Page 1

PowerBook G4 17-inch
(Legacy)
2003-03-01
Page 2

Apple Inc.
© 2003 Apple Computer, Inc.
All rights reserved.
No part of thispublication may bereproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in
any form or by any means, mechanical,
electronic, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise, without prior written permission of
Apple Inc., with the following exceptions: Any
person is hereby authorized to store
documentation on a single computer for
personal use only and to print copies of
documentation for personal use provided that
the documentation contains Apple’s copyright
notice.
The Apple logo is a trademark of Apple Inc.
No licenses, express or implied, are granted
with respectto anyof the technology described
in this document. Apple retains all intellectual
property rights associated with thetechnology
described in this document. This document is
intended to assist application developers to
develop applications only for Apple-labeled
computers.
Apple Inc.
1 Infinite Loop
Cupertino, CA 95014
408-996-1010
ASSUMING THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO ITS QUALITY
AND ACCURACY.
IN NO EVENT WILL APPLE BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGESRESULTING FROMANY
DEFECT ORINACCURACYIN THIS DOCUMENT,even
if advised of the possibility of such damages.
THE WARRANTY AND REMEDIESSET FORTH ABOVE
ARE EXCLUSIVE AND INLIEU OFALL OTHERS, ORAL
OR WRITTEN, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. No Apple
dealer, agent, or employee is authorized to make
any modification, extension, or addition to this
warranty.
Some statesdo notallow the exclusionor limitation
of implied warranties or liability for incidental or
consequential damages, so the above limitation or
exclusion may not applyto you. This warranty gives
you specific legal rights, and you may also have
other rights which vary from state to state.
Apple, theApple logo, AirPort, AirPort Extreme,
eMac, FireWire, Instruments, Mac, Mac OS,
Macintosh, PowerBook, SuperDrive, and
Velocity Engine are trademarks of Apple Inc.,
registered in the United States and other
countries.
DEC is a trademark of Digital Equipment
Corporation.
GeForce4 isa trademark of NVIDIA Corporation.
Intel and Intel Core are registered trademarks
of Intel Corportation or its subsidiaries in the
United States and other countries.
OpenGL is a registered trademark of Silicon
Graphics, Inc.
PowerPC and and the PowerPC logo are
trademarks ofInternational Business Machines
Corporation, used under license therefrom.
Even though Apple has reviewed this document,
APPLE MAKESNO WARRANTY ORREPRESENTATION,
EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH RESPECT TO
THIS DOCUMENT, ITS QUALITY, ACCURACY,
MERCHANTABILITY, ORFITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. AS A RESULT, THIS DOCUMENT IS
PROVIDED “AS IS,” AND YOU, THE READER, ARE
Page 3
Contents
Introduction
Chapter 1
Chapter 2
Introduction to PowerBook G4 17-inch 9
Organization of This Document 9
Overview of PowerBook G4 17-inch 11
PowerBook G4 17-inch Features 11
Appearance 12
Peripheral Devices 14
System Software 14
Open Firmware 14
Computer Identification 14
Power Saving Features 15
Architecture 17
Block Diagram and Buses 17
Block Diagram 17
Main ICs and Buses 18
Microprocessor and Caches 18
PowerPC G4 Microprocessor 18
Level 2 Cache 19
Level 3 Cache 19
Intrepid Controller and Buses 19
System RAM 20
Boot ROM 20
FireWire Controllers 20
Ethernet Controller 20
Video Display Subsystem 20
I/O Controller 21
DMA Support 21
Interrupt Support 22
USB Interface 22
Ultra ATA-100 Interface 22
ATA-33 Interface 22
Modem Support 22
Sound Circuitry 23
Power Controller 23
AirPort Extreme Interface 23
CardBus Controller IC 24
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
3
Page 4

CONTENTS
Chapter 3
Devices and Ports 25
USB Ports 25
USB Connectors 25
USB Storage Devices 26
FireWire Ports 26
FireWire 400 Connector 26
FireWire 800 Connector 27
Booting from a FireWire Device 29
Target Disk Mode 29
Ethernet Port 29
Internal Modem 30
AirPort Extreme 31
Data Security 31
AirPort Extreme Hardware 32
AirPort Extreme Software 32
Bluetooth Technology 32
Hard Disk Drive 33
Hard Disk Dimensions 33
Hard Disk Connector 34
SuperDrive (DVD-R /CD-RW) 37
Trackpad 38
Keyboard 38
Changing the Operation of the Keyboard 39
Flat-Panel Display 44
External Monitors 45
Dual Display and Mirror Mode 45
Analog Monitor Resolutions 45
Digital Display Resolutions 46
DVI-I Connector 46
External Video Port 48
Sound System 49
Sound Inputs 49
Sound Outputs 50
Digitizing Sound 51
Chapter 4
4
Expansion Features 53
RAM Expansion Slots 53
Accessing the RAM Slots 53
Mechanical Design of DDR RAM SO-DIMMs 54
Electrical Design of DDR RAM SO-DIMMs 54
RAM SO-DIMM Electrical Limits 56
CardBus Slot 57
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 5

CONTENTS
Appendix A
Appendix B
Supplemental Reference Documents 59
Apple Technical Notes 59
3D Graphics 59
PowerPC G4 Microprocessor 59
Velocity Engine (AltiVec) 60
Mac OS X 60
I/O Kit 60
Open Firmware 60
RAM Expansion Modules 61
PC Card Manager 61
ATA Devices 62
USB Interface 62
FireWire Interface 62
Digital Visual Interface 63
Wireless Networks 63
Bluetooth 63
Abbreviations 65
Abbreviations and Standard Units 65
Other Abbreviations 65
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
5
Page 6

CONTENTS
6
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 7
Figures and Tables
Chapter 1
Chapter 2
Chapter 3
Overview of PowerBook G4 17-inch 11
Figure 1-1 Front view of the computer 13
Figure 1-2 Side views showing I/O ports 13
Architecture 17
Figure 2-1 Block diagram 17
Table 2-1 Buses supported by the Intrepid IC 19
Devices and Ports 25
Figure 3-1 USB Type A port 25
Figure 3-2 6-pin FireWire connector 27
Figure 3-3 9-pin FireWire 800 connector 28
Figure 3-4 Maximum dimensions of the internal hard disk 34
Figure 3-5 Hard disk connector and location 35
Figure 3-6 Keyboard layout 39
Figure 3-7 Alternate operations of function and control keys 40
Figure 3-8 Embedded numeric keypad operation 41
Figure 3-9 DVI-I connector 47
Figure 3-10 S-video connector 48
Table 3-1 Pin assignments on the USB port 25
Table 3-2 Pin assignments on the 6-pin FireWire connector 27
Table 3-3 Signals on the 9-pin FireWire 800 connector 28
Table 3-4 Signals for 10Base-T and 100Base-T operation 29
Table 3-5 Signals for 1000Base-T operation 30
Table 3-6 Pin assignments on the ATA hard disk connector 35
Table 3-7 Signals on the ATA hard disk connector 36
Table 3-8 Media read and written by the SuperDrive 37
Table 3-9 The function keys as control buttons 42
Table 3-10 Embedded keypad keys 43
Table 3-11 Control keys that change 43
Table 3-12 Picture sizes on the flat-panel display 44
Table 3-13 Picture sizes on an analog monitor 45
Table 3-14 Picture sizes on a digital display 46
Table 3-15 Main signals on the DVI-I connector 47
Table 3-16 MicroCross signals on the DVI-I connector 47
Table 3-17 Pin assignments for the S-video output connector 48
Table 3-18 Picture sizes for S-video output 48
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
7
Page 8
FIGURES AND TABLES
Chapter 4
Expansion Features 53
Figure 4-1 Removing RAM expansion slot cover 53
Table 4-1 Sizes of RAM expansion modules and devices 55
Table 4-2 Types of DRAM devices 56
8
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 9

INTRODUCTION
Introduction to PowerBook G4 17-inch
Important: The information in this document is obsolete and should not be used for new development.
Links to downloads and other resources may no longer be valid.
This developer note is a technical description of the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer. The note provides
information about the computer’s internal design, input-output features, and expansion capabilities.
This developer note is intended to help hardware and software developers design products that are compatible
with the Macintosh products described here. If you are not already familiar with Macintosh computers or if
you would like additional technical information, you may wish to read thesupplementary reference documents
described in Appendix A (page 59).
Organization of This Document
The information in this note is arranged in four chapters and two appendixes.
● Chapter 1, “Introduction”, (page 11) introduces the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer and describes its
features.
● Chapter 2, “Architecture”, (page 17) describes the internal logic of the computer, including the main ICs
that appear in the block diagram.
● Chapter 3, “Devices and Ports”, (page 25) describes the standard I/O ports and the built-in I/O devices.
● Chapter 4, “Expansion Features”, (page 53) describes the expansion features of interest to developers.
It includes development guides for expansion-bay devices, the RAM expansion modules, and the PC
Card slot.
● Appendix A (page 59) contains links to supplemental reference documents.
● Appendix B (page 65) is a list of the abbreviations used in this developer note.
Organization of This Document 9
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 10

INTRODUCTION
Introduction to PowerBook G4 17-inch
10
Organization of This Document
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 11

CHAPTER 1
Overview of PowerBook G4 17-inch
This chapter outlines the features of the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer.
PowerBook G4 17-inch Features
Here is a list of the features of the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer. Each feature is described in a later
chapter, as indicated.
● Processor The computer has a PowerPC G4 microprocessor running at a clock speed of 1 GHz. For more
information, see “PowerPC G4 Microprocessor” (page 18).
● System bus The speed of the system bus is 167 MHz.
● Cache location and speed In additionto the L2 cache, which is internal to the processor IC, the computer
also has a 1MB 5:1 L3 cache. See “Level 2 Cache” (page 19) and “Level 3 Cache” (page 19).
● RAM The computer has two standard PC2700 (333 MHz) DDR SO-DIMM expansion slots for SDRAM
modules. The computer comes with 512 MB of SDRAM installed in one slot. See “RAM Expansion
Slots” (page 53).
● ROM The computer has 1 MB of boot ROM used by Open Firmware at startup. For information about
the ROM, see “Boot ROM” (page 20). For information about Open Firmware, see “Open Firmware” (page
60).
● Hard disk storage The computer comes with a built-in hard disk drive with a capacity of 60 GB. For more
information, see “Hard Disk Drive” (page 33).
● Display The display is a 100 dpi,17 inch wide-screen TFT with a resolution of 1440x900. See “Flat-Panel
Display” (page 44).
● External monitor The computer supports an external video monitor, using the DVI connector for a digital
video display and an S-video connector for a PAL or NTSC video monitor. Included with the computer
are a DVI-to-VGA adapter and an S-video-to-composite adapter; a DVI-to-ADC Apple Display Connector
adapter is available separately. See “External Monitors” (page 45).
● Graphics IC and memory The nVidia GeForce4 440 Go graphics controller operates on the AGP-4x bus
along with 64 MB of DDR video SRAM. For more information, see “Video Display Subsystem” (page 20).
● Battery bay The computer has a single battery bay. The battery uses lithium ion cells and provides 55
watt-hours at 10.8 V (nominal) for up to 4.5 hours.
● Power adapter The computer comes with a 65 W power adapter with safety ground.
● SuperDrive (DVD-R/CD-RW drive) The computer has a built-in DVD-R/CD-RW SuperDrive drive. For
more information, see “SuperDrive (DVD-R /CD-RW)” (page 37).
PowerBook G4 17-inch Features 11
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 12

CHAPTER 1
Overview of PowerBook G4 17-inch
● CardBus slot The computer has a CardBus slot that accepts one Type I or Type II PC Card or a CardBus
Card. For more information, see “CardBus Slot” (page 57).
● USB ports The computer has two USB 1.1ports for an external keyboard, a mouse, andother USBdevices,
described in “USB Ports” (page 25).
● FireWire ports The computer has one IEEE-1394a 400 Mbps serial FireWire 400 port and one IEEE-1394b
800 Mbps serial FireWire 800 port. For more information, see “FireWire Ports” (page 26).
● Target disk mode The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer can act like a FireWire storage device connected
to another computer. See “Target Disk Mode” (page 29).
● Modem The computer has a built-in modem with 56 Kbps data rate and V.34, V.90, and V.92 support.
For more information, see “Internal Modem” (page 30).
● Ethernet The computer has a built in Ethernet port with an RJ-45 connector for 10Base-T, 100Base-T,
and 1000Base-T operation. For more information, see “Ethernet Port” (page 29).
● AirPort Extreme The fully-integrated, 54 Mbps AirPort Extreme provides a wireless LAN connection. For
more information, see “AirPort Extreme” (page 31).
● Bluetooth support Fully-integrated Bluetooth support enablesshort-range wireless connections between
desktop and laptop computers and a host of other peripheral devices. For more information, see
“Bluetooth Technology” (page 32).
● Sound The computer has a built-in microphone, stereo speakers, a stereo headphone jack, and a sound
input jack. See “Sound System” (page 49).
● Keyboard The keyboard has an embedded numeric keypad and inverted-T arrow keys. Some of the
function keys are used to control the display brightness and speaker volume. See “Keyboard” (page 38).
● Trackpad The integrated trackpad includes tap/double-tap and drag features and palm-rejection
capabilities. For more information, see “Trackpad” (page 38).
● Weight The basic configuration weighs 6.8 pounds.
● Size The computer is 15.4 inches (39.2 cm ) wide, 10.2 inches (25.9 cm) deep, and 1.0 inches (2.6 cm)
thick.
● Illuminated keyboard The computer has abacklit keyboard for optimal usability in all lighting conditions.
For more information, see “Keyboard” (page 38).
● Ambient light sensor The computer has an ambient light sensor which monitors lightlevels and activates
the illuminated backlit keyboard and adjusts the display brightness.
Appearance
Figure 1-1 (page 13) is a front view of the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer. Figure 1-2 (page 13) provides
side views showing the I/O ports.
12
Appearance
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 13

CHAPTER 1
Overview of PowerBook G4 17-inch
Figure 1-1 Front view of the computer
Figure 1-2 Side views showing I/O ports
Appearance 13
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 14

CHAPTER 1
Overview of PowerBook G4 17-inch
Peripheral Devices
Included with the computer are a 65 W Apple Portable Power Adapter, an S-video-to-composite cable, and
a DVI-to-VGA cable. In addition to these devices, the following peripheral devices are available separately:
● The PowerBook G4 Rechargeable Battery is available as an additional or replacement battery.
● The 65 W Apple Portable Power Adapter, which comes with the computer, is also available separately.
The adapter can fully recharge a completely depleted battery in three hours or less while the computer
is shut down or in sleep mode.
● The Apple DVI to ADC Adapter, which enables the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer to support Apple’s
ADC displays.
● The Apple Pro Keyboard, a full-featured USB keyboard.
● The Apple Pro Mouse, an optical USB mouse.
● The AirPort Extreme Base Station.
● A power cable for use on airliners is also available. The airline power cable should have a sense resistor
of 24.3 K ohms +/-5% connected between the power plug's shell and ground. For more information, see
“Power Controller” (page 23).
System Software
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer comes with Mac OS X version 10.2. For the latest information, see the
references listed in “Mac OS X” (page 60).
Here are a few items of interest about the system software on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer.
Open Firmware
System software on all current Macintosh models uses a design based on Open Firmware. With this approach,
the ROM on the main logic board contains only the Open Firmware code needed to initialize the hardware
and load an operating system. The rest of the system code is loaded into RAM from disk or from the network.
For more information, see the references listed in “Open Firmware” (page 60).
14
Computer Identification
Rather than reading the box flag or the model string and then making assumptions about the computer’s
features, applications that need to find out the features of the computer should use IORegistry calls to test
for the features they require. IORegistry calls are part of the I/O Kit API. For more information, see the references
listed at “I/O Kit” (page 60).
Peripheral Devices
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 15

CHAPTER 1
Overview of PowerBook G4 17-inch
Asset management software that reports the kind of computer it is running on can obtain the value of the
model property from the IOService plane of the IORegistry. For the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer, the
value of the model property is PowerBook5,1.
Power Saving Features
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has several profiles to save power. These profiles are labeled on the
Energy Saver panel of System Preferences.
Reduced Processor Performance
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer reduces both processor speed and voltage to save power. Reduced
processor speed allows the software to change the processor’s clock speed, slowing down to conserve power
or speeding up when more speed is needed. The slower clock speed is 667 MHz and the L3 cache is turned
off.
The user interface for the reduced processor speed is located in the options tab under the Energy Saver panel
in System Preferences.
Operating Modes
The power management protocols on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computersupport two power-saving modes:
idle and sleep.
● Idle: The system is idling with the main processor stopped in a halted, low-power state. All clocks are
running; the system can return to running code within a few nanoseconds. Cache coherency is maintained
in this state.
● Sleep: The system is completely shut down, with only the DRAM state preserved for quick recovery. All
processors are powered off with their state preserved in DRAM. All clocks in the system are suspended
except for the 32.768 kHz timebase crystal on the PMU99 IC.
The computer automatically enters idle mode after several seconds of inactivity. If the computer is attached
to a network, it is able to respond to service requests and other events directed to the computer while it is
in idle mode.
While it is connected to an AC power supply, the computer can also respond to network activity when it is
in sleep mode. The user can enable this feature by selecting Wake-on-LAN in the Energy Saver panel of
System Preferences.
When operating on the battery in sleep mode, the computer consumes less than 1 watt of power, meeting
the Energy Star power-saving standard. When operating on the power adapter in sleep mode, the combined
computer and adapter consume 3 to 4 watts of power.
Important: Peripherals such as PCMCIA cards and USB devices that do not conform to the computer’s power
management protocols preventthe computer from switching to sleep mode and so deny the user the benefits
of this energy-saving mode. When such peripherals are attached to the computer, the operating system
displays a dialog to inform the user that the computer no longer meets the Energy Star requirements.
System Software 15
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 16

CHAPTER 1
Overview of PowerBook G4 17-inch
16
System Software
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 17

CHAPTER 2
Architecture
This chapter describes the architecture of the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer. It includes information about
the major components on the main logic board: the microprocessor, the other main ICs, and the buses that
connect them to each other and to the I/O interfaces.
Block Diagram and Buses
This section is an overview of the major ICs and buses on the computer’s main logic board.
Block Diagram
Figure 2-1 (page 17) is a simplified block diagram of the main logic board. The diagram shows the input and
output connectors, the main ICs, and the buses that connect them together.
Figure 2-1 Block diagram
Block Diagram and Buses 17
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 18

CHAPTER 2
Architecture
Main ICs and Buses
The architecture of the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer is designed around the PowerPC G4 microprocessor
and Intrepid IC that contains the memory controller and I/O device controller.
The PowerPC G4 microprocessor is connected to the Intrepid IC by a MaxBus bus. The bus clock speed is 167
MHz. Other buses that connect with the Intrepid IC are summarized in Table 2-1 (page 19), which is in the
section “Intrepid Controller and Buses” (page 19).
The Intrepid I/O controller has a 32-bit PCI bus with a bus clock speed of 33 MHz. That bus also connects to
the Boot ROM and the CardBus controller. The Intrepid IC has other buses that connect with the hard disk
drive and the optical drive, the power controller IC, the sound IC, the internal modem module, and the
wireless LAN module.
Each of the components listed here is described in one of the following sections.
Microprocessor and Caches
The microprocessor communicates with the rest of the system by way of a 64-bit MaxBus bus to the Intrepid
IC. The microprocessor has a separate bus to its internal second-level cache.
PowerPC G4 Microprocessor
The PowerPC G4 microprocessor used in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has many powerful features,
including an efficient pipelined system bus called MaxBus.
Features of the PowerPC G4 include
● 32-bit PowerPC implementation
● superscalar PowerPC core
● Velocity Engine (AltiVec technology): 128-bit-wide vector execution unit
● dual 32 KB instruction and data caches
● an on-chip level 2 (L2) cache consisting of 256 KB with a clock speed ratio of 1:1
● high bandwidth MaxBus (also compatible with 60x bus)
● fully symmetric multiprocessing capability
18
The PowerPC G4 microprocessor in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer runs at a clock speed of 1 GHz.
Microprocessor and Caches
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 19

CHAPTER 2
Architecture
Level 2 Cache
The data storage for the L2 cache consists of 256 KB of fast static RAM that is built into the microprocessor
chip along with the cache controller and tag storage. The built-in L2 cache runs at the same clock speed as
the microprocessor.
Level 3 Cache
The data storage for the L3 cache is 1 MB of DDR SRAM running at a clock speed ratio of 5:1. The tag storage
for the L3 cache is built into the microprocessor.
Intrepid Controller and Buses
The Intrepid IC provides cost and performance benefits by combining several functions into a single IC. It
contains the memory controller, the PCI bus bridge, the Ethernet and FireWire interfaces, and the AGP
interface.
Each of the separate communication channels in the Intrepid IC can operate at its full capacity without
degrading the performance of the other channels.
In addition to the buses listed in Table 2-1 (page 19), the Intrepid IC also has separate interfaces to the
physical layer (PHY) ICs for Ethernet and FireWire, and an IIC (inter-IC control bus) interface that is used for
configuring the memory subsystem.
Table 2-1 Buses supported by the Intrepid IC
Bus clock speedWidth of data pathDestinationsBus
167 MHz64 bitsMicroprocessorMaxBus
333 MHz64 bitsSystem RAMMemory
33 MHz32 bitsAirPort Extreme, CardBus, Boot ROMPCI
66 MHz32 bitsGraphics ICAGP4X
100 Mbps16 bitsHard driveUltra ATA-100
33 MHhz16 bitsSuperDriveATA-33
The microprocessor and the I/O controller IC are described in their own sections. The following sections
describe the other subsystems that are connected to the Intrepid IC.
Intrepid Controller and Buses 19
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 20

CHAPTER 2
Architecture
System RAM
The memory subsystem in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computersupports twoslots for 333 MHz DDR (PC2700)
SO-DIMMs (small-outline dual inline memory modules). The data bus to the RAM and DIMM is 64 bits wide,
and the memory interface is synchronized to the MaxBus bus interface at 167 MHz. See “RAM Expansion
Slots” (page 53).
Boot ROM
The boot ROM is connected to the Intrepid IC by way of the high byte of the PCI bus plus three additional
control signals: chip select, write enable, and output enable. The boot ROM is a 1 MB by 8 bit device.
FireWire Controllers
The Intrepid IC FireWire controller supports IEEE 1394a for a maximum data rate of 400 Mbps (50 MBps) and
IEEE 1394b for a maximum data rate of 800 Mbps (100 MBps). The Intrepid IC provides DMA (direct memory
access) support for the FireWire interface.
The controller in the Intrepid IC implements the FireWire link layer. A physical layer IC, called a PHY, implements
the electrical signaling protocol of the FireWire interface and provides the electrical signals to the port. For
more information, see “FireWire 400 Connector” (page 26) and “FireWire 800 Connector” (page 27).
Ethernet Controller
The Intrepid IC includes an Ethernet media access controller (MAC) that implements the link layer. The Intrepid
IC provides DB-DMA support for the Ethernet interface.
The Ethernet controller in the Intrepid IC is connected to a PHY interface IC that provides the electrical signals
to the port. The PHY is capable of operating in either 10Base-T, 100Base-T, or 1000Base-T mode: The actual
speed of the link is automatically negotiated by the PHY and the bridge or router to which it is connected.
For more information, see “Ethernet Port” (page 29).
The PHY supports Auto-MDIX, which allows the use of straight-through cables in crossover situations (and
conversely). For more information, see “Ethernet Port” (page 29).
Video Display Subsystem
The video display subsystem contains the graphics controller IC along with 64 MB of DDR SDRAM memory.
The graphicsIC, an nVidia GeForce4 440 Go, contains 2D and 3D acceleration engines, front-end and back-end
scalers, a CRT controller, and an AGP4x bus interface with bus master capability.
20
The features of the nVidia GeForce4 440 Go include
● graphics processor clock speed of 189 MHz
● memory clock speed of 202.5 MHz
Intrepid Controller and Buses
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 21

CHAPTER 2
Architecture
● support for 64 MB of DDR video memory with 128-bit interface
● 2D and 3D graphics acceleration
● transform acceleration
● lighting acceleration
● video acceleration
● support for MPEG decoding
● support for video mirror mode
● support for dual-display mode
● S-video output for a TV monitor
The interface between the graphics IC and the rest of the system is an AGP4x (accelerated graphics port,
quadruple speed) bus on the Intrepid IC. The AGP bus has 32 data lines, a clock speed of 66 MHz, and supports
deeply pipelined read and write operations.
The graphics IC uses a graphics address remapping table (GART) to translate AGP logical addresses into
physical addresses. The graphics driver software can allocate memory in both the graphics SDRAM and the
main memory.
The graphics IC supports the internal flat-panel display and an external monitor. The external monitor can
either mirror the built-in display or show additional desktop space (dual-display mode). For information
about the displays and supported resolutions, see “Flat-Panel Display” (page 44) and “External Monitors” (page
45).
I/O Controller
The I/O controller IC in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer is a custom IC called Intrepid. It provides the
interface and control signals for the devices and functions described in the following sections.
Note: In the device tree, the I/O controller is named “mac-io”.
DMA Support
The Intrepid IC provides DB-DMA (descriptor-based direct memory access) support for the following I/O
channels:
● Ultra DMA ATA interface to the the internal hard drive
● modem slot interface to the built-in modem
● IIS channel to the sound IC
I/O Controller 21
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 22

CHAPTER 2
Architecture
The DB-DMAsystem provides a scatter-gather process based on memory resident data structures that describe
the data transfers. The DMA engine is enhanced to allow bursting of data files for improved performance.
Interrupt Support
The Intrepid IC has an interrupt controller (MPIC) that handles interrupts generated within the IC as well as
external interrupts, such as those from the Ethernet and FireWire controllers.
USB Interface
The Intrepid IC implements three independent USB controllers (root hubs), two of which are each connected
to one of the ports on the side of the computer. The use of independent controllers allows both USB ports
to support high data rate devices at the same time with no degradation of their performance. If a user
connects a high-speed (12 Mbps) device to one port and another high-speed device to the other, both devices
can operate at their full data rates.
The third independent USB controller supports the internal modem and Bluetooth modules.
The two external USB connectors support USB devices with data transfer rates of 1.5 MBps (12 Mbps). For
more information about the connectors, see “USB Connectors” (page 25).
USB devices connected to the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer are required to support USB-suspend mode
as defined in the USB specification. Information about the operation of USB-suspend mode on Macintosh
computers is included in the Mac OS USB DDK API Reference. To obtain it, see the reference at “USB
Interface” (page 62).
The USB ports on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer comply with the Universal Serial Bus Specication
1.1 Final Draft Revision.The USB controllers comply with the Open Host Controller Interface (OHCI) specification.
Ultra ATA-100 Interface
The Intrepid IC provides an Ultra ATA-100 channel that is connected to the internal hard disk drive. The
Intrepid IC provides DB-DMA (descriptor-based direct memory access) support for the ATA-100 interface.
The internal hard disk drive is connected as device 0 (master) in an ATA Device 0/1 configuration. For more
information, see “Hard Disk Drive” (page 33).
ATA-33 Interface
22
The Intrepid IC provides an ATA bus that supports the SuperDrive (DVD-R/CD-RW) drive and the wireless LAN
module. The SuperDrive is an ATAPI drive and is device-selected as master in an ATA device configuration.
Modem Support
The internal modem is connected to an internal USB port. The Intrepid IC provides DB-DMA support for the
modem interface. The modem provides digital call progress signals to the sound circuitry.
I/O Controller
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 23

CHAPTER 2
Architecture
The internal modem is a separate module that contains the data pump IC and the interface to the telephone
line (DAA). For more information about the modem, see “Internal Modem” (page 30).
Sound Circuitry
The sound circuitry, called Snapper, is connected to the Intrepid IC by a standard IIS (inter-IC sound) bus. The
Intrepid IC provides DB-DMA (descriptor-based direct memory access) support for the IIS port.
Note: In the device tree, the sound circuitry is named “sound”.
The Snapper circuitry includes a signal processing IC that handles the equalization and volume control
functions, a codec IC that performs A-to-D and D-to-A conversion, and a power amplifier that drives the
headphone jack.
All audio is handled digitally inside the computer. The Snapper circuitry performs digital-to-analog conversion
for the audio signals to the internal speakers and the headphone jack.
For a description of the features of the sound system, see “Sound System” (page 49).
Power Controller
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer can operate from a 15 volt power outlet on an airline, but for safety
reasons, the computer will not allow battery charging. In order for the computer to detect the connection
to airline power, the airline power cable should have a sense resistor of 24.3 Kohms +/-1% connected between
the power plug's shell and ground.
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has a variable speed fan control circuit and a thermal circuit that will
force the unit into reduce-processor mode at 72 degrees Celsius and into sleep mode if the processor
temperature exceeds 79 degrees Celsius.
The power management controller in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer is a custom IC called the PMU99.
It supports several power-saving modes of operation, including idle, doze, and sleep.
Note: In the device tree, the power controller is named “via-pmu”.
A device’sID voltage limits determines how the PMU identifies the power adapter. The PowerBook G4 17-inch
computer is designed to use the 65-Watt Apple Portable Power Adapter which ships with it. Although you
can use a 45-Watt Apple portable power adapter with a 17-inch PowerBook G4 computer, it may not provide
sufficient power during some activities and power may be drawn temporarily from the battery. Should the
battery become discharged, you may need to plug in the 65-Watt Apple Portable Power Adapter that came
with the computer in order to start it up.
AirPort Extreme Interface
AirPort Extremecontains a media access controller (MAC), a digital signal processor (DSP),and a radio-frequency
(RF) section.
I/O Controller 23
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 24

CHAPTER 2
Architecture
Two antennas are built into the computer’s case. To improve reception, a diversity module between the
antennas and the card measures the signal strength from both antennas and selects the stronger signal for
AirPort Extreme.
AirPort Extreme is based on the IEEE draft specification of the 802.11g standard. The card transmits and
receives data at up to 54 Mbps and is compatible with 802.11b-standard 11 Mbps systems and older
802.11b-standard systems. For information about its operation, see “AirPort Extreme” (page 31).
CardBus Controller IC
The interface to the PC Card slot is connected to the PCI bus. The CardBus controller IC is a PCI1510A device
made by Texas Instruments. It supports both 16-bit PC Cards and 32-bit CardBus Cards.
24
I/O Controller
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 25

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
This chapter describes both the built-in I/O devices and the ports for connecting external I/O devices. Each
of the following sections describes an I/O port or device.
USB Ports
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has two external USB v1.1 ports that can be used to connect additional
I/O devices such as a USB mouse, printers, scanners, and low-speed storage devices.
The USB ports on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer comply with the Universal Serial Bus Specification
1.1 Final Draft Revision. For more information about USB on Macintosh computers, consult the references at
“USB Interface” (page 62).
USB Connectors
The USB ports use USB Type A connectors, which have four pins each. Two of the pins are used for power
and two for data. Figure 3-1 (page 25) is an illustration of a Type A port and matching connector. Table 3-1
shows the pin assignments.
Figure 3-1 USB Type A port
Table 3-1 Pin assignments on the USB port
DescriptionSignal namePin
+5 VDCVCC1
Data –D–2
Data +D+3
GroundGND4
The computer provides 5-volt power at 500 mA for each of the two ports.
The USB ports support both low-speed and high-speed data transfers, at up to 1.5 Mbits per second and 12
Mbits per second, respectively. High-speed operation requires the use of shielded cables.
USB Ports 25
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 26

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer supports all four data transfer types defined in the USB specification.
USB devices can provide a remote wakeup function for the computer. The USB root hub in the computer is
set to support remote wakeup whenever a device is attached to the bus.
USB Storage Devices
Class drivers are software components that are able to communicate with many USB devices of a particular
kind. If the appropriate class driver is present, any number of compliant devices can be plugged in and start
working immediately without the need to install additional software.
FireWire Ports
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has one FireWire 400 (IEEE 1394a) port and one FireWire 800 (IEEE
1394b) port. Both FireWire ports
● support booting the system from a mass storage device
● support target disk mode
The two FireWire ports share a single power supply that can provide up to 14 watts total. Both ports are on
the same FireWire bus and can connect to up 62 other FireWire devices.
The FireWire hardware and software provided with the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer are capable of all
asynchronous and isochronous transfers defined by IEEE standard 1394a and 1394b.
For additional information about the FireWire interface and the Apple API for FireWire device control, refer
to the resources listed at “FireWire Interface” (page 62).
FireWire 400 Connector
The 6-pin FireWire 400 technology
● supports serial I/O at 100, 200, and 400 Mbps
● provides up to 7 watts ofpower when the computer system is on or when the power adapter is connected
and in sleep mode
The FireWire 400 connector has six contacts, as shown in Figure 3-2 (page 27). The connector pin assignments
are shown in Table 3-2 (page 27).
26
FireWire Ports
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 27

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Figure 3-2 6-pin FireWire connector
Table 3-2 Pin assignments on the 6-pin FireWire connector
DescriptionSignal namePin
Unregulated DC; 12.8 VPower1
Ground return for power and inner cable shieldGround2
Twisted-pair B, differential signalsTPB-3
Twisted-pair B, differential signalsTPB+4
Twisted-pair A, differential signalsTPA-5
Twisted-pair A, differential signalsTPA+6
Outer cable shield—Shell
When the computer is on or the power adapter is connected, the power pin provides a maximum voltage
of 12.8 V (no load) and 7 W power per port. Maximum output current for both ports combined is 1.5 A and
is controlled by a self-resetting fuse.
Pin 2 of the 6-pin FireWire connector is groundfor both power and the inner cable shield. If a 4-pin connector
is used on the other end of the FireWire cable, its shell should be connected to the wire from pin 2.
The signal pairs are crossed in the cable itself so that pins 5 and 6 at one end of the cable connect with pins
3 and 4 at the other end. When transmitting, pins 3 and 4 carry data and pins 5 and 6 carry clock; when
receiving, the reverse is true.
FireWire 800 Connector
The FireWire 800 port on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer is based on IEEE 1394b and enables a 800
Mbps transfer rate. FireWire 800 uses a 9-pin connector and is backwards compatible with original 1394
FireWire devices with 6-pin or 4-pin connectors. With the appropriate cable, the new 9-pin port works
seamlessly with legacy FireWire devices. Cables are available to go from both 6-pin and 4-pin connectors to
a 9-pin, and 9-pin to 9-pin.
FireWire Ports 27
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 28

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Note: FireWire adapter cables are not included with the computer.
The 9-pin FireWire 800 connector is shown in Figure 3-3 (page 28). Its connector signals and pin assignments
are shown in Table 3-3 (page 28).
Figure 3-3 9-pin FireWire 800 connector
Table 3-3 Signals on the 9-pin FireWire 800 connector
DescriptionSignal namePin
Twisted-pair B MinusTPB–1
Twisted-pair B PlusTPB+2
Twisted-pair A MinusTPA–3
Twisted-pair A PlusTPA+4
Twisted-pair A Ground ReferenceTPA (R)5
Power GroundVG6
Status Contact (no connection; reserved)SC7
Power Voltage (approximately 12.8 V DC)VP8
Twisted-pair B Ground ReferenceTPB (R)9
VP (pin 8) provides up to 7 W power, shared with the other FireWire connectors. The voltage on the power
pin is approximately 12.8 V.
The 9-pin FireWire 800 port is capable of operating at 100, 200, 400, and 800 Mbps, depending on the device
to which it is connected. The FireWire 800 port is bilingual in that it supports both IEEE 1394a and 1394b.
Using a cable with a 9-pin connector at one end and a 4-pin or 6-pin connector at the other, the 9-pin port
is capable of directly connecting to all existing FireWire devices. Using a cable with 9-pin connectors at both
ends, the 9-pin port is capable of operating at 800 Mbps.
28
The IEEE 1394b standard defines long-haul media using Cat 5 UTP and several kinds of optical fiber. The
PowerBook G4 17-inch computer is interoperable with such cablesbut cannot be directly connected to them.
To use long-haul cables, connect the computer to a 1394b hub that has the desired kind of long-haul
connectors. If the hub has a bilingual port, that port can be connected to any of the computer’s FireWire
ports. If the hub has a beta-only port, it can be connected only to the computer’s 9-pin port.
FireWire Ports
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 29

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Booting from a FireWire Device
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer can boot from a FireWire storage device that implements SBP-2 (Serial
Bus Protocol) with the RBC (reduced block commands) command set. Detailed information is available from
Developer Technical Support at dts@apple.com.
Target Disk Mode
One option at boot time is to put the computer into a mode of operation called target disk mode.
When the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer is in target disk mode and connected to another Macintosh
computer by a FireWire cable, the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer operates like a FireWire mass storage
device with the SBP-2 (Serial Bus Protocol) standard. Target disk mode has two primary uses:
● high-speed data transfer between computers
● diagnosis and repair of a corrupted internal hard drive
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer can operate in target disk mode as long as the other computer has a
FireWire 1394a or 1394b port and is running either Mac OS X (any version) or Mac OS 9 with FireWire software
version 2.3.3 or later.
To put the computer into target disk mode, hold down the T key while the computer is starting up. When
Open Firmware detects the T key during the boot process, it transfers control to special Open Firmware code.
To take the computer out of target disk mode, press the power button.
When running target disk mode from a PowerBook G4 17-inch computer using a 45 W adapter, the screen
dims and the battery icon displays the battery level, giving the appearance of operating on battery power.
Ethernet Port
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has a built-in Ethernet port that supports 10Base-T, 100Base-T, and
1000Base-T transfer rates. In operation, the actual speed of the link is auto-negotiated betweenthe computer’s
PHY device and the network bridge or router to which it is connected.
The connector for the Ethernet port is an RJ-45 connector on the right side of the computer. Table 3-4 (page
29) shows the signals and pin assignments for 10Base-T and 100Base-T operation. Table 3-5 (page 30) shows
the signals and pin assignments for 1000Base-T operation.
Table 3-4 Signals for 10Base-T and 100Base-T operation
Signal definitionSignal namePin
Transmit (positive lead)TXP1
Transmit (negative lead)TXN2
Receive (positive lead)RXP3
Ethernet Port 29
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 30

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Signal definitionSignal namePin
Not used–4
Not used–5
Receive (negative lead)RXN6
Not used–7
Not used–8
Table 3-5 Signals for 1000Base-T operation
Signal definitionSignal namePin
Transmit and receive data 0 (positive lead)TRD+(0)1
Transmit and receive data 0 (negative lead)TRD–(0)2
To interconnect two computers for 1000Base-T operation, you must use 4-pair cable (Category 5 or 6).
The Ethernet port on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer supports Auto-MDIX. It switches between MDI
(Medium Dependent Interface) and MDI-X operation automatically, so it can be connected to another device
by either a straight-through cable or a cross-over cable.
The Ethernet interface in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer conforms to the ISO/IEC 802.3 specification,
where applicable, and complies with IEEE specifications 802.3i (10Base-T), 802.3u-1995 (100Base-T), and
802.3ab (1000Base-T).
Internal Modem
Transmit and receive data 1 (positive lead)TRD+(1)3
Transmit and receive data 2 (positive lead)TRD+(2)4
Transmit and receive data 2 (negative lead)TRD–(2)5
Transmit and receive data 1 (negative lead)TRD–(1)6
Transmit and receive data 3 (positive lead)TRD+(3)7
Transmit and receive data 3 (negative lead)TRD–(3)8
30
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer comes with a built-in modem. The connector for the modem is an
RJ-11 connector on the left side of the computer.
The modem has the following features:
● modem bit rates up to 56 Kbps (supports V.34, V.90, and V.92 modem standards)
Internal Modem
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 31

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
● fax modem bit rates up to 14.4 Kbps
The modem is connected to an internal USB port and is a vendor-specific USB device. The modem driver
controls the modem hardware and presents a virtual serial port to the operating system and applications.
Applications that bypass the operating system’s modem driver and communicate directly with the SCC will
not work properly.
Note: 56 Kbps technology refers to download speeds only and requires compatible modems at server sites.
Other conditions may limit modem speed. FCC limitations allow a maximum of 53 Kbps during download
transmissions.
AirPort Extreme
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer supports AirPort Extreme, a fully-integrated, internal wireless LAN
module based on the IEEE draft specification of the 802.11g standard. By communicating wirelessly with a
base station, AirPort Extreme can be used for internet access, email access, and file exchange. A base station
provides the connection to the Internet or the bridge between the wireless signals and a wired LAN or both.
The AirPort Extreme Base Station has connectors for a wired LAN, a DSL or cable modem, or a standard
telephone line using the optional 56K modem that is built-in on some models.
AirPort Extreme transmits and receives data at speeds up to 54 Mbps, comparable to wired networking
speeds. Airport Extreme is also compatible with other devices that follow the IEEE 802.11b standard, including
PC's. For more information about compatibility, see the reference at “Wireless Networks” (page 63).
Note: As is the case with the existing IEEE 802.11b standard, actual data throughput speeds will be lower
than the indicated maximum connection speeds. Inherent in wireless LAN systems, bandwidth overhead is
required for wireless routing, scrambling, security error correction, and other processes.
Data Security
AirPort Extreme has several features designed to maintain the security of the user’s data.
● In 802.11b mode, the system uses direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) technology that uses a
multi-bit spreading code that effectively scrambles the data for any receiverthat lacks the corresponding
code.
● The system can use an Access Control List of authentic network client ID values (wireless and MAC
addresses) to verify each client’s identity before granting access to the network.
● When communicating with a base station, AirPort Extreme uses 64-bit and 128-bit WEP encryption to
encode data while it is in transit. Additional security features may be available via firmware upgrades as
802.11b standards are ratified by IEEE or as the 802.11g draft standard matures.
● The AirPort Extreme Base Station can be configured to use NAT (Network Address Translation), protecting
data from Internet hackers.
AirPort Extreme 31
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 32

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
● The AirPort Extreme Base Station can authenticate users by their unique Ethernet IDs, preventing
unauthorized computers from logging into your network. Network administrators can take advantage
of RADIUS compatibility, used for authenticating users over a remote server. Smaller networks can offer
the same security using a local look-up table located within the base station.
As an additional data security measure, VPNcan be used in conjunction with the AirPort Extreme data security.
AirPort Extreme Hardware
AirPort Extreme is a fully-integrated, wireless LAN module based on the IEEE draft specification of the 802.11g
standard using both OFDM (orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing) and DSSS technologies. Using DSSS,
AirPort Extreme is interoperable with PC-compatible wireless LANs that conform to the 802.11b standard at
speeds of 11 Mbps, 5.5 Mbps, 2 Mbps, and 1 Mbps. Using OFDM, AirPort Extreme is compatible with all
802.11g draft standard speeds.
Two antennas are built into the computer, on either side of the flat-panel display. One antenna is always
used for transmitting. Either of the two antennas may be used for receiving. Using a diversity technique,
AirPortExtreme may select the antenna that gives the best reception. The secondary antenna is used for
Bluetooth.
AirPort Extreme Software
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer includes software for setting up and using AirPort Extreme:
● AirPort Extreme Setup Assistant, an easy-to-use program that guides users through the steps necessary
to set up AirPort Extreme or set up an AirPort Extreme Base Station.
● Users can switch between wireless networks and can create and join peer-to-peer networks. These
functions are accessed via the AirPort Extreme status menu.
● AirPort Extreme Admin Utility, a utility for advanced users and system administrators. With it the user
can edit the administrative and advanced settings needed for some advanced configurations.
Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth is a fully integrated, open specification that enables short-range wireless connections between
desktop and laptop computers and a host of other peripheral devices. Bluetooth support is built into Mac
OS X and compliant with Bluetooth specification v1.1. It operates on a globally available 2.4 GHz frequency
band (ISM band) for worldwide compatibility and has a maximum throughput of 1Mbps.
The Bluetooth technology supports the following profiles:
32
● synchronization —enables synchronization of devices over Bluetooth
● serial —provides a wireless serial connection to other Bluetooth devices
● dial-up networking (DUN) — enables a mobile phone to act as a modem
Bluetooth Technology
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 33

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
● object push —enables the transfer of files between Bluetooth devices
For more information on Bluetooth technology, refer to “Bluetooth” (page 63).
Bluetooth and AirPort Extreme share the antennas in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer’s display housing.
Hard Disk Drive
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has an internal hard disk drive with a storage capacity of 60 GB. The
drive has fluid dynamic bearings for quieter operation. The drive uses the Ultra DMA IDE (integrated drive
electronics) interface and is ATA-5 compatible. Current Data Transfer Mode for the drive is ATA-100.
The software that supports the internal hard disk is the same as that in previous models with internal IDE
drives and includes DMA support. For the latest information about that software, see Technical Note TN1098,
ATA Device Software Guide Additions and Corrections. The web page for Technical Note TN1098 includes a
link to a downloadable copy of ATA Device Software Guide.
To obtain the reference documents listed here, see the reference links at “ATA Devices” (page 62).
Hard Disk Dimensions
Figure 3-4 (page 34) shows the maximum dimensions of the hard disk and the location of the mounting
holes. The minimum clearance between any conductive components on the drive and the bottom of the
mounting envelope is 0.5 mm.
Hard Disk Drive 33
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 34

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Figure 3-4 Maximum dimensions of the internal hard disk
Hard Disk Connector
The internal hard disk has a 48-pin connector that carries both the ATA signals and the power for the drive.
The connector has the dimensions of a 50-pin connector, but with one row of pins removed, as shown in
Figure 3-5 (page 35). The remaining pins are in two groups: pins 1–44, which carry the signals and power,
and pins 45–48, which are reserved. Pin 20 has been removed, and pin 1 is located nearest the gap, rather
than at the end of the connector.
34
Hard Disk Drive
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 35

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Figure 3-5 Hard disk connector and location
Signal Assignments
Table 3-6 (page 35) shows the signal assignments on the 44-pin portion of the hard disk connector. A slash
(/) at the beginning of a signal name indicates an active-low signal.
Table 3-6 Pin assignments on the ATA hard disk connector
Signal namePin numberSignal namePin number
GROUND2/RESET1
DD84DD73
DD96DD65
DD108DD57
DD1110DD49
DD1212DD311
DD1314DD213
DD1416DD115
DD1518DD017
KEY20GROUND19
GROUND22DMARQ21
GROUND24/DIOW, /STOP23
GROUND26/DIOR, /HDMARDY, HSTROBE25
Hard Disk Drive 35
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 36

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Signal namePin numberSignal namePin number
CSEL28IORDY, /DDMARDY, DSTROBE27
GROUND30/DMACK29
/IOCS1632INTRQ31
/PDIAG, /CBLID34/DA133
/DA236/DA035
/CS138/CS037
GROUND40/DASP39
+5V MOTOR42+5V LOGIC41
Reserved44GROUND43
/IOCS16 is not used; see Table 3-7 (page 36).
ATA Signal Descriptions
Table 3-7 (page 36) describes the signals on the ATA hard disk connector.
Table 3-7 Signals on the ATA hard disk connector
Signal descriptionSignal name
/DA(0–2)
DD(0–15)
/CBLID
/CS0
/CS1
Device address; used by the computer to select one of the registers in the ATA drive. For
more information, see the descriptions of the CS0 and CS1 signals.
Data bus; buffered from IOD(16–31) of the computer’s I/O bus. DD(0–15) are used to transfer
16-bit data to and from the drive buffer. DD(8–15) are used to transfer data to and from the
internal registers of the drive, with DD(0–7) driven high when writing.
The host checks this signal after power on or hardware reset to detect whether an
80-conductor cable is present.
Register select signal. It is asserted low to select the main task file registers. The task file
registers indicate the command, the sector address, and the sector count.
Register select signal. It is asserted low to select the additional control and status registers
on the ATA drive.
36
Cable select; not available on this computer (n.c.).CSEL
Device active or slave present; not available on this computer (n.c.)./DASP
Drive ready to receive Ultra DMA data./DDMARDY
I/O data read strobe./DIOR
Hard Disk Drive
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 37

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Signal descriptionSignal name
I/O data write strobe./DIOW
Used by the host to initiate a DMA transfer in response to DMARQ./DMACK
Strobe for Ultra DMA data transfers to host.DSTROBE
Ultra DMA data ready./HDMARDY
Strobe for Ultra DMA data transfers from host.HSTROBE
IORDY
INTRQ
/PDIAG
The built-in ATA devices are connected to the I/O bus through bidirectional bus buffers.
I/O ready; when driven low by the drive, signals the CPU to insert wait states into the I/O
read or write cycles.
I/O channel select; not used on this computer./IOCS16
Asserted by the device when it is ready to transfer data to or from the host.DMARQ
Interrupt request. This active high signal is used to inform the computer that a data transfer
is requested or that a command has terminated.
Asserted by device 1 to indicate to device 0 that ithas completed the power-on diagnostics;
not available on this computer (n.c.).
Hardware reset to the drive; an active low signal./RESET
Stop request; an active low signal./STOP
This pin is the key for the connector.Key
SuperDrive (DVD-R /CD-RW)
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has a slot-loading DVD-R/CD-RW SuperDrive.
The SuperDrive can read and write DVD media and CD media, as shown in Table 3-8. The DVD-R/CD-RW drive
also provides DVD-Video playback. The G4 microprocessor provides the MPEG-2 decoding.
Table 3-8 Media read and written by the SuperDrive
Writing speedReading speed (maximum)Media type
1x (CLV)4x (CAV max)DVD-R
_8x (CAV max, single layer) 6x (CAV max, dual layer)DVD-ROM
8x (CLV)24x (CAV max)CD-R
4x (CLV)12x (CAV max)CD-RW
SuperDrive (DVD-R /CD-RW) 37
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 38

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Writing speedReading speed (maximum)Media type
–24x (CAV max)CD or CD-ROM
The Apple SuperDrive writes to DVD-R 4.7 gigabyte General Use media. These discs are playable in most
standard DVD players and computer DVD-ROM drives. For a list of players tested by Apple for playability,
refer to
http://www.apple.com/dvd/compatibility/
For compatibility information regarding recordable DVD formats, refer to
http://dvddemystified.com/dvdfaq.html#4.3
Digital audio signals from the SuperDrive can be played through the sound outputs under the control of the
System Preferences.
The SuperDrive is an ATAPI drive.
Trackpad
The pointing device in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer is a trackpad. The trackpad is a solid-state device
that emulates a mouse by sensing the motions of the user’s finger over its surface and translating those
motions into ADB commands.
The user makes selections either by pressing the trackpad button (below the trackpad) or by tapping and
double tapping on the pad itself. The trackpad responds to one or two taps on the pad itself as one or two
clicks of the button. The user can tap and drag on the trackpad in much the same manner as clicking and
dragging with the mouse. The tap and double-tap functions are optional and can be activated or deactivated
by means of the mouse pane in System Preferences.
The trackpad on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has palm-rejection capabilities that help prevent
unintended trackpad input while typing is being performed. When the “Ignore trackpad while typing”
checkbox is selected on the mouse pane of Systems Preferences, the system software attempts to filter out
unintended contact with the trackpad. The trackpad will not respond when a mouse is present and the
“Ignore trackpad when mouse is present” checkbox is selected on the mouse pane of Systems Preferences.
Note: If the trackpad is not responding to intended input, check to see if the “Ignore trackpad while typing”
checkbox is selected.
Keyboard
The keyboard is a full-size, 19 mm pitch, low-profile design with a row of function keys and inverted-T cursor
motion keys. A dedicated media eject key is located to the right of the F12 function key.
38
Trackpad
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 39

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has a fiber-optic backlit keyboard and ambient light sensors that control
the brightness of the display and the keyboard backlighting. In low light, the computer automatically
illuminates the backlit keyboard and lowers the display brightness. As light levels increase, the display
brightness is re-adjusted automatically and the keyboard backlighting is turned off. There are two light
sensors, one under each speaker grill.
Access to internal components and expansion connectors is no longer via the keyboard, so the keyboard is
not latched for removal. Access to the memory cards is via the RAM expansion slot and is explained in “RAM
Expansion Slots” (page 53).
Changing the Operation of the Keyboard
Several of the keys on the keyboard have more than one mode of operation.
● Function keys F1–F10 can also control features such the display brightness, the speaker volume, the dual
display feature, the Num Lock function, and the illuminated keyboard brightness. Refer to Table 3-9 (page
42) for the entire list. A media eject key is located to the right of the F12 function key.
● Certain control keys can be used as page-control keys.
● The keys on the right side of the keyboard can be used as a numeric keypad.
The next sections describe these groups of keys and the way their alternate modes of operation are selected
by using the Fn key, and the Num Lock key.
Keyboard Illustrations
Figure 3-6 (page 39) shows the actual appearance of the keyboard. Figure 3-7 (page 40) shows the alternate
modes of operation of the function and control keys. Figure 3-8 (page 41) shows the embedded numeric
keypad.
Figure 3-6 Keyboard layout
Keyboard 39
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 40

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Figure 3-7 (page 40) and Figure 3-8 (page 41) include duplicate versions of some keys in order to show their
alternate modes of operation. In some cases, the alternate key captions shown in the figures do not appear
on the keyboard. For the actual appearance of the keyboard, refer to Figure 3-6 (page 39).
Figure 3-7 Alternate operations of function and control keys
40
Keyboard
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 41

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Figure 3-8 Embedded numeric keypad operation
Keyboard 41
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 42

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Using the Fn Key
Pressing the Fn key affects three sets of keys: the function keys F1–F12, the embedded numeric keypad, and
certain modifier keys.
● It toggles the function keys between their control-button operationand their F1–F10 functions, as shown
in Table 3-9 (page 42) and Figure 3-7 (page 40).
● It selects the embedded numeric keypad on the right portion of the alphanumeric keys, as shown in
Table 3-10 (page 43) and Figure 3-8 (page 41).
● It changes certain control keys, including the cursor control keys, to page control keys, as shown in Table
3-11 (page 43) and Figure 3-8 (page 41).
Note: In Mac OS X, a third-party utility is needed to implement user-programmable function key assignments.
Using the Num Lock Key
Pressing the Num Lock key affects two sets of keys: the embedded keypad and the rest of the alphanumeric
keys.
● It selects the embedded numeric keypad, as shown in Table 3-10 (page 43) and Figure 3-8 (page 41).
● It makes the rest of the alphanumeric keys functionless (NOPs), as shown in Figure 3-8 (page 41).
The Function Keys
Table 3-9 (page 42) defines the operation of the function keys.
Table 3-9 The function keys as control buttons
Control buttonKey name
Decrease display brightnessF1
Increase display brightnessF2
Mute the speakerF3
Decrease speaker volumeF4
Increase speaker volumeF5
42
Num LockF6
Switch between dual display and mirroring modesF7
Keyboard illumination controlF8
Decrease keyboard illuminationF9
Keyboard
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 43

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Control buttonKey name
Increase keyboard illuminationF10
The Embedded Keypad
A certain group of alphanumeric keys can also function as an embedded keypad. The user selects this mode
by using the Fn key or the Num Lock key. Figure 3-8 (page 41) shows the keys making up the embedded
keypad and Table 3-10 (page 43) lists them.
Table 3-10 Embedded keypad keys
Keypad functionKey nameKeypad functionKey name
* (multiply)PClear6
1J77
2K88
3L99
– (subtract);/ (divide)0
0M= (equals)-
NOP,4U
. (decimal).5I
+ (add)/6O
When the embedded keypad is made active by the Num Lock key, the other alphanumeric keys have no
operation (NOP), as shown in Figure 3-8 (page 41). The affected keys include certain special character keys:
plus and equal sign, right and left brackets, vertical bar and backslash, and straight apostrophe.
Other Control Keys
The cursor control keys can also be used as page control keys. Other control keys can take on the functions
of certain keys on a PC keyboard, for use with PC emulation software. The Fn key controls the modes of
operation of this group of keys. Table 3-11 (page 43) is a list of these keys and their alternate functions. These
control keys are also show in Figure 3-8 (page 41).
Table 3-11 Control keys that change
Alternate functionKey name
Right shift keyShift
Right control keyControl
Alt gr (right Alt key)Option
Keyboard 43
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 44

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Alternate functionKey name
Windows keyCommand
Menu key (for contextual menus)Enter
HomeLeft arrow
Page upUp arrow
Page downDown arrow
EndRight arrow
Flat-Panel Display
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has a built-in, wide-screen, 100 dpi, color flat-panel display with a
resolution of 1440 by 900 pixels and measures 17 inches diagonally.
The display is backlit by a cold cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL). The display uses TFT (thin-film transistor)
technology for high contrast and fast response.
In addition to its native resolution (1440 by 900) the display also supports several non-native resolutions, as
shown in Table 3-12. The graphics controller IC includes a scaling function that expands displays with those
smaller resolutions to fill the screen.
The display’s native resolution, 1440 by 900, has an aspect ratio of 16:10. When selecting a picture resolution
with an aspect ration of 4:3, the user can choose to have it displayed with square pixels and black margins
on the sides, or with stretched pixels that fill the display from side to side. These options are shown in Table
3-12 (page 44).
Table 3-12 Picture sizes on the flat-panel display
Shape of pixelsBlack marginsDisplay area usedPicture size
squareyes1200 by 900800 by 600
stretchedno1440 by 900800 by 600
squareno1440 by 9001024 by 640
squareyes1200 by 9001024 by 768
44
stretchedno1440 by 9001024 by 768
squareno1440 by 9001152 by 720
square (native)no1440 by 9001440 by 900
Flat-Panel Display
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 45

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
External Monitors
The computer has a Digital Visual Interface (DVI) port for connecting to flat panel displays, a VGA monitor,
or projection devices. The DVI connector supports DVI-equipped displays and projectors. A DVI-to-VGA
adapter is included for use with analog monitors. With a DVI-to-ADC adapter, available separately, the
PowerBook G4 17-inch computer can be used with any Apple flat panel display.
The computer also has an S-video-to-composite cable that supplies a video signal for an NTSC or PAL video
monitor or VCR. See “External Video Port” (page 48).
Dual Display and Mirror Mode
An external monitor or projection device connected to the computer can increase the amount of visible
desktop space. This way of using an external monitor is called dual display to distinguish it from mirror mode,
which shows the same information on both the external display and the built-in display. Use the F7 key to
switch between the dual display mode and the mirror mode.
When mirror mode is selected, the scaling function is available on the internal display, and on the internal
display and an external monitor when both are operating. However, the monitors could have black borders
during mirroring, depending on the supported timings between the two displays and on the monitor’s
selection algotithm. Both displays show full-sized images only when the display resolution for the external
monitor is set to the internal display’s native resolution: 1440 by 900. Both displays can operate with other
resolution settings, but in mirror mode, one of them has a display that is smaller than the full screen and has
a black border around it. With the resolution for the external monitor set to 640 by 480 or 800 by 600, the
image on the internal display is smaller than its screen. For resolution settings larger than 1440 by 900, the
image on the external monitor is smaller than its screen.
Analog Monitor Resolutions
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer comes with an adapter for use with an analog video monitor. Table
3-13 (page 45) lists the standard picture sizes and frame rates supported.
Table 3-13 Picture sizes on an analog monitor
Frame ratePicture size (pixels)
85 Hz800 by 600
85 Hz1024 by 768
85 Hz1280 by 960
85 Hz1280 by 1024
85 Hz1600 by 1024
85 Hz1600 by 1200
85 Hz1920 by 1080
External Monitors 45
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 46

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Frame ratePicture size (pixels)
85 Hz1920 by 1200
85 Hz1920 by 1440
75 Hz2048 by 1536
Note: Table 3-13 (page 45) lists the most common resolutions; additional resolutions are possible.
When the flat-panel display and an external video monitor are operating at the same time, the system allocates
enough video memory for each to support the full 24-bit pixel depth at resolutions up to 2048 by 1536 pixels.
Digital Display Resolutions
Table 3-14 (page 46) shows the resolutions supported on flat-panel (digital) displays. The 64 MB of video
RAM on the accelerated graphics card supports pixel depths up to 24 bits per pixel at all resolutions.
Table 3-14 Picture sizes on a digital display
640 by 480
800 by 500
800 by 600
1024 by 640
1024 by 768
1280 by 800
1280 by 1024
1600 by 1200
1920 by 1200
DVI-I Connector
46
The external monitor connector is a DVI-I connector. It carries both digital and analog video signals. Figure
3-9 (page 47) shows the contact configuration; Table 3-15 (page 47) and Table 3-16 (page 47) list the signals
and pin assignments.
External Monitors
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 47
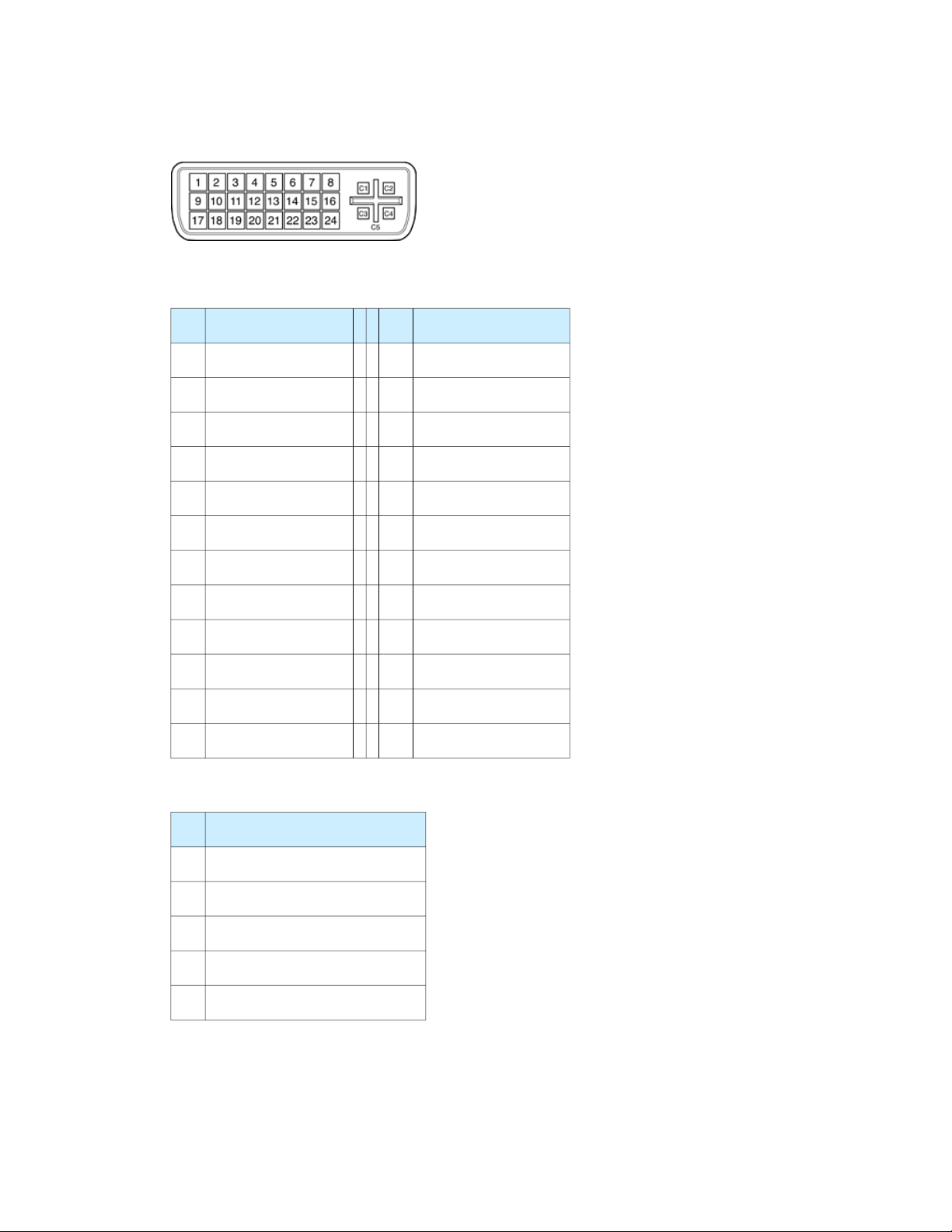
CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Figure 3-9 DVI-I connector
Table 3-15 Main signals on the DVI-I connector
Signal namePinSignal namePin
TMDS Data3+13TMDS Data2–1
+5V Power14TMDS Data2+2
Ground for +5V Power15TMDS Data2/4 Shield3
Hot Plug Detect16TMDS Data4–4
TMDS Data0–17TMDS Data4+5
TMDS Data0+18DDC Clock6
TMDS Data0/5 Shield19DDC Data7
TMDS Data5–20Analog Vertical Sync8
TMDS Data5+21TMDS Data1–9
TMDS Clock Shield22TMDS Data1+10
TMDS Clock+23TMDS Data1/3 Shield11
TMDS Clock–24TMDS Data3–12
Table 3-16 MicroCross signals on the DVI-I connector
Signal namePin
Analog Red VideoC1
Analog Green VideoC2
Analog Blue VideoC3
Analog Horizontal SyncC4
Analog Common Ground ReturnC5
The graphics data sent to the digital monitor use transition minimized differential signaling (TMDS). TMDS
uses an encoding algorithm to convert bytes of graphics data into characters that are transition-minimized
to reduce EMI with copper cables, and DC-balanced for transmission over fiber optic cables. The TMDS
External Monitors 47
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 48

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
algorithm also provides robust clock recovery for greater skew tolerance with longer cables or low-cost short
cables. For additional information about TMDS, see the references shown in “Digital Visual Interface” (page
63).
External Video Port
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer has a video port that provides S-video output to a PAL or NTSC video
monitor or VCR. The video output connector is a 7-pin S-video connector. Figure 3-10 (page 48) shows the
arrangement of the pins and Table 3-17 (page 48) shows the pin assignments on the S-video connector.
Figure 3-10 S-video connector
Table 3-17 Pin assignments for the S-video output connector
S-video output connectorPin number
Analog GND1
Analog GND2
Video Y (luminance)3
Video C (chroma)4
composite video5
Unused6
Unused7
An S-video-to-composite adapter is included and accepts an RCA plug for connecting to a composite video
device.
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer provides video output at picture sizes and frame rates compatible with
the NTSC and PAL standards; the picture sizes are listed in Table 3-18 (page 48). Those picture sizes produce
underscanned displays on standard monitors.
48
Table 3-18 Picture sizes for S-video output
Pixel depthPicture size
24 bpp512 by 384
External Video Port
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 49

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Sound System
Pixel depthPicture size
24 bpp640 by 480
24 bpp60 Hz NTSC only 720 by 480
24 bpp50 Hz PAL only 720 by 576
24 bpp800 by 600
24 bpp832 by 624
24 bpp1024 by 768
The sound system for the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer supports stereo sound output and input, available
simultaneously. The sound circuitry handles audio data as 16-bit samples at a 44.1 kHz sample rate.
The sound circuitry and system software can create sounds digitally and either play the sounds through the
built-in speakers or send the sound signals out through the sound output jack or one of the USB ports.
The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer can record sound data from the built-in microphone, an audio CD, the
audio input jack, or a USB audio device. For each sound input source, sound play-through can be enabled
or disabled. Sound data from digital sources is converted to analog form for output to the speakers and the
sound output jack.
Sound Inputs
The sound system accepts inputs from the following sources:
● the built-in microphone
● the audio input jack
● a CD or DVD in the DVD-R/CD-RW SuperDrive via IIS
● a digital audio device connected to a USB or FireWire port via IIS
The audio input jack and microphone preamp share a dedicated analog input channel in the Snappercircuitry;
the other inputs send digital data. The analog input can be set for play-through or recording. The digital
inputs can be selected or mixed by the Snapper sound circuitry.
The computer also accepts digitalsound data from the DVD-R /CD-RW SuperDrive or from devices connected
to the USB or FireWire ports. Sound data from those sources can be sent to the sound system to be converted
to analog form for output to the speakers and the output jack.
Sound System 49
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 50

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Built-in Microphone
The built-in microphone is located at the bottom of the left speaker grill.
The sound signal from the built-in microphone goes through a dedicated preamplifier that raises its nominal
30 mV level to a nominal 150 mV (peak-to-peak) signal to the sound circuitry. That signal level assures good
quality digitizing without driving the analog input into clipping.
Audio Input Jack
The audio input jack is a 3.5 mm mini phone jack that accepts line-level stereo signals. It also accepts a stereo
miniplug-to-RCA cable adapter for connecting stereo equipment to the computer.
The sound input jack signal connections are
● tip: audio left channel
● ring: audio right channel
● sleeve: audio ground
Modem Activity Sound Signals
Modem activity sound signals from the communications slot are sent to the Snapper sound circuitry as 8-bit
digital data.
Sound Outputs
The sound system sends sound output signals to the built-in speakers and the external sound output jack.
Headphone Jack
The headphonejack is located on the left side of the computer. The headphone jack provides enough current
to drive a pair of low-impedance headphones. It can also be used as a line-level output.
The headphone jack has the following electrical characteristics:
● impedance suitable for driving standard 32-ohm headphones
● output level 2.0 V peak-to-peak (1.41 V RMS)
50
● signal-to-noise (SNR) 90 dB unweighted (typical)
● total harmonic distortion (THD) 0.03% or less
Sound System
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 51

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
Internal Speakers
The computer has two internal speakers, one on either side of the keyboard. The computer turns off the
sound signals to the speakers when an external device is actively connected to the sound output jack and
during power management.
Digitizing Sound
The sound circuitry digitizes and records sound as 44.1 kHz 16-bit samples. If a sound sampled at a lower
rate on another computer is played as output, the Sound Manager transparently upsamples the sound to
44.1 kHz prior to outputting the audio to the sound circuitry.
When recording sound from a microphone, applications that may be affected by feedback should disable
sound play-through by calling the Sound Manager functions.
Sound System 51
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 52

CHAPTER 3
Devices and Ports
52
Sound System
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 53

CHAPTER 4
Expansion Features
This chapter describes the expansion features of the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer’s RAM expansion slots
and the CardBus slot.
RAM Expansion Slots
The computer has two RAM expansion slots that accommodate standard SO (small outline) DIMMs using
DDR SDRAM devices. One slot may is occupied by factory-installed SO-DIMM. The slots are accessible for user
installation of an additional SO-DIMM.
The SO-DIMMs must use DDR SDRAM devices. If the user installs an SO-DIMM that uses Single Data Rate
(SDR) devices, the boot process will fail when the user attempts to restart the computer and the computer
will not operate.
The address logic for the RAM slots supports up to 1 GB total RAM. Using the highest-density devices currently
available, an SO-DIMM can contain up to 512 MB of RAM, so the two RAM expansion slots can accommodate
up to 1 GB total RAM.
Accessing the RAM Slots
The user can access the RAM expansion slots by removing the memory slot cover on the back of the computer,
as shown in Figure 4-1 (page 53). For complete instructions on accessing and replacing the RAM memory,
refer to the PowerBook G4 17-inch Getting Started guide that came with the computer.
Figure 4-1 Removing RAM expansion slot cover
RAM Expansion Slots 53
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 54

CHAPTER 4
Expansion Features
Mechanical Design of DDR RAM SO-DIMMs
The RAMexpansion modulesused in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer are PC2700 DDR333 RAMSO-DIMMs,
as defined in the JEDEC specifications.
The mechanical characteristics of the RAM expansion SO-DIMM are given in the JEDEC specification for the
DDR SO-DIMM. The specification number is JEDEC JESD95. To obtain a copy of the specification, see the
references listed at “RAM Expansion Modules” (page 61).
The specification defines SO-DIMMs with nominal heights of 1.0, 1.25, 1.5, and 2.0 inches. The PowerBook
G4 17-inch computer can accommodate SO-DIMMS with heights of 1.25 inches or less.
Important: The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer can not accept a 1.5 or 2-inch SO-DIMM.
The JEDEC specification defines the maximum depth or thickness of an SO-DIMM as 3.8 mm. Modules that
exceed the specified thickness can cause reliability problems.
Electrical Design of DDR RAM SO-DIMMs
SO-DIMMs for the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer are required to be PC2700 compliant. For information
about the PC2700 specifications, see the references at “RAM Expansion Modules” (page 61).
The electrical characteristics of the DDR RAM SO-DIMM are given in section 4.5.6 of the JEDEC Standard 21-C,
release 7 (JESD-21C). To obtain a copy of the specification, see the references listed at “RAM Expansion
Modules” (page 61).
The JEDEC and Intel specifications define several attributes of the DIMM, including storage capacity and
configuration, connector pin assignments, and electrical loading. The specifications support SO-DIMMs with
either one or two banks of memory.
Important: The memory controller on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer uses a separate CKE signals for
each bank, as called out in the JEDEC specification. SO-DIMMs that have all the CKE pins connected together
do not operate properly.
The JEDEC specification for the SO-DIMM defines a Serial Presence Detect (SPD) feature that contains the
attributes of the module. SO-DIMMs for use in PowerBook computers are required to have the SPD feature.
Information about the required values to be stored in the presence detect EEPROM is in section 4.1.2.5 and
Figure 4.5.6–C (200-pin DDR SDRAM SO–DIMM, PD INFORMATION) of the JEDEC standard 21-C specification,
release 7.
54
Important: For a DIMM to be recognized by the startup software, the SPD feature must be programmed
properly to indicate the timing modes supported by the DIMM.
Capacitance of the data lines must be kept to a minimum. Individual DRAM devices should have a pin
capacitance of not more than 5 pF on each data pin.
RAM Expansion Slots
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 55

CHAPTER 4
Expansion Features
DDR SDRAM Devices
The DDR SDRAM devices used in the RAM expansion modules must be self-refresh type devices for operation
from a 2.5 V power supply. The speed of the DDR SDRAM devices must be 167 MHz or higher.
The devices are programmed to operate with a CAS latency of 2.5 or 3. At these CAS latencies, the access
time from the clock transition must be +/- 0.6 ns or less for data strobes and +/- 0.7 ns for data lines. The
burst length must be at least 4 and the minimum clock delay for back-to-back random column access cycles
must be a latency of 1 clock cycle.
When the computer is in sleep mode, the RAM modules are in self-refresh mode and the maximum
power-supply current available for each RAM module is 6 mA/128 MB (see the section “RAM SO-DIMM
Electrical Limits” (page 56)). Developers should specify DDR SDRAM devices with low power specifications
so as to stay within that limit.
Configuration of DDR RAM SO-DIMMs
Table 4-1 (page 55) shows information about the different sizes of DDR SDRAM devices used in the memory
modules. The first two columns show the memory size and configuration of the SO-DIMMs. The next two
columns show the number and configuration of the DDR SDRAM devices making up the memory modules.
Table 4-1 Sizes of RAM expansion modules and devices
SO-DIMM size
* 1 GB is a theoretical max and
is reserved for future expansion.
1GB dual die package is not
supported.
SO-DIMM
configuration (MB x
bits)
Number of
devices
Device
configuration (MB x
bits)
Number of
banks
116 x 8816 x 64128 MB
28 x 16816 x 64128 MB
216 x 81632 x 64256 MB
132 x 8832 x 64256 MB
216 x 16832 x 64256 MB
232 x 81664 x 64512 MB
2x 8128 x 64*1 GB
RAM Expansion Slots 55
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 56

CHAPTER 4
Expansion Features
Note: The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer does not use memory interleaving, so installing two SO-DIMMs
of the same size does not result in any performance gain.
Address Multiplexing
Signals A[0] – A[12] and BA[0] – BA[1] on each RAM SO-DIMM make up a 15-bit multiplexed address bus that
can support several different types of DDR SDRAM devices. Table 4-2 (page 56) lists the types of devices that
can be used in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer by size, configuration, and sizes of row, column, and
bank addresses.
Important: The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer supports only the types of DDR SDRAM devices specified
in Table 4-2 (page 56). Other types of devices should not be used with this computer.
Table 4-2 Types of DRAM devices
Column address bitsRow address bitsDevice configuration (bytes x bits x banks)Device size
10124 M x 8 x 4128 Mbits
9122 M x 16 x 4128 Mbits
8121 M x 32 x 4128 Mbits
10138 M x 8 x 4256 Mbits
9134 M x 16 x 4256 Mbits
111316 M x 8x 4512 Mbits
RAM SO-DIMM Electrical Limits
Each RAM SO-DIMM must not exceed the following maximum current limits on the 2.5 V supply:
Active: 1.2 A (8 devices at 150 mA each)
Sleep: 6 mA/128 MB
Important: The restriction on sleep current is required not only to maximize the battery life but to meet the
limitations of the backup battery during sleep swapping of the main battery. Developers of RAM expansion
modules thatexceed the limit on sleep current mustinclude a warning to theuser that battery sleep swapping
may not work with those modules installed.
56
The Intrepid memory controller does not support 4-bit-wide SDRAM devices in any RAM expansion module.
RAM Expansion Slots
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 57

CHAPTER 4
Expansion Features
CardBus Slot
The CardBus slot accepts one Type I or Type II card. The slot supports both 16-bit PC Cards and 32-bit CardBus
Cards. The card can be removed and replaced while the computer is operating.
Note: The CardBus slot does not provide 12 V power.
For information about the CardBus and the PC Card, refer to the CardBus DDK and the PC Card Manager SDK.
To obtain the DDK and the SDK, see the reference at “PC Card Manager” (page 61).
CardBus Slot 57
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 58

CHAPTER 4
Expansion Features
58
CardBus Slot
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 59

APPENDIX A
Supplemental Reference Documents
For more information about the technologies mentioned in this developer note, you may wish to consult
some of the following references.
For information about older models of Macintosh computers, refer to the developer notes archive at
http://developer.apple.com/documentation/HardwareDrivers/index.html
Apple Technical Notes
Apple Technical Notes answer many specific questions about the operation of Macintosh computers and the
Mac OS. The notes are available on the Technical Note website at
http://developer.apple.com/technotes/
3D Graphics
Developers of 3D graphics for games should know about OpenGL for Macintosh¬®, a new version of SGI’s
application programming interface (API) and software library for 3D graphics.
Information is available on the World Wide Web at
http://www.apple.com/opengl
Developer support and documentation is available at
http://developer.apple.com/opengl/
PowerPC G4 Microprocessor
Information about the PowerPC G4 microprocessor is available on the World Wide Web at
http://www.freescale.com/webapp/sps/site/homepage.jsp?nodeId=0162468rH3bTdG
Apple Technical Notes 59
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 60

APPENDIX A
Supplemental Reference Documents
Velocity Engine (AltiVec)
Velocity Engine is Apple’s name for the AltiVec vector processor in the PowerPC G4 microprocessor. Apple
provides support for developers who are starting to use the Velocity Engine in their applications.
Documentation, development tools, and sample code are available on the World Wide Web, at
http://developer.apple.com/hardwaredrivers/ve/index.html
and
http://developer.apple.com/documentation/Performance/Conceptual/vDSP/vDSP_Library.pdf
AltiVec Technology Programming Environments Manual (AltiVec PEM) is a reference guide for programmers.
It contains a description for each instruction and information to help in understanding how the instruction
works. You can obtain a copy of the AltiVec PEM through the Motorola AltiVec site on the World Wide Web,
at
http://www.freescale.com/webapp/sps/site/overview.jsp?nodeId=02VS0l81285Nf2
Mac OS X
Mac OS X version 10.2 is installed by default on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer. For access to Apple’s
developer documentation for Mac OS X, see the Apple Developer Connection (ADC) website at
http://developer.apple.com/documentation/index.html
O'Reilly & Associates publishes a series of books about Mac OS X development. The books in this series have
been technically reviewed by Apple engineers and are recommended by the Apple Developer Connection.
I/O Kit
The I/O Kit is part of Darwin, the operating system foundation for Mac OS X. The documentation for I/O Kit
is available on Apple’s Darwin website at
http://developer.apple.com/documentation/Darwin/Darwin.html
Open Firmware
60
The software architecture implemented on current Macintosh computers follows the standard defined by
the Open Firmware IEEE 1274-1994 specification. Three Technical Notes provide an introduction to Open
Firmware on the Macintosh platform. They are:
TN1061: Open Firmware, Part I, available at
http://developer.apple.com/technotes/tn/tn1061.html
Velocity Engine (AltiVec)
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 61

APPENDIX A
Supplemental Reference Documents
TN1062: Open Firmware, Part II, available at
http://developer.apple.com/technotes/tn/tn1062.html
TN1044: Open Firmware, Part III, available at
http://developer.apple.com/technotes/tn/tn1044.html
Other Technical Notes provide additional information about Open Firmware on the Macintosh.
TN2000: PCI Expansion ROMs and You, at
http://developer.apple.com/technotes/tn/tn2000.html
TN2001: Running Files from a Hard Drive in Open Firmware, at
http://developer.apple.com/technotes/tn/tn2001.html
TN2004: Debugging Open Firmware Using Telnet, available at
http://developer.apple.com/technotes/tn/tn2004.html
RAM Expansion Modules
The mechanical characteristics of the DDR RAM SO-DIMM are given in JEDEC specification number JESD95.
The specification can be found by using the search string JESD95 on the Electronics Industry Association’s
website at
http://www.jedec.org/DOWNLOAD/default.cfm
The electrical characteristics of the RAM SO-DIMM are given in JEDEC Standard 21-C. The specification can
be found by using the search string JESD-21C on the Electronics Industry Association’s website at
http://www.jedec.org/DOWNLOAD/default.cfm
The DDR RAM DIMMs are required to be PC2700 compliant. Information about the PC2700 specifications is
available from Intel’s website at
http://developer.intel.com/technology/memory/
PC Card Manager
For information about the CardBus and the PC Card, refer to the CardBus DDK and the PC Card Manager SDK.
The DDK and SDK are available on the Apple Developer World web page at
http://developer.apple.com/sdk/index.html
RAM Expansion Modules 61
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 62

APPENDIX A
Supplemental Reference Documents
ATA Devices
ATA (AT Attachment), also referred to as integrated drive electronics (IDE), is a standard interface used with
storage devices such as hard disk drives. For more information on ATA, refer to the following Apple website
at
http://developer.apple.com/documentation/Hardware/DeviceManagers/ata/ata.html
ATA Manager 4.0 supports driver software for internal IDE drives and includes DMA support. For the latest
information about ATA Manager 4.0, see Technical Note TN1098, ATA Device Software Guide Additions and
Corrections, available on the world wide web at
http://developer.apple.com/technotes/tn/tn1098.html
The web page for Technical Note TN1098 includes a link to a downloadable copy of ATA Device Software
Guide.
Information about the ATA standards is available at the Technical Committee T13 AT Attachment website,
at
http://www.t13.org/
USB Interface
For more information about USB on Macintosh computers, refer to Apple Computer’s Mac OS USB DDK API
Reference. Information is also available on the World Wide Web, at
http://developer.apple.com/documentation/Hardware/DeviceManagers/usb/usb.html
USB game controllers are supported by the InputSprocket componentof the Apple Games Sprockets software
architecture. InputSprocket software and information about the InputSprocket API can be found at
http://developer.apple.com/games/
For full specifications of the Universal Serial Bus, you should refer to the USB Implementation Forum on the
World Wide Web, at
http://www.usb.org/developers/docs
FireWire Interface
62
For additional information about the FireWire IEEE 1394a and 1394b interfaces and the Apple API for FireWire
software, refer to the resources available on the Apple FireWire website at
http://developer.apple.com/hardwaredrivers/firewire/
The IEEE 1394 standards are available from the IEEE. Ordering information can be found on the World Wide
Web at
ATA Devices
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 63

APPENDIX A
Supplemental Reference Documents
http://shop.ieee.org/store
You may also find useful information at the 1394 Trade Association’s website:
http://www.1394ta.org/
Digital Visual Interface
For information about transition minimized differential signaling (TMDS) used with digital video monitors,
see the specification, Digital Visual Interface DVI Revision 1.0, available on the website of the Digital Display
Working Group (DDWG) at
http://www.ddwg.org/
Wireless Networks
More information about Wi-Fi and wireless networks using the IEEE 802.11 standards is available on the
website of the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance, at
http://www.wirelessethernet.org/OpenSection/
Bluetooth
For more information regarding Bluetooth technology, refer to the following locations on the World Wide
Web.
Bluetooth specification:
http://www.bluetooth.com/
Bluetooth SIG:
http://www.bluetooth.org
Bluetooth developer tools on the Apple web site at:
http://developer.apple.com/hardwaredrivers/bluetooth/
Digital Visual Interface 63
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 64

APPENDIX A
Supplemental Reference Documents
64
Bluetooth
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 65

APPENDIX B
Abbreviations
Here a lists of abbreviations used in this developer note.
Abbreviations and Standard Units
Standard units of measure used in this note include:
megabytesMBamperesA
milliampere-hoursmAh
Other Abbreviations
Other abbreviations used in this note include:
an Ethernet standard for data transmission at rates up to 10 Mbits per second10Base-T
megabits per secondMbpsdecibelsdB
megabitsMbitsgigabytesGB
megahertzMHzhertzHz
millimetersmmkilobytesKB
nanosecondsnskilogramskg
voltsVkilohertzkHz
volts direct currentVDCmilliamperesmA
an Ethernet standard for data transmission at rates up to 100 Mbits per second100Base-T
an Ethernet standard for data transmission at rates up to 1000 Mbits per second1000Base-T
accelerated graphics portAGP
ATA Interface ModuleAIM
American National Standards InstituteANSI
application programming interfaceAPI
Abbreviations and Standard Units 65
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 66

APPENDIX B
Abbreviations
application-specific integrated circuitASIC
AT attachmentATA
column address strobe, a memory control signalCAS
compact discCD
compact disc read-only memoryCD-ROM
central processing unitCPU
cathode ray tube, a video display deviceCRT
data access adapter (a telephone line interface)DAA
digital-to-analog converterDAC
display data channelDDC
G4
Dual Inline Memory ModuleDIMM
descriptor-based direct memory accessDB-DMA
device developer’s kitDDK
double data rate, a type of SDRAMDDR
direct memory accessDMA
Digital Visual InterfaceDVI
extended data outEDO
enhanced integrated device electronicsEIDE
Generation 4, the fourth generation of PowerPC microprocessors, incorporating AltiVec
technology
groundGND
hierarchical file systemHFS
human interface device, a class of USB devicesHID
integrated circuitIC
66
integrated device electronicsIDE
International Electrotechnical CommissionIEC
inter-IC control busIIC
inter-IC sound busIIS
input and outputI/O
Other Abbreviations
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 67

APPENDIX B
Abbreviations
International Organization for StandardizationISO
Joint Electron Device Engineering CouncilJEDEC
level 1 or first level, a type of CPU cacheL1
level 2 or second level, a type of CPU cacheL2
level 3 or third level, a type of CPU cacheL3
light emitting diodeLED
Macintosh Operating SystemMac OS
Medium Dependent InterfaceMDI
Medium Dependent Interface with Cross-OverMDI-X
modem
modulator-demodulator, a data communications interface for use with analog telephone
lines
nonmaskable interruptNMI
no operationNOP
nonvolatile random-access memoryNVRAM
orthogonal frequency-division multiplexingOFDM
Open Host Controller InterfaceOHCI
operating systemOS
Peripheral Component Interconnect, an industry-standard expansion busPCI
phase-locked loopPLL
random-access memoryRAM
Radio Corporation of AmericaRCA
root mean squarerms
read-only memoryROM
Serial Bus ProtocolSBP
Small Computer System InterfaceSCSI
software developer’s kitSDK
Single Data RateSDR
synchronous dynamic RAMSDRAM
signal to noise ratioSNR
Other Abbreviations 67
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 68

APPENDIX B
Abbreviations
Small Outline Dual Inline Memory ModuleSO-DIMM
Serial Presence Detect, a feature of the SO-DIMMSPD
transition minimized differential signalingTMDS
Universal Serial Bus, an industry-standard expansion busUSB
positive supply voltage (voltage for collectors)VCC
68
Other Abbreviations
Legacy Document | 2003-03-01 | © 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...