Page 1

User Manual
EtherNet/IP Network Configuration
Catalog Numbers 1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2F, 1756-EN2T, 1756-EN2TR, 1756-EN2TXT, 1756-EN3TR, 1756-EN2TSC, 1756-EN2TRXT,
1768-ENBT, 1769-L23E-QB1B, 1769-L23E-QBFC1B, 1769-L32E, 1769-L35E, 1769-AENTR, 1783-ETAP, 1783-ETAP1F, 1783-ETAP2F,
1794-AENT, 20-COMM-E, 22-COMM-E, 1734-AENT, 1734-AENTR
Page 2

Important User Information
Read this document and the documents listed in the additional resources section about installation, configuration, and
operation of this equipment before you install, configure, operate, or maintain this product. Users are required to
familiarize themselves with installation and wiring instructions in addition to requirements of all applicable codes, laws,
and standards.
Activities including installation, adjustments, putting into service, use, assembly, disassembly, and maintenance are required
to be carried out by suitably trained personnel in accordance with applicable code of practice.
If this equipment is used in a manner not specified by the manufacturer, the protection provided by the equipment may be
impaired.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or consequential damages resulting from the
use or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many variables and
requirements associated with any particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or
liability for actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or
software described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation,
Inc., is prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary, we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
WARNING: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can cause an explosion in a hazardous environment,
which may lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death, property
damage, or economic loss. Attentions help you identify a hazard, avoid a hazard, and recognize the consequence.
IMPORTANT
Identifies information that is critical for successful application and understanding of the product.
Labels may also be on or inside the equipment to provide specific precautions.
SHOCK HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that dangerous
voltage may be present.
BURN HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that surfaces may
reach dangerous temperatures.
ARC FLASH HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a motor control center, to alert people to
potential Arc Flash. Arc Flash will cause severe injury or death. Wear proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Follow ALL
Regulatory requirements for safe work practices and for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Allen-Bradley, CompactLogix, ControlLogix, DriveLogix , FactoryTalk, FLEX, FlexLogix, Lo gix5000, NetLinx, PanelBuilder, PanelView, PLC-5, POINT I/O, PowerFlex,, Rockwell Automation, RSLinx, RSLogix, R SView,
SLC, and Studio 5000 are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Trademarks not belonging to Rockwell Automation are property of their respective companies.
Page 3

Summary of Changes
Introduction
Updated Information
This release of this document contains new and updated information. To find
new and updated information, look for change bars, as shown next to this
paragraph.
The document contains these changes.
Topic Page
Added the 1769-AENTR to system-level figures 12, 34, 36, 45
Added information about the 1769-AENTR diagnostic web pages 116
Added information about troubleshooting the 1769-AENTR with the web pages 136
Additional, less-significant changes have been made throughout the document.
Change bars mark all changes.
For more information about publications that assist you when you use the
products described in this publication, see
Additional Resources on page 10.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 3
Page 4

Summary of Changes
Notes:
4 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 5

Table of Contents
Preface
EtherNet/IP Overview
Configure a Workstation to Operate
on an EtherNet/IP Network
Configure an EtherNet/IP
Communication Module to Operate
on the Network
About This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Studio 5000 Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Additional Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Chapter 1
EtherNet/IP Communication Modules in a Control System. . . . . . . . . 11
Chapter 2
Configure the Ethernet Communication Driver in RSLinx Software . 14
Chapter 3
Determine Network Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Set the Network IP Address on a Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Set the Network IP Address with the Rotary Switches . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Set the Network IP Address with the BOOTP/DHCP Server. . . . 21
Set the Network IP Address with RSLinx Software or the
Studio 5000 Environment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Reset the Module IP Address to Factory Default Value . . . . . . . . . . 29
Duplicate IP Address Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Duplicate IP Address Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
IP Address Swapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
DNS Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Use EtherNet/IP Communication Modules in a Logix5000
Controller Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Configure a Supervisor on a Devicelevel Ring Network
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 5
Chapter 4
DLR Nodes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Supervisor Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Ring Node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Construct the Physical Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Configure Supervisor Nodes on a DLR Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configure a Ring Supervisor in the Studio 5000 Environment. . . . 37
Enable Ring Supervisor in the Studio 5000 Environment . . . . . . . . 40
Configure and Enable a Ring Supervisor in RSLinx
Classic Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Complete the Physical Connections of the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Verify Supervisor Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Page 6

Table of Contents
Control I/O
Interlocking and Data Transfer
between Controllers
Chapter 5
Set Up the Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Add Distributed I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Add an I/O Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Select a Communication Format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Choosing a Direct or Rack-optimized Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Ownership . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Select a Remote Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Set the Requested Packet Interval (RPI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Access Distributed I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Chapter 6
Set Up the Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Logix5000 Controller Combinations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Tag Guidelines for Produced or Consumed Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Connections for Produced and Consumed Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Produce a Tag. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Configure the Produced Tag. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Consume Data Produced by Another Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Add the Producer Controller to the Consumer’s I/O
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Create the Consumed Tag. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Guidelines for Message (MSG) Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Connections for Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Cache Message Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Enter Message Logic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Add the EtherNet/IP Communication Module to the Local
Controller’s I/O Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Enter a Message. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Configure a MSG Instruction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Communicate with PLC-5 or SLC Controllers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Converting between INTs and DINTs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Mapping Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Receive MSGs from PLC-5 or SLC 500 Controllers . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
6 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 7

Send Email
Communicate with PanelView
Terminals
Table of Contents
Chapter 7
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
EtherNet/IP Communication Module as an Email Client . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Send Email via a Controller-initiated Message Instruction . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Create String Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Enter the Ladder Logic. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Configure the MSG Instruction that Identifies the Mail
Relay Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Configure the MSG Instruction That Contains the Email Text . . 94
Enter Email Text. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Possible Email Status Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Chapter 8
Set Up the Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Logix5000 Controller Combinations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Connections to PanelView Terminals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Add a PanelView Terminal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Organize Controller Data for a PanelView Terminal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Connections to
FactoryTalk View Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Diagnostic Web Pages
Chapter 9
1756-EN2TR Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Diagnostic Overview Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Ethernet Statistics Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Connection Manager Cmd Object Info Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Ring Statistics Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
1756-ENBT Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Diagnostic Overview Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
1769-AENTR Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Diagnostic Overview Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 7
Page 8

Table of Contents
Troubleshoot an EtherNet/IP
Communication Module with
Diagnostic Web Pages
Index
Chapter 10
Access Web Browser Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Troubleshoot the
1756-ENBT Communication Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Diagnostic Overview Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Message Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
I/O Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Troubleshoot the
1756-EN2TR Communication Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Diagnostic Overview Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Troubleshoot the
1769-AENTR Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Diagnostic Overview Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
I/O Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Switch Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Internet Group Multicast Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Virtual Local Area Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
8 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 9

Preface
About This Manual
Studio 5000 Environment
This manual describes how you can use EtherNet/IP communication modules
with your Logix5000
controller and communicate with various devices on the
Ethernet network.
Use this manual if you program applications that use EtherNet/IP networks with
these Logix5000 controllers:
controller
controller
controller
• CompactLogix
• ControlLogix
• SoftLogix
Be sure to understand these concepts and tools:
• Use of networking
• Studio 5000
• RSLinx
• RSNetWorx
environment
Classic software
for EtherNet/IP software
The Studio 5000 Engineering and Design Environment combines engineering
and design elements into a common environment. The first element in the Studio
5000 environment is the Logix Designer application. The Logix Designer
application is the rebranding of RSLogix
5000 software and will continue to be
the product to program Logix5000 controllers for discrete, process, batch,
motion, safety, and drive-based solutions.
The Studio 5000 environment is the foundation for the future of Rockwell
Automation® engineering design tools and capabilities. This environment is the
one place for design engineers to develop all of the elements of their control
system.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 9
Page 10
Preface
Additional Resources
These documents contain additional information concerning related products
from Rockwell Automation.
Resource Description
EtherNet/IP Communication Modules Installation Instructions,
publication
EtherNet/IP Media Planning and Installation Manual Provides details about how to use the required media components and how to plan for, install, verify, troubleshoot,
EtherNet/IP Secure Communication Module User Manual,
publication
Ethernet Design Considerations Reference Manual, publication
ENET-RM002
EtherNet/IP Socket Interface Application Technique, publication
ENET-AT002
EtherNet/IP Embedded Switch Technology Application Guide,
publication
Integrated Architecture and CIP Sync Configuration Application
Technique, publication
Integrated Motion on the EtherNet/IP Network Reference Manual,
publication
Network Technology Web page,
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/rockwellautomation/
products-technologies/network-technology/overview.page?
Industrial Automation Wiring and Grounding Guidelines,
publication
Product Certifications website,
ENET-IN002
ENET-UM003
ENET-AP005
IA-AT003
MOTION-RM003
1770-4.1
http://www.ab.com Provides declarations of conformity, certificates, and other certification details.
Provides information about how to complete these tasks with EtherNet/IP communication modules in a Logix5000
control system:
• Install the module
• Configure initial application setup
• Troubleshoot application anomalies related to EtherNet/IP communication module use
and certify your EtherNet/IP network.
This manual is available from the Open DeviceNet Vendor Association (ODVA) at:
Provides information on setting up authentication, encryption, and firewalls, typical architectures, and diagnostics
for modules equipped with secure communication functionality.
Provides explanation of the following Ethernet concepts:
• Overview
• Network layout and components
• Network infrastructure devices
• Network infrastructure features
• Protocol
Describes the socket interface that you can use to program MSG instructions to communicate between a Logix5000
controller via an EtherNet/IP module and Ethernet devices that do not support the EtherNet/IP application
protocol, such as bar code scanners, RFID readers, or other standard Ethernet devices.
Provides details about how to install, configure, and maintain linear and Device-level Ring (DLR) networks by
using Rockwell Automation EtherNet/IP devices equipped with embedded switch technology.
Provides information on CIP Sync and the IEEE 1588-2008 Precision Time Protocol.
Reference descriptions of the AXIS_CIP_DRIVE attributes and the Studio 5000 Logix Designer application Control
Modes and Methods
Provides information on reference architectures and white papers on networking.
Provides general guidelines for installing a Rockwell Automation industrial system.
http://www.odva.org.
You can view or download publications at
http:/www.rockwellautomation.com/literature/. To order paper copies of
technical documentation, contact your local Allen-Bradley distributor or
Rockwell Automation sales representative.
10 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 11

Chapter 1
EtherNet/IP Overview
EtherNet/IP networks are communication networks that offer a comprehensive
suite of messages and services for many automation applications.
These are examples of applications that use EtherNet/IP networks:
• Real Time Control
• Time Synchronization
• Motion
This open network standard uses off-the-shelf Ethernet communication products
to support real-time I/O messaging, information exchange, and general
messaging.
EtherNet/IP Communication Modules in a Control System
EtherNet/IP networks also support CIP Safety, making the simultaneous
transmission of safety and standard control data and diagnostics information over
a common network possible.
Depending on the type, Rockwell Automation EtherNet/IP communication
modules provide some of this functionality:
• Support for messaging, produced/consumed tags, and distributed I/O
• Encapsulate messages within standard TCP/UDP/IP protocol
• Share a common application layer with ControlNet and DeviceNet
network protocols
• Interface via RJ45, category 5, unshielded, twisted-pair cable connectors
• Fiber connectors
• Support for half/full duplex 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps operation
• No network scheduling or routing table requirements
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 11
Page 12
Chapter 1 EtherNet/IP Overview
OUT
DC
OUT
DC
CompactLogix L3
Controller
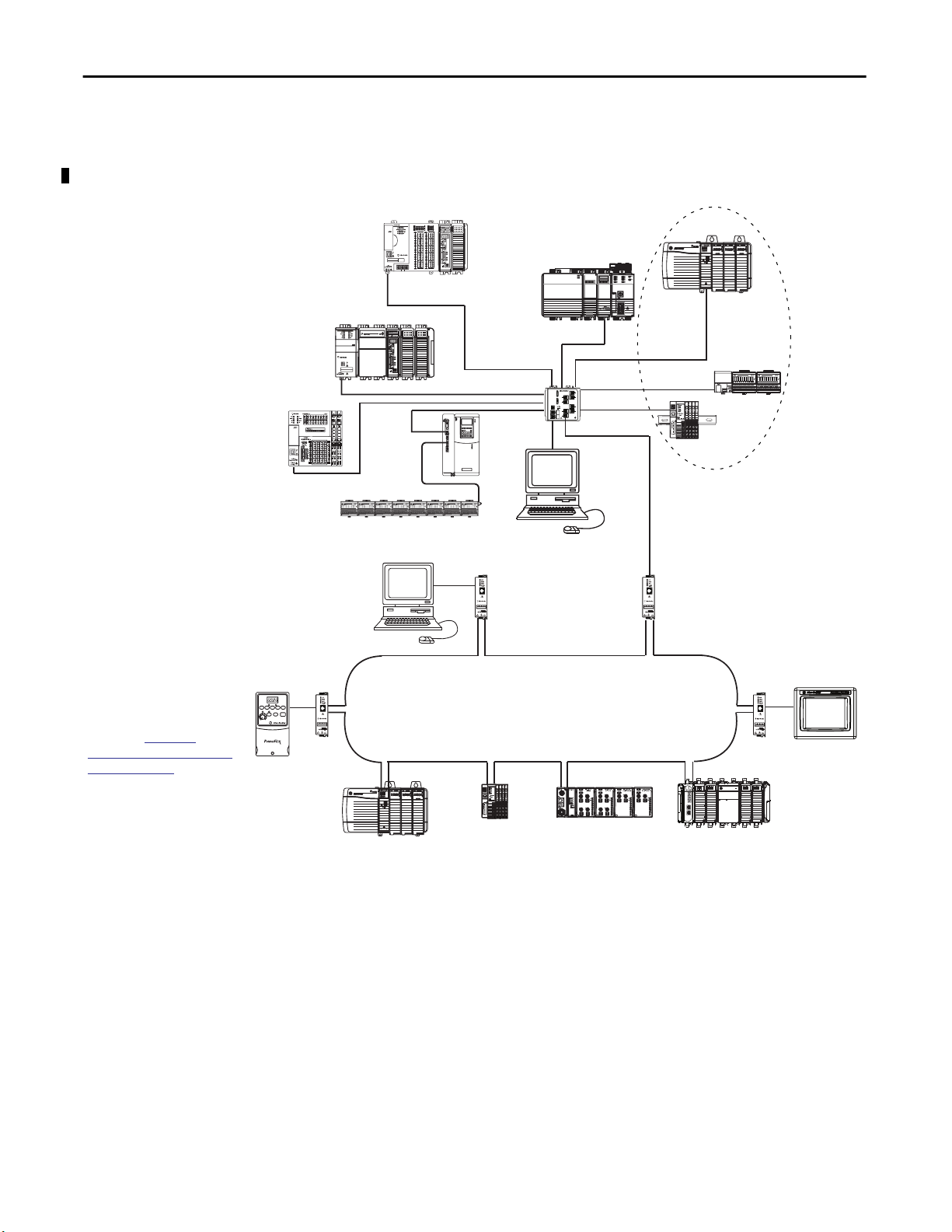
This graphic shows how Rockwell Automation EtherNet/IP communication
modules fit into a control system.
Figure 1 - EtherNet/IP Communication Modules in a Control Systems
CompactLogix L2 Controller
L27ERM
A0B0 Z0
01234567
A0B0 Z0
01234567
INOUT
DC
A1B1 Z1
89 10 1112 1314 15
SINK\
INOUT
24VDC
INPUT
DC
SOURCE
QBFC1B
A1B1 Z1
89 10 111213 1415
SINK\
24VDC
INPUT
SOURCE
02FUSE
COUNTER
01234567
DC
HIGH SPEED
02FUSE
COUNTER
01234567
DC
24VDC
OUTPUT
SOURCE
HIGH SPEED
13OK
24VDC
1112 1314 15
8910
OUTPUT
SOURCE
13OK
1112 1314 15
8910
DC IN
HSC
A0+
A0-
00
08
B0+
B0-
01
09
Z0+
Z0-
02
10
A1+
A1-
03
11
B1+
B1-
04
12
Z1+
Z1-
05
13
+V
+V
06
14
OUT
OUT
07
15
2
0
OUT
0UT
COM
COM
1
3
0
1
COMCOM
NC
NC
V
V
in
in
+V
+V
0+
2+
I
I
in
in
00
08
2+
0+
V/I
V/I
in
in
01
09
2-
0-
V
CJC
in
02
10
+
3+
I
CJC
in
03
11
3+
V
V/I
in
in
04
12
1+
3V/I
I
00:00:BC:2E:69:F6
in
in
05
13
1-
1+
V
V
OUT
OUT
06
14
1+
0+
I
I
OUT
in
07
15
0+
1+
COM
COM
COMCOM
0
1
ANALOG
DC OUT
+24VDC COM FG
+24VDC COM FG
1768-L4x
1768-ENBT
Distributed I/O
1756-EN2T
1756 I/O Modules
Linear Topology
CompactLogix L1
Controller
Device-level Ring Topology
For more information on using
EtherNet/IP communication
modules and taps in a DLR
network, see
Supervisor on a Device-level Ring
Network on page 33.
Configure a
1783-ETAP
PowerFlex Drive
00:00:BC:2E:69:F6
1 (Front)1 (Front)1 (Front)
2 (Rear)
PowerFlex
Drive
Switch
Workstation
1783-ETAP
Workstation
1734-AENT
1734 I/O Modules
1783-ETAP
MOD
LINK 1
NET
LINK 2
Comm Adapter
X 100
X 10
X 1
LINK 1LINK 2
1794-AENT
1794 I/O Modules
1783-ETAP
PanelView Terminal
1756-EN2TR
1734-AENTR
1734 I/O Modules
1738-AENTR
1738 I/O Modules
1756 I/O Modules
In this example, these actions can occur over the EtherNet/IP network:
• Controllers produce and consume tags.
• Controllers initiate MSG instructions that send and receive data or
configure devices.
• Workstations upload or download projects to the controllers
12 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
1769-AENTR
1769 I/O Modules
Page 13

Chapter 2
Configure a Workstation to Operate on an
EtherNet/IP Network
This chapter describes how to configure a workstation to operate on an
EtherNet/IP network.
You must configure an Ethernet communication driver in RSLinx software for
the workstation.
A workstation needs the driver to perform these tasks:
• Upload and download Studio 5000 environment project information to
controllers over an EtherNet/IP network.
• Configure EtherNet/IP network parameters for devices via RSNetWorx
for EtherNet/IP software.
• Collect controller data for electronic operator interfaces, for example,
PanelView
FactoryTalk
You can choose either of these Ethernet drivers:
• AB_ETHIP
• AB_ETH
Before you add a new driver, confirm these conditions exist:
• Workstation is properly connected to the EtherNet/IP network
• IP address and other network parameters are correctly configured for the
workstation
Plus terminals, and visualization software, for example,
View software.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 13
Page 14
Chapter 2 Configure a Workstation to Operate on an EtherNet/IP Network
Configure the Ethernet Communication Driver in RSLinx Software
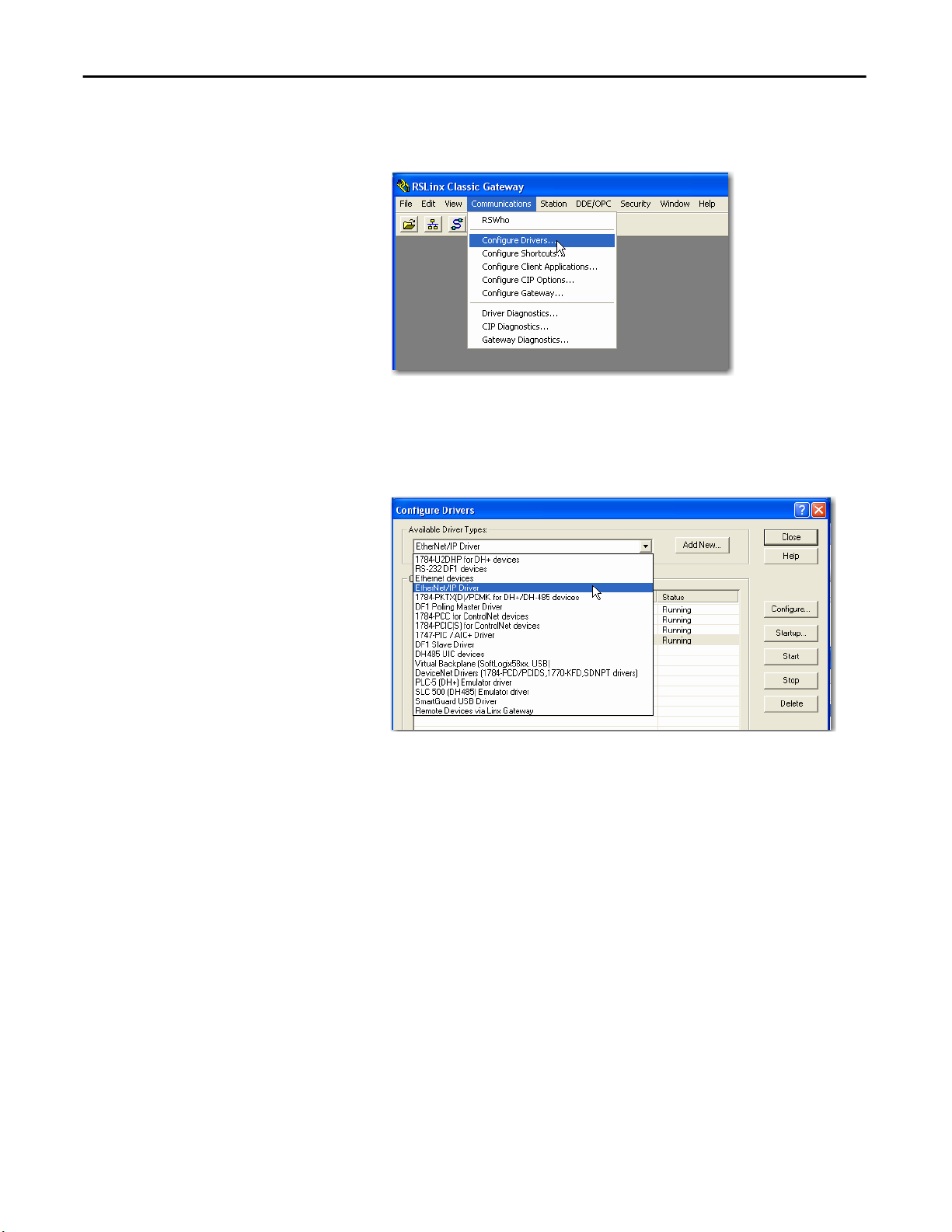
To configure the EtherNet/IP driver, follow these steps.
1. From the Communications menu, choose Configure Drivers.
The Configure Drivers dialog box appears.
2. From the Available Driver Types pull-down menu, choose EtherNet/IP
Driver or Ethernet devices and click Add New.
The Add New RSLinx Driver dialog box appears.
14 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 15
Configure a Workstation to Operate on an EtherNet/IP Network Chapter 2
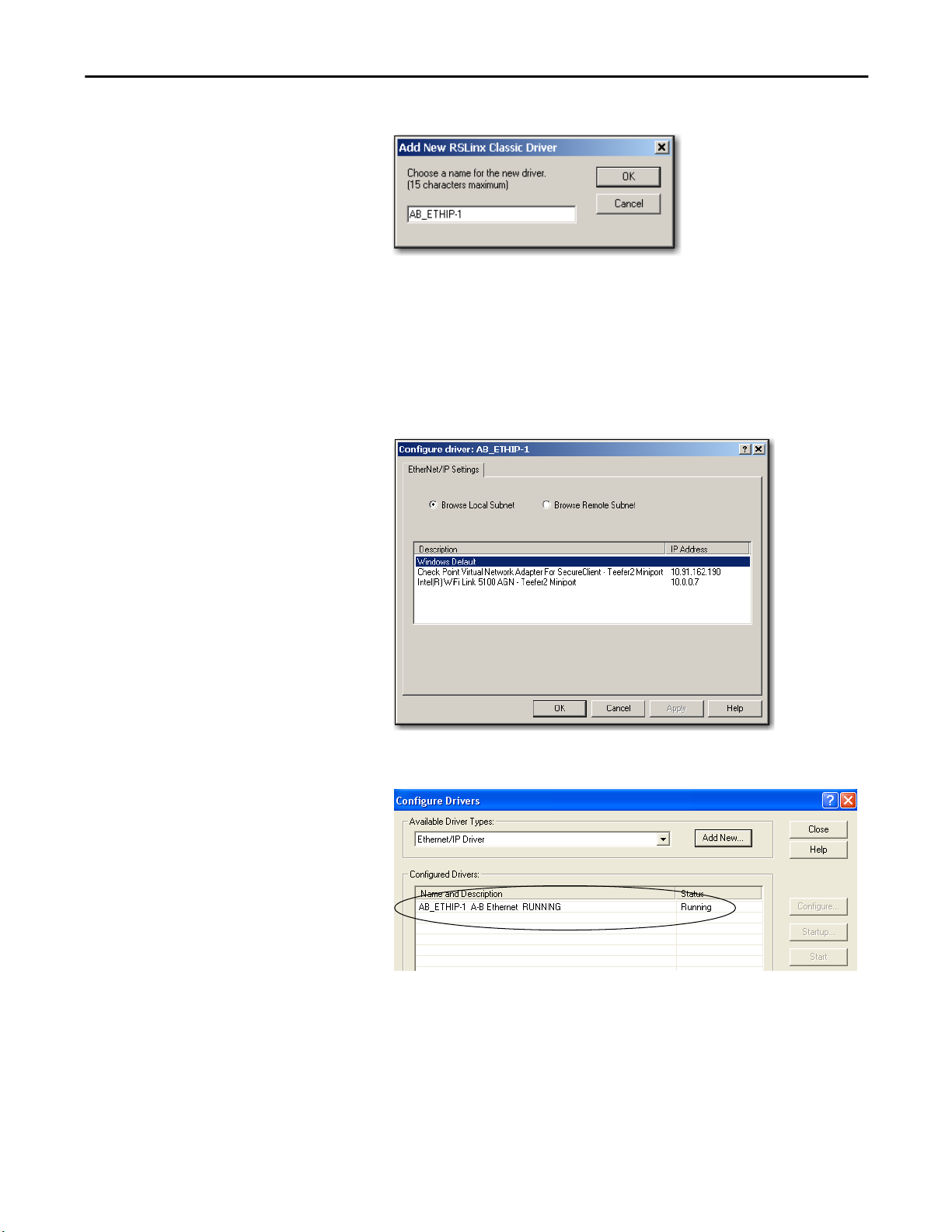
3. Type a name for the new driver and click OK.
The Configure driver dialog box appears.
4. Click Browse Local Subnet.
TIP
To view devices on a different subnet or VLAN from the workstation running
RSLinx software, click Browse Remote Subnet.
5. Click OK to close the dialog box.
This new driver is available.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 15
Page 16

Chapter 2 Configure a Workstation to Operate on an EtherNet/IP Network
Notes:
16 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 17
Chapter 3
Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication
Module to Operate on the Network
This chapter describes how to configure an EtherNet/IP communication module
to operate on an EtherNet/IP network.
Topic Page
Determine Network Parameters 17
Set the Network IP Address on a Module 18
Duplicate IP Address Detection 29
IP Address Swapping 30
DNS Addressing 31
Use EtherNet/IP Communication Modules in a Logix5000 Controller Application 32
Determine Network
To operate an EtherNet/IP network, you must define these parameters.
Parameters
EtherNet/IP Network Parameter Description
IP address The IP address uniquely identifies the module. The IP address is in the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx where each xxx is a number
Subnet mask Subnet addressing is an extension of the IP address scheme that allows a site to use a single network ID for multiple
Gateway A gateway connects individual physical networks into a system of networks. When a node needs to communicate with
from 000…254.
There are some reserved values that you cannot use as the first octet in the address. These numbers are examples
of values you cannot use:
• 001.xxx.xxx.xxx
• 127.xxx.xxx.xxx
• 223 to 255.xxx.xxx.xxx
The specific reserved values that cannot be used vary according the conditions of each application. The previous values
are only examples of reserved values.
physical networks. Routing outside of the site continues by dividing the IP address into a net ID and a host ID via the
class. Inside a site, the subnet mask is used to redivide the IP address into a custom network ID portion and host ID
portion. This field is set to 0.0.0.0 by default.
If you change the subnet mask of an already-configured module, you must cycle power to the module for the change
to take effect.
a node on another network, a gateway transfers the data between the two networks. This field is set to 0.0.0.0 by
default.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 17
Page 18

Chapter 3 Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network
If you use DNS addressing, or reference the module via host name in MSG
instructions, define these parameters.
Table 1 - EtherNet/IP Network Parameters for DNS Addressing
EtherNet/IP Network Parameter Description
Host name A host name is part of a text address that identifies the host for a module. The full text address of a module is
Domain name A domain name is part of a text address that identifies the domain in which the module resides. The full text address of a module is
Primary DNS server address This identifies any DNS servers used in the network. You must have a DNS server configured if you specified a domain name or a host
Secondary DNS server address
host_name.domain_name.
host_name.domain_name. The domain name has a 48-character limit.
If you specify a DNS server, you must type a domain name. Also, if you send email from the module, some mail relay servers require a
domain name during the initial handshake of the SMTP session.
name in the module’s configuration. The DNS server converts the domain name or host name to an IP address that can be used by the
network.
For more information on DNS addressing, see
page 31.
Check with your Ethernet network administrator to determine if you need to
specify these parameters.
Set the Network IP Address on a Module
Depending on the EtherNet/IP communication module, you can use some or all
of these tools to set the network Internet Protocol (IP) address:
• Rotary switches - Switches are physical parts on the module. Remember
the following as you read this chapter:
– Some EtherNet/IP communication modules use thumbwheel switches.
that function similarly to rotary switches. This chapter uses the term
rotary switches to describe both switch types.
– Some EtherNet/IP communication modules do not have rotary
switches. If your module does not have switches, skip Set the Network
IP Address with the Rotary Switches on
Network IP Address with the BOOTP/DHCP Server on
page 20 and go to Set the
page 21.
– 1783-ETAPx EtherNet/IP taps use DIP switches to set the network IP
address. For more information on how to use the DIP switches, see the
publications for those products.
• Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP)/Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) server
• RSLinx Classic software
• Studio 5000 environment
The module uses these tools sequentially to set the IP address.
18 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 19
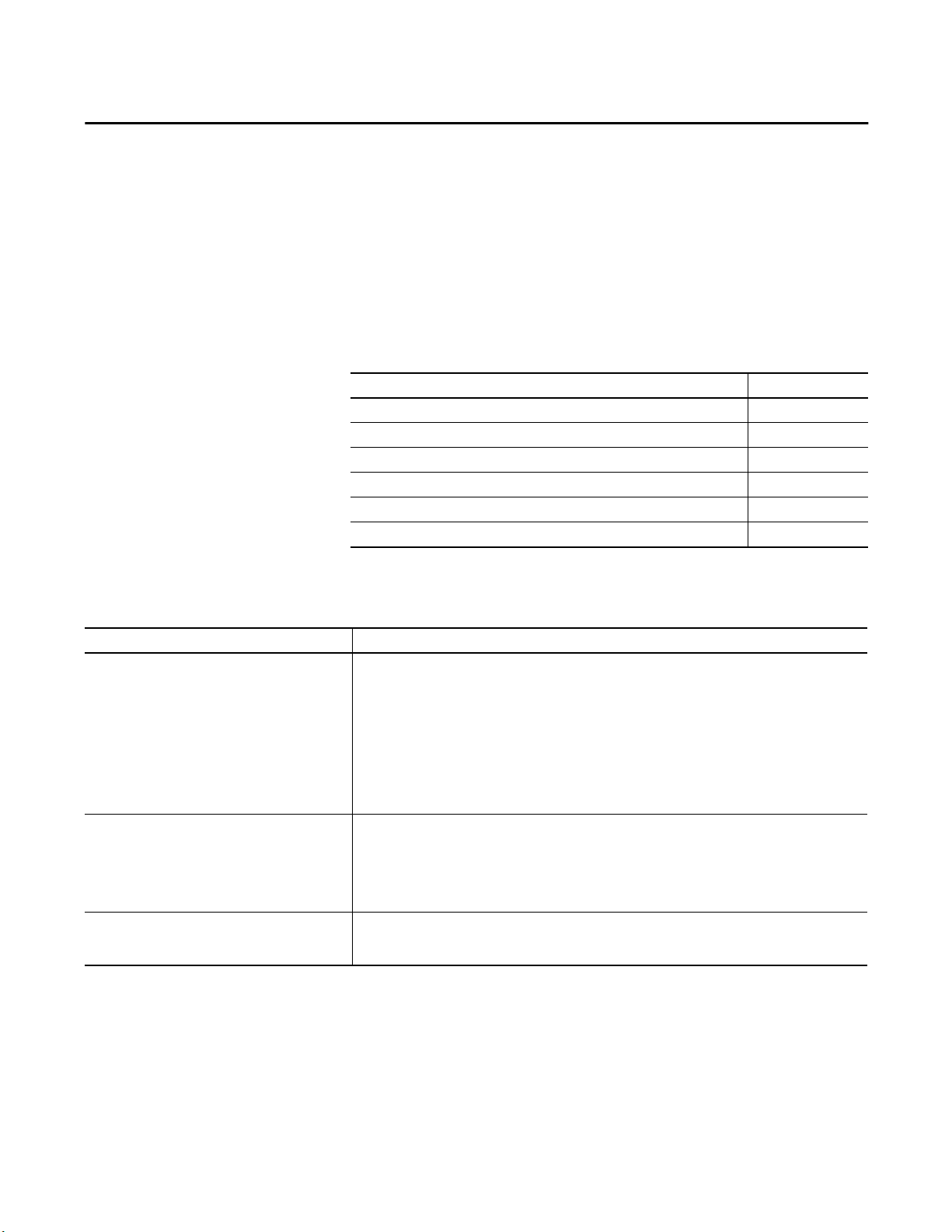
Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network Chapter 3
EtherNet/IP communication modules are shipped with this configuration:
• BOOTP/DHCP enabled
• Rotary switches set to 999 - when applicable
This graphic shows the process used to set your module’s IP address.
Figure 2 - How Your Module’s IP Address is Set
Module Powerup
Module uses IP address
stored in nonvolatile
memory.
Is DHCP or
BOOTP
enabled?
Switches set
from
001…254?
YesNo
Module requests
address from DHCP/
BOOTP server.
Module has an IP
address.
YesNo
If you need to reset your module’s settings to its factory default settings during
normal module operation,
Reset the Module IP Address to Factory Default Value
on page 29.
The tools are used in this sequence to set the network IP address:
Set the Network IP Address with the Rotary Switches
1.
2.
Set the Network IP Address with the BOOTP/DHCP Server
3.
Set the Network IP Address with RSLinx Software or the Studio 5000
Environment
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 19
Page 20

Chapter 3 Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network
Set the Network IP Address with the Rotary Switches
This graphic shows the rotary switches on a 1756 EtherNet/IP communication
module. The location of the switches is dependant on the module.
At powerup, the module reads the rotary switches to determine if they are set to a
valid number for the last portion of the IP address. Valid numbers range from
001…254.
If the settings are a valid number, these conditions result:
• IP address = 192.168.1.xxx (where xxx represents the switch settings)
• Subnet mask = 255.255.255.0
• Gateway address = 0.0.0.0
TIP
Some modules now provide a gateway address of 192.168.1.1 when the
network address is set with rotary switches. Refer to the product
documentation to determine the correct gateway address the module uses.
• The module does not have a host name assigned, nor does it use any
Domain Name System
We recommend that you set the rotary switches to a valid number before
installing the module.
If either of these conditions exist, the module attempts to use the BOOTP/
DHCP server to set the IP address:
• Rotary switches are not set to a valid number
• Module does not have rotary switches
For more information on using the BOOTP/DHCP server to set the IP address,
page 21.
see
20 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 21

Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network Chapter 3
Set the Network IP Address with the BOOTP/DHCP Server
The BOOTP/DHCP server is a standalone server you can use to set an IP
address. When used, the BOOTP/DHCP server sets an IP address and other
Transport Control Protocol (TCP) parameters.
You can use the BOOTP/DHCP server to set the module’s IP address if one of
these conditions exists at powerup:
• The module’s rotary switches are not set to a number and the module is
BOOTP/DHCP enabled.
• The module does not have rotary switches and the module is BOOTP/
DHCP enabled.
Access the BOOTP/DHCP server from one of these locations:
• Programs > Rockwell Software > BOOTP-DHCP Server
If you have not installed the server, you can download and install it from
http://www.ab.com/networks/ethernet/bootp.html.
• Tools directory on the Studio 5000 environment installation CD
IMPORTANT
Before you start the BOOTP/DHCP server, make sure you have the
module’s hardware (MAC) address. The hardware address is on a sticker
on the side of the communication module and uses an address in a
format similar to the following:
00-00-BC-14-55-35
To set the module’s IP address with a BOOTP/DHCP server, follow these steps.
1. Start the BOOTP/DHCP software.
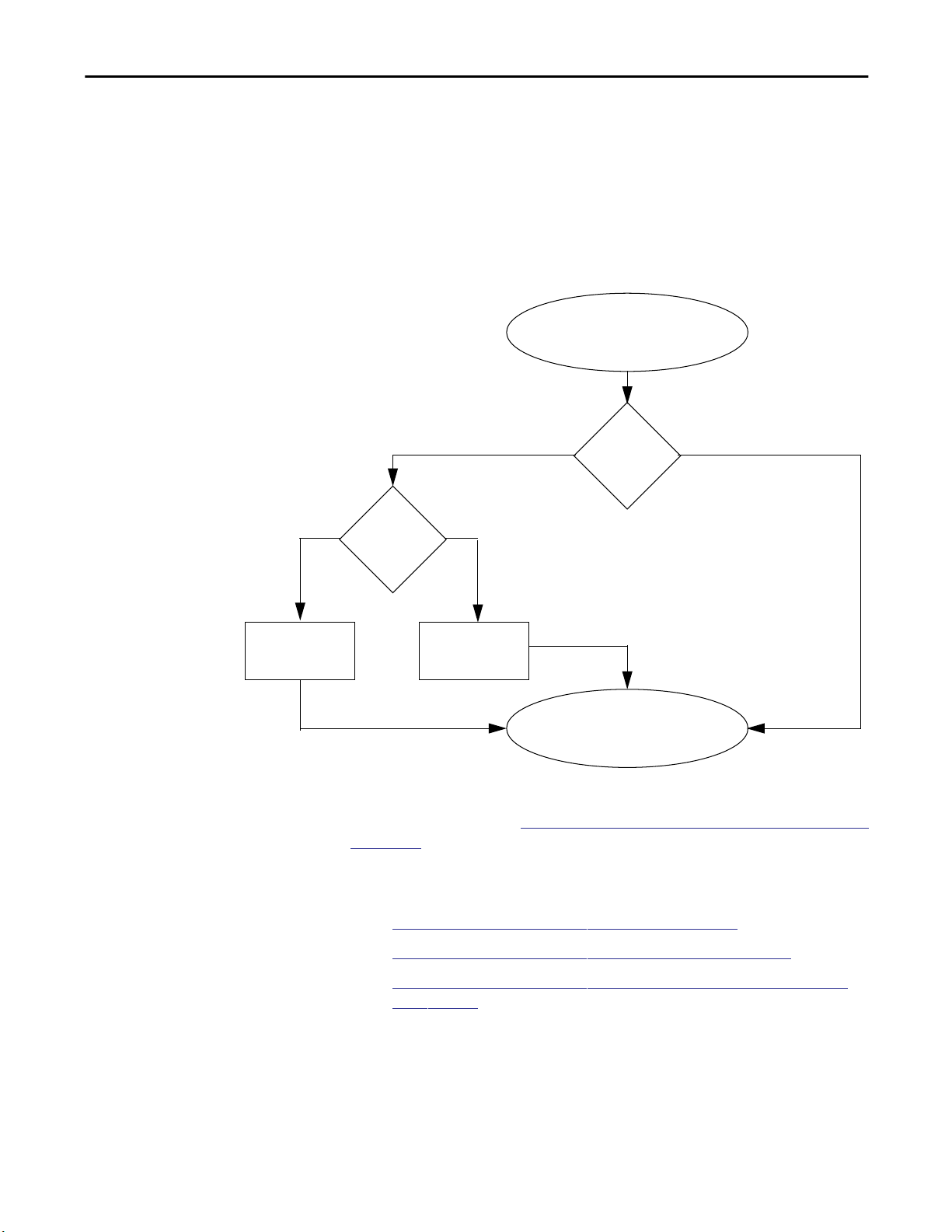
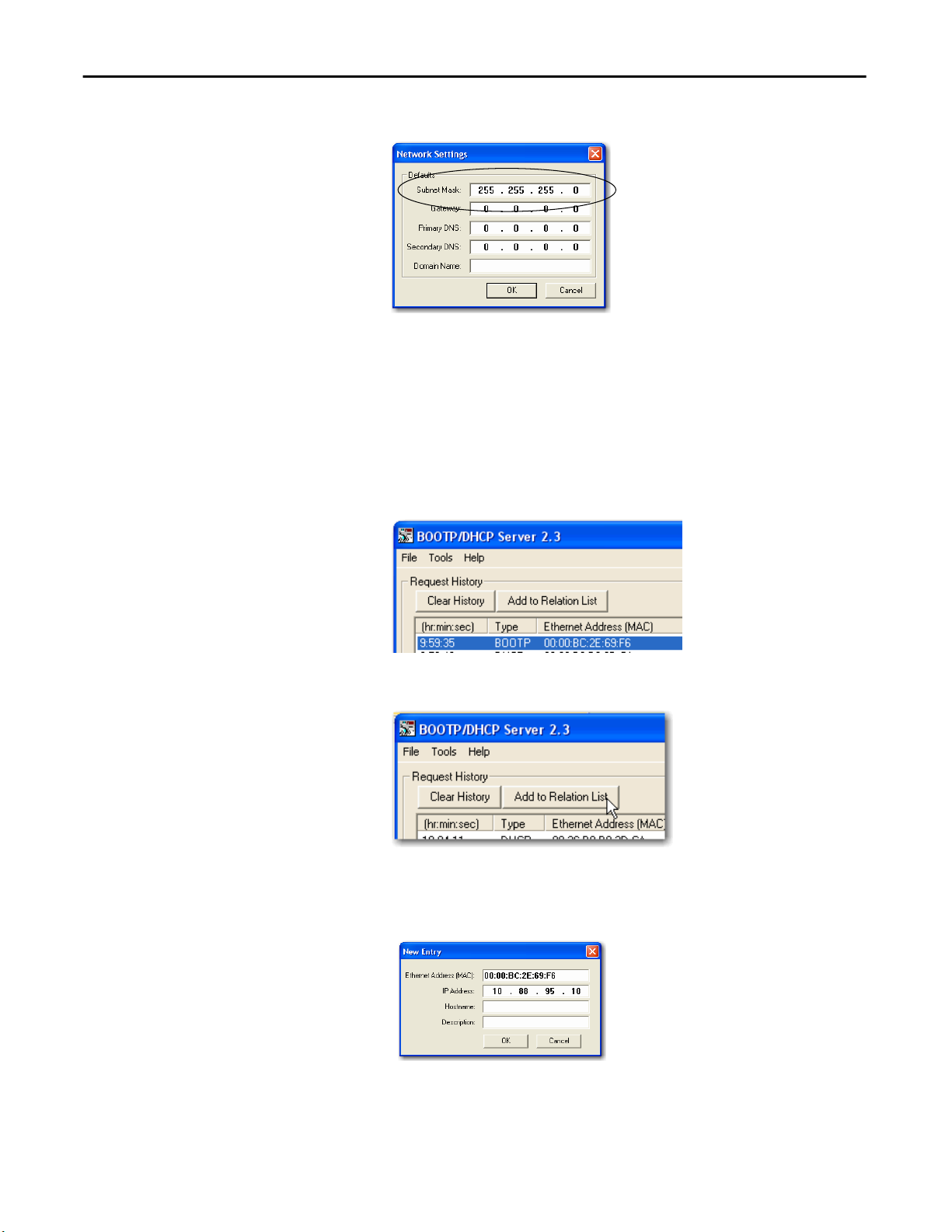
2. From the Tools menu, choose Network Settings.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 21
Page 22
Chapter 3 Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network
3. Type the Subnet Mask of the network.
The Gateway address, Primary and/or Secondary DNS address, and
Domain Name fields are optional.
4. Click OK.
The Request History panel appears with the hardware addresses of all
modules issuing BOOTP requests.
5. Select the appropriate module.
6. Click Add to Relation List.
The New Entry dialog box appears.
7. Type an IP Address, Hostname, and Description for the module.
8. Click OK.
22 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 23

Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network Chapter 3
9. To permanently assign this configuration to the module, wait for the
module to appear in the Relation List panel and select it.
10. Click Disable BOOTP/DHCP.
When power is recycled, the module uses the assigned configuration and
does not issue a BOOTP request.
IMPORTANT
If you do not click Disable BOOTP/DHCP, on a power cycle, the host
controller clears the current IP configuration and begins sending
BOOTP requests again.
Use DHCP Software
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) software automatically assigns
IP addresses to client stations logging onto a TCP/IP network. DHCP is based
on BOOTP and maintains some backward compatibility. The main difference is
that BOOTP allows for manual configuration (static), while DHCP allows for
both static and dynamic allocation of network addresses and configurations to
newly attached modules.
Be cautious when using DHCP software to configure a module. A BOOTP
client, such as the EtherNet/IP communication modules, can start from a DHCP
server only if the DHCP server is specifically written to also handle BOOTP
queries. This is specific to the DHCP software package used. Consult your
system administrator to see if a DHCP package supports BOOTP commands
and manual IP allocation.
ATTENTION: The EtherNet/IP communication module must be assigned a
fixed network address. The IP address of this module must not be dynamically
provided.
Failure to observe this precaution may result in unintended machine motion or
loss of process control.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 23
Page 24

Chapter 3 Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network
Set the Network IP Address with RSLinx Software or the Studio 5000 Environment
This table describes when to set the network IP address with RSLinx software or
the Studio 5000 environment.
Conditions Software to Use Page
• A BOOTP server is not available
• The EtherNet/IP communication module is connected to another NetLinx
network
The Studio 5000 Logix Designer project is online with a controller that
communicates to or through the EtherNet/IP communication module
Consider these factors when you determine how to set the network IP address:
• Network isolation from or integration into the plant/enterprise network
• Network size - For large networks, isolated networks, it might be more
convenient and safer to use a BOOTP/DHCP server rather than the
Studio 5000 Environment or RSLinx software. The BOOTP/DHCP
server also limits the possibility of assigning duplicate IP addresses.
RSLinx software 25
Studio 5000 environment 28
• Company policies and procedures dealing with plant floor network
installation and maintenance
• Level of involvement by IT personnel in plant-floor network installation
and maintenance
• Type of training offered to control engineers and maintenance personnel
If you use the Rockwell Automation BOOTP or DHCP server in an uplinked
subnet where an enterprise DHCP server exists, a module may get an address
from the enterprise server before the Rockwell Automation utility even sees the
module. You might have to disconnect from the uplink to set the address and
configure the module to retain its static address before reconnecting to
the uplink. This is not a problem if you have node names configured in the
module and leave DHCP enabled.
24 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 25
Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network Chapter 3
Set the Network IP Address with RSLinx Software
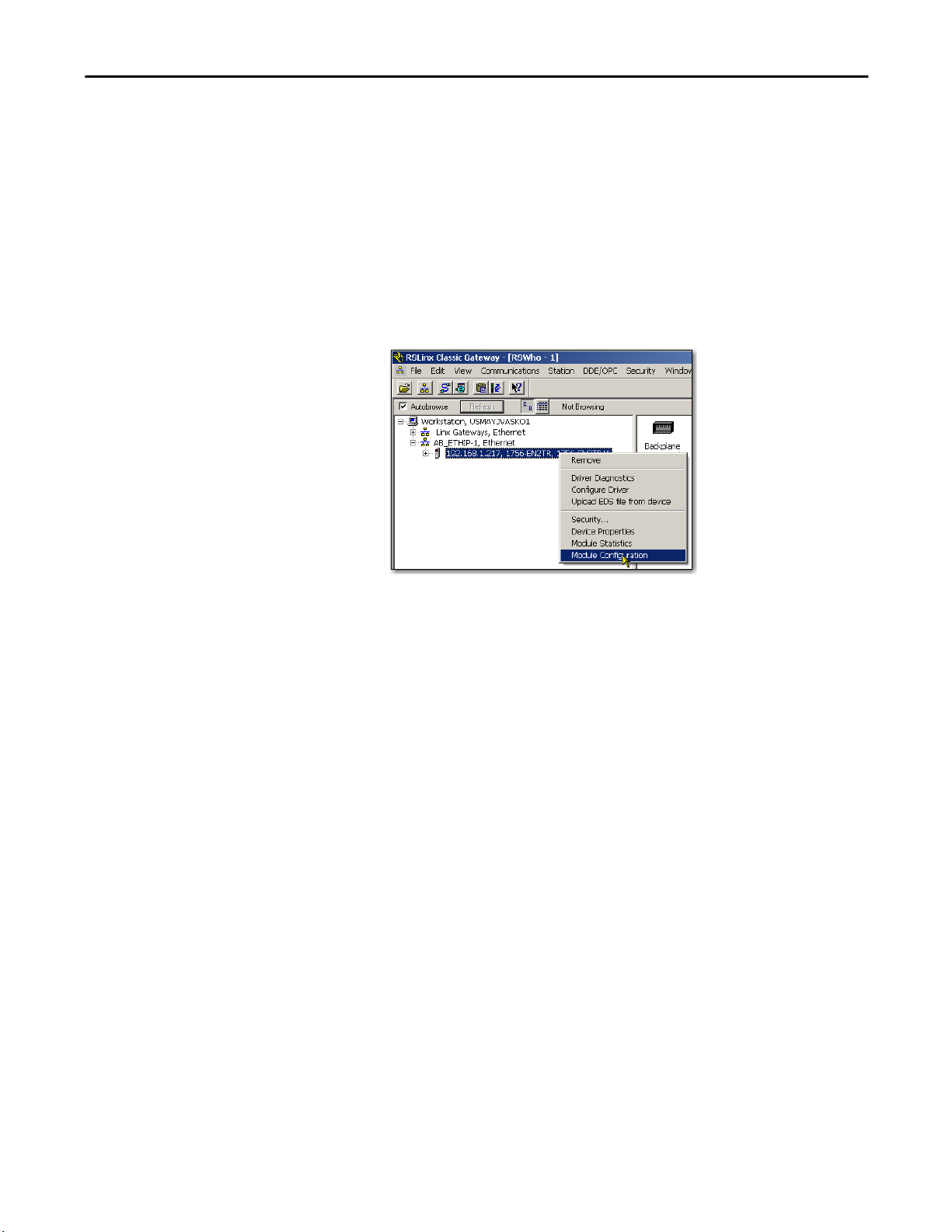
To use RSLinx software to set the communication module’s IP address, follow
these steps.
1. From the Communications menu, choose RSWho.
The RSWho dialog box appears.
2. Navigate to the Ethernet network.
3. Right-click the EtherNet/IP module and choose Module Configuration.
The Module Configuration dialog box appears.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 25
Page 26
Chapter 3 Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network
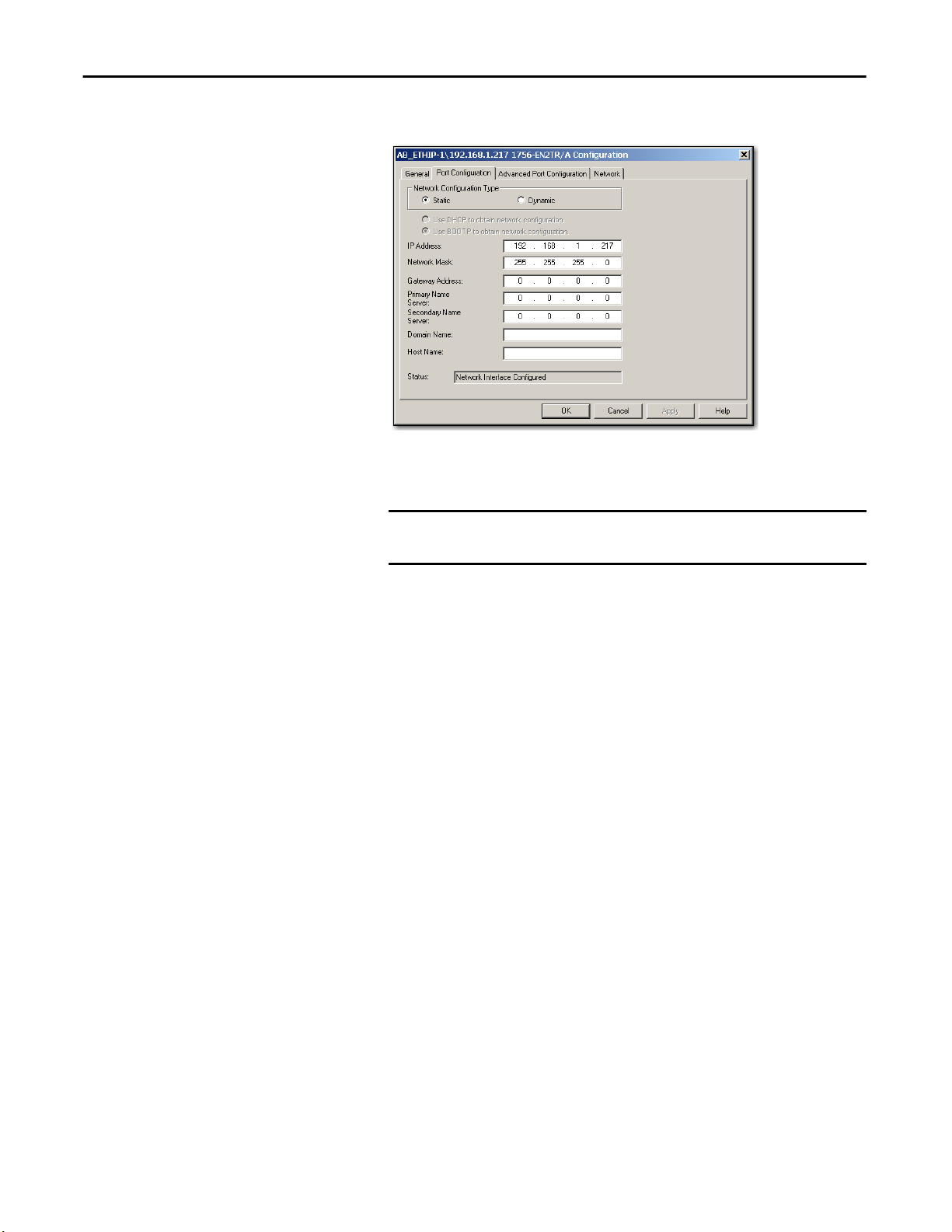
4. Click the Port Configuration tab.
5. For Network Configuration Type, click Static to permanently assign this
configuration to the port.
IMPORTANT
If you click Dynamic, on a power cycle, the controller clears the current
IP configuration and resumes sending BOOTP requests.
6. Type this information in the appropriate fields:
• In the IP Address field, type the IP address.
• In the Network Mask field, type the network mask address.
• In the Gateway Address field, type the gateway address.
• In the Primary Name Server field, type the name of the primary server.
• In the Secondary Name Server field, type the name of the secondary
server.
• In the Domain Name field, type the domain name.
• In the Host Name field, type the host name.
26 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 27

Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network Chapter 3
7. Configure the port settings.
To Then
Use the default port speed and
duplex settings
Manually configure your port’s
speed and duplex settings
Leave Auto-negotiate port speed and duplex checked.
This setting determines the actual speed and duplex setting.
Follow these steps.
1. Clear the Auto-negotiate port speed and duplex checkbox.
2. From the Current Port Speed pull-down menu, choose a port
speed.
3. From the Current Duplex pull-down menu, choose the appropriate
Duplex value, that is, Half Duplex or Full Duplex.
IMPORTANT
8. Click OK.
Consider the following when you configure the module’s port settings:
• If the module is connected to an unmanaged switch, leave Autonegotiate port speed and duplex checked or the module will fail.
• If you are forcing the port speed and duplex with a managed
switch, the corresponding port of the managed switch must be
forced to the same settings or the module will fail.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 27
Page 28
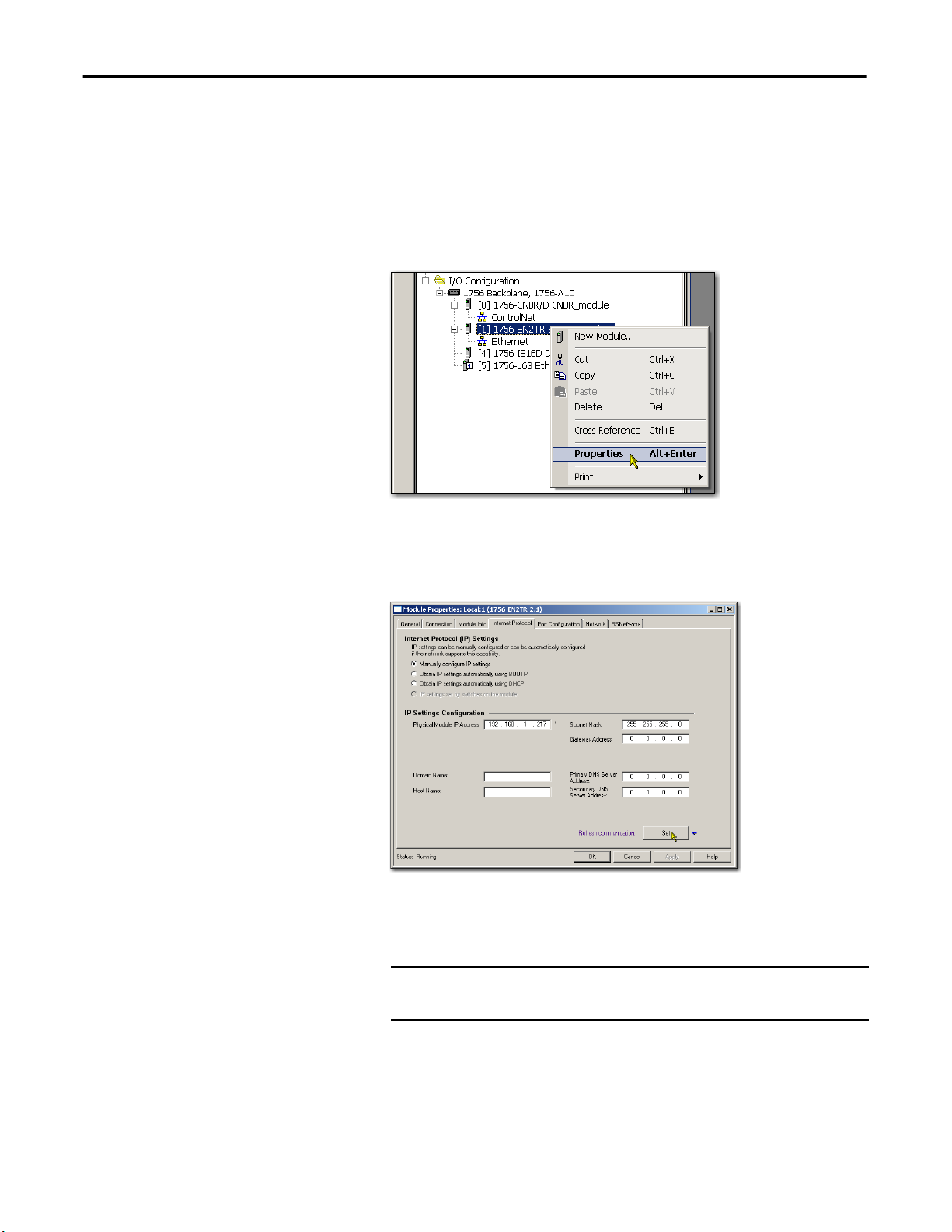
Chapter 3 Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network
Set the Network IP Address with the Studio 5000 Environment
To use the Studio 5000 environment to set the communication module’s IP
address, follow these steps.
1. In the Controller Organizer, right-click the EtherNet/IP module and
choose Properties.
The Module Properties dialog box appears.
2. Click the Port Configuration tab.
3. In the IP Address field, type the IP address.
4. In the other fields, type the other network parameters, if needed.
IMPORTANT
The fields that appear vary from one EtherNet/IP
module to another.
5. Click Set.
6. Click OK.
28 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 29

Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network Chapter 3
Reset the Module IP Address to Factory Default Value
You can reset the module’s IP address to its factory default value with the
following methods:
• If the module has rotary switches, set the switches to 888 and cycle power.
• If the module does not have rotary switches, use a MSG instruction to the
reset the IP address.
Duplicate IP Address Detection
Some EtherNet/IP communication modules support duplicate IP
address detection. The module verifies that its IP address does not match any
other network device’s IP address when you perform either of these tasks:
• Connect the module to a EtherNet/IP network.
• Change the module’s IP address.
If the module’s IP address matches that of another device on the network, the
module’s EtherNet/IP port transitions to Conflict mode. In Conflict mode, these
conditions exist:
• OK status indicator is blinking red.
• Network (NET) status indicator is solid red.
• On some EtherNet/IP communication modules, the module status display
indicates the conflict.
The display scrolls:OK <IP_address_of_this_module> Duplicate IP
<Mac_address_of_duplicate_node_detected>
For example: OK 10.88.60.196 Duplicate IP - 00:00:BC:02:34:B4
• On some EtherNet/IP communication modules, the module’s diagnostic
webpage displays information about duplicate IP address detection.
For more information on which EtherNet/IP communication modules
support displaying duplicate IP address on their diagnostic webpage, see
the Technical Note titled Logix modules Duplicate IP address detection
enhancement, #118216, in the Technical Support Knowledgebase
available at
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 29
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/knowledgebase/.
Page 30
Chapter 3 Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network
Duplicate IP Address Resolution
When two EtherNet/IP communication modules on a network have conflicting
IP addresses, the resolution depends on the conditions in which the duplication is
detected. This table describes how duplicate IP addresses are resolved.
Duplicate IP Address Detection Conditions Resolution Process
• Both modules support duplicate IP address detection
• Second module is added to the network after the first
module is operating on the network
• Both modules support duplicate IP address detection
• Both modules were powered up at approximately the same
time
One module supports duplicate IP address detection and a
second module does not
1. The module that began operation first uses the IP address and continues to operate without interruption.
2. The module that begins operation second detects the duplication and enters Conflict mode.
To assign a new IP address to the module and leave Conflict mode, see
on page 18.
Both EtherNet/IP devices enter Conflict mode.
To resolve this conflict, follow these steps:
a. Assign a new IP address to one of the modules by using the methods described in
Address on a Module on page 18.
b. Cycle power to the other module.
1. Regardless of which module obtained the IP address first, the second module, that is, the module that does not
support IP address detection, uses the IP address and continues to operate without interruption.
2. The module that supports duplicate IP address detection detects the duplication and enters Conflict mode.
To assign a new IP address to the module and leave Conflict mode, see
on page 18.
Set the Network IP Address on a Module
Set the Network IP
Set the Network IP Address on a Module
IP Address Swapping
Devices experiencing duplicate IP address conditions behave differently
depending on whether connections have been established to either of the
modules and whether both modules support duplicate IP address detection.
Some EtherNet/IP communication modules support IP address swapping. This
functionality is used in ControlLogix enhanced redundancy systems. During a
system switchover, partnered EtherNet/IP communication modules swap IP
addresses.
For more information about IP address swapping, see the ControlLogix
Enhanced Redundancy System User Manual, publication
1756-UM535.
30 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 31

Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network Chapter 3
DNS Addressing
To further qualify a module’s address, use DNS addressing to specify a host name
for a module, which also includes specifying a domain name and DNS servers.
DNS addressing makes it possible to set up similar network structures and IP
address sequences under different domains.
DNS addressing is necessary only if you refer to the module by host name, such as
in path descriptions in MSG instructions.
To use DNS addressing, follow these steps.
1. Assign a host name to the module.
A network administrator can assign a host name. Valid host names must be
IEC-1131-3 compliant.
2. Configure the module's parameters.
3. In addition to the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address, configure
a host name for the module, domain name, and primary/secondary DNS
server addresses.
In the DNS server, the host name must match the IP address of the
module.
IMPORTANT
Make sure the DNS enable bit is set.
If you configure your module by using RSLinx software, version
2.41, the enable bit is cleared and DNS addressing will not work. If
you configure your module by using the Port Configuration tab in
the Studio 5000 environment, the enable bit is set, so DNS
addressing will work.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 31
Page 32

Chapter 3 Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication Module to Operate on the Network
4. In the Studio 5000 environment, add the module to the I/O configuration
tree.
Add an I/O Module on page 50.
See
Use EtherNet/IP Communication Modules in a Logix5000 Controller Application
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
After installing an EtherNet/IP communication module and setting its IP
address, add the module to the Controller Organizer in a Studio 5000
Environment project. This addition establishes I/O control.
You must download that project to the host controller before operation can
begin. When the controller begins operation, it establishes a connection with the
EtherNet/IP communication module. The module’s configuration determines its
behavior.
If a child module resides in the same domain as its parent module,
just type the host name. If the child module’s domain differs from
that of its parent module, type the host name and the domain
name (host.domain)
You can also use DNS addressing in a module profile in the I/O
controller tree or in a message path. If the destination module’s
domain name differs from that of the source module, use a fullyqualified DNS name (hostname.domainname). For example, to
send a message from ENBT1.location1.companyA to
ENTB1.location2.companyA, the host names match, but the
domains differ. Without the entry of a fully qualified DNS name, the
module adds the default domain name to the specified host name.
For more information on connecting a workstation to and configuring it for use
on an EtherNet/IP network, see
EtherNet/IP Network on page 13.
For more information on controlling I/O, see
32 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Configure a Workstation to Operate on an
Control I/O on page 47.
Page 33

Chapter 4
Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring
Network
A Device-level Ring (DLR) network is a single-fault tolerant ring network
intended for the interconnection of automation devices.
Topic Page
Construct the Physical Network 36
Configure Supervisor Nodes on a DLR Network 37
Complete the Physical Connections of the Network 45
Verify Supervisor Configuration 46
Modules that support the DLR network have an 'R' in the catalog number; for
example, 1756-EN2TR. Check you module specifications to determine whether
the module supports the DLR network.
The ring topology offers these advantages:
• Media redundancy
• Fast network fault detection and reconfiguration
• Resiliency of a single-fault tolerant network
• Easy implementation without any additional hardware requirements
IMPORTANT
This section describes how to configure a ring supervisor on a DLR network.
This section does not fully describe a DLR network itself.
See EtherNet/IP Embedded Switch Technology Application Guide, publication
ENET-AP005, for information on these topics:
• DLR network overview
• Fully configuring a DLR network, that is, configuring all nodes on the DLR
network
• Monitoring a DLR network
• Troubleshooting a DLR network
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 33
Page 34

Chapter 4 Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network
Figure 3 - Example Device-level Ring Topology
DLR Nodes
1783-ETAP
1783-ETAP
1756-EN2TR
1734-AENTR
1734 I/O Modules
1738-AENTR
1738 I/O Modules
1756 I/O Modules
A DLR network uses these types of nodes:
Supervisor Node
•
1756-EN2TR
1783-ETAP
MOD
LINK 1
NET
LINK 2
Comm Adapter
X 100
X 10
X 1
LINK 1LINK 2
1769-AENTR
1769 I/O Modules
Ring Node
•
Supervisor Node
A DLR network requires at least one node to be configured as ring supervisor.
For a list of supervisor-capable modules, see the EtherNet/IP Embedded Switch
Technology Application Guide, publication
IMPORTANT
Out of the box, the supervisor-capable devices have their supervisor function
disabled so they are ready to participate in either a linear/star network
topology, or as a ring node on an existing DLR network.
In a DLR network, you must configure at least one of the supervisor-capable
devices as the ring supervisor before physically connecting the ring. If not, the
DLR network will not work.
Active Ring Supervisor
When multiple nodes are enabled as supervisor, the node with the numerically
highest precedence value becomes the active ring supervisor; the other nodes
automatically become back-up supervisors.
ENET-AP005.
34 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 35

Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network Chapter 4
The ring supervisor provides these main functions:
• Manage traffic on the DLR network
• Collect diagnostic information for the network
Back-up Supervisor Node
At any point in time, there can be only one active supervisor on a DLR network.
However, we recommend that you can configure at least one other supervisorcapable node to act as back-up supervisor nodes. During normal operation, a
back-up supervisor behaves like a ring node. If the active supervisor node faults,
the back-up supervisor with the next numerically highest precedence becomes
the active supervisor.
If multiple supervisors are configured with the same precedence value (the
factory default value for all supervisor-capable devices is 0), the node with the
numerically highest MAC address becomes the active supervisor.
IMPORTANT
We recommend that you execute these tasks:
• Configure at least one back-up supervisor.
• Configure the desired active ring supervisor with a numerically higher
precedence value as compared to the back-up supervisors.
• Keep track of the DLR network’s supervisor-precedence values for all
supervisor-enabled nodes.
For more information about how to configure a supervisor, see
Supervisor Nodes on a DLR Network on page 37.
While a back-up supervisor is not required on a DLR network, we recommend
that you configure at least one back-up supervisor for your ring network.
Configure
Ring Node
A ring node is any node that operates on the network to process data that is
transmitted over the network or to pass on the data to the next node on the
network. When a fault occurs on the DLR network, these reconfigure themselves
and relearn the network topology. Additionally, ring nodes can report fault
locations to the active ring supervisor.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 35
Page 36

Chapter 4 Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network
Construct the Physical Network
Last physical
connection is not
made.
The first thing you must do to create a new DLR network is physically connect
all necessary devices to the network. However, leave at least one connection
unmade, that is, temporarily omit the physical connection between two nodes on
the ring, as the factory default settings of DLR devices are set to operate in linear/
star mode or as ring nodes on existing DLR networks.
This figure shows an example of a new DLR network with one physical
connection left open.
Figure 4 - Example Device-level Ring Topology with One Connection Left Unmade
MOD
LINK 1
NET
LINK 2
Comm Adapter
X 100
X 10
X 1
LINK 1LINK 2
36 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 37

Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network Chapter 4
Configure Supervisor Nodes on a DLR Network
After you have installed all devices on the DLR network, you must configure the
supervisor node. Ring nodes do not require any configuration.
IMPORTANT
Before you can complete a DLR network, that is, configure all devices on the
network and make all physical connections, you must configure and enable a ring
supervisor with one of these options:
• the Studio 5000 environment
• RSLinx Classic software
This section assumes that you set the IP address for each device on the
EtherNet/IP network when you installed that device.
If you have not done so already, configure the IP address for the supervisorcapable devices before configuring them to be supervisors.
For more information on setting IP addresses, see
on a Module on page 18.
Set the Network IP Address
Configure a Ring Supervisor in the Studio 5000 Environment
Consider the following before you use the Studio5000 environment to configure
an EtherNet/IP communication module as a ring supervisor:
• Depending on the module’s firmware revision, you must use a specific
Add-on Profile (AOP) version. For example, if you use a 1756-EN2TR
module, firmware revision 3.x, you must use AOP, version 2.x or later.
For more information on module firmware revisions and required AOP
versions, go to
LogixProfiler.asp
• The Major Revision parameter in a module’s configuration must match
the Major Revision of the physical module.
If the Major Revision levels do not match, The Studio 5000 environment
alerts you to the mismatch when you attempt to configure the Internet
Protocol, Port Configuration and Network tabs for that device.
• Some supervisor-capable devices require you to configure more parameters
than others.
This chapter describes how to configure a 1756-EN2TR module as a ring
supervisor. For more information on configuring other modules as ring
supervisors, see the EtherNet/IP Embedded Switch Technology
Application Guide, publication
http://support.rockwellautomation.com/controlflash/
ENET-AP005.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 37
Page 38

Chapter 4 Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network
To configure the ring supervisor in the Studio 5000 environment, follow these
steps.
1. In the Controller Organizer, right-click 1756 Backplane and choose
New Module.
The Select Module dialog box appears.
2. Choose the module you wish to add and click OK.
Depending on the module type, the Select Major Revision dialog box
may appear. If the dialog box appears, choose the module’s major revision
and click OK.
38 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 39

Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network Chapter 4
3. Complete the rest of the module configuration in your RSLogix 5000
software project.
The graphic below shows the I/O configuration for an example DLR
network.
4. Download to your Logix controller.
5. Go online with the controller and leave it in Program mode.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 39
Page 40

Chapter 4 Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network
Enable Ring Supervisor in the Studio 5000 Environment
After you add a supervisor-capable module to the Studio 5000 environment
project and configure it, you must enable the module to function as a
ring supervisor.
This chapter describes how to enable a 1756-EN2TR module as a ring supervisor.
For more information on enabling other modules as ring supervisors, see
EtherNet/IP Embedded Switch Technology Application Guide, publication
ENET-AP005.
IMPORTANT
You must be online to enable a ring supervisor in the Studio 5000
environment.
To enable a ring supervisor, follow these steps.
1. With your project online, double-click the supervisor-capable device in
the I/O configuration tree.
40 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 41

Click here to enable Supervisor
mode.
Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network Chapter 4
2. Click the Network tab and check Enable Supervisor Mode.
Configuration takes effect immediately. You do not need to click Apply
or OK.
3. Click Advanced to configure supervisor-related parameters.
This table describes the Ring Parameters.
4. Configure desired supervisor-related parameters. This table describes the
parameters.
IMPORTANT
We recommend that you use the default values for Beacon Interval,
Beacon Timeout and Ring Protocol VLAN ID.
Table 2 - Supervisor Mode Parameters
Functionality Description Default
Supervisor
Precedence
Beacon Interval Frequency of the active ring supervisor transmitting a beacon frame
Beacon Timeout The beacon timeout is amount of time nodes wait before timing out
You must configure a supervisor precedence number for each device
configured as a ring supervisor. The highest possible supervisor
precedence value is 255.
When multiple nodes are enabled as supervisor, the node with the
highest precedence value is assigned as the active ring supervisor; the
other nodes automatically become back-up supervisors.
We recommend that you complete these tasks:
• Configure back-up supervisor nodes.
• Set your desired Active Ring Supervisor with a relatively high
supervisor-precedence value compared to the back-up nodes.
• Keep track of your network’s supervisor-precedence values.
If multiple supervisors are configured with the same precedence value
(the factory default value for all supervisor-capable devices is 0), the
node with the numerically highest MAC address becomes the active
supervisor.
through both of its Ethernet ports. This parameter is user configurable
for any time between 200S and 100mS.
the reception of beacon frames and taking appropriate action.
Supervisors support a range from 400S to 500mS.
Setting
0
400 S
1960 S
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 41
Page 42

Chapter 4 Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network
Table 2 - Supervisor Mode Parameters
Functionality Description Default
Ring Protocol
VLAN ID
Reserved for future use. 0
5. Click Set.
6. Click Close.
Setting
42 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 43

Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network Chapter 4
Configure and Enable a Ring Supervisor in RSLinx Classic Software
Depending on the module’s firmware revision, you must use a specific RSLinx
software version to configure and enable the module with RSLinx Classic
software.
For more information on module firmware revisions and required RSLinx
Classic software versions, go to
ControlFlash/.
To configure and enable a ring supervisor in RSLinx Classic software, follow
these steps.
1. Launch RSLinx software.
2. Browse to the DLR network that you are setting up.
http://support.rockwellautomation.com/
TIP
If you do not have the Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) file installed on the
module configured to be the ring supervisor, it will appear with a question
mark (?).
You can use these methods to obtain and use the EDS file:
– Right-click the module and choose to upload the EDS file
– Download the EDS file from: http://www.rockwellautomation.com/resources/
eds/
3. Access the supervisor-capable node’s properties.
4. Right-click the node and choose Module Configuration.
The General tab appears with information about the module that is not
configurable.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 43
Page 44

Chapter 4 Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network
5. Click the Network tab and check Enable Ring Supervisor.
Configuration takes effect immediately. You do not need to click Apply or
OK.
6. Click Advanced to configure supervisor-related parameters.
7. Configure desired supervisor-related parameters and click Set.
8. Click Close.
IMPORTANT
For Beacon Interval, Beacon Timeout and Ring Protocol VLAN ID, we
recommend that you only use the default values.
44 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 45

Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network Chapter 4
Complete the Physical Connections of the Network
Last physical
connection is
made.
After you configure and enable your ring supervisor nodes, you must complete
the physical connection of your new DLR network to make it complete and fully
functional.
This figure shows an example DLR network with all physical
connections complete.
Figure 5 - Example Device-level Ring Topology with All Connections Complete
MOD
LINK 1
NET
LINK 2
Comm Adapter
X 100
X 10
X 1
LINK 1LINK 2
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 45
Page 46

Chapter 4 Configure a Supervisor on a Device-level Ring Network
Verify Supervisor Configuration
Verify these fields.
You may want to verify that your supervisor configuration has taken place and
that the ring network is functioning properly. You can verify that configuration
and a normally functioning network in either the Studio 5000 environment or
RSLinx Classic software.
1. Access the module properties as described previously.
2. Click the Network tab.
3. Verify the Network Topology and Network Status fields.
They should display Ring and Normal respectively, as shown below.
You can also verify the supervisor configuration through the module’s diagnostic
web pages. For more information on monitoring diagnostics via an EtherNet/IP
communication module’s web pages, see
Diagnostic Web Pages on page 107.
46 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 47

Chapter 5
Control I/O
This chapter describes how a controller controls distributed I/O over an
EtherNet/IP network. An EtherNet/IP communication module connects the
controller to the network.
Topic Page
Set Up the Hardware 47
Select a Remote Adapter 57
Set the Requested Packet Interval (RPI) 58
Access Distributed I/O 59
Set Up the Hardware
Local Chassis with
Logix5000 Controller
In this example, the Logix5000 controller uses an EtherNet/IP communication
module to connect to the EtherNet/IP network. The distributed (remote) I/O
uses an EtherNet/IP adapter to connect to the EtherNet/IP network.
Figure 6 - Distributed I/O over an EtherNet/IP Network
EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP
Redundancy Module
Logix5575
OKFORCESDRUN
PRI COM OK
LNK1 LNK2 OK
R
M
E
P
R
N
U
O
G
R
1 2
EtherNet/IP
ControlNet
ControlNet
10/100 BASE T
LNK NET OK
LNK NET OK
EtherNet/IP Switch
Data
Workstation
Remote Chassis with
EtherNet/IP Adapter and
I/O Modules
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 47
Page 48

Chapter 5 Control I/O
A Logix5000 controller establishes direct or rack-optimized connections to
communicate with I/O modules. Digital I/O modules support either connection
type, but analog I/O modules support only direct connections.
You must complete these tasks before your controller can communicate with
distributed I/O modules over an EtherNet/IP network:
• Set the IP addresses for each EtherNet/IP communication module.
• Connect all wiring and cabling.
• Configure a communication driver (such as AB-ETHIP-1) for the
programming workstation.
Add Distributed I/O
To communicate with distributed I/O modules, add the following components
to the controller’s I/O Configuration folder:
• Local EtherNet/IP communication module
• Remote adapter
• I/O modules in the same chassis as the remote adapter
Within the folder, organize the modules into a hierarchy (tree/branch, parent/
child).
This graphic shows a system that uses a 1756-EN2TR module as the local
communication module, a remote 1794-AENT adapter and distributed
FLEX I/O modules.
Controller
Logix5575
M
R
E
U
N
R
EtherNet/IP
10/100 BASE T
OKFORCESDRUN
LNK1 LNK2 OK
P
R
O
G
1 2
Local Communication
Module
EtherNet/IP
ControlNet
10/100 BASE T
LNK1 LNK2 OK
1 2
Remote Adapter and I/O Modules
Device
48 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 49

Control I/O Chapter 5
To build the I/O configuration for a typical distributed I/O network, follow
these steps.
1. Add the local communication module, that is, the bridge.
2. Add the remote adapter for the distributed I/O chassis or DIN rail.
3. Add the I/O module.
This graphic shows the consumer controller’s I/O configuration after distributed
I/O modules are added.
IMPORTANT
I/O is controlled on the same subnet and cannot be
processed via a router.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 49
Page 50

Chapter 5 Control I/O
Add an I/O Module
To add a module to the I/O Configuration folder, follow these steps.
1. In the Controller Organizer, right-click the remote communication
module and choose New Module.
The Select Module dialog box appears.
2. Choose the module you wish to add and click OK.
Depending on the I/O module, the Select Major Revision dialog box
may appear. If the dialog box appears, choose the module’s major revision
and click OK.
50 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 51

Control I/O Chapter 5
The Module Properties dialog box appears.
3. In the Name field, type the name of your I/O module.
4. In the Slot field, type the slot number in which your I/O module will
reside.
5. From the Comm Format pull-down menu, choose a communication
format.
For more information on the selection of communication formats, see
the Requested Packet Interval (RPI) on page 58.
6. Click OK to see the rest of the Module Properties dialog box.
7. Configure the module as necessary.
Use the Help button to view module-specific configuration information.
8. Click Finish.
Set
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 51
Page 52

Chapter 5 Control I/O
Select a Communication Format
When configuring an I/O module, you must select a communication format.
The type of communication format determines the data structure for the
module’s tags. Many I/O modules support different formats. Each format uses a
different data structure.
The communication format determines these parameters:
• Direct or rack-optimized connection
• Ownership
Table 3 - Communication Formats
I/O Module
Type
Digital A rack-optimized connection Rack Optimization
Digital A direct connection Scheduled Data
Analog A direct connection
Desired Connection Type Required Communication Format
To use specialty features of the module,
such as diagnostics, timestamps, or
electronic fuses
(only direct connection is supported for
analog modules)
Full Diagnostics
CST Timestamped
Input Data
Output Data
Float Data
Integer Data
CST Timestamped
See the Studio 5000 environment online help for specific communication
formats per I/O module.
Choosing a Direct or Rack-optimized Connection
The Logix5000 controller uses connections to transmit I/O data. These
connections can be direct connections or rack-optimized connections. The
connection types that are available are module-dependant.
Term Definition
Direct connection A direct connection is a real-time, data transfer link between the controller and an I/O module.
The controller maintains and monitors the connection with the I/O module. Any break in the
connection, such as a module fault or the removal of a module while under power, sets fault bits
in the data area associated with the module.
A direct connection
is any connection
that does not use
the Rack
Optimization
Comm Format.
52 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 53

Term Definition
Rack-optimized
connection
For digital I/O modules, you can choose rack-optimized communication. A rack-optimized
connection consolidates connection usage between the controller and all the digital I/O modules
in the chassis (or DIN rail). Rather than having individual, direct connections for each I/O module,
there is one connection for the entire chassis (or DIN rail).
Rack-optimized
connection
Control I/O Chapter 5
IMPORTANT
If you use different 1756 EtherNet/IP communication modules in a remote
chassis, such as a 1756-ENBT module and a 1756-EN2T module, do not use
a rack-optimized communication format to the remote chassis.
If you must use a rack-optimized communication format with a remote
1756 chassis, install the 1756-ENBT and 1756-EN2T modules in a separate
remote chassis.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 53
Page 54

Chapter 5 Control I/O
Direct Connections For I/O Modules
In this example, assume that each distributed I/O module is configured for a
direct connection to the controller.
Controller with EtherNet/IP
Communication Module
EtherNet/IP Network
EtherNet/IP
Logix5575
OKFORCESDRUN
LNK1 LNK2 OK
M
R
E
P
R
U
O
N
G
R
EtherNet/IP
ControlNet
10/100 BASE T
10/100 BASE T
LNK1 LNK2 OK
EtherNet/IP Adapters with I/O
Modules
1 2
1 2
Switch
LNK1 LNK2 OK
EtherNet/IP
1 2
DC OUTPUT
10/100 BASE T
ST
AT
ST
AT
Diagnostic
DC OUTPUT
DC OUTPUT
ST
ST
AT
AT
ST
ST
AT
AT
Diagnostic
Diagnostic
Two Digital I/O Modules Three Analog I/O Modules Four Digital I/O
Modules
Table 4 - Example - System Connections
System Connections Amount
Controller to local EtherNet/IP communication module 0
Controller to EtherNet/IP adapter
Direct connection for digital I/O modules
Direct connection for analog I/O modules
Total connections used 9
6
3
If you have many modules, direct connections to each module may not be feasible
because you could use up the number of connections and packets per second
supported by the module.
Rack-optimized Connections for I/O Modules on page 55 to conserve
See
connection use and network traffic.
54 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 55

Control I/O Chapter 5
Rack-optimized Connections for I/O Modules
In this example, assume that each digital I/O module is configured for a rackoptimized connection to the controller. Analog modules must be configured for
direct connections.
Controller with EtherNet/IP
Communication Module
EtherNet/IP Network
EtherNet/IP
Logix5575
10/100 BASE T
OKFORCESDRUN
LNK1 LNK2 OK
M
R
E
P
R
U
O
N
G
R
ControlNet
LNK1 LNK2 OK
EtherNet/IP
10/100 BASE T
EtherNet/IP Adapters with I/
O Modules
1 2
1 2
Switch
LNK1 LNK2 OK
EtherNet/IP
1 2
DC OUTPUT
10/100 BASE T
ST
AT
ST
AT
Diagnostic
DC OUTPUT
DC OUTPUT
ST
ST
AT
AT
ST
ST
AT
AT
Diagnostic
Diagnostic
Two Digital I/O Modules Three Analog I/O Modules Four Digital I/O
Modules
Example - System Connections
System Connections Amount
Controller to local EtherNet/IP communication module 0
Controller to EtherNet/IP adapter with digital modules
(rack-optimized connection to each adapter)
Controller to EtherNet/IP adapter with analog modules
(direct connection for each analog I/O module)
Total connections used 5
2
3
The rack-optimized connection conserves connections, but can limit the status
and diagnostic information that is available from the I/O modules.
To optimize the number of available connections, use a rack-optimized
connection between any digital I/O that allows it and the remote adapter that
connects the distributed I/O to the controller via the communication module.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 55
Page 56

Chapter 5 Control I/O
Ownership
In a Logix5000 system, modules multicast data. Therefore, multiple modules can
receive the same data at the same time from a single module. When choosing a
communication format, decide whether to establish an owner-controller or
listen-only relationship with the module.
Ownership Type Description
Owner controller The controller that creates the primary configuration and communication connection to a module. The owner controller writes configuration
data and can establish a connection to the module.
An owner connection is any connection that does
not include Listen-Only in its Comm Format.
Listen-only connection An I/O connection where another controller owns/provides the configuration data for the I/O module. A controller using a listen-only
connection monitors only the module. It does not write configuration data and can only maintain a connection to the I/O module when the
owner controller is actively controlling the I/O module.
Listen-only connection
Table 5 - Choosing a Type of Module Ownership
Module Type Another Controller Desired Conditions Use This Connection Type
Input module Does not own the module Owner
Owns the module Maintain communication with the module if it loses
communication with the other controller
Stop communication with the module if it loses
communication with the other controller
Output module Does not own the module Owner
Owner
Use the same configuration as the other owner
controller.
Listen-only
Owns the module Listen-only
56 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 57

Control I/O Chapter 5
Table 6 - Input and Output Modules - Differences in Ownership
Control This Ownership Description
Input modules Owner An input module is configured by a controller that establishes a connection as an owner. This configuring controller is the first
Listen-only Once an input module has been configured and owned by a controller, other controllers can establish a listen-only connection to
Output modules Owner An output module is configured by a controller that establishes a connection as an owner. Only one owner connection is allowed for
Listen-only Once an output module has been configured and owned by one controller, other controllers must establish listen-only connections
controller to establish an owner connection.
Once an input module has been configured and owned by a controller, other controllers can establish owner connections to that
module. This allows additional owners to continue to receive multicast data if the original owner controller breaks its connection to
the module. Additional owners must have the identical configuration data and communication format as the original owner
controller; otherwise, the connection attempt is rejected.
that module. These controllers can receive multicast data while another controller owns the module. If all owner controllers break
their connections to the input module, all controllers with listen-only connections no longer receive multicast data.
an output module. If another controller attempts to establish an owner connection, the connection attempt is rejected.
to that module. These controllers can receive multicast data while another controller owns the module. If the owner controller
breaks its connection to the output module, all controllers with listen-only connections no longer receive multicast data.
Select a Remote Adapter
The type of distributed I/O modules that you need to access determines which
adapter to use.
Table 7 - Choice of Remote Adapter
Type of Distributed I/O Available Remote Adapters
1756 ControlLogix I/O 1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2T, 1756-EN2TR, 1756-EN2TXT,
1794 FLEX I/O 1794-AENT
1734 POINT I/O 1734-AENT
1769 Compact I/O 1769-AENTR
1756-EN2F, or 1756-EN3TR communication module
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 57
Page 58

Chapter 5 Control I/O
Set the Requested Packet Interval (RPI)
When you configure an I/O module, you define the requested packet interval
(RPI) for the module. Only data-producing modules require an RPI. For
example, a local EtherNet/IP communication module requires no RPI because it
produces no data for the system. Instead it functions only as a bridge.
To set an RPI, follow these steps.
1. Make sure the module is installed, started and connected to the controller
via a serial, or other network, connection.
2. In the Controller Organizer, right-click the EtherNet/IP communication
module and choose Properties.
The Module Properties dialog box appears.
3. Click the Connection tab.
58 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 59

Control I/O Chapter 5
4. From the Requested Packet Interval (RPI) menu, enter the rate at which
you want data to be updated over a connection.
Only set the RPI to the rate the application requires.
Access Distributed I/O
IMPORTANT
The RPI determines the number of packets per second that the
module produces on a connection. Each module can produce only
a limited number of packets per second. Exceeding this limit
prevents the module from opening more connections.
5. Click OK.
Unlike EtherNet/IP communication modules, in Logix5000 controllers, I/O
values update at an interval set via the project’s I/O configuration folder. The
values update asynchronously to the execution of logic. At the specified interval,
the controller updates a value independently from the execution of logic.
I/O information is presented as a structure of multiple fields, which depends on
the specific features of the I/O module. The name of the structure is based on the
location of the I/O module in the system. Each I/O tag is automatically created
when you configure the I/O module through the programming software.
Each tag name follows this format:
Location:SlotNumber:Type.MemberName.SubMemberName.Bit
This address variable Is
Location Identifies network location
LOCAL = local DIN rail or chassis
ADAPTER_NAME = identifies remote adapter or bridge
SlotNumber Slot number of I/O module in its chassis
Type Type of data
I = input
O = output
C = configuration
S = status
MemberName Specific data from the I/O module, which depends on the type of data the module can store
For example, Data and Fault are possible fields of data for an I/O module. Data is the common name for values the are sent to or received
from I/O points.
SubMemberName Specific data related to a MemberName
Bit (optional) Specific point on the I/O module, which depends on the size of the I/O module (0...31 for a 32-point module)
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 59
Page 60

Chapter 5 Control I/O
EXAMPLE
Example Module Example Tag Names (automatically created by the software)
1 Remote 1794-AENT adapter “FLEX_io_adapter” FLEX_io_adapter:I
FLEX_io_adapter:I.SlotStatusBits
FLEX_io_adapter:I.Data
FLEX_io_adapter:O
FLEX_io_adapter:O.Data
2 Remote 1794-IA16
“input_module” in slot 0
Rack-optimized connection
3 Remote 1794-OB16
“output_module” in slot 1
Rack-optimized connection
4 Remote 1794-IF2XOF2I
“combo_analog” in slot 2
Direct connection
FLEX_io_adapter:0:C
FLEX_io_adapter:0:C.Config
FLEX_io_adapter:0:C.DelayTime_0
FLEX_io_adapter:0:C.DelayTime_1
FLEX_io_adapter:0:C.DelayTime_2
FLEX_io_adapter:0:C.DelayTime_3
FLEX_io_adapter:0:C.DelayTime_4
FLEX_io_adapter:0:C.DelayTime_5
FLEX_io_adapter:0:I
FLEX_io_adapter:1:C
FLEX_io_adapter:1:C.SSData
FLEX_io_adapter:1:O
FLEX_io_adapter:1:O.Data
FLEX_io_adapter:2:C
FLEX_io_adapter:2:C.InputFIlter
FLEX_io_adapter:2:C.InputConfiguration
FLEX_io_adapter:2:C.OutputConfiguration
FLEX_io_adapter:2:C.RTSInterval
FLEX_io_adapter:2:C.SSCh0OuputData
FLEX_io_adapter:2:C.SSCH1OutputData
FLEX_io_adapter:2:I
1
2
3
4
Using rack optimization for an I/O module creates tags as aliases for the adapter
module’s tags. This logic displays the device’s tag as an alias for the adapter
module’s tag. In this example, the tag name of the adapter is in angle brackets.
Tag Name of the I/O Device Tag Name of the Adapter
Conveyor:2:I.0
<Conveyor:I.Data[2].0>
60 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 61

Chapter 6
Interlocking and Data Transfer
between Controllers
This chapter describes how to share data by interlocking controllers (producing
and consuming tags) and transferring messages between controllers via an
EtherNet/IP network.
Topic Page
Set Up the Hardware 62
Tag Guidelines for Produced or Consumed Data 63
Connections for Produced and Consumed Tags 64
Produce a Tag 66
Consume Data Produced by Another Controller 68
Guidelines for Message (MSG) Instructions 73
Connections for Messages 74
Enter Message Logic 75
Configure a MSG Instruction 79
Communicate with PLC-5 or SLC Controllers 83
Table 8 - Communication Methods
If you want to And the data Then Page
Interlock operations Resides on Logix5000 controllers Produce and consume a tag 63
Transfer data Needs regular delivery at an interval
that you specify
Is sent when a specific condition
occurs in your application
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 61
Produce and consume a tag 63
Execute a message (MSG)
instruction
73
Page 62

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
Set Up the Hardware
Local Chassis with Logix5000
Controller and EtherNet/IP
Communication Module
In this example, the controller in the local chassis produces a tag that the
Logix5000 controller in the remote chassis consumes. The local controller can
also send a MSG instruction to the remote controller.
Figure 7 - Sharing Data and Transferring Messages
Data
EtherNet/IP Switch
Workstation
Remote Chassis with Logix5000
Controller and EtherNet/IP
Communication Module
Logix5000 Controller Combinations
Your controller type determines which communication module to use.
Table 9 - Choosing a Communication Module
Controllers Communication Modules
ControlLogix • 1756-ENBT
1768 CompactLogix 1768-ENBT communication module
1769-L1x CompactLogix Controllers Built-in EtherNet/IP port
• 1769-L30ER
• 1769-L30ER-NSE
• 1769-L30ERM
• 1769-L33ER
• 1769-L33ERM
• 1769-L36ERM
• 1769-L24ER-QB1B
• 1769-L24ER-QBFC1B
• 1769-L27ERM-QBFC1B
• 1769-L16ER-BB1B
• 1769-L18ER-BB1B
• 1769-L18ERM-BB1B
• 1756-EN2F
• 1756-EN2T
• 1756-EN2TR
• 1756-EN2TXT
• 1756-EN3TR
• 1756-EN2TRXT
• 1756-EN2TSC
Built-in EtherNet/IP port
62 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 63

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
You must complete these tasks before Logix5000 controllers can share tags over
an EtherNet/IP network:
• Set the IP addresses and other network parameters for each EtherNet/IP
communication module.
• Connect all wiring and cabling.
• Configure a communication driver (such as AB-ETHIP-1) for the
programming workstation.
Tag Guidelines for Produced or Consumed Data
IMPORTANT
If you are sharing tags between ControlLogix controllers and the
controllers are sharing only tags, not sending messages, set the
communication format of the 1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2F, 1756-EN2T,
1756-EN2TR, 1756-EN2TXT, 1756-EN3TR, 1756-EN2TSC and
1756-EN2TRTXT module to None.
To properly organize tags for produced or consumed data (shared data), follow
these guidelines.
Table 10 - Guidelines for the Organization of Tags
Guideline Details
Create the tags at the
controller scope.
Use one of these data types:
• DINT
• REAL
• array of DINTs or REALs
• user-defined
Limit the size of the tag
to 500 bytes.
Combine data that goes to the same
controller.
You can share only controller-scoped tags.
• To share other data types, create a user-defined data type that contains the
required data.
• Use the same data type for the produced tag and corresponding consumed
tag or tags.
If transferring more than 500 bytes, create logic to transfer the data in packets.
A size of < 125 DINT words will keep total bytes within 500. This helps reduce
the total number of packets for transactions.
If producing several tags for the same controller:
• Group the data into one or more user-defined data types. This method uses
fewer connections than does producing each tag separately.
• Group the data according to similar update intervals. To conserve network
bandwidth, use a greater RPI for less critical data.
For example, you could create one tag for data that is critical and another tag for
data that is not as critical.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 63
Page 64

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
Terminology
A Logix5000 controller can produce (broadcast) and consume (receive) systemshared tags.
Table 11 - Tag Definitions
Term Definition
Produced tag A tag that a controller makes available for use by other controllers. Multiple
Consumed tag A tag that receives the data of a produced tag. The data type of the consumed
To share produced or consumed tags, two controllers must be attached to the
same EtherNet/IP subnet. Two controllers cannot bridge produced or consumed
tags over two subnets.
controllers can simultaneously consume (receive) the data. A produced tag
sends its data to one or more consumed tags (consumers) without using logic.
The produced tag sends its data at the RPI of the consuming tag.
tag must match the data type (including any array dimensions) of the produced
tag. The RPI of the consumed tag determines the period at which the data
updates.
Connections for Produced and Consumed Tags
Logix controllers can produce (broadcast) and consume (receive) system-shared
tags that are sent and received via the EtherNet/IP communication module.
Produced and consumed tags each require connections.
Table 12 - Required Connections for Produced and Consumed Tags
Tag Type Required Connections
Produced The local controller (producing) must have one connection for the produced tag
and the first consumer and one more connection for each additional consumer
(heartbeat). The produced tag requires two connections.
As you increase the number of controllers that can consume a produced tag, you
also reduce the number of connections the controller has available for other
operations, such as communication and I/O.
Consumed Each consumed tag requires one connection for the controller that is consuming
the tag.
IMPORTANT: When you configure a consumed tag, you must add a remote
module to the producing controller’s Studio 5000 environment project to
configure the consuming controller. The default Comm Format when adding a
remote module to the project is Rack Optimized.
Change the Comm Format to None when adding the remote communication
module.
64 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 65

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
All EtherNet/IP communication modules support as many as 32 produced
multicast connections. Because each tag that passes through an EtherNet/IP
communication module uses a single connection, the number of available
connections limits the total number of tags that can be produced or consumed. If
the communication module uses all of its connections for I/O and other
communication modules, no connections remain for produced and consumed
tags.
IMPORTANT
Table 13 - Number Connections for Produced and Consumed Tags
Type of Tag Device Number of Connections Used
Produced tag Logix5000 controller Number_of_consumers + 1
Consumed tag Logix5000 controller
This graphic shows a Logix5000 controller producing a single tag for
consumption by another Logix5000 controller. In this example, the producing
controller uses 2 connections and every other Logix module/controller uses only
1 connection.
Figure 8 - Logix5000 Controller in Local Chassis Producing a Single Tag for a Logix5000 Controller
in a Remote Chassis
Local Controller (producer controller)- 1768 CompactLogix controller
Connections Used = 2 (1 + Number of consumers)
Depending on whether it is producing or consuming a tag, a Logix5000
controller uses its connections differently.
EtherNet/IP communication
module
EtherNet/IP communication
module
Remote Controller (consumer controller) - ControlLogix controller
Connections Used = 1
1
1
Local Communication Module 1768-ENBT
Connections Used = 1
EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP
ControlNet
Logix5575
10/100 BASE T
10/100 BASE T
OKFORCESDRUN
LNK1 LNK2 OK
LNK1 LNK2 OK
M
R
E
P
R
U
O
N
G
R
Remote Communication Module
- 1756-EN2T
1 2
1 2
Connections Used = 1
At its limits, a Logix5000 controller that produced 125 tags, each with only 1
consumer, the controller would use all of its available 250 connections. In this
example, the EtherNet modules used to communicate the tags would use only
125 connections. An example of the different.
For more information on using connections over an EtherNet/IP network, see
Ethernet Design Considerations Reference Manual, publication
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 65
ENET-RM001.
Page 66

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
Produce a Tag
To produce a tag, configure the produced tag in the Studio 5000 Logix Designer
project for the local (producer) controller. You do not have to configure the
consumer controllers in the I/O Configuration folder of the producer controller.
Configure the Produced Tag
To configure the produced tag, follow these steps.
1. In the producer’s Controller Organizer, right-click the Controller Tags
folder and choose Edit Tags.
The Controller Tags dialog box appears.
You can produce only controller-scoped tags.
2. In the Controller Tags window, right-click the tag that you want to
produce and choose Edit Tag Properties.
66 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 67

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
The Tag Properties dialog box appears.
3. From the Type pull-down menu, choose Produced.
4. Click Connection.
The Produced Tag Connection dialog box appears.
5. In the Max Consumers field, type the maximum number of controllers
that will consume (receive) the tag.
6. Click OK.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 67
Page 68

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
Consume Data Produced by Another Controller
Local Controller (consumer controller) - ControlLogix controller
Connections Used = 1
Local Communication Module 1756-EN2T
Connections Used = 1
To consume a produced tag, specify both the producer controller and the
produced tag in the Studio 5000 Logix Designer project for the remote
(consumer) Logix5000 controller.
Add the Producer Controller to the Consumer’s I/O Configuration
Add the producer controller to the remote controller’s I/O Configuration folder.
In the folder, organize the controllers and communication modules into a
hierarchy of tree/branch and parent/child.
Figure 9 - Logix5000 Controller in Local Chassis Consuming a Single Tag for a Logix5000 Controller
in a Remote Chassis
Remote Controller (producer controller)- 1768 CompactLogix controller
Connections Used = 2 (1 + Number of consumers)
EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP
ControlNet
Logix5575
10/100 BASE T
10/100 BASE T
OKFORCESDRUN
LNK1 LNK2 OK
LNK1 LNK2 OK
M
R
E
P
R
U
O
N
G
R
Remote Communication
1 2
1 2
Module - 1768-ENBT
Connections Used = 1
To add a producer controller to the consumer controller’s I/O, follow these steps.
1. Add the local communication module for the consumer controller.
2. Add the remote communication module for the producer controller.
3. Add the producer controller.
This graphic shows the consumer controller’s I/O configuration after the
modules are added.
68 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 69

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
To add a producer controller to the I/O Configuration folder, follow these steps.
1. In the Controller Organizer, right-click the remote backplane and choose
New Module.
The Select Module Type dialog box appears.
2. Click the By Category tab and choose your producer controller.
3. Click OK.
Depending on the controller type, the Select Major Revision dialog box
may appear. If the dialog box appears, choose the module’s major revision
and click OK.
The New Module dialog box appears.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 69
Page 70

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
4. Configure your new module.
• In the Name field, type the name of your module.
• In the Slot field, type the chassis slot number.
• From the Electronic Keying pull-down menu, choose the keying level
that fits your application.
5. Click OK.
IMPORTANT
The number and type of configuration parameters on the New Module
dialog box varies according to the controller type.
Create the Consumed Tag
To create the consumed tag, follow these steps.
1. In the consumer controller’s project in the Studio 5000 environment,
right-click the Controller Tags folder and choose Edit Tags.
The Controllers Tag dialog box appears.
Only controller-scoped tags can consume data.
70 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 71

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
2. In the Controller Tags window, right-click the tag that will consume the
data and choose Edit Tag Properties.
The Tag Properties dialog box appears.
3. From the Type pull-down menu, choose Consumed.
4. In the Data Type field, type a data type that matches the type assigned to
the produced tag.
5. Click Connection.
The Consumed Tag Connection dialog box appears.
6. From the Producer pull-down menu, choose the controller that produces
the data.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 71
Page 72

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
7. In the Remote Data field, type the tag name or instance number of the
produced data.
8. In the RPI field, type the requested packet interval (RPI) for the
connection.
Only set the RPI to the rate the application requires.
IMPORTANT
The RPI determines the number of packets per second that the
module will produce on a connection. Each module can only
produce a limited number of packets per second. Exceeding this
limit prevents the module from opening more connections.
For information on RPI and how it affects the actual packet interval
(API), see the Ethernet Design Considerations Reference Manual,
publication
ENET-RM001.
9. Click OK.
72 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 73

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
Guidelines for Message (MSG) Instructions
Follow these guidelines.
Table 14 - MSG Instruction Guidelines
Guideline Description
For each MSG instruction, create a
control tag.
Keep the source and destination
data at the controller scope.
If your MSG is to a module that uses
16-bit integers, use a buffer of INTs
in the MSG and DINTs throughout
the project.
Cache the connected MSGs that
execute most frequently.
If you want to enable more than 16
MSGs at one time, use some type of
management strategy.
Keep the number of unconnected
and uncached MSGs less than the
number of unconnected buffers.
Each MSG instruction requires its own control tag:
• Data type = MESSAGE
• Scope = controller
• The tag cannot be part of an array or a user-defined data type.
A MSG instruction can only access tags that are in the Controller Tags folder.
If your message is to a module that uses 16-bit integers, such as a PLC-5 or SLC
500 controller, and it transfers integers (not REALs), use a buffer of INTs in the
message and DINTs throughout the project.
This increases the efficiency of your project because Logix5000 controllers
execute more efficiently and use less memory when working with 32-bit
integers (DINTs).
Cache the connection for those MSG instructions that execute most frequently,
up to the maximum number permissible for your controller revision.
This optimizes execution time because the controller does not have to open a
connection each time the message executes.
If you enable more than 16 MSGs at one time, some MSG instructions may
experience delays in entering the queue. To guarantee the execution of each
message, perform one of these tasks:
• Enable each message in sequence.
• Enable the messages in groups.
• Program a message to communicate with multiple modules.
• Program logic to coordinate the execution of messages.
The controller can have 10...40 unconnected buffers. The default number is 10.
• If all the unconnected buffers are in use when an instruction leaves the
message queue, the instruction errors and does not transfer the data.
• You can increase the number of unconnected buffers to a maximum of 40.
For more information on programming MSG instructions, see the Logix5000
Controller General Instructions Reference Manual, publication
1756-RM003.
The individual system user manuals for Logix5000 controllers also provide MSG
examples unique to specific controller platforms.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 73
Page 74

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
Connections for Messages
Messages transfer data to other modules, such as other controllers or operator
interfaces. Each message uses one connection, regardless of how many modules
are in the message path. To conserve connections, you can configure one message
to read from or write to multiple modules.
These connected messages can leave the connection open (cache) or close the
connection when the message is done transmitting.
Table 15 - Message Connections
Type of Message Communication Method Used Connection Used
CIP data table read or write CIP Yes
PLC-2, PLC-3, PLC-5, or SLC (all types) CIP No
CIP with Source ID No
DH+ Yes
CIP generic CIP Your choice
Block-transfer read or write Yes
(1) You can connect CIP generic messages, but for most applications we recommend you leave CIP generic messages unconnected.
(1)
Cache Message Connections
Use the message’s execution rate to determine whether to cache a connection
or not.
Table 16 - Guidelines for Caching Message Connections
Message Execution Instruction Configuration
Repeated Cache the connection.
Important: Caching keeps the connection open and optimizes execution time.
Opening a connection each time the message executes increases execution time.
Infrequent Do not cache the connection.
Important: Not caching closes the connection upon completion of the message,
freeing up the connection for other uses.
74 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 75

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
Enter Message Logic
Local Communication
Module - 1756-ENBT
To send or receive data from an EtherNet/IP communication module via a
message, you must program a MSG instruction in the local controller’s logic. If
the target module is configured in the I/O Configuration folder of the controller,
browse to select the module or manually type the message path in the MSG
instruction.
Add the EtherNet/IP Communication Module to the Local Controller’s I/O Configuration
To use the Browse button to select the target device of a MSG instruction, add
that remote device to the I/O Configuration folder of the local controller.
Within the I/O Configuration folder, organize the local and remote devices into
a hierarchy of tree/branch, parent/child.
Figure 10 - Logix5000 Controller in Local Chassis Sending a Message to a Logix5000 Controller in a
Remote Chassis
Remote Controller - ControlLogix ControllerLocal Controller - ControlLogix Controller
EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP
ControlNet
Logix5575
10/100 BASE T
10/100 BASE T
OKFORCESDRUN
LNK1 LNK2 OK
LNK1 LNK2 OK
M
R
E
P
R
U
O
N
G
R
1 2
1 2
EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP
ControlNet
Logix5575
10/100 BASE T
10/100 BASE T
OKFORCESDRUN
LNK1 LNK2 OK
LNK1 LNK2 OK
M
R
E
P
R
U
O
N
G
R
Remote Communication
1 2
1 2
Module - 1756-ENBT
For a typical local/remote MSG structure, following the steps.
1. Add the local communication module for the local controller.
2. Add the remote communication module for the remote controller.
3. Add the remote controller.
This graphic shows the local controller’s I/O configuration after a local
EtherNet/IP communication module is added.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 75
Page 76

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
Select a communication format for a communication module based on the
modules in its remote chassis.
Table 17 - Module Communication Formats
Conditions Use This Communication Format
The remote chassis contains only analog modules, diagnostic
digital modules, fused output modules, or communication
modules
The remote chassis contains only standard, digital input and
output modules (no diagnostic modules or fused output
modules)
You want to receive I/O module and chassis slot information
from a rack-optimized remote chassis owned by another
controller
To add a module to the I/O Configuration folder, follow these steps.
None
Rack Optimization
Listen-Only Rack Optimization
1. In the Studio 5000 environment, right-click the level to which you want to
add the new module and choose New Module.
The Select Module Type dialog box appears.
76 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 77

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
2. Click the By Category tab and choose your EtherNet/IP
communication module.
3. Click OK.
Depending on the EtherNet/IP communication module, the Select Major
Revision dialog box may appear. If the dialog box appears, choose the
module’s major revision and click OK.
The New Module dialog box appears.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 77
Page 78

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
4. Configure your new module.
• In the Name field, type the name of your module.
• In the IP Address field, type the module IP address.
• In the Slot field, type the chassis slot number.
• Click Change to configure these parameters:
–Module Revision
–Electronic Keying
–Communication Format
5. Click OK.
IMPORTANT
The number and type of configuration parameters on the New Module
dialog box varies according to the EtherNet/IP communication module
type.
Enter a Message
To enter a message, follow these steps.
1. Use relay ladder logic to enter a MSG instruction.
2. Click to configure the MSG instruction.
EXAMPLE
If count_send = 1 and count_msg.EN = 0 (MSG instruction is not already enabled), then execute a MSG instruction that sends data to another controller.
count_send
Enter a MSG instruction
count_msg.en
/
...
Type - Uncongured
Message Control count_msg
MSG
EN
DN
...
ER
78 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 79

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
Configure a MSG Instruction
To configure a MSG instruction, follow these steps.
1. Click in the MSG box.
...
The Message Configuration dialog box appears.
2. Click the Configuration tab and specify the type of MSG instruction.
Configure a MSG to a Logix5000 Controller
If you want to For this item Type or choose
Read (receive) the data Message Type CIP Data Table Read
Source Element First element of the tag that contains data in the other controller
Number of Elements Number of elements to transfer
Destination Tag First element of the tag (controller-scoped) in this controller for the data
Write (send) the data Message Type CIP Data Table Write
Source Tag First element of the tag (controller-scoped) in this controller that contains the data
Number of Elements Number of elements to transfer
Destination Element First element of the tag for the data in the other controller
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 79
Page 80

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
Configure a MSG to an SLC 500 Controller
If the data is And you want to For this item Type or choose
Integer Read (receive) data Message Type SLC Typed Read
Source Element Data table address in the SLC 500 controller (for example, N7:10)
Number of Elements Number of integers to transfer
Destination Tag First element of int_buffer
Write (send) data Message Type SLC Typed Write
Source Tag First Element of int_buffer
Number of Elements Number of integers to transfer
Destination Element Data table address in the SLC 500 controller (for example, N7:10)
Floating-point (REAL) Read (receive) data Message Type SLC Typed Read
Source Element Data table address in the SLC 500 controller (for example, F8:0)
Number of Elements Number of values to transfer
Destination Tag First element of the tag (controller-scoped) in this controller for the data
Write (send) data Message Type SLC Typed Write
Source Tag First element of the tag (controller-scoped) in this controller that contains the data
Number of Elements Number of values to transfer
Destination Element Data table address in the SLC 500 controller (for example, F8:0)
Configure a MSG to a PLC-5 Controller
If the data is And you want to For this item Type or choose
Integer Read (receive) data Message Type PLC5 Typed Read
Source Element Data table address in the PLC-5 controller (for example, N7:10)
Number of Elements Number of integers to transfer
Destination Tag First element of int_buffer
Write (send) data Message Type PLC5 Typed Write
Source Tag First element of int_buffer
Number of Elements Number of integers to transfer
Destination Element Data Table address in the PLC-5 controller (for example, N7:10)
Floating-point (REAL) Read (receive) data Message Type PLC5 Typed Read
Source Element Data table address in the PLC-5 controller (for example, F8:0)
Number of Elements Number of values to transfer
Destination Tag First element of the tag (controller-scoped) in this controller for the data
Write (send) data Message Type PLC5 Typed Write
Source Tag First element of the tag (controller-scoped) in this controller that contains the data
Number of Elements Number of values to transfer
Destination Element Data table address in the PLC-5 controller (for example, F8:0)
3. Click the Communication tab.
4. In the Path field, type the communication path.
80 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 81

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
For a message to a ControlLogix controller, this Studio 5000 environment
Message Configuration dialog box appears.
For a message to a SLC 500 or PLC-5 processor, this RSLogix Message
Configuration dialog box appears.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 81
Page 82

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
5. If the target module is configured in the I/O Configuration folder of the
originating controller, click Browse to select the module or manually type
the path to the target module.
A manually typed path begins with the name of the local EtherNet/IP
communication module, the port the message exits (2 for EtherNet/IP),
and the IP address of the next module in the path, which could be the
target module.
EXAMPLE
Communication path from a Logix5000 controller to a Logix5000 controller over
an EtherNet/IP network
5575E
Ethernet Network
N
2T
Message
IP Address
168.127.127.12
5575E
N
2T
washer, 2, 168.127.127.12, 1, 0
Where Indicates
Washer Name of the 1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2F, 1756-EN2T, 1756-EN2TR,
2 Ethernet port of the 1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2F, 1756-EN2T, 1756-
168.127.127.12 IP address of the 1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2F, 1756-EN2T, 1756-EN2TR,
1 Backplane port of the 1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2F, 1756-EN2T, 1756-
0 Slot number of the destination controller
1756-EN2TXT, or 1756-EN3TR module
EN2TR, 1756-EN2TXT, or 1756-EN3TR module
1756-EN2TXT, or 1756-EN3TR Module in the destination chassis
EN2TR, 1756-EN2TXT, or 1756-EN3TR Module in the destination
chassis
82 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 83

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
Communicate with PLC-5 or SLC Controllers
If the message is to a PLC-5 or SLC 500 processor and it reads or writes integers
(not REALs), use a buffer of INTs in the message. Remember these
considerations:
• Logix5000 controllers execute more efficiently and use less memory when
working with 32-bit integers (DINTs).
• PLC-5 and SLC 500 processors require 16-bit integers.
• Messages require an INT buffer.
• Data can be moved into or out of the buffer as needed.
Converting between INTs and DINTs
If the message is to a device that uses 16-bit integers, such as a PLC-5 or SLC 500
controller, and it transfers integers (not REALs), use a buffer of INTs in the
message and DINTs throughout the project. This increases the efficiency of your
project.
1
2
Read 16-Bit Integers Data From
the Device
Word 1
Word 2
Word 3
Buffer of INTs DINTs For Use In
the Project
INT_Buffer[0] DINT_Array[0]
INT_Buffer[1] DINT_Array[1]
INT_Buffer[2] DINT_Array[2]
1. The Message (MSG) instruction reads 16-bit integers (INTs) from the
device and stores them in a temporary array of INTs.
2. An File Arith/Logical (FAL) instruction converts the INTs to DINTs for
use by other instructions in your project.
Write 16-Bit Integers DINTs From the
Project
1
Buffer of INTs Data For the
2
Device
DINT_Array[0] INT_Buffer[0] Word 1
DINT_Array[1] INT_Buffer[1] Word 2
DINT_Array[2] INT_Buffer[2] Word 3
1. An FAL instruction converts the DINTs from the Logix5000 controller to
INTs.
2. The MSG instruction writes the INTs from the temporary array to the
device.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 83
Page 84

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
Mapping Tags
A Logix5000 controller stores tag names on the controller so that other devices
can read or write data without having to know physical memory locations. Many
products only understand PLC/SLC data tables, so the Logix5000 controller
offers a PLC/SLC mapping function that enables you to map Logix tag names to
memory locations.
• You have to map only the file numbers that are used in messages; the other
file numbers do not need to be mapped.
• The mapping table is loaded into the controller and is used whenever a
logical address accesses data.
• You can access only controller-scoped tags (global data).
• For each file that is referenced in a PLC-5 or SLC command, make a map
entry with one of these methods:
– Typing the PLC/SLC file number of the logical address
– Typing or selecting the Logix5000 controller-scoped (global) tag that
supplies or receives data for the file number (You can map multiple files
to the same tag.)
• For PLC-2 commands, specify the tag that supplies or receives the data.
When mapping tags, remember these guidelines:
• Do not use file numbers 0, 1, and 2. These files are reserved for Output,
Input, and Status files in a PLC-5 processor.
• Use PLC-5 mapping only for tag arrays of data type INT, DINT, or
REAL. Attempting to map elements of system structures may produce
undesirable effects.
• Use the PLC file identifier of N or B when accessing elements in an INT
tag array.
This example shows how to use a buffer of INTs.
84 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 85

Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers Chapter 6
EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE
Read integers from a PLC-5 controller.
ATTENTION: When condition turns on, reads 16-bit integer values (INTs) and stores them in int_buffer. Then the FAL
instruction moves the values to dint_array. This converts the values to 32-bit integers (DINTs), for use by other instructions
in the ControlLogix controller.
Write integers to a PLC-5 controller.
ATTENTION: When condition turns on, moves the values in dint_array to int_buffer. This converts the values to 16-bit
integers (INTs). Then the message instruction sends int_buffer to the other controller.
42424
Where Is an
dint_array Array of DINTs that are used in the ControlLogix controller
int_buffer Array of INTs with the same number of elements as dint_array
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 85
Page 86

Chapter 6 Interlocking and Data Transfer between Controllers
Receive MSGs from PLC-5 or SLC 500 Controllers
To receive MSGs from PLC-5 or SLC 500 processors, follow these steps.
1. If the originating controller is a PLC-5 or SLC 500 processor, in the MSG
instruction, select PLC5.
If the controller is a For this section And this item Specify
PLC-5 This PLC-5 Communication Command PLC-5 Typed Read or PLC-5 Typed Write
Data Table Address Starting address of the data in the PLC-5 controller
Size in Elements Number of elements to read or write
Port Number 2
Target Device Data Table Address Type, in quotation marks [“ “], the name of the tag in the ControlLogix
MultiHop Select Yes.
SLC 500 This Controller Communication Command PLC5 Read or PLC5 Write
Data Table Address Starting address of the data in the SLC 500 controller
Size in Elements Number of elements to read or write
Channel 1
Target Device Data Table Address Type, in quotation marks [“ “], the name of the tag in the ControlLogix
MultiHop Select Yes
controller (for example, “count”).
controller (for example, “count”).
2. On the MultiHop tab, specify the following:
• IP address of the EtherNet/IP communication module that is local to
the Logix5000 controller
• Slot number of the Logix5000 controller
86 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 87

Send Email
Chapter 7
Introduction
This chapter describes how to send an email through an EtherNet/IP
communication module.
IMPORTANT
Topic Page
EtherNet/IP Communication Module as an Email Client 87
Send Email via a Controller-initiated Message Instruction 89
Create String Tags 89
Enter the Ladder Logic 92
Configure the MSG Instruction that Identifies the Mail Relay Server 92
Configure the MSG Instruction That Contains the Email Text 94
Enter Email Text 96
Possible Email Status Codes 96
The 1756-EN2TSC module does not support this capability.
For email, the EtherNet/IP communication module can be remote or local to
the controller.
EtherNet/IP Communication Module as an Email Client
The EtherNet/IP communication module is an email client that uses a mail relay
server to send email.
IMPORTANT
The EtherNet/IP communication module can send an email to only one
recipient at a time. It cannot mail to a distribution list.
Table 18 - Ethernet Email
Desired Action Required Tasks
Send an email to specific personnel when a controller
application generates an alarm or reaches a certain
condition
Send controller or application status information on a
regular basis to a project manager
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 87
Program the controller to send a MSG instruction to the
EtherNet/IP communication module
The MSG instruction then instructs the
EtherNet/IP communication module to send the email text
(contained within the MSG instruction) to the mail relay
server.
Multiple controllers can use the same EtherNet/IP
communication module to initiate email.
Page 88

Chapter 7 Send Email
Firewall/Router
The EtherNet/IP communication module sends only the content of a MSG
instruction as an email to a mail relay server. Delivery of the email depends on the
mail relay server. The EtherNet/IP communication module does not
receive email.
Figure 11 - Sample System
ControlLogix Controller With 1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2F, 1756-EN2T, 1756EN2TR, 1756-EN2TXT, or 1756-EN3TR Module
EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP
Redundancy Module
Logix5575
10/100 BASE T
OKFORCESDRUN
PRI COM OK
LNK1 LNK2 OK
M
R
E
P
R
U
O
N
G
R
1 2
EtherNet/IP
ControlNet
ControlNet
LNK NET OK
LNK NET OK
Ethernet Switch
Ethernet Switch
Mail Relay
Server
1769-L35E CompactLogix Controller
Table 19 - Sample System Capabilities
Device Capability
ControlLogix controller Send a MSG instruction to the 1756-ENBT module to initiate sending an email to
CompactLogix controller
1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2F, 1756-EN2T,
1756-EN2TR, 1756-EN2TXT,
EN2TRXT, or 1756-EN3TR module
Mail relay server Send email to specified recipients.
the mail relay server.
Use the path of the MSG instruction to identify the 1756-ENBT module as the
target of the MSG instruction.
Send an email to the mail relay server from the email interface on the Send an
Email link.
This interface requires entry of all email information.
The mail relay server determines the delivery of any email sent through an
EtherNet/IP communication module, whether via a MSG instruction or from its
built-in interface.
88 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 89

Send Email Chapter 7
Send Email via a Controllerinitiated Message
Instruction
A Logix controller can send a generic CIP message instruction to the EtherNet/
IP communication module that instructs the module to send an email message to
a SMTP mail relay server using the standard SMTP protocol. This automatically
communicates controller data and application conditions to appropriate
personnel.
IMPORTANT
Some mail relay servers require a domain name be provided during the initial
handshake of the SMTP session. For these mail relay servers, specify a domain
name when configuring the EtherNet/IP communication module’s network
settings.
For additional information, see
Module to Operate on the Network on page 17.
Be careful to write the ladder logic to be sure the MSG instructions are not
continuously triggered to send email messages.
Configure an EtherNet/IP Communication
Create String Tags
You need three controller-scoped string tags. Each tag performs one of
these functions:
• Identifies the mail server
• Contains the email text
• Contains the status of the email transmission
The default STRING data type supports up to 82 characters. In most cases, this
is sufficient to contain the address of the mail server. For example, to create tag
EmailConfigstring of type STRING, follow these steps.
1. Click in the Value column of the Controller Tags dialog box.
...
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 89
Page 90

Chapter 7 Send Email
The String Browser dialog box appears.
2. Type the IP address or host name of the mail server.
3. Click OK.
The tags for the email text and transmission status can contain up to 474
characters. For these tags, you must create a user-defined STRING data type. The
default STRING data type in the Studio 5000 environment is not large enough
for most email text.
To create a user-defined STRING data type, follow these steps.
1. In the Data Types folder in the Studio 5000 environment, navigate to and
right-click the Strings folder, and choose New String Type.
90 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 91

Send Email Chapter 7
2. Create the EmailString data type.
3. Create one controller-scoped tag, such as EWEB_EMAIL, of this new
data type to contain the email text.
4. Create a second controller-scoped tag, such as EmailDstStr, of this new
data type to contain the transmission status.
Tag for Status
Tag for Email Text
Both of these tags are of type EmailString.
5. Click in the Value column of the Controller Tags dialog box.
...
The String Browser dialog box appears.
6. Type your email.
The text of the email does not have to be static. You can program a
controller project to collect specific data to be sent in an email.
7. Click OK.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 91
Page 92

Chapter 7 Send Email
SetServer
For more information on using ladder logic to manipulate string data, see the
Logix5000 Controllers Common Procedures Programming Manual, publication
1756-PM001.
Enter the Ladder Logic
Ladder logic requires two MSG instructions. One MSG instruction configures
the mail server and needs to be executed only once. The second MSG instruction
triggers the email. Execute this email MSG instruction as often as needed.
The first rung configures the mail server. The second rung sends the email text.
Configure the MSG Instruction that Identifies the Mail Relay Server
To configure the MSG instruction that identifies the mail relay server, follow
these steps.
1. In the MSG instruction, click the Communication tab.
92 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 93

Send Email Chapter 7
2. In the Path field, type the path for the MSG instruction. The path starts
with the controller initiating the MSG instruction.
Type the number of the port from which the message exits and the address
of the next module in the path.
For example, if the EtherNet/IP communication module is in the same
chassis as the controller and is in slot 2, the path is: 1, 2.
For more information on configuring the path of a MSG instruction, see
the Logix5000 Controllers General Instructions Reference Manual,
publication
1756-RM003.
3. Click the Configuration tab.
4. Configure the MSG parameters for sending an email.
• From the Service Type pull-down menu, choose Attribute Single
• In the Instance field, type 1.
• In the Class field, type 32f.
• In the Attribute field, type 5.
• From the Source Element pull-down menu, choose the tag that contains
your email text.
• In the Source Length field, type the number of characters in the email
plus four.
The Source Length is the number of characters in the STRING tag
that identifies the mail relay server plus 4 characters.
In this example, the tag contains 13 characters.
In this example, you would enter 13 for the number of characters plus 4
for a total of 17.
After the MSG instruction that configures the mail relay server executes
successfully, the controller stores the mail relay server information in
nonvolatile memory. The controller retains this information, even through
power cycles, until another MSG instruction changes the information.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 93
Page 94

Chapter 7 Send Email
Configure the MSG Instruction That Contains the Email Text
To configure the MSG instruction that contains the email text, perform this
procedure.
1. Click the Configuration tab.
The Source Length is the number of characters in the email tag plus 4
characters.
In this example, the email text contains 65 characters.
2. Configure the MSG parameters for sending an email.
• From the Service Type pull-down menu, choose Custom.
• In the Service Code field, type 4b.
• In the Instance field, type 1.
• In the Class field, type 32f.
• In the Attribute field, type 0.
• From the Source Element pull-down menu, choose the tag that contains
your email text.
• In the Source Length field, type the number of characters in the email
plus four.
In this example, you would enter 65 for the number of characters plus 4
for a total of 69.
• From the Destination pull-down menu, choose a tag to contain the
status of your email transmission.
94 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 95

Send Email Chapter 7
3. Click the Communication tab.
4. In the Path field, type the path from the controller to the EtherNet/IP
communication module.
The path starts with the controller initiating the MSG instruction. The
second number in the path represents the port from which the message
exits and the address of the next module in the path.
For example, if the EtherNet/IP communication module is in the same
chassis as the controller and is in slot 2, the path is: 1, 2.
5. If all the devices in the path are configured in the initiating controller’s I/O
Configuration tree, click Browse to select the target module.
The software automatically fills in the path.
6. Click OK.
For more information on configuring the path of an MSG instruction, see the
Logix5000 Controllers General Instructions Reference Manual, publication
1756-RM003.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 95
Page 96

Chapter 7 Send Email
Enter Email Text
Possible Email Status Codes
Use the string browser to type the text of the email. To include To:, From:, and
Subject: fields in the email, use <CR><LF> symbols to separate each of these
fields. The To: and From fields are required; the Subject: field is optional. For
example:
To: email address of recipient <CR><LF>
From: email address of sender <CR><LF>
Subject: subject of message <CR><LF>
body of email message
An email message must not exceed 474 characters in length. An additional 4-byte
string-length value is added to the tag. As a result, the maximum source length is
478 characters.
Examine the destination element of the email MSG to see whether the email was
successfully delivered to the mail relay server. A successful delivery indicates that
the mail relay server placed the email message in a queue for delivery, but it does
not mean the intended recipient received the email message. These are the
possible codes that a destination element could contain.
Table 20 - Email Status Code Descriptions
Error
Code
(Hex)
0x00 None Delivery successful to the mail relay server.
0x02 None Resource unavailable. The email object was unable to obtain memory resources to
0x08 None Unsupported Service Request. Make sure the service code is 0x4B and the Class is
0x11 None Reply data too large. The Destination string must reserve space for the SMTP
0x13 None Configuration data size too short. The Source Length is less than the Source
0x15 None Configuration data size too large. The Source Length is greater than the Source
0x19 None Data write failure. An error occurred when attempting to write the SMTP server
0xFF 0x0100 Error returned by email server; check the Destination string for reason. The email
Extendederror Code
(Hex)
0x0101 SMTP mail server not configured. Attribute 5 was not set with a SMTP server
0x0102 ‘To : ’ address not specified. Attribute 1 was not set with a ‘To: ’ address AND there is
0x0103 ‘From:’ address not specified. Attribute 2 was not set with a ‘From:’ address AND
Description
initiate the SMTP session.
0x32F.
server reply message. The maximum reply can be 470 bytes.
Element string size plus the 4-byte length. The Source Length must equal the
Source Element string size + 4.
Element string size plus the 4-byte length. The Source Length must equal the
Source Element string size + 4.
address (attribute 4) to nonvolatile memory.
message was not queued for delivery.
address.
not a ‘To :’ field header in the email body.
there is not a ‘From:’ field header in the email body.
96 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 97

Table 20 - Email Status Code Descriptions
Send Email Chapter 7
Error
Code
(Hex)
Extendederror Code
(Hex)
Description
0xFF 0x0104 Unable to connect to SMTP mail server set in Attribute 5. If the mail server address
is a host name, make sure that the device supports DNS, and that a Name Server is
configured. If the host name is not fully qualified, for example, ‘mailhost’ and not
‘mailhost.xx.yy.com’ then the domain must be configured as ‘xx.yy.com’. Try ‘ping
<mail server address>’ to insure the mail server is reachable from your network.
Also try ‘telnet <mail server address> 25’, which attempts to initiate a SMTP
session with the mail server via telnet over port 25. (If you connect then type
‘QUIT’).
0x0105 Communication error with SMTP mail server. An error occurred after the initial
connection with the SMTP mail server.
See the ASCII text following the error code for more details as to the type of error.
0x0106 SMTP mail server host name DNS query did not complete. A previous send service
request with a host name as the SMTP mail server address did not yet complete.
Note that a timeout for a DNS lookup with an invalid host name can take up to 3
minutes. Long timeouts can also occur if a domain name or name server is not
configured correctly.
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 97
Page 98

Chapter 7 Send Email
Notes:
98 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
Page 99

Chapter 8
Communicate with PanelView Terminals
This chapter describes how a controller uses an EtherNet/IP communication
module to communicate with PanelView and PanelView Plus terminals over an
EtherNet/IP network.
Topic Page
Set Up the Hardware 99
Connections to PanelView Terminals 100
Add a PanelView Terminal 101
Organize Controller Data for a PanelView Terminal 105
Connections to FactoryTalk View Applications 106
Set Up the Hardware
Local Chassis Containing a
Logix5000 Controller with
an EtherNet/IP Connection
In this example, the controller in the local chassis shares data with an HMI
application on the EtherNet/IP network. This application could be running
these components:
• PanelView terminal
• PanelView Plus terminal
• Workstation running Factory Talk View software
• Workstation running a FactoryTalk Enterprise application, such as
FactoryTalk View Machine Edition or FactoryTalk View Supervisory
Edition
Figure 12 - Ethernet Communication with PanelView Terminal
EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP
Redundancy Module
Logix5575
OKFORCESDRUN
PRI COM OK
LNK1 LNK2 OK
M
R
E
P
R
U
O
N
G
R
1 2
EtherNet/IP
ControlNet
ControlNet
10/100 BASE T
LNK NET OK
LNK NET OK
Data
HMI with EtherNet/IP
Connectivity
EtherNet/IP Switch
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014 99
Page 100

Chapter 8 Communicate with PanelView Terminals
Logix5000 Controller Combinations
Your controller type determines which communication module to use.
Table 21 - Choosing a Communication Module
Controllers Communication Modules
ControlLogix 1756-ENBT, 1756-EN2F, 1756-EN2T, 1756-EN2TR, 1756-
1768 CompactLogix 1768-ENBT communication module
1769-L23E-Q1B, 1769-L23E-QBFC1B, 1769-L32E, or 1769L35E CompactLogix
PowerFlex 700S with DriveLogix 1788-ENBT EtherNet/IP communication module
You must complete these tasks before your controller can communicate with
PanelView terminals over an EtherNet/IP network:
• Set the IP addresses for the controller’s EtherNet/IP communication
module and the HMI terminal.
EN2TXT, 1756-EN3TR, or
1756-EN2TSC communication modules
A built-in EtherNet/IP port
Connections to PanelView Terminals
• Connect all wiring and cabling.
To establish communication between a PanelView or PanelView Plus terminal,
specify controller connections.
Table 22 - PanelView Terminal Connections
Terminal Type
Type of Communication
Implicit (connected)
• Logix controller communicates to the PanelView terminal like
an I/O module.
• You must add the PanelView terminal to the I/O configuration
tree for the controller project.
Explicit (unconnected)
• Communication is set up in PanelBuilder or RSView ME
software.
• All communication is initiated by the PanelView or PanelView
Plus terminal.
PanelView PanelView Plus
Supported Not supported
Supported Supported
100 Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
 Loading...
Loading...