ATL IP250 User Manual

IP 250
Thank you for choosing your Atl IP250 telephone. You have selected a carefully designed
telephone that incorporates the very latest technology, offering a stylish instrument, and
providing many years of excellent service.
This booklet will ensure you obtain the best use of your IP telephone.
User Guide

IP250 IP Phone
Web Conguration Manual
To access the web conguration and status pages for your phone simply open up your
preferred web browser and enter the IP address of your IP250 into the address URL eld.
The web interface has two privilege levels: Administrator and User. Both privilege levels are
password protected by default. The user names for the Administrator and User are “admin”
and “user” respectively. And the default password for both privilege levels is “voip”.
The major difference between an Administrator and a User is that the Administrator has full
control over the IP250 device while the User mode only allows limited changes.
2

Table of Contents
IP250 IP Phone
1 HOME 5
2 LAN 6
2.1 LAN Status 6
2.2 LAN Settings 7
2.3 PPPoE 8
2.4 IPSEC 9
3 SIP 10
3.1 Server 10
3.2 Extension 11
3.3 Digit Map 13
3.4 User 1 14
3.5 OOB Signaling 15
3.6 Tos/Diffserv 15
3.7 Tone 16
3.8 Ring 17
3.9 Service Code 18
3.10 Phonebook 19
4 CODECS 20
5 SYSTEM 21
5.1 Security 21
5.2 Timeout 22
5.3 Localization 23
5.4 Handset 24
5.5 Port Number 25
5.6 Ringer Tone 25
5.7 SNMP 26
6 DOWNLOAD 27
6.1 HTTP Download method 27
6.2 AutoUpdate 28

7 CONFIGURATION 29
7.1 Backup 29
7.2 Restore 30
8 RESET 31
PHONE FUNCTIONS
MESSAGE 32
ENTER 32
DELETE 32
STORE 32
FORWARD 32
SET 32
CLID 32
MUTE 33
HOLD 33
CONF 33
AUTO RD 33
REDIAL/OUT 33
SPEAKER/HEADSET 33
VOLUME UP AND DOWN 33
TRANSFER 33
OPERATION 33
CALLER ID 35
PHONE BOOK 35
PHONE SETTING 37
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS 39
32
GUARANTEE 39
MANUFACTURER’S DECLARATION 40
4 37

1 HOME
This following page is the rst page displayed when the device is logged in to. Figure 1
and 2 show the variations in pages dependent on an Administrator or a User logging in. As
the screenshots show below, the user level privilege (Figure 1) doesn’t have access to the
conguration page of CODECS, Download and Conguration.
It displays how long the device has been running since its last reboot, the IP address the
device is currently using, whether or not the device is password protected, and also displays
the main application and downloader application rmware versions. In addition, the MAC
address of the WAN port, and serial number of the device, if it has one, are also displayed in
this page.
Figure 1 - User Privilege Mode
Figure 2 - Administrator Privilege

2 LAN
2.1 LAN Status
The following page allows conguration of the phone’s local network settings. Sub-pages
are available for the following on the left of page: the LAN interface status, conguration of
the LAN interface settings, and conguration of DHCP server settings, and Port Forwarding
(NAPT) Settings.
2.1 LAN Status
The page displays the current status of the LAN interface, including the IP address and other
network settings the interface is currently using.
6 35

2.2 LAN Settings
The following page allows the user to congure the private LAN interface settings. Assign an
IP address to the LAN Ethernet port. This IP address is also the default router address for the
devices on the private LAN. The default LAN interface IP address is set to 192.168.1.1. Enter
the subnet mask for the private LAN. If you wish to set the broadcast and multicast limits for
the bridge/router, enter these values as percentages of the LAN interface Ethernet bit rate.
Leaving these values blank will imply values of 100%.
Press “Save LAN Settings” to save and apply the LAN interface settings. Any new settings will
take effect immediately.

2.3 PPPoE
This page allows you to congure the phone to authenticate to your network using PPPoE. If
you wish to use this authentication method please ll out the appropriate elds and select Yes
in the Enable PPPoE’s selection Box. Please note that you will need to obtain your username
and password from who ever provides your network service.
8 33

2.4 IPSEC
UPDATE TO FOLLOW

3 SIP
3.1 Server
The following page allows conguration of the SIP server and endpoint settings.
Enter the address and port value of the SIP server. The address may be an IP address or
the name of the server. If no SIP server address is entered, the device will attempt to self
provision a SIP server using a DNS query. For this to be successful, ensure that the DNS
settings on the device include a DNS server address which is congured with the SIP server
address and will respond to the query, and the appropriate domain name of the network.
If you wish to specify a special SIP domain name, you may enter the domain name here. If
no domain name is entered, the SIP domain name will be set to that of the network (i.e. that
which is obtained via DHCP, or specied on the LAN settings page).
The currently provisioned SIP Server and Domain are displayed beside “SIP Server Settings”
for informational purposes. Select whether or not to send a Registration Request to the SIP
server by checking the box next to “Send Registration Request”.
For the endpoint, set the dial plan to be used by all lines, and select the transport method to
be used for SIP signaling (either UDP or TCP). For each line on the endpoint (NOTE: The IP
Phone has a single line), enter the Line Phone Number, Caller-ID Name, signaling port value,
authentication Username and Password, and select if AEC is to be performed on this line.
Press “Save SIP Settings” to save the new values.
10 31
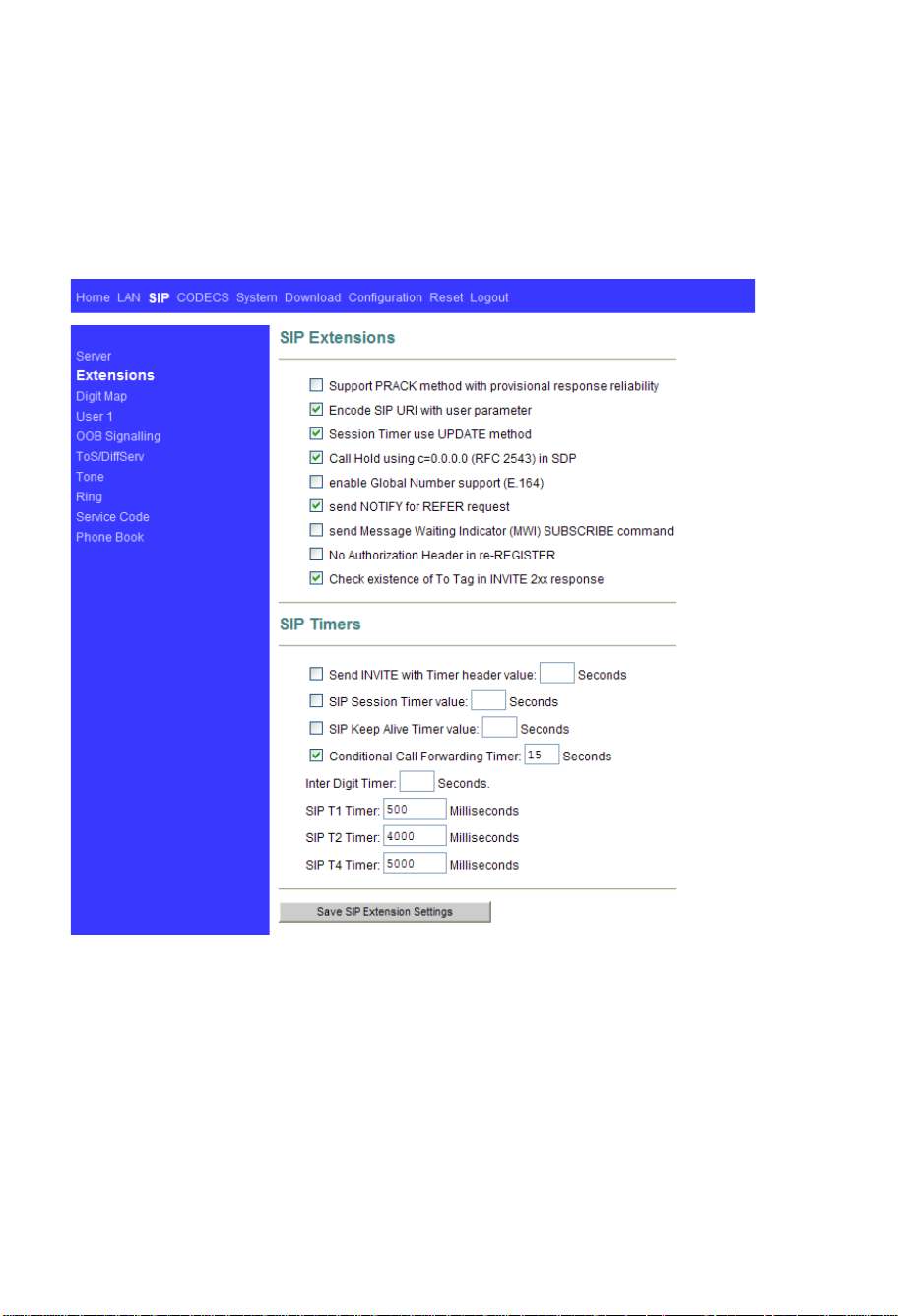
3.2 Extension
The following page allows specication of the SIP signaling stack behavior under certain
scenarios.
Support PRACK method: If you wish for the SIP stack to implement reliable transmission
►
of provisional responses according to RFC 3262 (using the PRACK method) ,check
the option.
Encode SIP URI with user parameter: include the user parameter “user=phone” in the
►
SIP URI headers.
Session Timer use UPDATE method: Session timer use update instead of reinvite.
►
Call Hold using C=0.0.0.0: using the call hold method described in RFC2543. If
►
unchecked, the call hold would follow RFC3263 method.

Enable Global Number support (E.164): add prex “+” for dialed numbers in sip
►
invitation.
Send NOTIFY for REFER request: send out NOTIFY request to transferer for
►
unattended and attended call transfer.
Send Message Waiting Indicator (MWI) SUBSCRIBE command: send SUBCRIBE
►
after registered to server to check if there are any messages to be read.
Send INVITE with Timer header: encode Timer header in all INVITE requests for
►
ringing timeout.
Enable SIP session timer: If you wish for the SIP stack to implement a session timer
►
according to “draft-sipsession-timer”, select the option.
SIP T1 Timer, SIP T2 Timer, and SIP T4 Timer: please refer to RFC3261.
►
Press “Save SIP Extension Settings” to save the new values.
12 29
 Loading...
Loading...