Page 1

hp driver
preconfiguration
Page 2

Page 3

hp preconfiguration
support guide
Page 4

(c) Copyright Hewlett-Packard Company,
2003
All Rights Reserved. Reproduction,
adaptation, or translation without prior written
permission is prohibited, except as allowed
under the copyright laws.
The information contained in this document
is subject to change without notice.
Edition 1, 03/2003
Trademark Credits
Microsoft (R) is a U.S. registered trademark
of Microsoft Corp.
Netscape (TM) is a U.S. trademark of
Netscape Communications Corporation.
Netscape Navigator (TM) is a U.S. trademark
of Netscape Communications Corporation.
PostScript (R) is a trademark of Adobe
Systems Incorporated.
Windows (R) and MS Windows (R) are U.S.
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corp.
Windows NT (R) is a U.S. registered
trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Hewlett-Packard Company
11311 Chinden Boulevard
Boise, Idaho 83714 U.S.A.
Page 5

Table of Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
HP driver preconfiguration overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Driver acquisition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Driver preconfiguration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
File format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Lockable features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Applying the configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Driver installation and deployment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Product/driver coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Environmental support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Direct installation - workstation/Windows print server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Windows Point and Print . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
True connect. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
False connect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Windows Point and Print configuration scenarios. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Novell Point and Print . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
HP Printer Server Appliance Point and Print . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Windows Terminal Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Windows Terminal Server (Citrix Metaframe Printer Auto-Create) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Windows Cluster Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
HP Driver Configuration Editor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Access/installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
HP Web JetAdmin Driver Configuration Plugin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Access/installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
HP Product Installation Software - Customization Utility/Silent Installer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 3
Page 6

4
HP Drive
r Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 7

List of Figures
Figure 1. Information dialog box .................................................................................................................. 17
Figure 2. Digital Signature Not Found dialog box ........................................................................................ 17
Figure 3. Device Settings tab ......................................................................................................................18
Figure 4. Printing Preferences tab ............................................................................................................... 19
Figure 5. Invalid Selection - duplexing for transparencies ........................................................................... 20
Figure 6. Driver selection .............................................................................................................................21
Figure 7. Configurable drivers .....................................................................................................................22
Figure 8. Driver Configuration - Select an Existing Configuration ...............................................................23
Figure 9. Driver Configuration - Device Settings ........................................................................................24
Figure 10. Driver Configuration - Printing Preferences ...............................................................................25
Figure 11. Invalid selection - duplexing for transparencies .........................................................................26
Figure 12. Driver configuration - Replace an Existing Configuration ...........................................................27
Figure 13. Driver configuration - Save as a New Configuration ..................................................................28
Figure 14. CD-ROM browser window ..........................................................................................................30
Figure 15. Choose Setup Language dialog box ..........................................................................................31
Figure 16. Option dialog box - Create Customized Installer ........................................................................ 31
Figure 17. Installer Type - Silent Installer ....................................................................................................32
Figure 18. Language and Operating System(s) dialog box .........................................................................32
Figure 19. Printer Model(s) dialog box ........................................................................................................33
Figure 20. Components dialog box ..............................................................................................................33
Figure 21. Port selection dialog box ............................................................................................................ 34
Figure 22. Driver Configuration dialog box .................................................................................................. 34
Figure 23. Configuration dialog box - Printing Preferences tab ................................................................... 35
Figure 24. Configuration dialog box - Device Settings tab ..........................................................................35
Figure 25. Invalid Selection dialog box ........................................................................................................36
Figure 26. Printer Name dialog box .............................................................................................................37
Figure 27. Destination Path dialog box ........................................................................................................37
Figure 28. Support Summary dialog box .....................................................................................................38
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 5
Page 8

HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide6
Page 9

List of Tables
Table 1. HP driver preconfiguration support ...........................................................................................................12
Table 2. Point and Print configuration scenarios ....................................................................................................14
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 7
Page 10

HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide8
Page 11

Introduction
This HP Driver Pr econfiguration Support Guide describes HP driver preconfiguration, the tools to
use it, and the printing environments in which it can be used. Three distinct tools for using HP
Driver Configuration are described in detail:
● HP Driver Configuration Editor
● HP Web JetAdmin Driver Configuration Plugin
● HP Customization Utility/Silent Installer
HP driver preconfiguration is a software architecture and set of tools that information technology
(IT) administrators in corporate and enterprise environments can use to preconfigure the printing
and device defaults for HP printer drivers before installing the drivers in the network environment.
For example, a company has purchased several HP Color LaserJet printers that are to be shared
among several workgroups. To keep printing costs to a minimum, management wants all of the
print queues to print on both sides of the paper (duplex) by default. To save costs further, they
want to restrict the ability of certain groups to print in color, thereby minimizing toner
consumption. Several different printer servers are in use, each of which has one or more queues
to the new devices. Some users can print directly to the new printers over the network, but IT
wants to apply the same driver configuration to those print queues.
In the past, the printers in such a case would have to be installed on each print server and then
manually configured for the required settings. The printers would also have to be manually
configured in accordance with the required specifications on each direct-print workstation. By
taking advantage of HP’s preconfiguration technology, however, this process can be greatly
simplified. The following examples show how the various tools can be used to support different
corporate environments:
● If the company uses HP Web JetAdmin, its queue management capability can be used to
preconfigure and create the queue on each specific Windows printer server in one step.
Furthermore, the configuration can be saved and used for later deployments of the same
product (regardless of which specific driver will be used for that product). Each print server
can then vend properly configured drivers to all Windows clients. HP Web JetAdmin can also
be installed directly on workstations.
● If the company has an internally developed printer and driver deployment process, HP driver
preconfiguration can be used to define the proper driver settings before the driver enters that
process. After the driver is configured, every subsequent deployment of the driver is installed
with the same settings.
● If the company uses Novell or the HP Printer Server Appliance, HP driver preconfiguration
can be used before drivers are loaded to the servers, thereby ensuring that clients are using
properly configured drivers when they connect to the shared print queues.
● If the company wants a silent executable file that users can run to create printers on their
workstations, the HP Installer Customization Utility can be used to create a silent, executable
package that contains preconfigured drivers.
● If the company has Windows print servers or workstations, then any of the three tools can be
used to preconfigure the drivers that are installed. Both Web JetAdmin and the HP Installer
handle both the configuration and the installation of the printers. The HP Driver
Configuration Editor only modifies the driver so that it reflects the specified settings when it is
installed (through any method).
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 9
Page 12

HP driver preconfiguration overview
Network administrators can use the HP driver preconfiguration solution to preconfigure a printer
driver before deploying and installing it in an operating environment. It is most beneficial when
configuring printer drivers for multiple workstations or print servers for print queues that share the
same configuration. Two classes of features can be configured: printer accessories and driver
feature settings. The driver is configured to match the printer hardware so that access to all of
the printer accessories through the driver is enabled appropriately (for example, for duplexing
units and additional input trays and output bins). Most driver feature settings can also be
configured.
Basically, the preconfiguration process consists of three steps:
● driver acquisition
● driver preconfiguration
● driver installation and deployment
The steps can be accomplished in different ways, depending on the tool that is being used to
define the configuration.
Driver acquisition
Software acquisition takes place in one of several ways:
● by getting drivers-only from the CD-ROM that came with the printer
● by downloading drivers from the HP Web site
● by using drivers that are already in the organization (for example, using a driver that has
already been certified by internal testing procedures for use within the organization)
Driver preconfiguration
The process of configuring drivers and other software occurs in advance of installation. This
allows the driver to be configured once and installed on any number of server or client systems.
File format
The driver configuration information is stored in a small configuration file that is separate from the
‘standard’ driver files (dynamic link libraries [DLLs] that are used to render and present a user
interface [UI]). Although it is maintained as a separate file, the driver configuration information is
included in the driver package and referenced in the driver .INF file. The configuration process
involves reading the default information from this file and allowing an administrator to select new
default settings for existing features. The file is then saved and used when the associated driver
is installed.
The configuration file is a text file, but the text is in XML format. The file contains a list of features
and their available options on a product-specific basis. The file structure is quite specific, and
one purpose of HP driver preconfiguration is to maintain the specific structure. HP driver
preconfiguration maintains consistency in the configuration file through dynamic constraint
checking. Before setting a value, the utility determines whether the proposed setting is valid
within the pre-established constraints that were placed upon the device at the factory. The utility
also ensures consistency by preserving the correct structure of the configuration file. This
structure is assumed by the device that uses the configuration information, and must therefore
be strictly maintained.
10 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 13

The configuration file has an extension of .CFG. It is typically compressed in the driver package
that is supplied with the driver, so it is not generally editable except with a tool specifically suited
to the task (see the following “Tools” section for a description of the editing options that HP
provides). When one of the HP tools is used to preconfigure driver settings, the contents of the
.CFG file are modified to reflect the settings, which become the default settings for any printer
that uses the preconfigured driver.
Lockable features
Although the developers of each individual product define the feature set that is configurable, the
general rule is that all driver features are supported. This means that both the device settings
(such as Optional Paper Sources and Duplex Unit) and the printing preferences (such as
default Paper Source and default Output Bin) are customizable in advance of installation. In
addition, a number of features can be locked to a particular state if an IT administrator wants
greater control over the way compatible devices are used. These are the ‘lockable’ settings:
● Print on Both Sides (Duplex)
● Print in Grayscale
● Media Type
● Paper Source
● Output Bin
Constraints
To ensure that an invalid configuration is not applied to the driver when it is installed, the .CFG
file defines the valid relationships between specific settings included in the file. For example, the
.CFG file prohibits having the media type set to Transparency when Print on Both Sides is
selected. The prohibition ensures that when the driver is finally installed, it can successfully
integrate the settings into its internal settings format.
Applying the configuration
When a preconfigured driver is installed, the modified .CFG file is accessed and the settings are
applied to the driver's own internal settings format. When installation is complete, the printer's
default settings reflect the settings selected in the CFG file. From this point forward, the printer
and driver behave like any printer, in terms of settings management. Users can modify the
printer's settings through the Printers folder and modify jobs within applications. By simply
creating two differently configured driver packages and installing them in turn, administrators can
install multiple printers using differently configured instances of the same driver.
Driver installation and deployment
The process of deploying and installing printer software varies widely across organizations.
While some companies have tightly controlled server and client software configurations, others
have a highly informal distribution network of software that is under no centralized controlling IT
body. For HP driver preconfiguration to be usable within a wide range of these computing
environments, it must be compatible with the standard deployment and installation methods that
are used by corporate and enterprise customers. In a practical sense, this means that the
preconfiguration must be compatible with any installation process that uses the system
application program interfaces (APIs) defined by Microsoft to install drivers and printers.
Product/driver coverage
Because driver preconfiguration is a new feature for HP printers, it is available for new mid-range
and high-end HP LaserJet products, and for some HP Business InkJet products, beginning with
the fall 2002 product introductions.
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 11
Page 14
This includes the following printers:
● HP LaserJet 4200
● HP LaserJet 4300
● HP LaserJet 5500
● HP Business InkJet 2280
● HP Business InkJet 3000
In addition, drivers for several HP LaserJet products that are currently being shipped have been
updated to include support for preconfiguration. This includes the following printers:
● HP LaserJet 4100
● HP LaserJet 4600
● HP LaserJet 8150
● HP LaserJet 9000
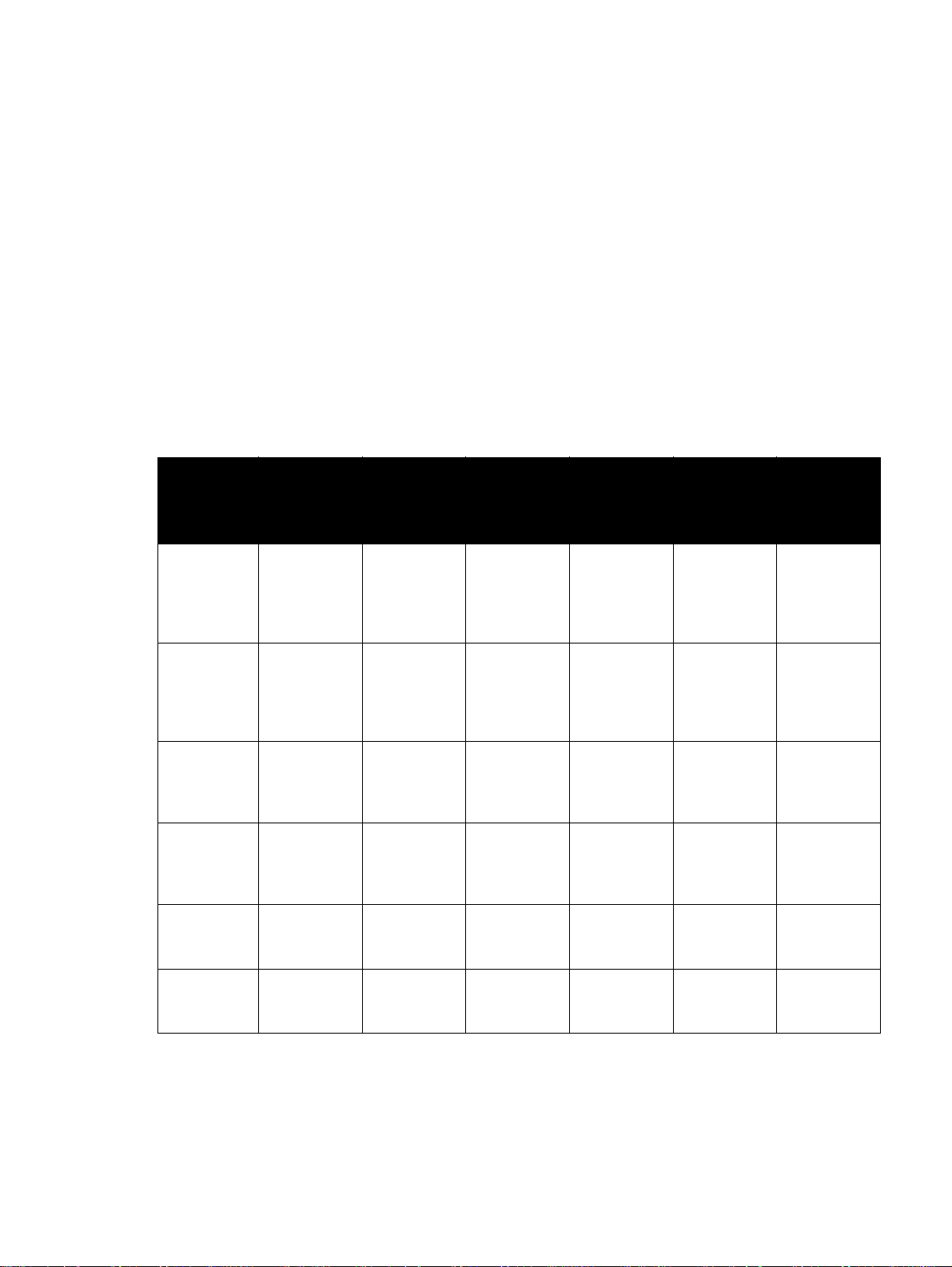
For the products that are supported, the following table shows drivers and operating systems that
support HP preconfiguration.
Table 1 HP driver preconfiguration support
Driver Windows
95 (TM)
HP
traditional
PCL 5c/e
driver
HP
traditional
PCL 6
driver
HP
traditional
PS driver
HP PCL
5c/e
unidriver
HP PCL 6
unidriver
Ye s Ye s Ye s Ye s Ye s N/A
Ye s Ye s Ye s Ye s Ye s N/A
No No No No N/A N/A
N/A N/A N/A N/A Ye s Ye s
N/A N/A N/A N/A Ye s Ye s
Windows 98Windows MeWindows
NT 4.0
(TM)
Windows
2000
Windows
XP
HP PS
unidriver
N/A: Not applicable; the driver is not supported in this operating system.
N/A N/A N/A N/A Ye s Ye s
12 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 15

Environmental support
Hewlett-Packard has gone to great lengths to ensure that driver configuration supports the most
common corporate and enterprise printing environments. This document provides detailed
information about specific workflow requirements for these environments, as well as limitations
that they might impose on the preconfiguration solution.
The descriptions that follow assume that the drivers to be used have been preconfigured before
they are installed. For Windows servers, some of the preconfiguration tools can handle the
preconfiguration and installation steps at the same time. For all other server platforms, the driver
must be preconfigured with the standalone version of the HP driver preconfiguration software,
the HP Driver Configuration Editor, and then installed by using the server installation method.
Direct installation - workstation/Windows print server
Direct installation is the common method that is used when a printer is being created on either a
Windows workstation or print server by using almost any installation method (such as Add
Printer Wizard, HP Installer, HP Web JetAdmin, and other "homegrown" installation
applications). As long as the driver for the printer being installed has been preconfigured by
using one of the tools described in this document, and the installation method follows the
standard Microsoft process for printer creation, the printer will reflect the defined settings when
installation is complete.
Windows Point and Print
The term "true connect" refers to any Windows Point and Print environment in which the server
and connecting clients share printer setting information. Whenever the server is Windows
NT 4.0, Windows 2000, or Windows XP, and the clients are Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, or
Windows XP, settings are shared.
The term "false connect" refers to Windows Point and Print environments in which the server and
connecting clients do not share printer setting information. Windows 95, Windows 98, and
Windows Me clients connecting to any Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, or Windows XP server
operate in this mode.
True connect
In true-connect environments, when the preconfigured server-side driver is installed, the settings
are stored so that all connecting clients receive them when they connect. The only limitation to
this behavior is for Windows NT 4.0-to-Windows NT 4.0 connections, where Point and Print does
not provide the Printing Preferences settings to connecting clients. Otherwise, all server-side
settings are vended to the clients.
False connect
In false-connect environments, the client receives no printer configuration information from the
server, aside from the port through which to print. When both the server-side and client-side
drivers support preconfiguration, the client driver calls back to the server and asks for the
preconfigured settings of the server-side driver for the shared printer. Only Windows 95,
Windows 98, and Windows Me drivers have this ability to ask the server directly for configuration
information, and it is used only in false-connect Point and Print scenarios.
If the client is unable to communicate with the server, then the configuration that was defined as
part of the vended Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows Me driver is used instead.
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 13
Page 16

Windows Point and Print configuration scenarios
The following table shows various server-client configuration scenarios for true-connect and
false-connect Windows Point and Print environments.
Table 2 Point and Print configuration scenarios
Server Client Configure
Printer
Properties
Windows
NT 4.0
Windows 2000 Windows 95,
Windows 95,
98, and Me
Windows
NT 4.0
Windows 2000 Yes No
98, and Me
Windows
NT 4.0
Windows 2000 Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Yes No
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Configure
Printing
Preferences
Windows XP Yes Yes
WinXP Windows 95,
98, and Me
Windows
NT 4.0
Windows 2000 Yes Yes
Windows XP Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Novell Point and Print
There are three main categories for preconfiguration in Novell environments:
● NetWare Directory Services (NDS)
● ZenWorks
● Novell Distributed Print Services (NDPS)
14 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 17

In the case of NDS and ZenWorks, at most one preconfiguration definition is available per
product (that is, one preconfiguration definition for each HP printer model). This is because
Novell stores all printer drivers to be vended in the same physical directory on the server. Driver
preconfiguration uses the same file name for all drivers for a given product to store the
configuration information, thus making the file both portable and consistent across all drivers for
a particular product. For this reason, only one configuration can be stored at a time.
In the case of NDPS printer objects, multiple instances of the same driver can be stored on the
server, each with its own preconfiguration data. These resources can then be associated with the
desired NDPS print queues and vended to printing clients accordingly. If a need exists to have
multiple configurations for the same driver model (for instance, the HP LaserJet 4200 PCL6
driver for Windows 2000) on the server, the Novell Resource Manager allows each new instance
of the driver to be used with a different name. See Novell documentation for step-by-step
instructions for adding drivers in this manner.
Regardless of the queue type, all Windows client platforms are supported in terms of using the
configurations that are defined on the server.
HP Printer Server Appliance Point and Print
The HP Print Server Appliance (PSA) supports preconfigured drivers to a limited degree. The
PSA is restricted to cases in which a single instance of a driver and its associated setting
information are on the server at any given point in time, which means that only a single
preconfiguration can be stored for each driver.
Windows Terminal Server
Driver preconfiguration is supported in the Windows Terminal Server environment for both the
Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 versions of the product. When a preconfigured driver is
installed on the server, all terminal clients receive that configuration when they connect to the
server. The only limitation in this scenario is that as printers are being added, the server
administrator must be working on the server directly, not working from a terminal session. This
limitation is related to the Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) infrastructure in the
Terminal Server environment.
Windows Terminal Server (Citrix Metaframe Printer Auto-Create)
Citrix Metaframe provides a feature whereby the workstation on which the terminal clients for a
server are running can install a local printer and gain access to the printer within the context of a
terminal session. This allows terminal users to print to locally defined printers even when they
are working from within a terminal session. The feature is called Printer Auto-Create because the
Citrix environment creates a server side printer for the printers that are dynamically installed on
the terminal workstation (that is, when the user logs on to the server during a terminal session).
The client workstation and server must both have the same driver installed for the client-side
printer.
If the driver installed on the client workstation is preconfigured, then the preconfigured settings
will be applied to the server-side printer when the terminal session is started.
Note This functionality is available only on Metaframe 1.8 and later versions that run in a Windows 2000
Terminal Server environment.
Windows Cluster Server
Driver preconfiguration is not supported in Windows Cluster Server environment.
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 15
Page 18

Tools
The configuration process for driver preconfiguration is supported through three distinct tools. All
three are designed with the same basic UI controls for interacting with the .CFG file, but are
packaged differently, either to support established printer installation workflows or to leave the
deployment and installation of the driver entirely up to the user. These tools are:
● the HP Driver Configuration Editor, a standalone tool for Windows operating system
environments
● the HP Web JetAdmin Driver Configuration Plugin, a Web-based tool
● the HP Customization Utility/Silent Installer
Note It is strongly recommended that .CFG files be modified only with the editing tools that are provided.
Manual editing of the XML can result in both invalid XML and incompatible settings within the file.
HP Driver Configuration Editor
Description
The HP Driver Configuration Editor is a small Windows application that the user can use to open
the .CFG file associated with a particular driver and make modifications that are applied when
that driver is installed on the target computer. It is used in the way that any ordinary Windows
application is used.
This tool does not handle any part of the deployment or installation of the driver. Rather, the
.CFG file is modified and saved back to the same driver directory in which it was opened. It is
intended for use in environments where there is an established process for deploying drivers or
where the server platform is not Windows-based. To support any Novell or PSA Point and Print
environments, this is the preconfiguration tool of choice.
Access/installation
The HP Driver Configuration Editor can be downloaded from hp.com at the following URL:
http://www.hp.com
After it has been downloaded, the compressed package can be expanded into a local or network
directory. No formal installation process is required; as soon as the package has been
expanded, it is ready to be run. The application can be run by double-clicking HPBCFGAP.EXE
in the destination directory.
This application shares functional features and user interface with the Customization Utility and
Web-based versions of the HP driver preconfiguration.
Procedure
In order to use the HP Driver Configuration Editor, the driver(s) to be configured must be in their
standard .INF-file driver packages that are obtained from HP (either from the HP Web site or
from the product in-box CD-ROM). The driver(s) must be stored in a location for which the user
of the tool has write-access. The driver must also support driver preconfiguration. If the tool is
used to browse to a driver directory and there is no .CFG file, the driver cannot be preconfigured.
1 Run HPBCFGAP.EXE from the download directory
To run the HP Driver Configuration Editor, double-click HPBCFGAP.EXE.
16 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 19

2 The Information dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Information dialog box
This dialog box warns users that, depending on how the driver is installed, a Windows
Hardware Quality Labs (WHQL) Digital Signature Warning will appear.
Because the .CFG file that is shipped with the drivers is part of the .INF-file package (and
referenced in the .INF file as a dependent file of the driver), modifying this file invalidates the
digital signature that Microsoft provides when the driver is WHQL-certified.
Figure 2 shows the Microsoft warning dialog that appears at install time.
Figure 2 Digital Signature Not Found dialog box
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 17
Page 20

This dialog appears only in Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows 2003 Server, and
only when drivers are being installed directly on the machine (not when they are being
installed as a Point and Print client).
3 Modify the configuration to meet your requirements.
The UI consists of two tabs: Device Settings and Printing Preferences.
Device Settings tab
The settings in the Device Settings tab, illustrated in Figure 3, are related to the installed
hardware on the device. Certain features on the Printing Preferences tab rely on the
installation of various hardware accessories in order to be used.
Bundle Selection
The Bundle Selection field lists the various hardware bundles available for the product
and, when changed, modifies the individual settings to reflect the bundle contents.
Figure 3 Device Settings tab
18 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 21

Printing Preferences tab
Settings in the Printing Preferences tab, illustrated in Figure 4, are related to the actual
formatting of documents as they are printed. By modifying the feature settings, the default
behavior of the driver is altered. For example, if Media Type is changed to Letterhead, then
every job printed will default to being printed on Letterhead paper. The user can modify this
setting both on a per-document and a per-printer basis.
Figure 4 Printing Preferences tab
Feature locking
HP driver preconfiguration supports the ability to lock five settings:
• Print on Both Sides (Duplex)
• Print in Grayscale
• Media Type
• Paper Source
• Output Bin
When a feature is locked, the selected default option is the only option that is available to users.
Generally, the feature is simply disabled in the driver UI after it has been installed. In the
preceding figure (Figure 4), the Print on Both Sides (Duplex) setting has been locked to True.
A small icon showing a padlock appears next to the setting in the UI. As a result, the user is
unable to print from this driver on only one side of the page. If the driver is installed on a server,
clients connecting to that printer are also unable to print on only one side of the page.
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 19
Page 22

Constraints
The .CFG file is encoded with all of the same constraints that the drivers enforce. As a result,
if the user of the HP Driver Configuration Editor attempts to set features to an invalid
combination, a warning dialog box appears, and the feature change that triggered the
warning is returned to its original state. For example, if the Media Type option is set to
Transparency when Print on Both Sides (Duplex) is set to True, an Invalid Selection
dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Invalid Selection - duplexing for transparencies
4 Save the file back to the driver directory.
Note The file should be saved back to the same driver directory in which it was opened.
Once the file is saved, the driver package is ready to be installed with the new settings.
5 Install the driver and create a printer using any preferred method.
Driver preconfiguration is compatible with any installation method that relies on the
published Microsoft procedures for installing a printer. See the Microsoft Developer Network
documentation for details about the published methods. All commercially available
installation methods, including driver vending from Novell and Samba servers, adhere to
these guidelines. For more information, see the Microsoft Developer Network Web site:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/default.asp
6 Exit the HP Driver Configuration Editor.
7 Install the driver on a server or workstation.
At this point the driver can be installed on a Windows workstation, or a Point and Print server
(Windows, Novell, or HP Printer Server Appliance). All queues that use the driver default to
the settings that were selected within the configuration editor, and any features that were set
to Locked are locked for all users, regardless of how they gain access to the driver (whether
through the server or the client).
HP Web JetAdmin Driver Configuration Plugin
Description
HP Web JetAdmin provides a queue creation application that can be used to create printers on
any Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, or Windows XP server or workstation. The HP Web
JetAdmin Driver Configuration Plugin adds a number of screens to the existing queue creation
workflow from which the drivers that are being installed for the queues can be customized as part
of the process.
IT administrators can also use the plugin to manage the configurations that are created for
specific queues by allowing them to be saved (with a name) and used in subsequent
installations.
20 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 23

The HP Driver Configuration Plugin uses ActiveX to deliver some of its functionality (in a fully
signed and certified ActiveX control). This requires that the client browser security be set to
accept third-party ActiveX content.
The plugin is also limited to Internet Explorer browsers. Netscape Navigator (TM) is not
supported.
Access/installation
The HP Driver Configuration plugin is available as part of the WJA Product Update -> Install
wizard dialog. After you select the HP Driver Configuration Plugin and select the installation
command, Web JetAdmin continues automatically.
To use the plugin, you must follow the Web JetAdmin queue-creation workflow and install a driver
that can be preconfigured.
Procedure
1 Open Web JetAdmin Queue Creation.
Follow the Web JetAdmin queue-creation workflow through the driver selection pages (see
Figure 6). When driver selection is complete, use the Skip button to continue. If more than
one driver is selected and all the drivers support preconfiguration, they will all be configured
in the same way through the following process.
Figure 6 Driver selection
At this point, the Driver Configuration Plugin examines the selected drivers to determine
whether they can be preconfigured. If they cannot, then the Web JetAdmin queue creation
workflow continues as if the Driver Configuration Plugin were not installed.
Driver Configuration - configuration options
If the drivers can be preconfigured, then the Driver Configuration Plugin is launched. The
first page (shown in Figure 7) lists the selected drivers that are configurable. The user can
then decide whether to preconfigure the drivers.
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 21
Page 24

Figure 7 Configurable drivers
2 Make the configuration selection.
This page lists the selected drivers that support preconfiguration. Depending on the drivers
that are selected for installation, some might not support preconfiguration (specifically,
Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows Me PostScript [PS] drivers).
The user is offered either two or three configuration options. If the Driver Configuration
Plugin has been used for the same product previously, and the configuration that was
created as part of that workflow was saved, then the user will have the following options:
• Yes - Create a New Configuration
• Yes - Use an Existing Configuration (this option appears only if a configuration has
been saved previously)
• No - Continue Creating Print Queue (select this option to skip driver configuration)
3 If existing configurations are available for the product that is being installed and the user
selects the Use an Existing Configuration setting, the dialog box shown in Figure 8
appears.
When the user selects an existing configuration, the appropriate configuration file is loaded
into the Configuration Editor pages (as shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10), just as a new
configuration would be. This allows changes to be made to that configuration, but does not
require them.
22 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 25

When the existing configuration has been selected, the configuration page appears, and the
remainder of the flow is the same as when a new configuration is being created.
Figure 8 Driver Configuration - Select an Existing Configuration
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 23
Page 26

4 If the user selects Yes - Create a New Configuration, the Driver Configuration dialog box
appears.
The onscreen user interface consists of two separate tabs: Device Settings (see Figure 9)
and Printing Preferences (see Figure 10).
Figure 9 Driver Configuration - Device Settings
24 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 27

Settings on the Device Settings tab are related to the installed hardware on the device.
Certain features on the Printing Preferences tab rely on various hardware accessories that
must be installed in order to be used.
Figure 10 Driver Configuration - Printing Preferences
Settings on the Printing Preferences tab are related to the actual formatting of documents
as they are printed. By modifying the feature settings the default behavior of the driver will be
altered. For example, if the Media Type setting is changed to Letterhead, then every job
printed will default to being printed on Letterhead paper. The user can modify this setting
both on a per-document or per-printer basis.
Feature locking
HP driver preconfiguration supports the ability to lock five settings:
• Print on Both Sides (Duplex)
• Print in Grayscale
• Media Type
• Paper Source
• Output Bin
When a feature is locked, the selected default option is the only option that is available to
users. Generally, the feature is simply disabled in the driver UI after it has been installed. In
Driver Configuration - Printing Preferences, for example, the Print on Both Sides (Duplex)
setting has been locked to True. A small icon showing a padlock appears next to the setting
in the UI. As a result, the user is unable to print from this driver on only one side of the page.
If the driver is installed on a server, clients connecting to that printer are also unable to print
on only one side of the page.
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 25
Page 28

Constraints
The .CFG file is encoded with all of the same constraints that the drivers enforce. As a result,
if the user of the HP Driver Configuration Editor attempts to set features to an invalid
combination, a warning dialog box appears, and the feature change that triggered the
warning is returned to its original state. For example, if the Media Type option is set to
Transparency when Print on Both Sides (Duplex) is set to True, an Invalid Selection
dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 11.
Figure 11 Invalid selection - duplexing for transparencies
5 Save the configuration.
Customers often have a set of standard configurations that are used for a given product. The
Driver Configuration plugin allows these configurations to be saved within Web JetAdmin for
future use.
Configurations are saved on a product-by-product basis. Therefore, a saved configuration
for an HP Color LaserJet 5500, for example, is available only when the queue creation is
installing a driver for the HP Color LaserJet 5500.
Each configuration is saved with a unique name. If an existing name is reused, the old
configuration is replaced.
26 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 29

Figure 12 shows the dialog box that appears when a configuration has been saved
previously. If there are no existing saved configurations, then the Replace an Existing
Configuration option does not appear, and the dialog box shown in Figure 13 appears.
Figure 12 Driver configuration - Replace an Existing Configuration
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 27
Page 30

Figure 13 Driver configuration - Save as a New Configuration
6 Complete queue creation.
After the configuration has been modified, clicking the Next button sends Web JetAdmin to
the summary screen for the queue(s) to be created. From this point, the standard Web
JetAdmin queue creation workflow continues in the same manner as when driver
preconfiguration is not present. For detailed information about the queue creation process,
see Web JetAdmin documentation at the following Web site:
hp.com/go/webjetadmin
HP Product Installation Software - Customization Utility/Silent
Installer
The Customization Utility features an install-time mode of HP driver preconfiguration. IT
administrators can use the utility to preconfigure the drivers for a printing system software driver
installation with the silent installer.
Description
You can use the HP LaserJet printing system software to create a silent installer that runs the
SETUP.EXE program without user interaction. This installation method is useful when you want
to use the default selections that the installer provides or when you want to run the installation
without being prompted. You also have the option of creating a custom disk image that contains
specific drivers and utilities, which allows users to run the installer without further interaction.
28 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 31

Installation
Silent installation can be performed in one of two ways:
● customized silent installer
● command-line silent installer
Customized silent installer
Use the customized silent installer to select the printing-system components to include in the
silent installation. You can select the operating system, language, printer models, drivers,
utilities, and documentation to install.
Command-line silent install
Command-line silent installation cannot be customized. It installs only the printing-system
components that are included in the Typical Installation.
Values that follow equal signs ( = ) in a command line must not contain intervening spaces.
Method 1: Command line
Type the following at the command line (do not type the beginning and ending quotation marks):
"<CD-ROM-ROOT>/SETUP/SETUP.EXE /U /PORT=XXXX /PRINTER=N /PD=N"
Method 2: SETUP.LST
Use the SETUP.LST file to specify command-line arguments to the installer for an unattended
installation. You can send command-line arguments in one of the following ways:
● Send the command directly to the installer.
● Send the command using the SETUP.LST file that is located in the setup directory.
● Use a combination of the two methods.
For example, this file contains two options: /port and /printer. The installer operates as normal
because the /u option has not been specified. If you use setup /u for the installer, it operates in
unattended mode and uses the two values that are specified in the defaults section of the
SETUP.LST file. If you use setup /u /printer=4 for the HP Color LaserJet 5500 installer, for
example, it operates in unattended mode and selects the HP LaserJet 5500hdn. The options
specified on the command line override the options specified in the SETUP.LST file.
The options available can also include the /u option. Using this option key makes the installer
always operate as unattended. The following descriptions explain the available options:
● /u signals the installer to use the specified port and printer that are identified in the command
line (or in this file), and to use all default selections. Installation then proceeds without
prompting the user.
● /port=xxxx is used to specify the default port when performing an unattended installation.
The value specified by xxxx should be a valid port and should contain no spaces (for
example, LPT1).
● /printer=n is used to specify the default printer when performing an unattended installation.
The value specified by n is an integer that references the list of available printers. For
example, the following printers are available for the HP Color LaserJet 5500 series printer
installation:
• 0 = HP LaserJet 5500 printer
• 1 = HP LaserJet 5500dn printer
• 2 = HP LaserJet 5500dtn printer
• 3 = HP LaserJet 5500 printer
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 29
Page 32

• 4 = HP LaserJet 5500hdn printer
• 5 = HP LaserJet 5500n printer
● /pd=n is used to specify whether the selected printer is the default printer when you have
multiple printers connected to your network. The value specified by n is an integer (that is, 0
or 1). For this argument, using 1 (one) sets the selected printer as the default printer. Using
zero (0) or not specifying a value at all sets the printer as a non-default printer.
You can preset these options in the SETUP.LST file that is located in the root directory of the
HP LaserJet software CD-ROM. In the defaults section, add the following syntax:
[Defaults]
Options= /port=<value> /printer=<number> /pd=<number>
For example, <value> = LPT1,
Procedure
To enable HP preconfiguration, follow these steps during installation:
1 In the software CD-ROM browser screen, click Customization Utility.
Figure 14 CD-ROM browser window
30 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 33

2 In the Choose Setup Language dialog box, select the language of your choice, and then
click OK.
Figure 15 Choose Setup Language dialog box
3 In the Option dialog box, click the Create Customized Installer option button, and then
click Next.
Figure 16 Option dialog box - Create Customized Installer
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 31
Page 34

4 In the Installer Type dialog box, click Silent Installer.
Figure 17 Installer Type - Silent Installer
5 In the Language and Operating System(s) dialog box, select the language and operating
systems of your choice, and then click Next.
Figure 18 Language and Operating System(s) dialog box
32 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 35

6 In the Printer Model(s) dialog box, select the printer model(s) to include, and then click
Next.
Figure 19 Printer Model(s) dialog box
7 In the Components dialog box, select the components that you want to install, and then click
Next.
Figure 20 Components dialog box
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 33
Page 36

8 In the Port dialog box, select the printer port, and then click Next.
Figure 21 Port selection dialog box
9 In the Driver Configuration dialog box, select the Yes, allow me to configure the drivers
option button, and then click Next to proceed with the installation.
Figure 22 Driver Configuration dialog box
34 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 37

10 In the Configuration dialog box, click the Printing Preferences tab. Scroll through the list
and select the settings that you want.
Figure 23 Configuration dialog box - Printing Preferences tab
11 Click the Device Settings tab. Scroll through the list and select the features that you want.
When you are finished, click Next.
Figure 24 Configuration dialog box - Device Settings tab
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 35
Page 38

Feature locking
HP driver preconfiguration supports the ability to lock five settings:
• Print on Both Sides (Duplex)
• Print in Grayscale
• Media Type
• Paper Source
•Output Bin
When a feature is locked, the selected default option is the only option that is available to
users. Generally, the feature is simply disabled in the driver UI after it has been installed. In
Driver Configuration - Printing Preferences, for example, the Print on Both Sides (Duplex)
setting has been locked to True. A small icon showing a padlock appears next to the setting
in the UI. As a result, the user is unable to print from this driver on only one side of the page.
If the driver is installed on a server, clients connecting to that printer are also unable to print
on only one side of the page.
Constraints
The .CFG file is encoded with all of the same constraints that the drivers enforce. As a result,
if the user attempts to set features to an invalid combination, a warning dialog box appears,
and the feature change that triggered the warning is returned to its original state. For
example, if the Media Type option is set to Transparency when Print on Both Sides
(Duplex) is set to True, an Invalid Selection dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 25 Invalid Selection dialog box
36 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 39

12 In the Printer Name dialog box, type a printer name (or use the default name), and then click
Next.
Figure 26 Printer Name dialog box
13 In the Destination Path dialog box, select a destination path (or use the default path), and
then click Next.
Figure 27 Destination Path dialog box
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 37
Page 40

14 Review the information in the Support Summary dialog box. If the information is incorrect,
click the Back buttons until you reach the screen where you can select the options you want,
and then continue with the installation sequence. If the information is correct, click Next.
Note The information varies, depending on the language, your operating system, and the features that
you selected.
Figure 28 Support Summary dialog box
The software creates a custom installation file. Note the location of the file.
15 Click Finish.
The installation file is now available to install using the silent installer. To install the driver,
navigate to the directory where the installation file is located, click SETUP.EXE, and proceed
with the installation.
38 HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide
Page 41

Index
Symbols
.CFG files 10, 16
.INF files 10
A
accessories, preconfiguration 10
acquisition, driver 10
ActiveX support 21
Auto-Create feature 15
B
bins, locking
features supported 11
with Customization Utility 36
with HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
with HP Web JetAdmin 25
browsers supported 21
Bundle Selection, HP Driver Configuration Editor 18
C
CFG files 10, 16
Citrix Metaframe environment 15
Cluster Server, not supported 15
command-line silent installation 29
constraints
Customization Utility 36
defined 11
HP Driver Configuration Editor 20
HP Web JetAdmin 26
Customization Utility
command-line installation 29
constraints, invalid configuration 36
Device Settings 35
features 28
locking features 36
Printing Preferences 35
setting up 30
D
default settings 19
deployment, driver 11, 13
Device Settings
Customization Utility 35
HP Driver Configuration Editor 18
HP Web JetAdmin 24
digital signature warning messages 17
direct installation environments 13
DLLs (dynamic link libraries) 10
downloading
drivers 10
HP Driver Configuration Editor 16
driver preconfiguration
CFG files 10, 16
defined 9
direct installation environments 13
environments supported 13
HP Print Server Appliance (PSA) 15
INF files 10
Novell environments 14
supported printers and drivers 11
tools 16
Windows Point and Print environments 13
Windows Terminal Server environments 15
drivers
acquisition 10
installation 11, 13
supported 11
duplex, locking
Customization Utility 36
features supported 11
HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
HP Web JetAdmin 25
dynamic link libraries (DLLs) 10
E
editing tools 16
environments supported 13
error messages, WHQL Digital Signature 17
F
false-connect environments 13
files, preconfiguration
about 11
editing 16
G
grayscale printing, locking
Customization Utility 36
features supported 11
HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
HP Web JetAdmin 25
H
HP Driver Configuration Editor
Device Settings 18
installation 16, 20
invalid configuration constraints 20
locking features 19
Printing Preferences 19
HP Print Server Appliance (PSA)
environments supported 15
tools, recommended 16
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 39
Page 42

HP Web JetAdmin
Device Settings 24
driver configuration 21
Driver Configuration Plugin features 20
installation 21
invalid configuration constraints 26
locking features 25
preconfiguration features 9
Printing Preferences 25, 27
queue-creation 21, 28
saving configurations 26
Web site 28
HP Web site 16
I
INF files 10
installation
Customization Utility 29
driver 11, 13
HP Driver Configuration Editor 16, 20
HP Web JetAdmin Driver Configuration Plugin 21
Internet Explorer support 21
invalid configurations
Customization Utility 36
defined 11
HP Driver Configuration Editor 20
HP Web JetAdmin 26
J
JetAdmin
Device Settings 24
driver configuration 21
Driver Configuration Plugin features 20
installation 21
invalid configuration constraints 26
locking features 25
preconfiguration features 9
Printing Preferences 25, 27
queue-creation 21, 28
saving configurations 26
Web site 28
L
locking features
defined 11
with Customization Utility 36
with HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
with HP Web JetAdmin 25
M
Media Type, locking
Customization Utility 36
features supported 11
HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
HP Web JetAdmin 25
messages, WHQL Digital Signature 17
Metaframe environment 15
Microsoft Developer Network Web site 20
Microsoft warning messages 17
N
NDPS (Novell Distributed Print Services) 14
NDS (NetWare Directory Services) 14
Netscape, not supported 21
Novell environments
supported 14
tools, recommended 16
O
operating systems supported 12
Output Bin, locking
Customization Utility 36
features supported 11
HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
HP Web JetAdmin 25
P
Paper Source, locking
Customization Utility 36
features supported 11
HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
HP Web JetAdmin 25
PCL drivers, supported 12
platforms supported 12
Point and Print environments
HP Printer Server Appliance (PSA) 15
Novell 14
tools, recommended 16
Windows 13
preconfiguration
CFG files 10, 16
defined 9
direct installation environments 13
environments supported 13
HP Print Server Appliance (PSA) 15
INF files 10
Novell environments 14
supported printers and drivers 11
tools 16
Windows Point and Print environments 13
Windows Terminal Server environments 15
Print in Grayscale, locking
Customization Utility 36
features supported 11
HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
HP Web JetAdmin 25
Print on Both Sides (Duplex), locking
features supported 11
with Customization Utility 36
with HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
with HP Web JetAdmin 25
Printer Auto-Create feature 15
printer drivers
acquisition 10
installation 11, 13
supported 11
printers supported 11
Printing Preferences
Customization Utility 35
HP Driver Configuration Editor 19
HP Web JetAdmin 25, 27
PS drivers, supported 12
PSA (HP Print Server Appliance)
environments supported 15
tools, recommended 16
S
settings
default 19
invalid 11
locking 11
user modification 11
SETUP.EXE program 28
SETUP.LST 29
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide40
Page 43

Silent Installer
command-line installation 29
constraints, invalid configuration 36
Device Settings 35
features 28
locking features 36
Printing Preferences 35
setting up 30
software acquisition 10
T
Terminal Server environment 15
tools, driver preconfiguration 16
true-connect environments 13
W
warning messages 17
Web JetAdmin
Device Settings 24
driver configuration 21
Driver Configuration Plugin features 20
installation 21
invalid configuration constraints 26
locking features 25
preconfiguration features 9
Printing Preferences 25, 27
queue-creation 21, 28
saving configurations 26
Web site 28
Web sites
HP 16
Microsoft Developer Network 20
Web JetAdmin 28
Windows
Cluster Server, not supported 15
direct installation environments 13
Hardware Quality Labs (WHQL) Digital Signature Warning 17
Point and Print 13
Terminal Server environment 15
versions supported 12
X
XML files 10, 16
Z
ZenWorks 14
HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide 41
Page 44

HP Driver Preconfiguration Support Guide42
Page 45

Page 46

copyright2003
Hewlett-Packard Company
©
 Loading...
Loading...