S
A
A
1-/2-Channel 15 V Digital Potentiometer
FEATURES
256 positions
AD5260: 1 channel
AD5262: 2 channels (independently programmable)
Potentiometer replacement
20 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 200 kΩ
Low temperature coefficient: 35 ppm/°C
4-wire, SPI-compatible serial data input
5 V to 15 V single-supply; ±5.5 V dual-supply operation
Power on midscale preset
APPLICATIONS
Mechanical potentiometer replacement
Instrumentation: gain, offset adjustment
Stereo channel audio level control
Programmable voltage-to-current conversion
Programmable filters, delays, time constants
Line impedance matching
Low resolution DAC replacement
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD5260/AD5262 provide a single- or dual-channel, 256position, digitally controlled variable resistor (VR) device.
These devices perform the same electronic adjustment function
as a potentiometer or variable resistor. Each channel of the
AD5260/AD5262 contains a fixed resistor with a wiper contact
that taps the fixed resistor value at a point determined by a
digital code loaded into the SPI-compatible serial-input register.
The resistance between the wiper and either end point of the
fixed resistor varies linearly with respect to the digital code
transferred into the VR latch. The variable resistor offers a
completely programmable value of resistance, between the A
terminal and the wiper or the B terminal and the wiper. The
fixed A-to-B terminal resistance of 20 Ω, 50 Ω, or 200 Ω has a
nominal temperature coefficient of 35 ppm/°C. Unlike the
majority of the digital potentiometers in the market, these
devices can operate up to 15 V or ±5 V provided proper supply
voltages are furnished.
Each VR has its own VR latch that holds its programmed
resistance value. These VR latches are updated from an internal
serial-to-parallel shift register, which is loaded from a standard
3-wire serial-input digital interface. The AD5260 contains an
8-bit serial register whereas the AD5262 contains a 9-bit serial
register. Each bit is clocked into the register on the positive
1
AD5260/AD5262
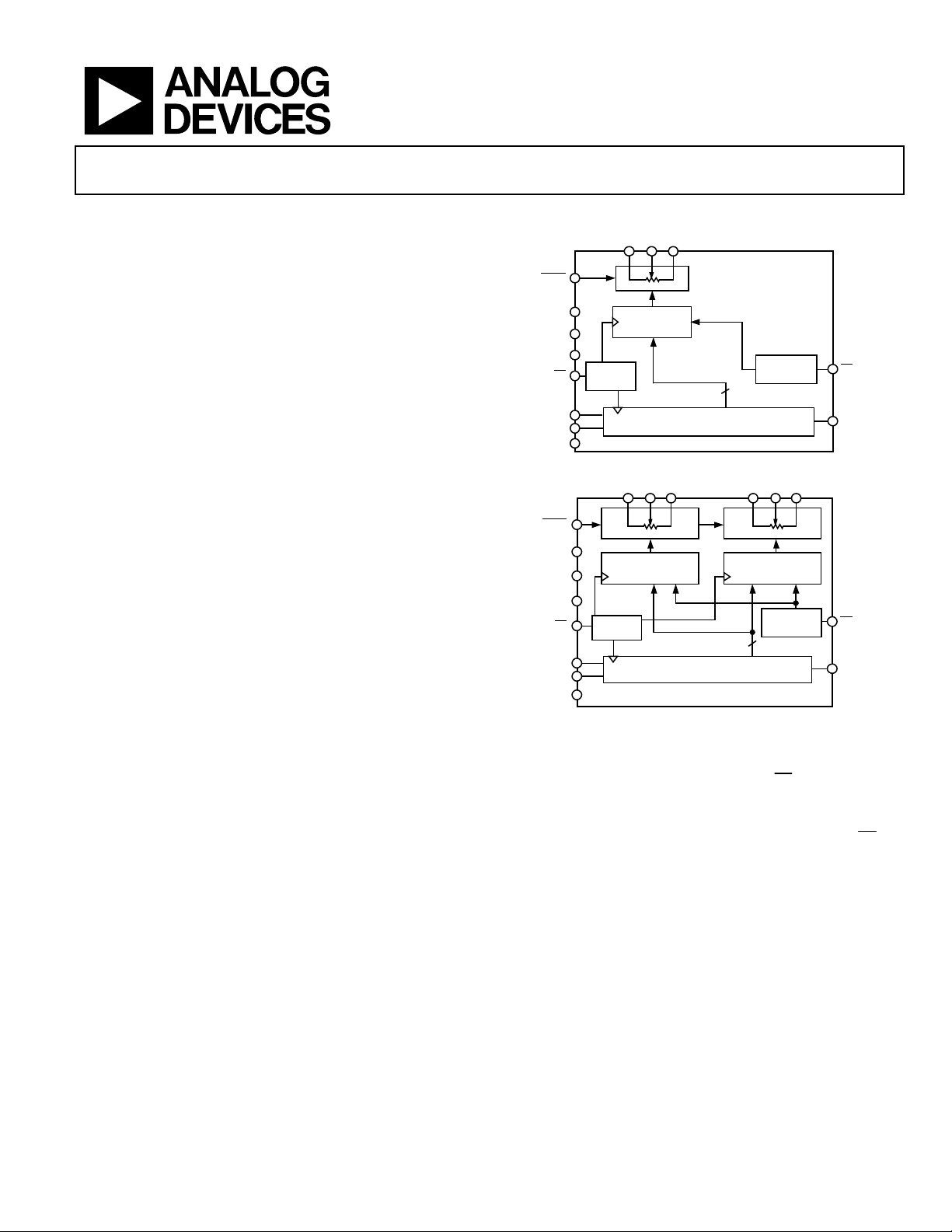
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAMS
WB
HDN
V
V
CS
CLK
SDI
GND
DD
SS
V
L
LOGIC
RDAC
REGISTER
SERIAL INPUT REGISTER
Figure 1. AD5260
1W1B1 A2W2B2
SHDN
V
V
CS
CLK
SDI
GND
DD
SS
V
L
LOGIC
RDAC1
REGISTER
SERIAL INPUT REGIST ER
AD5262
Figure 2. AD5262
edge of the CLK pin. The AD5262 address bit determines the
corresponding VR latch to be loaded with the last eight bits of
the data word during the positive edging of
data output pin at the opposite end of the serial register enables
simple daisy-chaining in multiple VR applications without
additional external decoding logic. An optional reset pin (
forces the wiper to the midscale position by loading 0x80 into
the VR latch.
The AD5260/AD5262 are available in thin surface-mount
14-lead TSSOP and 16-lead TSSOP packages. All parts are
guaranteed to operate over the extended industrial temperature
range of −40°C to +85°C.
1
The terms digital potentiometers, VR, and RDAC are used interchangeably.
AD5260
8
POWER-ON
RESET
RDAC2
REGISTER
POWER-ON
RESET
8
CS
strobe. A serial
PR
SDO
PR
SDO
PR
02695-001
02695-002
)
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2002–2010 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD5260/AD5262
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagrams............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Electrical Characteristics—20 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 200 kΩ Versions .. 3
Timing Diagrams.......................................................................... 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 6
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 6
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ........................... 7
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 9
Test Circuits..................................................................................... 14
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 15
Digital Interfacing ......................................................................15
Daisy-Chain Operation .............................................................16
RDAC Structure.......................................................................... 16
Programming the Variable Resistor......................................... 16
Programming the Potentiometer Divider............................... 17
Layout and Power Supply Bypassing ....................................... 18
Terminal Voltage Operating Range ......................................... 18
Power-Up Sequence................................................................... 18
RDAC Circuit Simulation Model............................................. 18
Macro Model Net List for RDAC............................................. 18
Applications Information.............................................................. 19
Bipolar DC or AC Operation from Dual Supplies................. 19
Gain Control Compensation.................................................... 19
Programmable Voltage Reference ............................................ 19
8-Bit Bipolar DAC...................................................................... 19
Bipolar Programmable Gain Amplifier................................... 20
Programmable Voltage Source with Boosted Output ........... 20
Programmable 4 mA-to-20 mA Current Source ................... 20
Programmable Bidirectional Current Source......................... 21
Programmable Low-Pass Filter ................................................ 21
Programmable Oscillator.......................................................... 21
Resistance Scaling ...................................................................... 22
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 23
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 24
REVISION HISTORY
8/10—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Updated Format..................................................................Universal
Deleted Figure 1; Renumbered Sequentially................................. 1
Changes to General Description Section ...................................... 1
Changes to Conditions of Channel Resistance Matching
(AD5262 only) Parameter, Voltage Divider Temperature
Coefficient Parameter, Full-Scale Error Parameter, and Zero-
Scale Error Parameter, Table 1........................................................ 3
Changes to Table 2 and Table 3....................................................... 5
Changes to Table 4............................................................................ 6
Changes to Table 5............................................................................ 7
Changes to Table 6............................................................................ 8
Changes to Figure 11 Caption and Figure 12 ................................9
Changes to Figure 31...................................................................... 12
Changes to Figure 35 Caption ...................................................... 13
Changes to Figure 43 and Figure 46............................................. 14
Deleted Potentiometer Family Selection Guide ......................... 18
Change to Programmable Voltage Source with Boosted Output
Section.............................................................................................. 20
Changes to Figure 64...................................................................... 21
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 23
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 24
3/02—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 24
AD5260/AD5262
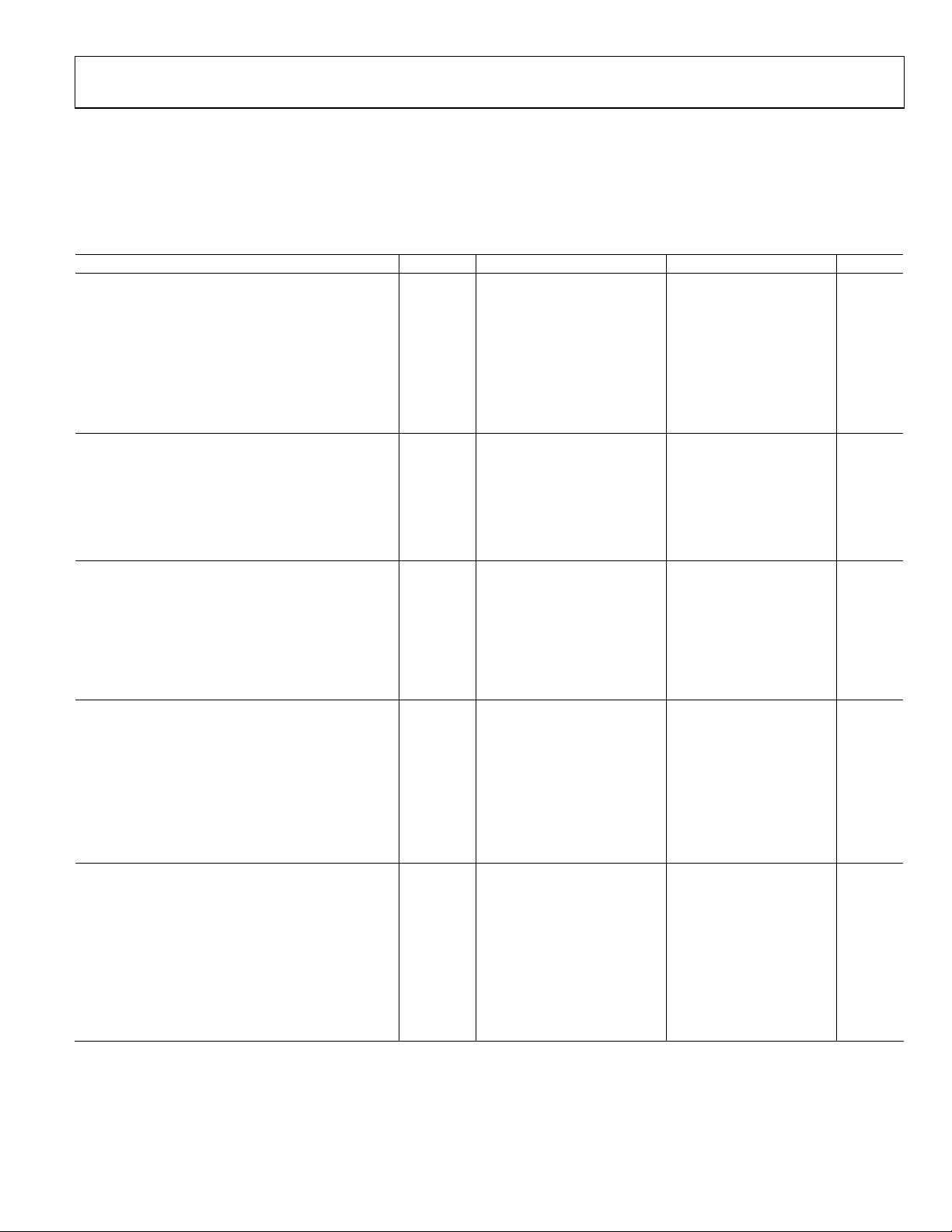
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS—20 kΩ, 50 kΩ, 200 kΩ VERSIONS
VDD = +15 V, VSS = 0 V, or VDD = +5 V, VSS = –5 V; VL = +5 V; VA = +5 V, VB = 0 V, −40°C < TA < +85°C, unless otherwise noted.
The AD5260/AD5262 contain 1968 transistors. Die size: 89 mil × 105 mil (9345 sq mil).
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ1 Max Unit
DC CHARACTERISTICS RHEOSTAT MODE Specifications apply to all VRs
Resistor Differential Nonlinearity2 R-DNL RWB, VA = no connect −1 ±¼ +1 LSB
Resistor Nonlinearity2 R-INL RWB, VA = no connect −1 ±½ +1 LSB
Nominal Resistor Tolerance3 ΔRAB TA = 25°C −30 30 %
Resistance Temperature Coefficient ΔRAB/ΔT Wiper = no connect 35 ppm/°C
Wiper Resistance RW IW = 1 V/RAB 60 150 Ω
Channel Resistance Matching (AD5262 only) ΔRWB/RWB Channel 1 and Channel 2 RWB,
= 0x80
D
X
Resistance Drift ΔRAB 0.05 %
DC CHARACTERISTICS POTENTIOMETER DIVIDER MODE Specifications apply to all VRs
Resolution N 8 Bits
Differential Nonlinearity4 DNL −1 ±1/4 +1 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity4 INL −1 ±1/2 +1 LSB
Voltage Divider Temperature Coefficient ΔVW/ΔT Code = half scale 5 ppm/°C
Full-Scale Error W
Zero-Scale Error V
Code = full scale −2 −1 +0 LSB
FSE
Code = zero scale 0 1 2 LSB
WZSE
RESISTOR TERMINALS
Voltage Range5 V
Ax and Bx Capacitance6 C
VSS VDD V
A, B, W
f = 5 MHz, measured to GND,
A,B
code = half scale
Wx Capacitance6 CW f = 1 MHz, measured to GND,
code = half scale
Common-Mode Leakage Current ICM VA = VB = VDD/2 1 nA
Shutdown Current7 I
5 μA
SHDN
DIGITAL INPUTS and OUTPUTS
Input Logic High VIH 2.4 V
Input Logic Low VIL 0.8 V
Input Logic High VIH VL = 3 V, VSS = 0 V 2.1 V
Input Logic Low VIL VL = 3 V, VSS = 0 V 0.6 V
Output Logic High (SDO) VOH R
Output Logic Low (SDO) VOL IOL = 1.6 mA, V
= 2 kΩ to 5 V 4.9 V
PULL-UP
= 5 V 0.4 V
LOGIC
Input Current8 IIL VIN = 0 V or 5 V ±1 μA
Input Capacitance6 CIL 5 pF
POWER SUPPLIES
Logic Supply VL 2.7 5.5 V
Power Single-Supply Range V
Power Dual-Supply Range V
VSS = 0 V 4.5 16.5 V
DD RANGE
DD/SS RANGE
±4.5 ±5.5 V
Logic Supply Current IL VL = 5 V 60 μA
Positive Supply Current IDD VIH = 5 V or VIL = 0 V 1 μA
Negative Supply Current ISS VSS= −5 V 1 μA
Power Dissipation9 P
V
DISS
= 5 V or VIL = 0 V,
IH
V
DD
= +5 V, VSS = –5 V
Power Supply Sensitivity PSS ΔVDD= +5 V, ±10% 0.003 0.01 %/%
0.1 %
25 pF
55 pF
0.3 mW
Rev. A | Page 3 of 24

AD5260/AD5262
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ1 Max Unit
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
Bandwidth –3 dB BW RAB = 20 kΩ/50 kΩ/200 kΩ 310/130/30 kHz
Total Harmonic Distortion THDW VA = 1 V
VW Settling Time tS VA = +5 V, VB = −5 V, ±1 LSB
Crosstalk11 CT VA = VDD, VB = 0 V, measure VW
Analog Crosstalk CTA VA1 = VDD, VB1 = 0 V, measure VW1
Resistor Noise Voltage e
INTERFACE TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Clock Frequency f
Input Clock Pulse Width tCH, tCL Clock level high or low 20 ns
Data Setup Time tDS 10 ns
Data Hold Time tDH 10 ns
CLK to SDO Propagation Delay13 tPD RL = 1 kΩ, CL< 20 pF 1 160 ns
CS
Setup Time
CS
High Pulse Width
Reset Pulse Width tRS 50 ns
CLK Fall to CS Rise Hold Time
CS
Rise to Clock Rise Setup
1
Typical values represent average readings at 25°C and VDD = +5 V, VSS = −5 V.
2
Resistor position nonlinearity error (R-INL) is the deviation from an ideal value measured between the maximum resistance and the minimum resistance wiper
positions. R-DNL measures the relative step change from ideal between successive tap positions. Parts are guaranteed monotonic. IW = VDD/R for both VDD = +5 V and
VSS = −5V.
3
VAB = VDD, wiper = no connect.
4
INL and DNL are measured at VW with the RDAC configured as a potentiometer divider similar to a voltage output digital-to-analog converter. VA = VDD and VB = 0 V.
DNL specification limits of ±1 LSB maximum are guaranteed monotonic operating conditions.
5
Resistor Terminal A, Terminal B, and Terminal W have no limitations on polarity with respect to each other.
6
Guaranteed by design and not subject to production test.
7
Measured at the Ax terminals. All Ax terminals are open-circuit in shutdown mode.
8
Worst-case supply current consumed when all logic-input levels set at 2.4 V, which is the standard characteristic of CMOS logic.
9
P
is calculated from (IDD × VDD). CMOS logic level inputs result in minimum power dissipation.
DISS
10
All dynamic characteristics use VDD = +5 V, VSS = −5 V, VL = +5 V.
11
Measured at VW where an adjacent VW is making a full-scale voltage change.
12
See Figure 5 for location of measured values. All input control voltages are specified with tR = tF = 2 ns (10% to 90% of 3 V) and timed from a voltage level of 1.5 V.
Switching characteristics are measured using VL = 5 V.
13
Propagation delay depends on value of VDD, RL, and CL.
6, 10
= 20 kΩ
R
AB
, VB = 0 V, f = 1 kHz,
RMS
0.014 %
5 μs
error band, R
= 20 kΩ
AB
1 nV-sec
with adjacent RDAC making
full-scale code change (AD5262
only)
–64 dB
= 5 V p-p at f = 10 kHz,
with V
W2
= 20 kΩ/200 kΩ (AD5262
R
AB
only)
RWB = 20 kΩ, f = 1 kHz 13
6, 12
Specifications apply to all parts
N_WB
25 MHz
CLK
t
5 ns
CSS
t
20 ns
CSW
t
0 ns
CSH
t
10 ns
CS1
nV/√Hz
Rev. A | Page 4 of 24
AD5260/AD5262
V
V
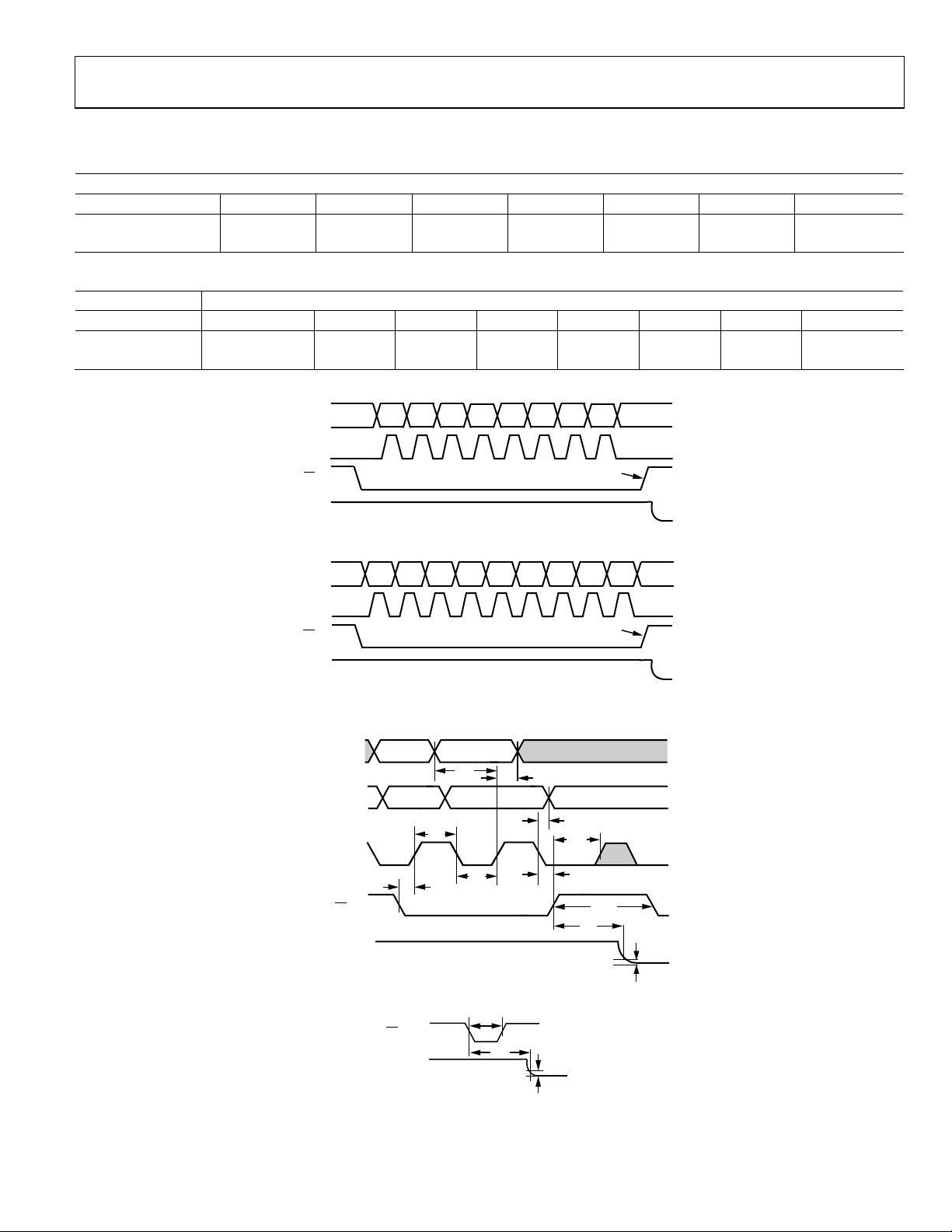
TIMING DIAGRAMS
Table 2. AD5260 8-Bit Serial Data Word Format
Data
B7 (MSB) B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 (LSB)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
27 26 2
Table 3. AD5262 9-Bit Serial Data Word Format
ADDR Data
B8 B7 (MSB) B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 (LSB)
A0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
8
2
2
7
26 2
5
2
5
2
SDI
CLK
CS
OUT
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 3. AD5260 Timing Diagram
SDI
CLK
CS
OUT
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
D7A0 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 4. AD5262 Timing Diagram
4
2
3
2
4
2
RDAC REGIST ER L O AD
RDAC REGISTE R L OAD
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
2
2695-004
02695-005
0
0
SDI
(DATA IN)
SDO
(DATA OUT)
CLK
CS
V
OUT
V
0V
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
DD
Ax OR Dx
A'x OR D'x
Dx
t
DS
t
DH
D'x
t
CH
t
CL
t
CSS
±1 LSB ERROR BRAND
Figure 5. Detailed Timing Diagram
t
1
PR
0
V
DD
±1 LSB ERRO R B AND
0V
RS
t
S
Figure 6. Preset Timing Diagram
Rev. A | Page 5 of 24
t
PD
t
±1 LSBD
CS1
t
CSH
t
CSW
t
S
±1 LSB
02695-006
02695-007

AD5260/AD5262
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA =25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
Parameter Rating
VDD to GND −0.3 V to +17 V
VSS to GND 0 V to −7 V
VDD to VSS 17 V
VL to GND 0 V to +7 V
VA, VB, VW to GND VSS, V
AX to BX, AX to WX, BX to W
X
DD
Intermittent1 ±20 mA
Continuous ±5 mA
Digital Inputs and Output Voltage
to GND
−0.3 V to VL + 0.3 V, or
+7 V (whichever is less)
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
Maximum Junction Temperature
)
(T
J MAX
150°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering,10 sec) 300°C
Vapor Phase (60 sec) 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) 220°C
Thermal Resistance2 θ
JA
14-Lead TSSOP 206°C/W
16-Lead TSSOP 150°C/W
1
Maximum terminal current is bounded by the maximum current handling of
the switches, maximum power dissipation of the package, and maximum
applied voltage across any two of the A, B, and W terminals at a given
resistance setting.
2
Package power dissipation = (T
J MAX
− TA)/θJA.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. A | Page 6 of 24
AD5260/AD5262
S
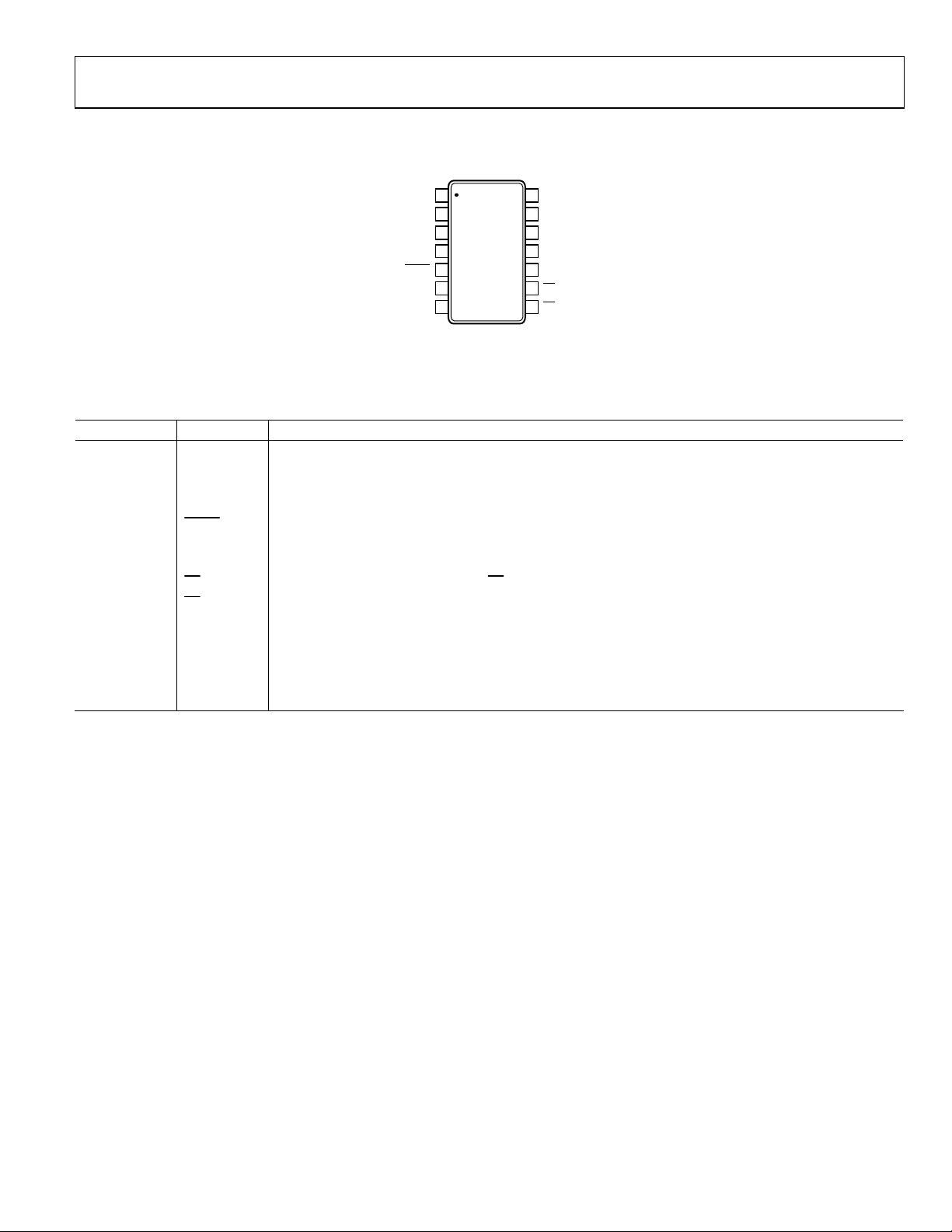
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
1
A
2
W
3
B
4
V
DD
5
HDN
6
CLK
7
SDI
NC = NO CONNECT
AD5260
TOP VIEW
(Not to S cale)
14
SDO
13
NC
12
V
L
11
V
SS
10
GND
9
PR
8
CS
2695-008
Figure 7. AD5260 Pin Configuration
Table 5. AD5260 Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 A A Terminal.
2 W Wiper Terminal.
3 B B Terminal.
4 VDD Positive Power Supply. Specified for operation at both 5 V or 15 V (sum of |VDD| + |VSS| ≤ 15 V).
5
SHDN
Active Low Input. Terminal A, open-circuit. Shutdown controls variable resistor.
6 CLK Serial Clock Input, Positive Edge Triggered.
7 SDI Serial Data Input.
8
9
CS
PR
Chip Select Input, Active Low. When CS
returns high, data is loaded into the RDAC register.
Active Low Preset to Midscale. Sets RDAC registers to 0x80.
10 GND Ground.
11 VSS Negative Power Supply. Specified for operation from 0 V to −5 V.
12 VL Logic Supply Voltage. Needs to be the same voltage as the digital logic controlling the AD5260.
13 NC No Connect. Users should not connect anything other than a dummy pad on this pin.
14 SDO Serial Data Output. Open-drain transistor requires a pull-up resistor.
Rev. A | Page 7 of 24
AD5260/AD5262
SDO
W1
V
SHDN
CLK
SDI
A1
B1
DD
1
2
3
AD5262
TOP VIEW
4
(Not to Scale)
5
6
7
8
16
A2
15
W2
14
B2
V
13
L
12
V
SS
11
GND
10
PR
9
CS
02695-009
Figure 8. AD5262 Pin Configuration
Table 6. AD5262 Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 SDO Serial Data Output. Open-drain transistor requires a pull-up resistor.
2 A1 A Terminal RDAC 1.
3 W1 Wiper RDAC 1, Address A0 = 0.
4 B1 B Terminal RDAC 1.
5 VDD Positive Power Supply. Specified for operation at both 5 V or 15 V. (Sum of |VDD| + |VSS| ≤ 15 V)
6
SHDN
Active Low Input. Terminal A, open-circuit. Shutdown controls variable Resistor 1 through Resistor R2.
7 CLK Serial Clock Input, Positive Edge Triggered.
8 SDI Serial Data Input.
9
CS
Chip Select Input, Active Low. When CS
returns high, data in the serial input register is decoded, based on the
Address Bit A0, and loaded into the target RDAC register.
10
PR
Active Low Preset to Midscale. Sets RDAC registers to 0x80.
11 GND Ground.
12 VSS Negative Power Supply. Specified for operation at either 0 V or −5 V (sum of |VDD| + |VSS| < 15 V).
13 VL Logic Supply Voltage. Needs to be same voltage as the digital logic controlling the AD5262.
14 B2 B Terminal RDAC 2.
15 W2 Wiper RDAC 2, Address A0 = 1.
16 A2 A Terminal RDAC 2.
Rev. A | Page 8 of 24
 Loading...
Loading...