Page 1

MVI71-GEC
PLC 5 Platform
Generic ASCII Ethernet
Communication Module
May 11, 2011
USER MANUAL
Page 2

Your Feedback Please
We always want you to feel that you made the right decision to use our products. If you have suggestions, comments,
compliments or complaints about our products, documentation, or support, please write or call us.
How to Contact Us
ProSoft Technology
5201 Truxtun Ave., 3rd Floor
Bakersfield, CA 93309
+1 (661) 716-5100
+1 (661) 716-5101 (Fax)
www.prosoft-technology.com
support@prosoft-technology.com
Copyright © 2011 ProSoft Technology, Inc., all rights reserved.
MVI71-GEC User Manual
May 11, 2011
ProSoft Technology ®, ProLinx ®, inRAx ®, ProTalk ®, and RadioLinx ® are Registered Trademarks of ProSoft
Technology, Inc. All other brand or product names are or may be trademarks of, and are used to identify products
and services of, their respective owners.
ProSoft Technology® Product Documentation
In an effort to conserve paper, ProSoft Technology no longer includes printed manuals with our product shipments.
User Manuals, Datasheets, Sample Ladder Files, and Configuration Files are provided on the enclosed CD-ROM in
Adobe® Acrobat Reader file format (.PDFs). These product documentation files may also be freely downloaded from
our web site: www.prosoft-technology.com
Page 3

Important Installation Instructions
Power, Input, and Output (I/O) wiring must be in accordance with Class I, Division 2 wiring methods, Article 501-4 (b)
of the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70 for installation in the U.S., or as specified in Section 18-1J2 of the Canadian
Electrical Code for installations in Canada, and in accordance with the authority having jurisdiction. The following
warnings must be heeded:
WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - SUBSTITUTION OF COMPONENTS MAY IMPAIR SUITABILITY FOR CLASS
I, DIV. 2;
WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - WHEN IN HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS, TURN OFF POWER BEFORE
REPLACING OR WIRING MODULES
WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - DO NOT DISCONNECT EQUIPMENT UNLESS POWER HAS BEEN
SWITCHED OFF OR THE AREA IS KNOWN TO BE NON-HAZARDOUS.
THIS DEVICE SHALL BE POWERED BY CLASS 2 OUTPUTS ONLY.
MVI (Multi Vendor Interface) Modules
WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - DO NOT DISCONNECT EQUIPMENT UNLESS POWER HAS BEEN
SWITCHED OFF OR THE AREA IS KNOWN TO BE NON-HAZARDOUS.
AVERTISSEMENT - RISQUE D'EXPLOSION - AVANT DE DÉCONNECTER L'ÉQUIPEMENT, COUPER LE
COURANT OU S'ASSURER QUE L'EMPLACEMENT EST DÉSIGNÉ NON DANGEREUX.
Warnings
North America Warnings
A Warning - Explosion Hazard - Substitution of components may impair suitability for Class I, Division 2.
B Warning - Explosion Hazard - When in Hazardous Locations, turn off power before replacing or rewiring
modules.
Warning - Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect equipment unless power has been switched off or the area is
known to be nonhazardous.
C Suitable for use in Class I, division 2 Groups A, B, C and D Hazardous Locations or Non-Hazardous Locations.
ATEX Warnings and Conditions of Safe Usage:
Power, Input, and Output (I/O) wiring must be in accordance with the authority having jurisdiction
A Warning - Explosion Hazard - When in hazardous locations, turn off power before replacing or wiring modules.
B Warning - Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect equipment unless power has been switched off or the area is
known to be non-hazardous.
C These products are intended to be mounted in an IP54 enclosure. The devices shall provide external means to
prevent the rated voltage being exceeded by transient disturbances of more than 40%. This device must be used
only with ATEX certified backplanes.
D DO NOT OPEN WHEN ENERGIZED.
Warning: This module is not hot-swappable! Always remove power from the rack before inserting or removing this
module, or damage may result to the module, the processor, or other connected devices.
Battery Life Advisory
The MVI46, MVI56, MVI56E, MVI69, and MVI71 modules use a rechargeable Lithium Vanadium Pentoxide battery to
backup the real-time clock and CMOS. The battery should last for the life of the module. The module must be
powered for approximately twenty hours before the battery becomes fully charged. After it is fully charged, the battery
provides backup power for the CMOS setup and the real-time clock for approximately 21 days. When the battery is
fully discharged, the module will revert to the default BIOS and clock settings.
Note: The battery is not user replaceable.
Page 4

Markings
Electrical Ratings
Backplane Current Load: 800 mA @ 5 Vdc
Operating Temperature: 0°C to 60°C (32°F to 140°F)
Storage Temperature: -40°C to 85°C (-40°F to 185°F)
Shock: 30 g operational, 50 g non-operational; Vibration: 5 g from 10 Hz to 150 Hz
Relative Humidity 5% to 95% (with no condensation)
All phase conductor sizes must be at least 1.3 mm(squared) and all earth ground conductors must be at least
4mm(squared).
Label Markings
Agency Approvals and Certifications
Agency Applicable Standards
ANSI / ISA ISA 12.12.01 Class I Division 2, GPs A, B, C, D
CSA/cUL C22.2 No. 213-1987
CSA CB Certified IEC61010
ATEX EN60079-0 Category 3, Zone 2
EN60079-15
243333
Page 5

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Contents
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Contents
Your Feedback Please ........................................................................................................................ 2
How to Contact Us .............................................................................................................................. 2
ProSoft Technology® Product Documentation .................................................................................... 2
Important Installation Instructions ....................................................................................................... 3
MVI (Multi Vendor Interface) Modules ................................................................................................ 3
Warnings ............................................................................................................................................. 3
Battery Life Advisory ........................................................................................................................... 3
Markings .............................................................................................................................................. 4
Guide to the MVI71-GEC User Manual 7
1 Start Here 9
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.6.1
System Requirements ............................................................................................. 10
Package Contents ................................................................................................... 11
Setting Jumpers ...................................................................................................... 12
Install the Module in the Rack ................................................................................. 13
Connect your PC to the Processor .......................................................................... 15
Download the Sample Program to the Processor ................................................... 16
Configuring the RSLinx Driver for the PC COM Port .............................................. 17
Connect your PC to the Module .............................................................................. 19
2 Module Configuration 21
2.1
2.2
2.1.1
2.1.2
2.1.3
2.1.4
2.1.5
Using ProSoft Configuration Builder ....................................................................... 22
Set Up the Project ................................................................................................... 22
Renaming PCB Objects .......................................................................................... 24
[Module] ................................................................................................................... 25
[Server x] ................................................................................................................. 25
Downloading the Project to the Module Using a Serial COM Port .......................... 27
IP Address ............................................................................................................... 28
3 Ladder Logic 29
3.1
3.2
Adding the Module to an Existing PLC5 Project ..................................................... 30
GECServerStat (Server Status Object) ................................................................... 32
4 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting 33
4.1
4.1.1
4.1.2
4.1.3
4.2
4.2.1
4.2.2
4.2.3
LED Status Indicators .............................................................................................. 34
Ethernet LED Indicators .......................................................................................... 34
Clearing a Fault Condition ....................................................................................... 35
Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................... 35
Using ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) for Diagnostics.................................... 36
Using the Diagnostic Window in ProSoft Configuration Builder .............................. 36
Navigation ............................................................................................................... 38
Main Menu ............................................................................................................... 39
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 5 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 6

Contents MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
4.2.4
4.3
Network Menu ......................................................................................................... 42
Reading Status Data from the Module ................................................................... 43
5 Reference 45
5.1
5.2
5.3
5.4
5.5
5.1.1
5.1.2
5.1.3
5.2.1
5.3.1
5.3.2
5.3.3
5.5.1
Product Specifications ............................................................................................ 46
General Specifications ............................................................................................ 46
Hardware Specifications ......................................................................................... 46
Functional Specifications ........................................................................................ 47
Functional Overview ............................................................................................... 48
General Concepts ................................................................................................... 48
Cable Connections ................................................................................................. 66
Ethernet Connection ............................................................................................... 66
RS-232 Configuration/Debug Port .......................................................................... 67
DB9 to RJ45 Adaptor (Cable 14) ............................................................................ 69
MVI71-GEC Status Data Area ................................................................................ 70
MVI71-GEC Configuration Data ............................................................................. 74
MVI71-GEC Server Communication Module Configuration ................................... 74
6 Support, Service & Warranty 77
Contacting Technical Support .......................................................................................................... 77
6.1
6.2
6.1.1
6.1.2
6.1.3
6.2.1
6.2.2
6.2.3
6.2.4
6.2.5
6.2.6
6.2.7
6.2.8
6.2.9
6.2.10
Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions ............................... 79
Returning Any Product ............................................................................................ 79
Returning Units Under Warranty ............................................................................. 80
Returning Units Out of Warranty ............................................................................. 80
LIMITED WARRANTY ............................................................................................ 81
What Is Covered By This Warranty ........................................................................ 81
What Is Not Covered By This Warranty .................................................................. 82
Disclaimer Regarding High Risk Activities .............................................................. 82
Intellectual Property Indemnity ............................................................................... 83
Disclaimer of all Other Warranties .......................................................................... 83
Limitation of Remedies ** ....................................................................................... 84
Time Limit for Bringing Suit ..................................................................................... 84
No Other Warranties ............................................................................................... 84
Allocation of Risks .................................................................................................. 84
Controlling Law and Severability ............................................................................ 84
Index 85
Page 6 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 7

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Guide to the MVI71-GEC User Manual
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Guide to the MVI71-GEC User Manual
Function
Introduction
(Must Do)
Diagnostic and
Troubleshooting
Reference
Product Specifications
Support, Service, and
Warranty
Index
Section to Read Details
Start Here (page 8) This section introduces the customer to the
→
Diagnostics and
→
Troubleshooting
(page 33)
Reference (page 45)
→
Product
Specifications (page
46)
Support, Service
→
and Warranty (page
77)
Index
module. Included are: package contents,
system requirements, hardware installation, and
basic configuration.
This section describes Diagnostic and
Troubleshooting procedures.
These sections contain general references
associated with this product and its
Specifications..
This section contains Support, Service and
Warranty information.
Index of chapters.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 7 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 8

Guide to the MVI71-GEC User Manual MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Page 8 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 9

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Start Here
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
1 Start Here
In This Chapter
System Requirements ........................................................................... 10
Package Contents ................................................................................. 11
Setting Jumpers .................................................................................... 12
Install the Module in the Rack ............................................................... 13
Connect your PC to the Processor ........................................................ 15
Download the Sample Program to the Processor .................................. 16
Connect your PC to the Module ............................................................ 19
To get the most benefit from this User Manual, you should have the following
skills:
Rockwell Automation® RSLogix™ software: launch the program, configure
ladder logic, and transfer the ladder logic to the processor
Microsoft Windows: install and launch programs, execute menu commands,
navigate dialog boxes, and enter data
Hardware installation and wiring: install the module, and safely connect
GEC and PLC devices to a power source and to the MVI71-GEC module’s
application port(s)
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 9 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 10

Start Here MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
1.1 System Requirements
The MVI71-GEC module requires the following minimum hardware and software
components:
Rockwell Automation PLC processor, with compatible power supply and one
free slot in the rack, for the MVI71-GEC module. The module requires 800mA
of available power.
The PLC Processor must provide for at least 64 words of BTR/BTW area,
otherwise the module may not function correctly.
Rockwell Automation RSLogix 5 programming software.
Rockwell Automation RSLinx communication software
Pentium® 100 MHz minimum. Pentium III 700 MHz (or better) recommended
Supported operating systems:
o
Microsoft Windows XP
o
Microsoft Windows 2000
o
Microsoft Windows NT v4.0 with Service Pack 3 or greater
o
Microsoft Windows ME
o
Microsoft Windows 98
64 Mbytes of RAM minimum, 256 Mbytes of RAM recommended
100 Mbytes of free hard disk space (or more based on application
requirements)
256-color VGA graphics adapter, 800 x 600 minimum resolution (True Color
1024 × 768 recommended)
CD-ROM drive
Page 10 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 11

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Start Here
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
1.2 Package Contents
The following components are included with your MVI71-GEC module, and are
all required for installation and configuration.
Important: Before beginning the installation, please verify that all of the following items are
present.
Qty. Part Name Part Number Part Description
1 MVI71-GEC Module MVI71-GEC Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication
1 Cable Cable #15, RS232
3 Cable Cable #14, RJ45 to
2 Adapter 1454-9F Two Adapters, DB9 Female to Screw
1 ProSoft Solutions CD Contains sample programs, utilities and
Module
For RS232 Connection to the CFG Port
Null Modem
For DB9 Connection to Module’s Port
DB9 Male Adapter
cable
Terminal. For RS422 or RS485
Connections to Port 1 and 2 of the Module
documentation for the MVI71-GEC module.
If any of these components are missing, please contact ProSoft Technology
Support for replacement parts.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 11 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 12
Start Here MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
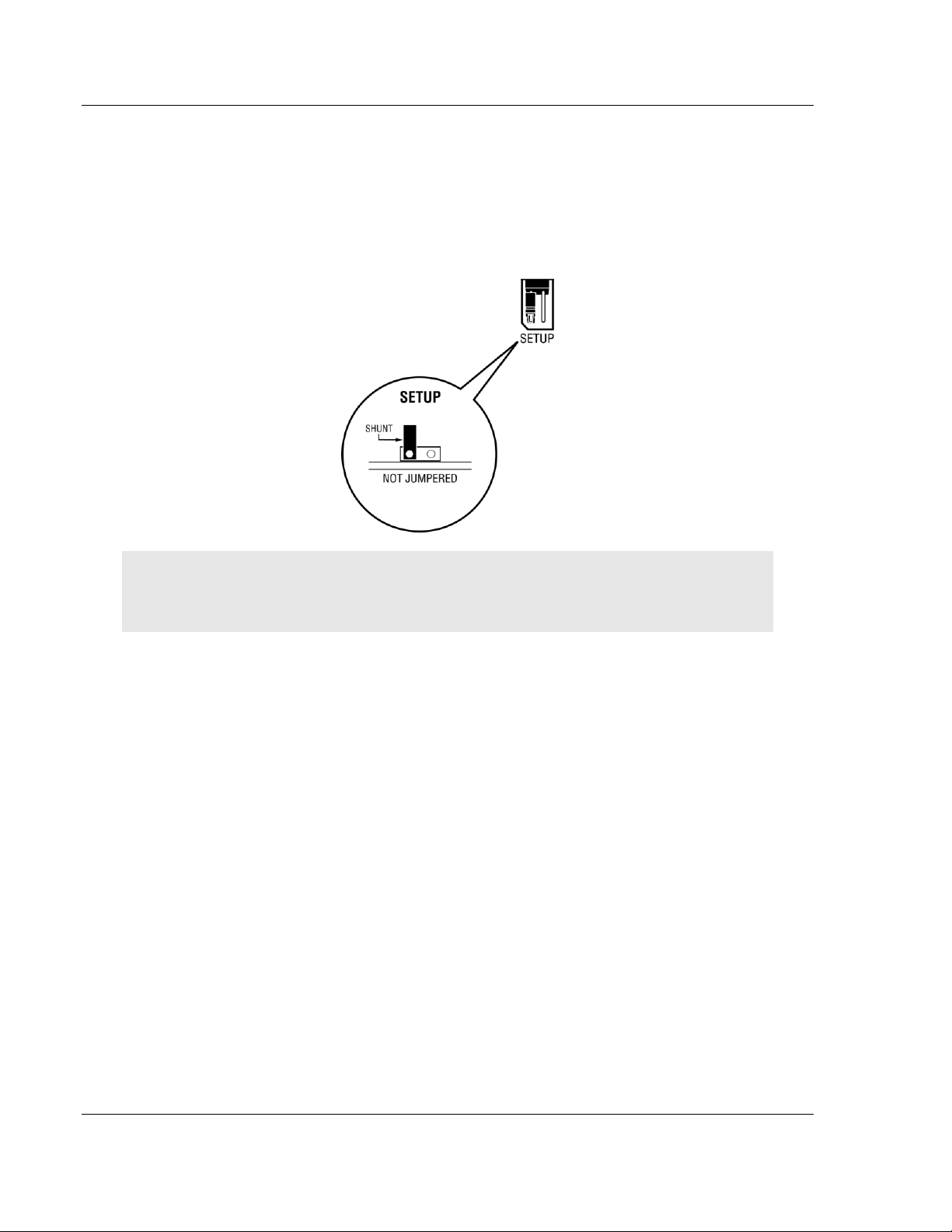
1.3 Setting Jumpers
The Setup Jumper acts as "write protection" for the module’s flash memory. In
"write protected" mode, the Setup pins are not connected, and the module’s
firmware cannot be overwritten. Do not jumper the Setup pins together unless
you are directed to do so by ProSoft Technical Support.
The following illustration shows the MVI71-GEC jumper configuration.
Note: If you are installing the module in a remote rack, you may prefer to leave the Setup pins
jumpered. That way, you can update the module’s firmware without requiring physical access to
the module.
Page 12 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 13
MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Start Here
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
1.4 Install the Module in the Rack
If you have not already installed and configured your PLC processor and power
supply, please do so before installing the MVI71-GEC module. Refer to your
Rockwell Automation product documentation for installation instructions.
Warning: You must follow all safety instructions when installing this or any other electronic
devices. Failure to follow safety procedures could result in damage to hardware or data, or even
serious injury or death to personnel. Refer to the documentation for each device you plan to
connect to verify that suitable safety procedures are in place before installing or servicing the
device.
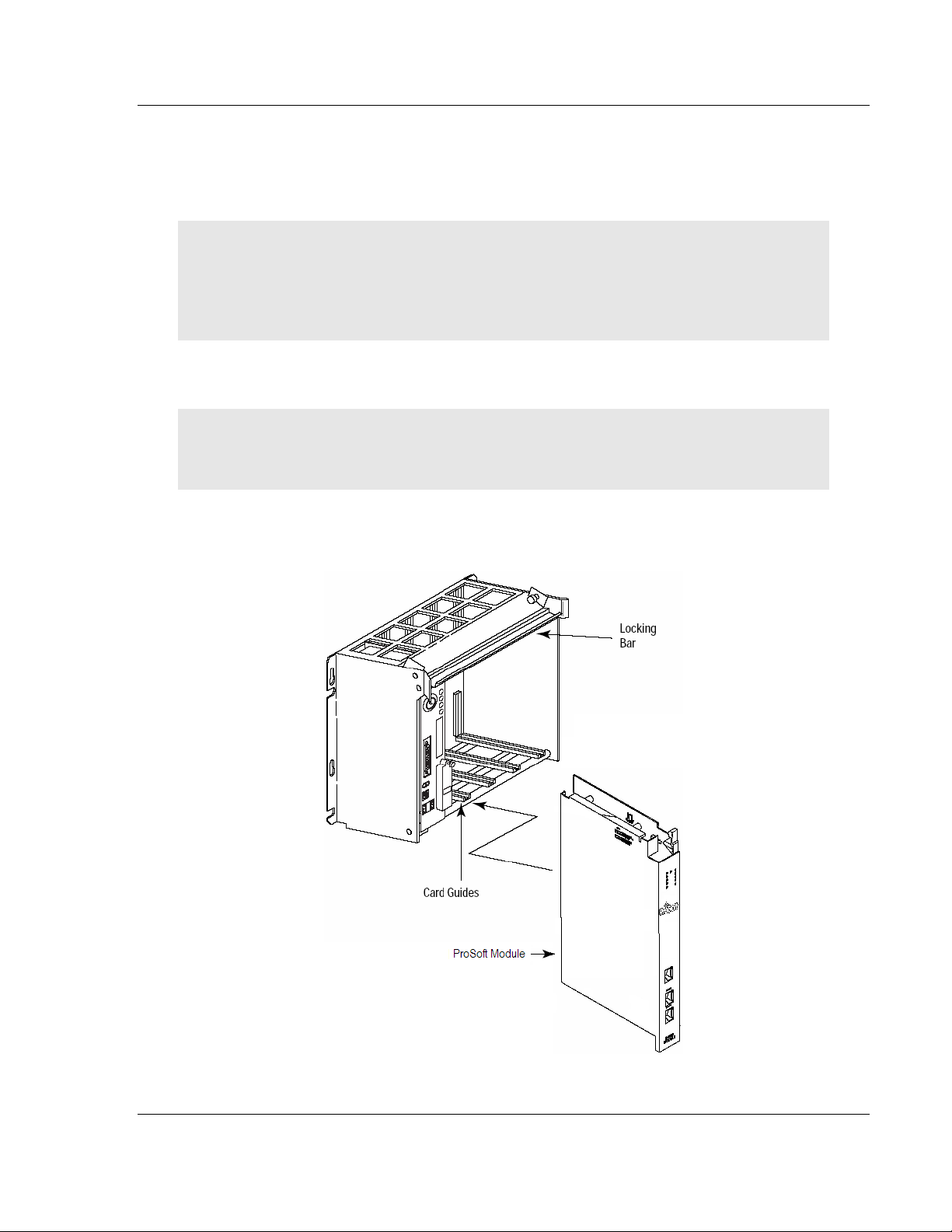
After you have checked the placement of the jumpers, insert MVI71-GEC into the
PLC™ chassis. Use the same technique recommended by Rockwell Automation
to remove and install PLC modules.
Warning: This module is not hot-swappable! Always remove power from the rack before
inserting or removing this module, or damage may result to the module, the processor, or other
connected devices.
1 Turn power OFF.
2 Align the module with the top and bottom guides, and slide it into the rack
until the module is firmly against the backplane connector.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 13 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 14

Start Here MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
3 With a firm but steady push, snap the module into place.
4 Check that the holding clips on the top and bottom of the module are securely
in the locking holes of the rack.
5 Make a note of the slot location. You will need to identify the slot in which the
module is installed in order for the sample program to work correctly. Slot
numbers are identified on the green circuit board (backplane) of the PLC
rack.
6 Turn power ON.
Note: If you insert the module improperly, the system may stop working, or may behave
unpredictably.
Page 14 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 15
MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Start Here
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
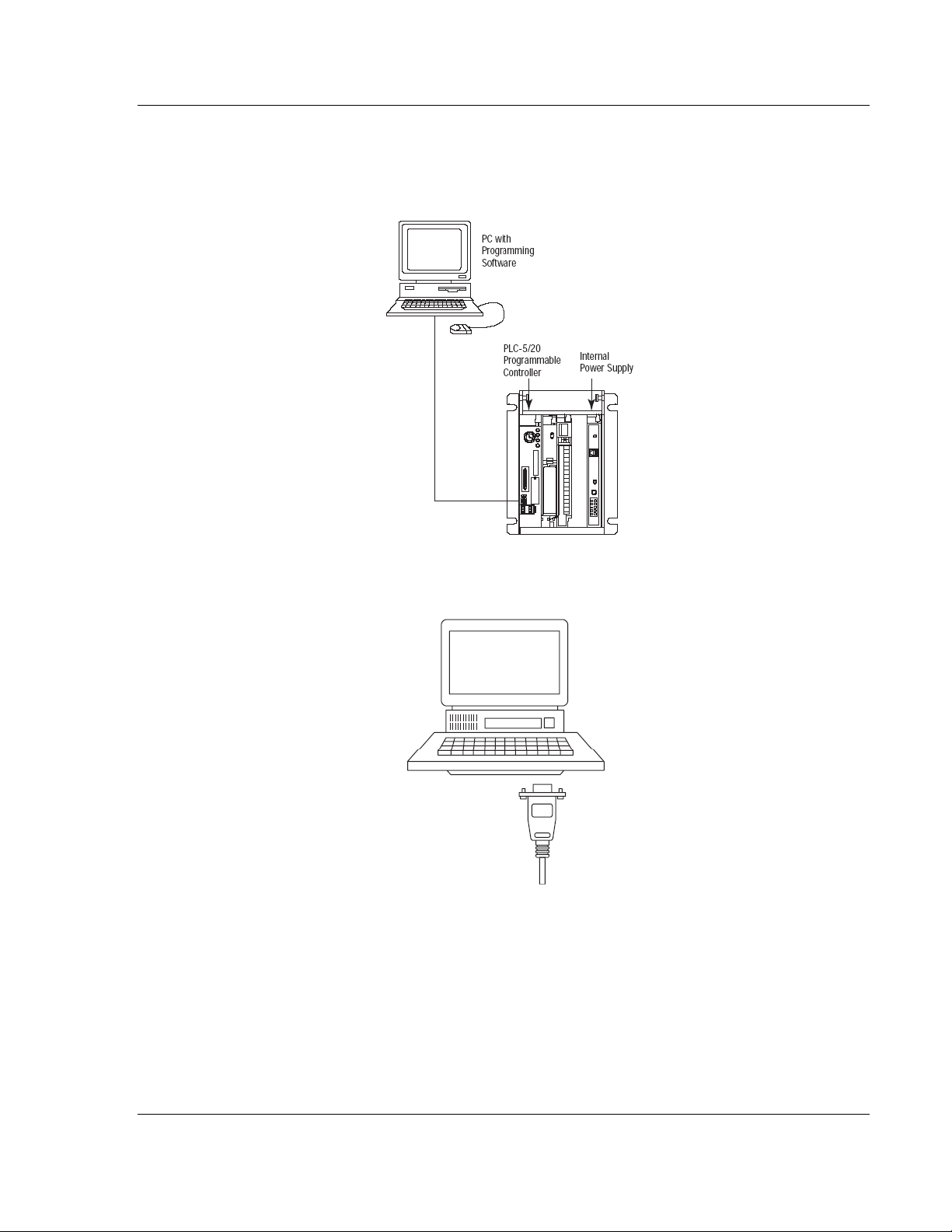
1.5 Connect your PC to the Processor
1 Connect the right-angle connector end of the cable to your controller at the
communications port.
2 Connect the straight connector end of the cable to the serial port on your
computer.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 15 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 16
Start Here MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
1.6 Download the Sample Program to the Processor
To download the sample program from RSLogix 5 to the PLC processor:
Note: The key switch on the front of the PLC processor must be in the REM position.
1 If you are not already online to the processor, open the Communications
menu, and then choose Download. RSLogix will establish communication
with the processor.
2 Click the Download button to transfer the sample program to the processor.
3 When prompted, choose Computer to PLC
4 RSLogix will compile the program and transfer it to the processor. This
process may take a few minutes.
Page 16 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 17
MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Start Here
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5 When the download is complete, RSLogix will open another confirmation
dialog box. Click OK to switch the processor from Program mode to Run
mode.
Note: If you receive an error message during these steps, refer to your RSLogix documentation to
interpret and correct the error.
1.6.1 Configuring the RSLinx Driver for the PC COM Port
If RSLogix is unable to establish communication with the processor, follow these
steps.
1 Open RSLinx.
2 Open the C
OMMUNICATIONS
menu, and choose C
ONFIGURE DRIVERS
.
This action opens the Configure Drivers dialog box.
Note: If the list of configured drivers is blank, you must first choose and configure a driver from the
Available Driver Types list. The recommended driver type to choose for serial communication with
the processor is RS-232 DF1 Devices.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 17 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 18
Start Here MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
3 Click to select the driver, and then click C
ONFIGURE
. This action opens the
Configure RS-232 DF1 Devices dialog box.
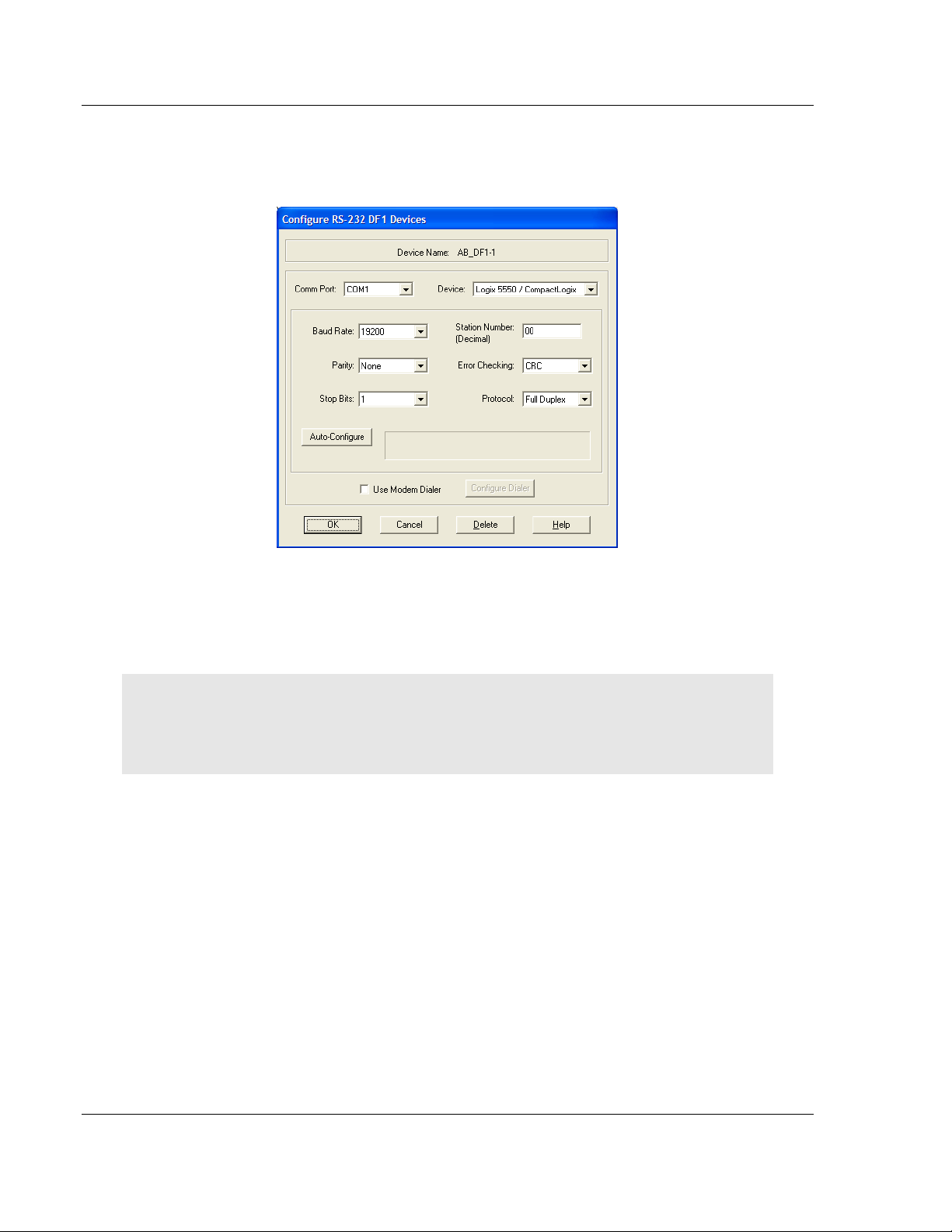
4 Click the A
UTO-CONFIGURE
button. RSLinx will attempt to configure your
serial port to work with the selected driver.
5 When you see the message Auto Configuration Successful, click the OK
button to dismiss the dialog box.
Note: If the auto-configuration procedure fails, verify that the cables are connected correctly
between the processor and the serial port on your computer, and then try again. If you are still
unable to auto-configure the port, refer to your RSLinx documentation for further troubleshooting
steps.
Page 18 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 19
MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Start Here
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
1.7 Connect your PC to the Module
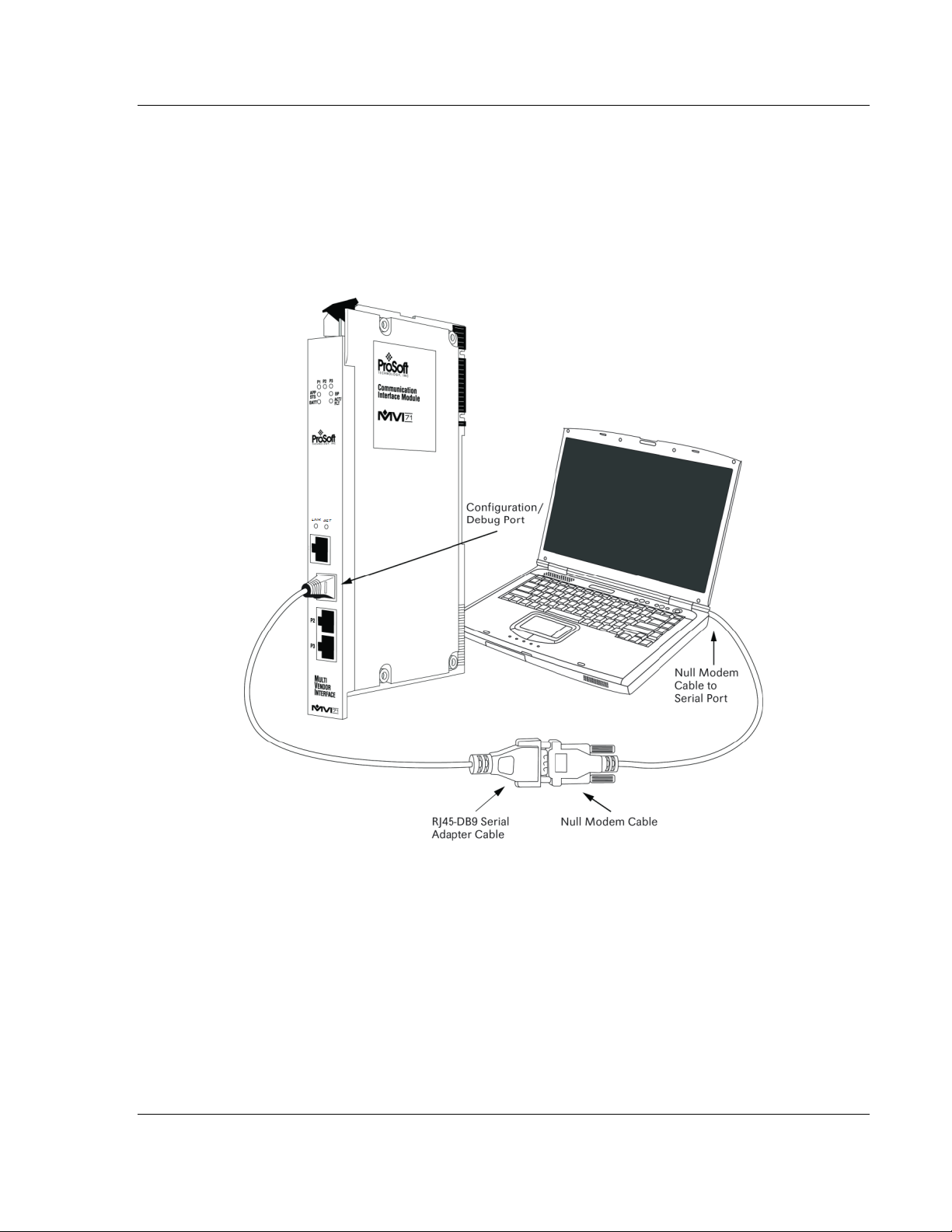
With the module securely mounted, connect your PC to the Configuration/Debug
port using an RJ45-DB-9 Serial Adapter Cable and a Null Modem Cable.
1 Attach both cables as shown.
2 Insert the RJ45 cable connector into the Configuration/Debug port of the
module.
3 Attach the other end to the serial port on your PC.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 19 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 20

Start Here MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Page 20 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 21

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Module Configuration
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
2 Module Configuration
In This Chapter
Using ProSoft Configuration Builder ...................................................... 22
IP Address ............................................................................................. 28
This section contains the setup procedure, data, and ladder logic for successful
application of the MVI71-GEC module. Each step in the setup procedure is
defined in order to simplify the use of the module.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 21 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 22
Module Configuration MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
2.1 Using ProSoft Configuration Builder
ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) provides a convenient way to manage
module configuration files customized to meet your application needs. PCB is not
only a powerful solution for new configuration files, but also allows you to import
information from previously installed (known working) configurations to new
projects.
2.1.1 Set Up the Project
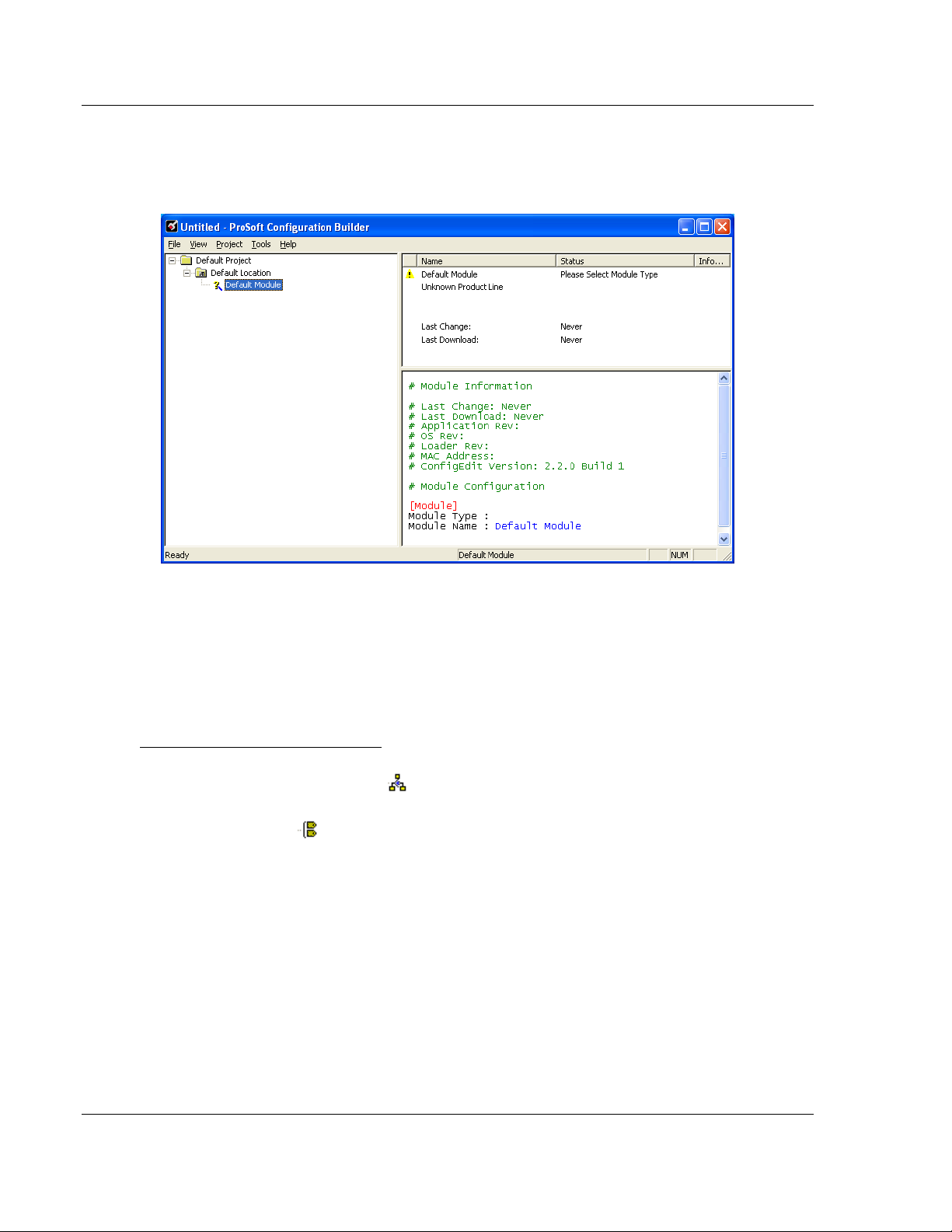
To begin, start ProSoft Configuration Builder. If you have used other Windows
configuration tools before, you will find the screen layout familiar. ProSoft
Configuration Builder’s window consists of a tree view on the left, an information
pane and a configuration pane on the right side of the window. When you first
start ProSoft Configuration Builder, the tree view consists of folders for Default
Project and Default Location, with a Default Module in the Default Location
folder. The following illustration shows the ProSoft Configuration Builder window
with a new project.
Your first task is to add the MVI71-GEC module to the project.
1 Use the mouse to select "Default Module" in the tree view, and then click the
right mouse button to open a shortcut menu.
Page 22 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 23
MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Module Configuration
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
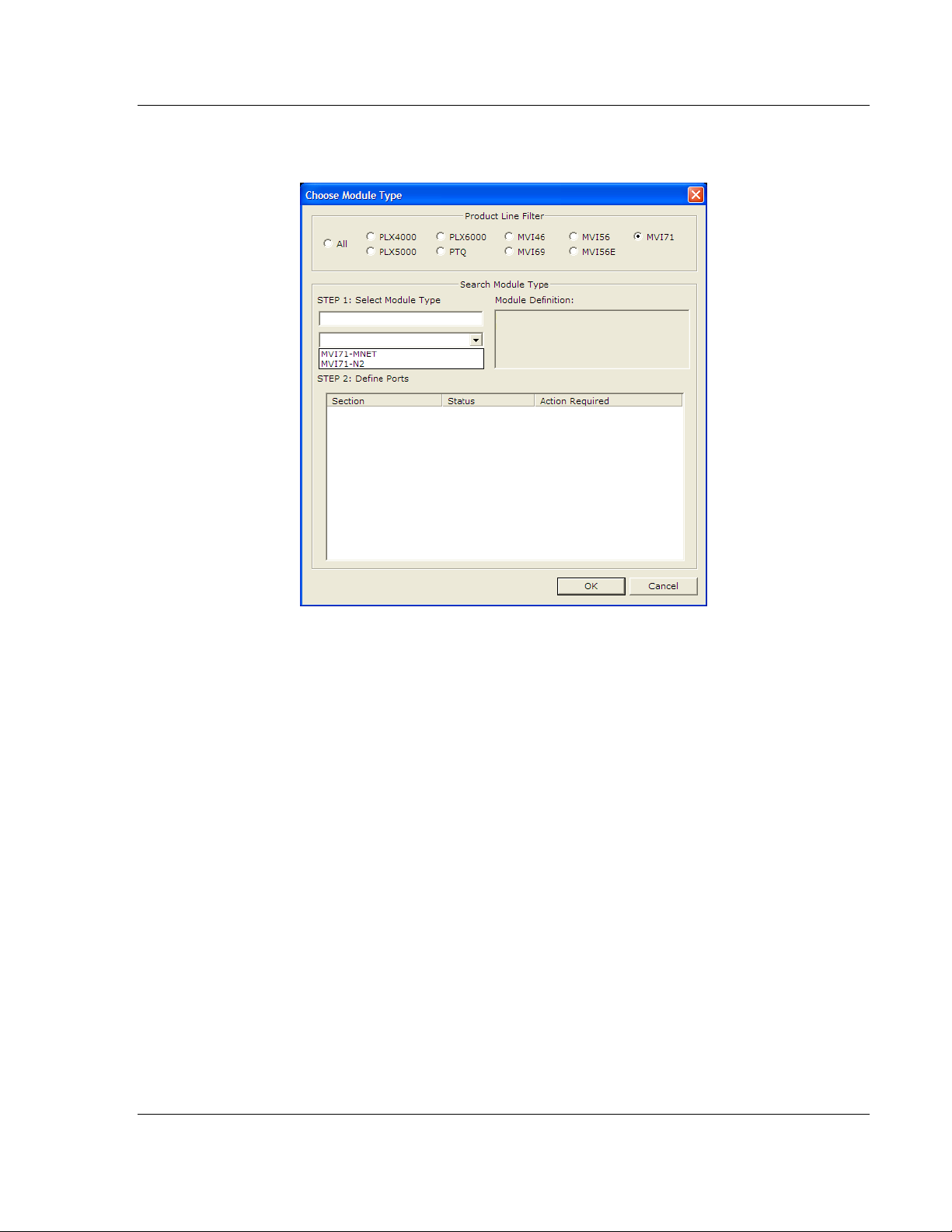
2 On the shortcut menu, choose "Choose Module Type". This action opens the
Choose Module Type dialog box.
3 In the Product Line Filter area of the dialog box, select MVI71. In the Select
Module Type dropdown list, select MVI71-GEC, and then click OK to save
your settings and return to the ProSoft Configuration Builder window.
The next task is to set the module parameters.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 23 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 24
Module Configuration MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
2.1.2 Renaming PCB Objects
Notice that the contents of the information pane and the configuration pane
changed when you added the module to the project.
At this time, you may wish to rename the Default Project and Default Location
folders in the tree view.
1 Select the object, and then click the right mouse button to open a shortcut
menu. From the shortcut menu, choose R
ENAME
.
2 Type the name to assign to the object.
3 Click away from the object to save the new name.
Configuring Module Parameters
1 Click the [+] sign next to the module icon to expand module information.
2 Click the [+] sign next to any icon to view module information and
configuration options.
3 Double-click any icon to open an Edit dialog box.
4 To edit a parameter, select the parameter in the left pane and make your
changes in the right pane.
5 Click OK to save your changes.
Page 24 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 25
MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Module Configuration
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
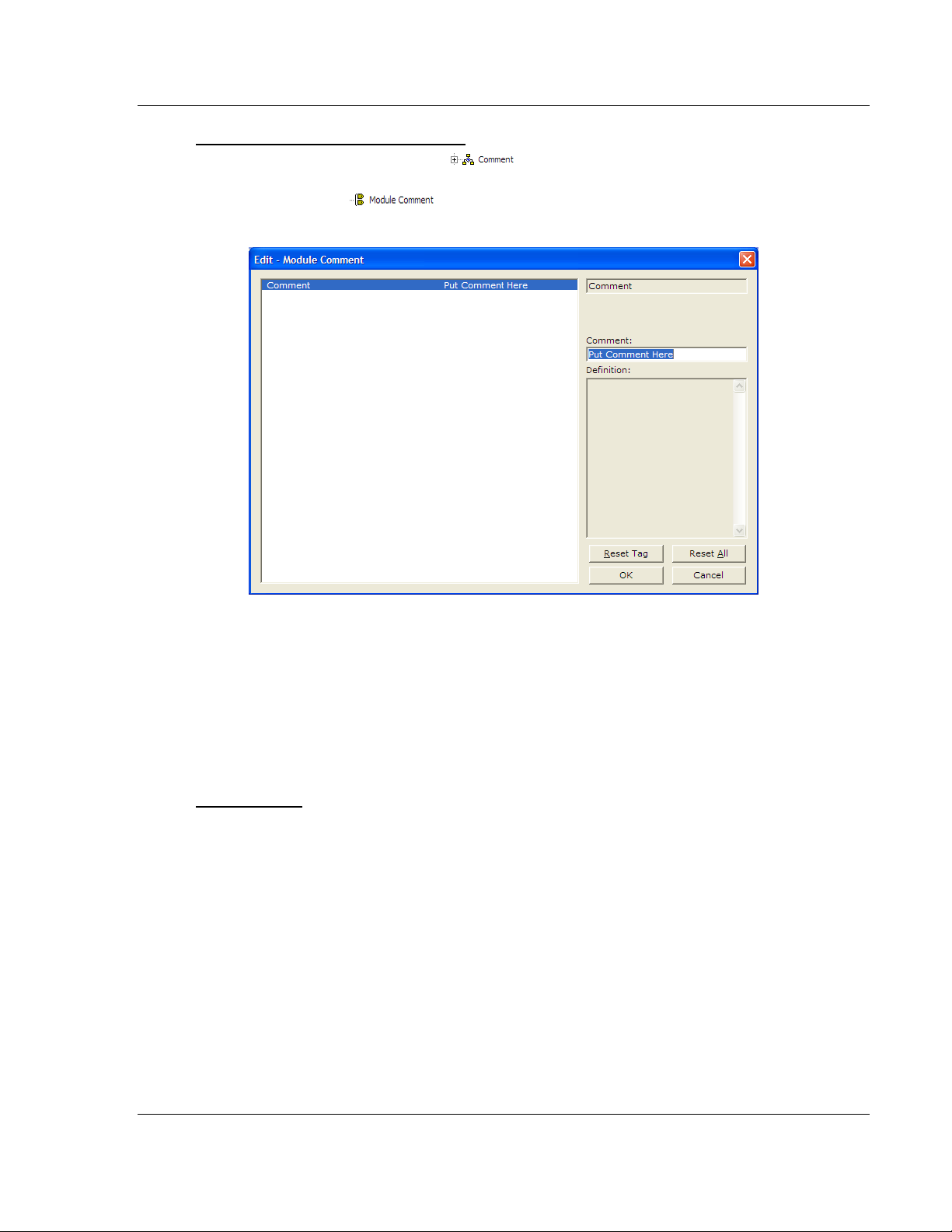
Creating Optional Comment Entries
1 Click the [+] to the left of the icon to expand the module
comments.
2 Double-click the icon. The Edit - Module Comment dialog box
appears.
3 Enter your comment and click OK to save your changes.
2.1.3 [Module]
This section of the file describes the database setup and module level
parameters.
[Module]
Module Name: MVI71-GEC Communication Module DEFAULT
Module Name
0 to 80 characters
This parameter assigns a name to the module that can be viewed using the
configuration/debug port. Use this parameter to identify the module and the
configuration file.
2.1.4 [Server x]
You can configure up to five servers ([Server 0] through [Server 4]). The
configuration section for each server contains the same set of parameters. You
can configure the parameters for each server to meet the requirements of your
application.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 25 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 26

Module Configuration MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Enabled
Yes or No
This parameter determines if the server will be utilized by the module. If a value
of "Yes" is entered, the server will be used. Any other value will disable the
server.
Service Port Number
1 to 65535
This parameter sets the TCP/IP service port for this server. Each server can
have its own unique service port or can share the same number with other
servers.
Connection Timeout
0 or 5000 to 65535
This parameter specifies the number of milliseconds the server will permit the
server to be inactive after a connection is made before closing the socket. This
timeout period is reset on each read or write packet. If the parameter is set to 0,
the connection will not timeout.
Connection Close Type
0, 1 or 2
This coded parameter defines the personality of the server after a connection is
made. If the parameter is set to 0, the socket will only be closed when a request
from the client is received or the connection timeout is exceeded. If a value of 1
is selected, the server will close the socket after it transmits a single message. If
a value of 2 is selected, the server will close the socket after it receives a
message.
Swap Rx Data Bytes
Yes or No
This parameter determines if the data received by the server will have the byte
order of the data swapped. If the parameter is set to No, no byte swapping will
occur. If the parameter is set to Yes, the odd byte will be swapped with the even
byte in each word of data received.
Swap Tx Data Bytes
Yes or No
This parameter determines if the data to be transmitted by the module will have
the byte order of the data swapped. If the parameter is set to No, no byte
swapping will occur. If the parameter is set to Yes, the odd byte will be swapped
with the even byte in each word of data received.
Page 26 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 27

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Module Configuration
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
2.1.5 Downloading the Project to the Module Using a Serial COM
Port
For the module to use the settings you configured, you must download (copy) the
updated Project file from your PC to the module.
To download the project file
1 In the tree view in ProSoft Configuration Builder, click once to select the
module.
2 Right-click the module icon to open a shortcut menu. From the shortcut
menu, choose D
PC for a valid com port (this may take a few seconds). When PCB has found
a valid COM port, the Download dialog box will open.
OWNLOAD FROM PC TO DEVICE
. The program will scan your
3 Choose the COM port to use from the dropdown list, and then click the
D
OWNLOAD
button.
The module will perform a platform check to read and load its new settings.
When the platform check is complete, the status bar in the Download dialog
box will display the message Module Running.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 27 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 28

Module Configuration MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
2.2 IP Address
In addition to the GEC.CFG, the MVI71-GEC module requires a second
configuration file that identifies its Ethernet configuration. Without this
configuration file, the module will not communicate properly on the network.
This file contains the Ethernet address information to be used by the module and
may be transferred to and from the module from the Network command
available on the debug port of the module. Please consult your network
administrator for the correct settings for your network before placing this or any
other Ethernet TCP/IP device upon your network.
Important: If the field "my_ip" does not exist, or if the wattcp.cfg file is corrupted or does not exist,
the module will not function.
To set the Module’s IP Address
1 Locate the sample configuration files for your module on the ProSoft
Solutions CD.
2 Copy the configuration files and ladder to a location on your PC’s hard drive.
We recommend C:\temp.
3 After you move the files, right-click on each of the files, choose Properties,
and clear the READ ONLY check box.
4 Start Notepad.exe, or any other editor that can save plain text files.
5 Open the file WATTCP.CFG. The following example shows the contents of a
typical WATTCP.CFG file.
# ProSoft Technology
# Default private class 3 address
my_ip=192.168.0.100
# Default class 3 network mask
netmask=255.255.255.0
# The gateway I wish to use
gateway=192.168.0.1,192.168.0.0,255.255.255.0
6 Edit the file, using the IP addresses supplied by your network administrator.
Important: The module does not support DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) for
obtaining an IP address from a server. This module must have its own static IP address that does
not duplicate the IP address of any other device on the Ethernet network.
7 Save the file as WATTCP.CFG. You must now transfer the file to the module.
Refer to Transferring WATTCP.CFG to the module (page 43) for the correct
procedure.
Page 28 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 29

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Ladder Logic
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
3 Ladder Logic
In This Chapter
Adding the Module to an Existing PLC5 Project .................................... 30
GECServerStat (Server Status Object) ................................................. 32
Ladder logic is required for the MVI71-GEC module to work. Tasks that must be
handled by the ladder logic are module data transfer, special block handling, and
status data receipt. Additionally, a power-up handler may be needed to handle
the initialization of the module’s data and to clear any processor fault conditions.
The sample ladder logic, on the inRAx CD-ROM, is extensively commented, to
provide information on the purpose and function of each rung. For most
applications, the sample ladder will work without modification.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 29 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 30

Ladder Logic MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
3.1 Adding the Module to an Existing PLC5 Project
1 Add the MVI71-GEC module to the project. Right-click the mouse button
on the I/O Configuration option in the Controller Organization window to
display a pop-up menu. Select the New Module option from the I/O
Configuration menu.
This action opens the following dialog box:
Page 30 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 31

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Ladder Logic
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
2 Select the 1769-Module (Generic 1769 Module) from the list and click OK.
3 Enter the Name, Description and Slot options for your application, using the
values in the illustration above. You must select the Comm Format as Data INT in the dialog box, otherwise the module will not communicate over the
backplane of the CompactLogix rack.
Click OK to continue.
4 Select the Request Packet Interval value for scanning the I/O on the module.
This value represents the minimum frequency the module will handle
scheduled events. This value should not be set to less than 1 millisecond.
Values between 1 and 10 milliseconds should work with most applications.
5 Save the module. Click OK to dismiss the dialog box. The Controller
Organization window now displays the module's presence. The following
illustration shows the Controller Organization window:
6 Copy the Controller Tags from the sample program.
7 Copy the User Defined Data Types from the sample program.
8 Copy the Ladder Rungs from the sample program.
9 Save and Download the new application to the controller and place the
processor in run mode.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 31 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 32

Ladder Logic MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
3.2 GECServerStat (Server Status Object)
The GECServerStat object stores the status information related to each server
on the module. All messages are counted for both receive and transmit
operations. The object also contains the CfgErrword member. The following table
describes the structure of this object.
Name Data Type Description
Enabled INT Flag to indicate if server is enabled
(1=Yes,0=No)
State INT Current state of server
IP INT[2] IP address of host connected to server
Port INT TCP port for host connected to server
Open INT Number of times server performed an open
Est INT Number of times connection established
Close INT Number of times socket closed
Rx INT Number of messages received
RxOverflow INT Number of receive buffer overflows
Tx INT Number of messages transmitted
TxOverflow INT Number of transmit buffer overflows
Timeout INT Number of socket timeout conditions
CfgErrword INT Configuration error word value for server
Page 32 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 33

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
4 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
In This Chapter
LED Status Indicators ............................................................................ 34
Using ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) for Diagnostics................... 36
Reading Status Data from the Module .................................................. 43
The module provides information on diagnostics and troubleshooting in the
following forms:
LED status indicators on the front of the module provide general information
on the module's status.
Status data contained in the module can be viewed through the
Configuration/Debug port, using the troubleshooting and diagnostic
capabilities of ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB).
Status data values can be transferred from the module to processor memory
and can be monitored there manually or by customer-created logic.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 33 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 34

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
4.1 LED Status Indicators
The LEDs indicate the module’s operating status as follows:
LED Color Status Indication
CFG Green On Data is being transferred between the module and a remote
Off No data is being transferred on the Configuration/Debug port.
P1 Green On Port not used
Off Port not used
P2 Green On Port not used
Off Port not used
APP Amber Off The MVI71-GEC is working normally.
On The MVI71-GEC module program has recognized a
BP ACT Amber On The LED is on when the module is performing a write
Off The LED is off when the module is performing a read
OK Red/
Green
BAT Red Off The battery voltage is OK and functioning.
Off The card is not receiving any power and is not securely
Green The module is operating normally.
Red The program has detected an error or is being configured. If
On The battery voltage is low or battery is not present. Allow
terminal using the Configuration/Debug port.
communication error.
operation on the backplane.
operation on the backplane. Under normal operation, the LED
should blink rapidly on and off.
plugged into the rack.
the LED remains red for over 10 seconds, the program has
probably halted. Remove the card from the rack and re-insert
the card to restart the module’s program.
battery to charge by keeping module plugged into rack for 24
hours. If BAT LED still does not go off, contact ProSoft
Technology, as this is not a user serviceable item.
4.1.1 Ethernet LED Indicators
LED State Description
Data OFF No activity on the Ethernet port.
GREEN Flash The Ethernet port is actively transmitting or receiving data.
Link OFF No physical network connection is detected. No Ethernet
communication is possible. Check wiring and cables.
GREEN Solid Physical network connection detected. This LED must be ON
solid for Ethernet communication to be possible.
Page 34 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 35

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
4.1.2 Clearing a Fault Condition
Typically, if the OK LED on the front of the module turns RED for more than ten
seconds, a hardware problem has been detected in the module or the program
has exited.
To clear the condition, follow these steps:
1 Turn off power to the rack.
2 Remove the card from the rack.
3 Verify that all jumpers are set correctly.
4 If the module requires a Compact Flash card, verify that the card is installed
correctly.
5 Re-insert the card in the rack and turn the power back on.
6 Verify correct configuration data is being transferred to the module from the
PLC controller.
If the module's OK LED does not turn GREEN, verify that the module is inserted
completely into the rack. If this does not cure the problem, contact ProSoft
Technology Technical Support.
4.1.3 Troubleshooting
Use the following troubleshooting steps if you encounter problems when the
module is powered up. If these steps do not resolve your problem, please contact
ProSoft Technology Technical Support.
Processor Errors
Problem description Steps to take
Processor fault Verify that the module is plugged into the slot that has been configured
for the module in the I/O Configuration of RSLogix.
Verify that the slot location in the rack has been configured correctly in
the ladder logic.
Processor I/O LED
flashes
This indicates a problem with backplane communications. A problem
could exist between the processor and any installed I/O module, not just
the MVI71-GEC. Verify that all modules in the rack are correctly
configured in the ladder logic.
Module Errors
Problem description Steps to take
BP ACT LED (not
present on MVI56E
modules) remains OFF
or blinks slowly
MVI56E modules with
scrolling LED display:
<Backplane Status>
condition reads ERR
OK LED remains RED The program has halted or a critical error has occurred. Connect to the
This indicates that backplane transfer operations are failing. Connect to
the module’s Configuration/Debug port to check this.
To establish backplane communications, verify the following items:
The processor is in RUN or REM RUN mode.
The backplane driver is loaded in the module.
The module is configured for read and write data block transfer.
The ladder logic handles all read and write block situations.
The module is properly configured in the processor I/O configuration
and ladder logic.
Configuration/Debug port to see if the module is running. If the program
has halted, turn off power to the rack, remove the card from the rack and
re-insert it, and then restore power to the rack.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 35 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 36

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
4.2 Using ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) for Diagnostics
The Configuration and Debug menu for this module is arranged as a tree
structure, with the Main menu at the top of the tree, and one or more sub-menus
for each menu command. The first menu you see when you connect to the
module is the Main menu.
Because this is a text-based menu system, you enter commands by typing the
[command letter] from your computer keyboard in the Diagnostic window in
ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB). The module does not respond to mouse
movements or clicks. The command executes as soon as you press the
[
COMMAND LETTER
[
COMMAND LETTER
] — you do not need to press [E
NTER].
When you type a
], a new screen will be displayed in your terminal application.
4.2.1 Using the Diagnostic Window in ProSoft Configuration Builder
Tip: You can have a ProSoft Configuration Builder Diagnostics window open for more than one
module at a time.
Page 36 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 37

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
To connect to the module’s Configuration/Debug serial port
1 Start PCB, and then select the module to test. Click the right mouse button to
open a shortcut menu.
2 On the shortcut menu, choose D
IAGNOSTICS
.
This action opens the Diagnostics dialog box.
3 Press [?] to open the Main menu.
If there is no response from the module, follow these steps:
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 37 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 38

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
1 Click to configure the connection. On the Connection Setup dialog box, select
a valid com port or other connection type supported by the module.
2 Verify that the null modem cable is connected properly between your
computer’s serial port and the module. A regular serial cable will not work.
3 On computers with more than one serial port, verify that your communication
program is connected to the same port that is connected to the module.
If you are still not able to establish a connection, contact ProSoft Technology for
assistance.
4.2.2 Navigation
All of the submenus for this module contain commands to redisplay the menu or
return to the previous menu. You can always return from a submenu to the next
higher menu by pressing [M] on your keyboard.
The organization of the menu structure is represented in simplified form in the
following illustration:
The remainder of this section shows the menus available for this module, and
briefly discusses the commands available to you.
Page 38 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 39

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Keystrokes
The keyboard commands on these menus are usually not case sensitive. You
can enter most commands in lowercase or uppercase letters.
The menus use a few special characters (?, -, +, @) that must be entered exactly
as shown. Some of these characters will require you to use the SHIFT, CTRL, or
ALT keys to enter them correctly. For example, on US English keyboards, enter
the ? command as SHIFT and /.
Also, take care to distinguish the different uses for uppercase letter "eye" (I),
lowercase letter "el" (L), and the number one (1). Likewise, uppercase letter "oh"
(O) and the number zero (0) are not interchangeable. Although these characters
look alike on the screen, they perform different actions on the module and may
not be used interchangeably.
4.2.3 Main Menu
When you first connect to the module from your computer, your terminal screen
will be blank. To activate the main menu, press the [?] key on your computer’s
keyboard. If the module is connected properly, the following menu will appear.
Caution: Some of the commands available to you from this menu are designed for advanced
debugging and system testing only, and can cause the module to stop communicating with the
processor or with other devices, resulting in potential data loss or other communication failures.
Use these commands only if you fully understand their potential effects, or if you are specifically
directed to do so by ProSoft Technology Technical Support Engineers.
There may be some special command keys that are not listed on the menu but that may activate
additional diagnostic or debugging features. If you need these functions, you will be advised how to
use them by Technical Support. Please be careful when pressing keys so that you do not
accidentally execute an unwanted command.
Redisplaying the Menu
Press [?] to display the current menu. Use this command when you are looking
at a screen of data, and want to view the menu choices available to you.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 39 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 40

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Viewing Block Transfer Statistics
Press [B] to view the Block Transfer Statistics screen.
Use this command to display the configuration and statistics of the backplane
data transfer operations between the module and the processor. The information
on this screen can help determine if there are communication problems between
the processor and the module.
Tip: Repeat this command at one-second intervals to determine the number of blocks transferred
each second.
Viewing Module Configuration
Press [C] to view the Module Configuration screen.
Use this command to display the current configuration and statistics for the
module.
Transferring the Configuration File from the PC to the Module
On the Diagnostics Menu this is referred to as Receive Module Configuration.
Press [R] to receive (download) the configuration file from your PC to the module
and store the file on the module’s Compact Flash Card (Personality Module) or
Flash RAM.
Press [Y] to confirm the file transfer, and then follow the instructions on the
terminal screen to complete the file transfer process.
After the file has been successfully downloaded, the module will restart the
program and load the new configuration information. Review the new
configuration using menu commands [6] and [0] to verify that the module is
configured correctly.
Transferring the Configuration File from The Module to the PC
On the Diagnostics Menu this is referred to as Send Module Configuration.
Press [S] to send (upload) the configuration file from the module to your PC.
Press [Y] to confirm the file transfer, and then follow the instructions on the
terminal screen to complete the file transfer process.
After the file has been successfully uploaded, you can open and edit the file to
change the module’s configuration.
Resetting Diagnostic Data
Press [U] to reset the status counters for the Client and/or server(s) in the
module.
Page 40 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 41

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Viewing Version Information
Press [V] to view version information for the module.
Use this command to view the current version of the software for the module, as
well as other important values. You may be asked to provide this information
when calling for technical support on the product.
Values at the bottom of the display are important in determining module
operation. The Program Scan Counter value is incremented each time a
module’s program cycle is complete.
Tip: Repeat this command at one-second intervals to determine the frequency of program
execution.
Warm Booting the Module
Press [W] from the Main menu to warm boot (restart) the module.
This command will cause the program to exit and reload, refreshing configuration
parameters that must be set on program initialization. Only use this command if
you must force the module to reboot.
Viewing Server Communication Status (Servers 0 to 4)
Use commands [1] [2] [3] [4] or [5] to view the communication status and
statistics of the specified server. This information can be useful when troubleshooting communication problems.
Viewing Client Communication Status (Clients 10 to 14)
Use commands [E] [F] [G] [H] or [I] to view the communication status and
statistics of the specified client. This information can be useful when
troubleshooting communication problems.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 41 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 42

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Viewing Server Configuration (Servers 0 to 4)
Use commands [6] [7] [8] [9] or [0] to view the configuration of the specified
server.
Opening the Network Menu
Press [@] to open the Network menu.
The Network menu allows you to send, receive and view the WATTCP.CFG file
that contains the IP, gateway and other network specification information. For
more information about this submenu, see Network Menu (page 42).
Exiting the Program
Press [ESC] to restart the module and force all drivers to be loaded. The module
will use the configuration stored in the module's flash memory to configure the
module.
4.2.4 Network Menu
From the IEC-870-5-104 Server menu press [@] to display the IEC-870-5-104
Network menu screen. The Network menu allows you to send, receive, and view
the WATTCP.CFG file that contains the IP and module addresses, and other
network information.
Page 42 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 43

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Transferring WATTCP.CFG to the Module
Press [R] to transfer a new WATTCP.CFG file from the PC to the module. Use
this command to change the network configuration for the module (for example,
the module’s IP address).
Press [Y] to confirm the file transfer, and then follow the instructions on the
terminal screen to complete the file transfer process.
Transferring WATTCP.CFG to the PC
Press [S] to transfer the WATTCP.CFG file from the module to your PC.
Press [Y] to confirm the file transfer, and then follow the instructions on the
terminal screen to complete the file transfer process.
After the file has been successfully transferred, you can open and edit the file to
change the module’s network configuration.
Viewing the WATTCP.CFG File on the module
Press [V] to view the module’s WATTCP.CFG file. Use this command to confirm
the module’s current network settings.
Returning to the Main Menu
Press [M] to return to the Main menu.
4.3 Reading Status Data from the Module
The MVI71-GEC module returns a status data set to the PLC processor in each
read block. This data is transferred to the PLC processor continuously with each
read block.
The Configuration/Debug port provides the following functionality:
Full view of the module’s configuration data
View of the module’s status data
Version Information
Control over the module (warm boot and cold boot)
Facility to upload and download the module’s configuration file
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 43 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 44

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Page 44 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 45

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5 Reference
In This Chapter
Product Specifications ........................................................................... 46
Functional Overview .............................................................................. 48
Cable Connections ................................................................................ 66
MVI71-GEC Status Data Area ............................................................... 70
MVI71-GEC Configuration Data ............................................................ 74
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 45 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 46

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
5.1 Product Specifications
The MVI71 Generic ASCII Ethernet Interface module is designed to allow PLC
processors to interface easily with ASCII devices using the TCP/IP protocol.
Compatible devices may be either ASCII instruments with built-in Ethernet or
Ethernet connection via a thin server to the existing ASCII device.
Five servers and Clients are present on the module permitting both the reception
and transmission of data between the Rockwell Automation processor and attached
devices.
The MVI71-GEC module is a powerful communication interface for PLC processors.
Developed under license from Rockwell Automation, the module incorporates
proprietary backplane technology that enables powerful data access between the
module and the PLC processor.
5.1.1 General Specifications
Single Slot - 1771 backplane compatible
The module is recognized as an Input/Output module and has access to
processor memory for data transfer between processor and module
Ladder Logic is used for data transfer between module and processor.
Sample ladder file included.
5.1.2 Hardware Specifications
Specification Description
Form Factor Single Slot 1771 chassis compatible
BTR/BTW data transfer
Local or remote rack
Backplane current load 800 mA @ 5 V
Operating temperature 32 to 140°F (0°C to 60°C)
Storage temperature -40°F to 185°F (-40°C to 85°C)
Shock 30g operational
50g non-operational
Vibration 5 g from 10150 Hz
Relative Humidity 5% to 95%, RH with no condensation
LED Indicators Module status
Backplane transfer status
Application status
Serial activity and error LED status
Configuration Serial Port (CFG) DB-9M PC compatible
RS-232
Hardware handshaking
Ethernet Port (Ethernet
modules)
RJ45 Connector
Link and activity LED indicators
Electrical Isolation 1500 V rms at 50 Hz to 60 Hz
for 60 s, applied as specified in section 5.3.2 of IEC
60950: 1991
Ethernet Broadcast Storm Resiliency = less than or
equal to 5000 [ARP] frames-per-second and less
than or equal to 5 minutes duration
Page 46 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 47

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5.1.3 Functional Specifications
Five Servers and Clients to receive and/or transmit data
10/100 Base-T Ethernet-compatible interface
Configurable parameters
o
Service port number
o
Connection timeout
o
Close type
Simple ladder logic operation
Setup and monitoring through RS-Logix 5 software and user-constructed
configuration file (GEC.CFG)
PLC backplane interface via I/O access
Each Server monitors
o
State
o
IP and port number of connected Client
o
Error codes
Each Client monitors
o
State
o
IP and port number of connected Server
o
Message related parameters
ASCII character strings up to 2048 characters in length supported
Full hardware handshaking control, providing radio, modem, and multi-drop
support
User-definable module memory usage, supporting the storage and transfer of
up to 4000 bytes to/from the control processor
Module error and status conditions returned to processor for diagnostic
purposes
o
Module status
o
Port error status word (bit mapped)
o
Port receive state
o
Port receive character count
o
Port receive block count
o
Port transmit state
o
Port transmit character count
o
Port transmit block count
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 47 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 48

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
5.2 Functional Overview
5.2.1 General Concepts
The following discussion explains several concepts that are important for
understanding module operation.
Module Power Up
On power up the module begins performing the following logical functions:
1 Initialize hardware components
o
Initialize PLC backplane driver
o
Test and clear all RAM
o
Initialize the serial communication ports
2 Read configuration for module from GEC.CFG file on Compact Flash Disk
3 Initialize servers
4 Set up the serial communication interface for the debug/configuration port
After the module has received the configuration, the module will begin receiving
and transmitting messages with devices on the Ethernet network.
Main Logic Loop
Upon completing the power-up configuration process, the module enters an
infinite loop that performs the functions shown in the following diagram.
Page 48 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 49

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Block Transfer Backplane Data Transfer
The MVI71-GEC module communicates directly over the PLC backplane. Data is
paged between the module and the PLC processor across the backplane using
BTR and BTW operations. Data is transferred from the module to the processor
using the BTR blocks, and data is transferred from the processor to the module
using BTW blocks.
The following illustration shows the data transfer method used to move data
between the PLC processor, the MVI71-GEC module, and the Ethernet network.
All data transferred between the module and the processor over the backplane is
through the BTR and BTW blocks. Ladder logic must be written in the PLC
processor to interface the block data with user data files.
Normal Data Transfer
Normal data transfer includes the transferring of data received or to be
transmitted on the servers and the status data. These data are transferred
through read (BTR) and write (BTW) blocks. Refer to Module Configuration for
a description of the ladder logic required to perform the data movement within the
PLC processor. The structure and function of each block is discussed in the
following topics.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 49 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 50

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Read Block
These blocks of data transfer information from the module to the PLC processor.
When data is received on one of the servers, a data block is built. The structure
of this block type is shown in the following table.
Word
Offset
0 Block Sequence Number (Bumped each scan by module)
Received
Data
58 Server 0 State
1 Server Number for data received. If the word contains a value of -1 or -2,
2 Number of characters (0 to 110) in receive block (3 to 57). If the receive
3 to 57 110 bytes of data received for specified server.
59 Server 1 State
60 Server 2 State
61 Server 3 State
62 Server 4 State
63 Number of characters processed from last write block.
Description
no receive data is present and the block contains status data. If the word
contains a value from 0 to 4, the block contains data from one of the
servers in the module.
data in the module is larger than 110 bytes, multiple blocks will be
transferred. Any block with a value of -1 in this field represents the first or
continuation block and the block contains 110 bytes of data. The last block
of data will contain a positive number in this field that represents the
number of characters in the last block.
Word Offset 0 contains an index value used to signal to the PLC processor that a
new block is ready for processing. The ladder logic must recognize a change in
this value and process the data encapsulated. If data is available for a server, a
block containing data received is passed to the processor.
Word Offset 1 contains the server index (0 to 4) that is sending the data to the
processor.
Word Offset 2 contains a value that determines the number of characters (or
bytes) in the data area of the block. If the server receives a message longer than
110 bytes, it must send the received message in multiple blocks to the processor.
In this case, the byte count field of the block will be set to -1 for each block where
more than 110 characters are being sent by the server. Each block with a byte
count field of -1 contains 110 bytes of data. The data set is located in the block
starting at word offset 3. When the last block of data to send by the server is less
than or equal to 110 bytes, the byte count field will be set to a number from 1 to
110. This signifies to the processor that this is the last block. The ladder logic
must handle data received on each server enabled in the module.
If no data is available, the module will page one of the two status data images to
the processor. If word 1 of the BTR block is set to -1, the data for the first three
servers, the product and block transfer data is sent in the block. The format of
this block is as follows:
Page 50 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 51

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Object in GSCInStat Block
Offset
Start
Seq Number 0 Sequence number for this block.
Server Index 1 For this status data block, this word is set to a value of -1.
PassCnt 2 Program cycle counter
Product 3 Product name as ASCII string
Rev 5 Revision level as ASCII string
OP 7 Operating system level as ASCII string
Run 9 Run number as ASCII string
BlkErrs.Read 11 Number of blocks transferred from module to processor
BlkErrs.Write 12 Number of blocks transferred from processor to module
BlkErrs.Parse 13 Number of blocks parsed by module
BlkErrs.Err 14 Number of block errors in module
Server[0].Enabled 15 This flag defines if the server is utilized. A value of 0
Server[0].State 16 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Server[0].IP 17 This double-word value contains the IP address of the client
Server[0].Port 19 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[0].Open 20 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[0].Established 21 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[0].Closed 22 This status value contains the total number of times a close
Server[0].RxCount 23 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[0].RxOverflow 24 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[0].TxCount 25 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[0].TxOverflow 26 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Server[0].Timeout 27 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[0].CfgErrWord 28 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors for the
Server[1].Enabled 29 This flag defines if the server is utilized. A value of 0
Server[1].State 30 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Server[1].IP 31 This double-word value contains the IP address of the client
Description
indicates the server is not used. Any other value indicates
the server is used.
connected to the server.
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
operation was performed on the socket.
received by the server.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the server.
transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer size
for the server.
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
server.
indicates the server is not used. Any other value indicates
the server is used.
connected to the server.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 51 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 52

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Object in GSCInStat Block
Offset
Start
Server[1].Port 33 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[1].Open 34 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[1].Established 35 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[1].Closed 36 This status value contains the total number of times a close
Server[1].RxCount 37 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[1].RxOverflow 38 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[1].TxCount 39 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[1].TxOverflow 40 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Server[1].Timeout 41 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[1].CfgErrWord 42 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors for the
Server[2].Enabled 43 This flag defines if the server is utilized. A value of 0
Server[2].State 44 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Server[2].IP 45 This double-word value contains the IP address of the client
Server[2].Port 47 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[2].Open 48 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[2].Established 49 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[2].Closed 50 This status value contains the total number of times a close
Server[2].RxCount 51 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[2].RxOverflow 52 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[2].TxCount 53 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[2].TxOverflow 54 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Server[2].Timeout 55 This status value contains the total number of times a
Description
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
operation was performed on the socket.
received by the server.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the server.
transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer size
for the server.
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
server.
indicates the server is not used. Any other value indicates
the server is used.
connected to the server.
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
operation was performed on the socket.
received by the server.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the server.
transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer size
for the server.
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
Page 52 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 53

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Object in GSCInStat Block
Offset
Start
Server[2].CfgErrWord 56 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors for the
Reserved 57 to 62 This data area is reserved for future use.
Last Write Count 63 This word contains the number of characters written on
Description
server.
server from last BTR block.
If the word 1 of the BTR block is set to -2, the data for the last two servers is
passed to the processor. The format of this block is as follows:
Object in GSCInStat Block
Offset
Start
Seq Number 0 Sequence number for this block.
Server Index 1 For this status data block, this word is set to a value of -2.
PassCnt 2 Program cycle counter
Product 3 Product name as ASCII string
Rev 5 Revision level as ASCII string
OP 7 Operating system level as ASCII string
Run 9 Run number as ASCII string
BlkErrs.Read 11 Number of blocks transferred from module to processor
BlkErrs.Write 12 Number of blocks transferred from processor to module
BlkErrs.Parse 13 Number of blocks parsed by module
BlkErrs.Err 14 Number of block errors in module
Server[3].Enabled 15 This flag defines if the server is utilized. A value of 0
Server[3].State 16 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Server[3].IP 17 This double-word value contains the IP address of the client
Server[3].Port 19 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[3].Open 20 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[3].Established 21 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[3].Closed 22 This status value contains the total number of times a close
Server[3].RxCount 23 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[3].RxOverflow 24 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[3].TxCount 25 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[3].TxOverflow 26 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Description
indicates the server is not used. Any other value indicates
the server is used.
connected to the server.
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
operation was performed on the socket.
received by the server.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the server.
transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer size
for the server.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 53 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 54

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Object in GSCInStat Block
Offset
Start
Server[3].Timeout 27 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[3].CfgErrWord 28 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors for the
Server[4].Enabled 29 This flag defines if the server is utilized. A value of 0
Server[4].State 30 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Server[4].IP 31 This double-word value contains the IP address of the client
Server[4].Port 33 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[4].Open 34 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[4].Established 35 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[4].Closed 36 This status value contains the total number of times a close
Server[4].RxCount 37 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[4].RxOverflow 38 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[4].TxCount 39 This status value contains the total number of messages
Server[4].TxOverflow 40 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Server[4].Timeout 41 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[4].CfgErrWord 42 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors for the
Reserved 43 to 62 This data area is reserved for future use.
Last Write Count 63 This word contains the number of characters written on
Description
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
server.
indicates the server is not used. Any other value indicates
the server is used.
connected to the server.
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
operation was performed on the socket.
received by the server.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the server.
transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer size
for the server.
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
server.
server from last BTR block.
If word 1 of the Input Image block is set to -3, the data for the first three clients is
passed to the processor. The format of this block is as follows:
Parameter Block Offset
Start
Seq Number 0 Sequence number for this block.
Server Index 1 For this status data block, this word is set to a value of -3.
PassCnt 2 Program cycle counter
Product 3 Product name as ASCII string
Rev 5 Revision level as ASCII string
Description
Page 54 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 55

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Parameter Block Offset
Start
OP 7 Operating system level as ASCII string
Run 9 Run number as ASCII string
BlkErrs.Read 11 Number of blocks transferred from module to processor
BlkErrs.Write 12 Number of blocks transferred from processor to module
BlkErrs.Parse 13 Number of blocks parsed by module
BlkErrs.Err 14 Number of block errors in module
Client[0].Connected 15 This flag defines if the client is utilized and connected to a
Client[0].State 16 This flag defines the current state of the client.
Client[0].IP 17 & 18 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Client[0].Port 19 This word value contains the port address for the server
Client[0].RxCount 20 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[0].RxOverflow 21 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[0].TxCount 22 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[0].TxOverflow 23 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Client[0].spare 24 Reserved for future use
Client[1].Connected 25 This flag defines if the client is utilized and connected to a
Client[1].State 26 This flag defines the current state of the client.
Client[1].IP 27 & 28 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Client[1].Port 29 This word value contains the port address for the server
Client[1].RxCount 30 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[1].RxOverflow 31 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[1].TxCount 32 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[1].TxOverflow 33 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Client[1].spare 34 Reserved for future use
Description
server. A value of 0 indicates the client is not connected
and can be utilized for a connection. Any other value
indicates the client is connected and being used.
server connected to the client.
connected to the client.
received by the client.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the
client.
transmitted by the client.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the client.
server. A value of 0 indicates the client is not connected
and can be utilized for a connection. Any other value
indicates the client is connected and being used.
server connected to the client.
connected to the client.
received by the client.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the
client.
transmitted by the client.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the client.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 55 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 56

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Parameter Block Offset
Start
Client[2].Connected 35 This flag defines if the client is utilized and connected to a
Client[2].State 36 This flag defines the current state of the client.
Client[2].IP 37 & 38 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Client[2].Port 39 This word value contains the port address for the server
Client[2].RxCount 40 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[2].RxOverflow 41 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[2].TxCount 42 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[2].TxOverflow 43 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Client[2].spare 44 Reserved for future use
Reserved 45 to 57 This data area is reserved for future use.
Server States 58 to 62 State of each of the five servers.
Last Write Count 63 This word contains the number of characters written on
Description
server. A value of 0 indicates the client is not connected
and can be utilized for a connection. Any other value
indicates the client is connected and being used.
server connected to the client.
connected to the client.
received by the client.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the
client.
transmitted by the client.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the client.
server from last BTR block.
If word 1 of the Input Image block is set to -4, the data for the last two clients is
passed to the processor. The format of this block is as follows:
Parameter Block Offset
Start
Seq Number 0 Sequence number for this block.
Server Index 1 For this status data block, this word is set to a value of -4.
PassCnt 2 Program cycle counter
Product 3 Product name as ASCII string
Rev 5 Revision level as ASCII string
OP 7 Operating system level as ASCII string
Run 9 Run number as ASCII string
BlkErrs.Read 11 Number of blocks transferred from module to processor
BlkErrs.Write 12 Number of blocks transferred from processor to module
BlkErrs.Parse 13 Number of blocks parsed by module
BlkErrs.Err 14 Number of block errors in module
Client[3].Connected 15 This flag defines if the client is utilized and connected to a
Client[3].State 16 This flag defines the current state of the client.
Description
server. A value of 0 indicates the client is not connected
and can be utilized for a connection. Any other value
indicates the client is connected and being used.
Page 56 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 57

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Parameter Block Offset
Start
Client[3].IP 17 & 18 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Client[3].Port 19 This word value contains the port address for the server
Client[3].RxCount 20 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[3].RxOverflow 21 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[3].TxCount 22 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[3].TxOverflow 23 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Client[3].spare 24 Reserved for future use
Client[4].Connected 25 This flag defines if the client is utilized and connected to a
Client[4].State 26 This flag defines the current state of the client.
Client[4].IP 27 & 28 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Client[4].Port 29 This word value contains the port address for the server
Client[4].RxCount 30 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[4].RxOverflow 31 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[4].TxCount 32 This status value contains the total number of messages
Client[4].TxOverflow 33 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Client[4].spare 34 Reserved for future use
Reserved 35 to 57 This data area is reserved for future use.
Server States 58 to 62 State of each of the five servers.
Last Write Count 63 This word contains the number of characters written on
Description
server connected to the client.
connected to the client.
received by the client.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the
client.
transmitted by the client.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the client.
server. A value of 0 indicates the client is not connected
and can be utilized for a connection. Any other value
indicates the client is connected and being used.
server connected to the client.
connected to the client.
received by the client.
received that exceed the specified buffer size for the
client.
transmitted by the client.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the client.
server from last BTR block.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 57 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 58

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Write Block
These blocks of data transfer information from the PLC processor to the module.
The structure of the BTW blocks used to transfer this data is shown in the
following table.
Word
Offset
0 Block Sequence Number (Read block number as set by module)
Transmit
Data
62 Server Control Word
1 Server Number for data to transmit. If the word contains a value of -1, no
2 Number of characters to transmit to server. Each block can transmit up to
3 to 61 118 bytes of data to transmit on specified server.
63 Module Control Word
Description
transmit data is present. If the word contains a value from 0 to maximum
number of servers -1, the block contains data to send to the specified
server in the module..
118 bytes of data. If this word contains a value of -1, the block contains 118
bytes of data and more blocks of data are to follow. When the module
received the last block containing a positive value representing the number
of bytes in the
block, the server will transmit the data to the client.
In Word Offset 0 the Block Sequence Number is the value set by the module
received on the last read block transfer through the BTR on the module. The
ladder logic should copy this value from word 0 of the BTR image to word 0 of
BTW image in the ladder logic. This is the last operation performed when
constructing the write block. The module’s program will trigger the process write
block function when a new value is recognized in word 0 of the BTW image.
Word 1 of the block defines the server index that should receive the message. If
the word is set to a value of -1, there is no data in the message. A value of 0 to 4
will cause the enclosed message to be sent to the server if the message length is
set to a value other than zero and the server has an open connection. Word 2 of
the block defines the length of data in the block. Up to 118 bytes of data can be
sent in each block starting at word offset 3 in the block. If the message to be sent
to a server is longer than 118 bytes, multiple blocks are required. As long as
more than 118 bytes are required to send, the message length field should be set
to a value of -1 and 118 bytes of data should be placed in the block. When 118 or
fewer bytes remain to be sent, the message length field should be set to that
value and the remaining data placed in the block. The server will accept
messages up to a length of 8192 bytes. If a message longer than 8192 bytes is
sent to a server, a transmit overflow error will be recorded and the message will
be sent when 8192 bytes are received. The remaining part of the message will
be sent as it is received.
Page 58 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 59

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
The last two words of the image control the server or the module. The server
control word (word offset 62) controls the server. The following table lists the
values recognized by the module:
Word
Offset
62 0 No operation to perform
Code Definition
1 Close socket after transmit operation
2 Abort socket after transmit operation
If a value of 0 is present in the field, no action is taken by the server. If a value of
1 is present in the field, the server will close the socket after it transmits the
message contained in the block. If a value of 2 is present, the server will send the
message contained in the block and then force the connection closed by sending
a reset message to the client.
Word 63 is utilized to control the module. Two commands are recognized by the
module as displayed in the following table.
Word
Offset
63 0 No operation to perform
Code Definition
-1 Warm boot module
-2 Cold boot module
-30 Close server 0
-31 Close server 1
-32 Close server 2
-33 Close server 3
-34 Close server 4
The module performs the action specified in the command control word.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 59 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 60

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Handling Multiple Blocks
An important concept to understand about the MVI71-GEC module is how
multiple blocks are handled.
The buffer size supports 4096 bytes, but the module can only send 110 bytes at
each scan to the processor. For example, if a device sends a message that
contains 550 bytes to the module, it will break it down to five blocks of 110 bytes.
The first four blocks will set the number of characters parameter to -1, indicating
that each block is part of the same message. The last block will have the number
of characters parameter set to 110, indicating that there are no more blocks from
that message.
The same holds true for writing data from the processor to the module, in which
case you can write 118 bytes each time to the module. The module buffers all the
data until it receives a block that has the number of characters parameter set to
>=0. In this case, it sends all data to the client connected to that server.
The ladder logic should handle multiple blocks. The main example ladder logic is
very simple and will only handle up to 110 bytes since it does not check the
status of the number of characters parameter. Refer to the Reference chapter for
an example of ladder logic that handles messages containing multiple blocks.
Important: You should be aware that messages are usually broken down into smaller frames by
the IP layer in a specific LAN or WAN according to the Maximum Transmit Unit (MTU) of the
network.
For example, a message that contains 2000 bytes can be broken down into two messages by the
IP layer in the network (after it is sent to the module). The same issue is applied when a client
sends data to the server; although a client sends a single message to the module, it could be
broken down into smaller fragments before it gets to the module. In this case, the module would
interpret it as two different messages.
It is the application layer’s responsibility to define when a message is finished. Therefore, you
should consider using some kind of control that allows the ladder to identify different messages as
part of a single message. This could be accomplished by using a specific character at the end of
each message or by using a fixed length for each message.
Page 60 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 61

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Side-Connect Backplane Data Transfer
The side-connect interface is the simplest method to implement the module.
Minimal ladder logic is required for the interface because the driver handles data
movement between the module and the processor automatically. Additionally,
this interface is much faster than the block transfer interface. The data flow
associated with this interface is shown in the following diagram:
The value found in the SC_DATA.TXT file on the module determines the starting
file number for the side-connect interface. The following table lists the files
required for the side-connect interface:
File Number Example Size Description
Cfg File N10 250 Data transferred from the processor to the module
Cfg File+1 N11 250 Data transferred from the module to the processor
The first file is used by the module to read data placed in the file by the
processor. The second file places received data from the network into the
processor. It is very important that these files be defined to prevent the processor
from faulting.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 61 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 62

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
These files have fixed formats that are discussed below. Data received by the
servers on the modules is passed to the read data file. The format of this file is
shown in the following table.
Word
Offset
0 Server Number for data received. If the word contains a value of -1, no
Received
Data
Module
Status
185 to 247 Spare data area for future use.
1 Number of characters (0 to 200) in receive block (2 to 101). If the receive
2 to 101 200 bytes of data received for specified server.
102 to 184 This data area contains the status data block. Each block transferred to
248 Number of characters processed from last write block.
249 Block Sequence Number (Bumped each scan by module)
Description
receive data is present. If the word contains a value from 0 to 4, the block
contains data from one of the servers in the module.
data in the module is larger than 200 bytes, multiple blocks will be
transferred. Any block with a value of -1 in this field represents the first or
continuation block and the block contains 200 bytes of data. The last
block of data will contain a positive number in this field that represents
the number of characters in the last block.
the processor contains this set of information.
Word 249 is used as a sequence number for the block of data presented to the
processor. When this number changes, the processor should read the new block
of data. Word 248 of the block informs the PLC processor of the number of bytes
processed from the last write block. Word 0 of the block informs the processor
the source of the data. If the word is set to a value of -1, the block does not
contain any received data and only the status data (words 102 to 184) is
significant in the block. If the word contains a value of 0 to 4, this value
represents the server that received the message. Ladder logic should be written
to handle each enabled server in the module and to process the data received.
Word 1 of the image contains a byte count of the number of characters in the
received message that begins at word 2.
Page 62 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 63

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
After the processor has processed the read block, it should prepare a write block
for the module. The format of this block (built in the write file) is shown in the
following table.
Word
Offset
0 Block Sequence Number (Read block number as set by module)
Transmit
Data
203 to 245 Reserved for future use
1 Server Number for data to transmit. If the word contains a value of -1, no
2 Number of characters to transmit to server. Each block can transmit up to
3 to 202 Data to transmit on specified server.
246 Server Control Word
247 Module Control Word
Description
transmit data is present. If the word contains a value from 0 to max
number of servers -1, the block contains data to send to the specified
server in the module..
400 bytes of data. If this word contains a value of -1, the block contains
400 bytes of data and more blocks of data are to follow. When the
module received the last block containing a positive value representing
the number of bytes in the block, the server will transmit the data to the
client.
Words 246 and 247 control the server and module as discussed in the previous
section. If data is to be transmitted to a server, word 1 should be set to the
appropriate server index value. If a value of -1 is placed in the word, no transmit
data will be processed by the module (null transmit block). The number of bytes
in the message to transmit must be placed in word 2 and the data placed in the
block starting at word 3. After the block is constructed, the ladder logic should
copy the last block sequence number received in the last read block into word 0
of the write block. This will trigger the module to process the new write data block
and to construct a new read block.
Network Data Transfer
In order for data to be transferred between the module and another device, a
TCP/IP connection must be made between a client and a server on the module.
The MVI71-GEC module contains five servers that listen on the user assigned
service ports waiting for a connection. When a client devices wishes to send data
to the module, it must open a TCP/IP connection to the module. After the
connection is established, either device can send and receive data. When either
device is finished with the connection, the connection must be closed. This
operation can be initiated from either end device.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 63 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 64

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
The MVI71-GEC module servers are configured to handle their TCP/IP session
independently. The user parameter Connection Timeout is utilized to determine
the amount of time a connection can remain idle before the server will close the
connection. If the parameter is set to 0, the server will not perform the timeout
logic and the socket will never be closed by the server on an idle condition. If this
feature is utilized, it can prevent connections that may be lost and were not
properly closed. For example, if the link between the client and the server is lost
(broken connection), the server will attempt to gently close the connection after
the timeout expires. When no response is received from the client, the server will
abort the connection and set up to accept a new connection. If the connection
timeout feature was not utilized in the situation above, the server will not be
available until the TCP/IP stack closes the socket.
Each server on the module is assigned its own server port number. This does not
mean that two or more servers cannot share the same port number. In fact this
might be desirable in some instances. It is up to the ladder logic to keep track of
each message and to insure that a request/response transaction is associated
with the correct connection. Information to keep track of each connection is
passed in each input image. The status data set provides the IP address and
TCP port address for the connection on each server. Each message transferred
between the module and the processor has a server index word. This word
associates the message with a server, which is associated with a connection to a
specific IP address and TCP port address. Therefore, each connection is
specified to the processor by the server index. The following illustration shows a
snapshot of the modules status data:
Server Status Data Description of Server
Server 0 IP of Host (192.168.0.100) Port of
Host (1243) State = 1
Server 1 IP of Host (192.168.0.100) Port of
Host (1244) State = 1
Server 2 IP of Host (192.168.0.101) Port of
Host (56443) State = 1
Server 3 IP of Host (192.168.0.102) Port of
Host (7943) State = 1
Server 4 IP of Host (0.0.0.0) Port of Host (0)
State = 0
This server is connected (State=1) to IP
address 192.168.0.100 on TCP port 1243.
This server is connected (State=1) to IP
address 192.168.0.100 on TCP port 1244.
This server is connected (State=1) to IP
address 192.168.0.101 on TCP port 56443.
This server is connected (State=1) to IP
address 192.168.0.102 on TCP port 7943.
This server is not connected (State not equal
to 1) and is waiting for a connection.
Ladder logic can send messages to the clients connected to servers 0 to 3.
Messages sent to server 4 will not be sent from the module because there is no
connection active on that server.
Page 64 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 65

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Each server has a state value in the status data area. This value is utilized by the
ladder logic to determine if a connection is present on server. The following table
defines the state status values used by each server:
State Value Definition
-1 Server is initializing and is being set up to listen.
0 The server is waiting for a client to establish a connection.
1 The server has established a connection with a client and can send or receive
data.
1000 The server has initiated a close operation on the connection.
1001 The server is waiting for the close on the connection to complete.
1002 The server is issuing an abort (reset) on the connection. The socket is forced
closed.
3000 The client is issuing the ARP command request and waiting for the response.
3001 The client has received the ARP response and has opened the socket.
Ladder logic should only direct messages to servers that have a state status
value of 1. The module will ignore all messages sent to servers with any other
state value.
When the ladder logic sends a message to a server, it can request that the
socket be closed after the message is sent. The server control word in the output
image is used for this purpose. Place a value of 1 in this register to gently close
the connection after the message is sent. If a value of 2 is placed in the register,
the server will abort the connection to force the socket closed (send a message
with the Reset Flag set to the client). Most applications will have the client close
the socket.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 65 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 66

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
5.3 Cable Connections
The MVI71-GEC module has the following functional communication connections
installed:
One Ethernet port (RJ45 connector)
One RS-232 Configuration/Debug port (RJ45 connector)
5.3.1 Ethernet Connection
The MVI71-GEC module has an RJ45 port located on the front of the module,
labeled Ethernet, for use with the TCP/IP network. The module is connected to
the Ethernet network using an Ethernet cable between the module’s Ethernet
port and an Ethernet switch or hub.
Note: Depending on hardware configuration, you may see more than one RJ45 port on the
module. The Ethernet port is labeled Ethernet.
Warning: The MVI71-GEC module is NOT compatible with Power Over Ethernet (IEEE802.3af /
IEEE802.3at) networks. Do NOT connect the module to Ethernet devices, hubs, switches or
networks that supply AC or DC power over the Ethernet cable. Failure to observe this precaution
may result in damage to hardware, or injury to personnel.
Important: The module requires a static (fixed) IP address that is not shared with any other device
on the Ethernet network. Obtain a list of suitable IP addresses from your network administrator
BEFORE configuring the Ethernet port on this module.
Ethernet Port Configuration - wattcp.cfg
The wattcp.cfg file must be set up properly in order to use a TCP/IP network
connection. You can view the current network configuration in ProSoft
Configuration Builder (PCB), as shown:
You may also view the network configuration using a PC serial port connection
and an ASCII terminal program (like Windows HyperTerminal) by selecting [@]
(Network Menu) and [V] (View) options when connected to the Debug port. For
more information on serial port access, see the chapter on Diagnostics and
Troubleshooting (page 33).
Page 66 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 67

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5.3.2 RS-232 Configuration/Debug Port
This port is physically an RJ45 connection. An RJ45 to DB-9 adapter cable is
included with the module. This port permits a PC-based terminal emulation
program to view configuration and status data in the module and to control the
module. The cable pinout for communications on this port is shown in the
following diagram.
Disabling the RSLinx Driver for the Com Port on the PC
The communication port driver in RSLinx can occasionally prevent other
applications from using the PC’s COM port. If you are not able to connect to the
module’s configuration/debug port using ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB),
HyperTerminal or another terminal emulator, follow these steps to disable the
RSLinx driver.
1 Open RSLinx and go to C
2 Make sure that you are not actively browsing using the driver that you wish to
stop. The following shows an actively browsed network.
OMMUNICATIONS
> RSWHO.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 67 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 68

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
3 Notice how the DF1 driver is opened, and the driver is looking for a processor
on node 1. If the network is being browsed, then you will not be able to stop
this driver. To stop the driver your RSWho screen should look like this:
Branches are displayed or hidden by clicking on the or the icons.
4 When you have verified that the driver is not being browsed, go to
C
OMMUNICATIONS
> C
ONFIGURE DRIVERS
.
You may see something like this:
If you see the status as running, you will not be able to use this com port for
anything other than communication to the processor. To stop the driver press
the S
TOP
button on the side of the window:
5 After you have stopped the driver you will see the following.
Page 68 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 69

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
6 You may now use the com port to connect to the debug port of the module.
Note: You may need to shut down and restart your PC before it will allow you to stop the driver
(usually only on Windows NT machines). If you have followed all of the above steps, and it will not
stop the driver, then make sure you do not have RSLogix open. If RSLogix is not open, and you
still cannot stop the driver, then reboot your PC.
5.3.3 DB9 to RJ45 Adaptor (Cable 14)
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 69 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 70

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
5.4 MVI71-GEC Status Data Area
This section contains a listing of the data contained in the MVI71-GEC status
data object.
Object In GSCInStat Block Offset
Start
PassCnt 102 Program cycle counter
Product 103 Product name as ASCII string
Rev 105 Revision level as ASCII string
OP 107 Operating system level as ASCII string
Run 109 Run number as ASCII string
BlkErrs.Read 111 Number of blocks transferred from module to processor
BlkErrs.Write 112 Number of blocks transferred from processor to module
BlkErrs.Parse 113 Number of blocks parsed by module
BlkErrs.Err 114 Number of block errors in module
Server[0].Enabled 115 This flag defines if the server is utilized. Y indicates
Server[0].State 116 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Server[0].IP 117 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Server[0].Port 119 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[0].Open 120 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[0].Established 121 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[0].Closed 122 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[0].RxCount 123 This status value contains the total number of
Server[0].RxOverflow 124 This status value contains the total number of
Server[0].TxCount 125 This status value contains the total number of
Server[0].TxOverflow 126 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Server[0].Timeout 127 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[0].CfgErrWord 128 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors
Server[1].Enabled 129 This flag defines if the server is utilized. Y indicates
Server[1].State 130 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Description
that the server is enabled. N indicates that the server is
disabled as ASCII string.
client connected to the server.
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
close operation was performed on the socket.
messages received by the server.
messages received that exceed the specified buffer
size for the server.
messages transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the server.
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
for the server.
that the server is enabled. N indicates that the server is
disabled as ASCII string.
Page 70 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 71

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Object In GSCInStat Block Offset
Start
Server[1].IP 131 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Server[1].Port 133 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[1].Open 134 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[1].Established 135 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[1].Closed 136 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[1].RxCount 137 This status value contains the total number of
Server[1].RxOverflow 138 This status value contains the total number of
Server[1].TxCount 139 This status value contains the total number of
Server[1].TxOverflow 140 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Server[1].Timeout 141 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[1].CfgErrWord 142 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors
Server[2].Enabled 143 This flag defines if the server is utilized. Y indicates
Server[2].State 144 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Server[2].IP 145 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Server[2].Port 147 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[2].Open 148 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[2].Established 149 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[2].Closed 150 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[2].RxCount 151 This status value contains the total number of
Server[2].RxOverflow 152 This status value contains the total number of
Server[2].TxCount 153 This status value contains the total number of
Server[2].TxOverflow 154 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Description
client connected to the server.
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
close operation was performed on the socket.
messages received by the server.
messages received that exceed the specified buffer
size for the server.
messages transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the server.
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
for the server.
that the server is enabled. N indicates that the server is
disabled as ASCII string.
client connected to the server.
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
close operation was performed on the socket.
messages received by the server.
messages received that exceed the specified buffer
size for the server.
messages transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the server.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 71 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 72

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Object In GSCInStat Block Offset
Start
Server[2].Timeout 155 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[2].CfgErrWord 156 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors
Server[3].Enabled 157 This flag defines if the server is utilized. Y indicates
Server[3].State 158 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Server[3].IP 159 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Server[3].Port 161 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[3].Open 162 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[3].Established 163 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[3].Closed 164 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[3].RxCount 165 This status value contains the total number of
Server[3].RxOverflow 166 This status value contains the total number of
Server[3].TxCount 167 This status value contains the total number of
Server[3].TxOverflow 168 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Server[3].Timeout 169 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[3].CfgErrWord 170 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors
Server[4].Enabled 171 This flag defines if the server is utilized. Y indicates
Server[4].State 172 This flag defines the current state of the server.
Server[4].IP 173 This double-word value contains the IP address of the
Server[4].Port 175 This word value contains the port address for the client
Server[4].Open 176 This status value contains the total number of times the
Server[4].Established 177 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[4].Closed 178 This status value contains the total number of times a
Description
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
for the server.
that the server is enabled. N indicates that the server is
disabled as ASCII string.
client connected to the server.
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
close operation was performed on the socket.
messages received by the server.
messages received that exceed the specified buffer
size for the server.
messages transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the server.
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
for the server.
that the server is enabled. N indicates that the server is
disabled as ASCII string.
client connected to the server.
connected to the server.
server performed an open operation.
connection was established on the socket.
close operation was performed on the socket.
Page 72 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 73

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Object In GSCInStat Block Offset
Start
Server[4].RxCount 179 This status value contains the total number of
Server[4].RxOverflow 180 This status value contains the total number of
Server[4].TxCount 181 This status value contains the total number of
Server[4].TxOverflow 182 This status value contains the total number of transmit
Server[4].Timeout 183 This status value contains the total number of times a
Server[4].CfgErrWord 184 This bit mapped word defines the configuration errors
Description
messages received by the server.
messages received that exceed the specified buffer
size for the server.
messages transmitted by the server.
messages that exceeded the specified maximum buffer
size for the server.
connection timeout occurred on the socket.
for the server.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 73 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 74

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
5.5 MVI71-GEC Configuration Data
This section contains a listing of the parameters and their definitions for the
MVI71-GEC module configuration file definition.
5.5.1 MVI71-GEC Server Communication Module Configuration
[Section]/Item Value Range Description
[MODULE] Module parameter definitions
Module Name: 0 to 80
characte
rs
[Section]/Item Value Range Description
[Server 0] Server definitions
Enabled: Yes or
No
Service Port Number: 1 to
65535
Connection Timeout: 0 or
5000 to
65535
Connection Close Type: 0, 1 or 2 This coded parameter defines the personality of the
Swap Rx Data Bytes: Yes or
No
Swap Tx Data Bytes: Yes or
No
This parameter assigns a name to the module that
can be viewed using the configuration/debug port.
Use this parameter to identify the module and the
configuration file.
This parameter determines if the server will be
utilized by the module. If a value of "Yes' is entered,
the server will be used. Any other value will disable
the server.
This parameter sets the TCP/IP service port for this
server. Each server can have its own unique
service port or can share the same number with
other servers.
This parameter specifies the number of
milliseconds the server will permit the server to be
inactive after a connection is made before closing
the socket. This timeout period is reset on each
read or write packet. If the parameter is set to 0, the
connection will not timeout.
server after a connection is made. If the parameter
is set to 0, the socket will only be closed when a
request from the client is received or the connection
timeout is exceeded. If a value of 1 is selected, the
server will close the socket after it transmits a
single message. If a value of 2 is selected, the
server will close the socket after it receives a
message.
This parameter is determines if the data received
by the server will have the byte order of the data
swapped. If the parameter is set to No, no byte
swapping will occur. If the parameter is set to Yes,
the odd byte will be swapped with the even byte in
each word of data received.
This parameter is determines if the data to be
transmitted by the server will have the byte order of
the data swapped. If the parameter is set to No, no
byte swapping will occur. If the parameter is set to
Yes, the odd byte will be swapped with the even
byte in each word of data received.
Note: Add other [Server n] sections for each server to be utilized.
Page 74 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 75

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Reference
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
[Section]/Item Value Range Description
[Server n] Server definitions
Enabled: Yes or
No
Service Port Number: 1 to
65535
Connection Timeout: 0 or
5000 to
65535
Connection Close Type: 0, 1 or 2 This coded parameter defines the personality of the
Swap Rx Data Bytes: Yes or
No
Swap Tx Data Bytes: Yes or
No
This parameter determines if the server will be
utilized by the module. If a value of "Yes' is entered,
the server will be used. Any other value will disable
the server.
This parameter sets the TCP/IP service port for this
server. Each server can have its own unique
service port or can share the same number with
other servers.
This parameter specifies the number of
milliseconds the server will permit the server to be
inactive after a connection is made before closing
the socket. This timeout period is reset on each
read or write packet. If the parameter is set to 0, the
connection will not timeout.
server after a connection is made. If the parameter
is set to 0, the socket will only be closed when a
request from the client is received or the connection
timeout is exceeded. If a value of 1 is selected, the
server will close the socket after it transmits a
single message. If a value of 2 is selected, the
server will close the socket after it receives a
message.
This parameter is determines if the data received
by the server will have the byte order of the data
swapped. If the parameter is set to No, no byte
swapping will occur. If the parameter is set to Yes,
the odd byte will be swapped with the even byte in
each word of data received.
This parameter is determines if the data to be
transmitted by the server will have the byte order of
the data swapped. If the parameter is set to No, no
byte swapping will occur. If the parameter is set to
Yes, the odd byte will be swapped with the even
byte in each word of data received.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 75 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 76

Reference MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Page 76 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 77

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Support, Service & Warranty
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
6 Support, Service & Warranty
In This Chapter
Contacting Technical Support ............................................................... 77
Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions ............... 79
LIMITED WARRANTY ........................................................................... 81
Contacting Technical Support
ProSoft Technology, Inc. (ProSoft) is committed to providing the most efficient
and effective support possible. Before calling, please gather the following
information to assist in expediting this process:
1 Product Version Number
2 System architecture
3 Network details
If the issue is hardware related, we will also need information regarding:
1 Module configuration and associated ladder files, if any
2 Module operation and any unusual behavior
3 Configuration/Debug status information
4 LED patterns
5 Details about the serial, Ethernet or fieldbus devices interfaced to the module,
if any.
Note: For technical support calls within the United States, an after-hours answering system allows
24-hour/7-days-a-week pager access to one of our qualified Technical and/or Application Support
Engineers. Detailed contact information for all our worldwide locations is available on the following
page.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 77 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 78

Support, Service & Warranty MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
Internet
Web Site: www.prosoft-technology.com/support
E-mail address: support@prosoft-technology.com
Asia Pacific
(location in Malaysia)
Asia Pacific
(location in China)
Europe
(location in Toulouse,
France)
Europe
(location in Dubai, UAE)
Tel: +603.7724.2080, E-mail: asiapc@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Chinese, English
Tel: +86.21.5187.7337 x888, E-mail: asiapc@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Chinese, English
Tel: +33 (0) 5.34.36.87.20,
E-mail: support.EMEA@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: French, English
Tel: +971-4-214-6911,
E-mail: mea@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: English, Hindi
North America
(location in California)
Tel: +1.661.716.5100,
E-mail: support@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: English, Spanish
Latin America
(Oficina Regional)
Tel: +1-281-2989109,
E-Mail: latinam@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Spanish, English
Latin America
(location in Puebla, Mexico)
Tel: +52-222-3-99-6565,
E-mail: soporte@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Spanish
Brasil
(location in Sao Paulo)
Tel: +55-11-5083-3776,
E-mail: brasil@prosoft-technology.com
Languages spoken include: Portuguese, English
Page 78 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 79

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Support, Service & Warranty
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
6.1 Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions
The following Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions
(collectively, "RMA Policies") apply to any returned product. These RMA Policies
are subject to change by ProSoft Technology, Inc., without notice. For warranty
information, see Limited Warranty (page 81). In the event of any inconsistency
between the RMA Policies and the Warranty, the Warranty shall govern.
6.1.1 Returning Any Product
a) In order to return a Product for repair, exchange, or otherwise, the
Customer must obtain a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number
from ProSoft Technology and comply with ProSoft Technology shipping
instructions.
b) In the event that the Customer experiences a problem with the Product for
any reason, Customer should contact ProSoft Technical Support at one of
the telephone numbers listed above (page 77). A Technical Support
Engineer will request that you perform several tests in an attempt to
isolate the problem. If after completing these tests, the Product is found to
be the source of the problem, we will issue an RMA.
c) All returned Products must be shipped freight prepaid, in the original
shipping container or equivalent, to the location specified by ProSoft
Technology, and be accompanied by proof of purchase and receipt date.
The RMA number is to be prominently marked on the outside of the
shipping box. Customer agrees to insure the Product or assume the risk
of loss or damage in transit. Products shipped to ProSoft Technology
using a shipment method other than that specified by ProSoft Technology,
or shipped without an RMA number will be returned to the Customer,
freight collect. Contact ProSoft Technical Support for further information.
d) A 10% restocking fee applies to all warranty credit returns, whereby a
Customer has an application change, ordered too many, does not need,
etc. Returns for credit require that all accessory parts included in the
original box (i.e.; antennas, cables) be returned. Failure to return these
items will result in a deduction from the total credit due for each missing
item.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 79 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 80

Support, Service & Warranty MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
6.1.2 Returning Units Under Warranty
A Technical Support Engineer must approve the return of Product under ProSoft
Technology’s Warranty:
a) A replacement module will be shipped and invoiced. A purchase order will
be required.
b) Credit for a product under warranty will be issued upon receipt of
authorized product by ProSoft Technology at designated location
referenced on the Return Material Authorization
i. If a defect is found and is determined to be customer generated, or if
the defect is otherwise not covered by ProSoft Technology s warranty,
there will be no credit given. Customer will be contacted and can
request module be returned at their expense;
ii. If defect is customer generated and is repairable, customer can
authorize ProSoft Technology to repair the unit by providing a
purchase order for 30% of the current list price plus freight charges,
duties and taxes as applicable.
6.1.3 Returning Units Out of Warranty
a) Customer sends unit in for evaluation to location specified by ProSoft
Technology, freight prepaid.
b) If no defect is found, Customer will be charged the equivalent of $100
USD, plus freight charges, duties and taxes as applicable. A new
purchase order will be required.
c) If unit is repaired, charge to Customer will be 30% of current list price
(USD) plus freight charges, duties and taxes as applicable. A new
purchase order will be required or authorization to use the purchase order
submitted for evaluation fee.
The following is a list of non-repairable units:
ScanPort Adapters
o
1500 - All
o
1550 - Can be repaired only if defect is the power supply
o
1560 - Can be repaired only if defect is the power supply
inRAx Modules
o
3150 - All
o
3170 - All
o
3250
o
3300
o
3350
o
3600 - All
o
3700
o
3750
o
3800-MNET
ProLinx Standalone Gateways
o
Page 80 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
4xxx - All (No hardware available to do repairs)
Page 81

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Support, Service & Warranty
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
6.2 LIMITED WARRANTY
This Limited Warranty ("Warranty") governs all sales of hardware, software, and
other products (collectively, "Product") manufactured and/or offered for sale by
ProSoft Technology, Incorporated (ProSoft), and all related services provided by
ProSoft, including maintenance, repair, warranty exchange, and service
programs (collectively, "Services"). By purchasing or using the Product or
Services, the individual or entity purchasing or using the Product or Services
("Customer") agrees to all of the terms and provisions (collectively, the "Terms")
of this Limited Warranty. All sales of software or other intellectual property are, in
addition, subject to any license agreement accompanying such software or other
intellectual property.
6.2.1 What Is Covered By This Warranty
a) Warranty On New Products: ProSoft warrants, to the original purchaser,
that the Product that is the subject of the sale will (1) conform to and
perform in accordance with published specifications prepared, approved
and issued by ProSoft, and (2) will be free from defects in material or
workmanship; provided these warranties only cover Product that is sold as
new. This Warranty expires three (3) years from the date of shipment for
Product purchased on or after January 1st, 2008, or one (1) year from the
date of shipment for Product purchased before January 1st, 2008 (the
"Warranty Period"). If the Customer discovers within the Warranty Period
a failure of the Product to conform to specifications, or a defect in material
or workmanship of the Product, the Customer must promptly notify
ProSoft by fax, email or telephone. In no event may that notification be
received by ProSoft later than 39 months from date of original shipment.
Within a reasonable time after notification, ProSoft will correct any failure
of the Product to conform to specifications or any defect in material or
workmanship of the Product, with either new or remanufactured
replacement parts. ProSoft reserves the right, and at its sole discretion,
may replace unrepairable units with new or remanufactured equipment.
All replacement units will be covered under warranty for the 3 year period
commencing from the date of original equipment purchase, not the date of
shipment of the replacement unit. Such repair, including both parts and
labor, will be performed at ProSoft’s expense. All warranty service will be
performed at service centers designated by ProSoft.
b) Warranty On Services: Materials and labor performed by ProSoft to repair
a verified malfunction or defect are warranteed in the terms specified
above for new Product, provided said warranty will be for the period
remaining on the original new equipment warranty or, if the original
warranty is no longer in effect, for a period of 90 days from the date of
repair.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 81 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 82

Support, Service & Warranty MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
6.2.2 What Is Not Covered By This Warranty
a) ProSoft makes no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, that
the operation of software purchased from ProSoft will be uninterrupted or
error free or that the functions contained in the software will meet or
satisfy the purchaser’s intended use or requirements; the Customer
assumes complete responsibility for decisions made or actions taken
based on information obtained using ProSoft software.
b) This Warranty does not cover the failure of the Product to perform
specified functions, or any other non-conformance, defects, losses or
damages caused by or attributable to any of the following: (i) shipping; (ii)
improper installation or other failure of Customer to adhere to ProSoft’s
specifications or instructions; (iii) unauthorized repair or maintenance; (iv)
attachments, equipment, options, parts, software, or user-created
programming (including, but not limited to, programs developed with any
IEC 61131-3, "C" or any variant of "C" programming languages) not
furnished by ProSoft; (v) use of the Product for purposes other than those
for which it was designed; (vi) any other abuse, misapplication, neglect or
misuse by the Customer; (vii) accident, improper testing or causes
external to the Product such as, but not limited to, exposure to extremes
of temperature or humidity, power failure or power surges; or (viii)
disasters such as fire, flood, earthquake, wind and lightning.
c) The information in this Agreement is subject to change without notice.
ProSoft shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions
made herein; nor for incidental or consequential damages resulting from
the furnishing, performance or use of this material. The user guide
included with your original product purchase from ProSoft contains
information protected by copyright. No part of the guide may be duplicated
or reproduced in any form without prior written consent from ProSoft.
6.2.3 Disclaimer Regarding High Risk Activities
Product manufactured or supplied by ProSoft is not fault tolerant and is not
designed, manufactured or intended for use in hazardous environments requiring
fail-safe performance including and without limitation: the operation of nuclear
facilities, aircraft navigation of communication systems, air traffic control, direct
life support machines or weapons systems in which the failure of the product
could lead directly or indirectly to death, personal injury or severe physical or
environmental damage (collectively, "high risk activities"). ProSoft specifically
disclaims any express or implied warranty of fitness for high risk activities.
Page 82 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 83

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Support, Service & Warranty
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
6.2.4 Intellectual Property Indemnity
Buyer shall indemnify and hold harmless ProSoft and its employees from and
against all liabilities, losses, claims, costs and expenses (including attorney’s
fees and expenses) related to any claim, investigation, litigation or proceeding
(whether or not ProSoft is a party) which arises or is alleged to arise from Buyer’s
acts or omissions under these Terms or in any way with respect to the Products.
Without limiting the foregoing, Buyer (at its own expense) shall indemnify and
hold harmless ProSoft and defend or settle any action brought against such
Companies to the extent based on a claim that any Product made to Buyer
specifications infringed intellectual property rights of another party. ProSoft
makes no warranty that the product is or will be delivered free of any person’s
claiming of patent, trademark, or similar infringement. The Buyer assumes all
risks (including the risk of suit) that the product or any use of the product will
infringe existing or subsequently issued patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
a) Any documentation included with Product purchased from ProSoft is
protected by copyright and may not be duplicated or reproduced in any
form without prior written consent from ProSoft.
b) ProSoft’s technical specifications and documentation that are included
with the Product are subject to editing and modification without notice.
c) Transfer of title shall not operate to convey to Customer any right to make,
or have made, any Product supplied by ProSoft.
d) Customer is granted no right or license to use any software or other
intellectual property in any manner or for any purpose not expressly
permitted by any license agreement accompanying such software or other
intellectual property.
e) Customer agrees that it shall not, and shall not authorize others to, copy
software provided by ProSoft (except as expressly permitted in any
license agreement accompanying such software); transfer software to a
third party separately from the Product; modify, alter, translate, decode,
decompile, disassemble, reverse-engineer or otherwise attempt to derive
the source code of the software or create derivative works based on the
software; export the software or underlying technology in contravention of
applicable US and international export laws and regulations; or use the
software other than as authorized in connection with use of Product.
f) Additional Restrictions Relating To Software And Other Intellectual
Property
In addition to compliance with the Terms of this Warranty, Customers
purchasing software or other intellectual property shall comply with any
license agreement accompanying such software or other intellectual
property. Failure to do so may void this Warranty with respect to such
software and/or other intellectual property.
6.2.5 Disclaimer of all Other Warranties
The Warranty set forth in What Is Covered By This Warranty (page 81) are in lieu
of all other warranties, express or implied, including but not limited to the implied
warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 83 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 84

Support, Service & Warranty MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
6.2.6 Limitation of Remedies **
In no event will ProSoft or its Dealer be liable for any special, incidental or
consequential damages based on breach of warranty, breach of contract,
negligence, strict tort or any other legal theory. Damages that ProSoft or its
Dealer will not be responsible for include, but are not limited to: Loss of profits;
loss of savings or revenue; loss of use of the product or any associated
equipment; loss of data; cost of capital; cost of any substitute equipment,
facilities, or services; downtime; the claims of third parties including, customers of
the Purchaser; and, injury to property.
** Some areas do not allow time limitations on an implied warranty, or allow the exclusion or
limitation of incidental or consequential damages. In such areas, the above limitations may not
apply. This Warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights which vary
from place to place.
6.2.7 Time Limit for Bringing Suit
Any action for breach of warranty must be commenced within 39 months
following shipment of the Product.
6.2.8 No Other Warranties
Unless modified in writing and signed by both parties, this Warranty is
understood to be the complete and exclusive agreement between the parties,
suspending all oral or written prior agreements and all other communications
between the parties relating to the subject matter of this Warranty, including
statements made by salesperson. No employee of ProSoft or any other party is
authorized to make any warranty in addition to those made in this Warranty. The
Customer is warned, therefore, to check this Warranty carefully to see that it
correctly reflects those terms that are important to the Customer.
6.2.9 Allocation of Risks
This Warranty allocates the risk of product failure between ProSoft and the
Customer. This allocation is recognized by both parties and is reflected in the
price of the goods. The Customer acknowledges that it has read this Warranty,
understands it, and is bound by its Terms.
6.2.10 Controlling Law and Severability
This Warranty shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of
the United States and the domestic laws of the State of California, without
reference to its conflicts of law provisions. If for any reason a court of competent
jurisdiction finds any provisions of this Warranty, or a portion thereof, to be
unenforceable, that provision shall be enforced to the maximum extent
permissible and the remainder of this Warranty shall remain in full force and
effect. Any cause of action with respect to the Product or Services must be
instituted in a court of competent jurisdiction in the State of California.
Page 84 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
Page 85

MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform Support, Service & Warranty
Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
G
GECServerStat (Server Status Object) • 32
Index
General Concepts • 48
General Specifications • 46
Guide to the MVI71-GEC User Manual • 7
[
[Module] • 25
[Server x] • 25
A
Adding the Module to an Existing PLC5 Project • 30
Allocation of Risks • 84
B
Battery Life Advisory • 3
Block Transfer Backplane Data Transfer • 49
C
Cable Connections • 66
Clearing a Fault Condition • 35
Configuring Module Parameters • 24
Configuring the RSLinx Driver for the PC COM Port •
17
Connect your PC to the Module • 19
Connect your PC to the Processor • 15
Connection Close Type • 26
Connection Timeout • 26
Contacting Technical Support • 77, 79
Controlling Law and Severability • 84
Creating Optional Comment Entries • 25
D
DB9 to RJ45 Adaptor (Cable 14) • 69
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting • 7, 33, 66
Disabling the RSLinx Driver for the Com Port on the
PC • 67
Disclaimer of all Other Warranties • 83
Disclaimer Regarding High Risk Activities • 82
Download the Sample Program to the Processor • 16
Downloading the Project to the Module Using a Serial
COM Port • 27
E
Enabled • 26
Ethernet Connection • 66
Ethernet LED Indicators • 34
Ethernet Port Configuration - wattcp.cfg • 66
Exiting the Program • 42
F
Functional Overview • 48
Functional Specifications • 47
H
Handling Multiple Blocks • 60
Hardware Specifications • 46
How to Contact Us • 2
I
Important Installation Instructions • 3
Install the Module in the Rack • 13
Intellectual Property Indemnity • 83
IP Address • 28
K
Keystrokes • 39
L
Ladder Logic • 29
LED Status Indicators • 34
Limitation of Remedies ** • 84
LIMITED WARRANTY • 79, 81
M
Main Logic Loop • 48
Main Menu • 39
Markings • 4
Module Configuration • 21
Module Name • 25
Module Power Up • 48
MVI (Multi Vendor Interface) Modules • 3
MVI71-GEC Configuration Data • 74
MVI71-GEC Server Communication Module
Configuration • 74
MVI71-GEC Status Data Area • 70
N
Navigation • 38
Network Data Transfer • 63
Network Menu • 42
No Other Warranties • 84
Normal Data Transfer • 49
O
Opening the Network Menu • 42
P
Package Contents • 11
Pinouts • 3, 66, 69
Product Specifications • 7, 46
ProSoft Technology® Product Documentation • 2
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 85 of 86
May 11, 2011
Page 86

Support, Service & Warranty MVI71-GEC ♦ PLC 5 Platform
User Manual Generic ASCII Ethernet Communication Module
R
Read Block • 50
Reading Status Data from the Module • 43
Redisplaying the Menu • 39
Reference • 7, 45
Renaming PCB Objects • 24
Resetting Diagnostic Data • 40
Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and
Conditions • 79
Returning Any Product • 79
Returning to the Main Menu • 43
Returning Units Out of Warranty • 80
Returning Units Under Warranty • 80
RS-232 Configuration/Debug Port • 67
Warnings • 3
What Is Covered By This Warranty • 81, 83
What Is Not Covered By This Warranty • 82
Write Block • 58
Y
Your Feedback Please • 2
S
Service Port Number • 26
Set Up the Project • 22
Setting Jumpers • 12
Side-Connect Backplane Data Transfer • 61
Start Here • 7, 9
Support, Service & Warranty • 7, 77
Swap Rx Data Bytes • 26
Swap Tx Data Bytes • 26
System Requirements • 10
T
Time Limit for Bringing Suit • 84
Transferring the Configuration File from The Module to
the PC • 40
Transferring the Configuration File from the PC to the
Module • 40
Transferring WATTCP.CFG to the Module • 28, 43
Transferring WATTCP.CFG to the PC • 43
Troubleshooting • 35
U
Using ProSoft Configuration Builder • 22
Using ProSoft Configuration Builder (PCB) for
Diagnostics • 36
Using the Diagnostic Window in ProSoft Configuration
Builder • 36
V
Viewing Block Transfer Statistics • 40
Viewing Client Communication Status (Clients 10 to
14) • 41
Viewing Module Configuration • 40
Viewing Server Communication Status (Servers 0 to 4)
• 41
Viewing Server Configuration (Servers 0 to 4) • 42
Viewing the WATTCP.CFG File on the module • 43
Viewing Version Information • 41
W
Warm Booting the Module • 41
Page 86 of 86 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
May 11, 2011
 Loading...
Loading...