
Colour Television Chassis
EM1A
AA
CL 06532111_000.eps
171000
Contents Page Contents Page
1. Technical specifications, connection facilities &
chassis overview 2
2. Safety- and maintenance instructions, 4
warnings and notes.
3. Directions for use 6
4. Mechanical instructions 11
5. Faultfinding and repair tips 15
Block-, wiring diagrams and testpoint overviews
6.
Blockdiagram video processing 27
Blockdiagram audio & control 28
Blockdiagram Large Signal Panel: supply 29
Powerlines overview 30
Wiring diagram 31
2
C overview 32
I
Testpoint overview LSP 33
Testpoint overview SSB / DW / CRT panel 34
Electrical diagram’s en PWB’s Diagram PWB
7.
Main supply (Diagram A1) 35 43-48
Standby supply (Diagram A2) 36 43-48
Line deflection (Diagram A3) 37 43-48
Frame deflection (Diagram A4) 38 43-48
Audio amplifier (Diagram A5) 39 43-48
Headphone amplifier (Diagram A6) 40 43-48
Tuner, I/O, SIMM-connector (Diagram A7) 41 43-48
Front control (Diagram A8) 42 43-48
SSB: SIMM-connector (Diagram B1) 49 55-60
IF, I/O, videoprocessing (Diagram B2) 50 55-60
Feature box (Diagram B3) 51 55-60
HOP (Diagram B4) 52 55-60
Audio demodulator (Diagram B6) 53 55-60
Painter (Diagram B7) 54 55-60
Multi PIP controller (Diagram C1) 61 65/66
Tuner (Diagram C2) 62 65/66
I/O processing (Diagram C3) 63 65/66
©
Copyright 2000 Philips Consumer Electronics B.V. Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
IF video sync (Diagram C4) 64 65/66
Side I/O panel (Diagram D) 67 67
Top control panel (Diagram E) 69 69
CRT panel (Diagram F) 70 71
DC-shift panel (Diagram G) 71 71
Horizontal DAF panel (Diagram I1) 72 74
Vertical DAF panel (Diagram I2) 73 74
Mains switch panel (Diagram J) 75 75
Mains harmonic panel (Diagram Y) 76 76
8. Alignments 77
9. Circuit description and 82
list of abbreviations 96
10. Spareparts list 98
Published by CO 0070 Service PaCE Printed in the Netherlands Subject to modification 5 3122 785 10850
GB 2 EM1A1.
Technical specifications, connection facilities & chassis overview
1. Technical specifications, connection facilities & chassis
overview
1.1 Technical specifications
1.1.1 Reception
Tuning system : PLL
Colour systems (off-air) : NTSC M (3.58 &
4.43 MHz),
: PAL B/G/D/K/I/M/N,
: SECAM B/G/D/K/L
Sound systems : FM/FM,
: 2SC B/G,
: NICAM B/G/D/K/I/L
A/V connections : PAL B/G,
:SECAM,
: NTSC M (3.58 &
4.43 MHz).
Channel selections : 100 channels,
: UVSH-channels
Frequency range : 44.25 - 855.25 MHz
Aerial input : 75 Ω, Coax
1.1.2 Miscellaneous
Set stroke numbers : /56, /57, /69, /79,
/93
Mains voltage : 160 - 276 V
(± 10 %),
: 50 / 60 Hz (± 5 %)
Ambient temperature : + 5 to + 45 deg. C.
Standby Power consumption : < 1 W.
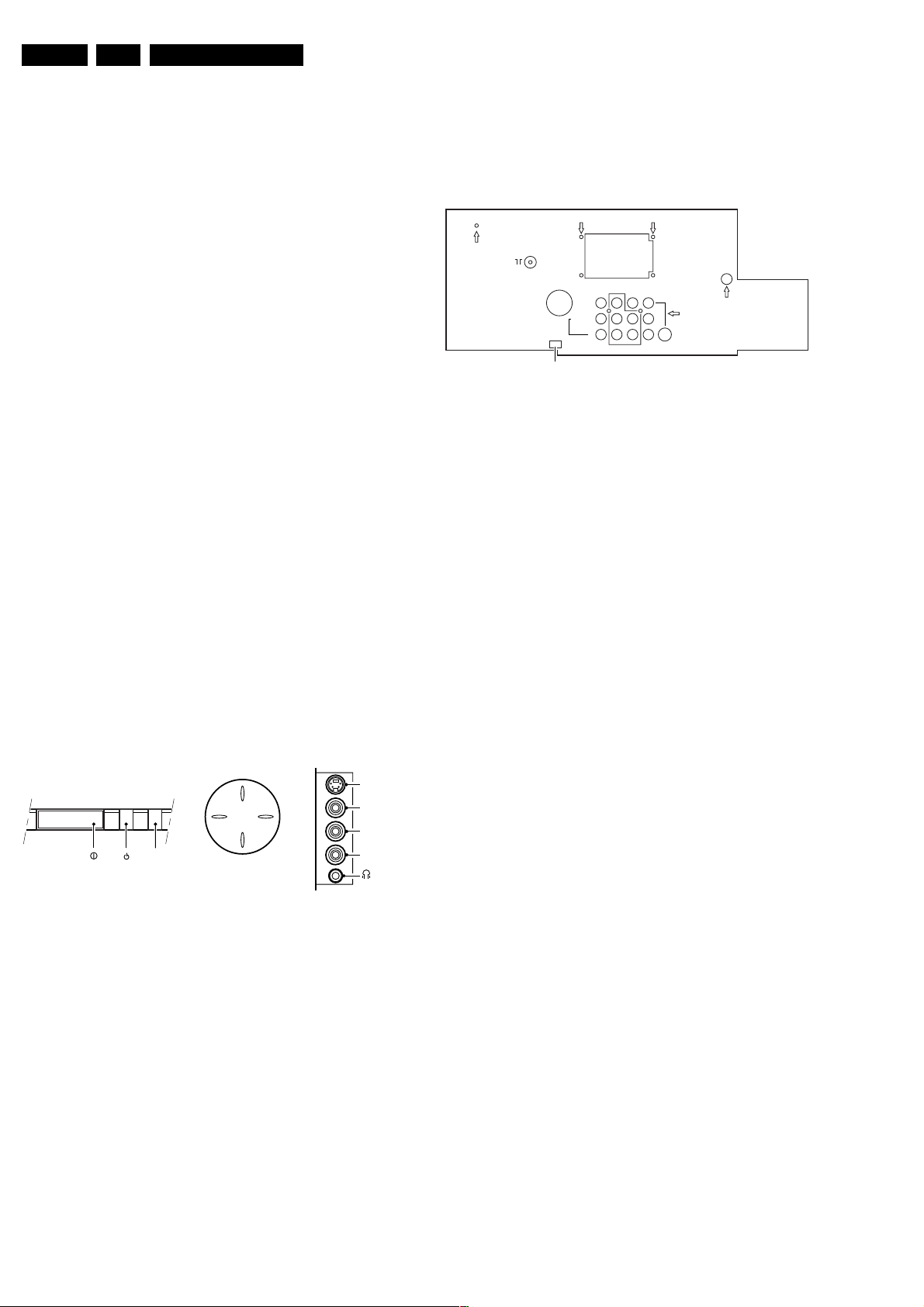
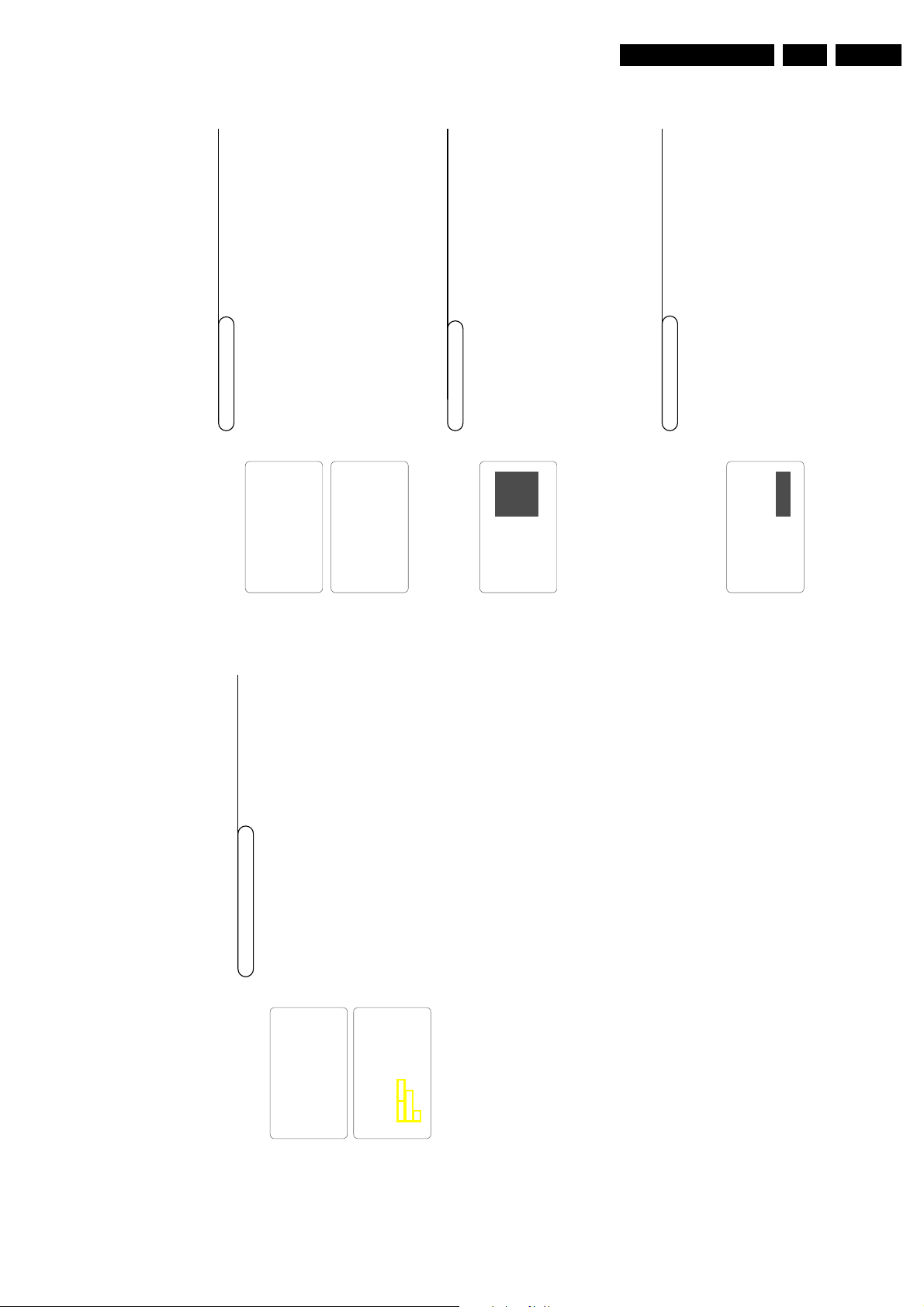
1.2.2 Rear connections
75Ω
MONITOR
OUT
VIDEO
L/MONO
AUDIO
R
COMPONENT VIDEO INPUT
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
Figure 1-2
Monitor out
1 - Video 1 Vpp / 75 Ω
2 - Audio L (0.5 Vrms / 10 kΩ)
3 - Audio R (0.5 Vrms / 10 kΩ)
AV1 in
1 - Y 0.7 Vpp / 75 Ω
2 - Pb 0.7 Vpp / 75 Ω
3 - Pr 0.7 Vpp / 75 Ω
AV1 in
4 - Video 1 Vpp / 75 Ω
5 - Audio L (0.5 Vrms / 10 kΩ)
6 - Audio R (0.5 Vrms / 10 kΩ)
AV1
AV2
IN
IN
Y
Pb
Pc
S-VIDEO
CL 06532130_001.eps
021000
kq
kq
q
jq
jq
jq
jq
jq
jq
1.2 Connection facilities
1.2.1 Control buttons & Side I/O connections
TOP CONTROL
P+
V+V-
IR
RED
Figure 1-1
SVHS
1 - gnd
2 - gnd
3 - Y 1 Vpp / 75 Ω
4 - C 0.3 Vpp / 75 Ω
Audio / video
1 - Video 1 Vpp / 75 Ω
2 - Audio L (0.2 Vrms / 10 kΩ)
3 - Audio R (0.2 Vrms / 10 kΩ)
4 - Headphone 32 - 2000 Ω / 10 mW
P-
SIDE I/OFRONT CONTROL
S-Video
Video
L
Audio
R
CL 06532130_002.eps
031000
j
j
jq
jq
jq
rt
v
v
AV2 in
1 - Video 1 Vpp / 75 Ω
2 - Audio L (0.5 Vrms / 10 kΩ)
3 - Audio R (0.5 Vrms / 10 kΩ)
AV2 in (SVHS)
1 - gnd
2 - gnd
3 - Y 1 Vpp / 75 Ω
4 - C 0.3 Vpp / 75 Ω
jq
jq
jq
v
v
j
j
Technical specifications, connection facilities & chassis overview
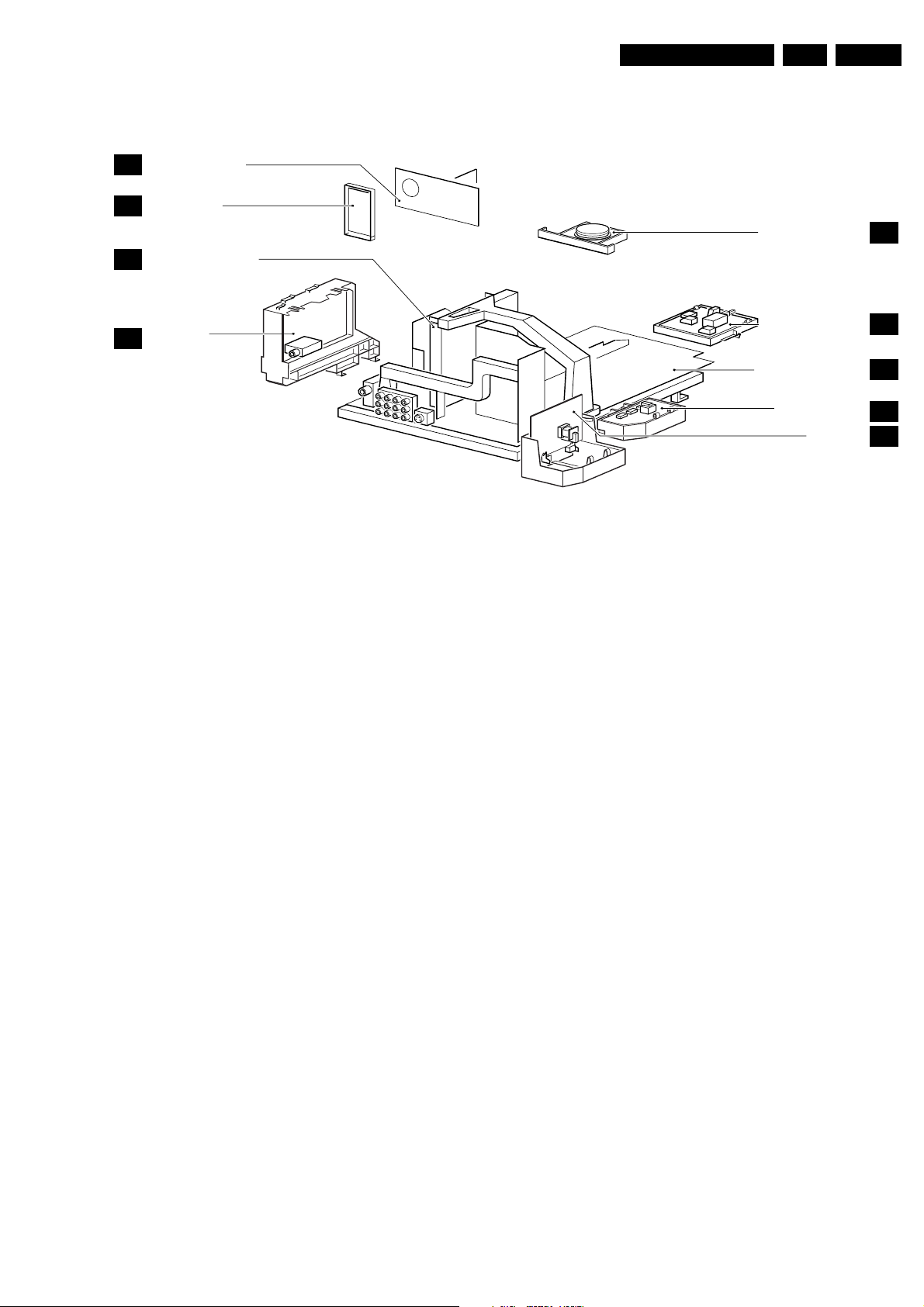
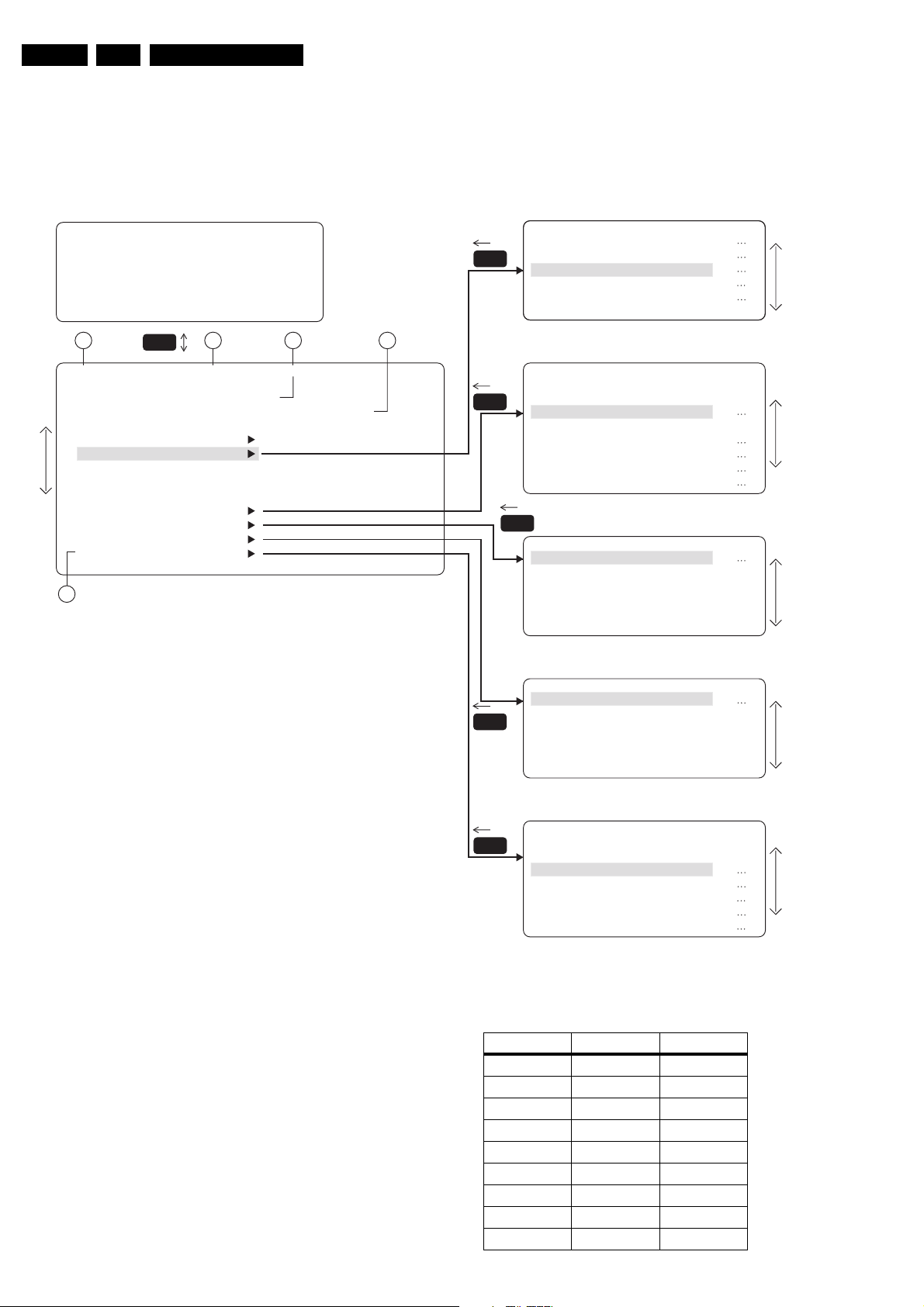
1.3 Chassis overview
CRT/SCAVEM PANEL
F
SIDE I/O PANEL
D
SMALL SIGNAL BOARD
B
TOP CONTROL PANEL
GB 3EM1A 1.
E
PIP/DOUBLE
C
WINDOW PANEL
Figure 1-3
MAINS SWITCH PANEL
LARGE SIGNAL PANEL
MAINS HARMONIC
PANEL
DAF PANEL
CL 06532130_003.eps
J
A
Y
I
181000
GB 4 EM1A2.
Safety & maintenance instructions, warnings and notes
2. Safety & maintenance instructions, warnings and notes
2.1 Safety instructions for repairs
Safety regulations require that during a repair:
• Safety components, indicated by the symbol ∆, should be
replaced by components identical to the original ones;
• When replacing the CRT, safety goggles must be worn.
Safety regulations require that after a repair, the set must be
returned in its original condition. In particular attention should
be paid to the following points:
• General repair instruction: as a strict precaution, we
advise you to resolder the solder joints, through which
the horizontal deflection current is flowing, in particular:
– All pins of the line output transformer (LOT);
– Fly-back capacitor(s);
– S-correction capacitor(s);
– Line output transistor;
– Pins of the connector with wires to the deflection coil;
– Other components through which the deflection
current flows.
Note: This resoldering is advised to prevent bad connections
due to metal fatigue in solder joints and is therefore only
necessary for television sets older than 2 years.
• The wire trees and EHT cable should be routed correctly
and fixed with the mounted cable clamps.
• The insulation of the mains lead should be checked for
external damage.
• The mains lead strain relief should be checked for its
function in order to avoid touching the CRT, hot
components or heat sinks.
• The electrical DC resistance between the mains plug and
the secondary side should be checked (only for sets
which have a mains isolated power supply). This check
can be done as follows:
– Unplug the mains cord and connect a wire between
the two pins of the mains plug;
– Set the mains switch to the 'ON' position (keep the
mains cord unplugged!);
– Measure the resistance value between the pins of
the mains plug and the metal shielding of the tuner or
the aerial connection on the set. The reading should
be between 4.5 MΩ and 12 MΩ.
– Switch off the TV and remove the wire between the
two pins of the mains plug.
• The cabinet should be checked for defects to avoid
touching of any inner parts by the customer.
2.2 Maintenance instructions
2.3 Warnings
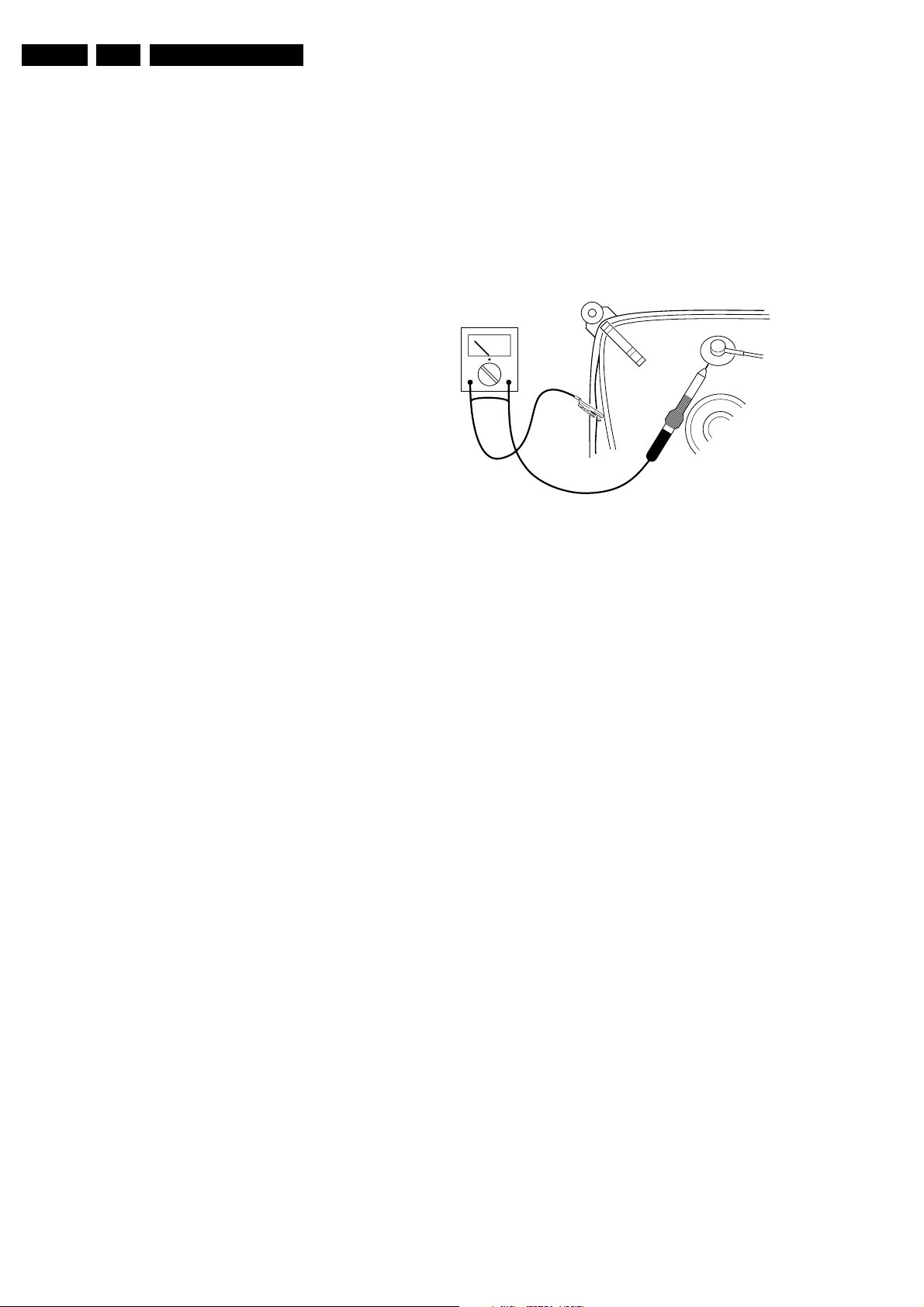
• In order to prevent damage to IC's and transistors, all
high-voltage flashovers must be avoided. In order to
prevent damage to the picture tube, the method shown in
Fig. 2-1 should be used to discharge the picture tube.
Use a high-voltage probe and a multimeter (position
VDC). Discharge until the meter reading is 0 V (after
approx. 30 s).
V
Figure 2-1
• All IC's and many other semiconductors are susceptible
to electrostatic discharges (ESD). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. When repairing,
make sure that you are connected with the same
potential as the mass of the set by a wristband with
resistance. Keep components and tools also at this same
potential. Available ESD protection equipment:
– Complete kit ESD3 (small table mat, wristband,
connection box, extension cable and earth cable)
4822 310 10671.
– Wristband tester 4822 344 13999.
• Together with the deflection unit and any multipole unit,
the used flat square picture tubes form an integrated unit.
The deflection and the multipole units are set optimally at
the factory. Adjustment of this unit during repair is
therefore not recommended.
• Be careful during measurements in the high-voltage
section and on the picture tube.
• Never replace modules or other components while the
unit is switched ON.
• When making settings, use plastic rather than metal
tools. This will prevent any short circuits and the danger
of a circuit becoming unstable.
CL 26532098/042
140792
It is recommended to have a maintenance inspection carried
out by a qualified service employee. The interval depends on
the usage conditions:
• When the set is used under normal circumstances, for
example in a living room, the recommended interval is 3
to 5 years.
• When the set is used in circumstances with higher dust,
grease or moisture levels, for example in a kitchen, the
recommended interval is 1 year.
• The maintenance inspection contains the following
actions:
– Execute the above-mentioned 'general repair
instruction'.
– Clean the power supply and deflection circuitry on
the chassis.
– Clean the picture tube panel and the neck of the
picture tube.

2.4 Notes
Safety & maintenance instructions, warnings and notes
GB 5EM1A 2.
• The direct voltages and oscillograms should be
measured with regard to the tuner earth (
(
) as this is called.
I
• The direct voltages and oscillograms shown in the
diagrams are indicative and should be measured in the
Service Default Mode (see chapter 5) with a colour bar
signal and stereo sound (L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated
otherwise) and picture carrier at 475.25 MHz.
• Where necessary, the oscillograms and direct voltages
are measured with (
Voltages in the power supply section are measured both
for normal operation (
values are indicated by means of the appropriate
symbols.
• The picture tube PWB has printed spark gaps. Each
spark gap is connected between an electrode of the
picture tube and the Aquadag coating.
• The semiconductors indicated in the circuit diagram and
in the parts lists are completely interchangeable per
position with the semiconductors in the unit, irrespective
of the type indication on these semiconductors.
• DOLBY, the double D symbol and PRO LOGIC are
trademarks of Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corporation.
Manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories
Licensing Corporation.
) and without (E) aerial signal.
D
) and in Standby (F). These
G
), or hot earth
H
GB 6 EM1A3.
2
A/CH
MENU SURF
SMARTSMART
CH
V
¬
i
bh
f◊
h
î
gU
XC
5
1
3
2
4
6
7
9
8
0
AV
PIP
PIP CH
UP DN
ACTIVE CONTROL
PROGRAM LIST
DOLBY V.
D
æ
q©
ßê
S
M
a
B
Sleep
D
Allows you to select a time period after which
the set will switch to standby mode
automatically.
Standby
B
• Switch set off temporarily to standby mode.
(The red light indicator lights up when set is
on standby mode).
• To switch on set from standby mode, press
button again.
(Alternate Channel)
A/CH
Allows you to alternate between the last
viewed channel and the present channel.
PIP (Picture in Picture)/Dual Window On/Off
æ
ßê©
PIP CH UP/DOWN
(if provided) See p. 12
Freeze
S
Allows you to freeze the main picture.
Screen format
q
Press this key repeatedly to select another
screen format:Auto, 4:3, Expand 4:3 and
Compress 16:9. See also p. 11.
Digit
(0-9)
Allows you to select a channel.
Note: For a 2-digit number,the second digit
must be entered before the “-”sign disappears.
Smart Sound
M
Allows you to select your desired sound setting
from 4 types of sound settings.
Press the key repeatedly to select the different
settings.
Smart Picture
a
Allows you to select 5 types of picture settings.
Press the key repeatedly to select the different
settings.
Preparation
Your remote control
DOLBY V
◊
Dolby Virtual (with Dolby Surround signals)
Dolby Virtual (Virtual Dolby Surround) enables you to experience the effect
of Dolby Pro Logic Surround,reproducing a rear sound effect.
Incredible Surround
In
Stereo
sound mode, when
Incredible Surround
is selected, it seems as
though the loudspeakers are spread further apart from one another.
In
Mono
sound mode, this feature,when switched on, enables you to hear
a spatial effect of sound.
Active Control On/Off
h
Measures and corrects all incoming signals in order to provide the best picture
quality settings. Press to select the Active Control values On or Off.
ON: Sharpness and Noise Reduction are controlled automatically.The Picture
settings are being adapted continuously and automatically. The menu items cannot
be selected.
PROGRAM LIST
î
Allows you to navigate through a list of installed programmes for a quick overview
of the channels and activate the channel you have selected.
MENU
Displays main menu.
Also exits the menu from the screen or returns
to a higher menu level.
SURF
Allows you to select up to a maximum of 10
favourite channels or sources and view quickly
the selected channels or sources.
To add a new channel or source:
• Select the channel number or source you
want to add to the surf list.
• Press the SURF key.
The request ADD? appears next to the
selected channel number or source.
• Press the cursor right to add.
To delete a channel or source:
• Select the channel number or source you
want to remove from the surf list.
• Press the SURF key.
The request DELETE? appears next to the
selected channel number or source.
• Press the cursor right to delete.
Press the SURF key repeatedly to scroll
through the selected channels or sources.
Cursor
Up/Down: allows you to select the next or
previous item on the menu and to
select another picture format
Left/Right:
allows you to access the sub-menus
and adjust the settings.
V
Volume
+/-
Increases or decreases volume.
¬
Mute
Mutes the sound.To restore the sound,press
the button again.
CH +/-
Selects channels in ascending or
descending order.
AV
Allows you to select the AV channels.
i
On Screen Display
• Displays the channel number, sound
transmission mode, the clock and the status
of the sleeptimer.
• Also allows you to exit menu from screen.XAllows you to switch from Stereo to Mono
sound during stereo transmission or to choose
between Language Y or Language Z during
dual sound transmission.
C
Timer
Allows you to set the clock to switch to
another channel at a specified time while you
are watching another channel or when the
set is on standby mode.
Colour keys,
bhUf
Teletext
(if provided) See p. 13
Allows you to access teletext information.
g
for future use
A/CH
MENU
SURF
SMARTSMART
CH
V
¬
i
i
bhgU
XC
5
1
3
2
4
6
7
9
8
0
AV
VIDEO MOVIES
PIP
PIP CH
UP DN
D
æ
q©
ßê
S
M
a
B
3. Directions for use
Directions for use
Installation
MENU
Press the
&
Use the cursor in the up/down directions to select a menu item.
Note: Sometimes not all the menu items are visible on the screen;press the cursor
é
down until all the items are displayed.“Use the cursor in the left/right directions to access the sub-menu and to
To use the menus
key to display/cancel the main menu.
adjust the settings.
Press the menu key to return.(Press the i key to switch the menu off.
‘
select menu
return
PICTURE
SOUND
item
switch
menu off
FEATURES
INSTALL
Note: If no action is executed, the menu automatically disappears after about 12
seconds.
key.
MENU
Press the
First, select your language.
&
Select the menu language
Store TV channels
PICTURE
SOUND
FEATURES
INSTALL
.
LANGUAGE
with the cursor down.
INSTALL
Select
é
key to return to the main menu.
MENU
Press the cursor right to select
Press the cursor right again.
Select your language with the cursor up/down.§Press the
“
‘
(
LANGUAGE
AUTO STORE
MANUAL STORE
SORT
CHANNEL EDIT
INSTALL
NAME
From now onwards, all on-screen displays will appear in the language that you
have chosen.
You can now search for and store the TV channels in two different ways: using
Auto store or Manual store (tuning in channel by channel).
key to return to the
MENU
menu.
INSTALL
in the
menu or press the i key to switch the menu off.
AUTO STORE
Select
&
Automatic tuning of channels
Press the cursor right to start the searching.
All TV channels are searched for and stored automatically.“When the tuning is completed, press the
é
INSTALL
SORT
CHANNEL EDIT
NAME
LANGUAGE
AUTO STORE
MANUAL STORE
INSTALL
Note: Channel numbers will always be written in Latin characters, even when a
language has been selected which uses other characters.
Installation
4
Directions for use
6
Installation
Sorting of channels
According to your preference you can change the order of the stored TV
channels.
&
Select
SORT
in the
INSTALL
menu.
é
Press the cursor right to enter the menu.“Key in the channel number in the
FROM
column you want to swap from. Use
the digit keys or the cursor left/right.
‘
Press the cursor down and select
TO
.
(
Key in the channel number in the
TO
column you want to swap to.
§
Press the cursor down and select
EXCHANGE
.
è
Press the cursor right.
The message
EXCHANGED
appears and the selected channels are exchanged.
!
Repeat steps
“
to
è
until all TV channel are allocated as you like.
ç
Press the
MENU
key to return to the
INSTALL
menu or press the i key to
switch menu off.
This feature allows you to edit or skip channels from the channel list which
have bad or weak signals or channels which you do not watch often.
Note: Once a channel is skipped, you cannot select it with the
CH -
or
+
key.
You can only access the channel with the digit keys.
&
Select
CHANNEL EDIT
in the
INSTALL
menu.
é
Press the cursor right to enter the channel list.
“
Select the channel you want to skip with the cursor up/down.‘Press the cursor right to skip the selected channel.
The message
SKIPPED
is displayed.
(
Press the cursor up/down to select another channel and repeat step
‘
.
§
Press the cursor left or the
MENU
key to return to the install menu or the
i key to switch menu off.
Note: to add back channels to the list, repeat steps
&
to
‘
and press the
i key to switch menu off.
Editing of channels
It is possible to assign a name to a TV channel.This feature allows you to
enter a new name or modify an existing name of a channel, including
peripherals.
Note: Even when you have selected another language in the language menu, only
the English language character set is offered to enter names to the TV channels
stored.
&
Select a TV channel or peripheral you want to assign a name or modify the
existing name.éSelect
NAME
in the
INSTALL
menu.
“
Press the cursor right to enter the menu.‘Key in the selected character with the cursor up/down.(Move to the next character with the cursor right and key in the next
character.You can key up to a maximum of 5 characters.
§
Press the
MENU
key to store the named channel.
Naming of channels
INSTALL
LANGUAGE
AUTO STORE
MANUAL STORE
SORT
CHANNEL EDIT
NAME
INSTALL
LANGUAGE
AUTO STORE
MANUAL STORE
SORT
CHANNEL EDIT ƒ
NAME
SORT
FROMTOEXCHANGE/EXCHANGED
34567 SKIPPED
INSTALL
LANGUAGE
AUTO STORE
MANUAL STORE
SORT
CHANNEL EDIT
NAME
CNN
GB 7EM1A 3.
Manual tuning of channels
menu.
INSTALL
in the
MANUAL STORE
Manual tuning allows you to store channel by channel.
You must go through every step of the manual store menu.&Select
LANGUAGE
AUTO STORE
MANUAL STORE
SORT
INSTALL
and press the cursor right.
is selected, the respective colour system will be automatically
COLOUR SYSTEM
AUTO
If
selected according to the transmission system.
Press the cursor right to enter the menu.“Select
é
If the reception is poor, select another colour system with the cursor up/down.
CHANNEL EDIT
NAME
COLOUR SYSTEM
SOUND SYSTEM
MANUAL STORE
and press the cursor right.
key or the cursor left.
MENU
is selected, the respective sound system will be automatically
SOUND SYSTEM
AUTO
selected according to the transmission system.
If
Press the
Select
‘
(
SEARCH
CHANNEL
STORE/STORED
FINE TUNE
PLL
key or the cursor left.
and press the cursor left or right to start the searching.
MENU
SEARCH
Note: If the reception is poor,select another sound system with the cursor up/down.
Searching stops once a transmitting channel is found.
Note: If the reception is poor, select another colour and/or sound system.
Press the
Select
§
è
.
CHANNEL
Select
Key in the desired channel number with the digit keys or with the cursor
!
ç
left/right.0Press the cursor down.
and press the cursor left/right to adjust.
FINE TUNE
In case of poor reception, you can improve the reception by adjusting the
frequency.1Select
In rare cases certain TV channels may reproduce distorted or unstable
pictures.
2
menu or press the i key to
.
STORE
(Phase Locked Loop) to switch to the setting 2 with the cursor
PLL
left/right to restore the picture for the respective transmission.
Select
Press the cursor down to select
Press the cursor right.
3
4
INSTALL
to continue searching for another transmitting
4
to
appears and the search menu item is highlighted again.
è
key to return to the
STORED
MENU
switch menu off.
channel.
The message
Now repeat steps
Press the
5
6
5
Installation
GB 8 EM1A3.
16
Connect Peripheral Equipment
75
CABLE
VCR
AV 2
in
AV 1
in
Monitor
out
COMPONENT VIDEO INPUT
VIDEO
L/Mono
R
Y
Pb
Pr
AUDIO
S-VIDEO
OUT
OUT
OUT IN
j x
4
1
3
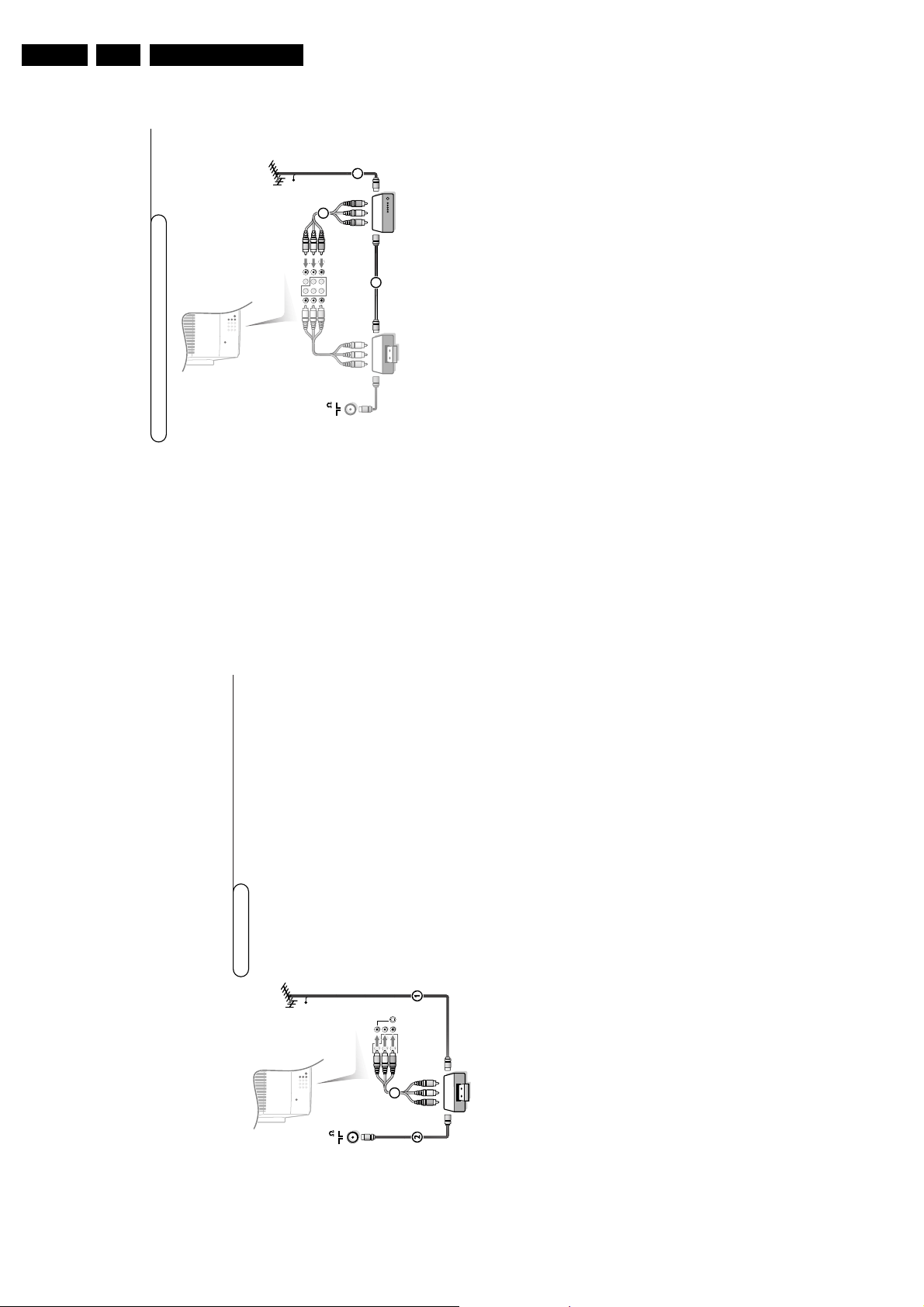
Video recorder and other A/V peripherals
&
Interconnect your video recorder with extra RF cables 3.éTo obtain better picture quality, also connect the Video,Audio left and Audio
right (only for stereo equipment) cables to the
VIDEO
,
AUDIO L/
Mono and
AUDIO R
input of
AV2 IN
sockets 4.
Note: in case of mono equipment, only the left loudspeaker reproduces sound.
Use a mono to stereo adaptor (not supplied) for sound reproduction via all
internal loudspeakers.
When a video recorder is not connected to
MONITOROUT
you can only record a
programme from the aerial or from the cable system.
Only when a video recorder is connected to
MONITOROUT
it is possible to record a
programme from other equipment connected to the TV. See Record with your video
recorder, p.18.
CABLE
VCR
75
OUT
j x
AV 2
in
AV 1
in
Monitor
out
COMPONENT VIDEO INPUT
VIDEO
L/Mono
R
Y
Pb
Pr
AUDIO
S-VIDEO
3
Directions for use
There is a wide range of audio and video equipment that can be connected
to your TV.The following connection diagrams show you how to connect
them.
Video recorder
Connect Peripheral Equipment
Connect the RF cable 1 to the RF socket x of your video recorder.éConnect another RF cable 2 from the output j of your video recorder to
&
15
,
VIDEO
input instead of connecting the video
.
AV2 IN
input
R
Mono and
Use a mono to stereo adaptor (not supplied) for sound reproduction via all
internal loudspeakers.
Better playback quality can be obtained if you also connect the Video,Audio
Left and Right (only for stereo equipment) cables 3 to the
Note: in case of mono equipment, only the left loudspeaker reproduces sound.
AUDIO L/
the input x of your TV.
connectors can be used for daisy chaining or to record
MONITOR OUT
The
programmes from your TV. See Record with your video recorder, p. 18.
S-VIDEO
input. (See the instructions of your video recorder.)
cable with the
VIDEO
quality with a S-VHS video recorder is obtained by connecting
S-VHS-Video
recorder to the
the
S-VHS-Video
If the cables 3 are not used the following steps are required:
Search for and store the test signal of the video recorder
Unplug the RF cable 1 from the RF socket x of your video recorder.éSwitch on your TV and put the video recorder on the test signal or play a
&
prerecorded tape (See the handbook for your video recorder.).“Search for the test signal of your video recorder in the same way as you
searched for and stored the TV signals. See Installation, Store TV Channels,
Manual Tuning, p. 5.‘Store the test signal under programme number 0 or between 90 and 99.
Replace the RF cable in the RF socket x of your video recorder after
(
Connect Peripheral Equipment
you have stored the test signal.
Directions for use
18
Record
Equipment connected with an aerial cable only :
Select the channel number under which you have stored the test signal with
the digit keys.
Equipment connected to the back or to the right side of the TV
Press the
AV
key repeatedly to select
AV1
,
CVI
,
AV2
or
FRONT
, according to
where you connected your equipment at the back or the right side of your
TV.
Select
CVI
to view the playback of DVD discs if you used the Component
Video Input sockets (
Y-Pb-Pr
and
AUDIO L
/
Mono
and
R
inputs).
If you want to change to TV channels?
Enter the channel number of the TV channel which you want to watch with
the digit keys.
To select connected equipment
A/CH
AV
MENU
SURF
SMARTSMART
CH
V
¬
i
bh
f◊
h
gU
XC
5
1
3
2
4
6
7
9
8
0
AV
PIP
PIP CH
UP DN
DOLBY V.
ACTIVE CONTROL
PROGRAM LIST
D
æ
q©
ßê
M
a
B
S
To record S-VHS quality, connect an S-VHS peripheral directly to the video
recorder.
Record a TV programme&Select the channel number on your video recorder.éSet your video recorder to record.
See the handbook for your video recorder.
Switching channel numbers on your TV does not disturb recording !
Record a programme on your video recorder connected to
MONITOR OUT
from Audio/Video equipment connected to
AV1,AV2
or to sockets on the right side of the TV
&
Switch on the equipment.
é
Select the correct external on your TV and on your video recorder.“Set your video recorder to record.
You record what you are watching on the screen.
Do not switch channel numbers or do not switch off your TV when you are recording !
Record with your video recorder
L
A
U
D
IO
V
ID
E
O
S
•V
ID
E
O
3
2
1
AV 2
in
AV 1
in
Monitor
out
COMPONENT VIDEO INPUT
VIDEO
L/Mono
R
Y
Pb
Pr
AUDIO
S-VIDEO
1 2
DVD
GB 9EM1A 3.
1 for mono
AUDIO L
2 and
VIDEO
equipment.
Connect your camera or camcorder to sockets at the right side of your TV.éConnect the equipment to
&
Camera & camcorder
AUDIO
2) and
VIDEO
1.
AUDIO R
input 3 (instead of
S-VIDEO
S-VHS quality with an S-VHS camcorder is obtained by connecting the S-VHS
cables with the
For stereo equipment also connect
inputs 1.
“
DVD-player
input
Y-Pb-Pr
.
VIDEO
input.
R
Mono and
in sockets on the TV.
(See the handbook of your DVD player.)
For correct picture reproduction also connect to
Connect the cables of your Y-Pb-Pr DVD player 1 to the
AV1
Connect the Audio left and right (only for stereo equipment) cables to the
AUDIO L/
&
é
Insert the plug into the headphone socket L at the right side of the TV.éPress ¬ on the remote control to switch off the internal loudspeakers
&
Headphone
17
to adjust the headphone volume and
Headphone
Connect Peripheral Equipment
menu select
SOUND
of the TV.
balance.
The headphone impedance must be between 8 and 4000 Ohm.
The headphone socket has a 3.5 mm jack.
In the
GB 10 EM1A3.
Directions for use
Personal notes:
Using a highly directional antenna may improve the picture .
Then re-insert the plug into the mains socket and turn on the television again.
Items to Check and Actions to follow
• This may be caused by obstruction to the antenna due to high rise buildings or hills.
• Check that the television's AC power cord is plugged into the mains socket.
• Unplug the television, wait for 60 seconds.
• Check the antenna connection at the rear of the television to see if it is properly connected to the
television input terminal.
• Possible broadcast station trouble. Try another channel.
• Adjust the contrast and brightness settings or select another picture setting with the smart picture key.
• Increase the VOLUME.
• Check that the television is not muted, press the ¬ button on the remote control.
• When no signal is detected, the television automatically switches off the sound.
This is proper operation and does not indicate a malfunction.
• Check the transmission system’s sound settings of this set.
connected to the right side of of your TV and another peripheral is connected to AV1 or AV2 at the
• Adjust the contrast and brightness setting or select another picture setting with the smart picture key.
same time. In this case, switch off one of the other peripherals.
• Check the transmission system’s colour settings of this set.
• Sometimes, poor picture quality occurs when having activated an S-VHS camera or camcorder
• Check the antenna connection.
• This may be caused by electrical interference (e.g. hairdryer, nearby neon lights,etc.)
• Turn off the equipment.
• Turn off the television immediately and consult a qualified service personnel.
• Check whether the batteries are working. Replace if necessar y.
• Clean the remote control sensor lens on the television.
• Operating range between television and the remote control should not be more than 6 meters.
• You can still use the keys at the top of your TV.
• This could be due to antenna siting or reflected signal.
• Switch over to “MONO” mode by pressing the X key.
• Press the i key again to exit from the menu.
19
Before Calling Service
Before Calling Service
Please make these simple checks before calling service.These tips may save you time and money since charges for television installation and
adjustments of customer controls are not covered under your warranty.
Symptoms
“Ghost” or double images
No power
No picture
Good picture but no sound
Good sound but poor
colour or no picture
Poor picture
Snowish picture and noise
Horizontal dotted line
One white line across the
screen
Television not responding to
remote control
NICAM sound distortion
(crackling noise)
Wrong menu
If your problem is not solved
Turn your TV off and then on again once.
Never attempt to repair a defective TV yourself.
Check with your dealer or call a TV technician.
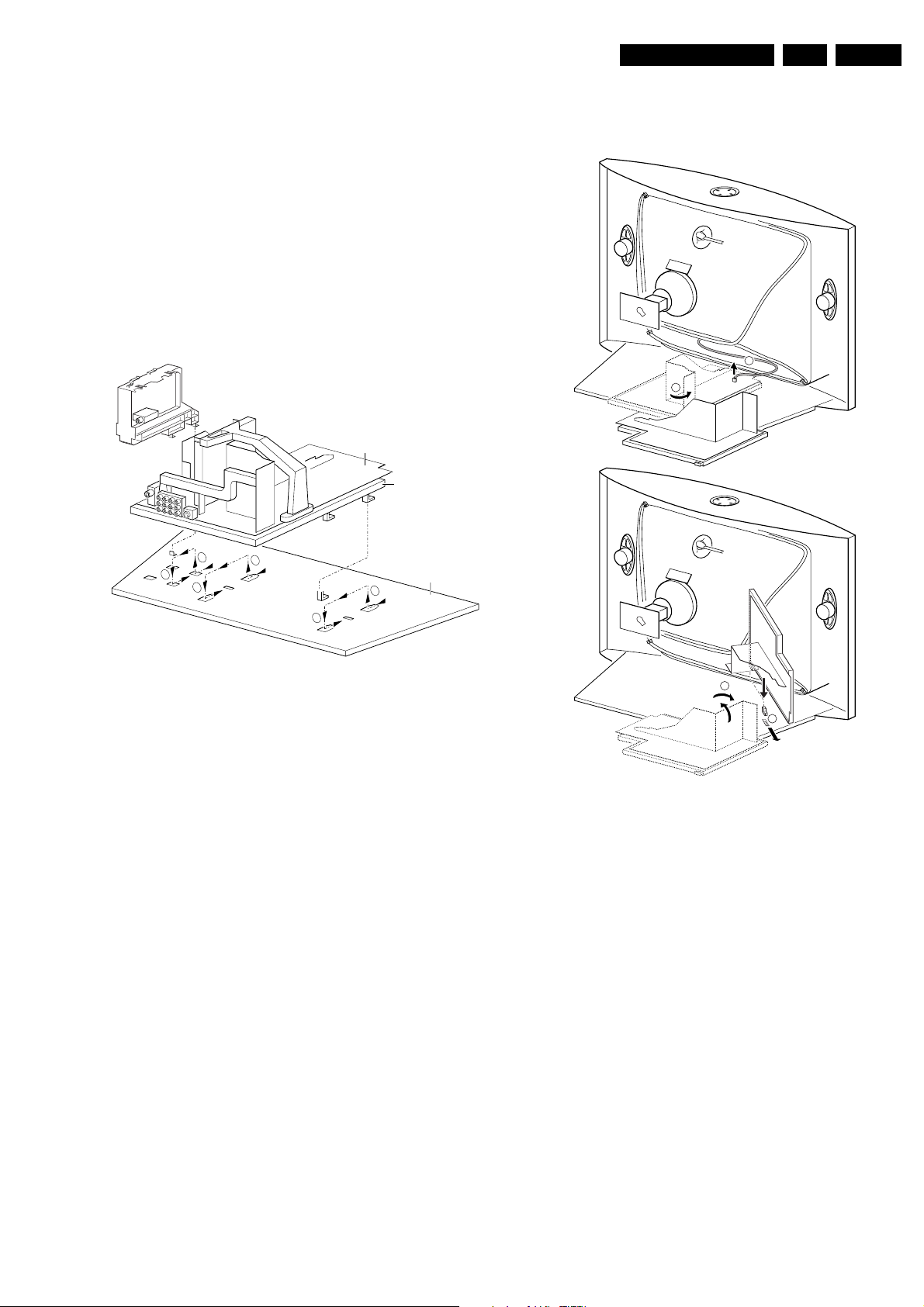
4. Mechanical instructions
4.1 Removing the Rear Cover
1. Remove all the fixation screws of the rear cover.
2. Now the rear cover can be removed by pulling it
backward.
4.2 Service positions
4.2.1 Service position LSP
Position 1: For better accessibility of the LSP, do the
following:
SSB
LSP
LSP - bracket
Mechanical instructions
GB 11EM1A 4.
1
2
A
3
4
2
1
1
2
Bottom tray
CL 06532130_004.eps
031000
Figure 4-1
1. Remove the LSP-module from the bottom tray by pulling
the complete module back- and then upward.
2. Hook the bracket in the first row of fixation holes of the
cabinet bottom. In other words reposition the bracket
from [1] to [2].
3. The same can be done with the DW-module (position [3]
to [4]).
Position 2: This service position is comparable to that of the
A10A. To get access to the bottom side (solder side) of the
LSP, do the following:
3
4
CL 06532130_006.eps
B
121000
Figure 4-2
1. Disconnect the CRT/SCAVEM panel from the CRTsocket.
2. Release LSP and DW-module, and pull backward.
3. Remove Mains switch module from bottomplate (see
description below).
4. Free the necessary wiring from their fixation clamps, for
the ease of handling.
5. Sometimes a cable must be disconnected for the ease of
handling, like the degaussing coil (0020) and
loudspeaker (1735, 1736 & 1737) cables.
6. Now reposition following modules, in order to cope with
the LSP service position:
– DAF-module from the LSP-bracket by pressing lever
while pushing the module forward in the direction of
the CRT (see also description below).
– Mains Harmonic module from the LSP-bracket by
removing 1 screw and then slide the module
backward, away from the CRT (see also description
below).
7. Turn the chassis tray 90 degrees counter clockwise (see
figure 4.2 - [2]).
8. Flip the chassis tray with the rear I/O panel towards the
CRT [3].
9. Place the hook of the tray in the fixation hole at the right
side of the cabinet bottom and pull the chassis tray
backward [4].
GB 12 EM1A4.
Mechanical instructions
10. Reconnect cables (except degaussing cable 0020),
panels and modules.
Alternative position 2: A somewhat easier way to access the
bottom side (solder side) of the LSP is the following (only
possible when the high tension cable is long enough):
2
1
1
3
A
Figure 4-3
1. Disconnect the CRT/SCAVEM panel from the CRTsocket.
2. Release LSP and DW-module, and pull backward.
3. Remove Mains switch module from bottomplate (see
description below).
4. Free the necessary wiring from their fixation clamps, for
the ease of handling.
5. Sometimes a cable must be disconnected for the ease of
handling, like the degaussing coil (0020), loudspeaker
(1735, 1736 & 1737) cables and 0325 (frame deflection).
6. Now reposition following modules, in order to cope with
the LSP service position:
– DAF-module from the LSP-bracket by pressing lever
while pushing the module forward in the direction of
the CRT (see also description below).
– Mains Harmonic module from the LSP-bracket by
removing 1 screw and then slide the module
backward, away from the CRT (see also description
below).
7. Flip the chassis tray 90 degrees clockwise [2].
8. Place the hook of the tray in fixation hole [A] of the
cabinet bottom and pull the chassis tray backward [3].
9. Reconnect the cables (except degaussing cable 0020),
panels and modules.
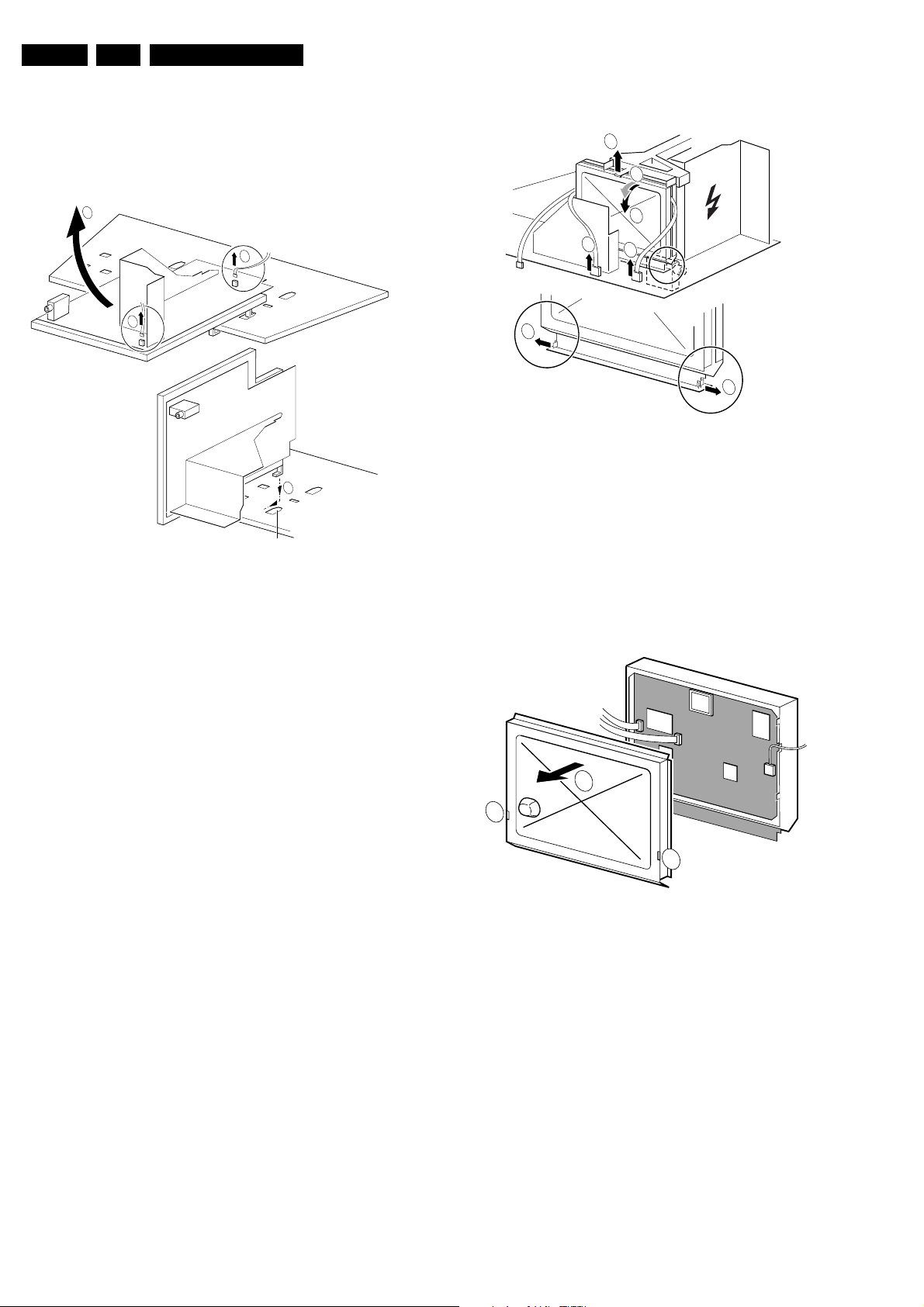
4.2.2 Service position SSB
All relevant test points can be accessed with the SSB in
original position, but for ease of use a 'SSB extension board'
is available under number 9965 000 05769.
Before usage of this board, the 'LSP top-bracket' has to be
taken out. This can be done by:
1. Remove the DAF panel (see 4.2.5).
2. Remove the 2 screws which hold the bracket at the right
side.
3. Lift the bracket at the same side. It hinges at the cooling
plate.
Note: For some type numbers, the LSP has to be moved
slightly to the right side in order to create enough space for
the SSB extension board.
CL 06532130_007.eps
131000
To get access to the test points of the SSB, the shielding has
to be removed:
2
3
5
11
1
FROM
PIP/DW MODULE (0205)
4
0948
0946
4
CL 06532130_008.eps
131000
Figure 4-4
1. Put the LSP in service position 1 (as described above).
2. If a PIP/DW module is present, then disconnect the IFcable from connector 1946, flatcable from connector
1948 and flatfoil on DW-module connector 0205 [1].
3. Release the 'top fixation clamp' which holds the SSB [2]
and pull the SSB slightly towards the Tuner [3]. At the
same time, the 2 metal clamps at both sides of the SIMMconnector must be released [4] . The complete SSB can
be taken out now by pulling the topside of the SSB
towards the Tuner [5]. It 'hinges' in the SIM-connector.
2
1
1
CL 06532130_009.eps
Figure 4-5
1. Once the SSB has been taken out of the connector, the
shielding can be removed.
2. After removal of the shielding, the panel can be replaced
in its connector in reverse order. Don't forget to
reconnect the cables.
3. If necessary for the measurement, the LSP can be put in
'service position 2' (as described above).
031000
Mechanical instructions
GB 13EM1A 4.
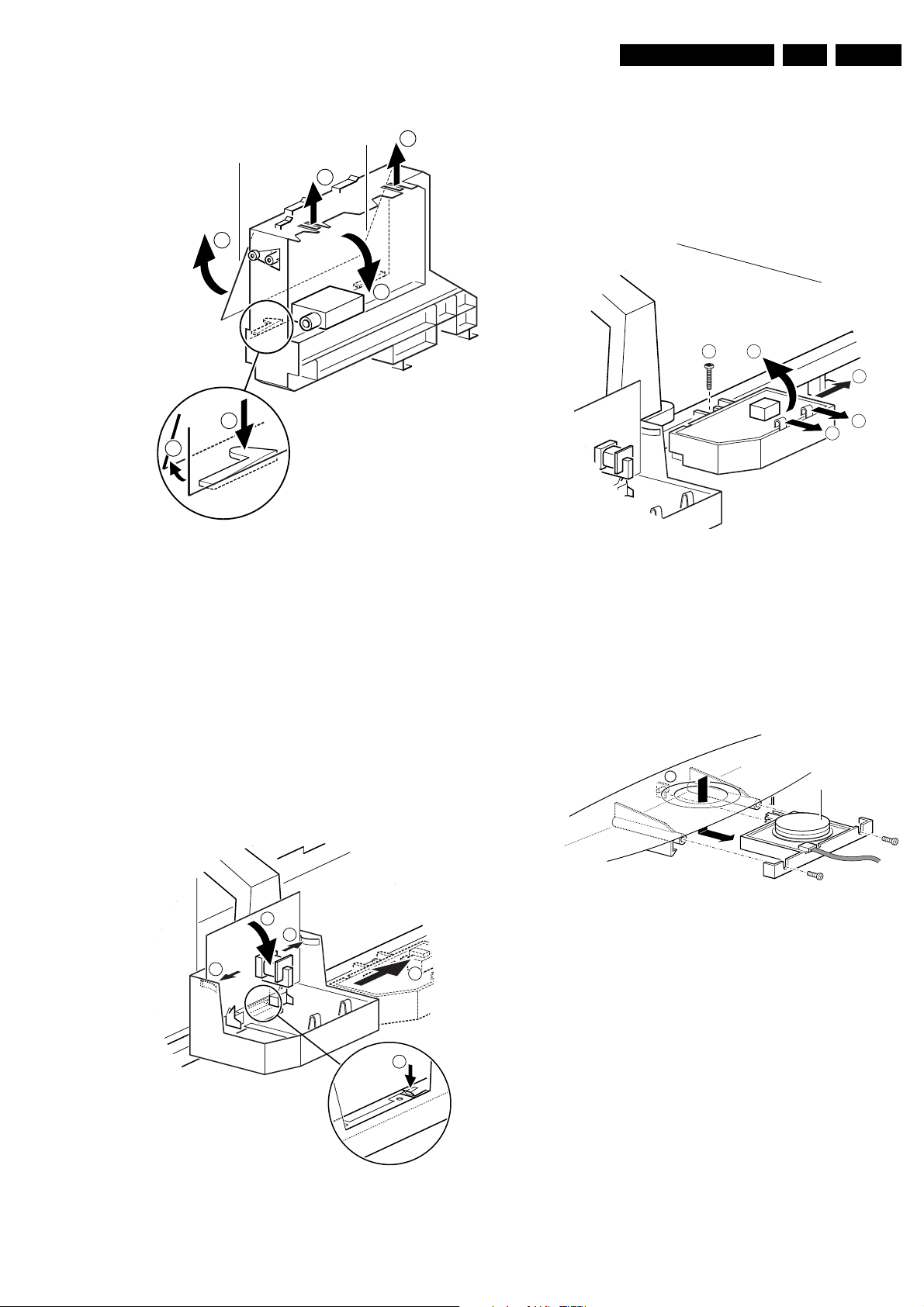
4.2.3 Accessing the Double Window (DW) panel
PIP/Double Window
1
Multi Voltage
1
4
2
3
4
CL 06532130_015.eps
Figure 4-6
1. Remove the DW bracket from the bottom tray by pulling
it backward (after pressing the fixation clamp).
2. The board can easily be lifted out of the bracket [2] after
releasing the 2 fixation clamps [1].
4.2.4 Accessing the Multi Voltage panel (if present)
031000
1. The complete module can be removed from the LSPbracket by pressing its fixation clamp [1] (located behind
the PWB), while sliding the module in the direction of the
CRT [2].
2. The board can easily be lifted from its bracket after
releasing the 2 fixation clamps [3].
4.2.6 Accessing the Mains Harmonic panel
31
CL 06532130_017.eps
Figure 4-8
1. The complete module can be removed from the LSPbracket (after removal of the DAF-panel) by removing
screw [1] and then slide the module in the opposite
direction of the CRT [2].
2. The board can easily be lifted from its bracket after
releasing the 2 fixation clamps [3].
3
2
3
131000
1. Remove the DW bracket from the bottom tray by pulling
it backward.
2. Press the 2 fixation clamps downward [3] (see figure 4-
7).
3. The board can easily be lifted out of the bracket after
releasing the 2 fixation clamps [4].
4.2.5 Accessing the Double Astigmatic Focus (DAF) panel
3
3
3
2
1
4.2.7 Accessing the Top Control panel
M
Figure 4-9
1. Remove the two fixation screws, which hold the panel.
2. Pull the board backward (w.o.w. release it from its front
hinge [M]).
3. The board can easily be lifted from its bracket after
releasing the 2 fixation clamps at the connector side.
Top control board
CL 06532012_003.eps
030200
Figure 4-7
CL 06532130_016.eps
031000
GB 14 EM1A4.
Mechanical instructions
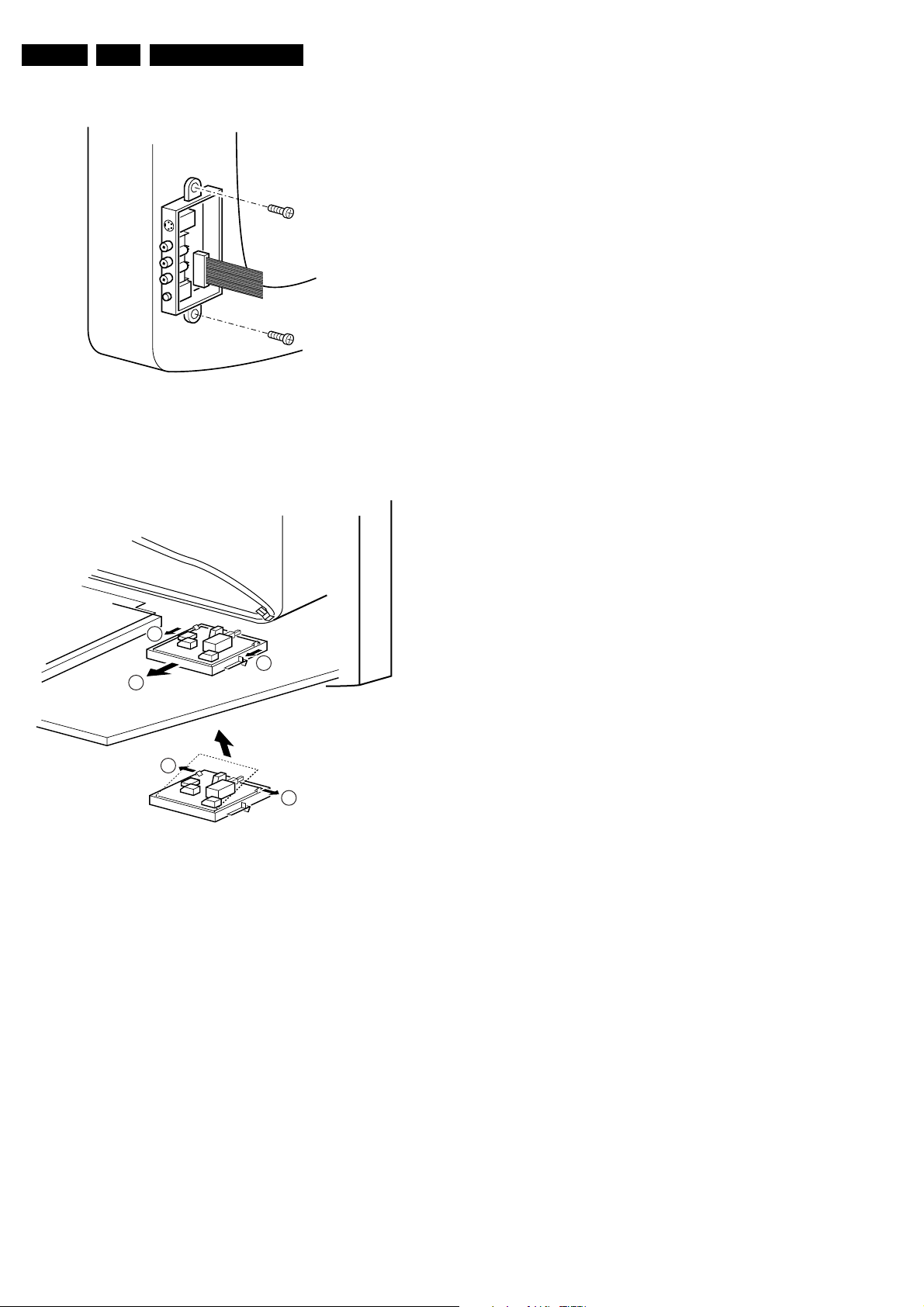
4.2.8 Accessing the Side I/O panel
CL 06532012_004.eps
Figure 4-10
4.2.9 Accessing the Mains Switch panel
1. The complete Side I/O-assembly can easily be removed
by unscrewing the 2 fixation screws.
2. The board can easily be lifted out of the bracket after
releasing the 2 fixation clamps.
030200
1
1
2
3
3
Figure 4-11
The easiest way to access this module is with the LSP in
service position 2.
1. Release the two fixation clamps by pulling them
backward [1].
2. At the same time, the complete assy must be pulled
backward [2].
3. If the board has to be removed, release the 2 clamps at
the bracket sides and lift panel up [3].
4.3 Mounting the Rear Cover
Before mounting the Rear Cover, some checks has to be
performed:
• Check whether the Mains Cord is mounted correctly in
the guiding brackets.
• Check whether all cables are replaced in their original
position. This is very important due to the large 'hot' area
of the set.
CL 06532130_018.eps
021000
Fault finding and repair tips
5. Fault finding and repair tips
GB 15EM1A 5.
In this chapter the following paragraphs are included:
1. Test points.
2. Service Modes.
3. Problems and solving tips (related to CSM).
4. ComPair.
5. Error codes.
6. The 'blinking LED' procedure.
7. Protections.
8. Repair tips.
5.1 Test points
The EM1A chassis is equipped with test points in the service
printing. These test points are referring to the functional
blocks:
• A1-A2-A3, etc.: Test points for the audio processing
circuitry [A5, A6, and B6].
• C1-C2-C3, etc.: Test points for the control circuitry [B7].
• F1-F2-F3, etc.: Test points for the frame drive and frame
output circuitry [A4, B4] and Double Window [C].
• F1F-F2F, etc.: Test points for the RGB-signals on the
CRT panel [F].
• I1-I2-I3, etc.: Test points for the intermediate frequency
circuitry [A7, B2].
• L1-L2-L3, etc.: Test points for the line drive and line
output circuitry [A3, B4].
• P1-P2-P3, etc.: Test points for the power supply [A1, A2].
• SC1-SC2, etc.: Test points for the synchronisation
circuitry on the CRT panel [F].
• V1-V2-V3, etc.: Test points for the video processing
circuitry [B].
• Via grounding the 'Front Detect'-line on the Side I/O
panel during switch ON (pins 1 and 7 of connector
0936).
• By the 'DEFAULT' button on the DST while the set is in
the normal operation mode.
CAUTION: Entering SDM by grounding the 'Front Detect'line will override the 5V-protection. This should only be
done for a short period of time. In case of SW-protections
(errors 1 - 4), the set will shutdown in 15 s.
When doing this, the service-engineer must know what
he is doing as it could lead to damaging the set.
After entering SDM, the following screen will be shown with
'SDM' at the upper right side for recognition.
SDM Menu
HRS: 0001 SWID: EM11A1-1.0
ERR: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
SDM
PICTURE BRIGHTNESS
+
i
SDM
SOUND COLOUR
MENU
FEATURES CONTRAST
INSTALL SHARPNESS
COLOUR TEMP
CL 06532130_010.eps
SDM
031000
Figure 5-1
Explanation
The numbering is done, in a for diagnostics logical sequence;
always start diagnosing within a functional block in the
sequence of the relevant test points for that functional block.
Measurements are performed under the following conditions:
• Service mode: SDM.
• Video: colour bar signal.
• Audio: 3 kHz left, 1 kHz right.
5.2 Service modes
5.2.1 Service Default Mode (SDM)
Purpose
• To provide a situation with predefined settings to get the
same measurement results as given in this manual.
• Start the 'Blinking LED' procedure.
• Have the possibility to override the 5V-protection.
Specification
• Tuning frequency 475.25 MHz for PAL/SECAM sets and
at channel 3 (61.25 MHz) for NTSC-sets.
• All picture settings at 50 % (brightness, colour, contrast,
hue).
• All sound settings at 50 % except volume at 25 % (so
bass, treble, balance at 50 %, volume at 25 %).
• All service-unfriendly modes are disabled, like timer,
sleep timer, parental lock, blue mute, hospitality mode
and no-ident timer (normally the set is automatically
switched off when no video signal - IDENT - was received
for 15 minutes).
Entering
• Via a standard RC-handset by entering the code
'062596' followed by the 'MENU' button.
• Via ComPair.
Access to normal user menu
Pressing the 'MENU' button on the remote control, switches
between the SDM and the normal user menus (with the SDM
mode still active in the background).
Error buffer
Pressing the 'OSD' button [i+] of the remote control, shows /
hides the error buffer. OSD can be hidden to prevent
interference with oscillogram measurements.
Access to SAM
By pressing the 'VOLUME +' and 'VOLUME -' buttons on the
local keyboard simultaneously for a few seconds, the set
toggles from SDM to SAM.
Exiting
There are 2 ways to exit this mode:
• Switch the set to 'STANDBY', the error buffer will also be
cleared (by switching the set OFF-ON with the mains
switch, the set will come up again in the SDM).
• By pressing the 'EXIT' button on the DST.
5.2.2 Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
Purpose
• To perform alignments.
• To change option settings.
• To display / clear the error code buffer.
Specification
• Software alignments (see chapter 8).
• Option settings (see chapter 8).
• Error buffer reading and erasing. The most recent error
code is displayed on the left side.
• Operation counter.
• Software version.
GB 16 EM1A5.
Fault finding and repair tips
Entering
• Via a standard RC-handset by entering the code
'062596' followed by the 'OSD' button [i+].
• Via ComPair.
SAM Menu
PICTURE BRIGHTNESS
SOUND COLOUR
FEATURES CONTRAST
INSTALL SHARPNESS
1
HRS: 0003 SWID: EM11A1-1.0
ERR: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
OPT: 254 100 128 0 0 0 0 0
CLEAR ERRORS
OPTIONS
AKB ON/OFF
OPC ON/OFF
VSD ON/OFF
TUNER
WHITE TONE
GEOMETRY
SOUND
COLOUR TEMP
MENU
2 3 4
SAM
SAM
• By the 'ALIGN' button on the DST while the set is in the
normal operation mode.
The following screen will be shown, with 'SAM' at the upper
right side for recognition.
SAM
SAM
SAM
MENU
MENU
NPRG
WSSB
SYSTEM
OB1
OB2
TUNER
IF-PLL OFFSET
AGC
2ND
AFA
AFB
MENU
NORMAL RED
5
Explanation
The Service Alignment Mode menu will now appear on the
screen. The following information is displayed:
1. Operation hours timer (hexadecimal).
2. Software identification of the main micro controller
(AAABBB-X.Y).
• AAA is the chassis name (EM1= Painter processor,
EM2= OTC processor).
• B = Software code belonging to a certain stroke
number (see table below).
• X = (main version number).
• Y = (subversion number).
3. Error buffer (7 errors possible).
4. Option bytes (8 codes possible), summary of options are
explained below.
Figure 5-2
VER-SLOPE
MENU
MENU
SOUND
NIC-FMAM
2CS-FM
PS-FM
PS-NIC-BGDK
PS-NIC-I
CL 06532130_011.eps
5. Sub menus are listed in a scroll-menu.
Country Strokenumber Software
Singapore /69 2A1
Thailand
Malaysia
Indonesia
Middle East /56 2A2
China /93 1A1
Hong Kong /57 2A1
Australia /79
New Zealand
SAM
SAM
021000

Fault finding and repair tips
GB 17EM1A 5.
Menu control
Menu items can be selected with the 'CURSOR UP/DOWN'
key. The selected item will be highlighted. When not all menu
items fit on the screen, moving the 'CURSOR UP/DOWN' will
display the next/previous menu items.
With the 'CURSOR LEFT/RIGHT' keys, it is possible to:
• (De)activate the selected menu item (e.g. GEOMETRY).
• Change the value of the selected menu item (e.g. VER-
SLOPE).
• Activate the selected submenu (e.g. SERV-BLK).
Access to normal user menu
Pressing the 'MENU' button on the remote control switches
between the SDM and the normal user menus (with the SAM
mode still active in the background). Pressing the 'MENU'
key in a submenu will go to the previous menu.
The menus and submenus
• CLEAR ERRORS. Erasing the contents of the error
buffer. Select the CLEAR ERRORS menu item and press
the 'CURSOR RIGHT' key. The content of the error
buffer is cleared.
• The functionality of the OPTIONS and ALIGNMENTS
(TUNER, WHITE TONE, SOUND, GEOMETRY and
SMART SETTING) sub menus is described in chapter 8.
Exiting
There are 2 ways to exit this mode:
• Switch the set to 'STANDBY', the error buffer will also be
cleared (by switching the set OFF-ON with the mains
switch, the set will come up again in the SAM).
• By pressing the 'EXIT' button on the DST.
5.2.3 Customer Service Mode (CSM)
Purpose
The 'Customer Service Mode' is a special service mode,
which can be activated and deactivated by the customer
upon request of the service technician/dealer during a
telephone conversation, in order to identify the status of the
set. This CSM is a 'read only' mode, therefore modifications
in this mode are not possible.
Entering
The Customer Service Mode will switch ON after pressing
the 'MUTE' key on the remote control handset and any of the
top control buttons on the TV for at least 4 seconds
simultaneously. This activation only works if there is no menu
on the screen.
HRS:
Hexadecimal
counter of operating hours (example: 1B
(hex) = 0001 1011 (bin) = 27 (dec)). Standby hours are not
counted as operating hours.
SWID: Software identification of the main micro controller
(see paragraph 5.2.2). Details on available software versions
can be found in the chapter 'Software Survey' of the
publication 'Product Survey - Colour Television'.
Line 2:
Error code buffer (for more details see paragraph 5.3).
Displays the last 7 errors of the error code buffer.
Line 3:
Software and hardware functionality of the EM1A is
controlled by option bits. An option byte or option number
represents 8 of those bits. Each option number is displayed
as a decimal number between 0 and 255. The set may not
work correctly when an incorrect option code is set. See
chapter 8 for more information on correct option settings
Line 4:
Indicates which colour and sound system is installed for the
selected pre-set:
Line 5:
Indicates that the set is not receiving an 'ident' signal on the
selected source.
Note: On some models, BLUE MUTE is displayed (if the BM
option is ON) when no signal is received.
Line 6:
Indicates whether the SLEEPTIMER function is ON/OFF.
Line 7:
Indicates whether the CHILD LOCK function is ON/OFF.
Line 8:
Indicates whether the current pre-set is defined as SKIPPED
or NON-PREFERRED.
Line 9:
Indicates whether the HOTEL MODE is activated.
Line 10:
Indicates which SOURCE is installed for this pre-set: EXT1,
SVHS2, EXT2, and Tuner.
Line 11:
Indicates which sound mode is installed for this pre-set:
Mono, NICAM, Stereo, L1, L2, SAP or Virtual
Line 12 to 17:
Value indicates parameter levels at CSM entry.
Explanation
After switching on the Customer Service Menu the following
screen will appear:
CSM Menu
1 HRS: 0005 SWID: EM11A1-1.0
2 CODES: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 OPT: 254 100 128 0 0 0 0 0
4 SYSTEM: AUTO 11 SOUND: MONO
5 NO SIGNAL 12 VOLUME:
6 TIMER ON 13 BALANCE: +/7 CHANNEL BLOCKED 14 HUE: +/8 NOT PREFERRED 15 COLOUR:
9 HOTELMODE ON 16 BRIGHTNESS:
10 SOURCE: 1 17 CONTRAST:
CL 06532130_012.eps
CSM
131000
Figure 5-3
Line 1:
Exiting
The Customer Service Mode will switch OFF after pressing
any key of the remote control handset (with exception of the
'P+' and 'P-' keys) and switching OFF the TV set with the
mains switch.
5.3 Problems and solving tips (related to CSM)
5.3.1 Picture problems
No colours / noise in picture
Check CSM line 4. Wrong colour system installed. To change
the setting:
1. Press the 'MENU' button on the remote control.
2. Select the INSTALL sub menu.
3. Select the MANUAL STORE sub menu.
4. Select and change the COLOUR SYSTEM setting until
picture and sound are correct.
5. Select the STORE menu item.

GB 18 EM1A5.
Fault finding and repair tips
Colours not correct / unstable picture
Check CSM line 4. Wrong colour system installed. To change
the setting:
1. Press the 'MENU' button on the remote control.
2. Select the INSTALL sub menu.
3. Select the MANUAL STORE sub menu.
4. Select and change the COLOUR SYSTEM setting until
picture and sound are correct.
5. Select the STORE menu item.
TV switches off or changes channel without any user
action
The TV-set switches off after 'TV SWITCHING OFF' was
displayed.
Auto standby switched the set off because:
• There was no ident signal for more than 15 minutes.
• There was no remote control signal received or local key
pressed for > 2 hours.
See chapter 8 for a description on the options to enable/
disable auto standby
Picture too dark or too bright
• Press 'Smart Picture' button on the remote control. In
case the picture improves, increase / decrease the
brightness value or increase / decrease the contrast
value. The new 'Personal Preference' value is
automatically stored after 3 minutes.
• After switching on the Customer Service Mode the
picture is OK. Increase / decrease the brightness value
or increase / decrease the contrast value. The new
'Personal Preference' value is automatically stored after
3 minutes.
White line around picture elements and text
• Press 'Smart Picture' button on the remote control. In
case the picture improves, decrease the sharpness
value. The new 'Personal Preference' value is
automatically stored after 3 minutes.
• After switching on the Customer Service Mode the
picture is OK. Decrease the sharpness value. The new
'Personal Preference' value is automatically stored after
3 minutes.
Snowy picture
Check CSM line 5. If this line indicates NO SIGNAL, check
following:
• no or bad antenna signal; connect a proper antenna
signal
• antenna not connected; connect the antenna
• no channel / pre-set is stored at this program number; go
to the INSTALL menu and store a proper channel at this
program number
• the tuner is faulty (in this case the CODES line will
contain number 13 or 16); check the tuner and replace/
repair if necessary
Snowy picture and/or unstable picture
• A scrambled or decoded signal is received.
Black and white picture
• Press 'Smart Picture' button on the remote control. In
case picture improves, increase the COLOUR value. The
new 'Personal Preference' value is automatically stored
after 3 minutes.
• After switching on the Customer Service Mode the
picture is OK. Increase the COLOUR value. The new
'Personal Preference' value is automatically stored after
3 minutes.
Menu text not sharp enough
• Press 'Smart Picture' button on the remote control. In
case the picture improves, decrease the CONTRAST
value. The new 'Personal Preference' value is
automatically stored after 3 minutes.
• After switching on the Customer Service Mode the
picture is OK. Decrease the CONTRAST value. The new
'Personal Preference' value is automatically stored after
3 minutes.
5.3.2 Sound problems
No sound or sound too loud (after channel change /
switching on)
• After switching on the Customer Service Mode the
volume is OK. Increase / decrease the volume level. The
new 'Personal Preference' value is automatically stored
after 3 minutes.
5.4 ComPair
5.4.1 Introduction
ComPair (Computer Aided Repair) is a service tool for Philips
Consumer Electronics products. ComPair is a further
development on the DST service remote control allowing
faster and more accurate diagnostics. ComPair has three big
advantages:
1. ComPair helps you to quickly get an understanding how
to repair the EM1A in short time by guiding you step by
step through the repair procedures.
2. ComPair allows very detailed diagnostics (on I2C level)
and is therefore capable of accurately indicating problem
areas. You do not have to know anything about I2C
commands yourself; ComPair takes care of this.
3. ComPair speeds up the repair time since it can
automatically communicate with the EM1A (when the
microprocessor is working) and all repair information is
directly available. When ComPair is installed together
with the SearchMan EM1A electronic manual,
schematics and PWBs are only a mouse-click away.
ComPair consists of a Windows based faultfinding program
and an interface box between PC and the (defective)
product. The ComPair interface box is connected to the PC
via a serial or RS232 cable. In case of the EM1A chassis, the
ComPair interface box and the TV communicate via a bidirectional service cable via the service connector at the rear
side of the set (located at the left side of the rear cinch
connectors, see also figure 1-2).
The ComPair faultfinding program is able to determine the
problem of the defective television. ComPair can gather
diagnostic information in 2 ways:
1. Communication to the television (automatic)
2. Asking questions to you (manually)
ComPair combines this information with the repair
information in its database to find out how to repair the TVset.
Automatic information gathering
Reading out the error buffer, ComPair can automatically read
out the contents of the entire error buffer.
Diagnosis is done on I2C level. ComPair can access the I2C
bus of the television. ComPair can send and receive I2C
commands to the micro controller of the television. In this
way it is possible for ComPair to communicate (read and
write) to devices on the I2C busses of the TV-set.
Manual information gathering
Automatic diagnosis is only possible if the micro controller of
the television is working correctly and only to a certain
extend. When this is not the case, ComPair will guide you
through the faultfinding tree by asking you questions and
showing you examples. You can answer by clicking on a link
(e.g. text or a waveform picture) that will bring you to the next
step in the faultfinding process.

Fault finding and repair tips
A question could be: Does the screen give a picture? (Click
on the correct answer)
YES / NO
An example can be: Measure test-point I7 and click on the
correct oscillogram you see on the oscilloscope
GB 19EM1A 5.
I7 B7502
1V / div DC
10µs / div
Figure 5-4
By a combination of automatic diagnostics and an interactive
question/answer procedure, ComPair will enable you to find
most problems in a fast and effective way.
Additional features
Beside fault finding, ComPair provides some additional
features like:
• Uploading/downloading of pre-sets.
• Managing of pre-set lists.
• Emulation of the Dealer Service Tool.
5.4.2 SearchMan (Electronic Service Manual)
If both ComPair and SearchMan are installed, all the
schematics and the PWBs of the faulty set are available
when clicking on the hyper-link of a schematic or a PWB in
ComPair. Example: Measure the DC-voltage on capacitor
C2568 (Schematic/Panel) at the Monocarrier.
Clicking on the PWB hyper-link automatically shows the
PWB with a highlighted capacitor C2568. Clicking on the
schematic hyper-link automatically shows the position of a
highlighted capacitor at the schematic.
5.4.3 Connecting the ComPair interface
The ComPair Browser software should be installed and setup before connecting the ComPair interface to the TV-set
(see the ComPair Browser Quick Reference Card for
installation instructions).
1. Connect the RS232 interface cable to a free serial (COM)
port on the PC and the ComPair interface PC connector
(connector marked with 'PC').
2. Connect the mains adapter to the connector marked
'POWER 9V DC' on the ComPair interface.
3. Switch the ComPair interface 'OFF'.
4. Switch the television set 'OFF' with the mains switch.
5. Connect the interface cable to the connector on the rear
side of the ComPair interface that is marked 'I
figure 5-6).
6. Connect the other end of the interface cable to the
ComPair connector on the monocarrier (left to the rear
cinch connectors).
7. Plug the mains adapter in the mains outlet and switch
'ON' the interface. The green and red LEDs light up
together. The red LED extinguishes after approx. 1
second (the green LED remains lit).
8. Start-up ComPair and select 'File' menu, 'Open...:; select
'EM1A Fault finding' and click 'OK'.
9. Click on the icon to switch 'ON' the communication mode
(the red LED on the ComPair interface will light up).
10. Switch 'ON' the TV-set with the mains switch.
11. When the set is in standby, click on 'Start-up in ComPair
mode from standby' in the ComPair EM1A faultfinding
tree, otherwise continue.
2
C' (see
EXTERNAL 2
L
R
AUDIO EXTERNAL 1
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
PC VCR I2CPower
9V DC
Figure 5-5
The set has now started up in ComPair mode. Follow the
instruction in the EM1A faultfinding tree to diagnose the set.
Note that the OSD works but that the actual user control is
disabled
5.4.4 Pre-set installation
Pre-sets can be installed via the service cable:
• sending TO the television and reading FROM the
television
• the rear cover does NOT have to be removed
Click on 'File', 'Open' and select 'EM1A fault finding' to use
the cable.
Pre-sets can be installed via menu 'Tools', 'Installation' and
'Pre-sets'.
5.4.5 Ordering ComPair
ComPair order codes:
• Starter kit ComPair + SearchMan software + ComPair
interface (excluding transformer): 4822 727 21629
• ComPair interface (excluding transformer): 4822 727
21631
• Starter kit ComPair software: 4822 727 21634
• Starter kit SearchMan software: 4822 727 21635
• Starter kit ComPair + SearchMan software: 4822 727
21636
• ComPair CD (update): 4822 727 21637
• SearchMan CD (update): 4822 727 21638
• ComPair interface cable (for EM1A): 4822 727 21641
5.5 Error codes
5.5.1 Error buffer
The error code buffer contains all errors detected since the
last time the buffer was erased. The buffer is written from left
to right. When an error occurs that is not yet in the error code
buffer, the error is written at the left side and all other errors
shift one position to the right.
The error code buffer will be cleared in the following cases:
• By activating 'CLEAR ERRORS' in the SAM menu:
– Exiting SDM or SAM with the 'Standby' command on
the remote control (by leaving SDM or SAM with the
mains switch, the error buffer is not reset).
– Transmitting the commands 'DIAGNOSE 99 OK' with
the DST (RC7150) or with ComPair
• Automatically reset if the content of the error buffer has
not changed for 50 hours
Examples:
ERROR: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 : No errors detected
ERROR: 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 : Error code 6 is the last and only
detected error
CL96532160_029.eps
110100

GB 20 EM1A5.
Fault finding and repair tips
ERROR: 9 6 0 0 0 0 0 : Error code 6 was first detected and
error code 9 is the last detected (newest) error
The contents of the error buffer can also be made visible
through the 'blinking LED' procedure. This is especially
useful when there is no picture. See paragraph 5.6 'The
blinking LED procedure '.
5.5.2 Error codes
In case of non-intermittent faults, clear the error buffer before
starting the repair. This is to prevent that 'old' error codes are
still present.
If possible, check the entire content of the error buffer. In
some situations an error code is only the result of another
Error Device Description Def. item Diagram
0
1 FBX 3V3 prot FBX 3V3 protection 5703 B3
2 No HFB No Horizontal Flyback 0325 A4
3 X-Ray protection X-Ray protection
4 5 V protection 5 V protection 1200/7651 A7/B6
5 No HOP POR Startup failure B4
6 General I
7 Mains Dip error HW-error
10 MC24C32 NVM communication error 7012 B7
11 MC24C32 NVM identification error 7012
12 SAA5667 Main µP, int. RAM test failure 7001 B7
13 TEDE9 Main Tuner 1200 A7
14 MSP3415D MSP34xx 7651 B6
15 CY7C1019 SRAM test failure 7011 B7
16 TELE9 PIP/DW Tuner 7201 C2
17 SAB9081H Multi PIP-IC 7801 C1
18 M62320P PIP/DW IO-expander 7403 C3
23 TDA888xx PIP/DW BOCMA-IC 7301 C4
27 Virtual Dolby Virtual Dolby error
30 TDA9320 HIP I/O-video processing 7323 B2
31 SAA4978 PICNIC 7709 B3
32 TDA9330 HOP video control/geometry 7301 B4
2
C bus error General I2C bus error
error code (and not the actual cause). E.g. a fault in the
protection detection circuitry can also lead to a protection.
Explanation of error codes:
Error 0
No errors.
Error 1
This protection is activated, when the PICNIC (pos. 7709 on
diagram B3) can not communicate via I2C for a certain time.
This could mean that stabiliser 7713 is defective. When e.g.
2704 makes a short circuit to ground, 7713 will become very
hot. For safety reasons the set will be switched to protection
mode.
Error 2
The absence of an HFB-pulse (pin 4 of connector 0324 on
LSP, diagram A3) is detected by the HOP (pos. 7301 on
diagram B4). A bit will be set in the HOP. After filtering by the
software, the set will switch to protection mode.
Error 3
Reserved.
Error 4
When the +5 V protection is active, the set is switched to
protection and error code 4 is placed in the error buffer. The
LED will blink 4 times (repeatedly). A 5 V failure can cause
a drop in the 5 V supply output, resulting in an undefined
behaviour of the set. Therefore, some I2C devices (Tuner
and MSP) connected to the 5 V supply are constantly
monitored. When none of these devices responds to the
micro controller for a prolonged time, the micro controller
assumes that there is a failure in the 5 V supply. By starting
up the set via grounding of the FRONT_DETECT-line (on the
side I/O), the +5 V protection will be overruled and it will be
easier to determine the cause. The +5V protection will be
activated when these I2C devices fail (no I2C
communication):
– Main Tuner (pos. 1200 on the LSP),
– MSP34xx sound processor (pos. 7651 on the SSB).
The following tips are useful to isolate the problem area, after
overriding the +5 V protection. Determine whether:
– The MSP sound processor is loading the +5 V; isolate
3650 and/or 4604 (see diagram B6).
– The main Tuner is loading the +5 V source; isolate coil
5200.
Caution! Overriding the +5 V protection when there is a 5 V
failure can increase the temperature in the set and may
cause permanent damage to components. Do not override
the +5V-protection for a prolonged time.
Error 5

Fault finding and repair tips
GB 21EM1A 5.
This error is covered by the Flash/Main routine described at
error 7. When during restart the 8 V remains absent, error 5
will be generated.
Error 6
This will occur in the following cases:
– SCL or SDA is shorted to ground.
– SCL is shorted to SDA.
– SDA or SCL connection at the micro controller is open
circuit.
Error 7
Flash detection: From the EHT-info, via D6303 and T7303 a
flash will stop the H-drive and line output stage immediately.
The FLS-bit in the status register of the HOP is set to ‘high’.
As the duration of a flash is very short the FLS-bit will be reset
to ‘low’ again after the flash refresh, so via a slow start the set
will be started again. If this interrupt occurs 5 times within an
interval of 10 seconds (indicating a mains interruption), the
set will go into protection and will generate error 7.
Error 10
Non Volatile Memory (EEPROM - pos. 7012) does not
respond to the micro controller.
Error 11
During the last start-up, the NVM and the micro controller did
not recognise each other (e.g. one of them was replaced or
the NVM memory has been changed/adapted or lost),
therefore the NVM was loaded with default values.
Error 12
Microprocessor (Painter - pos. 7001) internal RAM test
failure.
Error 13
Tuner (pos. 1200) is corrupted, the I
2
C line to the tuner is low,
or there is no supply voltage at pins 7, 4 and 5 of the tuner.
Error 14
Sound controller MSP34xx (pos. 7651) does not respond to
the micro controller.
Error 15
SRAM test failure (pos. 7011).
Error 16
The Tuner (pos. 7201) on the PIP/DW-panel does not
respond to the micro controller.
Error 17
Multi PIP IC SAB9081 I
2
C communication failure (pos. 7801
on the PIP/DW-panel).
Error 18
I/O expander IC M62320P I
2
C communication failure (pos.
7403 on the PIP/DW-panel).
Error 23
BOCMA IC TDA888xx I
2
C communication failure (pos. 7301
on the PIP/DW-panel).
Error 27
Virtual Dolby IC error.
Error 30
TDA 9320 HIP I/O-video processing (pos. 7323 on the SSB).
Error 31
SAA4978 PICNIC error (pos. 7709 on the SSB).
Error 32
TDA 9330 HOP video control/geometry error (pos. 7301 on
the SSB).
Note:
Error codes 1, 2 and 4 are protection codes and in this case
supplies of some circuits will be switched off. Also in
protection, the LED will blink the number of times equivalent
to the most recent error code.
5.6 The 'blinking LED' procedure
The contents of the error buffer can also be made visible
through the 'blinking LED' procedure. This is especially
useful when there is no picture.
When the SDM is entered, the LED will blink the contents of
the error-buffer. Error-codes ≥ 10 are shown as follows. A
long blink of 750 msec. which is an indication of the decimal
digit, followed by a pause of 1500 msec, followed by n short
blinks. When all the error-codes are displayed, the sequence
is finished with a LED display of 3 seconds. Then the
sequence starts again.
Example:
Error code position 1 2 3 4 5
Error buffer: 12 9 6 0 0
After entering SDM: 1 long blink (750 ms.) - pause (1500 ms.)
- 2 short blinks - pause (3 s.) - 9 short blinks - pause (3 s.) -
6 short blinks - pause (3 s.) - long blink (3 s.) - etc.
Note: If errors 1, 2 or 4 occur, the LED
always
occurred error, even if the set is NOT in service mode.
5.7 Protections
5.7.1 General
The EM1A has only one microprocessor (Painter) which
remains active during Standby. This because power of the
microprocessor and the memories is coming from the 3V3
supply, which is derived from the 5V Standby-circuitry. So in
both Power-on as in Standby-mode the microprocessor is
connected to this power supply.
If a fault situation is detected an error code will be generated
and if necessary the set will be put in the protection-mode.
The protection-mode is indicated by blinking of the red LED
at a frequency of 3 Hz. In some error cases the
microprocessor does not put the set in the protection-mode.
The error codes of the error buffer can be read via the
service-menu (SAM), the blinking LED procedure or via DST/
ComPair. The DST diagnose functionality will force the set
into the Service-standby, which is alike the usual Standby,
however the microprocessor has to remain in normal
operation completely.
To get a quick diagnosis the EM1A has 3 service-modes
implemented:
• The Customer Service Mode (CSM).
• The Service Default Mode (SDM). Start-up of the set in a
predefined way.
• The Service Alignment Mode (SAM). In this mode items
of the set can be adjusted via a menu and with the help
of test patterns.
The 'Protection Diagram' shows the structure of the
protection system. See diagram below.
gives the last

GB 22 EM1A5.
HFB X-RAY PROTECT
X-RAY PROTECT
EHT-INFO BCL
FLASH DETECT
Fault finding and repair tips
positioned in ‘Standby’-mode. The Painter will now try to restart the set. If this will not succeed after 5 times (after ≈ 30 60 s.), the Painter will generate error 7 (this error can have
several causes, such as a Flash, BRIDGE_PROT,
DEFL_PROT or a serious mains dip). A blinking red LED will
XPR (43)
HOP
FLS (5)
be started.
5.8 Repair tips
I2C SLOW BUS
HIP
HOP
PICNIC
TUNER
NVM
MSP
FBX
PROTECTION
TUNER
PROTECTION
HFB
PICNIC 3V3
TUNER 8V
+5V2
I2C
NHF (13)
I2C
I2C
CL 06532111_055.eps
PAINTER
121000
Figure 5-6
There are several types of protections:
• I2C related protections (e.g. +5V supply check).
• HOP related protections (mainly for deflection items).
• Hardware errors which are not sensed by the Painter
(e.g. BRIDGE_PROT)
I2C related protections
In normal operation some registers of the I2C controlled IC's
will be refreshed every 200 msec. During this sequence the
I2C-busses and the I2C -IC's as well will be checked. The I2C
protection will take place if the SDA and SCL are whether
short-circuited to ground or to each other. An I2C error can
also occur, if the power supply of the IC is missing (e.g.
FBX_PROT; error 1).
HOP related protections
Every 200 msec. the status register of the HOP is read by the
Painter via I2C. If a protection signal is detected on one of the
inputs of the HOP, then the relevant error bit in the HOP
register is set to ‘high’. If the error bit is still ‘high’ after 1 sec.,
the Painter will store the error code in the error buffer (NVM)
and depending on the relevancy of the error bit the set will
either go into the protection-mode or not.
• HFB: Horizontal Flyback. If the horizontal flyback is not
present, then this is detected via the HOP (HFB_XRAY_PROT). One status bit is set to ‘high’. The error
code is stored in the error buffer and the set will go into
the protection mode
• Flash detection. From the EHT-info, via D6303 and
T7303 a flash will stop the H-drive and line output stage
immediately. The FLS-bit in the status register of the
HOP is set to ‘high’. As the duration of a flash is very
short the FLS-bit will be reset to ‘low’ again after the flash
refresh, so via a slow start the set will be started again.
5.8.1 General
RESET
73
PAINTER
79
STANDBY-POR
IF NOT POR: ERROR 5 IS
GENERATED
13
(OUT)
STANDBY INFO
(TEMPORARELY LOW THEN HIGH
LIKE STARTING A CAR)
MAIN SUPPLY
NON-VFB
7308
7013
BRIDGE-PROT
I2C-bus
STANDBY-POR
STANDBY
POR-bit
7324
5V STANDBY
START/
STOP
22
START/
STOP
DEFL.
HOP
Figure 5-7
The start-up of the set is very different as of other sets (see
fig. 5-7 & 5-8):
1. When the set is switched ‘ON’, first the HOP is placed in
'low power start-up' mode (HOP-standby-mode). This
means that 5 V (derived from available Standby-supply)
is connected to pin 22 of the HOP-IC.
2. Now the HOP is driving the line-circuitry with 50 kHz
pulses. At the base of the line-transistor this is sensed via
the 'STANDBY’-line.
3. This signal triggers the Main supply to operate. Now the
line-stage has 'BAT'-voltage (141 V), it will also start.
4. After the 5 and 8 V-supply lines are sensed by the Painter
2
C), it will read the POR-bit from the HOP via the
(via I
I2C-bus.
5. Now the HOP is switched in ‘ON’-mode and the set will
start-up further with normal drive (31.25 kHz for PAL).
6. The last step will be the unblanking of the picture.
So standby is not controlled via a standby-line from
microprocessor, but is achieved indirectly via the HOPcircuitry.
OUT
4429
CUT OFF
7306
CL 06532111_056.eps
HOTCOLD
121000
Hardware related protections
Due to the architecture (with 'hot' deflection) there are two
protections that are 'unknown' to the microprocessor, namely
the 'BRIDGE_PROT' (coming from the line stage) and the
'DEFL_PROT' protection (coming from the frame deflection
stage). If one of these protections is triggered, the set is

Fault finding and repair tips
off
Standby supply starts oscillating
GB 23EM1A 5.
Standby-supply is running; +3.3V, +5V2 ready
'Standby-info' = high; µP has been reset by POR
Degaussing is activated automatically and should
be acivated after 12 seconds
Standby bit set in NVM?
yes
'Standby-info' remains
no
Initialize I/O pins of the OTC
Make 'Standby-info' low
Supply is in standby-mode
Mute
5V2 present on the HOP. HOP starts in low power start up mode
Deflection starts on 50kHz; +5V and +8V become present
+5V and +8V levels can be detected by the Painter. Vcc of the HOP is present.
Activate protection for +8V and +5V
Low_power_standby
High_power_standby
high
Main_power_on
Standby high
Go to protection
Error code 05
'HOP POR
not successfull'
Wait 1500ms and reset MSP
(Sound-IC)
read POR bit from the HOP
no
POR available within 1 second ?
yes
Put 'Standby-INFO' high again
Give HOP_start_commando within 23.5 ms after a
POR is obtained from the HOP
DISABLE I2C while EHT is starting up: 250ms
Activate I2C protection. Set protection algorithms active for
I2C, +5V, +8V, HFB, FBX
Initialize I2C IC's
From here onwards,
I2C communication is
possible
HOP_on
Set Black Current Stabilisation = Active
on
Figure 5-8
CL 06532130_021.eps
171000

GB 24 EM1A5.
• Notice that a very big part of the set (Large Signal Panel)
is 'hot', meaning the primary part of the Standby supply,
the whole Main supply (except for the secondary Audio
supply) and the complete deflection circuit. So notice
that the deflection-coil is hot!
• This set does not have an IR transmitting-LED. In its
place, a Service (ComPair) connector is implemented at
the rear of the set, which is directly accessible. In addition
to this, there is a blinking LED procedure to show the
contents of the error buffer.
• The relay you hear during switching 'ON' (via the main
switch) is from the degaussing-circuitry. So it is not used
for switching the supply as in the MG-chassis.
• When there is a menu in the picture, entry of servicemodes cannot be performed. So see to it that there is no
menu on the picture.
5.8.2 Repair tips
'Repair-tips how to repair the Main power supply:
• Simplest way is to replace components of the Main
supply with repair kit (3122 785 90260)
• More detailed way:
– Replace FET 7504 and zener 6505
– Remove SSB-panel
– Short-circuit BE of TS7529 in order to put supply in
‘on’-mode (TS7529 is blocking then)
– Load capacitor C2515 (VBAT) with a load of 500
ohm. Supply can not work without a minimum load.
– Use a variac to slowly increase the VMAINS.
Measure over sensing-resistors R3514/15 whether a
nice sawtooth-voltage becomes available. Also
measure the VBAT-output
– VBAT may never exceed 141 V. If so there is
something wrong in the feedback-circuitry (e.g.
regulator 7506)
Fault finding and repair tips
Repair-tips how to repair the Standby power supply:
• Simplest way is to replace components of the Standby
supply with repair kit (3122 785 90270)
Repair-tips how to repair the Deflection-circuitry:
• Simplest way is to replace components of the Deflectioncircuitry with repair kit (3122 785 90120)
Service-tips:
• Be careful measuring on gate of FET 7504. Circuitry is
very high ohmic and can easily be damaged.
• Take care not to touch ‘hot’ heatsink while disconnecting
SSB, despite the fact that mains cord is out of mains
socket. There still is an annoying rest-voltage for a short
while.
• Do not try to measure on side of SSB directed to the hot
heatsink. This is dangerous. All service test points are
guided to the Tuner side and are pointed out by service
printing. Where the circuitry was too crowded to place
this service-printing it has been explained on the Test
point overviews in this manual

Fault finding and repair tips
Phenomenon Possible Cause Repair tip
No picture, no LED. Standby Supply defective. Measure circuitry (see diagram A2). Start at test-point P16.
No picture, red LED
(high intensity).
Despite expectation,
the set should be ON
(this looks like
Standby). After some
There are 2 protections (which
are not ’seen’ by the processor)
that force the set in protection
(after 5 restart attempts):
BRIDGE_PROT or MAINS DIP
error.
time LED will start
blinking.
Set going into
protection after 5
restarts (error 7),
taking about 30 - 60 s.
No picture, red LED
blinking (3 Hz)
180 V missing on CRT-panel
(diagr. F). Most probably R3341
is interrupted, or RGB-amplifier
IC7307 is defective.
Set is in protection due to
various causes. For error codes
see error code list.
No picture, red LED
blinking (code 6, 6, 6)
No communication on I2C1-bus
(’devices’ bus) to processor. Set
is in protection-mode
No picture, red LED
blinking (code 10, 10,
10)
No picture, no sound,
set is making audible
squeaking sound
No picture, no sound,
No communication on I2C3-bus
(’NVM’ bus) to processor. Set is
in protection-mode
Supply could be in hiccup-mode
which can be heard via supply-
transformer squeaking
Supply does not work correctly If e.g. V
LED works fine
No RC5-reception.
Red LED does not
Processor-circuitry or RC-
receiver is wrong.
echo RC-commands.
Relay-activation
Processor not working correctly. Check RESET-circuitry on diagram B5. When switching on the set all I/o(degaussing) not
audible when switch
set on from off .
No sound, but picture. Measure P7 on diagram A1.
Possible sound-amplifier is
defect (but not short-circuited),
or sound-enable line is high
(see diagram A5).
Further the audio-signal path
must be measured (HIP, MSP,
switch-IC s, amplifier).
No sound at
headphone output.
Discrete amplifiers or supply to
it could be damaged.
Picture is rotated. Rotation-circuitry or supply to it
could be damaged (if present).
No picture. Check functionality and cabling
Tuner to SSB.
Picture looks like
cushion, further OK
Or NVM-content is overwritten
or E/W-MOSFET is short-
circuited
Very white picture,
180 V is missing on CRT-panel Probably R3468 on LSP (diagram A3) is interrupted, or bad connection
with flyback lines
visible
Un-sharp picture Focus could be misaligned or
SCAVEM-circuitry does not
work correctly
Un-synced picture Sync is derived in HIP-IC from
X-tals 1309 and/or 1310
Picture distorted. Check video-path, service
default mode.
No menu, OSD. Probably processor is defective. Measure test points C7, C8, C9, C10 on diagram B7.
Regardless the mode of the set, this voltage should always be available.
If protection is activated due to an absence of the Frame deflection, this
can be measured on test-point F10 (diagr. A4). Error 33 will be generated.
The BRIDGE_PROT could be triggered by an E/W failure.
An MAINS_DIP error (error 7) will be generated in both cases after 5
restart attempts, and will be visible via the blinking LED procedure.
ComPair is very useful here.
Measure 180 V behind R3341 (diagr. F) while operating, or measure
resistance of R3341 while set is of.
You have no picture, so:
Read out the error buffer via ComPair.
Read out blinking LED information via ’DIAGNOSE X’ with DST.
When error is known, check circuitry related to supply voltage and I
communication.
Measure, dependent of the error, on the I2C-bus which device is loading
the bus. This protection can be overruled via SDM-entry (via shortcircuiting FRONT_DETECT to GND on Side I/O).
No contact of processor with the NVM. A lot of settings will therefore be
wrong.
This could be caused by:
Short-circuited V
Short-circuited sound-winding (amplifier is short-circuiting 28 V) or
Short-circuited D6514 (due to a too high V
Delete excessive load to see where failure is caused by or check feed
(caused by short circuited line transistor 7421) or
BAT
).
BAT
back circuit. See repair-tip main power supply (supply needs a minimal
load).
is only about 90 V, regulator-IC 7506 could be damaged.
BAT
In case set reacts on local keyboard operation, error must be found in the
IR-receiver circuitry (diagram J).
pins of processor should become high for a moment, so also the degaussinput signal.
Measure and repair. With ComPair there is a beep-test that can determine
where the signal stops (use loudspeakers, headphone).
Measure A12, A13, A14, A15 and supply-line on diagram A6.
Measure test-points F3, R1, R2 on diagram A4.
Notice cable 1946.
First check in Service Alignment Mode, whether geometry can be
restored. If not check test point L4 and diagram A3, or measure with an
ohmmeter whether TS7480 is defective.
plug 0324 to 0224 (CRT-panel).
Align focus-potmeter of Line Transformer; check SCAVEM-circuitry on
CRT-panel [F].
Maybe an X-tal is making bad contact.
Investigate whether there exists an error code in the error buffer.
In case there is an error code, check I
2
C-bus and/or supply-lines (see
overview supply-lines).
Measure and check signal path Tuner, HIP, PICNIC, HOP, RGB-amplifier.
In case it is a geometry-issue, check Frame-circuitry, alignments or
possible corrupted NVM (7012)
GB 25EM1A 5.
2
C -
CL 06532111_057.EPS
121000

GB 26 EM1A5.
Personal notes:
Fault finding and repair tips

8. Alignments
Note: The Service Default Mode (SDM) and Service
Alignment Mode (SAM) are described in chapter 5.
8.1 General alignment conditions
All electrical adjustments should be performed under the
following conditions:
• Supply voltage: 110 / 220 V (± 10 %); 50 / 60 Hz (± 5 %)
• Warm-up time: ≈ 20 minutes
• The voltages and oscillograms are measured in relation
to the tuner earth (with exception to the voltages on the
primary side of the power supply). Never use the cooling
fins / plates as ground.
• Test probe: Ri > 10 MΩ; Ci < 2.5 pF.
• Use an isolated trimmer / screwdriver for the alignments.
Alignments
0V Ref.
8.2.2 Focusing
max.
V
CUTOFF
Figure 8-2
[VDC]
GB 77EM1A 8.
CL 06532130_014.eps
131000
8.2 Alignments on the large signal panel (LSP)
Large Signal panel (LSP)
Warning
All alignments
are on hot-part !
SSB
LOT
Focus 1
Focus 1
Screen
H.AMPL
3603 36093480
V.AMPL
V.SHIFT
CL 06532130_013.eps
031000
TUNER
CINCH
Figure 8-1
8.2.1 Vg2 adjustment
Rough method
Using a pattern generator displaying a black pattern (PAL
BG, 475.25 MHz), adjust the Vg2 potmeter of LOT (item
5430) to obtain normal picture (without visible fly-back lines).
1. Tune the set to a circle or crosshatch test pattern (use an
external video pattern generator).
2. Adjust the 1st Focus potmeter (upper LOT potmeter, see
figure 8-1) until the horizontal and vertical lines at 1/4
from east and west, at the height of the centre line, are of
minimum width without visible haze.
3. Adjust the 2nd Focus potmeter (middle LOT potmeter,
see figure 8-1) until the horizontal and vertical lines at 1/
4 from north and south, at the height of the centre line,
are of minimum width without visible haze.
8.3 Alignments and settings in the Service
Alignment Menu
8.3.1 General
With the software alignments of the Service Alignment Mode
the Geometry, White tone and Tuner (IF)can be aligned. Put
the set in the SAM mode (see chapter 5). The SAM menu will
now appear on the screen.
Menu navigation is done with the 'CURSOR UP, DOWN,
LEFT or RIGHT' keys of the RC-handset.
8.3.2 Geometry
The geometry alignments menu contains several items to
align the set, in order to obtain a correct picture geometry.
East/West Trapezium
Accurate method
1. Connect the RF output of the pattern generator to the
antenna-input of the TV. Test pattern is a 'black' pattern
(blank screen on CRT without any OSD info).
2. Set the channel of the oscilloscope to 50 V/div and the
time base to 5 ms. Select 'external triggering' on the
vertical pulse (anode of diode 6619, located near
connector 0325 to frame deflection coil).
3. Measure the black level pulse during the vertical flyback
(1st full line after the frame blanking) at the R, G and B
cathodes of the CRT (pin 8, 6 and 11 of the CRT
connector). Select the cathode with the highest V
DC
value for the measurement.
4. Adjust Vcutoff with the Vg2 (SCREEN) potmeter of the
LOT to 170 ± 2 V
.
DC
East/West Parabola
Horizontal Bow
Figure 8-3
CL 96532156_012.eps
250100

GB 78 EM1A8.
Alignments
Initial set-up
1. Connect an external video pattern generator (PAL BG,
475.25 MHz) to the aerial input of the TV-set with a
crosshatch test pattern.
2. Set 'Smart Picture' to NATURAL.
3. Activate the SAM-menu (see chapter 5).
4. Go to sub-menu GEOMETRY. Now the following
alignments can be performed:
Vertical slope (VER. SLOPE)
Align the vertical centre of the picture to the vertical centre of
the CRT.This is the first alignment to be performed of the
vertical alignments. For an easy alignment set SERV.BLK to
ON.
Service blanking (SERV. BLK)
Switch the blanking of the lower half of the screen ON/OFF
(to be used in combination with the vertical slope alignment).
Vertical amplitude alignment
Align the vertical amplitude with potentiometer R3603 on the
LSP (see Fig. 8-1) so that the complete test pattern is visible.
Vertical shift alignment
Align the vertical centering with potentiometer R3609 on the
LSP (see Fig. 8-1) so that the test pattern is located vertically
in the middle. Repeat the 'vertical amplitude' alignment if
necessary.
4. If the frequency showed in the line 'Fine tune' is between
471.18 MHz and 471.31 MHz, you don't need to re-adjust
the IF-AFC.
5. If not, adjust the frequency in the 'Fine tune' line to
471.25 MHz and store the program by leaving the menu
(this is very important because this will disable the AFC
algorythm).
6. Now go to the SAM and select 'Alignments' - 'General' 'IF AFC'.
7. First you must align the 'IF AFC'-parameter such that you
come into the AFC-window (AFA = 1)
8. Then you must look for the point where the AFBparameter changes from 1 to 0. This level is the value
you are looking for.
9. After adjustment store the value by returning to the
former menu.
10. Now return to the 'Installation' menu.
11. Select 'Manual Installation' - 'Search' - '47' - 'OK' and
store it. This will set the AFC 'on' again.
12. During the 'IF PLL'-parameter adjustment, one can see
feedback at the screen, by means of the 'AFA' and 'AFB'
indication (see table).
AFA AFB IF-PLL offset
0 0 Decrease offset value
0 1 Increase off-set value
10Correct
11Correct
Horizontal shift (HOR. SHIFT)
Align the horizontal centre of the picture to the horizontal
centre of the CRT.
Horizontal bow (HOR. BOW)
Align straight horizontal lines in the top and the bottom;
horizontal rotation around the centre.
Horizontal parallelogram (HOR. PARALLEL)
Align straight vertical lines in the top and the bottom; vertical
rotation around the centre.
East West width (EW. WIDTH)
Align the picture width until the complete test pattern is
visible.
East West parabola (EW. PARA)
Align straight vertical lines at the sides of the screen.
East West Trapezium (EW. TRAP)
Align straight vertical lines in the middle of the screen.
East West Upper Corner (EW. UCORN)
Align straight vertical lines in the upper corners of the screen.
East West Lower Corner (EW. LCORN)
Align straight vertical lines in the lower corners of the screen.
8.3.3 Tuner (Large Signal Panel and Double Window)
AGC
Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) to a colour bar video
signal and connect the RF output to aerial input. Set
amplitude to at least 1 mV and set frequency for PAL-BG to
471.25 MHz.
1. Activate the SAM-menu. Go to the sub-menu TUNER,
and select the 'AGC' sub-menu.
2. Connect a DC multi-meter to pin 1 of the tuner (item
1200 on LSP).
3. Adjust the AGC until the voltage at pin 1 of the Tuner is
just below 3.8 V.
4. The value can be incremented or decremented by
pressing the MENU LEFT/RIGHT button on the RC.
5. Switch the set to STANDBY.
2ND AGC
Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) to a colour bar video
signal and connect the RF output to aerial input. Set
amplitude to at least 1 mV and set frequency for PAL-BG to
471.25 MHz.
1. Activate the SAM-menu. Go to the sub-menu TUNER,
and select the '2nd AGC' sub-menu.
2. Connect a DC multi-meter to pin 1 of the tuner (7201 on
DW panel).
3. Adjust the 2nd AGC until the voltage at pin 1 of the Tuner
is just below 3.8 V.
4. The value can be incremented or decremented by
pressing the MENU LEFT/RIGHT button on the RC.
5. Switch the set to STANDBY.
Note: Described alignments are only necessary when HIP or
NVM is changed.
IF PLL OFFSET
Supply, via a video generator (e.g. PM5518), a TV-signal
(e.g. colour bar) with a signal-strength of at least 1 mV and a
frequency of 471.25 MHz (use BG if possible, otherwise
match the system of your generator with the received signal
in the set).
Alignment procedure:
1. Go to the 'Installation' menu.
2. Select 'Manual installation'.
3. Tune the TV-set to the system and frequency described
above via 'Search' - '471' - 'OK'.
8.3.4 Black cut off
In the WHITE TONE sub menu, the values of the black cut off
level can be adjusted. The colour temperature mode
(NORMAL, DELTA COOL, DELTA WARM) or the colour (R,
G, B) can be selected with the UP/DOWN RIGHT/LEFT
cursor keys. The value can be changed with the RIGHT/
LEFT cursor keys.
First the values for the NORMAL colour temperature should
be selected. Then the offset values for the DELTA COOL and
DELTA WARM mode can be selected (note that the
alignment values are non-linear).
• +1 to +63 represent a positive offset (63 is the maximum
positive offset).

Alignments
GB 79EM1A 8.
• -63 to -1 represent a negative offset (-63 is the minimum
negative offset).
1. Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) to a white spot
(chess board) pattern and connect RF output with aerial
input. Set amplitude to 1 mV and set frequency for PALBG to 475.25 MHz.
2. Set CONTRAST to the maximum value (99).
3. NORMAL settings
– NORMAL RED = 32
– NORMAL GREEN = 32
– NORMAL BLUE =32
4. COOL settings
– DELTA COOL RED = -3
– DELTA COOL GREEN = 0
– DELTA COOL BLUE = 3
5. WARM settings
– DELTA WARM RED = 4
– DELTA WARM GREEN = 0
– DELTA WARM BLUE = -8
6. CUT OFF (default) settings
– BLACK LEVEL R = 7
– BLACK LEVEL G = 7
7. Measure with a colour analyser (calibrated with the
spectra) on the centre of a white square on the screen.
Adjust the values of BLACK LEVEL R and BLACK
LEVEL G to get the right XY-coordinates for Tint =
Normal (see table 8-1).
Note: When there is no colour analyser available, use the
default settings mentioned above.
8.4 Options
8.4.1 Options
Options are used to control the presence / absence of certain
features and hardware. There are two ways to change the
option settings (see also fig. 8-3):
Changing a single option
An option can be selected with the MENU UP/DOWN keys
and its setting can be changed with the MENU LEFT/RIGHT
keys.
Changes in the option settings are saved by leaving the
OPTION submenu. Some changes will only take affect after
the set has been switched OFF and ON with the mains switch
(cold start).
Changing multiple options by changing option byte
values
Changing the option bytes directly, makes it possible to set
all options very fast. An option byte (OB1..8) can be selected
with the MENU UP/DOWN keys and its setting can be
changed with the MENU LEFT/RIGHT keys. An option byte
represents a number of different options. All options of the
EM1A are controlled via 8 option bytes. Select the option
byte (OB1..OB8) and key in the new value.
Changes in the option byte settings are saved by leaving the
OPTION submenu. Some changes will only take affect after
the set has been switched OFF and ON with the mains switch
(cold start).
8.3.5 Light output
In the WHITE TONE sub menu, also the light output of the
CRT can be adjusted. In this case a colour analyser is
necessary.
1. Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) to a white spot
pattern and connect RF output to aerial input. Set
amplitude to 1 mV and set frequency for PAL-BG to
475.25 MHz.
2. Set CONTRAST to the maximum value (99).
3. Measure with a colour analyser (calibrated with the
spectra) on the centre of the white square on the screen.
Adjust the level of NORMAL RED, NORMAL GREEN
and NORMAL BLUE in a simultaneous way to get the
360 cd light output.
8.3.6 White drive
In the WHITE TONE sub menu, the values of the WHITE
DRIVE level can be adjusted. The colour temperature mode
(NORMAL, DELTA COOL, DELTA WARM) or the colour (R,
G, B) can be selected with the UP/DOWN RIGHT/LEFT
cursor keys. The value can be changed with the RIGHT/
LEFT cursor keys.
1. Set pattern generator (e.g. PM5418) to a white spot
pattern and connect RF output to aerial input. Set
amplitude to 1 mV
475.25 MHz.
2. Set CONTRAST to the maximum value (99).
3. Measure with a colour analyser (calibrated with the
spectra) on the centre of the white square on the screen.
Adjust the level of NORMAL BLUE and NORMAL RED to
get the right XY-coordinates. See table 8-1.
and set frequency for PAL-BG to
RMS
Option bits/bytes
An option byte value is calculated in the following way:
Value 'option bit 1' x 1 =
Value 'option bit 2' x 2 =
Value 'option bit 3' x 4 =
Value 'option bit 4' x 8 =
Value 'option bit 5' x 16 =
Value 'option bit 6' x 32 =
Value 'option bit 7' x 64 =
Value 'option bit 8' x 128 =
========================
Total: value 'option byte' =
2 Software versions are used: 1A1 and 2A1/2A2. Below find,
in table 8-2 and 8-3, the option definition for both versions (for
an explanation of the SW-version versus country code see
table in chapter 5.2.2, page 16).
Table 8-1
Tint Temperature (K) X Y
Warm 8700 289 299
Normal 13500 266 274
Cool 18300 256 264

GB 80 EM1A8.
Alignments
Option table (version 1A1):
Table 8-2
Byte Bit Abbr. Feature Description (OFF = 0, ON = 1)
OB1 1 AUSB Auto Standby After 2hrs OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB1 2 AV3 Side AV source OFF = side AV source not available / ON = available
OB1 3 HOSP Hospitality mode OFF = hospital mode disabled / ON = enabled
OB1 4 E149 Picture setting for expand 14:9 OFF = not available in FORMAT menu / ON = available
OB1 5 C169 Pict. setting for compress 16:9 OFF = not available in FORMAT menu / ON = available
OB1 6 CVI External source selection for PIP OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB1 7 SBNP Auto Standby with no picture OFF = no switch to stdby / ON= switch to stdby after 10m. when no ident
OB1 8 ASBY Auto Standby After 2 hours OFF = disabled / ON = active after 2 hrs of no RC or keyboard response
OB2 1 PIPC PIP Control OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB2 2 BLMU Blue Mute OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB2 3 SOSD Smart OSD OFF = full display of OSD not available / ON = available
OB2 4 PLST Program List OFF = access to Command is ignored / ON = access is processed
OB2 5 PITN Philips tuner OFF = ALPS compatible tuner used / ON= Philips compatible tuner used
OB2 6 VDBY Virtual Dolby OFF = Virtual Dolby not available / ON = Virtual Dolby is available
OB2 7 IPMU Incredible picture via menu OFF = menu item 'INCR. PICT' not available / ON = available
OB2 8 CBFL Comb filter OFF = no comb filter on the SSB / ON = comb filter present on the SSB
OB3 1 SURF Surf OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB3 2 CHNA China set OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB3 3 VSLC Vertical slicing OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB3 4 W169 Double Window 16:9 OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB3 5 W4X3 Double Window 4:3 OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB3 6 PIPF PIP Functionality OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB3 7 PIPT PIP Tuner OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB3 8 PIPS PIP Surf OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB4 1 APC Auto Picture Control OFF = Time Window is set to 2 s. / ON = Time window is set to 5 s.
OB4 2 INCF Internal Combfilter OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB4 3 TMWIN Time Window OFF = Time Window is set to 2 s. / ON = Time window is set to 5 s.
OB4 4 SNIC Sound IC MSP3451 OFF = sound IC MSP3451 not present / ON = present
OB4 5 ROTI Rotation tilt OFF = menu item 'ROTATION' not available / ON = available
OB4 6 CHLK Child Lock OFF = function disabled / ON = enabled
OB4 7 AAVL Automatic Volume Leveller OFF = menu item 'AVL' not available / ON = menu item available
OB4 8 TIME Timer OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB5 1 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB5 2 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB5 3 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB5 4 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB5 5 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB5 6 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB5 7 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB5 8 PAGC PICNIC AGC OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB6 1..8 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB7 1..8 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB8 1..8 N/A (RESERVED) N/A

Alignments
GB 81EM1A 8.
Option table (version 2A1 / 2A2):
Table 8-3
Byte Bit Abbr. Feature Description (OFF = 0, ON = 1)
OB1 1 AV3 Side AV source OFF = side AV source not available / ON = available
OB1 2 SMCK Smart clock OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB1 3 HOSP Hospitality mode OFF = hospital mode disabled / ON = enabled
OB1 4 E149 Picture setting for expand 14:9 OFF = not available in FORMAT menu / ON = available
OB1 5 C169 Pict. setting for compress 16:9 OFF = not available in FORMAT menu / ON = available
OB1 6 CVI External source selection for PIP OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB1 7 SBNP Auto Standby with no picture OFF = no switch to stdby / ON= switch to stdby after 10m. when no ident
OB1 8 ASBY Auto Standby After 2 hours OFF = disabled / ON = active after 2 hrs of no RC or keyboard response
OB2 1 SOSD Smart OSD OFF = full display of OSD not available / ON = available
OB2 2 PLST Program List OFF = access to Command is ignored / ON = access is processed
OB2 3 PITN Philips tuner OFF = ALPS compatible tuner used / ON= Philips compatible tuner used
OB2 4 VDBY Virtual Dolby OFF = Virtual Dolby not available / ON = Virtual Dolby is available
OB2 5 NTSC NTSC playback OFF = not possible via EXT-in / ON= function enabled
OB2 6 IPMU Incredible picture via menu OFF = menu item 'INCR. PICT' not available / ON = available
OB2 7 CBFL Comb filter OFF = no comb filter on the SSB / ON = comb filter present on the SSB
OB2 8 AUSB Auto Standby auto on OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB3 1 W4X3 Double Window 4:3 OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB3 2 ISUR Incredible Surround OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB3 3 PIPF PIP Functionality OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB3 4 PIPT PIP Tuner OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB3 5 PIPS PIP Surf OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB2 6 PIPC PIP Control OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB3 7 BLMU Blue Mute OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB3 8 FAPG Favorite page OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB4 1 CHLK Child Lock OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB4 2 AAVL Automatic Volume Leveller OFF = menu item 'AVL' not available / ON = menu item available
OB4 3 TIME Timer OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB4 4 DTXT Double window TXT OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB4 5 TXT Teletext available OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB4 6 SURF Surf OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB4 7 VSLC Vertical slicing OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB4 8 W169 Double Window 16:9 OFF = function disabled / ON= function enabled
OB5 1 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB5 2 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB5 3 APC Auto Picture Control OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB5 4 PAGC PICNIC AGC OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB5 5 INCF Selection colour delay line OFF = disabled / ON = enabled
OB5 6 TMWIN Time Window OFF = Time Window is set to 2 s. / ON = Time window is set to 5 s.
OB5 7 SNIC Sound IC MSP3451 OFF = sound IC MSP3451 not present / ON = present
OB5 8 ROTI Rotation tilt OFF = menu item 'ROTATION' not available / ON = available
OB6 1..8 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB7 1..8 N/A (RESERVED) N/A
OB8 1..8 N/A (RESERVED) N/A

GB 82 EM1A9.
Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
9. Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
9.1 Circuit descriptions
The following circuits are described:
1. Introduction
2. Block diagrams
3. Power supply
4. Control & Teletext
5. Tuner & IF
6. Video: High-end Input Processor
7. Video: Feature box
8. Video: High-end Output Processor
9. Synchronisation
10. Horizontal deflection
11. Vertical deflection
12. Audio
13. CRT & SCAVEM
14. Double Window (DW)
9.1.1 Introduction
The EM1A is a lower specified MG-chassis. EM stands for
Eco-MG, 1 for the used processor (Painter) and A stands for
Asian Pacific.
The user interface and processor are the same as used in the
A10A set. In the EM1A however, a HIP, PICNIC and HOP are
used for the 100 Hz function i.s.o. the BOCMA in the A10A.
So the HIP and HOP have the same functionality as the
BOCMA (to let the set work in 2fH-mode), while the PICNIC
is used for video features like AutoTV and Freeze.
The architecture consists of a conventional Large Signal
Panel (LSP) a Double Window panel (DW) and a Small
Signal Board (SSB) module, placed into a so-called SIMMconnector (Standard Interface, 80 pins).
The LSP is built up very conventional, with hardly any surface
mounted components on the copper side. Difference with the
MG-chassis is that the EM1A LSP has a very large 'hot' part,
including the deflection coil.
The SSB is a high tech module (2 sides reflow technology,
full SMC) with very high component density and complete
shielding for EMC-reasons. Despite this, it is designed in
such a way, that repair on component level will be possible.
To achieve this, attention has been paid to:
• The position of service test lands (Tuner side).
• Accessibility (Tuner side).
• Clearance around surface mounted IC's (for replacing).
• Diagnostics & Fault Finding via ComPair.
Warning: Be aware that half of the LSP-circuitry is 'hot',
including the deflection coil.
Protection: The start-up behaviour of the EM1A is different
then that of the MG-chassis, meaning that there does not
exist a situation as in the MG where we have 'supply ON/
deflection circuit OFF'.
This means that isolating failures in the EM1A must be done
in a different way. See Chapter 5 of this manual.
9.1.2 Block diagrams
PIP/DW MODULE
TUNER
SPLITTER
PIP/DW
VIDEO-EXT
EXT
AUDIO-EXT
I/O
MONITOR-OUT (A+V)
TOP
CONTROL
IR
REC.
POWER
SUPPLY
LOW
POWER
STBY
EHT
180V
141V
28V
ETC.
5V2
MULTI
VOLTAGE
IF
FILTER
TUNER
FBL
VIF
SIF
BOCMA
IF
FILTER
COMB
FILTER
YUV
VIF
SIF
DW
PROC.
YUV50AUDIO-PIP
HA
VA
HIP
CVBS-TEXT
(V)
AUDIO-PIP
AUDIO-EXT
(A) MONITOR-OUT
PICNIC (FBX)PAINTER
SIF
MSP
PROZONIC
YUV VD
VD100
HD100
FBL-TEXT
RGB-TEXT
L
R
HP
NVM
TXT
RAM
AMPL
VDHOP
HOP
L
S/W
R
HP
VERT
HD
E/W
CRT
SCAVEM
HOR
E/W
R
G
+
B
SCAVEM
CRT
POWER
ON/OFF
MAINS
Figure 9-1
CL 06532130_019.eps
131000

Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
GB 83EM1A 9.
The tuner type is a PLL tuner and delivers the IF-signal, via
audio & video SAW-filters, to the HIP (High-end Input
Processor). The HIP has the following functions:
• IF modulation.
• Video source- and record select.
• Colour decoder.
• Synchronisation.
Two EXT-connectors can be used: AV1 is fully equipped and
AV2 is meant for VCR. There is also a possibility for Y/C in.
The MON-out can be used for WYSIWYR (What You See Is
What You Record).
The HIP delivers the signal to the PICNIC. This IC takes care
of:
• Analogue to Digital conversion and vice versa.
• 50 to 100 Hz conversion.
• Panorama mode.
• Noise reduction.
• Dynamic contrast.
Digital Scan
For
the PROZONIC is required, which can be
connected to the PICNIC.
After the PICNIC the, now doubled, YUV- and H/V-signals
are fed to the HOP (High-end Output Processor). This IC
handles the video control and geometry part. The RGBsignals from TXT/OSD are also inserted via the HOP. The
video part delivers the RGB signals to the CRT-panel and the
geometry part delivers the H-drive, V-drive and also a drivesignal for rotation (as a variable DC-level on the V-drive
signal).
Both deflection circuits are 'hot' and located on the LSP and
are driven by the HOP. To make the galvanic separation, the
line drive is driven via transformer 5410 and the framedrive
via optocoupler 7610.The horizontal output stage generates
some supply voltages, the EHT-, focus- and Vg2-voltages.
The RGB amplifiers on the CRT-panel are integrated in one
IC and are supplied with 180 V from the LOT.
The SCAVEM circuit modulates transitions of the Luminance
(Y) signal on the horizontal deflection current, giving a
sharper picture.
The sound part is built around the MSP34xx (Multichannel
Sound Processor) for IF sound detection, sound control and
source selection. Amplification is done via an integrated
power amplifier IC, the TDA2616.
The microprocessor, called Painter (OSD, Teletext and
Control) takes care of the analogue TXT input- and output
processing. The Painter processor and RAM (if present) are
supplied with 3.3 V, which is derived from the +5VSTANDBY.
The NVM (Non Volatile Memory) is used to store the settings,
the Painter is an OTP (One Time Programmable) chip with
programmed ROM-code and the (optional) DRAM is used for
storing the Teletext pages.
In the EM1A there is a separate Standby Supply in order to
reduce the Standby power consumption. During Standby, the
Main Supply is switched off (via TS7529). A relay is used to
switch the Degaussing circuit.
The Main Supply, a SOPS supply based on the 'downconverter' principle, generates the 141 V (VBAT) and the 28
V for the audio part.
Difference with former MG-sets is that VBAT is not mains
isolated ('hot') and is alignment free.
• Mains filter
• Degaussing picture tube
• Standby power supply
• Main supply
Mains filter (diagram A1)
1501
3521
4M7
3509
2507
0001
14
23
5503
3500
1R5
6501
6502
6503
6504
CL 96532156_019.eps
+375V
+
2510
220µ
GND
180100
3501
Figure 9-2
The mains filter has 2 functions: it prevents high-frequency
signals to be transferred into the mains and it protects the set
from lightning damage.
C2507 prevents the high-frequency signals, generated by the
set, to be conveyed into the mains by short-circuiting them.
In case of a lightning surge between the 2 phases (differential
mode) the energy is immediately bled away through the VDR
(R3509) to the other phase.
In case of a lightning surge on both phases of the mains in
relation to the aerial earth, the mains filter acts as a high
resistance (UEMK=L * dI/dt) as a result of which the voltage
across coil L5503/04 increases. A spark gap (0001) prevents
that the voltage increases too much, which would lead to a
damaged coil. When ignited, the current will be discharged
via this spark gap.
The two networks using R3503//0002 and R3502//0003 are
also used for lightning protection. They lead the energy of a
common-mode lightning surge from the 'cold' to the 'hot' side
in case of insertion on the aerial or from the 'hot' to the 'cold'
side in case of insertion via the mains-input.
Resistor R3500 is used for limiting the inrush-current.
Degaussing picture tube (diagram A1)
After switching 'ON' the set via the mains switch, the
DEGAUSS_INPUT signal from the processor (Painter) will
be made high, transistor 7528 will conduct and relay 1002 will
be activated. Initially a considerable current will flow, via PTC
3516, through the degaussing coil. The PTC will heat up,
resistance will rise and the current will decay rapidly. The
Painter will switch off the relay after 12 seconds.
Standby power supply (diagram A2)
This power supply is of a SOPS type (Self-Oscillating Power
Supply) and is regulated by the controlled switching of an
oscillator. It uses the so-called 'Flyback' principle:
S
Id
+
375V
-
S
-
375V
+
D
-
+
D
+
Isec
-
C
C
+
+
96532156_020.eps
RL
RL
210100
U
out
U
out
9.1.3 Power supply (diagram A1 & A2)
General
The power supply has a number of main functions. These
functions are dealt with in succession:
Figure 9-3
• After closing switch 'S', the current ID will increase linear
in time. The magnetic energy in the primary coil is directly
proportional with the self-inductance of the coil and
current ID (thus with the time the switch is closed). The

GB 84 EM1A9.
voltage polarity at the secondary winding is negative
(due to different winding direction), meaning that diode D
will block. Capacitor C will discharge via RL, UOUT will
decrease.
• Opening switch 'S' will generate a counter-e.m.f. in the
primary winding, trying to maintain current ID. Through
this the polarity of the secondary voltage will inverse. The
magnetic energy, stored in the coil, will now be
transformed to the secondary side. Diode D will now
conduct, capacitor C will be charged and UOUT will
increase.
6103
3107
2K2
5102
2102
10µ
3106
2K2
+
3125
15R
7100
3126
10K
2101
2n2
3103
1K
3102
1K
3117
47R
6105
15V
3127
5K6
+375V
-20V
3120
10R
Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
HOT COLD
8
9
U
I
MAIN
PRIM
I
U
A
U
D
SEC
6111
6107
ON OFF
t0 t1 t2
3114
220R
I
SEC
3124 6122
68R 3V9
3101
6M8
GND-STB
U
MAINS
6106
20V
3110
10R
3104
47R
6108
G
7101
U
A
2
1
2114
10n
3
5
I
PRIM
U
D
7102
3108
//3118
GND-STB
5101
D
S
2104
2µ2
N.Usec
+5V2
U
RL
OUT
t
3113
t
15R
t
2109
t
330N
To apply this on the EM1A (diagram A2): replace Switch 'S'
by FET TS7102, coil L by L5101, diode D by D6107//D6111
and C by C2104.
Time interval t0 - t1:
After switching on the set, the gate of MOSFET TS7102 will
be high (max. 15 V due to zenerdiode D6105). This will drive
the FET into saturation (UDS = 0 V). The DC-voltage
UMAINS will be transposed across the primary winding of
L5101 (3, 5) resulting in a linear increasing current through
this coil.
The voltage across the co-coupled coil (1, 2) is also positive
and will keep the FET into conductivity via C2101, R3103,
R3105, R3102 and R3117 for some time. The slope of the
primary current is determined by the self-induction of the coil
and on the magnitude of the supply voltage (+375 V).
The maximum current is determined by the time the FET
stays into conductance (t0 - t1). This time is directly
determined by the voltage across R3108//R3118. This
voltage is a measure of the current and if it exceeds 1.4 V,
TS7101 will be driven into conductivity and consequently
connect the gate of TS7102 to earth; the FET will block. The
current will be: 1.4 V/(10//4.7 ohm) = 0.43 A.
The voltage across the secondary winding (8, 9) will be
negative, diodes D6111 and D6107 will block.
Time interval t1 - t2:
The sudden current interruption in the primary coil, will
induce a counter-e.m.f. that wants to maintain the current.
The voltage on the drain of the FET will increase. The
secondary voltage (8, 9) will become positive and will charge
Figure 9-4
7103/04
CL 96532156_021.eps
250100
C2104 via D6107 and D6111. All energy that was stored in
L5101 during t0 - t1 will be transferred into the load. Due to
the transformer principle, a voltage will now be induced in the
primary winding (3, 5) and the co-coupled winding (1, 2). This
voltage will be: N * USEC (N = winding ratio).
The voltage across the co-coupled coil will be negative,
keeping the FET blocked.
Time t2:
At t2, the current through the secondary coil will be reduced
to zero, as C2104 is no longer charged. As a consequence,
the voltages will decay and will change polarity. The gate of
the FET will be again made positive, is driven into
conductivity and the cycle starts again.
Feedback, stabilisation:
The Standby Power Supply always oscillates at maximum
power; the only limiting factor is the maximum primary
current that has been pre-set with R3108//3118.
UOUT is determined by R3114, R3124 and zenerdiode
D6122. If the voltage across R3114 exceeds the threshold
voltage of the diode of the optocoupler 7104 (±1 V) or, in
other words, UOUT exceeds 5.2 V the transistor of the
optocoupler will conduct.
Transistor TS7100 will be driven and a negative voltage will
be transposed to the emitter of TS7101. When TS7101
conducts, the gate of the FET is at earth potential forcing the
oscillator stop. Due to the load, the secondary voltage UOUT
will decrease. At a certain voltage, optocoupler TS7103/04
will block and the oscillator will start again.

Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
GB 85EM1A 9.
Since there are no capacitors and there is a high
amplification-factor in the feedback circuit, the feedback is
ultra-fast. This is why the ripple on UOUT is minimal. The
negative supply voltage (-20 V) used in the feedback circuit
originates from the co-coupling coil and is rectified through
D6103.
Stabilisation is not effected through duty-cycle control but
through burst-mode of TS7100.
Burst-mode is load dependent. If the power supply is less
loaded, the secondary voltage will have the tendency to
increase more rapidly. If the load on the power supply
increases, then the oscillator stops less often, right up to the
moment that the oscillator is operating continuously:
maximum load. If the power supply is now loaded even more,
the output voltage will decay. The maximum load is
determined by the maximum primary current set by R3108//
3118.
Protection:
If the optocoupler would fail, the secondary voltage will
increase. This would have disastrous consequences since
many IC's (e.g. Painter, flash-RAM, DRAM) are fed with this
5.2 V. In other words, very expensive repairs would be
required.
We already know that the negative supply is directly
dependent upon the secondary 5.2 V, as a consequence of
which the negative supply will increase proportionally as the
secondary voltage increases.
If the negative supply in the mean time reaches -30 V, D6106
will start to zener and as a consequence TS7101 will start
conducting. Basically, D6106 will take over the stabilisation
task of the optocoupler, however, with a considerable
spread: from -20 V to -30 V is a 50 % increase, thus UOUT
will increase from 5.2 V to max. 7.5 V.
Main supply (diagram A1)
Some important notes on beforehand:
V
is not isolated from the mains supply ('hot').
BAT
V
is alignment free.
BAT
The Main Power Supply generates the 141 V (VBAT) and the
28 V for the audio part, and is based on the so-called 'down
converter' principle.
S
L
V
BAT =
V
BAT
R
L
V
BAT
R
L
. δT
V
IN
T
060100
Vin
Vin
I
T
S
S
closedSopen
I
T
δT
T
D
+
C
I
D
L
D
+
C
I
D
96532156_022.eps
• After closing switch 'S', the linear in time increasing
current IT, , will charge capacitor C.
• Opening switch 'S' will generate a counter-e.m.f. in coil L,
trying to maintain current IT. This is possible via diode D
(this diode is also called 'freewheel diode'). So after
opening 'S', the magnetic energy stored in coil L will be
transferred to electrostatic energy in capacitor C. The
VIN will only supply current during the time that 'S' is
closed while a constant current is flowing through RL.
• VBAT is directly proportional with VIN and the time that
'S' is closed and reverse proportional with period time 'T'.
So by changing the duty cycle, it will be possible to
control VBAT.
U
in
U
R3514
3514 3515
0
-1.4V
V
GS
+12V
-0.7V
6506
3504
T
OFFTOFF
1503
7502
6508
5505
UMAINS
180V
i.s.o. 240V
ca 10 µs
3513
A
I
D
7504
D
G
S
V
GS
3508
6505
15V
5506
3
1
2515
t
t
6510
3518
15V
120K
3511
3512
68K
B
V
BAT
R
LOAD
COLDHOT
2503
5
7
4
5506
8
Figure 9-6
At start-up of the main supply, C2515 can be assumed as
being a shortcircuit. UAB will be 15 V (R3513, D6510) and
UGS of the FET will be +5.4 V (voltage division over R3512
and R3518). The FET will be driven into saturation (same as
closing switch 'S' ). The drain-current will increase linear in
time. With other words: resistors R3513 and R3518 will start
the oscillator.
The voltage across the co-coupled coil (4, 5) is also positive
and will keep the FET into conductivity.
The drain-current will also flow through R3514//R3515. The
voltage on the base of TS7502 will be +0.8 V due to the
stabilisation circuit (which is explained further). At increasing
current, the emitter-voltage of TS7502 will get more negative.
When this voltage reaches -0.7 V, TS7502 will be driven into
conductivity and consequently connect the gate of TS7504 to
earth; the FET will block (same as opening switch 'S'). The
maximum drain-current is: 0.7 V/(R3514//R3515) = 1.4 A.
The voltage polarities on L5506 will invert, keeping the gate
of TS7504 negative via the co-coupled coil (4, 5). The voltage
on the secondary winding of L5506 (7, 8) will be positive,
generating the +28 V audio supply voltage via D6507 and
C2512.
The sudden current interruption in the primary coil, will
induce a counter-e.m.f. that wants to maintain the current via
the 'freewheel' diode D6508. This current is linear decreasing
in time and as it is also flowing through R3414//R3415,
TS7502 will be blocked after a certain time period. The gate
of the FET will be again made positive, is driven into
conductivity and the cycle starts again.
Stabilisation of VBAT:
The output voltage VBAT will be determined by: VBAT = VIN
* TON/(TON + TOFF) = VIN * duty-cycle.
1502 6507
CL 96532156_014.eps
2512
210100
V
S
(28V)
Figure 9-5

GB 86 EM1A9.
Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
To stabilise the output voltage, a feedback loop is
implemented, which will reduce TON when VBAT increases
and vice versa.
Via a voltage divider, excisting of (1 %) resistors R3507,
R3510 and R3527, a voltage of 2.5 V (when VBAT = 141 V)
is fed to the input of precision shunt regulator 7506. This
regulator will conduct, a current will flow through R3524 and
TS7505 will be driven into conductivity. The base of TS7502
will now be set at a certain positive voltage. As this transistor
switches the FET TS7504 on and off, this circuit can
determine the dutycycle.
E.g. when the load increases, VBAT will decrease. As a
consequence, the input-voltage of regulator 7506 will
decrease, resulting in a lower current. Through that, the
emitter-base voltage of TS7505 will diminish.
The current through R3504 will decline, changing the basevoltage of TS7502 and through that the TON (will increase)
of the FET. The output voltage VBAT will rise.
If the load continues to increase, the regulator will block at a
certain moment, the collector-current of TS7505 will now be
zero. If there flows no current through R3504, TON will now
be maximum (IMAX = 1.4 A). This is the point where VBAT
will be below 141 V, and at further increasing load will be
switched off (The voltage across the co-coupled coil (4, 5) will
decrease due to the increasing load. Therefore the voltage
on the gate of TS7504 comes below the threshold voltage.
The supply switches off and an audible hiccuping can be
heard).
On the other hand when the load decreases, VBAT will rise.
As a consequence, the input-voltage of 7506 will also rise
resulting in a higher current. The current through R3504 will
rise, changing the base-voltage of TS7502 and through that
the TON (will decrease) of the FET. The output voltage VBAT
will be reduced.
If, for instance, VIN will decrease (e.g. UMAINS is 180 V i.s.o.
240 V), the slope of the drain-current will be flattened,
through which the FET will be longer into conductance,
keeping VOUT constant.
If, for any reason, the stabilisation circuit might fail, the output
voltage VBAT can never exceed 200 V (via D6514). D6514
will form a shortcircuit, VBAT will drop and the set will switch
off (this will result in an audible hick-uping of the supply).
Set to 'STANDBY" (via RC):
When the set is switched to 'STANDBY' via the Remote
Control, the Main supply will be switched off.
This is done by the circuit around TS7529 (see diagram A1):
During 'ON'-state the Main supply is fed with line pulses via
the STANDBY line. They are rectified and smoothed via
D6517, D6516 and C2530 and fed to TS7529. Because they
are less than -20 V, this transistor will be blocked.
When these pulses are stopped (STANDBY), TS7529 will be
saturated and TS7502 will be switched off. This will switch off
the Main supply.
Set to 'ON' (via 'STANDBY'):
At the moment the set is switched 'ON', the HOP is not
working (as much as possible IC's are made voltageless
during 'STANDBY'). Therefore it is impossible that the
STANDBY line carries line-pulses, so the main supply cannot
start up. This problem is solved via the 'low power start-up'
possibility of the HOP.
Via pin 22, the HOP receives, via the STANDBY_INFO line
from the Painter, a voltage of 5.2 V coming from the Standby
supply. The result will be that the HOP will generate pulses
with a nominal TOFF and TON growing from 0 to 30 % of the
nominal value.
This signal is unchanged until the Main supply is switched
'ON' and the HOP the correct I
2
C-command POR-bit) has
received.
Guarding circuit:
The negative pulses on the secondary winding of L5506 are
rectified by D6520 and smoothed by C2535. The resulting
negative DC-voltage will keep TS7510 blocked, even as
TS7511.
When something happens in the Main supply through which
these pulses will decrease, the DC-voltage will increase.
TS7510 starts to conduct, even as TS7511. Via R3541 and
D6522 this situation will be maintained (thyristor principle).
The collector of TS7511 drives via R3538 a positive pulse
back to the Painter (named STANDBY(POR)). The Painter
will now switch off the Main supply via the STANDBY_INFO
signal.
SSB
There are 3 voltages used for the SSB: +8 V, +5.2 V and +5
V.
+5.2 V is the Standby voltage; it should always be present.
The 8 V is derived from the 11D V with stabiliser 7906 (on
LSP). This 11D voltage is only present when the line-drive
pulses start the deflection.
The 8 V is used to switch the +5.2 V with transistor 7905 to
supply the +5 V.
9.1.4 Control & Teletext (diagram B7)
Painter
The SAA5667 (IC7001) is called the Painter (OSD, TXT and
Control). In this IC, the microprocessor and the TXT-decoder
(level 2.5) are integrated.
Some of its functions are:
• Set control.
• TXT/OSD acquisition.
• RGB-outputs to the HOP
• Menu blending; for blending the contrast is software
controlled.
• I/O-ports for I2C, RC5, LED, and service modes.
• Error code generation.
The software for EM1A can be 192 kB.
For TXT-data 100 pages can be stored in IC7011.
The Non Volatile Memory IC7011 is a 4-kb version M24C32.
All ICs in this part are supplied with 3V3. For this voltage a
3V3 stabiliser is used (IC7005).
When the 3.3 V is available, a POR is generated with
TS7003/7004 to wake up the Painter. During the reset all I/O
pins are high. When a POR is generated the TV-set is in
Standby mode.
The horizontal (HD100) and vertical (VSYNC) sync pulses
are also fed to the Painter for stable OSD and TXT.
Teletext
The TXT-decoder in the Painter gets its video signal directly
on pin 31 (from the HIP).
The RGB-outputs are available on pins 46/47/48. Fast
blanking is realised via pen 52.
A separate memory is used to store the TXT information
(IC7011).
2222
I
C
In the EM1A-chassis with Painter-processor there are two
2
C-busses used:
I
• Slow (max. 100 kHz) hardware I
used for all IC communication.
• Separate short bus (called I
2
C-bus (called I2C1),
2
C3) for the Non Volatile
Memory (NVM) to avoid data corruption.

Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
GB 87EM1A 9.
NVM
The Non Volatile Memory contains all set related data that
must be kept permanently, such as:
• Software identification.
• Operational hours.
• Error-codes.
• Option codes.
• All factory alignments.
• Last Status items for the customer + a complete factory
recall.
• TXT featuring (keeping habit watch data).
9.1.5 Tuner & IF (diagram A7 & B2)
The tuner is I2C-controlled and is capable of receiving off-air,
S- (cable) and Hyperband channels:
The tuning is done via I2C. The reference voltage on pin 9 is
33 V. This voltage is derived from the 180 V (from the LOT)
via 2 resistors of 120 kΩ (diagram F) and a zenerdiode. The
Painter together with the HIP controls the tuning procedure.
There is also automatic switching for the different video
systems.
The IF-filter is integrated in a SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave)
filter. The type of this filter is depending of the standard(s)
that has to be received. Two SAW filters are used: One for
filtering picture-IF and one for filtering sound-IF.
The output of the tuner is controlled via an IF-amplifier with
AGC-control. This is a voltage feedback from pin 62 of the
HIP to pin 1 of the tuner. AGC take-over point is adjusted via
the service alignment mode ’Tuner AGC’. If there is too much
noise in the picture, then it could be that the AGC setting is
wrong. The AGC-setting could also be mis-aligned if the
picture deforms with perfect signal. The IF-amplifier amplifies
too much.
The video IF-signal is fed to pins 2 & 3 of the PLL-controlled
IF-demodulator. The voltage controlled oscillator of the PLL
is adjusted via the service menu ‘IF AFC’. If the alignment is
correct then the displayed frequency in the installation menu
is the same as the applied frequency from a generator. The
external coil L5408 connected between pins 7 & 8 is used as
reference. The demodulated IF-video signal is available at
pin 10 of the HIP. In this video signal there is a rest of sound
carrier, which is filtered by the sound trap 1406 or 1407
(depends on the received standard).
Then the signal is fed to the HIP again (pin 12) where the
group delay can be corrected, dependent on the standard
that is received. On pin 13 the CVBS-signal becomes
available which is used for further processing in the TV. Via
TS7322 the signal is supplied to AV1 (PIP/DW) and back into
the HIP (pin 14) to the I/O selection.
To realise quasi split sound, the IF-signal is fed to the HIP on
pin 63 & 64 via SAW-filter 1405. The FM (or AM for L-norm)
-modulated signal is available on pin 5 and is fed to the audio
demodulator MSP34xx.
9.1.6 Video: High-end Input Processor (HIP, diagram B2)
In the EM1A the TDA932xH input processor is used, which
contains the following functions:
• IF demodulation.
• Group delay correction.
• AFC signal generation, used to track drifting transmitters.
• Sound carrier re-generation (SIF).
• AM demodulation.
• Sync acquisition, delivering HA and VA.
• Switching off IF-filtering.
The HIP has various inputs.
• Full matrix switch with:
– 2 CVBS inputs
– 2 Y/C (or additional CVBS) inputs
– 1 CVBS front end input
• Two RGB and 1 YUV-input
Outputs: Three separate switchable outputs can be used:
• 1 YUV-output is fed to the PICNIC
• 2 CVBS outputs: One for Teletext Dual Screen and the
other for output to MONITOR OUT to have WYSIWYR
(What you see is what you record)
The input signals from the Front I/O are fed to the HIP and
front detection is fed to the Painter.
AV1 is a CVBS- and a YUV input (e.g. for DVD), while AV2 is
meant for CVBS and Y/C (SVHS). The 3rd option is a
MONITOR OUT-output.
Video processing
The sandcastle-pulse of the HIP will not be used for
synchronisation. The HOP will generate synchronisation
signal derived from the feature box (PICNIC) signals. The
HIP itself (no external voltage) controls the Y/C switch in the
HIP.
The chrominance decoder in the HIP is full multistandard:
PAL/SECAM/NTSC.
Two different crystals can be connected to the pins 54 & 57
without any alignment. The crystals are also used as a
reference for the synchronisation. A digital control circuit that
is locked to the reference signal of the colour decoder
determines the start-up of the sync. This crystal may only be
replaced by the original one. If just a crystal is taken, the
internal capacitance will be different and the effect will be that
there is no colour.
In the HIP, a sync separation circuit has been integrated; the
HIP delivers the HA and VA (50/60 Hz) to the PICNIC and
PIP/DW module. On pin 59 there is the 1fH sandcastle but
this is not connected to any circuit and only used internally for
the colour demodulator. The 2fH-sandcastle signal is
generated by the HOP.
9.1.7 Video: Feature box (PICNIC, diagram B3)
Introduction
The basic function of the Feature box (FBX6) is picture
improvement, and depending on the version several scan
conversion methods can be applied. The PICNIC is the
central key component.
In the EM1A-chassis the featurebox is integrated on the SSB.
The PICNIC is used for the 100 Hz conversion. In the PICNIC
the following functions are present:
• The ADC.
• The DAC.
• The 100 Hz conversion.
• The noise limiter (DNR).
• The contrast improvement.
All these functions are integrated in one IC: SAA4978H, a
160 pins QFP
ADC/DAC
Analogue to Digital conversion is done with three identical 9bit ADC's.
Digital to Analogue conversion uses three identical 10-bit
DAC's.
In the PICNIC there are three 9 bits ADCs present for Y, U &
V. For digitising the Y (luminance) 9 bits are used, to realise
a more detailed picture. The 9 bits are only internally used.
Via dithering the 9 bits are reduced to 8 bits and that data is
stored into the memory. The data in the memory is fed back
to the PICNIC and via undithering the data is again
reproduced 9 bits for processing.
U/V (colour difference signals) is also sampled with 9 bits.
These two 9 bit data streams are multiplexed to 4 bits data
streams. This reduction can be allowed, as the perception for
colours by the human eye is less sensitive as for luminance.

GB 88 EM1A9.
Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
100 Hz conversion
The main task of the PICNIC is the conversion from 50 Hz to
100 Hz for YUV and HV-sync. In order to remove 'large area
flicker' (especially visible in a white picture), the field-rate of
the video is doubled by the FBX6. A 50 Hz frame frequency
is converted to 100 Hz. Also the line frequency (16 kHz) is
doubled (32 kHz). Basically, when the video input contains
fields A, B etc..., the conversion provides an AABB sequence
on the display. The actual conversion is done in the first Field
Memory by reading it twice at double speed, while writing it
once.
Automatic Aspect Ratio Adaptation (AARA)
This feature uses data from the 'black bar detection circuit' to
adapt the vertical and horizontal amplitude to an aspect ratio
belonging to the display without showing the black bars.
CTI
At CVBS video signals, the bandwidth of colour signals is
limited to 1/4 of the luminance bandwidth. Transients
between areas of different colours are therefore not very
sharp. The PICNIC can steepen these transients artificially
with a time manipulation algorithm.
Dynamic Contrast
To make the contrast (black/white) range wider, Philips has
invented Dynamic Contrast. It uses the digital memory used
in 100 Hz sets. It measures every A-field (25 x/s) and digitally
analyses where on the greyscale most of the image is
located. If it's a relatively dark image, the lighter part of that
image is stretched towards white, so that more contrast will
become visible in that picture. If it's a relatively light image,
the darker part of that image is stretched towards black, so
that these darker parts will have more contrast. When the
image is in the middle of the greyscale, both dark and light
parts are stretched.
PROZONIC
M
E
M
1
When applying this, the 2nd Field Memory has to be
installed. The following functions are available:
• Line flicker reduction (Digital Scan): this is a feature to
reduce the 25 Hz interlace line flicker.
• Dynamic Noise Reduction: noise affected signals can be
improved by combining the pixel values of the current
and past video fields. This is however only possible in
areas without movement.
• Variable Vertical Sample Rate Conversion
• Synchronous No Parity Eight bit Reception an
Transmission interface (SNERT-bus)
Depending on the chassis model, the FBX6 can have the
following specification:
Featurebox 6 diversity
Set Chipset
EM1A 1fH N.A.
EM1A 2fH 1 Memory
EM1A 2fH DNR 1 Memory incl. DNR
EM1A 2fH Dig. Scan PROZONIC + 2 Memories
9.1.8 Video: High-end Output Processor (HOP, diagram B4)
General
In the HOP (High-end Output Processor, TDA9330) the video
processor and digital deflection processor are integrated.
The main functions of the HOP are:
• Video control (contrast, brightness, saturation, etc.).
• 2nd RGB interface for OSD/TXT.
• Peak White Limiting.
• Cut-off control and White Drive (RGB outputs).
• Geometry control.
The YUV-signals from the PICNIC are fed to the HOP. In the
HOP, the video and geometry control parts are integrated.
Also the RGB-signals from TXT/OSD are inserted via the
HOP. This IC has all functions from a video processor and
geometry control (like the DDP in MD2). The geometry part
delivers the H-drive, EW-drive and also a drive signal for
rotation. The internal V-drive circuit of the HOP is not used (is
explained further on).
BUS A BUS
BUS A BUS
BBUS BUS CBUS BUS D
2
I C
100Hz CONFIGURATION
BBUS BUS CBUS BUS D
2
I C
DIGITAL SCAN
PICNIC/SAA4978H
M
E
M
1
PICNIC/SAA4978H
P
R
O
Z
N
I
C
Y FEATY DEC
U FEATU DEC
V FEATV DEC
HD100HA
VD100VA
M
E
M
2
Y FEATY DEC
U FEATU DEC
V FEATV DEC
HD100HA
VD100VA
CL 96532156_017.eps
110100
Figure 9-7
To the PICNIC external IC's are connected dependent of the
features.
If EM1A has only 100 Hz, then only one memory-IC is used
to store one frame.
For sets with Digital Scan the PROZONIC (IC7708,
SAA4990H) is added with two memory-ICs (IC7714 & 7715).
It is an abbreviation for PROgressive scan Zoom and Noise
reduction IC.
Video Control
After conversion to RGB again, the signals can be controlled
for Saturation, Contrast and Brightness.
2nd RGB interface for OSD/TXT
On pins 35 - 38 the RGB and fast blanking from the Painter
(OSD and TXT) are inserted.
Peak White Limiting
On pin 43 there is a Peak White Limiting signal line (PWL). If
the beam current (EHT-info line) increases, then the EHTinfo voltage will decrease. PWL is controlled by average
limiting via R3343/C2333.
Cut-off control
Switching the TV to Standby:
1. Vertical scan is completed.
2. Vertical flyback is completed (the horizontal output is
gated with the flyback pulse, so that the horizontal output
transistor cannot be switched on during the flyback
pulse).
3. Slow stop of the horizontal output is started, by gradually
reducing the 'on' time at the horizontal output from
nominal to zero (this will take 50 ms).
4. At the same time the fixed beam current is forced via the
black current loop for 25 ms. This is done by setting the
RGB outputs to a maximum voltage of 5.6 V.
In the EM1A a 'one-point' cut-off control is used:
A current of 8 µA (for cut-off) is fed to pin 44 of the HOP. This
is done with a measurement pulse during the frame flyback.

Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
GB 89EM1A 9.
During the 1st frame, 3 pulses are generated to adjust the
cut-off voltage at a current of 8 µA. With this measurement
the black level at the RGB-outputs is adjusted. So at start-up
there is no monitor pulse anymore.
At start-up, the HOP measures the pulses, which come back
via pin 44. The RGB-outputs have to be between 1.5 V and
3.5 V. If one of the outputs is higher than 3.5 V or one of them
lower then 1.5 V, the RGB-outputs will be blanked.
Geometry control
All geometry control is done via I2C and the data is stored in
the NVM (IC7012) of the SSB.
Line drive (LINEDRIVE1).
Line drive is derived from an internal VCO. As a reference an
external resonator is used (1301). The internal VCO is locked
with the HD100-pulse, which comes from the PICNIC. The
'PHI-2' part in the HOP receives the HFB_X-RAY_PROT (pin
13) to correct the phase of the line drive. The EHT-info is
supplied to pin 14 (DYN-PHASE-CORR) to compensate
picture breathing depending on the beam current.
Frame drive (FRAMEDRIVE+).
The VD100 signal from the PICNIC will be extended for 16.5
lines by the circuit around TS7309 and 7311. The resulting
signal (VDHOP) will drive TS7310. This will result in the
(asymmetric) FRAMEDRIVE+ signal.
Note: The Frame outputs (pins 1/2) of the HOP are not used!
East/West drive.
At pin 3 the E/W-drive is available. Pin 4 is a feedback input
for the EHT-info and is used to prevent pumping of the
picture. EHT varies also dependent of the beam current.
Frame rotation.
For frame rotation a control voltage is used from pin 25 of the
HOP. This voltage can vary from 0.4 till 4 V.
Guarding protections:
• Flash detection:
When a flash occurs, the EHT-info will become negative very
fast. Via D6303/D6304/R3316, TS7303 starts to conduct.
This makes pin 5 of HOP high. When pin 5 of HOP is high,
then the output (pin 8) is immediately stopped. If the H-drive
stops, then also pin 5 will be low again, which will reset the
flash detection. A bit (FLS) will be set in an output status
register, so via the Painter it can be seen when there was a
flash. This FLS-bit will be reset when the Painter has read
that register.
• HFB protection:
If the HFB is not present then this will be detected via the
HOP. The Painter puts the TV into protection and an error
code will be generated.
9.1.9 Synchronisation (diagram B3 & B4)
The HIP video processor provides vertical and horizontal
sync pulses V
and HA, which are synchronised with the
A
incoming CVBS signal. These pulses are fed to the PICNIC
where they are doubled to be synchronous with the 100 Hz
picture. The outgoing pulses, V
D100
and H
D100
HOP that supplies the vertical and horizontal drive pulses
and the 2f
sandcastle pulse.
H
The VD100 pulse from the PICNIC is only one line long.
Therefore this pulse is converted into a VDHOP signal by a
530 µs monostable oscillator (extended by 16.5 lines). This
signal is on block function level equal to VSYNC and
FRAMEDRIVE+.
The Painter is synchronised on the HD100 pulse from the
FBX and on the VSYNC for the synchronisation of TXT/OSD.
are fed to the
When no CVBS is offered to the video processor, the VA and
HA pulses are switched off by the HIP, and the VD and HD
pulses are then generated by the PICNIC. This to assure a
stable OSD.
9.1.10 Horizontal (line) deflection (diagram A3)
Driving the line output stage
LINEDRIVE 1
HOTCOLD
MAIN SUPPLY +11D
STANDBY SUPPLY +5V2
T
ON
T
OFF
STARTNORMAL
T7421 conducting
3406
2402
(HOP)
EW_DRIVE
(HOP)
6408
6407
3411
2412
2414
7409
3414
3407
2415
3486
3487
3404
3484
7481
3485
3409
5410
5411
7408
+8V
3483
7482
141V
7421
2417
3417
141V
3418
3481
6481 2480
5
5430
1
2420
6480 2426 6422
7480
Figure 9-8
The HOP (located on the SSB) generates the line-drive
pulses (LINEDRIVE1), which have a frequency of 31250 Hz
(T = 32 µs).
When the LINEDRIVE1 signal is high, TS7409 and TS7408
will conduct. A constant DC voltage will be applied across
L5410, causing a linear increasing current through this coil.
The secondary voltage of L5410 has a negative polarity so
that TS7421 will block. When switching on the set, the
current through L5410 is supplied by the 5V2 Standby supply
(via D6407), and taken over by the +11D voltage (via D6408)
of the main supply.
When the LINEDRIVE1 signal becomes low, TS7409 and
TS7408 will block. The voltage polarity across the primary
winding of L5410 will invert. The positive voltage on the
secondary winding will now drive TS7421 into conductivity.
Because of the storage time of the line transistor (TS7421),
L5410 cannot transfer its energy immediately to the
secondary side. This may result in high voltage peaks on the
collector of TS7409 and TS7408. To prevent that these
peaks will damage the transistors, a 'snubber' circuit (C2414,
C2412 and R3411) will suppress them.
When the LINEDRIVE1 signal is high again, the abovedescribed sequence starts again. Circuit L5411 and R3409
will increase the switch-off time of the line transistor.
The line stage will be started via the 'slow start' principle.
During start-up, the HOP generates line drive pulses with a
small TON and a high frequency (50 kHz); TOFF will be
constant and TON will be gradually increased until the dutycycle is 50 % (normal condition). The time interval from start
to normal condition takes about 150 ms. When switching off,
the same procedure is followed, but now in reverse order.
Operation of the line output stage
To explain the operation of the line output stage, we use the
following start conditions:
• C2433 is charged to max. 141 V (VBAT)
• TS7421 is driven into conductivity.
1
*
2
*
2425 6423
S-correction
X
Deflection centre
Linearity Correction
YX
X > Y
2421
4
3
Caused by
serial losses in
the line output stage
1
LINE DEFL. COIL.
2
LINEARITY
(*1)
COIL.
5421
2432//33//34
(
2)
*
2
5422
1
CL 96532156_013.eps
3431
2431
260100

GB 90 EM1A9.
Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
5430
141V
7421
2420
I
Defl
t2t1
100V
6423
6422
Line defl.
2425
+
2433
141V
-
2421
41V
2426
41V
5422
5430
141V
7421
2420
Figure 9-9
Period t1 - t2:
When TS7421 is driven into conductivity, the capacitor
voltage of 141 V, will be divided across bridgecoil L5422 and
the deflection coil (conn. 0317). Due to the chosen
inductance values, there will be 100 V across the deflection
coil and 41 V across L5422. The linear increasing current in
the deflection coil will result in a spot moving from the centre
of the picture tube to the right.
The voltage across L5422 will also charge C2421 (41 V - 0.7
V).
Period t2 - t3:
At the moment the LINEDRIVE signal becomes high,
TS7421 will stop conducting. In the coils a voltage will be
induced, trying to maintain the current. The current through
the line deflection coils continues to flow through C2425 and
C2421 and the current through L5422 continues to flow
through C2426 and C2421. The energy stored in the line
deflection coil is passed to C2425, and the energy of L5422
to C2426.
The resonance-frequencies of these 2 LC-circuits define the
flyback time of the spot from the right side of the picture tube
to the left.
On average no current flows through C2421 and thus the
voltage across this capacitor remains constant.
5430
141V
7421
I
Defl
t3 t4
Line defl.
2425
6423
2420
6422
2433
2421
41V
2426
5422
5430
141V
7421
6423
2420
6422
Figure 9-10
Period t3 - t4:
As for the period t2 - t3; but now the current flows in the
opposite direction, since the voltage across C2425 and
C2426 is higher than the voltage across C2433 and C2421.
Period t4 - t5:
The coils want to maintain the negative current and will
charge the capacitors negative. Because of this, D6422 and
D6423 will conduct. The voltage is 100 V across the
deflection coil and 41 V across L5422. As both diodes
conduct, we may consider the voltage to be constant. A linear
current flows with the same changing characteristics as in
period t1 - t2. The spot now moves from the extreme left of
the picture tube to the centre. Before the current becomes
zero, and the spot is located in the centre of the frame,
TS7421 reverts back into conductivity. First a short negative
current will flow. The cycle starts again.
The linearity correction
I
Defl
t2 t3
A constant voltage across the horizontal deflection coil
should result in a linear increasing saw-tooth current. This
however is not the case as the resistance of the coil is not
negligible. In order to compensate for this, a pre-magnetised
2425
2421
2426
CL 96532156_024.eps
Line defl.
2433
5422
060199
6423
6422
coil L5421 in series with the deflection coil is used. This coil
ensures that during time interval t1 - t3 the circuit-resistance
will be higher than during t4 - t5. L5421 is called the linearity
coil.
To avoid self-oscillation, R3431 and C2431 are placed
parallel to L5421.
The S-correction
Since the sides of the picture are further away from the point
of deflection than the centre, a linear saw-tooth current would
result in a non-linear image (the centre would be scanned
slower than the sides). To solve this, the deflection current for
the right- and left side will be reduced.
C2433 is charged quadratic during time interval t1 - t2. Left
and right the voltage across the deflection coil decreases,
causing the deflection to slow down. In the centre, the
voltage increases and the deflection will be faster. An Sshaped current will have to be superimposed onto the sawtooth current. This correction is called finger-length
correction or S-correction. C2433 is relatively small, as a
result of which the saw-tooth current will generate a parabolic
voltage with negative voltage peaks. The current also results
in a parabolic voltage across C2421, resulting in the fingerlength correction, proportionally increasing with the picture
width. The EW-DRIVE signal will ensure the largest picture
width in the centre of the frame. Here the largest correction is
applied. The larger the picture width, the higher the deflection
current through C2433.
The E/W-correction
A line, written at the upper- or lower side of the screen, will
be larger at the screen centre when a fixed deflection current
is used. Therefore the amplitude of the deflection current
must be increased when the spot approaches the screen
centre. This is called East/West correction.
The EW-DRIVE signal is generated in the HOP and will drive
I
Defl
FET TS7480 via TS7481 and optocoupler TS7482. TS7480
will charge capacitor C2423 more or less, increasing the
deflection current when reaching the centre of the screen.
t5t4
2425
2421
41V
2426
Line defl.
100V
+
2433
-
141V
5422
CL 96532156_025.eps
231299
41V
Secondary line-voltages
During the blocking time of TS7421, the magnetic energy of
coil 1 - 5 of the LOT will be transferred to electrical energy in
the secondary winding. Via rectifying and smoothing, the
several secondary supply voltages will be generated:
• EHT, Focus and Vg2-voltage
• +180V for the CRT panel (pin 8 LOT)
• +11D for the line deflection (pin 12 LOT)
• +13VLOT for the frame deflection (pin 6 LOT)
• -15VLOT for the frame deflection (pin 3 LOT)
• Filament voltage (pin 9 LOT)
•
The EHT-INFO signal is derived via R3450//R3451. This
signal decreases while the beam current increases. It is fed
to the HOP to compensate for loss of picture width and
picture height.
The DYN-FASE-CORR signal is fed to the HOP via C2455
and drives a dynamic phase correction necessary because of
beam current variations. This is done by regulating TON of
the line transistor TS7421.
East-West circuit
The moment TS7480 is driven into saturation, C2421 will
discharge during the flyback. As a consequence of which
C2421 must be charged again during the scan via the
conduction diode D6422 (as long as C2421 is not charged to
the voltage across L5422, D6422 will conduct). The current
in the deflection coil is therefore larger than the current

Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
GB 91EM1A 9.
flowing in L5422 (1-2). The voltage across the deflection coil
increases, so the picture width increases. When TS7480
blocks, C2421 will not discharge anymore and the voltage
across C2421 will remain constant. The result is that the
voltage across the deflection coil is minimal. The voltage
across coil L5422, however, is maximal. This coil (L5422)
consists of a transformer:
• As the current through the coil 1-2 increases (smaller
picture width), the current through coil 3-4 decreases.
Because of the transformer characteristic a higher
voltage will be subjected to coil 3-4, which will counteract
the current. The current will diminish even further.
• When the current through coil 1-2 diminishes (larger
picture width), the current through coil 3-4 increases.
The EW Drive
The EW drive signal originates in the HOP and is supplied to
TS7480. The shape of this signal determines the various
geometric correction parameters:
• H amplitude
• EW-parabola
• EW-corner
• EW-trapezium
• Horizontal parallelogram
• Horizontal bow
Beam current correction
The EHT-info at point 10 of the LOT is dependent on the
value of the beam current and the voltage divider R3450,
R3451 and C2450. The EHT-info is fed to the HOP to trim the
contrast and to compensate for the changes in picture-width
as a function of the EHT-info, when the high-voltage is
decreased. The EHT-info is integrated via C2450 and sent
to the gate of the E/W FET (TS7480) as a DC-voltage to
correct the EW-current.
9.1.11 Vertical (frame) deflection (diagram A4)
Driving the frame output stage
HOTCOLD
HOP
(6-BITS DAC) 25
V
FRAMEDRIVE+
+13V_LOT
7610
3440
ROTAT I ON
CIRCUIT
+8V
3389
3390
3394
DHOP
3386
3391
7312
3388
7310
V
SYNC
3630
3631
+13V_LOT 141V
36193632
7606
7605
Figure 9-11
The HOP drives the frame output stage. As the HOP is 'cold'
and the frame output stage is 'hot', they must be galvanic
isolated. This is done by means of an optocoupler. In the MGchassis the HOP generates 3 signals needed for the frame
output stage: VDPOS, VDNEG and FRAME ROTATION. To
avoid the costs of 3 optocouplers, the frame drive pulse and
rotation DC-voltage are added together and then fed to
optocoupler TS7610.This is done as follows:
The VD100 signal from the PICNIC (diagram B3 pin 19) is
extended for 16.5 lines and inverted via a monostable
multivibrator (TS7311 & TS7309, diagram B4). The output
signal VDHOP is then superimposed on a DC-voltage from
pin 25 of the HOP. The resulting signal is called
FRAMEDRIVE+ and is fed to optocoupler 7610 (diagram
A4). So this signal contains info for both the frame deflection
and the frame rotation (if present).
The circuit around IC7440 will amplify this signal and the
output current will flow through the rotation coil. The vertical
pulses on this signal are filtered by C2445 to ensure that only
a DC-voltage will be supplied to the rotation coil.
The output voltage of the rotation circuit is between -8 and +8
V.
141V
3600
3601 3633
A
2601
+13V +12V
2600
7600
3602
3603
V. AMPL.
36123614
7603
3618
3615
+13V
3606
3607
7602
3608
3605
-15V
E/W
1
-
5
7620
7
+
3609
2602
V. SHIFT
3610
FRAME
3623
DEFL.
V
OUT
I
COIL
COIL
3620//21//22
CL 96532156_027.eps
070100
Figure 9-12
The sawtooth voltage for the frame output stage is not
generated by the HOP but by a discrete circuit after the
optocoupler 7610: via R3600 and R3601 a linear increasing
voltage over C2601 is built up with a large time constant.
The circuit around TS7603 is a current source, driving C2601
with a current value derived from the E/W modulator. This will
result in an S-shaped voltage on C2601 (also known as EWcorrection).
Flyback generator
The frame output stage is supplied via the +13 V and -15 V
coming from the LOT. The output of the amplifier is 0 VDC,
so a coupling capacitor is not required.
During the (forward) scan, a supply of +13 and -15 V is
sufficient to respond to the slow changing current. The
flyback generator puts a voltage of -15 V on pin 3. Because
of the voltage drop over zenerdiode D6622 (8.2 V), C2622
will be charged to 19 V: being 13 + (15 - 8.2 - 0.7) V.
During the flyback scan, the change in current per time is
3600
2M2
3601
2M2
A
2601
6600
470n
much larger, so a higher voltage is required. The flyback
generator will now generate a voltage of +13 V on pin 3.
Added to the charge on C2622 this will give a flyback voltage
of 32 V (depending on the CRT size, this value can differ).
The IC amplifier (IC7620, pin 5) supplies the sawtooth
current to the frame deflection coil. The current through this
coil is measured via R3620//R3621//R3622 and fed back to
CL 96532156_026.eps
210100
the inverting input of the amplifier.
R3624 and C2624 on the output of the amplifier, form a filter
for high frequencies and in that way also prevents
oscillations.
Peak voltages on the output, e.g. as a result of a possible
flash, are damped by the clamp circuit consisting of D6619,
C2627 and R3627. The network consisting of R3625, R3629
and C2629 form an extra damping circuit.
Protection circuit for bridge-coil and frame output stage
The secondary voltage of bridge coil L5422 is guarded at the
diode modulator (D6421/22) via a detection circuit consisting
of an 8.2 V zenerdiode (diagram A3). When the bridge-coil is
working properly, the average voltage on D6422 is such that
this zenerdiode will conduct and will drive TS7652 into
saturation via the BRIDGE_PROT signal (see diagram A4).
When, for any reason, the secondary side of the bridge-coil
is shorted, the average voltage on D6422 will drop below the
zener-voltage and TS7652 will block. Now capacitor C2642
will be charged. Transistor TS7407 will start conducting and
the STANDBY signal will be grounded via R3403. This will
switch off the main supply (see diagram A1).

GB 92 EM1A9.
Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
Via the circuit built around TS7641 the frame output stage is
guarded. If the frame output stage is working properly,
TS7641 and TS7652 will both conduct and thereby
discharging C2642. TS7407 is blocked now, causing the
STANDBY signal to be high ohmic.
If there are frame pulses missing, TS7641 will block and
capacitor C2642 can be charged. Transistor TS7407 will now
start conducting and the STANDBY signal will be grounded
via R3403. This will switch off the main supply (see diagram
A1).
9.1.12 Audio (diagram B6, A5 & A6)
Introduction
All EM1A sets contain one of ITT's Multistandard Sound
Processing IC's for sound decoding. The diversity arises
because each member of the MSP-family handles its own set
of sound standards:
• MSP3415D: Europe & AP decoding, Stereo incl.
NICAM.
• MSP3451G: Global decoding, Virtual Dolby.
This IC takes care of the main FM sound decoding. AM
decoding for the L system is done by the HIP. The
demodulated L sound is then again source selected and
processed in the MSP. The reason for this is the bad AM
detection performance of the MSP. In case of NICAM L
however, this is handled by the MSP.
All MSP versions contain digital audio processing, used for
the basic left/right stereo sound, such as bass, treble,
balance, incredible sound and spatial. In addition to that, the
MSP3451 is also able to perform Virtual Dolby, a Dolby
approved sound mode for surround sound reproduction with
left/right speakers only.
Audio source selection
MSP3515D (stereo)
This IC is an economised version of the MSP3410 that is
used in the MG-chassis. It can cover 2 stereo and 1 mono
(AM) input. Since more inputs are required, a separate
source selector is used (HEF4052, IC7675). This selector
has AV1, AV2, FRONT and MON-OUT (Tuner) as input and
is connected to the EXT1 input of the MSP3415. The EXT2
input is not used.
Since the MSP3415 has only one EXT output, which is
connected to the EXT1, a constant level output and
connection to EXT2 is not available. This is fixed by
connecting the HEF4052 input selector to the constant level
output and to EXT2 via a so-called 'Régimbeau' switch
(IC7652).
This switch is needed to prevent feedback (Larsen effect).
When EXT2 is chosen as input signal, and the output of
EXT2 is selected, this means that the main picture is also
EXT2 and will cause the Larsen effect. To prevent this, the
record select must be switched to Tuner. This is especially
important when decoders are used, behind a 'transparent'
VCR connected to EXT2.
To get a constant level output if the Tuner is selected, the
EXT1 output (Tuner at any time), has to be fed back to the
input selector and selected as input for the MSP (EXT1
input).
The MSP3415 has no separate output to drive a headphone.
The headphone is therefore hardwired (on the LSP) to the
main sound output.
MSP3451G (Virtual Dolby)
The MSP3451, which is used in all versions supporting
Virtual Dolby, is capable of supporting 4 stereo inputs and 1
mono (AM) INPUT. Therefore the extra input selector
(HEF4052) is not needed.
The MSP3451 is also capable of supporting 2 EXT outputs,
so the trick used in the MSP3415 set-up to get a constant
level output is not needed.
The MSP3451 has a separate headphone output, so sound
control be done separate from the speakers.
Audio decoding
At the input a choice can be made between two IF-signals;
SIF and SIFM.
The selected signal is fed to the AGC. After this, an ADC
converts the IF-signal to digital.
This digital signal can be processed by 2 demodulation
channels. The first one is able to handle FM and NICAM
signals. The second one can handle FM and AM signals.
Each channel contains a mixer to shift the incoming signal in
the frequency domain. This shift is determined by the value
of a DCO (Digital Controlled Oscillator)..
After the down-mix, the signal is fed, via a filter, to a
discriminator. From here the AM, FM or NICAM
demodulation can be performed.
Both channels contain an 'automatic carrier mute' function,
which automatically mutes the output of the analogue section
when no carrier is detected.
After demodulation, the FM-signals are subjected to a deemphasis operation. After that the matrix of the stereo
system is applied.
Audio processing
The sound processing in EM1A is completely done by the
MSP3415D for 'Stereo' sets and the MSP3451G for 'Virtual
Dolby' sets:
• Volume control is done by the user via the SOUND
menu.
• Tone control is done via the BASS/TREBLE control.
• Headphone control in 'Stereo'-sets is done via the
loudspeaker output of the MSP, no sound control
possible. In 'Virtual Dolby'-sets, the MSP has a separate
Headphone output so separate sound control is possible.
• Mute control can be done in different ways:
– Via the SOUND_ENABLE line of the Painter. Used
during start-up/switch-off conditions, in order to avoid
audible plops. This line is active low (high = mute).
– Via the decoding part of the MSP.
– Via the processing part of the MSP.
The mute on the RC or in the UI is per today a combination
of processing mute and SOUND_ENABLE line. When a user
mute is done, the processing mute will turn down the volume,
after which the SOUND_ENABLE line is switched. De-muting
is the other way around. The reason for this is a technical
problem with crosstalk of the headphone into the
loudspeakers.
Automatic Volume Levelling (AVL)
One of the features of the MSP-family is AVL. If used, it limits
the big volume differences in the broadcast between e.g.
news transmissions and commercials or within a movie.
To be able to get a Dolby approval (for the Virtual Dolby sets),
the AVL feature must be switchable. Therefore, the AVL
feature is customer switchable via the menu.
Audio amplification
The audio amplifier part is very straightforward. It uses 2
integrated power amplifier ICs (TDA2616). It delivers an
output of 2 x 10 WRMS to 2 full range speakers and/or
subwoofer.

Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
GB 93EM1A 9.
The supply voltage is +28 V, generated by the main supply
via L5506.
Muting is done via the SOUND-ENABLE line connected to
pin 2 of the amplifier-IC and coming from the Painter. This
signal is inverted by TS7730, as a result of which at a high
level of the SOUND-ENABLE signal, current is sinked from
pin 2 and the IC mutes.
9.1.13 CRT & SCAVEM (diagram F)
RGB amplifiers
On the CRT panel, the RGB amplifier (TDA6108, IC7307) is
located. Via the outputs 9, 8 and 7 the cathodes of the picture
tube are driven.
The supply voltage for the amplifier is 180 V and is derived
from the LOT.
SCAVEM
The SCAVEM-circuitry is implemented in the layout of the
picture tube panel. It is thus not an extra module. SCAVEM
means SCAn VElocity Modulation. This means that the
picture content influences the horizontal deflection. In an
ideal square wave, the sides are limited in slope by a limited
bandwidth (5 MHz).
SCAVEM will improve the slope as follows: At a positive
slope, an SCAVEM-current is generated which supports the
deflection current. The first half of the slope the spot is
accelerated and the picture is darker, while at the second half
of the slope, the spot is delayed and the slope becomes
steeper.
At the end of the slope, the SCAVEM-current decays to zero
and the spot is at the original position. An overshoot occurs
which improves the impression of sharpness. At the negative
slope, the SCAVEM-current counteracts the deflection.
During the first half of the slope, the spot is delayed and the
slope becomes steeper.
During the second half the spot accelerates, the SCAVEMcurrent is zero at the end of the slope.
Via the three resistors R33315, R33317 and R3320, Red,
Green and Blue are added together and offered to the emitter
TS7300. On the collector of this transistor, configured in a
common base, the sum of these 3 signals is obtained. Via the
emitter follower formed with TS7301, this signal is conveyed
to the differentiator C2303, R3309 and R3318. Only the high
frequencies are differentiated (small RC-time).
The positive and negative pulses of this signal drive
respectively TS7303 and TS7302 into conductivity. The DC
setting of the output stage is set by R3304, R3308, R3316
and R3319. The working voltage of the transistors is settled
at half the supply voltage.
At the positive section of the pulse, the current flows through
R3318, C2307, the SCAVEM-coil and TS7303. At the
negative section of the pulse, the current flows through
R3318, C2409, the SCAVEM-coil and TS7302.
between the two tuners need to be swapped, then the tuner
RF frequency is swapped.
The AV-switching is the same for all regions.
Key components
• Tuner (7201):
– AP Non-China TEDE9X700A
– China TEDE9X701A
• SAW Filter (1352):
– AP Non-China OFWK7260M (39.8MHz)
– China OFWK6287K (38.0 MHz)
• IF + Video processor (7301):
– AP/China & LATAM TDA8889H
• PIP processor (7801) SAB9081H
• Switching IC's TDA8601 (7803), HEF4053 (7401 &
7402)
• IO expander (7403) M62320P
9.1.14 Double Window (DW)
Introduction
The Double Window (DW) panel provides the option for
viewer to see two pictures or programs on the displayed area
of a TV screen. The displayed pictures can be in PIP mode
or DW mode. The viewer can also select the size and position
of the 'second' picture.
The DW-models always have 2 tuners. In the AP execution,
the TV uses one RF signal, which is connected, to the tuner
with splitter located on the DW panel. The 2nd tuner on the
main panel is fed with the signal from this splitter. Due to this
connection, the Main PCB tuner (Tuner 1) always processes
the Main Picture, and the tuner located on the DW panel
(Tuner 2) always process the DW picture. If the picture

GB 94 EM1A9.
Block Diagram
There is one configuration as shown below.
Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
DVSYNC
DHSYNC
V-MAIN-OUT
U-MAIN-OUT
Y-MAIN-OUT
0205
43 1
V-PIP+MAIN-IN
Y-PIP+MAIN-IN
PIP-AUDIO
U-PIP+MAIN-IN
9
10
68
RF to Main Tuner
TUNER - 7201
SPLITTER
LATAM & AP
CVBS-PIP_TUN1-2-CVBS-IN
CVBS_TER_OUT
SEL_TUNER1
NAFTA & AP-NTSC 24
CVBS-SC1_AV1-IN
CVBS-SC2_AV2-IN
SEL-MAIN-R1R2
Y-CVBS-FRONT-IN
C-SC2_SVHS-IN
C-FRONT-IN
SDA
SCL
2
1
12
13
2
1
7402-B
10
7402-A
11
7401-B
12
13
3
7403
2
EXPANDER
15
14
SEL_TUNER2
5
15
3
7401-A
11
IO
11
1
PIP-AUDIO
AP & LATAM
4305
1333
7401-C
14
SEL-FRNT-RR
4
SEL-MAIN-R1R2
5
SEL-FRNT-RR
6
SEL_TUNER1
7
SEL_TUNER2
9
FBLK
10
RESET
11
SEL-YUV_RGB
12
SEMI-STD-BY
1352
4
DOUBLE WINDOW PROCESSOR
4
5
2
1
TDA888X
8
16
IF
IC7301
+ +
29
26 60
GUIDE+
20
54
7402-C
5
3
9470
IC7801
SAB9081H
8772
SVSYNC
5649
4
SEL_PIP_CVBS
982100
SV
81
SHSYNC
7
MY
MU
SY
SU
8379
SYNC
RGB/YUV
MATRIX
COLOUR
DECODING
RGB/
YUV
INPUT2
41 42 43
R-SC1-IN_V-IN
G-SC1-IN_Y-IN
7501
V-CHIP
MV
8
DY
12
DU
10
DV
68
YUV INTERFACE
40 45 46
B-SC1-IN_U-IN
14
SDA
15
SCL
NAFTA ONLY
6
7
8
RBG/YUV
MATRIX
7803
234
12
11
10
TDA8601
RGB
OUTPUT
RGB
INPUT1
CL 06532045_070.eps
010800
Circuit Description
IF & Video section
The TV uses one RF input to the DW’s tuner with a splitter.
The tuner on the main board receives RF from the splitter.
Due to this configuration, the main board tuner always
processes the Main picture while the DW tuner always
processes the Sub picture. If the picture between the two
tuners needs to be swapped, then the tuners’ RF frequencies
are swapped.
Figure 9-13
IF-TER from the tuner is fed to pin-1 & 2, IF circuits of
TDA888x IC7301 via a SAW filter. The AGC voltage for the
tuner can be adjusted in the SAM’s tuner menu.
Dependant of the region execution, different SAW-filters are
applied.Therefore circuit diversity is unavoidable as shown in
figure below. The RESET-signal is used to set the SAW-filter
to different IF frequency modes. Table below shows IF
frequency settings by the RESET signal.

Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
CL06532045_072.eps
100500
Figure 9-14
SAW-filter (pos. 1352) RESET = Low RESET = High
AP P/M (38.9MHz) NTSC-M/N PAL BG/DK/I
China (38.0MHz) NTSC-M/N PAL BG/DK/I
In order to display the external AV sources by the DW panel,
source selection circuit is incorporated on the panel. In
EM1A, 4 external AV sources are possible (AV1, AV2/SVHS1, AV3/S-VHS2 & YUV). The selection between these
sources is done by IC7401 HEF4053.
Note: When S-VHS is inserted from the rear, AV2 source will
be disabled. Likewise when S-VHS is inserted from the sideAV. The YUV is fed directly to video processor IC7301. This
source selection is done internally by the IC.
The video processor IC7301 will decode the CVBS at pin-24
or pin-29 into YC signal and further process it into YUV signal
and output at pin-40, 45 & 46. The IC7301 internal FM
demodulator is used to produce mono audio and is available
at the pin-8 of IC7301. This audio signal PIP-AUDIO is fed to
the SSB sound processor as such that DW sound appeared
at the headphone
GB 95EM1A 9.
Power supplies
The power supplies used by DW panel are from the main
board 5V, 8V and 33V (for tuner only). The 5V is regulated to
+3.3V, +3V & +3VD by IC7802 LM317T. These voltages are
mainly used by DW processor circuitry. The 8V is mainly
supplied to IC7301 TDA888x IF + video processing circuitry
and also to fast switching IC7803.
DW/PIP processing
IC7801 SAB9081 is a multi-standard PIP controller, which
can be used in double window or PIP applications. The YUV
from the video processor IC7301 is fed to pin-79, 81 & 83.
IC7801 will inserts YUV from the IC7301 with reduced size
into the main picture YUV source in PIP environment. The
main picture YUV is fed to pin-100, 2 & 98 respectively.
These signals are mainly used during the DW mode.
Inside IC7801, the conversion to the digital environment is
done on chip with ADCs. Processing and storage (1 MB
DRAM) of the video data is done entirely in the digital
domain. The conversion back to the analogue domain is
done by DACs. Internal clocks are generated by PLLs, which
lock on to the applied horizontal and vertical syncs from the
main & sub pictures. The main picture syncs are applied to
pin-70 (vert.) & pin-94 (hor.) and the sub picture syncs are
applied to pin-72 (vert.) and pin-87 (hor.).
For DW mode, the main picture is compressed horizontally
by a factor of two and directly fed to the output. After
compression, a horizontal expansion of two is possible for
the main picture. The sub picture is also compressed
horizontally by a factor of two but stored in memory before it
is fed to the outputs.
Post-processed YUV signals are fed to fast switching IC7803
TDA8601 pin-6, 7 & 8. In normal operation (w/o DW), the
main picture YUV signals (at pin-2, 3 & 4) are bypassed by
IC7803, and returned back to the main video processor.
When DW mode is active, the compressed YUV signals
(main & sub pictures) are used and fed to main video
processor. During the PIP mode, only sub-picture YUV
signals are used. The insertion control is made possible by
fast blanking signal from IC7801 pin-68.

GB 96 EM1A9.
Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
9.2 Abbreviation list
AARA Automatic Aspect Ratio Adaptation:
algorithm that adapts aspect ratio to
remove horizontal black bars;
keeping up the original aspect ratio
ACI Automatic Channel Installation:
algorithm that installs TV sets
directly from cable network by
means of a predefined TXT page
ADC Analogue Digital Converter
AFC Automatic Frequency Control:
control signal used to tune to the
correct frequency
AGC Automatic Gain Control: algorithm
that controls the video input of the
featurebox
AI Artificial Intelligence
AM Amplitude Modulation
ANR Automatic Noise Reduction: one of
the algorithms of Auto TV
AR Aspect Ratio: 4 by 3 or 16 by 9
ASF Auto Screen Fit: algorithm that
adapts aspect ratio to remove
horizontal black bars but without
throwing away video information
ATV See Auto TV
AUDIO_C Audio Centre
AUDIO_L Audio Left
AUDIO_R Audio Right
AUDIO_SL Audio Surround Left
AUDIO_SW Audio Subwoofer
AUDIO-L-PROC Audio left processed
AUDIO-R-PROC Audio right processed
AUDIO-SR Audio surround right
Auto TV Name for the combination of picture
features/improvements, which work
automatically (ANR/Auto sharpness/
Auto Histo/ambient light).
BC-PROT Beam current protection
BG System B and G
BLC-INFO Black current information
B-SC1-IN Blue EXT1 in
B-SC2-IN Blue EXT2 in
B-TXT Blue teletext
CENTER Centre speaker
C-FRONT Chrominance front input
CL Constant Level: audio output to
connect with an external amplifier
ComPair Computer aided rePair
CRT Cathode Ray Tube or picture tube
CSM Customer Service Mode
CTI Colour Transient Improvement:
manipulates steepness of chroma
transients
CVBS Composite Video Blanking and
Synchronisation
CVBS-SC1-IN CVBS EXT1 in
CVBS-SC2 OUT CVBS EXT2 out
CVBS-SC2-IN CVBS EXT2 in
CVBS-SC3-IN CVBS EXT3 in
CVBS-SC4-IN CVBS EXT4 IN
CVBS-TER CVBS terrestrial
CVBS-TXT-DSOUT CBVBS teletext Dual Screen out
CVBS-TXT-OUT CVBS teletext out
CVBS-Y-FRONT CVBS luminance front input
DAC-HOP Digital analogue converter HOP IC
DBE Dynamic Bass Enhancement: extra
low frequency amplification
DC-filament Filament supply voltage
DC-PROT DC protection
DFU Direction For Use: description for the
end user
DNR Digital Noise Reduction: noise
reduction feature of the box
DSP Digital Signal Processing
DST Dealer Service Tool: special remote
control designed for dealers to enter
e.g. service mode
DVD Digital Versatile Disc
DYN-FASE-COR Dynamic phase correction
EHT Extra High Tension
EHT-INFO Extra High Tension information
EPG Electronic Program Guide: system
used by broadcasters to transmit TV
guide information (= NexTView)
EW East West, related to horizontal
deflection of the set
EXT External (source), entering the set
via EXT or via cinches
FBL Fast Blanking: DC signal
accompanying RGB signals
FBL-SC1-IN Fast blanking signal for EXT1 in
FBL-SC2-IN Fast blanking signal for EXT2 in
FBL-TXT Fast Blanking Teletext
FBX Feature Box: part of small signal /
separate module which contains 100
Hz processing, extra featuring and
AutoTV algorithms
FEAT-U U from Feature Box
FEAT-V V from Feature Box
FEAT-Y Y from Feature Box
FILAMENT Filament of CRT
FLASH Flash memory
FM Field Memory or Frequency
Modulation
FMS Functional Module Specification:
document that describes an isolated
hardware function
FRONT-C Front input chrominance (SVHS)
FRONT-DETECT Front input detection
FRONT-Y_CVBS Front input luminance or CVBS
(SVHS)
FRS Functional Requirement
Specification: software specification
document
G-SC1-IN Green EXT1 in
G-SC2-IN Green EXT2 in
G-TXT Green teletext
HA Horizontal Acquisition: horizontal
sync pulse coming out of the HIP
HD100 Horizontal Drive: horizontal sync
pulse coming out of the featurebox
HDTV High Definition TV: highest
resolution defined by the ATSC
standard (1080 lines and 1920
horizontal pixels, referred to as
1080i) The second HDTV standard,
720p x 1280 is not used in EM1A
chassis (3fH standard not feasible)
Headroom Extra margin provision to avoid
clipping of signals
HEATER Heater (Filament)
HFB Horizontal Flyback Pulse: horizontal
sync pulse from large signal
deflection
HFB+13V Non rectified output 13V-winding
LOT
HIP High-end video Input Processor:
video and chroma decoder of EM1A
HOP High-end video Output Processor:
video, sync and geometry controller
of EM1A
HP Headphone
HSI Hardware Software Interface
IN-FRONT-SNDL Sound left front in
IN-FRONT-SNDR Sound right front in
IN-SC1-B In EXT1 Blue

Circuit descriptions and abbreviation list
GB 97EM1A 9.
IN-SC1-G In EXT1 Green
IN-SC1-R In EXT1 Red
IN-SC1-SNDL In EXT1 sound left
IN-SC1-SNDR In EXT1 sound right
IN-SC2-B In EXT2 Blue
IN-SC2-CVBS_Y In EXT2 CVBS or luminance (SVHS)
IN-SC2-FBL In EXT2 fast blanking
IN-SC2-G In EXT2 Green
Interlaced Scan mode where two fields are
used to form one frame. Each field
contains half the number of the total
amount of lines. The fields are
written in “pairs”, causing line flicker.
IO-BUS In/Out - Bus
Last Status The settings last chosen by the
customer and read and stored in
RAM or in the NVM. They are called
at start-up of the set to configure it
according the customers wishes
LDP Line Deflection Protection
LED Light Emitting Diode
LINE-DRIVE Line drive signal
LNA Low Noise Adapter
LSP Large signal panel
MSP Multistandard Sound Processor: ITT
sound decoder of EM1A
MUTE Mute-Line
NC Not Connected
NDF No vertical DeFlection: vertical
flyback protection
NHF No Horizontal deflection: horizontal
flyback protection
NVM Non Volatile Memory: IC containing
TV related data e.g. alignments
O/C Open Circuit
ON/OFF LED On/Off control signal for the LED
OSD On Screen Display
Painter On screen display Teletext and
Control; also named Artistic
(SAA5800)
P50 Project 50 communication: protocol
between TV and peripherals
PCB Printed Circuit board
PICNIC Peripheral Integrated Combined
Network IC: main IC for 100 Hz
featuring and feature processing
PILOT Pilot Signal
PILOTMUTE Pilot Mute signal
Progressive Scan Scan mode where all scan lines are
displayed in one frame at the same
time, creating a double vertical
resolution.
PTP Picture Tube Panel
RAM Random Access Memory
RC Remote Control
RC5 RC5 signal from the remote control
receiver
RESET Reset signal
ROM Read Only Memory
SAM Service Alignment Mode
SC Sandcastle: pulse derived from sync
signals
SCAVEM Scan Velocity Modulation
S/C Short Circuit
SC1-OUT EXT output of the MSP audio IC
SC2-B-IN Scart2 Blue in
SC2-C-IN Scart2 chrominance in
SC2-OUT EXT output of the MSP audio IC
SIF Sound Intermediate Frequency
SIMM 80-fold connector between LSP and
SSB
SLDP Smart Local Dooming Prevention
(HW and SW)
SNDL-SC1-IN Sound left EXT1 in
SNDL-SC1-OUT Sound left EXT1 out
SNDL-SC2-IN Sound left EXT2 in
SNDL-SC2-OUT Sound left EXT2 out
SNDR-SC1-IN Sound right EXT1 in
SNDR-SC1-OUT Sound right EXT1 out
SNDR-SC2-IN Sound right EXT2 out
SNDR-SC2-OUT Sound right EXT2 out
SNDS-VL-OUT Surround sound left variable level
out
SNDS-VR-OUT Surround sound right variable level
out
SNERT Synchronous No parity Eight bit
Reception and Transmit
SSB Small Signal Board
STBY Standby
SW Subwoofer
TXT Teletext
TXT DS Teletext Dual Screen
µP microprocessor
VA Vertical Acquisition
VBAT main supply for deflection (mostly
141 V)
VD100 Vertical Drive: vertical sync pulse
from deflection
VFB Vertical Flyback Pulse: vertical sync
pulse coming from the feature box
VL Variable Level out: processed audio
output towards external amplifier
WYSIWYR What You See Is What You Record:
record selection that follows main
picture and sound
XTAL Quartz crystal
Y-OUT Luminance-signal to HOP IC

GB 98 EM1A10.
10. Spare parts list
Spare parts list
[A] Large Signal Panel + [F] CRT
Panel
Various
3122 785 90260 Main Supply Repair Kit
3122 785 90270 Standby Supply Repair Kit
3122 785 90120 Line Supply Repair Kit
0010 2422 025 16374 2P male V
0020 4822 267 10774 2P male red
0029 3104 304 22832 Chassis frame
0032 4822 492 70788 Fix IC
0036 4822 265 20723 2P
0037 3104 304 21114 LOT SSB support
0045 4822 267 10734 5P
0050 4822 466 93461 20 X 25
0065 3104 304 22031 LOT Spacer EMG
0102 3104 304 21601 Support bracket AP
0125 3104 304 90361 Insulation plate EMG
0150 4822 265 11253 Fuse holder
0153 4822 265 11253 Fuse holder
0203 4822 265 30734 4P
0204 2422 025 04854 6P female V
0224 4822 265 41113 7P
0298 2422 500 80036 CRT V 9P female
0317 4822 265 20723 2P
0324 4822 265 41113 7P
0325 2422 025 16382 3P male V
0340 4822 267 10968 11P
0383 4822 267 10735 3P
0391 4822 267 10973 1P
0395 4822 492 70789 Fix transistor
0396 4822 492 70789 Fix transistor
0480 4822 492 70789 Fix transistor
0504 4822 492 63524 Fix transistor
0505 3122 121 24785 Spring for bracket
0620 4822 492 70789 Fix transistor
0750 3122 121 24785 Spring for bracket
0760 3122 121 24785 Spring for bracket
1001 4822 252 60151 Spark gap
1002 2422 132 07411 Relay 1P 5V 5A
1200 2422 542 90067 TUN V+U PLL PH Dk
1200 2422 542 90072 TUN TV V+U
1401 4822 071 51601 Fuse 160mA
1501 4822 070 34002 Fuse 4A
1503 4822 070 12502 Fuse 2.5A
1735 2422 025 16407 3P male V
1736 2422 025 16382 3P male V
1737 4822 267 10735 3P
1900 2422 026 05064 Cinch 12P female H
1901 2422 026 04926 4P female H
1920 4822 265 30735 5P
1921 2422 025 04851 3P
1922 2422 025 04851 3P
1923 2422 025 16599 80P female V
1936 2422 025 12485 11P male V
1937 4822 267 10557 10P
1940 4822 267 10968 11P
1943 4822 267 10748 3P
1945 4822 267 10735 3P
1946 5322 268 90415 2P
1947 4822 267 10734 5P
1948 4822 265 31215 3P
g
2101 5322 122 32818 2n2F 10% 100V
2102 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2104 4822 123 14025 2200µF 20% 16V
2106 5322 126 10223 4n7F 10% 63V
2108 4822 121 70162 10nF 5% 400V
2109 4822 126 13482 470nF 20-80% 16V
2110 5322 121 42498 680nF 5% 63V
2111 4822 121 43526 47nF 5% 250V
2112 4822 124 11913 22nF 20% 275V
2113 4822 122 33127 2n2F 10% 63V
2114 4822 121 10711 100nF 20% 275V
2120 5322 121 42386 100nF 5% 63V
2200 4822 124 80195 470µF 20% 10V
2201 4822 126 14076 220nF 25V
2202 4822 126 13473 220nF 80-20% 50V
2203 4822 124 40433 47µF 20% 25V
2300 4822 124 40764 22µF 100 V
2301 4822 124 40196 220µF 20% 16V
2303 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2304 4822 121 41856 22nF 5% 250V
2305 3198 017 44740 470nF 10V
2306 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2307 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2309 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2313 4822 124 11565 10µF 20% 250V
2315 4822 122 33216 270pF 5% 50V
2316 4822 121 40518 100nF 10% 250V
2317 5322 121 44356 4n7F 5% 2kV
2318 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2319 4822 122 30043 10nF 80% 63V
2320 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2325 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2400 4822 124 11575 7µF 20% 160V
2402 4822 126 13599 3n3F 10% 500V
2411 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2412 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2413 4822 124 12255 10µF 20% 50V
2414 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2415 4822 122 33575 220pF 5% 63V
2416 4822 126 14133 1nF 20% 250V
2417 4822 126 14076 220nF 25V
2419 4822 126 14237 470pF 10% 2kV
2420 4822 121 70595 1n2F 5% 2kV
2421 4822 121 42634 560nF 5% 250V
2424 4822 126 10206 2n2F 10% 500V
2425 4822 121 10526 9n1F 5% 2kV
2426 2222 375 90218 18nF 5% 630V
2429 4822 121 43343 4n7F 10% 400V
2430 4822 121 41857 10nF 5% 250V
2431 4822 126 10206 2n2F 10% 500V
2433 2222 479 90022 0.43µF 250V
2446 5322 122 32268 470pF 10% 50V
2447 5322 122 32268 470pF 10% 50V
2448 5322 122 32268 470pF 10% 50V
2450 5322 121 42578 100nF 5% 250V
2455 5322 122 34099 470pF 10% 63V
2459 4822 122 31177 470pF 10% 500V
2460 4822 124 40784 3300µF 20% 16V
2461 4822 122 31177 470pF 10% 500V
2462 4822 124 80061 1000µF 20% 25V
2463 4822 122 31177 470pF 10% 500V
2464 4822 124 80061 1000µF 20% 25V
2465 4822 122 31177 470pF 10% 500V
2466 4822 124 41584 100µF 20% 10V
2467 4822 124 41584 100µF 20% 10V
2468 4822 124 12297 4.7µF 20% 350V
2469 4822 122 31169 1n5F 10% 500V
2471 2222 460 90025 18nF 2% 63V
2480 4822 121 43856 4n7F 5% 250V
2485 2222 460 90022 10nF 2% 63V
2489 4822 124 40433 47µF 20% 25V
2492 4822 126 14076 220nF 25V
2493 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2494 4822 126 14076 220nF 25V
2495 4822 126 14076 220nF 25V
2496 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2497 4822 126 14076 220nF 25V
2498 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2499 4822 122 33891 3.3nF10% 63V
2501 4822 126 14588 2n2F 10% 1kV
2502 5322 122 32818 2n2F 10% 100V
2503 5322 121 42489 33nF 5% 250V
2505 2020 554 90148 470pF 20% 250V
2506 4822 121 43913 470nF 10% 100V
2507 4822 126 13589 470nF 275V
2508 4822 124 11913 22nF 20% 275V
2509 4822 124 11913 22nF 20% 275V
2510 4822 124 12415 20µF 20% 400V
2512 4822 124 12056 1000µF 20% 35V
2513 5322 122 34099 470pF 10% 63V
2514 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2515 2020 021 91543 47µF 20% 160V
2518 4822 126 13249 150pF 10% 500V
2519 5322 122 32818 2n2F 10% 100V
2520 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2521 4822 122 33216 270pF 5% 50V
2528 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2530 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2531 4822 122 31169 1n5F 10% 500V
2536 4822 124 21913 1µF 20% 63V
2538 5322 126 10223 4n7F 10% 63V
2601 4822 121 51319 1µF 10% 63V
2602 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2603 2020 552 95447 16V 2U2
2604 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2607 4822 124 40769 4.7µF 20% 100V
2609 4822 124 40196 220µF 20% 16V
2610 4822 122 33127 2n2F 10% 63V
2620 4822 126 14076 220nF 25V
2621 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2622 4822 124 40255 100µF 20% 63V
2624 4822 121 51252 470nF 5% 63V
2625 4822 121 51252 470nF 5% 63V
2627 5322 124 40641 10µF 20% 100V
2639 2238 780 15654 220n 10% 16V
2640 4822 124 21913 1µF 20% 63V
2642 4822 124 40255 100µF 20% 63V
2653 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2704 4822 124 41751 47µF 20% 50V
2730 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2731 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2732 4822 124 40255 100µF 20% 63V
2733 4822 124 40255 100µF 20% 63V
2734 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2735 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2738 4822 124 80791 470µF 16V 20%
2739 4822 124 80791 470µF 16V 20%
2756 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2758 4822 124 40769 4.7µF 20% 100V
2759 4822 124 40769 4.7µF 20% 100V
2760 4822 124 80061 1000µF 20% 25V
2761 4822 124 80061 1000µF 20% 25V
2762 4822 124 80061 1000µF 20% 25V
2765 4822 124 40255 100µF 20% 63V
2766 4822 124 40255 100µF 20% 63V
2767 4822 124 80144 220µF 20% 25V
2768 4822 124 80144 220µF 20% 25V
2775 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2776 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2782 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2784 4822 121 43526 47nF 5% 250V
2785 4822 121 43526 47nF 5% 250V
2786 5322 121 42498 680nF 5% 63V
2906 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2910 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2912 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2913 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2917 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2920 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2923 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2925 5322 122 31863 330pF 5% 63V
2926 4822 124 11767 470µF 20% 25V
2927 4822 124 41751 47µF 20% 50V
2928 4822 126 13482 470nF 20-80% 16V
2941 5322 122 31865 1n5F 10% 63V
2942 5322 122 31865 1n5F 10% 63V
2944 4822 121 10779 1n5F 10% 50V
2946 5322 122 31865 1n5F 10% 63V
2951 4822 124 21913 1µF 20% 63V
2952 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2953 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
f
3101 4822 053 20106 10M 5% 0.25W
3102 4822 050 26801 680Ω 1% 0.6W
3103 4822 050 26801 680Ω 1% 0.6W
3104 4822 116 52195 47Ω 5% 0.5W
3105 4822 050 26801 680Ω 1% 0.6W
3106 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3107 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3108 4822 116 52176 10Ω 5% 0.5W
3109 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3110 4822 052 10109 10Ω 5% 0.33W
3113 4822 116 52186 22Ω 5% 0.5W
3114 4822 116 83872 220Ω 5% 0.5W
3117 4822 116 52195 47Ω 5% 0.5W
3118 4822 050 24708 4Ω7 1% 0.6W
3120 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3123 4822 116 52176 10Ω 5% 0.5W
3124 4822 116 52199 68Ω 5% 0.5W
3125 4822 116 52182 15Ω 5% 0.5W
3126 4822 050 21003 10k 1% 0.6W
3127 4822 116 52289 5k6 5% 0.5W
3130 4822 116 52195 47Ω 5% 0.5W
3200 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3201 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3202 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3203 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3230 4822 053 11223 22k 5% 2W
3300 4822 052 10109 10Ω 5% 0.33W
3301 4822 053 12472 4k7 5% 3W
3303 4822 117 10965 18k 1% 0.1W
3304 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3307 4822 051 20109 10Ω 5% 0.1W
3308 4822 117 11148 56k 1% 0.1W
3309 4822 117 10353 150Ω 1% 0.1W
3310 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3311 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3312 4822 117 11449 2k2 5% 0.1W

Spare parts list
GB 99EM1A 10.
3316 4822 117 11148 56k 1% 0.1W
3318 4822 051 20478 4Ω7 5% 0.1W
3319 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3321 4822 053 12472 4k7 5% 3W
3322 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3334 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3335 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3336 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3337 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3338 3198 013 01020 1k 20% 0.5W
3339 3198 013 01020 1k 20% 0.5W
3340 3198 013 01020 1k 20% 0.5W
3341 4822 052 10151 150Ω 5% 0.33W
3342 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3343 4822 050 22202 2k2 1% 0.6W
3345 4822 116 52191 33Ω 5% 0.5W
3347 3198 013 01520 1k5 20% 0.5W
3348 4822 050 22202 2k2 1% 0.6W
3349 3198 013 01020 1k 20% 0.5W
3350 4822 116 83883 470Ω 5% 0.5W
3351 4822 116 83883 470Ω 5% 0.5W
3352 4822 116 83883 470Ω 5% 0.5W
3354 4822 117 11449 2k2 5% 0.1W
3355 4822 051 20478 4Ω7 5% 0.1W
3356 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3357 4822 051 20478 4Ω7 5% 0.1W
3358 4822 117 11139 1k5 1% 0.1W
3365 4822 051 20478 4Ω7 5% 0.1W
3402 4822 117 10837 100k 1% 0.1W
3403 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3404 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3406 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3407 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3408 4822 117 11504 270Ω 1% 0.1W
3409 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3410 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3411 4822 116 52193 39Ω 5% 0.5W
3414 4822 117 13577 330Ω 1% 1.25W
3415 3198 012 31590 15Ω 5% 3W
3417 4822 116 52176 10Ω 5% 0.5W
3418 4822 050 23303 33k 1% 0.6W
3431 4822 052 10331 330Ω 5% 0.33W
3450 4822 116 52238 12k 5% 0.5W
3451 4822 116 52303 8k2 5% 0.5W
3460 4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3461 4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3462 4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3463 4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3464 4822 052 11108 1Ω 5% 0.5W
3465 4822 052 11108 1Ω 5% 0.5W
3466 4822 052 10228 2Ω2 5% 0.33W
3467 4822 052 10228 2Ω2 5% 0.33W
3468 4822 052 11688 6Ω8 5% 0.5W
3469 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3470 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3471 4822 117 11507 6k8 1% 0.1W
3472 4822 051 20393 39k 5% 0.1W
3473 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3474 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3476 4822 116 83874 220k 5% 0.5W
3477 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3478 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3481 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3484 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3485 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3486 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3487 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3489 4822 117 11449 2k2 5% 0.1W
3490 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3495 4822 050 23303 33k 1% 0.6W
3496 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3497 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3498 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3499 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3500 4822 117 12074 1Ω5 10% 7W
3501 3198 013 04710 470Ω 20% 0.5W
3504 4822 116 83883 470Ω 5% 0.5W
3505 4822 051 20683 68k 5% 0.1W
3506 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3507 4822 050 21604 160k 1% 0.6W
3508 3198 012 16820 6.8k.1W
3509 2322 595 90022 VDR DC 1mA/612V
3510 4822 117 11951 2k 1% 0.1W
3511 4822 116 52276 3k9 5% 0.5W
3512 4822 116 52297 68k 5% 0.5W
3513 4822 116 52272 330k 5% 0.5W
3514 3198 012 16870 0Ω68 5% 1W
3515 2322 193 53128 1Ω2 5%
3516 4822 116 10075 9Ω 220V
3517 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3518 4822 116 52234 100k 5% 0.5W
3519 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3520 4822 053 11333 33k 5% 2W
3521 4822 117 10118 1M 5% 0.5W
3522 4822 116 83961 6k8 5%
3523 4822 051 20105 1M 5% 0.1W
3524 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3525 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3526 4822 116 83303 10Ω 2W
3527 4822 117 11454 820Ω 1% 0.1W
3528 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3529 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3530 4822 116 52297 68k 5% 0.5W
3531 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3533 4822 051 20159 15Ω 5% 0.1W
3535 4822 051 20184 180k 5% 0.1W
3536 4822 051 20684 680k 5% 0.1W
3537 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3540 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3542 3198 012 11570 0Ω15 5% 1W
3543 4822 117 11504 270Ω 1% 0.1W
3544 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3545 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3600 4822 050 24704 470k 1% 0.6W
3601 4822 050 24704 470k 1% 0.6W
3602 4822 051 20822 8k2 5% 0.1W
3603 4822 101 11186 470Ω 30% lin 0.1W
3604 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3605 4822 051 20273 27k 5% 0.1W
3606 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3607 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3608 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3609 4822 101 11192 22k 30% lin 0.1W
3610 4822 051 20333 33k 5% 0.1W
3612 4822 051 20274 270k 5% 0.1W
3613 4822 051 20274 270k 5% 0.1W
3614 4822 050 21504 150k 1% 0.6W
3615 4822 116 52292 560k 5% 0.5W
3616 4822 116 52285 470k 5% 0.5W
3617 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3618 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3619 4822 051 20562 5k6 5% 0.1W
3620 4822 116 80176 1Ω 5% 0.5W
3621 4822 116 80176 1Ω 5% 0.5W
3622 4822 116 80176 1Ω 5% 0.5W
3623 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3624 4822 052 10158 1Ω5 5% 0.33W
3625 4822 116 83872 220Ω 5% 0.5W
3626 4822 116 83872 220Ω 5% 0.5W
3627 4822 116 52238 12k 5% 0.5W
3628 5322 116 53564 3Ω3 5% 0.5W
3630 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3631 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3632 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3633 4822 117 11449 2k2 5% 0.1W
3639 4822 051 20105 1M 5% 0.1W
3640 4822 116 52257 22k 5% 0.5W
3641 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3642 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3643 4822 051 20223 22k 5% 0.1W
3644 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3645 4822 116 52272 330k 5% 0.5W
3652 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3653 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3661 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3662 4822 051 20225 2M2 5% 0.1W
3663 4822 051 20332 3k3 5% 0.1W
3665 4822 051 20684 680k 5% 0.1W
3701 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3702 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3703 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3705 4822 051 20122 1k2 5% 0.1W
3706 4822 051 20122 1k2 5% 0.1W
3707 4822 051 20122 1k2 5% 0.1W
3708 4822 116 83961 6k8 5%
3710 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3711 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3714 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3715 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3716 4822 117 11139 1k5 1% 0.1W
3717 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3718 4822 116 52243 1k5 5% 0.5W
3719 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3730 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3731 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3732 4822 051 20822 8k2 5% 0.1W
3733 4822 051 20822 8k2 5% 0.1W
3734 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3735 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3736 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3737 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3738 4822 117 11148 56k 1% 0.1W
3739 4822 117 11148 56k 1% 0.1W
3740 4822 051 20683 68k 5% 0.1W
3741 4822 051 20683 68k 5% 0.1W
3742 4822 116 52199 68Ω 5% 0.5W
3743 4822 116 52199 68Ω 5% 0.5W
3744 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3745 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3750 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3756 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3757 4822 117 10837 100k 1% 0.1W
3758 4822 117 10837 100k 1% 0.1W
3762 4822 051 20828 8Ω2 5% 0.1W
3763 4822 117 10837 100k 1% 0.1W
3765 4822 117 11507 6k8 1% 0.1W
3770 4822 117 10834 47k 1% 0.1W
3773 4822 051 20154 150k 5% 0.1W
3784 4822 051 20828 8Ω2 5% 0.1W
3789 4822 051 20828 8Ω2 5% 0.1W
3790 4822 051 20822 8k2 5% 0.1W
3792 4822 051 20822 8k2 5% 0.1W
3794 4822 116 52195 47Ω 5% 0.5W
3798 4822 116 52249 1k8 5% 0.5W
3908 4822 116 52201 75Ω 5% 0.5W
3909 4822 116 52201 75Ω 5% 0.5W
3910 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3911 4822 116 52201 75Ω 5% 0.5W
3913 4822 116 52201 75Ω 5% 0.5W
3915 4822 116 52201 75Ω 5% 0.5W
3919 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3920 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3925 4822 052 10688 6Ω8 5% 0.33W
3928 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3929 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3930 4822 051 20561 560Ω 5% 0.1W
3932 4822 116 52201 75Ω 5% 0.5W
3935 4822 116 52201 75Ω 5% 0.5W
3936 4822 117 10353 150Ω 1% 0.1W
3937 4822 117 10353 150Ω 1% 0.1W
3940 4822 117 10353 150Ω 1% 0.1W
3941 4822 117 10353 150Ω 1% 0.1W
3944 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3946 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3950 4822 116 52249 1k8 5% 0.5W
3970 4822 051 20121 120Ω 5% 0.1W
3971 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3972 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3991 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3992 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3993 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3995 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3996 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
3997 4822 116 52175 100Ω 5% 0.5W
4xxx 4822 051 10008 0Ω 5% 0.25W
4xxx 4822 051 20008 0Ω 5% 0.25W
b
5101 8204 000 73591 TFM standby
5102 4822 157 70436 8.2µH
5103 4822 526 10704 Bead 100mHz
5104 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5105 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5110 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5115 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5120 3198 018 16870 680nF 10%
5200 4822 157 11775 6.8µH 5%
5203 4822 157 71206 Coil
5204 4822 157 71206 Coil
5205 4822 157 71206 Coil
5400 4822 157 11869 33µH 10%
5410 2422 531 02447 TFM sig driver
5411 4822 157 71097 0.56µH
5421 2422 536 00102 Coil lincor 6µH
5422 2422 531 02357 Bridge coil
5426 4822 157 70826 2.4µH
5430 3128 138 21091 TFM LOT slot
5461 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5463 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5465 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5466 4822 157 11869 33µH 10%
5467 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5468 4822 157 11737 22µH 10%
5469 3198 018 11890 18U 5%
5494 4822 157 11855 68µH 10%
5502 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5504 2422 549 43286 Bridge coil
5505 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5506 2422 531 98042 TFM SMT
5510 4822 157 11411 Bead 100mHz
5620 4822 157 11771 0.09µH 10%
d
6103 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6105 4822 130 34281 BZX79-B15
6106 4822 130 34398 BZX79-B24
6108 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6109 4822 130 31083 BYW55

GB 100 EM1A10.
Spare parts list
6111 4822 130 83865 SB360
6120 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6121 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6122 3198 010 53980 BZX79-B3V9
6200 9322 149 10685 BZM55-C33
6204 9322 129 38685 BZM55-C6V8
6205 9322 129 38685 BZM55-C6V8
6206 9322 129 38685 BZM55-C6V8
6207 9322 129 38685 BZM55-C6V8
6305 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6306 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6307 4822 130 30842 BAV21
6308 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6309 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6310 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6405 9322 149 10685 BZM55-C33
6406 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6407 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6408 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6421 4822 130 10753 BY359X-1500
6422 4822 130 10218 BY229X-800
6442 9322 129 42685 BZM55-C15
6461 4822 130 83796 BYV29F-500
6463 4822 130 83796 BYV29F-500
6465 4822 130 83796 BYV29F-500
6466 4822 130 83796 BYV29F-500
6468 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6480 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6481 4822 130 31024 BZX79-B18
6482 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6492 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6493 4822 130 11594 BZX284-C47
6499 9322 129 39685 BZM55-C8V2
6504 4822 130 10741 GBU6J
6505 4822 130 34281 BZX79-B15
6506 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6507 9340 550 66112 BYV28-200/24
6508 4822 130 11415 BYV28-400/20
6510 4822 130 34281 BZX79-B15
6511 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6512 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6514 5322 130 31932 BZT03-C200
6515 4822 130 32904 BZV85-C5V6
6516 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6517 4822 130 31983 BAT85
6518 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6519 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6600 4822 130 30621 1N4148
6616 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6619 4822 130 42488 BYD33D
6620 5322 130 31938 BYV27-200
6623 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6660 4822 130 31983 BAT85
6665 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6731 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6732 4822 130 83757 BAS216
ce
7100 4822 130 44568 BC557B
7101 4822 130 40959 BC547B
7102 4822 130 11417 STP3NB60FP
7104 4822 130 11418 TCDT1102G
7228 4822 209 73852 PMBT2369
7300 4822 130 44154 BF199
7301 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7302 5322 130 41888 BD140-16
7303 5322 130 41886 BD139-16
7304 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7307 9352 561 40112 TDA6108
7407 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7408 5322 130 44647 BC368
7409 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7421 9340 210 30127 BU2520DX
7440 4822 209 70672 LM358N
7480 4822 130 11417 STP3NB60FP
7481 4822 130 44568 BC557B
7482 4822 130 11418 TCDT1102G
7501 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7502 4822 130 61675 BF487
7504 9322 126 65687 STP5NB60FP
7505 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7506 4822 209 14933 TL431IZ
7510 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7528 4822 130 40981 BC337-25
7529 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7600 4822 130 44461 BC546B
7602 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7603 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7605 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7606 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7610 4822 130 11418 TCDT1102G
7620 4822 209 90009 TDA8177
7640 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7641 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7652 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7653 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7654 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7655 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7701 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7702 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7720 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7721 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7722 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7723 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7724 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7725 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7730 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7731 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7732 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7733 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7740 4822 209 32269 TDA2616/N1
7750 4822 209 32269 TDA2616/N1
7901 4822 130 40959 BC547B
7905 5322 130 44647 BC368
7906 4822 209 12334 L4940V85
7907 5322 130 60159 BC846B
8001 4822 320 20233 cable
8036 3104 311 01421 2P3 220mm
8203 3104 311 02441 4P 400mm
8204 3104 311 02521 6P 280mm
8317 3104 311 01421 2P3 220mm
8324 3104 311 01881 7P 480mm
8325 4822 320 20189 EHT cable
8326 4822 320 20216 EHT cable
8340 3104 311 02321 11P 400mm
8400 2422 025 16691 3P 2.5mm H
8501 3104 311 01892 JST 560mm
8737 3104 311 01101 3P 1m
8920 3104 311 02511 5P 280mm
8921 3104 311 01831 3P 280mm
8922 3104 311 01831 3P 280mm
8937 3104 311 02071 10P 280mm
9312 4822 051 20008 Jumper
[B] Small Signal Board
Various
0002 3104 301 23991 Shielding frame
0003 3104 301 24001 Shielding top cover
0026 3104 301 24011 Shielding bottom cover
0302 2422 025 16542 2P male V
1001 2422 543 89018 Crystal 12MHz
1020 3104 328 06281 SSB multi AP virtual DS
1020 3104 328 06291 SSB China virtual DS
1020 3104 328 10991 SSB Middle East virtual DS
1301 2422 540 98456 Crystal 12MHz
1309 2422 543 01184 Crystal 4.433619MHz
1310 2422 543 01183 Crystal 3.579545MHz
1405 2422 549 44374 Saw Filter OFWK9352L
1405 2422 549 44389 Saw Filter OFWK9361L
1406 2422 549 44324 Crystal 5.5-5.74MHz
1407 2422 549 44043 Crystal 4MHz
1408 2422 549 44376 Saw Filter
1408 2422 549 44388 Saw Filter
1409 2422 549 44373 Saw Filter OFWK3955L
1651 2422 543 89019 Crystal 18.432MHz
1681 2422 025 16835 3P male H
1682 2422 025 16729 10P female V
1701 2422 543 89018 Crystal 12MHz
g
2001 4822 126 11671 33pF
2002 4822 126 11671 33pF
2004 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2005 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2006 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2007 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2008 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2010 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2011 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2012 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2013 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2014 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2015 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2016 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2017 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2020 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V
2030 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2031 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2300 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2301 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2302 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2303 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V
2304 4822 122 33741 10pF 10% 50V
2306 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2307 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2308 4822 122 33741 10pF 10% 50V
2313 4822 121 70159 0.1µF 16V
2314 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2315 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2317 4822 126 14491 2.2µF 10V
2318 4822 126 14494 22nF 10% 25V
2319 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V
2320 4822 122 33741 10pF 10% 50V
2321 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2322 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2323 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2324 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V
2325 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2328 4822 122 33761 22pF 5% 50V
2329 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2330 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2331 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2332 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2333 4822 126 14491 2.2µF 10V
2334 4822 126 14491 2.2µF 10V
2335 4822 124 80349 47µF 20% 6.3V
2336 4822 126 14491 2.2µF 10V
2338 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V
2340 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2341 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2342 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2343 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2350 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2351 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2352 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2353 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2354 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2356 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2357 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2358 5322 126 11579 3n3F 10% 63V
2359 4822 122 33752 15pF 5% 50V
2360 3198 016 31280 1p5F 50V
2361 3198 016 31280 1p5F 50V
2362 4822 126 11663 12pF
2365 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2366 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2367 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2368 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2369 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2370 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2371 4822 126 13193 4n7F 10% 63V
2372 4822 126 14043 1µF 20-80% 16V
2373 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2374 4822 126 14491 2.2µF 10V
2375 4822 126 14494 22nF 10% 25V
2376 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2377 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2378 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2384 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2385 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2409 4822 126 14491 2.2µF 10V
2410 4822 126 14472 1µF 10% 10V
2411 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2412 4822 126 13193 4n7F 10% 63V
2413 4822 124 80151 47µF 16V
2417 3198 017 44740 470nF 10V
2418 3198 016 38280 8p2F 50V
2418 4822 122 33741 10pF 10% 50V
2420 4822 122 33753 150pF 5% 50V
2422 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2424 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2425 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2426 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2501 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2502 4822 122 32927 20nF 20-80% 50V
2503 4822 122 32927 20nF 20-80% 50V
2504 4822 122 32927 20nF 20-80% 50V
2505 4822 122 32927 20nF 20-80% 50V
2508 2020 021 91557 100µF 20% 16V
2509 4822 122 33752 15pF 5% 50V
2510 4822 122 33752 15pF 5% 50V
2550 4822 126 14241 50V 330P
2602 4822 126 14107 330nF 20-80% 25V
2603 4822 126 14107 330nF 20-80% 25V
2604 4822 126 14107 330nF 20-80% 25V
2605 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2609 3198 016 31020 1nF 25V
2610 4822 126 14238 50V 2N2
2611 5322 126 11578 1nF 10% 50V
2629 4822 126 14107 330nF 20-80% 25V
2632 4822 126 14107 330nF 20-80% 25V
2634 3198 016 31020 1nF 25V
2637 4822 126 14107 330nF 20-80% 25V
2639 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V

Spare parts list
GB 101EM1A 10.
2640 4822 126 13879 20nF 20-80% 16V
2651 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2652 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2653 4822 122 32927 20nF 20-80% 50V
2654 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2655 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2656 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2657 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2658 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2661 4822 122 32927 20nF 20-80% 50V
2662 4822 122 32927 20nF 20-80% 50V
2663 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2664 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2665 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2666 4822 124 12095 100µF 20% 16V
2667 3198 016 33380 3p3F 50V
2668 3198 016 33380 3p3F 50V
2669 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2670 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2673 3198 016 31020 1nF 25V
2674 3198 016 31020 1nF 25V
2675 4822 124 23002 10µF 16V
2677 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2678 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2679 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2680 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2681 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2682 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2685 3198 016 31020 1nF 25V
2686 3198 016 31020 1nF 25V
2693 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2694 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2702 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2703 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2704 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2706 2020 021 91557 100µF 20% 16V
2707 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2708 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2709 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2710 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2712 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2713 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2728 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2729 4822 126 14225 56pF 5% 50V
2730 4822 126 14494 22nF 10% 25V
2731 4822 122 31765 100pF 2% 63V
2733 4822 126 14494 22nF 10% 25V
2738 4822 126 14494 22nF 10% 25V
2743 4822 126 14494 22nF 10% 25V
2747 4822 126 14507 18pF 5% 50V
2748 4822 126 14507 18pF 5% 50V
2755 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2756 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2757 2020 021 91554 10µF 20% 16V
2758 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2759 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2760 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2761 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2762 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2763 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2764 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2765 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2766 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2767 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2770 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2771 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2772 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2773 3198 016 31020 1nF 25V
2774 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2776 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2785 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2786 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2788 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2790 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2792 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2795 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2796 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2798 3198 016 36810 680pF 25V
2900 5322 126 11582 6n8F 10% 63V
2901 5322 126 11582 6n8F 10% 63V
2902 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V
2903 5322 126 11582 6n8F 10% 63V
2904 5322 126 11582 6n8F 10% 63V
2906 5322 126 11582 6n8F 10% 63V
2908 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2909 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2910 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2911 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2912 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2913 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2914 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2915 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2916 4822 126 13883 220pF 5% 50V
2917 5322 126 11582 6n8F 10% 63V
f
3001 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3002 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3003 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3004 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3005 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3006 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3007 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3008 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3009 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3010 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3011 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3012 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3013 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3014 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3015 4822 051 30474 470k 5% 0.062W
3016 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3017 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3018 4822 117 13525 24k 1% 0.62W
3019 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3026 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3027 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3028 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3029 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3030 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3031 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3032 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3033 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3034 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3035 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3036 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3037 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3038 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3039 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3040 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3041 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3042 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3043 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3044 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3045 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3049 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3050 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3051 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3052 4822 051 30682 6k8 5% 0.062W
3053 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3055 2422 086 11013 Fuse 1Ω5
3056 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3057 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3059 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3060 4822 051 30272 2k7 5% 0.062W
3061 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3062 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3063 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3064 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3300 2322 750 63908 Fuse 3Ω9 5%
3301 4822 117 13632 100k 1% 0.62W
3302 2322 750 63908 Fuse 3Ω9 5%
3304 2322 750 63908 Fuse 3Ω9 5%
3306 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3307 4822 051 30183 18k 5% 0.062W
3308 4822 051 30684 680k 5% 0.062W
3310 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3311 4822 117 13632 100k 1% 0.62W
3314 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3315 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3316 4822 051 30123 12k 5% 0.062W
3317 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3318 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3320 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3321 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3322 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3324 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3327 4822 117 13632 100k 1% 0.62W
3328 4822 051 30393 39k 5% 0.062W
3329 4822 117 13568 6Ω8 5% 1206
3330 4822 051 30332 3k3 5% 0.062W
3331 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3333 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3335 4822 051 30332 3k3 5% 0.062W
3336 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3337 4822 051 30153 15k 5% 0.062W
3338 4822 051 30682 6k8 5% 0.062W
3340 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3341 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3342 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3343 4822 051 30683 68k 5% 0.062W
3344 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3345 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3346 4822 051 30333 33k 5% 0.062W
3347 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3348 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3351 4822 051 30109 10Ω 5% 0.062W
3352 4822 117 13632 100k 1% 0.62W
3353 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3354 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3355 4822 051 30109 10Ω 5% 0.062W
3356 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3358 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3359 4822 117 13632 100k 1% 0.62W
3360 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3361 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3362 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3363 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3364 4822 051 30683 68k 5% 0.062W
3365 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3366 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3367 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3370 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3371 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3372 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3376 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3377 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3378 4822 051 30153 15k 5% 0.062W
3382 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3384 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3385 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3386 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3388 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3389 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3390 4822 051 30183 18k 5% 0.062W
3391 4822 051 30683 68k 5% 0.062W
3393 4822 117 13632 100k 1% 0.62W
3394 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3395 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3400 4822 117 11152 4Ω7 5%
3407 4822 051 30562 5k6 5% 0.063W
3410 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3411 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3415 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3416 4822 117 13568 6Ω8 5% 1206
3418 4822 051 30391 390Ω 5% 0.062W
3419 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3419 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3421 4822 051 30562 5k6 5% 0.063W
3423 4822 051 30562 5k6 5% 0.063W
3433 4822 051 30392 3k9 5% 0.063W
3434 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3435 4822 051 30562 5k6 5% 0.063W
3436 4822 051 30271 270Ω 5% 0.062W
3437 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3439 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3439 4822 051 30561 560Ω 5% 0.062W
3441 4822 051 30393 39k 5% 0.062W
3446 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3453 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3530 4822 157 71593 10µH 10%
3532 4822 051 30273 27k 5% 0.062W
3544 4822 117 12864 82k 5% 0.6W
3545 4822 117 12864 82k 5% 0.6W
3550 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3601 4822 117 12864 82k 5% 0.6W
3602 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3603 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3604 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3605 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3606 4822 051 30154 150k 5% 0.062W
3610 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3611 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3621 4822 051 30273 27k 5% 0.062W
3624 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3625 4822 051 30333 33k 5% 0.062W
3630 4822 051 30273 27k 5% 0.062W
3634 4822 051 30121 120Ω 5% 0.062W
3637 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3651 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3652 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3653 4822 051 30682 6k8 5% 0.062W
3654 4822 051 30682 6k8 5% 0.062W
3655 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3656 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3658 4822 051 30273 27k 5% 0.062W
3660 4822 051 30154 150k 5% 0.062W
3662 4822 051 30271 270Ω 5% 0.062W
3680 4822 051 30271 270Ω 5% 0.062W
3684 4822 051 30682 6k8 5% 0.062W
3685 4822 051 30682 6k8 5% 0.062W
3686 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3687 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3688 4822 051 30682 6k8 5% 0.062W
3689 4822 051 30682 6k8 5% 0.062W
3690 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3691 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3702 4822 117 12139 22Ω 5% 0.062W
3703 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3705 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W

GB 102 EM1A10.
Spare parts list
3706 4822 051 30109 10Ω 5% 0.062W
3707 4822 051 30392 3k9 5% 0.063W
3708 4822 051 30272 2k7 5% 0.062W
3709 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3711 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3714 4822 117 12139 22Ω 5% 0.062W
3716 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3717 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3718 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3719 4822 117 13574 1Ω5 5% 1206
3720 4822 117 13574 1Ω5 5% 1206
3725 4822 051 30105 1M 5% 0.062W
3728 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3731 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3732 4822 051 10102 1k 2% 0.25W
3733 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3739 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3740 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3741 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3744 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3745 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3746 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3747 4822 051 30689 68Ω 5% 0.063W
3748 4822 051 30689 68Ω 5% 0.063W
3749 4822 051 30689 68Ω 5% 0.063W
3754 4822 051 30109 10Ω 5% 0.062W
3755 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3757 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3759 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3790 3198 031 11010 4X100Ω 5%
3791 3198 031 11010 4X100Ω 5%
3792 3198 031 11010 4X100Ω 5%
3793 3198 031 11010 4X100Ω 5%
3794 3198 031 11010 4X100Ω 5%
3795 3198 031 11010 4X100Ω 5%
3796 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3797 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
b
5301 4822 157 11876 6.8µH 10%
5302 4822 157 11876 6.8µH 10%
5401 3198 018 33370 0U33 10%
5401 4822 157 71303 Coil MLF2012DR39KT
5405 3198 018 33980 3U9 10%
5406 4822 157 11876 6.8µH 10%
5407 2422 535 95427 Bead 100mHz
5408 2422 549 44459 IND VAR 78mHz
5409 2422 535 95427 Bead 100mHz
5410 3198 018 51080 1U 10%
5639 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5640 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5641 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5642 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5643 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5644 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5645 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5651 2422 549 43769 100mHz 30R
5652 2422 549 43769 100mHz 30R
5653 2422 549 43769 100mHz 30R
5654 4822 157 11716 Coil BLM21P300SPT
5655 3198 018 56880 6U8 10%
5656 4822 157 71593 10µH 10%
5701 4822 157 71206 Coil
5702 2422 535 95427 Bead 100mHz
5703 4822 157 11716 Coil BLM21P300SPT
5704 4822 157 11716 Coil BLM21P300SPT
5705 2422 535 95427 Bead 100mHz
5706 4822 157 11778 5U6 10%
5707 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5711 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5713 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5718 3198 018 33370 0U33 10%
5720 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5911 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5912 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5913 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5914 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5915 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5916 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5917 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5918 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5919 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5920 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5921 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5922 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5923 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5924 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5925 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5926 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5927 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5928 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5929 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5930 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5931 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5932 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5933 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5935 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5940 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5943 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5944 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5945 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5946 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5947 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5948 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5949 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5950 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
5951 4822 157 11781 Coil BLM11A601SPT1
d
6303 4822 130 11594 BZX284-C47
6304 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6306 9322 129 37685 BZM55-C5V6
6307 4822 130 11528 1PS76SB10
6309 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6310 9322 129 38685 BZM55-C6V8
6311 9322 149 08685 BZM55-C22
6319 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6320 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6321 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6322 4822 130 83757 BAS216
6403 4822 130 11525 1SS356
6404 4822 130 11525 1SS356
6405 4822 130 11525 1SS356
6406 9322 149 08685 BZM55-C22
6652 9322 129 40685 BZM55-C10
6654 4822 130 83757 BAS216
ce
7001 9352 641 92557 SAA5667
7001 9352 659 94557 SAA5647HL/M1
7002 4822 130 60373 BC856B
7003 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7004 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7005 9322 116 74668 LD1117D33
7006 4822 209 73852 PMBT2369
7007 4822 209 73852 PMBT2369
7011 9322 156 63668 CY7C1019V33-15VC
7012 4822 209 17377 M24C32-WMN6
7301 9352 625 23518 TDA9330H/N2
7303 5322 130 42756 BC857C
7307 9352 630 99118 Comb filter multi TDA9181
7308 9340 310 30215 PDTC144ET
7309 9340 310 30215 PDTC144ET
7310 9340 310 30215 PDTC144ET
7311 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7312 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7313 4822 209 73852 PMBT2369
7314 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7315 4822 209 73852 PMBT2369
7320 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7322 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7323 9352 625 24518 TDA9321H/N2
7324 5322 130 63679 BC847CW
7401 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7405 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7406 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7407 5322 130 42756 BC857C
7411 5322 130 60159 BC846B
7651 9322 151 17671 MSP3411G-FH-A2
7656 9340 425 30115 BC847BPN
7661 9340 425 30115 BC847BPN
7682 9340 425 30115 BC847BPN
7701 5322 130 42756 BC857C
7702 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7704 4822 209 73852 PMBT2369
7708 4822 209 90034 SAA4990H/V0
7709 9352 640 20557 SAA4978H/V203
7713 9322 116 74668 LD1117D33
7714 4822 209 17307 MSM54V12222A-30JS
7715 4822 209 17307 MSM54V12222A-30JS
7716 2422 486 80737 32P female V
8681 3104 311 00121 3P 280mm
8682 3104 311 02951 10P 280mm
[C] PIP DW Panel
Various
0172 3104 301 08351 Phone 120 phone
0175 3104 304 22073 multi voltage bracket
0200 4822 267 10734 5P
0201 4822 267 10557 10P
0205 2422 025 16587 10P female V
0207 4822 267 10565 4P
0236 4822 267 10735 3P
0272 2422 025 16382 3P male V
0273 2422 025 12482 6P male V
1327 4822 242 10694 Crystal 12MHz
1333 2422 549 44311 Filter 5.8-6.5MHz
1352 2422 549 44202 Saw Filter OFWK6287K
1352 2422 549 44223 Saw Filter OFWK7260M
g
2261 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2262 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2265 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2269 4822 126 13751 47nF 10% 63V
2301 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2302 5322 126 10184 820P 5% 50V 3
2303 5322 126 10223 4n7F 10% 63V
2306 5322 126 11583 10nF 10% 50V
2309 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2312 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2313 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2314 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2316 4822 126 14494 22nF 10% 25V
2317 4822 126 13879 20nF 20-80% 16V
2319 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2321 5322 126 10465 3.9nF 10% 50V
2322 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2324 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2327 4822 126 11671 33pF
2328 4822 126 11671 33pF
2331 4822 124 22652 2.2µF 20% 50V
2332 4822 126 14076 220nF 25V
2333 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2334 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2335 4822 126 14043 1µF 20-80% 16V
2336 5322 126 10184 820P 5% 50V 3
2338 4822 122 33127 2n2F 10% 63V
2342 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2345 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2348 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2349 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2350 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2351 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2354 4822 126 13482 470nF 20-80% 16V
2355 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2356 4822 126 13482 470nF 20-80% 16V
2357 5322 122 32448 10pF 5% 63V
2372 5322 126 10223 4n7F 10% 63V
2373 4822 124 21913 1µF 20% 63V
2374 5322 122 32654 22nF 10% 63V
2375 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2376 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2377 5322 126 10511 1nF 5% 50V
2380 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2385 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2386 4822 126 13881 470pF 5% 50V
2390 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2391 4822 122 31765 100pF 2% 63V
2392 4822 126 14507 18pF 5% 50V
2393 4822 122 31765 100pF 2% 63V
2401 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2402 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2403 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2404 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2405 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2411 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2412 4822 126 13879 20nF 20-80% 16V
2415 4822 126 13879 20nF 20-80% 16V
2431 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2432 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2434 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2436 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2811 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2812 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2813 4822 122 33753 150pF 5% 50V
2814 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2816 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2817 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2818 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2819 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2821 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2822 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2823 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2824 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2825 5322 122 33538 150pF 2% 63V
2826 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2827 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2828 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2829 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2831 4822 126 14043 1µF 20-80% 16V

Spare parts list
GB 103EM1A 10.
2832 4822 126 14043 1µF 20-80% 16V
2833 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2834 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2836 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2837 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2838 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2839 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2841 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2842 4822 122 33753 150pF 5% 50V
2843 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2844 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2846 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2847 5322 122 33538 150pF 2% 63V
2848 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2849 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2851 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2852 4822 126 14585 100nF 10% 50V
2853 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2854 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2856 5322 122 33538 150pF 2% 63V
2857 4822 122 33753 150pF 5% 50V
2861 4822 124 40248 10µF 20% 63V
2862 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2863 4822 124 81151 22µF 50V
2864 3198 017 34730 47nF 16V
2866 3198 017 34730 47nF 16V
2867 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2868 4822 126 14305 100nF 10% 16V
2869 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2871 3198 017 41050 1µF 10V
2872 3198 017 34730 47nF 16V
2873 3198 017 34730 47nF 16V
2874 4822 051 30008 Jumper
2876 4822 051 30008 Jumper
2877 4822 051 30008 Jumper
2878 4822 126 13838 100nF 20-80% 50V
2882 4822 051 20008 Jumper
2883 4822 051 20008 Jumper
2891 5322 122 31647 1nF10% 63V
2892 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2893 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2894 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2895 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2896 4822 126 13692 47pF 1% 63V
2897 4822 122 33777 47pF 5% 63V
2898 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
2899 4822 124 40207 100µF 20% 25V
f
3263 4822 117 11449 2k2 5% 0.1W
3264 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3267 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3268 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3270 4822 051 20008 Jumper
3301 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3305 4822 117 12955 2k7 1% 0.1W
3311 4822 051 20273 27k 5% 0.1W
3312 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3315 4822 117 12708 39k 1% 0.1W
3316 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3318 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3321 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3322 4822 117 12902 8k2 1% 0.063W
3324 4822 051 20391 390Ω 5% 0.1W
3326 5322 117 12487 1k 1% 0.125W
3327 4822 051 30561 560Ω 5% 0.062W
3329 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3330 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3333 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3334 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3335 4822 051 20121 120Ω 5% 0.1W
3338 4822 051 20008 Jumper
3339 4822 117 10833 10k 1% 0.1W
3340 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3341 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3344 4822 051 20479 47Ω 5% 0.1W
3345 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3346 4822 051 30561 560Ω 5% 0.062W
3348 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3349 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3352 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3353 4822 051 30682 6k8 5% 0.062W
3354 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3355 4822 051 30273 27k 5% 0.062W
3356 4822 051 30183 18k 5% 0.062W
3370 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3371 4822 116 83933 15k 1% 0.1W
3372 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3374 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3381 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3382 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3383 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3384 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3385 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3386 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3387 4822 051 30393 39k 5% 0.062W
3388 4822 051 30103 10k 5% 0.062W
3389 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3390 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3401 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3402 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3403 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3404 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3405 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3411 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3412 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3413 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3414 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3415 4822 117 12925 47k 1% 0.063W
3416 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3431 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3432 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3437 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3438 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3439 4822 051 20008 Jumper
3440 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3441 4822 051 30152 1k5 5% 0.062W
3444 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3453 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3456 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3457 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3460 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3462 4822 052 10228 2Ω2 5% 0.33W
3465 4822 051 20471 470Ω 5% 0.1W
3801 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3802 4822 117 10361 680Ω 1% 0.1W
3803 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3804 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3805 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3806 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3807 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3808 4822 117 10361 680Ω 1% 0.1W
3809 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3810 4822 051 30681 680Ω 5% 0.062W
3811 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3812 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3813 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3814 4822 051 30223 22k 5% 0.062W
3816 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3817 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3818 4822 051 30479 47Ω 5% 0.062W
3821 4822 051 30151 150Ω 5% 0.062W
3823 4822 117 10361 680Ω 1% 0.1W
3825 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3826 4822 051 30332 3k3 5% 0.062W
3827 4822 117 12903 1k8 1% 0.063W
3828 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3829 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3831 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3832 4822 051 30393 39k 5% 0.062W
3833 4822 051 30332 3k3 5% 0.062W
3834 4822 117 12903 1k8 1% 0.063W
3836 4822 051 30332 3k3 5% 0.062W
3837 4822 117 12903 1k8 1% 0.063W
3838 4822 051 30393 39k 5% 0.062W
3839 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3846 4822 117 11503 220Ω 1% 0.1W
3852 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3854 4822 051 30101 100Ω 5% 0.062W
3860 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3862 4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3863 4822 052 10108 1Ω 5% 0.33W
3866 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3868 4822 117 12903 1k8 1% 0.063W
3869 4822 051 30332 3k3 5% 0.062W
3871 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3872 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3873 4822 051 30152 1k5 5% 0.062W
3874 4822 051 30152 1k5 5% 0.062W
3876 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3878 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
3879 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3880 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3881 4822 051 30391 390Ω 5% 0.062W
3882 4822 051 30472 4k7 5% 0.062W
3883 4822 051 30332 3k3 5% 0.062W
3884 4822 117 10361 680Ω 1% 0.1W
3886 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3887 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3888 4822 051 30008 Jumper
3889 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3890 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3891 4822 051 30339 33Ω 5% 0.062W
3892 4822 051 20472 4k7 5% 0.1W
3893 4822 051 30152 1k5 5% 0.062W
3894 4822 051 30222 2k2 5% 0.062W
3895 4822 051 30471 470Ω 5% 0.062W
3896 4822 051 30152 1k5 5% 0.062W
3897 4822 051 30221 220Ω 5% 0.062W
3898 4822 051 30102 1k 5% 0.062W
4xxx 4822 051 10008 0Ω 5% 0.25W
4xxx 4822 051 20008 0Ω 5% 0.25W
b
5261 4822 157 11778 5U6 10%
5309 4822 157 71334 0.68µH
5332 4822 157 71334 0.68µH
5333 4822 157 71334 0.68µH
5334 4822 157 71334 0.68µH
5349 4822 157 71694 0U82 10%
5350 3198 018 61590 15U 5%
5351 3198 018 61590 15U 5%
5352 4822 157 71334 0.68µH
5816 4822 157 11506 12uF
5818 4822 157 11506 12uF
5827 4822 157 11506 12uF
5834 4822 157 11506 12uF
5839 4822 157 11506 12uF
5848 4822 157 11506 12uF
5849 4822 157 11506 12uF
5851 4822 157 11506 12uF
5853 4822 157 11506 12uF
d
6301 4822 130 11525 1SS356
6412 4822 130 11397 BAS316
6415 4822 130 11397 BAS316
6801 4822 130 11564 UDZ3.9B
6802 4822 130 11564 UDZ3.9B
ce
7201 2422 542 90075 Tuner TEDE9X700A ALPS
7201 2422 542 90076 TUN SPL V+U PLL IEC Dk
7301 9352 638 73557 TDA8889H/N1
7305 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7307 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7331 5322 130 42756 BC857C
7332 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7385 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7386 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7401 5322 209 14481 HEF4053BT
7403 4822 209 17345 M62320FP
7411 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7412 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7438 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7801 9352 639 81557 SAB9081H/N4
7802 4822 209 80591 LM317T
7803 4822 209 12776 TDA8601T/C1
7804 9352 457 50115 74HC1G32GW
7805 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7806 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7807 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7808 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7809 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7810 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7828 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7871 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7874 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7876 5322 130 42756 BC857C
7891 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7892 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7893 3198 010 42310 BC847BW
7894 5322 130 42756 BC857C
[D] Side I/O Panel
Various
0044 3139 124 30421 Side I/O bracket
1901 2422 026 04926 4P female H
1902 4822 267 10975 3P
1903 4822 267 31014 Headphone socket
1936 2422 025 12485 11P male V
g
2903 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2904 5322 122 32531 100pF 5% 50V
2905 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V
2906 4822 122 33177 10nF 20% 50V

GB 104 EM1A10.
Spare parts list
f
3901 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3902 4822 116 52201 75Ω 5% 0.5W
3903 4822 051 20101 100Ω 5% 0.1W
3904 4822 116 52201 75Ω 5% 0.5W
3905 4822 116 52249 1k8 5% 0.5W
3906 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3908 4822 050 11002 1k 1% 0.4W
3910 4822 116 52276 3k9 5% 0.5W
3911 4822 050 21003 10k 1% 0.6W
3912 4822 050 21003 10k 1% 0.6W
8936 3104 301 07753 11P 560mm
[E] Top Control Panel
Various
0215 4822 267 10748 3P
1091 4822 276 13775 Switch
1092 4822 276 13775 Switch
1093 4822 276 13775 Switch
1094 4822 276 13775 Switch
f
3091 4822 051 20561 560Ω 5% 0.1W
3092 4822 051 20391 390Ω 5% 0.1W
3093 4822 051 20561 560Ω 5% 0.1W
3094 4822 117 11504 270Ω 1% 0.1W
3095 4822 051 20332 3k3 5% 0.1W
3096 4822 117 11139 1k5 1% 0.1W
d
6091 4822 130 31983 BAT85
8345 4822 320 12511 3P 1500mm
[J] Mains Switch Panel
Various
0132h4822 276 14024 Power switch
3139 124 30431 Front interface bracket
0187
h
0214 2422 025 06353 5P male H
1002 9322 127 54667 IR receiver TSOP1836UH1
9322 050 99682 LED
1008
h
g
2001 4822 124 40207 100uF 20% 25V
2002 4822 122 30043 10nF 80% 63V
f
3003 4822 116 52228 680Ω 5% 0.5W
3004 4822 116 80176 1Ω 5% 0.5W
3008 4822 053 21475 4M7 5% 0.5W
3009 4822 053 21225 2M2 5% 0.5W
[Y] Mains Harmonic Panel
Various
0030 3139 124 33211 Mains harmonic bracket
0061 4822 265 20723 2P
g
2061 4822 122 33799 1nF 10% 1kV
b
5066 8204 000 74291 Coil Mains harmonic
[G] DC Shift Panel
Various
0317 4822 265 20723 2P
0318 4822 265 20723 2P
1001 3104 328 06231 DC shift assy EMG
1430 2422 086 10581 Fuse 400mA 65V
b
5430 3128 138 38911 DC shift coil
d
6432 9340 317 00133 BYD33V
6433 9340 317 00133 BYD33V
8318 3104 301 08731 2P3 220mm
[I] DAF Panel
Various
0030 3104 304 21651 DAF DC-SHIFT BRACKET
0317 4822 265 20723 2P
0318 2422 025 16374 2P male V
0391 3104 311 02452 JST 340mm
0397 4822 267 10973 1P
g
2800 2222 375 90504 820pF 5% 2kV
2890 2222 375 90504 820pF 5% 2kV
f
3898 4822 116 21211 VDR 420V
3899 4822 116 21211 VDR 420V
b
5800 2422 531 02437 TFM SIG DAF S21975-03
 Loading...
Loading...