will automatically be set to
54.000 MHz.
High TX Power Adjustment (HI POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 5.0 W
(±0.3 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.

Alignment
High TX Power Adjustment (L3 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 2.5 W
(±0.2 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
High TX Power Adjustment (L2 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 1.0 W
(±0.1 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
High TX Power Adjustment (L1 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 50 mW
(+50/-30 mW) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M
button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
TX Deviation Adjustment (MAX DEV)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 50mV (rms) to
the MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and
adjust the deviation for 4.5 kHz (±0.2 kHz) (USA Version: 4.2 kHz (±0.2 kHz)) by rotating the DIAL, then
press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
Press the BAND button to activate the 145 MHz band
internal alignment routine.
The alignment frequency will automatically be set to
145.100 MHz (USA Version: 146.100 MHz).
144 MHz Band Alignment
Squelch Hysteresis Adjustment (HIS SQL)
m Rotate the DIAL for minimum squelch hysteresis. Press
the V/M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
Squelch Preset Threshold (THLD SQL)
m Inject a –15.0 dBµ RF signal (1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz
deviation), then press the V/M button, then press the
MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button, then rotate
the DIAL to select the next setting.
Squelch Preset Tight (TIGH SQL)
m Adjust the generator level to –4.0 dBµ, then press the
V/M button, then press the MON/F button twice. Press
the V/M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
AM Modulation (AM MOD)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 100mV (rms) to
the MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and
adjust the modulation for 60% (±10%) by rotating the
DIAL.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 67.0)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (+0.05/-0.1 kHz) by rotating the
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to
select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 183.5)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 254.1)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
S-Meter S-1 Adjustment (S1 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to –7.0 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
S-Meter Full-Scale Adjustment (S9 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to +19 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
Wide-FM S-Meter S-1 Adjustment (S1 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to 0 dBµ (1 kHz tone @ ±20
kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then press
the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button, then
rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
Wide-FM S-Meter Full-Scale Adjustment (S9 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to +20 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±20 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
DCS Tx Deviation Adjustment (DCS DEV)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.6 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
The alignment frequency will now be automatically set
to 144.000 MHz.
15

Alignment
High TX Power Adjustment (HI POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 5.0 W
(±0.3 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
L3 Tx Power Adjustment (L3 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 2.5 W
(±0.2 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
L2 Tx Power Adjustment (L2 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 1.0 W
(±0.1 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
L1 Tx Power Adjustment (L1 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 50 mW
(+50/-30 mW) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M
button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
TX Deviation Adjustment (MAX DEV)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 50mV (rms) to
the MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and
adjust the deviation for 4.5 kHz (±0.2 kHz) (USA Version: 4.2 kHz (±0.2 kHz)) by rotating the DIAL, then
press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 67.0)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (+0.05/-0.1 kHz) by rotating the
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to
select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 183.5)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 254.1)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
DCS Tx Deviation Adjustment (DCS DEV)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.6 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
Press the MON/F to activate the TX Power and Devia-
tion alignment routine.
The alignment frequency will automatically be set to
146.000 MHz (USA Version: 148.000 MHz).
High TX Power Adjustment (HI POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 5.0 W
(±0.3 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
High TX Power Adjustment (L3 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 2.5 W
(±0.2 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
High TX Power Adjustment (L2 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 1.0 W
(±0.1 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
High TX Power Adjustment (L1 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 50 mW
(+50/-30 mW) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M
button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
TX Deviation Adjustment (MAX DEV)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 50mV (rms) to
the MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and
adjust the deviation for 4.5 kHz (±0.2 kHz) (USA Version: 4.2 kHz (±0.2 kHz)) by rotating the DIAL, then
press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 67.0)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (+0.05/-0.1 kHz) by rotating the
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to
select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 183.5)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 254.1)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
16

Alignment
DCS Tx Deviation Adjustment (DCS DEV)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.6 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
NOTE: The next step depends on the geographical "version"
of the transceiver being aligned:
EXP Version: Alignment of the "SUB Band " follows
(see page 18.)
USA Version: Press the BAND button to activate the
222 MHz band internal alignment routine. In this case,
the alignment frequency will automatically be set to
222.000 MHz.
222 MHz Band Alignment
L2 Tx Power Adjustment (L2 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 0.3 W
(±0.1 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
L1 Tx Power Adjustment (L1 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 50 mW
(+50/-30 mW) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M
button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
DCS Tx Deviation Adjustment (DCS DEV)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.6 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating DIAL, then
press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
Press the MON/F to activate the TX Power and Devia-
tion alignment routine.
The alignment frequency will automatically be set to
224.995 MHz.
High Tx Power Adjustment (L2 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 0.3 W
(±0.1 W) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
High Tx Power Adjustment (L1 POWER)
m Transmit, and adjust the output power level for 50 mW
(+50/-30 mW) by rotating the DIAL, then press the V/M
button. Rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
TX Deviation Adjustment (MAX DEV)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 50mV (rms) to
the MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and
adjust the deviation for 4.2 kHz ±0.2 kHz by rotating
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to
select the next setting.
TX Deviation Adjustment (MAX DEV)
m Inject a 1 kHz audio tone at a level of 50mV (rms) to
the MIC jack. Press the V/M button, then transmit and
adjust the deviation for 4.2 kHz (±0.2 kHz) by rotating
the DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL
to select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 67.0)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (+0.05/-0.1 kHz) by rotating the
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to
select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 183.5)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 254.1)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 67.0)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (+0.05/-0.1 kHz) by rotating the
DIAL, then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to
select the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 183.5)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
CTCSS Tx Deviation Adjustment (TN 254.1)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.5 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
DCS Tx Deviation Adjustment (DCS DEV)
m Press the V/M button, then transmit and adjust the de-
viation for 0.6 kHz (±0.1 kHz) by rotating the DIAL,
then press the V/M button. Rotate the DIAL to select
the next setting.
17

Alignment
Press the SUB button to activate the SUB band inter-
nal alignment routine.
The alignment frequency will automatically be set to
435.100 MHz (USA Version: 440.100 MHz) on the SUB
band.
SUB Band Alignment
430 MHz Band Alignment
Squelch Hysteresis Adjustment (HIS SQL)
m Rotate the DIAL for minimum squelch hysteresis. Press
the V/M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
Squelch Preset Threshold (THLD SQL)
m Inject a –13.0 dBµ RF signal (1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz
deviation), then press the V/M button, then press the
MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button, then rotate
the DIAL to select the next setting.
Squelch Preset Tight (TIGH SQL)
m Adjust the generator level to –4.0 dBµ, then press the V/M
button, then press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/
M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
S-Meter S-1 Adjustment (S1 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to –7.0 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
S-Meter Full-Scale Adjustment (S9 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to +20 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button.
Press the BAND button to activate the 50 MHz SUB
band internal alignment routine.
The alignment frequency will automatically be set to
52.100 MHz.
50 MHz SUB Band Alignment
Squelch Hysteresis Adjustment (HIS SQL)
m Rotate the DIAL for minimum squelch hysteresis. Press
the V/M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
Squelch Preset Threshold (THLD SQL)
m Inject a –13.0 dBµ RF signal (1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz
deviation), then press the V/M button, then press the
MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button, then rotate
the DIAL to select the next setting.
Squelch Preset Tight (TIGH SQL)
m Adjust the generator level to –4.0 dBµ, then press the
V/M button, then press the MON/F button twice. Press
the V/M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next
setting.
S-Meter S-1 Adjustment (S1 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to –7.0 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
S-Meter Full-Scale Adjustment (S9 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to +19 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button.
Press the BAND button to activate the 144 MHz SUB band
internal alignment routine.
The alignment frequency will automatically be set to
145.100 MHz (USA Version: 146.100 MHz).
144 MHz SUB Band Alignment
Squelch Hysteresis Adjustment (HIS SQL)
m Rotate the DIAL for minimum squelch hysteresis. Press the
V/M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
Squelch Preset Threshold (THLD SQL)
m Inject a –15.0 dBµ RF signal (1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz
deviation), then press the V/M button, then press the
MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button, then rotate
the DIAL to select the next setting.
Squelch Preset Tight (TIGH SQL)
m Adjust the generator level to –4.0 dBµ, then press the V/M
button, then press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/
M button, then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
S-Meter S-1 Adjustment (S1 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to –7.0 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
press the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button,
then rotate the DIAL to select the next setting.
S-Meter Full-Scale Adjustment (S9 LEVEL)
m Adjust the generator level to +19 dBµ (1 kHz tone @
±3.5 kHz deviation), then press the V/M button, then
presses the MON/F button twice. Press the V/M button.
This completes the internal alignment routine for all
bands. To save all settings and exit, press the HM/RV
button.
18
 Loading...
Loading...