Page 1

VHF/UHF
ULTRA-COMPACT DUAL-BAND TRANSCEIVER
WITH WIDE BAND COVERAGE
VX-3R
Technical Supplement
©2007 VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD. EH028M90A
Introduction
This manual provides the technical information necessary for servicing the VX-3R Ultra-Compact Dual-Band Transceiver.
Servicing this equipment requires expertise in handing surface-mount chip components.
Attempts by non-qualified persons to service this equipment may result in permanent
damage not covered by the warranty, and may be illegal in some countries.
Two PCB layout diagrams provided for each double-sided board in this transceiver.
Each side of the board is referred to by the type of the majority of components installed
on that side (“Side A” or “Side B”). In most cases one side has only chip components,
and the other has either a mixture of both chip and leaded components (trimmers, coils,
electrolytic capacitors, ICs, etc.), or leaded components only.
VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
4-8-8 Nakameguro, Meguro-Ku, Tokyo 153-8644, Japan
VERTEX STANDARD
US Headquarters
10900 Walker Street, Cypress, CA 90630, U.S.A.
YAESU EUROPE B.V.
P.O. Box 75525, 1118 ZN Schiphol, The Netherlands
YAESU UK LTD.
Unit 12, Sun Valley Business Park, Winnall Close
Winchester, Hampshire, SO23 0LB, U.K.
VERTEX STANDARD HK LTD.
Unit 5, 20/F., Seaview Centre, 139-141 Hoi Bun Road,
Kwun Tong, Kowloon, Hong Kong
VERTEX STANDARD (AUSTRALIA) PTY., LTD.
Normanby Business Park, Unit 14/45 Normanby Road
Notting Hill 3168, Victoria, Australia
While we believe the information in this manual to be correct, VERTEX STANDARD
assumes no liability for damage that may occur as a result of typographical or other
errors that may be present. Your cooperation in pointing out any inconsistencies in the
technical information would be appreciated.
Important Note
This transceiver was assembled using Pb (lead) free solder, based on the RoHS specification.
Only lead-free solder (Alloy Composition: Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu) should be used for repairs performed on this apparatus. The solder stated above utilizes the alloy composition required for compliance with the lead-free specification,
and any solder with the above alloy composition may be used.
Contents
Specification .......................................................................................................................................... 2
Exploded View & Miscellaneous Parts.............................................................................................4
Block Diagram .......................................................................................................................................5
Circuit Description .............................................................................................................................. 7
Alignment...............................................................................................................................................9
Board Unit (Schematics, Layouts & Parts)
MAIN Unit ....................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Filter Unit .........................................................................................................................................................................31
SW Unit ............................................................................................................................................................................. 35
VCO Unit ..........................................................................................................................................................................39
1
Page 2

Specifications
General
Frequency Ranges: RX 0.5-1.8 MHz (AM Broadcast)
(USA Version) 1.8-30 MHz (SW Band)
30-76 MHz (50 MHz HAM)
76-108 MHz (FM)
108-137 MHz (Air Band)
137-174 MHz (144 MHz HAM)
174-222 MHz (VHF TV)
222-420 MHz (ACT1)
420-470 MHz (430 MHz HAM)
470-800(729) MHz (UHF TV)
(757-774) MHz (UHF TV)
800-999 MHz (GEN2; USA Cellular Blocked)
TX 144-146(148) MHz
430-440(450) MHz
Channel Steps: 5/9/8.33/10/12.5/15/20/25/50/100 kHz
Frequency Stability: ±5 ppm (–10 °C to +60 °C)
Repeater Shift: ±600 kHz (144 MHz)
±1.6/5.0/7.6 MHz (430 MHz)
Emission Type: F2D, F3E, F2A
Antenna Impedance: 50 W
Supply Voltage: Nominal: 3.7 V DC, Negative Ground
Operating: 3.7 ~ 7.0 V, Negative Ground (EXT DC Jack)
5.0 ~ 7.0 V, Negative Ground (EXT DC Jack w/Charging)
Current Consumption: 120 mA (Receive)
60 mA (Standby, Saver Off)
30 mA (Standby, Saver On, Save Ratio 1:2)
50 mA (Radio Band Receive)
100 μA (Auto Power Off)
1.3 A (1.5 W Tx , 144 MHz) 3.7 V DC
1.6 A (3 W Tx , 144 MHz) 6 V DC
1.2 A (1 W Tx , 430 MHz) 3.7 V DC
1.8 A (2 W Tx , 430 MHz) 6 V DC
Operating Temperature: –20 °C to +60 °C
Case Size (W x H x D): 1.9” x 3.2” x 0.9” (47 x 81 x 23 mm) (W/O knob & antenna)
Weight: 4.6 oz (130 g) With FNB-82LI & antenna
Transmitter
RF Power Output: 1.5 W (@ 4.5 V AA x 3 or 3.7 V FNB-82LI 144 MHz)
3 W (@ 6 V or EXT DC 144 MHz)
1 W (@4.5 V AA x 3 or 3.7 V FNB-82LI 430 MHz)
2 W (@ 6 V or EXT DC 430 MHz)
Low 0.1 W (@ 4.5 V AA x 3 or 3.7 V FNB-82LI)
Low 0.3 W (@ 6 V or EXT DC)
Modulation Type: Variable Reactance F2D , F3E, F2A
Maximum Deviation: ±5 kHz (F2D , F3E)
Spurious Emission: At least 60 dB below (HIGH)
At least 50 dB below (LOW or less than 1 W)
Microphone Impedance:2 kΩ
2
Page 3

Receiver
Circuit Type: AM, NFM: Double-Conversion Superheterodyne
WFM: Triple-Conversion Superheterodyne
AM Radio/FM Radio: Single-Conversion Superheterodyne
Intermediate Frequencies: 1st: 47.25 MHz (AM, NFM)
1st: 45.8 MHz (WFM)
1st: 130 kHz (AM Radio/FM Radio)
2nd: 450 kHz (AM, NFM)
2nd: 10.7 MHz (WFM)
3rd: 1 MHz (WFM)
Sensitivity:3 μV for 10 dB SN (0.5-1.8 MHz, AM Radio)
3 μV for 10 dB SN (1.8-30 MHz, AM)
0.35 μV TYP for 12 dB SINAD (30-54 MHz, NFM)
1 μV TYP for 12 dB SINAD (54-76 MHz, NFM)
3 μV TYP for 12 dB SINAD (76-108 MHz, FM Radio)
1.5 μV TYP for 10 dB SN (108-137 MHz, AM)
0.2 μV for 12 dB SINAD (137-140 MHz, NFM)
0.16 μV for 12 dB SINAD (140-150 MHz, NFM)
0.2 μV for 12 dB SINAD (150-174 MHz, NFM)
1 μV TYP for 12 dB SINAD (174-225 MHz, NFM)
0.5 μV for 12 dB SINAD (300-350 MHz, NFM)
0.2 μV for 12 dB SINAD (350-400 MHz, NFM)
0.18 μV for 12 dB SINAD (400-470 MHz, NFM)
1.5 μV for 12 dB SINAD (470-540 MHz, WFM)
3 μV TYP for 12 dB SINAD (540-800 MHz, WFM)
1.5 μV TYP for 12 dB SINAD (800-999 MHz, NFM)
USA Version Cellular Blocked
Selectivity: NFM, AM: 12 kHz/35 kHz (–6 dB /–60 dB)
WFM : 200 kHz / 300 kHz (–6 dB/–20 dB)
AF Output: 50 mW @ 8 Ω for 10 % THD (@ 3.7 V)
100 mW @8 W for 10 % THD (@ 6 V)
Specifications
Specifications are subject to change without notice, and are guaranteed within the 144 and 430 MHz amateur bands only. Frequency
ranges will vary according to transceiver version; check with your dealer.
3
Page 4
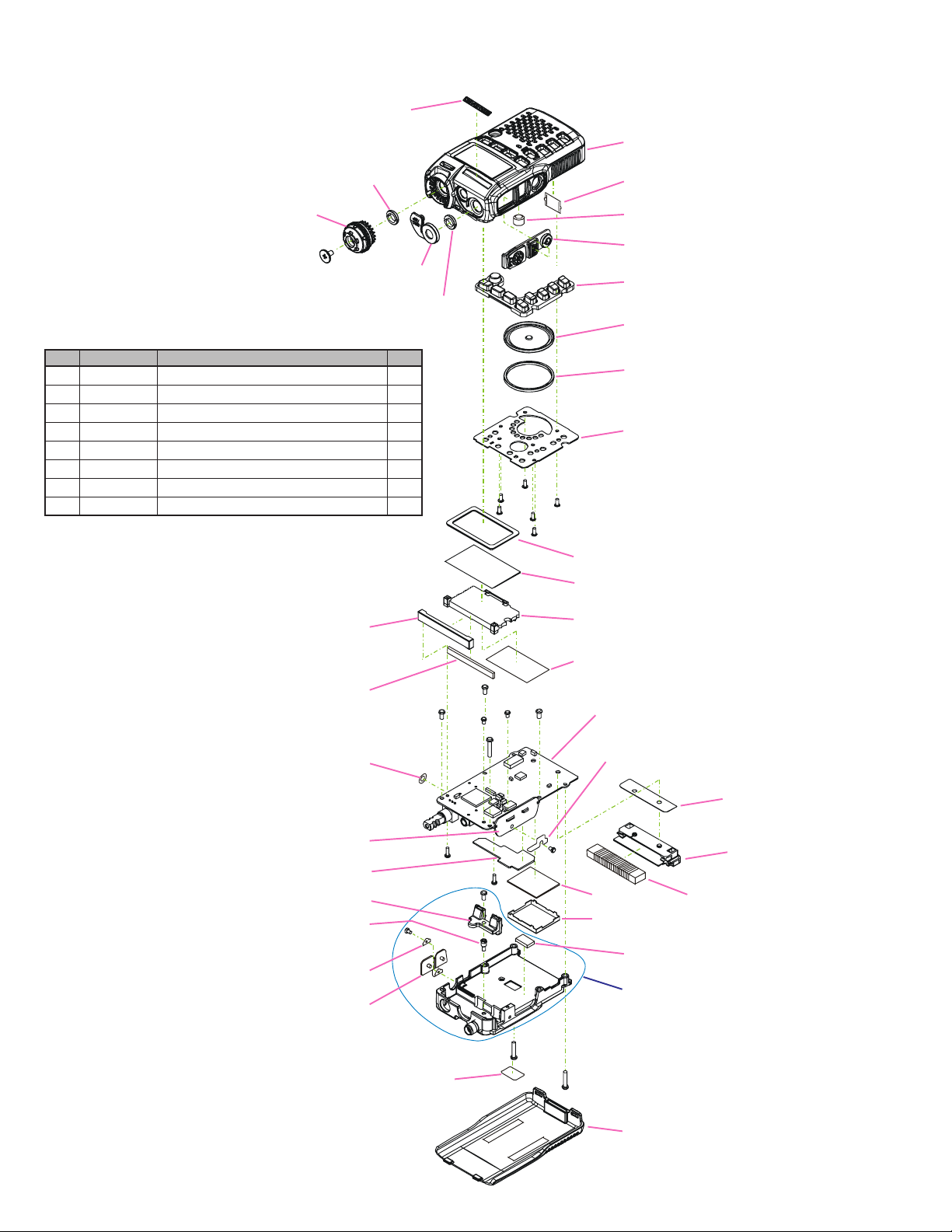
Exploded View & Miscellaneous Parts
RA0951900
NAME PLATE (YAESU)
RA0111400
RING NUT
RA0947300
ENCODER KNOB ASSY
No.
VXSTD P/N
U9900220
U9900068
U07125302
U9900156
U9900044
U44110002
RA0918600
U07240302
FLAT HEAD TAPTITE-B 1.7X4NI #1
PAN HEAD TAPTITE-B M2X4NI#3
PAN HEAD SCREW M1.7X2.5NI#3
PAN HEAD SCREW M2X11NI#3
PAN HEAD TAPTITE-P 1.7X5NI#3 GUIDE
PAN HEAD TAPTITE-B M2X10NI
SPECIAL SCREW (2.6X5X8)
PAN HEAD SCREW M2X4NI#3
Description
Non-designated parts are available only as part of a
designated assembly.
RA0922600
FRAME
RA0922700
INTER CONNECTOR
RA0955400
MASK SHEET (EXT)
RA094680A
MIC CAP
RA0023500
RING NUT(SMA)
Qty.
6
3
4
1
2
2
1
1
RA0954400
SHIELD SHEET (LCD)
G6090181
LCD
RA0922500
LIGHT GUIDE
RA0952400
LCD SHEET
MAIN Unit
RA0965600
THERMAL CONDUCTOR
RA095220A
CASE ASSY
RA0503600
LATCH NAIL
M3290048
MICROPHONE ELEMENT
RA094660A
RUBBER KNOB (PTT)
RA095230A
KEY PAD
M4090159
SPEAKER 0.5W/8-OHM
RA0948400
RUBBER RING
RA094830A
HOLDER PLATE
RA0950500
DOUBLE FACE (ANT)
SW Unit
FILTER Unit
RA0966900
CONTACT HOLDER ASSY
RA0532100
STUD
RA0955500
SUPPORT
RA094690B
EXT CAP
VCO Unit
RA0400300
SHIELD CASE VCO
RA0511800
SPONGE RUBBER (BOAD)
CP8973001
CHASSIS ASSY
RA0924200
HOLDER (ANT)
Q9000881
BAR ANTENNA
RA0952500
MASK SHEET (CHA)
RA0963700
BATTERY COVER ASSY
4
Page 5
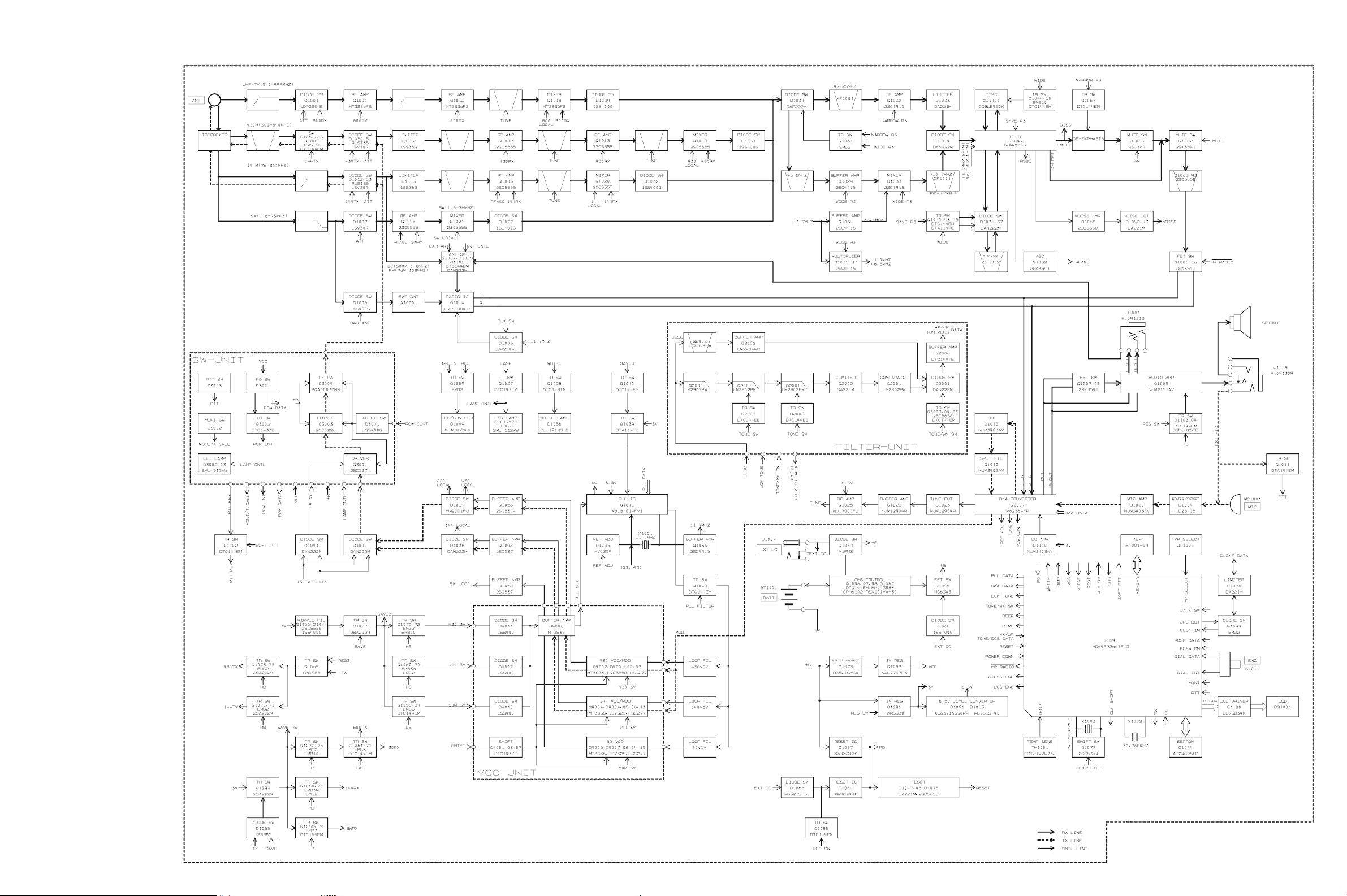
Block Diagram
5
Page 6

Note
6
Page 7

Circuit Description
The VX-3R consists of a MAIN-UNIT, a FILTER-UNIT, a
SW-UNIT, and a VCO-UNIT. The MAIN-UNIT contains
the receiver front end, PLL IC, power and switching circuits, the CPU, audio ICs, and the power circuitry for the
LCD, the IF, and audio ICs and the VCO-UNIT for transmit and receive local signal oscillation.
Receiver Signal Flow
The VX-3R includes four receiver front ends, each optimized for a particular frequency range and mode combination.
(1) Triplexer
Received 145 MHz signals, after passing through a lowpass filter to the VHF T/R switch circuit composed of diode switch D1052 (RLS135) and D1053 (1SV307).
Received 430 MHz signals, after passing through a lowpass filter to the UHF T/R switch circuit composed of diode switch D1050 (RLS135) and D1051 (1SV307).
(2) VHF Bands Reception
Received signals between 140 and 150 MHz pass through
the Triplexer circuit, low-pass filter/high-pass filter circuit, VHF T/R switch circuit and protector diode D1003
(1SS362) before additional filtering by a band-pass filter
prior to application to RF amplifier Q1003 (2SC5555). The
amplified RF signal is pass through the band-pass filter
to first mixer Q1020 (2SC5555). Meanwhile, VHF output
from the VCO-UNIT is amplified by Q1048 (2SC5374)
and applied through diode T/R switch D1038 (DAM222M)
to mixer Q1020 (2SC5555) as the first local signal.
The 47.25 MHz intermediate frequency product of the
mixer is delivered to the IF circuit.
The TUNE voltage from the CPU is amplified by DC amplifier Q1025 (NJU7007F3) and applied to varactors
D1011 (1SV325), D1012 (1SV325), D1013 (HVC369B),
D1014 (1SV325), D1015 (1SV325), D1016 (HVC369B),
D1025 (1SV325), and D1026 (1SV325) in the variable fre-
quency band-pass filters. By changing the electrostatic capacitance of the varactors, optimum filter characteristics
are provided for each specific operating frequency.
(3) UHF Bands Reception
Received signals between 430 and 450 MHz pass through
the Triplexer circuit, low-pass filter/high-pass filter circuit, UHF T/R switch circuit and protector diode D1002
(1SS326) before additional filtering by a band-pass filter
prior to application to RF amplifier Q1002 (2SC5555). The
amplified RF signal is pass through the band-pass filter,
RF amplifier Q1013 (2SC5555) and band-pass filter to first
mixer Q1019 (2SC5555). Meanwhile, UHF output from
the VCO-UNIT is amplified by Q1056 (2SC5374) and ap-
plied through diode T/R switch D1039 (DAM222M) to
mixer Q1019 (2SC5555) as the first local signal.
The 47.25 MHz intermediate frequency product of the
mixer is delivered to the IF circuit.
The TUNE voltage from the CPU is amplified by DC amplifier Q1025 (NJU7007F3) and applied to varactors
D1005, D1010, D1023, and D1024 (all HVC358B) in the
variable frequency band-pass filters. By changing the electrostatic capacitance of the varactors, optimum filter characteristics are provided for each specific operating frequency.
(4) 47.25-MHz First Intermediate Frequency
The 47.25 MHz first intermediate frequency from first
mixers is delivered from the first mixer to IF circuit. On
the MAIN-UNIT, the IF for AM and FM-narrow signals
is passed through diode switch D1030 (DAP222M) and
47.25 MHz monolithic crystal filter (MCF) XF1001 to narrow IF amplifier Q1030 (2SC4915) for input to IF IC Q1047
(NJM2552V) after amplitude limiting by D1033
(DA221M).
Meanwhile, a portion of the output of 11.7 MHz crystal
X1001 is multiplied fourfold by Q1035 and Q1037 (both
2SC4915) to provide the 46.8 MHz second local signal,
applied to the Narrow IF IC. Within the IC, this signal is
mixed with the 47.25 MHz first intermediate frequency
signal to produce the 450 kHz second intermediate frequency.
This second IF is filtered by ceramic filter CF1002 and
amplified by the limiting amplifier within the Narrow IF
IC before quadrate detection by ceramic discriminator
CD1001.
Demodulated audio is output from pin 11 of the Narrow
IF IC through narrow mute analog switch Q1068
(2SJ364).
The resulting audio is amplified by AF amplifier Q1005
(NJM2151AV), and output through MIC/EAR jack J1004
to internal speaker SP1001 or an external earphone.
Transmitter Signal Flow
(1) 145 MHz Band Transmit/Receive Switching
Closing PTT switch S3003 on the SW-UNIT pulls the base
of Q1011 (DTA144EM) low, causing the collector to go
high. This signal is input to pin 44 (PTT) of CPU Q1095
(HD64F2266TF13V), allowing the CPU to recognize that
the PTT switch has been pushed. When the CPU detects
closure of the PTT switch, pin 70 (TX/RX) goes high. This
control signal switches Q1069 (RN4985) to produce the
TX control signal that activates Q1071 (2SA2029). At the
same time, PLL division data is input to PLL IC Q1041
(MB15A01PFV1) from the CPU, to disable the receiver
power saver. Also, switching Q1070 (EMG2) to disable
the receiver circuits. Then causing the red side of BUSY/
TX lamp D1009 (CL-165HR/YG) to light.
7
Page 8

Circuit Description
(2) Modulation
Voice signal input from either built-in microphone
MC1001 on MAIN-UNIT or external jack J1004 on the
MAIN-UNIT is pre-emphasized by C1056 and R1033, and
processed by microphone amplifier Q1010 (NJM3403AV),
IDC (instantaneous deviation control) circuit Q1010
(NJM3403AV) to prevent over-modulation, and active
low-pass filter Q1010 (NJM3403AV).
During CTCSS operation, the voice signal is mixed with
the TONE ENC subaudible tone signal from pin 43 of the
CPU and delivered to the VCO. During DTMF operation,
the DTMF tones from pin 55 of the CPU are input to the
IDC stage.
(3) 145 MHz Band Transmission
Modulating audio passes through deviation setting D/A
converter Q1017 (M62364FP) to VHF MOD of the VCOUNIT mounted on the MAIN-UNIT. This signal is applied
to varactor D4005 (HSC277TRF) in the tank circuit of VHF
VCO Q4004 (MT3S36FS), which oscillates at the desired
VHF transmitting frequency. The modulated VCO signal
is buffered by amplifier Q4006 (MT3S36FS) and Q1048
(2SC5374) and delivered through VHF T/R diode switch
D1038 to the MAIN-UNIT. The modulated low-level VHF
transmit signal from the VCO is passed through diode
switch D1040 (DAN222M) to amplifier Q3001 (2SC5374).
The modulated VHF transmit signal from the VCO is
amplified by Q3001 (2SC5374) and RF power amplifier
Q3003 (2SC5226) up to 0.3 or 3 W (depending on the pow-
er source). The RF output passes through TX diode switch
D1052 (RLS135). RF output is passed by T/R switch and
low-pass filter to suppress harmonics and spurious products before output to the antenna at the antenna terminal.
(4) 435 MHz Band Transmission
Modulating audio passes through deviation setting D/A
converter Q1017 (M62364FP) to UHF MOD of the VCOUNIT mounted on the MAIN-UNIT. This signal is applied
to varactor D4002 (HSC277TRF) in the tank circuit of UHF
VCO Q4002 (MT3S36FS), which oscillates at the desired
UHF transmitting frequency. The modulated VCO signal
is buffered by amplifier Q4006 (MT3S36FS) and Q1056
(2SC5374) and delivered through UHF T/R diode switch
D1039 (DAN222M) to the MAIN-UNIT. The modulated
low-level UHF transmit signal from the VCO is passed
through diode switch D1040 (DAN222M) to amplifier
Q3004 (RQA0003DNS). The modulated UHF transmit sig-
nal from the VCO is amplified by Q3001 (2SC5374) and
RF power amplifier Q3003 (2SC5226) up to 0.3 or 2 W
(depending on the power source). The RF output passes
through TX diode switch D1050 (RLS135). RF output is
passed by T/R switch and low-pass filter to suppress harmonics and spurious products before output to the antenna at the antenna terminal.
PLL Frequency Synthesizer
PLL IC Q1041 (MB15A01PFV1) on the MAIN-UNIT con-
sists of a data shift register, reference frequency divider,
phase comparator, charge pump, intermittent operation
circuit, and band selector switch. Serial PLL data from
the CPU is converted into parallel data by the shift register in the PLL IC and is latched into the comparative frequency divider and reference frequency divider to set a
frequency dividing ratio for each. An 11.7 MHz reference
signal produced by X1001 is input to REF pin 1 of the PLL
IC. The internal reference frequency divider divides the
11.7 MHz reference by 2,050 (or 1,640) to obtain a reference frequency of 5 kHz (or 6.25 kHz), which is applied
to the phase comparator. Meanwhile, a sample of the output of VHF VCO Q4004 or UHF VCO Q4002 on the VCOUNIT, buffered by Q4006, is input to the PLL IC, where it
is frequency-divided by the internal comparative frequency divider to produce a comparative frequency also applied to the phase comparator. The phase comparator compares the phase between the reference frequency and comparative frequency to output a pulse corresponding to the
phase difference between them. This pulse is input to the
charge pump, and the output from the charge pump passes through a loop filter composed of R1280, R1281, C1185,
R1169 and either R1171, C1187, R1174 and C1190 for VHF,
or R1170, C1186, R1173 and C1189 for UHF, which convert the pulse into a corresponding smoothed varactor
control voltage (VCV). The VCV is applied to varactor
D4004 and D4013 (both 1SV325) in the VHF VCO tank
circuit, or to varactor D4001 (HVC355B) in the UHF VCO
tank circuit, to eliminate phase difference between the reference frequency and comparative frequency, and so locking the VCO oscillation frequency to the reference crystal. The VCO frequency is determined by the frequencydividing ratio sent from the CPU to the PLL IC. During
receiver power save operation, the PLL circuit operates
intermittently to reduce current consumption, for which
the intermittent operation control circuit reduces the lockup time.
8
Page 9

Alignment
Introduction
The VX-3R is carefully aligned at the factory for the
specified performance across the amateur band. Realign-
ment should therefore not be necessary except in the event
of a component failure. Only an authorized VERTEX
STANDARD representative should perform all compo-
nent replacement and service, or the warranty policy may
be void. The following procedures cover adjustments that
are not normally required once the transceiver has left
the factory. However, if damage occurs and some parts
are subsequently replaced, realignment may be required.
If a sudden problem occurs during normal operation, it is
likely due to component failure; realignment should not
be done until after the faulty component has been re-
placed. We recommend that servicing be performed only
by authorized VERTEX STANDARD service technicians
who are experienced with the circuitry and fully equipped
for repair and alignment. If a fault is suspected, contact
the dealer from whom the transceiver was purchased for
instructions regarding repair. Authorized VERTEX STAN-
DARD service technicians realign all circuits and make
complete performance checks to ensure compliance with
factory specifications after replacing any faulty compo-
nents. Those who do undertake any of the following align-
ments are cautioned to proceed at their own risk. Prob-
lems caused by unauthorized attempts at realignment are
not covered by the warranty policy. In addition, VERTEX
STANDARD reserves the right to change circuits and
alignment procedures in the interest of improved perfor-
mance, without notifying owners.
Under no circumstances should any alignment be at-
tempted unless the normal function and operation of the
transceiver is clearly understood, the cause of the mal-
function has been clearly pinpointed, any faulty compo-
nents are replaced, and realignment is determined to be
absolutely necessary.
The following test equipment (and familiarity with its
use) is necessary for complete realignment. Correction of
problems caused by misalignment resulting from use of
improper test equipment is not covered under the war-
ranty policy. While most steps do not require all of the
equipment listed, the interactions of some adjustments
may require that additional adjustments be performed.
Do not attempt to perform only a single step unless it is
clearly isolated electrically from all other steps. Have all
test equipment ready before beginning and, follow all of
the steps in a section in the order presented.
Required Test Equipment
P RF Signal Generator with calibrated output level at 500 MHz
P Deviation Meter (linear detector)
P In-line Wattmeter with 5% accuracy at 500 MHz
P 50-ohm, 10-W RF Dummy Load
P 8-ohm AF Dummy Load
P Regulated DC Power Supply adjustable from 3 to 15 V DC, 3A
P Frequency Counter: 0.2-ppm accuracy at 500 MHz
P AF Signal Generator
P AC Voltmeter
P DC Voltmeter: high impedance
P UHF Sampling Coupler
P SINAD Meter
Alignment Preparation & Precautions
A 10 W RF dummy load and in-line wattmeter must
be connected to the main antenna jack in all procedures
that call for transmission, alignment is not possible with
an antenna. After completing one step, read the next step
to see if the same test equipment is required. If not, re-
move the test equipment (except dummy load and watt-
meter, if connected) before proceeding.
Correct alignment requires that the ambient tempera-
ture of the transceiver be the same as that of the test equip-
ment, and that the temperature be held constant between
68 ~ 86 °F (20 ~ 30 °C). When the transceiver is brought
into the shop from hot or cold air, it should be allowed
some time to come to room temperature before alignment.
Whenever possible, alignments should be made with os-
cillator shields and circuit boards firmly affixed in place.
The test equipment must be thoroughly warmed up be-
fore beginning.
Note: Signal levels in dB referred to in the alignment procedure
are based on 0 dBμ=0.5 μV (closed circuit).
Test Setup
Set up the test equipment as shown below for transceiv-
er alignment, and apply 4.4 V DC power to the transceiver.
Refer to the drawings for Alignment Points.
RF Signal
Generator
In-Line
Wattmeter
50-ohm RF
Dummy Load
Deviation
Meter
Frequency
Counter
Sampling
Coupler
Alignment Setup
8-ohm
AF Load
SINAD
Meter
9
Page 10

Alignment
Internal System Alignment Routine
This uses a programmed routine in the transceiver, which
simplifies many previously complex discrete component
settings and adjustments with digitally controlled settings
via front panel buttons and LCD indications.
To enter the alignment mode:
U Program the alignment password "AH028M" into
the CW ID memory via the Set Mode Item 19: CW ID.
(See the box below for programming the alignment
password.)
U Turn off the transceiver.
U Press and hold in the [TXPO] button while powering
the radio on to enter the alignment mode.
U In the alignment mode, each adjustment item is shown
on the LCD in the Memory Channel Number display
slot, and is selected by rotating the DIAL knob.
To exit the alignment mode:
U Press the [HM/RV] button.
U Clear the alignment password from the CW ID mem-
ory, and program the user's CW ID, if needed.
Warning!: Do not change the alignment items which are
not described in the adjustment procedures.
Programming the Alignment Password
1. Press and hold in the [TXPO] key for one second to
enter the Set mode.
2. Rotate the DIAL knob to select Set Mode Item 19: CW
ID.
Note: Do not forget to pull the DIAL knob to rotate the
DIAL knob.
3. Press the [TXPO] key momentarily to enable adjust-
ment of this Set Mode Item.
4. Rotate the DIAL knob to set this Item to "ON".
5. Press the [V/M] key momentarily to display any previ-
ously stored callsign.
Note the previously stored call sign, so you can re-
enter it later.
6. Press and hold the [HM/RV] key for 2 seconds to clear
any previous callsign.
7. Rotate the DIAL knob to select the "A", then press the
[V/M] key momentarily to save the "A" and move on
to the next character.
8. Repeat the previous step to complete the alignment
password "AH028M".
9. Press the [TXPO] key momentarily, then press the PTT
switch to save the settings and exit to normal opera-
tion.
PLL Reference Frequency Adjustment (REF)
P Rotate the DIAL knob to select the alignment item "rEF".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that
the Frequency Counter reading is 440.000 MHz ±200
Hz.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
430 MHz band
RX Tune Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to -10 dBμV at the 435.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Connect the SINAD meter to the MIC/SP jack
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click counter-clockwise to
select the alignment item "tUn".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Rotate the DIAL knob for minimum defection of the
SINAD meter.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
Squelch Threshold Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and then
set the output level to -12 dBμV at the 435.100 MHz (with 1
kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob three clicks clockwise to select the
alignment item "tHL".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key again.
Squelch Tight Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and then
set the output level to -5 dBμ at the 435.100 MHz (with 1 kHz
tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "tIg".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key again.
NFM S-Meter S-1 Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and then
set the output level to -7 dBμV at the 435.100 MHz (with 1
kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "S1".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key again.
10
Page 11
Alignment
NFM S-Meter Full Scale Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and then
set the output level to +20 dBμV at the 435.100 MHz (with 1
kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "S9".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key again.
WFM S-Meter S-1 Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and then
set the output level to 0 dBμV at the 435.100 MHz (with 1
kHz tone @ ±20 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "S1".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key again.
WFM S-Meter Full Scale Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and then
set the output level to +20 dBμV at the 435.100 MHz (with 1
kHz tone @ ±20 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "S9".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key again.
High TX Power Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load and Wattmeter to the
ANT jack.
P Increase the DC power supply voltage to 6.0 V.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "HHP".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that the
Wattmeter reading is 2.0 W ±0.1 W.
P Reduce the DC power supply voltage to 4.4 V.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "HP".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that the
Wattmeter reading is 1.0 W ±0.1 W.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
Low TX Power Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load and Wattmeter to the
ANT jack.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "LP".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that the
Wattmeter reading is 0.1 W ±0.05 W.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
MAX Deviation Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load, Wattmeter, and Devia-
tion Meter to the ANT jack.
P Connect the AF Generator to the MIC/SP jack, and then set
the output level to 50 mV at 1 kHz.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "dEV".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that the
Deviation meter reading is 4.2 kHz ±0.1 kHz.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
CTCSS Tone Deviation Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load, Wattmeter, and Devia-
tion Meter to the ANT jack.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "100".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that the
Deviation meter reading is 0.65 kHz ±0.05 kHz.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
DCS Deviation Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load, Wattmeter, and Devia-
tion Meter to the ANT jack.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the align-
ment item "dCS".
P Press the [V/M] key.
Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that the
Deviation meter reading is 0.65 kHz ±0.05 kHz.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
11
Page 12

Alignment
50 MHz band
Press the [BAND] button to switch the alignment band to
50 MHz Band.
Squelch Threshold Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to -4 dBμV at the 52.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "tHL".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
Squelch Tight Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to +3 dBμV at the 52.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "tIg".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
WFM S-Meter S-1 Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to +8 dBμV at the 52.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±20 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "S1".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
WFM S-Meter Full Scale Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to +25 dBμV at the 52.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±20 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "S9".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
NFM S-Meter S-1 Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to 0 dBμV at the 52.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "S1".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
NFM S-Meter Full Scale Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to +20 dBμV at the 52.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "S9".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
12
Page 13
Alignment
144 MHz Band
Press the [BAND] button to switch the alignment band to
144 MHz Band.
RX Tune Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to -10 dBμV at the 145.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Connect the SINAD meter to the MIC/SP jack
P Rotate the DIAL knob clockwise until the alignment
item "tUn" appears.
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Rotate the DIAL knob for minimum defection of the
SINAD meter.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
Squelch Threshold Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to -12 dBμV at the 145.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob counter-clockwise until the align-
ment item "tHL" appears
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
Squelch Tight Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to -5 dBμV at the 145.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "tIg".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
NFM S-Meter S-1 Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to -7 dBμV at the 145.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "S1".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
NFM S-Meter Full Scale Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to +20 dBμV at the 145.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±3.5 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "S9".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
WFM S-Meter S-1 Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to 0 dBμV at the 145.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±20 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "S1".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
WFM S-Meter Full Scale Adjustment
P Connect the RF Signal Generator to the ANT jack, and
then set the output level to +20 dBμV at the 145.100 MHz
(with 1 kHz tone @ ±20 kHz deviation).
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "S9".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the [F/W] key twice, and then press the [V/M] key
again.
High TX Power Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load and Wattmeter to
the ANT jack.
P Increase the DC power supply voltage to 6.0 V
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "HHP".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that
the Wattmeter reading is 2.9 W ±0.1 W.
P Reduce the DC power supply voltage to 4.4 V
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "HP".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that
the Wattmeter reading is 1.5 W ±0.1 W.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
13
Page 14

Alignment
Low TX Power Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load and Wattmeter to
the ANT jack.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "LP".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that
the Wattmeter reading is 0.1 W ±0.05 W.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
MAX Deviation Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load, Wattmeter, and
Deviation Meter to the ANT jack.
P Connect the AF Generator to the MIC/SP jack, and then
set the output level to 50 mV at 1 kHz.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "dEV".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that
the Deviation meter reading is 4.2 kHz ±0.1 kHz.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
CTCSS Tone Deviation Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load, Wattmeter, and
Deviation Meter to the ANT jack.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "100".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that
the Deviation meter reading is 0.65 kHz ±0.05 kHz.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
DCS Deviation Adjustment
P Connect the 50-Ohm Dummy Load, Wattmeter, and
Deviation Meter to the ANT jack.
P Rotate the DIAL knob one click clockwise to select the
alignment item "dCS".
P Press the [V/M] key.
P Press the PTT switch, then rotate the DIAL knob so that
the Deviation meter reading is 0.65 kHz ±0.05 kHz.
P Press the [V/M] key again.
This completes the internal alignment routine for all
bands. To save all settings and exit, press the [HM/RV]
button.
14
Page 15

MAIN Unit
Circuit Diagram
15
Page 16

MAIN Unit
Note
16
Page 17

BA C
MAIN Unit
Parts Layout (Side A)
HD64F2266TF13V
(Q1095)
LC75834W
(Q1100)
LV24100LP
(Q1014)
1
M62364FP
(Q1017)
NJM2151AV
(Q1005)
NJM3403AV
(Q1010)
AT24C256
(Q1094)
NJM12904R
(Q1023)
2
2SK3541
(Q1006, 1007, 1008,
1016, 1032, 1082)
2SA2029 (F*)
(Q1057, 1071, 1073,
1092)
2SC5374 (NA)
(Q1077)
2SC5658 (B*)
(Q1055, 1078, 1088, 1093)
DTA114TE (94)
(Q1039, 1042, 1043)
DTA144EM (16)
(Q1039, 1042, 1043)
3
DTC143TM (03)
(Q1039, 1042, 1043)
DTC144EM (26)
(Q1004, 1040, 1045, 1050,
1059, 1061, 1085, 1089,
1102, 1104, 1105)
EMB10 (B10)
(Q1044, 1072)
EMB3 (B3)
(Q1058, 1060, 1074)
EMD2 (D2)
(Q1099)
4
EMG2 (G2)
(Q1009, 1070, 1075)
SSM6J25FE (PH)
5
(Q1103)
MT3S36FS (21)
(Q1001, 1012, 1018)
TAR5S30
(Q1086)
NJU7007F3 (B3)
(Q1025)
XC61GN3002HR
(Q1084, 1087)
NJU7747F4
(Q1083)
1SS385 (09)
(D1055)
DAN222M (N)
(D1008)
RN4985
(Q1069)
DA221M (K)
(D1047, 1048, 1070)
17
Page 18

MAIN Unit
Parts Layout (Side B)
ba c
NJM2552V
(Q1047)
MB15A02PFV1
(Q1041)
MM1438BWLE
(Q1097)
1
2SJ364 (4M)
(Q1068)
2
2SC4915-O (QY)
(Q1029, 1030, 1033, 1034,
1035, 1036, 1037)
2SC5374 (NA)
(Q1038, 1048, 1056)
2SC5555ZD (ZD-)
(Q1002, 1003, 1013, 1015,
1019, 1020, 1021)
2SC5658 (B*)
(Q1065)
CPH6102 (AB)
(Q1096)
DTC144EM (26)
(Q1049, 1067, 1098)
3
EMG2 (G2)
(Q1031)
MCH6305 (JE)
(Q1090)
XC6371A650PR (AF0)
(Q1091)
4
5
18
1SS362 (C3)
(D1002, 1003)
DA221M (K)
(D1033, 1042, 1043)
1SS385 (09)
(D1055)
DAN222M (N)
(D1034, 1036, 1037, 1038,
1039, 1040, 1041)
DAP222M (P)
(D1030)
Page 19

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
P.C.B. with Components (W/ SW Unit, VCO Unit) CP8966001 DST:USA TYP:A2U
CP8966003 DST:EXP TYP:A1
CP8966004 DST:EXP TYP:A2
CP8966005 DST:EXP TYP:A3
CP8966006 DST:EU TYP:B1
CP8966007 DST:EU TYP:B2
CP8966008 DST:EXP TYP:B3
CP8966009 DST:EU TYP:C1
CP8966010 DST:EU TYP:C2
CP8966011 DST:EXP TYP:C3
CP8966012 DST:EU TYP:D1
CP8966013 DST:EU TYP:D2
CP8966014 DST:AUS TYP:H1
CP8966015 DST:AUS TYP:H2
Printed Circuit Board FR0158600 1C 1001 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK UMK105CK020CW-F K22178250 1- A A1
C 1002 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c3
C 1003 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B c2
C 1004 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B c2
C 1005 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A A1
C 1006 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- B c3
C 1007 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c2
C 1008 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c2
C 1009 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH UMK105CH150JW-F K22178262 1- A B1
C 1010 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c2
C 1011 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B5
C 1012 CHIP CAP. 68pF 50V CH UMK105CH680JW-F K22178278 1- A B1
C 1013 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A A5
C 1014 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A A5
C 1015 CHIP TA.CAP. 47uF 4V TEESVP0G476M8R K78060050 1- A A2
C 1016 CHIP TA.CAP. 47uF 4V TEESVP0G476M8R K78060050 1- A A2
C 1017 CHIP TA.CAP. 100uF 4V TEESVA0G107M8R K78060051 1- A C5
C 1018 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A3
C 1019 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A3
C 1020 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK GRM1554C1H2R0CZ01D K22178204 1- A A1
C 1021 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH UMK105CH050CW-F K22178253 1- A A1
C 1022 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1- A A1
C 1023 CHIP CAP. 12pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H120JZ01D K22178214 1- A A1
C 1024 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH UMK105CH070DW-F K22178255 1- A A1
C 1025 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- A B3
C 1026 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B c3
C 1028 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c3
C 1029 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH UMK105CH040CW-F K22178252 1- B c3
C 1030 CHIP CAP. 220pF 25V CH GRM36CH221J25PT K22148203 1- B c3
C 1031 CHIP CAP. 68pF 50V CH UMK105CH680JW-F K22178278 1- B c2
C 1032 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- B c2
C 1034 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B c3
C 1035 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B c2
C 1036 CHIP CAP. 22pF 50V CH UMK105CH220JW-F K22178266 1- A B1
C 1037 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c3
C 1038 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B c3
C 1039 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B c3
C 1040 CHIP CAP. 22pF 50V CH UMK105CH220JW-F K22178266 1- B b3
C 1041 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b3
C 1042 CHIP CAP. 47pF 50V CH UMK105CH470JW-F K22178274 1- A B1
C 1043 CHIP CAP. 56pF 50V CH UMK105CH560JW-F K22178276 1- A B1
C 1044 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A5
C 1045 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A B5
C 1046 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B5
C 1047 CHIP TA.CAP. 100uF 4V TEESVA0G107M8R K78060051 1- A A2
C 1051 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A B4
C 1052 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A B4
C 1054 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A B4
C 1055 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A4
C 1056 CHIP CAP. 0.0047uF 25V B TMK105B472KW-F K22148831 1- A B4
C 1057 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B4
C 1058 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B4
C 1059 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A B3
C 1060 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ UMK105CJ030CW-F K22178251 1- A B3
C 1061 CHIP CAP. 8pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H8R0DZ01D K22178210 1- A B3
C 1062 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ UMK105CJ030CW-F K22178251 1- A B3
C 1063 CHIP CAP. 0.5pF 50V CK UMK105CK0R5CW-F K22178247 1- B c3
C 1064 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK UMK105CK020CW-F K22178250 1- B c3
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
19
Page 20

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
C 1065 CHIP CAP. 56pF 50V CH UMK105CH560JW-F K22178276 1- B c3
C 1066 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH UMK105CH040CW-F K22178252 1- B c3
C 1067 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b3
C 1068 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A B3
C 1069 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c3
C 1070 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH UMK105CH040CW-F K22178252 1- B b3
C 1071 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B c3
C 1072 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b3
C 1073 CHIP CAP. 8pF 50V CH UMK105CH080DW-F K22178256 1- B b3
C 1074 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b3
C 1075 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B c3
C 1076 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b3
C 1077 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B b3
C 1078 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b3
C 1079 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A A5
C 1080 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A A2
C 1084 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A B4
C 1085 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B4
C 1086 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B4
C 1087 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B4
C 1088 CHIP CAP. 180pF 25V CH TMK105CH181JW-F K22148244 1- A B4
C 1089 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B3
C 1090 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 4V TESVSP0G226M-8R K78060047 1- A B3
C 1091 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A C4
C 1092 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH UMK105CH180JW-F K22178264 1- A B4
C 1093 CHIP CAP. 1pF 50V CK UMK105CK010CW-F K22178248 1- A B3
C 1094 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK GRM1554C1H2R0CZ01D K22178204 1- A B3
C 1095 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH UMK105CH180JW-F K22178264 1- A B4
C 1096 CHIP CAP. 12pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H120JZ01D K22178214 1- A C3
C 1097 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK GRM1554C1H2R0CZ01D K22178204 1- A B3
C 1098 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ UMK105CJ030CW-F K22178251 1- A B3
C 1099 CHIP CAP. 56pF 50V CH UMK105CH560JW-F K22178276 1- B b3
C 1100 CHIP CAP. 1pF 50V CK UMK105CK010CW-F K22178248 1- B b3
C 1101 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK UMK105CK020CW-F K22178250 1- B b3
C 1102 CHIP CAP. 56pF 50V CH UMK105CH560JW-F K22178276 1- B b3
C 1103 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ UMK105CJ030CW-F K22178251 1- B b3
C 1104 CHIP CAP. 3pF 50V CJ UMK105CJ030CW-F K22178251 1- B b3
C 1105 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH UMK105CH050CW-F K22178253 1- A B3
C 1106 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b3
C 1107 CHIP CAP. 8pF 50V CH UMK105CH080DW-F K22178256 1- B b2
C 1108 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH UMK105CH090DW-F K22178257 1- B b3
C 1109 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK UMK105CK020CW-F K22178250 1 B b3
C 1109 CHIP CAP. 1pF 50V CK GRM1554C1H1R0BZ01D K22178287 2- B b3
C 1110 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1 B b3
C 1110 CHIP CAP. 1pF 50V CK GRM1554C1H1R0BZ01D K22178287 2- B b3
C 1111 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B5
C 1112 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A B5
C 1113 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A C5
C 1114 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A C5
C 1115 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B4
C 1116 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B4
C 1117 CHIP CAP. 0.0033uF 50V B GRM155B11H332KA01D K22178815 1- A B4
C 1118 CHIP CAP. 0.0033uF 50V B UMK105B332KW-F K22178835 1- A B4
C 1119 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B4
C 1120 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- B a3
C 1121 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a3
C 1122 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b3
C 1123 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A B3
C 1124 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a3
C 1125 CHIP CAP. 68pF 50V CH UMK105CH680JW-F K22178278 1- B b3
C 1126 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b2
C 1127 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B a3
C 1128 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c5
C 1129 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A C4
C 1130 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A C4
C 1131 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a3
C 1132 CHIP CAP. 0.22uF 10V B GRM155B31A224KE18D K22108808 1- A C4
C 1133 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a4
C 1134 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a2
C 1135 CHIP CAP. 22pF 50V CH UMK105CH220JW-F K22178266 1- B a2
C 1136 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B a3
C 1137 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B a3
C 1138 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c5
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
20
Page 21

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
C 1139 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B b4
C 1140 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b4
C 1141 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1- B b4
C 1142 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b5
C 1143 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b4
C 1144 CHIP CAP. 56pF 50V CH UMK105CH560JW-F K22178276 1- B b4
C 1145 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- B b4
C 1146 CHIP CAP. 470pF 25V B TMK105B471K-F K22148816 1- B c5
C 1147 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 4V TESVSP0G226M-8R K78060047 1- B c4
C 1148 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B c4
C 1149 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B c4
C 1150 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH UMK105CH150JW-F K22178262 1- B a3
C 1151 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1- B a3
C 1152 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a2
C 1153 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a3
C 1154 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b5
C 1155 CHIP CAP. 180pF 25V CH GRM36CH181J25PT K22148201 1- B b5
C 1156 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH UMK105CH050CW-F K22178253 1- B b5
C 1157 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b4
C 1158 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b5
C 1159 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a5
C 1160 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a4
C 1161 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B c3
C 1162 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B c4
C 1163 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B c4
C 1164 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B b4
C 1165 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1- B c4
C 1166 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B c4
C 1167 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH UMK105CH180JW-F K22178264 1- B c4
C 1168 CHIP CAP. 220pF 25V CH GRM36CH221J25PT K22148203 1- B c4
C 1169 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c4
C 1170 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c3
C 1171 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b4
C 1172 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- B c4
C 1173 CHIP TA.CAP. 100uF 4V TEESVA0G107M8R K78060051 1- A C3
C 1179 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a4
C 1180 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 10V B GRM155B11A473KA01D K22108801 1- B a4
C 1181 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B UMK105B471KW-F K22178825 1- B b4
C 1182 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a4
C 1183 CHIP CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V B JMK107BJ475MA-T K22084803 1- B a4
C 1184 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH UMK105CH070DW-F K22178255 1- B b4
C 1185 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V TESVSP0J475M-8R K78080053 1- B c4
C 1186 CHIP TA.CAP. 0.1uF 20V SKF-1D104M-RP K78130049 1- B c4
C 1187 CHIP TA.CAP. 0.1uF 20V SKF-1D104M-RP K78130049 1- B c4
C 1188 CHIP TA.CAP. 0.1uF 20V SKF-1D104M-RP K78130049 1- B c4
C 1189 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c4
C 1190 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 10V B GRM155B11A473KA01D K22108801 1- B c3
C 1191 CHIP CAP. 0.033uF 10V B GRM155B11A333KA01D K22108803 1- B c5
C 1192 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c4
C 1193 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- B c4
C 1194 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c4
C 1195 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- B c4
C 1197 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c3
C 1198 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c3
C 1204 CHIP CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V B JMK107BJ475MA-T K22084803 1- B a4
C 1205 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B UMK105B471KW-F K22178825 1- B b4
C 1206 CHIP CAP. 0.0047uF 25V B GRM36B472K25PT K22148830 1- B b4
C 1207 CHIP CAP. 0.0056uF 25V B GRM155B11E562KA01D K22148802 1- B b4
C 1209 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b4
C 1210 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a4
C 1211 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B a4
C 1212 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a4
C 1213 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b4
C 1214 CHIP CAP. 56pF 50V CH UMK105CH560JW-F K22178276 1- B b4
C 1215 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50V B UMK105B471KW-F K22178825 1- B b5
C 1216 CHIP CAP. 0.0018uF 50V B UMK105B182KW-F K22178832 1- B b5
C 1217 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH UMK105CH070DW-F K22178255 1- B b3
C 1218 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 4V TESVSP0G226M-8R K78060047 1- A A4
C 1219 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A4
C 1220 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c4
C 1226 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b3
C 1227 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B a3
C 1228 CHIP CAP. 0.0022uF 50V B UMK105B222KW-F K22178833 1- B a3
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
21
Page 22

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
C 1229 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b4
C 1230 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 16V B EMK105B223KW-F K22128813 1- B b4
C 1231 CHIP CAP. 0.0039uF 50V B UMK105B392KW-F K22178836 1- B b4
C 1232 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a4
C 1233 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b4
C 1234 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A C5
C 1235 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 4V TESVSP0G226M-8R K78060047 1- A A4
C 1236 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A4
C 1237 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A4
C 1240 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b4
C 1241 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B a3
C 1242 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 10V B GRM155B11A473KA01D K22108801 1- B a3
C 1243 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 10V B GRM155B11A473KA01D K22108801 1- A C2
C 1244 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H150JZ01D K22178216 1- A B2
C 1245 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H150JZ01D K22178216 1- A B2
C 1246 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H150JZ01D K22178216 1- A C2
C 1247 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH UMK105CH050CW-F K22178253 1- A C2
C 1248 CHIP CAP. 6pF 50V CH UMK105CH060DW-F K22178254 1- A C2
C 1249 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A C1
C 1250 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H150JZ01D K22178216 1- A C2
C 1251 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1 B c2
C 1251 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH UMK105CH090DW-F K22178257 AUSTRALIA 2- B c2
C 1251 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 EUROPE 2- B c2
C 1251 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH UMK105CH090DW-F K22178257 EXPORT 2- B c2
C 1251 CHIP CAP. 9pF 50V CH UMK105CH090DW-F K22178257 USA 2- B c2
C 1252 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1- B c2
C 1253 CHIP TA.CAP. 100uF 4V TEESVA0G107M8R K78060051 1- A B2
C 1254 CHIP TA.CAP. 100uF 4V TEESVA0G107M8R K78060051 1- A B2
C 1255 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B1
C 1256 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A C2
C 1257 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A C2
C 1259 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A C2
C 1261 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A C2
C 1263 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A B4
C 1264 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH UMK105CH180JW-F K22178264 1- B c2
C 1266 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c2
C 1267 CHIP CAP. 56pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H560JD01D K22178230 1 B c2
C 1267 CHIP CAP. 51pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H510JZ01D K22178229 2- B c2
C 1268 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c3
C 1269 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c2
C 1270 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1 B c2
C 1270 CHIP CAP. 47pF 50V CH UMK105CH470JW-F K22178274 2- B c2
C 1271 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c2
C 1274 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c2
C 1275 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A C2
C 1276 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A C2
C 1277 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A C1
C 1280 CHIP CAP. 0.0068uF 25V B GRM155B11E682KA01D K22148803 1- A B4
C 1281 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B5
C 1282 CHIP CAP. 820pF 50V B GRM155B11H821KA01D K22178808 1- A B5
C 1284 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH UMK105CH050CW-F K22178253 1 B c2
C 1284 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH UMK105CH070DW-F K22178255 2- B c2
C 1285 CHIP CAP. 12pF 50V CH UMK105CH120JW-F K22178260 1- B c1
C 1287 CHIP CAP. 8pF 50V CH UMK105CH080DW-F K22178256 1- B c1
C 1288 CHIP CAP. 27pF 50V CH UMK105CH270JW-F K22178268 1- B c2
C 1290 CHIP CAP. 27pF 50V CH UMK105CH270JW-F K22178268 1- B b2
C 1292 CHIP CAP. 39pF 50V CH UMK105CH390JW-F K22178272 1- B c1
C 1293 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH UMK105CH150JW-F K22178262 1- B c1
C 1294 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- B c1
C 1296 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B1
C 1297 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 4V TESVSP0G226M-8R K78060047 1- B b2
C 1298 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B4
C 1299 CHIP TA.CAP. 33uF 10V TEMSVB21A336M-8R K78100047 1- B b2
C 1300 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TEESVP1A106M8R K78100074 1- B c4
C 1301 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b2
C 1302 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b2
C 1303 CHIP CAP. 820pF 50V B GRM155B11H821KA01D K22178808 1- A B4
C 1304 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B5
C 1306 CHIP CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V B JMK107BJ475MA-T K22084803 1- A B5
C 1307 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B2
C 1308 CHIP CAP. 68pF 50V CH UMK105CH680JW-F K22178278 1- B c1
C 1309 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH UMK105CH150JW-F K22178262 1- B c1
C 1310 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH UMK105CH180JW-F K22178264 1- B c1
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
22
Page 23

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
C 1311 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH UMK105CH150JW-F K22178262 1- B c1
C 1312 CHIP CAP. 7pF 50V CH UMK105CH070DW-F K22178255 1- B c1
C 1313 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- B c1
C 1314 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 1315 CHIP CAP. 8pF 50V CH UMK105CH080DW-F K22178256 1- B c1
C 1316 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b1
C 1318 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H101JD01D K22178236 1- A A4
C 1319 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 16V F GRM155F11C473ZA01D K22129004 1- A B1
C 1320 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A A1
C 1321 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A A1
C 1322 CHIP CAP. 680pF 50V B UMK105B681KW-F K22178827 1- A A2
C 1323 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b1
C 1324 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b1
C 1325 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B a2
C 1326 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H101JD01D K22178236 1- A A4
C 1327 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 16V F GRM155F11C473ZA01D K22129004 1- A B1
C 1329 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 4V TESVSP0G226M-8R K78060047 1- B a1
C 1330 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A A2
C 1331 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A A2
C 1332 CHIP CAP. 220pF 50V B UMK105B221KW-F K22178821 1- B a4
C 1333 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A A2
C 1334 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A2
C 1335 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A B5
C 1336 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 47uF 10V RV5-10V470M K48100011 1- B b1
C 1337 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 47uF 10V RV5-10V470M K48100011 1- B b1
C 1338 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A A4
C 1339 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A B4
C 1340 CHIP CAP. 0.33uF 6.3V B GRM155B10J334KE18D K22088801 1- B c4
C 1341 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 4V TESVSP0G226M-8R K78060047 1- A A4
C 1342 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A C1
C 1346 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A C3
C 1347 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B c2
C 1348 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- A A1
C 1349 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- A A1
C 1350 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- A C1
C 1351 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- A B1
C 1352 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- A B1
C 1353 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- A A2
C 1356 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1C 1356 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 4C 1357 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174809 1C 1357 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 4C 1358 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1C 1358 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 4C 1360 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1CD1001 CERAMIC DISC CDBLB450KCAY07-B0 H7900930 1CF1001 CERAMIC FILTER SFECF10M7GA00-R0 H3900577 1- B a3
CF1002 CERAMIC FILTER ELFC450F H3900552 1- B a4
D 1001 DIODE JDP2S04E(TAPE) G2071180 1- A A1
D 1002 DIODE 1SS362(TE85R.F) G2070268 1- B c2
D 1003 DIODE 1SS362(TE85R.F) G2070268 1- B c2
D 1004 DIODE UDZS TE-17 5.1B G2070908 1- A A4
D 1005 DIODE HVC358B TRF-E G2070590 1- B c3
D 1006 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- A B5
D 1007 DIODE 1SV307(TPH3.F) G2070638 1- B c3
D 1007 DIODE JDP2S04E(TAPE) G2071180 4- B c3
D 1008 DIODE DAN222M T2L G2070936 1- A A5
D 1009 LED CL-165HR/YG-D-T G2070860 1- A C1
D 1010 DIODE HVC358B TRF-E G2070590 1- B c3
D 1011 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- B b2
D 1012 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- B b3
D 1013 DIODE HVC369B TRF-E G2070872 1- B b3
D 1014 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- B b3
D 1015 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- B b2
D 1016 DIODE HVC369B TRF-E G2070872 1- B b2
D 1017 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A A4
D 1018 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A A3
D 1019 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A C3
D 1020 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A C3
D 1021 DIODE 1SV331(TPH3.F) G2071044 1- A B3
D 1022 DIODE 1SV331(TPH3.F) G2071044 1- A C4
D 1023 DIODE HVC358B TRF-E G2070590 1- B b3
D 1024 DIODE HVC358B TRF-E G2070590 1- B b3
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
23
Page 24

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
D 1025 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- B b2
D 1026 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- B b2
D 1027 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- B b3
D 1028 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A A5
D 1029 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- A B3
D 1030 DIODE DAP222M T2L G2070938 1- B a3
D 1031 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- B b3
D 1032 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- B b3
D 1033 DIODE DA221M T2L G2070940 1- B a4
D 1034 DIODE DAN222M T2L G2070936 1- B a3
D 1035 DIODE HVC359 TRF-E G2070708 1- B c4
D 1036 DIODE DAN222M T2L G2070936 1- B a4
D 1037 DIODE DAN222M T2L G2070936 1- B a4
D 1038 DIODE DAN222M T2L G2070936 1- B b4
D 1039 DIODE DAN222M T2L G2070936 1- B c3
D 1040 DIODE DAN222M T2L G2070936 1- B c3
D 1041 DIODE DAN222M T2L G2070936 1- B c3
D 1042 DIODE DA221M T2L G2070940 1- B a3
D 1043 DIODE DA221M T2L G2070940 1- B a3
D 1044 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- A A4
D 1047 DIODE DA221M T2L G2070940 1- A C2
D 1048 DIODE DA221M T2L G2070940 1- A C2
D 1050 DIODE RLS135 TE-11 G2070128 1- B c2
D 1051 DIODE 1SV307(TPH3.F) G2070638 1- B c2
D 1052 DIODE RLS135 TE-11 G2070128 1- B c2
D 1053 DIODE 1SV307(TPH3.F) G2070638 1- B c2
D 1055 DIODE 1SS385(TE85L.F) G2070880 1- A C3
D 1056 LED WH104S(TAPE) G2071174 1- A C1
D 1061 DIODE 1SV271(TPH3.F) G2070476 1- B c1
D 1063 DIODE RB751S-40TE61 G2070850 1- B b2
D 1065 DIODE 1SV307(TPH3.F) G2070638 1- B c1
D 1066 DIODE RB521S-30 TE61 G2070642 1- B b2
D 1067 DIODE RSX101VA-30TR G2070984 1- B b2
D 1068 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- B b1
D 1069 DIODE M1FM3-5063 G2071090 1- B b2
D 1070 DIODE DA221M T2L G2070940 1- A A4
D 1071 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- A A3
D 1072 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- A A3
D 1073 DIODE RB521S-30 TE61 G2070642 1- A B1
D 1074 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- B c3
D 1075 DIODE JDP2S04E(TAPE) G2071180 1- A A4
D 1076 SURGE ABSORBER EZAEG3A50AV Q9000867 1 A A1
D 1076 SURGE ABSORBER EZAEG2A50AX Q9000868 2- A A1
D 1077 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1D 1077 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 4DS1001 LCD 912-641A-1373(VER A) G6090181 1- A B2
F 1001 CHIP FUSE 0.63A FCC10 631ABPA Q0000114 1- B b2
FB1001 FERRITE BEADS BLM15BD102SN1D L9190133 1- B a2
FB1002 FERRITE BEADS BLM15BD102SN1D L9190133 1- B b2
FB1003 FERRITE BEADS BLM15BD102SN1D L9190133 1- B a1
FB1004 FERRITE BEADS BLM15BD102SN1D L9190133 1- B b1
FB1005 FERRITE BEADS BLM15BD102SN1D L9190133 1- B c1
FB1006 FERRITE BEADS BLM15BD102SN1D L9190133 1- B b1
FB1007 FERRITE BEADS BLM15BD102SN1D L9190133 1- B b1
FB1008 FERRITE BEADS BLM15BD102SN1D L9190133 1- B c1
FB1009 CHIP COIL BLM21PG300SN1D L1690840 1- B b2
FB1010 CHIP COIL BLM21PG300SN1D L1690840 1- B a2
J 1001 CONNECTOR MJC-041-B1Z-3.5T P1091312 1- B a1
J 1002 SHIELD FINGER 1674954-1 S5000255 1- A C5
J 1003 SHIELD FINGER 1674954-1 S5000255 1- A B5
J 1004 CONNECTOR MJC-046-C1-3.5-T P1091309 1- B b1
J 1005 CONNECTOR AXK6F10345YP P0091378 1- B c4
J 1006 CONNECTOR AXK6F10345YP P0091378 1- B b4
J 1007 CONNECTOR AXK6F10345YP P0091378 1- B c3
J 1009 CONNECTOR MJC-051-A1-1-T P1091311 1- B a2
L 1001 M.RFC 0.0082uH TFL0510-8N2 L1690810 1- A A1
L 1002 M.RFC 0.033uH 2% C1608CB-33NG L1691038 1- B c3
L 1003 M.RFC 0.12uH 2% C1608CB-R12G L1691100 1- A A1
L 1004 M.RFC 0.68uH LK1608 R68K-T L1690416 1- A A5
L 1005 M.RFC 0.0082uH TFL0510-8N2 L1690810 1- A A1
L 1006 M.RFC 0.0047uH TFL0510-4N7 L1690807 1- A A1
L 1008 M.RFC 0.0068uH 5% C1608CB-6N8J L1691093 1- B c3
L 1009 M.RFC 0.01uH 2% C1608CB-10NG L1691032 1- B c3
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
24
Page 25

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
L 1010 M.RFC 0.15uH 2% C1608CB-R15G L1691101 1- B b2
L 1011 M.RFC 0.056uH 2% C1608CB-56NG L1691041 1- B b2
L 1012 M.RFC 0.1uH 2% C1608CB-R10G L1691045 1- A B1
L 1013 M.RFC 0.15uH 2% C1608CB-R15G L1691101 1- B c3
L 1014 M.RFC 0.18uH 2% C1608CB-R18G L1691102 1- A A1
L 1015 M.RFC 0.1uH 2% C1608CB-R10G L1691045 1- A B1
L 1016 M.RFC 4.7uH LK1608 4R7K-T L1690688 1- A A5
L 1018 M.RFC 0.01uH TFL0510-10N L1690811 1- A B3
L 1019 M.RFC 0.0068uH TFL0510-6N8 L1690809 1- A B3
L 1020 M.RFC 0.0027uH C1005C-2N7K L1691338 1- A B3
L 1021 M.RFC 0.01uH 2% C1608CB-10NG L1691032 1- B c3
L 1022 M.RFC 0.01uH 2% C1608CB-10NG L1691032 1- B b3
L 1023 M.RFC 0.082uH 2% C1608CB-82NG L1691044 1- B b2
L 1024 M.RFC 0.082uH 2% C1608CB-82NG L1691044 1- B b3
L 1026 M.RFC 0.0027uH C1005C-2N7K L1691338 1- A C4
L 1027 M.RFC 0.01uH 2% C1608CB-10NG L1691032 1- B b3
L 1028 M.RFC 0.0047uH TFL0510-4N7 L1690807 1- A B3
L 1029 M.RFC 0.082uH 2% C1608CB-82NG L1691044 1- B b2
L 1030 M.RFC 0.15uH LK1608 R15K-T L1690409 1- B a3
L 1031 M.RFC 0.39uH LK1608 R39K-T L1690413 1- B a3
L 1032 M.RFC 0.33uH LK1608 R33K-T L1690412 1- B a2
L 1033 M.RFC 0.22uH LK1608 R22K-T L1690410 1- B c4
L 1034 M.RFC 0.47uH LK1608 R47K-T L1690414 1- B b5
L 1035 M.RFC 1uH LK1608 1R0K-T L1690687 1- B b4
L 1036 M.RFC 0.22uH LK1608 R22K-T L1690410 1- B b4
L 1037 M.RFC 33uH LK1608 330M-T L1690690 1- B c4
L 1038 M.RFC 0.33uH 2% C1608CB-R33G L1691106 1- B a4
L 1041 M.RFC 0.022uH TFL0510-22N L1690815 1- B b4
L 1043 M.RFC 0.022uH TFL0510-22N L1690815 1- B c3
L 1044 M.RFC 0.015uH TFL0510-15N L1690813 1- B b3
L 1045 M.RFC 10uH 2% KQ1008TE100G L1691216 1- B b5
L 1046 M.RFC 150uH FLC32T-151J L1690229 1- A C2
L 1047 COIL E2 0.28-1.0-4.5T-R L0022395 1- B c2
L 1049 COIL E2 0.4-1.3-2T-L L0022580 1- B c2
L 1050 M.RFC 4.7uH LK1608 4R7K-T L1690688 1- B c2
L 1051 COIL E2 0.28-1.0-4.5T-R L0022395 1- B c2
L 1052 M.RFC 4.7uH LK1608 4R7K-T L1690688 1- B c2
L 1053 COIL E2 0.25-1.9-5.5T-R L0022610 1- B c2
L 1054 COIL E2 0.35-1.4-3.5T-L-B L0022729 1- B c2
L 1055 COIL E2 0.35-1.4-3.5T-L-B L0022729 1- B c1
L 1056 COIL E2 0.25-1.9-6.5T-L L0022401 1- B c2
L 1057 COIL E2 0.25-1.9-6.5T-L L0022401 1- B c2
L 1058 M.RFC 150uH FLC32P-T-151K L1690661 1- B b2
L 1059 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- B c1
L 1060 COIL E2 0.35-1.6-4T-L L0022456 1- B c1
L 1061 COIL E2 0.25-1.9-6.5T-L L0022401 1- B c1
L 1062 COIL E2 0.25-1.9-6.5T-L L0022401 1- B c1
MC1001 MICROPHONE ELEMENT OB-22S44-C1033MG M3290048 1- A B3
Q 1001 TRANSISTOR MT3S36FS(TE85L.F) G3070377 1- A B3
Q 1002 TRANSISTOR 2SC5555ZD-TR G3355557 1- B c3
Q 1003 TRANSISTOR 2SC5555ZD-TR G3355557 1- B b2
Q 1004 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A A5
Q 1005 IC NJM2151AV(TAPE) G1094420 1- A A2
Q 1006 FET 2SK3541 T2L G3835417 1- A B5
Q 1007 FET 2SK3541 T2L G3835417 1- A B5
Q 1008 FET 2SK3541 T2L G3835417 1- A B4
Q 1009 TRANSISTOR EMG2 T2R G3070304 1- A C1
Q 1010 IC NJM3403AV-TE1 G1092215 1- A B4
Q 1011 TRANSISTOR DTA144EM T2L G3070310 1- A A4
Q 1012 TRANSISTOR MT3S36FS(TE85L.F) G3070377 1- A B3
Q 1013 TRANSISTOR 2SC5555ZD-TR G3355557 1- B c3
Q 1014 IC LV24100LP-TLM-E G1094371 1- A A5
Q 1015 TRANSISTOR 2SC5555ZD-TR G3355557 1- B b3
Q 1016 FET 2SK3541 T2L G3835417 1- A B5
Q 1017 IC M62364FP 600D G1093033 1- A C4
Q 1018 TRANSISTOR MT3S36FS(TE85L.F) G3070377 1- A C3
Q 1019 TRANSISTOR 2SC5555ZD-TR G3355557 1- B b3
Q 1020 TRANSISTOR 2SC5555ZD-TR G3355557 1- B b3
Q 1021 TRANSISTOR 2SC5555ZD-TR G3355557 1- B b3
Q 1023 IC NJM12904R-TE1 G1093337 1- A C5
Q 1025 IC NJU7007F3-TE1 G1093617 1- A C5
Q 1027 TRANSISTOR DTC143TM-T2L G3070372 1- A A3
Q 1028 TRANSISTOR DTC143TM-T2L G3070372 1- A C1
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
25
Page 26

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
Q 1029 TRANSISTOR 2SC4915-O(TE85L.F) G3349158O 1- B a2
Q 1030 TRANSISTOR 2SC4915-O(TE85L.F) G3349158O 1- B a3
Q 1031 TRANSISTOR EMG2 T2R G3070304 1- B a3
Q 1032 FET 2SK3541 T2L G3835417 1- A C3
Q 1033 TRANSISTOR 2SC4915-O(TE85L.F) G3349158O 1- B a3
Q 1034 TRANSISTOR 2SC4915-O(TE85L.F) G3349158O 1- B c4
Q 1035 TRANSISTOR 2SC4915-O(TE85L.F) G3349158O 1- B b5
Q 1036 TRANSISTOR 2SC4915-O(TE85L.F) G3349158O 1- B c5
Q 1037 TRANSISTOR 2SC4915-O(TE85L.F) G3349158O 1- B b4
Q 1038 TRANSISTOR 2SC5374-TL G3353748 1- B b4
Q 1039 TRANSISTOR DTA114TE TL G3070264 1- A A4
Q 1040 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A A4
Q 1041 IC MB15A01PFV1-G-BND-EFE1 G1092545 1- B b4
Q 1042 TRANSISTOR DTA114TE TL G3070264 1- A C4
Q 1043 TRANSISTOR DTA114TE TL G3070264 1- A C3
Q 1044 TRANSISTOR EMB10 T2R G3070302 1- A C4
Q 1045 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A C4
Q 1047 IC NJM2552V-TE1 G1094382 1- B a4
Q 1048 TRANSISTOR 2SC5374-TL G3353748 1- B b4
Q 1049 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- B c4
Q 1050 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A C4
Q 1055 TRANSISTOR 2SC5658 T2L Q/R G3356588 1- A A4
Q 1056 TRANSISTOR 2SC5374-TL G3353748 1- B b3
Q 1057 TRANSISTOR 2SA2029 T2L Q/R G3120298 1- A A4
Q 1058 TRANSISTOR EMB3 T2R G3070303 1- A A4
Q 1059 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A B4
Q 1060 TRANSISTOR EMB3 T2R G3070303 1- A B4
Q 1061 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A B4
Q 1065 TRANSISTOR 2SC5658 T2L Q/R G3356588 1- B b3
Q 1067 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- B b4
Q 1068 FET 2SJ364-P(TX) G3703648P 1- B b4
Q 1069 TRANSISTOR RN4985(TE85L.F) G3070333 1- A A4
Q 1070 TRANSISTOR EMG2 T2R G3070304 1- A A4
Q 1071 TRANSISTOR 2SA2029 T2L Q/R G3120298 1- A A4
Q 1072 TRANSISTOR EMB10 T2R G3070302 1- A B4
Q 1073 TRANSISTOR 2SA2029 T2L Q/R G3120298 1- A A4
Q 1074 TRANSISTOR EMB3 T2R G3070303 1- A B4
Q 1075 TRANSISTOR EMG2 T2R G3070304 1- A A4
Q 1077 TRANSISTOR 2SC5374-TL G3353748 1- A C2
Q 1078 TRANSISTOR 2SC5658 T2L Q/R G3356588 1- A C2
Q 1082 FET 2SK3541 T2L G3835417 1- A B4
Q 1083 IC NJU7747F4-03-TE1 G1094425 1- A B1
Q 1084 IC XC61GN3002HR G1094470 1- A C2
Q 1085 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A C2
Q 1086 IC TAR5S30(TE85L.F) G1093570 1- A C1
Q 1087 IC XC61GN3002HR G1094470 1- A C2
Q 1088 TRANSISTOR 2SC5658 T2L Q/R G3356588 1- A B4
Q 1089 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A A1
Q 1090 FET MCH6305-TL G3070301 1- B b2
Q 1091 IC XC6371A650PR G1094017 1- B b2
Q 1092 TRANSISTOR 2SA2029 T2L Q/R G3120298 1- A C3
Q 1093 TRANSISTOR 2SC5658 T2L Q/R G3356588 1- A B5
Q 1094 IC AT24C256B-10TU-1.8 G1094384 1- A B2
Q 1095 IC HD64F2266TF13V(FLASH) G1093813 1- A B2
Q 1096 TRANSISTOR CPH6102-TL G3070223 1- B b2
Q 1097 IC MM1438BWLE G1093814 1- B b2
Q 1098 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- B b2
Q 1099 TRANSISTOR EMD2 T2R G3070312 1- A A4
Q 1100 IC LC75834W G1093288 1- A A1
Q 1102 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A A2
Q 1103 FET SSM6J25FE(TAPE) G3070379 1- A C1
Q 1104 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A C1
Q 1105 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A A5
R 1001 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A A1
R 1002 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B c2
R 1003 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- B c2
R 1004 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- A C2
R 1005 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A A3
R 1006 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A B3
R 1007 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A B3
R 1008 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- B c3
R 1009 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B c3
R 1010 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B c3
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
26
Page 27

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
R 1011 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- B b3
R 1012 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B b3
R 1013 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b3
R 1014 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A A5
R 1015 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A A5
R 1016 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A A5
R 1017 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1 A A5
R 1017 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 2- A A5
R 1018 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A A5
R 1019 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A A2
R 1020 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A A2
R 1021 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B5
R 1022 CHIP RES. 39k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 393JTH J24189044 1- A A2
R 1023 CHIP RES. 560 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 561JTH J24189022 1- A A2
R 1024 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B4
R 1025 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- A B4
R 1026 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B4
R 1027 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B4
R 1028 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- A B4
R 1029 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A C1
R 1030 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A B1
R 1031 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- A B4
R 1032 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- A B4
R 1033 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 562JTH J24189034 1- A B4
R 1034 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A B4
R 1035 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A B4
R 1036 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- A B4
R 1037 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B4
R 1039 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 470JTH J24189009 1- A B3
R 1040 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A B3
R 1041 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A B3
R 1042 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A B3
R 1043 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B c3
R 1044 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B c3
R 1045 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B c3
R 1046 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A B3
R 1047 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B b3
R 1048 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b3
R 1049 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b2
R 1050 CHIP RES. 1.5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 152JTH J24189027 1- B c3
R 1051 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B b3
R 1052 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B b3
R 1053 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B5
R 1054 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B5
R 1055 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- A B5
R 1056 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B5
R 1057 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- A B5
R 1058 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B5
R 1059 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A C5
R 1060 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A C5
R 1061 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B5
R 1062 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B4
R 1063 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A A4
R 1064 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A A3
R 1065 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 184JTH J24189052 1- A B4
R 1066 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A C3
R 1067 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A C3
R 1068 CHIP RES. 270k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 274JTH J24189054 1 A B4
R 1068 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 2- A B4
R 1069 CHIP RES. 270k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 274JTH J24189054 1- A B4
R 1070 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B4
R 1071 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B4
R 1072 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A B4
R 1073 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A B4
R 1074 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- A B3
R 1075 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 562JTH J24189034 1- A B4
R 1076 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 562JTH J24189034 1- A B4
R 1077 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A A4
R 1078 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B4
R 1079 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B4
R 1080 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A C3
R 1081 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b3
R 1082 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b3
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
27
Page 28

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
R 1083 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b3
R 1084 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 470JTH J24189009 1- B b3
R 1085 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B b3
R 1086 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b2
R 1087 CHIP RES. 270k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 274JTH J24189054 1- B b3
R 1088 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b3
R 1089 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- B b3
R 1090 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1 B b3
R 1090 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 331JTH J24189019 2- B b3
R 1091 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B b2
R 1092 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 331JTH J24189019 1- B b3
R 1093 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 331JTH J24189019 1- B b3
R 1094 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A A4
R 1095 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A A4
R 1096 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD3903 J24189331 1- A C5
R 1097 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD4703 J24189332 1- A C5
R 1098 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD3303 J24189330 1- A C5
R 1099 CHIP RES. 560k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD5603 J24189335 1- A C5
R 1100 CHIP RES. 270k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD2703 J24189329 1- A C5
R 1101 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 1% MCR01MZSF1004 J24189333 1- A C5
R 1102 CHIP RES. 820k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD8203 J24189336 1- A C5
R 1103 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A C5
R 1104 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 470JTH J24189009 1- A C1
R 1105 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A C4
R 1106 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A B4
R 1107 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A B4
R 1108 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- A B4
R 1109 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- A C3
R 1110 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- A B3
R 1111 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- B a3
R 1112 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- B a3
R 1113 CHIP RES. 270k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD2703 J24189329 1- A B4
R 1114 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 0.5% RR0510R-104-D J24189167 1- A B4
R 1115 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A C4
R 1116 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B4
R 1117 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A C4
R 1118 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- B a3
R 1119 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- B a3
R 1120 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B a3
R 1121 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A C4
R 1123 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A C4
R 1124 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B a2
R 1125 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- B a3
R 1126 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 154JTH J24189051 1- B c5
R 1127 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b5
R 1128 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B b4
R 1129 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B b5
R 1130 CHIP RES. 560 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 561JTH J24189022 1- B c4
R 1131 CHIP RES. 120k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 124JTH J24189050 1- B c4
R 1132 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B c4
R 1133 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B a4
R 1134 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B a4
R 1135 CHIP RES. 330 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 331JTH J24189019 1- B a2
R 1136 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B a3
R 1137 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b4
R 1138 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- B b3
R 1139 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B b4
R 1140 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B b4
R 1141 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B c4
R 1142 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- B c4
R 1143 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B c4
R 1144 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 681JTH J24189023 1- B c4
R 1145 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 105JTH J24189061 1- B c4
R 1146 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B c4
R 1147 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b4
R 1148 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B b4
R 1157 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B a4
R 1158 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B a4
R 1159 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- B a4
R 1160 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B a4
R 1161 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- B a5
R 1162 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B a5
R 1163 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B a5
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
28
Page 29

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
R 1164 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a5
R 1165 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a4
R 1166 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a4
R 1167 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 183JTH J24189040 1- B b3
R 1168 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B b4
R 1169 CHIP RES. 1.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 122JTH J24189026 1- B c4
R 1170 CHIP RES. 1.5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 152JTH J24189027 1- B c4
R 1171 CHIP RES. 1.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 182JTH J24189028 1- B c4
R 1172 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B c4
R 1173 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- B c4
R 1174 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- B c4
R 1175 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B c5
R 1176 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- B c3
R 1183 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b4
R 1184 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- B b3
R 1185 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b4
R 1186 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 681JTH J24189023 1- B a4
R 1187 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- B a4
R 1188 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B b4
R 1189 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a5
R 1190 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B a4
R 1191 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B b5
R 1192 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A A4
R 1193 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b3
R 1194 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A A4
R 1195 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B c3
R 1202 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- B b3
R 1203 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b3
R 1204 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- B a4
R 1205 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B a3
R 1206 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b4
R 1207 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b4
R 1208 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A A4
R 1209 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B4
R 1210 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A A4
R 1216 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B a3
R 1217 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B a3
R 1219 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b4
R 1220 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- B b4
R 1221 CHIP RES. 180k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 184JTH J24189052 1- B a3
R 1222 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b4
R 1223 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b4
R 1224 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A C3
R 1225 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A C2
R 1226 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 105JTH J24189061 1- A C2
R 1227 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A C2
R 1228 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD3303 J24189330 1- A C2
R 1230 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- A C2
R 1231 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 0.5% RR0510R-683-D J24189163 1- A C2
R 1232 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B4
R 1234 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- A B4
R 1235 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B c2
R 1236 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B c2
R 1237 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A C2
R 1238 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A C2
R 1239 CHIP RES. 2.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 272JTH J24189030 1- A B4
R 1240 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A B5
R 1241 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B4
R 1242 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- A B5
R 1243 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 154JTH J24189051 1- A B4
R 1244 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- A C2
R 1245 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- A C2
R 1247 CHIP RES. 22 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 220JTH J24189005 1- B b2
R 1248 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A C2
R 1249 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A C3
R 1250 CHIP RES. 1.5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 152JTH J24189027 1- A B5
R 1251 CHIP RES. 2.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 225JTH J24189065 1- A B5
R 1252 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B5
R 1253 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- A B3
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER.USA A2 1-
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. A1 1-
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. A2 1-
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. B1 1-
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
29
Page 30

Main Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. B2 1-
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. C1 1-
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. C2 1-
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. D1 1-
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. D2 1-
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. H1 1-
R 1254 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 VER. H2 1-
R 1255 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A A1
R 1256 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b2
R 1257 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- B b2
R 1258 CHIP RES. 150 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 151JTH J24189015 1- B b2
R 1259 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b2
R 1260 CHIP RES. 4.7 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 4R7JTH J24189066 1- B b2
R 1261 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A A4
R 1262 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- B c3
R 1263 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A A3
R 1264 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B c3
R 1265 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A B1
R 1266 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A B1
R 1267 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A A2
R 1268 CHIP RES. 0.2 1/2W 1% RLC32-R200FTP J24279031 1- A C2
R 1269 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A A4
R 1270 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B3
R 1271 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B3
R 1272 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A C3
R 1273 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A C3
R 1275 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A A5
R 1276 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 470JTH J24189009 1- B b4
R 1277 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A C1
R 1278 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 183JTH J24189040 1- A B5
R 1279 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 183JTH J24189040 1- A B5
R 1280 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 681JTH J24189023 1- B c4
R 1281 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 681JTH J24189023 1- B c4
R 1282 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1R 1283 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 000JATP J24185000 1-3
R 1284 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1R 1285 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1R 1286 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1R 1287 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 332JATP J24185332 1R 1287 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 4R 1288 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16 101JATP J24185101 1R 1288 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 4R 1289 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1S 1001 TACT SWITCH SKRWAEE010 N5090156 1- A A3
S 1002 TACT SWITCH SKRWAEE010 N5090156 1- A A3
S 1003 TACT SWITCH SKRWAEE010 N5090156 1- A A4
S 1004 TACT SWITCH SKRWAEE010 N5090156 1- A A4
S 1005 TACT SWITCH SKRWAEE010 N5090156 1- A A5
S 1006 TACT SWITCH SKRWAEE010 N5090156 1- A B3
S 1007 TACT SWITCH SKRWAEE010 N5090156 1- A B3
S 1008 TACT SWITCH SKRWAEE010 N5090156 1- A C3
S 1009 TACT SWITCH SKRWAEE010 N5090156 1- A C3
S 1010 DETECTION SWITCH SPPW811203 N4090160 1- B b3
S 1011 ROTARY ENCODER TP70N00E20 RY-8401 Q9000880 1- B a1
TH1001 THERMISTOR ERTJ1VV473J G9090122 1- A C2
X 1001 XTAL XV00117 11.7MHz 11.7MHZ H0103330A 1- B c4
X 1002 XTAL SSP-T7-F 32.768kHz 32.768KHZ H0103327 1- A B2
X 1003 XTAL AT-38 3.579545MHz 3.579545MHZ H0103292 1-
XF1001 XTAL FILTER 47S15A 47.25MHZ H1102411 1- B a3
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
30
Page 31

Filter Unit
Circuit Diagram
31
Page 32

Filter Unit
Parts Layout (Side A)
1
2
BA C
DA221M (K)
(D2002)
DAN222M (N)
(D2001)
LM2902PWR
(Q2001)
LM2904PWR
(Q2002)
Parts Layout (Side B)
a c
1
2
2SC5658 (B*)
(Q2003)
b
DTC144EM (26)
(Q2004, 2005,
2007, 2008)
DTC144TEM (96)
(Q2006)
32
Page 33

Filter Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
P.C.B. with Components CB4006001
Printed Circuit Board FR0167700 1C 2001 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1- A A1
C 2002 CHIP CAP. 0.0047uF 25V B TMK105B472KW-F K22148831 1- A B1
C 2003 CHIP CAP. 0.0047uF 25V B TMK105B472KW-F K22148831 1- A B1
C 2004 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V TESVSP0J475M-8R K78080053 1- A A1
C 2005 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A1
C 2006 CHIP CAP. 0.0027uF 50V B UMK105B272KW-F K22178834 1- A A1
C 2007 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 16V B GRM155B11C223KA01D K22128806 1- A A1
C 2008 CHIP CAP. 0.015uF 16V B EMK105B153KW-F K22128811 1- A A1
C 2009 CHIP CAP. 560pF 50V B UMK105B561KW-F K22178826 1- A A1
C 2010 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 2011 CHIP CAP. 0.015uF 16V B EMK105B153KW-F K22128811 1- A A1
C 2012 CHIP CAP. 220pF 25V CH TMK105CH221JW-F K22148246 1- A A1
C 2013 CHIP CAP. 220pF 25V CH TMK105CH221JW-F K22148246 1- A A1
C 2014 CHIP CAP. 560pF 50V B UMK105B561KW-F K22178826 1- A A1
C 2015 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 10V B GRM155B11A473KA01D K22108801 1- A A1
C 2017 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 4V TESVSP0G226M-8R K78060047 1- A A1
C 2018 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B1
C 2019 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 16V B GRM155B11C223KA01D K22128806 1- A A1
C 2020 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A2
C 2021 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H330JZ01D K22178224 1- A B1
D 2001 DIODE DAN222M T2L G2070936 1- A B1
D 2002 DIODE DA221M T2L G2070940 1- A A2
J 2001 CONNECTOR AXK5F10347YG P1091326 1- B c1
Q 2001 IC LM2902PWR G1094009 1- A A1
Q 2002 IC LM2904PWR G1094010 1- A B1
Q 2003 TRANSISTOR 2SC5658 T2L Q/R G3356588 1- A A2
Q 2004 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A A2
Q 2005 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A A1
Q 2006 TRANSISTOR DTC144TE-TL G3070280 1- A A1
Q 2007 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A A1
Q 2008 TRANSISTOR DTC144EM T2L G3070309 1- A A1
R 2001 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A A1
R 2002 CHIP RES. 680 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 681JTH J24189023 1- A B1
R 2003 CHIP RES. 560k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 564JTH J24189058 1- A B1
R 2004 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A B1
R 2005 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A B1
R 2006 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B1
R 2007 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B1
R 2008 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A A1
R 2009 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A B1
R 2011 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A A1
R 2012 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 154JTH J24189051 1- A A1
R 2013 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A A1
R 2015 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A A1
R 2016 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- A A1
R 2017 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- A A1
R 2018 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- A A1
R 2019 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- A A1
R 2020 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- A A1
R 2021 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- A A1
R 2022 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 123JTH J24189038 1- A A1
R 2023 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A A1
R 2024 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A A1
R 2025 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A A1
R 2026 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- A A1
R 2027 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A A1
R 2028 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- A A1
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
33
Page 34

Filter Unit
Note
34
Page 35

SW Unit
Circuit Diagram
35
Page 36

SW Unit
Parts Layout (Side A)
1
RQA0003DNS
(Q3004)
BA C
Parts Layout (Side B)
a c
1
2SC5226 (R22)
(Q3003)
2SC5374 (NA)
(Q3001)
DTC143ZE (E23)
(Q3003)
b
36
Page 37

SW Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
P.C.B. with Components CS1944003 DST:USA
CS1944004 DST:EXP
CS1944005 DST:EU
CS1944006 DST:AUS
Printed Circuit Board FR0165100 1C 3002 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1- B a1
C 3003 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B a1
C 3004 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B a1
C 3005 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B a1
C 3006 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH UMK105CH101JW-F K22178282 1- B b1
C 3007 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B c1
C 3008 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- B a1
C 3010 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B a1
C 3011 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B a1
C 3012 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B1
C 3013 CHIP CAP. 39pF 50V CH UMK105CH390JW-F K22178272 1- B a1
C 3015 CHIP CAP. 22pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H220JZ01D K22178220 1- B a1
C 3016 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b1
C 3017 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B b1
C 3019 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- B b1
C 3020 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B1
C 3021 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- B a1
C 3025 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- B b1
C 3028 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 3033 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 10V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A B1
D 3001 DIODE 1SS400G T2R G2070934 1- A B1
D 3002 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- B b1
D 3003 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- B b1
D 3004 SURGE ABSORBER EZAEG2A50AX Q9000868 1-3
D 3005 SURGE ABSORBER EZAEG2A50AX Q9000868 1-3
D 3006 SURGE ABSORBER TVSF0603 Q9000847 1D 3007 SURGE ABSORBER TVSF0603 Q9000847 1D 3008 DIODE UDZS TE-17 8.2B G2070890 1D 3008 DIODE EDZ TE-61 8.2B G2071188 4L 3001 M.RFC 0.033uH TFL0510-33N L1690817 1- B a1
L 3002 M.RFC 0.033uH ELJ-RE33NJF2 L1690720 1- B a1
L 3003 CHIP COIL 0.012uH 2% LQW18AN12NG00D L1690881 1- B a1
L 3004 M.RFC 0.0047uH ELJ-RE4N7JF2 L1690710 1- B a1
L 3005 COIL E2 0.25-1.9-6.5T-L L0022401 1- B a1
Q 3001 TRANSISTOR 2SC5374-TL G3353748 1- B a1
Q 3002 TRANSISTOR DTC143ZE TL G3070102 1- B b1
Q 3003 TRANSISTOR 2SC5226-5-TL G3352268E 1- B a1
Q 3004 FET RQA0003DNS G3070363 1- A A1
R 3001 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B a1
R 3002 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a1
R 3004 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- B a1
R 3005 CHIP RES. 10 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 100JTH J24189001 1- B a1
R 3006 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b1
R 3007 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- B c1
R 3008 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 562JTH J24189034 1- B a1
R 3009 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B1
R 3012 CHIP RES. 10 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 100JTH J24189001 1- B a1
R 3013 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A B1
R 3014 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- B a1
R 3015 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B b1
R 3016 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B b1
R 3017 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B b1
R 3018 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B b1
S 3001 TACT SWITCH SOT-152HST N5090131 1- A B1
S 3002 TACT SWITCH SOT-152HST N5090131 1- A B1
S 3003 TACT SWITCH SOT-152HST N5090131 1- A A1
TH3001 THERMISTOR TN05-3M154J G9090171 1-
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
37
Page 38

SW Unit
Note
38
Page 39

VCO Unit
Circuit Diagram
39
Page 40

VCO Unit
Parts Layout (Side A)
1
2
BA
DTC143ZE (E23)
(Q4001, 4003, 4007)
MT3S36FS (21)
(Q4002, 4004, 4005,
4006)
Parts Layout (Side B)
a
1
2
b
40
Page 41

VCO Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
P.C.B. with Components CB3815001
Printed Circuit Board FR0158700 1C 4001 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 4002 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A1
C 4003 CHIP CAP. 0.5pF 50V CK GRM1554C1HR50BZ01D K22178285 1- A A1
C 4004 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A1
C 4005 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A1
C 4006 CHIP CAP. 2pF 50V CK GRM1554C1H2R0BZ01D K22178289 1- A A1
C 4007 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A1
C 4008 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H4R0BZ01D K22178291 1- A A1
C 4009 CHIP CAP. 22pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H220GZ01D K22179707 1- A A1
C 4010 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH UMK105CH040CW-F K22178252 1- A A1
C 4011 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 4012 CHIP CAP. 12pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H120JZ01D K22178214 1- A A1
C 4013 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A2
C 4014 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 4015 CHIP CAP. 1pF 50V CK GRM1554C1H1R0BZ01D K22178287 1- A A1
C 4017 CHIP CAP. 1pF 50V CK GRM1554C1H1R0BZ01D K22178287 1- A A1
C 4018 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A2
C 4019 CHIP CAP. 27pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H270JZ01D K22178222 1- A A1
C 4020 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A1
C 4021 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 4022 CHIP CAP. 51pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H510GZ01D K22179710 1- A A1
C 4023 CHIP CAP. 47pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H470GZ01D K22179709 1- A A1
C 4024 CHIP CAP. 4pF 50V CH UMK105CH040CW-F K22178252 1- A A1
C 4025 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 4026 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A2
C 4027 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B2
C 4028 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- A A1
C 4031 CHIP CAP. 68pF 50V CH UMK105CH680JW-F K22178278 1- A A1
C 4032 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 4033 CHIP CAP. 5pF 50V CH UMK105CH050CW-F K22178253 1- A A1
C 4034 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A A1
C 4035 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B1
C 4036 CHIP CAP. 47pF 50V CH UMK105CH470JW-F K22178274 1- A B1
C 4037 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1- A A1
C 4038 CHIP CAP. 15pF 50V CH UMK105CH150JW-F K22178262 1- A B1
C 4039 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 4040 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A A1
C 4041 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1- A B1
C 4042 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B1
C 4043 CHIP CAP. 10pF 50V CH UMK105CH100DW-F K22178258 1- A B1
C 4044 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B1
C 4045 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50V B UMK105B102KW-F K22178829 1- A B1
C 4047 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B1
C 4048 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 16V B GRM36B103K16PT K22128804 1- A B2
C 4049 CHIP CAP. 33pF 50V CH UMK105CH330JW-F K22178270 1- A B1
D 4001 DIODE HVC355B TRF-E G2070588 1- A A1
D 4002 DIODE HSC277TRF-E G2070584 1- A A1
D 4003 DIODE HSC277TRF-E G2070584 1- A A1
D 4004 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- A A1
D 4005 DIODE HSC277TRF-E G2070584 1- A A1
D 4006 DIODE HSC277TRF-E G2070584 1- A A1
D 4007 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- A A1
D 4008 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- A A2
D 4010 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A B1
D 4011 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A B1
D 4012 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A B1
D 4013 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- A A1
D 4014 DIODE HSC277TRF-E G2070584 1- A B1
D 4015 DIODE 1SV325(TPH3.F) G2070848 1- A B1
J 4001 CONNECTOR AXK5F10335YP P1091136 1- B b1
J 4002 CONNECTOR AXK5F10335YP P1091136 1- B a1
L 4001 M.RFC 1uH LK1608 1R0K-T L1690687 1- A A1
L 4002 M.RFC 0.0082uH 2% C1608CB-8N2G L1691226 1- A A1
L 4003 M.RFC 0.0082uH 2% C1608CB-8N2G L1691226 1- A A1
L 4004 M.RFC 1uH LK1608 1R0K-T L1690687 1- A A1
L 4005 M.RFC 2.2uH LK1608 2R2K-T L1690634 1- A A1
L 4006 CHIP COIL 0.022uH 2% LQW18AN22NG00D L1690884 1- A A1
L 4007 M.RFC 0.015uH 2% C1608CB-15NG L1691034 1- A A1
L 4008 M.RFC 1uH LK1608 1R0K-T L1690687 1- A A1
L 4009 M.RFC 4.7uH LK1608 4R7K-T L1690688 1- A A2
L 4010 M.RFC 0.1uH 2% C1608CB-R10G L1691045 1- A B1
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
41
Page 42

VCO Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
L 4011 M.RFC 1uH LK1608 1R0K-T L1690687 1- A B1
L 4012 M.RFC 0.33uH LK1608 R33K-T L1690412 1- A B1
L 4013 M.RFC 0.01uH HK1608 10NJ-T L1690516 1- A B1
L 4014 M.RFC 0.1uH LK1608 R10K-T L1690407 1- A B1
L 4015 M.RFC 0.22uH 2% C1608CB-R22G L1691103 1- A B1
Q 4001 TRANSISTOR DTC143ZE TL G3070102 1- A A1
Q 4002 TRANSISTOR MT3S36FS(TE85L.F) G3070377 1- A A1
Q 4003 TRANSISTOR DTC143ZE TL G3070102 1- A A2
Q 4004 TRANSISTOR MT3S36FS(TE85L.F) G3070377 1- A A1
Q 4005 TRANSISTOR MT3S36FS(TE85L.F) G3070377 1- A A1
Q 4006 TRANSISTOR MT3S36FS(TE85L.F) G3070377 1- A B1
Q 4007 TRANSISTOR DTC143ZE TL G3070102 1- A B2
R 4001 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A A1
R 4002 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A A1
R 4003 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- A A1
R 4004 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A A1
R 4005 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 470JTH J24189009 1- A A1
R 4006 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A A1
R 4007 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 470JTH J24189009 1- A A1
R 4008 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A A1
R 4009 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A A1
R 4010 CHIP RES. 470 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- A A1
R 4011 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A A1
R 4012 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A A1
R 4013 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A A1
R 4014 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A A1
R 4016 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B2
R 4017 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A A1
R 4018 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A B1
R 4019 CHIP RES. 220 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A A1
R 4020 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A A1
R 4021 CHIP RES. 390 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 391JTH J24189020 1- A A1
R 4022 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 470JTH J24189009 1- A B1
R 4023 CHIP RES. 2.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 272JTH J24189030 1- A B1
R 4024 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A A1
R 4025 CHIP RES. 100 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A B1
R 4026 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A A1
R 4027 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A A1
SHIELD CASE VCO RA0400300 1STICK FINGER 97-542-02(1/80) S5000211 1-
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
42
Page 43

Page 44

Copyright 2007
VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
All rights reserved
No portion of this manual
may be reproduced without
the permission of
VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
44
 Loading...
Loading...