
NetComm GAteWAy™ SerieS
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
USER GUIDE

Preface
This manual provides information related to the installation, operation, and application of this device. The individual reading this manual is
presumed to have a basic understanding of telecommunications terminology and concepts.
If you nd the product to be broken or malfunctioning, please contact technical support for immediate service by email at
technicalsupport@netcomm.com.au
For product update, new product release, manual revision, or software upgrades, please visit our website at
www.netcommlimited.com
Important Safety Instructions
With reference to unpacking, installation, use and maintenance of your electronic device, the following basic guidelines are recommended:
• Do not use or install this product near water, to avoid re or shock hazard. For example, near a bathtub, kitchen sink or laundry tub,
or near a swimming pool. Also, do not expose the equipment to rain or damp areas (e.g. a wet basement).
• Do not connect the power supply cord on elevated surfaces. Allow it to lie freely. There should be no obstructions in its path and no
heavy items should be placed on the cord. In addition, do not walk on, step on or mistreat the cord.
• Use only the power cord and adapter that are shipped with this device.
• To safeguard the equipment against overheating, make sure that all openings in the unit that offer exposure to air are not blocked.
• Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of electric shock from
lightening. Also, do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
• Never install telephone wiring during stormy weather conditions.
WARNING
• Disconnect the power line from the device before servicing.
Copyright
Copyright©2010 NetComm Limited. All rights reserved. The information contained herein is proprietary to NetComm Limited. No part of
this document may be translated, transcribed, reproduced, in any form, or by any means without prior written consent of NetComm Limited
NOTE:This document is subject to change without notice.
Save Our Environment
When this equipment has reached the end of its useful life, it must be taken to a recycling centre and processed separate from domestic
waste.The cardboard box, the plastic contained in the packaging, and the parts that make up this router can be recycled in accordance
with regionally established regulations. Never dispose of this electronic equipment along with your household waste. You may be subject to
penalties or sanctions under the law. Instead, ask for disposal instructions from your municipal government.
Please be responsible and protect our environment.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
2 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Table of Contents
Introduction ...............................................................................................................................................................................................4
Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................................................................5
Application .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................5
LED Indicators..................................................................................................................................................................................................................5
Back Panel Connectors ....................................................................................................................................................................................................6
Factory Default Settings ...................................................................................................................................................................................................7
Hardware Requirements ...................................................................................................................................................................................................7
System Requirements ......................................................................................................................................................................................................7
Package Contents............................................................................................................................................................................................................7
Installation & Setup ...................................................................................................................................................................................8
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router Conguration .......................................................................................................................... 14
Web User Interface ..................................................................................................................................................................................17
Web Conguration Overview ..........................................................................................................................................................................................18
Accessing the ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router Web User Interface ....................................................................................................................18
Quick Start ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Interface Setup ........................................................................................................................................................................................22
Internet ..........................................................................................................................................................................................................................23
LAN ...............................................................................................................................................................................................................................24
Wireless .........................................................................................................................................................................................................................25
Wireless Security ............................................................................................................................................................................................................26
WPS Settings .................................................................................................................................................................................................................26
Advanced Setup ......................................................................................................................................................................................27
Firewall ...........................................................................................................................................................................................................................28
Routing ..........................................................................................................................................................................................................................28
QoS ...............................................................................................................................................................................................................................30
VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................................................................................31
ADSL .............................................................................................................................................................................................................................32
Access Management ..............................................................................................................................................................................33
ACL Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................34
Filtering ..........................................................................................................................................................................................................................34
Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP) ......................................................................................................................................................................................36
DDNS ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................37
CWMP ...........................................................................................................................................................................................................................37
Maintenance ............................................................................................................................................................................................40
Admin Setting ................................................................................................................................................................................................................40
System Time ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................40
Firmware Update ............................................................................................................................................................................................................41
System Reset .................................................................................................................................................................................................................41
Diagnostics ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................41
Status ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 43
Device Info .....................................................................................................................................................................................................................43
System Log ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................44
Statistics ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................44
Appendix A: Installing UPnP in Windows Example ............................................................................................................................... 46
Installing UPnP in Windows Me ......................................................................................................................................................................................46
Installing UPnP in Windows XP .......................................................................................................................................................................................47
Using UPnP in Windows XP Example .............................................................................................................................................................................48
Auto-discover Your UPnP-enabled Network Device ........................................................................................................................................................48
Web Conguration Easy Access .....................................................................................................................................................................................50
Appendix B: Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................................................52
Appendix C: Technology Glossary .........................................................................................................................................................55
Appendix D: Legal and Regulatory Information .....................................................................................................................................58
Customer Information .....................................................................................................................................................................................................58
Federal Communication Comission Interference statement ............................................................................................................................................59
Product Warranty ...........................................................................................................................................................................................................59
Limitations of Warranty ...................................................................................................................................................................................................60
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 3

Introduction

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Introduction
The NetComm NB14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router allows you to connect to a broadband Internet service and share the
connection with multiple users. Also including a host of other features that exist to make your experience as seamless as possible, the
NB14WN is an ideal entry level Wireless N ADSL2+ product.
With a built-in Wireless N access point providing speeds of up to 150Mbps, multiple users are able to connect any Internet enabled device
to the NB14WN without wires and access the Internet from a location convenient to them. On top of this, the NB14WN also comes with a
built-in 4 port Ethernet switch, allowing for other devices to access the Internet over a wired connection.
The NB14WN also has a number of handy features that assist in delivering you the best possible user experience. These include a WPS
push button that allows for an easy set-up of your wireless network, a push button to easily turn your wireless signal on and off, advanced
security options to ensure your network remains safe and an easy to navigate web interface if you need to change any settings.
Features
• Fully featured ADSL2+ modem router
• Wireless N access point for speeds of up to 150Mbps
• 4 LAN ports for multiple wired connections
• WPS button for simple set up of your wireless network
• Advanced wireless security to maintain the integrity of your network
• Easy to use web based setup and conguration
Application
Wireless N
150Mbps
Power
Point
PDA
Switch
Once you have connected to an ADSL service, you are able to share the Internet with a wireless or wired connection.
Power
Adapter
Laptop
Computer
Gaming
Console
LED Indicators
The front panel LED indicators are shown and explained below
LED Icon Description
Power Lights up when powered ON.
ADSL
Internet
Lights up when the router is connected via ADSL.
Lights up when connected to the Internet.
Wireless
WPS
Ethernet
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 5
Lights up when specic Wireless connection is established, Blinks on WAN / LAN trafc and Blinks on Temporarily
overridden to LAN mode.
Lights up when Wi-Fi protected Set Up is being used
Lights up when the corresponding LAN port is being used

LED Color On Flash Off
Green Ready Waiting for device ready Power Off
Green Connect to DSLAM Disconnect to DSLAM N/A
Green The device has a WAN IP address from ISP Transmit / Receive Data N/A
Green WLAN Ready Transmit / Receive Data WLAN Off
Green N/A Start WPS peer within 2 minutes WPS Idle
Green Ethernet Connected Transmit / Receive Data Ethernet Disconnected
Back Panel Connectors
The below table shows the function of each connector and switch of the NB14WN’s back panel. The image illustrates the connectors.
Connector Description
POWER Connects to your NB14WN’s 12VAC power adaptor
ON/OFF Power Switch
LAN1~4 RJ-45 Jack (Ethernet Cable) connection to your PC or switch
LINE Connects to your ADSL2+ line – for ADSL2+ Line input
RESET Reset button, RESET the NB14WN to its default settings
Side Panel
Connector Description
WPS Start WPS(Wi-Fi Protected Setup) peer within 2 minutes.
WLAN WLAN On/Off switch
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
6 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Factory Default Settings
Before conguration, please refer to following default settings,
Web interface:
Username: admin
Password: admin
LAN IP Settings:
IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
DHCP:
DHCP Server: Enable
Hardware Requirements
To use the ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router, please have following hardware / accessories ready.
A PC with a pre-installed Ethernet Adapter (Required)
12VAC power adaptor (Included in the package)
RJ-45 Ethernet cable (Included in the package)
RJ-11cable (Included in the package)
System Requirements
1. Pentium 200MHZ processor or above
2. Windows 98SE / Windows Me / Windows 2000 / Windows XP / Windows Vista / Windows 7 or MAC 10.3 or later
3. 64MB of RAM or above
4. 25MB free disk space
Package Contents
• ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
• CD-ROM (Software & Manual)
• Quick Start Guide
• 1 x Telephone Cable (RJ-11)
• Ethernet Cable (RJ-45)
• Power Adaptor
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 7

Installation and SetUp

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Installation & Setup
Follow each step carefully and only go to the next step once you have completed the previous step.
Connection of the ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
1. Connect the supplied RJ-11 cable to the ADSL port on the back of your router to the phone port that supplies your ADSL.
2. Connect the supplied RJ-45 Ethernet cable from one of the LAN ports on the back of the router to your computer
3. Connect the supplied power adapter to your router and press the on/off button to power the router on.
Computer
Phone port
Power
Adapter
Power
Point
Conguration Procedures
Before beginning the NB14WN conguration, please kindly congure your PC as below, to enable automatic IP address / DNS Server.
For Windows 98SE/ME/2000/XP
1. Click on “Start” -> “Control Panel” (in Classic View). In the Control Panel; double click on “Network Connections” to continue.
2. Single RIGHT click on “Local Area connection”, then click “Properties”.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 9
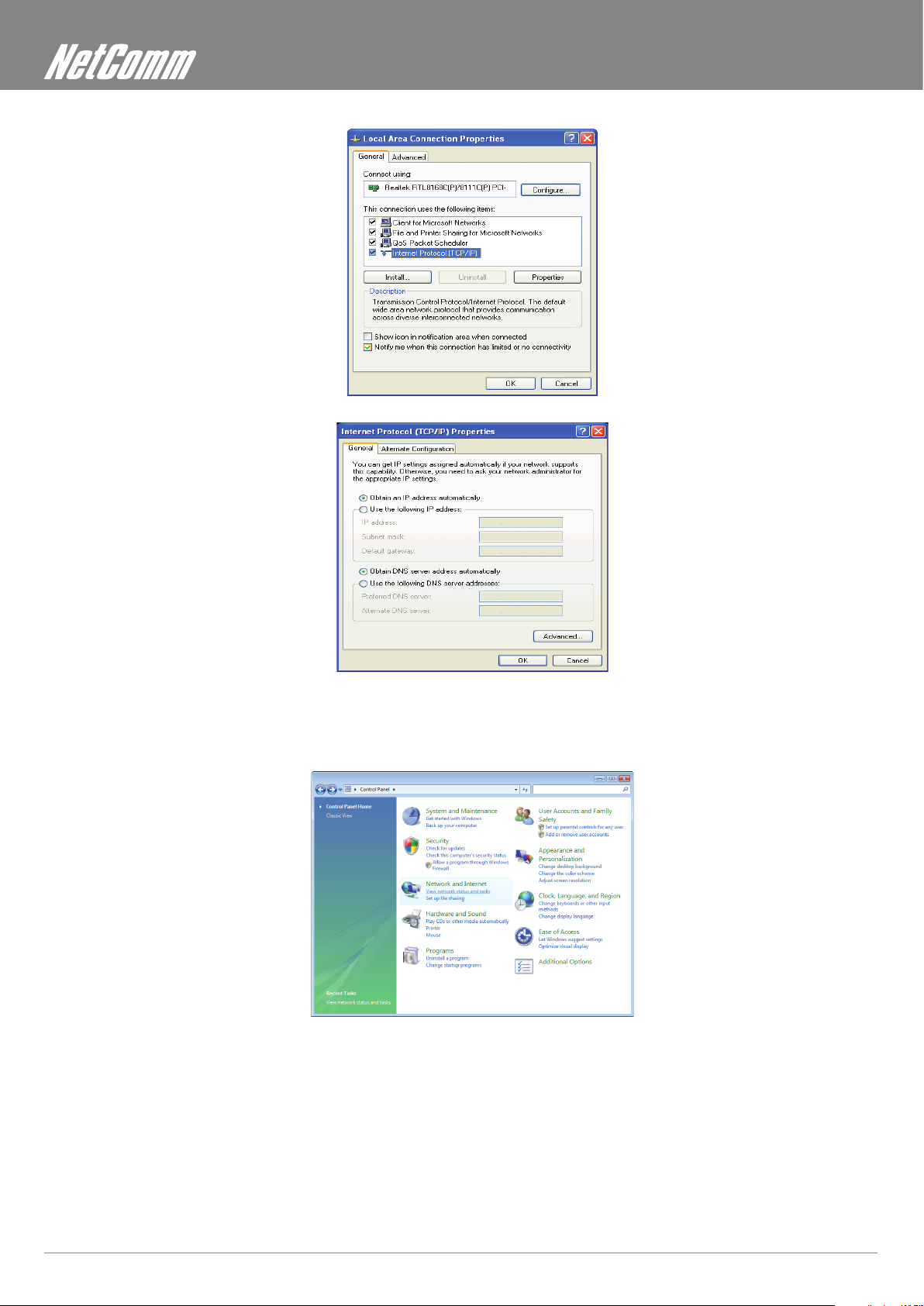
3. Double click on “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)”.
4. Check “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically” then click on “OK” to continue.
5. Click “Show icon in notication area when connected” (see screen image in 3. above) then click on “OK” to complete the setup
procedures.
For Windows Vista-32/64
1. Click on “Start” -> “Control Panel” -> “Network and Sharing Center”.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
10 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
2. In the Manage network connections, click on “Manage network connections” to continue.
3. Single RIGHT click on “Local Area connection”, then click “Properties”.
4. The screen will display the information “User Account Control” and click “Continue” to continue.
5. Double click on “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)”.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 11
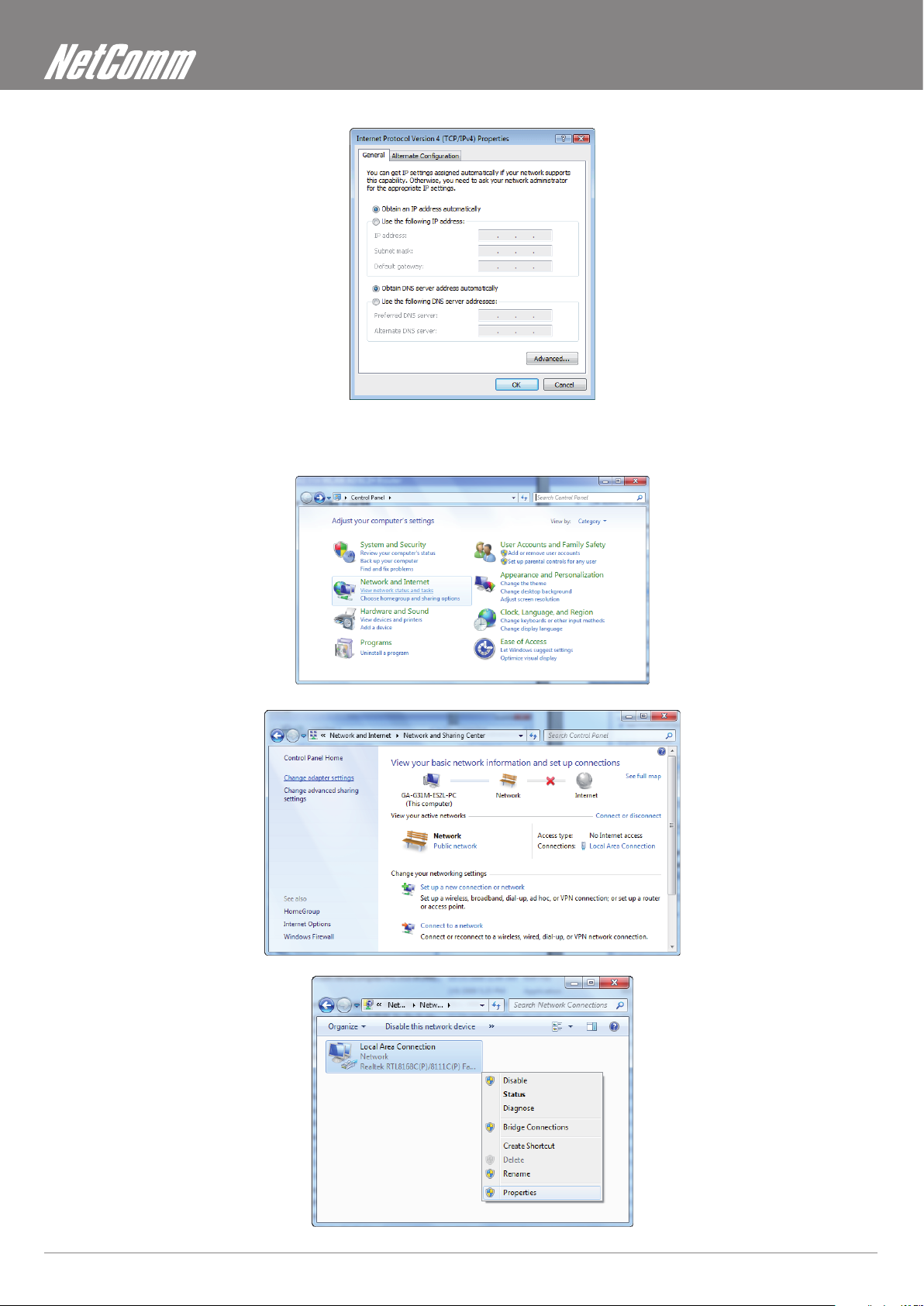
6. Check “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically” then click on “OK” to continue.
For Windows 7-32/64
1. Click on “Start” -> “Control Panel” (in Category View) -> “View network status and tasks”.
2. In the Control Panel Home, click on “Change adapter settings” to continue.
3. Single RIGHT click on “Local Area Connection”, then click “Properties”.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
12 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
4. Double click on “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)”.
5. Check “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically” then click on “OK” to continue.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 13

ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router Conguration

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem
Router Conguration
1. Please insert the supplied CD into your CD-ROM drive.
2. The CD should auto-start, displaying the window shown below. If your CD does not start automatically, go to Windows Explorer,
Select your CD drive and double click “autorun.exe”.
3. To congure the device, please click “Easy Conguration”.
4. Enter the VPI, VCI, Username and Password your ISP (Internet Service Provider) provided, and Protocol mode. Then press “Next”.
5. Please enter the “ESSID” and Wireless “Default Channel” if you want to change from the defaults. The default settings are;
Network = Enable, ESSID = NetComm Wireless, Default Channel = Auto
6. Choose the Encryption type if necessary. Options are;
- Off – No Encryption
- 64 Bit Encryption
- 128 Bit Encryption
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (TKIP)
- Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (AES-CCMP)
- WPA Mixed Mode.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 15

7. Please click the “Setup” button once you have entered all of your desired settings. Allow a short time for your device to apply these
settings
8. A window will pop up informing you of the status
9. Another window will open informing you that the easy conguration is complete. Click on “Exit” to complete the procedure.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
16 www.netcomm.com.au

Web User Interface

Web User Interface
Web Conguration Overview
The embedded web conguration allows you to manage the ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router from anywhere through a browser
such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator.
Accessing the ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Web User Interface
Step 1. Make sure your ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router is properly connected
Step 2. Prepare your computer/computer network to connect to the Router
Step 3. Launch your web browser.
Step 4. Type “192.168.1.1”.
Step 5. An Enter Network Password window displays. Enter the user name and password (“admin” is the default for both) and click OK.
Step 6. You should now see the Site Map screen.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
18 www.netcomm.com.au

Quick Start

Quick Start
You can use “Quick Start” to setup the router’s ADSL connection with ease.
Click “Quick Start” to get into the quick setup procedures.
Click “RUN WIZARD” to start up this procedure.
Step 1 – Please click “Next” to setup your new administrator’s password.
Step 2 – Please click “Next” to setup your time zone.
Step 3 – Please click “Next” to setup your Internet connection type. This information is supplied to you by your Internet Service Provider.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
20 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Step 4 - Enter the connection information provided by your ISP and click “Next”.
Step 5 - Enter the connection information provided by your ISP and click “Next”.
Step 6 – Please click “NEXT” to conrm your changes.
Step 7 – Please click “CLOSE” to exit the Quick Start Wizard
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 21

Interface Setup

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Interface Setup
Internet
VC Conguration
Go to Interface Setup -> Internet. To add or delete an ADSL VC (virtual channel) conguration, enter the information that has been supplied
to you by your ISP.
WAN Conguration
The router can be connected to your service provider in any of the following ways:
• Dynamic IP Address: Obtain an IP address automatically from your service provider.
• Static IP Address: Uses a static IP address. Your service provider gives a static IP address to access Internet services.
• PPPoE: PPP over Ethernet is a common connection method used for ADSL
• PPPoA: PPP over ATM is a common connection method used for ADSL
• Bridge: Bridge mode is a common connection method used for ADSL modems.
Dynamic Routing
The dynamic routing feature of the router can be used to allow the router to automatically adjust to physical changes in the network’s
layout. The router uses the dynamic RIP protocol. It determines the route that the network packets take based on the fewest number of
hops between the source and the destination. The RIP protocol regularly broadcasts routing information to other routers on the network
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 23

LAN
DNS
Go to Interface -> LAN to enable DHCP server. You can then set DNS server for the router. A Domain Name System (DNS) server is like
an index of IP addresses and Web addresses. If you type a Web address into your browser, a DNS server will nd that name in its index
and nd the matching IP address.
Most ISPs provide a DNS server for speed and convenience. Since your Service Provider may connect to the Internet with dynamic IP
settings, it is likely that the DNS server IP addresses are also provided dynamically. However, if there is a DNS server that you would
rather use, you need to specify the IP address below.
LAN Conguration
The ‘LAN Settings’ option enables you to congure the LAN port.
If DHCP Relay is selected, the DHCP requests from local PCs are forward to the DHCP server that runs on the WAN side. To have this
function working properly, disable the NAT to run on router mode only, disable the DHCP server on the LAN port, and make sure the
routing table has the correct routing entry.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
24 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Wireless
Wireless Settings
Go to Interface -> Wireless to setup the wireless parameters.
There are a number of options you can change. Two of the more basic and common options you may wish to change are:
SSID
The name of your wireless network. You can change the SSID. Only devices with the same SSID can interconnect.
Channel
The channel number is used for wireless networking. The channel setting of the wireless devices within a network should be the same.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 25

Wireless Security
It is recommended that you change your wireless security to ensure that your network remains free from any unwanted guests.
The Authentication type supports “WEP 64Bits”, “WEP 128Bits”, “WPA-PSK”, “WPA2-PSK”, and ‘WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK”.
Choose which type of security you would like to use and follow the instructions to set the password. The security authentication types in
the drop down box are listed from least secure to most secure.
WPS Settings
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) provides a convenient way to establish the connection between this broadband router and wireless clients.
Any WPS-compatible wireless client can establish secure connection with this broadband router with simple push-button type conguration
or Pin Code type conguration.
Here are descriptions of every setup items:
Item Name Description
Use WPS Check this box to enable WPS function,uncheck it to disable WPS.
WPS mode Select your WPS mode to PIN Code or PBC
AP self PIN code This is the WPS PIN code of this wireless router. This code is useful when you need to build
enrollee PIN code Please input the PinCode displayed at the conguration software of WPS-enabled wireless client,
Start WPS Start WPS peer within 2 minutes.
Reset to OOB Click on Reset to OOB button to Reset WPS AP to the OOB(out of box) conguration.
SSID The SSID of this wireless router will be displayed here.
Authentication Type The wireless security authentication mode of this wireless router will be displayed here.
PIN (Personal Information Number) PBC (Push Button Conguration)
wireless connection by WPS with other WPS-enabled wireless devices.
and click ‘Start WPS’ to establish connection with the wireless client.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
26 www.netcomm.com.au

Advanced Setup

Advanced Setup
Firewall
Go to Advanced Setup ->Firewall to setup Firewall features. Selecting this option can automatically detect and block Denial of Service (DoS)
attacks, such as Ping of Death, SYN Flood, Port Scan and Land Attack.
Routing
Routing Table
Go to Advanced Setup -> Routing to see the Routing Table. The Routing table allows you to see how many routings on your routing table
and interface information
Static Routing
Click on ADD ROUTE to setup static route features.
The static routing function determines the path that the router follows over your network before and after it passes through your router. You
can use static routing to allow different IP domain users to access the Internet through this device.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
28 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
NAT
Go to Advanced Setup->NAT to setup the NAT features. Network Address Translation (NAT) allows multiple users at your local site to
access the Internet through a single public IP address or multiple public IP addresses. NAT can also prevent hacker attacks by mapping
local addresses to public addresses for key services such as the Web or FTP.
Virtual Server
Go to Advanced Setup ->NAT -> Virtual Server to set a virtual server (known as Port Mapping).You can congure the router as a virtual
server so that remote users accessing services such as the Web or FTP at your local site via public IP addresses can be automatically
redirected to local servers congured with private IP addresses. In other words, depending on the requested service (TCP/UDP port
numbers), the router redirects the external service request to the appropriate server (located at another internal IP address). For some
applications, you need to assign a set or a range of ports (example 4000-5000) to a specied local machine to route the packets. The
router allows the user to congure the needed port mappings to suit such applications.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 29
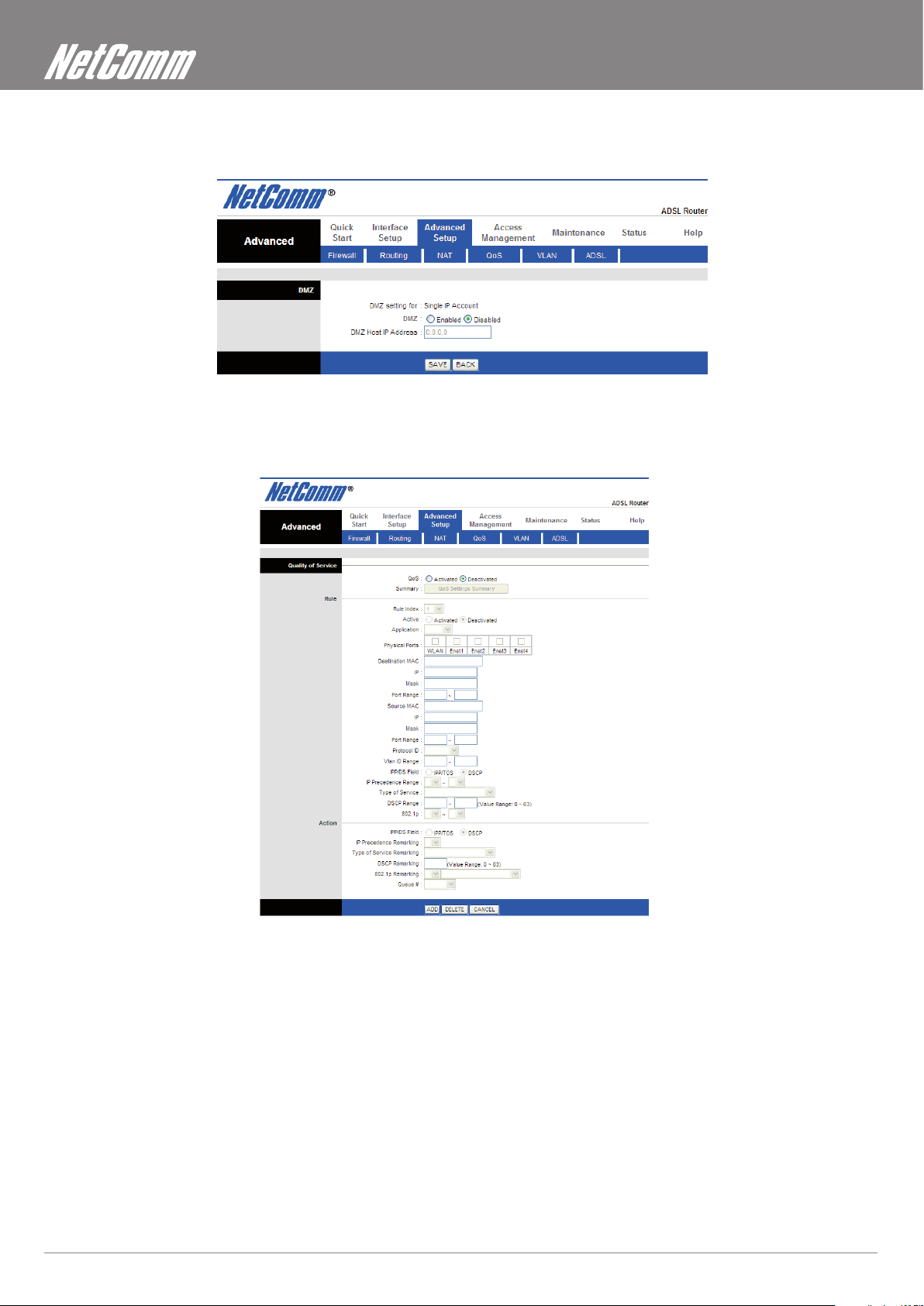
DMZ Setting
Go to Advanced Setup ->NAT -> DMZ to set DMZ parameters. If you have a local client PC that cannot run an Internet application properly
from behind the NAT rewall, you can open the client up to unrestricted two-way Internet access by dening a virtual DMZ Host.
QoS
Go to Advanced Setup -> QoS to setup QoS features. This option will provide better service of selected network trafc over various
technologies.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
30 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
VLAN
Go to Advanced Setup -> VLAN to enable VLAN features. Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a group of devices on one or more LANs that are
congured so that they can communicate as if they were attached to the same wire, when in fact they are located on a number of different
LAN segments. Because VLANs are based on logical instead of physical connections, it is very exible for user/host management,
bandwidth allocation and resource optimization.
VLAN PVID
Go to VLAN PVID for each interface to setup VLAN PVID features. Each physical port has a default VID called PVID
Go to VLAN PVID for each interface to setup VLAN PVID features. Each physical port has a default VID called PVID (Port VID). PVID is
assigned to untagged frames or priority tagged frames (frames with null (0) VID) received on this port.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 31

VLAN Group
Go to Dene VLAN Group to setup VLAN group features.
ADSL
Go to Advanced Setup > ADSL to dene and set your ADSL mode and ADSL Type.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
32 www.netcomm.com.au

Access Management

Access Management
ACL Setting
Go to Access Management -> ACL to enable remote management. The user may remotely access the ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem
Router once setting their IP as a Secure IP Address through selected applications. With the default IP 0.0.0.0, any client would be allowed
to remotely access the ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router.
Filtering
IP Filtering
Go to Access Management -> IP Filtering to block some packets from the WAN. The router provides extensive rewall protection by
restricting connection parameters to limit the risk of intrusion and defence against a wide array of common hacker attacks. The user can
set different IP lter rules of a given protocol (TCP, UDP or ICMP) and a specic direction (incoming, outgoing, or both) to lter the packets.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
34 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Application Filter
Select Application Filter from the drop down box to deny service to a number of precongured programs and services
URL Filter
Select URL Filter from the drop down box to deny service to any URL that you specify
SNMP
Go to Access Management -> SNMP to setup the SNMP feature. Simple Network Management Protocol is used for exchanging
information between network devices.
Get Community: Select to set the password for the incoming Get- and GetNext requests from the management station.
Set Community: Select to set the password for incoming Set requests from the management station.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 35

Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
Universal Plug and Play Overview
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a distributed, open networking standard that uses TCP/IP for simple peer-to-peer network connectivity
between devices. An UPnP device can dynamically join a network, obtain an IP address, convey its capabilities and learn about other
devices on the network. In turn, a device can leave a network smoothly and automatically when it is no longer in use.
How do I know if I’m using UPnP?
UPnP hardware is identied as an icon in the Network Connections folder (Windows XP). Each UPnP compatible device installed on your
network will appear as a separate icon. Selecting the icon of a UPnP device will allow you to access the information and properties of that
device.
NAT Traversal
UPnP NAT traversal automates the process of allowing an application to operate through NAT. UPnP network devices can automatically
congure network addressing, announce their presence in the network to other UPnP devices and enable exchange of simple product and
service descriptions. NAT traversal allows the following:
• Dynamic port mapping
• Learning public IP addresses
• Assigning lease times to mappings
Windows Messenger is an example of an application that supports NAT traversal and UPnP.
See the Network Address Translation (NAT) chapter for further information about NAT.
Cautions with UPnP
The automated nature of NAT traversal applications in establishing their own services may present network security issues. Network
information and conguration may also be obtained and modied by users in some network environments.
All UPnP-enabled devices may communicate freely with each other without additional conguration. Disable UPnP if this is not your
intention.
UPnP broadcasts are only allowed on the LAN.
See later sections for examples of installing UPnP in Windows XP and Windows Me as well as an example of using UPnP in Windows.
Conguring UPnP
From the Site Map in the main menu, click UPnP under Access Management to display the screen shown next.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
UPnP Select this checkbox to activate UPnP. Be aware that anyone could use a UPnP application to open the web conguration’s login screen without
Auto congured Select this check box to allow UPnP-enabled applications to automatically congure the NB14WN so that they can communicate through the
Apply Click Apply to save your settings back to home screen.
entering NB14WN’s IP address (although you must still enter the password to access the web conguration).
device. For example by using NAT traversal, UPnP applications automatically reserve a NAT forwarding port in order to communicate with another
UPnP enabled device; this eliminates the need to manually congure port forwarding for the UPnP enabled application.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
36 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
DDNS
Go to Access Management -> DDNS to setup your DDNS parameters. Dynamic DNS allows you to update your dynamic IP address with
one or many dynamic DNS services. So anyone can access your FTP or Web service on your computer using DNS-like address.
CWMP
The CWMP page is used to congure the TR-069 CPE. Here you may change the settings for the ACS’s parameters.
WAN Management Protocol (TR-069) allows an Auto-Conguration Server (ACS) to perform auto-conguration, provision, collection, and
diagnostics to this router.
CWMP: Activated/Deactivated TR-069 client on the CPE.
Login ACS
URL: URL for the CPE to connect to the ACS using the CPE WAN Management Protocol. This parameter MUST be in the form of a
valid HTTP or HTTPS URL. An HTTPS URL indicates that the ACS supports SSL. The “host” portion of this URL is used by the CPE for
validating the certicate from the ACS when using certicate-based authentication.
User Name: Username used to authenticate the CPE when making a connection to the ACS using the CPE WAN Management Protocol.
This username is used only for HTTP-based authentication of the CPE.
Password: Password used to authenticate the CPE when making a connection to the ACS using the CPE WAN Management Protocol.
This password is used only for HTTP-based authentication of the CPE.
Connection Request
Path: The path of the device ConnectionRequestURL. The device ConnectionRequestURL should be congured based on the Device_IP,
Path and Port as follows:
http://Device_IP:Port/Path
Port: The port of the device ConnectionRequestURL
User Name: Username used to authenticate an ACS making a Connection Request to the CPE.
Password: Password used to authenticate an ACS making a Connection Request to the CPE.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 37

Periodic Inform
Activated: When this eld is enabled, the DSL device will send an Inform RPC to the ACS server at the system startup, and will continue to
send it periodically at an interval dened in Periodic Inform Interval eld;
Deactivated: When this eld is disabled, the DSL device will only send Inform RPC to the ACS server once at the system startup.
Interval: Time interval in seconds to send Inform RPC.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
38 www.netcomm.com.au

Maintenance

Maintenance
Admin Setting
Go to Maintenance-> Administration to set a new username and password to restrict management access to the router.
The default is admin (Username) and admin (Password)
System Time
Go to Maintenance->Time Zone and select system time as you wish.
Connecting to a Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) server allows the router to synchronize the system clock to the global Internet.
The synchronized clock in the router is used to record the security log and control client ltering.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
40 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Firmware Update
Go to Maintenance -> Firmware to upgrade the rmware. The new rmware for your router can improve functionality and performance.
Enter the path and name of the upgrade le then click the UPGRADE button below. You will be prompted to conrm the upgrade.
System Reset
Go to Maintenance -> SysRestart to restart your system. In the event that the router stops responding correctly or in some way stops
functioning, you can perform a reset. Your settings will not be changed. To perform the reset, select “Current Setting” and click on the
“RESTART” button below. The router will reboot with current setting. Select “Factory Default Setting” and click on the “RESTART” button,
the router will reboot with factory default setting.
Diagnostics
The Diagnostics menu provides feedback on the connection status of the router and the DSL link. The individual tests are listed below. If
the test continues to fail, click Help and follow the troubleshooting procedures provided onscreen.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 41

Status
NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Status
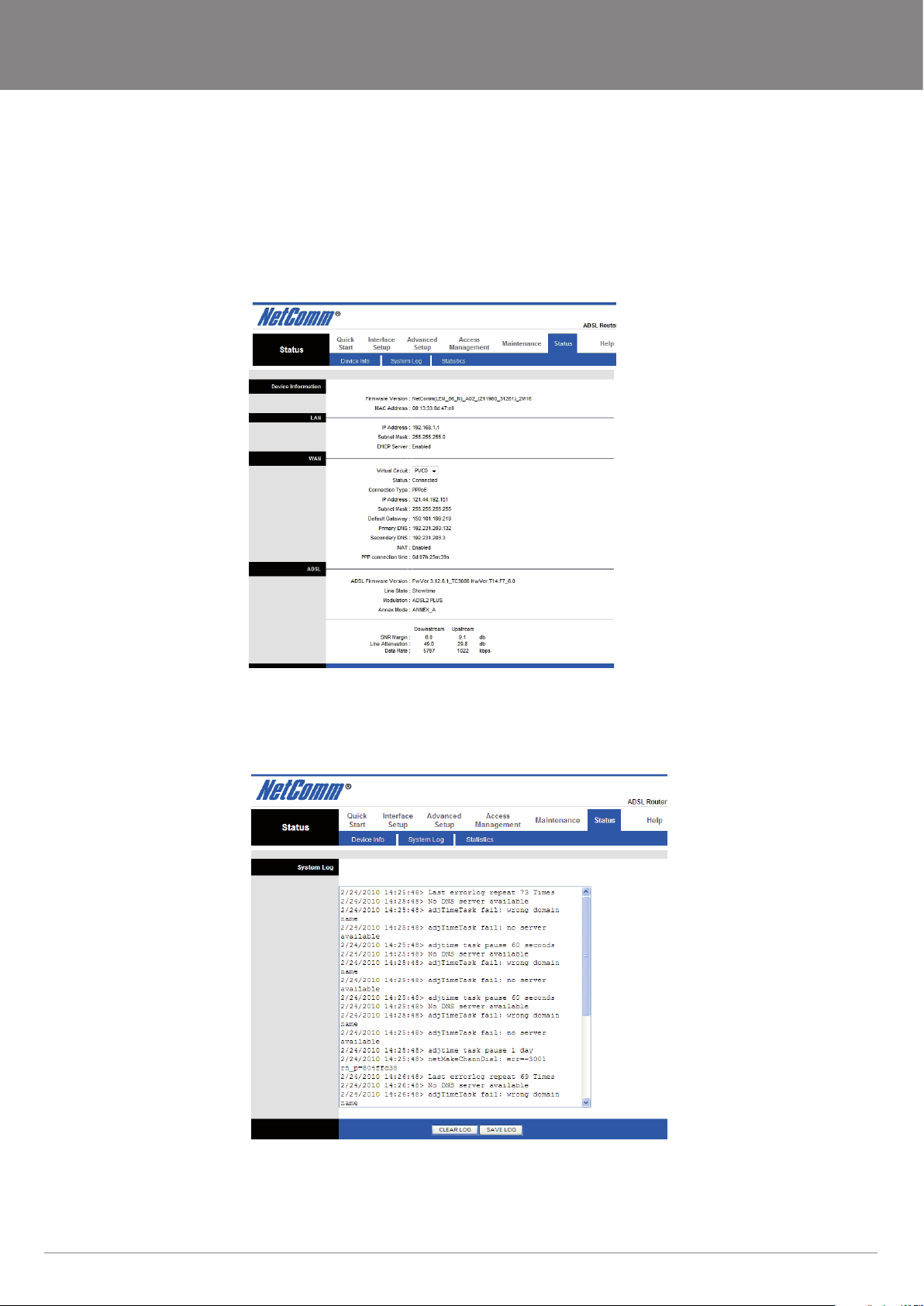
Device Info
System Status
Go to Status -> Device Info to see the router’s information. The System Status page shows the WAN, LAN and the router’s rmware
version.
The ‘ADSL Line Status’ enables you to check the status of your ADSL connection including how fast data is being transferred.
System Log
Go to Status -> System Log and you can see the system log le. Click “Save Log” to save system log le.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 43

Statistics
Ethernet
Go to Status-> Statistics and select Ethernet interface. You can see the trafc Statistics of Ethernet activity.
ADSL
Go to Status-> Statistics and select ADSL interface. You can see the trafc Statistics of ADSL interface.
WLAN
Go to Status-> Statistics and select WLAN interface. You can see the trafc Statistics of Wireless interface.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
44 www.netcomm.com.au

Appendix

Appendix A: Installing UPnP in
Windows Example
This section shows how to install UPnP in Windows Me and Windows XP.
Installing UPnP in Windows Me
Follow the steps below to install the UPnP in Windows Me.
Step 1. Click Start and Control Panel. Double-click Add/Remove Programs.
Step 2. Click on the Windows Setup tab and select Communication in the Components selection box. Click Details.
Step 3. In the Communications window, select the Universal Plug and Play check box in the Components selection box.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
46 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Step 4. Click OK to go back to the Add/Remove Programs Properties window and click Next.
Step 5. Restart the computer when prompted.
Installing UPnP in Windows XP
Follow the steps below to install the UPnP in Windows XP.
Step 1. Click Start and Control Panel.
Step 2. Double-click Network Connections.
Step 3. In the Network Connections window, click Advanced in the main menu and select Optional Networking Components.
The Windows Optional Networking Components Wizard window displays.
Step 4. Select Networking Service in the Components selection box and click Details.
Step 5. In the Networking Services window, select the UPnP User Interface check box.
Step 6. Click OK to go back to the Windows Optional Networking Component Wizard window and click Next.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 47
Using UPnP in Windows XP Example
This section shows you how to use the UPnP feature in Windows XP. You must already have UPnP installed in Windows XP and UPnP
activated on the NB14WN.
Make sure the computer is connected to a LAN port of the NB14WN. Turn on your computer and the NB14WN.
Auto-discover Your UPnP-enabled Network Device
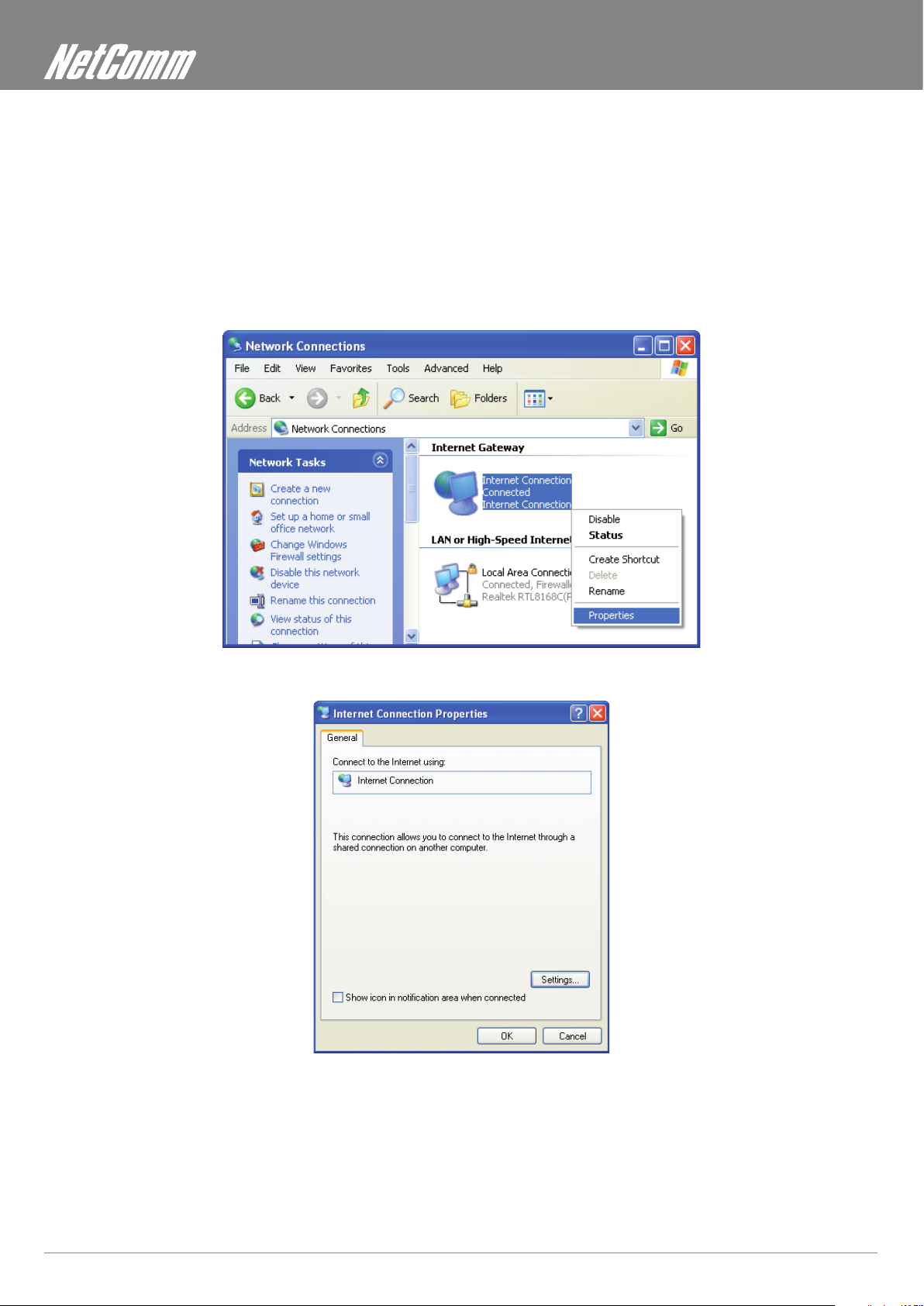
Step 1. Click start and Control Panel. Double-click Network Connections. An icon displays under Internet Gateway.
Step 2. Right-click the icon and select Properties.
Step 3. In the Internet Connection Properties window, click Settings to see the port mappings that were automatically created.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
48 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Step 4. You may edit or delete the port mappings or click Add to manually add port mappings.
Step 5. Select Show icon in notication area when connected option and click OK. An icon displays in the system tray
Step 6. Double-click on the icon to display your current Internet connection status.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 49

Web Conguration Easy Access
With UPnP, you can access the web-based conguration on the NB14WN without nding out the IP address of the device rst. This comes
helpful if you do not know the IP address of the NB14WN.
Follow the steps below to access the web conguration.
Step 1. Click Start and then Control Panel.
Step 2. Double-click Network Connections.
Step 3. Select My Network Places under Other Places.
Step 4.An icon with the description for each UPnP-enabled device displays under Local Network.
Step 5. Right-click on the icon for your NB14WN and select Invoke. The web conguration login screen displays.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
50 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Step 6. Right-click on the icon for your NB14WN and select Properties. A properties window displays with basic information about the
device.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 51
Appendix B: Troubleshooting
Using LEDs to Diagnose Problems
The LEDs are useful aides for nding possible problem causes.
Power LED
The PWR LED on the front panel does not light up.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Make sure that the NB14WN’s power adaptor is connected to the device and plugged in to an appropriate power source. Use only the
2 Check that the NB14WN and the power source are both turned on and device is receiving sufcient power.
3 Turn the NB14WN off and on.
4 If the error persists, you may have a hardware problem. In this case, you should contact your vendor.
LAN LED
The LAN LED on the front panel does not light up.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the Ethernet cable connections between your NB14WN and the computer or
2 Check for faulty Ethernet cables.
3 Make sure your computer’s Ethernet card is working properly.
4 If these steps fail to correct the problem, contact your local distributor for assistance.
supplied power adaptor.
hub.
DSL LED ( ACT & LINK)
The DSL LED on the front panel does not light up.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the telephone wire and connections between the devices’ DSL port and the
2 Make sure that the telephone company has checked your phone line and set it up for
3 Reset your ADSL line to reinitialize your link to the DSLAM.
4 If these steps fail to correct the problem, contact your local distributor for assistance.
wall jack.
DSL service.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
52 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Telnet
I cannot telnet into the NB14WN.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the LAN port and the other Ethernet connections.
2 Make sure you are using the correct IP address of the NB14WN. Check the IP address of the device.
3 Ping the NB14WN from your computer. If you cannot ping the device, check the IP addresses of the NB14WN
4 Make sure you entered the correct password. The default password is “admin”.
5 If these steps fail to correct the problem, contact the distributor.
and your computer. Make sure your computer is set to get a dynamic IP address; or if you want to use a static
IP address on your computer, make sure that it is on the same subnet as the NB14WN.
Web Conguration
I cannot access the web conguration.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Make sure you are using the correct IP address of the NB14WN. Check the IP address of the device.
2 Make sure that there is not a console session running.
3 Check that you have enabled web service access. If you have congured a secured client IP address, your
4 For WAN access, you must congure remote management to allow server access from the Wan (or all).
5 Your computer’s and the NB14WN’s IP addresses must be on the same subnet for LAN access.
6 If you changed the devices LAN IP address, then enter the new one as the URL.
7 Remove any lters in LAN or WAN that block web service.
The web conguration does not display properly.
computer’s IP address must match it.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Delete the temporary web les and log in again. In Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options and then
click the Delete Files ... button. When a Delete Files window displays, select Delete all ofine content and click
OK. (Steps may vary depending on the version of your Internet browser.)
Login Username and Password
I forgot my login username and/or password.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 If you have changed the password and have now forgotten it, you will need to upload the default
2 Press the Reset button for ve seconds, and then release it. When the LINK LED begins to blink, the defaults
3 The default username is “admin”. The default password is “admin”. The Password and Username elds are
4 It is highly recommended to change the default username and password. Make sure you store the username
conguration le. This will erase all custom congurations and restore all of the factory defaults including the
password.
have been restored and the NB14WN restarts.
case-sensitive. Make sure that you enter the correct password and username using the proper casing.
and password in a save place.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 53

LAN Interface
I cannot access the NB14WN from the LAN or ping any computer on the LAN.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the Ethernet LEDs on the front panel. A LAN LED should be on if the port is
2 Make sure that the IP address and the subnet mask of the NB14WN and your
connected to a computer or hub.
computer(s) are on the same subnet.
WAN Interface
Initialization of the ADSL connection failed.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the cable connections between the ADSL port and the wall jack. The DSL LEDs
2 Check that your VPI, VCI, type of encapsulation and type of multiplexing settings are
3 Restart your device. If you still have problems, you may need to verify your VPI, VCI,
I cannot get a WAN IP address from the ISP.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 The ISP provides the WAN IP address after authenticating you. Authentication may be
2 The username and password apply to PPPoE and PPoA encapsulation only. Make
on the front panel of the device should be on.
the same as what you collected from your telephone company and ISP.
type of encapsulation and type of multiplexing settings with the telephone company
and ISP.
through the user name and password, the MAC address or the host name.
sure that you have entered the correct Service Type, User Name and Password (be
sure to use the correct casing).
Internet Access
I cannot access the Internet.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Make sure the NB14WN is turned on and connected to the network.
2 Verify your WAN settings.
3 Make sure you entered the correct user name and password.
Internet connection disconnects.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the schedule rules.
2 If you use PPPoA or PPPoE encapsulation, check the idle time-out setting.
3 Contact your ISP.
Remote Node Connection
I cannot connect to a remote node or ISP.
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check WAN screen to verify that the username and password are entered properly.
2 Verify your login name and password for the remote node.
3 If these steps fail, you may need to verify your login and password with your ISP.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
54 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Appendix C: Technology Glossary
10Base-T
An adaptation of the Ethernet standard for Local Area Network (LAN). 10Base-T uses a twisted pair cable with maximum length of 100
meters.
AAL
ATM Adaptation Layer that denes the rules governing segmentation and reassembly of data into cells. Different AAL types are suited to
different trafc classes.
Address mask
A bit mask used to select bits from an Internet address for subnet addressing. The mask is 32 bits long and selects the network portion of
the Internet address and one or more bits of the local portion. Sometimes called subnet mask.
ADSL
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, as it’s name showing, is an asymmetrical data transmission technology with high trafc rate
downstream and low trafc rate upstream. ADSL technology satises the bandwidth requirement of applications, which demand
“asymmetric” trafc, such as web surng, le download and Video-on-demand (VOD).
ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode is a layer 2 protocol supporting high-speed asynchronous data with advanced trafc management and quality
of service features.
bps
Bits per second. A standard measurement of digital transmission speeds.
Bridge
A device that connects two or more physical networks and forwards packets between them. Bridges can usually be made to lter packets,
that is, to forward only certain trafc. Related devices are: repeaters which simply forward electrical signals from one cable to the other, and
full-edged routers which make routing decisions based on several criteria.
CPE
Customer Premises Equipment, such as ADSL router, USB modem.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol. Used for assigning dynamic IP address to devices on a network. Used by ISPs for dialup users.
DNS
Domain Name Server, translates domain names into IP
addresses to help user recognize and remember. However, the Internet actually runs on numbered IP addresses, DNS servers needs to
translate domain names back to their respective IP addresses.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 55

DSL
Digital Line Subscriber (DSL) technology provides high-speed access over twisted copper pair for connection to the Internet, LAN
interfaces, and to broadband services such as video-on-demand, distance learning, and video conferencing.
FTP
File Transfer Protocol. The Internet protocol (and program) used to transfer les between hosts.
IPoA (RFC 1577)
Classical IP and ARP over ATM. Considers ATM congured as a Logic IP Sub-network(LIS) to replace Ethernet local LAN segments.
ISP
Internet service provider. A company that allows home and corporate users to connect to the Internet.
LAN
Local area network. A limited distance (typically under a few kilometers or a couple of miles) high-speed network (typically 4 to 100 Mbps)
that supports many computers.
MAC
Media Access Control Layer. A sub-layer of the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the ISO OSI Model responsible for media control.
MTU
Maximum Transmission Unit
NAT
Network Address Translator as dened by RFC 1631. Enables a LAN to use one set of IP address for internal trafc. A NAT box located
where the LAN meets the Internet provides the necessary IP address translation. This helps provide a sort of rewall and allow for a wider
address range to be used internally without danger of conict.
PPP
Point-to-Point-Protocol. The successor to SLIP, PPP provides router-to-router and host-to-network connections over both synchronous
and asynchronous circuits.
PPPoA (RFC 2364)
The Point-to-Point Protocol(PPP) provides a standard method for transporting multi-protocol datagrams over point-to-point links. This
document describes the use of ATM Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL5) for framing PPP encapsulated packets.
PPPoE (RFC 2516)
This document describes how to build PPP sessions and encapsulate PPP packets over Ethernet. PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) provides the
ability to connect a network of hosts over a simple bridging access device to a remote Access Concentrator.
PVC
Permanent Virtual Circuit. Connection-oriented permanent leased line circuit between end-stations on a network over a separate ATM
circuit.
RFC
Request for Comments. The document series, begun in 1969, which describes the Internet suite of protocols and related experiments. Not
all RFCs describe Internet standards, but all Internet standards are written up as RFCs
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
56 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
RFC 1483
Multi-protocol encapsulation over AAL-5. Two encapsulation methods for carrying network interconnect trafc over ATM AAL-5. The rst
method allows multiplexing of multiple protocols over a single ATM virtual circuit. The protocol of a carried PDU is identied by prexing the
PDU by an IEEE 802.2 Logical Link Control (LLC) header. This method is in the following called “LLC Encapsulation”. The second method
does higher-layer protocol multiplexing implicitly by ATM Virtual Circuits (VCs). It is in the following called “VC Based Multiplexing”.
Router
A system responsible for making decisions about which of several paths network (or Internet) trafc will follow. To do this, it uses a routing
protocol to gain information about the network and algorithms to choose the best route based on several criteria known as “routing metrics.
Spanning Tree
Spanning-Tree Bridge Protocol (STP). Part of an IEEE standard. A mechanism for detecting and preventing loops from occurring in a multibridged environment. When bridges connect three or more LAN segments, a loop can occur. Because a bridge forwards all packets that
are not recognized as being local, some packets can circulate for long periods of time, eventually degrading system performance. This
algorithm ensures only one path connects any pair of stations, selecting one bridge as the ‘root’ bridge, with the highest priority one as
identier, from which all paths should radiate.
TELNET
The virtual terminal protocol in the Internet suite of protocols. Allows users of one host to log into a remote host and act as normal terminal
users of that host.
VCI
Virtual Circuit Identier. Part of the ATM cell header, a VCI is a tag indicating the channel over which a cell will travel. The VCI of a cell can be
changed as it moves between switches via Signaling.
VPI
Virtual Path Identier. Part of the ATM cell header, a VPI is a pipe for a number of Virtual Circuits.
WAN
Wide area network. A data communications network that spans any distance and is usually provided by a public carrier (such as a
telephone company or service provider)
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 57

Appendix D: Legal & Regulatory
Information
This manual is copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purposes of private study, research, criticism or review, as permitted under
the Copyright Act, no part may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form, by any means, be it electronic,
mechanical, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of NetComm Limited. NetComm Limited accepts no liability or
responsibility, for consequences arising from the use of this product.
NetComm Limited reserves the right to change the specications and operating details of this product without notice.
NetComm is a registered trademark of NetComm Limited.
All other trademarks are acknowledged the property of their respective owners.
Customer Information
ACA (Australian Communications Authority) requires you to be aware of the following information and warnings:
(1) This unit shall be connected to the Telecommunication Network through a line cord which meets the requirements of the ACA TS008
Standard.
(2) This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the Standards for C-Tick and or A-Tick as set by the ACA . These standards
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio noise and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions detailed within this manual, may
cause interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur with the installation of this
product in your home or ofce. If this equipment does cause some degree of interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, we encourage the user to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Change the direction or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between this equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an alternate power outlet on a different power circuit from that to which the receiver/TV is connected.
• Consult an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
(3) The power supply that is provided with this unit is only intended for use with this product. Do not use this power supply with any other
product or do not use any other power supply that is not approved for use with this product by NetComm. Failure to do so may cause
damage to this product, re or result in personal injury.
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
58 www.netcomm.com.au

NetComm Gateway Series - ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router
Product Warranty
The warranty is granted on the following conditions:
1. This warranty extends to the original purchaser (you) and is not transferable;
2. This warranty shall not apply to software programs, batteries, power supplies, cables or other accessories supplied in or with the
product;
3. The customer complies with all of the terms of any relevant agreement with NetComm and any other reasonable requirements of
NetComm including producing such evidence of purchase as NetComm may require;
4. The cost of transporting product to and from NetComm’s nominated premises is your responsibility; and,
5. NetComm does not have any liability or responsibility under this warranty where any cost, loss, injury or damage of any kind,
whether direct, indirect, consequential, incidental or otherwise arises out of events beyond NetComm’s reasonable control. This
includes but is not limited to: acts of God, war, riot, embargoes, acts of civil or military authorities, re, oods, electricity outages,
lightning, power surges, or shortages of materials or labour.
6. The customer is responsible for the security of their computer and network at all times. Security features may be disabled within the
factory default settings. NetComm recommends that you enable these features to enhance your security.
YML14WN ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide
www.netcomm.com.au 59

GNU General Public License
This product includes software code that is subject to the GNU General Public License (“GPL”) or GNU Lesser General Public License
(“LGPL”). This code is subject to the copyrights of one or more authors and is distributed without any warranty. A copy of this software can be
obtained by contacting NetComm Limited on +61 2 9424 2059.
The warranty is automatically voided if:
1. You, or someone else, use the product, or attempts to use it, other than as specied by NetComm;
2. The fault or defect in your product is the result of a voltage surge subjected to the product either by the way of power supply or
communication line, whether caused by thunderstorm activity or any other cause(s);
3. The fault is the result of accidental damage or damage in transit, including but not limited to liquid spillage;
4. Your product has been used for any purposes other than that for which it is sold, or in any way other than in strict accordance with
the user manual supplied;
5. Your product has been repaired or modied or attempted to be repaired or modied, other than by a qualied person at a service
centre authorised by NetComm; and,
6.
The serial number has been defaced or altered in any way or if the serial number plate has been removed.
Limitations of Warranty
The Trade Practices Act 1974 and corresponding State and Territory Fair Trading Acts or legalisation of another Government (“the relevant
acts”) in certain circumstances imply mandatory conditions and warranties which cannot be excluded. This warranty is in addition to and
not in replacement for such conditions and warranties.
To the extent permitted by the Relevant Acts, in relation to your product and any other materials provided with the product (“the Goods”)
the liability of NetComm under the Relevant Acts is limited at the option of NetComm to:
• Replacement of the Goods; or
• Repair of the Goods; or
• Payment of the cost of replacing the Goods; or
• Payment of the cost of having the Goods repaired.
All NetComm ACN 002 490 486 products have a standard 12 months warranty from date of purchase. However some products have an
extended warranty option (refer to packaging). To be eligible for the extended warranty you must supply the requested warranty information
to NetComm within 30 days of the original purchase by registering on-line via the NetComm web site at
www.netcomm.com.au
ADSL2+ Wireless N150 Modem Router User Guide YML14WN
60 www.netcomm.com.au

NETCOMM LIMITED Head Ofce
PO Box 1200, Lane Cove NSW 2066 Australia
P: 02 9424 2070 F: 02 9424 2010
E: int.sales@netcomm.com.au
W: www.netcommlimited.com.
DYNALINK NZ 12c Tea Kea Place, Albany, Auckland,
New Zealand
P: 09 448 5548
F: 09 448 5549
E: sales@dynalink.co.nz
W: www.dynalink.co.nz
How to congure WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Wireless Security
Product Warranty
NetComm products have a standard 12 months warranty from date of purchase. However some products have an extended
registering your product online at the NetComm website www.netcommlimited.com.
warranty option, via
Technical Support
If you have any technical difculties with your product, please refer to the support section of our website.
www.netcomm.com.au/support
Note: NetComm Technical Support for this product only covers the basic installation and features outlined in the Quick Start Guide. For further information regarding the advanced features of this product, please
refer to the conguring sections in the User Guide or contact a Network Specialist.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of NetComm Limited or their respective owners. Specications are subject to change without notice. Images shown
may vary slightly from the actual product.
 Loading...
Loading...