ANALOG DEVICES AD5273 Service Manual
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
64-Position OTP Digital Potentiometer
FEATURES
64 positions
One-time programmable (OTP)
Resistance setting—low cost alternative over EEMEM
Unlimited adjustments prior to OTP activation
1 kΩ, 10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ end-to-end terminal resistance
Compact 8-lead SOT-23 standard package
Ultralow power: I
Fast settling time: t
2
I
C-compatible digital interface
Computer software
= 5 μA maximum
DD
= 5 μs typical during power-up
S
2
replaces microcontroller in
factory programming applications
Wide temperature range: −40°C to +105°C
Low operating voltage: 2.7 V to 5.5 V
OTP validation check function
APPLICATIONS
System calibrations
Electronics level settings
Mechanical potentiometers and trimmer replacement
Automotive electronics adjustments
Transducer circuit adjustments
Programmable filters up to 6 MHz BW
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD5273 is a 64-position, one-time programmable (OTP)
digital potentiometer
achieve permanent program setting. This device performs the
same electronic adjustment function as most mechanical
trimmers and variable resistors. It allows unlimited adjustments
before permanently setting the resistance values. The AD5273 is
programmed using a 2-wire, I
During write mode, a fuse blow command is executed after the
final value is determined, thereby freezing the wiper position at
a given setting (analogous to placing epoxy on a mechanical
trimmer). When the permanent setting is achieved, the value
does not change, regardless of the supply variations or environmental stresses under normal operating conditions. To verify the
success of permanent programming, Analog Devices, Inc.,
patterned the OTP validation such that the fuse status can be
discerned from two validation bits in the read mode.
4
that employs fuse link technology to
1
set-and-forget
3
2
C®-compatible digital control.
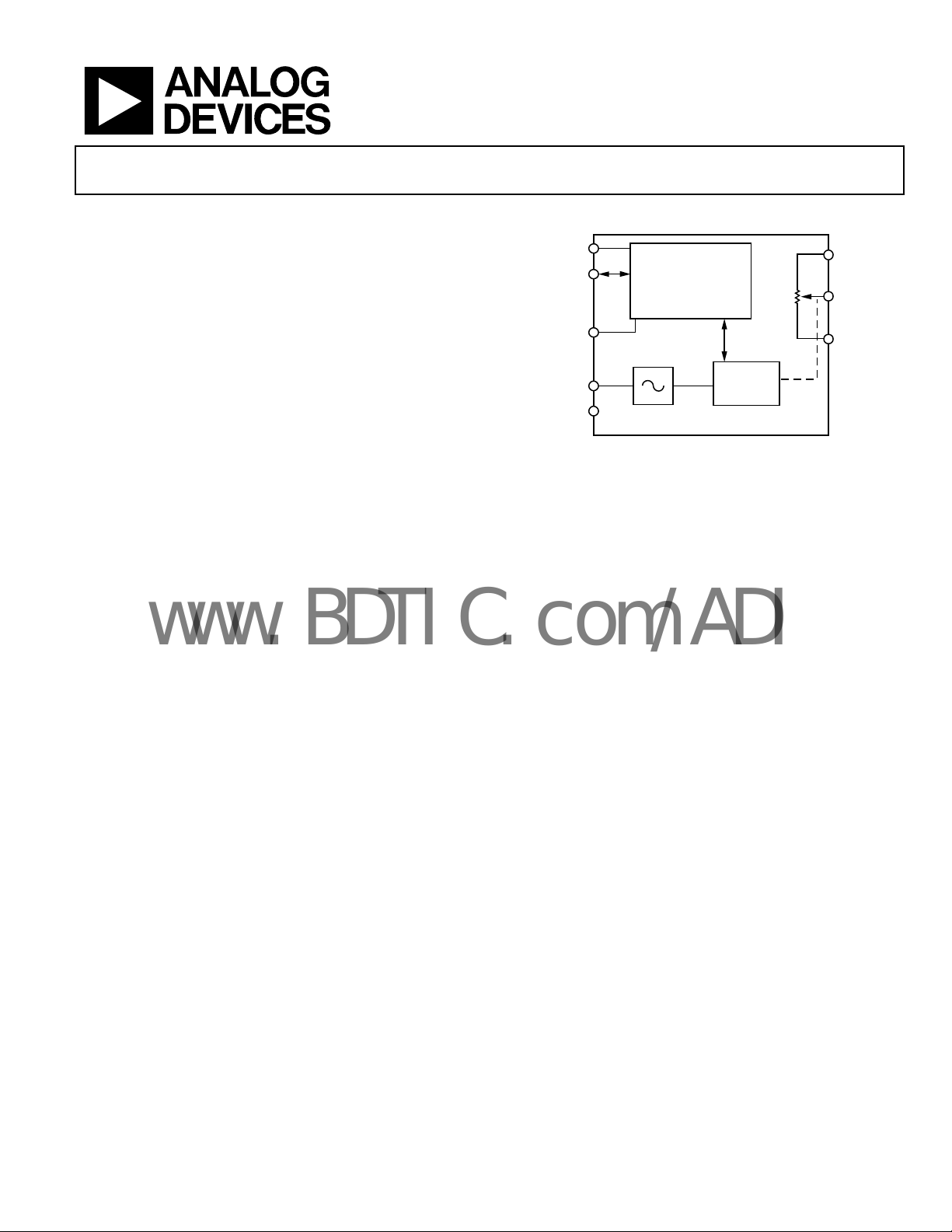
AD5273
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
SCL
2
I
SDA
AD0
V
GND
DD
C INTERFACE
AND
CONTROL LOGIC
AD5273
FUSE
LINK
Figure 1.
WIPER
REGISTER
In addition, for applications that program the AD5273 at the
factory, Analog Devices offers device programming software
running on Windows® NT®, Windows 2000, and Windows XP
operating systems. This software application effectively replaces
any external I
2
C controllers, which in turn enhances the user
system’s time-to-market.
The AD5273 is available in 1 kΩ, 10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, and 100 kΩ
resistances and in a compact 8-lead SOT-23 standard package.
It operates from −40°C to +105°C.
Along with its unique OTP feature, the AD5273 lends itself
well to general digital potentiometer applications due to its
effective resolution, array resistance options, small footprint,
and low cost.
An AD5273 evaluation kit and software are available. The kit
includes the connector and cable that can be converted for
factory programming applications.
For applications that require dynamic adjustment of resistance
settings with nonvolatile EEMEM, users should refer to the
AD523x and AD525x families of nonvolatile memory digital
potentiometers.
1
OTP allows unlimited adjustments before permanent setting.
2
Analog Devices cannot guarantee the software to be 100% compatible to all
systems due to the wide variation in computer configurations.
3
Applies to 1 kΩ parts only.
4
The terms digital potentiometer, VR, and RDAC are used interchangeably.
A
W
B
03224-001
2
Rev. G
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2002–2008 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD5273
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 4
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 6
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 6
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ............................. 7
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 8
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 13
One-Time Programming ........................................................... 13
Variable Resistance and Voltage for Rheostat Mode ............. 14
Variable Resistance and Voltage for Potentiometer Mode .... 14
ESD Protection ........................................................................... 15
Terminal Voltage Operating Range .......................................... 15
Power-Up/Power-Down Sequences ......................................... 15
Power Supply Considerations ................................................... 15
Controlling the AD5273 ................................................................ 16
Software Programming ............................................................. 16
I2C Controller Programming .................................................... 17
Controlling Two Devices on One Bus ..................................... 18
Applications Information .............................................................. 19
DAC .............................................................................................. 19
Programmable Voltage Source with Boosted Output ........... 19
Programmable Current Source ................................................ 19
Gain Control Compensation .................................................... 19
Programmable Low-Pass Filter ................................................ 20
Level Shift for Different Voltages Operation .......................... 20
RDAC Circuit Simulation Model ............................................. 20
Evaluation Board ............................................................................ 21
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 22
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 22
REVISION HISTORY
6/08—Rev. E to Rev. F
Updated Fuse Blow Condition to 400 ms Throughout ............... 5
1/08—Rev. E to Rev. F
Changes to Table 1 ............................................................................ 4
Changes to Table 2 ............................................................................ 6
Changes to Table 3 ............................................................................ 7
Inserted Figure 28 ........................................................................... 12
Changes to One-Time Programming Section ............................ 13
Changes to Power Supply Considerations Section ..................... 15
Deleted Figure 35 ............................................................................ 15
Changes to Figure 36 ...................................................................... 15
Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 22
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 22
1/05—Rev. D to Rev. E
Changes to Features .......................................................................... 1
Changes to Specifications ................................................................ 3
Changes to Table 3 ............................................................................ 6
Changes to Power Supply Considerations Section ..................... 15
Changes to Figure 35 and Figure 37............................................. 15
Changes to DAC Section ............................................................... 19
Changes to Level Shift for Different Voltages
Operation Section........................................................................... 20
Deleted the Resistance Scaling Section ....................................... 20
Deleted the Resolution Enhancement Section ........................... 20
12/04—Rev. C to Rev. D
Updated Format .................................................................. Universal
Changes to Specifications ................................................................. 3
Changes to Theory of Operation Section.................................... 13
Changes to Power Supply Consideration Section ...................... 15
Changes to Figure 35, Figure 36, and Figure 37 ......................... 15
11/03—Rev. B to Rev. C
Changes to SDA Bit Definitions and Descriptions .................... 10
Changes to One-Time Programming (OTP) Section................ 11
Changes to Table III ....................................................................... 11
Changes to Power Supply Considerations .................................. 13
Changes to Figure 8, Figure 9, and Figure 10 ............................. 13
Rev. G | Page 2 of 24

AD5273
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
10/03—Rev. A to Rev. B
Changes to Features .......................................................................... 1
Changes to Applications ................................................................... 1
Changes to Specifications ................................................................. 2
Changes to Absolute Maximum Ratings ........................................ 4
Changes to Pin Function Descriptions ........................................... 5
Changes to TPC 7, TPC 8, TPC 13, and TPC 14 Captions ......... 7
Deleted TPC 20; Renumbered Successive TPCs ........................... 9
Change to TPC 21 Caption .............................................................. 9
Change to the SDA Bit Definitions and Descriptions ................ 10
Replaced Theory of Operation Section ........................................ 11
Replaced Determining the Variable Resistance and
Voltage Section ................................................................................ 11
Replaced ESD Protection section .................................................. 12
Replaced Terminal Voltage Operating Range Section ............... 12
Replaced Power-Up Sequence Section ......................................... 12
Replaced Power Supply Considerations Section ......................... 13
Changes to Application section ..................................................... 16
Change to Equation 9 ..................................................................... 17
Deleted Digital Potentiometer Family Selection Guide ............. 19
6/03—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Change to Specifications .................................................................. 2
Change to Power Supply Considerations Section ....................... 12
Updated Outline Dimensions ........................................................ 20
12/02—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. G | Page 3 of 24
AD5273
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V, VA < VDD, VB = 0 V, −40°C < TA < +105°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ1Max Unit
DC CHARACTERISTICS—RHEOSTAT MODE
Resolution N 6 Bits
Resistor Differential Nonlinearity
2
R-DNL
10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ RWB, VA = NC −0.5 +0.05 +0.5 LSB
1 kΩ R
Resistor Nonlinearity
2
R-INL LSB
, VA = NC −1 +0.25 +1 LSB
WB
10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ RWB, VA = NC −0.5 +0.10 +0.5 LSB
1 kΩ RWB, VA = NC −5 +2 +5 LSB
Nominal Resistance Tolerance
3
ΔRAB/RAB T
= 25°C
A
10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ −30 +30 %
Nominal Resistance, 1 kΩ RAB 0.8 1.2 1.6 kΩ
Rheostat Mode Temperature
Coefficient
4
(ΔR
)/∆T Wiper = NC 300 ppm/°C
AB/RAB
Wiper Resistance RW IW = VDD/R, VDD = 3 V or 5 V 60 100 Ω
DC CHARACTERISTICS—POTENTIOMETER
DIVIDER MODE
Differential Nonlinearity
Integral Nonlinearity
5
5
INL −0.5 +0.5 LSB
DNL −0.5 +0.1 +0.5 LSB
Voltage Divider4 Temperature Coefficient (ΔVW/VW)/ΔT Code = 0x20 10 ppm/°C
Full-Scale Error V
Code = 0x3F −1 0 LSB
WFSE
10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ −1 0 LSB
1 kΩ −6 0 LSB
Zero-Scale Error V
Code = 0x00 −6 0 LSB
WZSE
10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ 0 1 LSB
1 kΩ 0 5 LSB
RESISTOR TERMINALS
Voltage Range
Capacitance7 A, B CA, CB f = 5 MHz, measured to GND, code =
6
VA, VB, VW GND VDD V
25 pF
0x20
Capacitance7 W CW f = 1 MHz, measured to GND, code =
55 pF
0x20
Common-Mode Leakage ICM V
= VB = VW 1 nA
A
DIGITAL INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Input Logic High (SDA and SCL)
8
VIH 0.7
V
V
DD
DD
0.5
Input Logic Low (SDA and SCL)8 VIL −0.5 +0.3
V
DD
Input Logic High (ADO) VIH 3.0 VDD V
Input Logic Low (ADO) VIL V
= 0 V or 5 V 0 0.4 V
IN
Input Logic Current IIL 0.01 1 μA
Input Capacitance
7
C
3 pF
IL
Output Logic Low (SDA) VOL 0.4 V
Three-State Leakage Current IOZ ±1 μA
Output Capacitance
7
C
3 pF
OZ
+
V
V
Rev. G | Page 4 of 24
AD5273
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ1Max Unit
POWER SUPPLIES
Power Supply Range VDD 2.7 5.5 V
OTP Power Supply
Supply Current IDD V
OTP Supply Current
Power Dissipation
Power Supply Sensitivity PSRR RAB = 1 kΩ −0.3 +0.3 %/%
PSRR RAB = 10 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 100 kΩ −0.05 +0.05 %/%
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
Bandwidth, −3 dB BW_1 kΩ RAB = 1 kΩ, code = 0x20 6000 kHz
BW_10 kΩ RAB = 10 kΩ, code = 0x20 600 kHz
BW_50 kΩ RAB = 50 kΩ, code = 0x20 110 kHz
BW_100 kΩ RAB = 100 kΩ, code = 0x20 60 kHz
Total Harmonic Distortion THDW
Adjustment Settling Time tS1
Power-Up Settling Time—
After Fuses Blown
Resistor Noise Voltage e
INTERFACE TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
SCL Clock Frequency f
t
Bus Free Time Between
BUF
Stop and Start
t
Hold Time
HD; STA
(Repeated Start)
t
Low Period of SCL Clock t3 1.3 μs
LOW
t
High Period of SCL Clock t4 0.6 50 μs
HIGH
t
Setup Time for
SU; STA
Start Condition
t
Data Hold Time t6 0.9 μs
HD; DAT
t
Data Setup Time t7 0.1 μs
SU; DAT
tF Fall Time of Both SDA and
SCL Signals
tR Rise Time of Both SDA and
SCL Signals
t
Setup Time for Stop Condition t10 0.6 μs
SU; STO
OTP Program Time t11 400 ms
1
Typical values represent average readings at 25°C, VDD = 5 V, and VSS = 0 V.
2
Resistor position nonlinearity error, R-INL, is the deviation from an ideal value measured between the maximum resistance and the minimum resistance wiper
positions. R-DNL measures the relative step change from ideal between successive tap positions. Parts are guaranteed monotonic.
3
VAB = VDD, wiper (VW) = no connect.
4
∆RWB/∆T = ∆RWA/∆T. Temperature coefficient is code-dependent; see the Typical Performance Characteristics section.
5
INL and DNL are measured at VW. INL with the RDAC configured as a potentiometer divider similar to a voltage output DAC. VW with the RDAC configured as a
potentiometer divider similar to a voltage output DAC. V
conditions.
6
The A, B, and W resistor terminals have no limitations on polarity with respect to each other.
7
Guaranteed by design; not subject to production test.
8
The minimum voltage requirement on the VIH is 0.7 × VDD. For example, VIH min = 3.5 V when VDD = 5 V. It is typical for the SCL and SDA resistors to be pulled up to VDD.
However, care must be taken to ensure that the minimum V
9
Different from the operating power supply; the power supply for OTP is used one time only.
10
Different from the operating current; the supply current for OTP lasts approximately 400 ms for the one time it is needed.
11
See Figure 28 for the energy plot during the OTP program.
12
P
is calculated from (IDD × VDD). CMOS logic level inputs result in minimum power dissipation.
DISS
13
Bandwidth, noise, and settling time depend on the terminal resistance value chosen. The lowest R value results in the fastest settling time and highest bandwidth.
The highest R value results in the minimum overall power consumption.
14
All dynamic characteristics use VDD = 5 V.
15
See Figure 29 for the location of the measured values.
8, 9
12
8, 10 ,11
7, 13 , 14
V
T
DD_OTP
I
T
DD_OTP
P
V
DISS
= 25°C 4.75 5 5.25 V
A
= 5 V or VIL = 0 V 0.1 5 μA
IH
= 25°C, V
A
= 5 V or VIL = 0 V, VDD = 5 V 0.5 27.5 µW
IH
= 5 V 100 mA
DD_OTP
= 1 V rms, RAB = 1 kΩ, VB = 0 V, f = 1
V
A
0.05 %
kHz
= 5 V ± 1 LSB error band, VB = 0 V,
V
A
measured at V
t
S2
= 5 V ± 1 LSB error band, VB = 0 V,
V
A
measured at V
RAB = 1 kΩ, f = 1 kHz, code = 0x20 3 nV/√Hz
7, 14, 15
N_WB
Applies to all parts
400 kHz
SCL
1.3 μs
t
1
t
2
After this period, the first clock pulse is
W
, VDD = 5 V
W
5 μs
5 μs
0.6 μs
generated
0.6
t
5
0.3 μs
t
8
t
0.3 μs
9
= VDD and VB = 0 V. DNL specification limits of ±1 LSB maximum are guaranteed monotonic operating
A
is met when the SCL and SDA are driven directly from a low voltage logic controller without pull-up resistors.
IH
Rev. G | Page 5 of 24

AD5273
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
VDD to GND −0.3 V +6.5 V
VA, VB, VW to GND GND, VDD
Maximum Current
IWB, IWA Pulsed ±20 mA
IWB Continuous (RWB ≤ 1 kΩ, A Open)
IWA Continuous (RWA ≤ 1 kΩ, B Open) ±4 mA
Digital Input and Output Voltage to GND 0 V, VDD
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +105°C
Maximum Junction Temperature (TJ max) 150°C
Storage Temperature −65°C to +150°C
Reflow Soldering
Peak Temperature 260°C
Time at Peak Temperature 20 sec to 40 sec
Thermal Resistance θJA, SOT-23
1
Maximum terminal current is bounded by the maximum current handling
of the switches, the maximum power dissipation of the package; the maximum applied voltage across any two of the A, B, and W terminals at a given
resistance.
2
Package power dissipation = (TJ max – TA)/θJA.
1
±4 mA
2
230°C/W
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. G | Page 6 of 24
AD5273
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
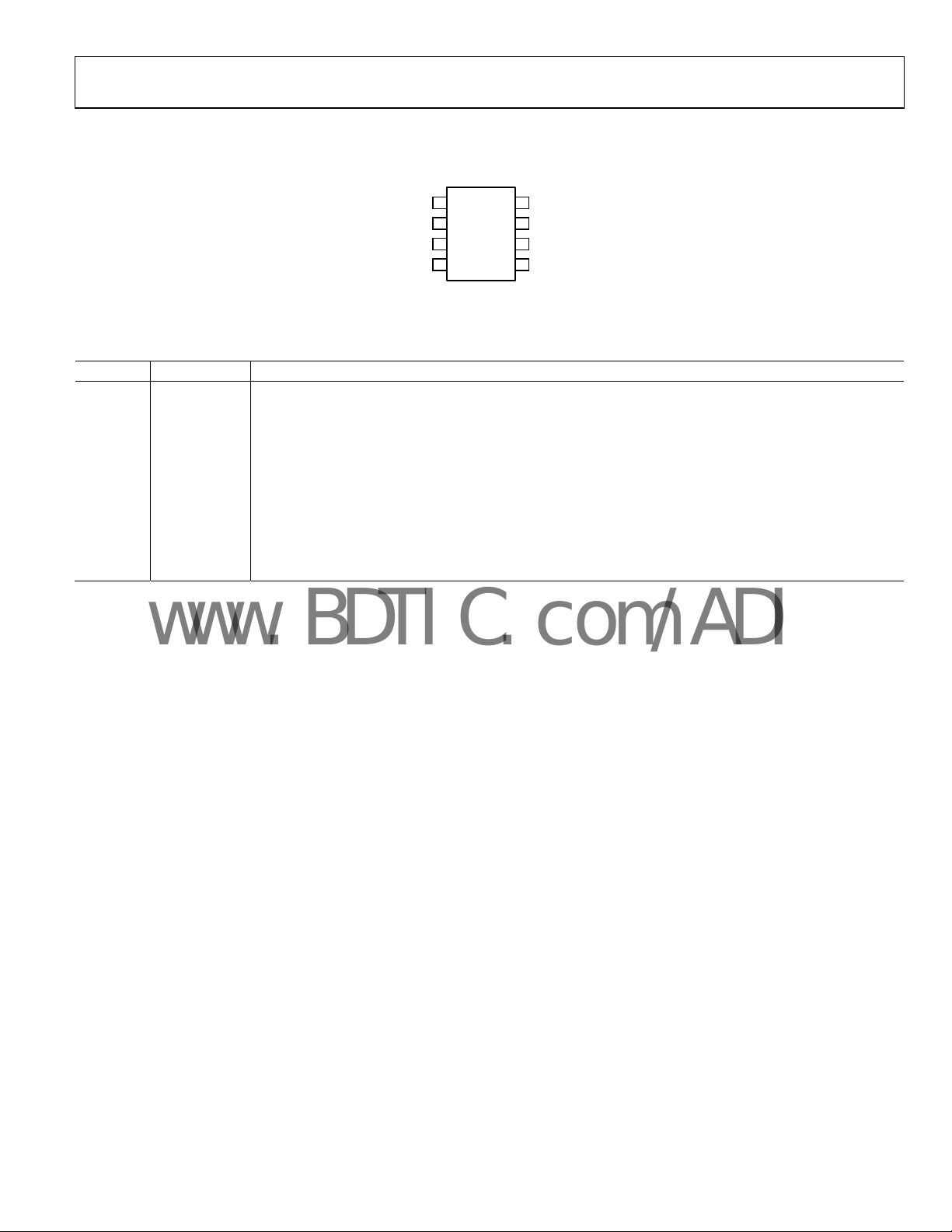
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
W
1
AD5273
2
V
DD
GND
SCL
TOP VIEW
3
(Not to Scale)
4
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
Table 3. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 W Wiper Terminal W. GND ≤ VW ≤ VDD.
2 VDD
Positive Power Supply. Specified for nonOTP operation from 2.7 V to 5.5 V. For OTP programming, V
be within the window of 4.75 V and 5.25 V and be capable of driving 100 mA.
3 GND Common Ground.
4 SCL
5 SDA
Serial Clock Input. Requires a pull-up resistor. If it is driven directly from a logic controller without the pull-up
resistor, ensure that the V
minimum is 0.7 × VDD.
IH
Serial Data Input/Output. Requires a pull-up resistor. If it is driven directly from a logic controller without the
pull-up resistor, ensure that the V
minimum is 0.7 × VDD.
IH
6 AD0 I2C Device Address Bit. Allows a maximum of two AD5273 devices to be addressed.
7 B Resistor Terminal B. GND ≤ VB ≤ VDD.
8 A Resistor Terminal A. GND ≤ VA ≤ VDD.
A
8
B
7
AD0
6
SDA
5
03224-002
must
DD_OTP
Rev. G | Page 7 of 24
AD5273
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
0.5
0.3
0.1
VDD = 3V
RAB = 10kΩ
T
= 25°C
A
0.10
0.06
0.02
RAB = 10kΩ
TA = –40°C
TA = +85°C
TA = +125°C
–0.1
= 5V
V
RHEOSTAT MODE INL (LSB)
–0.3
–0.5
0648 16 24 32 40 48 56
Figure 3. R
0.25
0.15
0.05
–0.05
RHEOSTAT MODE DNL (LSB)
–0.15
–0.25
0648 16 24 32 40 48 56
Figure 4. R
DD
CODE (Decimal)
vs. Code vs. Supply Voltages
INL
= 3V
V
DD
CODE (Decimal)
vs. Code vs. Supply Voltages
DNL
VDD = 5V
RAB = 10kΩ
T
= 25°C
A
03224-003
03224-004
–0.02
–0.06
POTENTIOMETER MODE DNL (LSB)
–0.10
0.10
0.06
0.02
–0.02
–0.06
POTENTIOMETER MODE INL (LSB)
–0.10
0648
16 24 32 40 48 56
CODE (Decimal)
Figure 6. DNL vs. Code vs. Temperature
3V
0648
16 24 32 40 48 56
CODE (Decimal)
Figure 7. INL vs. Code vs. Supply Voltages
5V
T
= +25°C
A
RAB = 10kΩ
T
= 25°C
A
03224-006
03224-007
0.10
0.06
TA = +85°C
0.02
–0.02
T
= +25°C
A
–0.06
POTENTIOMETER MODE INL (LSB)
–0.10
0648 16 24 32 40 48 56
CODE (Decimal)
Figure 5. INL vs. Code vs. Temperature
RAB = 10kΩ
TA = +125°C
TA = –40°C
03224-005
Rev. G | Page 8 of 2
0.10
0.06
0.02
–0.02
–0.06
POTENTIOMETER MODE DNL (LSB)
–0.10
0648
16 24 32 40 48 56
Figure 8. DNL vs. Code vs. Supply Voltages
4
3V
CODE (Decimal)
5V
RAB = 10kΩ
T
= 25°C
A
03224-008
 Loading...
Loading...