ATL IP300S User Manual

IP300S
User Guide
www.atltelecom.com

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
Directory
DIRECTORY ...............................................................................................................................................................2
1. OVERVIEW....................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.1. FEATURES................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.2. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS ......................................................................................................................7
1.2.1. CALL CONTROL CAPABILITY ......................................................................................................................7
1.2.2. REAL-TIME VOICE STREAMING................................................................................................................... 8
1.2.3. NAT AND FIREWALL .................................................................................................................................. 8
1.2.4. MANAGEMENT............................................................................................................................................ 8
2. LAYOUT......................................................................................................................................................... 10
2.1. HARDWARE .............................................................................................................................................. 10
2.1.1. FRONT VIEW .............................................................................................................................................10
2.1.2. REAR VIEW............................................................................................................................................... 10
2.1.3. BACK VIEW .............................................................................................................................................. 11
2.2. KEYS ........................................................................................................................................................ 11
2.3. KEYPAD.................................................................................................................................................... 14
3. OPERATION.................................................................................................................................................... 15
3.1. KEY DEFINITIONS IN MENU MODE ........................................................................................................... 15
3.2. ENTER ALPHABETS AND NUMBERS........................................................................................................... 16
3.3. ADDRESS-OF-RECORD (SIP AOR) ............................................................................................................ 16
4. STARTUP........................................................................................................................................................17
4.1. PREREQUISITE...........................................................................................................................................17
4.1.1. NETWORK................................................................................................................................................. 17
4.1.1.1. DHCP .................................................................................................................................................. 18
4.1.1.2. STATIC IP (FIXED IP) ...........................................................................................................................18
4.1.1.3. PPPOE ................................................................................................................................................. 18
4.1.1.4. VERIFY NETWORK CONFIGURATION.................................................................................................... 19
4.1.2. SIP SERVICE ............................................................................................................................................. 19
4.1.3. CONFIGURE NAT AND FIRE WALL .............................................................................................................20
4.2. INITIALIZATION.........................................................................................................................................21
4.3. REGISTRATION ..........................................................................................................................................22
5. SHUTDOWN ................................................................................................................................................... 22
5.1. UNREGISTRATION .....................................................................................................................................22
6. IDLE............................................................................................................................................................... 23
6.1. REGISTERED ............................................................................................................................................. 23
6.2. NOT REGISTERED YET OR REGISTRATION EXPIRES .................................................................................... 23
6.3. REGULAR REGISTRATION ......................................................................................................................... 23
7. TAKE CALLS ..................................................................................................................................................24
[2/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
RINGING ................................................................................................................................................... 24
7.1.
7.2. REJECT CALL............................................................................................................................................ 25
7.3. FORWARD CALL ....................................................................................................................................... 25
7.4. ANSWER CALL.......................................................................................................................................... 25
7.5. CONNECTED.............................................................................................................................................. 26
7.6. DISCONNECTED ........................................................................................................................................ 26
7.7. FORWARD AND DND ................................................................................................................................ 28
7.7.1. DO NOT DISTURB (DND) ......................................................................................................................... 28
7.7.2. CALL FORWARD ....................................................................................................................................... 28
7.7.2.1. ALL CALLS FORWARD ......................................................................................................................... 29
7.7.2.2. BUSY FORWARD .................................................................................................................................. 29
7.7.2.3. NO ANSWER FORWARD........................................................................................................................ 29
7.7.3. FORWARDING RULES ................................................................................................................................29
8. MAKE CALLS................................................................................................................................................. 30
8.1. DIAL SCHEME ...........................................................................................................................................31
8.1.1. GUARDING TIME ....................................................................................................................................... 34
8.1.2. ENUM SAMPLE ........................................................................................................................................ 35
8.2. REDIAL .....................................................................................................................................................37
8.3. ADDRESS BOOK ........................................................................................................................................37
8.4. CALL HISTORY ......................................................................................................................................... 38
8.5. SPEED DIAL .............................................................................................................................................. 39
8.6. CALL RETURN .......................................................................................................................................... 41
8.7. CALLING ................................................................................................................................................... 41
8.8. CALL FAILURE.......................................................................................................................................... 42
8.9. AUTO-REDIAL ........................................................................................................................................... 42
8.10. ONE-TOUCH DIAL..................................................................................................................................... 43
9. CALL PROCESSING......................................................................................................................................... 45
9.1. HANDSET, SPEAKER-PHONE, EAR-PHONE AND LOUD-SPEAKER ................................................................ 45
9.2. HOLD........................................................................................................................................................ 45
9.3. MUTE........................................................................................................................................................ 46
9.4. TRANSFER.................................................................................................................................................46
9.4.1. CONSULTATIVE TRANSFER .......................................................................................................................47
9.4.2. BLIND TRANSFER......................................................................................................................................48
9.4.3. PHONE LOCKED ........................................................................................................................................ 48
9.5. CONFERENCE ............................................................................................................................................49
9.5.1. HEURISTICS AND CONSTRAINT.................................................................................................................. 49
9.5.2. CONFERENCE TIPS .................................................................................................................................... 50
9.6. BLOCK CALLS........................................................................................................................................... 51
10. CALL PREFERENCE ................................................................................................................................... 54
[3/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
CALL WAITING .........................................................................................................................................54
10.1.
10.2. DIAL TIMEOUT .......................................................................................................................................... 55
10.3. HOLD RECALL ..........................................................................................................................................55
10.4. AUTO HOLD ON CALL SWITCH ................................................................................................................. 56
10.5. AUTO REDIAL........................................................................................................................................... 56
10.6. SILENTLY FOLLOW REDIRECTION............................................................................................................. 57
10.7. DIAL PLAN................................................................................................................................................ 57
10.7.1. INTER-DIGIT TIMEOUT .........................................................................................................................57
10.7.2. DIAL KEY .............................................................................................................................................58
10.7.3. LAN DIAL ........................................................................................................................................... 58
10.7.4. CALL COMMAND ................................................................................................................................. 59
10.7.4.1. CALL RETURN...................................................................................................................................... 60
10.7.4.2. ANONYMOUS CALL (CLIP & CLIR) .................................................................................................... 60
10.8. MESSAGE ALERT....................................................................................................................................... 61
10.9. AUTO-ANSWER......................................................................................................................................... 61
10.10. CODEC PREFERENCE.......................................................................................................................... 64
10.10.1. ENABLE PERSONAL PREFERENCE......................................................................................................... 67
10.11. COMFORT NOISE GENERATION ............................................................................................................ 67
10.12. REGISTRATION ON DEMAND ................................................................................................................ 68
10.13. MULTI-DOMAIN REGISTRATION .......................................................................................................... 70
11. VOICE VOLUME ADJUSTMENT.................................................................................................................. 72
11.1. RINGER ..................................................................................................................................................... 72
11.2. HANDSET .................................................................................................................................................. 72
11.3. SPEAKER PHONE .......................................................................................................................................72
11.4. EAR PHONE............................................................................................................................................... 73
12. SERVICE.................................................................................................................................................... 74
12.1. VOICE MAIL ............................................................................................................................................. 74
12.1.1. SET UP VOICE MAIL............................................................................................................................. 75
12.1.2. ACCESS VOICE MAIL ...........................................................................................................................76
12.2. INSTANT MESSAGING ............................................................................................................................... 76
12.3. SYNCHRONIZE TIME ................................................................................................................................. 77
12.4. AUTO PROVISION...................................................................................................................................... 79
12.5. SOFT-SWITCH (PBX) FEATURE ACCESS ...................................................................................................82
13. NAT TRAVERSAL ..................................................................................................................................... 85
13.1. PUBLIC INTERNET CONFIGURATION.......................................................................................................... 85
13.2. LAN CONFIGURATION TO TRAVERSE NAT AND FIREWALL ..................................................................... 86
13.2.1. STATIC NAT ROUTE ............................................................................................................................ 86
13.2.2. NAT TRAVERSAL BY STUN................................................................................................................ 89
APPENDIX A - AVAILABLE NTP SERVERS ............................................................................................................... 91
[4/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
PPENDIX B – TROUBLE SHOOTING ........................................................................................................................ 96
A
APPENDIX C – TONES............................................................................................................................................ 100
[5/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
1. Overview
1.1. Features
z DHCP or PPPoE for host IP, gateway, network mask, DNS (optional, 2 DNS at most), TFTP
server, NTP server, and TTL; all those settings could be static assigned as well.
z If provided by DHCP server, it could use DHCP to get NTP server.
z Ear-phone, speaker-phone for hand-free, handset and loud-speaker support (all are volume
adjustable). Changeable ringing tone.
z Supports 2 concurrent calls.
z Multiple service domains for easy access to different ISPs (3 domains at most).
z Address book (up to 500 entries) and call history (10 most recently received calls, 10 most
recently missed calls and 10 most recently dialed numbers).
z Call return, speed dials (20 numbers), redial, auto-redial, call-screening (20 numbers) and
detail records of the latest three calls.
z Call forwarding: configurable forwarding number, unconditionally forward all calls, forward
calls on busy and forward calls on no response (adjustable waiting time).
z Call processing includes: hold (music on hold), mute, Caller ID, Call waiting (alerting tone,
LED indication and screen popup), call transfer (blind transfer, consultative transfer,
semi-supervised transfer, and take-back), call forward, call reject, do not disturb (DND).
z Call preferences include: call waiting, auto-answer (server-side invoked, locally activated
and selectively auto-answer), dial-timeout, adjustable hold recall timer, auto-hold on call
switch, auto-redial criterion (stop-on-ringing or stop-on-connected), accept call diversion or
not, inter-digit time-out, message alerting, and per call Calling Line Identification
Restriction.
z 3-way local conferencing
z Message Waiting Indication (MWI)
z 180 locally generated ringing and 183 remotely generated call progress tone.
z Out-of-dialog instant messaging, and flashing SMS without user interaction.
z NAT & firewall support by STUN or pre-configured NAT Gateway port mapping;
Auto-update or notify the change of NAT IP by STUN if NAT employs DHCP as well (such
as xDSL dial-up).
z Symmetric RTP flow for cases where only one endpoint is behind a NAT.
z Voice activity detection to reduce network bandwidth consumption.
z Comfort noise generation and dynamic de-jitter buffer to deliver better voice quality.
z 8 Programmable DSS keys.
z One-touch dialing (Hot lines)
【
z Configurable dial-key (#, *, & or dedicated DSS key as
inclusion of “#, *, or &” in dial strings.
Dial-】key ) to facilitate the
[6/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
z Regular alarm and one-time alarm.
z Prompt user on call diversion for better security support (Configurable)
z Menu driven configuration by keypad, Web browser or TELNET.
z Use of Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) to synchronize time with network time server
and adjust to time-zone (configurable) and daylight saving time (configurable).
z Use of Trivial File Transport Protocol (TFTP) and HTTP for auto-provisioning and image
update
z IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging support
z Support both 802.1P link layer precedence bits and IP layer type-of-service (ToS) bits for
voice streaming, such that IP SIP Phone would perfectly replace your desktop analog phone
within a switched network.
z SNMPv2 for network management and supervision.
z Call-related statistics, including total inbound/outbound calls, average conversation duration,
connected ratio of the last 50 calls, and the conversation time distribution (less than 3
minutes, 3-20 minutes and longer than 20 minutes) during the last 72 hours, or since system
startup.
1.2. Technical Specifications
1.2.1. Call Control Capability
z Fully complies with RFC 3261 (SIP) with RFC 2543 backward compatible.
z Fully complies with RFC 2327 (SDP) and RFC 3264 for capability negotiation based on SDP
offer and answer model.
z Multiple Outbound Proxy, Registrar and Redirect server support, up to 3 different service
domains.
z Support SIP server authentication procedure (HTTP digest authentication scheme)
z On-demand registration and re-registration on network configuration changed (auto-detect
the changed IP of host, NAT, Dynamic DNS)
z Auto-locating SIP server (RFC 3263) by DNS NAPTR/SRV record (RFC 2782) lookup
z Supports SIP multicast registration to 224.0.1.75
z Call Transfer (RFC3515 for REFER method, RFC3420 for sipfrag support, RFC3891 for
replaces header and RFC3892 for Referred-by header).
z Message waiting indication, MWI, (RFC 3842).
z Fully Implementation of RFC 2916 (E.164 and DNS) for ENUM translation by NAPTR
(RFC 2915)
z Configurable SIP signaling port (default 5060), support both UDP and TCP.
z Support rport and received in VIA header (RFC3581) (Configurable)
z Redundancy SIP proxy server support by DNS NAPTR/SRV/AAAA records.
[7/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
z Support REGISTER, INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, BYE, OPTION, REFER, MESSAGE,
SUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, INFO methods
z Support “alert-info” header for distinctive ring.
1.2.2. Real-time Voice Streaming
z Fully complies with RFC 1889 (RTP / RTCP), RFC 1890 (AVT profiles), RFC 3551 (RTP
Profile for Audio and Video Conference with Minimal Control) and RFC 3555 (MIME Type
Registration of RTP Payload Formats).
z Support both in-band DTMF mixed with RTP voice stream and out-of-band DTMF over RTP
(RFC2833).
z Dynamic RTP de-jitter buffer and lost packets concealment management.
z Speech CODEC supports: G.711 (A-law and µ-law), G.723.1/G.723.1A (both 5.3 and 6.4
kbps), and G.729A/G.729AB. CODEC precedence is configurable to adjust to your network
link speed.
z 3-way local conferencing
z Voice activity detection (VAD) and comfort noise generation (CNG).
z Voice and ringer volume control
z Real-time acoustic echo canceller.
z IP Type of Service (ToS) bits set for RTP/RTCP packet prioritization
z 802.1P precedence bits support to prioritize RTP voice frames within switched network.
z Configurable RTP / RTCP ports.
1.2.3. NAT and Firewall
z Support static NAT mapping (both NAT IP and SIP/RTP ports are configurable)
z Support Simple Traversal of UDP through NAT, (RFC 3489 STUN).
z Support auto-detect (auto-update) the change of NAT IP by STUN (in case the NAT has no
static IP and employ dial-up to public internet).
z draft-ietf-mmusic-sdp4nat-03.txt (RTCP attribute in SDP)
z Symmetric RTP flow for the cases where only one endpoint behind NAT.
z Support STUN server redundancy by DNS SRV/AAAA records
1.2.4. Management
z TFTP and HTTP for Auto-Provision
z HTTP configuration by web browser
z Key-pad configuration
z TELNET configuration
[8/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
z SNMPv2 for network management:
MIB2: RFC1213
Get and Set operation for internal state (Proprietary Enterprise MIB for system
configuration access).
Trap:
System startup
System shutdown (by command/SNMP/Image upgrade)
SIP Registrar availability
Call-Channel Status.
[9/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
2. Layout
2.1. Hardware
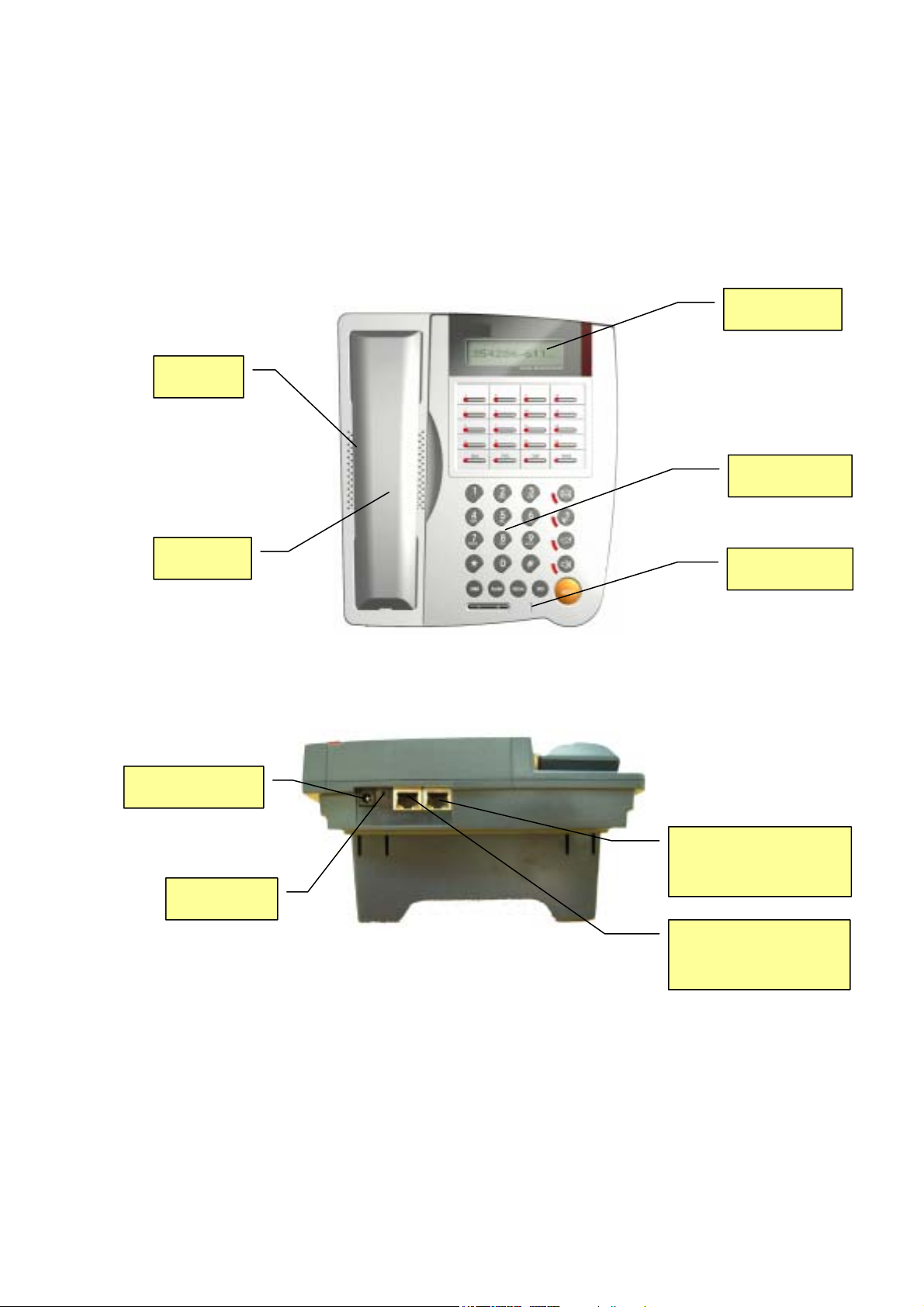
2.1.1. Front View
Speaker
2x16 LCD
Keypad
Handset
2.1.2. Rear View
Power adaptor
Reset SW
Microphone
RJ-45 Ethernet
switch to PC
RJ-45 Ethernet Jack
to LAN
[10/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
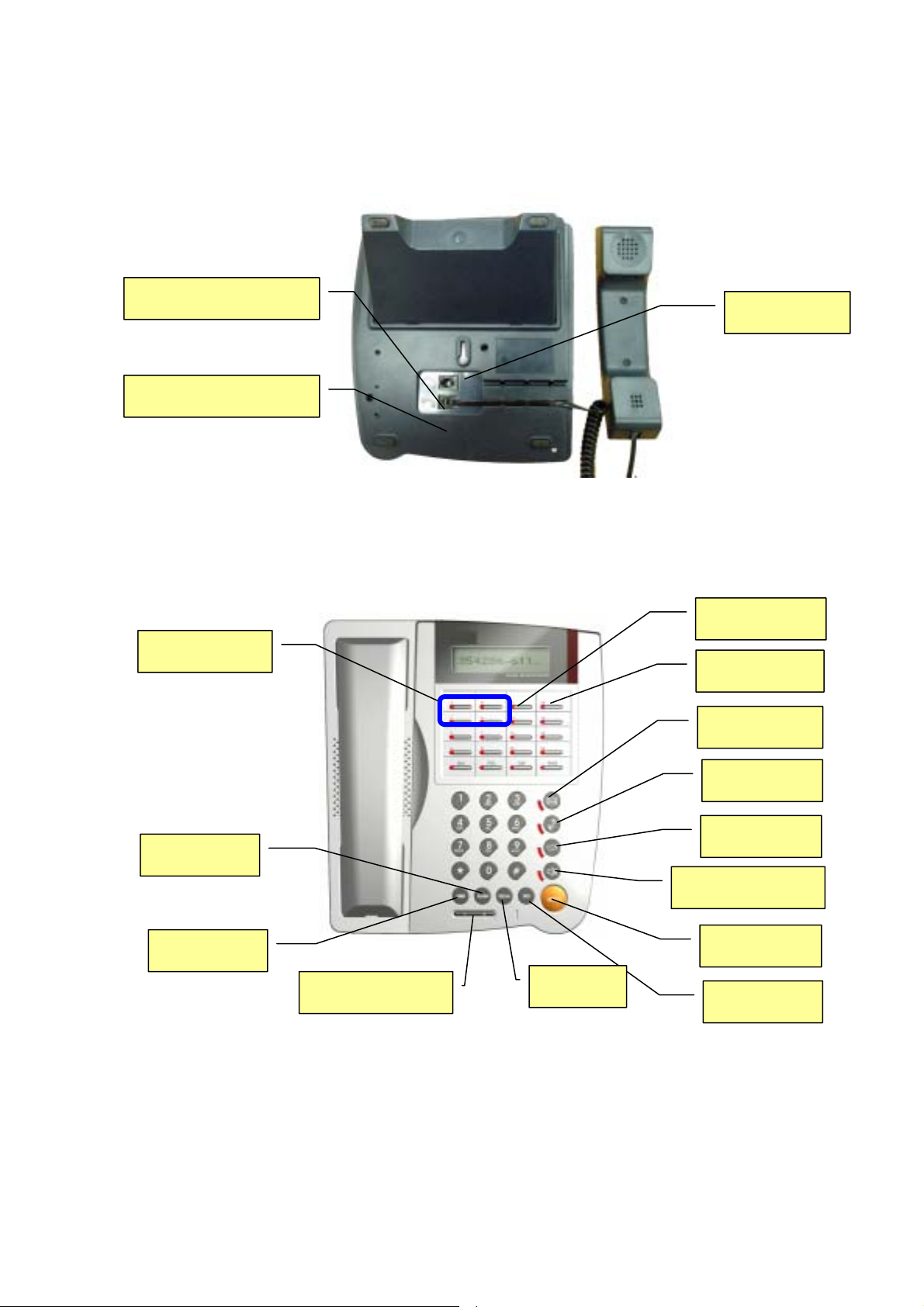
2.1.3. Back View
RJ-11 Earphone Jack
RJ-11 Handset Jack
Wall mount
2.2. Keys
A/B Channel
FLASH
XFER
Volume【−,+】
REDIAL
Service Realm
Reject
MWI
MUTE
FUNC
SPK/Hands-free
HOLD
SPD
【
Keys
】:
Function when in-call or idle | Fun c tion on menu mode
【A / B Channel】:Call lines (2 concurrent calls at most) / Review the calling information on this
channel during conversation.
【Service Realm】:Display the registration status of each active service domain on idle; switch
target service domain (ISP) while making calls.
[11/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
【Reject】:Reject incoming waiting calls
【MWI】:Message Waiting Indication, MWI: Access to voice mail system
【MUTE】: Mute | Delete character
【FUNC】:Menu | Return to upper level submenu
【SPK】:Hands-free | Exit menu
【HOLD】:Hold | Confirm, Save
【SPD】:Speed Dial
【Redial】:Redial the last dialed number.
【FLASH】:Take back or cancel transferring calls; cancel conference.
【XFER】:Transfer
【Volume】:
【+】:Volume UP (Ringer, headset, handset, speaker) | Next item、Move cursor to right
【-】:Volume down (Ringer, headset, handset, speaker) | Previous item、Move cursor to left
Registration
URL
Auto-redial Address Book
DSS: F1-F8
DND
Call History
Forward
Conference
【Registration】:Re-register. The LED indicates the registration status of each active service
domain:
Green LED On: Successfully register to all active service domains.
Red LED On: At least one service domain could not be registered.
Green LED Flashes: Registration is in progress. Note, IP SIP Phone will regularly refresh
SIP Address-or-Record registration as necessary.
Red LED Flashes: No service domains have ever registered successfully.
LED is off: Users explicitly logs out all SIP service and goes off-line ‘till user presses the
【Registration】key again to go on-line (re-register to all SIP service).
【Auto-redial】:Auto-redial the last dialed number ‘till connected (ringing)
【DND】:Do Not Disturb (red LED indicates on)
[12/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
【Forward】:Forward incoming waiting calls
【URL】:Use keypad to enter alphabets and numbers (red LED on).
【Address Book】:Access to address book (search an entry or list all entries).
【Call History】:Missed calls / Received calls / Dialed Number. If the red LED is on, it indicates
there are unread records of missed calls.
【Conference】:Three-way local conferencing
【F1-F8】:User programmable DSS keys for easy access to various phone features. The default
mappings of these function keys are:
【F1】:Forward menu – shortcut to activate incoming calls forwarding menu.
【F2】: Channel info–show information of the last call on each call channel【A / B】.
【F3】: Call Detail - show detail records of the latest three connected and finished calls.
【F4】: Speed dials – activate speed dial list.
【F5】
: Messaging; Out-of-dialog instant messaging.
【F6】: Packetization - adjust the voice packetization based on your network link speed.
【F7】: Network Info - show the current active host IP, MAC address and DNS IP(s).
【F8】: Call Return - place a call to the last incoming call, either a missed or received one.
[13/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
i
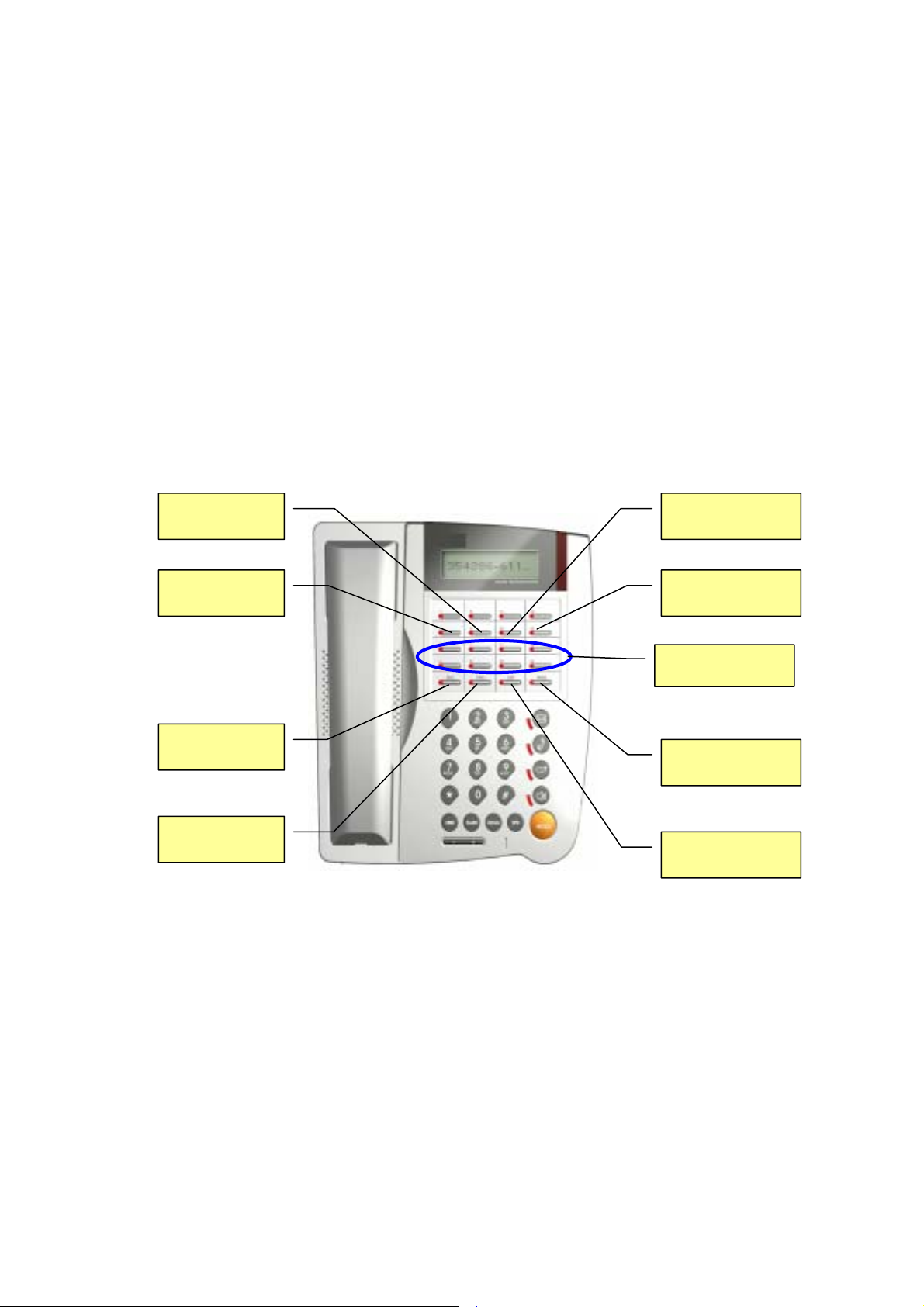
2.3. Keypad
LCD 2x16
Lamp
R
ng
A Call B Call
Service Realm
Reject
Auto-Redial Registration
URL Addr. Book
Fwd Menu
Channel info
Call detail(CDR)
Speed dials
Messaging
Packetization
Network info
Call Return
DND Forward Conference
Call History
1 2(abc) 3(def) MWI
4(ghi) 5(jkl) 6(mno) MUTE
7(pqrs) 8(tuv) 9(wxyz) FUNC
*
0(oper)
#
SPK
XFER
Flash SPD
Re-Dial
HOLD
Vol Down Vol Up
Those keys in blue font (which are referred as DSS function keys hereafter) can be
dynamically re-configured by user from menu-3.2 DSS Functions.
[14/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
3. Operation
3.1. Key Definitions in Menu Mode
【】HOLD
【MUTE】
【】FUNC
【】SPK
【Õ】 / 【Ö】
Enter the selected menu item or confirm the modification.
Delete the current character or the previous character if the cursor is
positioned at the end.
Return to upper level menu.
Exit the menu
Circle through the selected menu items and adjust volume.
【0 - 】 9
Cursor
Direct-selection / setting / jump-to-specific-item.
1. Insert mode only
2. Positioned on the currently setting value.
3. Positioned on the 1
st
menu item.
[15/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
)
3.2. Enter Alphabets and Numbers
Circular input by pressing the same key
Key Alphabet & Number
1 1
2 2->a->b->c->A->B->C
3 3->d->e->f->D->E->F
4 4-> g->h->i->G-> H->I
5 5->j->k->l->J->K->L
6 6->m->n->o->M->N->O
7 7->p->q->r->s->P->Q->R->S
8 8->t->u->v->T->U->V
9 9->w->x->y->z->W->X->Y->Z
0 0->[Space]
* Punctuation Table:
. @ - * # _ ? & $ / \ , : ; + (
‘ ! “ ¥ % < > | § = ٪ {}Φ ±
# #
3.3. Address-of-Record (SIP AoR)
The general form of SIP address-of-record is:
“Display” <protocol:email-like-address>;tag=param
z The “Display” field is optional. If present, it consists of any ASCII characters except
for ‘<’ and ‘>’. If the “Display” is present, the following address must be enclosed in a
paired ‘<’ and ‘>’.
z Protocol: Usually in lower case, such as “sip”, “tel” or “sips”. Note, “sip”, “tel” and
“sips” protocol names MUST be specified in lower case, which is stipulated on
RFC3261.
z email-like-address: in the form of “user-part@domain” where user-part is optional and
the domain part could be either a dotted IP or a domain name record, such as:
3200@SIP.isp.com
mike@192.168.192.100
192.168.3.100 (Note, the user-part is optional in direct IP dialing mode)
+886-3-5639025
z “tag=param”: Multiple parameters could be present (separated by ‘;’)
Example Note
Michael <sip:Michael@SIP.isp.com>
[16/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
Mike Jackson <sip:3200@SIP.isp.com>
“Voice Mailbox” <sip:8888@vms.SIP.isp.com> Display with enclosing ‘”’.
sip:300@SIP.isp.com AoR without display
sip:192.168.3.100 AoR without user part (in dotted IP)
tel:+886-3-5639025 ENUM AoR
sip:+88635639025@SIP.isp.com;user=phone ENUM AoR with SIP proxy support
4. Startup
Basically you have the following ways to configure your IP SIP Phone.
z Press
keypad.
z Use any modern web browser to configure the phone from a PC. The default login
password for both privileged and user-level password is “0000”.
z TELNET into the phone by any TELNET client. The default TELNET port is TCP port
23, login password is as the same as your phone password set in menu-3.1 on “IP SIP
Phone v2 Keypad-TELNET Administration“ (the default phone password is “0000”)
and the max concurrency is 4. IP-Range will not apply the changes until user presses
[Ctrl] +’s’ to apply the modifications or the client disconnected by [Ctrl] +’c’.
z Auto-provision on phone startup. Please refer to “Menu-7.4 Auto-provision.” on “IP SIP
Phone v2 Keypad- TELNET Administration”.
Note, before you can configure your phone-set from your PC, such as by a TELNET
【】
FUNC +
client or poi nt you r brows er to t he pho ne-set , you must have configured its IP via
keypad properly.
【】
# to activate the configuration menu and configure it via
4.1. Prerequisite
Initially, your phone can only be configured via keypad since it bears no valid IP yet. After
finishing configuring your network, you could use either a web browser (HTTP port 80) or a
TELNET client (TCP port 23) if you have a small number phone-sets to configure.
However, we recommend you to use TFTP for auto-provision if you have to administer
large amounts of phone-sets. For TFTP provision, please refer to 12.4 Auto Provisioning on this
document.
4.1.1. Network
To configure your network:
z Press 【FUNC】+ 【#】
z Go to 【6.Network】\【1.General】
Please configure the phone based on your network configuration: DHCP, static IP or
[17/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
PPPoE.
4.1.1.1. DHCP
z Pick【1.Mode】\【1.DHCP】
z Disable【4.Use Static DNS】by choosing 【2.DHCP】
Note: if you want to assign a different domain name server instead of using those obtained by
DHCP, you should choose【1.Static DNS】and set the IP of your specific DNS into
【5.Static DNS】, such as “1.Primary DNS” = 192.168.3.254
The supported DHCP options are:
z Client PC address
z DHCP option 1—Client Subnet Mask
z DHCP option 3—Gateway IP on the client’s subnet
z DHCP option 6—One or two Domain Name servers
z DHCP option 15—Domain name
(
modify this as necessary)
.
z DHCP option 42—Network Time Protocol servers
z DHCP option 66 (TFTP server name)
【
Note: To make DHCP option 6 take effect, you must disable
MENU】=>【6.Network】
/ 【1.General” /【4.Use static DNS】 by picking 【2.DHCP】
Note: If DHCP option 42 is present, it will overwrite the SNTP server in menu-7.3.2
【
Server IP】
Note: DHCP option 66 will overwrite the Auto-provision server in Menu-7.4.2 【TFTP
server】
4.1.1.2. Static IP (Fixed IP)
z Pick【1.Mode】\【2.Static assign】
z Go to【2.Static Settings】, and enter your network configurations based on your ISP.
For example:
1. Host IP = 210.201.210.132
2. Network mask = 255.255.255.0
3. Gateway IP = 210.201.210.128
z Enable【4.Use Static DNS】by choosing【1.Static DNS】
(modify this as necessary)
(modify this as necessary)
(modify this as necessary)
】
z Assign【5.Static DNS】, such as: 【1.Primary DNS
= “168.95.1.1” (modify this as
necessary)
4.1.1.3. PPPoE
z Pick【1.Mode】\【3.PPPoE】
z Go to【3.PPPoE settings】and enter your PPPoE authentication information, such as:
1. Login ID = MyPPPoEAccount
2. Password = PPPoEDialupPassword
(modify this as necessary)
(modify this as necessary)
[18/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
3. Service Name = Optional, some ISP requires it
(modify this as necessary).
4.1.1.4. Verify Network Configuration
Press 【F7】 (which default is a shortcut to menu【8.Advanced】\【4.System Status】\
【1.Network】) to check current active network settings:
1 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 2 1 0 . 1 1 3
MA C :
1 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 2 1 0 . 1
It will display the host IP, Ethernet MAC address and the active DNS IP (secondary DNS IP
will be shown if available) in order.
Once finishing network configuration, you should be able to place a point-to-point call. For
example, if your phone IP is “192.168.1.10” and you want to dial another SIP phone which IP is
“192.168.1.20”, please dial “*20**5060” (or just “*20” if the target phone listens on UDP port
5060; otherwise you must dial the target UDP port as well). This is “LAN dialing” (Refer to
section 8.1-“Dialing Scheme” on this document). If the call could be set up correctly, then your
network configuration is fine; otherwise, please refer to B-1 on Appendix B-“Trouble Shooting”.
Note, if you reside on a LAN without gateway, you should specify the gateway IP as
“0.0.0.0” rather than assigning a non-existent or an invalid IP; otherwise the network packets may
not be routed correctly (which may result in no voice packets could be sent from this phone)!
This constrain applies to DHCP and PPPoE as well: DHCP and PPPoE server should not
designate a non-existent or invalid gateway.
4.1.2. SIP Service
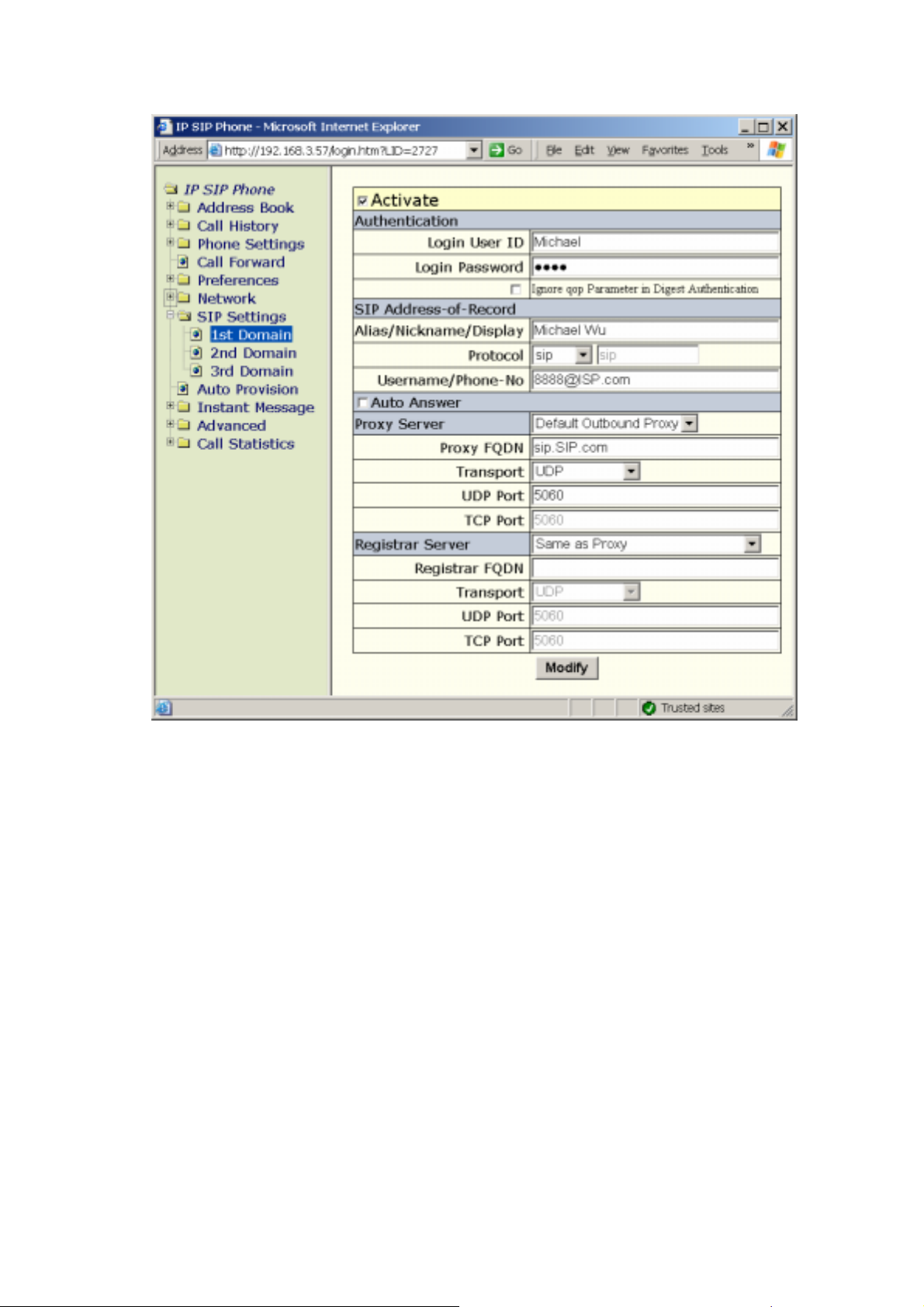
Before you start, you should ensure you have SIP-related data from your ISP. For example,
if you get the following information from your SIP ISP:
i. Account: Michael
ii. Password: secret
iii. SIP address-of-record: 8888@isp.com
iv. SIP Proxy / Registrar Server: sip.isp.com, which serves on UDP port 5060
Then you could configure your IP SIP Phone by a web browser as below:
[19/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
Alternatively, you mayo to 『Main Menu』=>”6.Network” / ”2.SIP settings” / ”1.1
to configure these information by keypad.
i. If you have applied for more than one service domains, please repeat step I and II
until all active domains are properly configured. IP SIP Phone supports three
different service domains at most.
ii. After saving the configuration, the system will try to register to those activated SIP
domains. The flashing green LED of 【Registration】 key indicates that the
registration is undergoing. Once the green LED stops flashing, you could know the
registration result by the LED. Please refer to section-10.11 “Registration on
Demand” and section-10.12 “Multi-domain Registration” on this user’s guide for
detail.
iii. If you failed to register your phone to SIP registrar, please refer to Appendix
B-“Trouble Shooting” on this document.
4.1.3. Configure NAT and Firewall
st
Realm”
If your SIP server locates on public internet, whereas your phone resides on a local area
[20/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
network, please refer to chapter 13-“NAT Traversal” on this user’s guide if your phone-set is
behind network address translator (NAT) and / or firewall.
4.2. Initialization
(a) Startup:
I P S I P P
V ersion
hone
(b) Check for auto-provision. Please refer to section 12.4 Auto Provisioning on this
document for detail
i. Auto-provision is on but no TFTP server specified:
A u t o - p r o v i s i o n
N o T F T P s e r v e r !
ii. Download configuration files from TFTP server
T F T P servername
i p r a n g e r . c f g . . . .
iii. Download failed:
T F T P ipranger.cF
T i m e d o u t
iv. Download successfully and apply changes:
A u t o - p r o v i s i o n
v. If auto-provision does not apply any changes to current settings:
(c) Check Date and Time:
Note:
IP SIP Phone will go the Idle ready Mode after 5 seconds if user dose not enter
any digit. The default system time on start-up is January 1, 1970, 00:00,
GMT.
i p r a n g e r . c f G . . . .
A u t o - p r o v i s i o n
U s e R O M s e t t i n g s
C u r R e n t d a t e :
MM/ DD/ YYYY
C u r R e n t t i m e :
h h: mm: s s
[21/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
User entry any digit for Time & Date. It must press 【HOLD】Key to be Idle
Ready Mode Display.
The phone will synchronize its time by Simple Network Time Protocol, SNTP,
with network time server regularly if SNTP is enabled. If you want to keep the
time you manually set previously, you must disable SNTP. Please refer to
section-4.4.1 “Date/Time” on “IP SIP Phone v2 Web Administration” for
detail.
You can just ignore the date & time settings on boot, leaving the phone to
synchronize its clock with network time server. Please check menu-3.3.4:
“Time zone” (by TELNET or keypad) to adjust your time zone otherwise the
synchronized time may be several hours late (earlier) than your local time.
Please refer to section-4.4.1 “Date/Time” on “IP SIP Phone v2 Web
Administration” for detail.
4.3. Registration
(a) Registering
R eg t o r egistrar
. si p . f c i .com.tw
The registered on-line timeout is 3600 seconds (1 hour).
(b) Registration Done
R eg i s t e r ed
E xp i r e s in 3600s
System will refresh registration after 90% of the expiration interval elapsed.
(c) Registration Failed
R eg e r r : host unr
r ac h a b l e
This message will freeze the screen for a while, such as 5 seconds, for the user to figure
out the reason. Failed registration will shorten the re-registration interval to 90 seconds.
5. Shutdown
5.1. Unregistration
U nr e g i s t ering...
[22/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
6. Idle
6.1. Registered
F ri M M / D D hh:mm
M ic h a e l Wu
6.2. Not registered yet or registration expires
F ri M M / D D hh:mm
M ic h a e l Wu
The registration LED will flash to indicate that the phone set has not been registered to any
service domain. That is, the phone set could only be reached via “Intra-domain Dialing”, “IP
Dialing” or “LAN Dialing” methods; please refer to section 8.1- “Dial Scheme” on this user’s
guide for detail.
6.3. Regular Registration
1. Registering
R eg t o r egistrar
. si p . f c i .com.tw
2. Registration Done
R eg i s t e r ed
E xp i r e s in 3600s
3. Registration Failed
R eg e r r : host unr
r ac h a b l e
This error message will freeze the screen for a while on idle state, such as 5 seconds,
for the user to figure out the reason. Failed registration will shorten the re-registration
interval to 90 seconds. You could perform registration on demand by pressing
【】
Registration to force an immediate registration.
[23/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
7. Take Calls
In menu mode, you cannot receive calls. If there is incoming calls when you are configuring
your phone, the call will be silently rejected with a 486 busy response.
Besides, if you enter menu by DSS keys (see menu-3.2 DSS features), the phone will start
ringing when incoming calls are waiting. To pick up the incoming call, you must exit menu first
then take it as a normal incoming call (lifting the handset has no effect in menu mode).
7.1. Ringing
Play rings, and blink both red and green lamp of related 【A / B / 】C Call
(a) On Idle State
F ro m mm:ss
S co t t S u n
(b) Other calls are in progress:
1. Pop up the caller ID for 7 seconds. It may show the display name if the caller ID
could be found on the address book. The “mm:ss” keeps track of the time elapsed
after the call arrived.
F ro m mm:ss
S co t t S u n
2. The channel LED of this incoming waiting call,
【】
3.
Forward and
call.
4. Call waiting alarm will alert the user twice in 7 seconds.
Note: If the caller ID is too long to accommodate into a line or you want to review the caller ID
after the screen pop-up disappeared, you can review the call information on each channel
【】
by pressing
Those records (with their caller IDs, AoR, shown) are volatile in memory such that they
F2 , which is mapped to “Channel info” by default.
A . C A l l e r I D ( A o R )
B . C A l l e r I D ( A o R )
【】
Reject LEDs will be on for the user to handle this incoming
【
A / B / 】C Call , will flash fast.
will be clean up every time the system reboots. If you review them on idle mode, you may
press 【Redial】to dial a specific number. Each record keeps the following call-related
information:
[24/100]

IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
1 . C A l l e r I D ( A o R )
2 . F r o m ( C O n t a c t )
3 . C O D E C
4 . U s e r A g e n t
5 . M e d i a S e s s i o n
1. Caller ID: address-of-record of the peer (press 【Redial】to dial this number).
2. From: Contact IP of the peer for SIP signaling (press 【Redial】to dial this number).
3. CODEC: CODEC employed for the call.
4. User agent: The phone tool used by the peer for this call.
5. Media session: display the local and remote RTP/RTCP session.
1 . L o c a l R T P
2 . R e m o t e R T P
Display the RTP IP and port pair of CPE for RTP/RTCP media stream.
1 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 3 . 1 : 6 2 2 6
2 / 6 2 2 6 3
The format comes in the format “xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:RTP/RTCP”, which specifies the IP
of CPE and the UDP port used for RTP and RTCP session. The information will be
timely updated in call connection and the unavailable information will be shown as
“N/A”.
7.2. Reject Call
【】
Press
“received call”.
Reject on an incoming ringing call to reject it as busy and recorded it as a
7.3. Forward Call
【】
Press
available or reply it as busy if not available. This forwarded call will be recorded as a “received
call”.
Forward on an incoming ringing call to forward it to a preconfigured number if
To configure the target number to forward to, please go to menu “4.Call Forward” / “1.
Target Number.” (by TELNET or keypad); alternatively, you may refer to section 4.5 “Call
Forward” on “IP SIP Phone v2 Web Administration” for detail.
This may also be a network feature, handled from a network configuration by the system
administrator.
7.4. Answer Call
mm:ss
[25/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
S co t t S u n
The “mm:ss” keeps track of the time elapsed after answered.
(A) On Idle State:
a. Press
b. Pick up the handset or turn on the speaker phone to answer it. Note: if you turn the
(B) Other calls are in progress
a. Press
b. The
【
A / B / 】C Call to answer the call
ear-phone on, the voice will be output to ear-phone and the speaker LED will flash
to notify that ear-phone is active.
【
A / B / 】C Call to answer the call
【】
Reject and
incoming waiting call as busy by pressing
target number by pressing
【】
Forward LEDs will be on such that you may reject the
7.5. Connected
mm:ss
S co t t S u n DTMF
7.6. Disconnected
【】
Reject or forward it to a predefined
【】
Forward .
(a) Peer hangs up
R el e a s e d mm:ss
S co t t S u n
Where “mm:ss” indicates the duration of the call. If the user is on speaker phone mode, it
will return to IDLE state in 5 seconds.
(b) User hands up
1. Ringing calls are waiting => Back to Ringing State
2. Answered calls are waiting:
The “Holding calls recall” will be triggered on expiry to alarm the user that
there are still some holding calls. User could pick up the holding call by hooking up
again; otherwise the holding call will be disconnected after ringing for 1 minute.
After disconnected, you may review the call detail record (CDR) by pressing
which is mapped to “Call detail” by default. “Call detail” keeps track of CDR of the latest three
connected and finished calls (either incoming or outgoing). Those records (with their caller IDs,
【】
F3 ,
AoR, shown) are sorted by their finished time with latest comes first. Besides, they are volatile
in memory such that they will be clean up every time the system reboots.
[26/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
)
1 . C A l l e r I D ( A o R )
2 . C A l l e r I D ( A o R )
3 . C A l l e r I D ( A o R )
You may press 【Redial】to dial the target’s SIP address-of-record.
Each record keeps the following call-related information:
1 . C A l l e r I D ( A o R
2 . T i m e o f c a l l
3 . D u r a t i O n
4 . F r o m ( C O n t a c t )
5 . C O D E C
6 . U s e r a g e n t
7 . M e d i a T r a f f i c
1. Caller ID: address-of-record of the peer (press 【Redial】to dial this number).
2. Time of call
3. Duration: call active time.
4. From: Contact IP of the peer for SIP signaling (press
【
Redial】to dial this number).
5. CODEC: CODEC employed for the call.
6. User agent: The phone tool used by the peer for this call.
7. Media traffic:
The media-related information will be available only when the call lasted for more
than 20 seconds. But the information about RTP session such as local and remote IP
/ port for RTP session is always available.
1 . R T P s e s s i o n
2 . P a c k e t s
3 . B y t e s
4 . P a c k e t l o s t
5 . D e l a y
7-1 RTP session:
1 . L o c a l R T P
2 . R e m o t e R T P
Display the RTP IP and port pair of CPE for RTP media stream.
1 9 2. 168. 3. 1: 6226
2 / 62263
The format comes in the format “xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:RTP/RTCP”, which
specifies the IP of CPE and the UDP port used for RTP and RTCP session.
7-2 Packets: Received / Sent RTP packets
[27/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
@
S e nt : 1, 234, 567
R c vd: 1, 234, 567
7-3 Bytes: Received / Sent bytes, including IP / UDP / RTP header and payload
S e nt : 1, 234, 567KB
R c vd: 1, 234, 567KB
7-4 Packet lost: Received / Sent RTP packet lost ratio.
S e nt : 11. 21%
R c v d : 9 . 3%
7-5 Delay: One-way / Round-trip delay
O n e- way: 1, 234 mS
R o Und-trip:N/A
7.7. Forward and DND
You can configure the target number to forward to while this phone is busy or not answered
within a predefined guarding interval. This forwarding number is also employed while the phone
is engaged in Do Not Disturb (DND) mode or while the user presses
【】
Forward key on an
incoming waiting call.
The system forwarding rules will check Do Not Disturb mode first, then All Calls Forward,
Busy Forward, finally going to No Answer Forward while no-answer timer expires.
7.7.1. Do Not Disturb (DND)
You can block incoming calls by configuring the Do Not Disturb feature. Blocked calls are
logged in the Missed Calls.
【】
Press
DND to toggle Do Not Disturb feature.
7.7.2. Call Forward
To configure the target number to forward to while this phone is busy or not answered within
a predefined guarding interval:
z By keypad or TELNET:
Press
【】
FUNC
【】
+ # to activate menu.
Go to submenu “4. Call forward” / “1. Target number”.
Press
【】
HOLD to pick an entry from address book. . Use 【Õ】and 【 Ö】to
view the current number.
M I c h a e l < s i P : 8 8 8 8
Q u a n t i e r T e c h . c o
【】
Press MUTE to remove the current mapping of forward number.
[28/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
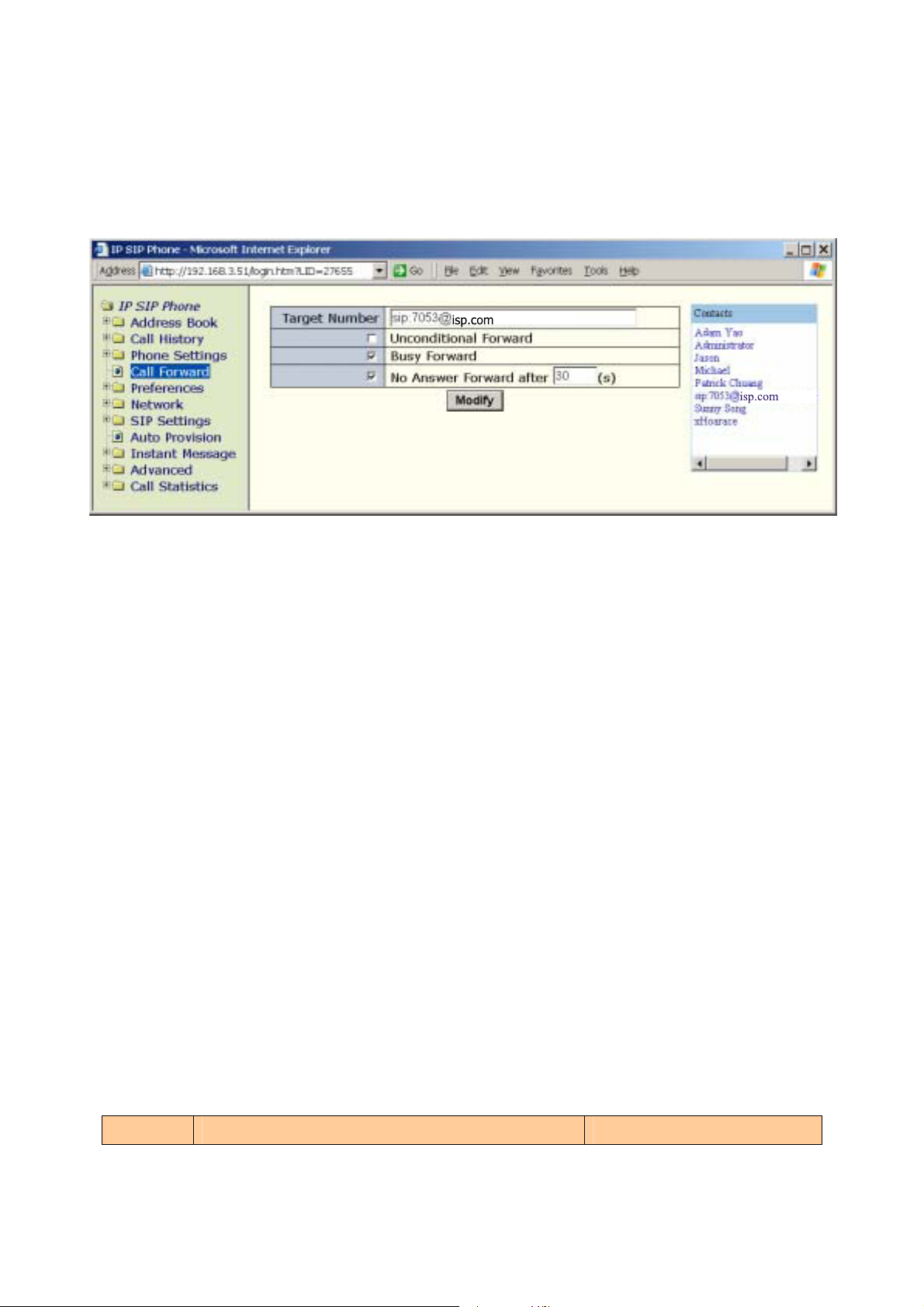
z By web browser:
Go to
an entry from the address book to set it as “Target Number”.
Delete the number in the text input to remove it.
Note: by default,
This target forwarding number is also employed while the phone is engaged in Do Not
Disturb (DND) mode or while the user presses
『
Call Forward』 page, then click the “Contacts” on the right panel to pick
isp.com
isp.com
【F1】
is mapped to the “Call Forward” menu.
【】
Forward key on an incoming waiting call.
7.7.2.1. All Calls Forward
You can configure to unconditionally forward all incoming calls by enable the All Calls
Forward feature from menu 4-2 “All Calls Fwd” or on 『Call Forward』 web page. Forwarded
calls are logged in the Missed Calls, menu 2-1. If this feature is enabled, the corresponding
【】
Forward LED will blink slowly to remind user. Default is disabled.
7.7.2.2. Busy Forward
You can configure to forward incoming waiting calls when the system is busy, on which time
all lines are occupied, from menu 4-3 “Busy Forward” or on 『Call Forward』 web page.
Forwarded calls are logged in the Missed Calls, menu 2-1. Default is disabled.
7.7.2.3. No Ans wer Forward
You can configure to forward incoming waiting calls after ringing for a predefined interval
from menu 4-4 “No answer fwd” or on 『Call Forward』 web page. Forwarded calls are logged
in the Missed Calls, menu 2-1.
7.7.3. Forwarding Rules
Priority Conditions Results
[29/100]
IP SIP Phone v2 User’s Guide Mar. 2005
All Calls
Forward
Busy
Forward
【】
DND is on1
Forwarding number is
available
Forward the incoming call to
the target forwarding number.
1. Reply as 480 Temporarily
Forwarding number is
unavailable.
unavailable
2. Recorded as a missed call
Both
1. All calls forward feature is on
2. Forwarding number is available
Forward the incoming call to
the target forwarding
number.
Others Normal incoming call
Both
1. Busy forward feature
Forward the incoming call to
the target forwarding number.
is on
System call capacity is
2. The forwarding
full loaded
number is available.
1. Reply as busy.
others
2. Record as a missed call.
No
Answer
【】
Press
Forward on a
ringing call.
Both
1. No answer forward
feature is on
Forwarding number is
available
Forwarding number is
unavailable
Forwarding number is
available
Forward the incoming call to
the target forwarding number.
1. Reply as busy
2. Record as a received call.
Forward the incoming call to
the target forwarding number.
1. Reply as no-answer.
Forwarding number is
Forward
2. No-answer timer
2. Recorded as a missed call.
unavailable
expires.
Note: Those not-forwarded calls should be recorded as “Missed Calls” and retrievable at a later
time to review. The call history LED should turn on to inform users and turn off after the user
has reviewed them.
Note: Whenever there are un-reviewed missed calls, the Call history LED will be on. Moreover, it
will directly enter into Missed calls menu while the call history LED is on and go into Call
history menu if the LED is off.
8. Make Calls
If system is busy or there is no enough resource available, such as no suitable codec or no call
manager available, to make a call, it will play “Network congestion tone” and show the
following prompt.
S Y S T E M B U S Y
1
【】
DND , Do Not Disturb, will turn on the corresponding LED.
[30/100]
 Loading...
Loading...