ISUZU 4HK-1 Service Manual

FOR SERVICE TRAINING
4HK1-TC ENGINE
-Engine Mechanical Features-
-Engine Control System & Diagnosis-
Applicable Model
Model Year |
Vehicle Model |
Main Market |
|
2005 |
NPR & NQR |
General Export (Euro 3 Regulation) |
|
Europe, Australia, Thailand, South Africa & etc. |
|||
|
|
ISUZU MOTORS LIMITED

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-1
INTRODUCTION & ENGINE MECHANICAL FEATURES
The 2005 model year NPR/NQR truck, the 4HK1-TC inline 4 cylinder engine replaces the 4HE1-TC engine for advanced exhaust emission countries. The 4HK1-TC engine has been newly developed on the basis of previous 4HE1-TC engine, with additional features including the employment of four valve mechanism per a cylinder that are operated via a single camshaft, common rail fuel injection system, water-cooled exhaust gas re-circulation (EGR) system, and the change of combustion chamber form. The larger engine displacement and the common rail fuel injection system have resulted in an increase both in maximum output and torque, and met Euro 3 emission regulation standard. Most conspicuous items are listed below.
Multi fuel injection type high-pressure common rail system and is made with Denso.
Single overhead camshaft (OHC) with 4 valves per a cylinder.
Electrical control EGR valve, water-cooled EGR cooler.
Turbocharger with intercooler.
Engine Type |
Maximum Output |
Maximum Toruque |
4HK1-TCS |
129kw (175ps)/2600RPM |
500Nm (51kgm)/1500-2000RPM |
4HK1-TCN |
110kw (150ps)/2600RPM |
404Nm (41kgm)/1500-2600RPM |
The base transmission is MYY for 4HK1-TCN low output engine, MZZ for 4HK1-TCS high output engine. The Smoother system is available for only MYY transmission.

|
|
|
N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-2 |
|
|
|
|
Major mechanical changed items are listed below. |
|
Part |
Status |
|
Description or Reason in Comparison with 4HE1-TC Engine |
|
Cylinder Block |
Change |
|
Bore size is upped (110mm to 115mm / 4.33in to 4.53in) |
|
Crankshaft |
Carry-over |
|
- |
|
Cylinder Head |
Change |
|
Four valve type with camshaft position sensor hole |
|
Cylinder Head Gasket |
Change |
|
Cylinder head is changed |
|
Camshaft |
Change |
|
Four valve type is employed |
|
Camshaft Gear |
Change |
|
Scissors gear type is employed |
|
Inlet Valve |
Change |
|
Four valve type is employed |
|
Exhaust Valve |
Change |
|
Four valve type is employed |
|
Valve Spring |
Change |
|
Four valve type is employed |
|
Rocker Arm |
Change |
|
Four valve type is employed |
|
Cylinder Head Cover |
Change |
|
Four valve type is employed |
|
Timing Gear Train |
Change |
|
Fuel system is changed |
|
Flywheel |
Change |
|
Crankshaft position sensor is ring added |
|
Flex Plate |
Carry-over |
- |
|
|
Flywheel Housing |
Change |
|
Common rail system is employed & crankshaft position sensor |
|
|
hole |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Engine Hanger |
Change |
|
Cylinder head and EGR layout is changed |
|
Piston |
Change |
|
Bore size is upped |
|
Piston Ring |
Change |
|
Bore size is upped |
|
Connecting Rod |
Carry-over |
- |
|
|
Oil Pan |
Change |
|
Oil level switch is added |
|
Oil Pump |
Carry-over |
- |
|
|
Oil Cooler |
Change |
|
Engine size is changed |
|
Front Cover |
Carry-over |
- |
|
|
Water Pump |
Carry-over |
- |
|
|
Cooling Fan |
Change (4HK1-TCS) |
|
4HK1-TCS: Size is changed to improve performance |
|
Carry-over (4HK1-TCN) |
|
|
||
EGR Cooler |
New |
|
Newly adopted |
|
EGR Pipe |
Change |
|
EGR layout is changed |
|
EGR Valve |
Change |
|
Electrical control type |
|
PCV System |
Carry-over |
- |
|
|
Fuel Pump |
Change |
|
Common rail system is employed (supply pump) |
|
Injection Nozzle |
Change |
|
Common rail system is employed |
|
Injection Pipe |
Change |
|
Common rail system is employed |
|
Fuel Pipe |
Change |
|
Common rail system is employed |
|
Intake Duct |
Change |
|
Layout is changed & boost pressure sensor are added |
|
Intake Manifold |
Change |
|
Layout is changed |
|
Intercooler |
Change |
|
Size is upped |
|
Exhaust Manifold |
Carry-over |
- |
|
|
Turbocharger |
Change |
|
Wastegate valve actuator setting is changed |
|
ACG |
Change |
|
|
|
Starter |
Carry-over |
- |
|
|
Engine Harness |
Change |
|
Common rail system is employed |
|

|
|
N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-3 |
|
ENGINE MAIN DATA & SPECIFICATIONS |
|
|
|
Engine Model |
4HE1-TC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Engine Type |
Diesel, Four Cycle |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cylinder Layout - Number of Cylinders |
Inline-Four Cylinders |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel Injection Order |
1-3-4-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bore x Stroke (mm/in) |
110.0 x 125.0 / 4.33 x 4.92 |
115.0 x 125.0 / 4.53 x 4.92 |
|
|
|
|
|
Total Displacement (cc) |
4751 |
5193 |
|
|
|
|
|
Compression Ratio |
18.0 |
18.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
Compression Pressure at 200 rpm (MPa / psi) |
3.0 / 441 |
3.3 / 478 |
|
|
|
|
|
Combustion Camber Type |
Direct Injection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cylinder Liner |
Dry Type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idle Speed (rpm) |
800±25 |
650±25 |
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel System |
Mechanical Type Governor |
Common Rail System |
|
|
|
|
|
Injection Pump Type |
BOSCH In-line Type (MITICS) |
DENSO (HP3) Supply Pump |
|
|
|
Electrical Controlled Injector |
|
Injection Nozzle Type |
Hole Nozzle (Mechanical Type) |
|
|
(G2) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Number of Injection Hole |
6 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
Diameter of Injection Hole (mm) |
0.21 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
|
|
Injection Nozzle Operating Pressure (MPa) |
17.65 |
Electrically Controlled |
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel Filter Type |
Cartridge Paper Element & Water Separator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Valve System |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Valve Layout |
Overhead Valve |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Drive Type |
Gear Drive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intake Valve Open At BTDC (deg) |
14.0 |
19.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Intake Valve Close At ABDC (deg) |
51.0 |
53.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Exhaust Valve Open At BBDC (deg) |
49.0 |
48.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Exhaust Valve Close At ATDC (deg) |
16.0 |
14.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Intake Valve Clearance At Cold (mm) |
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhaust Valve Clearance At Cold (mm) |
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cooling System |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cooling Method |
Water Cooled |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Water Capacity (litter/gal) |
14 (3.7) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Water Pump Type |
Centrifugal Impeller Type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thermostat Type |
Wax Pellet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thermostat Opening Temperature (deg. C / deg. F) |
82 & 85 / 180 & 185 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lubricating System |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lubricating Method |
Full Flow Pressure Circulation |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oil Pump Type |
Gear |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Oil Capacity (litter/gal) |
13 (3.4) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Oil Filter Type |
Cartridge Paper Element |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Air Cleaner Type |
Dry Paper Element |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
EGR System |
W/O Cooler & Vacuum Control |
|
W/Cooler & Electrical Control |
|
EGR Valve |
|
EGR Valve |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
PCV System |
Open Type |
|
||
|
|
|
||
Preheating System |
Glow Plug |
|
||
Starting System |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Starter Motor Output (V-kW) |
24 - 3.0 |
|
||
Charge System |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Alternator Output (V-A) |
24 – 50, 60 or 80 |
|
||
Regulator Type |
IC |
|
|
|
Battery Size |
115E41R x 2 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|

GEAR TRAIN
Valve Train
N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-5
To rotate the fuel supply pump with engine speed, idle gear has changed with three steps. The crankshaft gear (42 teeth) corresponds with the large diameter of idle gear A (72 teeth). The fuel supply pump gear (35 teeth) corresponds with the middle diameter of idle gear A (60 teeth). The idle gear B (61 teeth) corresponds with the small diameter of idle gear A (30 teeth).
1.Camshaft Gear (Z=35)
2.Idle Gear C (Z=41)
3.Idle Gear B (Z=61)
4.Idle Gear A (Large) (Z=72)
5.Idle Gear A (Middle) (Z=60)
6.Idle Gear A (Small) (Z=30)
7.Fuel Supply Pump Gear (Z=35)
8.Crankshaft Gear (Z=42)
To improve exhaust emission and engine output performance, four valve mechanism is newly adopted for 4HK1-TC engine. Note that the adjustment method of valve clearance has been changed from 4HK1-TC engine as following steps.
1.Rotate the crankshaft to make the No.1 cylinder meet the compression top dead center (TDC). There are 2 marks stamped on the crank pulley. The mark (1) is used to bring the engine No.1 or No. 4 cylinder to TDC. The mark (2) is irrelevant. Do not use the mark (2).

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-6
Cylinder No. |
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Valve |
|
IN |
|
EX |
IN |
|
EX |
IN |
|
EX |
IN |
|
EX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No.1 |
Cylinder |
O |
|
O |
O |
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
Compression |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
TDC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No.4 |
Cylinder |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
X |
|
X |
Compression |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
TDC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.Loosen fully each adjusting screw (8) & (2) of the bridge and the rocker arm.
3.Insert a 0.4mm (0.016in) thickness gauge between the tip of the rocker arm and bridge cap (5), and adjust the clearance with the adjusting screw (3) on the rocker arm, and then fix it with a lock nut (4).
4.With a thickness gauge kept inserted, check that the adjusting screw (6) contacts the valve shaft end and the movement of the thickness gauge has become tight when the adjusting screw (6) on the bridge is tightened lightly.
5.Check the valve shaft end on the opposite side floats or it contacts obliquely. In case of a floating or oblique contact, loosen a little the adjusting screw (6) on the bridge side and adjust so that the valve shaft ends on both sides get in contact properly. Bridge (8) & valve shaft end clearance less than 0.1 mm (0.004in).
6.After the adjustment so that the end of the valves on both sides touch properly, tighten up the lock nut (7) on the bridge (8).
Note that unless the bridge is kept horizontal, the bridge is pressed obliquely, thus causing the bridge and bridge guide to be seized or damaged. Therefore, exact adjustment is required.
Valve clearance: 0.4mm (0.016in) intake & exhaust side at cold
Adjusting screw lock nut tightening torque: 22Nm (16lb ft)
At the No.1 cylinder compression top dead center, the valves with “O” mark in the following table, or at the No.4 cylinder compression top dead center, the valve with “X“ mark can be adjusted.

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-7
Fuel Supply Pump Installation
1. Apply white paint to the top of the fuel supply pump gear tooth directly above the stamped “O” mark.
2. Rotate the crankshaft to the compression top dead center (TDC). There are 2 marks stamped on the crank pulley. The mark (1) is used to bring the engine No.1 or No. 4 cylinder to TDC. The mark (2) is irrelevant. Do not use the mark (2).
3. Install the O-ring to the fuel supply pump.
4. Align a slit of the fuel supply pump bracket with a white paint on the gear and install the fuel supply pump in the gear case using the stud bolts as a guide.

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-8
5. Check through the hole (1) that a white paint (2) on the gear is in the position shown on the left.
Fixing nut tightening torque: 50Nm (37lb ft) Fixing bolt tightening torque: 76Nm (56lb ft)
CYLINDER HEAD COVER & HEAD COVER CASE
Along with the employment of a common rail type fuel injection system, the head cover is split and housed in a newly introduced head cover case attached with an intermediate connector for the injector. The head cover case is so designed that it is secured individually to the cylinder head with four bolts, and further it is tightened together with the head cover with nine bolts. Accordingly, the head cover is removable individually regardless of the injector harness, thus enabling easy inspection and service including the valve clearance adjustment.
1. Gasket
2. Oil Filler Cap
3. Head Cover Bolt
4. Head Cover
5. Gasket
6. Head Cover Case
7. Intermediate Harness Connector
8. Cylinder Head Cover Case Bolt
9. Cylinder Head
10. Gasket
11. Connector Fixing Bolt

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-9
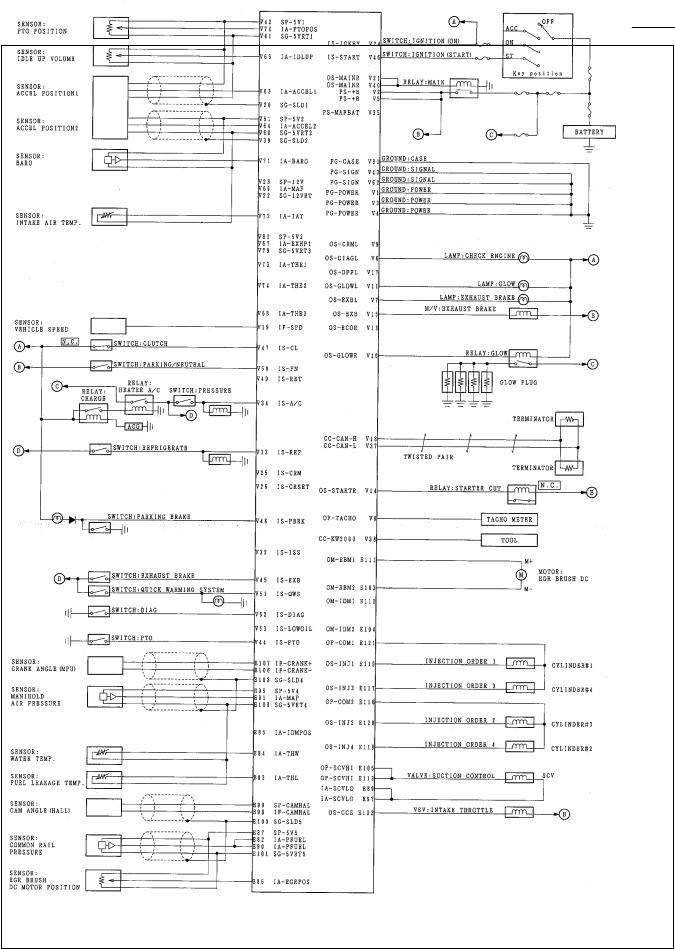
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located at inside of engine-side cover on the left via mounting bracket and is beside the engine. The ECM is made by Transtron. The ECM mainly controls the following.
Fuel injection control
Fuel timing control
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system control
Preheating system control
Exhaust brake control
Power take off (PTO) control
On-board diagnostics for engine control
The ECM constantly observes the information from various sensors. The ECM controls the systems that affect vehicle performance. The ECM performs the diagnostic function of the system. The ECM can recognize operational problems, alert the driver through the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), and store diagnostic trouble code (DTC). DTC identify the system faults to aid the technician in making repair.
This diagnostic applies to internal microprocessor integrity conditions within the ECM. The electronically erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM) memorize learning data and injector ID code data for engine control and communication with other control module.
Symbol “!” warns you of an electric shock hazard. To avoid shock and possible serious injury, DO NOT touch the terminals. When disconnecting the harness connector, always turn OFF the ignition switch or disconnect the battery cable.
Parts number of each ECM mainly differs with following contents.
Engine specification (output or torque) Transmission specification (MYY, MZZ or Smoother) Speed limiter application
Notice!
If the ECM is to be replaced the fuel injector ID Code Data (24, 0-9 or A-F characters for each fuel injector) MUST be programmed into the new ECM.
Notice!
This ECM does not have ability of re-flash function by Service Programming System (SPS) via Tech 2 scan tool.
N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-10

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ECM Connector Pin Assignment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin No. |
Pin Function |
|
Pin |
Pin Function |
|
Pin |
Pin Function |
|
|
No. |
|
No. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1 |
ECM Power Ground |
|
28 |
Not Used |
|
55 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
Main Relay Voltage |
|
29 |
Not Used |
|
56 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
ECM Power Ground |
|
30 |
Not Used |
|
57 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
ECM Power Ground |
|
31 |
Not Used |
|
58 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Main Relay Voltage |
|
32 |
Not Used |
|
59 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) |
|
33 |
Refrigerator Switch Input Signal |
|
60 |
APP Sensor 2, BARO Sensor, IAT |
|
Control |
|
|
Sensor Low Reference |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7 |
Exhaust Brake Lamp Control |
|
34 |
A/C Switch Input Signal |
|
61 |
APP Sensor 2, BARO Sensor, IAT |
|
|
|
Sensor 5V Reference |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
Engine Speed Signal Output to |
|
35 |
Not Used |
|
62 |
ECM Signal Ground |
|
IPC |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
Not Used |
|
36 |
Not Used |
|
63 |
APP Sensor 1 Input Signal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
Glow Plug Relay Control |
|
37 |
CAN Low Signal |
|
64 |
APP Sensor 2 Input Signal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
Glow Indicator Lamp Control |
|
38 |
Keyword 2000 Serial Data |
|
65 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
Not Used |
|
39 |
APP Sensor 2 Shield |
|
66 |
Idle Up Sensor Input Signal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
Not Used |
|
40 |
Main Relay Power Supply |
|
67 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
APP Sensor 1, Idle Up Sensor, |
|
|
|
|
14 |
Starter Cut Relay Control |
|
41 |
Remote PTO Accelerator |
|
68 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
Sensor Low Reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
APP Sensor 1, Idle Up Sensor, |
|
|
|
|
15 |
Exhaust Brake Solenoid Control |
|
42 |
Remote PTO Accelerator |
|
69 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
Sensor 5V Reference |
|
|
|
|
16 |
Not Used |
|
43 |
ECM Signal Ground |
|
70 |
Remote PTO Accelerator Sensor |
|
|
|
Input Signal |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
Not Used |
|
44 |
PTO Operation Switch Input |
|
71 |
BARO Sensor Input Signal |
|
|
Signal |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
CAN High Signal |
|
45 |
Exhaust Brake Switch Input |
|
72 |
IAT Sensor Input Signal |
|
|
Signal |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
VSS Input Signal |
|
46 |
Start Position Input Signal |
|
73 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
APP Sensor 1 Shield |
|
47 |
Clutch Switch Input Signal (M/T |
|
74 |
Not Used |
|
|
Only) |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
Main Relay Power Supply |
|
48 |
Park Brake Switch Input Signal |
|
75 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
Not Used |
|
49 |
Not Used |
|
76 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
Not Used |
|
50 |
Neutral Switch Input Signal |
|
77 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
Ignition ON Switch Input Signal |
|
51 |
Engine Warm Up Switch Input |
|
78 |
Not Used |
|
|
Signal |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
Not Used |
|
52 |
Diag Switch |
|
79 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
Not Used |
|
53 |
Not Used |
|
80 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
Not Used |
|
54 |
Not Used |
|
81 |
ECM Case Ground |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pin No. |
Pin Function |
|
Pin |
Pin Function |
|
Pin |
Pin Function |
|
|
No. |
|
No. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
82 |
FRP Sensor Input Signal |
|
96 |
Not Used |
|
110 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
83 |
FT Sensor Input Signal |
|
97 |
SCV Low Control |
|
111 |
EGR Valve DC Motor Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
84 |
ECT Sensor Input Signal |
|
98 |
CMP Sensor 12V Reference |
|
112 |
Not Used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
85 |
Not Used |
|
99 |
CMP Sensor Input Signal |
|
113 |
SCV High Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
86 |
EGR Valve Position Sensor Input |
|
100 |
FRP Sensor, CMP Sensor |
|
114 |
Not Used |
|
Signal |
|
Shield |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
87 |
FRP Sensor, EGR Valve Position |
|
101 |
FRP Sensor, EGR Valve |
|
115 |
Not Used |
|
Sensor Input Signal |
|
Position Sensor Low Reference |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
88 |
Not Used |
|
102 |
Intake Throttle Solenoid Valve |
|
116 |
Cylinder #2, #3 Injector Power |
|
|
Control |
|
Supply |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
89 |
SCV Low Control |
|
103 |
EGR Valve DC Motor Power |
|
117 |
Cylinder #4 Injector Control |
|
|
Supply |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 |
FRP Sensor Input Signal |
|
104 |
Not Used |
|
118 |
Cylinder #2 Injector Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
91 |
Boost Pressure Sensor Input |
|
105 |
SCV High Control |
|
119 |
Cylinder #1 Injector Control |
|
Signal |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
92 |
Not Used |
|
106 |
CKP Sensor Low Signal Input |
|
120 |
Cylinder #3 Injector Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
93 |
Not Used |
|
107 |
CKP Sensor High Signal Input |
|
121 |
Cylinder #1, #4 Injector Power |
|
|
|
Supply |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
94 |
Not Used |
|
108 |
Boost Pressure Sensor, CKP |
|
|
|
|
|
Sensor Shield |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Boost Pressure Sensor 5V |
|
|
Boost Pressure Sensor, ECT |
|
|
|
|
95 |
|
109 |
Sensor, FT Sensor Low |
|
|
|
|
|
Reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-13
ECM Inputs & Outputs
Sensor Input |
Fuel Injection Control Output |
||
• |
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor |
• |
Suction control valve (SCV) |
• |
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor |
• |
Fuel injector #1 |
• |
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor |
• |
Fuel injector #2 |
• |
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor |
• |
Fuel injector #3 |
• |
Fuel temperature (FT) sensor |
• |
Fuel injector #4 |
•Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor
•Barometric pressure (BARO) sensor
• |
Boost pressure sensor |
|
Actuator Control Output |
|
• |
Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor |
|
• |
Intake throttle solenoid valve |
• |
Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) |
|
• |
Exhaust brake solenoid valve |
• |
EGR valve position sensor |
|
• |
EGR valve motor |
• |
Idle up control sensor |
EC |
|
|
• |
Remote PTO accelerator sensor |
M |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Relay & Lamp Control Output |
|
|
|
|
• |
Glow relay |
Switch Input |
|
• |
Starter cut relay |
|
|
• |
Malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) |
||
• |
Ignition switch (ON/start position) |
|
||
|
• |
Glow indicator lamp |
||
• |
Clutch switch (M/T) |
|
||
|
• Exhaust brake indicator lamp |
|||
• |
Park brake switch |
|
||
|
|
|
||
•Park/Neutral switch
•Exhaust brake switch
•Engine warm up switch
•A/C switch
• |
PTO switch |
Communication |
|
• |
Refrigerator switch |
• |
Tech 2 (Keyword 2000) |
• |
Diag request switch |
• |
Controller area network (CAN) |

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-14
The ECM monitors the battery voltage through the ECM main relay load supply voltage terminals “2” and “5”, and the ignition voltage on the ignition voltage feed terminal “24” to make sure that the voltage stays within the proper range. When the charging system detects a malfunction, the charge indicator will light.
Related DTC
DTC |
DTC Name On Scan |
Condition for Running the DTC |
Condition for Setting the DTC |
|
Tool |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1625 |
ECM Main Relay |
DTC P1603 is not set. |
The ECM detects that a low |
|
Circuit |
The ignition switch is ON. |
voltage condition on the ECM |
|
|
The ignition switch ON time is |
main relay voltage feed circuit for |
|
|
longer than 3 seconds. |
longer than 3 seconds when the |
|
|
|
ECM main relay is commanded |
|
|
|
ON. |
|
|
|
|
P1625 |
ECM Main Relay |
The ignition switch is OFF. |
The ECM detects that a high |
|
Circuit |
|
voltage condition on the ECM |
|
|
|
main relay voltage feed circuit for |
|
|
|
longer than 5 seconds when the |
|
|
|
ECM main relay is commanded |
|
|
|
OFF. |
|
|
|
|
Suspected Cause
ECM main relay coil side power supply circuit is open circuit or high resistance.
ECM main relay voltage feed circuit is open circuit or high resistance.
Faulty ECM main relay.
ECM main relay coil side power supply circuit is short to battery voltage circuit.
ECM main relay voltage feed circuit is short to battery voltage circuit.
Faulty ECM main relay.

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-15
The engine control module (ECM) provides 5volts reference voltage through the reference circuit 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 to the following sensors.
5volts reference circuit 1
Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor 1 Idle up volume sensor
Remote PTO accelerator sensor 5volts reference circuit 2
APP sensor 2
Barometric pressure (BARO) sensor 5volts reference circuit 3 (Not Used) 5volts reference circuit 4
Boost pressure sensor 5volts reference circuit 5
Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor EGR valve position sensor

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-16
Related DTC
DTC |
DTC Name On Scan |
Condition for Running the DTC |
Condition for Setting the DTC |
|
Tool |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1631 |
5 Volt Reference |
DTC P1630 is not set. |
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
Circuit 1 |
The battery voltage is between 16 |
reference circuit 1 voltage is less |
|
|
– 32 volts. |
than 4.5 volts. |
|
|
The ignition switch is ON. |
OR |
|
|
|
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
|
|
reference circuit 1 voltage is more |
|
|
|
than 5.5 volts. |
P1632 |
5 Volt Reference |
DTC P1630 is not set. |
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
Circuit 2 |
The battery voltage is between 16 |
reference circuit 2 voltage is less |
|
|
– 32 volts. |
than 4.5 volts. |
|
|
The ignition switch is ON. |
OR |
|
|
|
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
|
|
reference circuit 2 voltage is more |
|
|
|
than 5.5 volts. |
|
|
|
|
Suspected Cause
APP sensor 1 5V reference circuit is short to ground, short to any 12V reference circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit.
Idle up sensor 5V reference circuit is short to ground, short to any 12V reference circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit.
PTO accelerator sensor 5V reference circuit is short to ground, short to any 12V reference circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit. Faulty APP sensor 1.
Faulty Idle up sensor.
Faulty PTO accelerator sensor. Faulty ECM.
Notice: APP sensor 1 is internal to APP sensor assembly.
APP sensor 2 5V reference circuit is short to ground, short to any 12V reference circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit.
BARO sensor 5V reference circuit is short to ground, short to any 12V reference circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit.
Faulty APP sensor 2. Faulty BARO sensor. Faulty ECM.
Notice: APP sensor 2 is internal to APP sensor assembly.

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-17
Related DTC
DTC |
DTC Name On Scan |
Condition for Running the DTC |
Condition for Setting the DTC |
|
Tool |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1633 |
5 Volt Reference |
DTC P1630 is not set. |
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
Circuit 3 |
The battery voltage is between 16 |
reference circuit 3 voltage is less |
|
|
– 32 volts. |
than 4.5 volts. |
|
|
The ignition switch is ON. |
OR |
|
|
|
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
|
|
reference circuit 3 voltage is more |
|
|
|
than 5.5 volts. |
|
|
|
|
P1634 |
5 Volt Reference |
DTC P1630 is not set. |
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
Circuit 4 |
The battery voltage is between 16 |
reference circuit 4 voltage is less |
|
|
– 32 volts. |
than 4.5 volts. |
|
|
The ignition switch is ON. |
OR |
|
|
|
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
|
|
reference circuit 4 voltage is more |
|
|
|
than 5.5 volts. |
|
|
|
|
Suspected Cause
-
Boost pressure sensor 5V reference circuit is short to ground, short to any 12V reference circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit. Faulty boost pressure sensor.
Faulty ECM.

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-18
Related DTC
DTC |
DTC Name On Scan |
Condition for Running the DTC |
Condition for Setting the DTC |
|
Tool |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1635 |
5 Volt Reference |
DTC P1630 is not set. |
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
Circuit 5 |
The battery voltage is between 16 |
reference circuit 5 voltage is less |
|
|
– 32 volts. |
than 4.5 volts. |
|
|
The ignition switch is ON. |
OR |
|
|
|
The ECM detects that the 5 volts |
|
|
|
reference circuit 5 voltage is more |
|
|
|
than 5.5 volts. |
|
|
|
|
Suspected Cause
FRP sensor 5V reference circuit is short to ground, short to any 12V reference circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit.
EGR valve position sensor 5V reference circuit is short to ground, short to any 12V reference circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit. Faulty FRP sensor.
Faulty EGR valve position sensor. Faulty ECM.
Notice: EGR valve position sensor is internal to EGR valve assembly.

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-19
The engine control module (ECM), the smoother control module, ABS control module (EHCU) and the DMU, interchange of data among each controller performed via a controller area network (CAN) communication bus. Following signals are communicated via a CAN bus.
•Accelerator pedal position signal
•Engine output torque
•PTO control signal
•Exhaust brake cut signal
•Engine speed signal
•Injection volume reduction signal
The ECM monitors CAN operational status by expecting a constant flow of messages from each module. If the ECM fails to receive an expected message from each module, DTC U2104, U2106 or U2108 will set depending on what communication is lost.

|
|
|
|
|
N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-20 |
|
Related DTC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DTC |
DTC Name On Scan |
Condition for Running the DTC |
Condition for Setting the DTC |
Suspected Cause |
|
|
|
Tool |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CAN high circuit is short to ground, short to |
|
U2104 |
CAN Bus Reset |
The ignition switch is ON. |
The ECM detects that the CAN |
|
||
|
Counter Overrun |
|
|
Bus OFF is detected. |
battery or ignition voltage. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CAN low circuit is short to ground, short to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
battery or ignition voltage. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrical interference. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faulty ECM. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faulty TCM. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faulty EHCU. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CAN high circuit is short to ground, short to |
|
U2106 |
Lost CAN |
The ignition switch is ON. |
|
The ECM detects that the CAN |
|
|
|
Communications With |
|
|
Bus messages from the TCM are |
battery or ignition voltage. |
|
|
Transmission Control |
|
|
not being received. |
CAN low circuit is short to ground, short to |
|
|
System |
|
|
|
battery or ignition voltage. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrical interference. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faulty ECM. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faulty TCM. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CAN high circuit is short to ground, short to |
|
U2108 |
Lost Communications |
The ignition switch is ON. |
The ECM detects that the CAN |
|
||
|
With ABS/TCS Control |
|
|
Bus messages from the EHCU |
battery or ignition voltage. |
|
|
System |
|
|
(ABS control unit) are not being |
CAN low circuit is short to ground, short to |
|
|
|
|
|
received. |
battery or ignition voltage. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrical interference. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faulty ECM. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faulty EHCU. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-21
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is fitted between the air cleaner and turbocharger. The IAT sensor is a variable resistor. The IAT sensor measures the temperature of the air entering the engine. The engine control module (ECM) supplies 5 volts to the IAT sensor signal circuit and a ground for the IAT sensor low reference circuit. When the IAT sensor is cold, the sensor resistance is high. When the air temperature increases, the sensor resistance decreases. With high sensor resistance, the ECM detects a high voltage on the IAT sensor signal circuit. With lower sensor resistance, the ECM detects a lower voltage on the IAT sensor signal circuit. The ECM uses to this value to calculate a fuel injection quantity, injection timing and EGR control.
|
IAT Sensor Characteristic -Reference- |
|
|
Ohms |
|||
|
|
|
Volts |
||||
|
30000 |
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
27500 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22500 |
|
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Ohms) |
20000 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
17500 |
|
|
|
|
2.5 |
|
|
Resistance |
|
|
|
|
|
Output (Volts) |
|
15000 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
12500 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
||
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
|||
10000 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
7500 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2500 |
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
-20 -10 |
0 |
10 20 30 40 50 60 |
70 |
80 |
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
Temperature (C) |
|
|
|
|
The characteristic of the IAT sensor is displayed in the graph and table. Calculated intake air temperature can be found on the Tech 2 by unit “°C” or “°F”. The output voltage also can be found on the Tech 2.
Notice!
In data display “°C” or “°F” will be fixed to a default value when DTC is set relating to the IAT sensor open or short circuit. To diagnose this DTC, observe the “Volts” in the data display.
°C |
°F |
Ohms |
Volts |
90 |
194 |
240 |
0.2 |
80 |
176 |
320 |
0.3 |
70 |
158 |
450 |
0.4 |
60 |
140 |
660 |
0.6 |
50 |
122 |
960 |
0.8 |
40 |
104 |
1440 |
1.1 |
30 |
86 |
2300 |
1.6 |
20 |
68 |
3430 |
2.1 |
10 |
50 |
5410 |
2.7 |
0 |
32 |
9770 |
3.3 |
-10 |
14 |
16410 |
3.8 |
-20 |
-4 |
28560 |
4.2 |

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-22
IAT Sensor
Connector Face
Related DTC
DTC |
DTC Name On Scan |
Condition for Running the DTC |
Condition for Setting the DTC |
Suspected Cause |
|
Tool |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Sensor signal circuit is short to ground or short to |
|
P0112 |
Intake Air Temperature |
DTCs P1630 and P1632 are not |
The ECM detects that the IAT |
||
|
(IAT) Sensor Circuit |
set. |
sensor signal voltage is less than |
the low reference circuit. |
|
|
Low Voltage |
The ignition switch is ON. |
0.1 volts for 5 seconds. |
Faulty IAT sensor. |
|
|
|
The ignition voltage is more than 18 |
|
Faulty ECM. |
|
|
|
volts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sensor signal circuit is open circuit, high |
|
P0113 |
Intake Air Temperature |
DTCs P1630 and P1632 are not |
The ECM detects that the IAT |
||
|
(IAT) Sensor Circuit |
set. |
sensor signal voltage is more than |
resistance, short to any 5V or 12V reference |
|
|
High Voltage |
The ignition switch is ON. |
4.8 volts for 5 seconds. |
circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit. |
|
|
|
The ignition voltage is more than 18 |
|
Sensor low reference circuit is open circuit or |
|
|
|
volts. |
|
high resistance. |
|
|
|
The engine run time is longer than |
|
Poor harness connector connection. |
|
|
|
|
Faulty IAT Sensor. |
||
|
|
3 minutes. |
|
||
|
|
|
Faulty ECM. |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-23
ENGINE COOLTANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR
|
ECT Sensor Characteristic -Reference- |
|
|
Ohms |
|||||||
|
|
|
Volts |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
28000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
26000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
24000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
22000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
20000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Resistance (Ohms) |
18000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
16000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output (Volts) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
14000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.5 |
|||
12000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|||
10000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
8000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
-3 |
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
10 |
20 30 40 50 60 |
70 |
80 |
90 |
10 |
11 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
Temperature (C) |
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
°C |
°F |
Ohms |
Volts |
110 |
230 |
160 |
0.2 |
100 |
212 |
200 |
0.3 |
90 |
194 |
260 |
0.4 |
80 |
176 |
350 |
0.5 |
70 |
158 |
470 |
0.6 |
60 |
140 |
640 |
0.8 |
50 |
122 |
880 |
1.1 |
40 |
104 |
1250 |
1.5 |
30 |
86 |
1800 |
1.9 |
20 |
68 |
2650 |
2.3 |
10 |
50 |
4000 |
2.8 |
0 |
32 |
6180 |
3.3 |
-10 |
14 |
9810 |
3.8 |
-20 |
-4 |
16000 |
4.2 |
-30 |
-22 |
27000 |
4.5 |
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is installed to the coolant stream on the thermostat housing. It is a variable resistor. The ECT sensor measures the temperature of the engine coolant. The engine control module (ECM) supplies 5 volts to the ECT sensor signal circuit and a ground for the ECT sensor low reference circuit. When the ECT sensor is cold, the sensor resistance is high. When the air temperature increases, the sensor resistance decreases. With high sensor resistance, the ECM detects a high voltage on the ECT sensor signal circuit. With lower sensor resistance, the ECM detects a lower voltage on the ECT sensor signal circuit. The ECM uses to this value to calculate a fuel injection quantity, injection timing and EGR control and preheating control.
1.Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The characteristic of the ECT sensor is displayed in the graph and table. Calculated coolant temperature can be found on the Tech 2 by unit “°C” or “°F“. The output voltage also can be found on the Tech 2.
Notice!
In data display “°C” or “°F” will be fixed to a default value when DTC is set relating to the ECT sensor. To diagnose this DTC, observe the “Volts” in the data display.

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-24
ECT Sensor
Connector Face
Related DTC
DTC |
DTC Name On Scan |
Condition for Running the DTC |
Condition for Setting the DTC |
Suspected Cause |
|
Tool |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Sensor signal circuit is short to ground or short to |
|
P0117 |
Engine Coolant |
DTCs P1630 and P1634 are not |
The ECM detects that the ECT |
||
|
Temperature (ECT) |
set. |
sensor signal voltage is less than |
the low reference circuit. |
|
|
Sensor Circuit Low |
The ignition switch is ON. |
0.1 volts for 5 seconds. |
Faulty ECT sensor. |
|
|
Voltage |
The ignition voltage is more than |
|
Faulty ECM. |
|
|
|
18 volts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sensor signal circuit is open circuit, high |
|
P0118 |
Engine Coolant |
DTCs P1630 and P1634 are not |
The ECM detects that the ECT |
||
|
Temperature (ECT) |
set. |
sensor signal voltage is more than |
resistance, short to any 5V or 12V reference |
|
|
Sensor Circuit High |
The ignition switch is ON. |
4.8 volts for 5 seconds. |
circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit. |
|
|
Voltage |
The ignition voltage is more than |
|
Sensor low reference circuit is open circuit or |
|
|
|
18 volts. |
|
high resistance. |
|
|
|
The engine run time is longer than |
|
Poor harness connector connection. |
|
|
|
3 minutes. |
|
Faulty ECT Sensor. |
|
|
|
|
|
Faulty ECM. |
|
|
|
|
|
Engine overheat. |
|
P1173 |
Engine Overheat |
DTCs P0117, P0118, P1630 and |
The ECM detects that the ECT is |
||
|
|
P1634 are not set. |
more than 110°C (230°F) for 5 |
Faulty engine cooling system |
|
|
|
The ignition switch is ON. |
seconds. |
Faulty ECT sensor. |
|
|
|
The ignition voltage is more than |
|
|
|
|
|
18 volts. |
|
|
|
|
|
The engine is running. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-25
FUEL TEMPERATURE (FT) SENSOR
The fuel temperature (FT) sensor is installed to the supply pump. It is a variable resistor. The FT sensor measures the temperature of the fuel. The engine control module (ECM) supplies 5volts to the FT sensor signal circuit and a ground for the FT sensor low reference circuit. When the FT sensor is cold, the sensor resistance is high. When the air temperature increases, the sensor resistance decreases. With high sensor resistance, the ECM detects a high voltage on the FT sensor signal circuit. With lower sensor resistance, the ECM detects a lower voltage on the FT sensor signal circuit. The ECM uses to this value to calculate a fuel injection volume, injection timing and EGR control.
1. Fuel Temperature (FT) Sensor
2. Suction Control Valve (SCV)
|
|
FT Sensor Characteristic -Reference- |
|
|
Ohms |
|||
|
|
|
|
Volts |
||||
|
|
26000 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
24000 |
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
22000 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
20000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18000 |
|
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
(Ohms) |
|
16000 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
14000 |
|
|
|
|
2.5 |
||
|
12000 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Volts) |
||
Resistance |
|
10000 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
Output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
8000 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
|||
|
|
6000 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
4000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
||
|
|
2000 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
-30 |
-20 |
-10 |
0 |
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 |
80 |
90 |
100 110 |
|
|
|
|
|
Temperature (C) |
|
|
|
|
°C |
°F |
Ohms |
Volts |
110 |
230 |
140 |
0.2 |
100 |
212 |
180 |
0.3 |
90 |
194 |
240 |
0.4 |
80 |
176 |
310 |
0.5 |
70 |
158 |
420 |
0.6 |
60 |
140 |
580 |
0.9 |
50 |
122 |
810 |
1.1 |
40 |
104 |
1150 |
1.5 |
30 |
86 |
1660 |
1.8 |
20 |
68 |
2450 |
2.3 |
10 |
50 |
3700 |
2.8 |
0 |
32 |
5740 |
3.3 |
-10 |
14 |
9160 |
3.8 |
-20 |
-4 |
15000 |
4.2 |
-30 |
-22 |
25400 |
4.5 |
The characteristic of the FT sensor is displayed in the graph and table. Calculated coolant temperature can be found on the Tech 2 by unit “°C” or “°F “. The output voltage also can be found on the Tech 2.
Notice!
In data display “°C” or “°F” will be fixed to a default value when DTC is set relating to the FT sensor. To diagnose this DTC, observe the “Volts” in the data display.

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-26
FT Sensor
Connector Face
Related DTC
DTC |
DTC Name On Scan |
Condition for Running the DTC |
Condition for Setting the DTC |
Suspected Cause |
|
Tool |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Sensor signal circuit is short to ground or short to |
|
P0182 |
Fuel Temperature |
DTCs P1630 and P1634 are not |
The ECM detects that the FT |
||
|
Sensor Circuit Low |
set. |
sensor signal voltage is less than |
the low reference circuit. |
|
|
Voltage |
The ignition switch is ON. |
0.1 volts for 5 seconds. |
Faulty FT sensor. |
|
|
|
The ignition voltage is more than |
|
Faulty ECM. |
|
|
|
18 volts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sensor signal circuit is open circuit, high |
|
P0183 |
Fuel Temperature |
DTCs P1630 and P1634 are not |
The ECM detects that the FT |
||
|
Sensor Circuit High |
set. |
sensor signal voltage is more than |
resistance, short to any 5V or 12V reference |
|
|
Voltage |
The ignition switch is ON. |
4.8 votls for 5 seconds. |
circuit, short to battery or ignition voltage circuit. |
|
|
|
The ignition voltage is more than |
|
Sensor low reference circuit is open circuit or |
|
|
|
18 volts. |
|
high resistance. |
|
|
|
The engine run time is longer than |
|
Poor harness connector connection. |
|
|
|
3 minutes. |
|
Faulty FT Sensor. |
|
|
|
|
|
Faulty ECM. |
|
|
|
|
|
|

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-27
CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR & CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP) SENSOR
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is located on top of the flywheel housing. There are 56 notches spaced 6deg. apart and a 30deg. section that is uncut. This uncut portion allows for the detection of top dead center (TDC). The CKP sensor is a magnet coil type sensor, which generates an AC signal voltage based on the crankshaft rotational speed. If the CKP sensor fails, the camshaft position (CMP) sensor signals will substitute for the CKP sensor signal backup.
1. Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
2. Sensor Wheel

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-28
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor is installed on the cylinder head at the rear of the camshaft. The CMP sensor detects a total five through holes, four reference holes arranged equally every 90deg. space and one reference hole on the camshaft gear flange surface, and sends signals to the engine control module (ECM). Receiving these signals, the ECM determines cylinder #1 compression top dead center (TDC). If the CMP sensor fails, the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor signals will NOT substitute for the CMP sensor signal backup. Engine cranks but does not start.
1.Camshaft Gear
2.Gear Rotating Direction
3.Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor

N*R 4HK1-TC Engine-29
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No.1 TDC |
No.3 TDC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6deg.CA |
30deg.CA |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CH1
0V
CH2 |
30deg.CA |
90deg.CA |
No.1 TDC |
|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
0V |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90deg.CA |
|
|
90deg.CA |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The relationship of CKP sensor and CMP sensor is displayed on the above picture. The ECM detects 112 CKP sensor pulses (56 x 2) and 5 CMP sensor pulses per 2 crankshaft rotations (720 deg.CA). Both sensor wheels are mechanically bit with each other. Therefore, the relationship of each pulse is always constant. The injection timing suitable for the vehicle conditions is controlled based on the inputs from respective sensors.
 Loading...
Loading...