Nissan Primera User Manual
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
QG18DE
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INDEX..................................6
Alphabetical & P No. Index for DTC ...........................6
PRECAUTIONS ...............................................................9
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ‘‘AIR
BAG’’ and ‘‘SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER’’..............9
Precautions for On Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System of Engine ........................................................9
Engine Fuel & Emission Control System..................10
Precautions................................................................11
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnosis...................12
PREPARATION .............................................................13
Special Service Tools................................................13
Commercial Service Tool ..........................................13
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL
SYSTEM.........................................................................14
Engine Control Component Parts Location...............14
Circuit Diagram..........................................................17
System Diagram........................................................18
Vacuum Hose Drawing..............................................19
System Chart.............................................................20
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION...............................................21
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System .......................21
Electronic Ignition (EI) System..................................23
Air Conditioning Cut Control......................................24
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed)........................................................................25
Evaporative Emission System...................................25
Positive Crankcase Ventilation..................................28
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDURE...................................29
Fuel Pressure Release..............................................29
Fuel Pressure Check.................................................29
Fuel Pressure Regulator Check................................30
Injector.......................................................................30
Idle Speed/Ignition Timing/Idle Mixture Ratio
Adjustment.................................................................32
Idle Air Volume Learning...........................................43
SECTION
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION...............................................................45
Introduction................................................................45
Two Trip Detection Logic...........................................45
Emission-related Diagnostic Information...................46
Malfunction Indicator (MI)..........................................54
OBD System Operation Chart...................................59
CONSULT-II...............................................................64
Generic Scan Tool (GST)..........................................74
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INTRODUCTION...............76
Introduction................................................................76
Work Flow..................................................................78
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — BASIC INSPECTION ........80
Basic Inspection.........................................................80
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — GENERAL
DESCRIPTION...............................................................90
DTC Inspection Priority Chart....................................90
Fail-safe Chart...........................................................91
Symptom Matrix Chart...............................................92
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode..........................................................................96
Major Sensor Reference Graph in Data Monitor
Mode..........................................................................98
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................101
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR INTERMITTENT
INCIDENT.....................................................................108
Description...............................................................108
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................108
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR POWER SUPPLY........109
Main Power Supply and Ground Circuit..................109
DTC P0100 MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR (MAFS)......115
Component Description...........................................115
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................115
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................115
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................115
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................116
Wiring Diagram........................................................117
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................118
EC
EC

CONTENTS
(Cont’d)
Component Inspection.............................................120
DTC P0110 INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR ......................................................................121
Component Description...........................................121
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................121
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................121
Wiring Diagram........................................................122
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................123
Component Inspection.............................................124
DTC P0115 ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR(ECTS) (CIRCUIT)........................................125
Component Description...........................................125
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................125
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................125
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................126
Wiring Diagram........................................................127
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................128
Component Inspection.............................................129
DTC P0120 THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR ...........130
Component Description...........................................130
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................130
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................131
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................131
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................131
Wiring Diagram........................................................133
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................134
Component Inspection.............................................136
DTC P0130 FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(FRONT HO2S) (CIRCUIT)..........................................138
Component Description...........................................138
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................138
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................138
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................139
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................139
Overall Function Check...........................................140
Wiring Diagram........................................................141
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................142
Component Inspection.............................................143
DTC P0131 FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(FRONT HO2S) (LEAN SHIFT MONITORING)..........144
Component Description...........................................144
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................144
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................144
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................145
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................145
Overall Function Check...........................................146
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................146
Component Inspection.............................................148
DTC P0132 FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(FRONT HO2S) (RICH SHIFT MONITORING)...........150
Component Description...........................................150
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................150
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................150
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................151
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................151
Overall Function Check...........................................152
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................152
Component Inspection.............................................154
DTC P0133 FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(FRONT HO2S) (RESPONSE MONITORING)............156
Component Description...........................................156
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................156
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................156
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................157
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................157
Overall Function Check...........................................158
Wiring Diagram........................................................159
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................160
Component Inspection.............................................163
DTC P0134 FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(FRONT HO2S) (HIGH VOLTAGE).............................164
Component Description...........................................164
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................164
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................164
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................165
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................165
Wiring Diagram........................................................166
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................167
Component Inspection.............................................168
DTC P0135 FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
HEATER.......................................................................169
Description...............................................................169
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................169
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................169
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................169
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................170
Wiring Diagram........................................................171
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................172
Component Inspection.............................................173
DTC P0137 REAR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(REAR HO2S) (MIN. VOLTAGE MONITORING)........174
Component Description...........................................174
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................174
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................174
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................174
EC-QG-2

CONTENTS
(Cont’d)
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................175
Overall Function Check...........................................176
Wiring Diagram........................................................177
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................178
Component Inspection.............................................181
DTC P0138 REAR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(REAR HO2S) (MAX. VOLTAGE MONITORING)......182
Component Description...........................................182
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................182
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................182
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................182
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................183
Overall Function Check...........................................184
Wiring Diagram........................................................185
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................186
Component Inspection.............................................188
DTC P0139 REAR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(REAR HO2S) (RESPONSE MONITORING)..............190
Component Description...........................................190
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................190
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................190
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................190
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................191
Overall Function Check...........................................192
Wiring Diagram........................................................193
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................194
Component Inspection.............................................197
DTC P0140 REAR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(REAR HO2S) (HIGH VOLTAGE)...............................198
Component Description...........................................198
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................198
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................198
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................198
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................199
Overall Function Check...........................................199
Wiring Diagram........................................................200
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................201
Component Inspection.............................................202
DTC P0141 REAR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
HEATER.......................................................................204
Description...............................................................204
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................204
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................204
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................204
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................205
Wiring Diagram........................................................206
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................207
Component Inspection.............................................208
DTC P0171 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
FUNCTION (LEAN SIDE)............................................209
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................209
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................209
Wiring Diagram........................................................210
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................211
DTC P0172 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
FUNCTION (RICH SIDE).............................................215
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................215
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................215
Wiring Diagram........................................................216
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................217
DTC P0180 TANK FUEL TEMPERATURE
SENSOR ......................................................................221
Component Description...........................................221
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................221
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................221
Wiring Diagram........................................................222
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................223
Component Inspection.............................................224
DTC P0300 - P0304 NO.4-1CYLINDER
MISFIRE, MULTIPLE CYLINDER MISFIRE ...............225
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................225
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................225
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................226
DTC P0325 KNOCK SENSOR (KS)...........................231
Component Description...........................................231
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................231
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................231
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................231
Wiring Diagram........................................................232
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................233
Component Inspection.............................................234
DTC P0335 CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
(POS)............................................................................235
Component Description...........................................235
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................235
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................235
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................236
Wiring Diagram........................................................237
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................238
Component Inspection.............................................240
DTC P0340 CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
(CMPS) (PHASE).........................................................241
Component Description...........................................241
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................241
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................241
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................242
Wiring Diagram........................................................243
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................244
Component Inspection.............................................246
EC-QG-3

CONTENTS
(Cont’d)
DTC P0400 EGR FUNCTION (CLOSE)......................247
Description...............................................................247
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................248
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................248
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................248
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................249
Wiring Diagram........................................................251
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................252
Component Inspection.............................................254
DTC P0403 EGR VOLUME CONTROL VALVE
(CIRCUIT).....................................................................255
Description...............................................................255
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................256
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................256
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................256
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................256
Wiring Diagram........................................................257
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................258
Component Inspection.............................................259
DTC P0420 THREE WAY CATALYST FUNCTION ...260
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................260
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................260
Overall Function Check...........................................261
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................261
DTC P0443 EVAP CANISTER PURGE VOLUME
CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE (CIRCUIT) ................264
Description...............................................................264
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................264
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................265
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................265
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................265
Wiring Diagram........................................................266
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................267
Component Inspection.............................................268
DTC P0500 VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (VSS).........269
Component Description...........................................269
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................269
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................269
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................269
Wiring Diagram........................................................271
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................272
DTC P0505 IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE (IACV)
— AUXILIARY AIR CONTROL (AAC) VALVE ..........273
Description...............................................................273
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................274
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................274
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................274
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................274
Wiring Diagram........................................................275
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................276
Component Inspection.............................................277
DTC P0510 CLOSED THROTTLE POSITION
SWITCH .......................................................................278
Component Description...........................................278
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................278
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................278
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................278
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................279
Overall Function Check...........................................279
Wiring Diagram........................................................280
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................281
Component Inspection.............................................282
DTC P0605 ECM .........................................................284
Component Description...........................................284
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................284
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................284
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................284
DTC P1111 INTAKE VALVE TIMING CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE......................................................285
Component Description...........................................285
Operation.................................................................285
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................285
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................285
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................285
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................286
Wiring Diagram........................................................287
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................288
Component Inspection.............................................289
DTC P1131 SWIRL CONTROL VALVE CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE......................................................290
Description...............................................................290
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................290
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................291
Component Description...........................................291
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................291
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................291
Wiring Diagram........................................................292
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................293
Component Inspection.............................................294
DTC P1217 OVERHEAT (COOLING SYSTEM).........296
System Description..................................................296
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................296
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................297
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................297
Overall Function Check...........................................298
Wiring Diagram........................................................299
EC-QG-4

CONTENTS
(Cont’d)
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................301
Main 12 Causes of Overheating..............................305
Component Inspection.............................................306
DTC P1401 EGR TEMPERATURE SENSOR.............307
Component Description...........................................307
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................307
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................307
Wiring Diagram........................................................309
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................310
Component Inspection.............................................311
DTC P1402 EGR FUNCTION (OPEN)........................312
Description...............................................................312
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................313
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................313
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................313
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................314
Wiring Diagram........................................................316
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................317
Component Inspection.............................................318
DTC P1706 PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION (PNP)
SWITCH .......................................................................320
Component Description...........................................320
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................320
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................320
On Board Diagnosis Logic.......................................320
DTC Confirmation Procedure..................................320
Overall Function Check...........................................321
Wiring Diagram........................................................322
Diagnostic Procedure For M/T Models....................323
INJECTOR ...................................................................325
Component Description...........................................325
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................325
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................325
Wiring Diagram........................................................326
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................327
Component Inspection.............................................329
IGNITION SIGNAL.......................................................330
Component Description...........................................330
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................330
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................330
Wiring Diagram........................................................331
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................333
Component Inspection.............................................335
START SIGNAL...........................................................336
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................336
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................336
Wiring Diagram........................................................337
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................338
FUEL PUMP.................................................................340
System Description..................................................340
Component Description...........................................340
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................340
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................340
Wiring Diagram........................................................341
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................342
Component Inspection.............................................344
POWER STEERING OIL PRESSURE SWITCH.........345
Component Description...........................................345
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................345
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................345
Wiring Diagram........................................................346
Diagnostic Procedure ..............................................347
Component Inspection.............................................349
ELECTRICAL LOAD SIGNAL.....................................350
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode........................................................................350
ECM Terminals and Reference Value.....................350
Wiring Diagram........................................................351
MI & DATA LINK CONNECTORS..............................353
Wiring Diagram........................................................353
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS).......354
Fuel Pressure Regulator..........................................354
Idle Speed and Ignition Timing................................354
Mass Air Flow Sensor .............................................354
Intake Air Temperature Sensor...............................354
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor......................354
Throttle Position Sensor..........................................354
Front Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater......................354
Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater......................354
Tank Fuel Temperature Sensor ..............................355
Crankshaft Position Sensor (POS)..........................355
Camshaft Position Sensor (PHASE).......................355
EGR Volume Control Valve.....................................355
EGR Temperature Sensor.......................................355
EVAP Canister Purge Volume Control Valve..........355
IACV-AAC Valve......................................................355
Injector.....................................................................355
Ignition Coil with Power Transistor..........................356
Fuel Pump ...............................................................356
EC-QG-5
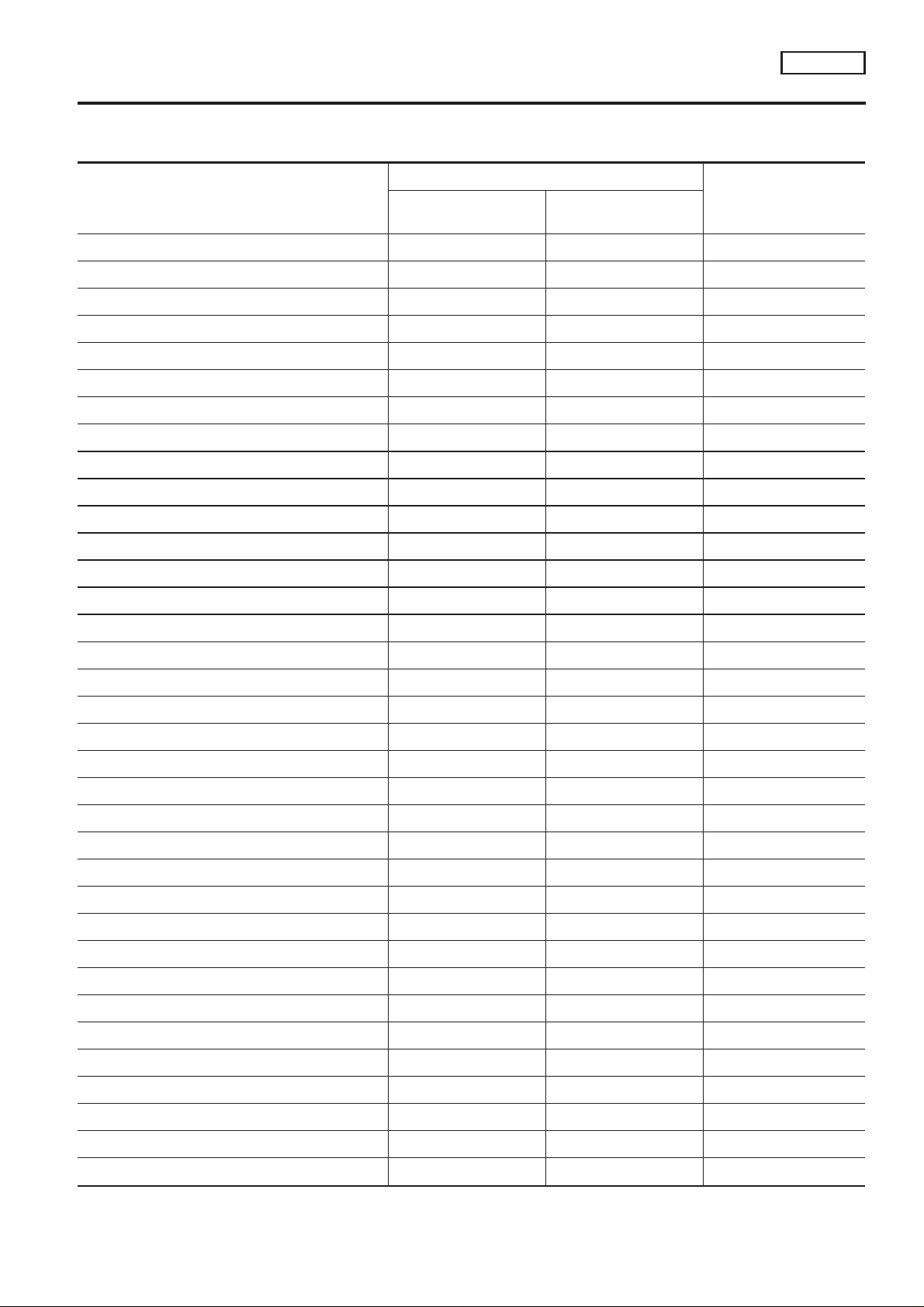
Alphabetical & P No. Index for DTC
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INDEX
QG18DE
Alphabetical & P No. Index for DTC
ALPHABETICAL INDEX FOR DTC
Items
(CONSULT-II screen terms)
Unable to access ECM — — EC-QG-91
AIR TEMP SEN/CIRC*6 P0110 0110 EC-QG-121
CAM POS SEN/CIRC P0340 0340 EC-QG-241
CLOSED TP SW/CIRC*6 P0510 0510 EC-QG-278
COOLANT T SEN/CIRC*3 P0115 0115 EC-QG-125
CPS/CIRCUIT (POS)*6 P0335 0335 EC-QG-235
CYL 1 MISFIRE*6 P0301 0301 EC-QG-225
CYL 2 MISFIRE*6 P0302 0302 EC-QG-225
CYL 3 MISFIRE*6 P0303 0303 EC-QG-225
CYL 4 MISFIRE*6 P0304 0304 EC-QG-225
ECM*6 P0605 0605 EC-QG-284
EGR SYSTEM*6 P0400 0400 EC-QG-247
CONSULT-II
GST*2
DTC*5
Reference page
ECM*1
NCEC0001
NCEC0001S01
EGR SYSTEM*6 P1402 1402 EC-QG-312
EGR TEMP SEN/CIRC*6 P1401 1401 EC-QG-307
EGR VOL CON/V CIR*6 P0403 0403 EC-QG-255
ENG OVER TEMP P1217 P1217 EC-QG-296
FR O2 SE HEATER-B1*6 P0135 0135 EC-QG-169
FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1*6 P0130 0130 EC-QG-138
FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1*6 P0131 0131 EC-QG-144
FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1*6 P0132 0132 EC-QG-150
FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1*6 P0133 0133 EC-QG-156
FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1*6 P0134 0134 EC-QG-164
FUEL SYS-LEAN/BK1*6 P0171 0171 EC-QG-209
FUEL SYS-RIGH/BK1*6 P0172 0172 EC-QG-215
FUEL TEMP SEN/CIRC*6 P0180 0180 EC-QG-221
IACV/AAC VLV/CIRC*6 P0505 0505 EC-QG-273
INT/V TIM V/CIR-B1*6 P1111 1111 EC-QG-285
KNOCK SEN/CIRC-B1 P0325 0325 EC-QG-231
MAF SEN/CIRCUIT*3 P0100 0100 EC-QG-115
MULTI CYL MISFIRE*6 P0300 0300 EC-QG-225
NATS MALFUNCTION P1610 - P1615 1610 - 1615 Refer to EL section.
NO SELF DIAGNOSTIC FAILURE INDICATED P0000 0000 —
NO SELF DIAGNOSTIC FAILUTRE INDICATED No DTC Flashing*4 EC-QG-55
P-N POS SW/CIRCUIT*6 P1706 1706 EC-QG-320
PURG VOLUME CONT/V*6 P0443 0443 EC-QG-264
EC-QG-6
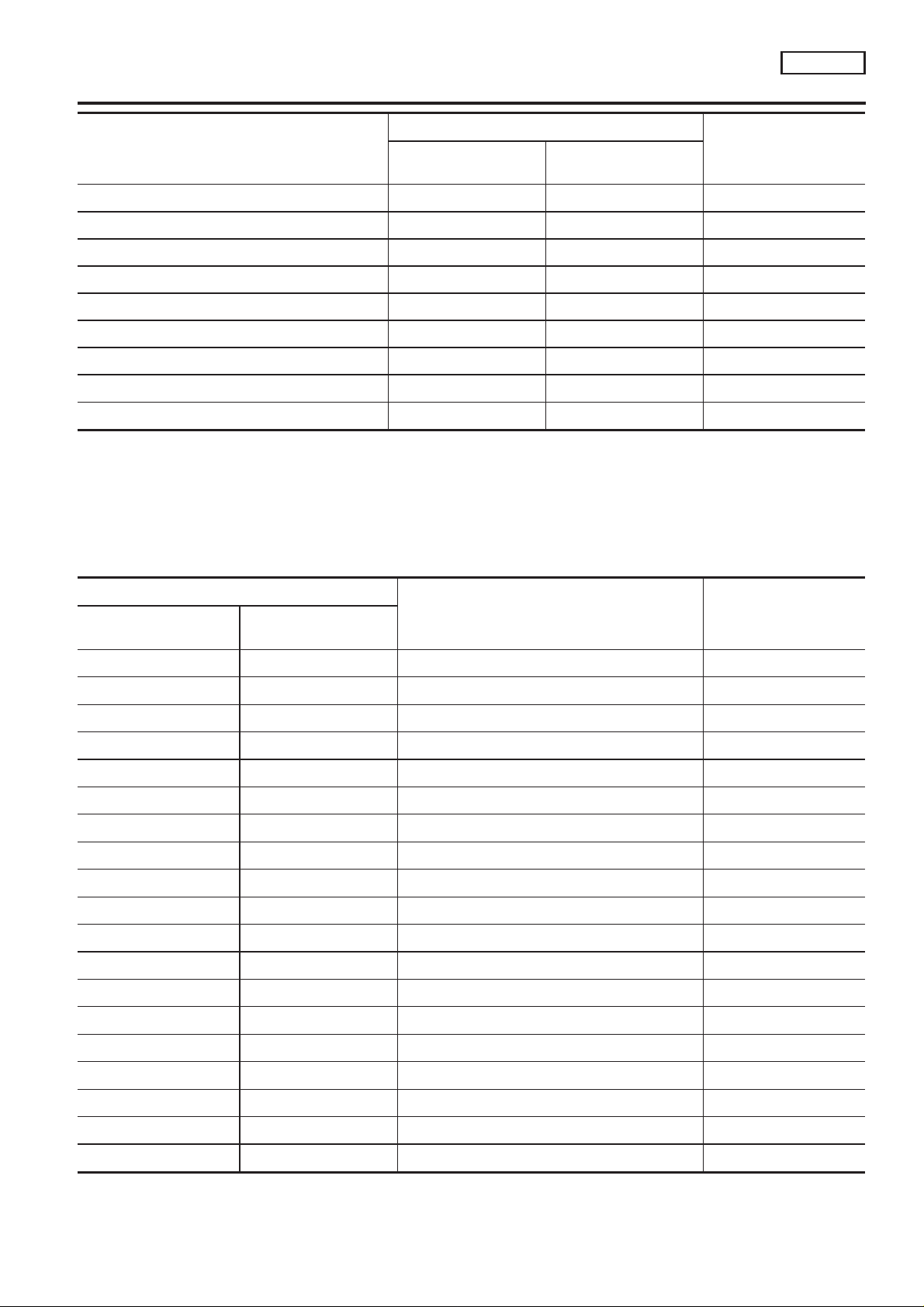
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INDEX
Alphabetical & P No. Index for DTC (Cont’d)
QG18DE
Items
(CONSULT-II screen terms)
REAR O2 SENSOR-B1*6 P0137 0137 EC-QG-174
REAR O2 SENSOR*6 P0138 0138 EC-QG-182
REAR O2 SENSOR*6 P0139 0139 EC-QG-190
REAR O2 SENSOR*6 P0140 0140 EC-QG-198
RR O2 SE HEATER-B1*6 P0141 0141 EC-QG-204
SWIRL CONT SOL/V*6 P1131 1131 EC-QG-290
THRTL POS SEN/CIRC*3 P0120 0120 EC-QG-130
TW CATALYST SYS-B1*6 P0420 0420 EC-QG-260
VEH SPEED SEN/CIRC P0500 0500 EC-QG-241
*1: In Diagnostic Test Mode II (Self-diagnostic results). These numbers are controlled by NISSAN.
*2: These numbers are prescribed by ISO15031-6.
*3: When the fail-safe operation occurs, the MI illuminates.
*4: While engine is running.
*5: 1st trip DTC No. is the same as DTC No.
*6: Not available for ‘‘Eastern Europe model’’.
CONSULT-II
GST*2
DTC*5
Reference page
ECM*1
P NO. INDEX FOR DTC
CONSULT-II
GST*2
DTC*5
ECM*1
(CONSULT-II screen terms)
Items
Reference page
NCEC0001S02
— — Unable to access ECM EC-QG-91
No DTC Flashing*4 NO SELF DIAGNOSTIC FAILURE INDICATED EC-QG-55
P0000 0000 NO SELF DIAGNOSTIC FAILURE INDICATED —
P0100 0100 MAF SEN/CIRCUIT*3 EC-QG-115
P0110 0110 AIR TEMP SEN/CIRC*6 EC-QG-121
P0115 0115 COOLANT T SEN/CIRC*3 EC-QG-125
P0120 0120 THRTL POS SEN/CIRC*3 EC-QG-130
P0130 0130 FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1 EC-QG-138
P0131 0131 FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1*6 EC-QG-144
P0132 0132 FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1*6 EC-QG-150
P0133 0133 FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1*6 EC-QG-156
P0134 0134 FRONT O2 SENSOR-B1*6 EC-QG-164
P0135 0135 FR O2 SE HEATER-B1*6 EC-QG-169
P0137 0137 REAR O2 SENSOR-B1*6 EC-QG-174
P0138 0138 REAR O2 SENSOR-B1*6 EC-QG-182
P0139 0139 REAR O2 SENSOR-B1*6 EC-QG-190
P0140 0140 REAR O2 SENSOR-B1*6 EC-QG-198
P0141 0141 RR O2 SE HEATER-B1*6 EC-QG-204
P0171 0171 FUEL SYS-LEAN/BK1*6 EC-QG-209
EC-QG-7
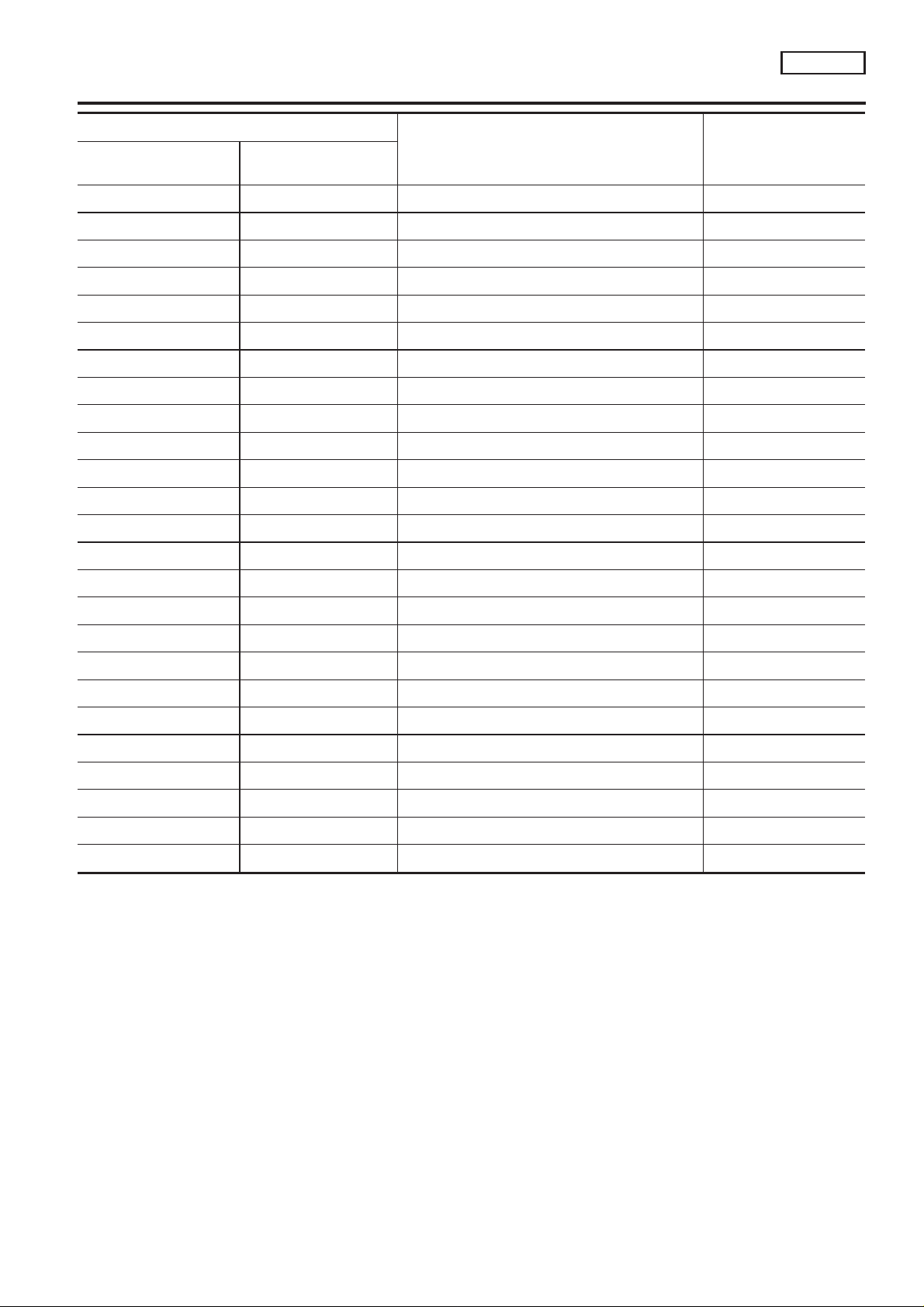
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INDEX
Alphabetical & P No. Index for DTC (Cont’d)
QG18DE
DTC*5
CONSULT-II
GST*2
P0172 0172 FUEL SYS-RICH/BK1*6 EC-QG-215
P0180 0180 FUEL TEMP SEN/CIRC*6 EC-QG-221
P0300 0300 MULTI CYL MISFIRE*6 EC-QG-225
P0301 0301 CYL 1 MISFIRE*6 EC-QG-225
P0302 0302 CYL 2 MISFIRE*6 EC-QG-225
P0303 0303 CYL 3 MISFIRE*6 EC-QG-225
P0304 0304 CYL 4 MISFIRE*6 EC-QG-225
P0325 0325 KNOCK SEN/CIRC-B1 EC-QG-231
P0335 0335 CPS/CIRCUIT (POS)*6 EC-QG-235
P0340 0340 CAM POS SEN/CIRC EC-QG-241
P0400 0400 EGR SYSTEM*6 EC-QG-247
P0403 0403 EGR VOL CON/V CIR*6 EC-QG-255
P0420 0420 TW CATALYST SYS-B1*6 EC-QG-260
P0443 0443 PURG VOLUME CONT/V*6 EC-QG-264
ECM*1
(CONSULT-II screen terms)
Items
Reference page
P0500 0500 VEH SPEED SEN/CIRC EC-QG-269
P0505 0505 IACV/AAC VLV/CIRC*6 EC-QG-273
P0510 0510 CLOSED TP SW/CIRC*6 EC-QG-278
P0605 0605 ECM EC-QG-284
P1111 1111 INT/V TIM V/CIR-V1*6 EC-QG-285
P1131 1131 SWIRL CONT SOL/V*6 EC-QG-290
P1217 1217 ENG OVER TEMP EC-QG-296
P1401 1401 EGR TEMP SEN/CIRC*6 EC-QG-307
P1402 1402 EGR SYSTEM*6 EC-QG-312
P1610 - 1615 1610 - 1615 NATS MALFUNCTION Refer to EL section.
P1706 1706 P-N POS SW/CIRCUIT*6 EC-QG-320
*1: In Diagnostic Test Mode II (Self-diagnostic results). These numbers are controlled by NISSAN.
*2: These numbers are prescribed by ISO15031-6.
*3: When the fail-safe operation occurs, the MI illuminates.
*4: While engine is running.
*5: 1st trip DTC No. is the same as DTC No.
*6: Not available for ‘‘Eastern Europe model’’.
EC-QG-8

PRECAUTIONS
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ‘‘AIR BAG’’ and ‘‘SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER’’
QG18DE
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ‘‘AIR
BAG’’ and ‘‘SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER’’
The Supplemental Restraint System ‘‘AIR BAG’’ and ‘‘SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER’’, used along with a seat
belt, help to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front passenger in a frontal collision. The
Supplemental Restraint System consists of air bag modules (located in the center of the steering wheel and
on the instrument panel on the passenger side), seat belt pre-tensioners, a diagnosis sensor unit, warning
lamp, wiring harness and spiral cable.
In addition to the supplemental air bag modules for a frontal collision, the supplemental side air bag used along
with the seat belt helps to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front passenger in a side collision. The supplemental side air bag consists of air bag modules (located in the outer side of front seats),
satellite sensor, diagnosis sensor unit (one of components of supplemental air bags for a frontal collision),
wiring harness, warning lamp (one of components of supplemental air bags for a frontal collision). Information
necessary to service the system safely is included in the RS section of this Service Manual.
WARNING:
+ To avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death
in the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be performed
by an authorized NISSAN dealer.
+ Improper maintenance, including incorrect removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to per-
sonal injury caused by unintentional activation of the system.
+ Do not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. SRS wiring harnesses (except ‘‘SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER’’ connector) can be
identified with yellow harness connector (and with yellow harness protector or yellow insulation
tape before the harness connectors).
NCEC0002
Precautions for On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System of Engine
The ECM has an on board diagnostic system. It will light up the malfunction indicator (MI) to warn the driver
of a malfunction causing emission deterioration.
CAUTION:
+ Be sure to turn the ignition switch ‘‘OFF’’ and disconnect the negative battery terminal before any
repair or inspection work. The open/short circuit of related switches, sensors, solenoid valves, etc.
will cause the MI to light up.
+ Be sure to connect and lock the connectors securely after work. A loose (unlocked) connector will
cause the MI to light up due to the open circuit. (Be sure the connector is free from water, grease,
dirt, bent terminals, etc.)
+ Certain systems and components, especially those related to OBD, may use a new style slide-
locking type harness connector.
For description and how to disconnect, refer to EL section, ‘‘Description’’, ‘‘HARNESS CONNECTOR’’.
+ Be sure to route and secure the harnesses properly after work. The interference of the harness with
a bracket, etc. may cause the MI to light up due to the short circuit.
+ Be sure to connect rubber tubes properly after work. A misconnected or disconnected rubber tube
may cause the MI to light up due to the malfunction of the EGR system or fuel injection system,
etc.
+ Be sure to erase the unnecessary malfunction information (repairs completed) from the ECM before
returning the vehicle to the customer.
NCEC0003
EC-QG-9
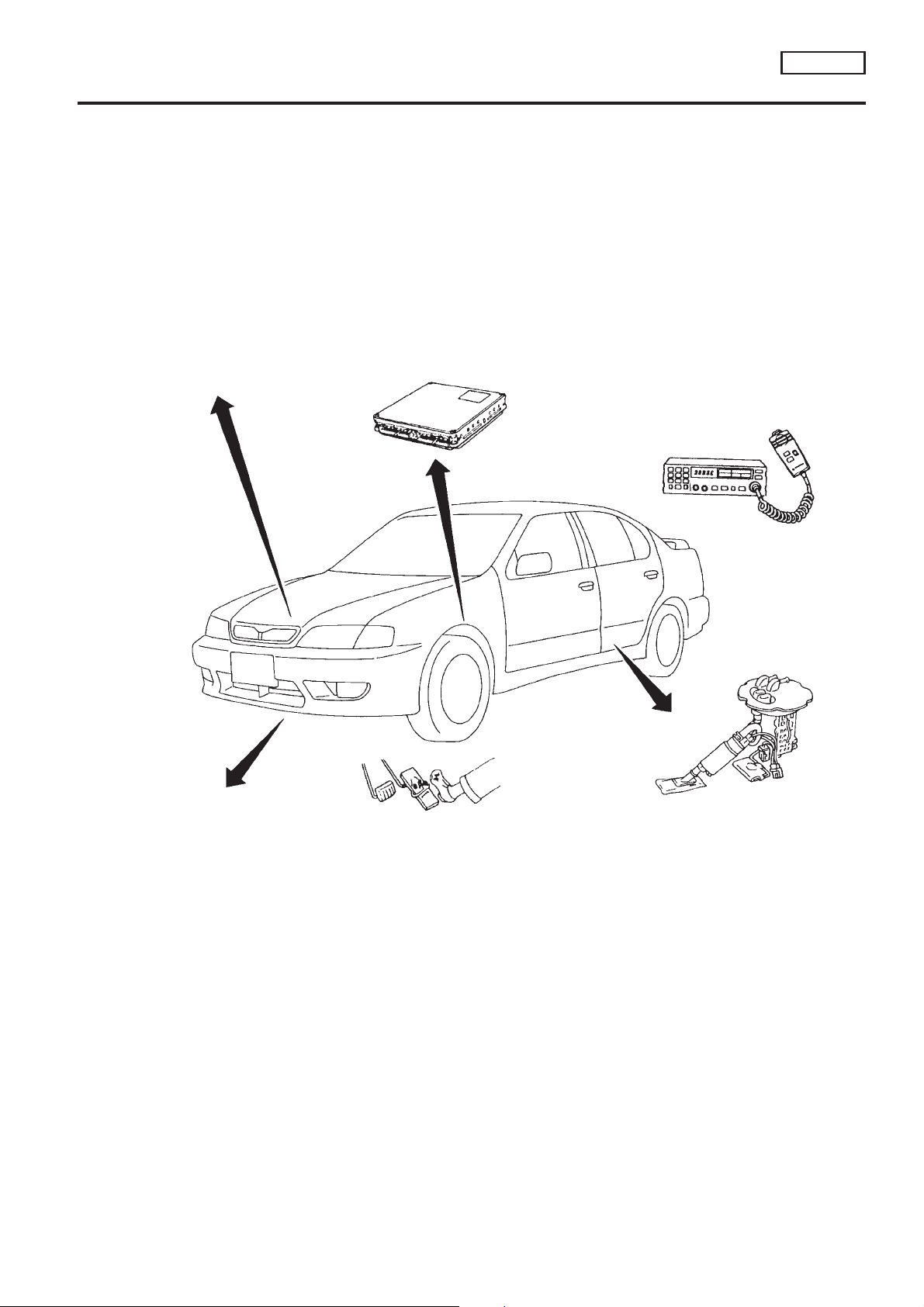
Engine Fuel & Emission Control System
PRECAUTIONS
QG18DE
BATTERY
● Always use a 12 volt battery as power
source.
● Do not attempt to disconnect battery
cables while engine is running.
Engine Fuel & Emission Control System
ECM
● Do not disassemble ECM.
● If a battery terminal is disconnected,
the memory will return to the ECM
value.
The ECM will now start to self-control
at its initial value. Engine operation can
vary slightly when the terminal is
disconnected. However, this is not an
indication of a problem. Do not replace
parts because of a slight variation.
WIRELESS EQUIPMENT
● When installing C.B. ham radio or a
mobile phone, be sure to observe the
following as it may adversely affect
electronic control systems depending
on installation location.
1) Keep the antenna as far as
possible from the electronic control units.
2) Keep the antenna feeder line more than
20 cm (8 in) away from the harness
of electronic controls.
Do not let them run parallel for a long
distance.
3) Adjust the antenna and feeder line so
that the standing-wave ratio can be
kept smaller.
4) Be sure to ground the radio to vehicle
body.
NCEC0004
ENGINE CONTROL PARTS HANDLING
● Handle mass air flow sensor carefully to
avoid damage.
● Do not disassemble mass air flow
sensor.
● Do not clean mass air flow sensor with
any type of detergent.
● Do not disassemble IAC valve-AAC valve.
● Even a slight leak in the air intake
system can cause serious problems.
● Do not shock or jar the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position
sensor.
WHEN STARTING
● Do not depress accelerator pedal when
starting.
● Immediately after starting, do not rev up
engine unnecessarily.
● Do not rev up engine just prior to
shutdown.
EC-QG-10
FUEL PUMP
● Do not operate fuel pump when there
is no fuel in lines.
● Tighten fuel hose clamps to the
specified torque.
ECM HARNESS HANDLING
● Securely connect ECM harness
connectors.
A poor connection can cause an
extremely high (surge) voltage to develop
in coil and condenser, thus
resulting in damage to ICs.
● Keep ECM harness at least 10 cm (4
in) away from adjacent harness, to
prevent an ECM system malfunction
due to receiving external noise,
degraded operation of ICs, etc.
● Keep ECM parts and harness dry.
● Before removing parts, turn off ignition
switch and then disconnect battery
ground cable.
SEF331WB
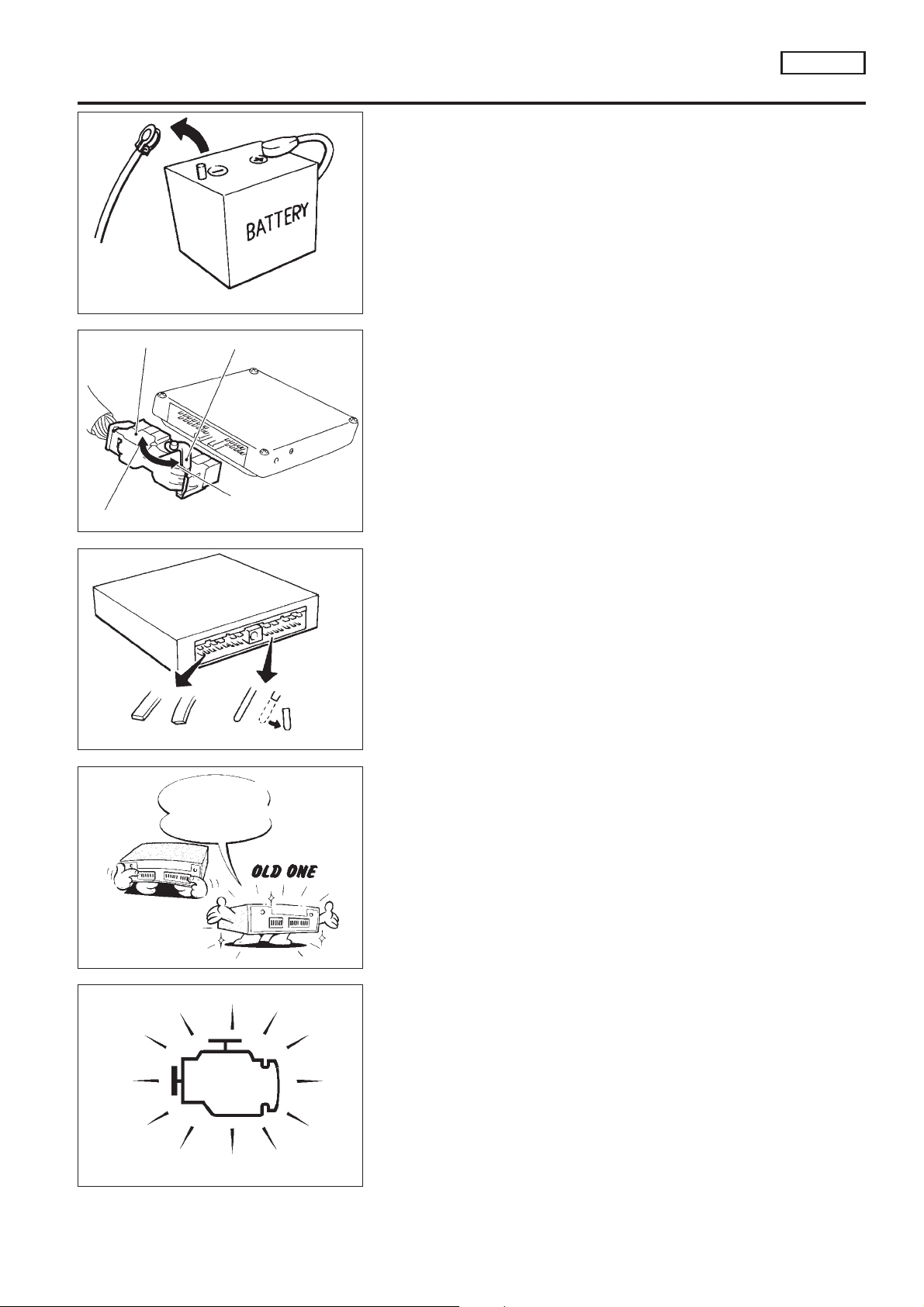
PRECAUTIONS
QG18DE
Precautions
Protector Lever
Fasten
Loosen
SEF289H
SEF908W
Precautions
NCEC0005
+ Before connecting or disconnecting the ECM harness
connector, turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect negative battery terminal. Failure to do so may damage the
ECM because battery voltage is applied to ECM even if
ignition switch is turned off.
+ When connecting or disconnecting ECM harness
connector, use lever as shown.
When connecting, fasten connector securely with lever
moved until it stops.
+ When connecting or disconnecting pin connectors into or
from ECM, take care not to damage pin terminals (bend or
break).
Make sure that there are not any bends or breaks on ECM
pin terminals when connecting pin connectors.
Bend Break
Perform ECM input/output signal
inspection before
replacement.
SEF291H
+ Before replacing ECM, perform Terminals and Reference
Value inspection and make sure ECM functions properly.
Refer to EC-QG-101.
MEF040D
+ After performing each TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS, perform
‘‘Overall Function Check’’ or ‘‘DTC Confirmation Procedure’’.
The DTC should not be displayed in the ‘‘DTC Confirmation Procedure’’ if the repair is completed. The ‘‘Overall
Function Check’’ should be a good result if the repair is
completed.
SAT652J
EC-QG-11

Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnosis
Battery
voltage
PRECAUTIONS
QG18DE
+ When measuring ECM signals with a circuit tester, never
allow the two tester probes to contact.
Accidental contact of probes will cause a short circuit and
damage the ECM power transistor.
Short
Solenoid valve
Harness connector
for solenoid valve
Circuit tester
ECM
NG
OK
SEF348N
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnosis
NCEC0006
When you read Wiring diagrams, refer to the followings:
+ ‘‘HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS’’ in GI section
+ ‘‘POWER SUPPLY ROUTING’’ for power distribution circuit in
EL section
When you perform trouble diagnosis, refer to the followings:
+ ‘‘HOW TO FOLLOW TEST GROUP IN TROUBLE DIAGNO-
SIS’’ in GI section
+ ‘‘HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN
ELECTRICAL INCIDENT’’ in GI section
EC-QG-12
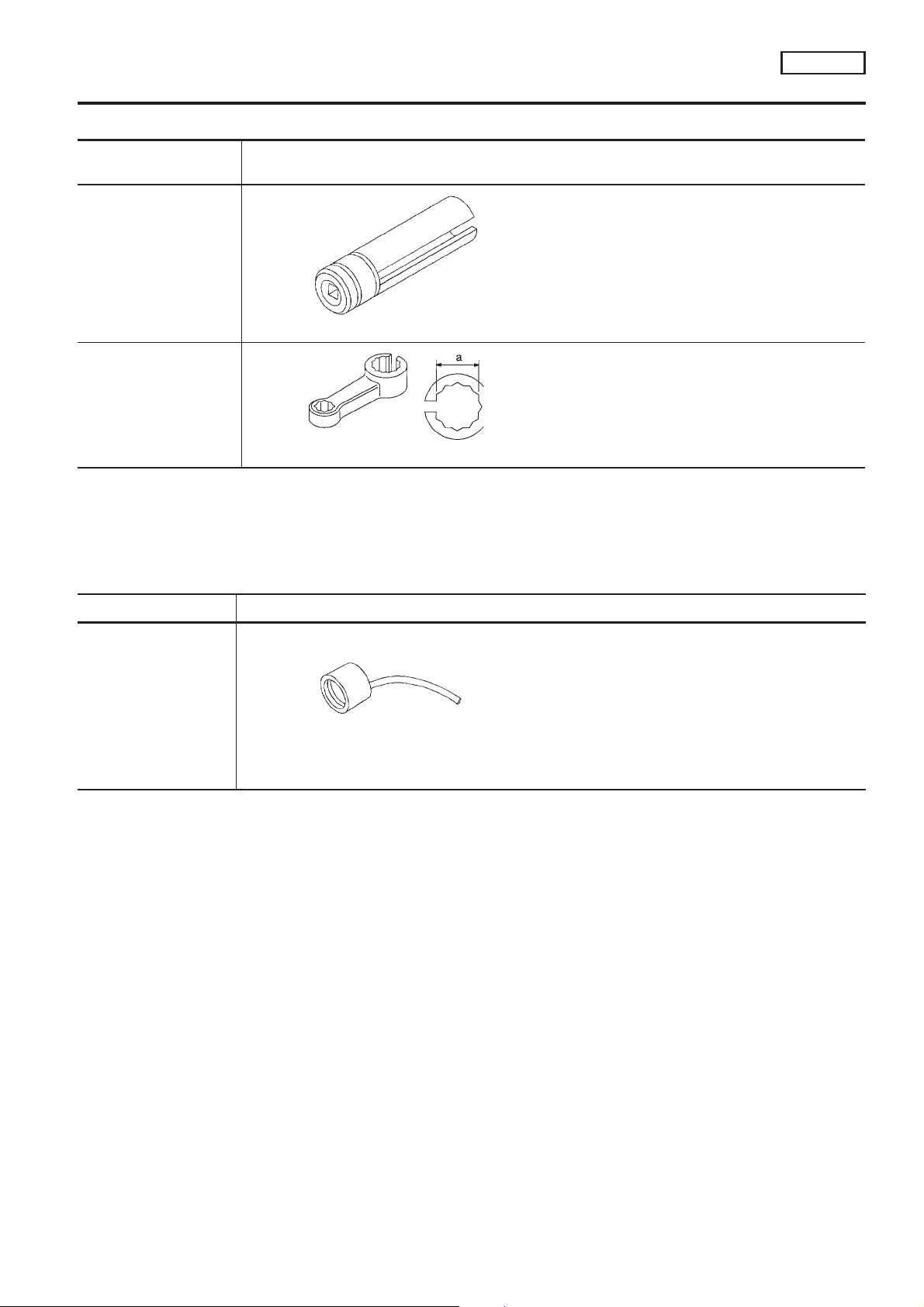
PREPARATION
QG18DE
Special Service Tools
Tool number
Tool name
KV10117100
Heated oxygen sensor
wrench
KV10114400
Heated oxygen sensor
wrench
Description
NT379
NT636
Special Service Tools
Loosening or tightening front heated oxygen sensor with 22 mm (0.87 in) hexagon nut
Loosening or tightening rear heated oxygen sensor
a: 22 mm (0.87 in)
NCEC0007
Tool name Description
Fuel filler cap adapter
NT653
Commercial Service Tool
Checking fuel tank vacuum relief valve opening
pressure
NCEC0008
EC-QG-13
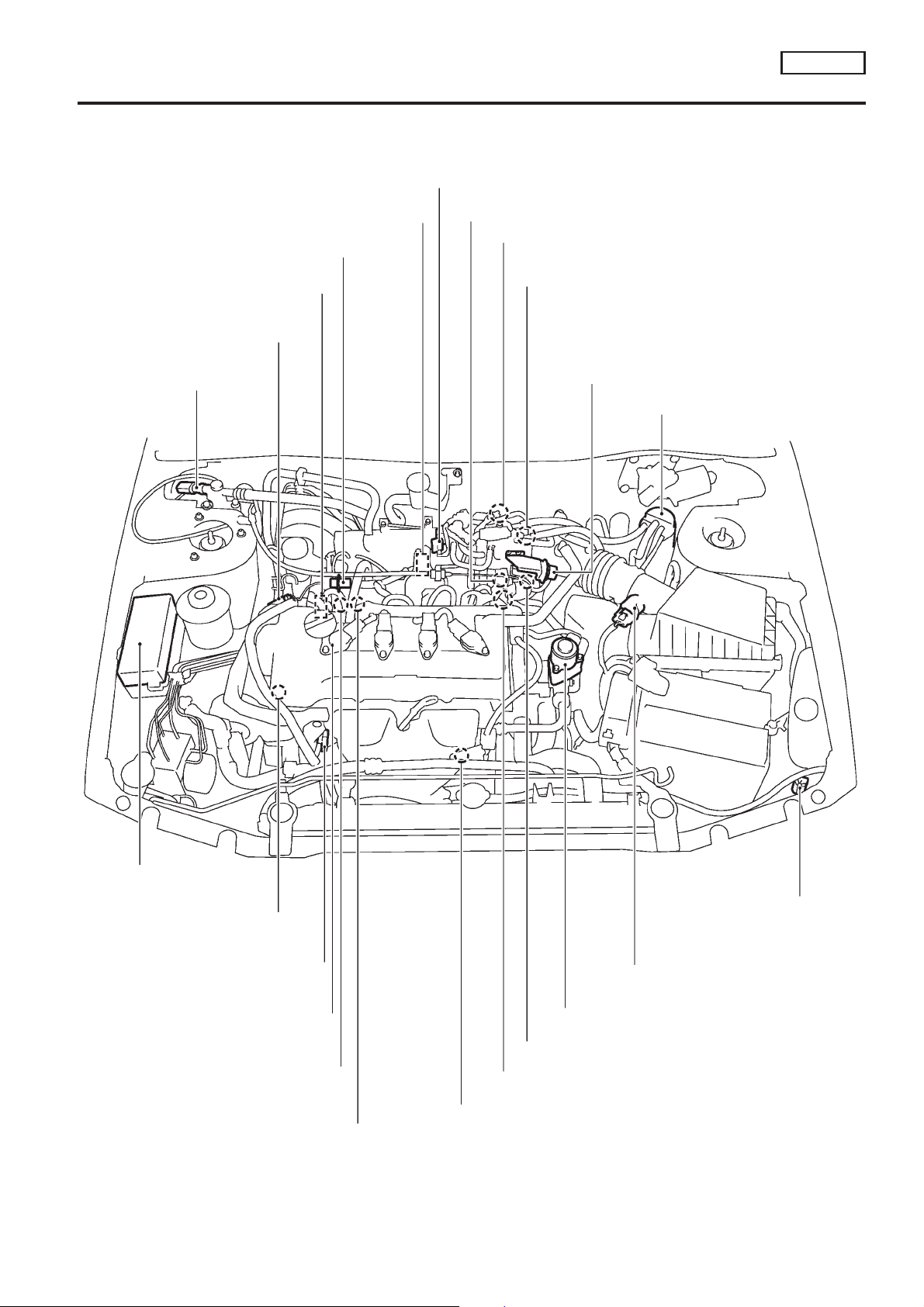
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEM
Engine Control Component Parts Location
QG18DE
Power steering oil
pressure switch
Fuel pressure regulator
Intake valve timing
control solenoid valve
Condenser
Engine Control Component Parts Location
EVAP canister purge
volume control valve
Swirl control valve
One-way valve
control solenoid valve
EGR temperature sensor
Throttle position sensor &
throttle position switch
Throttle opener
EVAP canister
NCEC0009
Relay box
Camshaft position sensor
(PHASE)
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Ignition coil (With power transistor)
and spark plugs
Fuel injectors
PCV valve
IACV-AAC valve
Swirl control valve actuator
Front heated oxygen sensor
EC-QG-14
Mass air flow sensor
EGR volume control valve
Intake air
temperature
sensor
SEF909W

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEM
Engine Control Component Parts Location (Cont’d)
QG18DE
Throttle opener
Fuel pressure
regulator
Intake valve timing
control solenoid valve
EVAP canister
purge volume
control valve
One-way valve
Condenser
Vacuum tank
Front
Front
Front
Front
EGR volume
control valve
EGR volume
control valve
Swirl control
valve actuator
IACV-AAC valve
Mass air flow
sensor
Air cleaner
Swirl control valve
control solenoid valve
Air duct
Mass air
flow sensor
Relay box
Rocker cover
Front
Camshaft position sensor
(PHASE)
View from the underside of the vehicle
Rear heated oxygen
sensor harness
connector
Rear heated
oxygen sensor
Front
Knock sensor
Oil filter
Crankshaft
position sensor
(POS)
SEF910W
EC-QG-15

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEM
Engine Control Component Parts Location (Cont’d)
ECM
QG18DE
Fuel pump
harness connector
Fuse block
Front
ECM harness
connector
Fuel pump fuse
Fuel pump
relay
Data link connector
Glove box
Fuel tank
gauge unit
harness connector
Under rear seat cushion
ECM relay
(Self-shutoff)
Relay box cover
Fan motor relay
EC-QG-16
SEF911W
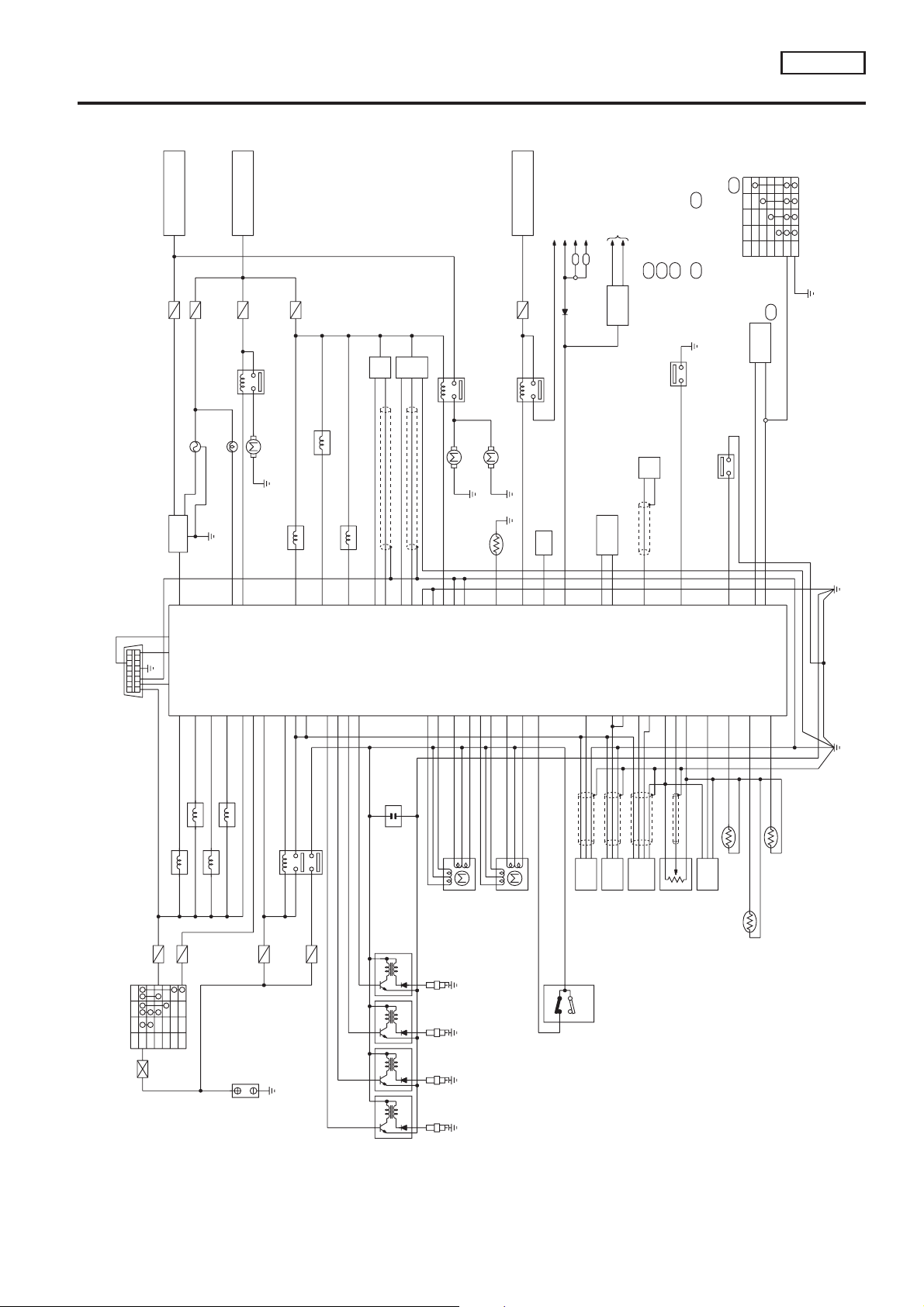
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEM
QG18DE
Circuit Diagram
BATTERY
FUSE
SPEED-
(Via fusible link
VEHICLE SPEED
SENSOR
OMETER
ON or START
IGNITION SWITCH
FUEL PUMP
RELAY
MALFUNCTION
INDICATOR
FUEL LAMP
EVAP CANISTER
PURGE VOLUME CONTROL
INTAKE VALVE
SOLENOID VALVE
TIMING CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE
SWIRL CONTROL
VALVE CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE
Circuit Diagram
REAR HEATED
OXYGEN SENSOR
FRONT HEATED
OXYGEN SENSOR
A/C
RELAY
COOLING
FAN RELAY
COOLING
FAN MOTOR-1
COOLING
FAN MOTOR-2
FUEL TANK
GAUGE UNIT
(FUEL TANK
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR)
ON
IGNITION SWITCH
NATS IMMU
To compressor
To headlamp LH
To lighting switch
XH
COMBINATION
To headlamp relay LH
HD
METER
TIME CONTROL UNIT
3
8811
To rear defogger system
13
14
: With air conditioner
: Without air conditioner
OA
AC
POWER STEERING
OIL PRESSURE
SWITCH
KNOCK
SENSOR
: With XENON headlamp or
HD
daytime light system
HD
: Except
XH
4
OA
123
FAN SWITCH
OFF
A/C CONTROL
PANEL
10
27
PARK/NEUTRAL
POSITION SWITCH
NCEC0010
AC
DATA LINK CONNECTOR
FUSE
ACCON STOFF
IGNITION SWITCH
86
114
93
115
101
No.2
No.1
INJECTOR
RELAY
1
14
1103135
112
22
21
41
No.3
43
105
107
67
No.4
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
103
104
363738
4623
CONDENSER
IGNITION COIL
(With POWER
63
106
108
TRANSISTOR)
SPARK
134857
ECM
15
PLUG
1667
IACV-AAC
VALVE
82
23
18
9178
EGR VOLUME
CONTROL
VALVE
116
40
THROTTLE
POSITION SWITCH
CLOSED
50
85
CRANKSHAFT
POSITION
WIDE
OPEN
32
34
66
SENSOR (POS)
CAMSHAFT
81
756173645892111
POSITION
SENSOR (PHASE)
MASS AIR
FLOW SENSOR
46
THROTTLE
POSITION
SENSOR
424451
INTAKE AIR
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
REFRIGERANT
PRESSURE
SENSOR
ENGINE COOLANT
727470
EGR
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
FUSIBLE
LINK
BATTERY
No. 1 No.2 No.3 No.4
EC-QG-17
YEC258
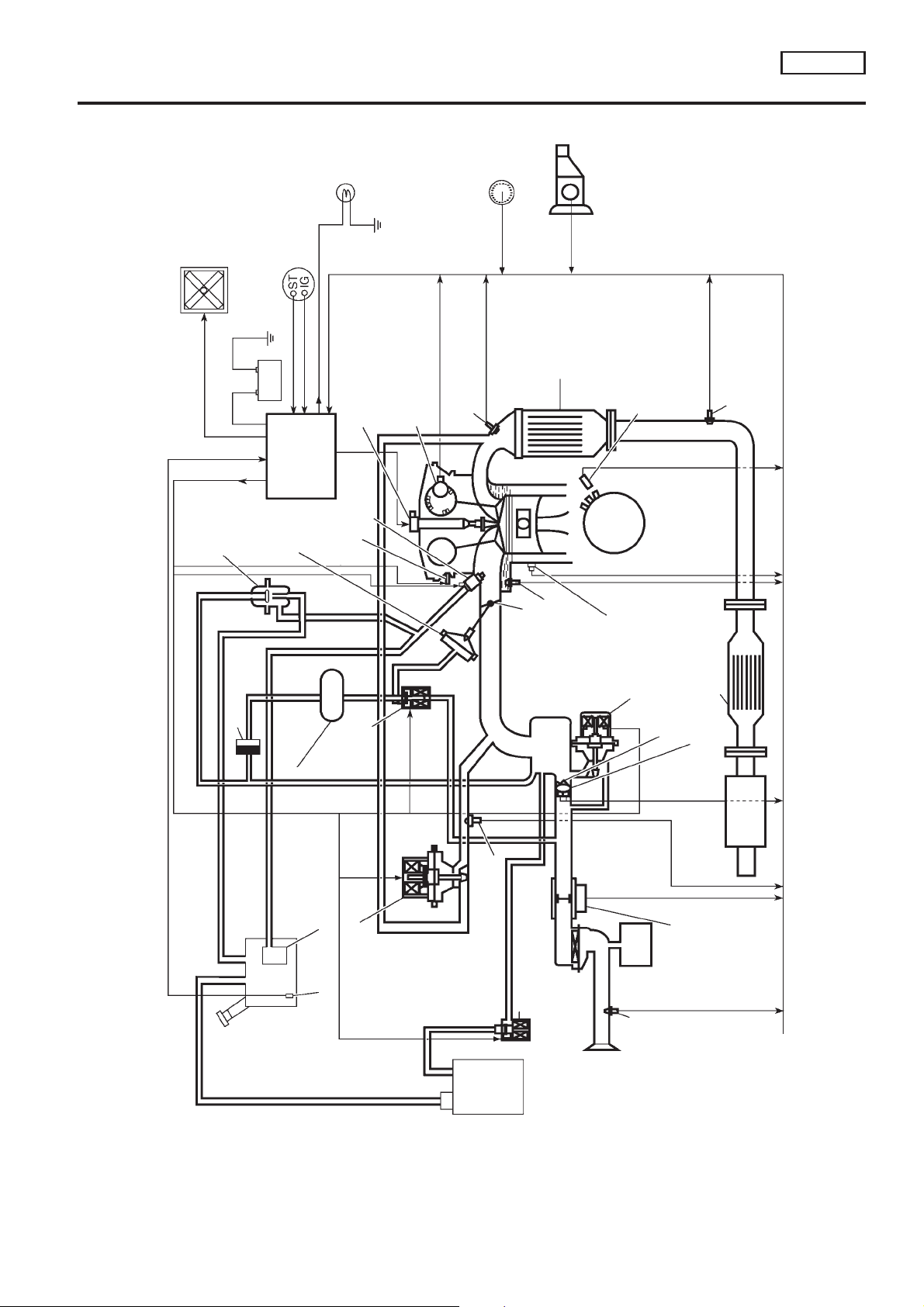
System Diagram
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEM
QG18DE
Cooling fan
Fuel
pressure
Ignition switch
Battery
Swirl
regulator
ECM
Control
Valve
actuator
Intake valve
System Diagram
Malfunction
indicator
Camshaft position sensor
(PHASE)
Ignition coil and power transistor
Fuel injector
timing control
solenoid valve
Front heated oxygen sensor
Vehicle speed
sensor
Three way catalyst
Park / Neutral
position switch
Crankshaft position
sensor (POS)
Rear heated oxygen
sensor
NCEC0011
One-way valve
Fuel tank
Vacuum tank
Fuel pump
Fuel temperature sensor
Swirl Control
Valve control
EGR volume control valve
solenoid valve
Swirl
EGR temperature sensor
control valve
EVAP canister purge
volume control
Engine coolant
temperature
sensor
solenoid valve
Air cleaner
Knock sensor
IACV-
AAC valve
Throttle position sensor
Mass air
flow sensor
Three way catalyst
Closed throttle position
switch
EC-QG-18
EVAP canister
Intake air temperature
sensor
SEF914W
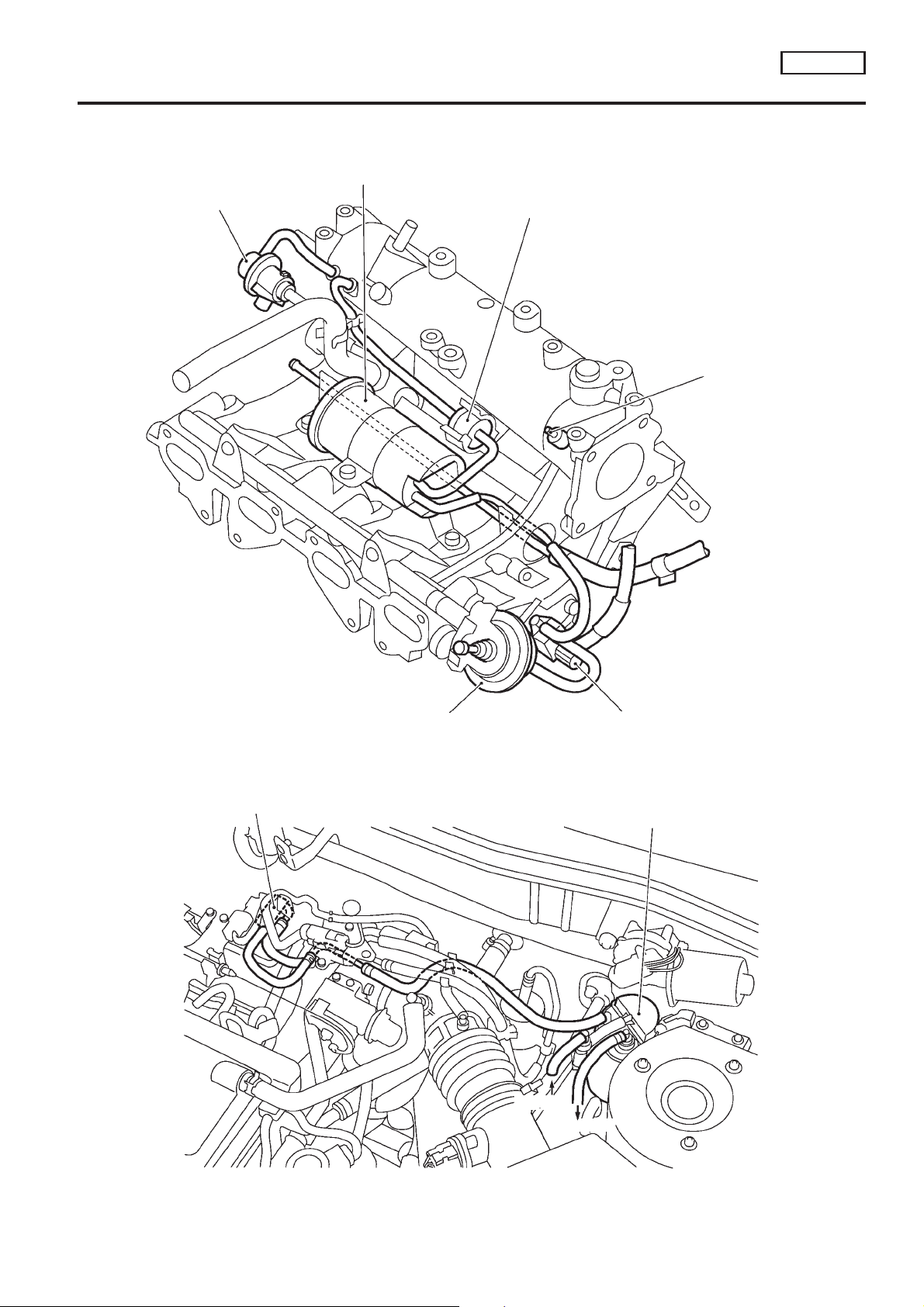
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEM
Vacuum Hose Drawing
QG18DE
Vacuum Hose Drawing
Refer to ‘‘System Diagram’’ on EC-QG-18 for vacuum control system.
Fuel pressure
regulator
Vacuum tank
One-way valve
(coloured side should
face the vacuum source)
EVAP canister
purge pipe
(to EVAP canister)
NCEC0012
EVAP canister purge volume
control solenoid valve
Swirl control valve
actuator
Swirl control valve
control solenoid valve
EVAP canister
SEF915W
EC-QG-19
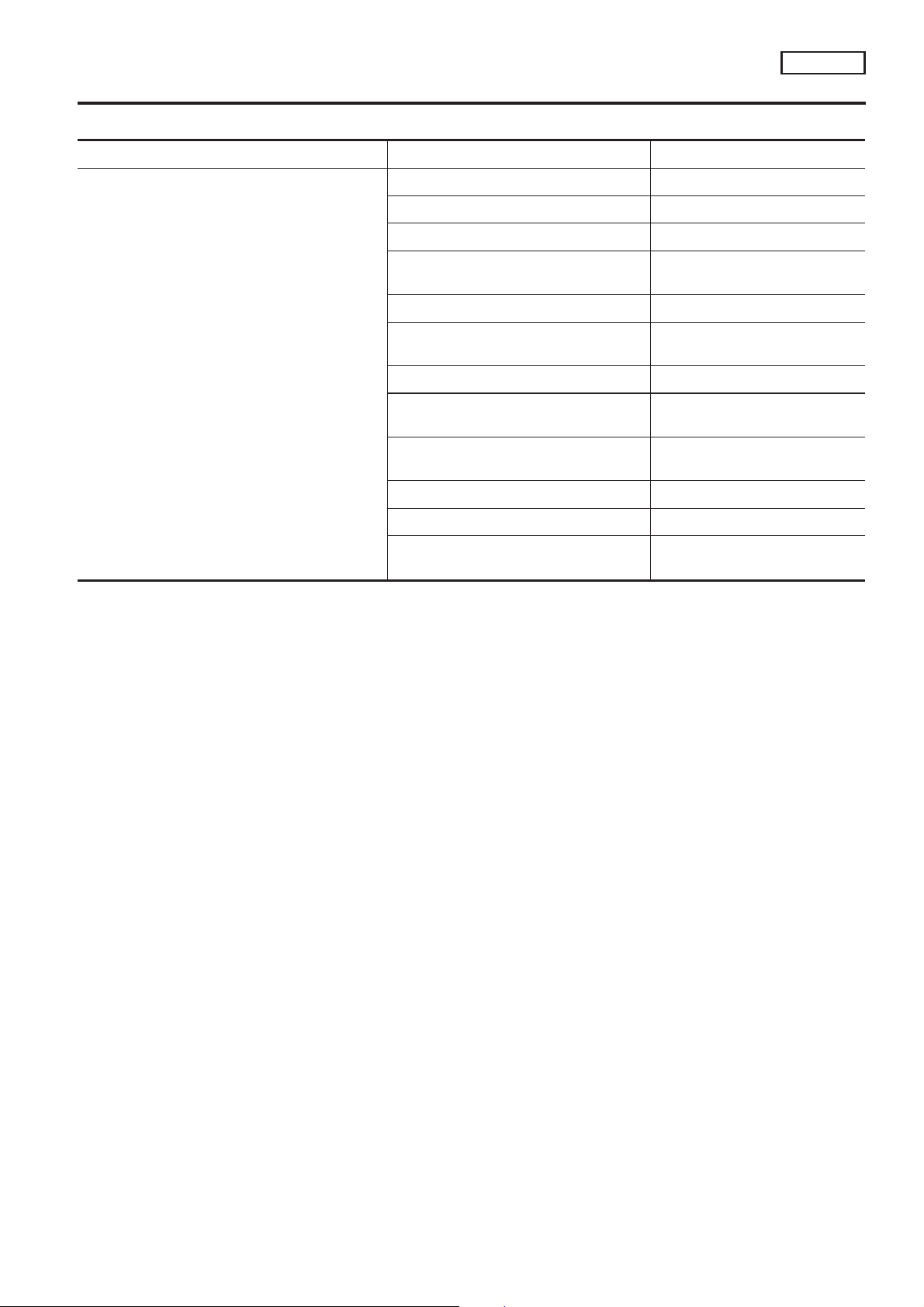
System Chart
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEM
QG18DE
Input (Sensor) ECM Function Output (Actuator)
+ Camshaft position sensor (PHASE)
+ Mass air flow sensor
+ Engine coolant temperature sensor
+ Front heated oxygen sensor
+ Ignition switch
+ Throttle position sensor
+ PNP switch
+ Air conditioner switch
+ Knock sensor
+ EGR temperature sensor*1
+ Crankshaft position sensor (POS)
+ Tank fuel temperature sensor*1
+ Battery voltage
+ Power steering oil pressure switch
+ Vehicle speed sensor
+ Intake air temperature sensor
+ Rear heated oxygen sensor*2
+ Closed throttle position switch
+ Electrical load
+ Refrigerant pressure sensor
System Chart
Fuel injection & mixture ratio control Injectors
Electronic ignition system Power transistor
Idle air control system IACV-AAC valve
Valve timing control
Fuel pump control Fuel pump relay
Front heated oxygen sensor monitor & on
board diagnostic system
EGR control EGR volume control valve
Front and rear heated oxygen sensor
heater control
EVAP canister purge flow control
Cooling fan control Cooling fan relay
Air conditioning cut control Air conditioner relay
Swirl control valve control
Intake valve timing control solenoid valve
Malfunction indicator
(On the instrument panel)
Heated oxygen sensor heater
EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve
Swirl Control Valve control solenoid valve
NCEC0013
*1: These sensors are not used to control the engine system. They are used only for the on board diagnosis.
*2: Under normal conditions, this sensor is not for engine control operation.
EC-QG-20
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System
DESCRIPTION
Input/Output Signal Chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed and piston position
Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Cylinder number
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Front heated oxygen sensor Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System
ECM func-
tion
Actuator
QG18DE
NCEC0014
NCEC0014S01
Throttle position sensor
PNP switch Gear position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Ignition switch Start signal
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner operation
Knock sensor Engine knocking condition
Electrical load Electrical load signal
Battery Battery voltage
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering operation
Rear heated oxygen sensor* Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
* Under normal conditions, this sensor is not for engine control operation.
Basic Multiport Fuel Injection System
Throttle position
Throttle valve idle position
Fuel injection & mixture ratio
control
Injector
NCEC0014S02
The amount of fuel injected from the fuel injector is determined by the ECM. The ECM controls the length of
time the valve remains open (injection pulse duration). The amount of fuel injected is a program value in the
ECM memory. The program value is preset by engine operating conditions. These conditions are determined
by input signals (for engine speed and intake air) from both the camshaft position sensor and the mass air
flow sensor.
Various Fuel Injection Increase/Decrease Compensation
NCEC0014S03
In addition, the amount of fuel injected is compensated to improve engine performance under various operating conditions as listed below.
<Fuel increase>
+ During warm-up
+ When starting the engine
+ During acceleration
+ Hot-engine operation
+ High-load, high-speed operation
<Fuel decrease>
+ During deceleration
+ During high engine speed operation
+ During high vehicle speed operation (M/T models)
+ Extremely high engine coolant temperature
EC-QG-21
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System (Cont’d)
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
QG18DE
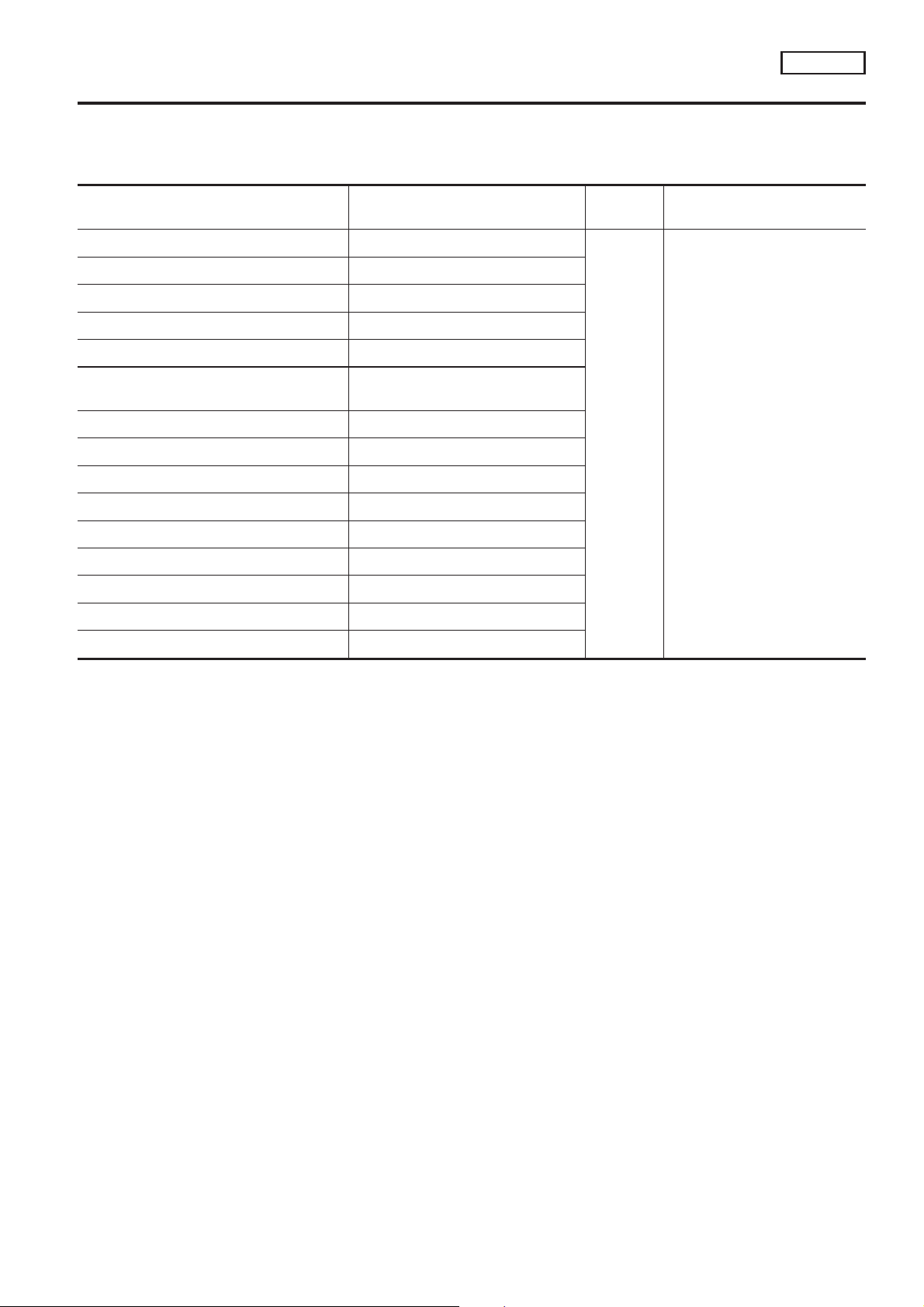
Mixture Ratio Feedback Control (Closed loop control)
CLOSED LOOP CONTROL
Injection pulse
Combustion
Feedback
signal
ECM
Front heated
oxygen sensor
Injectors
Engine
Fuel
injection
NCEC0014S04
SEF336W
The mixture ratio feedback system provides the best air-fuel mixture ratio for driveability and emission control. The three way catalyst can then better reduce CO, HC and NOx emissions. This system uses a front
heated oxygen sensor in the exhaust manifold to monitor if the engine operation is rich or lean. The ECM
adjusts the injection pulse width according to the sensor voltage signal. For more information about the front
heated oxygen sensor, refer to EC-QG-157. This maintains the mixture ratio within the range of stoichiometric
(ideal air-fuel mixture).
This stage is referred to as the closed loop control condition.
Rear heated oxygen sensor is located downstream of the three way catalyst. Even if the switching characteristics of the front heated oxygen sensor shift, the air-fuel ratio is controlled to stoichiometric by the signal from
the rear heated oxygen sensor.
Open Loop Control
NCEC0014S05
The open loop system condition refers to when the ECM detects any of the following conditions. Feedback
control stops in order to maintain stabilized fuel combustion.
+ Deceleration and acceleration
+ High-load, high-speed operation
+ Malfunction of front heated oxygen sensor or its circuit
+ Insufficient activation of front heated oxygen sensor at low engine coolant temperature
+ High engine coolant temperature
+ During warm-up
+ When starting the engine
Mixture Ratio Self-learning Control
NCEC0014S06
The mixture ratio feedback control system monitors the mixture ratio signal transmitted from the front heated
oxygen sensor. This feedback signal is then sent to the ECM. The ECM controls the basic mixture ratio as
close to the theoretical mixture ratio as possible. However, the basic mixture ratio is not necessarily controlled
as originally designed. Both manufacturing differences (i.e., mass air flow sensor hot film) and characteristic
changes during operation (i.e., injector clogging) directly affect mixture ratio.
Accordingly, the difference between the basic and theoretical mixture ratios is monitored in this system. This
is then computed in terms of ‘‘injection pulse duration’’ to automatically compensate for the difference between
the two ratios.
‘‘Fuel trim’’ refers to the feedback compensation value compared against the basic injection duration. Fuel trim
includes short term fuel trim and long term fuel trim.
‘‘Short term fuel trim’’ is the short-term fuel compensation used to maintain the mixture ratio at its theoretical
value. The signal from the front heated oxygen sensor indicates whether the mixture ratio is RICH or LEAN
compared to the theoretical value. The signal then triggers a reduction in fuel volume if the mixture ratio is
rich, and an increase in fuel volume if it is lean.
‘‘Long term fuel trim’’ is overall fuel compensation carried out long-term to compensate for continual deviation
of the short term fuel trim from the central value. Such deviation will occur due to individual engine differences,
wear over time and changes in the usage environment.
EC-QG-22
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System (Cont’d)
QG18DE
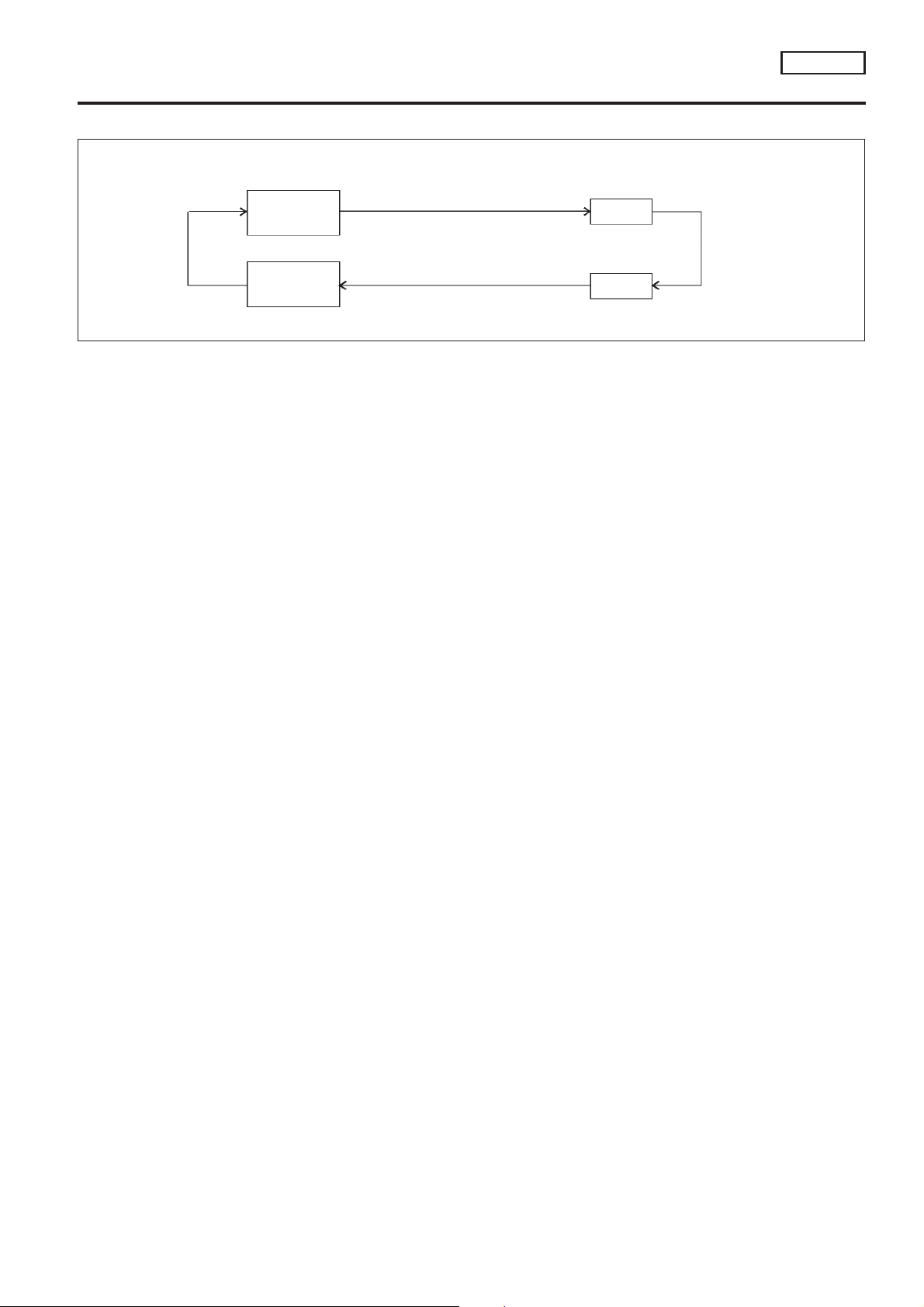
Fuel Injection Timing
● Sequential multiport fuel injection system
Injection pulse
No. 1 cylinder
No. 2 cylinder
No. 3 cylinder
No. 4 cylinder
1 engine cycle
● Simultaneous multiport fuel injection system
No. 1 cylinder
No. 2 cylinder
No. 3 cylinder
No. 4 cylinder
1 engine cycle
NCEC0014S07
SEF337W
Two types of systems are used.
Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System
NCEC0014S0701
Fuel is injected into each cylinder during each engine cycle according to the firing order. This system is used
when the engine is running.
Simultaneous Multiport Fuel Injection System
NCEC0014S0702
Fuel is injected simultaneously into all four cylinders twice each engine cycle. In other words, pulse signals of
the same width are simultaneously transmitted from the ECM.
The four injectors will then receive the signals two times for each engine cycle.
This system is used when the engine is being started and/or if the fail-safe system (CPU) is operating.
Fuel Shut-off
NCEC0014S08
Fuel to each cylinder is cut off during deceleration or operation of the engine at excessively high speeds.
Electronic Ignition (EI) System
DESCRIPTION
Input/Output Signal Chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed and piston position
Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Cylinder number
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Throttle position sensor
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Ignition switch Start signal
Knock sensor Engine knocking
PNP switch Gear position
Battery Battery voltage
Throttle position
Throttle valve idle position
ECM func-
tion
Ignition timing control
NCEC0015
NCEC0015S01
Actuator
Power transistor
EC-QG-23
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
Electronic Ignition (EI) System (Cont’d)
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
QG18DE
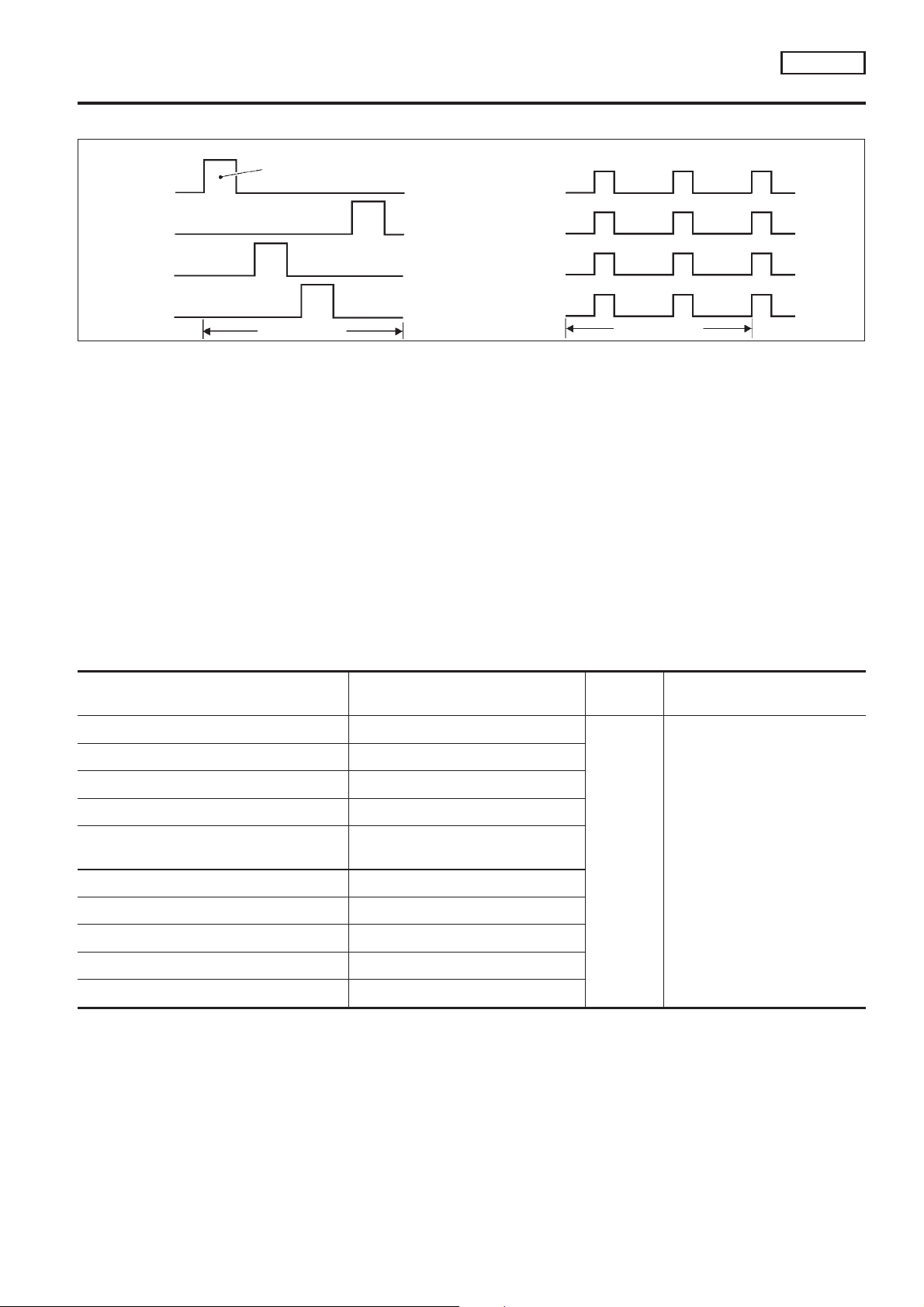
System Description
Tp
(msec)
1.75
1.50
1.25
1.00
0.75
Injection pulse width
600 1,000 1,400 1,800 2,200
Engine speed (rpm)
N
SEF742M
NCEC0015S02
The ignition timing is controlled by the ECM to maintain the best air-fuel ratio for every running condition of
the engine. The ignition timing data is stored in the ECM. This data forms the map shown above.
The ECM receives information such as the injection pulse width, crankshaft position sensor signal and camshaft position sensor signal. Computing this information, ignition signals are transmitted to the power transistor.
e.g., N: 1,800 rpm, Tp: 1.50 msec
A°BTDC
During the following conditions, the ignition timing is revised by the ECM according to the other data stored
in the ECM.
+ At starting
+ During warm-up
+ At idle
+ During acceleration
The knock sensor retard system is designed only for emergencies. The basic ignition timing is programmed
within the anti-knocking zone, if recommended fuel is used under dry conditions. The retard system does not
operate under normal driving conditions.
If engine knocking occurs, the knock sensor monitors the condition. The signal is transmitted to the ECM. The
ECM retards the ignition timing to eliminate the knocking condition.
Air Conditioning Cut Control
DESCRIPTION
Input/Output Signal Chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner ‘‘ON’’ signal
Throttle position sensor Throttle valve opening angle
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Ignition switch Start signal
Refrigerant pressure sensor Refrigerant pressure
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering operation
System Description
This system improves engine operation when the air conditioner is used.
Under the following conditions, the air conditioner is turned off.
+ When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed.
+ When cranking the engine.
+ At high engine speeds.
+ When the engine coolant temperature becomes excessively high.
ECM func-
Air conditioner cut
control
tion
NCEC0016
NCEC0016S01
Actuator
Air conditioner relay
NCEC0016S02
EC-QG-24
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine speed)
+ When operating power steering during low engine speed or low vehicle speed.
+ When engine speed is excessively low.
QG18DE
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed)
DESCRIPTION
Input/Output Signal Chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
PNP switch Neutral position
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
If the engine speed is above 3,950 rpm with no load, (for example, in Neutral and engine speed over 4,000
rpm) fuel will be cut off after some time. The exact time when the fuel is cut off varies based on engine speed.
Fuel cut will operate until the engine speed reaches 1,150 rpm, then fuel cut is cancelled.
NOTE:
This function is different from deceleration control listed under ‘‘Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI)
System’’, EC-QG-21.
ECM func-
tion
Fuel cut
control
Actuator
Injectors
NCEC0017
NCEC0017S01
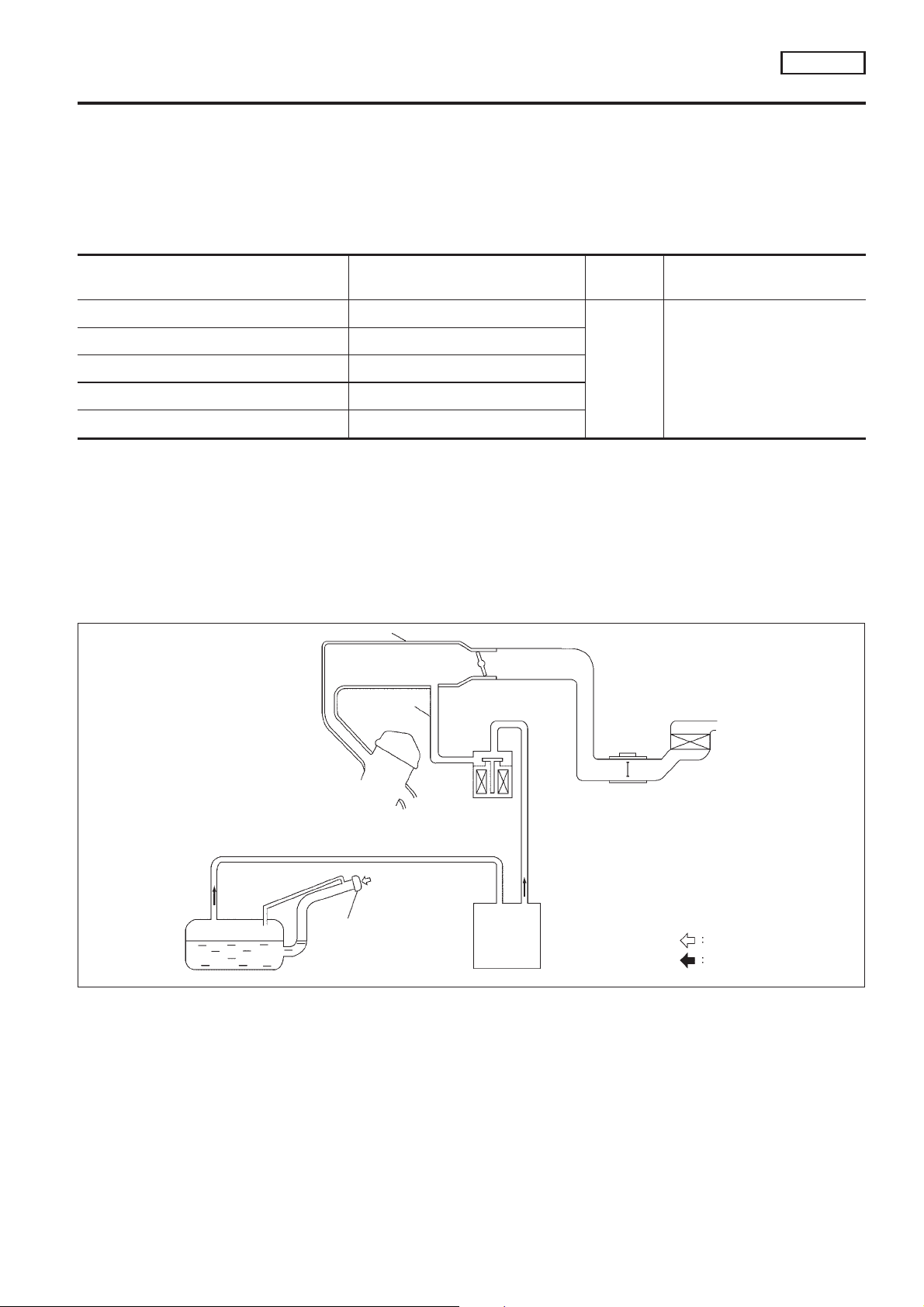
Evaporative Emission System
DESCRIPTION
Intake manifold
Purge line
EVAP canister
purge volume
control solenoid
valve
Relief of vacuum
Sealing gas cap with
pressure relief valve
and vacuum relief
valve
The evaporative emission system is used to reduce hydrocarbons emitted into the atmosphere from the fuel
system. This reduction of hydrocarbons is accomplished by activated charcoals in the EVAP canister.
The fuel vapor in the sealed fuel tank is led into the EVAP canister which contains activated carbon and the
vapor is stored there when the engine is not operating or when refueling to the fuel tank.
The vapor in the EVAP canister is purged by the air through the purge line to the intake manifold when the
engine is operating.
EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve is controlled by ECM. When the engine operates, the flow
rate of vapor controlled by EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve is proportionally regulated as
the air flow increases.
EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve also shuts off the vapor purge line during decelerating and
idling.
Throttle body
EVAP
canister
Air
Fuel vapor
NCEC0018
SEF916W
EC-QG-25
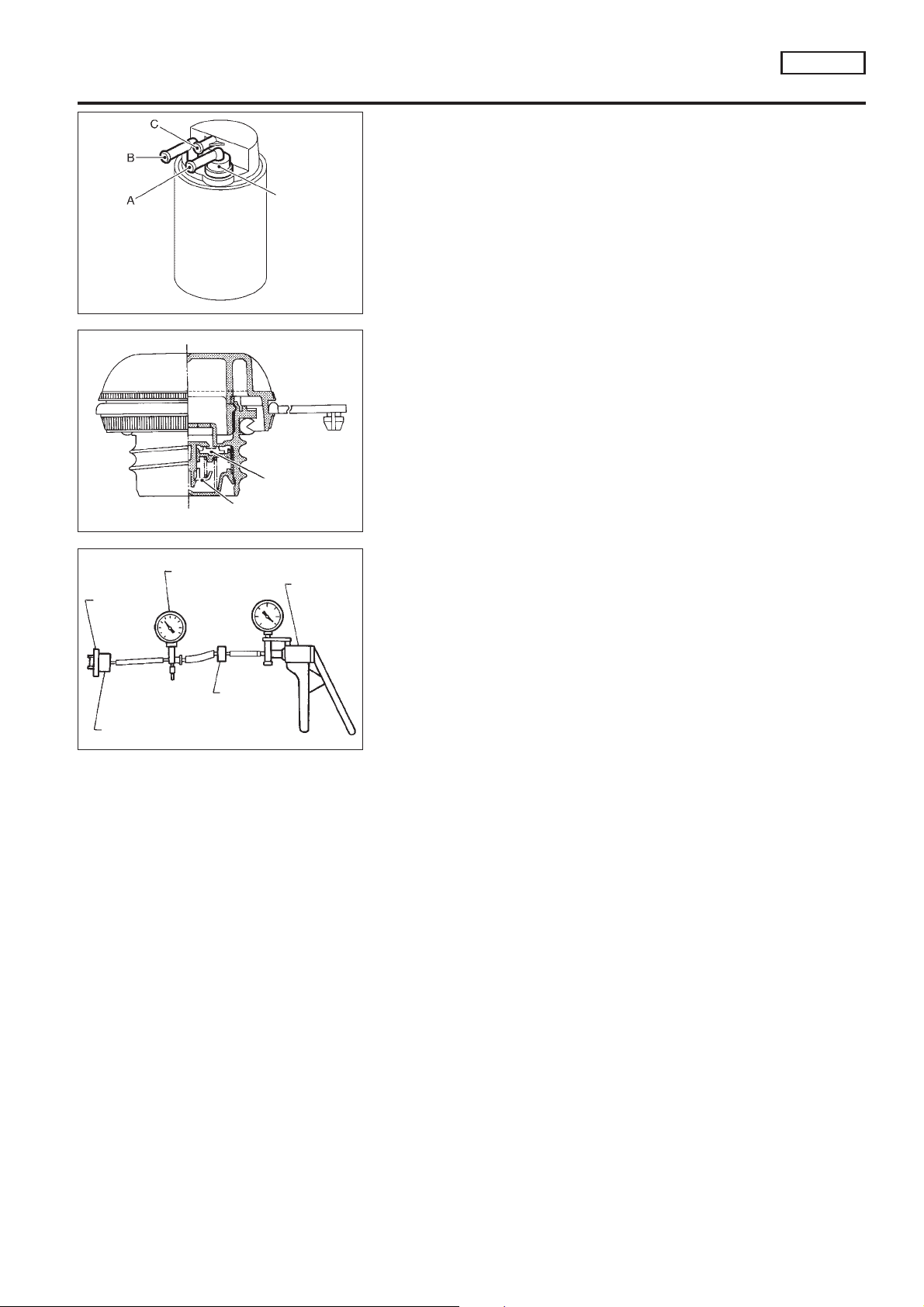
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
Evaporative Emission System (Cont’d)
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
QG18DE
Valve A
Valve B
Check valve
SEF917W
SEF918W
INSPECTION
EVAP Canister
NCEC0019
NCEC0019S01
Check EVAP canister as follows:
1. Block port B. Orally blow air through port A. Check that air
flows freely through port C with check valve resistance.
2. Block port A. Orally blow air through port B. Check that air
flows freely through port C.
Fuel Tank Vacuum Relief Valve (Built into fuel filler
cap)
1. Wipe clean valve housing.
2. Check valve opening pressure and vacuum.
Pressure:
16.0 - 20.0 kPa (0.16 - 0.20 bar, 0.163 - 0.204
2
kg/cm
Vacuum:
−6.0 to −3.5 kPa (−0.060 to −0.035 bar, −0.061 to
−0.036 kg/cm
3. If out of specification, replace fuel filler cap as an assembly.
, 2.32 - 2.90 psi)
2
, −0.87 to −0.51 psi)
NCEC0019S03
Vacuum/Pressure gauge
Fuel filler
cap
Fuel filler cap adapter
One-way
valve
Vacuum/
Pressure
pump
SEF943S
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge Volume
Control Solenoid Valve
Refer to EC-QG-268.
Tank Fuel Temperature Sensor
Refer to EC-QG-224.
NCEC0019S07
NCEC0019S08
EC-QG-26
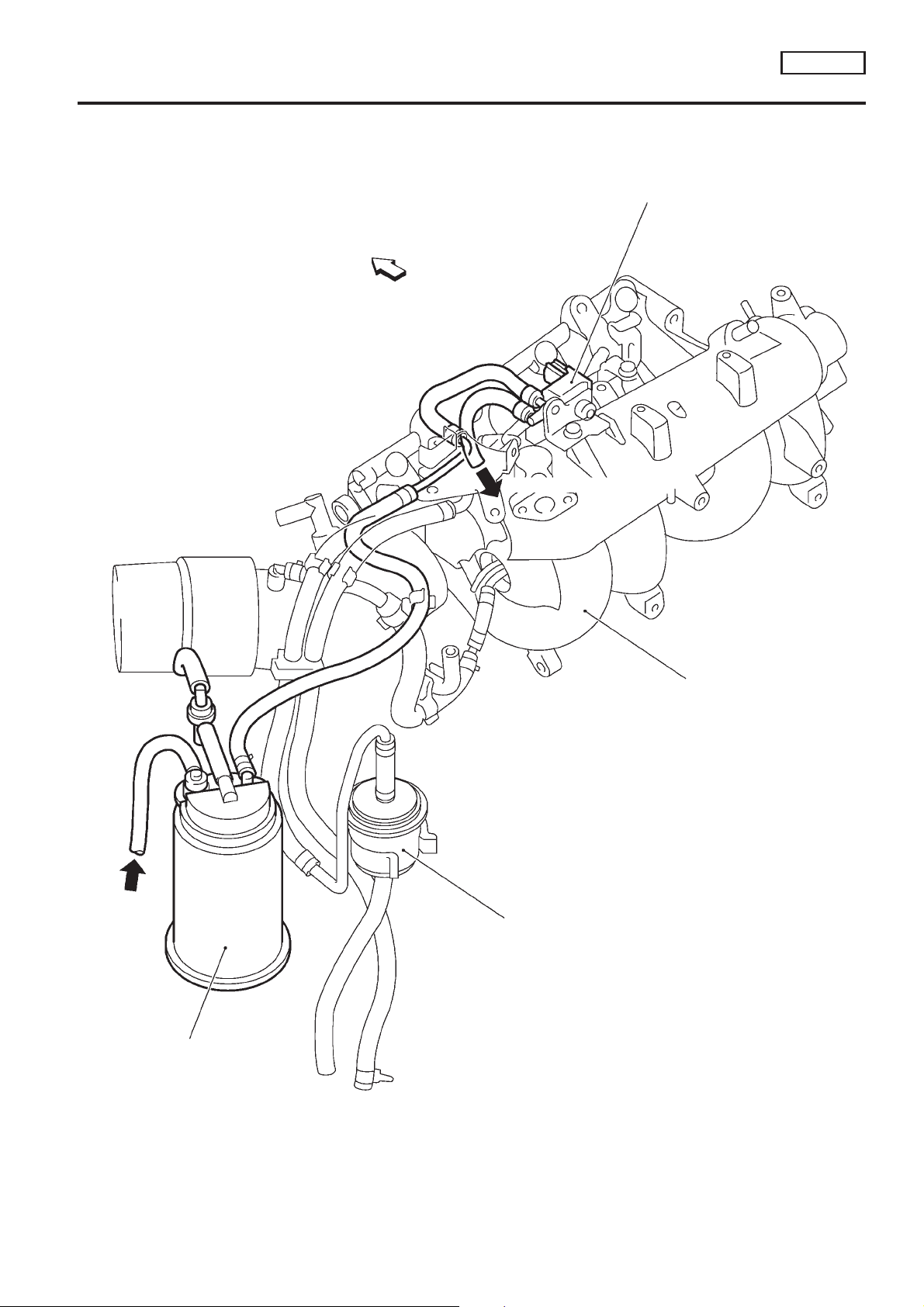
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Evaporative Emission System (Cont’d)
QG18DE
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION LINE DRAWING
Vehicle front
To intake manifold
EVAP canister purge volume
control solenoid valve
NCEC0020
From
fuel tank
Intake manifold
Fuel filter
EVAP canister
NOTE: Do not use soapy water or any type of solvent while installing vacuum hoses or purge hoses.
SEF919W
EC-QG-27
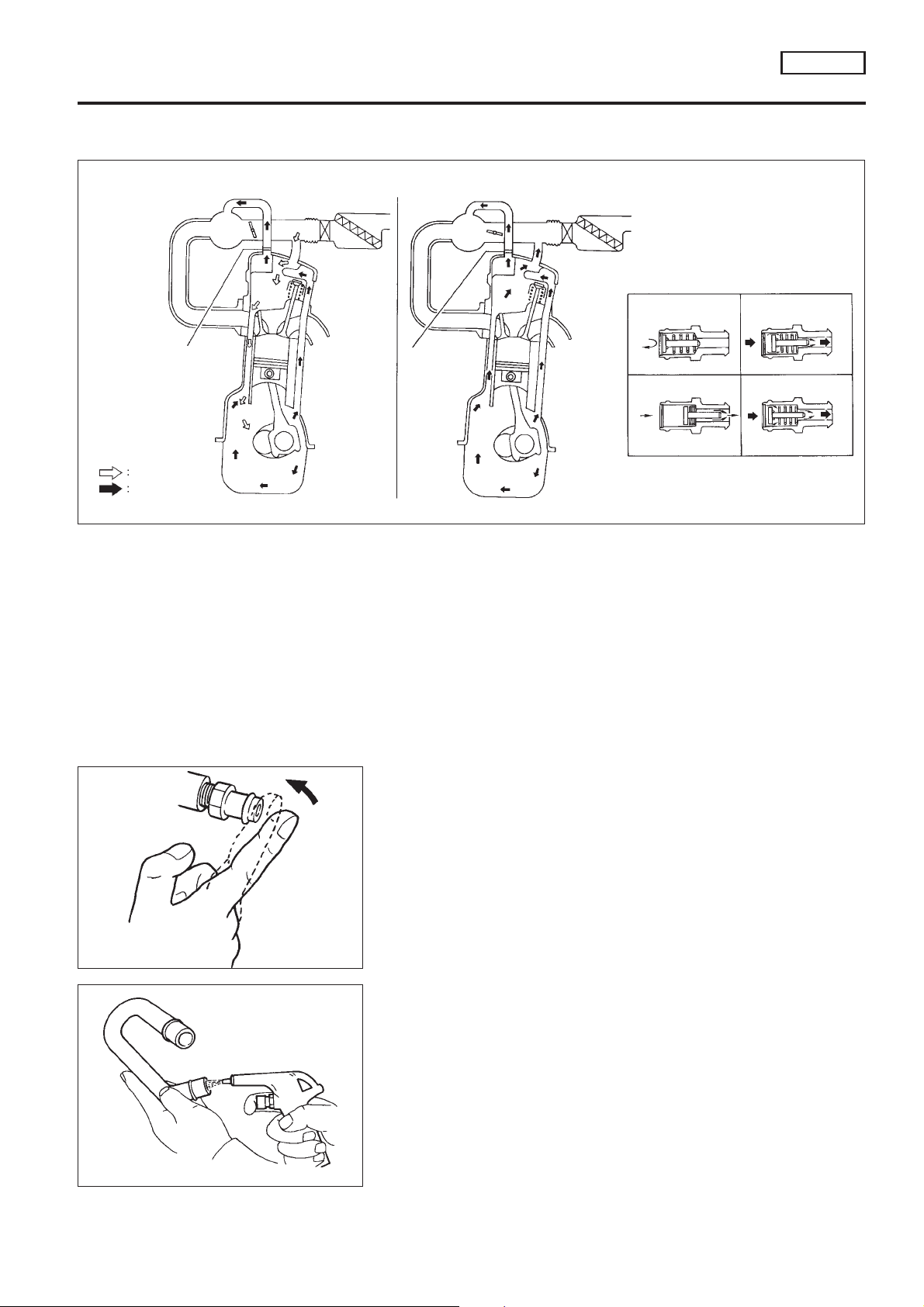
Positive Crankcase Ventilation
DESCRIPTION
Cruising Acceleration or high load
PCV valve PCV valve
Fresh air
Blow-by gas
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PCV valve operation
Engine not running
or backfiring
Idling or
decelerating
QG18DE
Cruising
Acceleration
or high load
NCEC0022
SEF921W
This system returns blow-by gas to the intake collector.
The positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve is provided to conduct crankcase blow-by gas to the intake
manifold.
During partial throttle operation of the engine, the intake manifold sucks the blow-by gas through the PCV
valve.
Normally, the capacity of the valve is sufficient to handle any blow-by and a small amount of ventilating air.
The ventilating air is then drawn from the air duct into the crankcase. In this process the air passes through
the hose connecting air inlet tubes to rocker cover.
Under full-throttle condition, the manifold vacuum is insufficient to draw the blow-by flow through the valve.
The flow goes through the hose connection in the reverse direction.
On vehicles with an excessively high blow-by, the valve does not meet the requirement. This is because some
of the flow will go through the hose connection to the intake collector under all conditions.
INSPECTION
PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) Valve
NCEC0023
NCEC0023S01
With engine running at idle, remove PCV valve from breather separator. A properly working valve makes a hissing noise as air passes
through it. A strong vacuum should be felt immediately when a finger is placed over the valve inlet.
SEC137A
Ventilation Hose
NCEC0023S02
1. Check hoses and hose connections for leaks.
2. Disconnect all hoses and clean with compressed air. If any
hose cannot be freed of obstructions, replace.
ET277
EC-QG-28

BASIC SERVICE PROCEDURE
QG18DE
Fuel Pressure Release
PEF823K
Fuel pump fuse
Fuel pump
relay
Fuel Pressure Release
NCEC0024
Before disconnecting fuel line, release fuel pressure from fuel
line to eliminate danger.
WITH CONSULT-II
NCEC0024S01
1. Start engine.
2. Perform ‘‘FUEL PRES RELEASE’’ in ‘‘WORK SUPPORT’’
mode with CONSULT-II.
3. Afterengine stalls, crank it two or three times to release all fuel
pressure.
4. Turn ignition switch OFF.
WITHOUT CONSULT-II
NCEC0024S02
1. Remove fuse for fuel pump. Refer to fuse block cover for fuse
location.
2. Start engine.
3. Afterengine stalls, crank it two or three times to release all fuel
pressure.
4. Turn ignition switch OFF and reconnect fuel pump fuse.
Data link connector
SEF922W
Fuel pressure gauge
Fuel filter
SEF925W
Fuel Pressure Check
NCEC0025
+ When reconnecting fuel line, always use new clamps.
+ Make sure that clamp screw does not contact adjacent
parts.
+ Use a torque driver to tighten clamps.
+ Use Pressure Gauge to check fuel pressure.
+ Do not perform fuel pressure check with system operat-
ing. Fuel pressure gauge may indicate false readings.
1. Release fuel pressure to zero.
2. Disconnect fuel hose between fuel filter and fuel tube (engine
side).
3. Install pressure gauge between fuel filter and fuel tube.
4. Start engine and check for fuel leakage.
5. Read the indication of fuel pressure gauge.
At idle speed:
With vacuum hose connected
Approximately 235 kPa (2.35 bar, 2.4 kg/cm
2
,34
psi)
With vacuum hose disconnected
Approximately 294 kPa (2.94 bar, 3.0 kg/cm
2
,43
psi)
EC-QG-29
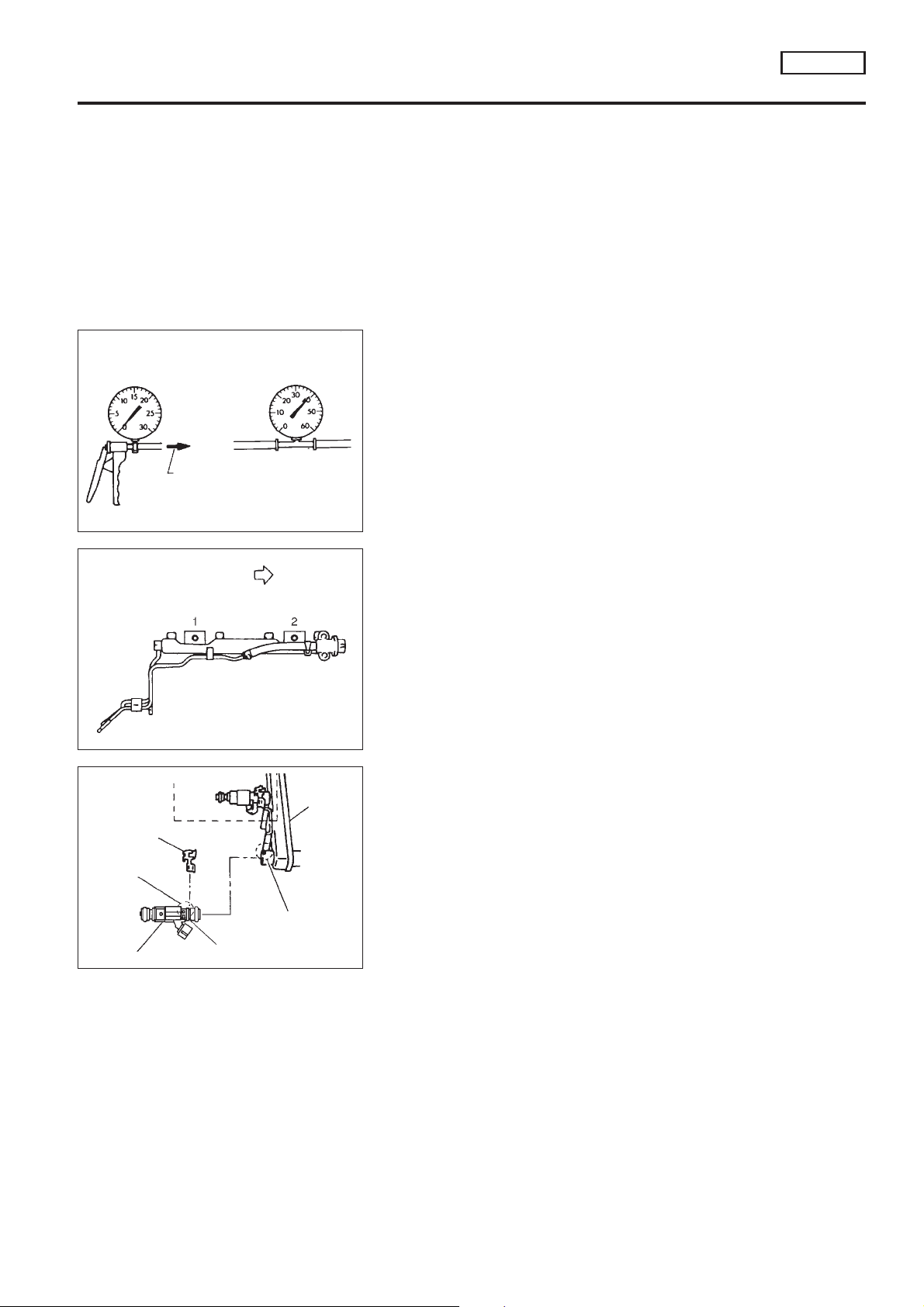
Fuel Pressure Regulator Check
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDURE
If results are unsatisfactory, perform Fuel Pressure Regulator
Check, EC-QG-30.
QG18DE
Vacuum Fuel pressure
To pressure regulator
Engine front
Installing condition
Clip
Align protrusions.
Fuel injector
Clip mounting groove
SEF718B
SEF926W
Fuel tube
Protrusion
SEF927W
Fuel Pressure Regulator Check
NCEC0026
1. Stop engine and disconnect fuel pressure regulator vacuum
hose from intake manifold.
2. Plug intake manifold with a rubber cap.
3. Connect variable vacuum source to fuel pressure regulator.
4. Start engine and read indication of fuel pressure gauge as
vacuum is changed.
Fuel pressure should decrease as vacuum increases. If results
are unsatisfactory, replace fuel pressure regulator.
Injector
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
1. Release fuel pressure to zero.
2. Remove fuel tube assemblies in numerical sequence as
shown in the Figure at left.
3. Expand and remove clips securing fuel injectors.
4. Extract fuel injectors straight from fuel tubes.
+ Be careful not to damage injector nozzles during removal.
+ Do not bump or drop fuel injectors.
+ Do not disassemble or adjust fuel injectors.
5. Install fuel injectors.
Carefully install O-rings, including the one used with the pressure regulator.
+ Use bare hands to install O-rings. Do not wear gloves.
+ Apply a coat of engine oil (with a low viscosity of 5W-30,
etc.) to O-rings before installation.
+ Do not use solvent to clean O-rings and other parts.
+ Make sure that O-rings and other parts are clean and free
from foreign particles.
+ Be careful not to damage O-rings with service tools or
finger nails. Do not expand or twist O-rings. If stretched,
do not insert them into fuel tubes immediately after
stretching.
+ Always insert O-rings straight into fuel tubes. Do not tilt
or rotate them during installation.
6. Position clips in grooves on fuel injectors.
+ Make sure that protrusions of fuel injectors are aligned
with cutouts of clips after installation.
NCEC0027
EC-QG-30
 Loading...
Loading...