Page 1

Compact® NSF and NSJ
150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Class 615
CONTENTS Page
Section 1—The Compact
Section 2—General Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Section 3—Circuit Breakers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Section 4—Trip Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Section 5—Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Section 6—Motor Circuit Protectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Section 7—Mounting Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Section 8—Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Section 9—Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Section 10—Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Section 11—Connection Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Section 12—Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
®
Circuit Breaker Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Page 2

Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
THE COMPACT® CIRCUIT BREAKER LINE ....................................................................................... 4
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS .......................................................................................................... 5
Compliance with Standards ............................................................................................................. 5
CIRCUIT BREAKERS ........................................................................................................................... 8
Ratings and Interrupting Ratings ..................................................................................................... 8
TRIP UNITS ........................................................................................................................................ 10
Trip Units for Compact® NSF150 and NSF250 Circuit Breakers .................................................. 10
Trip Units for Compact
Electronic Trip Unit Test Kits ......................................................................................................... 16
SWITCHES ......................................................................................................................................... 17
Ratings and Interrupting Ratings ................................................................................................... 17
MOTOR CIRCUIT PROTECTORS ..................................................................................................... 19
Ratings and Interrupting Ratings ................................................................................................... 19
MOUNTING CONFIGURATIONS ....................................................................................................... 21
Fixed Mounting .............................................................................................................................. 21
Connections .................................................................................................................................. 21
Plug-in Mounting ........................................................................................................................... 21
Drawout Mounting ......................................................................................................................... 22
CONNECTIONS ................................................................................................................................. 24
Front Connection ........................................................................................................................... 24
Rear Connection ........................................................................................................................... 25
ACCESSORIES .................................................................................................................................. 26
Location ......................................................................................................................................... 26
Connections .................................................................................................................................. 26
Automatic Secondary Disconnecting Blocks ................................................................................. 27
Auxiliary and Alarm Switches ........................................................................................................ 28
Shunt Trip and Undervoltage Trip ................................................................................................. 30
Motor Operator .............................................................................................................................. 31
Rotary Operating Handles ............................................................................................................. 33
Cable Operating Handles .............................................................................................................. 35
Locking Systems ........................................................................................................................... 36
Interlocking Accessories ................................................................................................................ 37
Front Panel Escutcheons .............................................................................................................. 39
DIMENSIONS ..................................................................................................................................... 41
Fixed Mounted ............................................................................................................................... 41
Plug-in and Drawout Mounting ...................................................................................................... 43
Cable Operating Handles .............................................................................................................. 47
Rotary Operating Handles ............................................................................................................. 48
Front Accessories .......................................................................................................................... 51
Interlocking Systems ..................................................................................................................... 52
CONNECTION DIMENSIONS ............................................................................................................ 53
WIRING DIAGRAMS .......................................................................................................................... 55
SUPPLEMENTARY TECHNICAL INFORMATION ............................................................................. 57
Reflex Tripping .............................................................................................................................. 62
Let-through Curves ........................................................................................................................ 63
Current Limiting Curves ................................................................................................................. 65
UL 489 Test Procedure ................................................................................................................. 67
IEC 947-2 Test Procedure ............................................................................................................. 70
Routine and Maintenance Guidelines ........................................................................................... 73
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Table of Contents
®
NSJ400 and NSJ600 Circuit Breakers ................................................... 11
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
3
Page 4
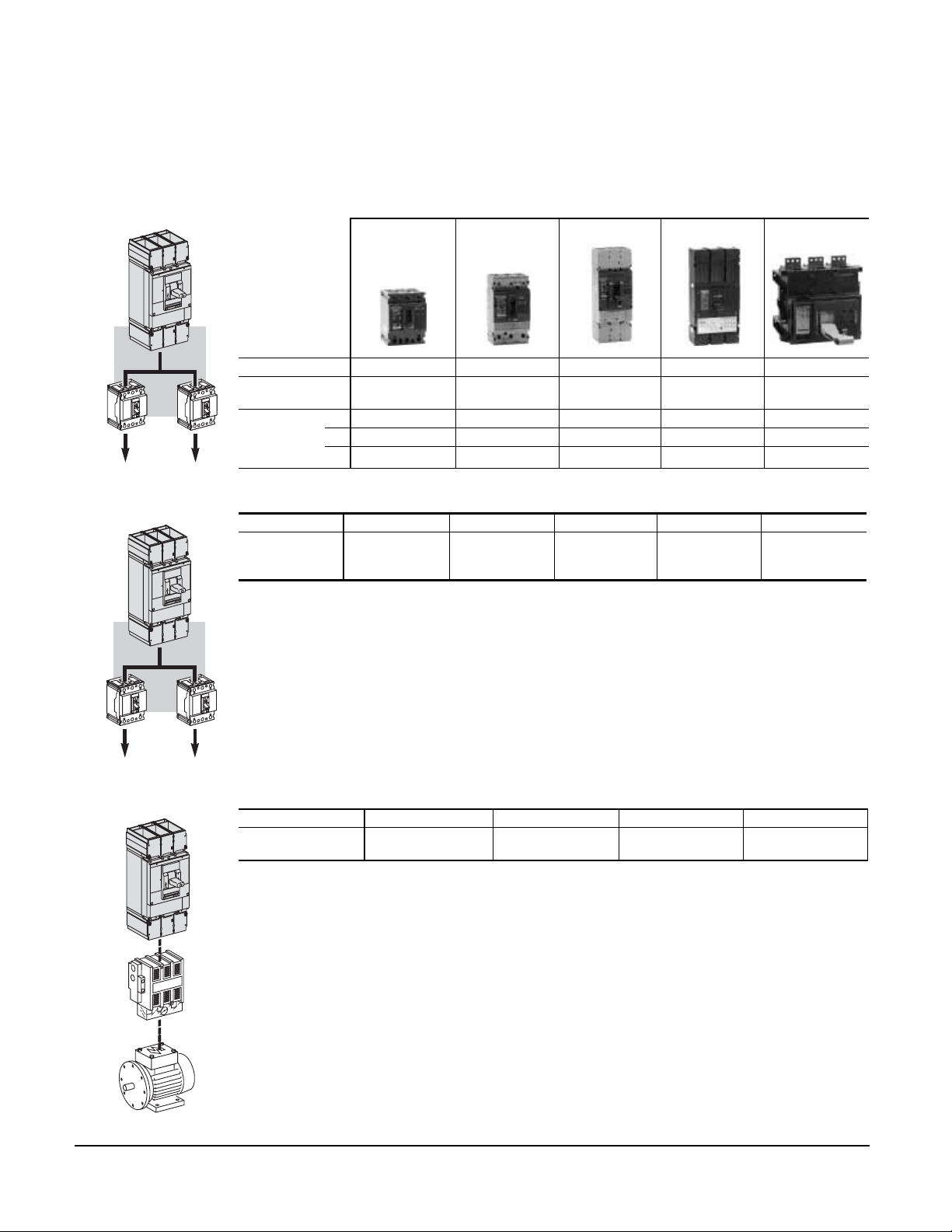
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 1—The Compact® Circuit Breaker Line
SECTION 1—THE COMPACT® CIRCUIT BREAKER LINE
CIRCUIT BREAKERS—PAGE 8
06153032
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
r
t
Rated Current (A)
COMPACT
Interrupting
Rating at 480 V
®
15–100 15–250 150–600 400–1200 1250–2500
NSE100
18 35 35 50 —
N
—65656585
H
——100150—
L
SWITCHES—PAGE 17
Rated Current (A)
06153032
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
tr
COMPACT
®
70 150, 250 400, 600 800, 1200 1600–2500
NSE100A
MOTOR CIRCUIT PROTECTORS—PAGE 19
3–75 100–250 400–600 800–1200
NSE100A
06153033
Rated Current (A)
COMPACT
®
NSF150
NSF250
NSF150A
NSF250A
NSF150A
NSF250A
NSJ400
NSJ600
NSJ400A
NSJ600A
CK400–CK1200 CM1250–CM2500
CK800NA
NSJ400A
NSJ600A
CK800NA
CM1600HA
CM2000HA
CM2500HA
h
s
u
p
o
t
ip
tr
For NSE, CK and CM circuit breakers see appropriate catalog.
4
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 5

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
SECTION 2—GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
COMPLIANCE WITH STANDARDS
MERLIN
compact
06153060
NSF 250 N
600Y/347V 50/60Hz
UL/CSA
interrupting ratings
RMS sym. Amps
240V ac
480V ac
600Y/347V ac
current limiting
(see curves in catalog)
IEC947.2
220/240V
380/415V~
Ics=100% Icu
Ui 750V
cat A
UTE VDE BS CEI UNE NEMA
~
65k
35k
18k
85kA
36kA
Uimp 8kV
Icu
Section 2—General Characteristics
Compliance with
North American
Standards
Compliance with
International
Standards
Compliance with
the Specifications
of Marine
Classification
Organizations
Compact® NS circuit breakers are built in accordance with Underwriters Laboratories Inc. UL 489
Standard and Canadian Standards Association CSA C22.2 No. 5.02 Standard. Circuit breakers,
switches and their accessories, except where noted, are Listed under UL files E63335, E103740,
E103955, and Certified under CSA files LR69561 and LR88980.
Compact NS circuit breakers and their accessories comply also with the following international
standards:
• IEC 60947-1: general rules
• IEC 60947-2: circuit breakers
• IEC 60947-3: switches, disconnectors, switch disconnectors, etc.
In that these standards are applied in most countries, Compact circuit breakers and their accessories
comply with European (EN 60947-1 and EN 60947-2) and the corresponding national standards:
• France NF
• Germany VDE
• U.K. BS
• Australia AS
• Italy CEI
Compact NS circuit breakers have been approved for marine application by the American Bureau of
Shipping, Bureau Veritas, Lloyd’s Register of Shipping, Registro Italiano Navale, Germanischer Lloyd’s
and Det Norske Veritas.
They comply with the following standards:
• UL 489 Supplement SA. Marine use on vessels over 65 feet in length
• US Coast Guard specifications
• IEC 92-504 and marine specifications: inclination, vibrations, insulation resistance
• IEC 803 Electromagnetic Disturbance Immunity
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
5
Page 6

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 2—General Characteristics
Tropicalization Compact
humidity at 45° C or 80% at 55° C, hot and humid climate conditions). The materials used in Compact
NS circuit breakers will not support the growth of fungus or mold.
They also comply with the following standards:
®
NS circuit breakers comply with NF C 63-100 standard level 2 conditions (95% relative
• IEC 68-2-30 damp heat
• IEC 68-2-2 dry heat
• IEC 68-2-11 salt spray
• IEC 68-2-1 low temperatures
Pollution Degree Compact NS circuit breakers are certified for operation in pollution degree III environments as defined
by IEC standard 947 (industrial environments).
Environmental
Protection
Compact NS circuit breakers take into account concerns for environmental protection. Most
components are recyclable and parts are marked as specified in applicable standards.
Suitability for
Isolation (Positive
Contact Indication)
06153037
Installation in
Class II
Switchboards
All Compact NS circuit breakers and switches are suitable for isolation as defined in the IEC 947-2
Standard:
• The isolation position corresponds to the O (OFF position).
• The operating handle cannot indicate the OFF position unless the contacts are open.
• Padlocks may not be installed unless the contacts are open
Installation of a rotary handle or a motor mechanism does not alter the functionality of the position
indication system.
The isolation function is certified by tests guaranteeing:
• The mechanical reliability of the position indication system
• The absence of leakage currents
• Overvoltage withstand capacity between upstream and downstream connections
Circuit Breaker Marking
06153038
All Compact NS circuit breakers, even when fitted with a rotary handle or a motor mechanism, can be
installed through the door of Class II IEC switchboards (as per IEC 664 Standard). Refer to circuit
breaker installation instructions prior to installing circuit breaker.
Installation requires no special insulation because Compact NS circuit breakers provide Class II
insulation between the front face and all internal circuits.
Switch Marking
06153039
6
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 7
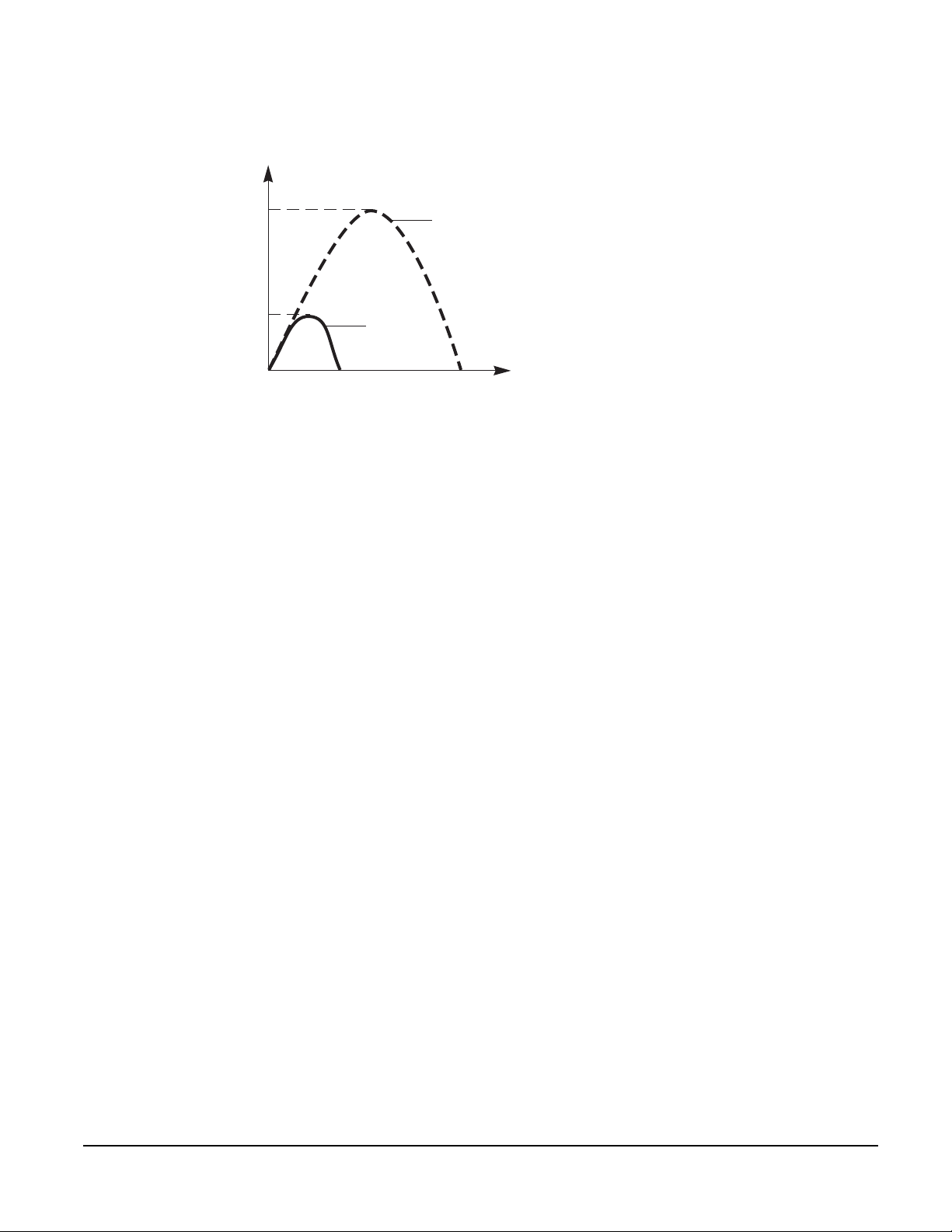
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 2—General Characteristics
Suitability for
Isolation (Positive
Contact Indication)
The limiting capacity of a circuit breaker is its ability to limit short-circuit currents.
Isc
06153040
The exceptional limiting capacity of the Compact
Prospective
Isc Peak
Limited
Isc Peak
Limited
Isc
tsc
Actual
Current
Prospective
Current
Prospective
Isc
t
®
NS line is due to the double break technique (rapid
natural repulsion of contacts and the appearance of two arc voltages in series with a steep wavefront).
The limiting capacity of the Compact NS line greatly reduces the forces created by fault currents in
devices. The result is a major increase in breaking performance. In particular, the service breaking
capacity Ics is equal to 100% of Icu.
The Ics value, defined by IEC 947-2, is guaranteed by tests comprising the following operations:
• Breaking a fault current equal to 100% of Icu three times consecutively
• Checking that the device continues to function normally
• Conduction of rated current without abnormal temperature rise
• Protection functions perform within the limits specified by the standard
• Suitability for isolation is not impaired
Longer Service
Current limiting circuit breakers greatly reduce the negative effects of short circuits on installations.
Life of Electrical
Installations
Thermal Effects Less temperature rise in conductors, therefore longer service life for cables.
Mechanical Effects Reduced electrodynamic forces, therefore less risk of electrical contacts or busbars being distorted or
broken.
Electromagnetic
Effects
Less disturbance for measuring devices located near electrical circuits.
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
7
Page 8
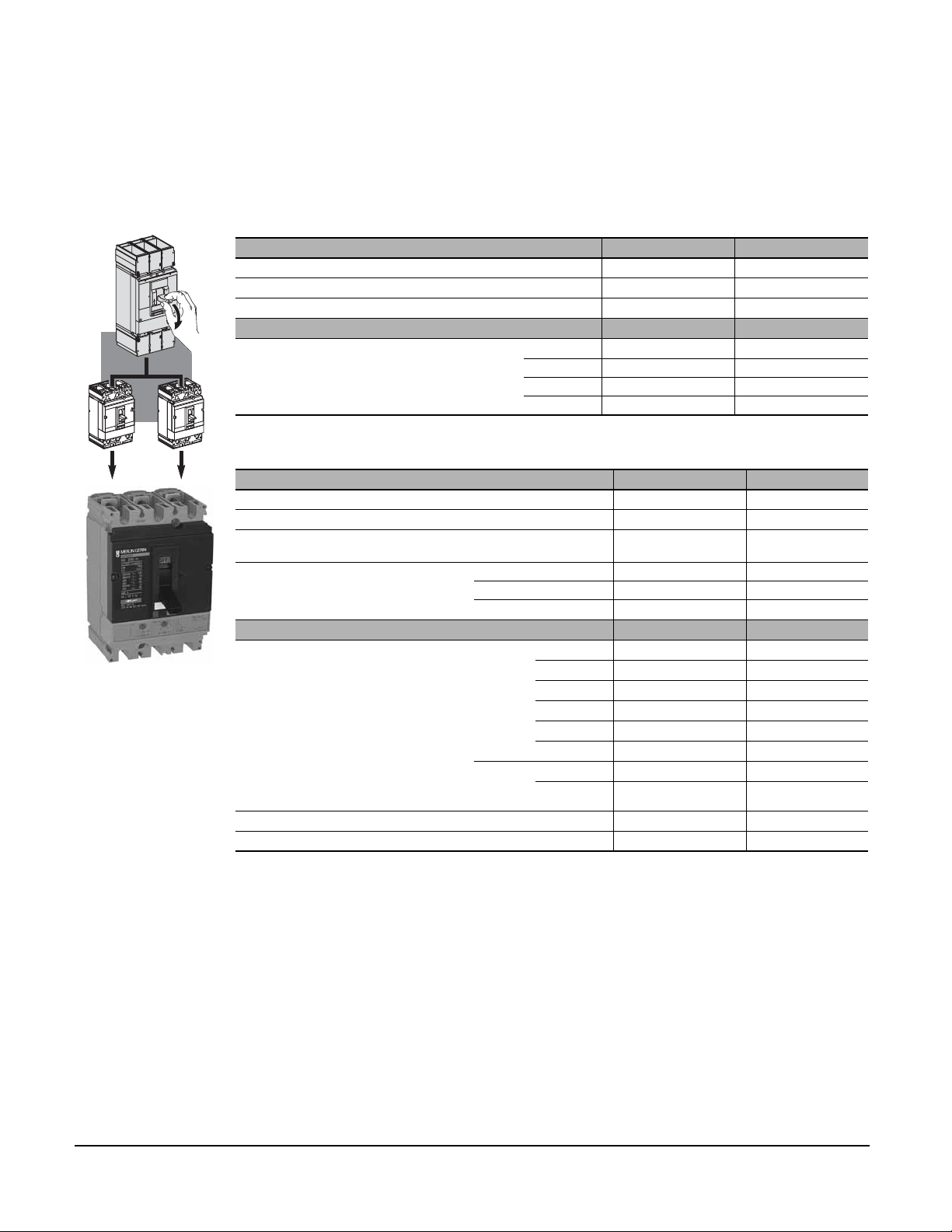
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 3—Circuit Breakers
SECTION 3—CIRCUIT BREAKERS
RATINGS AND INTERRUPTING RATINGS
UL 489 Listed Ratings
Compact® Circuit Breakers NSF150 NSF250
06153061
06153062
Number of Poles
Rated Voltage (V)
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
r
t
Rated Current (A) In
Interrupting Ratings (kA rms)
*Oversized Neutral Protection: four-pole OSN 125/250N and 150/250N are same ratings as NSF250A.
AC 50/60 Hz 600Y/347 600Y/347
40° C 150 250
240 V 65 100 65 100
480 V 35 65 35 65
600 Y/ 347 V 18 25 18 25
600 V — — — —
IEC 947-2 and EN 60947-2 Ratings
Compact® Circuit Breakers NSF150 NSF250
Number of Poles
Rated Insulation Voltage (V) Ui
Rated Impulse
Withstand Voltage (kV)
Rated Operational Voltage (V) Ue
Rated Current (A) In
Ultimate Breaking Capacity (kA rms) Icu
Service Breaking Capacity Ics
Utilization Category
*Oversized Neutral Protection: four-pole OSN 125/250N and 150/250N are same ratings as NSF250A.
Uimp
AC 50/60 Hz 690 690
DC 500 500
40° C 150 250
AC 50/50 Hz 220/ 240 V 85 100 85 100
380/ 415 V 36 70 36 70
440 V 35 65 35 65
500 V 30 50 30 50
525 V 22 35 22 35
600/ 690 V 8 10 8 10
DC 250 V (1 pole) 50 85 50 85
500 V (2 pole in
series)
(% Icu) 100% 100% 100% 100%
3, 4, 4 OSN* 3, 4
N H N H
3, 4, 4 OSN* 3, 4
750 750
88
N H N H
50 85 50 85
A A A A
8
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 9
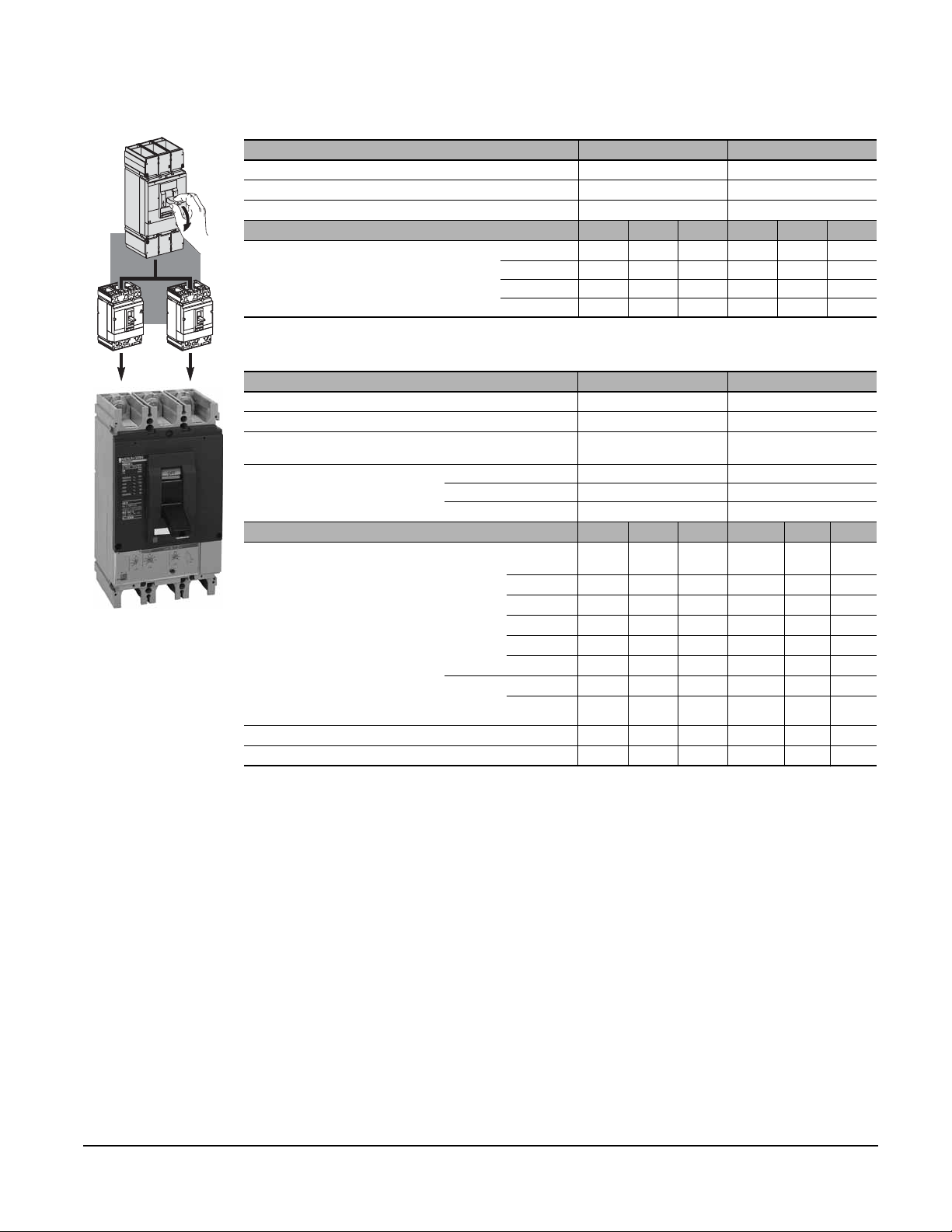
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 3—Circuit Breakers
UL 489 Listed Ratings
Compact® Circuit Breakers NSJ400 NSJ600
06153061
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
r
t
Number of Poles
Rated Voltage (V)
Rated Current (A) In
Interrupting Ratings (kA rms)
AC 50/60 Hz 600 600
40° C 400 (100% Rated Circuit Breaker) 600
240 V 65 100 150 65 100 150
480 V 35 65 100 35 65 100
600 Y/ 347 V — — — — — —
600 V 182525182525
*Oversized Neutral
IEC 947-2 and EN 60947-2 Ratings
Compact® Circuit Breakers NSJ400 NSJ600
Number of Poles
06153063
Rated Insulation Voltage (V) Ui
Rated Impulse
Withstand Voltage (kV)
Uimp
Rated Operational Voltage (V) Ue
Rated Current (A) In
Ultimate Breaking Capacity
(kA rms)
Icu
Service Breaking Capacity Ics
Utilization Category
*Oversized Neutral
AC 50/60 Hz 690 690
DC 500 500
40° C 400 600
AC 50/50 Hz 220/240 V 85 100 150 85 100 150
380/415 V 45 70 150 45 70 150
440 V 42 65 130 42 65 130
500 V 30 50 70 30 50 70
525 V 22 35 50 22 35 50
600/690 V 10 20 35 10 20 35
DC 250 V (1 pole) — 85 — — 85 —
500 V (2 pole
in series)
(% Icu) 100% 100% 100% 100% — 100%
3, 4, 4 OSN* 3, 4
N H L N H L
3, 4, 4 OSN* 3, 4
750 750
88
N H L N H L
—85—— 85—
A A A A — A
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
9
Page 10
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 4—Trip Units
SECTION 4—TRIP UNITS
TRIP UNITS FOR COMPACT® NSF150 AND NSF250 CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Compact NSF150 and NSF250 circuit breakers are equipped with thermal-magnetic (TM) trip units.
Protection • Against overload (1) with a fixed thermal protection
• Against short circuits (2) with fixed (on NSF150) or adjustable (on NSF250) magnetic protection
t
06153064
21
1
Ir
250 A
Trip Units for Compact® NSF150–NSF250
Circuit Breakers
Rating (A) In
3P 50° C 14.2 19 28.5 38 47.5 57 66.5 76 85 95 118 142 166 190 213 237
4P3T 60° C 13.5182736455463728190112 135158180203225
4P4T 70° C 12.8 17 25.6 34.2 43 51 60 68 77 85 107 128 150 171 192 214
Circuit Breaker
Rating (A) In
4P OSN 50° C 95 142 118 237 142 237
Overload Protection
Thermal
Short-circuit Protection
Magnetic
Neutral Protection
*Oversized Neutral
Compact® NSF150 N/H ■■■■■■■■■■ ■ ■
Compact® NSF250 N/H ■ ■■■
®
Compact
NSF150 400 500 1000 1250 1500
Compact® NSF250 5–10 x In
Im
10
9
TM15DP–TM250DP Trip Units
40° C 152030405060708090100125150 175200225250
TM100OSN–TM150OSN Trip Units
Phase Neutral Phase Neutral Phase Neutral
40° C 100 150 125 250 150 250
60° C 90 135 112 225 135 225
70° C 85 128 107 214 128 214
3P Non-adjustable
4P3T
4P4T
4P OSN*
Non-adjustable Adjustable
4P3T No Neutral Protection
4P4T 1000 1250 1500 5–10 x In
4P OSN*
8
7
x 250 A
5
6
Ir Im
TM 250 D
250A / 40°C
2
0
Ir Im
Non-adjustable, No Neutral Protection
Non-adjustable
Non-adjustable
1000 1250 1500
I
10
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 11
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 4—Trip Units
TRIP UNITS FOR COMPACT® NSJ400 AND NSJ600 CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Compact NSJ400 and NSJ600 circuit breakers are equipped with current sensors and electronic trip
units.
Current Sensors Four different sizes are available and can be mounted with all trip units:
• NSJ400—150, 250 and 400 A
• NSJ600—600 A
Trip Units
STR23SP,
STR53UP and
STR23SP-OSN
•
Protection for loads, from 60 to 600 A
— STR23SP and STR53UP for standard protection
— STR23SP-OSN for oversized neutral protection (factory-installed only)
— STR53UP for generator supplied network protection and long cable runs
• Trip units STR23SP and STR53UP can be mounted on all Compact NSJ400 and NSJ600 circuit
breaker types N, H and L
• Trip unit STR53UP offers a greater number of optional indication and measurement functions,
protection settings and ground-fault protection
• STR23SP and STR53UP available on four-pole circuit breakers with sealable, 3-position neutral
protection setting:
— 4P 3D (neutral unprotected)
— 4P 3D + N/2 (neutral protection at 0.5 x Ir) where Ir is trip unit current setting
— 4P 4D (neutral protection at Ir) where Ir is trip unit current setting
Trip Units for Compact® NSJ400 and NSJ600
Circuit Breakers
Overload Protection (Long Time)
Tripping
Threshold (A)
Tripping Time (s)
(Min–Max)
Short-circuit Protection (Short Time)
Tripping
Time Delay
(ms)
Short-circuit Protection (Instantaneous)
Tripping Threshold (A)
Adjustable Neutral Protection (Three Position Switch)
Other Functions
Indication of Fault Type ■ (Standard)
Equipment Ground-fault Protection (T) ■
Built-in Ammeter (I) ■
Zone-selective Interlocking (ZSI) ■
Communication (COM) ■
Ir
Im / Isd
Accuracy ± 15%
Max. Overcurrent Time Before Tripping Fixed ≤ 40
Total Breaking Time ≤ 60 ≤ 60 ≤ 140 ≤ 230 ≤ 350 ≤ 60
Switch Settings Protection Level
Position 1 4P 3D No Protection No Protection No Protection No Protection
Position 2 4P 3D + N/2 0.5 x Ir 0.5 x Ir 0.8 x Ir 0.75 x Ir
Position 3 4P 4D 1.0 x Ir 1.0 x Ir 1.6 x Ir 1.5 x Ir
20–70° C Adjustable (48 Settings) 0.4–1 x In
At 1.5 x Ir 120–180 17–25 34–50 69–100 138–200 277–400 120–180
At 6 x Ir 5–7.5 0.8–1 1.6–2 3.2–4 6.4–8 12.8–16 5–7.5
At 7.2 x Ir 3.2–5.0 0.5–0.7 1.1–1.4 2.2–2.8 4.4–5.5 8.8–11 3.2–5.0
STR23SP STR53UP
Fixed Adjustable Fixed
Adjustable (7 Settings)
2–9 x Ir
Fixed ≥ 9 x In Adjustable (7 Settings) 1.5–9 x In Fixed ≥ 9 x In
Adjustable (7 Settings) 1.5–7 x Ir Adjustable (7 Settings) 2–9 x Ir
Adjustable (4 Settings + Constant I2t Function)
≤ 15 ≤ 60 ≤ 140 ≤ 230
STR23SP OSN
(Oversized Neutral)
Fixed ≤ 40
NSJ250/400N NSJ400/600N
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
11
Page 12
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 4—Trip Units
Electronic Trip
Unit STR23SP and
STR23SP-OSN
(Oversized
Neutral)
t
7
06153065
1
6
3
1
2
3
4
5
Ir Im
test
+
Io = sensor
.7
.63
.5
-
short time
Im
56
4
3
2
90
%Ir
105
7
9
x Ir
ImIr
STR 23 SP
long time
Ir
.8
x In
.9
1
.85
.88
.93
.9
.95
.98
.8
1
x Io
alarm
0
Protection • Long-time (LT) overload protection, adjustable threshold, based on the actual rms current
— Adjustable threshold (1) using six lo base settings (0.5–1) and fine adjustment Ir with eight
settings ranging from (0.8–1)
— Non-adjustable tripping time (2)
• Short-time (ST) short-circuit protection
— Adjustable threshold Im (3)
— Fixed time delay (4)
• Instantaneous (I) short-circuit protection, fixed threshold (5)
• Neutral protection available on standard four-pole circuit breakers; protection level controlled using
three-position switch
— 4P 3D: no protection
— 4P 3D + N/2: neutral protection at 0.5 Ir
— 4P 4D: neutral protection at Ir
• Neutral protection for STR23SP-OSN (oversized neutral) available on four-pole circuit breakers
equipped with oversized neutral protection; protection level controlled using three-position switch
I
12
NSJ250/400N: NSJ400/600N:
— 4P 3D: no protection — 4P 3D: no protection
— 4P 3D + N/2: neutral protection at 0.8 x Ir — 4P 3D + N/2: neutral protection at 0.75 x Ir
— 4P 4D: neutral protection at 1.6 x Ir — 4P 4D: neutral protection at 1.5 x Ir
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 13

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 4—Trip Units
Indications Load indication (LED) in front (6):
• Lights solid at 90% of Ir threshold
• Flashes at >105% or greater of Ir threshold
Test Test connector in front (7) for connection to test kit to check circuit breaker operation after fitting the trip
unit or other accessories.
Setting Example Question: What is the overload protection threshold of a Compact NSJ400 circuit breaker equipped
with trip unit STR23SP where Io = 0.5 and Ir = 0.8?
Answer: In x Io x Ir = 400 x 0.5 x 0.8 = 160 A
The same trip unit with the same settings, mounted on an NSJ600 circuit breaker will have the following
tripping threshold: In x Io x Ir = 600 x 0.5 x 0.8 = 240 A.
.7
.8
Io
.9
1
06153066
.63
.5
x In
400 x 0.5 x 0.8 = 160 A
.88
.85
.8
.9
Ir
.93
.95
.98
1
x Io
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
13
Page 14
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 4—Trip Units
Electronic Trip
Unit STR53UP
t
4
8
test
1
Io
.7
.6
.5
Ir
.9
.8
x In
+
.90 .93
.88
1
.85
1
.8
x Io
tr
8
4
-
2
0,5
(s) @ 6 Ir
06153067
Protection • Long-time (LT) overload protection, adjustable threshold, based on actual rms current, as defined
2
STR 53 UP
.95
.98
1
tsd
8
Isd
(s)
3
4 5
3
6
2
7
1.5
x Ir
.3 .3
.2
.2
.1
0
0
on
I2t
off
5
%Ir >Ir >Isd >Ig
Ii
4 6
3
8
9
2
7
.1
9
1.5
x In
6
Ig
.4
.3
.2
tg
.3
(s)
.2
.1
on
.4 .4
.5
x In
I2t
9
.6
.7
.8
1
.3
.2
.1
off
7
test
μ P
> Ir
> Im
> Ih
In I1 I2 I3
1
2
6
7
A
tr
tsd
IsdIr li
0
Ir Isd I
3
4
5
by IEC 947-2, appendix F
— Adjustable threshold (1) using six lo base settings (0.5–1) and fine adjustment Ir with eight
settings ranging from (0.8–1)
— Adjustable tripping time (2)
• Short-time (ST) short-circuit protection
— Adjustable threshold Isd (3)
— Adjustable time delay (4), with or without constant I
2
t function
• Instantaneous (Ii) short-circuit protection, adjustable threshold (5)
• Neutral protection available on standard four-pole circuit breakers; protection level controlled using
three-position switch
— 4P 3D: no protection
— 4P 3D + N/2: neutral protection at 0.5 Ir
— 4P 4D: neutral protection at Ir
I
Overload Indications
(%Ir)
• LED (9) lights solid when current exceeds 0.9 Ir
• LED (9) flashes when current exceeds long-time threshold Ir
Fault Indications LEDs indicate the type of fault that caused tripping:
• Overload (LT protection) or abnormal component temperature (>Ir)
• Short-circuit (ST or instantaneous protection) (>Isd)
• Ground-fault (if earth-fault protection option is present) (>Ig)
• Microprocessor malfunction—both (>Ir) and (>Isd) LEDs go on, plus the (>Ig) LED, if the ground-
fault protection option is present
The LEDs are battery powered with spare batteries supplied in the adapter box. When a fault occurs,
the LED indicating type of fault shuts off after approximately 10 minutes to conserve battery power. The
fault data is stored in memory and the LED can be re-illuminated by pressing the battery/LED test
button (9). The LED automatically goes off and memory is cleared when the circuit breaker is reset.
Test
• Test connector in front (8) for connection to test kit (see page 16); used to check circuit breaker
operation after fitting trip unit or other accessories
• Test button (9) for (%Ir), (>Ir), (>Im) and (>Ig) LEDs and battery
Self-monitoring The circuit breaker trips for both microprocessor faults and abnormal temperatures.
14
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 15

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 4—Trip Units
Options for
Electronic Trip
Unit STR53UP
Equipment Ground-fault Protection (T)—see (6) and (7), page 14
Type
Tripping threshold
Tripping time (ms)
Ig Adjustable (8 Settings) 0.2–1 x In
Accuracy ± 15%
Max. overcurrent time before tripping (Tg) Adjustable (4 Settings + Constant I2t Function) 60, 140, 230, 350
Total Breaking Time -140, -230, -350, -500
Residual Current
Ammeter (I) A digital display continuously indicates the current of the phase with the greatest load. By pressing a
scroll button, it is also possible to display successively the readings of I1, I2, I3 and I neutral. LEDs
indicate the phase for which the current is displayed.
06153068
A
In I1 I2 I3
Zone-selective
Interlocking (ZSI)
A number of circuit breakers are interconnected one after another by a pilot wire. In the event of a
short-time or earth fault:
• If a given trip unit STR53UP detects the fault, it informs the upstream circuit breaker which applies
the set time delay
• If the trip unit STR53UP does not detect the fault, the upstream circuit breaker trips after its shortest
time delay
Opto-electronic
Outputs
Communication
(COM)
Possible
Combinations
In this way, the fault is cleared rapidly by the nearest circuit breaker. In addition, thermal stresses on
the circuits are minimized and time discrimination is maintained throughout the installation.
The use of opto-transistors ensures total isolation between the internal circuits of the trip unit and the
circuits wired by the user.
®
Transmission of the following data to Digipact
distribution monitoring and control modules:
• Settings
• Phase and neutral currents (rms values)
• Highest current of the three phases
• Overload condition alarm
• I
• T
• I + T
• I + COM
• I + T + COM
• ZSI
• ZSI + I
• ZSI + T
• ZSI + I + T
• ZSI + I + COM
• ZSI + I + T + COM
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
15
Page 16

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 4—Trip Units
ELECTRONIC TRIP UNIT TEST KITS
The test kits presented below are compatible with Compact® and Masterpact® MP/MC/M circuit
breakers.
Tests performed by test kits are only functional tests designed to electrically test the operating integrity
of the trip unit, the flux shifter and the mechanical operation of the circuit breaker. Tests are not
designed to calibrate the circuit breaker.
Mini Test Kit and
Hand-held Test Kit
Portable Test Kit
and Full-function
Test Kit
The Mini Test Kit and the new generation Hand-held Test Kit are portable units which require no
external power supply. Both are powered by five 9 V alkaline batteries, not supplied. These test kits are
used to check operation of the electronic trip unit and circuit breaker tripping. Connection of either test
kit is made via the test port on the front of the trip unit.
06153069
Mini Test Kit
06133786
Hand-held Test Kit
The Portable Test Kit and the new generation Full-function Test Kit are calibration units. Both require a
power supply of 110 or 240 Vac, 50/60 Hz (two-position selector). These test kits are used to check the
operation of the trip unit by measuring actual trip times:
• At 1.5 x Ir for long-time protection
• At 15 x Ir for short-time protection
• At 0.8 x In for ground-fault protection
16
06153070
Portable Test Kit
06133014
Full-function Test Kit
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 17
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
SECTION 5—SWITCHES
RATINGS AND INTERRUPTING RATINGS
UL 1087 Listed Ratings
Section 5—Switches
06153061
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
tr
Number of Poles
Rated Voltage (V)
Rated Current (A)
AC 50/60 Hz 600Y/ 347 600Y/ 347
*Oversized Neutral Protection: four-pole OSN 125/250 and 150/250 are same ratings as NSF250A.
3, 4, 4P OSN* 3, 4
150 250
IEC 947-3 Ratings
Compact® Switches NSF150A NSF250A
Compact® Switches NSF150A NSF250A
Number of Poles
Rated Insulation Voltage (V) Ui
Rated Impulse Withstand
Voltage (kV)
Uimp
Rated Operational Voltage (V) Ue
Rated Operational Current (V) Ie
Making Capacity (kA peak)
Short-time Withstand Current
(kA rms)
*Oversized Neutral Protection
Icw
AC 50/60 Hz 690 690
DC 500 500
AC23A 690 V 160 250
DC23A 250 V 160 250
DC23A 500 V (2 poles in series) 160 250
Icw (kA rms) 2.5 3.5
Duration (s) 3 3
3, 4, 4P OSN* 3, 4
750 750
88
3.6 4.9
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
17
Page 18
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 5—Switches
UL 489 Listed Ratings
06153061
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
r
t
Number of Poles
Rated Voltage (V)
AC 50/60 Hz 600 600
Rated Current (A)
*Oversized Neutral Protection: four-pole OSN 125/250 and 150/250 are same ratings as NSF250A.
3, 4, 4P OSN* 3, 4
400 600
IEC 947-3 Ratings
Compact® Switches NSF150A NSF250A
Compact® Switches NSJ400A NSJ600A
Number of Poles
Rated Insulation Voltage (V) Ui
Rated Impulse Withstand
Voltage (kV)
Uimp
Rated Operational Voltage (V) Ue
Rated Operational Current (V) Ie
Making Capacity (kA peak)
Short-time Withstand Current
(kA rms)
*Oversized Neutral Protection
Icw
AC 50/60 Hz 690 690
DC 500 500
AC23A 690 V 400 630
DC23A 250 V 400 630
DC23A 500 V (2 poles in series) 400 630
Icw (kA rms) 5 8
Duration (s) 3 3
3, 4, 4P OSN* 3, 4
750 750
88
7.1 8.5
Short-circuit
Withstand Current
Molded case switches are identical to molded case circuit breakers, except they are not equipped with
trip units and sensors. Molded case switches open when the handle is switched to the OFF position or
in response to an auxiliary tripping device such as a shunt trip or an undervoltage release.
These switches open instantaneously at a non-adjustable, factory preset, magnetic trip point calibrated
to protect only the molded case switch itself. Magnetic settings:
• NSF150/250 A switches: 2000 A
• NSJ 400/600 A switches: 6000 A
These switches are suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering not more than:
• 240 V: 100 kA for NSF switches and 150 kA for NSJ switches
• 480 V: 65 kA for NSF switches and 100 kA for NSJ switches
• 600 V (600Y/347 for NSF switches): 25 kA
Switches are Listed under UL file E103740 and Certified under CSA file LR 88980.
18
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 19
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
SECTION 6—MOTOR CIRCUIT PROTECTORS
RATINGS AND INTERRUPTING RATINGS
UL 489 Recognized Component
Compact® Circuit Breakers NSF150HC NSF250HC
06153033
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
tr
Number of Poles
Rated Voltage (V)
Rated Current (A) In
AC 50/60 Hz 600Y/347 600Y/347
40° C 150 200 250
Magnetic Trip Setting Im
IEC 947-2 and EN 60947-2 Ratings
Compact® Circuit Breakers NSF150HC NSF250HC
Number of Poles
Rated Insulation Voltage (V) Ui
Rated Impulse Withstand
Voltage (kV)
Rated Operational Voltage (V) Ue
Rated Current (A) In
Ultimate Breaking Capacity Icu
(kA rms) 380/415 V 70 70
Service Breaking Capacity Ics
Utilization Category
Uimp
AC 50/60 Hz 690 690
DC 500 500
40° C 150 200 250
AC 50/60 Hz 220/240 V 100 100
440 V 65 65
500 V 50 50
525 V 35 35
660/690 V 10 10
DC 250 V (1 pole) 85 85
500 V (2 poles in series) 85 85
(% Icu) 100% 100%
Section 6—Motor Circuit Protectors
33
900-1800
33
750 750
88
1000–
2000
HC HC
AA
1250–
2500
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
19
Page 20
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 6—Motor Circuit Protectors
UL 489 Recognized Component
Compact® Circuit Breakers NSJ400HC NSJ600HC
06153033
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
tr
Number of Poles
Rated Voltage (V)
Rated Current (A) In
AC 50/60 Hz 600 600
40° C
Magnetic Trip Setting Im
IEC 947-2 and EN 60947-2 Ratings
Compact® Circuit Breakers NSF150HC NSF250HC
Number of Poles
Rated Insulation Voltage (V) Ui
Rated Impulse Withstand
Voltage (kV)
Rated Operational Voltage (V) Ue
Rated Current (A) In
Ultimate Breaking Capacity Icu
(kA rms) 380/415 V 70 70
Service Breaking Capacity Ics
Utilization Category
Uimp
AC 50/60 Hz 690 690
DC 500 500
40° C 400 600
AC 50/60 Hz 220/240 V 100 100
440 V 65 65
500 V 30 30
525 V 35 35
660/690 V 20 20
DC 250 V (1 pole) 85 85
500 V (2 poles in series) 85 85
(% Icu) 100% 100%
33
400 (100% Rated
Circuit Breaker)
600
2000–4000 3000–6000
33
750 750
88
HC HC
AA
20
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 21
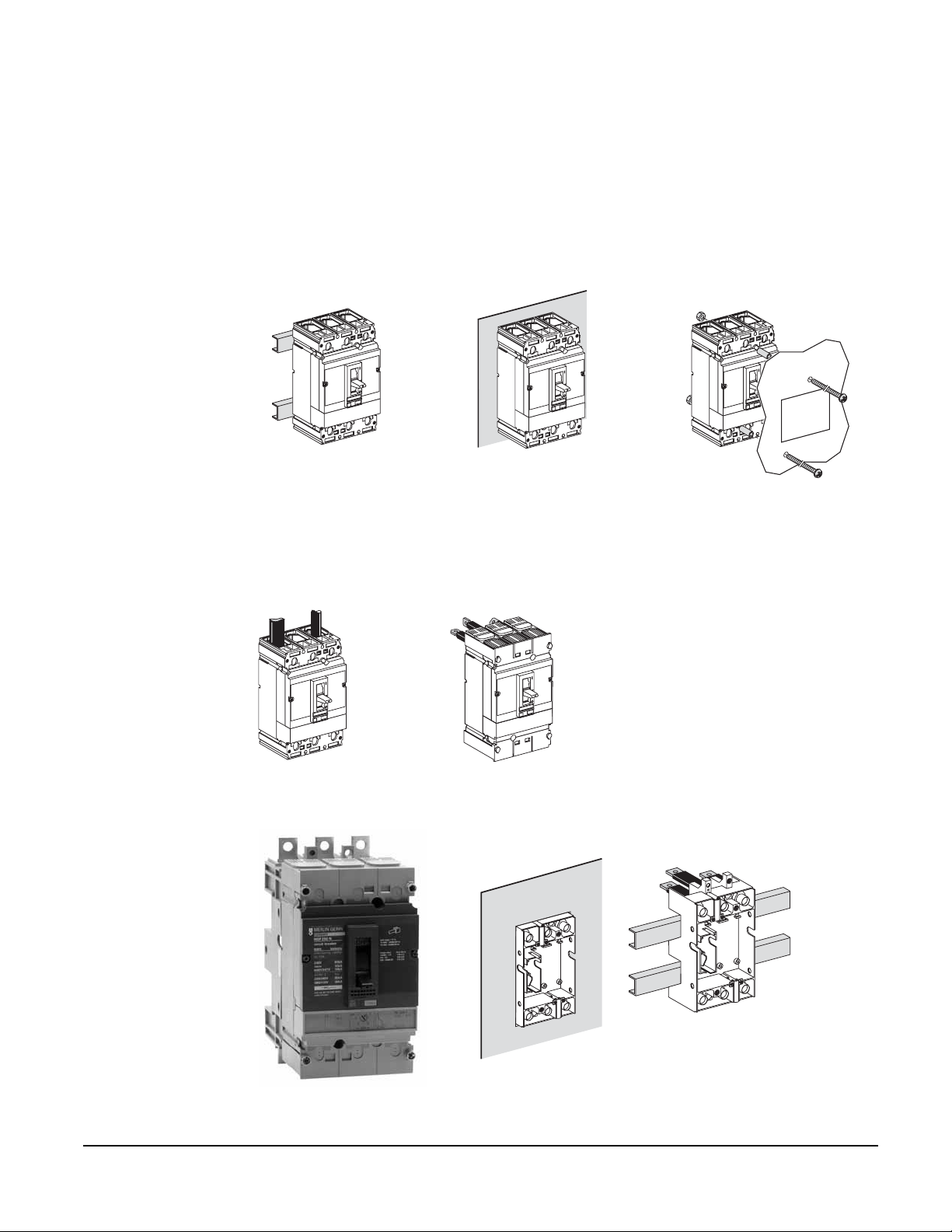
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
SECTION 7—MOUNTING CONFIGURATIONS
Refer to circuit breaker installation instructions before installing circuit breaker, accessories or wiring.
FIXED MOUNTING
Section 7—Mounting Configurations
CONNECTIONS
Mounting on Rails
06153071
h
s
pu
to
trip
Mounting on Backplate
06153072
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
r
t
Flush Mounting
06153073
h
s
pu
to
ip
r
t
See Section 8—Connections for details. Compact® NSF and NSJ circuit breakers suitable for reverse
feeding.
Front Connection
06153074
h
s
u
p
to
p
i
tr
Rear Connection
06153075
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
i
r
t
PLUG-IN MOUNTING
06153076
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Mounting through
Front Panel
06153077
Mounting on Rails
06153078
21
Page 22

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 7—Mounting Configurations
The plug-in configuration makes it possible to:
• Extract and/or rapidly replace the circuit breaker without having to touch connections
• Allow for addition of future circuits at a later date
When the circuit breaker is in the connected position, the primary voltage is fed through the circuit
breaker by means of multiple finger disconnects. Control voltage of internal accessories is provided
through secondary disconnects.
Parts of a Plug-in
Configuration
Compact® circuit breaker (fixed mounted)
• Set of power and secondary disconnects that are added to the circuit breaker
• Plug-in base for mounting through a front panel or on rails
• Safety trip, to be installed on the circuit breaker, which causes automatic tripping if the circuit
breaker is ON before engaging or withdrawing it; the safety trip does not prevent circuit breaker
operation, even when the circuit breaker is disconnected
• Mandatory short terminal shields
The plug-in mounting is Listed under UL file E113555 and Certified under CSA file LR 69561.
DRAWOUT MOUNTING
The chassis is made up of two side plates installed on the base and two other plates mounted on the
circuit breaker.
06153079
06153080
Connected
RemovedDisconnected
Chassis Functions All functions of the plug-in base, plus:
• Disconnected position: the power circuits are disconnected, the circuit breaker is simply
"withdrawn" and may still be operated (on, off, push-to-trip)
• Circuit breaker may be locked using 1 to 3 padlocks—diameter 0.19 to 0.31 inch (5 to 8 mm)—to
prevent connection
• Auxiliaries can be tested using manual auxiliary connector
Mounting • On a backplate, through a front panel or on rails
• Horizontally or vertically
22
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 23

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 7—Mounting Configurations
Accessories • Auxiliary switches for installation on the fixed part of the chassis, indicating the "connected" and
"disconnected" positions
• Toggle collar for circuit breakers with toggle through front panel, intended to maintain the degree of
protection whatever the position of the circuit breaker (supplied with a toggle extension)
• Keylock which, depending on the bolt fitted, can be used to:
— Prevent insertion for connection
— Lock the circuit breaker in connected or disconnected position
• Telescopic shaft for extended rotary handles
Connection of
Auxiliaries
Control voltage is provided through automatic secondary disconnects in the connected position only.
See Section 8—Connections for more details. Electrical accessories can be tested in the disconnected
position with an external wiring harness.
The drawout-mounted chassis is Listed under UL file E113555 and Certified under CSA file LR 69561.
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
23
Page 24

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 8—Connections
SECTION 8—CONNECTIONS
FRONT CONNECTION
Connection to
Cables
06153081
h
s
pu
o
t
p
i
tr
Copper or Aluminum
Cable
Cable connectors for Compact® NSF150 and NSF250 circuit breakers surround the circuit breaker
terminals. They are positioned by an insulating lug pack which is anchored to the circuit breaker case.
06153082
06153083
Cable connectors for Compact NSJ400 and NSJ600 circuit breakers bolt onto the circuit breaker
terminals or the terminals of the plug-in base.
06153084
One-wire Cable
NSF150 NSF150/250
Steel Lug (15–60 A) Aluminum Lug (70–250 A)
S
06153086
06153085
Two-wire Cable
#14 AWG–#3/0 AWG Cu (Solid or Stranded)
#12 AWG–#4/0 AWG Al (Stranded Only)
2.5–95 mm
2
CU/AL
#2/0 AWG–250 kcmil Cu (Stranded Only)
S
70–120 mm
#4/0 AWG–300 kcmil Al (Stranded Only)
95–150 mm
2
2
L
L
S
NSJ400 NSJ600
1 Cable 1–2 Cable
S
L
0.79 in.
20 mm
#2 AWG–600 kcmil Cu (Stranded Only)
35–300 mm
#2 AWG–500 kcmil Al (Stranded Only)
35–240 mm
1.2 in.
31 mm
2
2
Cu/AL
L
S
L
0.79 in.
20 mm
#2/0 AWG–350 kcmil Cu (Stranded Only)
70–185 mm
#2/0 AWG–500 kcmil Al (Stranded Only)
70–240 mm
1.2–2.4 in.
31–61 mm
2
2
24
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 25

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 8—Connections
Connection to
Bars
Compact® NSF150 to NSJ600 circuit breakers are equipped as standard with captive nuts and screws
for direct connection to bars:
• Compact NSF150/250 circuit breakers—M8 screws
• Compact NSJ400/600 circuit breakers—M10 screws
06153087
06153088
e
h
s
u
p
to
trip
∅
L
Compact®Circuit Breaker NSF150/250 NSJ400/600
Pole Pitch
L
d
D
e
∅
D
d
REAR CONNECTION
in. / mm 1.4 / 35 1.8 / 45
in. / mm -1 / 25 -1.3 / 32
in. / mm -0.4 / 10 -0.64 / 16
in. / mm < 0.35 / 9 < 0.51 / 13
in. / mm -0.23 / -6 0.11–0.39 / 3–10
in. / mm < 0.32 / 8 < 0.4 / 10
Fixed Mounting For connection of bars or cables with compression lugs. Rear connections are easily installed on the
circuit breaker terminals. The same connection may be installed flat, edgewise or at a 45° angle. All
combinations are possible. The circuit breaker is mounted on a backplate.
Plug-in Mounting
and Drawout
06153089
sh
u
p
o
t
trip
For connection of bars or cables with compression lugs. Rear connections are installed flat. The plug-in
base or the chassis are mounted through a front panel.
06153090
One Long + Two Short
06153091
Four Positions
Mounting
06153092
06153093
Plug-in Mounting Drawout Mounting
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
push
to
p
ri
t
25
Page 26
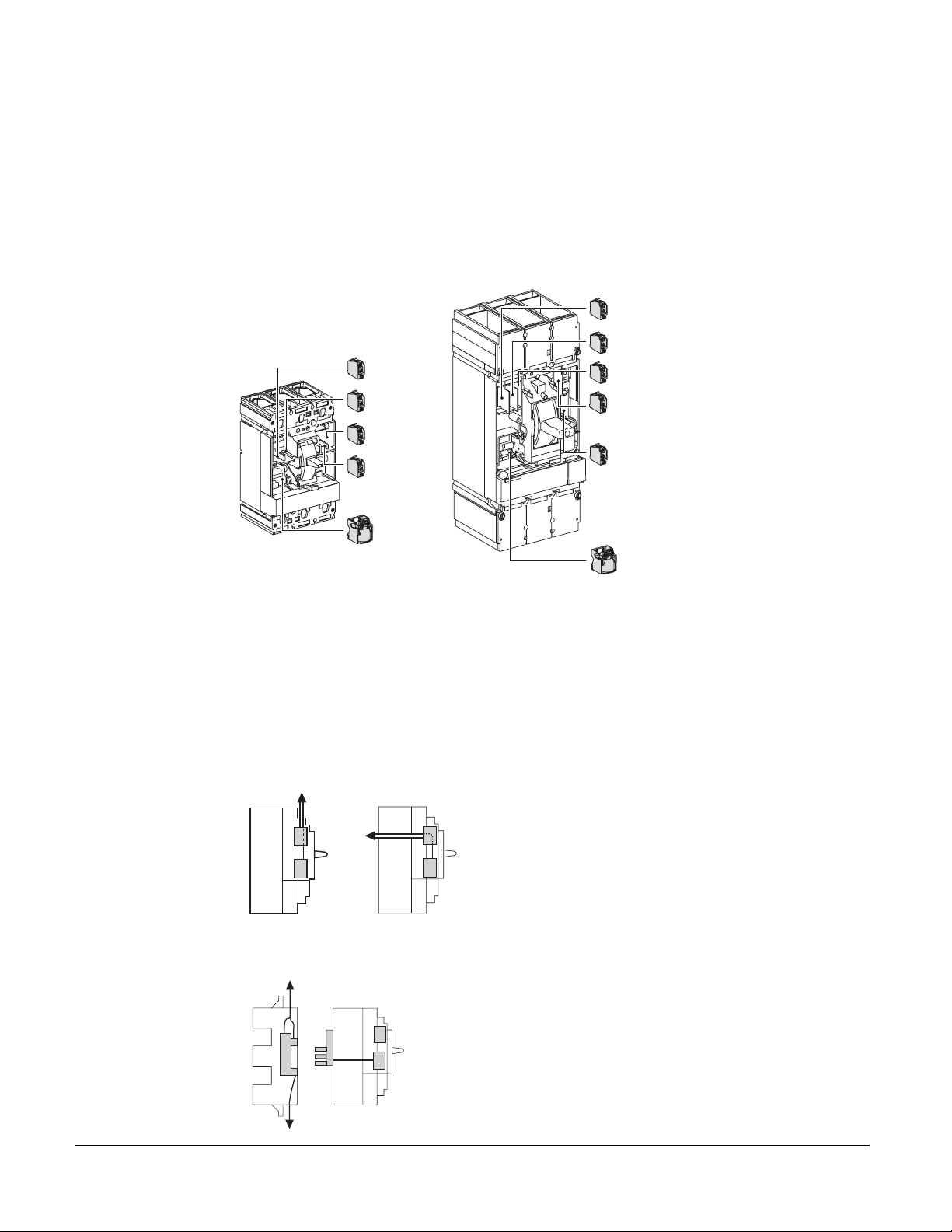
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
SECTION 9—ACCESSORIES
LOCATION
Internal accessories comply with requirements of Underwriters Laboratories Inc. UL 489 and Canadian
Standard Association C22.2 No. 5.1 Standards. All internal accessories are Listed for fixed installation
per UL file E103955 and Certified under CSA file LR 69561.
Auxiliary Switch
(OF1)
06153094
Auxiliary Switch
(OF1)
Alarm Switch
(SD)
Auxiliary Switch
(OF2)
Overcurrent
Trip Switch (SDE)
Shunt Trip (MX)
or Undervoltage
Trip (MN)
Auxiliary Switch
(OF2)
Auxiliary Switch
(OF3)
Alarm Switch
(SD)
Overcurrent
Trip Switch (SDE)
Shunt Trip (MX)
or Undervoltage
Trip (MN)
NSF150/250 NSJ400/600
CONNECTIONS
Each electrical accessory is fitted with numbered terminal blocks for wires with the following maximum
size:
• #16 AWG (1.5 mm
• #14 AWG (2.5 mm
Fixed Mounting Auxiliary circuits exit the device through a knock-out in the front cover.
06153095
Plug-in and
Drawout Mounting
06153097
2
) for auxiliary switches, undervoltage and shunt trip or undervoltage trip
2
) for the motor operator
06153096
26
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 27

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
AUTOMATIC SECONDARY DISCONNECTING BLOCKS
Accessory circuits exit the circuit breaker via one to three secondary disconnecting blocks (nine wires
each). For Compact
unit STR53UP also exit via the automatic secondary disconnecting blocks. These are made up of:
• A moving part connected to the circuit breaker via a support (one support per circuit breaker)
• A fixed part mounted on the plug-in base, equipped with connectors for wires up to
#14 AWG (2.5 mm
06153098
®
NSJ400/600 circuit breakers connection wires for the options installed with trip
2
)
06153099
Section 9—Accessories
OF1
SD
MN/MX
®
Compact
06153100
Nine-wire Manual Auxiliary Connector
OF2
SDE
MT
NSF150 and NSF250 Circuit Breakers
OF1
SD
MN/MX
Compact
OF2
SDE
MT
®
NSJ400 and NSJ600 Circuit Breakers
OF3
SDV
COM
R/T
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
27
Page 28

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
AUXILIARY AND ALARM SWITCHES
06153101
Changeover
Switches
Auxiliary switches provide remote information of the circuit breaker status and can thus be used for
indications, electrical locking, relays, etc.
Functions • OF (open/closed): auxiliary switch—indicates position of the circuit breaker contacts
• SD (trip indication): bell alarm—indicates that the circuit breaker has tripped due to
— Overload
— Short circuit
— Ground fault
— The operation of a shunt trip or undervoltage trip or the "push-to-trip" button which resets when
the circuit breaker is reset
• Operation of a plug-in base or chassis when attempting to withdraw the circuit breaker in ON
position; SDE (fault indication): indicates the circuit breaker has tripped due to an overload, short
circuit or ground fault; resets when circuit breaker is reset
• CAM (early-make or early-break function): indicates the position of the rotary handle; used in
particular for advanced-opening safety trip devices
• Connected/disconnected: indicates the position of a drawout circuit breaker
• Switching of very low loads: all above auxiliary switches are also available in low-level versions
capable of switching very low loads (e.g., for controlling PLCs or electronic circuits)
Standards Auxiliary switches comply with UL 489, CSA C22.2 No. 5.1 and IEC 947-5 Standards. “Low-level"
switches are not UL Listed.
Installation • Functions OF, SD and SDE:
— Switches snap into cavities under front accessory cover of the circuit breaker
— For Compact
depending on where it is fitted in the circuit breaker
®
NSF150–NSJ600 circuit breakers, one model serves for all indication functions
• SDE function of a circuit breaker equipped with a thermal-magnetic trip unit requires the SDE
actuator
• CAM: to be fitted in the rotary handle module; depending on how it is installed, it ensures either the
CAO (early-break) or the CAF (early-make) function "Connected/disconnected" function; two parts
to be fitted on the chassis and the drawout circuit breaker
28
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 29
Electrical Ratings
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
UL 489 and CSA C22.2 No. 5.1 Ratings
Minimum Rating
Maximum Current and Voltage
Maximum Rating
IEC 947 Ratings
Rated Thermal Current (A)
Minimum Rating
Maximum Current and Voltage
Utilization Category
(IEC 947-4)
Operational Current (A)
50/60 Hz 240 V 5 6
480 V 5 6
DC 48 V 2.5 2.5
600 V — 3
125 V 0.8 0.8
250 V 0.3 0.3
Low-level Switches Regular Switches
56
1 mA–4 V 10 mA–24 V
100 mA–10 V 6 A–480 V
If the maximum voltage and current are
exceeded, the low-level characteristics of
the switch will be compromised.
However, the switch will still function as a
standard switch to the following
specifications:
ac dc ac dc
AC12 AC15 DC12 DC14 AC12 AC15 DC12 DC14
24 V 5351662.51
48 V 5 3 2.5 0.2 6 6 2.5 0.2
110 V 5 2.5 0.8 0.05 6 5 0.8 0.05
220/240 V 5 2 — — 6 4 — —
250 V — — 0.3 0.03 — — 0.3 0.03
380/415 V 5 1.5 — — 6 3 — —
440 V 5 1.5 — — 6 3 — —
660/690 V — — — — 6 0.1 — —
Section 9—Accessories
Low-level Switches Regular Switches
1 mA–4 V 10 mA–24 V
100 mA–10 V 6 A–480 V
If the maximum voltage and
current are exceeded, the lowlevel characteristics of the switch
will be compromised. However,
the switch will still function as a
standard switch to the following
specifications:
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
29
Page 30
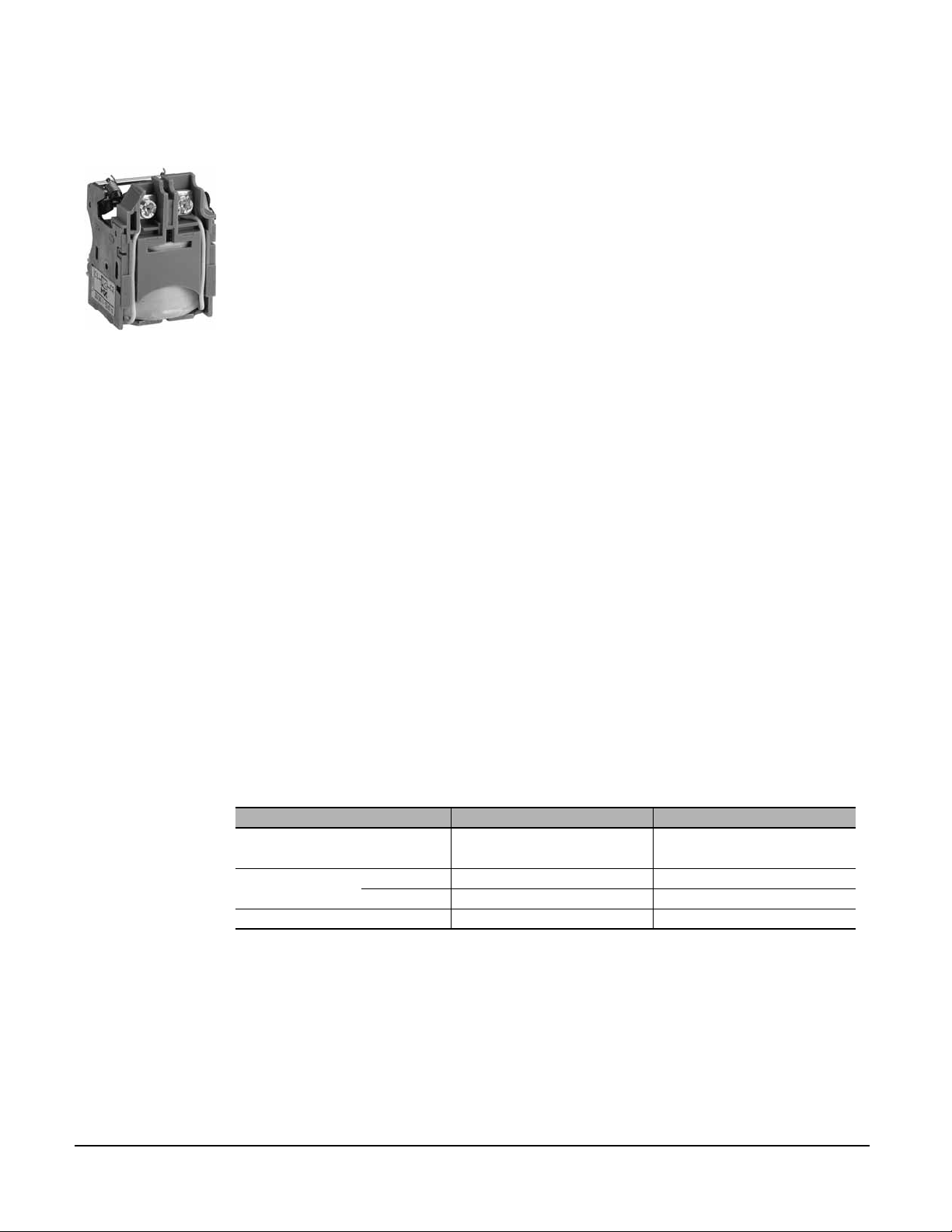
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
SHUNT TRIP AND UNDERVOLTAGE TRIP
A voltage release can be used to trip the circuit breaker via a control signal.
06153102
Undervoltage trip
(MN)
• Trips circuit breaker when the control voltage drops below a tripping threshold
• Drops out between 35% and 70% of rated voltage
• Circuit breaker closing is possible only if the voltage exceeds 85% of rated voltage
• Permanent type
• If an overvoltage condition exists, operation of circuit breaker closing mechanism will not permit the
main contacts to touch, even momentarily
Shunt trip (MX) • Trips the circuit breaker when control voltage rises above 70% of its rated voltage
• Impulse type ≥ 20 ms or maintained control signals
• AC shunt trips can be operated at 55% of their rated voltage, making them suitable for ground-fault
protection when combined with a Class I ground-fault sensing element
Operation • The circuit breaker must be reset locally after being tripped by shunt trip or undervoltage trip
(MN or MX)
• MN or MX tripping has priority over manual (or motor operator) closing; in the presence of a
standing trip order such an action does not result in any closing, even temporarily, of the main
Installation and
Connection
contacts
• Endurance: 50% of the rated mechanical endurance of the circuit breaker for Compact
NSJ600 circuit breakers
• Accessories are common to NSF and NSJ circuit breakers and are located within the circuit breaker
behind front accessory cover
• Each terminal may be connected by one #18–#14 AWG (1.0–2.5 mm
Electrical Characteristics
2
) stranded copper wire
®
NSF150–
30
Rated Voltage (V)
Consumption
Clearing Time (ms)
AC DC
24, 48, 110–130, 208–277, 380–480, 525, 600 12, 24, 30, 48, 60, 125, 250
Pickup (MX) < 10 VA < 5 W
Seal-in (MN) < 5 VA < 5 W
< 50 < 50
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 31

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
MOTOR OPERATOR
The motor operator remotely operates the circuit breaker featuring easy and sure operation:
• All circuit breaker indications and information remain visible and accessible, including trip units
06153103
Applications • Local motor-driven operation, centralized operation, automatic distribution control
settings and circuit breaker connection
• Suitability for isolation is maintained and padlocking remains possible
• Double insulation front face
• Normal/standby source changeover or switching to a replacement source to optimize energy costs
• Load shedding and reconnection to optimize energy costs
• Synchrocoupling—less than five cycle closing time
Automatic
Operation
• On and off by two impulse type or continuous control signals
• Depending on the wiring, resetting can be done locally, remotely or automatically
• Mandatory manual reset following tripping due to an electrical fault
Manual Operation • Transfer to manual mode using switch with possibility of remote mode indication
• On and off by two push buttons
• Recharging of stored-energy system by pumping the lever nine times
• Padlocking in off position
Installation and
Connection
• All installation (fixed, plug-in/drawout mounting) and connection capabilities are maintained
• Connection of the motor operator module behind its front cover to a built-in terminal block, for
stranded copper wire #14 AWG (2.5 mm
2
)
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
31
Page 32

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
Accessories for
NSJ400/600
• Keylock for locking in OFF position
• Operations counter, indicating the number of ON and OFF cycles; the counter must be installed on
the front of the motor operator module.
Characteristics
NSF NSJ
Response Time (ms)
Max. Cycles Frequency Per Minute
Control Voltage (V)
Consumption
Minimum Operating Order
Operating Voltage
AC 50/60 Hz 48–60 48–60
DC 24–30 24–30
AC (VA) Opening -500 —
DC (W) Opening -500 —
Opening < 500 —
Closing < 80 —
4—
110–130 110–130
208–277 208–277
380–480 380–415
440–480
48–60 48–60
110–130 110–130
250 250
Closing -500 —
Closing -500 —
700 ms —
85–110% Rated Voltage —
06153104
10
MERLIN GERIN
compact
NSJ 400 N
circuit breaker
600V
UL inter. ratings
RMS Sym Amps
240V
480V
600V
IEC947
.2
220/240V
380/415V
Ics = 100% Icu
Uimp = 8kV
UTE VDE BS CEI UNE NEMA
In = 400A
manu
1 3
50/60Hz
65k
35k
25k
Ic
u
85kA
45kA
auto
2
O OFF
O
push OFF
89
charged
I
push ON
7
4
5 6
2
2
1
1
1. Contact position indicator (suitability for isolation)
2. Outgoing circuit identification labels
3. Spring status indicator (charged, dischar ged)
4. Locking device (keylock) on NSJ400/600
5. Locking device (off position) using one to three padlocks, diameter
0.2–0.32 in. (5–8 mm), not supplied
6. Manual spring-charging handle
7. ON push button
8. OFF push button
9. Manual/auto mode selection switch; the position of the switch can be indicated
remotely
10. Operations counter (Compact
®
NSJ400/600 circuit breaker)
32
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 33

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
ROTARY OPERATING HANDLES
Operation • The direct rotary handle maintains
— Suitability for isolation
— Indication of three positions: O (off), I (on) and tripped
— Access to the "push-to-trip" button
— Visibility of, and access to, trip unit settings
Section 9—Accessories
Directly Mounted
tripped
ON
I
reset
O
OFF
06153105
Closing
I/ON
(Closed)
Tripped
Reset
O/OFF
(Open
Isolated)
• The circuit breaker may be locked in the off position by using one to three padlocks, padlock
shackle diameter 0.19–0.31 in. (5–8 mm); padlocks are not supplied
06153106
Installation Replaces the circuit breaker front accessory cover (secured by screws).
Models
• Standard with black handle
• VDE type with red handle and yellow bezel for machine tool control
Variations for
Compact
®
NSF150–
NSJ600 Circuit
Breakers
Accessories transform the standard direct rotary handle for the following situations:
• Motor control centers (MCCs)
— Opening of door prevented when circuit breaker is on
— Closing of circuit breaker inhibited when door is open
• Machine tool control; complies with CNOMO E03.81.501N; degree of protection IP54
The directly-mounted rotary operating handle is Listed under UL file E103955 and Certified under CSA
file LR 69561.
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
33
Page 34

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
Door Mounted Makes it possible to operate circuit breakers installed inside an enclosure from the front. The handle
mechanism can be used in NEMA 3R and 12 enclosure applications. Degree of protection: IP40 as per
IEC 529.
06153107
Operation
• The unit maintains:
— Suitability for isolation
— Indication of the three positions: O (off), I (on) and tripped
— Visibility of and access to trip unit settings when door is open
• Defeatable interlock prevents opening of door when circuit breaker is on
• Circuit breaker may be locked in the off position by using one to three padlocks, padlock shackle
diameter 0.19–0.31 in. (5–8 mm); padlocks are not supplied; locking prevents opening of the
switchboard door
Models
• Standard with black handle
• VDE type with red handle and yellow bezel for machine tool control
Installation The extended rotary operating handle is made up of:
• A unit that replaces the front accessory cover of the circuit breaker (secured by screws)
• An assembly (handle and front plate) on the door that is always secured in the same position,
whether the circuit breaker is installed vertically or horizontally
• An extension shaft that must be adjusted; the distances between back of circuit breaker and door
Variation for
Compact
NSJ600 Circuit
Breakers
®
NSF150–
are
— Compact
— Compact NSJ400/600 circuit breakers: 8.4–25 in. (210–625 mm)
For withdrawable configurations, the extended rotary handle is also available with a telescopic shaft
containing two stable positions. The extended rotary operating handle is Listed under UL file E103955
and Certified under CSA file LR 69561.
®
NSF150/250 circuit breakers: 7.4–24 in. (185–600 mm)
34
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 35

CABLE OPERATING HANDLE
The extended rotary operating handle is Listed under UL file E103955 and Certified under CSA file LR
69561.
06153108
h
s
u
p
o
t
p
tri
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
O
O
FF
Flange-mounted
Handle Cable
Operating
Mechanism
•
The cable operator maintains:
— Suitability for isolation
— Indication of three positions: O (Off), I (On) and tripped
— Access to push-to-test
• The circuit breaker may be locked in the off position by one to three padlocks, padlock shackle
diameter 0.19–0.31 in. (5–8 mm); padlocks are not supplied
• Door can be locked closed due to interlocking features of handle operator
Installation Handle is mounted on flange of enclosure using specified mounting dimensions while circuit breaker
and operating mechanism are mounted to inside of enclosure using two screws.
Cable lengths available in 3-, 5- or 10-foot lengths to accommodate a variety of mounting locations.
Handles are available in painted Nema 1, 3, 3R, 4 (sheet steel) and 12 ratings or chrome (Nema 4, 4x).
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
35
Page 36
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
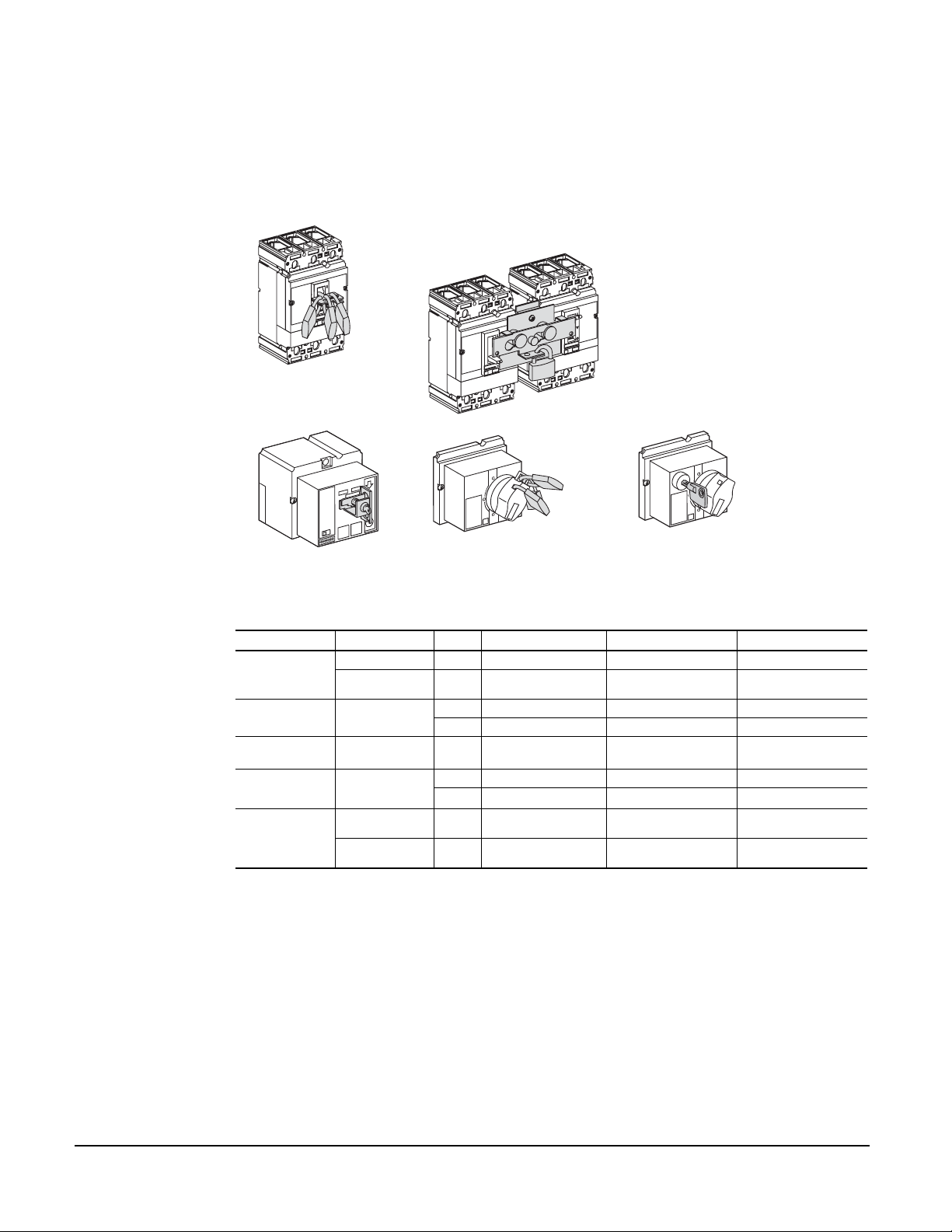
LOCKING SYSTEMS
Padlocking systems can receive up to three padlocks with diameters ranging from
0.19–0.31 in. (5–8 mm) ; padlocks not supplied.
Locking In the Off
Position
06153109
06153110
push
to
trip
push
to
trip
push
to
trip
Locking of the Toggle Using a
Fixed Device
Locking of the Toggle Using a
Stationary Device
06153111
I
ush
p
manu/auto
O
ON
ush
p
OFF
Locking of the Motor Operator
Using a Keylock
2
1
06153112
Locking of the Rotary Handle Using
a Padlock or a Keylock
ON
I
O
OFF
06153113
Locking of the Rotary Handle Using
a Keylock
profalux
profalux
ON
I
O
F
OF
Control Device Function Means Required Accessories Compact® NSF150/250 Compact® NSJ400/600
Toggle
Direct Rotary
Handle
MCC Rotary
Operating Handle
Extended Rotary
Operating Handle
Motor Operator
Lock In Off Position Padlock Removable Device ■■
Lock In Off or On
Position
Lock In Off Position
Padlock Stationary Device ■■
Padlock — ■■
Keylock Locking Device + Keylock
Lock In Off Position Padlock — ■■
Lock In Off Position,
Door Opening
Prevented
Lock In Off Position,
Motor
Mechanism Locked
Out
Padlock — ■■
Keylock Keylock
Padlock —
Keylock
Locking Device (Keylock
Incorporated)
■■
■
36
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 37

INTERLOCKING ACCESSORIES
Interlocking prevents simultaneous closing of two circuit breakers.
Control Device Means NSF150–NSJ600
Toggle
Rotary Handle (Directly or Door Mounted)
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
Sliding Bar Interlocking Mechanical Device ■
Mechanical Interlocking ■
2 Keylocks and 1 Key ■
Interlocking of
Circuit Breakers
with Toggle
Control
Interlocking of
Circuit Breakers
with Rotary
Handles
Two models:
• For Compact
• For Compact
®
NSF150–NSF250 circuit breakers (three-pole or four-pole)
®
NSJ400–NSJ600 circuit breakers (three-pole or four-pole)
Padlocking systems can receive one or two padlocks with diameters ranging from
0.19–0.31 inch (5–8 mm). Both interlocked circuit breakers should be fixed version or plug-in version.
Two sliding interlocking bars can be used to interlock three circuit breakers installed side-by-side, in
which case one circuit breaker is in the ON position and the two others in the OFF position.
06153114
push
to
trip
push
to
trip
Interlocking with Toggle Control
For Compact® NSF150–NSJ600 circuit breakers
06153115
ON
I
ON
I
tripped
push
to
trip
reset
O
OFF
O
OFF
ON
I
ON
I
ripped
t
push
to
p
ri
t
reset
O
OFF
O
OFF
Interlocking with Rotary Handles
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
37
Page 38
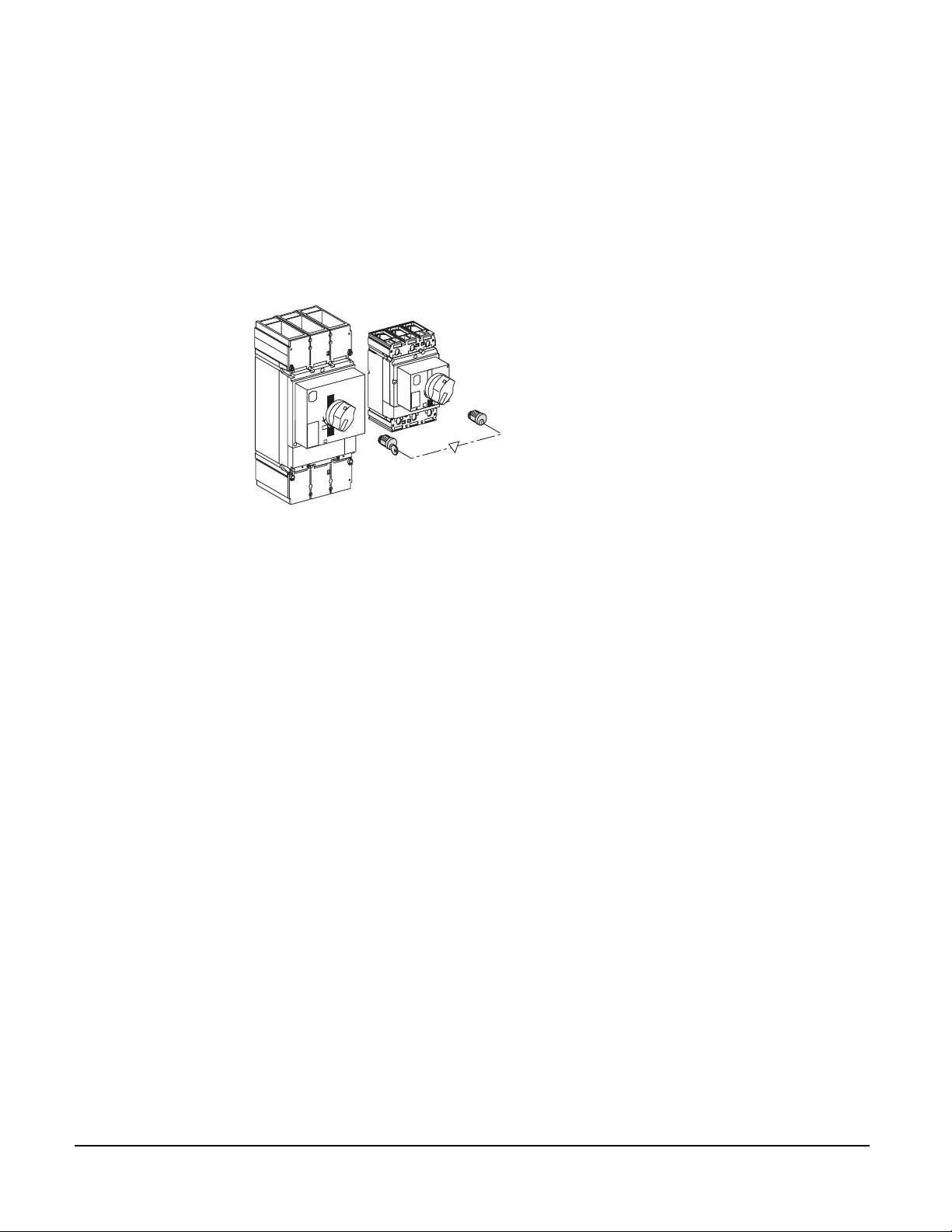
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
Interlocking with
Keys
For circuit breakers equipped with rotary handles or a motor mechanism. Interlocking with keys may be
easily implemented by equipping each of the Compact
®
circuit breakers, either fixed or drawout
mounted, with a directly mounted rotary operating handle and a standard keylock, but with only one key
for the two keylocks. This solution enables interlocking between two circuit breakers that are
geographically distant or that have significantly different characteristics.
Use:
• A keylock adapter (different for each device)
• Two identical keylocks with a single key
06153116
ON
I
ON
I
O
OFF
h
s
u
p
o
t
trip
sh
u
p
o
set
t
e
r
p
i
tr
O
OFF
Interlocking with Keys
38
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 39

FRONT-PANEL ESCUTCHEONS
∅
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
For Fixed or Plugin Mounting
Front-panel
Escutcheons for
Toggle
Front-panel
Escutcheon for
Motor Operator
Module or Rotaryoperating Handle
Door escutcheon provides better appearance of the door contact.
Secures to the panel, from the front.
06153117
h
s
pu
to
trip
Secures to the panel by four screws, from the front.
06153118
2
2
d
rge
d
scha
i
d
rge
scha
i
d
F
OF
O
OFF
O
5...8
5...8
∅
1
1
I
I
O
O
ON
push ON
sh
pu
push OFF
OFF
sh
pu
06153119
ON
I
O
h
us
p
F
to
OF
trip
Toggle Boot
• Protection up to NEMA 3M
• Fits on front of circuit breaker
06153120
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
39
Page 40

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 9—Accessories
For Drawout
Mounting
Toggle Collars The toggle collars make it possible to maintain degrees of protection regardless of the circuit breaker
position (connected, disconnected).
• Front panel escutcheons are obligatory (identical to those for rotary handle and ammeter module)
• Toggle collars secured by two screws on the circuit breaker
• Front panel escutcheons secured on the switchboard
• Toggle extension is supplied with the toggle collar
Front panel escutcheons for motor operator, rotary operating handles are the same as for the fixedmounted circuit breaker with the same equipment.
06153121
push
to
trip
Outgoing Circuit
Compact® NS circuit breakers come with labels designed for handwritten indications.
Identification
06153122
N
I
A
M
AIN
PUMP
M
push
trip
P
to
It is also possible to use preprinted Telemecanique labels, catalog No. AB1
• Compact
• Compact
®
NSF150–NSF250 circuit breakers: eight characters
®
NSJ400–NSJ600 circuit breakers: sixteen characters
Sealing Accessory This accessory includes the elements required to fit lead seals to prevent:
• Front accessory cover removal
• Rotary handle removal
06153123
• Opening of the motor operator
• Access to accessories
• Access to trip unit settings
06153124
• Access to ground-fault protection settings
• Trip unit removal
• Terminal cover removal
• Access to power connections
40
06153125
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 41

SECTION 10—DIMENSIONS
FIXED MOUNTED
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
Dimensions
06153126
H1
H3
H54
X
H
H2
H53
P1
P2
P4
Z
Mounting on Backplate
2P, 3P 4P
06153129
G1
G
∅T
K1 K1
K
K1
G5
X
G4
2P, 3P 4P
06153127
X
A
Y
L
L1
A—Short Terminal Covers
for Rear Connection
K1 K1 K1
K2
K
Electrical Clearances
13.8
35
06153128
X
13.8
35
0.4
10
0.4
10
Y
L
L2
Mounting on Rails
2P, 3P 4P
U (E)
06153130
X
∅T
G
K1
K
X
K2
K
X
∅T4 (D)
D—Only For Rear Connected Circuit Breakers
Y
Front Panel Cutouts
For Fixed or Plug-in Circuit Breakers
Cutout A
06153131
B/C
P5
P6
Z
A
X
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
06153132
R1
Y
E—U ≤ 0.78 in. (20 mm) When Using
Secondary Disconnecting Blocks
®
NSF150 and NSF250
(Compact
Circuit Breakers)
Cutout B
06153133
C1
X
C
Y
R
Y
R4(3P)
R5(4P)
R2
Y
Cutout C
06153134
C3
X
C2
Y
X
C2
Y
Dimensions: in. / mm
C3
41
Page 42
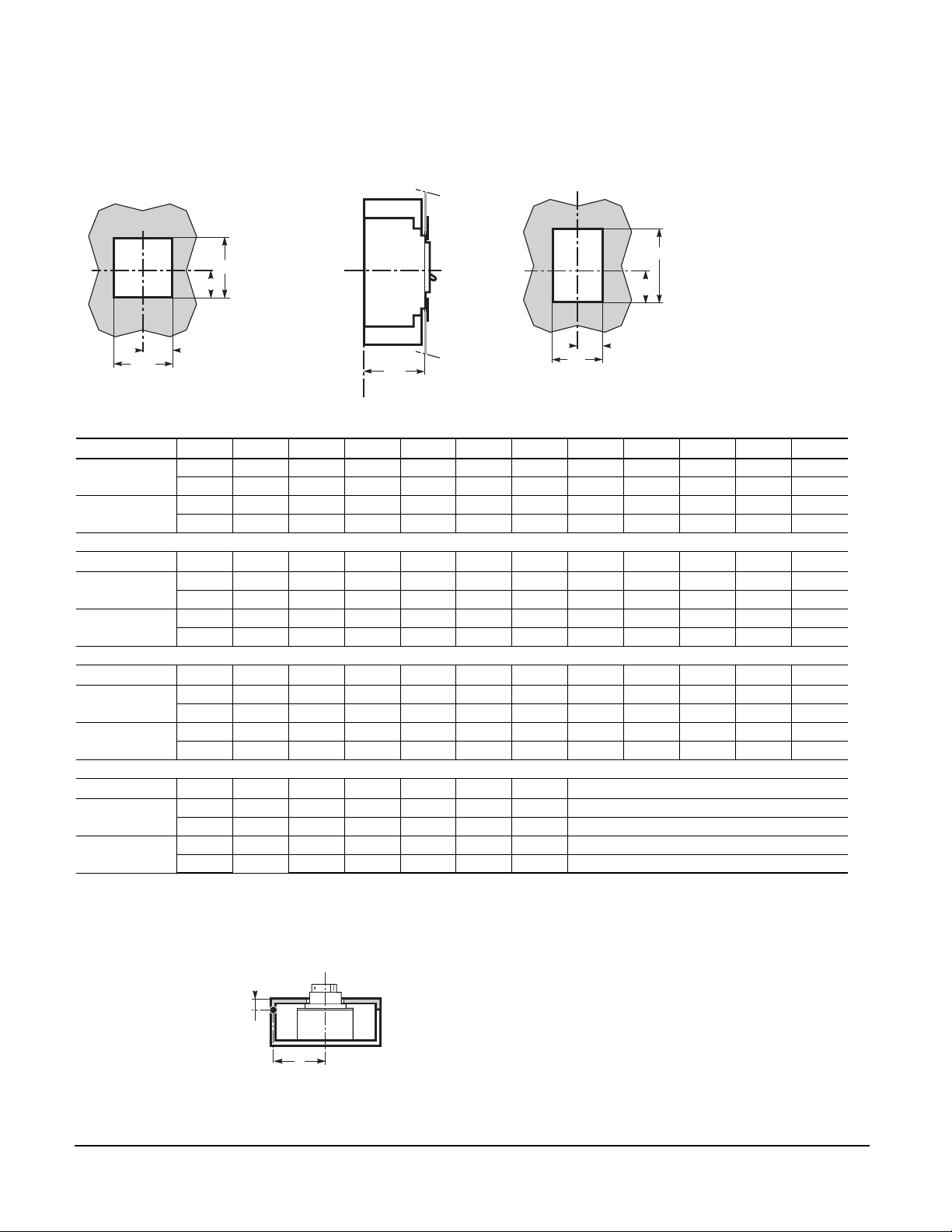
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
Front-panel Cutouts
With Toggle Boot
06153135
Y
R12
R13
Front Accessories: See Page 39
NSF150/250N/H/L
NSJ400/600N/H/L
NSF150/250N/H/L
NSJ400/600N/H/L
Inch 1.14 2.99 2.12 4.25 1.69 4.09 1.33 3.38 2.46 4.92 2.75
mm 29 76 54 108 43 104 34 86 62,5 125 70
Inch 1.63 4.56 3.64 7.24 2.08 5.74 1.83 4.96 3.93 7.87 4.46
mm 41.5 116 92.5 184 53 146 46.5 126 100 200 113.5
Inch 5.51 3.16 6.33 3.70 7.40 3.74 7.48 0.68 1.37 2.06 4.13
mm 140 80.5 161 94 188 95 190 17.5 35 52.5 105
Inch 8.93 5.01 10.03 5.61 11.22 6.69 13.38 0.88 1.77 2.75 5.51
mm 227 127.5 255 142.5 285 170 340 22.5 45 70 140
With Escutcheon
06153136
X
C21
X
C20
P6
Z
C C1C2C3C6C7C20C21G G1G4
G5H H1H2H3H53H54K K1 L L1
06153137
C7
X
C6
Y
R6
R7
Dimensions: in. / mm
L2 P1 P2 P4 P5 P6 R R1 R2 R4 R6
NSF150/250N/H/L
NSJ400/600N/H/L
Inch 5.51 3.18 3.38 4.37(*) 3.26 3.46 0.57 1.14 2.12 4.25 1.14
mm1408186111(*)838814.52954108 29
Inch 7.28 3.75 4.33 6.61 4.21 4.40 1.24 2.48 2.81 5.62 1.83
mm 185 95.5 110 168 107 112 31.5 63 71.5 143 46.5
R7 R12 R13 ØT ØT4 U**
NSF150/250N/H/L
NSJ400/600N/H/L
* P4 = 4.96 in./126mm for Compact® NSF250N/H/L Circuit Breaker
** U ≤ 0.78 in./20mm When Using Secondary Disconnecting Blocks (Compact® NSF150 and NSF250 Circuit Breakers)
Inch 2.28 1.69 3.38 0.23 0.86 - 1.25
mm 58 43 86 6 22 - 32
Inch 3.66 2.48 4.96 0.23 1.25 - 1.25
mm 93 63 126 6 32 - 32
NOTE: Door cutouts require a minimum distance between the center of the circuit breaker and the door
hinge point
06153138
h
Δ
3.93 in./100 mm + (h x 5).
Δ
42
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 43

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
PLUG-IN AND DRAWOUT MOUNTING
Dimensions
Plug-in (On Base)
Z
M
06153139
H17
(*)
2P, 3P 4P
K1
K1
06153140
X
Section 10—Dimensions
K1 K1
G11
G11
X
X
X
H16
P7
P8
P9
P4
Drawout (On Chassis)
M
06153141
H19
H18
Z
P7
P8
P9
P2 P12
P4
G10
G10
(*)
Y
Y
L
L
L1
L1
Y
L
L2
2P, 3P 4P
06153142
X
X
(*)
Y
L6
L7
L8
Y
X
(*)
L6
L9
L10
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Dimensions: in. / mm
43
Page 44

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
Mounting
Through a Backplate
(Plug-in Base)
K6
K1
K
G13
X
G12
Y
K5
2P, 3P 4P
06153143
E21525
G11
G10
T
On Rails (Plug-in Base or Chassis)
2P, 3P 4P
U
06153145
G21
K21
K20
X
E21526
K22
K20
K2
K7
Through a Backplate
(Chassis)
K
2P, 3P 4P
06153144
G11
X
G10
Y
K5
T
K1
K
G13
X
G12
Y
K11
K12
X
K2
K13
K
X
Y
K11
G20
∅T
Y
Front-panel Cutouts
Plug-in Mounting
See Fixed-mounted Installation Page 41
06153146
X
P44
Z
Y
Drawout with Extended Front-panel Escutcheons
06153147
Y
R8
R9
X
C11
C17
44
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 45
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
C11 C17 G10 G11 G12 G13 G20 G21 H16 H17 H18 H19 K K1
NSF150/250N/H/L
NSJ400/600N/H/L
NSF150/250N/H/L
NSJ400/600N/H/L
NSF150/250N/H/L
NSJ400/600N/H/L
* P4 = 4.96 in./126mm for Compact NSF250N/H/L Circuit Breaker
** U ≤ 0.78 in./20mm When Using Automatic Auxiliary Connectors (Compact NSF150 and NSF250 Circuit Breakers)
Inch 4.05 1.67 3.74 7.48 3.42 6.85 1.47 2.95 4.03 8.07 4.07 8.26 0.68 1.37
mm 103 42.3 95 190 87 174 37.5 75 102.5 205 103.5 210 17.5 35
Inch 6.10 1.65 5.90 11.8 5.39 10.7 2.95 5.90 6.20 12.40 5.51 11.02 0.88 1.77
mm 115 42 150 300 137 274 75 150 157.5 315 140 280 22.5 45
K5 K6 K11 K12 K13 K20 K21 L L1 L2 L6 L7 L8 L9
Inch 2.14 4.29 2.91 5.82 7.20 1.37 2.75 2.06 4.13 5.51 3.64 7.28 8.50 8.66
mm 54.5 109 74 148 183 35 70 52.5 105 140 92.5 185 216 220
Inch 2.81 2.81 7.40 3.60 7.20 8.97 1.96 2.75 5.51 7.28 4.33 8.66 98.46 10.43
mm 71.5 143 91.5 183 228 50 100 70 140 185 110 220 250 265
L10P2P4P7P8P9P12P44R8R9U**ØT
Inch 9.88 3.38 4.37(*) 1.06 1.77 2.95 1.25 4.84 2.91 5.82 ≤1.25 0.23
mm 251 86 111(*) 27 45 75 32 123 74 148 ≤ 32 6
Inch 11.61 4.33 6.61 1.06 1.77 3.93 1.25 5.78 3.54 7.08 ≤ 1.25 0.11
mm 295 110 168 27 45 100 32 147 90 180 ≤32 3
Section 10—Dimensions
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
45
Page 46
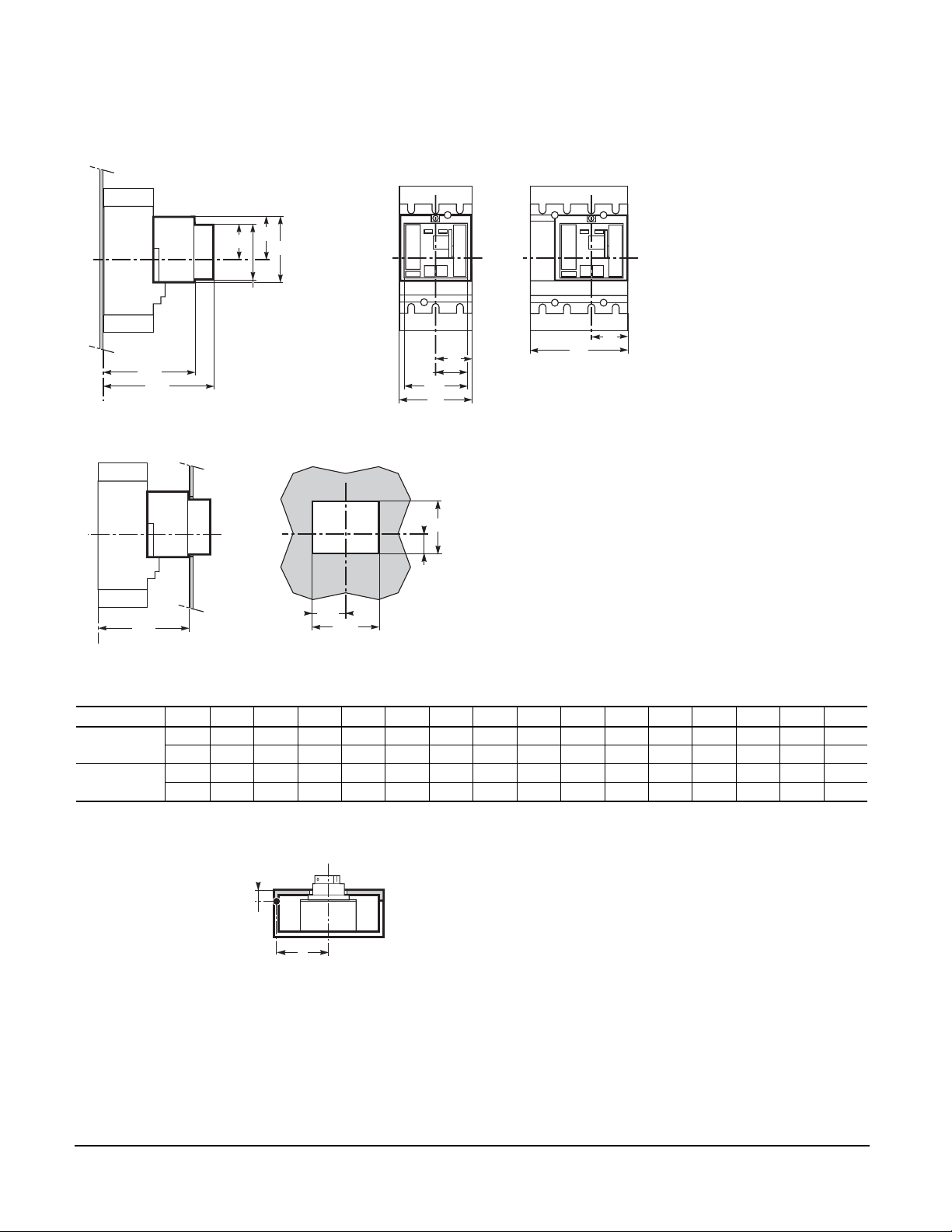
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
Motor Operators
2P, 3P 4P
06153148
06153149
H20
H22
P33
Z
P32
Front-panel Cutouts
H21
X
H23
L12
L11
X
Y
L
L1
L2
X
Y
L
06153150
P45
Z
Dimension Table
NSF150/250N/H/L
NSJ400/600N/H/L
Inch 1.14 2.99 2.46 3.81 1.79 2.87 2.06 4.13 5.51 3.58 1.79 7.00 5.62 5.70 1.90
mm 29 76 62.5 97 45.5 73 52.5 105 140 91 45.5 178 143 145 48.5
Inch 1.63 4.96 3.93 5.98 3.26 4.84 2.75 5.51 7.28 4.84 2.42 9.84 8.46 8.54 2.53
mm 41.5 126 100 152 83 123 70 140 185 123 61.5 250 215 217 64.5
06153151
C23
X
Y
R14
R15
C22 C23 H20 H21 H22 H23 L L1 L2 L11 L12 P32 P33 P45 R14
X
C22
NOTE: Door cutouts require a minimum distance between the center of the circuit breaker and the door
Δ
hinge point
06153138
h
3.93 in./100 mm + (h x 5).
46
Δ
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 47
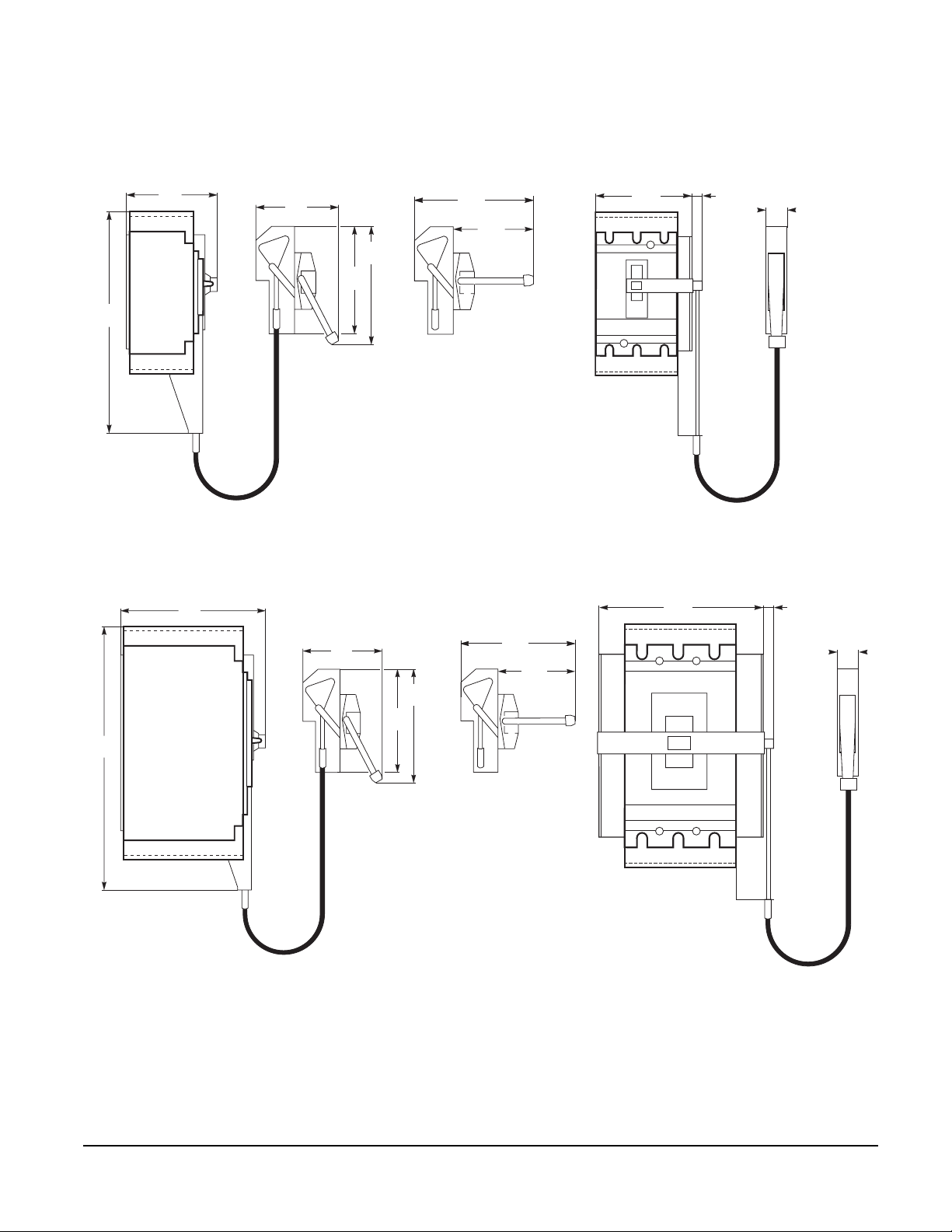
CABLE-OPERATING HANDLES
Compact NSF
5.19
06153152
8.75
222
132
4.31
109
9.38
238
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
10.38
264
11.32
11.32
287
287
7.01
178
06153153
4.86
123
0.31
8
1.06
27
Compact NSJ
06153154
13.5
343
4.31
184
4.31
109
9.38
238
10.38
264
11.32
11.32
287
287
7.01
178
06153155
7.996
203
0.31
8
1.06
27
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Dimensions: in. / mm
47
Page 48

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
ROTARY-OPERATING HANDLES
Dimensions
06153156
H23
X
H20
P34
P35 (A)
P36 (B)
P37 (C)
Z
A—Without Keylock
B—With Ronis™ Keylock
C—With Profalux™ Keylock
Ronis and Profalux are trademarks of HF Sécurité
Front-panel Cutouts
Fixed or Plug-in Mounted
06153158
X
06153151
2P, 3P 4P
L12
06153157
60°
60°
I
DD
O
H24
X
I
60
DD
60
O
X
Y
Y
L15
L
L2
L
L11
L1
Drawout Mounting
C23
X
06153159
06153147
X
C11
X
C22
Y
P43
Z
R14
R15
Mandatory to Fit Fron t Panel
Escutcheon
Motor Control Center Type Direct Rotary-operating Handle
Front-panel Cutout
06153160
G39
X
G38
Y
K14
K15
Dimensions
06153161
P42
0.04–0.12 in.
Max.
±
2
1–3 mm
C17
P44
Z
L8
L7
L12
06153162
Y
R8
R9
H24
H10
X
H9
Y
48
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 49
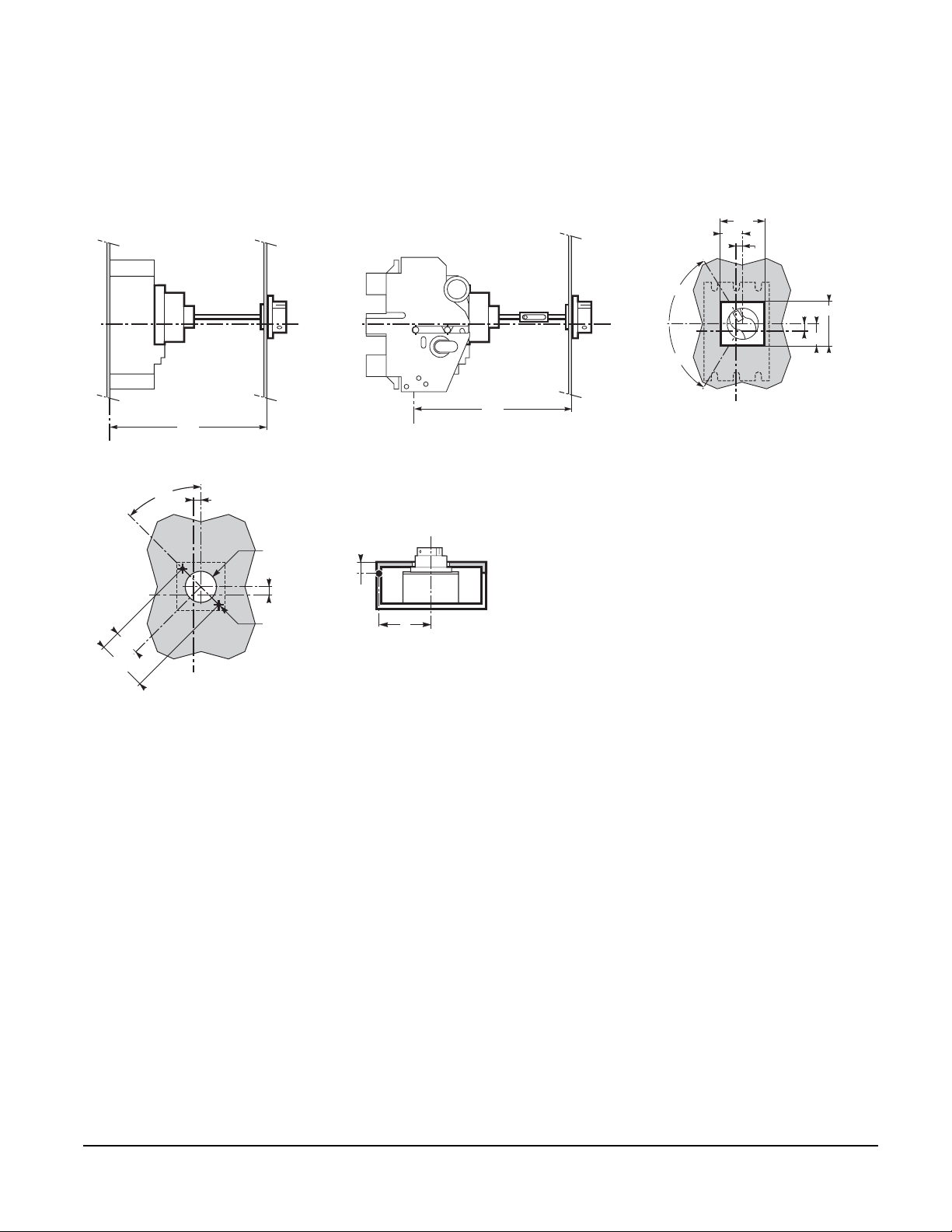
Dimensions
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
Fixed or Plug-in Mounted
Cut Shaft at Length:
P38—4.96 in. (126 mm) NSF150/250
P38—5.90 in. (150 mm) NSJ400/600
06153163
Z
P38
Front-panel Cutout
45°
06153166
G36
G37
L12
Y
X
∅T7
H24
∅T6
Drawout Mounting
Cut Shaft at Length:
P38—4.80 in. (122 mm) NSF150/250
P40—5.90 in. (150 mm) NSJ400/600
06153165
06153164
60°
X
Z
P40
X
60°
L13
O
L14
L12
I
Y
X
H24
H26
H25
NOTE: Door cutouts require a minimum distance between the center of
Δ
the circuit breaker and the door hinge point
06153138
h
Δ
3.93 in./100mm + (h x 5)
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
49
Page 50

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
C11 C17 C22 C23 G36 G37 G38 G39 H9 H10 H20 H23 H24 H25
NSF150/250N/H
NSJ400/600N/H/L
NSF150/250N/H
NSJ400/600N/H/L
NSF150/250N/H
NSJ400/600N/H/L
Inch 4.05 1.67 1.14 2.99 1.41 2.83 1.61 3.93 2.36 4.72 1.10 2.87 0.35 1.47
mm 103 42.5 29 76 36 72 41 100 60 120 28 73 9 37.5
Inch 6.10 1.65 1.63 4.96 1.41 2.83 2.00 5.70 3.26 6.29 1.47 4.84 0.96 1.47
mm 155 42 41.5 126 36 72 51 145 83 160 40 123 24.5 37.5
H26 K14 K15 L L1 L2 L7 L8 L11 L12 L13 L14 L15 P34
Inch 2.95 1.96 3.93 2.06 4.13 5.51 2.71 4.72 3.58 0.36 1.47 2.95 2.16 4.76
mm 75 50 100 52.5 105 140 69 120 91 9.25 37.5 75 55 121
Inch 2.95 2.85 5.70 2.75 5.51 7.28 3.34 6.29 4.84 0.19 1.47 2.95 2.61 5.70
mm 75 72.5 145 70 140 185 85 160 123 5 37.5 75 66.5 145
P35 P36 P37 P38 P40 P42 P43 P44 R8 R9 R14 R15 ØT6 ØT7
Inch 6.10/7.04
6.14 6.45 7.28 min.
23.6 max.
156 164 185 min.
mm 155/179
600 max.
7.08 7.08 7.40 8.22 min.
Inch
23.6 max.
180 180 188 209 min.
mm
600 max.
9.76
4.92 3.50 4.84 2.91 5.82 1.90 3.81 0.16 1.96
min.
23.6
max.
248
125 89 123 74 148 48.5 97 4.2 50
min.
600
max.
10.7
5.86 4.40 5.78 3.54 7.08 2.53 5.07 0.16 1.96
min.
23.6
max.
272
149 112 147 90 180 64.5 129 4.2 50
min.
600
max.
50
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 51

FRONT ACCESSORIES
Extended Escutcheons
For Toggle
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
06153167
Toggle Boot
06153170
Front-panel Escutcheons
For Toggle
06153173
06153171
06153168
M
A
06153169
D
06153172
M8
A3
06153174
M2
D3
06153175
M3
A1
D2D1
For Extended Escutcheon, Motor Operator Module or Rotary Handle
06153176
06153177
A2
A A1A2A3D D1D2D3M M2M3 M6M7M8
NSF150/250N/H
NSJ400/600N/H/L
Inch 3.58 2.71 6.18 3.70 1.37 0.13 0.25 1.57 2.87 4.52 4.01 4.48 3.97 3.70
mm 91 69 157 94 35 3.5 6.5 40 73 115 102 114 101 94
Inch 4.84 4.01 7.44 1.37 5.27 0.13 0.25 2.36 4.84 6.10 5.59 6.45 5.94 5.27
mm 123 102 189 35 134 3.5 6.5 60 123 155 142 164 151 134
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
M6
06153178
M7
D2D1
51
Page 52

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 10—Dimensions
INTERLOCKING SYSTEMS
Interlocking Systems with Rotary-operating Handles
Dimensions Front-panel Cutout
06153179
G
Z
NSF150/250
NSJ400/600
06153180
ABCDFGHJ KL MN
Inch 12.79 3.54 3.44 6.89 6.14 5.23 0.36 0.35 11.61 2.97 5.90 2.95
mm 325 90 87.5 175 156 133 9.25 9 295 75.5 150 75
Inch 16.38 4.53 3.94 7.87 8.27 6.18 0.20 0.97 15.20 3.94 6.89 2.93
mm 416 115 100 200 210 157 5 24.6 386 100 175 74.5
Interlocking Systems with Toggles
Dimensions
Three-pole
F
Y
H
H
A
J
X
C
B
06153181
D
F
K
L
N
M
Front-panel Cutout
06153182
P5
Z
NSF150/250N/H
NSJ400/600N/H/L
52
06153183
X
Y
L16
L17
C2 C3 L L16 L17 R2 R19 P5
Inch 2.12 4.25 2.06 5.51 9.64 2.12 5.51 3.26
mm 54 108 52.5 140 245 54 140 83
Inch 3.64 7.24 2.75 7.28 12.79 2.81 7.28 4.21
mm 92.5 184 70 185 325 71.5 185 107
L
06153184
C3
X
C2
Y
R19
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Y
R2R2
Page 53

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
SECTION 11—CONNECTION DIMENSIONS
Fixed Mounted
P13
NSF150/250N/H
06153185
06153186
G4
X
G5
X
NSJ400/600N/H/L
* P13 = 0.84 in./21.5 mm for Compact
Section 11—Connection Dimensions
G4 G5 K1 P13
Inch 2.75 5.51 1.37 0.76*
mm 70 140 35 19.5*
Inch 4.46 8.93 1.77 1.02
mm 113.5 227 45 526
®
NSF250N/H Circuit Breaker
Z
Front Connections
06153187
Rear Connections
06153193
Y
K1K1
Bar Connection
NSF 150/250 (M8 Screws)
Z
06153188
2.75
X
70
Cable Connection
NSF 150/250
Z
06153190
2.75
X
NSF 150/250
0.39
10
06153194
70
∅0.33
8.6
∅
∅0.78
20
∅
NSJ 400/600 (M10 Screws)
Z
06153189
X
NSJ 400/600
Z
06153191
X
0.51
13
0.55
14
4.46
113.5
NSJ 400/600
0.59
15
06153195
0.55
14
4.46
113.5
∅0.33
∅
13
∅0.91
∅
23.2
Z
06153192
X
0.55
14
1.83
46.5
4.46
113.5
0.70
18
1.69/43 (*)
3.46
0.23
6
(*) Short RC : 1.69
(**) Long RC : 3.46/
Dimensions of Energized Parts: See Section 8—Connections
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
/88
(**)
Z
/43
2.75
1.18
70
30
X
0.31
88
1.99/50 (*)
4.52
8
(*) Short RC : 1.96
(**) Long RC : 4.52/
/115
(**)
Z
/50
115
4.46
113.5
X
Dimensions: in. / mm
53
Page 54
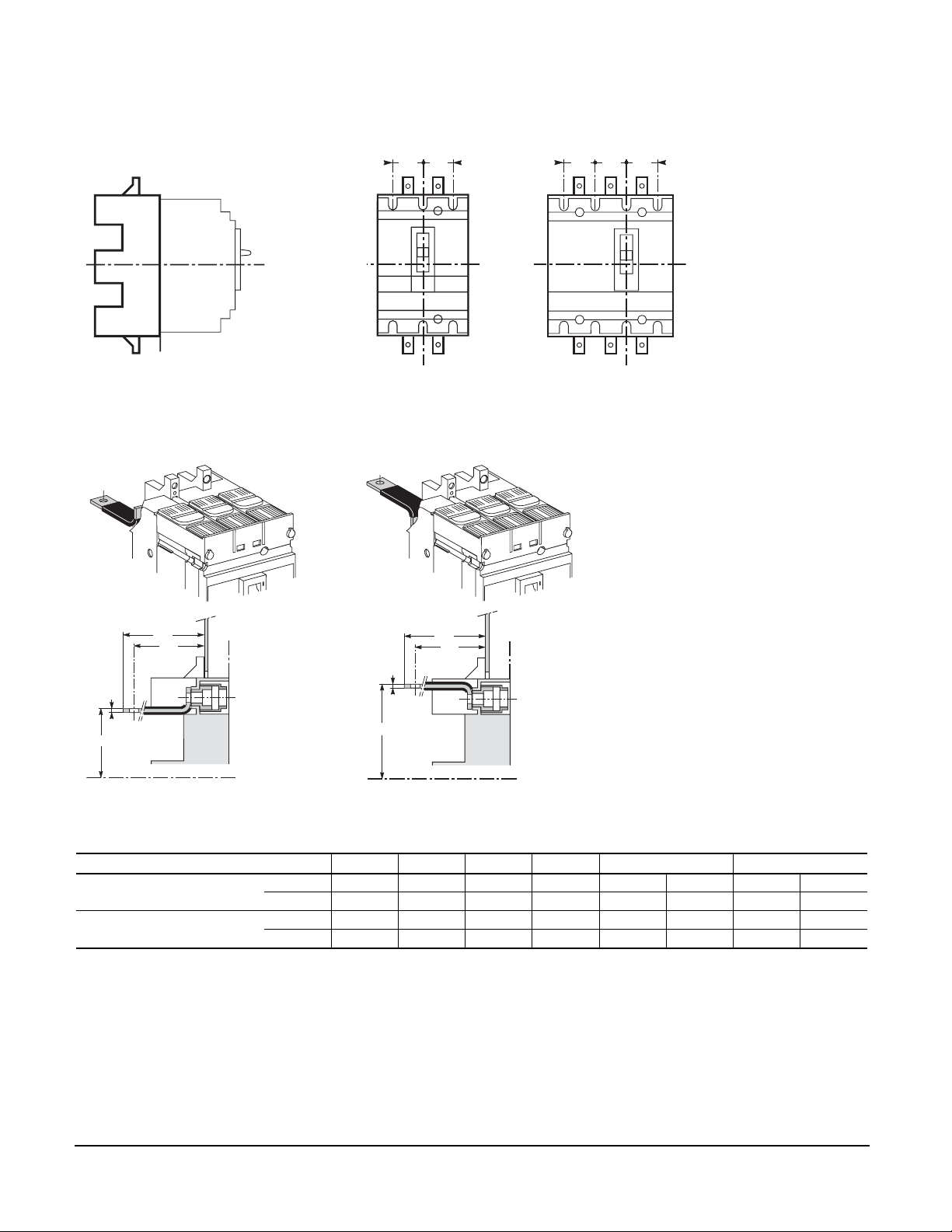
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 11—Connection Dimensions
Plug-in or Drawout Mounting
06153196
X
Z
Rear Connections
Rear Connections Fitted at Lower Limit
06153198
2P, 3P 4P
K1
06153197
K1
K1
X
Y
Rear Connections Fitted at Upper Limit
06153200
K1
K1
X
Y
06153199
G33
P22
P23
E
Z
X
06153201
G35
P22
P23
E
Z
X
EG33G35K1P22 P23
NSF150/250N/H Inch 0.15 2.5 3.16 1.37 2.93 4.86 2.59 4.52
mm 4 63.5 80.5 35 74.5 123.5 66 115
NSJ400/600N/H/L Inch 0.23 4.09 5.07 1.77 4.50 7.14 3.93 6.57
mm 6 1 04 129 45 114.5 181.5 100 167
54
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 55

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
SECTION 12—WIRING DIAGRAMS
Manually-operated Circuit Breaker
GY
312
GY
352 354
VT
Z11 e
T1
+
R1
92 94
C1
D1
12 14
22 24
06153202
VT
314
32 24
82 84
Section 12—Wiring Diagrams
BK
VT
YE
RD
CE
CD
1
31
351
YE
YE
trip unit (3)
I
d
BK
WHRDBL
Z12
Motor-operated Circuit Breaker
GY
312
GY
352 354
VT
Z11 e
BK
trip unit (3)
I
d
WHRDBL
VT
314
06153203
CE
YE
WH
OR
GN
D1
MN
D4
-
T2
D4
e
R2
T1
+
R1
D1
WH
OR
GN
D1
MN
D4
RD
GN
92 94
C1
(1)
SD
MX
91
C2
ORBLBL
91C2
92 94
C1
RD
GN
C1
92 94
(1)
SD
MX
C2
91
ORBLBL
12 14
OF1
12 14
YE
12 14
OF1
22 24
32 34
OF2
OF3
21
11
GY
11
22 24
YE
VT
22 24
OF2
11
GY
31
GY
GY
21
31
32 24
VT
YE
VT
32 34
OF3
21
GY
GY
31
72 74
(2)
SDV
72 74
SDV
GN
RD
82 84
CAF2CAF1
CAO1
SDE
81
71
81
BK
84
GN
RD
82 84
SDE
(2)
71
81
GN (4)
WH
B2 A2 A4 B4
BK (4)
A1 L1
BK
A2 B4A4
GY
RD
BL
OR
MT
GN
VT
YE
VT
YE
VT
CD
31
1
351
YE
YE
All schemes are shown without
the control voltage present, all
devices open and relays in the
de-energized position.
Switches CD, CE: on drawout
chassis.
Switches CAO, CAF: on rotary
handle.
Symbols
CAF = early-make switch
CAO = early-break switch
CE = "connected" position indication switch
CD = "disconnected" position indication switch
MN = undervoltage trip
MT = motor operator
MX = shunt trip
OF = position indication switch
SD = trip indication switch
SDE = overcurrent trip switch
SDV = ground-fault indication switch
-
T2
Z12
D4
e
R2
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
91C2
11
21
31
A1
Legend
(1) Undervoltage or shunt trip
(2) For plug-in/drawout versions, SDV
and OF2 switches can be installed
together, but only one of them will be
connected through automatic
secondary disconnecting blocks
(3) Options are only installed on trip
unit STR53UP
(4) Wiring supplied, mandatory to
connect
L1
Color code
VT: Purple
YE: Yellow
RD: Red
BK: Black
GN: Green
GY: Grey
WH: White
OR: Orange
BL: Blue
55
Page 56

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 12—Wiring Diagrams
Motor Operator—Automatic Resetting After Tripping
Use of the Motor Operator (Standard Wiring Diagram)
CN1 - CN 1
06153204
+
CN2 - CN 2
Ð
DP1
ON
OFF
RD
82 84
H1
(1)
GN
B2 A2A2A4A4B4
B4
BL
OR
WH
H2
trip unit
Motor Operator + Undervoltage Trip
06153205
ON
OFF
D1
A2 A4 B4
SDE
81
MT
BK (1)
A1 L1
BK
A1 L1
GN
Motor Operator + Shunt Trip
06153206
OFF
ON
C1
A2 A4 B4
Mandatory manual reset after tripping due to an electrical fault.
Symbols
DP1 = protection circuit breakers
OFF = opening push button
ON = closing push button
H2 = "manual" position indication
H1 = electrical fault indication
MT = motor operator
SDE = electrical fault indication switch
(1) Jumper is supplied and must be connected by user. Overcurrent trip switch is strongly recommended
to lock remote or automatic resetting after an overcurrent fault.
56
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 57
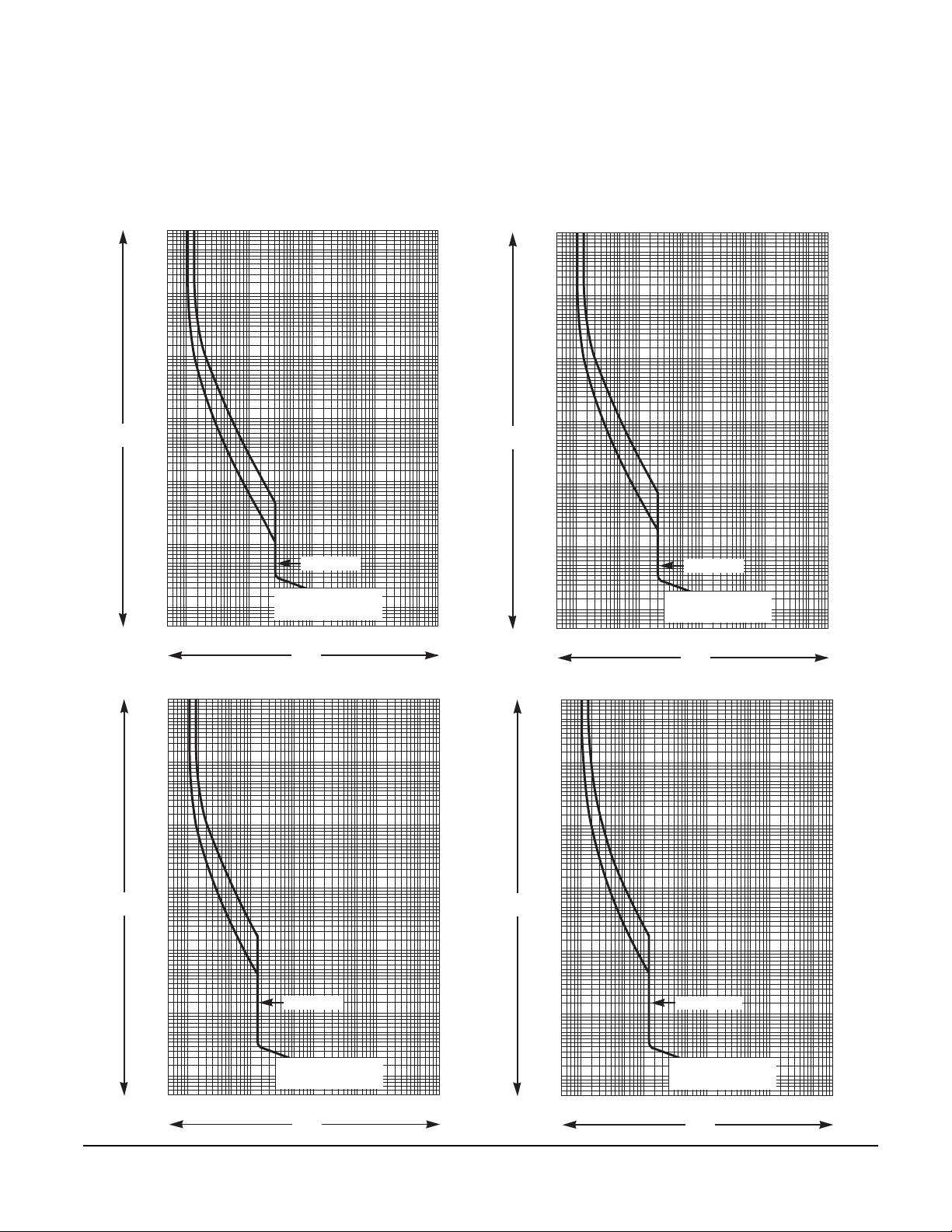
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
SECTION 13—SUPPLEMENTARY TECHNICAL INFORMATION
TRIP UNITS FOR COMPACT® NSF150–NSF250 CIRCUIT BREAKERS
TM15DP
10 000
5 000
06153207
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
TM30DP
TM30DP
10 000
10 000
5 000
5 000
06153209
2 000
2 000
1 000
1 000
500
500
200
200
100
100
50
50
20
20
10
10
t(s)
t(s)
5
5
2
2
1
1
.5
.5
.2
.2
.1
.1
.05
.05
.02
.02
.01
.01
.005
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
Reflex Tripping: See Page 62
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Im = 25 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
Im = 13 x In
Im = 13 x In
Reflex Tripping:
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
I / Ir
500 1000
500 1000
500 1000
10 000
10 000
10 000
TM20DP
10 000
5 000
06153208
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
TM40DP
10 000
5 000
06153210
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
Im = 20 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
Im = 12.5 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
500 1000
500 1000
10 000
10 000
57
Page 58

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
TM50DP
10 000
5 000
06153211
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
Im = 10 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
500 1000
10 000
TM60DP
10 000
5 000
06153212
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50
Im = 16 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
100
500 1000
I / Ir
10 000
TM70DP
10 000
5 000
06153213
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
Reflex Tripping: See Page 62
Im = 14.8 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
500 1000
10 000
TM80DP
10 000
5 000
06153214
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
Im = 13 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
500 1000
10 000
58
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 59

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
TM90DP
10 000
5 000
06153215
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
Im = 11.5 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
500 1000
10 000
TM100-225DP
10 000
5 000
06153216
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
Im = 5...10 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
500 1000
10 000
TM250DP
10 000
5 000
06153217
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
t(s)
5
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.5 1 2 5 10 20 50 100
Reflex Tripping: See Page 62
Im = 4.8...9.8 x In
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
500 1000
10 000
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
59
Page 60

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
EFFECT OF HIGH TEMPERATURES
When the ambient temperature is greater than 40° C, overload protection characteristics are slightly
modified. When determining tripping times using time/current curves, the Ir values corresponding to the
thermal setting on the circuit breaker must be reduced using the coefficients below:
45° C 50° C 55° C 60° C 65° C 70° C
0.975 0.95 0.925 0.90 0.875 0.85
Example What is the tripping time for a TM200DP circuit breaker with a 400A fault current and an ambient
temperature of 40° C?
• Ir = 200 A
• I/Ir = 400/200 = 2
On the time/current curve, t = 100 s.
Consider the same conditions, except an ambient temperature of 65° C. What is the tripping time?
• Ir = 200 x 0.875 = 175 A
• I/Ir = 400/175 = 2.28
On the time/current curve,
≈ 65 s.
60
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 61
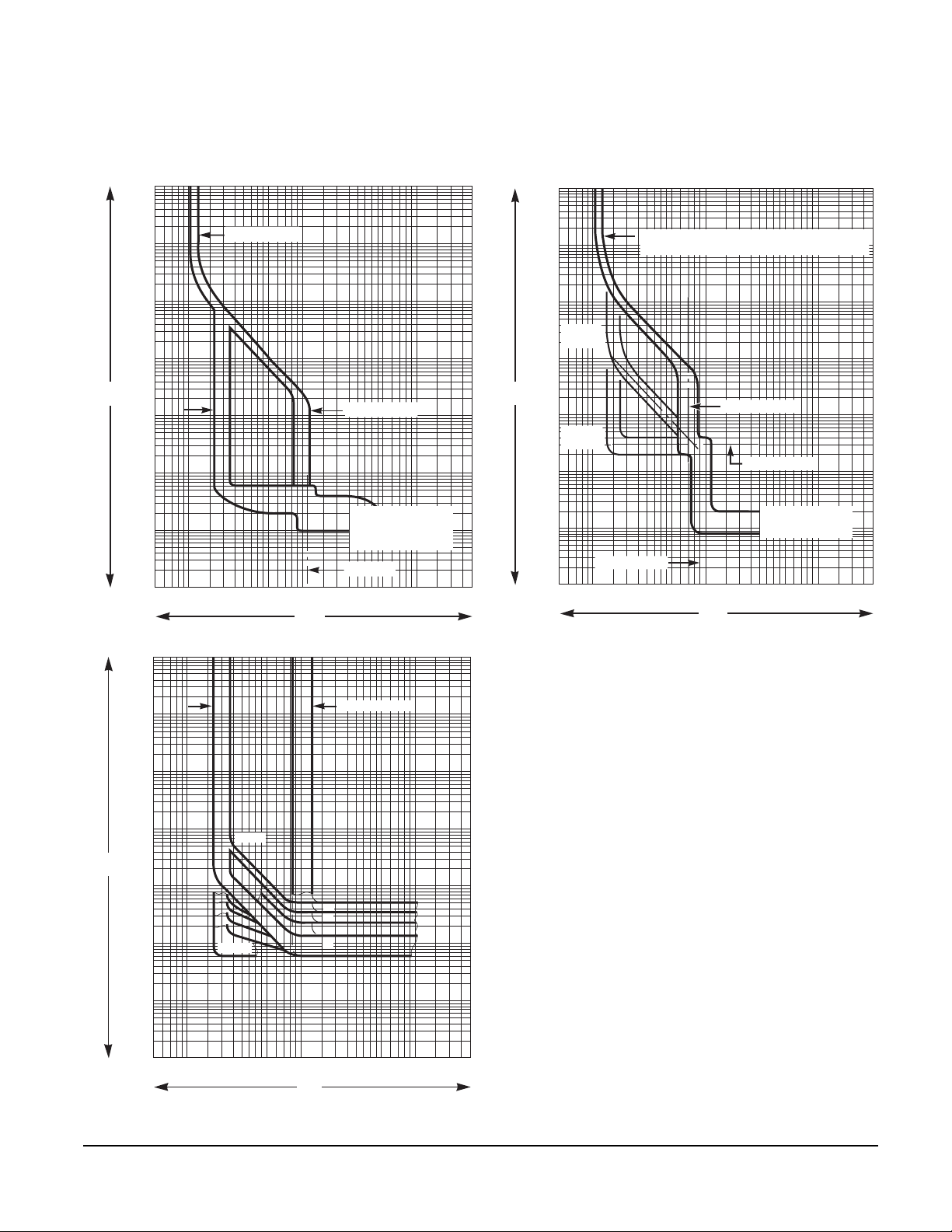
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
0
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
TRIP UNITS FOR COMPACT® NSJ400–NSJ600 CIRCUIT BREAKERS
STR23SP
10 000
5 000
06153218
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
5
t(s)
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.002
.001
.5 .7 1 2 3 4 5 7 10 20 30 50 70 100 200
Ir = 0.4–1 x In
I / Ir
Im = 2
–9 x Ir
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I = 11 x In
300
STR53UP
10 000
5 000
06153219
2 000
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
10
5
t(s)
2
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
.02
.01
.005
.002
.001
.5 .7 1 2 3 4 5 7 10 20 30 50 70100 200
Isd = 1.5
I2t = ON
Isd = 1.5
2
t = OFF
I
Ir = 0.4–1 x In
tr = 1–8 s (6 Ir)
Ii = 1.5–9 x in
For Hot Start (0.9 x Ir) Divide
Max. Time by 2, Min. Time by 4
Isd = 1.5–7 x Ir
Tsd = 0–0.3 s
Reflex Tripping:
t < 10 ms
I / Ir
3
STR53UP Ground-fault Protection
10 000
5 000
2 000
06153220
1 000
500
200
100
50
20
t(s)
10
5
2
I2t ON
1
.5
.2
.1
.05
I2t OFF
.02
.01
.005
.002
.001
.05 .07 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .7 1 2 3 5 7 10 20 3
Reflex Tripping: See Page 62
I / In
Ig = 0.2–1 x In
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
61
Page 62

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
REFLEX TRIPPING
All Compact® NS circuit breakers and switches incorporate the exclusive reflex tripping system.
This extremely simple system breaks very high fault currents by mechanically tripping the device via a
"piston" actuated directly by the pressure produced in the breaking units resulting from a short circuit.
For high short-circuit thermal withstand, this system provides a faster break. Reflex tripping curves are
exclusively a function of the circuit breaker rating.
06153221
20
NSJ600
NSJ400**
t
(ms)
10
8
7
6
5
TM70DP...TM250DP
...TM60DP
TM15DP
NSF250
4
3
NSF150*
2 3 4 6 10 20 30 40 60 100
I (kA RMS)
*4P OSN Compact® NSF125/250N and NSF 150/250N Ratings Are Same As NSF250
** 4P OSN NSJ 400/600N Ratings Are Same As NSJ600
200
62
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 63
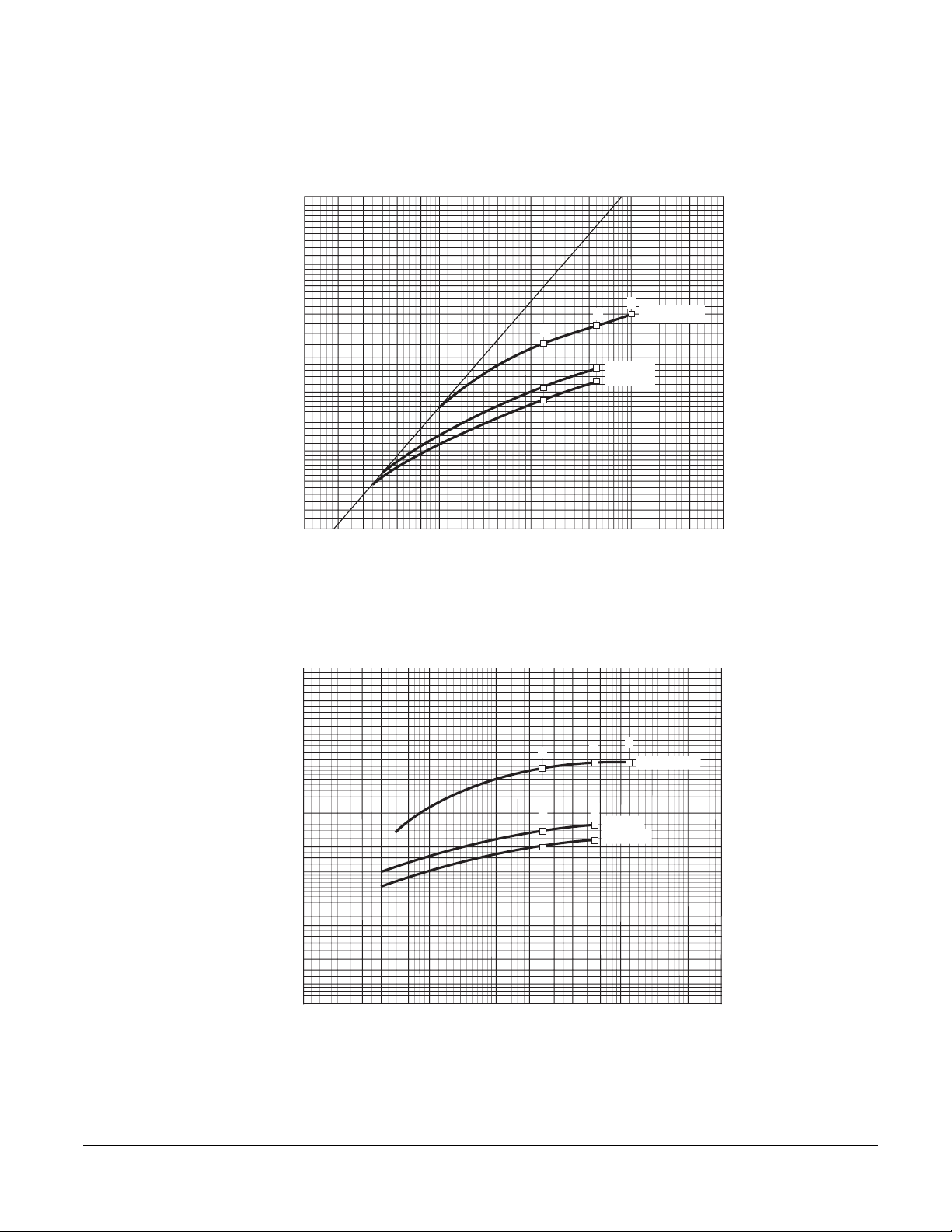
LET-THROUGH CURVES AT 480 V
Maximum Peak
Let-through
Current (Amperes)
200
06153222
)
3
100
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
8
7
6
Maximum (*) Peak Let-Through Current (Amperes x 10
5
(*) Based on maximum values obtained throughout the circuit breaker development and UL test programs.
4
2 3 4 6 10 20 30 40 60 100 200 300
Available Short Circuit Current (RMS Symmetrical Amperes x 103)
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
L
H
N
NSJ400/600
NSF250
NSF150**
Maximum Letthrough I
(Amperes
2
t
2
Seconds)
**4P OSN Compact® NSF125/250N and NSF 150/250N Ratings Are Same As NSF250
2
7
06153223
10
5
3
Seconds)
2
N
L
H
2
10
t (Amperes
2
5
6
N
H
NSF250
NSF150**
3
2
5
10
Maximum (*) Let-Through I
5
3
(*) Based on maximum values obtained throughout the circuit breaker development and UL test programs.
2
2 3 4 6 10 20 30 40 60 100 200 300
Available Short Circuit Current (RMS Symmetrical Amperes x 103)
NSJ400/600
**4P OSN Compact® NSF125/250N and NSF 150/250N Ratings Are Same As NSF250
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
63
Page 64

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
LET-THROUGH CURVES AT 600 V
Maximum Peak
Let-through
Current (Amperes)
200
06153224
)
3
100
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
N
N
10
8
7
Maximum (*) Peak Let-Through Current (Amperes x 10
6
5
(*) Based on maximum values obtained throughout the circuit breaker development and UL test programs.
4
2 3 4 6 10 20 30 40 60 100 200 300
Available Short Circuit Current (RMS Symmetrical Amperes x 103)
H/L
NSJ400/600
H
NSF250
NSF150**
Maximum Letthrough I
(Amperes
2
t
2
Seconds)
**4P OSN Compact® NSF125/250N and NSF 150/250N Ratings Are Same As NSF250
2
7
06153225
10
5
H/L
3
Seconds)
2
2
6
10
t (Amperes
2
N
N
NSJ400/600
H
NSF250
NSF150**
5
3
2
5
10
Maximum (*) Let-Through I
5
3
(*) Based on maximum values obtained throughout the circuit breaker development and UL test programs.
2
2 3 4 6 10 20 30 40 60 100 200 300
Available Short Circuit Current (RMS Symmetrical Amperes x 103)
**4P OSN Compact® NSF125/250N and NSF 150/250N Ratings Are Same As NSF250
64
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 65
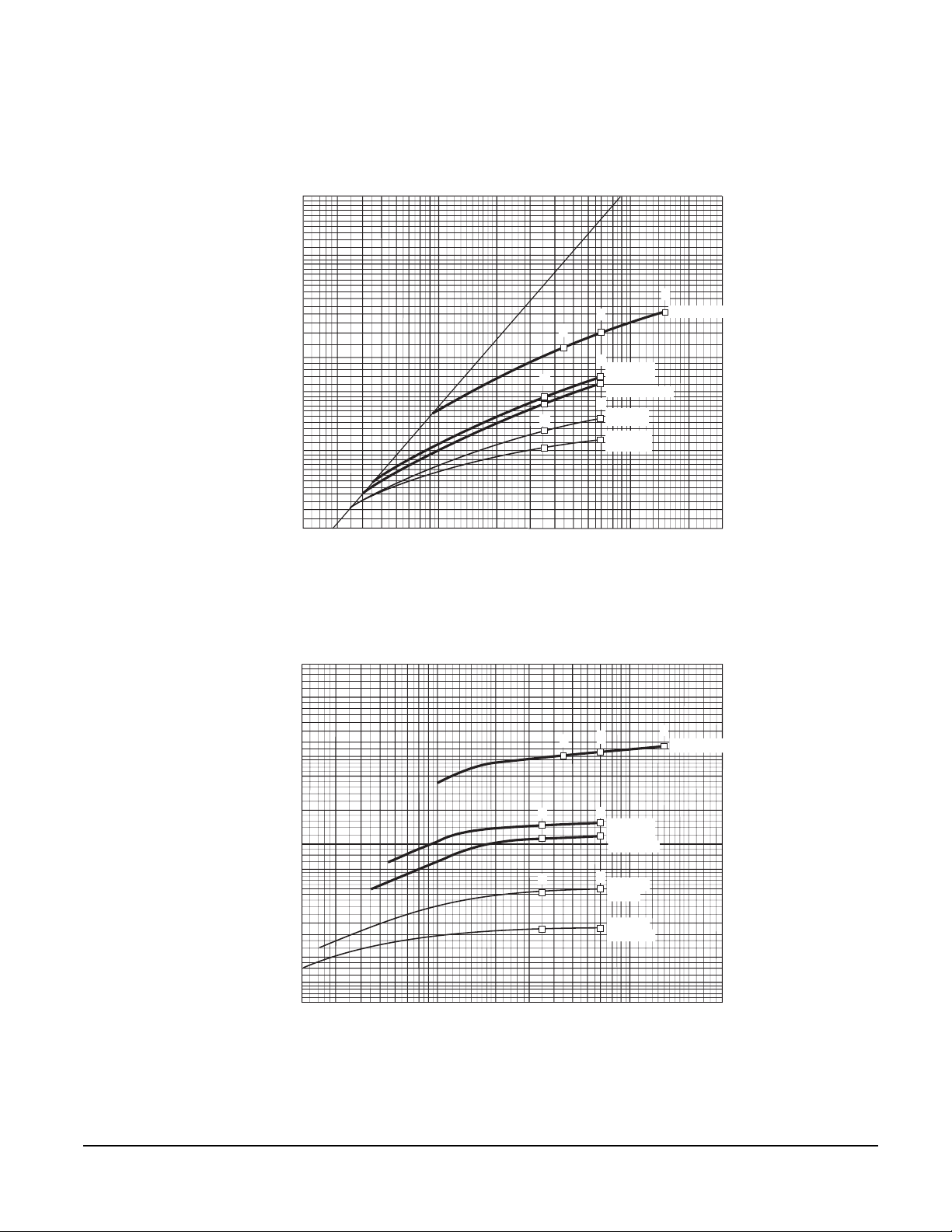
Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
CURRENT-LIMITING CURVES AT 380/415 V
Maximum Peak
Let-through
Current (Amperes)
200
06153226
)
3
100
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
8
7
Maximum (*) Peak Let-Through Current (Amperes x 10
6
5
(*) Based on maximum values obtained throughout the circuit breaker development and UL test programs.
4
2 3 4 6 10 20 30 40 60 100 200 300
Available Short Circuit Current (RMS Symmetrical Amperes x 103)
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
L
H
N
H
N
N
NSF250
NSF150**
TM40–150DP
H
NSF150
TM30DP
NSF150
TM15–20DP
NSJ400/600
Maximum Letthrough I
(Amperes
2
t
2
Seconds)
**4P OSN Compact® NSF125/250N and NSF 150/250N Ratings Are Same As NSF250
2
7
06153227
10
5
3
Seconds)
2
2
6
10
t (Amperes
2
5
3
2
5
10
Maximum (*) Let-Through I
5
3
(*) Based on maximum values obtained throughout the circuit breaker development and UL test programs.
2
N
N
H
N
H
NSF250
NSF150**
TM40–250DP
H
NSF150
TM30DP
NSF150
TM15–20DP
2 3 4 6 10 20 30 40 60 100 200 300
Available Short Circuit Current (RMS Symmetrical Amperes x 103)
L
L
NSJ400/600
**4P OSN Compact® NSF125/250N and NSF 150/250N Ratings Are Same As NSF250
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
65
Page 66

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
CURRENT-LIMITING CURVES AT 690 V
Maximum Peak
Let-through
Current (Amperes)
200
06153226
)
3
100
80
70
60
50
40
30
H
H
L
NSJ400/600
Maximum Letthrough I
(Amperes
2
t
2
Seconds)
N
N
H
NSF250
NSF150**
TM40...250DP
TM30DP
TM15...20DP
20
10
8
7
Maximum (*) Peak Let-Through Current (Amperes x 10
6
5
(*) Based on maximum values obtained throughout the circuit breaker development and UL test programs.
4
2 3 4 6 10 20 30 40 60 100 200 300
Available Short Circuit Current (RMS Symmetrical Amperes x 103)
**4P OSN Compact® NSF125/250N and NSF 150/250N Ratings Are Same As NSF250
2
7
06153226
10
5
3
Seconds)
2
2
10
t (Amperes
2
5
H
H
N
N
6
N
H
NSF250
NSF150**
TM40...250DP
L
NSJ400/600
3
TM30DP
TM15...20DP
10
2
5
66
Maximum (*) Let-Through I
5
3
(*) Based on maximum values obtained throughout the circuit breaker development and UL test programs.
2
2 3 4 6 10 20 30 40 60 100 200 300
Available Short Circuit Current (RMS Symmetrical Amperes x 103)
**4P OSN Compact® NSF125/250N and NSF 150/250N Ratings Are Same As NSF250
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 67

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
UL 489 TEST PROCEDURE
Standard Tests For electronic trip circuit breakers and uncompensated thermal-magnetic circuit breakers rated 40° C,
the test sequences are as shown in the table below:
Test Sequence
X Y Z
200% Calibration at 25° C (77° F) ■■■
135% Calibration at 25° C (77° F) ■
Calibration of Adjustable Instantaneous Trip ■
Overload ■
Tungsten Lamp Load
100% Calibration at 40° C (104° F)
Temperature and 100% Calibration at 25° C (77° F) ■
Endurance ■
200% Calibration at 25° C (77° F) Repeated ■
135% Calibration at 25° C (77° F) Repeated ■
Interrupting Ability (Y sequence) ■
Interrupting Ability (Z sequence) ■
200% Trip Out at 25° C (77° F) ■■
Dielectric Voltage Withstand ■■■
① Applies only to circuit breakers rated 50 A or less, and 125 or 125/250 V or less.
② Applies only to thermal-magnetic breakers rated 40° C.
①
②
Standard
Specifications
Temperature The temperature rise at the circuit breaker and at its terminals does not exceed specified limits when
connected with specified cables or bus bars (see below) and at its rated current.
Examples of specified wires and bus:
• 75° C Copper Wire
Rating Number Size
100 A
250 A 1 250 kcmil
400 A 2 3/0 AWG
600 A 2 350 kcmil
800 A 3 300 kcmil
1000 A 3 400 kcmil
1200 A 4 350 kcmil
1 #1 AWG (60° C)
1#3 AWG
• Copper Busbar
Rating Number Size
1600 A 2 1/4 x 3
2000 A 2 1/4 x 4
2500 A
3000 A 4 1/4 x4
(1200 A or Less—1000 A / in
2 1/4 x 5
4 1/4 x 2-1/2
2
)
Calibration 200% calibration at 25° C—the circuit breaker must trip within time limits which depend on the rating
from three minutes for 30 A rated circuit breakers to 30 minutes for over 2000 A rated circuit breakers.
135% calibration at 25° C—the circuit breaker must trip within two hours for circuit breakers rated more
than 50 A.
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
67
Page 68

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
Calibration of adjustable instantaneous trip—the circuit breaker must trip within the range of 80–120%
of the maximum marked tripping current and 75–125% of the minimum marked tripping current.
Overload
• Up to 1600 A—50 operations at 600% of rated current
• 2000 and 2500 A—25 operations at 600% of rated current
• 3000–6000 A—three operations at 600% of rated current followed by 25 operations at 200% of
rated current
The power factor shall be from to 0.45–0.50 lagging.
Endurance The circuit breaker must complete an endurance test:
• Operations at rated current and rated voltage
• Followed by no load operation.
The power factor shall be 0.75–0.80 lagging.
Frame Size Number of Cycles of Operations
With Current Without Current Total
100 A 6,000 4,000 10,000
225 A 4,000 4,000 8,000
400 A 1,000 5,000 6,000
600 A 1,000 5,000 6,000
800 A 500 3,000 3,500
1200 A 500 2,000 2,500
1600 A 500 2,000 2,500
2000 A 500 2,000 2,500
2500 A 500 2,000 2,500
3000 A 400 1,100 1,500
Interrupting Ability Interrupting ability (Y sequence)—after endurance tests and calibrations are repeated, the circuit
breaker completes an opening (O) followed by a close-open operation (O-t-CO), with specified current.
Frame Rating RMS Sym. Amperes
(3-pole O-and-CO)
100 A ① 3,000
225 A 3,000
400 A 5,000
600 A 6,000
800 A 10,000
1200 A 14,000
1600 A 20,000
2000 A 25,000
3000 A 35,000
① Above 250 V
Interrupting ability (Z sequence)—a three-pole circuit breaker rated 240, 480 or 600 V has to complete
an opening operation (O) and a close-open operation (O-and-CO) on each pole, at rated voltage,
followed by an opening operation (O) using all three poles.
Frame rating RMS Sym. Amperes
Each Pole Common
O-and-CO O
100 to 800 A 8,660 10,000
1000 to 1200 A 12,120 14,000
1600 A 14,000 20,000
2000 A 14,000 25,000
3000 A 25,000 35,000
68
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 69

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
Dielectric After testing, the circuit breaker must withstand for one minute a voltage of 1000 V plus twice the rated
voltage between:
• Line and load terminals with circuit breaker in open, tripped and off positions
• Terminals of opposite polarity with circuit breaker closed
• Live parts and the overall enclosure with circuit breaker open and closed
Optional Tests
Tests On
Accessories
• High available fault current—circuit breakers having passed all the standard tests may have the UL
Listing label applied at higher values than the standard; test sequence is as follows:
— 200% calibration
— Interrupting capacity: an opening operation followed by a close-open operation (O-and-CO) on
all poles are performed on the circuit breaker
The power factor over 20000 A shall be 0.15–0.2 lagging:
— Trip out at 250%
— Dielectric at twice the rated test voltage
• 100% rated—circuit breakers having passed all the standard tests may have the UL Listing label
applied to use the circuit breaker in an enclosure when carrying 100% of its maximum rating
The circuit breaker is submitted to additional temperature tests performed as standard tests, except
that the circuit breaker is installed in an enclosure. The dimensions and possible ventilations shall be
recorded and shall be marked on the circuit breaker.
Shunt trip and Undervoltage Trip—these devices are submitted to temperature, overvoltage, operation,
endurance and dielectric tests.
Overvoltage Test—the device must be capable of withstanding 110% of its rated voltage continuously
without damage (this test does not apply to a shunt trip with an "a" contact connected in series).
Operation:
Shunt Trip—must operate at 75% of its rated voltage (except shunt trip devices for use with groundfault protection shall operate at 55%).
Undervoltage Trip—must trip the circuit breaker when the voltage is less than 35% and may trip the
circuit breaker between 35 and 70% of its rated voltage and shall pick-up and seal when the voltage
is at 85% or more of its rated voltage.
Endurance—the device must be capable of performing successfully for 10% of the number of "with
current" operations of the circuit breaker.
Auxiliary and Alarm Switches—auxiliary and alarm switches must be submitted to temperature,
overload, endurance and dielectric tests.
Overload Test—the test consists of fifty operations making and breaking 150% of rated current at rated
voltage, with a 75–80% power factor in ac and non-inductive load in dc.
Endurance—the switch must make and break its rated current at rated voltage, with a 75–80% power
factor in ac, and non-inductive load in dc for 100% of the number of operations "with current" for
auxiliary switches, and 10% of this number for alarm switches.
Motor Operator—the motor operator shall perform the number of "without current" operations indicated
for the circuit breaker endurance tests. The first 25 operations shall be conducted at 85% of the motor
operator voltage rating. The circuit breaker is to be tripped during these tests. The next 25 operations
shall be conducted at 110% of the motor operator voltage rating. The balance shall be completed at
rated voltage without tripping the circuit breaker.
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
69
Page 70

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
IEC 947-2 TEST PROCEDURE
Standard Tests Consisting of seven parts, the IEC 947 Standard applies to all low-voltage equipment designed for
industrial application.
Three documents are to be consulted for circuit breakers and switches:
• IEC 947-1: general regulations
• IEC 947-2: circuit breakers
• IEC 947-3: switches
Two Categories of
Devices
Breaking Capacity
Ultimate Breaking
Capacity: Icu
Breaking
Performance During
Operation: Ics
The IEC 947-1 standard defines two categories of devices:
• Category A—devices not specifically designed to carry out chronometric selectivity
• Category B—devices specifically designed to carry out chronometric selectivity; these circuit
breakers possess a compulsory additional characteristic: short-time withstand (Icw)
Icu is the value to be taken into account when calculating an installation. The rule remains: Icu > Icc
(maximum fault current of the installation).
This characteristic indicates the ability of the device to eliminate short-circuit currents less than Icc and
with a greater likelihood of occurring, generally near the application. Ics is expressed in % of Icu (values
retained by the standard IEC 25-50-75-100% of Icu). This test sequence designed to check the Ics
performance, groups together on the same device, following the breaking test (O-CO-CO, see page
72), certain checks such as:
• Temperature rise under In
• Calibration at 1.45 In
• Leakage current (for devices suitable for disconnection)
The leakage current should not exceed 2 mA under the application voltage (0.5 mA when new). These
checks ensure that the device is able to carry out all its functions after elimination of a fault of Ics value
and to be put back in operation; hence the notion of breaking power performance during operation Ics.
70
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 71

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
Isolation
Function Recognition and definition of the disconnection capacity for industrial low-voltage equipment:
Until recently, circuit breaker standards have established no regulations concerning the isolation
function. Only the installation standards provided some rather vague information. The IEC 947
standard takes this function into account. In the "general regulations" section, it clearly states:
• The manufacturing regulation
• The tests to be performed
The circuit breaker standard should define the manner in which the tests are to be performed (under
study). The manufacturing regulations state, for example:
• Both the isolation and the inner contact distances (open > 8 mm)
• A device indicating the true position of the contacts (operating handle if representative of the state
of all the contacts)
• When a "locked" position is provided, this should only be possible with "open" contacts
The tests to be performed are as follow:
• Shock wave voltage strength (Uimp)
V
U
06153226
0.9
0.5
0.1
0t1 t2
1.2
12.3 kV
Uimp
50
tμs
1.2/50 μs–12.3 kV plus 25% between open contacts in comparison with devices not fitted with the
applied isolation function according to the figure below. The test is validated if no triggering occurs
between the contacts.
• Measurement of leakage current—under 110% of the device application voltage, maximum leakage
currents proposed per pole:
— 0.5 mA new device
— 2 mA device after Ics
— 6 mA device after Icu or after endurance tests, representative of the "end of service life."
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
71
Page 72

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
Test Sequences
Sequence Category of Devices Tests
• Trip Unit Control
• Dielectric Properties
• Mechanical and Electrical Endurance
1–General Characteristics All Circuit Breakers
2–Breaking Capacity During Operation All Circuit Breakers
3–Ultimate Breaking Capacity (Icu)
4–Admissible Short Duration Current (Icw) B
Combined Sequence
A
B if Icu > Icw
• Icw = Ics Replaces Sequences 2
and 4
• Icw = Ics = Icu Replaces
Sequences 2, 3 and 4
• Overload
• Dielectric Voltage Withstand
• Temperature Rise
• 145% Calibration (3 Phases Test)
• Breaking Capacity During Operation (Ot-CO-t-CO)
• Dielectric Voltage Withstand
• Temperature Rise
• 145% Calibration (3 Phases Test)
• 200% Calibration (Each Pole Separately)
• Ultimate Breaking Capacity (O-t-CO)
• Dielectric Voltage Withstand
• 250% Calibration (Each Pole Separately)
• 200% Calibration (Each Pole Separately)
• Short-time Current Withstand
• Temperature Rise
• Breaking Capacity at Admissible Short-time Current (O-t-CO)
• Dielectric Voltage Withstand
• 200% Calibration (Each Pole Separately)
• 200% Calibration (Each Pole Separately)
• Short-time Current Withstand Icw
• Breaking Capacity at Ics (O-CO-CO) at Maximum Relay Temp.
• Dielectric Voltage Withstand
• Temperature Rise
• 200% Calibration (Each Pole Separately)
72
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 73

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
ROUTINE AND MAINTENANCE GUIDELINES
Recommended
Inspection
Intervals
HAZARD OF ELECTRIC SHOCK, EXPLOSION, OR ARC FLASH
• Apply appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow safe electrical work practices.
See NFPA 70E.
• This equipment must only be installed and serviced by qualified electrical personnel.
• Turn off all power supplying this equipment before working on or inside equipment.
• Always use a properly rated voltage sensing device to confirm power is off.
• Replace all devices, doors and covers before turning on power to this equipment.
Failure to follow this instruction will result in Failure to follow these instructions will result
in death or serious injury.
HAZARD OF EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Molded case circuit breakers contain factory-sealed and calibrated elements. The seal must not be
broken and the circuit breaker must not be tampered with. Molded case circuit breakers should not
be field adjusted or repaired. In the case of a malfunction, the circuit breaker should be replaced or
inspected at the Schneider Electric factory, or by an authorized representative.
Failure to follow this instruction can result in equipment damage.
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
DANGER
CAUTION
Merlin Gerin circuit breakers are designed to be maintenance-free. However, all equipment with moving
parts requires periodic inspection to ensure optimum performance and reliability. It is recommended
that the circuit breakers be routinely inspected six months after installation, followed by annual
inspection. Intervals can vary depending on particular usages and environments.
Inspection of
Terminals
• Connections to circuit breaker terminals should be inspected. If there is discoloration due to
overheating, the connections should be disassembled and the surface cleaned before reinstallation.
It is essential that electrical connections be made carefully in order to prevent overheating.
• Check for terminal tightness.
Cleaning Remove dust and dirt that have accumulated on the circuit breaker surface and terminals.
Mechanical
Checks
Even over long periods of time, circuit breakers are not often required to operate on overload or shortcircuit conditions. Therefore it is essential to operate the circuit breaker periodically. To trip the circuit
breaker, push the push-to-trip button.
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
73
Page 74

Compact® NSF and NSJ 150 to 600 A Circuit Breakers
Section 13—Supplementary Technical Information
Insulation
Resistance Tests
When a circuit breaker is subjected to severe operating conditions, an insulation resistance test should
be performed as indicated in NEMA standard publication No. AB4-1996. An insulation resistance test is
used to determine the quality of the insulation between phases and phase-to-ground. The resistance
test is made with a dc voltage higher than the rated voltage to determine the actual resistance of the
insulation.
The most common testing method employs a "megger" type instrument. A 1000 V instrument will
provide a more reliable test because it is capable of detecting tracking on insulated surfaces.
Resistance values below one megohm are unsafe and should be investigated. An insulation test should
be made:
• Between line and load terminals of individual poles with the circuit breaker contacts open
• Between adjacent poles and from poles to the metallic supporting structure with the circuit breaker
contacts closed. The latter test may be done with the circuit breaker in place after the line and load
conductors have been removed, or with the circuit breaker bolted to a metallic base which simulates
the in-service mounting.
Electrical Tests These tests require equipment for conducting pole resistance, overcurrent and instantaneous tripping,
in accordance with NEMA Standard publication No. AB4. They are not within the scope of normal field
operation.
74
© 1995–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Page 75

Page 76

Square D Company
3700 Sixth St. SW
Cedar Rapids, IA 52404
1-888-SquareD
(1-888-778-2733)
www.SquareD.com
Schneider Canada Inc.
19 Waterman Avenue,
M4B 1 Y2
Toronto, Ontario
1-800-565-6699
www.schneider-electric.ca
Catalog No. 0615CT9901R4/03 10/2003 © 1997–2003 Schneider Electric All Rights Reserved
Replaces 0615CT9901 dated 03/1999.
 Loading...
Loading...