Page 1

4540
High Pressure Reactors
Operating Instruction Manual
394M
Page 2

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
PREFACE 3
Scope 3
Related Instructions 3
Intended Usage 3
Safety Information 3
General Specifications 3
Explanation of Symbols 4
Environmental Conditions 4
Unpack Carefully 4
Provisions for Lifting and Carrying 4
Cleaning & Maintenance 4
User’s Responsibility 5
FIXED HEAD OR REMOVABLE HEAD DESIGN 6
Vessel Head Design 6
PTFE Flat Gasket 6
INSTALLATION 7
Pressure and Temperature Limits 7
Assemble the Reactor 8
IDENTIFY THE VALVES 9
Gas Inlet Valves 9
Gas Release Valve 9
Liquid Sampling Valve 9
HOW TO USE THE VESSEL 13
Fixed Head Vessels 13
Removable Head Vessels 13
MAINTENANCE 15
General Maintenance Notes 15
Periodic Pressure Tests 16
Technical Support 16
4540 SERIES REACTION VESSEL PARTS LIST 17
Standard Vessel Fittings 17
Heaters Parts List 19
Overarm Parts List 20
4540 SERIES DRAWINGS 22
4540 Series Vessel with Fittings 22
1/4 HP Light Duty FH/RH Overarm and Motor 24
1/8 HP Light Duty FH/RH Vessel Overarm and Motor 25
4544 600 mL Removable Head Reactor 26
4545 600 mL Fixed Head Reactor 27
4544/4544A 600 mL Removable Head Reactor 28
4545/4545A 600 mL Fixed Head Reactor 29
4546 1200 mL Removable Head Reactor 30
4547 1200 mL Fixed Head Reactor 31
OTHER VESSEL HEAD FITTINGS 10
Safety Rupture Disc 10
Type J Thermocouple 10
Pressure Gage 10
Gage and Valve Adapters 10
ACCESSORIES 11
Serpentine Cooling Coil 11
Spare Parts Kit 11
Liners 11
Variable Speed Electric Motor 11
Air Motor 11
Pneumatic Lift for Fixed Head Vessels 12
2
Parr Instrument Company
Customer Service
Questions concerning the installation or operation
of this instrument can be answered by the Parr
Customer Service Department:
1-309-762-7716 • 1-800-872-7720
Fax: 1-309-762-9453
E-mail: parr@parrinst.com
www.parrinst.com
Page 3

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
PREFACE
Scope
These instructions describe the installation, operation and maintenance of Parr Series 4540 Pressure
Reactors offered in two sizes, 600 mL and 1200 mL.
They cover the basic steps to be followed when
installing these reactors and describe the function of
all standard components. They are intended to be
used in conjunction with several related instruction
sheets listed in the following section. This information
describes several components which are common to
most Parr pressure reaction equipment, and includes
safety precautions and other related information applicable to all reaction laboratories. The users should
study all of these instructions carefully before starting
to use these vessels so that they will fully understand
the capabilities and limitations of the equipment.
Related Instructions
The following Parr publications are also included to
further your understanding of this instrument and
its component parts:
No. Description
201M Limited Warranty
230M Safety Precautions to be Observed when
Operating Pressure Reaction Equipment
231M Operating Instructions for Parr Safety
Rupture Discs
234M Operating and Maintenance Instructions
for Parr Magnetic Drives
323M Operating Instructions for Parr Pressure
Relief Valves
548M Operating Instructions for 4848 Reactor
Controllers
FX004 Health & Safety Assurance Certification
Intended Usage
This system has been designed for use as a high
pressure reactor system. It has been designed, built,
and tested to strict physical and electrical standards.
However, it is the user’s responsibility to install and
operate it in conformance with local pressure and
electrical codes.
If this equipment is used in a manner beyond its
intended usage, the protection provided by the
equipment may be impaired.
Safety Information
To avoid electrical shock, always:
1. Use a properly grounded electrical outlet of
correct voltage and current handling capability.
2. Ensure that the equipment is connected to
electrical service according to local national
electrical codes. Failure to properly connect may
create a fire or shock hazard.
3. For continued protection against possible hazard,
replace fuses with same type and rating of fuse.
4. Disconnect from the power supply before
maintenance or servicing.
To avoid personal injury:
1. Do not use in the presence of flammable or
combustible materials; fire or explosion may
result. This device contains components which
may ignite such material.
2. Refer servicing to qualified personnel.
General Specifications
Electrical Ratings
Controller ratings are found in the Operating Instructions for the controller supplied with your reactor.
Before connecting a controller to an electrical outlet,
the user must be certain that the electrical outlet has
an earth ground connection and that the line, load
and other characteristics of the installation do not
exceed the following limits:
Voltage: Fluctuations in the line voltage should not
exceed 10% of the rated nominal voltage shown on
the data plate.
Frequency: Controllers can be operated from either
a 50 or 60 Hertz power supply without affecting their
operation or calibration.
Current: The total current drawn should not exceed
the rating shown on the data plate on the controller
by more than 10 percent.
Thermocouple: Unless otherwise specified, all
Series 4848 Controllers operate with a Type J (ironconstantan) thermocouple. The total resistance of
the thermocouple and the lead wires should not
exceed 100 ohms. If the resistance of the thermocouple circuit is higher, it will reduce the sensitivity
of the control system.
www.parrinst.com
3
Page 4

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Explanation of Symbols
II On position, full power heater switch
I On position, half power heater switch
O Off Position
~ Alternating Current (AC)
This CAUTION symbol may be present on the Product Instrumentation and
literature. If present on the product, the user must consult the appropriate
part of the accompanying product literature for more information.
This CAUTION symbol indicates that the surface may be hot.
Protective Earth (PE) terminal. Provided for connection of the Protective
Earth (green or green/yellow) supply system conductor.
Environmental Conditions
This instrument is intended to be used indoors.
Caution!
Do not use in hazardous atmospheres.
Operating: 15 ºC to 35 ºC; maximum relative humidity of 80% non-condensing. Installation Category II
(over voltage) in accordance with IEC 664.
Pollution degree 2 in accordance with IEC 664.
Altitude Limit: 2,000 meters.
Storage: -25 °C and 65 °C; 10% to 85% relative humidity.
Unpack Carefully
Unpack the equipment carefully and check all the
parts against the, packing list. If shipping damage is
discovered, report it immediately to the delivering
carriers. The vessel, motor, heater, and temperature
controller may be packed separately for convenience
in shipping, but these parts are easily reassembled.
Examine the components closely for any loose parts
or shipping damage and be sure to check all layers of
packing materials thoroughly so as not to overlook
any parts which might otherwise be discarded.
Provisions for Lifting and Carrying
Before moving ensure all cables are disconnected.
Use proper and safe lifting techniques when installing
or moving the 4540 Reactor and/or its components.
Cleaning & Maintenance
Periodic cleaning may be performed on the exterior
surfaces of the controller with a lightly dampened
cloth containing mild soap solution. All power
should be disconnected and the power cord should
be unplugged when cleaning the instrument.
There are no user serviceable parts inside the product other than what is specifically called out and
discussed in this manual. Advanced troubleshooting
instructions beyond the scope of this manual can
be obtained by calling Parr Instrument Company
in order to determine which part(s) may need to be
replaced or serviced.
Ensure that any hot surfaces have had
adequate time to cool before cleaning
or maintaining the reactor and/or its
components.
4
Parr Instrument Company
Page 5

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
User’s Responsibility
All Parr reactors and pressure vessels are designed and manufactured with great care to assure safe operation when used within their prescribed temperature and pressure limits.
But . . . the basic responsibility for safety when using this equipment rests entirely with the user; who must:
1. Select a reactor or pressure vessel that has the
capability, pressure rating, corrosion resistance
and design features that are suitable for its
intended use. Parr engineers will be glad to
discuss available equipment and material
options with prospective users, but the final
responsibility for selecting a reactor or pressure
vessel that will perform to the user’s satisfaction
in any particular reaction or test must rest with
the user – not with Parr.
In exercising the responsibility for the selection
of pressure equipment, the prospective user is
often faced with a choice between over-or underdesigned equipment. The hazards introduced
by under-designed pressure vessels are readily
apparent, but the penalties that must be paid for
over-designed apparatus are often overlooked.
Recognizing these criteria, Parr reactors and
pressure vessels are offered in several different
styles, each designed for convenient use in daily
operation within certain temperature and pressure limits, using gaskets, closures and other
elements carefully selected for safe operation
within the limits specified for that design. But in
order to preserve the validity of these designs,
all temperature and pressure limits must be
observed, and no attempt should be made to
increase these limits by making alterations or by
substituting components which are not recommended by Parr Instrument Company.
2. Install and operate the equipment within a
suitable barricade, if required, with appropriate
safety accessories and in full compliance with
local safety codes and rules.
All standard Parr pressure vessels are provided
with either suitable relief device or a means to
attach one (typically in the form of a plugged
opening). When a pressure vessel is delivered
without a pressure venting device, it is the
customer’s responsibility to provide pressure
relief in order to protect the operator and the
equipment from destructive high pressures. If
you need more information or need help in
selecting a proper relief device, please contact
Parr Instrument Company.
3. Establish training procedures to ensure that any
person handling the equipment knows how to
use it properly.
4. Maintain the equipment in good condition and
establish procedures for periodic testing to be
sure the vessel remains structurally sound.
www.parrinst.com
5
Page 6
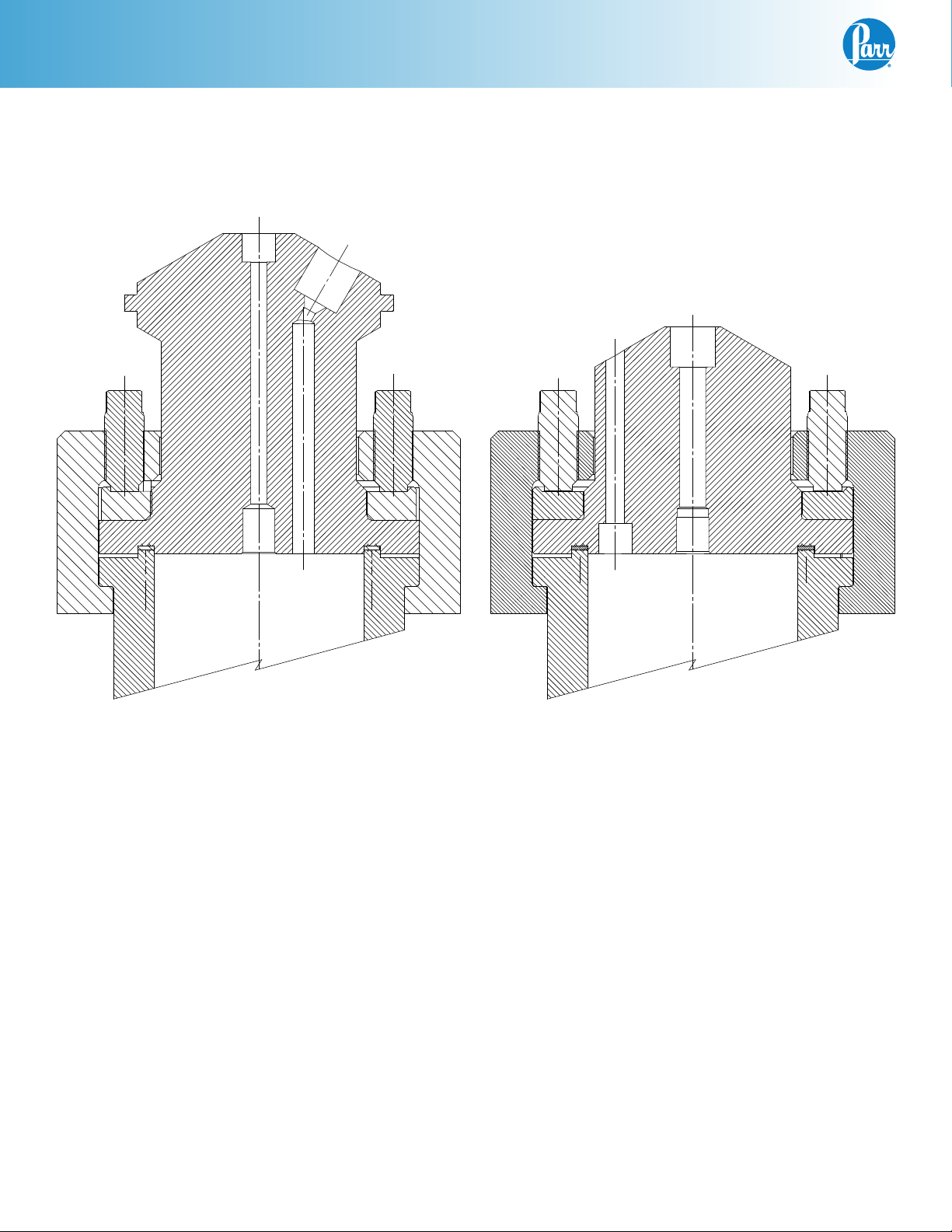
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
FIXED HEAD OR REMOVABLE HEAD DESIGN
Parr Series 4540 High Pressure Reactors are furnished with two structural options in addition to the size,
pressure range, stirrer motor, controller and similar options. These are:
Fixed Head Moveable Head
Vessel Head Design
There is no difference in the pressure or temperature
limits or basic operating instructions based upon the
fixed head or movable vessel options. There are differences in the design of the stand components which
adapt the vessels to the support system.
In the fixed head design, the head of the vessel may
remain fixed in the reactor support stand. All attachments to the head, gas and liquid feed and discharge
lines, cooling water, vapor take-off and condenser,
thermocouple, and any electrical leads can remain
permanently in place. The reactor is opened by
removing the cover clamp sections and lowering the
cylinder away from the head.
In the removable head vessel design, all connections to
the head are removed to allow the vessel to be opened.
PTFE Flat Gasket
The flat gasket is held in a recess in the vessel
head and a machine pilot on the cylinder closes the
recess to completely contain the gasket. The split
ring closure used with this gasket has eight compression bolts which must be tightened to develop
the loading on the gasket.
Maximum temperatures of a given system are
dependant upon the material of construction and
type of seal. Other accessories may limit operating
temperature. The PTFE flat gasket can be used to
operating temperatures as high as 350 °C.
Metal gaskets can be furnished for special applications. The metal gaskets are not interchangeable
with the flat gasket design, but require special
grooves machined into the head and cylinder.
Parr recommends the PTFE flat gaskets for most
applications.
6
Parr Instrument Company
Page 7

INSTALLATION
Pressure and Temperature Limits
The working pressure and temperature at which any
reactor or pressure vessel can be used will depend
upon the design of the vessel and the materials
used in its construction. Since all materials lose
strength at elevated temperatures, any pressure
rating must be stated in terms of the temperature at
which it applies. The standard material of construction for Parr Instrument Company is Type 316 Stainless Steel.
Limits for vessels made of other materials and for
other operating temperatures can be obtained from
Parr Customer Service. No attempt should be made
to increase these limits by making alterations or by
substituting components that are not recommended
by the Parr Instrument Company. It must also be
understood that lower pressure and temperature
limits may be required for modified reactors and for
vessels made of special alloys.
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Limits for vessels will be determined by the physical characteristics of the vessel material and will be
prescribed on an individual basis.
The maximum working pressure and temperature
for any vessel is governed by the design of the
vessel and the strength of the material from which
it is constructed. There is also a close relationship
between working pressure and temperature since
the strength of any material will normally fall off
as the temperature is increased. Temperature and
pressure limits are also affected by the physical
properties and temperature limits of the gaskets and
seals used in the vessel, and by any valves, gages
or other fittings attached to the vessel. Obviously,
the safe operating pressure of any system can be no
higher than that of its lowest rated component.
All Parr reactors show the maximum safe operating
pressure and temperature imprinted on the cylinder.
Pressure Vessel and Temperature Limits
The standard material of construction for Parr Instrument Company is Type 316 Stainless Steel. The working
pressure and temperature in these one and two liter reactors must not exceed the following maximum limits:
Vessel Material Maximum Pressure Maximum Temperature
T316 SS 5000 psig 350 °C PTFE Flat Gasket
www.parrinst.com
7
Page 8

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Assemble the Reactor
These reactors require at least 10 square feet of workspace in a well-ventilated area with convenient access
to an electric outlet, running water and a drain. This
unit needs to be placed at least 10 inches away from
walls or flammable materials.
1. Set the Reactor Controller near the reactor, leaving
a space of at least six inches between the controller
and the base of the reactor so that the controller
will not be unduly affected by radiant heat. Connect the reactor to the controller using information
contained in its Instruction Manual No. 548M or
follow the steps below.
Labeled connections are provided on the rear panel
of the controller.
Parr Cooling Only:
The Parr Cooling output connector is to be used
only with Parr Instrument Company cooling solenoid valve assemblies supplied with the appropriate cooling power cord.
Parr Heating Only:
2B. Vessels on stationary stand.
Bolt the stand to the bench/floor using
the holes in the base plate.
Loosen the panel screw holding the vessel retainer
to the front midplate. Open the vessel retainer to
allow the placement of the vessel assembly. If fixed
head style, position the head in the slot located in
the front midplate. If removable head style, place
vessel assembly such that the split ring rests on
midplate bracket. After installing the vessel, close
the vessel retainer and retighten the panel screw.
Pull up on the release knob located at the top of the
belt guard. This knob is attached to the upper drive
shaft and the universal coupling. Lifting the knob
will allow the alignment of the universal coupling
and the drive adapter attached to the magnetic
drive. Turn the knob to align the slot in the drive
adapter with the universal coupling.
3. Connect the power cord from the heater into the
heater socket on the rear panel of the controller.
4. Plug the motor power cord into the motor socket
on the rear of the controller.
Secure the clamp on the motor cord
with the provided screw next to the
motor socket for safety purposes.
The Parr Heating output connector is to be used
only with Parr Instrument Company heater assemblies supplied with the appropriate heater power
cord.
Note: Do not make connections to a Variac,
Powerstat or the like to attempt to control the
heating output. The heavy inductive load on
the primary side of such devices can destroy
the internal sold state relay located in the 4848
controller.
Parr Motor Only:
The Motor output connector is to be used only with
Parr Instrument Company motor assemblies supplied with the appropriate motor power cord.
2A. Vessels on movable cart.
The motor is contained in the overarm assembly
attached to the cart. The overarm assembly pivots
to the rear to allow the vessel to be placed in the
heater. The overarm is then aligned atop the vessel.
Pull up on the release knob to allow the upper
drive shaft to be connected to the magnetic stirrer.
8
Parr Instrument Company
5. Note the voltage requirement on the controller
identification label on the back panel, and then
plug the power cord into an appropriate outlet.
Power for these reactors should be drawn from a
3-slot, grounded outlet capable of carrying up to
the full current rating of the system.
6. Connect the thermocouple extension wire to both
the thermocouple and to the controller in the
“Primary Temp Input” position on the rear panel.
Insert the thermocouple into thermowell.
7. Connect leads from accessory packages such as
tachometer, pressure transducer and high temp
cut-off to the designated positions on the back
panel of the 4848 Reactor Controller.
8. Connect cooling water to internal cooling coil if
installed.
9. Connect cooling water to the magnetic stirrer. See
manual no. 234M.
10. Connect tubing to the rupture disc outlet and run
to a safely vented area. See manual no. 231M.
11. Using the switch on the Reactor Controller, turn on
the motor for a short run to check the stirrer drive
system.
Page 9

IDENTIFY THE VALVES
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Gas Inlet Valves
The gas inlet valve is easily identified when the
bomb is open by noting that it is connected to a dip
tube which extends to a point near the bottom of
the bomb cylinder. This is an angle valve with an
attached fitting which provides a socket for attaching
the pressure hose furnished with the reactor.
Gas Release Valve
The gas release valve is connected to a plain opening
on the underside of the bomb head. Gas released from
this valve will be drawn from the top of the reactor.
Gage Adapter
Liquid Sampling Valve
The liquid sampling valve is attached to the same
fitting as the gas inlet valve and connected to the
same dip tube. With this arrangement, incoming gas
is always introduced below the surface of the liquid
and the operator is provided with a means for clearing the dip tube to be sure that any liquid sample
taken during a run will be representative of the
charge. This can be done by opening the upper gas
inlet valve momentarily to allow the inlet gas to force
any liquid in the dip tube back into the reactor before
withdrawing a sample from the sampling valve.
Pressure Gage
Thermocouple
Gas Inlet Valve
Gas Hose Connection
Gas Release Valve
Split Ring Assembly
Shaft Assembly
Liquid Sampling Valve
Thermowell
Dip Tube
Cooling Coil
Stirrer Bracket
Impeller
Removable Head Vessel Vessel with Standard Magnetic Drive Shown
www.parrinst.com
9
Page 10

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
OTHER VESSEL HEAD FITTINGS
Safety Rupture Disc
There is a safety rupture disc attached to the head
that is intended to rupture and release the pressure
before it reaches a dangerous level. A metal tag
wired to the safety head identifies the burst pressure at room temperature for that particular disc.
A similar tag is furnished with each replacement
disc. This tag must remain with the apparatus at all
times so that both present and future operators will
be aware of the disc rating. Users should read the
discussion of rupture discs given in the Instruction
Sheet No. 231M for a complete description of the
characteristics of rupture discs and the precautions
to be observed when operating pressure equipment
protected by this type of safety device.
A typical pre-bulged disc can be used to 90% of the
rating on the tag. For additional protection, the user
should install an adequate and safe venting system
for removing any toxic, flammable or volatile material which would be released if the rupture disc
should burst. A connector for attaching 3/8” OD
tubing to the discharge port of the rupture disc is
provided for this purpose.
Type J Thermocouple
A Type J thermocouple in a 1/8” dia. Stainless steel
sheath is furnished with the reactor. Insert this thermocouple into the head thermowell and connect it
to the thermocouple socket on the rear panel of the
temperature controller using the A470E2 extension
wire furnished with the controller.
Pressure Gage
A pressure gage, usually 0-7500 psi with a T316
stainless steel Bourdon tube, is mounted on the
head using attachment fittings similar to those used
for the inlet/sampling valve assembly.
Gage and Valve Adapters
The pressure gage and the combined gas inlet and
sampling valves are attached to the head with an
adapter which allows these fittings to be drawn up
tightly when facing in any direction. To attach these
fittings to the head, screw the gage or valves firmly
into the adapter, then run the 209HC4 bushing onto
the threaded stem as far as it will go. Screw this
assembly into the head until the nose of the adapter
is seated; then back it off until the valve or gage is
facing in the desired direction. Now hold the fitting
firmly in place and close the joint by tightening the
209HC4 bushing. This connection can be made and
broken repeatedly without destroying the sealing
faces. A light coating of thread lubricant, such as
Parr No. 424HC2 High Temperature Anti-Seize Lube,
applied to the threads and to the nose of the adapter
will help to obtain a tight joint.
Note: PTFE tape should be used only on all
tapered (NPT) threads, not on the straight
threads of the 209HC4.
10
56HCPH
208HC15
1446HC
209HC4
PRESSURE GAGE
Parr Instrument Company
A451VB
A455VB2
491HCAD
208HC6
209HC4
INLET SAMPLING VALVE
A455VB2
208HC11
209HC4
GAS RELEASE VALVE
Page 11

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
ACCESSORIES
Serpentine Cooling Coil
A Serpentine Cooling Coil can be installed in any
of these reactors. The reactors are not drilled for a
cooling loop unless so ordered. Reactors purchased
without a serpentine cooling coil can have this feature added by returning the head assembly to Parr
Instrument Company.
If ordered the serpentine cooling coil is mounted to
the underside of the head and sealed with a ferrule
and compression nut arrangement.
A slow continuous flow of cold water through the
cooling loop is an effective means for controlling
temperature overshoot, particularly when operating
at temperatures below 150 °C. Alternately the cooling loop is used to effectively cool the system at the
completion of a reaction.
An optional solenoid valve package is available to
automate the cooling process. This package coordinates with the internal coil, with the water supply and
connects to the temperature control.
If the internal cooling is not required, the coil may be
removed and the alternate plugs installed.
Spare Parts Kit
Parr can furnish spare parts kits for these reactors
which will provide a reserve supply of parts and tools
sufficient to handle most normal replacements and
emergency repairs during a year of heavy usage.
These kits contain replacement gaskets, packing,
O-rings, shafts, bearings, and rupture discs. They can
be ordered from any Parr Dealer or direct from the Parr
Instrument Company. The order must specify the reactor size and indicate type of rupture disc, stirrer drive
and whether it has a flat-gasket or O-ring closure.
Liners
Glass or PTFE liners can be furnished to fit most
Parr reactors. These liners slide into the cylinder.
Although they will not keep corrosive vapors from
reaching the surfaces of the cylinder and head, they
make it much easier to add and remove liquid reactants, and they give some protection to the cylinder
when working with corrosive solutions. It must be
noted, however, that adding a PTFE liner will slow
the heat transfer rate into the vessel, and it may be
necessary to adjust the temperature control method
to prevent overheating.
Liner Part Numbers
Fits ID
Cylinder
Size
Glass
Liner
PTFE Liner
3.25” 600 mL 2312HC 2312HC3HA
3.25” 1200 mL 2312HC2 2312HC4HA
Variable Speed Electric Motor
Reactors are normally equipped with a DC variable
speed motor supplied and controlled through the
4848 Reactor Controller. Instructions for connecting and operating these motors are included in the
controller instruction sheet No. 232M. This motor
is usually installed in a drive system designed to
produce stirring speeds from 0 to 600 rpm. Higher
speeds up to 1700 rpm can be obtained by substituting larger diameter motor drive pulleys.
Air Motor
Variable stirring speeds from 100 to 2000 rpm with
no spark hazard can be obtained by replacing the
standard motor with an air motor. This motor operates on compressed air which must be supplied at 40
psig minimum pressure with at least 10CFM available
at that pressure. It is furnished with a speed control
valve and oiler, all assembled on a mounting bracket.
To operate reactors equipped with an air motor,
mount the drive system firmly on the heater and
connect the air hose to a compressed air line. Fill the
oiler with SAE 10 motor oil and adjust the oiler to
feed one drop per minute into the air stream.
For long continuous runs at high speeds the oiling
rate should be increased to three drops per minute.
If the motor becomes sluggish, flush it with a nonflammable solvent in a well ventilated area. Disconnect the air line and muffler and pour a small amount
of solvent into the inlet port. Rotate the shaft by hand
in both directions for a few minutes; then connect the
air line and run the motor until there is not further
trace of solvent in the exhaust.
If the muffler felts are dirty, wash them in solvent or
replace them. Relubricate the motor with a squirt of
oil into the chamber and reassemble.
If it becomes necessary to disassemble the motor
to replace the vanes, follow directions given in the
instruction sheet published by the Gast Manufacturing
Corp., Benton Harbor, Michigan.
www.parrinst.com
11
Page 12

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Pneumatic Lift for Fixed Head Vessels
For those models equipped with a
pneumatic lift package, the following
instructions apply:
Technical Support
This pressure reactor assembly uses
an A2760HC3 Pneumatic Lift Package
to raise and lower the Cylinder.
Cylinder Lift Assembly
Contact our customer service
department with questions
concerning the Pneumatic Lift
Package.
Toll Free: 1(800) 872-7720
E-mail: parr@parrinst.com
Hand Lever Valve Assembly “Joystick”
Lift up on joystick to go “UP” or
Push down on joystick to go “DOWN”.
Hose Bulkhead Flow Control Connector
A (1/4”) quick disconnect fitting has been
provided for the air line connection.
Pneumatic Lift Cylinder
Pressure Regulator with Gage
The air pressure has been preset
to 50 psi. The regulator can be
adjusted by lifting up on this cap
and then turning “clockwise” to
increase or “counterclockwise”
to decrease the amount of
pressure being sent to the
pneumatic cylinder.
Press cap back down after setting
pressure, this will prevent the
cap from being unintentionally
turned.
User is responsible for connecting to their
air supply.
Heater Assembly
Hose Coupler
Flow Control Valves
The flow control valves have been preset for optimum
performance. Both the speed and lifting capacity of the
Pneumatic lift package can be adjusted with the flow
control valves located on the input and output ports of
the pneumatic cylinder.
12
Parr Instrument Company
Page 13

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
HOW TO USE THE VESSEL
Fixed Head Vessels
First, lower the heater and push it aside before attempting to remove the split ring and cylinder. Raise
the support cylinder holder to the bottom of the
cylinder and open the gas release valve to discharge
any internal pressure.
To open the Vessel
Remove the split rings. For vessels with a confined,
flat PTFE gasket, loosen the six bolts. For vessels
with an O-ring closure, loosen the latches on each
side of the split rings. The split ring halves can now
be removed, and the head with all attached fittings
will remain in place. The cylinder can now be lowered away. Handle the cylinder carefully so as not to
damage the stirring shaft and other internals.
Before Closing the Vessel
Examine the head seal carefully to be sure that
it is in good condition. The seal should not have
any nicks or be hardened, discolored or deformed.
Examine the mating surfaces on the cylinder and
head to be sure they are clean and free from burrs;
then raise the cylinder up to the head.
To Open the Vessel
Remove the split rings. For vessels with a confined,
flat PTFE gasket, loosen the six bolts. For vessels
with an O-ring closure, loosen the latches on each
side of the split rings. The split ring halves can now
be removed, and the head with all attached fittings
wilt remain in place. The head with all attached fittings is free to be lifted from the cylinder. Handle the
head carefully so as not to damage the stirring shaft
and other internals.
Before Closing the Vessel
Examine the head seal carefully to be sure that
it is in good condition. The seal should not have
any nicks or be hardened, discolored or deformed.
Examine the mating surfaces on the cylinder and
head to be sure they are clean and free from burrs.
Then carefully set head on cylinder.
To Close the Vessel
Slide the two split ring halves around the cylinder
and head flanges. If equipped with a drop band,
position the split ring halves such that the indentation for one of the halves is located 180 degrees
away from the pressure gage. Slide the drop band
over the split ring halves and tighten the set screw
lightly to hold the band in place.
To Close the Vessel
Put the two split ring halves around the head and
cylinder flanges and fasten the latches or tighten the
bolts as assembled before.
Removable Head Vessels
First, open the gas release valve to discharge any
internal pressure. For vessels on a movable floor
cart, lift the vessel out of the heater before attempting to remove the split ring and head. For vessels
on a stationary stand, loosen the panel screw holding the vessel retainer, remove the vessel from the
stand and set it on a table.
For vessels on a movable floor cart, place the vessel
into the heater with the gage facing forward and
swing the drive arm into position, connecting the
splined coupling onto the stirrer drive. For vessels
on a stationary stand, place the vessel onto the
midplate such that the drop band set screw fits into
the slot on the back of the midplate.
Recommended Bolt Torque
Material Pressure (psi) Torque (ft-lb)
PTFE 0 - 3000 35 ft-lbs
PTFE 4000 - 5000 40 ft-lbs
Pick a starting bolt and tighten it to approximately
15 ft-lbs. Then by-pass the adjacent bolts and move
around the closure to a bolt approximately 180 degrees from the starting bolt. Torque all bolts to the
initial 15 ft-lbs. Then proceed with the same pattern
increasing the torque in 10 ft-lbs increments.
www.parrinst.com
13
Page 14

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Note: The following steps are common to both head configurations.
Gas Connections
Gas connections are dependent on applications.
For general usage, use the pressure hose furnished
with the reactor. Screw the Type “A” coned pressure
fitting into the adapter attached to the gas inlet valve
and tighten the compression nut firmly. Do not use
any thread dope on the coned fitting.
Pressurizing the Vessel
Check all valves carefully before admitting gas into
the system. The liquid sampling valve must remain
closed throughout the charging procedure. The gas
release valve must also be closed unless the vessel
is to be purged, or unless there is to be a continuous
flow through the reactor during a run. Always make
certain that the pressure in the gas tank is greater
than the pressure in the vessel; otherwise liquid
will be forced out of the vessel and into the gas
tank when the inlet valve is opened. If there is any
possibility that the tank pressure might not be high
enough to force gas into the reactor, install a one
way check valve (optional) in the gas line to prevent
any reverse flow. With the inlet valve open and the
flow control valve on the gas tank closed, open the
main valve on the gas tank only about one-quarter
turn; then use the flow control valve or the valve
on a pressure regulator to control the flow of gas
into the vessel. After the desired pressure has been
reached, close the tank valves and the vessel inlet
valve and disconnect the hose at the vessel end.
Do Not Overfill the Vessel
Always watch the pressure gage closely when
admitting gas so as not to exceed the maximum
working limit. Remember that any subsequent
increase in temperature will raise the pressure.
Also, be sure that the amount of liquid placed in the
vessel is carefully controlled. As a general rule, the
liquid charge should not exceed two-thirds of the capacity of the cylinder. Too much liquid in the vessel
can lead to development of dangerous pressures if
sufficient space is not provided for expansion when
the liquid is heated. This hazard is explained in
greater detail in a warning statement included in the
Instruction Manual No. 230M.
Releasing Pressure
Use the gas release valve to reduce the pressure in
the vessel if the reactor is accidentally overcharged
when filling. Use this valve also to release any
excess pressure during a run and to exhaust the
vessel at the end of a run. If the discharge gases are
flammable or toxic, discharge to an exhaust hood or
to any other safe release point.
Withdrawing Liquid Samples
Liquid samples may be withdrawn from the sampling
valve attached to the same adapter as the gas inlet
valve whenever the vessel is pressurized. Always
close the inlet valve before withdrawing a liquid
sample and open the sampling valve cautiously
because liquid will be discharged with considerable
force. Be particularly careful if the temperature of
the sample is above its boiling point at atmospheric
pressure. If so, it will “flash” and be lost as soon
as it is released from the vessel. This problem can
be avoided by connecting an optional 4352 Sample
Collection Vessel to the sampling valve to collect the
liquid into an appropriate receiver. The addition of
a small amount of gas can be used to clear the dip
tube between liquid samples so that the next sample
drawn through the tube will truly be representative of
the mixture.
Initial Operating Test
Read all operating instructions carefully so as to be
well acquainted with the correct procedures for handling the vessel and for operating the controller and
other accessories. An initial operating test should
be made, with only water, to check the apparatus
before starting the first experimental runs. For this
initial test, fill the cylinder not more than half full
of water and run the temperature up to 150ºC while
checking the apparatus for leaks and observing the
performance of the temperature controller
14
Parr Instrument Company
Page 15

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
MAINTENANCE
General Maintenance Notes
1. Periodically inspect all electrical wiring and pressure connections for excessive corrosion. Suspect parts should be replaced by components
only supplied by Parr Instrument Company.
2. Always use appropriate wrenches on all fittings
and valves. Never use pliers or pipe wrenches.
3. Head and cylinder service fixtures are available
for convenience and protection of components
during maintenance of your reactor.
4. To reinstall straight thread (NPS) fittings to the
head, screw the gage or valves firmly into the
adapter.
Run the bushing onto the threaded stem as far
as it will go. Screw this assembly into the head
until the nose of the adapter is seated; then
back it off until the valve or gage is facing in the
desired direction (no more than one full turn).
Hold the fitting firmly in place and close the
joint by tightening the bushing. This connection
can be made and broken repeatedly without
destroying the sealing surfaces. A light coating
of thread lubricant, such as Parr High Temperature Anti-Seize Lubricant, applied to the straight
threads and to the nose of the adapter will help
to obtain a tight joint.
Note: PTFE tape should be used only
on all tapered (NPT) threads not NPS
straight threads.
5. NPT (National Pipe Taper) threads should not be
disassembled any more than necessary. It will
become increasingly difficult to maintain a tight
seal with these tapered threads if the joint is
made and broken repeatedly.
6. Do not use oil or anti-seize lubricant on threads
or fittings if the vessel is to be used with oxygen.
7. If your vessel is equipped with a loose compression ring be sure that it is in place on the head
before attaching any head fittings. The compression ring cannot be installed after fittings have
been screwed into the head.
8. Clean all threads and gas passages thoroughly
and remove all tape fragments when overhauling a vessel. An ultrasonic bath is excellent for
cleaning metal parts, but do not place a thermocouple probe, pressure gage, face seals or ball
bearings in an ultrasonic bath. Periodic cleaning
may be performed on the exterior surfaces
of the reactor stand a lightly dampened cloth
containing mild soap solution. All power should
be disconnected when cleaning.
9. Routinely inspect cap screws on split ring
closure for lubrication and cleanliness. These
screws should not be allowed to dry because
the threads will seize. Regularly apply Parr High
Temperature Anti-Seize Lubricant before this
happens.
10. To operate reactors equipped with an air motor,
connect air hose to a compressed air line. For
best torque and speed control the piping to
the motor should be at least 3/8” IPS or larger.
Fill the oiler with SAE 10 motor oil and adjust
the oiler feed one drop per minute into the air
stream. For long continuous runs at high speeds
the oiling rate should be increased to three
drops per minute. If the motor becomes sluggish, flush it with a non-flammable solvent in a
well ventilated area.
Disconnect the air line and muffler and pour
a small amount of solvent into the inlet port.
Rotate the shaft by hand in both directions for
a few minutes; then connect the air line and
run the motor until there is not further trace of
solvent in the exhaust. If the muffler is dirty,
replace it. Relubricate the motor with a squirt of
oil into the chamber and reassemble.
11. If servicing assistance is needed, contact Parr
Instrument Company directly at the address
shown on the back of these instructions.
www.parrinst.com
15
Page 16

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Periodic Pressure Tests
Each cylinder used in a Parr stirred reactor is tested
under hydrostatic pressure to the higher of 1.43
times the rated working pressure at room temperature or 1.30 times the rated working pressure
corrected for temperature before it is released from
the factory. Micrometer caliper measurements are
taken during this test to check the deflection of the
walls under pressure. Excessive deflection or failure
of the metal to resume its original dimensions after
pressure is released indicates that a cylinder is potentially unsafe and it will be rejected. Similar tests
should be made at regular intervals during the life
of each cylinder, and particularly whenever the user
suspects that the equipment has been over-stressed
or damaged.
Some laboratories maintain hydraulic test facilities
and make it a rule that all pressure vessels must
be tested at regular intervals. Records are kept of
deflections at specific test pressures so that any
increase in deflection becomes a warning that the
metal has lost strength. Any cylinder that fails to
return to its original dimensions after application of
the prescribed hydrostatic test should be discarded
as unsafe for further use.
Users who do not have pressure test facilities can
return any Parr pressure vessel to the factory for hydrostatic testing and overhaul. This should be done
whenever the metal shows excessive damage from
corrosion or whenever an over-pressure or other
unusual occurrence raises any safety questions.
To return a vessel for repair, contact Parr Instrument
Company for a return authorization number (RMA).
Technical Support
Parr Instrument Company strives to provide our
customers with world class support. When contacting Parr for technical support, please provide the
complete serial number etched on the side of the
cylinder. Serial numbers are a long string of letters
and numbers. See highlighted text in figure below
for an example of a complete serial number.
PARR INSTRUMENT COMPANY
MOLINE, IL. USA
2430HC3 222315 T316 112409 4600-1003-14106
MAWP 1900 PSI AT 350C 2010
Each Parr operating instruction manual binder
comes with a customized Parts Lists that contains
a list of the parts in each major component of your
Parr Reactor. Do not discard this Parts List. You
should use this parts list for reordering consumable
and replacement parts to ensure that you order the
correct parts for your reactor system.
Apparatus returned for testing and overhaul should
be shipped prepaid to the following address:
Ship repair to:
Parr Instrument Company
Attn: Service Department
RMA # XXXXXX
211 53rd Street
Moline, Illinois 61265
An order or letter of instructions should be mailed to
the same address, as no repair work will be started
without specific instructions and a Health & Safety
Assurance Certification form (FX004) signed by a
responsible user.
16
Parr Instrument Company
Customer Service
Questions concerning the installation or operation
of this instrument can be answered by the Parr
Customer Service Department:
1-309-762-7716 • 1-800-872-7720
Fax: 1-309-762-9453
E-mail: parr@parrinst.com
www.parrinst.com
Page 17

4540 SERIES REACTION VESSEL PARTS LIST
Standard Vessel Fittings
(5000 psig/ 350 °C)
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Consult the itemized list for your reactor, provided
along with this manual. For purpose of reactor identification the following abbreviation codes are used:
RV - Removable Vessel FH - Fixed Head
FG - Flat Gasket Seal OR - O-ring Seal
MD - Magnetic Drive FMD - Footless Magnetic Drive
LD - Light Duty HD - Heavy Duty
Cylinders*
Part No. Description
2302HC Cylinder, 600 mL
2302HC2 Cylinder, 600 mL with BDV
2302HC10 Cylinder, 1200 mL
2302HC12 Cylinder, 1200 mL with BDV
Heads*
Part No. Description Code
2300HC14 Head RV
2300HC15 Head RV FMD
2301HC8 Head FH
2301HC7 Head FH FMD
* For parts made from alternate materials use the
codes shown below as a suffix to the standard part
number.
CM - Alloy 400 CC - Alloy 20Cb3
CT - Alloy 600 CA - Titanium G2 or G4
CG - Alloy b-2 CH - Alloy C-276
CX - Zirconium
Split Rings and Accessories
Part No. Description Code
A2305HC Split ring, 4140 alloy steel RV
A2305HC-T Split ring, T316SS (PED Vessels) RV
2304HC Compression Ring RV
A2315HC2 Split ring, with latches captive
compression ring, 4140 alloy
steel
A2315HC2-T Split ring, with latches captive
compression ring, T316SS
(PED Vessels)
1278HC6F Bolts, split ring 5/8”- 18-1/2” Hex
1368HC Torque Wrench 3/8” drive
1369HC2 Torque Adapter 3/8” drive x 1/2” hex
FH
FH
Gaskets & Seals
Part No. Description
48HC Gasket, silver, mag drive
48HCFG Gasket, gold plated, mag drive
2303HC Head Gasket, PTFE
Thermowell
Part No. Description
A2067HC Thermowell, 600 mL / 1200 mL
* For Special Fittings
Dip Tubes
Part No. Description
257HC39 Dip Tube with nut, 600 mL
257HC40 Dip Tube with nut, 1200 mL
www.parrinst.com
17
Page 18

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Shafts
Part No. Description Code
352HC10 Stub Shaft, mag drive RV
352HC11 Stub Shaft, mag drive FH
2141HC19 Shaft, 600 mL MV LD FMD
2141HC20 Shaft, 1200 mL MV LD FMD
2141HC21 Shaft, 600 mL FH LD FMD
2141HC22 Shaft, 1200 mL FH LD FMD
A449HC16 Shaft Assembly with coupling, 600 mL
387HC2 Coupling, T316 .50 OD
379HC Pin, shaft, coupling
448HC16 Shaft w/ bushing, 600 mL
A449HC17 Shaft Assembly with coupling, 1200 mL
387HC2 Coupling, .50 OD
379HC Pin, shaft, coupling
448HC17 Shaft w/ bushing, 1200 mL
447HC Shaft bushing, PTFE
448HC16 Shaft with 447HC bushing, 600 mL
448HC17 Shaft with 447HC bushing, 1200 mL
A2308HC Impeller with screws, 1.75” dia.
A2148HC4 FMD Impeller w/ screw, 1.75” diameter
358HC2F Screw for impeller
Stirrer Support Bracket
Part No. Description
A2307HC3 Stirrer Bracket with bushing
380HCF Cap Screw for bracket
299HC Bushing PTFE for bracket
External Fittings
Part No. Description
94CAAD Plug, ¼” NPTM
A451VB Needle Valve, straight regulating 1/4”
NPTM-M (Liquid Sample)
A455VB2 Valve, angle regulating 1/4” NPTF-F
(Gas Inlet & Gas Release)
1446HC Adapter, 1/4” NPTM
491HCAD Hex Nipple, 1/4” NPTM
491HC2AD Hex long nipple, 1/4” NPTM
208HC6 Valve Adapter, two 1/4” NPTF
208HC15 Gage Adapter, angled, two 1/4” NPTF
209HC4 Bushing
288VBAD Male Connector, 3/8” T-1/4” NPTM
396HC3 Stirrer Plug
35HC Compression Nut, for plug
A1357E2 Thermocouple, grounded, 600 mL, Type J
A1357E
A888HC2 Safety Rupture Disc assembly w/o disc
A2685HC Cooling Sleeve Assembly
Thermocouple, grounded, 1200 mL, Type J
(see 231M)
Magnetic Stirrer
Part No. Description
A1120HC Magnetic Drive Assembly
(rubber coupling)
A1120HC6 Magnetic Drive Assembly
(universal coupling)
See manual 234M for a full list of magnetic stirrers & parts.
Cooling Coils*
Part No. Description
3227HC6 Serpentine Cooling Coil, 600 mL
3227HC7 Serpentine Cooling Coil, 1200 mL
Cooling Loops
Part No. Description
3763HC Cooling Loop, 600 mL
3763HC2 Cooling Loop, 1200 mL
Cooling Loop Fittings
Part No. Description
A92HWAD Male Connector
217VB Nut for A92HWAD ¼T
218VB Ferrule for A92HWAD ¼” T
79HW Plug, Hex Head 1/8” NPTM
18
Parr Instrument Company
Gages
Part No. Description
56HCPA Pressure gage, 4-1/2”, 0-100 psi
56HCPB Pressure gage, 4-1/2”, 0-200 psi
56HCPC Pressure gage, 4-1/2”, 0-600 psi
56HCPD Pressure gage, 4-1/2”, 0-1000 psi
56HCPF Pressure gage, 4-1/2”, 0-2000 psi
56HCPH Pressure gage, 4-1/2”, 0-5000 psi
56HCPK Pressure gage, 4-1/2”, 0-10,000 psi
* For Special Fittings
Page 19

Heaters Parts List
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Heaters for Bench Top and Floor Stand Vessels
Part No. Description
A2256HC12EB
A2256HC12EE
A2256HC22EB
A2256HC32EE
Heater Assembly w/ thermowell
1000W 115V 600 mL
Heater Assembly w/ thermowell
1500W 230V 600 mL
Heater Assembly w/ thermowell
1500W 115V 1200 mL
Heater Assembly w/ thermowell
2000W 230V 1200 mL
Heaters for Moveable Cart Model
Part No. Description
A735HCEB*
A735HCEE*
A735HC8EE
A735HC3EB
A735HC3EE
* 600 mL without Bottom Drain Valve
1200 mL with or without Bottom Drain Valve
Heater Assembly 1500W 115V
600 mL
Heater Assembly 1500W 230V
600 & 1200 mL
Heater Assembly 2000W 230V
1200 mL w/o Bottom Drain Valve
Heater Assembly 1000W 115V
600 mL w/ Bottom Drain Valve
Heater Assembly 1000W 230V
600 mL w/ Bottom Drain Valve
www.parrinst.com
19
Page 20

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
Overarm Parts List
Motor
Part No. Description Code
1355EES Motor, VS/PM 130VDC 1/8HP
A1554EES
A1393HC Air Motor LD
A388E6 Air Motor HD
A388EES Motor 1/4 HP VS 90 VDC LD HD
A388E2ES Motor 1/2 HP VS 90VDC HD
A388EEQ Motor 1/4 HP EXP VS 90 VDC LD HD
A388E2ET Motor 1/2 HP VS 180 VDC HD
A388EER Motor 1/4 HP EXP VS 180 VDC LD HD
A388EET Motor 1/4 HP VS 180 VDC LD HD
Motor, VS/PM 130VDC 1/8HP
with EMC filter
Driven Pulley Assembly
Part No. Description Code
A2179HC Driven Pulley Assembly LD
839HC Ball Bearing LD
841HC Snap Ring, External .693” LD
842HC Snap Ring, 1.804” LD
858HC2 Pulley, Driven LD
862HC Support Hub LD
299HC2 Bushing, PTFE LD
Shaft Couplings
Part No. Description Code
A722HC2 Shaft Coupling .38 rubber RV
A722HC Shaft Coupling .50 rubber RV
2075HC2 Shaft Coupling .38 universal FH
2352HC Shaft Coupling .50 universal FH
Release Knobs
Part No. Description Code
845HC2 Release Knob, .38 Shaft LD
726HC Release Knob, .50 Shaft HD
Drive Pulleys (Motor)
Part No. Description Code
857HC Pulley 600 RPM LD
857HC3 Pulley 800 RPM LD
857HC4 Pulley 1000 RPM LD
857HC5 Pulley 1700 RPM LD
695HC5 Pulley 600 RPM .62 HD
695HC3 Pulley 1000 RPM .62 HD
695HC2 Pulley 1700 RPM .62 HD
Pulley Belt Combinations
A2519HC Driven Pulley Assembly HD
706HC2 Pulley, Driven HD
725HC Support Hub HD
730HC Ball Bearing HD
731HC Snap Ring Internal 2” HD
732HC Snap Ring External 1” HD
2429HC Bushing PTFE HD
Upper Drive Shafts
Part No. Description Code
A860HC Upper Drive Shaft RV
A742HC13
A2562HC Upper Drive Shaft FH
A2564HC Upper Drive Shaft 11.27” FH
* For Special Fittings
* For Special Fittings
Upper Drive Shaft,
standard Calrod heater only
RV
LD Drive RV-Belt FH-Belt
857HC 847HC6 847HC9
857HC3 847HC6 847HC9
857HC4 847HC6 847HC9
857HC5 847HC4 847HC10
HD Drive RV-Belt FH-Belt
695HC5 728HC 728HC5
695HC3 728HC 728HC5
695HC2 728HC3 728HC6
Optional Tach Parts
Part No. Description
1564HC Optical Wheel
A10 01E Tach Sensor Assembly (9.0”L)
20
Parr Instrument Company
Page 21

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
BELT GUARD
DRIVE PULLEY
OVERARM PLATE
ISOLATOR
ENCASEMENT
MOTOR
BACK PLATE
BELT
TACH SENSOR
ASSEMBLY
RELEASE KNOB
OPTICAL WHEEL
DRIVEN PULLEY
HUB ASSEMBLY
SNAP RING
UPPER DRIVE SHAFT
UNIVERSAL COUPLING
www.parrinst.com
21
Page 22

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
4540 SERIES DRAWINGS
4540 Series Vessel with Fittings
Shown with Standard Magnec Drive
A92HWAD MALE CONNECTOR
A888HC2 RUPTURE DISC HOLDER
366VBAA HEX COUPLING
288VBAD MALE CONNECTOR
A1120HC6 MAG DRIVE
352HC10 STUB SHAFT
299HC BUSHING (UNDERSIDE)
208HC15 GAGE ADAPTER
209HC4 ADAPTER BUSHING
2300HC14 HEAD
94CAAD PLUG
A1357E2 THERMOCOUPLE, 600mL
A1357E THERMOCOUPLE, 1200mL
A138CA MALE CONNECTOR
REMOVABLE VESSEL
A92HWAD MALE CONNECTOR
A1120HC6 MAG DRIVE REF
352HC11 STUB SHAFT
299HC BUSHING (UNDERSIDE) REF
56HC SERIES GAGE
A455VB2 VALVE
GAS INLET VALVE
2301HC8 HEAD
1446HC ADAPTER
GAS HOSE CONNECTION
FIXED HEAD VESSEL
A455VB2 VALVE
491HC2AD NIPPLE
GAS RELEASE VALVE
A2305HC SPLIT RING ASS'Y
2304HC COMPRESSION RING
A449HC16 SHAFT ASS'Y, 600mL
A449HC17 SHAFT ASS'Y, 1200mL
3227HC6 COOLING COIL, 600mL
3227HC7 COOLING COIL, 1200mL
2X A92HWAD MALE CONNECTOR
2X A2308HC IMPELLER
491HCAD NIPPLE
A451VB VALVE
LIQUID SAMPLING VALVE
208HC6 ADAPTER
209HC4 ADAPTER
A2067HC THERMOWELL
CUT TO LENGTH
257HC39 DIP TUBE, 600mL
257HC40 DIP TUBE, 1200mL
A2315HC2 SPLIT RING ASS'Y
A2307HC3 STR BRACKET
2302HC CYLINDER, 600mL
2302HC10 CYLINDER, 1200mL
2303HC GASKET
22
Parr Instrument Company
Page 23

4540 Series Vessel with Fittings
Shown with Footless Magnec Drive
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
A2140HC2 MAG DRIVE
1133HC BUSHING (UNDERSIDE)
2996HC COLLAR (UNDERSIDE)
2300HC15 HEAD
A2140HC2 MAG DRIVE REF
1133HC BUSHING (UNDERSIDE) REF
2996HC COLLAR (UNDERSIDE) REF
2301HC7 HEAD
FIXED HEAD VESSELREMOVABLE VESSEL
2141HC19 SHAFT, 600mL
2141HC20 SHAFT, 1200mL
2X A2148HC4 IMPELLER
2141HC21 SHAFT, 600mL
2141HC22 SHAFT, 1200mL
www.parrinst.com
23
Page 24

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
1/4 HP Light Duty FH/RH Overarm and Motor
Diagram of Overarm for: 4544A, 4545A, 4546A & 4547A
24
RPM
600 RPM 695HC5 Ø1.75 728HC5
1000 RPM 695HC3 Ø3.00 728HC5
1700 RPM 695HC2 Ø4.00 728HC6
Parr Instrument Company
RPM Table
Pulley Diameter Belt
Page 25

1/8 HP Light Duty FH/RH Vessel Overarm and Motor
Diagram of Overarm for: 4544A, 4545A, 4546A, & 4547A
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
RPM Table
RPM
600 RPM 857HC Ø1.19 847HC9
1000 RPM 857HC4 Ø1.85 847HC9
1700 RPM 857HC5 Ø3.00 847HC10
Pulley Diameter Belt
www.parrinst.com
25
Page 26

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
4544 600 mL Removable Head Reactor
Without Bottom Drain Valve
26
Parr Instrument Company
Page 27

4545 600 mL Fixed Head Reactor
Without Bottom Drain Valve
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
www.parrinst.com
27
Page 28

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
4544/4544A 600 mL Removable Head Reactor
With or Without Bottom Drain Valve
28
Parr Instrument Company
Page 29

4545/4545A 600 mL Fixed Head Reactor
With or Without Bottom Drain Valve
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
www.parrinst.com
29
Page 30

4540 High Pressure Reactor System
4546 1200 mL Removable Head Reactor
Without Bottom Drain Valve
30
Parr Instrument Company
Page 31

4547 1200 mL Fixed Head Reactor
Without Bottom Drain Valve
4540 High Pressure Reactor System
www.parrinst.com
31
Page 32

394M R02 12/30/14
 Loading...
Loading...