Page 1
2354235 11/2008
Altivar 71
Communication parameters
User manual
Software V2.7
11/2009
1755861
www.schneider-electric.com
Page 2

Contents
Document structure and directions for use__________________________________________________________________________ 5
Presentation _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7
Software enhancements ________________________________________________________________________________________ 9
Enhancements made to version V1.2 in comparison to V1.1 _____________________________________________________ 9
Enhancements made to version V1.6 in comparison to V1.2 ____________________________________________________ 10
Enhancements made to version V2.5 in comparison to V1.6 ____________________________________________________ 10
Enhancements made to version V2.7 in comparison to V2.5 ____________________________________________________ 10
Notations___________________________________________________________________________________________________ 11
Description of parameters _______________________________________________________________________________ 11
Drive terminal displays __________________________________________________________________________________ 11
Profiles ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 12
What is a profile? ______________________________________________________________________________________ 12
Functional profiles supported by the Altivar 71 _______________________________________________________________ 13
I/O profile __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 14
Definition ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 14
Control word - run on state [2 wire] (2C) ____________________________________________________________________ 16
Control word - run on edge [3 wire] (3C) ___________________________________________________________________ 17
Status word (ETA) _____________________________________________________________________________________ 18
Example: I/O profile with positioning by sensors function _______________________________________________________ 19
CiA402 profile_______________________________________________________________________________________________ 21
Functional description __________________________________________________________________________________ 21
CiA402 state chart _____________________________________________________________________________________ 22
Description of states ___________________________________________________________________________________ 23
Control word (CMD) ____________________________________________________________________________________ 25
Status word (ETA) _____________________________________________________________________________________ 27
Starting sequence _____________________________________________________________________________________ 28
Sequence for a drive powered by the power section line supply __________________________________________________ 29
Sequence for a drive with separate control section ____________________________________________________________ 31
Sequence for a drive with line contactor control ______________________________________________________________ 34
Command/reference switching__________________________________________________________________________________ 37
Channels ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 37
Not separate mode ____________________________________________________________________________________ 38
Separate mode _______________________________________________________________________________________ 38
Switching in not separate mode ___________________________________________________________________________ 39
Switching in separate mode ____________________________________ __________________________________________ 39
Channel switching _____________________________________________________________________________________ 40
Reference switching principle ____________________________________________________________________________ 42
Command switching principle _______________________________________________________________ _____________ 43
Assigning control word bits ______________________________________________________________________________ 44
Example: I/O profile with positioning by sensors function _______________________________________________________ 47
Copy on switching _____________________________________________________________________________________ 49
Forced local ________________________________________________________________________________________________ 50
Definition ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 50
Forced local mode and reference switching _________________________________________________________________ 51
Forced local mode and command switching _________________________________________________________________ 52
Priority stops________________________________________________________________________________________________ 54
Priority stops on the graphic display terminal ________________________________________________________________ 54
Priority stops via the terminals or the network ________________________________________________________________ 54
Communication monitoring_____________________________________________________________________________________ 56
Principle _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 56
Network monitoring criteria ______________________________________________________________________________ 56
Behavior in the event of a network fault _____________________________________________________________________ 57
Detailed operation _____________________________________________________________________________________ 58
Assignment of setpoints from a network___________________________________________________________________________ 60
Setpoint parameters ___________________________________________________________________________________ 60
Without PID regulator __________________________________________________________________________________ 61
With PID regulator _____________________________________________________________________________________ 62
Configuration saving and switching ______________________________________________________________________________ 63
Saving the configuration ________________________________________________________________________________ 63
Restore configuration ___________________________________________________________________________________ 65
Configuration switching via control word ____________________________________________________________________ 66
Configuration switching by selection _______________________________________________________________________ 70
Parameter set switching_______ ___________________________________________________ _____________________________ 72
Loading drive parameters______________________________________________________________________________________ 77
Requirement _________________________________________________________________________________________ 77
Procedure ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 77
Command parameters ________________________________________________________________________________________ 79
Setpoint parameters__________________________________________________________________________________________ 82
1755861 11/2009 3
Page 3

Sommaire
Status parameters ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 84
Output value parameters ______________________________________________________________________________________ 92
Output values (speed) __________________________________________________________________________________ 92
Output values (torque) ________________________________________ __________________________________________ 93
Output values (motor) __________________________________________________________________________________ 94
Reference parameters ________________________________________________________________________________________ 96
References (speed) ____________________________________________________________________________________ 96
References (torque) ____________________________________________________________________________ ________ 97
Reference (regulator) ___________________________________________________________________________________ 98
Measurement parameters______________________________________________________________________________________ 99
Input measurements ___________________________________________________________________________________ 99
Thermal states ________________________________________________________________________________________ 99
Time _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 100
I/O parameters _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 102
Logic I/O ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 102
Analog inputs ________________________________________________________________________________________ 103
Analog outputs _______________________________________________________________________________________ 104
Encoder ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 105
Fault parameters____________________________________________________________________________________________ 106
Log parameters_____________________________________________________________________________________________ 113
Log of the following faults ______________________________________________________________________________ 117
Identification parameters _____________________________________________________________________________________ 121
CiA402 standard configuration and adjustment parameters_______________________________________________ ____________ 124
ODVA standard configuration and adjustment parameters ___________________________________________________________ 128
Index of parameters codes____________________________________________________________________________________ 129
4 1755861 11/2009
Page 4

Document structure and directions for use
Installation Manual
This manual describes:
• Assembly
• How to connect the drive
Programming Manual
This manual describes:
• Functions
• Parameters
• How to use the drive's display terminal (integrated display terminal and graphi c display terminal)
Communication Parameters Manual
This manual describes:
• The operating modes specific to communication (state chart)
• The interaction between communication and local control
• The control, reference and monitoring parameters, with specific information for use via a bus or communication network
It does not include the drive adjustment and configuration parameters, which are contained in the Excel file supplied as an
appendix to this manual.
All the parameters are grouped together in an Excel file supplied as an appendix, with the following data:
-Code
-Name
- Addresses: logic, CANopen, INTERBUS, Device Net
- Category
- Read/write access
- Type: signed numerical, unsigned numerical, etc.
-Unit
- Factory setting
- Minimum value
- Maximum value
- Display on the graphic display terminal and the 7-segment integrated display termi nal
- Relevant menu
This file offers the option of sorting and arranging the data according to any criterion chosen by the user.
Data relating to operation, interdependences and limits of use are described in the Programming Manual.
The various documents are to be used as follows:
1. For information about the drive and its programming, refer to the Programming Manual.
2. For information about communication and its programming, refer to the Parameters Manual.
3. Use the Parameters file to define any addresses and values of the adj ustment and configuration parameters to be modified through
communication.
The section entitled "Loading drive parameters" on page 77
through communication.
describes the recommended procedure for loading parameters
Modbus, CANopen, Ethernet, Profibus, INTERBUS, Uni-Telway, FIPIO, Modbus Plus and Device Net
manuals
These manuals describe:
• Assembly
• Connection to the bus or network
• Diagnostics
• Configuration of the communication-specific parameters via the integrated display terminal or graphic display terminal
They describe the protocol communication services in detail.
"Controller Inside" Manual
This manual describes, for the "Controller Inside" card:
• Assembly
• Connection
• Functions
• Configuration
1755861 11/2009 5
Page 5

Documentation structure
Altivar 58/58F Migration Manual
This manual describes the differences between the Altivar 71 and the Altivar 58/58F.
It explains how to replace an Altivar 58 or 58F, including how to replace drives communicating on a bus or network.
Note: This Parameters Manual describes the parameters of the Altivar 71 profiles.
It does not describe the Altivar58/58F compatibility parameters (SE8 profile).
These are detailed in the Altivar 58/58F Communication Variables Manual and the Migration Manual.
Altivar 78 Migration Manual
This manual describes the differences between the Altivar 71 and the Altivar 78.
It explains how to replace an Altivar 78.
6 1755861 11/2009
Page 6
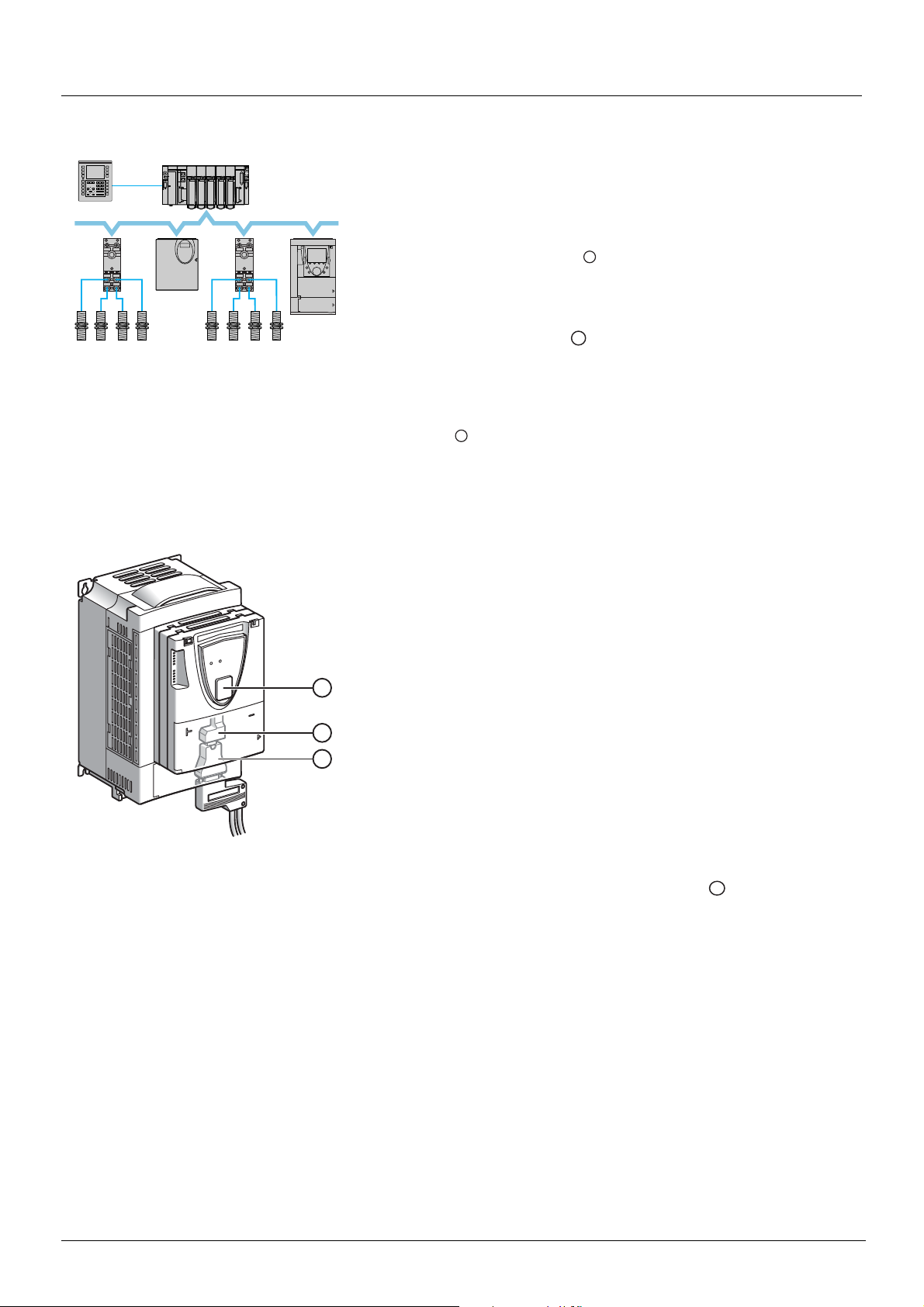
Presentation
2
1
3
1
2
1
3
Magelis XBT Premium
FTM FTM
ATV 31
ATV 71
Sensors Sensors
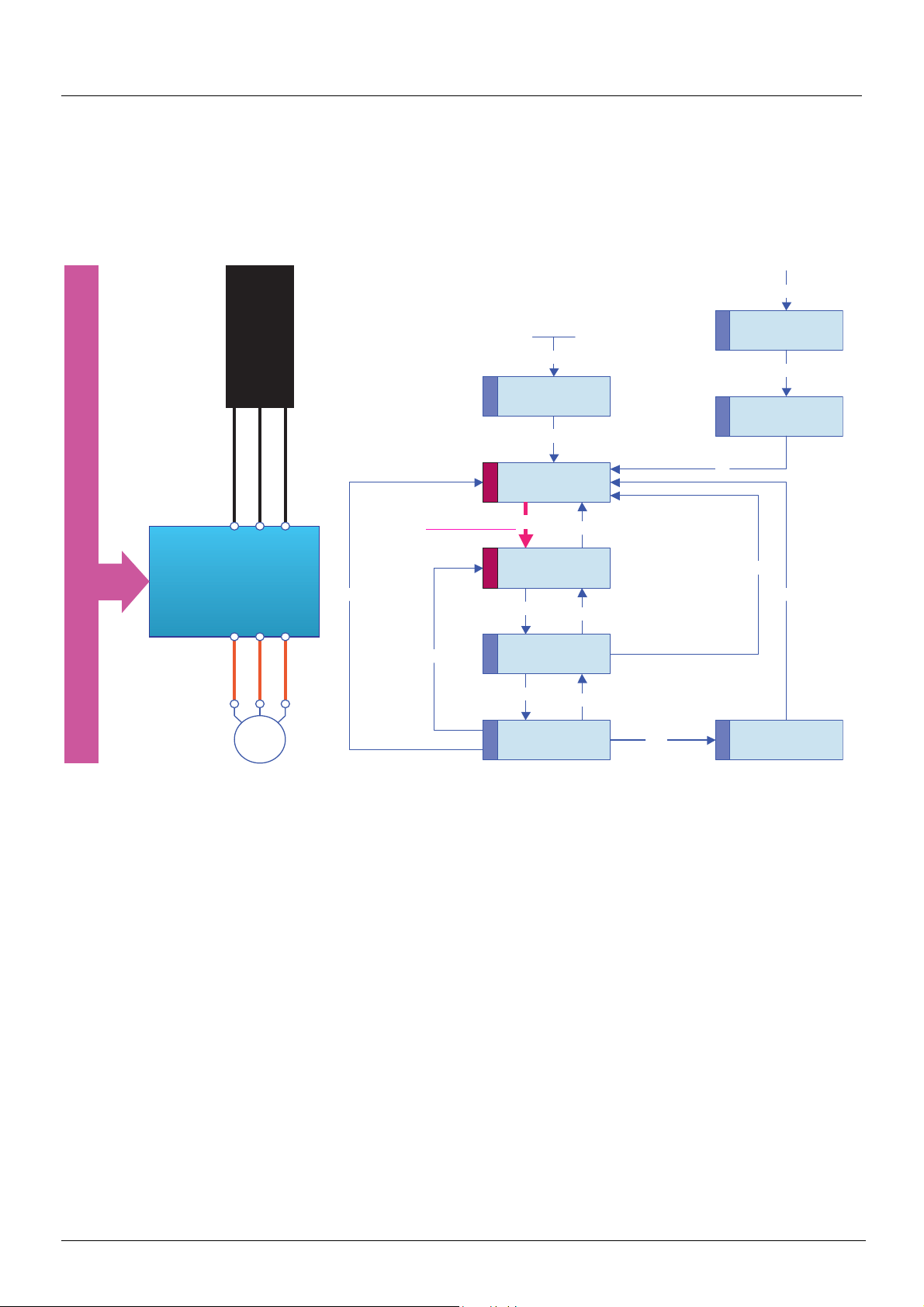
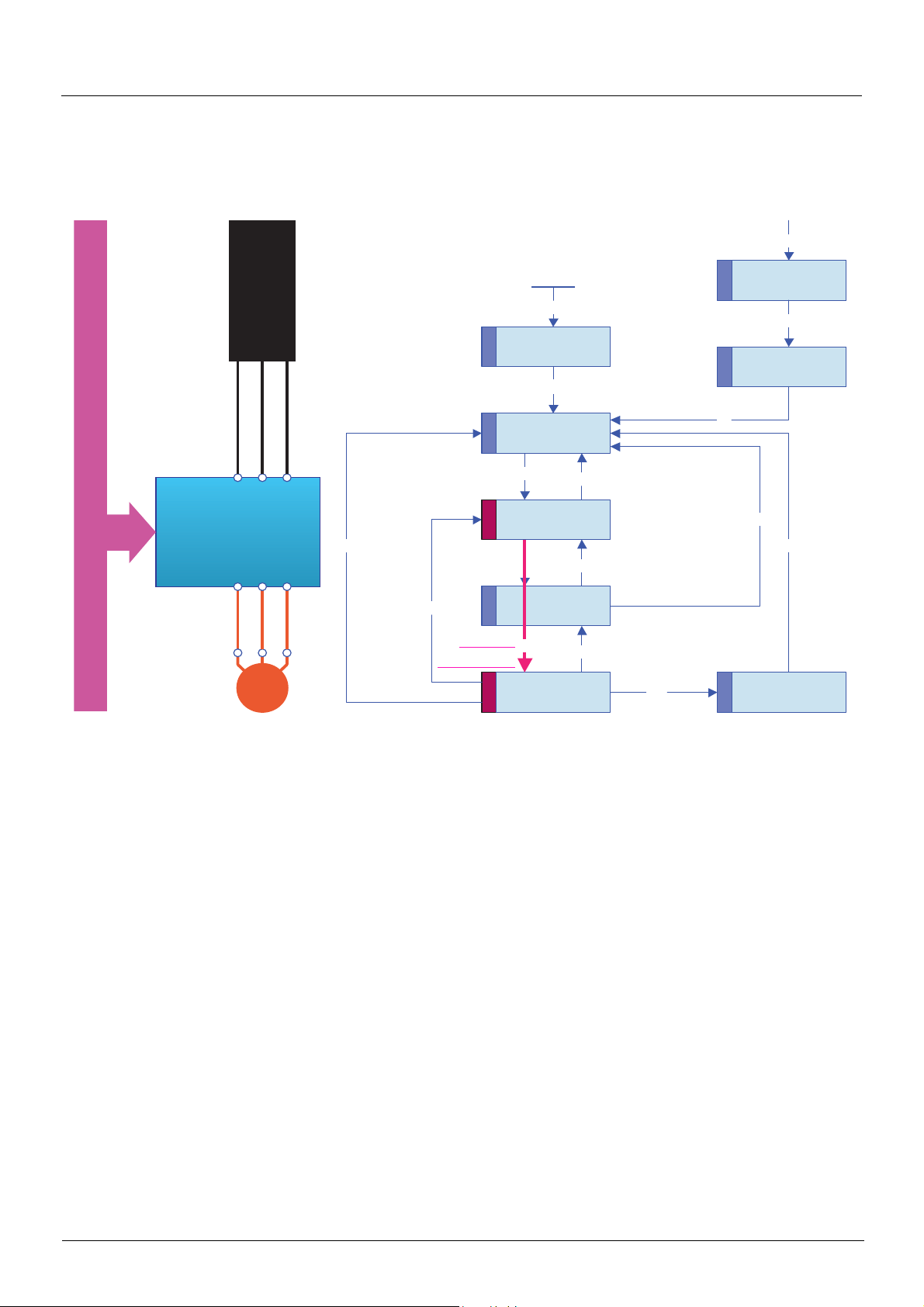
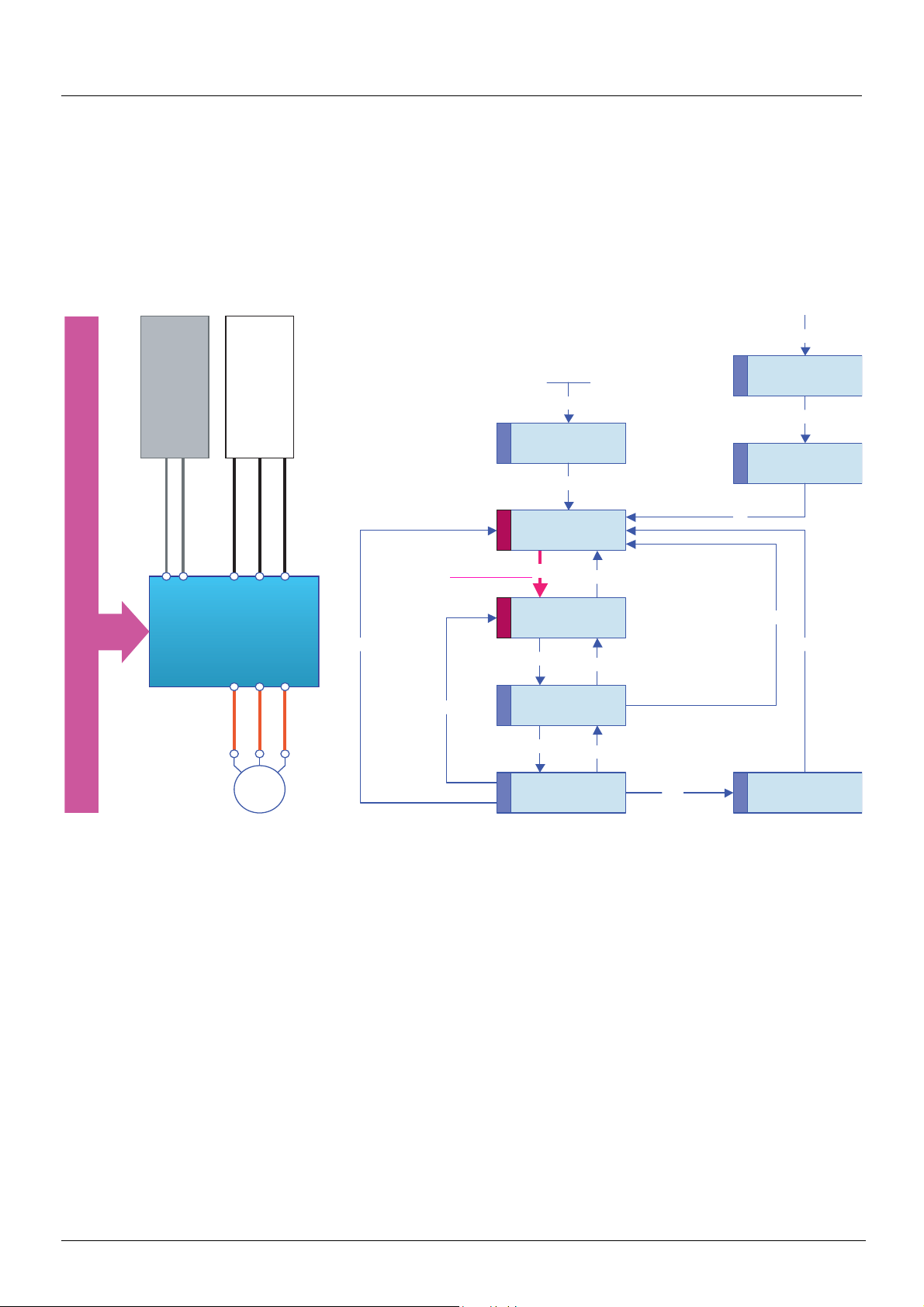
Example of configuration on the CANopen bus
The Altivar 71 drive has been designed to meet all the configuration requirements
encountered within the context of industrial communication installations.
It includes Modbus and CANopen communication protocols as standard.
Two integrated communication ports enable direct access to the Modbus protocol :
• One RJ45 Modbus connector port , located on the drive front panel,
which is used to connect:
• The remote graphic display terminal
• A Magelis industrial HMI terminal
• The PowerSuite software workshop
• One RJ45 Modbus network port , located on the drive’s control terminals,
which is dedicated to control and signaling by a PLC or other type of controller.
It can also be used to connect a display terminal or the PowerSuite software
workshop.
The CANopen protocol can be accessed from the Modbus network port via the
CANopen adapter (1).
The Altivar 71 can also be connected to other networks and industrial communication
buses by using one of the communication option cards:
• Ethernet TCP/IP
• Modbus/Uni-Telway. This card provides access to additional functions, which
complement those of the integrated ports: Modbus ASCII and 4-wire RS 485
•Fipio
• Modbus Plus
•Profibus DP
• DeviceNet
•INTERBUS
• etc. (Please refer to the catalog)
The control section can be powered separately, thus allowing communication
(monitoring, diagnostics) to be maintained even if the power supply section fails.
The main communication functions of Altivar 58 and Altivar 58F drives are compatible
with the Altivar 71 (2):
- Connection
- Communication services
- Drive behavior (profile)
- Control and monitoring parameters
- Basic adjustment parameters
The PowerSuite software workshop supports the transfer of configurations from
Altivar 58 and Altivar 58F drives to the Altivar 71.
(1) If the CANopen adapter is installed, Modbus will not be available on the network port .
(2) Please refer to the ATV 58(F)/ATV 71 Migration Manual supplied on the documentation CD-ROM.
1755861 11/2009 7
Page 7

Presentation
All the drive functions are accessible via the network:
• Control
• Monitoring
• Adjustment
• Configuration
If the "Controller Inside" programmable card is installe d on the drive , it s variables (%MW, etc.) can be acce ssed via the integ rated Modb us
ports or the Ethernet option card.
The speed/torque command and reference can come from different sources:
• The I/O terminals
• The communication ne twork
• The "Controller Inside" programmable card
• The remote graphic display terminal
• The PowerSuite software workshop (for commissioning and maintenance)
The Altivar 71 drive's advanced functions can be used to manage switching of these command and reference sources according to
application requirements.
The periodic communication variables can be selected via:
• The network configuration software (Sycon, etc.): CANopen, DeviceNet
• The Altivar 71’s communication scanner function: Profibus DP, Fipio, Modbus Plus
• The network's IO Scanner function: Ethernet TCP/IP
With the exception of DeviceNet, regardless of n etwork type, the Altivar 71 can be controlled:
• In accordance with the Drivecom profile (CANopen CiA DSP 402)
• In accordance with the I/O profile, whereby control is as straightforward and flexible as control via the I/O terminals
The DeviceNet card supports the ODVA standard profile.
Communication is monitored according to criteria specific to each protocol. Regardless of protocol type, the reaction of the drive to a
communication fault can be configured:
• Drive fault involving: Freewheel stop, stop on ramp, fast stop or braked stop
• Stop without drive fault
• Maintain the last command received
• Fallback position at a predefined speed
• Ignore the fault
A command from the CANopen bus is handled with the same priority as an input from the drive termi nals. This enables very good response
times to be achieved on the network port via the CANopen adapter.
8 1755861 11/2009
Page 8

Software enhancements
Since the Altivar ATV71 was first launched, it has benefited from the addition of several new functions. Software version has now been
updated to V2.7. The new version can be substituted to the previous versions without making any changes.
Although this documentation relates to versi on V2.7, it can st ill be used with previ ous versions, as the update s merely invol ves t he additi on
of new values and parameters. None of the previous versions parameters have been modified or removed.
The software version is indicated on the nameplate attached to the body of the drive.
Enhancements made to version V1.2 in comparison to V1.1
Factory setting
Note 1: In version V1.1, the analog input was 0 ± 10 V. For safety reasons, this input is co nfigured as 0 + 10 V in the new versi on.
Note 2: In version V1.1, the analog output AO1 was assigned to the motor frequency. In the new version, this output is not
assigned.
Except for these two parameters, the factory setting of version V1.1 is retained in the new version. The new functions are inactive in the
factory setting.
Motor frequency range
The maximum output frequency range is extended from 1000 to 1600 Hz (depending on rating and selected control profile).
New parameters and functions
[1.2 MONITORING] (SUP-) menu
Addition of states and internal values relating to the new fun ctions described below.
[1.3 SETTINGS] (SEt-) menu
• [High torque thd.] (ttH)
• [Low torque thd.] (ttL)
• [Pulse warning thd.] (FqL)
• [Freewheel stop Thd] (FFt)
[1.4 MOTOR CONTROL] (drC-) menu
• [rpm increment] (InSP)
• Extension to all drive ratings of the following configurat ions, formerly limited to 45 kW for ATV7 1
synchronous motor [Sync. mot.] (SYn), sinus filter [Sinus filter] (OFI), noise reduction [Noise reduction] (nrd), braking balance [Braking
balance] (bbA).
pppM3X and 75 kW for ATV71pppN4:
[1.5 INPUTS / OUTPUTS CFG] (I-O-) menu
• Input AI1 becomes configurable as 0 + 10 V or 0 ± 10 V using [AI1 Type] (AI1t).
• [AI net. channel] (AIC1)
• New options for assigning relays and logic outputs: rope slack, torque greater than high threshold, torque less than low threshold,
motor rotating in forward direction, motor rotating in reverse, measured speed th reshold attained, and load variation detection.
• Analog output AO1 becomes usable as a logic output and can be assigned to the relay and logic output functions.
• New option of modifying the scaling of the analog outputs using the parameters [Scaling AOx min] (ASLx) and [Scaling AOx max]
(ASHx).
• New options for assigning analog outputs: signed motor torque and measured motor speed.
• New options for assigning alarm groups: rope slack, torque greater than high threshold, torque less than low threshold, measured
speed threshold attained, and load variation detection.
1755861 11/2009 9
Page 9

Software enhancements
[1.7 APPLICATION FUNCT.] (Fun-) menu
• The summing, subtraction and multiplier reference functions become assignable to the network analog input [Network AI] (AIU1)
• New parameter [Freewheel stop Thd] (FFt) used to adjust a threshold for switching to freewheel at the end of a stop on ramp or fast stop.
• New parameter: Brake engage at controlled zero speed [Brake engage at 0] (b ECd).
• The weight sensor [Weight sensor ass.] (PES) becomes assignable to the network analog input [Network AI] (AIU1).
• New "rope slack" function, with the parameters [Rope slack config.] (rSd) and [Rope slack trq level] (rStL).
• Use of the ramp [Acceleration 2] (AC2) during PID function starts and wake-ups.
• Torque limitation [TORQUE LIMITATION] (tOL-) becomes configurable as a % or 0.1% using [Torque increment] (IntP) and can be
assigned to the network analog input [Network AI] (AIU1).
• New "stop at calculated distance after end of slowdown travel" function, wit h the parameters [Stop distance] (Std), [Rated linear
speed] (nLS) and [Stop corrector] (SFd).
• Positioning by sensor or limit switch [POSITIONING BY SENSORS] (LPO-) becomes configurable as positive or n egative logic usi ng
[Stop limit config.] (SAL) and [Slowdown limit cfg.] (dAL).
• Parameter switchi ng [PARAM.] (MLP-) becomes assignable to attained frequency thresholds [Freq. Th. attain.] (FtA) and
[Freq. Th. 2 attain.] (F2A).
• New half floor function: [HALF FLOOR] (HFF-) menu.
[1.8 FAULT MANAGEMENT] (FLt-) menu
• Option of reinitializing the drive without switching it off, using [Product reset] (rP).
• Option of reinitializing the drive using a logic input without switching it off, using [Product reset assig.] (r PA).
• Option of configuring the "output phase loss" fault [Output Phase Loss] (OPL) to [Output cut] (OAC) is extended to all drive ratings
(formerly limited to 45 kW for ATV71
• The external fault [EXTERNAL FAULT] (EtF-) becomes configurable as positive or negative logic using [External fault config] (LEt).
• New monitoring function by speed measurement via the "Pulse input", using the [FREQUENCY METER] (FqF-) menu.
• New load variation detection function, using the [DYNAMIC LOAD DETECT.] (dLd-) menu.
• The braking unit short-c i rc uit fault becomes configurable u si n g [Brake res. fault Mgt] bUb).
pppM3X and 75 kW for ATV71pppN4).
[7 DISPLAY CONFIG.] menu
• Addition in [7.4 TERMINAL ADJUSTMENT] of the [CONTRAST] and [STANDBY] parameters for adjusting the contrast of the graphic
display unit and setting it to standby.
Enhancements made to version V1.6 in comparison to V1.2
Extension of the range with addition of the drives ATV71pppY for network 500 to 690 V.
There are no new parameters, but the ranges of adjustment and factory settings of some parameters are adapted to the new voltage.
[1.5 INPUTS / OUTPUTS CFG] (I-O-) menu
Increase in adjustment range of delay parameters for relays and logic outputs : 0 to 600 00 ms instead of 0 to 9999 ms.
Enhancements made to version V2.5 in comparison to V1.6
[1.3 SETTINGS] (SEt-) menu
• New parameters [Skip Frequency] (JPF), [Skip Frequency 2] (JF2) and [3rd Skip Frequency] (JF3) allow to avo id critical speed which
generate resonances.
• New parameter [Skip.Freq.Hysteresis] (JFH) to adjust the range of skip frequency.
• Possibility to adjust the parameter [Torque ratio] (trt) (visible too in [TORQUE CONTROL] (tOr-) menu).
Important :
For V2.5 version, the behaviour of the following functions is different from the previous when type of stop "freewheel" is selected (factory
value):
• [LIMIT SWITCHES] (LSt-) function,
• [POSITIONING BY SENSORS] (LPO-) function,
• "shutdown" command by communication (see CiA402 state chart in communication parameters manual).
Actually, on previous versions, type of stop "freewheel" was not well done.
Enhancements made to version V2.7 in comparison to V2.5
[7 DISPLAY CONFIG.] menu
Addition in [7.4 KEYPAD PARAMETERS] of [Power up menu]. This parameter allows to choose the menu which displays on the drive on
power up.
[1.3 SETTINGS] (SEt-) menu
The adjustment range of [Time to restart] (ttr) can now be configured between 0.00 and 15.00 seconds.
10 1755861 11/2009
Page 10

Notations
Description of parameters
Identification
A parameter is defined by means of various character strings:
• Code: 4 charac
brt, tLIG
• Name: Description in plain text (used by the PowerSuite software workshop)
• Terminal name: Character string in square brackets for the graphic display terminal [Gen. torque lim]
Addresses
There are 4 formats for specifying parameter addresses:
• Logic address: Address for the Modbus messaging (RS485 and Ethernet TCI/IP) and the PKW indexed periodic variables (Fipio,
Profibus DP), in decimal and hexadecimal (preceded by 16#).
To optimize Modbus messaging performance, two addresses are given for the control word and the status word. The addresses
annotated "speed" are for use in rpm; the addresses annotated "frequency" are for use in Hz.
• CANopen index: CANopen index/subindex in hexadecimal fo rmat, to be used for va riabl e assign ment of PDOs and SDO messagi ng
• INTERBUS index: Index/subindex in hexadecimal for PCP messaging
• DeviceNet path: Class/instance/attribute i n hexadecimal
Read/write
• R: Read only
• R/W: Read and write
• R/WS: Read and write, but write only possible when motor is at standstill
ters max. The code makes it possible to identify the parameter on the integrated 7-segment display terminal (Examples:
)
Type
• WORD (bit register): Word where each bit represents an item of command, monitoring or configuration information
• WORD (listing): Word where each value represents a possible choice for a configuration or state
• INT: Signed integer
• UINT: Unsigned integer
• DINT: Signed double integer
• UDINT: Unsigned double integer
Format
Hexadecimal values are written as follows: 16#pppp
Drive terminal displays
The menus that appear on the graphic display terminal are shown in square brackets.
Example: [1.9 COMMUNICATION].
The menus that appear on the integrated 7-segment display terminal always end with a dash and appear between round brackets.
Example: (COM-).
Parameter names are displayed on the remote graphic display terminal in square brackets.
Example: [Fallback speed].
The parameter codes displayed on the integrated 7-segment display terminal are shown in round brackets.
Example: (LFF).
1755861 11/2009 11
Page 11

Profiles
What is a profile?
There are three types of profile:
• Communication profiles
• Functional profiles
• Application profiles
Communication profiles
A communication profile describes the characteristics of the bus or network:
• Cables
• Connectors
• Electrical characteristics
• Access protocol
• Addressing system
• Periodic exchange service
• Messaging service
•...
A communication profile is unique to a type of network (Fipio, Profibus DP, etc.) and is used by various different types of device.
Functional profiles
A functional profile describes the behavior of a type of device. It defines:
• Functions
• Parameters (name, format, unit, type, etc.)
• Periodic I/O variables
• State chart(s)
•...
A functional profile is common to all members of a device family (variable speed drives, encoders, I/O modules, displays, etc.).
Ideally, functional profiles should be network-independent, but in reality they are not. They can feature common or similar parts. The
standardized (IEC 61800-7) functional profiles of variable speed drives are:
• CiA402
• PROFIDRIVE
•CIP
DRIVECOM has been available since 1991.
CiA402 "Device profile for drives and motion control" represents the next stage of this standard’s development and is maintained by
CanInAutomation.
Some protocols also support the ODVA (Open DeviceNet Vendor Association) profile.
Application profiles
Application profiles define in their entirety the services to be provided by the devices on a machine. For example, "CiA DSP 417-2 V 1.01
part 2: CANopen application profile for lift control systems - virtual device definitions".
Interchangeability
The aim of communication and functional profiles is to achieve interchangeability of the devices connected via the network.
Although this aim is not always achieved, the profiles facilitate free competition.
12 1755861 11/2009
Page 12

Profiles
Functional profiles supported by the Altivar 71
I/O profile
Using the I/O profile simplifies PLC programming.
When controlling via the terminals or the display terminal, the I/O profile is used without knowing it.
With an Altivar 71, the I/O profile can also be used when controlling via a network.
The drive starts up as soon as the run command is sent.
The 16 bits of the control word can be assigned to a function or a terminal input.
This profile can be developed for simultaneous control of the drive via:
• The terminals
• The Modbus control word
• The CANopen control word
• The network card control word
• The "Controller Inside" control word
The I/O profile is supported by the drive itself and therefore in turn by all the communication ports (integrated Modbus, CANopen and the
Ethernet, Fipio, ModbusPlus, Modbus, Uni-Telway, Profibus DP, DeviceNet, and INTERBUS communication cards).
CiA402 profile
The drive only starts up following a command sequence.
The control word is standardized.
5 bits of the control word (bits 11 to 15) can be assigned to a function or a terminal input.
The CiA402 profile is supported by the drive itself and therefore in turn by all the communication ports (integrated Modbus, CANopen and
the Ethernet, Fipio, ModbusPlus, Modbus, Uni-Telway, Profibus DP, DeviceNet, and INTERBUS communication cards).
The Altivar 71 supports the CiA402 profile’s "Velocity mode".
In the CiA402 profile, there are two modes that are specific to the Altivar 71 and characterize command and reference management (see
section “Command/reference switching”, page 37
• Separate mode [Separate] (SEP)
• Not separate mode [Not separ.] (SIM)
):
ODVA profile
The drive starts up as soon as the run command is sent.
The control word is standardized.
The ODVA profile is supported by the DeviceNet communication card.
1755861 11/2009 13
Page 13
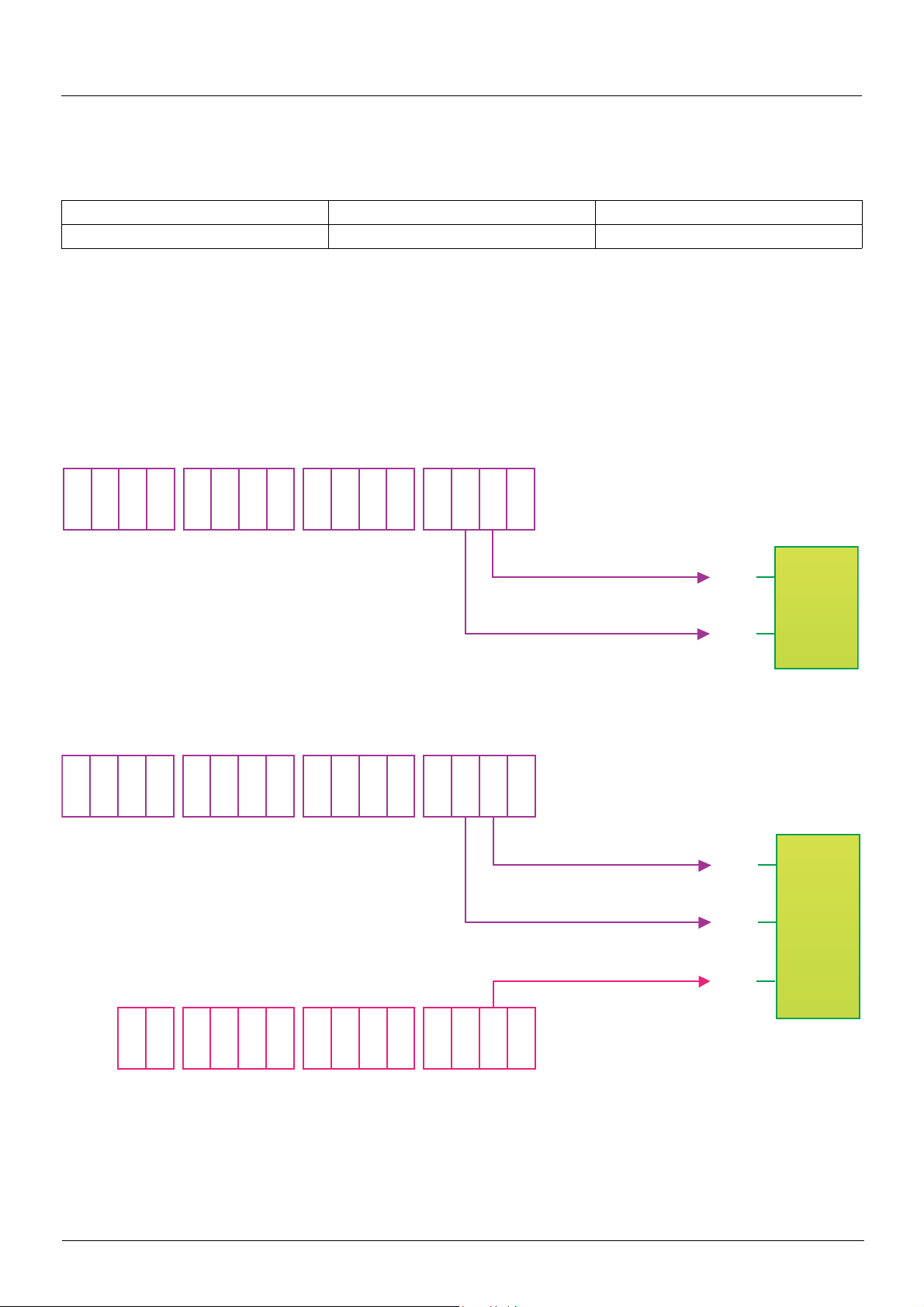
I/O profile
C201
C202
bit 9
bit 8
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 11
bit 10
bit 13
bit 12
bit 15
bit 14
A
B
CANopen control word
Function
C201
C202
bit 9
bit 8
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 11
bit 10
bit 13
bit 12
bit 15
bit 14
A
B
LI2
LI10
LI9
LI8
LI7
LI6
LI5
LI4
LI3
LI2
LI1
LI12
LI11
LI14
LI13
C
CANopen control word
Terminals
Function
Definition
The behavior of the drive is identical whether via the network or via the terminals.
The I/O profile is achieved via the following configuration:
Menu Parameter Value
[1.6 - COMMAND] (CtL-) [Profile] (CHCF) [I/O profile] (IO)
As well as to logic inputs of the terminals, drive functio n s can be assigned to control word bits.
A function input can be assigned to:
• A terminal input (LI2 to LI14)
• A Modbus control word bit (C101 to C115)
• A CANopen control word bit (C201 to C215)
• A network card control word bit (C301 to C315)
• A Controller Inside control word bit (C401 to C415)
• A switched bit (Cd00 to Cd15): See "Command/reference switching" section.
Schematic diagrams:
Fixed assignment on CANopen:
Fixed assignment to terminals and on CANopen: :
14 1755861 11/2009
Page 14
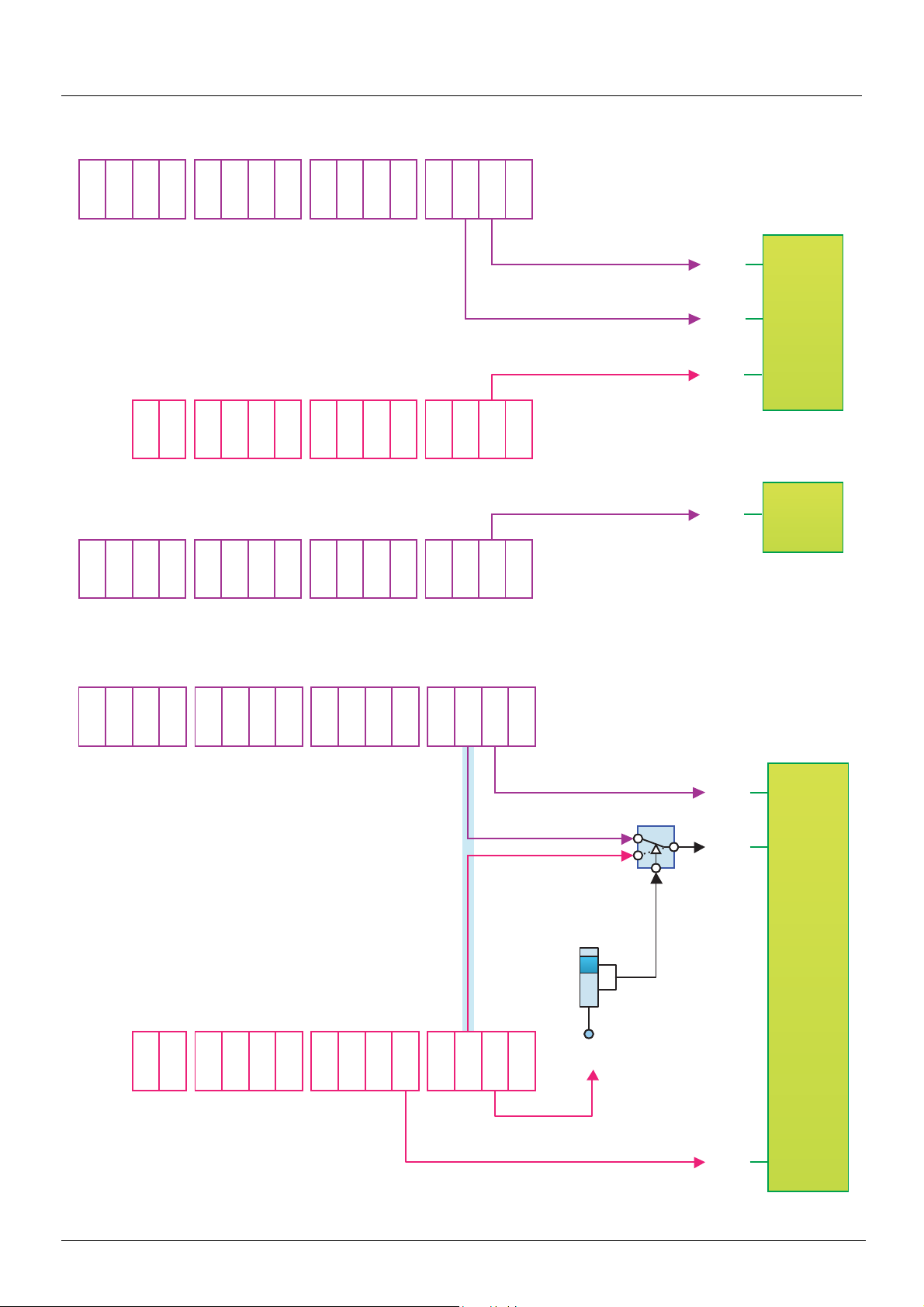
I/O profile
C201
C202
C401
bit 9
bit 8
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 11
bit 10
bit 13
bit 12
bit 15
bit 14
bit 9
bit 8
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 11
bit 10
bit 13
bit 12
bit 15
bit 14
A
B
LI2
LI10
LI9
LI8
LI7
LI6
LI5
LI4
LI3
LI2
LI1
LI12
LI11
LI14
LI13
C
Stop
CANopen control word
Terminals
Function
"Controller Inside" control word
Fast stop
C201
Cd02
LI5
LI10
LI9
LI8
LI7
LI6
LI5
LI4
LI3
LI2
LI1
LI12
LI11
LI14
LI13
bit 9
bit 8
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 11
bit 10
bit 13
bit 12
bit 15
bit 14
LI2
A
B
C
CANopen control word
Terminals
Function
CANopen
Terminals
Command
switching
CCS
Fixed assignment to terminals, on CANopen and on "Controller Inside" card:
Fixed assignment to terminals and on CANopen with command switching:
1755861 11/2009 15
Page 15
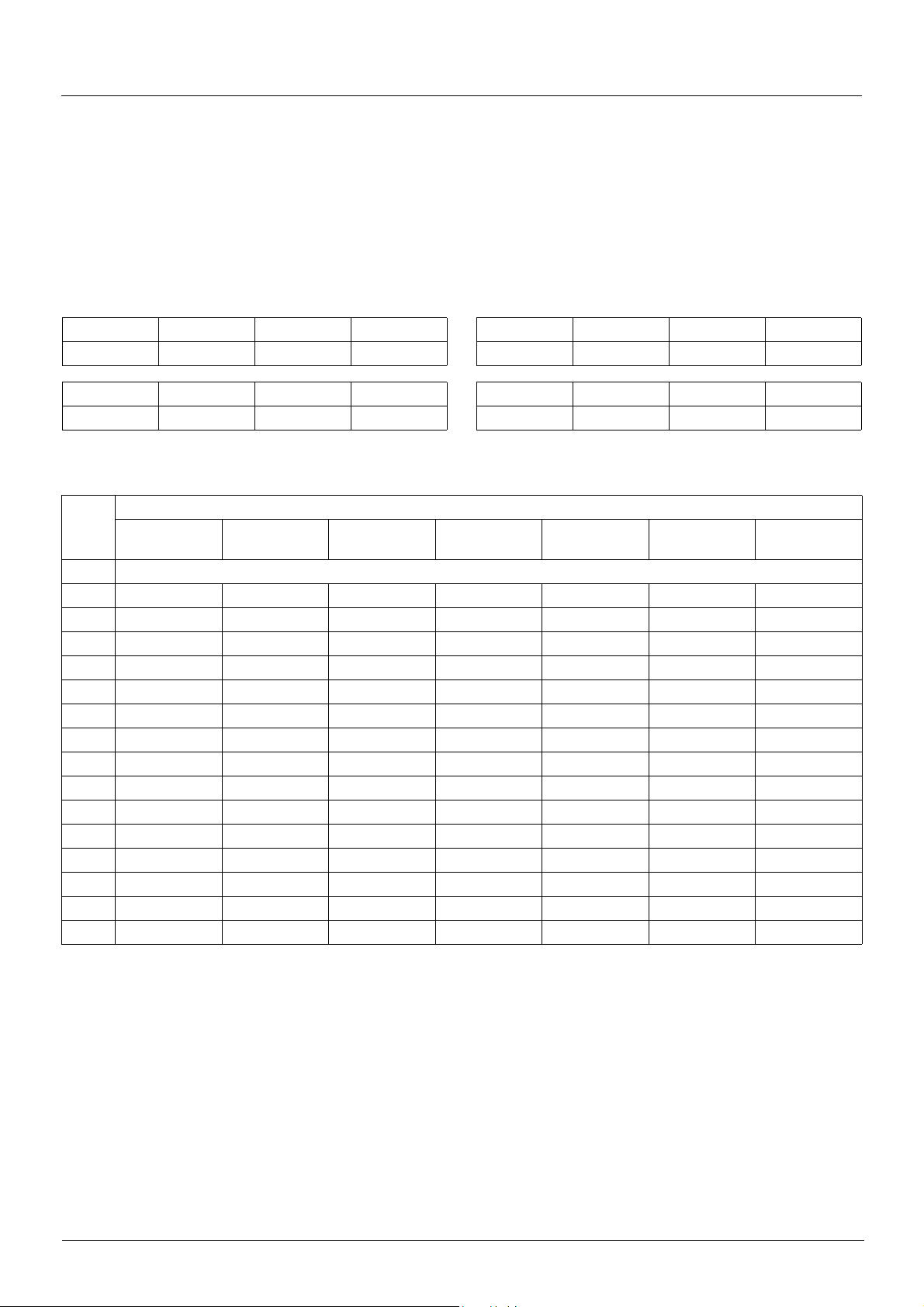
I/O profile
Control word - run on state [2 wire] (2C)
Please refer to the [1.5 INPUTS / OUTPUTS CFG] (I-O-) section of the Programming Manual.
The forward run command is automatically assigned to input LI1 and to bit 0 of the various control wo rds.
This assignment cannot be modified.
The run command is active on state 1:
• Of input LI1, if the terminals are active
• Of bit 0 of the control word, if the network is active
Bits 1 to 15 of the control words can be assigned to drive functions.
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Forward
bit 15 bit 14 bit 13 bit 12 bit 11 bit 10 bit 9 bit 8
Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable
In the case of a [2 wire] (2C) run on state command and I/O profile, fixed assignment of a function input is possible using the following
codes:
Fixed assignments
Bit
Drive terminals Logic I/O card
bit 0 Forward
bit 1 LI2 --C101 C201 C301 C401
bit 2 LI3 --C102 C202 C302 C402
bit 3 LI4 --C103 C203 C303 C403
bit 4 LI5 --C104 C204 C304 C404
bit 5 LI6 --C105 C205 C305 C405
bit 6 - LI7 - C106 C206 C306 C406
bit 7 - LI8 - C107 C207 C307 C407
bit 8 - LI9 - C108 C208 C308 C408
bit 9 - LI10 - C109 C209 C309 C409
bit10 - - LI11 C110 C210 C310 C410
bit11 - - LI12 C111 C211 C311 C411
bit12 - - LI13 C112 C212 C312 C412
bit13 - - LI14 C113 C213 C313 C413
bit14---C114 C214 C314 C414
bit15---C115 C215 C315 C415
Extended I/O
card
Modbus CANopen Network card
"Controller Inside"
card
For example, to assign the operating direction command to bit 1 of CANopen, simply conf igure the [Reverse ass ign.] (rrS) parameter with
the value [C201] (C201).
16 1755861 11/2009
Page 16
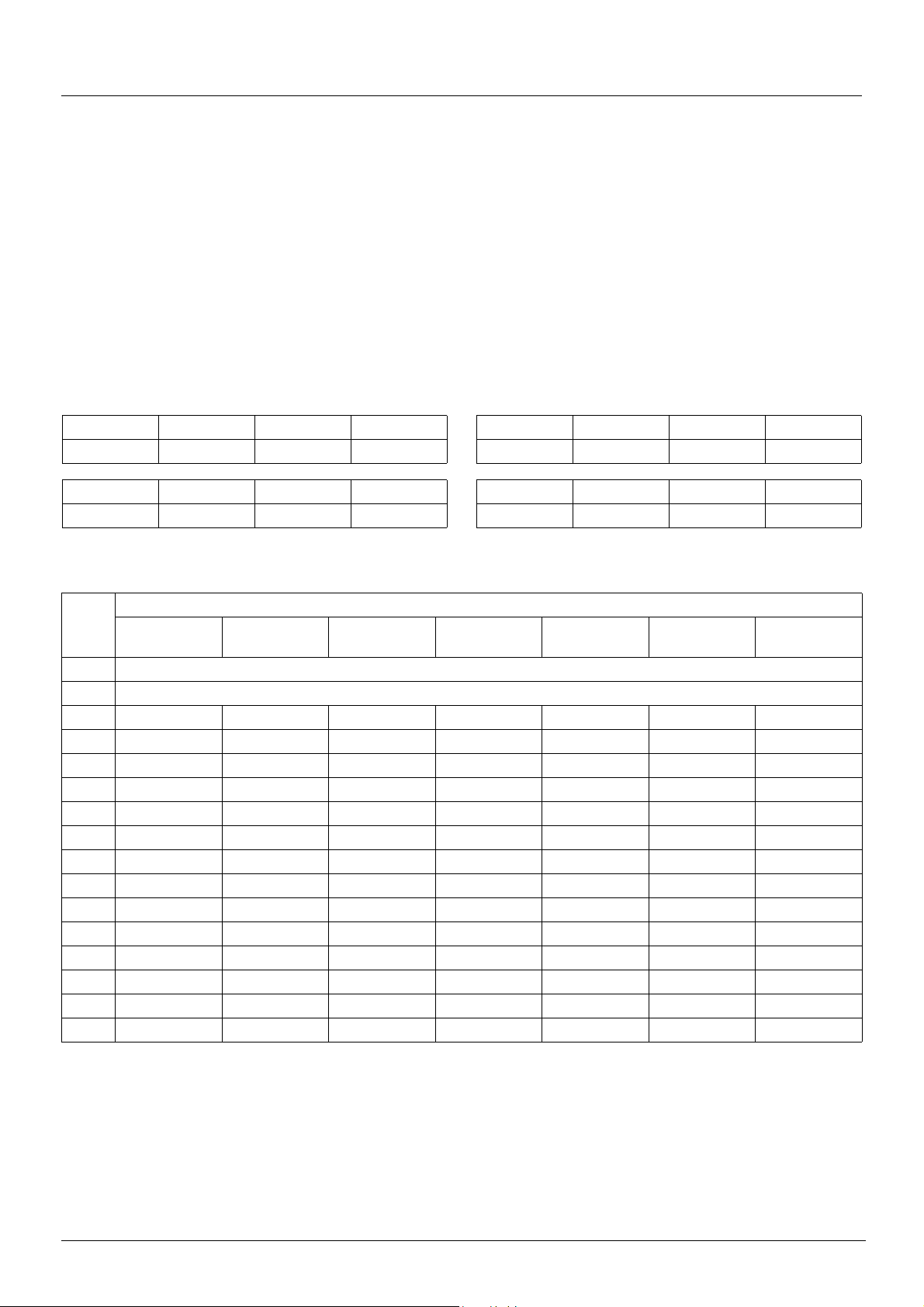
I/O profile
Control word - run on edge [3 wire] (3C)
Please refer to the [1.5 INPUTS / OUTPUTS CFG] (I-O-) section of the Programming Manual.
The stop command is automatically assigned to input LI1 and to bit 0 of the control words.
This assignment cannot be modified.
This command enables running on state 1:
• Of input LI1, if the terminals are active
• Of bit 0 of the control word, if the network is active
The forward run command is automatically assigned to input LI2 and to bit 1 of the control words.
This assignment cannot be modified.
The forward run command is active if the stop command is at 1 and on a rising edge (0 V 1):
• Of input LI2, if the terminals are active
• Of bit 1 of the control word, if the network is active
Bits 2 to 15 of the control words can be assigned to drive functions.
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Forward Stop
bit 15 bit 14 bit 13 bit 12 bit 11 bit 10 bit 9 bit 8
Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable Configurable
In the case of a [3 wire] (3C) run on state command and I/O profile, fixed assignment of a function input is possible using the following
codes:
Fixed assignments
Bit
Drive terminals Logic I/O card
bit 0 Authorization to run (Stop)
bit 1 Forward
bit 2 LI3 --C102 C202 C302 C402
bit 3 LI4 --C103 C203 C303 C403
bit 4 LI5 --C104 C204 C304 C404
bit 5 LI6 --C105 C205 C305 C405
bit 6 - LI7 - C106 C206 C306 C406
bit 7 - LI8 - C107 C207 C307 C407
bit 8 - LI9 - C108 C208 C308 C408
bit 9 - LI10 - C109 C209 C309 C409
bit10 - - LI11 C110 C210 C310 C410
bit11 - - LI12 C111 C211 C311 C411
bit12 - - LI13 C112 C212 C312 C412
bit13 - - LI14 C113 C213 C313 C413
bit14---C114 C214 C314 C414
bit15---C115 C215 C315 C415
Extended
I/O card
Modbus CANopen Network card
"Controller Inside"
card
For example, to assign the operating direction command to bit 2 of CANopen, simply conf igure the [Reverse ass ign.] (rrS) parameter with
the value [C202] (C202).
1755861 11/2009 17
Page 17
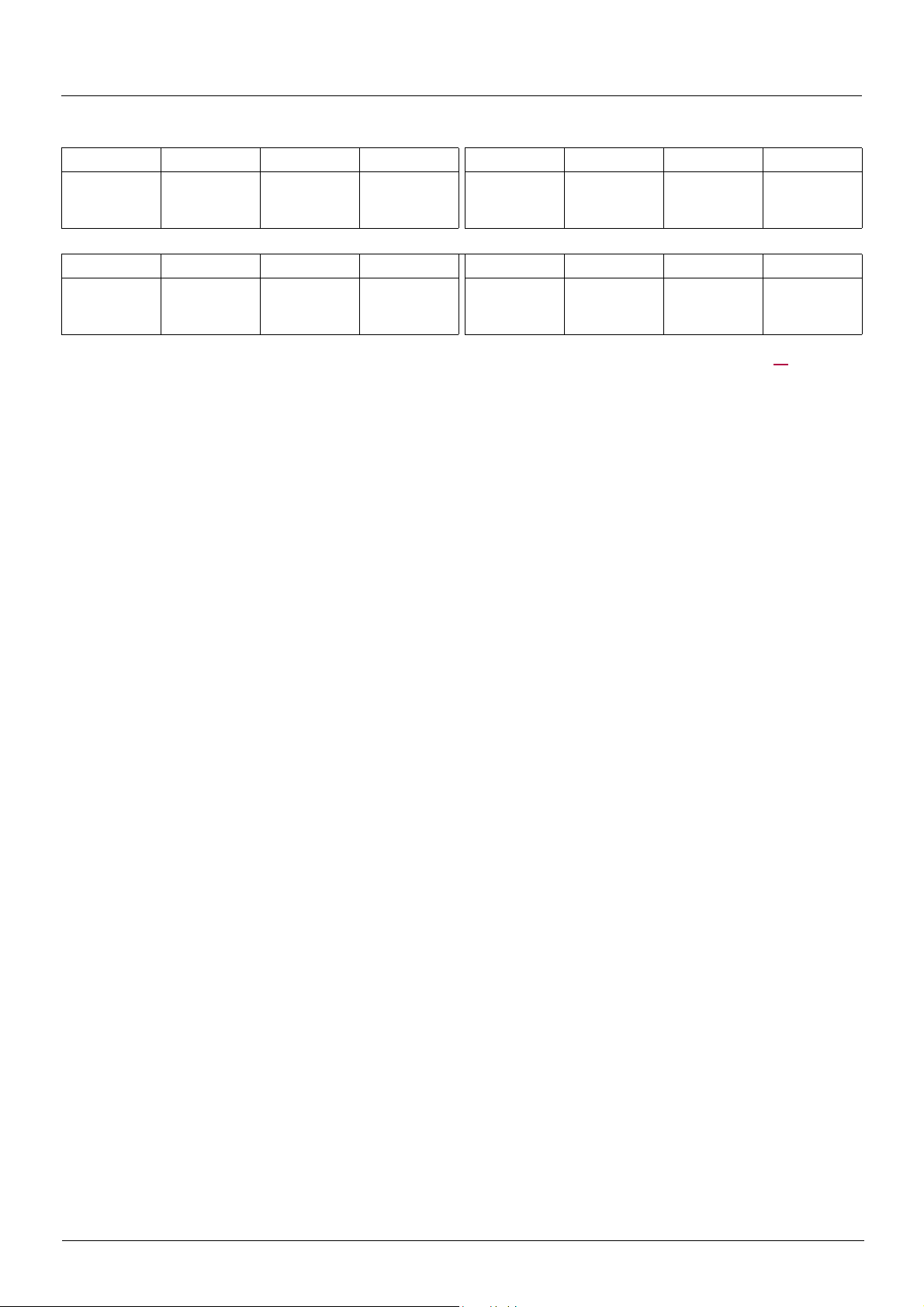
I/O profile
Status word (ETA)
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
Alarm
bit 15 bit 14 bit 13 bit 12 bit 11 bit 10 bit 9 bit 8
Direction of
rotation
The status word is identical in the I/O profile and the CiA402 profile. For more information, see section “CiA402 profile”, page21.
Reserved
(= 0 or 1)
Stop via STOP
key
Reserved (=1)
Reserved (=0) Reserved (=0)
Power section
line supply
present
Fault Running Ready
Reference
outside limits
Reference
reached
Command or
reference via
network
Reserved (=0)
Reserved
(= 0 or 1)
18 1755861 11/2009
Page 18
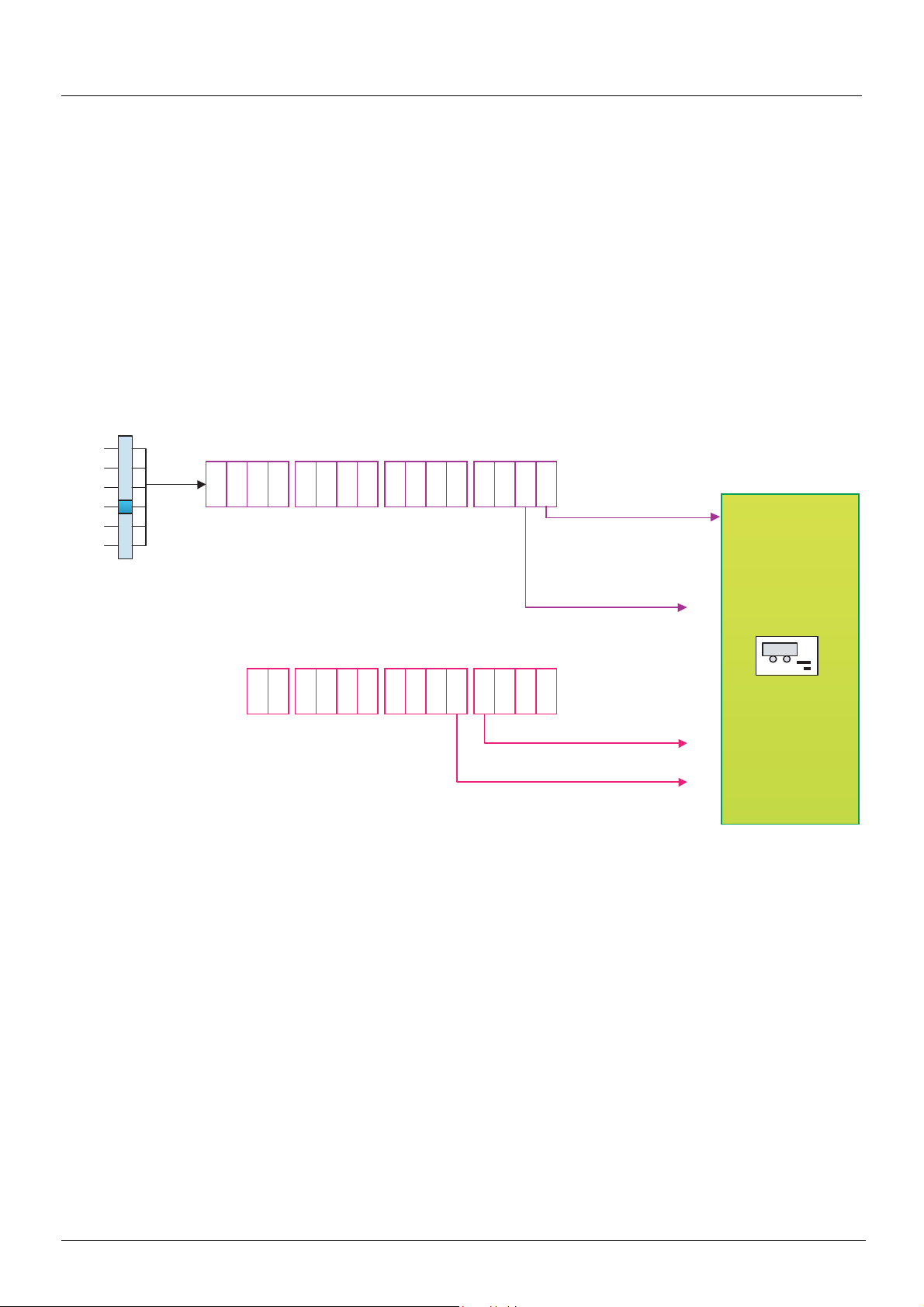
I/O profile
tEr
LCC
CAn
Mdb
nEt
APP
tEr
LCC
CAn
Mdb
nEt
APP
bit 9
bit 8
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
C201
LI4
LI6
LI5
LI8
LI10
LI9
LI8
LI7
LI6
LI5
LI4
LI3
LI2
LI1
LI12
LI11
bit 11
bit 10
bit 13
bit 12
bit 15
bit 14
LI14
LI13
CANopen control word
Terminals
Command channel 1
Cd1
Forward
Positioning
by sensors
Reverse
Disabling of sensors
Forward stop sensor
Reverse stop sensor
Forward slowdown sensor
Reverse slowdown sensor
Example: I/O profile with positioning by sensors function
Please refer to the [1.7 APPLICATION FUNCT.] (FUn-) section of the Programming Manual, under "Positioning by sensors".
In this example, a PLC is used to control the transfer of parts on a conveyor composed of transfer tables. Each table is controlled by a
variable speed drive. The PLC and the drives are connected via a CANopen network.
The PLC controls the operation of the installation via the CANopen bus.
The drive uses the stop sensor to inhibit transfer of the part if the next table is unavailable. In this case, the PLC enables the sensors.
If the next table is free, the drive transfers the part without stopping. In this case, the PLC disables the sensors.
The stop sensor is directly connected to the drive terminals.
The slowdown sensor, which is also directly connected (to the drive) enables a more precise st op.
Configuration schematic diagram:
1755861 11/2009 19
Page 19
I/O profile
Configure the following parameters:
Parameter Value Comment
Type of command On state (2 wire) The run command is obtained via bit 0 of the CANopen control
Profile I/O profile
Reference 1 configuration CANopen The reference comes from the CANopen card.
Command 1 configuration CANopen The command comes from the CANopen card.
Assignment of stop sensor Input LI4
Assignment of slowdown sensor Input LI5
Assignment of sensor disable command Bit 1 of CANopen control
word
Configuration via the remote graphic display terminal:
Menu Parameter Value
[1.5 INPUTS / OUTPUTS CFG] (I-O-) [2/3 wire control] (tCC ) [2 wire] (2C)
[1.6 - COMMAND] (CtL-) [Profile] (CHCF) [I/O profile] (IO)
[Ref. 1 channel] (Fr1) [CANopen] (CAn)
[Cmd channel 1] (Cd1) [CANopen] (CAn)
[1.7 APPLICATION FUNCT.] (FUn-)
[POSITIONING BY SENSORS] (LPO-)
[Stop FW limit sw.] (SAF) [LI4] (LI4)
[Slowdown forward] (dAF) [LI5] (LI5)
[Disable limit sw.] (CLS) [C201] (C201)
word.
Note: On a [2 wire] (2C) state command, the forward command is automatically assigned to bit 0 of the CANopen control word.
20 1755861 11/2009
Page 20
CiA402 profile
Controlword
(6040)
Statusword
(6041)
Statemachine
M
3
vl_target_velocity
(6042)
vl_velocity_demand
(6043)
Limit Ramp
Power device
vl_velocity_acceleration (6048)
vl_velocity_acceleration (6049)
vl_velocity_min_max amount (6046)
vl_control_effort
(6044)
Control word
(CMD)
Status word
(ETA)
State machine
M
3
Speed reference
(LFRD)
Speed reference
after ramp
(FRHD)
Reference limit Ramp
Power
module
Acceleration delta speed (SPAL)
Acceleration delta time (SPAT)
Deceleration delta speed (SPDL)
Deceleration delta time (SPDT)
Velocity min amount (SMIL)
Velocity max amount (SMAL)
Output speed
(RFRD)
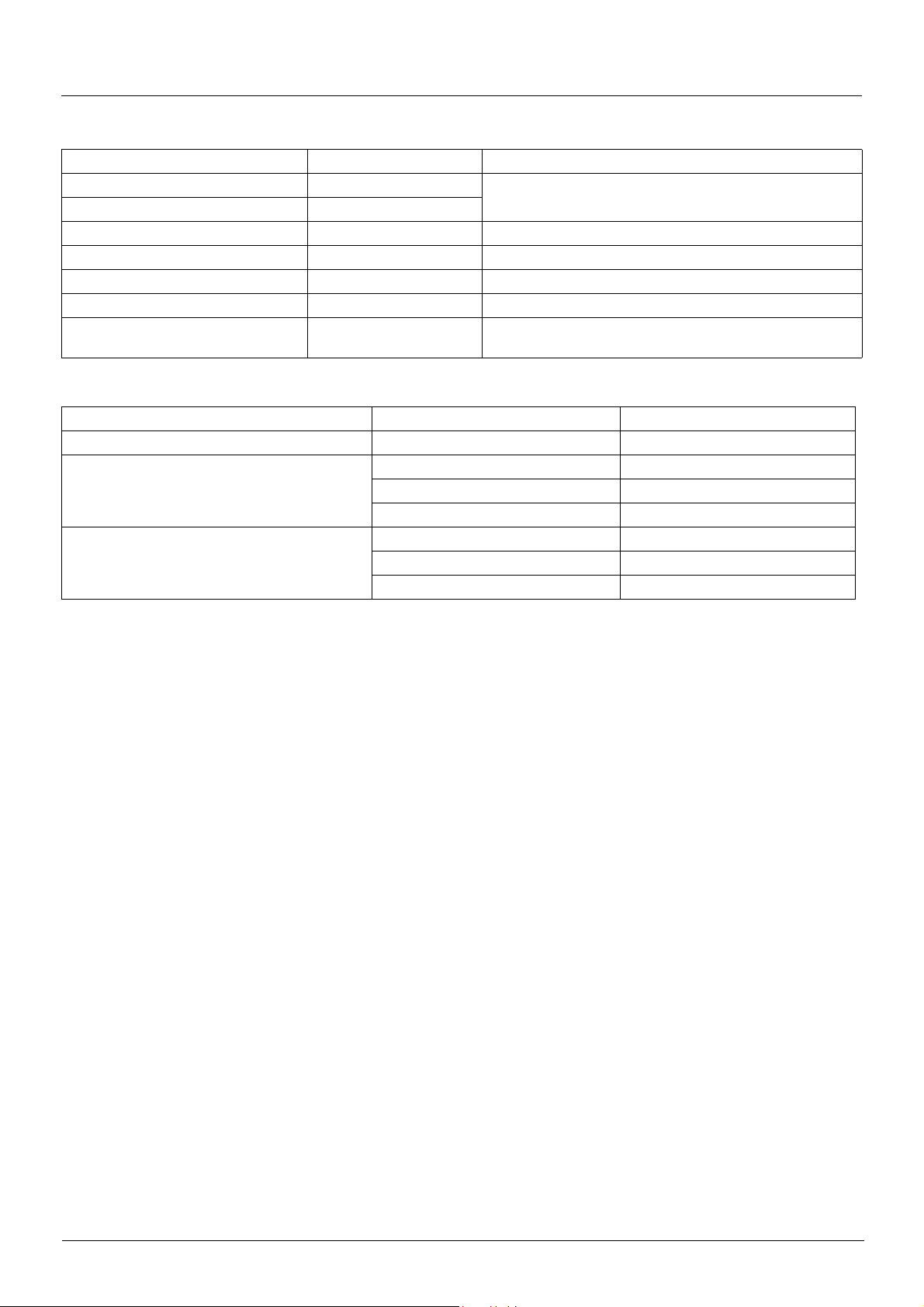
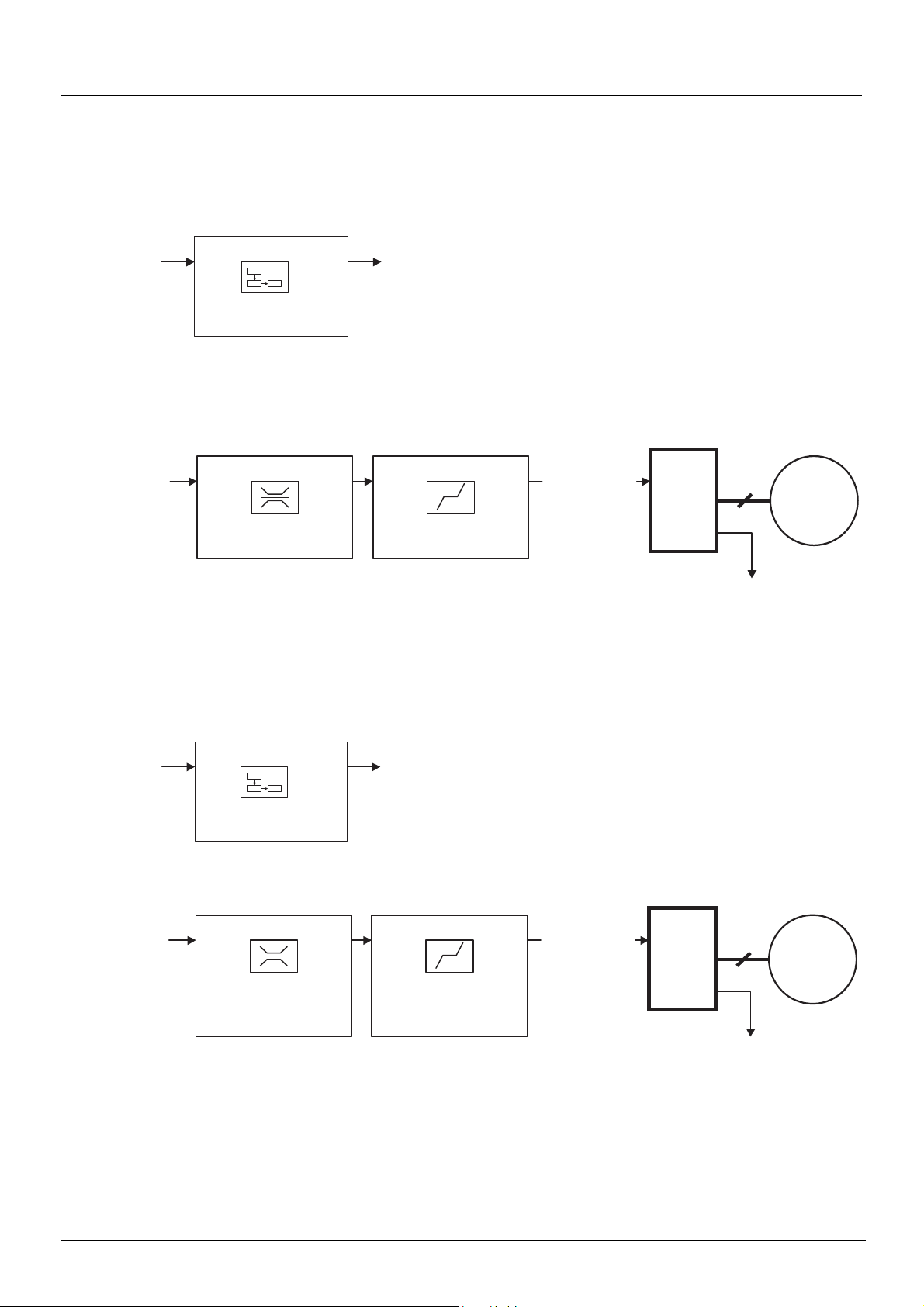
Functional description
b Drive operation involves two main functions, which are illustrated in the two diagrams below (the values in brackets are the CANopen
addresses of the parameters):
• Control diagram:
• Simplified diagram of speed control in "Velocity" mode:
b The main parameters are shown with their CiA402 name and their CiA402/Drivecom index (the values in brackets are the parameter
codes).
These diagrams translate as follows for the Altivar system:
• Control diagram:
• Simplified diagram of speed regulation in "Velocity" mode:
1755861 11/2009 21
Page 21
CiA402 profile
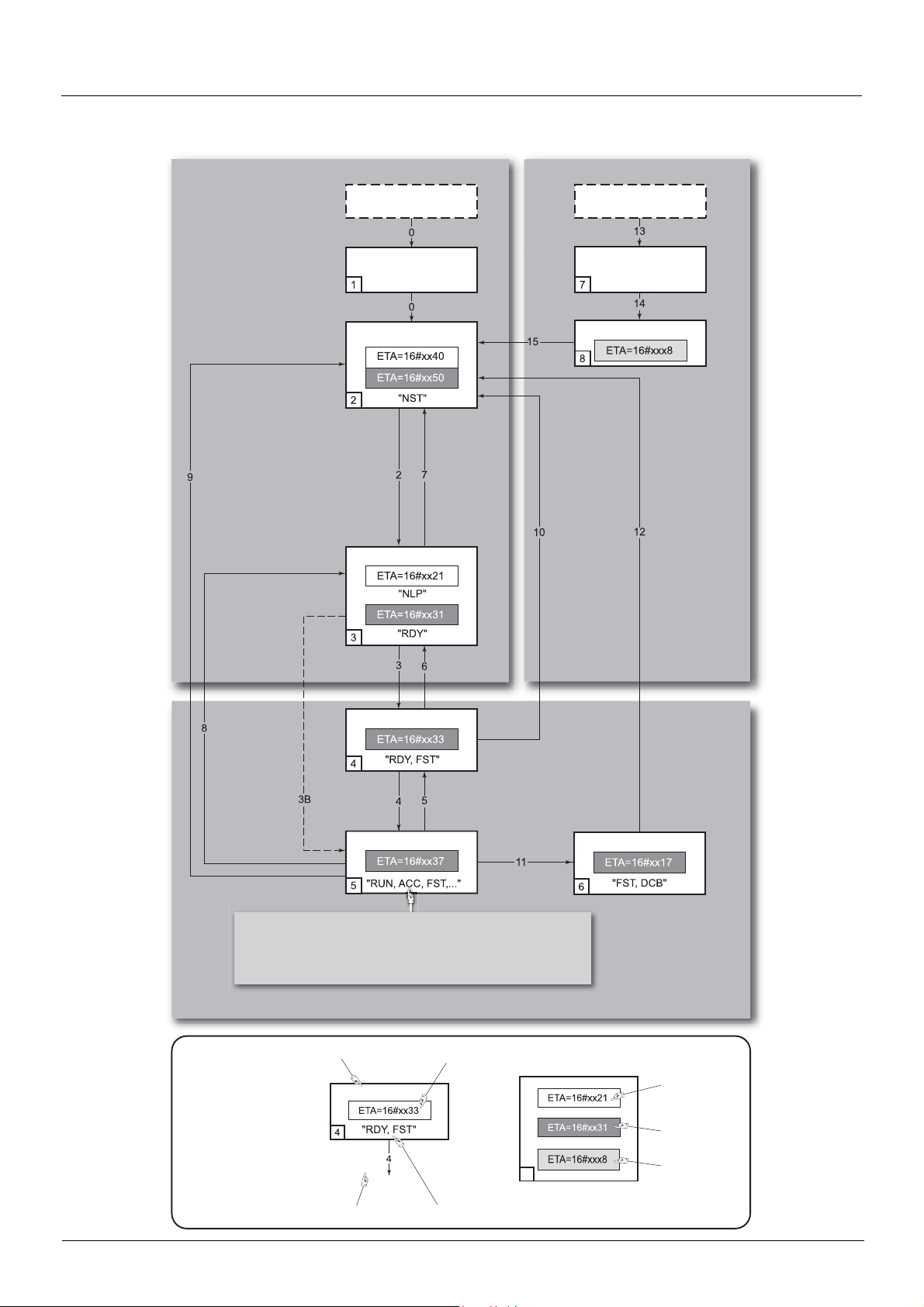
Fault
Power section line supply present or absent
Power section line supply present
Transition condition
with example of command
Value of
status word
Power
absent
Power
present
Status display on
graphic display terminal
State
Key:
Examples:
ETA=16#0637: Stop or forward, speed reached
ETA=16#8637: Stop or reverse, speed reached
ETA=16#0237: For w ar d, acce le ra ti ng or dece le r ati n g
ETA=16#8237: Reverse, accelerating or decelerating
Enable
operation
CMD=16#xxxF
Switched on
Ready to switch on
or
Switched on
Operation enabled
Power absent
or present
Enable
operation
CMD=16#xxxF
Disable
operation
CMD=16#0007
or
fast stop
Quick stop
CMD=16#0002
Quick stop active
Switch on
CMD=16#xxxF
Shutdown
CMD=16#0006
Switch on
CMD=16#0007
Shutdown
CMD=16#0006
Disable
voltage
CMD=16#0000
or
Quick stop
CMD=16#0002
or
STOP key
or
freewheel stop
at the terminals
or
modification
of a configuration
parameter
If Quick stop option code
= 2:
transition after stop.
If Quick stop option code
= 6:
Disable voltage
CMD=16#0000
or
STOP key
or
freewheel stop at
terminals
Disable
voltage
CMD=16#0000
or
Quick stop
CMD=16#0002
or
STOP key
Shutdown
CMD=16#0006
Disable voltage
CMD=16#0000
or
STOP key
or
freewheel stop at
the terminals
or
Power Removal
or
Switch on disabled
Fault disappeared
and faults reset
CMD=16#0080
Not ready to switch on
Entry into
state chart
Fault reaction active
From all states
Fault
Fault
CiA402 state chart
22 1755861 11/2009
Page 22

CiA402 profile
Description of states
Each state represents an internal reaction by the drive.
This chart will change depending on whether the control word is sent (CMD) or an event occurs (a fault, for example).
The drive state can be identified by the value of the status word (ETA).
1 - Not ready to switch on
Initialization starts. This is a transient state invisible to the communication network.
2 - Switch on disabled
The drive is inactive.
The drive is locked, no power is supplied to the motor.
For a separate control section, it is not necessary to supply AC power to the power section.
For a separate control section with line contactor, the contac tor is not controlled.
The configuration and adjustment parameters can be modified.
3 - Ready to switch on
Awaiting power section line supply.
For a separate control section, it is not ne cessa ry to s uppl y AC power to the p ower sec tion, b ut the sy ste m wil l expe ct it i n o rder to chan ge
to state "4 - Switched on".
For a separate control section with line contactor, the contac tor is not controlled.
The drive is locked, no power is supplied to the motor.
The configuration and adjustment parameters can be modified.
4 - Switched on
The drive is supplied with AC power but is stationary.
For a separate control section, the power section line supply must be present.
For a separate control section with line contactor, the contac tor is controlled.
The drive is locked, no power is supplied to the motor.
The power stage of the drive is ready to operate, but voltage has not yet been applied to the output.
The adjustment parameters can be modified.
Modification of a configuration parameter returns the drive to state "2- Switch on disabled".
5 - Operation enabled
The drive is running.
For a separate control section, the power section line supply must be present.
For a separate control section with line contactor, the contac tor is controlled.
The drive is unlocked, power is supplied to the motor.
The drive functions are activated and voltage is applied to the motor terminals.
However, in the case of an open-loop drive, if the reference is zero or the "Halt" command i s applied, no power is suppli ed to the motor and
no torque is applied.
Auto-tuning (tUn) requires an injection of current into the motor. The drive must therefore be in state "5 - Operation enabled" for this
command.
The adjustment parameters can be modified.
The configuration parameters cannot be modified.
Note: The command "4 - Enable operation" must be taken into consideration only if the channel is valid (see Communication monitoring
page 56
reference has been received for the first time.
The reaction of the drive to a "Disable operation" command depends on the value of the "Disable operation opti on code" (DOTD) parameter:
• If the "Disable operation option code" parameter has the value 0, the drive ch anges to "4 - Switche d on" and s tops i n free wheel st op.
• If the "Disable operation option code" parameter has the value 1, the drive stops on ramp and then changes to "4 - Switched on".
1755861 11/2009 23
). In particular, if the channel is involved in the command and the reference, transition 4 will take place only after the
Page 23
CiA402 profile
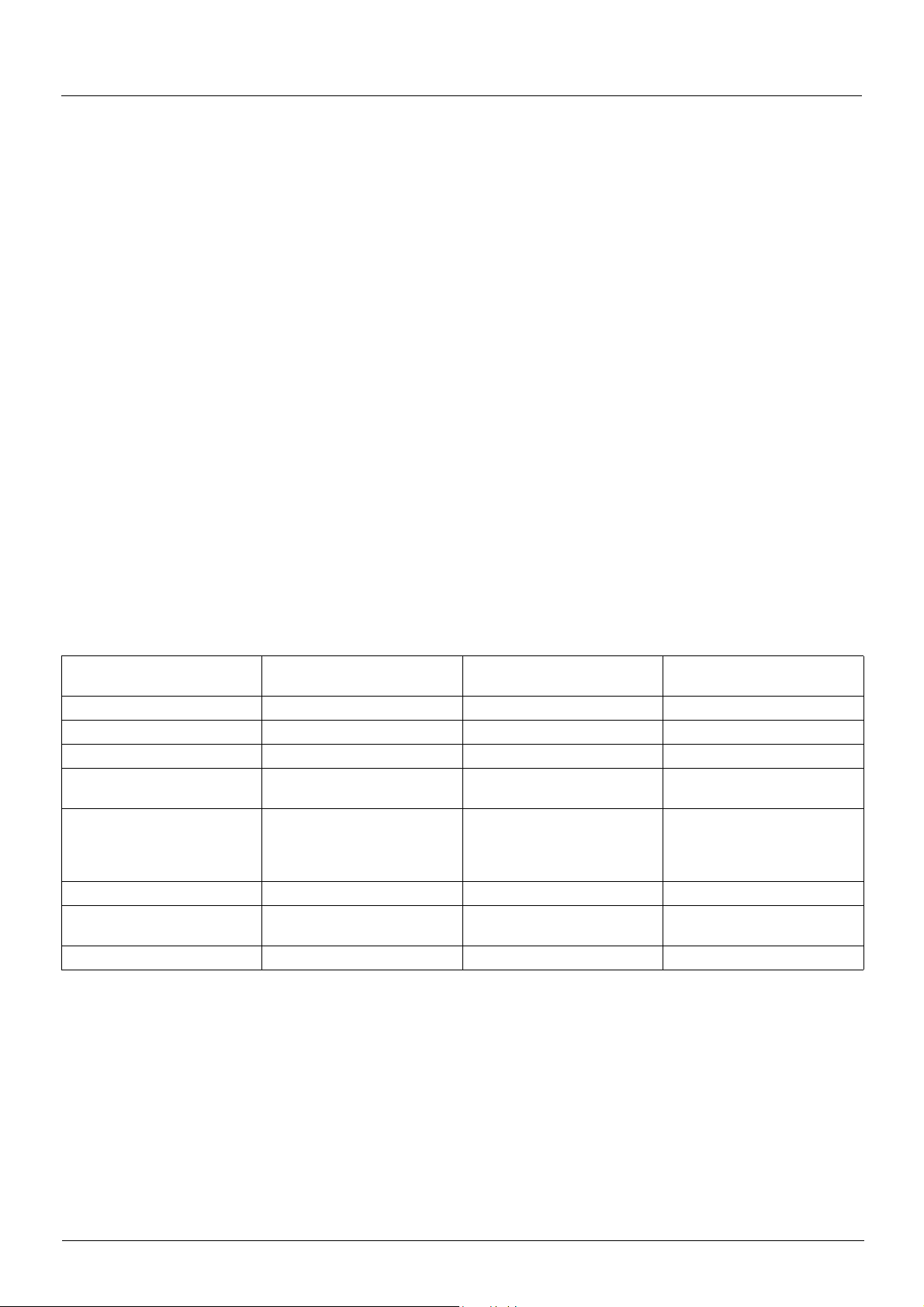
6 - Quick stop active
Emergency stop
The drive performs a fast stop, after which restarting will only be possible once the drive has changed to the "Switch on disabled" state.
During fast stop, the drive is unlocked and power is supplied to the motor.
The configuration parameters cannot be modified.
The condition for transition 12 to state "2 - Switch on disabled" depends on the value of the parameter "Quick stop option code" (QSTD):
• If the "Quick stop option code" parameter has the value 2, the drive stops according t o the fast st op ramp and then chang es to s tate
"2 - Switch on disabled".
• If the "Quick stop option code" parameter has the value 6, the drive stops according to the fast stop ramp and then remains in state
"6 - Quick stop active" until:
- A "Disable voltage" command is received
- Or the STOP key is pressed
- Or there is a freewheel stop command via the terminals
7 - Fault reaction active
Transient state during which the drive performs an action appropriate to the type of fault.
The drive function is activated or deactivated according t o the type of reaction configured in the fault management parameters.
8 - Fault
Drive faulty.
The drive is locked, no power is supplied to the motor.
Summary
State
1 - Not ready to switch on Not required No Yes
2 - Switch on disabled Not required No Yes
3 - Ready to switch on Not required No Yes
4 - Switched on Required No
5 - Operation enabled Required
6 - Quick stop active Required Yes, during fast stop No
7 - Fault reaction active
8 - Fault Not required No Yes
Power section line supply for
separate control section
Depends on fault management
configuration
Power supplied to motor
Yes, apart from an open-loop
drive with a zero reference or in
the event of a "Halt" command
for an open-loop drive.
Depends on fault management
configuration
Modification of configuration
Yes, return to "2 - Switch on
disabled" state
parameters
No
-
24 1755861 11/2009
Page 24
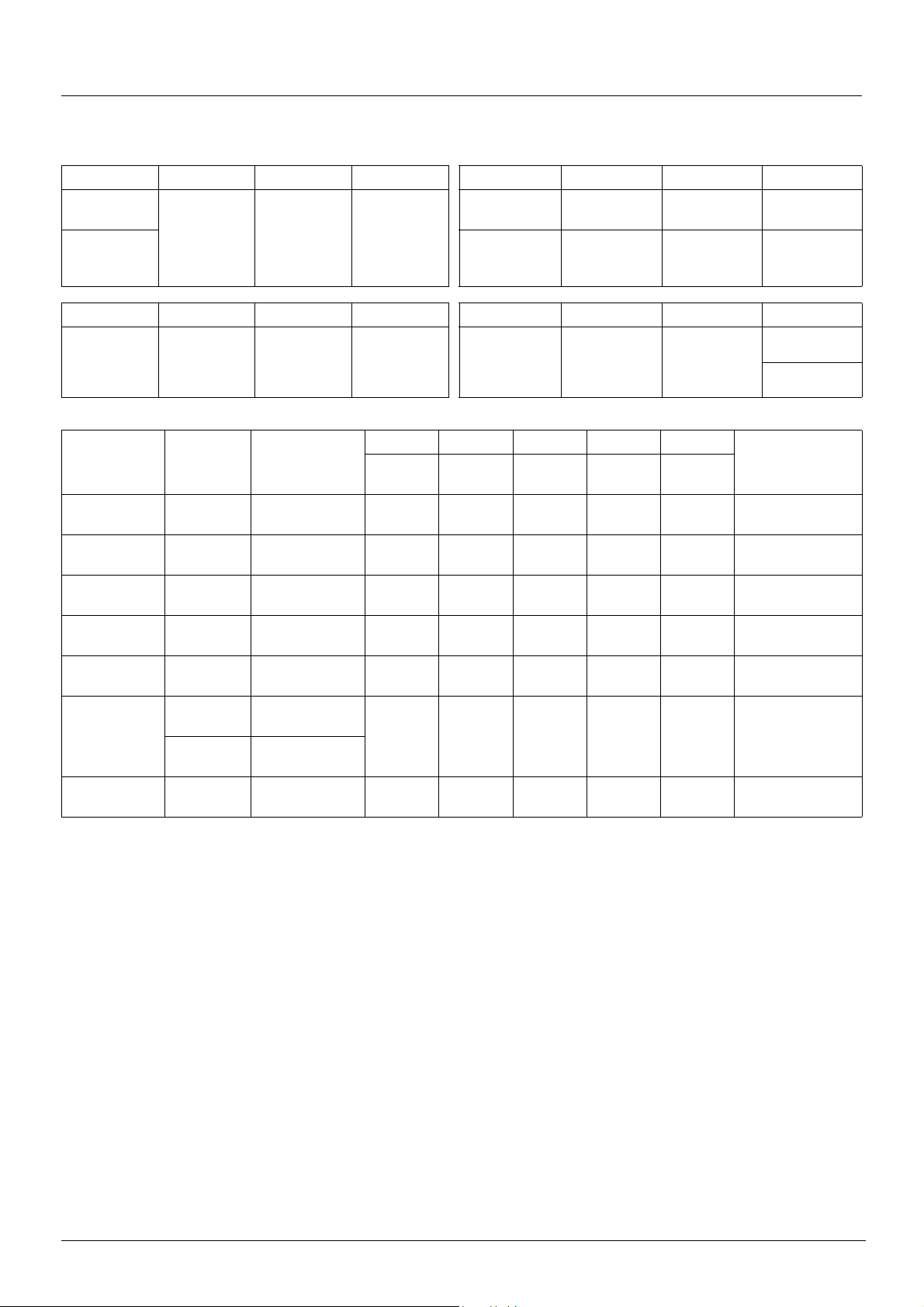
CiA402 profile
Control word (CMD)
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
Fault reset
Enable operation
Quick stop Enable voltage
Switch on
Reserved (=0) Reserved (=0) Reserved (=0)
Ack. fault
Assignable Assignable Assignable Assignable
Command
Shutdown 2, 6, 8
Switch on 3 4 - Switched on x x 1 1 1 16#0007
operation
operation
Disable voltage 7, 9, 10, 12
Quick stop
Fault reset 15
bit 15 bit 14 bit 13 bit 12 bit 11 bit 10 bit 9 bit 8
bit7 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Fault
reset
x x 1 1 0 16#0006
x 1 1 1 1 16#000F
x x x 0 x 16#0000
x x 0 1 x 16#0002
0 V 1 x x x x 16#0080
Enable
Disable
Transition
address
4
5 4 - Switched on x 0 1 1 1 16#0007
11
7, 10
Final state
3 - Ready to
switch on
5 - Operation
enabled
2-Switch on
disabled
6 - Quick stop
active
2-Switch on
disabled
2-Switch on
disabled
Run command
By default,
direction of
rotation
command.
Enable
operation
Quick
Emergency
stop
Reserved (=0) Reserved (=0)
Enable
stop
voltage
Authorization
to supply AC
power
Switch on
Example value
Contactor
control
Halt
Halt
x: Value is of no significance for this command.
0 V 1: Command on rising edge.
1755861 11/2009 25
Page 25
CiA402 profile
Stop commands:
The "Halt" command enables movement to be int errupted wi t hout ha vin g t o leave t he "5 - Operat ion ena bl ed" stat e. The st op is performed
in accordance with the [Type of stop] (Stt) parameter.
In the case of an open-loop drive, if the "Halt" command is active, no power is supplied to the motor and no torque is applied.
In the case of a closed-loop drive, if the "Halt" command is active , power c ontinues t o be supplie d to the motor and t orque is appl ied during
stopping.
Regardless of the assignment of the [Type of stop] (Stt) parameter ([Fast stop] (FSt), [Ramp stop] (rMP), [Freewheel] (nSt), or [DC
injection] (dCI)), the drive remains in the "5 - Operation enabled" state.
A Fast Stop command at the terminals or using a bit of the control word assigned to Fast Stop causes a change to the "4 - Switched on"
state. A "Halt" command does not cause this transition.
A Freewheel Stop command at the terminals or using a bit of the control word assigned to Freewheel Stop causes a change to the "2 Switch on disabled" state.
WARNING
RISK OF EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
When the braking loop is configured, it is necessary to use the "Halt" command (bit 8 of CMD command word) to stop.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury or equipment damage.
Assigning control word bits
In the CiA402 profile, fixed assignment of a function input is po ssible using the following codes:
Bit Integrated Modbus CANopen Network card "Controller Inside" card
bit 11 C111 C211 C311 C411
bit 12 C112 C212 C312 C412
bit 13 C113 C213 C313 C413
bit 14 C114 C214 C314 C414
bit 15 C115 C215 C315 C415
For example, to assign the DC injection braking to bit 13 of CANopen, simply configure the [DC injection assign.] (dCI) parameter with
the [C213] (C213) value.
Bit 11 is assigned by default to the operating direction command [Reverse assign.] (rrS).
26 1755861 11/2009
Page 26
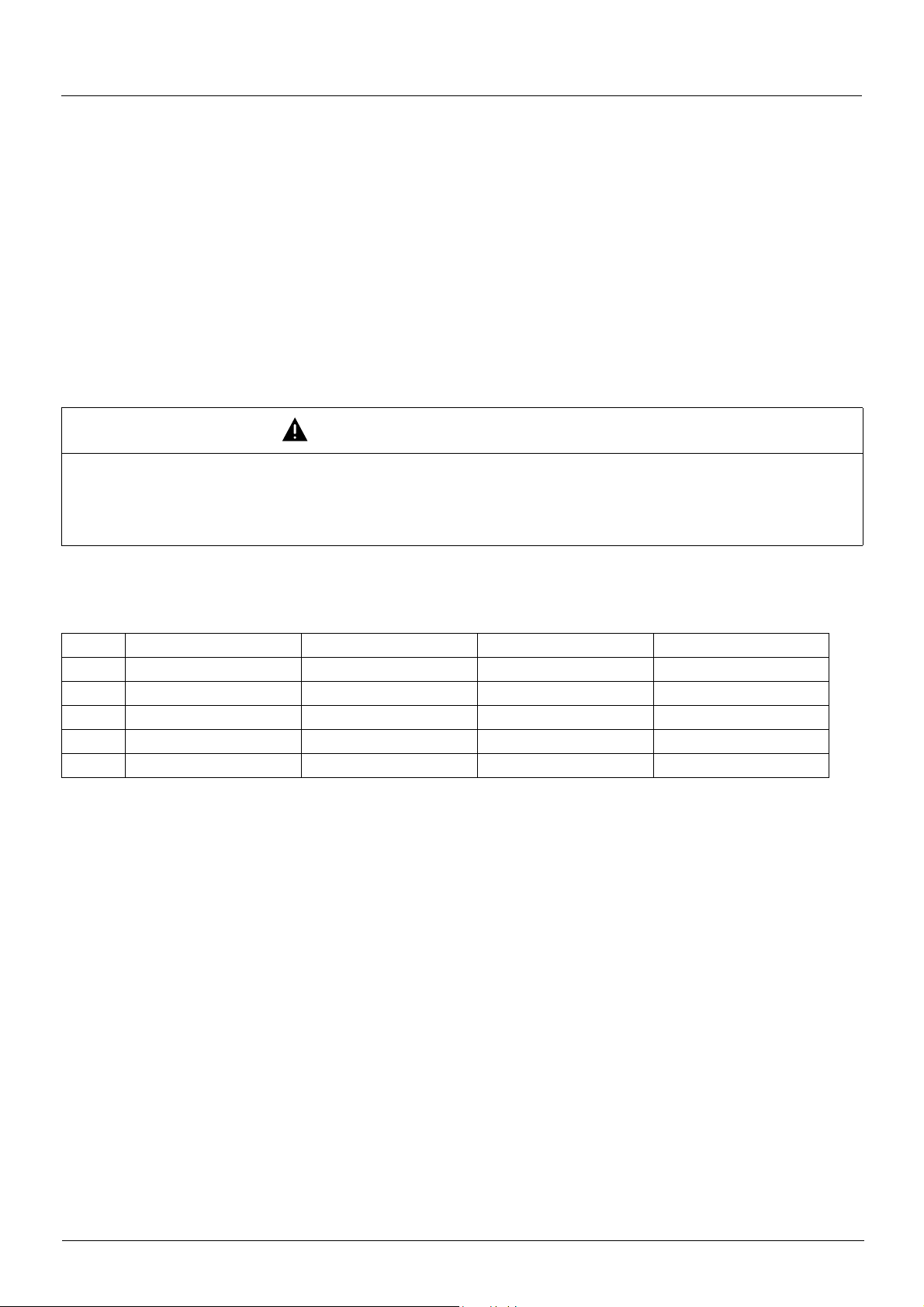
CiA402 profile
Status word (ETA)
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
Warning
Alarm
bit 15 bit 14 bit 13 bit 12 bit 11 bit 10 bit 9 bit 8
Direction of
rotation
Switch on
disabled
Power section
line supply
disabled
Stop via
STOP key
Quick stop
Emergency
stop
Reserved (=0) Reserved (=0)
Voltage
enabled
Power section
line supply
present
Fault
Fault
Internal limit
active
Reference
outside limits
Operation
enabled
Running Ready
Target
reached
Reference
reached
Switched on
Remote
Command or
reference via
network
Ready to
switch on
Awaiting
power section
line supply
Reserved (=0)
bit6 bit5 bit4 bit3 bit2 bit1 bit0
Status
1-Not ready to
switch on
2 -Swi tch on
disabled
3 -Ready to
switch on
4 -Switched on 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 16#0023
5 -Operation
enabled
6 -Qui ck stop
active
7 - Fault reaction
active
8-Fault 0xx1000
x: In this state, the value of the bit can be 0 or 1.
(1)
This mask can be used by the PLC program to test the chart state.
Switch on
disabled
0xx0000 -
1 x x 0 0 0 0 16#0040
0 1 x 0 0 0 1 16#0021
0 1 1 0 1 1 1 16#0027
0 0 1 0 1 1 1 16#0007
0xx1111 -
Quick
stop
Voltage
enabled
Fault
Operation
enabled
Switched onReady to
switch on
ETA
masked by
16#006F
16#0008
or 16#0028
(1)
(2)
(2)
Fault following state "6 - Quick stop active".
1755861 11/2009 27
Page 27
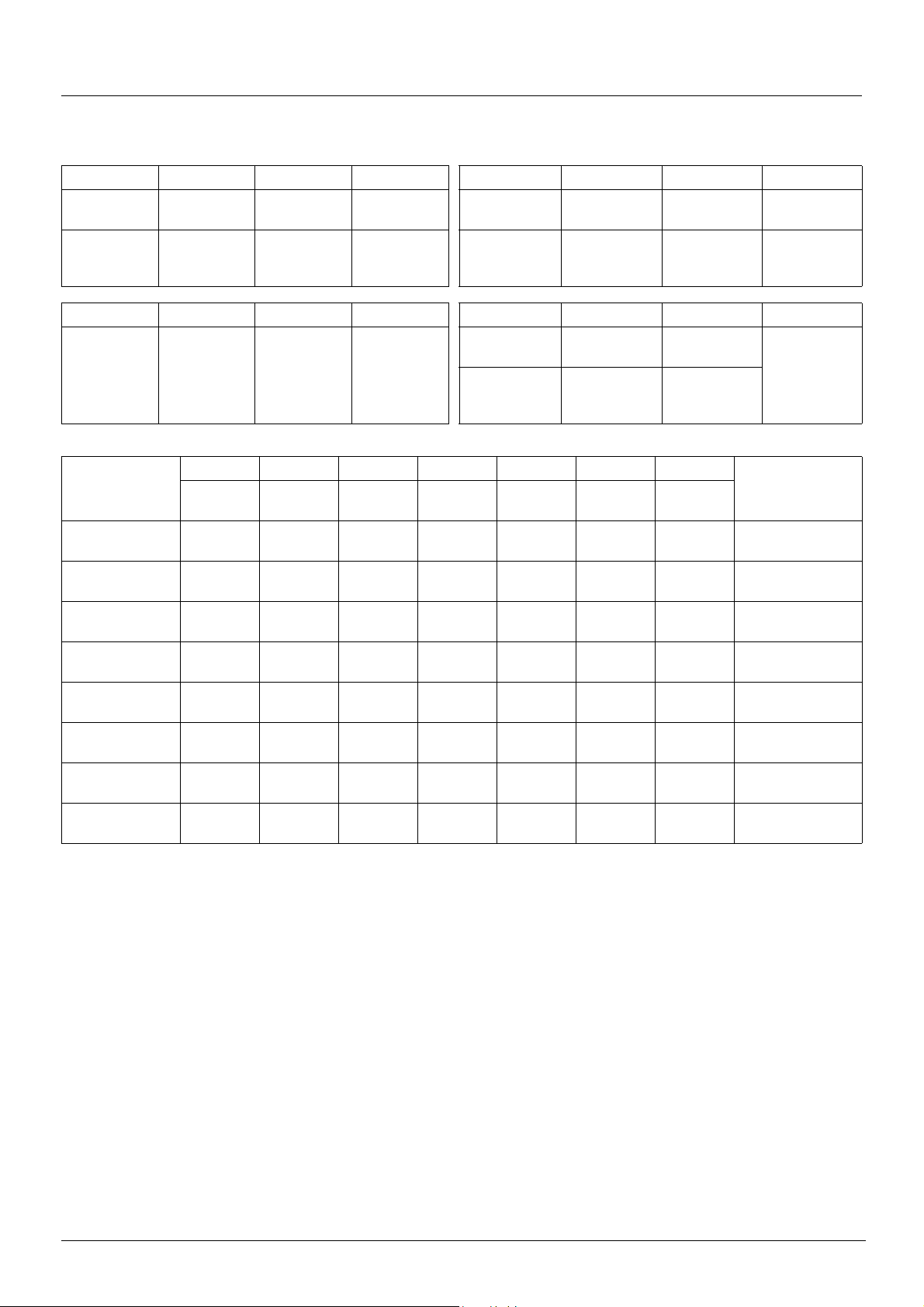
CiA402 profile
M MM M
Power section
line supply
Power section
line supply
Control section
power supply
Direct
Not separate
(1)
Direct
Separate
Line contactor
controlled by the drive
Separate
DRIVE DRIVE DRIVE
Power section
line supply
Power section
line supply
Control section
power supply
Control section
power supply
Starting sequence
The command sequence in the state chart depends on how power is being supplied to the drive.
There are three possible s cen a r io s :
(1)
The power section supplies the control section.
28 1755861 11/2009
Page 28
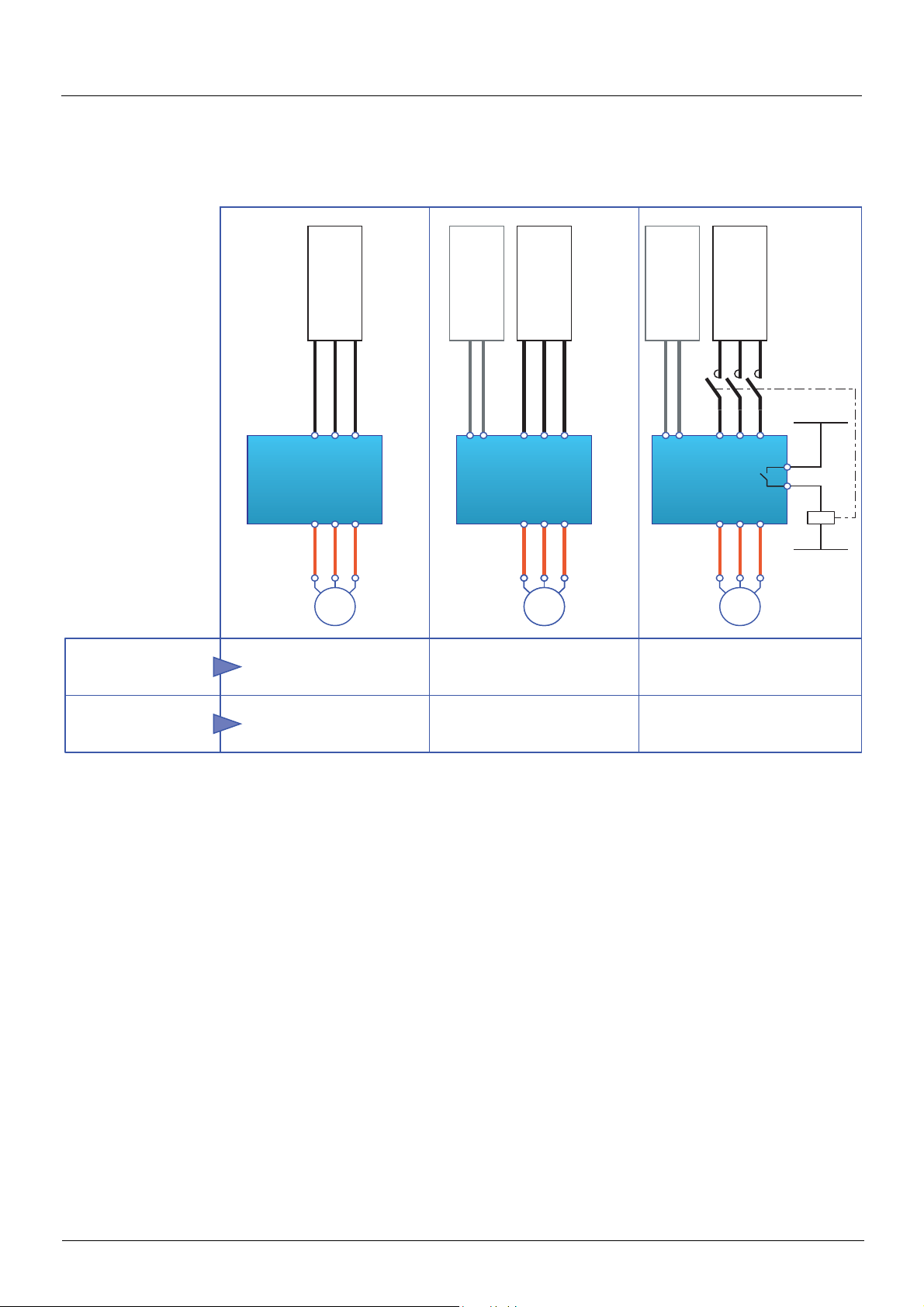
CiA402 profile
M
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
11
9
8
12
10
15
14
13
0
1
2
3
4
5 6
8
7
Power section
line supply
Bus or network
DRIVE
Not ready to
switch on
Entry into state chart
Switch on
disabled
Ready to
switch on
Switched on
Operation
enabled
Quick stop
active
Fault
Fault reaction
active
From all states
Shutdown
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Shutdown
Disable
operation
Disable
voltage
Enable
operation
Shutdown
Switch on
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Quick stop
Sequence for a drive powered by the power section line supply
Both the power and control sections are powered by the power section line supply.
If power is supplied to the control section, it has to be supplied to the power section as well.
The following sequence must be applied:
b Step 1
• Send the "2 - Shutdown" command
1755861 11/2009 29
Page 29
CiA402 profile
M
2
3
5
6
7
1
11
9
8
12
10
15
14
13
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
7
4
Not ready to
switch on
Entry into state chart
Switch on
disabled
Ready to
switch on
Switched on
Operation
enabled
Quick stop
active
Fault
Fault reaction
active
From all states
Switch on
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Shutdown
Disable
operation
Disable
voltage
Enable
operation
Shutdown
Switch on
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Quick stop
Power section
line supply
Bus or network
DRIVE
b Step 2
• Check that the drive is in the "3 - Ready to switch on" state.
• Then send the "4 - Enable operation" command.
• The motor can be controlled (send a reference not equal to zero).
Note: It is possible, but not necessary, to send the "3 - Switch on" command followed by the "4 - Enable Operation" command to switch
successively into the states "3 - Ready to Switch on", "4 - Switched on" and then "5 - Operation Enabled".
The "4 - Enable operation" command is sufficient.
30 1755861 11/2009
Page 30
CiA402 profile
M
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
11
9
8
12
10
15
14
13
0
1
2
3
4
5 6
8
7
Power section
line supply
Bus or network
DRIVE
Control section
power supply
Not ready to
switch on
Entry into state chart
Switch on
disabled
Ready to
switch on
Switched on
Operation
enabled
Quick stop
active
Fault
Fault reaction
active
Shutdown
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Shutdown
Disable
operation
Disable
voltage
Enable
operation
Shutdown
Switch on
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Quick stop
From all states
Sequence for a drive with separate control section
Power is supplied separately to the power and control sections.
If power is supplied to the control section, it does not have to be supplied to the power section as well.
The following sequence must be applied:
b Step 1
• The power section line supply is not necessarily present.
• Send the "2 - Shutdown" command
1755861 11/2009 31
Page 31

CiA402 profile
M
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
11
9
8
12
10
15
14
13
0
1
2
3
4
5 6
8
7
Power section
line supply
Bus or network
DRIVE
Control section
power supply
Not ready to
switch on
Entry into state chart
Switch on
disabled
Ready to
switch on
Switched on
Operation
enabled
Quick stop
active
Fault
Fault reaction
active
From all states
Shutdown Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Shutdown
Disable
operation
Disable
voltage
Enable
operation
Shutdown
Switch on
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Quick stop
b Step 2
• Check that the drive is in the "3 - Ready to switch on" state.
• Check that the power section line supply is present ("Voltage enabled" of the status word).
Power section line supply Terminal display Status word
Absent nLP 16#pp21
Present rdY 16#pp31
• Send the "3 - Switch on" command
32 1755861 11/2009
Page 32

CiA402 profile
M
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
11
9
8
12
10
15
14
13
0
1
2
3
4
5 6
8
7
Power section
line supply
Bus or network
DRIVE
Control section
power supply
Not ready to
switch on
Entry into state chart
Switch on
disabled
Ready to
switch on
Switched on
Operation
enabled
Quick stop
active
Fault
Fault reaction
active
From all states
Shutdown Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Shutdown
Disable
operation
Disable
voltage
Enable
operation
Shutdown
Switch on
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Quick stop
b Step 3
• Check that the drive is in the "4 - Switched on" state.
• Then send the "4 - Enable operation" command.
• The motor can be controlled (send a reference not equal to zero).
• If the power section line supply is still not pre sent in the "4 - Switched on" st ate after a t ime delay [Mains V. time out] (LCt), the drive
will switch to fault mode (LCF).
1755861 11/2009 33
Page 33

CiA402 profile
M
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
11
9
8
12
10
15
14
13
0
1
2
3
4
5 6
8
7
Power section
line supply
Bus or network
DRIVE
Control section
power supply
Not ready to
switch on
Entry into state chart
Switch on
disabled
Ready to
switch on
Switched on
Operation
enabled
Quick stop
active
Fault
Fault reaction
active
Shutdown
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Shutdown
Disable
operation
Disable
voltage
Enable
operation
Shutdown
Switch on
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Quick stop
From all states
Sequence for a drive with line contactor control
Power is supplied separately to the power and control sections.
If power is supplied to the control section, it does not have to be supplied to the power secti on as well. The drive controls the line contactor.
The following sequence must be applied:
b Step 1
• The power section line supply is not present as the line contactor is not being controlled.
• Send the "2 - Shutdown" command
34 1755861 11/2009
Page 34

CiA402 profile
M
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
11
9
8
12
10
15
14
13
0
1
2
3
4
5 6
8
7
Power section
line supply
Bus or network
DRIVE
Control section
power supply
Not ready to
switch on
Entry into state chart
Switch on
disabled
Ready to
switch on
Switched on
Operation
enabled
Quick stop
active
Fault
Fault reaction
active
From all states
Shutdown
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Shutdown
Disable
operation
Disable
voltage
Enable
operation
Shutdown
Switch on
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Quick stop
b Step 2
• Check that the drive is in the "3 - Ready to switch on" state.
• Send the "3 - Switch on" command, which will close the line contactor and switch on the power section line supply.
1755861 11/2009 35
Page 35

CiA402 profile
M
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
11
9
8
12
10
15
14
13
0
1
2
3
4
5 6
8
7
Power section
ine supply
Bus or network
DRIVE
Control section
power supply
Not ready to
switch on
Entry into state chart
Switch on
disabled
Ready to
switch on
Switched on
Operation
enabled
Quick stop
active
Fault
Fault reaction
active
From all states
Shutdown
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Shutdown
Disable
operation
Disable
voltage
Enable
operation
Shutdown
Switch on
Disable voltage
or Quick stop
Quick stop
b Step 3
• Check that the drive is in the "4 - Switched on" state.
• Then send the "4 - Enable operation" command.
• The motor can be controlled (send a reference not equal to zero).
• If the power section line supply is still not pre sent in the "4 - Switched on" st ate after a t ime delay [Mains V. time out] (LCt), the drive
will switch to fault mode (LCF).
36 1755861 11/2009
Page 36

Command/reference switching
Channels
A channel is the name given to the source of a command or reference.
The 6 Altivar 71 channels are:
• The terminals
• The graphic display terminal
• The integrated Modbus ports
• The integrated CANopen port
• A network card
• The "Controller Inside" card
The Altivar 71 has 2 integrated Modbus ports. These 2 ports are physicall y independent of one an other but together constitut e a single logic
channel.
The drive does not distinguish between commands and references that come from the Modb us network port and tho se that come from the
Modbus HMI port.
With the Altivar 71 drive, it is possible to select the active command channel and the active reference channel:
• Via configuration
• Via switching at the terminals or via a communication network
Channel commands and references
All the drive’s command and reference parameters are managed on a channel-by-channel basis.
Only the control word (CMd), speed reference (LFrd) and frequency reference (LFr) are switched.
It is possible to identify the last value written for each channel and each command or reference parameter:
Parameter name Parameter code
Taken into
account by the
drive
Control word CMd CMd1 CMd2 CMd3 CMd4
Extended control word CMI CMI1 CMI2 CMI3 CMI4
Speed setpoint (rpm) LFrd LFd1 LFd2 LFd3 LFd4
Frequency setpoint (0.1 Hz) LFr LFr1 LFr2 LFr3 LFr4
Torque setpoint Ltr Ltr1 Ltr2 Ltr3 Ltr4
PID regulator setpoint PISP PIr1 PIr2 PIr3 PIr4
Multiplying coefficient MFr MFr1MFr2MFr3MFr4
Modbus CANopen
Communication
card
Controller
inside
1755861 11/2009 37
Page 37

Command/reference switching
-10V
+10V
TERMINALS
ReferenceCommand
Digital
reference
TERMINALS
ReferenceCommand
CANopen
CANopen
Not separate mode
Command and reference come from the same channel.
In CiA402 profile, not separate mode is configured via the terminal:
Menu Parameter Value
[1.6 - COMMAND] (CtL-) [Profile] (CHCF) [Not separ.] (SIM)
Separate mode
Command and reference may come from different channels.
In CiA402 profile, separate mode is achieved via configuration with the terminal:
Menu Parameter Value
[1.6 - COMMAND] (CtL-) [Profile] (CHCF) [Separate] (SEP)
In I/O profile, the drive is automatically in separate mode.
Menu Parameter Value
[1.6 - COMMAND] (CtL-) [Profile] (CHCF) [I/O profile] (IO)
38 1755861 11/2009
Page 38

Command/reference switching
-10V
+10v
CANopen
CANopen
Control register
TERMINALS
ReferenceCommand
Digital reference
TERMINALS
ReferenceCommand
CANopen
CANopen
Digital reference
-10V
+10V
Switching in not separate mode
Switching takes place between 2 channels simultaneously for both reference and command.
In this example, the command and reference come either from CANopen or from the terminals.
Switching in separate mode
Switching can take place between 2 channels independently for the reference and command.
In this example, the command always comes from the terminals; the reference can come either from CANopen or from the terminals.
1755861 11/2009 39
Page 39

Command/reference switching
Channel switching
Reference channel configuration
Reference channel configuration enables reference sources to be predefined, which can be modified or switched subsequently via a
command.
There are 3 predefined reference channels:
• Reference channel 1
• Reference channel 1B
• Reference channel 2
Reference channels 1 and 1B are used for drive application functions.
Reference channel 2 is connected directly to the reference limiting function, bypassing the application functions.
The predefined reference channels are assigned via the [Ref. 1 channel] (Fr1), [Ref. 1B channel] (Fr1b) and [Ref. 2 channel] (Fr2)
configuration parameters, which can have the following values:
• [No] (nO): Not assigned
• [AI1] (AI1): Analog input AI1
• [AI2] (AI2): Analog input AI2
• [AI3] (AI3): Analog input AI3 (if extension card present)
• [AI4] (AI4): Analog input AI4 (if extension card inserted)
• [HMI] (LCC): Graphic display terminal
• [Modbus] (Mdb): Integrated Modbus
• [CANopen] (CAn): Integrated CANopen
• [Com. card] (nEt): Communication card (if inserted)
• [C.Insid. card] (APP): Controller Inside card (if inserted)
• [RP] (PI): Frequency input, (if card inserted)
• [Encoder] (PG): Encoder input (if card inserted)
Note: The "+speed/-speed" function is on reference channel 2. See the Programming Manual for more information.
Command channel configuration
Command channel configuration enables command sources to be predefined, which can be modified or switched subsequently via a
command.
There are 2 predefined command channels:
• Command channel 1
• Command channel 2
The predefined command channels are assigned via the [Cmd channel 1] (Cd1) and [Cmd channel 2] (Cd2) configuration parameters,
which can have the following values:
• [Terminals] (tEr): Terminals
• [HMI] (LCC): Graphic display terminal
• [Modbus] (Mdb): Integrated Modbus
• [CANopen] (CAn): Integrated CANopen
• [Com. card](nEt): Communication card (if inserted)
• [C.Insid. card] (APP): Controller Inside card (if inserted)
40 1755861 11/2009
Page 40

Command/reference switching
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
Switches
A channel switch is used to select predefined channels.
It can be:
• Defined via configuration
• Actuated either by an input (terminals) or a control word bit (network)
• Written via a network during operation (modification of a configuration parameter)
The possible switch values are:
Function reference
switching
[Ref 1B switching] (rCb)
Channel 1 Fr1 Fr1 Cd1
Channel 1B Fr1b
Channel 2 - Fr2 Cd2
Drive input LI1 ... LI6
Logic I/O card input LI7 ... LI10
Extended I/O card input LI11 ... LI14
Modbus command bit bit 0 = C100 ... bit 15 = C115
CANopen command bit bit 0 = C200 ... bit 15 = C215
Network command bit bit 0 = C300 ... bit 15 = C315
Controller Inside command bit bit 0 = C400 ... bit 15 = C415
The values Fr1, Fr1b, Fr2, Cd1 and Cd2 are either configured or written via the network during operation.
In I/O and CiA402 (separate mode) profiles, independent switching is possible:
Type Channel 1 Channel 2 Switching
Reference
Command
Function reference 1
[Ref. 1 channel] (Fr1)
Function reference 1 or 1B
[Ref. 1 channel] (Fr1)
[Ref. 1B channel] (Fr1b)
Command 1
[Cmd channel 1] (Cd1)
Function reference 1B
[Ref. 1B channel] (Fr1b)
Direct reference 2
[Ref. 2 channel] (Fr2)
Command 2
[Cmd channel 2] (Cd2)
Direct reference
switching
[Ref. 2 switching] (rFC)
--
Function reference switching
[Ref 1B switching] (rCb)
Direct reference switching
[Ref. 2 switching] (rFC)
Command switching
[Cmd switching] (CCS)
Command switching
[Cmd switching] (CCS)
In CiA402 profile (not separa t e m o de ) switching is simultaneous:
Type Channel 1 Channel 2 Switching
Function reference 1 or 1B
Reference
and
Command
1755861 11/2009 41
[Ref. 1 channel] (Fr1)
[Ref. 1B channel] (Fr1b)
Command 1
[Cmd channel 1] (Cd1)
Direct reference 2
[Ref. 2 channel] (Fr2)
Command 2
[Cmd channel 2] (Cd2)
Direct reference switching
[Ref. 2 switching] (rFC)
Page 41

Command/reference switching
rCb
rFC
Fr1
Fr2
LIpp
C1pp
C2pp
C3pp
C4pp
Fr1
Fr1b
LIpp
C1pp
C2pp
C3pp
C4pp
Fr1
CANopen
RØseau
AI1C
AI2C
LFr1
LFr2
LFr3
AI2
Modbus
AI1
TerminalLFr
Controller
LFr4
Fr1
AI1C
AI2C AI2
AI1
LFr
Fr1b
AI1C
AI2C
LFr1
LFr2
LFr3
AI1
AI2
LFr
LFr4
Fr2
AI1C
AI2C
LFr1
LFr2
LFr3
AI1
AI2
LFr
LFr4
Reference channel 1
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Reference channel 1B
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Reference channel 2
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Function
reference
switching
Application
function output
reference
Direct
reference 2
Direct reference
switching
Reference
limit
Ramp
Function
Reference switching principle
A detailed description is given in the Programming Manual.
This diagram shows reference switching as applicable to all the following modes:
• I/O profile
• CiA402 profile and separate mode
• CiA402 profile and not separate mode
42 1755861 11/2009
Page 42

Command/reference switching
CCS
Cd1
Cd2
LIpp
C1pp
C2pp
C3pp
C4pp
Cd1
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
CANopen
RØseau
LIx
CMD1
CMD2
CMD3
Terminal
Modbus
ControllerCMD4
Cd2
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
LIx
CMD1
CMD2
CMD3
Terminal
ControllerCMD4
Bornier
Command channel 1
Command
switching
Command channel 2
Run
Stop
Forward
Reverse
Terminals
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Terminals
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
rFC
Fr1
LIx
AI1
AI2
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
CMD1
CMD2
CMD3
CMD4
LIx
Fr2
LIx
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
CMD1
CMD2
CMD3
CMD4
Fr1
Fr2
LIpp
C111 ... C115
C211 ... C215
C311 ... C315
C411 ... C415
AI1
AI2
Reference channel 1
(1)
Direct
reference
switching
(1)
Reference channel 2
(1)
Run
Stop
Forward
Reverse
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Command switching principle
A detailed description is given in the Programming Manual.
I/O profile or CiA402 profile (separate mode)
CiA402 profile (not separate mode)
(1)In not separate mode, command switching follows reference switching. It is therefore reference switching that switches the command.
1755861 11/2009 43
Page 43

Command/reference switching
C201
Cd02
LI5
LI10
LI9
LI8
LI7
LI6
LI5
LI4
LI3
LI2
LI1
LI12
LI11
LI14
LI13
bit 9
bit 8
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 11
bit 10
bit 13
bit 12
bit 15
bit 14
LI2
A
C
B
CANopen control word
Terminals
Function
CANopen
Terminals
Command
switching
CCS
Assigning control word bits
I/O profile
The I/O profile is extremely flexible in terms of assigning and switching the 16 control word bits.
To switch a control word bit using:
• an input from the terminals
• or a control word bit from another communication channel
simply configure a switched assignment for the function input (CDpp), instead of a fixed assignment (Cppp).
Inputs and bits of the same order are switched.
Inputs LI1 to LI6 of the drive terminals can be used to switch control word bits 0 to 5.
With a logic I/O card using inputs LI7 to LI10, control word bits 6 to 9 can also be switc hed.
With an extended I/O card using inputs LI11 to LI14, control word bits 10 to 13 can al so be switched.
Once a bit has been assigned to a switchable assignment, it can no longer be assigned to a fixed assignment, and vice versa.
Example: Once a function input has been assigned to CD04, it can not be assigned to LI5, C104, C204, C304 or C404.
Example
Function input A is always controlled by bit 1 of the CANopen control word.
Function input B is always controlled by input LI5 on the terminals.
Depending on the value of LI2, function input C is controlled:
• Either by input LI3 on the terminals
• Or by bit 2 of the CANopen control word
44 1755861 11/2009
Page 44

Command/reference switching
The tables below show assignments on the basis of input or bit.
Run on state command [2 wire] (2C):
In all macro configurations, bit 1 is assigned by default to the operating direction command [Reverse assign.] (rrS).
Bit
bit 0 Forward
bit 1 Cd01 LI2 --C101 C201 C301 C401
bit 2 Cd02 LI3 --C102 C202 C302 C402
bit 3 Cd03 LI4 --C103 C203 C303 C403
bit 4 Cd04 LI5 --C104 C204 C304 C404
bit 5 Cd05 LI6 --C105 C205 C305 C405
bit 6 Cd06 - LI7 - C106 C206 C306 C406
bit 7 Cd07 - LI8 - C107 C207 C307 C407
bit 8 Cd08 - LI9 - C108 C208 C308 C408
bit 9 Cd09 - LI10 - C109 C209 C309 C409
bit10 Cd10 --LI11 C110 C210 C310 C410
bit11 Cd11 --LI12 C111 C211 C311 C411
bit12 Cd12 --LI13 C112 C212 C312 C412
bit13 Cd13 --LI14 C113 C213 C313 C413
bit14 Cd14 ---C114 C214 C314 C414
bit15 Cd15 ---
Switched
assignment
Drive
terminals
Logic I/O card
Extended
I/O card
Fixed assignments
Integrated
Modbus
C115 C215 C315 C415
CANopen Network card
"Controller
Inside" card
Run on edge command [3 wire] (3C):
In all macro configurations, bit 2 is assigned by default to the operating direction command [Reverse assign.] (rrS).
Bit
bit 0 Run authorization
bit 1 Forward
bit 2 Cd02 LI3 --C102 C202 C302 C402
bit 3 Cd03 LI4 --C103 C203 C303 C403
bit 4 Cd04 LI5 --C104 C204 C304 C404
bit 5 Cd05 LI6 --C105 C205 C305 C405
bit 6 Cd06 - LI7 - C106 C206 C306 C406
bit 7 Cd07 - LI8 - C107 C207 C307 C407
bit 8 Cd08 - LI9 - C108 C208 C308 C408
bit 9 Cd09 - LI10 - C109 C209 C309 C409
bit10 Cd10 --LI11 C110 C210 C310 C410
bit11 Cd11 --LI12 C111 C211 C311 C411
bit12 Cd12 --LI13 C112 C212 C312 C412
bit13 Cd13 --LI14 C113 C213 C313 C413
bit14 Cd14 ---C114 C214 C314 C414
bit15 Cd15 ---C115 C215 C315 C415
Switched
assignment
Drive
terminals
Logic I/O card
Extended
I/O card
Fixed assignments
Integrated
Modbus
CANopen Network card
"Controller
Inside" card
1755861 11/2009 45
Page 45

Command/reference switching
CiA402 profile
Control word bits of the same order are switched if the function inputs are assigned to swi tchable bits.
Switching may be poss ible using LI12, LI13 or LI14 on an extended I/O card.
Once a bit has been assigned to a switchable assignment, it can no longer be assigned to a fixed assignment, and vice versa.
Example: Once a function input has been assigned to Cd04, it c annot be assigned to LI5, C104, C204, C304 or C404.
The table below shows assignments on the basis of input or bit.
Bit
bit 0 - LI1 ---- - bit 1 - LI2 ---- - bit 2 - LI3 ---- - bit 3 - LI4 ---- - bit 4 - LI5 ---- - bit 5 - LI6 ---- - bit 6 - - LI7 --- - bit 7 - - LI8 --- - bit 8 - - LI9 --- - bit 9 - - LI10 --- - bit10 - - - LI11 -- - bit11 Cd11 --LI12 C111 C211 C311 C411
bit12 Cd12 --LI13 C112 C212 C312 C412
bit13 Cd13 --LI14 C113 C213 C313 C413
bit14 Cd14 ---C114 C214 C314 C414
bit15 Cd15 ---C115 C215 C315 C415
Switched
assignment
Drive
terminals
Logic I/O card
Extended I/O
card
Fixed assignments
Integrated
Modbus
CANopen Network card
"Controller
Inside" card
46 1755861 11/2009
Page 46

Command/reference switching
tEr
LCC
CAn
Mdb
nEt
APP
tEr
LCC
CAn
Mdb
nEt
APP
bit 9
bit 8
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
C201
LI4
LI6
LI5
LI8
LI10
LI9
LI8
LI7
LI6
LI5
LI4
LI3
LI2
LI1
LI12
LI11
bit 11
bit 10
bit 13
bit 12
bit 15
bit 14
LI14
LI13
CANopen control word
Terminals
Command channel 1
Cd1
Forward
Positioning
by sensors
Reverse
Disabling of sensors
Forward stop sensor
Reverse stop sensor
Forward slowdown sensor
Reverse slowdown sensor
tEr
LCC
CAn
Mdb
nEt
APP
bit 9
bit 8
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
CD01
LI4
LI5
LI10
LI9
LI8
LI7
LI6
LI5
LI4
LI3
LI2
LI1
LI12
LI11
bit 11
bit 10
bit 13
bit 12
bit 15
bit 14
tEr
LCC
CAn
Mdb
nEt
APP
LI8LI8
LI14
LI13
CANopen control word
Terminals
Command channel 1
Cd1
Forward
Positioning
by sensors
Reverse
Disabling of sensors
Forward stop sensor
Reverse stop sensor
Forward slowdown sensor
Reverse slowdown sensor
Command
switching
CCS
Command channel 2
Cd2
Example: I/O profile with positioning by sensors function
Let us return to the example given in the "I/O profile" section.
In the diagram below, the command comes from CANopen alone:
For a different application, provision must be made to enable the switching of the run commands and the disabling of the sensors and the
reference at the terminals.
The new diagram will look like this:
1755861 11/2009 47
Page 47

Command/reference switching
Configure the following parameters:
Parameter Value Comment
Type of command On state (2 wire) The run command is obtained via bit 0 of the CANopen control word.
Profile IO profile
Reference 1 configuration CANopen Reference 1 comes from the CANopen card.
Command 1 configuration CANopen Command 1 comes from the CANopen card.
Reference 1B configuration AI1 Reference 1B comes from analog input 1. Reference 1B has to be taken
rather than reference 2, as use is to be made of the positioning function.
Command 2 configuration Terminals Command 2 comes from the terminals.
Assignment of stop sensor Input LI4 The sensor inputs are not switched.
Assignment of slowdown sensor Input LI5
Assignment of sensor disable
command
Assignment of command switch Input LI8 The LI8 inputs enable the command and reference to be switched.
Assignment of application
reference switch 1/1B
Bit 1 switched.
Input LI8
Configuration via the graphic display terminal:
Menu/submenu Parameter Value
[1.5 INPUTS / OUTPUTS CFG] (I-O-) [2/3 wire control] (tCC) [2 wire] (2C)
[1.6 - COMMAND] (CtL-) [Profile] (CHCF) [I/O profile] (IO)
[Ref. 1 channel] (Fr1) [CANopen] (CAn)
[Cmd channel 1] (Cd1) [CANopen] (CAn)
[Cmd channel 2] (Cd2) [Terminals] (tEr)
[Cmd switching] (CCS) [LI8] (LI8)
[1.7 APPLICATION FUNCT.] (FUn-)
[POSITIONING BY SENSORS] (LPO-)
[Stop FW limit sw.] (SAF) [LI4] (LI4)
[Slowdown forward] (dAF) [LI5] (LI5)
[Disable limit sw.] (CLS) [Cd01] (Cd01)
[Ref. 1B channel] (Fr1b) [Ref. AI1] (AI1)
[Ref 1B switching] (rCb) [LI8] (LI8)
48 1755861 11/2009
Page 48

Command/reference switching
Copy on switching
When switching channels, it is possible to copy the re ference or command from function channel 1 to direct channel 2.
Menu Submenu
[1.6 COMMAND] (CtL-)
Parameter Possible values
[Copy channel 1 --> 2] No copy.
[No] (nO)
Copy reference
[Reference] (SP)
Copy command
[Command] (Cd)
Copy command and reference
[Cmd + ref.] (ALL)
If a copy is not made, the drive stops according to the configured stop type [Type of stop] (Stt) until the first command and reference are
received.
The reference before ramp (FrH) is copied unless the direct channel 2 reference is via +/- speed.
If the direct channel 2 reference is via +/- speed, the after ramp (rFr) reference is copied.
If the direct channel 2 command is via the terminals, the function channel 1 command is not copied even in pulse control (3-wire) [3 wire]
(3C).
If the direct channel 2 reference is via AI1, AI2, AI3, AI4, the encoder input or frequency input, the function channel 1 reference is not copied.
1755861 11/2009 49
Page 49

Forced local
Definition
Forced local mode supports switching to the terminals or display terminal.
This function complements channel switching and makes it pos sible to make use of an existing function from the Altivar58 range.
Forced local mode is only available in CiA402 profile, not in I/O profile.
All other communication takes priority over forced local mode.
Forced local mode can be configured via the display terminal:
Menu Submenu
[1.9 COMMUNICATION] (COM-) [FORCED LOCAL] (LCF-)
Parameter Possible values
Forced local switch
[Forced local assign.] (FLO)
Forced local channel
[Forced local Ref.] (FLOC)
Function inactive:
[No] (nO)
Assignment to a logic input LI1 ... LI14:
[LI1] (LI1) ... [LI14]
Forced local mode is active when the input is at state 1.
Forced local on stop
[No] (nO)
Assignment of the command to the terminals and of the reference to one of the analog inputs
AI1 ... A14
[AI2 ref.] (AI2), [AI3 ref.] (AI3), [AI4 ref.] (AI4)
Assignment of the command to the terminals and of the reference to the frequenc y inpu t (if card
present)
[Pulse Input] (PI)
Assignment of the reference [HMI Frequency ref.] (LFr) and of the command
(RUN/STOP/FWD/REV buttons) to the graphic display terminal
[HMI] (LCC)
(LI14)
In "forced local" state:
• Any attempts to write the parameter via one of these channels is rejected (applies to command, reference and adjustment
parameters).
• However, the parameters can be read.
• The drive does not register a communication fault.
On exiting "forced local" mode:
• The drive copies the run commands, the direction and the forced local reference to the active channel (maintained).
• Monitoring of the active command and reference channels resumes followi ng a time delay [Time-out forc. local] (FLOt).
• Drive control only takes effect once the drive has received the reference and
The time delay [Time-out forc. local] (FLOt) (default value = 10 s) can be configured via the remote graphic display terminal:
Menu Submenu Parameter
[1.9 COMMUNICATION] (COM-) [FORCED LOCAL] (LCF-) [Time-out forc. local] (FLOt)
the command.
50 1755861 11/2009
Page 50

Forced local
AI1C
AI2C
LFr1
LFr2
LFr3
AI2
AI1
LFr
LFr4
AI2
AI1
AI1C
AI2C
LFr1
LFr2
LFr3
AI1
AI2
LFr
LFr4
AI1C
AI2C
LFr1
LFr2
LFr3
AI1
AI2
LFr
LFr4
LI1
...
LI14
AI1C
AI2C
AI4C
LFr
AI3C
AI1
AI2
AI4
AI3
AI1
AI2
AI4
AI3
Fr1
Fr1b
LIpp
C111 ... C115
C211 ... C215
C311 ... C315
C411 ... C415
Fr1
Fr2
LIpp
C111 ... C115
C211 ... C215
C311 ... C315
C411 ... C415
Reference channel 1
Fr1
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Reference channel 1B
Fr1B
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Reference channel 2
Fr2
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Function
reference
switching rCB
Application
function output
reference
Direct
reference 2
Direct reference
switching
rFC
Reference
limit
Ramp
Function
Forced local
switching FLO
Display terminal
Forced local channel
FLOC
Forced local mode and reference switching
A detailed description is given in the Programming Manual.
This diagram shows reference switching as applicable to the following modes:
• CiA402 profile and separate mode
• CiA402 profile and not separate mode
1755861 11/2009 51
Page 51

Forced local
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
LIx
CMD1
CMD2
CMD3
CMD4
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
LIx
CMD1
CMD2
CMD3
CMD4
LIx
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
AI1
AI2
AI4
AI3
LI1 ... LI14
Cd1
Cd2
LIpp
C111 ... C115
C211 ... C215
C311 ... C315
C411 ... C415
Command channel 1
Cd1
Command
switching
CCS
Command channel 2
Cd2
Run
Stop
Forward
Reverse
Terminals
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Terminals
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Forced local channel
FLOC
Forced
local
switching
FLO
Display terminal
Forced local mode and command switching
A detailed description is given in the Programming Manual.
CiA402 profile (separate mode)
52 1755861 11/2009
Page 52

Forced local
LIx
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
AI1
AI2
AI4
AI3
LI1
...
LI14
LIx
AI1
AI2
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
CMD1
CMD2
CMD3
CMD4
LIx
LIx
RUN/STOP
FWD/REV
CMD1
CMD2
CMD3
CMD4
AI1
AI2
Fr1
Fr2
LIpp
C111 ... C115
C211 ... C215
C311 ... C315
C411 ... C415
Reference channel 1 (1)
Fr1
Direct
reference
switching
rFC
Reference channel 2 (1)
Fr2
Run
Stop
Forward
Reverse
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Display terminal
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Controller
Forced local channel
FLOC
Forced
local
switching
FLO
Display terminal
CiA402 profile (not separate mode)
(1)In not separate mode, command switching follows reference switching. It is therefore reference switching that switches the command.
1755861 11/2009 53
Page 53

Priority stops
Priority stops on the graphic display terminal
If the graphic display terminal is not the active command channel, pressing the STOP key on the graphic display terminal causes a
freewheel stop if:
• The
[Stop Key priority]
If the graphic display terminal is the active command channel, the STOP key causes a stop according to the type of stop configured in the
[Type of stop] (Stt) parameter, regardless of the value of the [Stop Key priority] (PSt) parameter.
The effect of the graphic display terminal is not dependent on the pr ofile.
Priority stops via the terminals or the network
I/O profile
In the I/O profile:
Stop and fault commands, configured as fixed assignments (LIpp, C1pp, C2pp, C3pp, C4pp), on terminal inputs or control word bits,
have priority even if the channel is not active.
Commands, configured as switched assignments (Cd00 ... Cd15), are active if and only if the channel is active.
(PSt) parameter in the
[1.6 - COMMAND]
(CtL-) menu is configured as
[Yes]
(YES) (factory setting).
Fixed assignments are configured using the following values :
Channel
Drive terminals LI2 ... LI6 LI3 ... LI6
Logic I/O card LI7 ... LI10
Extended I/O card LI11 ... LI14
Integrated Modbus C101 ... C115 C102 ... C115
CANopen C201 ... C215 C202 ... C215
Communication card C301 ... C315 C302 ... C315
"Controller Inside" card C401 ... C415 C402 ... C415
Command Configuration = 0 = 1 V a lu e for starting
Freewheel stop [Freewheel stop ass.] (nSt) Stop No stop 1
Fast stop [Fast stop assign.] (FSt) Stop No stop 1
DC injection braking [DC injection assign.] (dCI) No braking Braking 0
External fault [External fault ass.] (EtF) No fault Fault 0
(1)
If the assignment is fixed, this is the value necessary for starting, even if another channel is active.
In the case of a run on edge command, configured via [3 wire] (3C) :
The stop command (run enable) is assigned by factory default to switched order 0 (equivalent to Cd00):
• It is active at the terminals (LI1) only if the terminals are active.
• It is active via the network (bit 0) only if the network is active.
Run on state command
[2 wire] (2C)
Run on edge command
[3 wire] (3C)
(1)
54 1755861 11/2009
Page 54

Priority stops
CiA402 profile
In the CiA402 profile, separate or not separate mode:
External stop and fault commands, configured as fixed assig nments (LIpp, C1pp, C2pp, C3pp, C4pp), on terminal inputs or cont rol word
bits, have priority even if the channel is not active.
Commands, configured as switched assignments (Cd11 ... Cd15), are active if, and only if, the channel is active.
Fixed assignments are configured using the following values :
Channel
Drive terminals LI2 ... LI6 LI3 ... LI6
Logic I/O card LI7 ... LI10
Extended I/O card LI11 ... LI14
Integrated Modbus C111 ... C115
CANopen C211 ... C215
Communication card C311 ... C315
"Controller Inside" card C411 ... C415
Cp11 is assigned by default to the reverse direction command [Reverse assign.] (rrS).
Run on state command
[2 wire] (2C)
Run on edge command
[3 wire] (3C)
At the terminals:
Command Configuration = 0 = 1
Freewheel stop
Fast stop [Fast stop assign.] (FSt) Stop No stop 1 4-Switched on
DC injection braking
External fault [External fault ass.] (EtF) No fault Fault 0 8-Fault
(1)
If the assignment is fixed, this is the value necessary for starting, even if another channel is active.
In run on edge command, configured by [3 wire] (3C), the stop command (run enable) is assigned by factory default to LI1. This command
is active even if the terminals are not the active channel.
Via the network:
Command Configuration = 0 = 1
Fast stop [Fast stop assign.] (FSt) No stop Stop 0 4-Switched on
DC injection braking
External fault [External fault ass.] (EtF) No fault Fault 0 8-Fault
(1)
If the assignment is fixed, this is the value necessary for starting, even if another channel is active.
[Freewheel stop ass.]
(nSt)
[DC injection assign.]
(dCI)
[DC injection assign.]
(dCI)
Stop No stop 1 2-Switch on disabled
No braking Braking 0 5-Operation enabled
No braking Braking 0 5-Operation enabled
Value for
starting
Value for
starting
State reached since
(1)
5-Operation enabled
State reached since
(1)
5-Operation enabled
In the CiA402 profile, the freewheel stop comma nd [Freewheel stop ass .] (nSt) cannot be assigned to the control word. Freewheel stop is
obtained using the "5-Disable operation" or "Halt" commands with the type of stop [Type of stop] (Stt) parameter configured as
[Freewheel] (nSt).
1755861 11/2009 55
Page 55

Communication monitoring
The Altivar 71 drive incorporates communication monitoring mechanisms.
Principle
Following initialization (power-up), the drive waits until at least one command or reference parameter has been written for the first time by
the network.
Then, the network is monitored and, if a network fault occurs, the drive reacts according t o the configuration (ignore fault, stop on drive fault,
maintain speed, fallback speed, or stop without fault).
The drive can start only once all the command and reference parameters of the active network have been written.
Network monitoring criteria
The network is monitored in accordance with protocol-specific criteria, which are summarized in the table below and specified in the
corresponding protocol manual.
Protocol Network problem Related drive fault (1)
Integrated Modbus ports • Adjustable time-out for received requests destined for the drive [Modbus com.] (SLF1)
•Bus Off
• Life Guarding
Integrated CANopen port
Modbus TCP/IP Ethernet
card
Fipio card
Modbus Plus card
Modbus card
Uni-Telway card • Fixed time-out (10 s) for master polling
Profibus DP card
INTERBUS card
DeviceNet card
• CANoverrun
• Heartbeat
• NMT state machine transition
Network management fault:
• FDR fault
• IP address duplication fault
Communication fault:
• Adjustable time-out for received control word (I/O scanning or
messaging)
• Network overload
• Non-adjustable time-out for received periodic variables dest ined for
the drive
• Adjustable time-out:
• Either for received periodic variables (Peer cop) desti ned for the
drive
• Or for Modbus messages destined for the drive, if no periodic
variables (Peer cop) configured
• Fixed time-out (10 s) for received requests destined for the drive
• Adjustable time-out (via the network configuration software) for
received periodic variables (PZD and PKW) destined for the drive
• Time-out for received periodic variables destined for the drive
Communication fault:
• Adjustable time-out:
• Either for received periodic variables (Polling and COS)
destined for the drive
• Or for network activity, if no periodic variables configured
Configuration fault:
• The drive configuration is not compatible with the selected
assembly
[CANopen com.] (COF)
[External fault com.]
[Com. network] (CnF)
[External fault com.]
(EPF2)
(EPF2)
(1) If the drive is configured to trip on a fault in the event of a network fault
If an anomaly is detected, the port or network card indicates a network fault.
56 1755861 11/2009
Page 56

Communication monitoring
Behavior in the event of a network fault
In the event of a network fault (on a monitored cha nnel), the drive reacts as specified in the
MANAGEMENT]
•
[Modbus fault mgt]
•
[CANopen fault mgt]
•
[Network fault mgt]
The Modbus TCP/IP Ethernet card can also trigger an external fault (in the event of an FDR fault or IP address duplication fault), to which
the drive reacts as specified in the
mgt]
(EPL) parameter.
The drive can react in five possible ways:
1. Drive fault
[Freewheel] (YES) : Freewheel stop (factory setting)
[Ramp stop] (rMP):Stop on ramp
[Fast stop] (FSt): Fast stop
[DC injection] (dCI): DC injection stop
The fault displayed will depend on the source of the communication fault:
•
[Modbus com.]
•
[CANopen com.]
•
[Com. network]
•
[External fault com.]
The CiA402 state chart changes to "7 - Fault reaction active" and then to "8 - fault".
2. Stop without fault
(CLL-) submenu) by the following parameters:
(SLL) for integrated Modbus
(COL) for CANopen
(CLL) for a network card
[1.8 – FAULT MANAGEMENT]
(SLF1) for integrated Modbus
(COF) for CANopen
(CNF) for a network card
(EPF2) for Ethernet card FRD and IP faults
(FLt-) menu (
[1.8 - FAULT MANAGEMENT]
[EXTERNAL FAULT]
(EtF-) submenu) by the
(FLt-) menu (
[COM. FAULT
[External fault
[Per STT] (Stt): Stop according to configuration of [Type of stop] (Stt).
There is no drive fault.
If the CiA402 state chart is in "5-Operation enabled", it changes to "4-Switched on" after stopping.
3. Ignore fault
[Ignore] (nO): Fault ignored
4. Maintain speed
[Spd maint.] (rLS): The drive maintains the speed at the time the fa ult occurred, as long as the fault persists and the run command has
not been removed.
There is no drive fault.
If the CiA402 state chart is in "5-Operation enabled", it remains there.
5. Fallback speed
[Fallback spd] (LFF): Change to fallback speed, maintained as long as the fault persists and the run command has not been removed.
There is no drive fault.
If the CiA402 state chart is in "5-Operation enabled", it remains there.
The fallback speed can be configured in the [1.8 – FAULT MANAGEMENT] (FLt-) menu using the [Fallback spe e d] (LFF) parameter.
Note: The drive will not start up immediately at the fallback speed. If there is a l oss of co mmuni cat ion, th e dri ve wi ll o nly run at th e f al lba ck
speed if the run command was present when the communication fault occurred.
In the event of a control system being used to ensure switchover to an act ive safe state if there is a loss of communicati on, drives that ha ve
been stopped must always be left in the run state (5 - Operation enabled) with zero reference to ensure that they change to the fallback
speed.
1755861 11/2009 57
Page 57

Communication monitoring
Detailed operation
Monitoring of communication channels
• The drive monitors all its communication channels.
• Communication problems are indicated on the LEDs on the card or drive or on the graphic display te rminal. However, a problem d oes
not always trigger a network fault or a drive fault.
- Example:
If a drive is controlled via the I/O and only monito red via an Ethernet network, an Ethernet commun ication problem does not cause
a fault.
• As soon as a command or reference parameter has been written for the first time on a communication cha nnel, this channel is said
to be connected.
• A channel is said to be participant if it tran smits a command or referenc e parameter nece ssary for controlling th e drive (see list in the
table below).
Channel state Parameter Assignment
If the channel is the active
command channel
If the channel is the active
reference channel Frequency reference (LFr) or Speed reference (LFrd)
Whatever the channel state
Control word (CMd)
Control word (CMd) containing a command or reference switch
Frequency reference (LFr) or Speed reference (LFrd), either
summing or subtracting
Torque reference (Ltr) [Torque ref. channel] (Tr1)
PID regulator reference (PISP) [Ref. 1 channel] (Fr1)
Network analog input [Network AI] (AIU1)
Reference multiplication coefficient (MFr)
[Cmd channel 1] (Cd1)
or [Cmd channel 2] (Cd2)
[Ref. 1 channel] (Fr1)
or [Ref. 1B channel](Fr1b)
or [Ref. 2 channel](Fr2)
[Cmd switching]
or
[Ref 1B switching]
or
[Ref. 2 switching]
[Summing ref. 2] (SA2)
or [Summing ref. 3] (SA3)
or [Subtract ref. 2] (dA2)
or [Subtract ref. 3] (dA3)
[PID feedback ass.] (PIF)
or [AI net. channel] (AIC1)
[Multiplier ref. 2] (MA2)
or [Multiplier ref. 3] (MA3)
(CCS)
(rCb)
(rFC)
- Example:
If the operation on reference function [REF. OPERATIONS] (OAI-) is active and a summing reference [Summing ref. 2] (SA2)
has been assigned to [Modbus] (Mdb), the Modbus reference plays a part in control.
• If a communication problem occurs on a connected participant channel, then the dri ve triggers a network fault.
The drive reacts according to the network fault configuration (drive fault, stop without fault, ignore fault, maintai n speed or fallback
speed).
• If a communication problem occurs on a non-participant or disco nnected channel, the dri ve does not trigger a netwo rk fault or a drive
fault. This avoids, in particular, the occurrence of spurious faults when installations are powered up.
- Example:
A drive is controlled via CANopen and is powered up.
The PLC is powered up but is not in RUN mode. The network is operational but no parameter has been sent to the drive yet. If
the drive is disconnected from the CANopen network, a communication prob lem occurs, but no fault.
• The channel disconnects in the event of a communication problem.
Note: A control word (CMd) of a channel other than the active channel with fixed bit assignments, other than channel switches (fast stop,
preset speeds, etc.) is not considered to be participant. A communicati on problem will not cause a network fault.
- Example:
A drive is equipped with a "Controller Inside" card and an Ethernet card.
The "Controller Inside" card controls the drive (command and reference).
One bit of the Ethernet control word is assigned to "fast stop".
If the drive is disconnected from the Ethernet ne twork, th e drive can no longer be stopped via Ethernet (however, a drive fault is
not triggered).
58 1755861 11/2009
Page 58

Communication monitoring
4
1
2
=1
7
6
5
3
Channel disconnected
Connected
channel disabled
Channel
enabled
Network fault
Communication
problem and
non-participant
channel
Communication
problem and
non-participant
channel
Command or
reference
parameter
received
All parameters assigned
to drive functions have
been received
Communication
problem and
participant
channel
Communication
problem and
participant
channel
Enabling of communication channels
• A communication channel is enabled if all its parameters assigned to drive functions have been received.
- Example:
A drive is in I/O profile with speed control. Modbus constitutes both the command and reference channel.
The Modbus channel will be enabled as soon as the control word and speed reference have been received.
• The drive is only able to start if all participant channels are enabled.
- Example 1:
A drive in CiA402 profile is connected to Modbus, which is the active channel.
Unless the reference has been written at least o nce, i t wi ll no t be po ssi ble t o proce ed to the "5-Operat ion enable d" st ate , even if
the "4-Enable operation" command is sent.
- Example 2:
A drive is connected to Modbus.
The terminals are both the reference and command channel.
The operation on reference function [REF. OPERATIONS] (OAI-) is active and summing input 2 is assi gned to Modbus.
The drive will not start until the reference has been supplied by Modbus.
- Example 3:
A drive is configured for switching between the terminals and CANopen.
If the command switch is assigned to the Ethernet card, startup will only be possible once the Ethernet channel is enabled.
• A communication problem disables a communication channel.
• When switching from an enabled channel to a disabled channel, th e drive immediately triggers a network fault.
Special case involving Ethernet Modbus TCP/IP card
• The Ethernet card can generate two types of network fault: a network management fault and a commun ication fault.
• If a network management fault (FDR or IP address d uplication f ault) occurs, a drive fa ult is gen erated regardless of the state (active,
participant, etc.) of this channel.
1755861 11/2009 59
Page 59

Assignment of setpoints from a network
Setpoint parameters
The Altivar 71 supports a number of setpoint parameters, which must be selected according to the functions used in the drive.
Function used Input to be assigned Value Setpoint to be sent via the network
Speed reference
(rpm)
Frequency reference
(0.1 Hz or high
resolution)
Sum [Summing ref. 2] (SA2)
Subtraction [Subtract. ref. 2] (dA2)
Multiplication [Multiplier ref. 2] (MA2)
PID regulator [Ref.1 channel] (Fr1)
Torque control
[Ref.1 channel] (Fr1)
[Ref.2 channel] (Fr2)
[Ref.1B channel] (Fr1b)
[Ref.1 channel] (Fr1)
[Ref.2 channel] (Fr2)
[Ref.1B channel] (Fr1b)
[Summing ref. 3] (SA3)
[Subtract. ref. 3] (dA3)
[Multiplier ref. 3] (MA3)
[Ref.1B channel] (Fr1b)
[PID feedback ass.] (PIF) [Network AI] (AIU1) PID regulator feedback (AIU1)
[AI net. channel] (AIC1) [Modbus] (Mdb) or
[Torque ref. channel]
(Tr1)
[Modbus] (Mdb) or
[CANopen] (CAn) or
[Com. card] (nEt)
[Modbus] (Mdb) or
[CANopen] (CAn) or
[Com. card] (nEt)
[Modbus] (Mdb) or
[CANopen] (CAn) or
[Com. card] (nEt) or
[Network AI] (AIU1)
[Modbus] (Mdb) or
[CANopen] (CAn) or
[Com. card] (nEt) or
[Network AI] (AIU1)
[Modbus] (Mdb) or
[CANopen] (CAn) or
[Com. card] (nEt) or
[Network AI] (AIU1)
[Modbus] (Mdb) or
[CANopen] (CAn) or
[Com. card] (nEt)
[CANopen] (CAn) or
[Com. card] (nEt)
[Modbus] (Mdb) or
[CANopen] (CAn) or
[Com. card] (nEt)
Speed reference (LFRD)
Frequency reference (LFR)
Speed reference (LFRD) or Frequency reference (LFR)
Speed reference (LFRD) or Frequency reference (LFR)
[Multiplying coeff.] (MFr)
PID regulator reference (PISP)
Torque reference (LTR)
Example 1:
The drive is to be controlled by sending the speed reference to the PID regulator via CANopen. No application fu nction is used.
The following must be assigned: [Ref.1 channel] (Fr1) = [CANopen] (CAn)
The following must be sent: Speed reference (LFRD)
Example 2:
The drive is to be controlled by sending the PID regulator reference via Modbus.
The following must be assigned: [Ref.1 channel] (Fr1) = [Modbus] (Mdb)
The following must be sent: PID regulator reference (PISP)
Example 3:
The drive is to be controlled by sending the PID regulator reference and the feedback via the Ethernet card.
The following must be assigned:
- [Ref.1 channel] (Fr1) = [Com. card] (nEt)
- [PID feedback ass.] (PIF) = [Network AI] (AIU1)
- [AI net. channel] (AIC1) = [Com. card] (nEt)
The following must be sent:
- PID regulator reference (PISP)
- PID regulator feedback (AIU1)
60 1755861 11/2009
Page 60

Assignment of setpoints from a network
H/>
72H
279/
:52
H2/
2H%
279
;-%
;-&
@-%
@-&
8-%
8-&
2H$
2H$>
+/- speed around a
reference
Preset speeds
Jog
operation
PID not assigned
Graphic display
terminal
Forced local
Ramps
Parameter:
The black square represents the
factory setting assignment.
Key:
Channel 1
Channel 2
[Ref 1B switching]
[Ref.1 channel]
[Ref.1B channel]
[Summing ref. 2]
[Summing ref. 3]
[Subtract. ref. 2]
[Subtract. ref. 3]
[Multiplier ref. 2]
[Low speed]
[Multiplier ref. 3]
[PID REGULATOR]
AI1
[Ref.2 channel]
[Ref. 2 switching]
(FRA + SA2 + SA3 - dA2 - dA3) x MA2 x MA3
(SP1)
SP2
SP16
LI
LCC
FRA
nO
[High
speed]
nO
nO
nO
nO
FrH
AI2
AI3
HSP
LSP
ACC DEC
AC2 DE2
LI
AI4
nO
0V
Note: Forced local is not active in
[I/O profile].
FrO
FrOd
Power
stage
M
rFr
rFrd
FrHd
Network references
Fr1, Fr1b, Fr2:
• LFr or LFrd
SA2, SA3, dA2, dA3:
• LFr, LFrd, or AIU1
MA2, MA3:
•MFr or AIU1
Without PID regulator
1755861 11/2009 61
Page 61

Assignment of setpoints from a network
H/>
72H
279/
H2/
2H%
279
;-%
;-&
@-%
@-&
2H$
2H$>
Graphic display
terminal
Ramps (1)
Channel 1
Channel 2
PID
See diagram
below
A
Forced local
[Ref 1B switching]
[Ref.1 channel]
[Ref.1B channel]
[Summing ref. 2]
[Summing ref. 3]
[Subtract. ref. 2]
[Subtract. ref. 3]
[Low speed]
AI1
[Ref.2 channel]
[Ref. 2 switching]
FRA + SA2 + SA3 - dA2 - dA3
B
LCC
PIP1
[High
speed]
nO
FrH
FrO
AI2
AI3
HSP
LSP
ACC DEC
AC2 DE2
LI
AI4
nO
0V
Note: Forced local is not active in
[I/O profile].
FrHd
FrOd
Power
stage
M
rFr
rFrd
PIP2
•PISP
• LFr, LFrd, or AIU1
• LFr or LFrd
•AIU1
PAU
(manu)
Pr2
Pr4
nO
+
-
rP2
rP3
rP4
rIG
rPG
PIF
PIN
0
tLS
rSL
PIF1 / PIF2
PIP1 / PIP2
x(-1)
nO
nO
YES
PIC
nO
AI1
.....
AI4
LI
+
+
POH
POL
rdG
ACC DEC
FPI
x PSr
PII
SP2
SP16
rPI
A
B
nO
YES
PrP
AC2
(1)
Internal
reference
PID
feedback
Preset PID references
Error
inversion
Restart
(wake-up) error
threshold
Gains
Ramps
Parameter:
The black rectangle
represents the factory
setting assignment.
Key:
Ramp
Preset manual references
Scaling
[RP] (PI)
[Encoder] (PG)
[Network AI]
(AIU1)
Predictive
speed
reference
Manual
reference
Auto/
Manual
rPC
rPF
rPO
rPE
With PID regulator
(1)Ramp AC2 is only active at startup of the PID function and during PID "wake-ups".
62 1755861 11/2009
Page 62

Configuration saving and switching
Display
terminal
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Display
terminal
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Current
configuration
(RAM)
No
Industrial
HMI
terminal
PLC
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Saving the configuration
When a parameter is modified via the drive’s integrated display terminal or graphic display terminal, this parameter is automatically saved
to the EEPROM non-volatile memory.
When a parameter is modified using a PLC or an HMI terminal via a network (Modbus, CANopen or a network card), this parameter is written
to the current configuration in the RAM volatile memory. It is not saved to the EEPROM non-volatile memory. If the drive control voltage is
disconnected, when it is reconnected, the parameter reverts to the initial value and the setting is lost.
1755861 11/2009 63
Page 63

Configuration saving and switching
Display
terminal
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Industrial
HMI
terminal
PLC
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Extended control word:
Save (CMI,1)
Set to 1
To save the parameter, a save command must be executed using bit 1 of the extended control word (CMI).
The save command is only active if the drive is stopped and not in "5-Operation enabled" state.
64 1755861 11/2009
Page 64

Configuration saving and switching
Display
terminal
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Industrial
HMI
terminal
PLC
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Extended control word:
Restore configuration (CMI,2)
Set to 1
Display
terminal
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Industrial
HMI
terminal
PLC
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Extended control word:
Factory setting (CMI,0)
Set to 1
[Macro configuration]
(CFG)
Restore configuration
The restore configuration command is executed using bit 2 of the extended cont rol word (CMI).
The return to factory settings command is executed usi ng bit 0 o f the extend ed control word (CMI). The type of setting is determined by the
active macro configuration parameter [Macro configuration] (CFG) and by the [PARAMETER GROUP LIST] (FrY) parameter which
defines the parameter groups concerned.
The restore command is only active if the drive is stopped and not in "5-Operation enab led" state.
1755861 11/2009 65
Page 65

Configuration saving and switching
Display
terminal
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Configuration switching
[2 Configurations](CnF1)
[3 configurations](CnF2)
Active
configuration
(CNFS)
Terminals
00 01
10
11
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Display
terminal
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Control word:
Configuration switching
[2 Configurations](CnF1)
[3 configurations](CnF2)
Active
configuration
(CNFS)
00 01
10
11
Industrial
HMI
terminal
PLC
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Set to 0/1
Configuration switching via control word
The configuration or motor switching function (see the Programming Manual) can be used via the network or via the terminals.
To use this function via a network, simply assign one or two bits of the control word to the motor or configuration switching command via
the [2 Configurations] (CnF1) and [3 Configurations] (CnF2) parameters.
The active configuration can be read in the [Config. active] (CNFS) parameter.
66 1755861 11/2009
Page 66

Configuration saving and switching
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
PLC
Industrial
HMI
terminal
Display
terminal
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Extended control word:
Save configuration (CMI,1)
Active
configuration
(CNFS)
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Set to 1
1 2 3
Extended control word:
Restore configuration (CMI,2)
Set to 1
Display
terminal
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Active
configuration
(CNFS)
Industrial
HMI
terminal
PLC
Modbus
CANopen
Network
1 2 3
When the configuration or motor switching function is configured on inputs or on control word bits, to save a configuration that is already
active, set bit 1 of the extended control word (CMI) to 1.
When the configuration or motor switching funct i on i s co nfigu re d on in puts o r on c ontro l wo rd bits, b it 2 of th e ext en ded contr ol wo rd (CMI)
must be set to 1.
The configuration switching commands are only active if the drive is stopped and not in "5-Operation enabled" state.
1755861 11/2009 67
Page 67

Configuration saving and switching
Function parameters
Code Description
CNF1
CNF2
CNFS
Parameter name: Assignment for 2 configurations
Terminal display: [2 Configurations]
Logic address: 8021 = 16#1F55 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2032/16 Read/write: R/WS
INTERBUS index: 5FBC/9C Factory setting: 0
DeviceNet path: 9C/01/9C
See next page.
Parameter name: Assignment for 3 configurations
Terminal display: [3 Configurations]
Logic address: 8022 = 16#1F56 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2032/17 Read/write: R/WS
INTERBUS index: 5FBC/9D Factory setting: 0
DeviceNet path: 9C/01/9D
See next page.
Parameter name: Active configuration
Terminal display: [Config. active]
Logic address: 8020 = 16#1F54 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2032/15 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/CD
DeviceNet path: 89/01/15
0 = The parameter set switching function is not configured
1=(CNF0): Configuration no. 0 active
2=(CNF1): Configuration no. 1 active
3=(CNF2): Configuration no. 2 active
Value of the control bit assigned by [2 Configurat ions] (CnF1) 0101
Value of the control bit assigned by [3 Configurat ions] (CnF2) 0011
Value of [Config. active] (CnFS) 1233
Active configuration 0122
68 1755861 11/2009
Page 68

Configuration saving and switching
Assignment of logic inputs and control bits for CNF1 and CNF2
Value Assignment Description/Condition
0 Not assigned
129
to
134
135
to
138
139
to
142
187
to
191
203
to
207
219
to
223
235
to
239
[LI1] (LI1)
to
[LI6] (LI6)
[LI7] (LI7)
to
[LI10] (LI10)
[LI11] (LI11)
to
[LI14] (LI14)
[C111] (C111)
to
[C115] (C115)
[C211] (C211)
to
[C215] (C215)
[C311] (C311)
to
[C315] (C315)
[C411] (C411)
to
[C415] (C415)
Logic inputs
Drive with or without option
Logic inputs
With VW3A3201 logic I/O card
Logic inputs
With VW3A3202 extended I/O card
Control bit
With integrated Modbus regardless of profile
Control bit
With integrated CANopen regardless of profile
Control bit
With a communication card regardless of profile
Control bit
With Controller Inside card regardless of profile
Note: In [I/O profile] (IO), LI1 cannot be accessed and if [2/3 wire control] (tCC) = [3 wire] (3C), LI2 cannot be accessed either.
1755861 11/2009 69
Page 69

Configuration saving and switching
Display
terminal
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Save configuration
(SCS)
Industrial
HMI
terminal
PLC
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Write
1 2 3
Display
terminal
Configuration 0
(EEPROM)
Configuration 1
(EEPROM)
Configuration 2
(EEPROM)
Factory settings
Current
configuration
(RAM)
Restore configuration
(FCS)
Industrial
HMI
terminal
PLC
Modbus
CANopen
Network
Write
1 2 3 64
[Macro configuration]
(CFG)
Configuration switching by selection
The current configuration can be saved in one of the 3 non-volatile configurations in EEPROM using the "Save configuration" (SCS)
parameter. In this case, it is not necessary to assign a function in the control word.
One of the 3 non-volatile configurations in EEPROM can be restored to the current configuration using the "Restore configuration" (FCS)
parameter.
Note: Value 64 controls the return to factory settings.
The configuration switching commands are only active if the drive is stopped and not in "5-Operation enabled" state.
70 1755861 11/2009
Page 70

Configuration saving and switching
Function parameters
Code Description
SCS
FCS
FrY
Parameter name: Save configuration
Logic address: 8001 = 16#1F41 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2032/2 Read/write: R/WS
INTERBUS index: 5FBC/9A
DeviceNet path: 9C/01/9A
0=No save
1 = Save to configuration no. 0
2 = Save to configuration no. 1
3 = Save to configuration no. 2
Parameter name: Restore configuration
Logic address: 8002 = 16#1F42 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2032/3 Read/write: R/WS
INTERBUS index: 5FBC/9B
DeviceNet path: 9C/01/9B
0=No restore
1 = Restore configuration no. 0
2 = Restore configuration no. 1
3 = Restore configuration no. 2
64 = Factory setting
Parameter name: Parameter group list
Terminal display: [PARAMETER GROUP LIST]
Logic address: 3022 = 16#OBCE Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2000/17 Read/write: R/WS
INTERBUS index: 5FBC/06 Factory setting: 0
DeviceNet path: 70/01/17
Selection of menus to be loaded
Bit 0: = 1: [All] (ALL) : All parameters
Bit 1: = 1: [Drive menu] (drM): The [1 DRIVE MENU] menu without [1.9 COMMUNICATION] and [1.14 CONTROL
INSIDE MENU]. In the [7 DISPLAY CONFIG.] menu, [Return std name] returns to [No].
Bit 2: = 1: [Settings] (SEt): The [1.3 SETTINGS] menu without the [IR compensation] (UFr), [Slip compensation]
(SLP) and [Mot. therm. current] (ItH) parameters.
Bit 3: = 1: [Motor param] (MOt): Motor parameters:
[Rated motor power] (nPr) - [Rated motor volt.] (UnS) - [Rated mot. current] (nCr) - [Rated motor freq.] (FrS) -
[Rated motor speed] (nSP) - [Auto tuning] (tUn) - [Auto tuning state] (tUS) - [U0] (U0) to [U5] (U5) - [Freq pt
1on 5pt V/F] (F1) to [F5] (F5) - [V. constant power] (UCP) - [Freq. Const Power] (FCP) - [Nominal I sync.]
(nCrS) - [Nom motor spdsync] (nSPS) - [Pole pairs] (PPnS) - [Syn. EMF constant] (PHS) - [Autotune L d-axis]
(LdS) - [Autotune L q-axis] (LqS) - [Cust. stator R syn] (rSAS) - [IR compensation] (UFr) - [Slip compensation]
(SLP) - the motor parameters that can be accessed in [Expert] mode.
The following selections can only be accessed if [Config. Source] (FCSI) = [Macro-Conf]
Bit 4: = 1: [Comm. menu] (COM): The [1.9 COMMUNICATION] menu without either [Scan. IN1 address] (nMA1) to
[Scan. IN8 address] (nMA8) or [Scan.Out1 address] (nCA1) to [Scan.Out8 address] (nCA8).
Bit 5: = 1: [Control Inside menu] (PLC): The [1.14 CONTROL INSIDE MENU] menu
Bit 6: = 1: [Monitor config.] (MOn): The [6 MONITORING CONFIG.] menu
Bit 7: = 1: [Display config.] (dIS): The [7 DISPLAY CONFIG.] menu
Bits 8 to 15: Reserved (= 0 or 1)
(InI):
1755861 11/2009 71
Page 71

Parameter set switching
The parameter set switching function (see the Programming Manual) can be used via the network or via the terminals.
To use this function via a network, simply assign one or two bits of the control word to para meter set switching via the [2 Parameter sets]
(CHA1) and [3 Parameter sets] (CHA2) parameters.
The active set can be read in the "Active parameter set" (CFPS) parameter.
The parameter sets can be written via a network.
The parameter sets can be switched with the motor running.
Function parameters
Code Description
CHA1
CHA2
CFPS
Parameter name: Assignment for 2 sets
Terminal display: [2 Parameter sets]
Logic address: 12902 = 16#3266 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2063/3 Read/write: R/WS
INTERBUS index: 5FBD/54 Factory setting: 0
DeviceNet path: A1/01/67
See next page.
Parameter name: Assignment for 3 sets
Terminal display: [3 Parameter sets]
Logic address: 12903 = 16#3267 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2063/4 Read/write: R/WS
INTERBUS index: 5FBD/55 Factory setting: 0
DeviceNet path: A1/01/68
See next page.
Parameter name: Active parameter set
Logic address: 12900 = 16#3264 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2063/1 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/EC
DeviceNet path: A1/01/65
0 = The parameter set switching function is not configured
1=[Set 1 active] (CFP1): Parameter set no. 1 active
2=[Set 2 active] (CFP2): Parameter set no. 2 active
3=[Set 3 active] (CFP3): Parameter set no. 3 active
Value of the control bit assigned by [2 Parameter sets] (CHA1) 0101
Value of the control bit assigned by [3 Parameter sets] (CHA2) 0011
Value of "Active parameter set" (CFPS) 1233
Active parameter set 1233
72 1755861 11/2009
Page 72

Parameter set switching
CHA1 and CHA2 assignment values
Value Assignment Description/Condition
0 [No]
4 [Freq. Th. attain.] (FtA) Switching via [Freq. threshold] (Ftd)
13 [Freq. Th. 2 attain.]
129
to
134
135
to
138
139
to
142
160
to
170
171
to
175
177
to
186
187
to
191
193
to
202
203
to
207
209
to
218
219
to
223
225
to
234
235
to
239
(nO) Not assigned
(F2A)
[LI1] (LI1)
to
[LI6] (LI6)
[LI7] (LI7)
to
[LI10] (LI10)
[LI11] (LI11)
to
[LI14] (LI14)
[CD00] (Cd00)
to
[CD10] (Cd10)
[CD11] (Cd11)
to
[CD15] (Cd15)
[C101] (C101)
to
[C110] (C110)
[C111] (C111)
to
[C115] (C115)
[C201] (C201)
to
[C210] (C210)
[C211]
(C211)
to
[C215] (C215)
[C301] (C301)
to
[C310] (C310)
[C311] (C311)
to
[C315] (C315)
[C401] (C401)
to
[C410] (C410)
[C411] (C411)
to
[C415] (C415)
Switching via [Freq. threshold 2] (F2d)
Logic inputs
Drive with or without option
Logic inputs
With VW3A3201 logic I/O card
Logic inputs
With VW3A3202 extended I/O card
Switchable bit
In [I/O profile] (IO)
Switchable bit
Regardless of profile
Control bit
With integrated Modbus in [I/O profile] (IO)
Control bit
With integrated Modbus regardless of profile
Control bit
With integrated CANopen in [I/O profile] (IO)
Control bit
With integrated CANopen regardless of profile
Control bit
With a communication card in [I/O profile] (IO)
Control bit
With a communication card regardless of profile
Control bit
With Controller Inside card in [I/O profile] (IO)
Control bit
With Controller Inside card regardless of profile
Note: In [I/O profile] (IO), LI1 cannot be accessed and if [2/3 wire control] (tCC) = [3 wi re] (3 C) , LI2, C101, C201, C301 and C401
cannot be accessed either.
1755861 11/2009 73
Page 73

Parameter set switching
Parameter sets can be loaded via the following parameters:
Address table:
No. Code Logic address: CANopen index: INTERBUS index: DeviceNet path:
1 AD01 12911 = 16#326F 2063/C 5FBF/8C 9F/01/8C
2 AD02 12912 = 16#3270 2063/D 5FBF/8D 9F/01/8D
3 AD03 12913 = 16#3271 2063/E 5FBF/8E 9F/01/8E
4 AD04 12914 = 16#3272 2063/F 5FBF/8F 9F/01/8F
5 AD05 12915 = 16#3273 2063/10 5FBF/90 9F/01/90
6 AD06 12916 = 16#3274 2063/11 5FBF/91 9F/01/91
7 AD07 12917 = 16#3275 2063/12 5FBF/92 9F/01/92
8 AD08 12918 = 16#3276 2063/13 5FBF/93 9F/01/93
9 AD09 12919 = 16#3277 2063/14 5FBF/94 9F/01/94
10 AD10 12920 = 16#3278 2063/15 5FBF/95 9F/01/95
11 AD11 12921 = 16#3279 2063/16 5FBF/96 9F/01/96
12 AD12 12922 = 16#327A 2063/17 5FBF/97 9F/01/97
13 AD13 12923 = 16#327B 2063/18 5FBF/98 9F/01/98
14 AD14 12924 = 16#327C 2063/19 5FBF/99 9F/01/99
15 AD15 12925 = 16#327D 2063/1A 5FBF/9A 9F/01/9A
Table of values for set no. 1:
No. Code Logic address: CANopen index: INTERBUS index: DeviceNet path:
1 S101 12931 = 16#3283 2063/20 5FBF/9B 9F/01/9B
2 S102 12932 = 16#3284 2063/21 5FBF/9C 9F/01/9C
3 S103 12933 = 16#3285 2063/22 5FBF/9D 9F/01/9D
4 S104 12934 = 16#3286 2063/23 5FBF/9E 9F/01/9E
5 S105 12935 = 16#3287 2063/24 5FBF/9F 9F/01/9F
6 S106 12936 = 16#3288 2063/25 5FBF/A0 9F/01/A0
7 S107 12937 = 16#3289 2063/26 5FBF/A1 9F/01/A1
8 S108 12938 = 16#328A 2063/27 5FBF/A2 9F/01/A2
9 S109 12939 = 16#328B 2063/28 5FBF/A3 9F/01/A3
10 S110 12940 = 16#328C 2063/29 5FBF/A4 9F/01/A4
11 S111 12941 = 16#328D 2063/2A 5FBF/A5 9F/01/A5
12 S112 12942 = 16#328E 2063/2B 5FBF/A6 9F/01/A6
13 S113 12943 = 16#328F 2063/2C 5FBF/A7 9F/01/A7
14 S114 12944 = 16#3290 2063/2D 5FBF/A8 9F/01/A8
15 S115 12945 = 16#3291 2063/2E 5FBF/A9 9F/01/A9
74 1755861 11/2009
Page 74

Parameter set switching
Table of values for parameter set no. 2:
No. Code Logic address: CANopen index: INTERBUS index: DeviceNet path:
1 S201 12951 = 16#3297 2063/34 5FBF/AA 9F/01/AA
2 S202 12952 = 16#3298 2063/35 5FBF/AB 9F/01/AB
3 S203 12953 = 16#3299 2063/36 5FBF/AC 9F/01/AC
4 S204 12954 = 16#329A 2063/37 5FBF/AD 9F/01/AD
5 S205 12955 = 16#329B 2063/38 5FBF/AE 9F/01/AE
6 S206 12956 = 16#329C 2063/39 5FBF/AF 9F/01/AF
7 S207 12957 = 16#329D 2063/3A 5FBF/B0 9F/01/B0
8 S208 12958 = 16#329E 2063/3B 5FBF/B1 9F/01/B1
9 S209 12959 = 16#329F 2063/3C 5FBF/B2 9F/01/B2
10 S210 12960 = 16#32A0 2063/3D 5FBF/B3 9F/01/B3
11 S211 12961 = 16#32A1 2063/3E 5FBF/B4 9F/01/B4
12 S212 12962 = 16#32A2 2063/3F 5FBF/B5 9F/01/B5
13 S213 12963 = 16#32A3 2063/40 5FBF/B6 9F/01/B6
14 S214 12964 = 16#32A4 2063/41 5FBF/B7 9F/01/B7
15 S215 12965 = 16#32A5 2063/42 5FBF/B8 9F/01/B8
Table of values for set no. 3:
No. Code Logic address: CANopen index: INTERBUS index: DeviceNet path:
1 S301 12971 = 16#32AB 2063/48 5FBF/B9 9F/01/B9
2 S302 12972 = 16#32AC 2063/49 5FBF/BA 9F/01/BA
3 S303 12973 = 16#32AD 2063/4A 5FBF/BB 9F/01/BB
4 S304 12974 = 16#32AE 2063/4B 5FBF/BC 9F/01/BC
5 S305 12975 = 16#32AF 2063/4C 5FBF/BD 9F/01/BD
6 S306 12976 = 16#32B0 2063/4D 5FBF/BE 9F/01/BE
7 S307 12977 = 16#32B1 2063/4E 5FBF/BF 9F/01/BF
8 S308 12978 = 16#32B2 2063/4F 5FBF/C0 9F/01/C0
9 S309 12979 = 16#32B3 2063/50 5FBF/C1 9F/01/C1
10 S310 12980 = 16#32B4 2063/51 5FBF/C2 9F/01/C2
11 S311 12981 = 16#32B5 2063/52 5FBF/C3 9F/01/C3
12 S312 12982 = 16#32B6 2063/53 5FBF/C4 9F/01/C4
13 S313 12983 = 16#32B7 2063/54 5FBF/C5 9F/01/C5
14 S314 12984 = 16#32B8 2063/55 5FBF/C6 9F/01/C6
15 S315 12985 = 16#32B9 2063/56 5FBF/C7 9F/01/C7
1755861 11/2009 75
Page 75

Parameter set switching
Code Description
VAL
Parameter name: Load parameter set command
Logic address: 12901 = 16#3265 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2063/02 Read/write: R/W
INTERBUS index:
DeviceNet path: A1/01/66
0 = Function not used or a new set of parameters has been taken into account
1 = Request to write a new set of parameters
2 = A new set of parameters is being written
Procedure:
• Write the addresses and values of the sets.
• Set VAL to 1.
• Once the new sets have been taken into account, the drive resets (VAL) to 0.
76 1755861 11/2009
Page 76

Loading drive parameters
Requirement
Certain applications require parameters to be downloaded:
• When the installation starts up
• When the manufacturing range is changed
• When a faulty device is replaced
Neither the integrated ports nor the network cards of the drive provide a parameter file loading procedure (except for the faulty device
replacement (FDR) mechanism of the VW3 A3 310 Modbus Ethernet TCP/IP card).
Parameter loading is therefore based on write requests that have to be programmed in the controller (PLC, etc.).
If the controller is limited to writing para meters sequentially, the final configuration risks not being identical to the one desired.
The differences between the configuration to be loaded and the real configuration result from cons istency checking of the drive parame ters.
The drive checks relationships between the parameters, and if they are not correct:
• It automatically modifies a parameter which is offered for writing (pedestal, deadband) or
• Writing of the parameter is rejected
Examples illustrating this problem are given on page 78
The controller must therefore follow a procedure that includes a phase of disabling the consistency check function.
Procedure
.
All the operations described below must be carried out with the motor stopped, with no run command to the drive.
Saving the reference configuration
1. Identify the parameters of the reference drive that differ from the factory setting. These parameters can be identified easily using the
PowerSuite software (which displays the list of parameters).
2. Reserve a parameter map table in the controll er (PLC, etc. ). This map t abl e is a se ries of add re sses a nd values. Th e las t para m eter to
be loaded is identified by an address equal to -1.
3. Enter the addresses of the modified parameters into the controller's map table by copying the list given by the PowerSuite software.
4. Initialize the values in the map table . There are two possible methods:
- Enter the values manually.
- Program an automatic read function in the controller. Connect the controller to the reference drive. Save the reference
configuration in the map table.
Loading the configuration
The program in the controller (PLC, etc.) must perform the following operations:
1. Command a drive factory setting:
Write the value 16#0001 to the extended control word (8504-CMI).
2. Disable the parameter consistency check function:
Write the value 16#8000 to the extended control word (8504-CMI).
3. Load the configuration:
Write the parameters one after another using the map table.
4. Enable the parameter consistency check function:
Write the value 16#0000 to the extended control word (8504-CMI).
5. Check the drive configuration:
Read and compare the parameters one after another against the map table.
1755861 11/2009 77
Page 77

Loading drive parameters
Inconsistency examples
The two adjustment parameters [Low speed] (3105-LSP) and [High speed] (3104-HSP) comply with the consistency rule:
0
y [Low speed] (3105-LSP) y [High speed] (3104-HSP) y 16000.
Example 1
Initial configuration V Configuration to be loaded:
[High speed] (3104-HSP) = 30 Hz
[Low speed] (3105-LSP) = 20 Hz
• "Request n: Request to write [Low speed] (3105-LSP) to 40 Hz
• "Consistency check: The consistency rule [Low speed] (3105-LSP)
-The [Low speed] (3105-LSP) parameter actually written into the drive is 30 Hz.
• "Request n+1: Request to write [High speed] (3104-HSP) = 60 Hz
• "Consistency check: The consistency rules have been observed:
-The [High speed] (3104-HSP) parameter is correctly written as 60 Hz in the drive.
The loaded configuration differs from the configuration to be loaded:
[Low speed] (3105-LSP) = 30 Hz instead of [Low speed] (3105-LSP) = 40 Hz
The drive can operate between 30 Hz and 40 Hz, which is not desired.
Example 2
Initial configuration V Configuration to be loaded:
[High speed] (3104-HSP) = 60 Hz
[Low speed] (3105-LSP) = 40 Hz
V [High speed] (3104-HSP) = 60 Hz
V [Low speed] (3105-LSP) = 40 Hz
y [High speed] (3104-HSP) has not been observed:
V [High speed] (3104-HSP) = 30 Hz
V [Low speed] (3105-LSP) = 0 Hz
• "Request n: Request to write [High speed] (3104-HSP) to 30 Hz
• "Consistency check: The consistency rule [Low speed] (3105-LSP)
-The [High speed] (3104-HSP) parameter actually written into the drive is 40 Hz.
• "Request n+1: Request to write [Low speed] (3105-LSP) = 0 Hz
• "Consistency check: The consistency rules have been observed:
-The [Low speed] (3104-HSP) parameter is correctly written as 0 Hz in the drive.
The loaded configuration differs from the configuration to be loaded:
[High speed] (3104-HSP) = 40 Hz instead of [High speed] (3104-HSP) = 30 Hz
The drive can operate between 30 Hz and 40 Hz, which is not desired.
y [High speed] (3104-HSP) has not been observed:
78 1755861 11/2009
Page 78

Command parameters
Code Description
CMd
Parameter name: Co ntro l wo rd
Terminal display: [Cmd value]
CiA402 name: controlword
DRIVECOM name: Control word
Logic address: 8601 = 16#2199
or 8501 = 16#2135 (1)
CANopen index: 6040/0 Read/write: R/W
INTERBUS index: 6040/0
DeviceNet path: B7/01/01
(1)Note: This parameter is available at two logic addresses to optimize exchanges via Modbus messaging (Modbus
function 16 = 16#10 Write Multiple Registers):
- If the drive has to be controlled in terms of speed, it is preferable to use address 8601, since the speed refe rence
is at address 8602.
- If the drive has to be controlled in terms of frequency, it is preferable to use address 8501, since the frequency
reference is at address 8502.
Parameter conforming to CiA402 profile
Possible values in the IO profile
On state command [2 wire] (2C)
bit 0: Forward (on state) command
= 0: No forward command
= 1: Forward command
Type: WORD (bit register)
On edge command [3 wire] (3C)
bit 0: Stop (run authorization)
= 0: Stop
= 1: Run is authorized on a forward or reverse
command
bit 1: Forward (on 0 V 1 rising edge) command
The assignment of bit 0 cannot be mod ified. It corresp onds to
the assignment of the terminals. It can be switched. Bit 0
(Cd00) is only active if the channel of this control word is
active.
Bits 1 to 15 can be assigned to commands. Bits 2 to 15 can be assigned to commands.
For example, to change the direction of operation using bit 2 of the control word of the active channel, simply configure the
[Reverse assign.] (rrS) parameter:
• To the value [C102] (C102) ... [C402] (C402) for a fixed assignment
• To the value [CD02] (Cd02) for a switched assignment
The stop commands:
• Freewheel stop [Freewheel stop ass.] (nSt)
• Fast stop [Fast stop assign.] (FSt) are active at value 0, in the same way as on the terminals.
= 0: Stop
= 1: No stop command
DC injection braking [DC injection assign.] (dCI) is active at value 1, in the same way as on the terminals.
= 0: No braking command
= 1: Braking
If a fixed assignment is made [C101] (C101) to [C115] (C115) ... [C401] (C401) to [C415] (C415), the freewheel stop, fast
stop and DC injection braking commands are always active, even if the channel is not active. If these commands are
configured as fixed assignments, the following settings must be made in order to start, even if another channel is active:
• Freewheel stop = 1
• Fast stop = 1
• DC injection braking = 0
The assignment of bits 0 and 1 cannot be modified. It
corresponds to the assignment of the terminals. It can be
switched. Bits 0 (Cd00) and 1 (Cd01) are only active if the
channel of this control word is active.
If a switched assignment is made [CD00] (Cd00) to [Cd15] (Cd15) the freewheel stop, fast stop and DC injection braking
commands are only active if the channel is active.
1755861 11/2009 79
Page 79

Command parameters
Code Description
Possible values in CiA402 profile, separate or not separate mode
bit 0: "Switch on"/Contactor command
bit 1: "Disable voltage"/Authorization to supply AC power
bit 2: "Quick stop"/Emergency stop
bit 3: "Enable operation"/Run command
bit 4: Reserved (set to 0)
bit 5: Reserved (set to 0)
bit 6: Reserved (set to 0)
bit 7: "Fault reset"/Fault acknowledgment active on 0 V 1 rising edge
bit 8: Halt Stop according to the [Type of stop] (Stt) parameter without leaving the 5 - Operation enabled state
bit 9: Reserved (set to 0)
bit 10: Reserved (set to 0)
bit 11: Direction of rotation command Default assignment; this bit can be assigned to another command.
= 0: Forward rotation
= 1: Reverse rotation
bit 12: Can be assigned to a command
bit 13: Can be assigned to a command
bit 14: Can be assigned to a command
bit 15: Can be assigned to a command
For the description of bits 0, 1, 2, 3, 7 and 8, see the "CiA402 profile" section.
The CiA402 standard enables the drive manufacturer to use bits 11 to 15 in a specific way. On the Altivar 71, they can be
assigned to function commands. Bit 11 is assigne d by default t o control the di rection of rotation, al though it can be assigned
to another command. A new assignment deletes the assig nment to the di rection of ro tation co mmand. Bits 12 t o 15 have no
default assignment. For example, to control DC injection braking using bit 12 of the Modbus control word, simply set the
[DC injection assign.] (dCI)) parameter to value [C212] (C212).
The fast stop command configured by [Fast stop assign.] (FSt) is active at 1:
= 0: No stop command
= 1: Stop
The DC injection braking command configured by [DC injection assign.] (dCI) is active at 1:
= 0: No braking command
= 1: Braking
With a fixed assignment ([C1
stops, even if the channel is not active. If thes e commands are co nfigu red as fixe d assignment s, the f ollowing se ttin gs must
be made in order to start, even if another channel is active:
• Fast stop command = 0
• DC injection braking command = 0
With a switched assignment ([Cd
is active.
The freewheel stop [Freewheel stop ass.] (nSt) command cannot be assigned in CiA402 profile.
pp], [C2pp], [C3pp] or [C4pp]), the fast stop and DC injection braking commands are priority
pp]), the fast stop and DC injection braking commands are only operational if the channel
80 1755861 11/2009
Page 80

Command parameters
Code Description
CMI Parameter name: Extended control word
Logic address: 8504 = 16#2138 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2037/5 Read/write: R/W
INTERBUS index: 5FB6/1E
DeviceNet path: 8B/01/69
bit 0: RAM factory setting command according to the [PARAMETER GROUP LIST] (FrY) parameter (active at 1). If y ou
also wish to return the EEPROM to the factory setting, bit 1 must also be set to 1 (both commands can be executed
simultaneously).
bit 1: Save configuration to EEPROM non-volatile memory command (active at 1).
This bit automatically changes to 0 after the reque st is ta ken into accou nt. Th e command is only a ctive i f the dri ve
is stopped, and not in "5-Operation enabled" state.
Note: If CMI is a periodic network variable, the PLC program must write it to 0 after the first request is taken into
account. The life of the EEPROM memory is limited to 100,000 write operat ions.
Note: If the motor or configuration switching function is active, the configuration in the RAM is saved to the
EEPROM in the configuration designated by [Config. Active] (CnFS).
bit 2: Restore configuration to EEPROM non-volatile memory command (active on 0 to 1 rising edge).
This bit automatically changes to 0 after the request is taken into account.
The command is only active if the drive is stopped, and not in "5-Operation enabled" state.
Note: If CMI is a periodic network variable, the PLC program must write it to 0 after the first request is taken into
account.
This does not adversely affect the life of the EEPROM memory, but permanently copies the configuration
in the memory to the current configuration.
Note: If the motor or configuration switching function is active, the configuration in the EEPROM designated by
[Config. Active] (CnFS) is copied to the RAM.
bit 3: Reserved (= 0)
bit 4: Reserved (= 0)
bit 5: Reserved (= 0)
bit 6: Reserved (= 0)
bit 7: Reserved (= 0)
bit 8: Reserved (= 0)
bit 9: Definition of the frequency reference (LFr) and output frequency (rFr) unit:
=0: 0.1 Hz
=1: Standardized value 16 signed bits based on the maximum frequency. The value 32767 corresponds to
[Max frequency] (tFr). The default value of [Max frequency] (tFr) is 60 Hz, and the resolution is then
approximately 0.0018 Hz.
This function has no effect on the speed reference (LFrd) or the output speed (rFrd).
bit 10: Fast stop command (active at 1)
bit 11: DC injection braking command (active at 1). This command must no be used if [Motor control type] (Ctt) =
[Sync. mot.] (SYn).
bit 12: Direction of rotation command
= 0: Forward
= 1: Reverse
bit 13: Reserved (= 0)
bit 14: Reserved (= 0)
bit 15: Parameter consistency check
= 0: The check is activated. Each time a parameter is written, the drive checks the relationship between the written
parameter and the configuration in the drive. For example, the [High speed] (HSP) parameter must be less than
the [Max frequency] (tFr) parameter. If an attempt is made to write a val ue greater than the [Max frequency ] (tFr)
parameter to the [High speed] (HSP) parameter, the write operation is accepted, but the value i s limited to th at of
[Max frequency] (tFr).
= 1: The check is deactivated. The drive is locked in stop mode. In this drive state, the configuration can be written
parameter by parameter and the drive does not modify the values that are written.
1
V0: The change from 1 to 0 triggers a calculation of the consistency of the configuration. Some parameters can be
modified automatically by the drive.
1755861 11/2009 81
Page 81

Setpoint parameters
See section “Assignment of setpoints from a network”, page 60
Code Description
LFRD
LFR
Parameter name: Speed setpoint
CiA402 name: vl target velocity
DRIVECOM name: Speed-Setpoint
Logic address: 8602 = 16#219A Type: INT
CANopen index: 6042/0 Read/write: R/W
INTERBUS index: 6042/0 Unit: rpm
DeviceNet path: 2A/01/08 (1)
8C/01/03 (2)
Parameter conforming to CiA402 and ODVA profiles
Signed value. This parameter changes the direction of operation according to its si gn.
Parameter name: Freq uen cy reference
Terminal display: [Frequency ref.]
Logic address: 8502 = 16#2136 Type: INT
CANopen index: 2037/3 Read/write: R/W
INTERBUS index: 5FB6/1C Unit: 0.1 Hz or standardized
DeviceNet path: 8B/01/67
Signed value.
The unit depends on the value of bit 9 of the extended control word (CMI):
= 0: 0.1 Hz
= 1: High resolution: Standardized value at maximum frequency in 16 signed bits. The value 32767 = 16 # 7FFF
corresponds to [Max frequency] (tFr). The default value of [Max frequency] (tFr) is 60 Hz, and the resolution is
then approximately 0.0018 Hz.
16 signed bits based on the
maximum frequency (TFR)
LTR
(1)ODVA standard path. It can be used for explicit messaging. Do not use it for configuring an assembly.
(2)Altivar path. Avoid using it for explici t messaging, to ensure bet ter interc hangeabili ty. Thi s is the p ath that must be used for configuri ng
an assembly.
Parameter name: Torque reference
Terminal display: [HMI torque ref.]
CiA402 name: Target torque
DRIVECOM name: Torque-Setpoint-External
Logic address: 8505 = 16#2139 Type: INT
CANopen index: 6071/0 Read/write: R/W
INTERBUS index: 5FB6/1F Unit:
DeviceNet path: 8B/01/6A
Parameter conforming to CiA402 profile
Signed value.
The "Nominal motor torque" is not accessible as a drive parameter. I t is the result of a calculation on the o ther characteristics.
0.001 "Nominal motor torque"
82 1755861 11/2009
Page 82

Setpoint parameters
Code Description
Int Parameter name: Torque unit
Logic address: 9260 = 16#242C Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 203E/3D Read/write: R/WS
INTERBUS index: 5FBF/35 Factory setting: According to drive rating
DeviceNet path: 8F/01/3D
0 = 0.01 Nm
1 = 0.1 Nm
2=1 Nm
3 = 10 Nm
This parameter is only used and can only be configured wit h DeviceNet. It sets the u nit for the LTCR and OTRN parameters.
LtCr
PISP Parameter name: PID regulator setpoint
AIU1
Parameter name: Torque setpoint (Nm)
Logic address: 9261 = 16#242D Type: INT
CANopen index: 203E/3E Read/write: R/W
INTERBUS index: 5FB6/3D Unit: 0.01 - 0.1 - 1 - 10 Nm
DeviceNet path: 2A/01/0C
Logic address: 8503 = 16#2137 Type: INT
CANopen index: 2037/4 Read/write: R/W
INTERBUS index: 5FB6/1D Unit: 1
DeviceNet path: 8B/01/68
Signed value.
If the PID regulator is to be controlled via a network, this reference must be written, in accordance with the protocol:
• Either via messaging
• Or by assigning this parameter in the periodic variables
Parameter name: Network analog input
Terminal display: [Network AI]
Logic address: 5281 = 16 #14A1 Type: INT
CANopen index: 2016/52 Read/write: R/W
According to Int page 83
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/40 Unit: 1
DeviceNet path: 7B/01/52
MFr Parameter name: Multip ly in g c oe ffi ci e nt
Terminal display: [Multiplying coeff.]
Logic address: 11831 = 16#2E37 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2058/20 Read/write: R/W
INTERBUS index: 5FB6/3E Unit: 1%
DeviceNet path: 9C/01/20
1755861 11/2009 83
Page 83

Status parameters
Code Description
ETA
Parameter name: Status word
CiA402 name: Statusword
DRIVECOM name: Statusword
Logic address: 8603 = 16#219B
or 3201 = 16#0C81 (1)
CANopen index: 6041/0 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 6041/0
DeviceNet path: 71/01/02
(1)Note: This parameter is available at two logic addresses to optimize exchanges via Modbus messaging (Modbus
function 4 = 16#04 Read Input Registers):
- If the drive has to be monitored in terms of speed, it is preferable to use address 8603, since the output speed is
at address 8604.
- If the drive has to be monitored in terms of frequency, it is preferable to use address 3201, since the output
frequency is at address 3202.
Parameter conforming to CiA402 profile
Possible values in the IO profile
Note: The value is identical in the CiA402 profile and the I/O profile. In the I/O profile, the description of the values is
simplified and does not refer to the CiA402 (Drivecom) state chart.
bit 0: Reserved (= 0 or 1)
bit 1: Ready
= 0: Not ready, = 1: Ready
bit 2: Running
= 0: The drive will not start if a reference other than zero is applied.
= 1: Running, if a reference other than zero is applied, the drive can start.
bit 3: Fault
= 0: No fault, = 1: Fault
Type: WORD (bit register)
bit 4: Power section line supply present
= 0: Power section line supply absent, = 1: Power section line supply present
bit 5: Reserved (= 1)
bit 6: Reserved (= 0 or 1)
bit 7: Alarm
= 0: No alarm, = 1: Alarm
bit 8: Reserved (= 0)
bit 9: Command via a network
= 0: Command via the terminals or the graphic display terminal, = 1: Command via a network
Note: The network can be integrated Modbus, CANopen, a communication card or the Controller Inside card. This is not
necessarily the network via which the status word is read. Therefore, if the command comes from CANopen (CANopen
command channel active) and the status word (ETA) is read via an Ethernet card, the data item "Control via a network" = 1.
This does not mean that control can be carried out via the Ethernet card. For more information, see the "Active command
channel" (CCC) and "Active reference channel" (CRC) parameters.
bit 10: Reference reached
= 0: The reference is not reached, = 1: The reference has been reached
bit 11: Reference outside limits
= 0: The reference is within the limits, = 1: The reference is not within t he limits
When the drive is in speed mode, the limits are defined by the "Low speed (LSP)" and "High speed (HSP)"
parameters. When the torque function is activated, refer to the description of this function (see the Programming
Manual).
bits 12 and 13: Reserved (= 0)
bit 14: Stop via STOP key
= 0: STOP key not pressed, = 1: Stop triggered by the STOP key on the graphic display terminal
bit 15: Direction of rotation
= 0: Forward rotation at output, = 1: Reverse rotation at output
84 1755861 11/2009
Page 84

Status parameters
Code Description
Possible values in CiA402 profile
bit 0: "Ready to switch on", awaiting power section line supply
bit 1: "Switched on", ready
bit 2: "Operation enabled", running
bit 3: "Fault"
= 0: No fault,
= 1: Fault
bit 4: "Voltage enabled", power section line supply present
= 0: Power section line supply absent
= 1: Power section line supply present
When the drive is powered by the power section only, this bit is always at 1.
bit 5: Quick stop/Emergency stop
bit 6: "Switched on disabled", power section line supply locked
bit 7: Warning alarm
= 0: No alarm
= 1: Alarm
bit 8: Reserved (= 0)
bit 9: Remote: command or reference via the network
= 0: Command or reference via the terminals
= 1: Command or reference via the network
bit 10: Target reference reached
= 0: The reference is not reached
= 1: The reference has been reached
When the drive is in speed mode, this is the speed reference. When the torque function is activated, refer to the
description of this function (see the Programming Manual). Wh en the drive stops, the reference has been reached.
bit 11: "Internal limit active", reference outside limits
= 0: The reference is within the limits
= 1: The reference is not within the limits
When the drive is in speed mode, the limits are defined by the "Low speed (LSP)" and "High speed (HSP)"
parameters. When the torque function is activated, refer to the description of this function (see the Programming
Manual).
bit 12: Reserved (= 0)
bit 13: Reserved (= 0)
bit 14: "Stop key", STOP via stop key
= 0: STOP key not pressed
= 1: Stop triggered by the STOP key on the graphic display terminal
bit 15:"Direction", direction of rotation
= 0: Forward rotation at output
= 1: Reverse rotation at output
The combination of bits 0, 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6 defines the state in the DSP 402 state chart (see the CiA402 profile section).
1755861 11/2009 85
Page 85

Status parameters
Code Description
ETI Parameter name: Extended status word
Logic address: 3206 = 16#0C86 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/7 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/08
DeviceNet path: 71/01/07
bit 0: = 1: Access to the EEPROM non-volatile memory in progress
bit 1: = 0: No parameter consistency check
= 1: Parameter consistency check
bit 2: = 0: The drive is not in fault state or a fault is present
= 1: The drive is in fault state but the fault is no longer present (not acknowledged)
bit 3: Reserved (= 0)
bit 4: = 1: Drive in speed regulation mode
bit 5: = 1: DC injection braking (identical to LSR4, bit 11)
bit 6: = 0: Drive in steady state
= 1: Drive in transient state
bit 7: = 1: Motor thermal state threshold reached for the active motor
LRS1
bit 8: = 1: Overbraking (identical to LSR5, bit 1)
bit 9: = 1: Acceleration in progress (identical to LSR4, bit 13)
bit 10: = 1: Deceleration in progress (identical to LSR4, bit 14)
bit 11: = 1: Current or torque limiting in progress
bit 12: = 1: Fast stop in progress (identical to LSR4, bit 15)
bit 13: bit 13 = 0 and bit 14 = 0: Command via the terminals
bit 14: bit 13 = 1 and bit 14 = 0: Command via the graphic display terminal
bit 13 = 0 and bit 14 = 1: Command via Modbus
bit 13 = 1 and bit 14 = 1: Command via CANopen, the network card or the "Controller Inside" card
bit 15: = 0: Forward operation applied before the ramp
= 1: Reverse operation applied before the ramp
Parameter name: Extended status word 1
Logic address: 3250 = 16#0CB2 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/33 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/1C
DeviceNet path: 71/01/33
bit 0: Reserved (= 0)
bit 1: = 1: The drive is in fault state
bit 2: = 0: The drive is locked, the motor is not powered
= 1: The drive is unlocked, power can be supplied to the motor (RUN state)
bit 3: = 1: The output contactor is controlled
bit 4: = 1: Frequency threshold (ftd) reached: [Freq. Th. attained] (FtA)
bit 5: = 1: High speed (HSP) reached: [HSP attained] (FLA)
bit 6: = 1: Current threshold (Ctd) reached: [Current Th. attained] (CtA)
bit 7: = 1: Frequency reference reached: [Frequency ref. att.] (SrA)
bit 8: = 1: Motor 1 thermal state threshold [Motor therm. level] (ttd) reached: [Motor th. state att.] (tSA)
bit 9: = 1: Brake contactor command [Brake assignment] (bLC) active
bit 10: = 1: PID regulator error alarm: [PID error al] (PEE)
bit 11: = 1: PID regulator feedback alarm: [PID fdbk al.] (PFA)
bit 12: = 1: 4-20 mA alarm on analog input AI2: [4-20mA loss (AI2)] (LFF2)
bit 13: = 1: Second frequency threshold (ftd) reached: [Freq. Th. 2 attained] (FA2)
bit 14: = 1: Drive thermal state threshold [Drv therm. state al] (tHA) reached: [Th. drv. att.] (tAd)
bit 15: = 1: The "traverse control" function is active
86 1755861 11/2009
Page 86

Status parameters
Code Description
LRS2 Parameter name: Extended status word 2
Logic address: 3251 = 16#0CB3 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/34 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/1D
DeviceNet path: 71/01/34
bits 0 to 10: Reserved (= 0)
bit 11: = 1: Rope slack (see [Rope slack config.] (rSd)) parameter
bit 12: = 1: [High torque alarm] (ttHA): Motor torque greater than the high threshold [High torque thd.] (ttH)
Bit 13: = 1: [Low torque alarm] (ttLA): Motor torque less than the low threshold [Low torque thd.] (ttL)
Bit 14: = 1: [Forward] (MFrd): Motor rotating in the forward direction
Bit 15: = 1: [Reverse] (MrrS): Motor rotating in the reverse direction
LRS3
Parameter name: Extended status word 3
Logic address: 3252 = 16#0CB4 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/35 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/1E
DeviceNet path: 71/01/35
bit 0: = 0: Reference channel 1 or 1B (Fr1) or (Fr1b) is active
= 1: Reference channel 2 (Fr2) is active
bit 1: = 0: Command channel 1 (Cd1) is active
= 1: Command channel 2 (Cd2) is active
bit 2: = 0: Ramp set 1 (ACC) and (dEC )
= 1: Ramp set 2 (AC2) and (dE2)
bit 3: = 0: Current limit 1 (CLI) is active
= 1: Current limit 2 (CL2) is active
bit 4: Reserved (= 0)
bit 5: = 1: Motor 2 thermal state threshold [Motor2 therm. level] (ttd2) reached: [Th.mot2 att] (tS2)
bit 6: = 1: Motor 3 thermal state threshold [Motor3 therm. level] (ttd3) reached: [Th.mot3 att] (tS3)
bit 7: Reserved (= 0)
bit 8: = 1: 24 VDC external power supply present
bit 9: = 1: Stop on low speed time limit function [Low speed time out] (tLS)
bit 10: Reserved (= 0)
bit 11: Reserved (= 0)
bit 12: Reserved (= 0)
bit 13: Reserved (= 0)
bit 14: Reserved (= 0)
bit 15: = 0: The output torque is positive (forward)
= 1: The output torque is negative (reverse)
1755861 11/2009 87
Page 87

Status parameters
Code Description
LRS4 Parameter name: Extended status word 4
Logic address: 3253 = 16#0CB5 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/36 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/1F
DeviceNet path: 71/01/36
bit 0: = 1: Configuration 0 is active
bit 1: = 1: Configuration 1 is active [Cnfg.1 act.] (CnF1)
bit 2: = 1: Configuration 2 is active [Cnfg.2 act.] (CnF2)
bit 3: Reserved (= 0)
bit 4: = 1: Parameter set 1 is active: [Set 1 active] (CFP1)
bit 5: = 1: Parameter set 2 is active: [Set 2 active] (CFP2)
bit 6: = 1: Parameter set 3 is active: [Set 3 active] (CFP3)
bit 7: Reserved (= 0)
bit 8: = 0: Power section line supply present
= 1: Power section line supply absent
bit 9: = 1: Motor "fluxing" in progress: [In motor fluxing] (FLX)
bit 10: = 1: The motor is "fluxed"
bit 11: = 1: DC injection braking (identical to ETI, bit 5)
LRS5
bit 12: = 1: Current limiting in progress
bit 13: = 1: Acceleration in progress (identical to ETI, bit 9)
bit 14: = 1: Deceleration in progress (identical to ETI, bit 10)
bit 15: = 1: Fast stop in progress: [Fast stop in prog.] (FSt) (identical to ETI, bit 12)
Parameter name: Extended status word 5
Logic address: 3254 = 16#0CB6 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/37 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/20
DeviceNet path: 71/01/37
bit 0: = 1: Drive DC bus loading: [DC bus loading] (dbL)
bit 1: = 1: Drive braking [In braking] (brS)
bit 2: = 1: The "Power removal" function is active
bit 3: = 1: Automatic restart attempts in progress: [Auto restart] (AUtO)
bit 4: = 1: "Auto-tuning" in progress: [Auto-tuning] (tUn)
bit 5: = 1: Controlled stop in progress following loss of power section line supply (CTL)
bit 6: = 1: The drive cannot follow the configured deceleration ramp, deceleration automatically adapted (OBR)
bit 7: = 1: Controlled output cut in progress (SOC)
bit 8 : = 1: [Freq. meter Alarm] (FqLA): Measured speed threshold reached: [Pulse warning thd.] (FqL)
bit 9: = 1: The line contactor is active
bit 10: Reserved (= 0 or 1)
bit 11: Reserved (= 0 or 1)
bit 12: Reserved (= 0 or 1)
bit 13: = 1: Current present in the motor (MCP)
bit 14: = 1: If the "limit switch management" [LIMIT SWITCHES] function is activated. The [Stop FW limit sw.] or
[Stop RV limit sw.] stops are reached.
bit 15 : = 1: [Dynamic load alarm] (dLdA): Load variation detection (see [DYNAMIC LOAD DETECT.] (dLd -))
88 1755861 11/2009
Page 88

Status parameters
Code Description
LRS6 Parameter name: Extended status word 6
Logic address: 3255 = 16#0CB7 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/38 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/21
DeviceNet path: 71/01/38
bit 0: = 1: Alarm group 1 is active
bit 1: = 1: Alarm group 2 is active
bit 2: = 1: Alarm group 3 is active
bit 3: = 1: Probe 1 alarm: [PTC1 alarm] (PtC1)
bit 4: = 1: Probe 2 alarm: [PTC2 alarm] (PtC2)
bit 5: = 1: LI6 PTC probe alarm: [LI6 =PTC alarm] (PtC3)
bit 6: Reserved (= 0)
bit 7: = 1: External fault [External fault alarm] (EtF)
bit 8: = 1: Undervoltage alarm [Undervoltage] (USA)
bit 9: = 1: The power section line supply loss detection threshold for a controlled stop has been reached (undervoltage
warning)
bit 10: = 1: Slipping alarm: [Load slipping] (AnA)
bit 11: = 1: Drive overheat alarm (tHA)
LRS7
bit 12: Reserved (= 0)
bit 13: = 1: Speed alarm in the brake control sequence (BSA)
bit 14: = 1: Brake contact alarm in the brake control sequence (BCA)
bit 15: = 1: Current or torque limit alarm after time-out [Trq/I limit. time out] (StO)
Parameter name: Extended status word 7
Logic address: 3256 = 16#0CB8 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/39 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/22
DeviceNet path: 71/01/39
bit 0: = 1: Reference channel 1 or 1B (Fr1) or (Fr1b) is active
bit 1: = 1: Reference channel 2 (Fr2) is active.
bit 2: = 1: Command channel 1 (Cd1) is active.
bit 3: = 1: Command channel 2 (Cd2) is active.
bit 4: = 1: Reference channel 1B (Fr1b) is active.
bit 5: = 1: Spool end ("traverse control" function)
bit 6: = 1: Master-slave synchronization ("traverse control" function)
bit 7: = 1: Torque regulation alarm
bit 8: = 1: IGBT thermal state alarm
bit 9: = 1: Braking resistor overload alarm
bit 10: = 1: Alarm sent by the "Controller Inside" card
bit 11: = 1: 4-20 mA alarm on analog input AI3: [4-20mA loss (AI3)] (LFF3)
bit 12: = 1: 4-20 mA alarm on analog input AI4: [4-20mA loss (AI4)] (LFF4)
bit 13: = 1: DC bus precharging contactor controlled (DC0)
bit 14: Reserved (= 0)
bit 15: Reserved (= 0)
1755861 11/2009 89
Page 89

Status parameters
Code Description
LRS8 Parameter name: Extended status word 8
Logic address: 3257 = 16#0CB9 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/3A Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/23
DeviceNet path: 71/01/3A
bit 0: Reserved (= 0)
bit 1: Reserved (= 0)
bit 2: Reserved (= 0)
bit 3: Reserved (= 0)
bit 4: Reserved (= 0)
bit 5: Reserved (= 0)
bit 6: Reserved (= 0)
bit 7: Reserved (= 0)
bit 8: Reserved (= 0)
bit 9: Reserved (= 0)
bit 10: Reserved (= 0)
bit 11: Reserved (= 0)
CRC
bit 12: Reserved (= 0)
bit 13: Reserved (= 0)
bit 14: Reserved (= 0)
bit 15: = 1: Drive ready(rdY)
Parameter name: Active reference channel
Logic address: 8441 = 16#20F9 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2036/2A Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/CE
DeviceNet path: 8B/01/2A
bit 0: = 1: The terminals are the active reference channel via an analog input
bit 1: Reserved (= 0)
bit 2: = 1: The graphic display terminal is the active reference channel
bit 3: = 1: Modbus is the active reference channel
bit 4: Reserved (= 0)
bit 5: Reserved (= 0)
bit 6: = 1: CANopen is the active reference channel
bit 7: = 1: The terminals are the active reference channel in +/- speed
bit 8: = 1: The graphic display terminal is the active reference channel in +/- speed
bit 9: = 1: The network card is the active reference channel
bit 10: = 1: The "Controller Inside" card is the active reference channel
bit 11: Reserved (= 0)
bit 12: Reserved (= 0)
bit 13: Reserved (= 0)
bit 14: Reserved (= 0)
bit 15: = 1: The PowerSuite software workshop is the active reference channel
90 1755861 11/2009
Page 90

Status parameters
Code Description
CCC Parameter name: Active command channel
Logic address: 8442 = 16#20FA Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2036/2B Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/CF
DeviceNet path: 8B/01/2B
bit 0: = 1: The terminals are the active command channel
bit 1: Reserved (= 0)
bit 2: = 1: The graphic display terminal is the active command channel
bit 3: = 1: Modbus is the active command channel
bit 4: Reserved (= 0)
bit 5: Reserved (= 0)
bit 6: = 1: CANopen is the active command channel
bit 7: = 1: The terminals are the active command channel in +/- speed
bit 8: = 1: The graphic display terminal is the active command channel in +/- speed
bit 10: = 1: The "Controller Inside" card is the active command channel
bit 11: Reserved (= 0)
CFPS
CNFS
bit 12: Reserved (= 0)
bit 13: Reserved (= 0)
bit 14: Reserved (= 0)
bit 15: = 1: The PowerSuite software workshop is the active command channel
Parameter name: Active parameter set
Logic address: 12900 = 16#3264 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2063/01 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/EC
DeviceNet path: A1/01/65
0 : The parameter set switching function is not configured
1 = [Set 1 active] (CFP1): Parameter set no. 1 active
2 = [Set 2 active] (CFP2): Parameter set no. 2 active
3 = [Set 3 active] (CFP3): Parameter set no. 3 active
Parameter name: Active configuration
Terminal display: [Config. Active]
Logic address: 8020 = 16#1F54 Type: WORD (listing)
CANopen index: 2032/15 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/CD
DeviceNet path: 89/01/15
0 : The motor or configuration switching function is not configured
1 = (CNF0): Configuration no. 0 active
2 = (CNF1): Configuration no. 1 active
3 = (CNF2): Configuration no. 2 active
1755861 11/2009 91
Page 91

Output value parameters
Output values (speed)
Code Description
rFrd
rFr
Parameter name: Output velocity
CiA402 name: vl control effort
DRIVECOM name: Speed-Actual-Value
Logic address: 8604 = 16#219C Type: INT
CANopen index: 6044/0 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 6044/0 Unit: rpm
DeviceNet path: 2A/01/07 (1)
8C/01/05 (2)
Parameter conforming to CiA402 and ODVA profiles
Signed value.
If the drive is in open-loop mode, the speed value is estimated.
If the drive is in closed-loop mode, the speed value is measured on the sensor.
This parameter is linked to the "Output frequency" (rFr) parameter for which the unit is 0.1 Hz.
Parameter name: Output frequency
Terminal display: [Output frequency]
Logic address: 3202 = 16#C82 Type: INT
CANopen index: 2002/3 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/04 Unit: 0.1 Hz or standardized
DeviceNet path: 71/01/03
16 signed bits based on the
maximum frequency (TFR)
Signed value.
The unit depends on the value of bit 9 of the extended control word:
=0: 0.1 Hz
=1: Standardized value on 16 signed bits at maximum frequency. The value 32767 corresponds to [Max frequency]
(TFR). The default value of [Max frequency] (TFR) is 60 Hz, and the resolution is then approximately 0.0018 Hz.
(1) ODVA standard path. It can be used for explicit messaging. Do not use it for configuri ng an assembly.
(2) Altivar path. Avoid using it for explicit messaging, to ensure better interch angeability. Th is is the path that must b e used for configuring
an assembly.
92 1755861 11/2009
Page 92

Output value parameters
Output values (torque)
Code Description
Otr
Otrn
Parameter name: Output torque
Terminal display: [Motor torque]
CiA402 name: Torque actual value
DRIVECOM name: Torque-Actual-Value
Logic address: 3205 = 16#0C85 Type: INT
CANopen index: 6077/0 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/07 Unit:
DeviceNet path: 71/01/06
Parameter conforming to CiA402 profile
Signed value.
The "Nominal motor torque" is not accessible as a drive parameter. It is the result of other characteristics.
Parameter name: Output torque (Nm)
Logic address: 3216 = 16#0C90 Type: INT
CANopen index: 2002/11 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/10 Unit: 0.01 - 0.1 - 1 - 10 Nm
DeviceNet path: 2A/01/0B
0.001 "Nominal motor torque"
According to Int page 83
1755861 11/2009 93
Page 93

Output value parameters
Output values (motor)
Code Description
LCr
UOP
OPr Parameter name: Motor power
Parameter name: Mot or cu rrent
Terminal display: [Motor current]
Logic address: 3204 = 16#0C84 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2002/5 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/06 Unit: 0.1 A
DeviceNet path: 2A/01/09 (1)
71/01/05 (2)
Parameter conforming to ODVA profile
Parameter name: Motor voltage
Terminal display: [Motor voltage]
Logic address: 3208 = 16#0C88 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2002/9 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/0A Unit: 1 V
DeviceNet path: 71/01/09
Terminal display: [Motor power]
Logic address: 3211 = 16#0C8B Type: INT
CANopen index: 2002/C Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/0C Unit: 1%
DeviceNet path: 71/01/0C
UNT Parameter name: Units of parameters APH, PTH, and RTH
Logic address: 3234 = 16#0CA2 Type: WORD (bit register)
CANopen index: 2002/23 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/19
DeviceNet path: 71/01/23
The unit changes automatically when the value reaches the maximum format of the parameter.
bit 0 + bit 1 = unit of APH: 0 = Wh, 1 = kWh, 2 = MWh
bit 2 + bit 3 = unit of PTH: 0 = seconds, 1 = minutes, 2 = hours
bit 4 + bit 5 = unit of RTH: 0 = seconds, 1 = minutes, 2 = hours
bits 6 to 15:Reserved (= 0)
(1)ODVA standard path. It can be used for explicit messaging. Do not use it for configuring an assembly.
(2)Altivar path. Avoid using it for explici t messaging, to ensure bet ter interc hangeabili ty. Thi s is the p ath that must be used for configuri ng
an assembly.
94 1755861 11/2009
Page 94

Output value parameters
Code Description
APH
AUS Parameter name: ENA average speed
Parameter name: Mot or en ergy consum pti on
Terminal display: [Consumption]
Logic address: 3230 = 16#0C9E Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2002/1F Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/15 Unit: According to the preceding
DeviceNet path: 71/01/1F
Terminal display: [ENA avg speed]
Logic address: 12102 = 16#2F46 Type: INT
CANopen index: 205B/3 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/EA Unit: 0.1 Hz
DeviceNet path: 9D/01/67
UNT parameter
1755861 11/2009 95
Page 95

Reference parameters
References (speed)
Code Description
FrHd
FrOd Parameter name: Speed reference after ramp
Parameter name: Speed reference before ramp
Logic address: 8605 = 16#219D Type: INT
CANopen index: 2038/6 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 6043/0 Unit: rpm
DeviceNet path: 8C/01/06 F a ctory setting:
Terminal display:
CiA402 name: vl velocity demand
DRIVECOM name: Speed-Reference-Variable
Logic address: 8641 = 16#21C1 Type: INT
CANopen index: 6043/0 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/D8 Unit: rpm
DeviceNet path: 8C/01/2A F a ctory setting:
Parameter conforming to CiA402 profile
Signed value.
Adjustment range:
Adjustment range:
This parameter is linked to the "Frequency after ramp" (FRO) parameter for which the unit is 0.1 Hz.
FrH
FrO Parameter name: Frequency reference after ramp
Parameter name: Freq uen cy referenc e before ramp
Terminal display: [Frequency ref.]
Logic address: 3203 = 16#0C83 Type: INT
CANopen index: 2002/4 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/05 Unit: 0.1 Hz
DeviceNet path: 71/01/04
Logic address: 9021 = 16#233D Type: INT
CANopen index: 203C/16 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/D9 Unit: 0.1 Hz
DeviceNet path: 8E/01/16
96 1755861 11/2009
Page 96

Reference parameters
References (torque)
Code Description
trr
trO Parameter name: Torque reference after ramp
Parameter name: Torque reference before ramp
Terminal display: [Torque reference]
Logic address: 9231 = 16#240F Type: INT
CANopen index: 203E/20 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/DB Unit: 0.1%
DeviceNet path: 8F/01/20
Torque demand value Torque demand value
Torque-Command-Variable Torque-Command-Variable
Logic address: 9232 = 16#2410 Type: INT
CANopen index: 203E/21 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/DC Unit: 0.001 "Nominal motor torque"
DeviceNet path: 8F/01/21
Parameter conforming to CiA402 profile
Signed value.
The "Nominal motor torque" is not accessible as a drive parameter. It is the result of other characteristics.
1755861 11/2009 97
Page 97

Reference parameters
Reference (regulator)
See section “Assignment of setpoints from a network”, page 60.
Code Description
rPC
rPF Parameter name: PID regulator feedback reference
rPE Parameter name: PID regulator discrepancy
Parameter name: PID reference after ramp
Terminal display: [PID reference]
Logic address: 11982 = 16#2ECE Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2059/53 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/E7 Unit: 1
DeviceNet path: 9C/01/B7
Terminal display: [PID feedback]
Logic address: 11981 = 16#2ECD Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2059/52 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/E6 Unit: 1
DeviceNet path: 9C/01/B6
Terminal display: [PID error]
Logic address: 11980 = 16#2ECC Type: INT
CANopen index: 2059/51 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/E5 Unit: 1
DeviceNet path: 9C/01/B5
rPO Parameter name: PID regulator limit output reference
Terminal display: [PID Output]
Logic address: 11983 = 16#2ECF Type: INT
CANopen index: 2059/54 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/E8 Unit: 0.1 Hz
DeviceNet path: 9C/01/B8
98 1755861 11/2009
Page 98

Measurement parameters
Input measurements
Code Description
ULn
Parameter name: Power supply voltage
Terminal display: [Mains voltage]
Logic address: 3207 = 16#0C87 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2002/8 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/09 Unit: 0.1 V
DeviceNet path: 71/01/08
Thermal states
Code Description
tHd
tHr Parameter name: Mot or ther m a l st ate
Parameter name: Drive thermal state
Terminal display: [Drv. thermal state]
Logic address: 3209 = 16#0C89 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2002/A Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/0B Unit: 1 %
DeviceNet path: 71/01/0A
Terminal display: [Motor thermal state]
Logic address: 9630 = 16#259E Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2042/1F Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/DE Unit: 1 %
DeviceNet path: 91/01/1F
tHb Parameter name: DBR thermal state
Terminal display: [DBR thermal state]
Logic address: 14114 = 16#3722 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 206F/F Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FBD/7F Unit: 1%
DeviceNet path: A7/01/73
1755860 11/2009 99
Page 99

Measurement parameters
Time
Code Description
rtH
PtH Parameter name: Total drive operating time
tAC Parameter name: IGBT alarm time
Parameter name: Total motor operating time
Terminal display: [Run time]
Logic address: 3231 = 16#0C9F Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2002/20 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/16 Unit: According to UNT parameter
DeviceNet path: 71/01/20
Terminal display: [Power on time]
Logic address: 3233 = 16#0CA1 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2002/22 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/18 Unit: According to UNT parameter
DeviceNet path: 71/01/22
Terminal display: [IGBT alarm counter]
Logic address: 3235 = 16#0CA3 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 2002/24 Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/1A Unit: 1 s
(see page 94
(see page 94
)
)
DeviceNet path: 71/01/24
EbOt Parameter name: Current bobbin time
Logic address: 12209 = 16#2FB1 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 205C/A Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/EB Unit: 1 min
DeviceNet path: 9E/01/0A
100 1755860 11/2009
Page 100

Measurement parameters
Code Description
dAY
tIME Parameter name: Time
Parameter name: Date
Logic address: 7391 = 16#1CDF Type: UINT
CANopen index: 202B/5C Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/CE Unit: See below
DeviceNet path: 85/01/C0
Logic address: 7392 = 16#1CE0 Type: UINT
CANopen index: 202B/5D Read/write: R
INTERBUS index: 5FB9/CF Unit: See below
DeviceNet path: 85/01/C1
Format of "Date" and "Time" parameters
Date and time are binary-coded using the corresponding word bits indicated in the table below.
Note: The value 0 for year corresponds to the year 2000 (2006 = 36, for example).
Bits 1514131211109876543210
Year XXXXXXX
Date
Time
Month XXXX
Day XXXXX
Hours XXXXXXXX
Minutes XXXXXXXX
1755860 11/2009 101
 Loading...
Loading...