Denon DN408X, DN-412X User Manual

User Guide
English ( 3 – 8 )
Guía del usuario
Español ( 9 – 14 )
Guide d’utilisation
Français ( 15 – 20 )
Guida per l’uso
Italiano ( 21 – 26 )
Benutzerhandbuch
Deutsch ( 27 – 32 )
Appendix
English ( 33 – 34 )

3
User Guide (English)
Introduction
Box Contents
DN-408X
Power Cable
User Guide
Safety & Warranty Manual
Support
For the latest information about this product (system requirements, compatibility information,
etc.) and product registration, visit denonpro.com.
Quick Setup
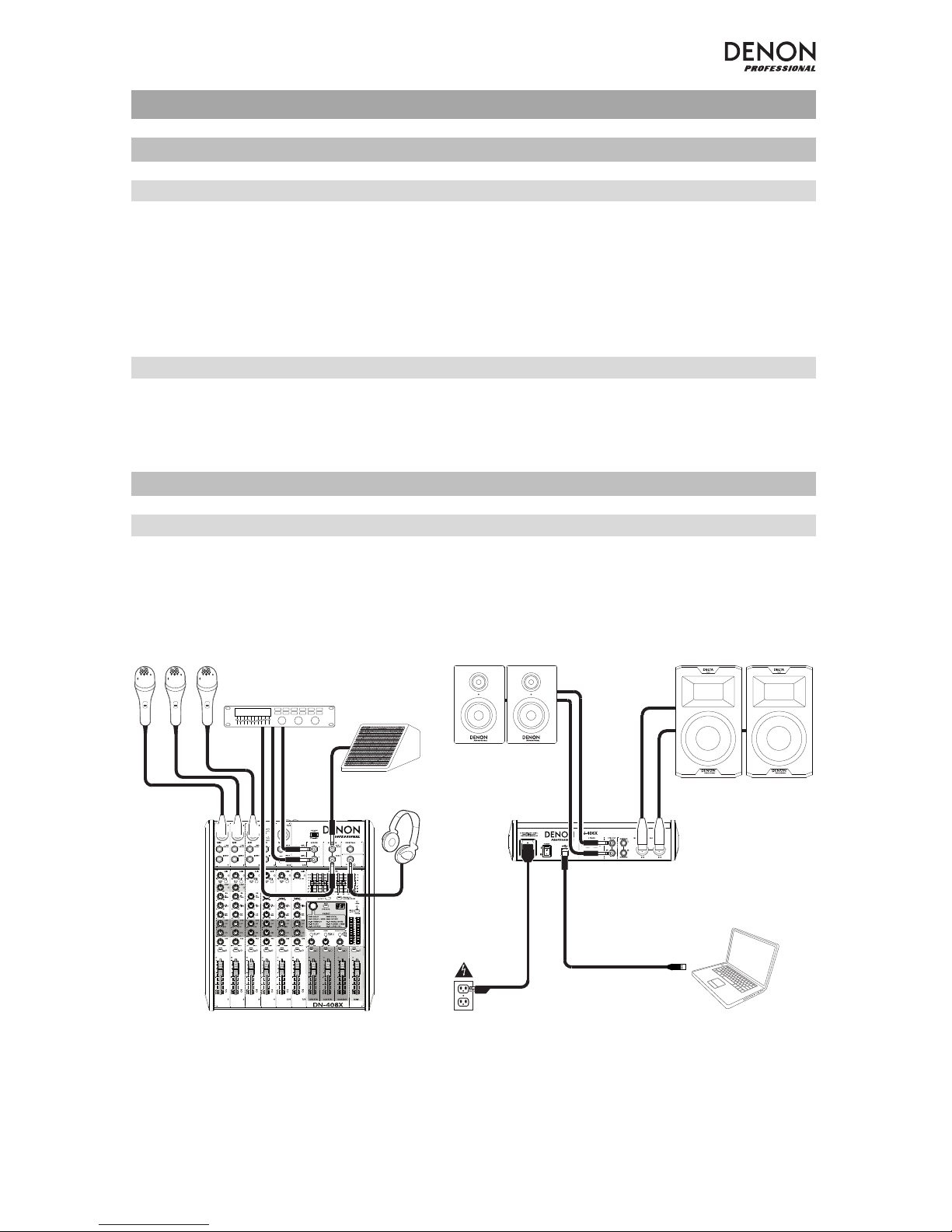
Connection Diagram (Example)
Items not listed under Introduction > Box Contents are sold separately.
Top Panel View
RearPanelView
Microphones
External Effects
Processor Stage
Monitor
Headphones
Booth
/
Cue Monitors Main Loudspeakers
Power
Computer
4
Features
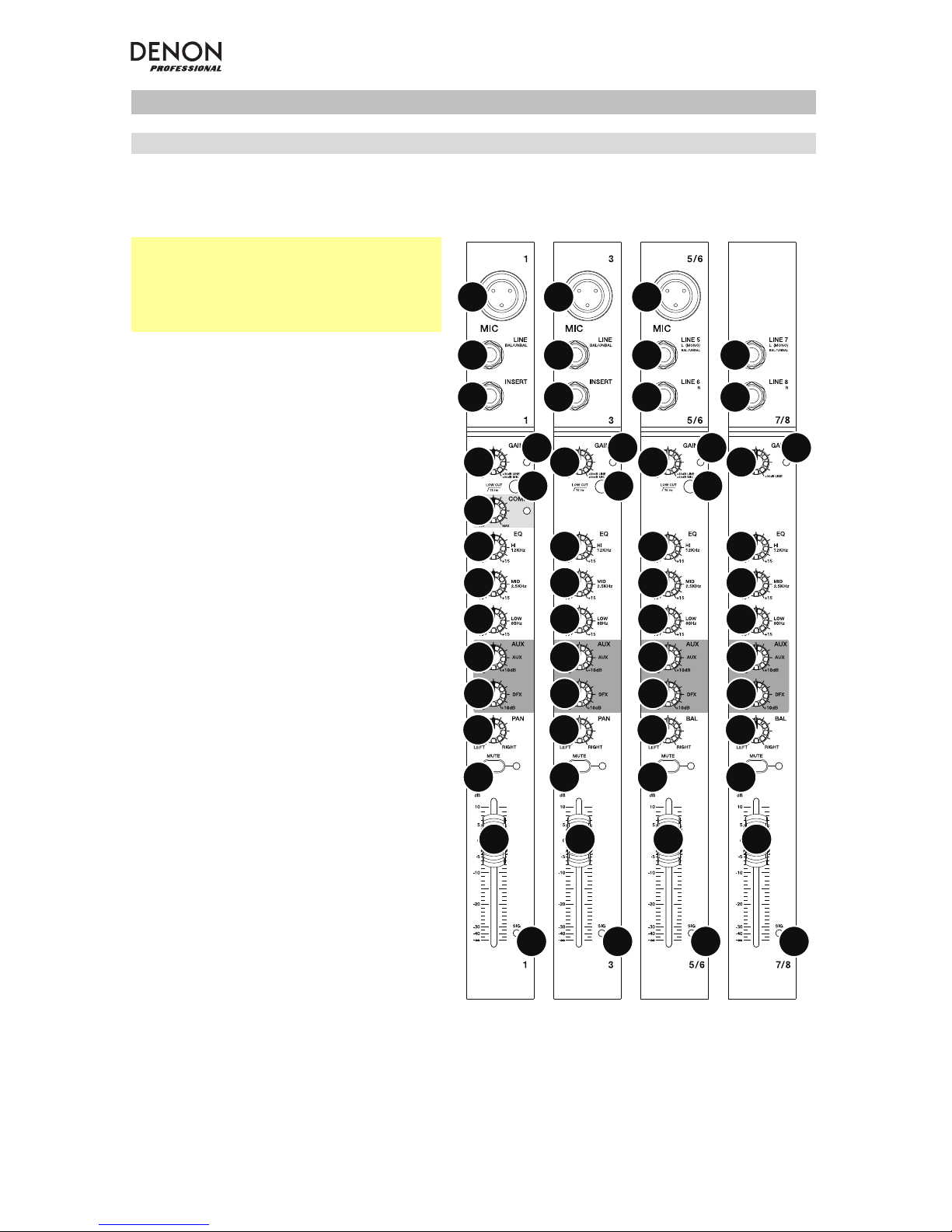
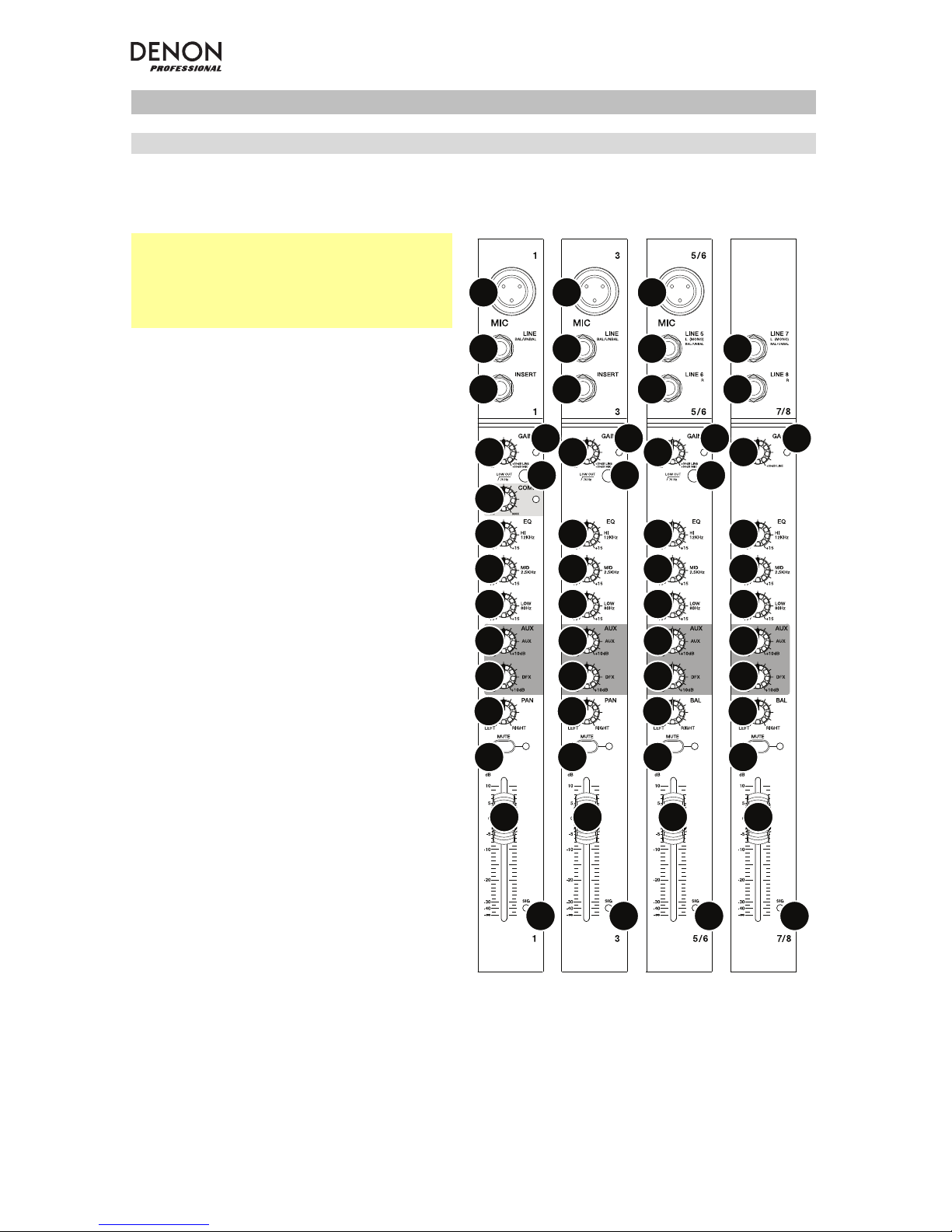
Top Panel
Channels
Note: The channels have essentially the
same controls with some minor variations
between Channels 1–2, 3–4, 5/6, and
7/8. The four different channel types are
shown here.
1. Mic Input: Connect a microphone or
line-level device to these inputs with
an XLR cable.
2. Line Input: Connect line-level
devices to these inputs with 1/4”
(6.35mm) cables.
3. Insert: Use a standard 1/4”
(6.35mm) TRS cable to connect an
external processor (such as a
compressor, limiter, external EQ unit,
etc.) to this jack. The signal will be
taken after the channel’s gain control
and returned before the channel’s
EQ controls. The tip of the TRS
connection is the send, and the ring
is the return.
4. Gain: Adjusts the channel audio level
(pre-fader and pre-EQ gain). Adjust
this so that the Signal LED lights up.
5. Peak LED: The LED will flash if the
signal is clipping. If this happens,
decrease the setting of the Gain
knob.
6. Low Cut Filter: When this button is
depressed, that channel’s audio will
be sent through a 75 Hz lowfrequency filter with a slope of 18 dB
per octave. This is useful for
reducing low-frequency noise when
using microphones.
7. Compressor: Adjusts the amount of
compression on the channel, applied
by the mixer’s built-in compressor.
The LED next to the knob will light up
when the compressor is on.
8. Hi EQ: Adjusts the high (treble) frequencies of the channel.
9. Mid EQ: Adjusts the mid-range frequencies of the channel.
10. Low EQ: Adjusts the low (bass) frequencies of the channel.
1
2
3
4
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
5
6
5
6
55
6

5
11. Monitor Knob: Adjusts the pre-fader level of the signal sent from that channel to the
Monitor Mix, whose level is controlled by the Monitor Fader.
12. DFX Knob: Adjusts the post-fader level of the signal sent to the mixer’s effects
processor, whose level is controlled by the DFX Return Fader (DFX Rtn).
13. Channel Pan / Balance: If this knob is labeled Pan, it adjusts the (mono) channel’s
position in the stereo field. If the knob is labeled Bal, it adjusts the balance between the
left and right channels of that stereo signal.
14. Channel Mute: Press this button to mute/unmute the channel. The LED next to the
button will light up when the channel is muted.
15. Channel Fader: Adjusts the audio level on the channel.
16. Signal LED (Sig): Indicates that the channel’s incoming audio signal is within an optimal
range.
Main Controls
17. Aux Send: Use 1/4” (6.35mm) TRS cables to
connect these outputs to the inputs of an external
amplifier or active monitor. Use the Monitor
Knob (Mon) on each channel to control the level
of the signal sent to Aux Send 1. This is useful for
creating a custom monitor mix for onstage
musicians.
18. Aux Return (Aux Rtn): Connect the outputs of an
external device to these inputs with 1/4” (6.35mm)
mono cables. If your source is mono, plug it into
the left jack and it will be heard on both the left
and right sides.
19. Aux Return Fader (Aux Rtn): Controls the audio
level sent into the Aux Return (Aux Rtn) inputs.
20. Graphic Equalizer: When the EQ On/Off switch
is on (depressed), you can use these controls to
adjust the equalization of the main mix.
21. EQ On/Off: Enables or disables the Graphic
Equalizer.
22. Main Out / Monitor Out: When this button is
raised, the Graphic Equalizer will affect the signal
sent to the Main Mix Outputs. When this button
is depressed, the Graphic Equalizer will affect the
signal sent to the Aux 1 (Mon) Output.
23. Effect Selector: This knob determines what
effect the mixer’s internal effects processor will
apply to the various channels. Turn the knob to
change the effect number, and push the knob to
select it. The display next to the DFX Mute button
will show the preset number. Each channel can
send different levels of audio to the processor by
adjusting its DFX Knob. See the Effects section
for an explanation of the available effects.
17
20
27
40
28
21 22
23
24
29
37
38
39
31
33
303234
25
18
1718
19
14 14 14 14
26
35 36

6
24. DFX Mute: Press this button to mute/unmute the effects.
25. DFX Peak LED: The LED will flash if the signal is clipping. If this happens, decrease the
setting of your source channels’ DFX Knobs. When the effects processor is muted, the
LED will be solidly lit.
26. DFX Return Fader (DFX Rtn): Adjusts the volume of the audio sent from the mixer’s
effects processor.
27. DFX Bypass: You can connect a standard 1/4” (6.35mm) latching-style footswitch (sold
separately) to this input and use it to bypass the mixer’s internal effects processor (when
the footswitch is in its “closed” position).
28. Phones Output: Connect 1/4” (6.35mm) stereo headphones to these outputs. The
Phones Volume knob controls the volume. The Phones Source button sets what signal
is sent to this output.
29. Phones Source: When this button is raised, the signal from the Main Mix Outputs will
be heard in the Phones Output. When this button is depressed, the signal from the
Control Room Outputs (Ctrl Out) will be heard in the Phones Output.
30. Phones Volume: Adjusts the volume of Phones Output.
31. USB In Source: When this button is raised, the signal sent to the mixer through its USB
Port will be sent to the Main Mix Outputs. When this button is depressed, the signal sent
to the mixer through its USB Port will be sent to the Control Room Outputs (Ctrl Out).
32. USB In Level: Adjusts the level of the signal sent to the mixer through its USB Port.
33. 2 Track In Source: When this button is raised, the signal from the 2 Track In will be sent
to the Main Mix Outputs. When this button is depressed, the signal from the 2 Track In
will be sent to the Control Room Outputs (Ctrl Out).
34. 2 Track In Level: Adjusts the level of the 2 Track In.
35. Monitor Fader: Adjusts the level of the Aux Send 1 (Mon)
output (the Monitor Mix).
36. Main Fader: Adjusts the level of the Main Mix Outputs.
37. LED Meters: Shows the audio level of the Main Mix Outputs. The Clip LED can light up
occasionally, but if it happens too often, reduce the volume of the mix and/or individual
channels.
38. Phantom Power: Activates/deactivates phantom power. When activated, phantom
power supplies +48V to the XLR mic inputs and the LED next to the button will light up.
Please note that most dynamic microphones do not require phantom power, while most
condenser microphones do. Consult your microphone’s documentation to find out
whether it needs phantom power.
39. Power LED: Illuminates when the mixer is on.
40. USB Power Connection: You can use this USB port to connect and power (or charge) a
device that requires power from a 5V, 1A USB bus.

7
Effects
To apply effects, turn the Effects Preset Knob and press it to select one of the available
presets. To send a channel's signal to the effects processor, turn up that channel's DFX Knob
(Aux 2). Each effect has 10 variations.
Numbers Effect Description
00–09 Delay Reproduces the signal after a small period of time.
10–19 Delay+Verb Delay effect with room reverb.
20–29 Tremolo Rapidly increases and decreases the signal volume at a
regular rate.
30–39 Plate Simulates bright plate reverb.
40–49 Chorus Simulates the full, complex, watery sound of several
instruments playing the same thing.
50–59 Vocal Reverb, simulating a room with a small delay time.
60–69 Rotary Simulates the classic Doppler effect of the spinning horn
inside an organ speaker.
70–79 Small Room Reverb simulating a bright studio space.
80–89 Flange+Verb Applies room reverb plus a classic stereo flanging effect.
90–99 Large Hall Reverb simulating a large acoustic space.
8
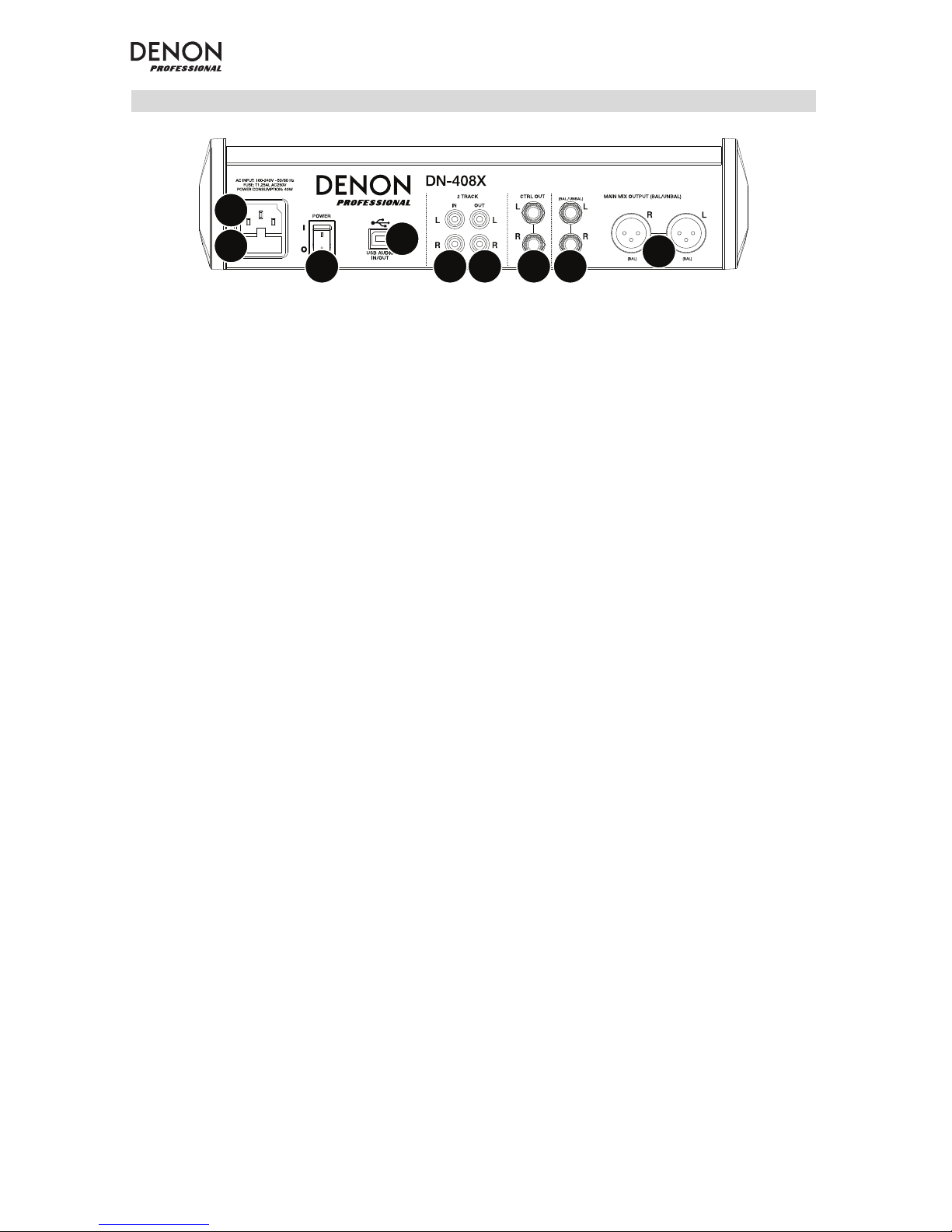
Rear Panel
1
2
3
4
45
6
7
8
1. Power In: Use the included power cable to connect the mixer to a power outlet. While
the power is switched off, connect the power cable into the mixer first, then connect the
power cable to a power outlet.
2. Fuse Cover: If the fuse is broken, use a screwdriver or other tool to lift this tab, and
replace the fuse with a fuse with the same rating (printed just above the Power In). Using
a fuse with an incorrect rating can damage the unit and/or fuse.
3. Power Switch: Powers the mixer on and off. Turn on the mixer only after connecting all
of your input devices but before turning on your amplifiers. Turn off amplifiers before you
turn off the mixer.
4. Main Mix Outputs: Use standard XLR or 1/4” (6.35mm) cables to connect either pair of
these outputs to your loudspeakers or amplifier system. Use the Main Fader to control
the level of these outputs.
5. Control Room Outputs (Ctrl Out): Use standard 1/4” (6.35mm) cables to connect these
outputs to your control room (booth) monitors or amplifier system.
6. USB Port: Use a standard USB cable to connect this USB port to a computer. The mixer
can send or receive audio to or from your computer through this connection.
• When sending audio, the main mix will be sent from the mixer to your computer.
• When receiving audio, it will be sent from your computer to the Main Mix Outputs
or Control Room Outputs (Ctrl Out), depending on the position of the mixer’s USB
In Source button.
7. 2-Track Inputs (2 Track In): Connect these inputs to the outputs of an external sound
source using a standard stereo RCA cable (sold separately). Use the 2 Track In Source
button to send this signal either to the Main Mix Outputs or to the Control Room
Outputs (Ctrl Out).
8. 2-Track Outputs (2 Track Out): Connect these outputs to the inputs of an external
recording device using a standard stereo RCA cable (sold separately).
9
Guía del usuario (Español)
Introducción
Contenido de la caja
DN-408X
Cable de alimentación
Guía del usuario
Manual sobre la seguridad y garantía
Soporte
Para obtener la información más completa acerca de este product (los requisitos del sistema,
compatibilidad, etc) y registro del producto, visite denonpro.com.
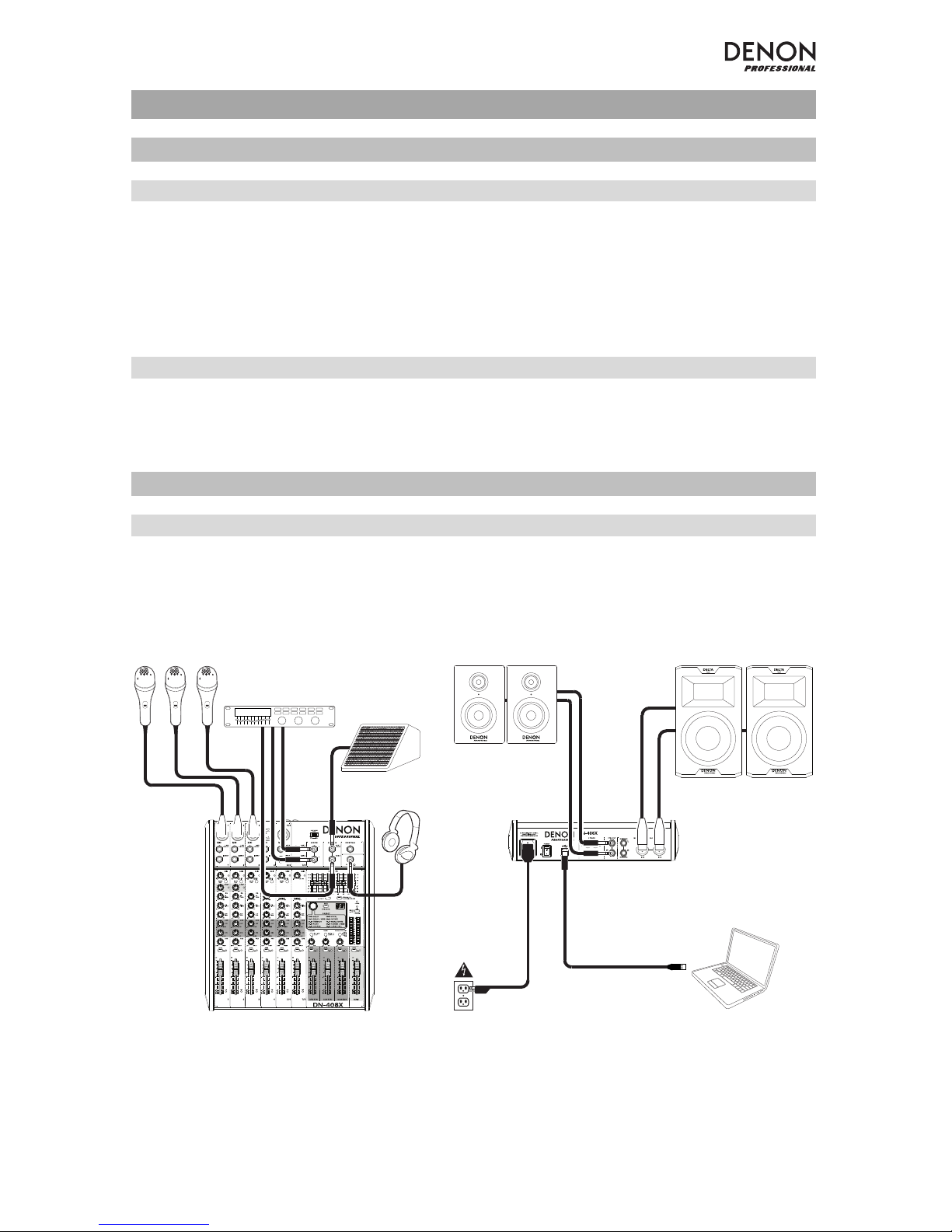
Instalación rápida
Diagrama de conexión (ejemplo)
Los elementos que no se enumeran en Introducción > Contenido de la caja se venden por separado.
V
ista del panel superio
r
V
ista del panel trasero
Micrófonos
Procesador de
efectos externo Monitor de
escenario
Auriculares
Monitores de cue/cabina Altavoces principales
Suministro eléctrico
Computadora
10
Características
Panel superior
Canales
Nota: Los canales tienen esencialmente los
mismos controles con algunas variaciones
menores entre los canales 1–2, 3–4, 5/6 y
7/8. Se muestran aquí los cuatro tipos de
canales diferentes.
1. Entrada de micrófono: Conecte a
estas entradas un micrófono o
dispositivo de nivel de línea con un
cable XLR.
2. Entrada de línea: Conecte a estas
entradas dispositivos de nivel de línea
con cables de 6,35mm (1/4 pulg.)
3. Inserción: Use un cable TRS de
6,35mm (1/4 pulg.) estándar para
conectar a este conector hembra un
procesador externo (como un
compresor, limitador, ecualizador
externo, etc.). La señal se toma
después del control de ganancia del
canal y retorna antes de los controles
del ecualizador del canal. La señal se
envía por la punta de la conexión TRS
y retorna por la nuca.
4. Ganancia: Ajusta el nivel de audio del
canal (ganancia pre-fader y preecualización). Ajuste esto para que el
LED de señal se encienda.
5. LED de pico: El LED destella si la
señal se está recortando. Si esto
sucede, disminuya el ajuste de la
perilla Gain (Ganancia).
6. Filtro pasabajos: Cuando se pulsa
este botón, el audio de ese canal se
envía a través de un filtro de baja
frecuencia de 75 Hz con una
pendiente de 18 dB por octava. Esto
resulta útil para reducir el ruido de
baja frecuencia cuando se usan
micrófonos.
7. Compresor: Ajusta la cantidad de compresión en el canal, aplicada por el compresor
incorporado del mezclador. El LED que está junto a la perilla se encenderá cuando el
compresor esté activado.
8. Ecualización de agudos: Ajusta las altas frecuencias (agudos) del canal.
9. Ecualización de medios: Ajusta las frecuencias medias del canal.
10. Ecualización de graves: Ajusta las bajas frecuencias (graves) del canal.
1
2
3
4
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
5
6
5
6
55
6

11
11. Perilla de monitor: Ajusta el nivel de pre-fader de la señal enviada desde ese canal a la
mezcla de monitor, cuyo nivel se controla con el fader del monitor.
12. Perilla de DFX (efectos digitales): Ajusta el nivel de post-fader de la señal enviada hacia
el procesador de efectos del mezclador, cuyo nivel se controla con el fader de retorno
de efectos digitales (DFX Rtn).
13. Paneo / balance del canal: Si esta perilla indica Pan, ajusta la posición del canal (mono)
en el campo estéreo. Si la perilla indica Bal, ajusta el balance entre los canales izquierdo
y derecho de esa señal estéreo.
14. Silenciamiento de canal: Pulse este botón para silenciar/anular el silenciamiento del
canal. El LED junto al botón se encenderá cuando el canal esté silenciado.
15. Fader de canal: Ajusta el nivel de audio del canal.
16. LED de señal (Sig): Indica que la señal entrante de audio del canal está dentro de un
rango óptimo.
Controles principales
17. Envío auxiliar: Use cables TRS de 6,35mm (1/4
pulg.) para conectar estas salidas a las entradas
de un amplificador o monitor activo externo. Use
la perilla de monitor (Mon) en cada canal para
controlar el nivel de la señal enviada a Aux Send
1 (Envío auxiliar 1). Esto es útil para crear una
mezcla de monitor personalizada para los
músicos en el escenario.
18. Retorno de auxiliares (Aux Rtn): Conecte las
salidas de un dispositivo externo a estas
entradas con cables mono de 6,35mm (1/4
pulg.) Si su fuente es mono, enchúfela en el
conector izquierdo y se escuchará en ambos
lados, izquierdo y derecho.
19. Fader del retorno de auxiliares (Aux Rtn):
Controla el nivel de audio enviado a las entradas
de retorno de auxiliares (Aux Rtn).
20. Ecualizador gráfico: Cuando el interruptor EQ
On / Off (Ecualizador encendido / apagado) está
conectado (pulsado), estos controles se pueden
usar para ajustar la ecualización de la mezcla
principal.
21. Ecualizador encendido/apagado: Activa o
desactiva el ecualizador gráfico.
22. Salida principal / Salida para monitor: Cuando
este botón está levantado, el ecualizador gráfico
afecta a la señal enviada a las salidas Main Mix
Output (Mezcla principal). Cuando este botón
está pulsado, el ecualizador gráfico afecta a la
señal enviada a la salida Aux 1 (Mon).
17
20
27
40
28
21 22
23
24
29
37
38
39
31
33
303234
25
18
1718
19
14 14 14 14
26
35 36
 Loading...
Loading...