
Fractionation of Fungal Fermentation
Broth using Solid-Phase Extraction
Application Note
Bioactive Pharmaceuticals, Agrochemicals
Authors
Liam Evans and Jonathan Steele
Hypha Discovery Ltd
Abstract
This application note describes a very effi cient clean-up and fractionation method
using a polymer-based, solid-phase extraction (SPE) product, Bond Elut Plexa.
This quick and effective method shows how unwanted sources of assay
interferences, such as proteins and oligosaccharides, can be removed allowing the
fractionation of the smaller bioactive pharmaceutical and agrochemical molecules
of interest from tropical higher fungi into more precise groups of polarity.
0
Introduction
Molecules from nature have an
excellent proven track record of
providing initial leads for development
into new pharmaceutical and
agrochemical products. To discover
new bioactive pharmaceutical and
agrochemical molecules from tropical
higher fungi, a new method that
stimulates fermentation of fungi has
been developed. The huge increase in
chemical production is shown in the
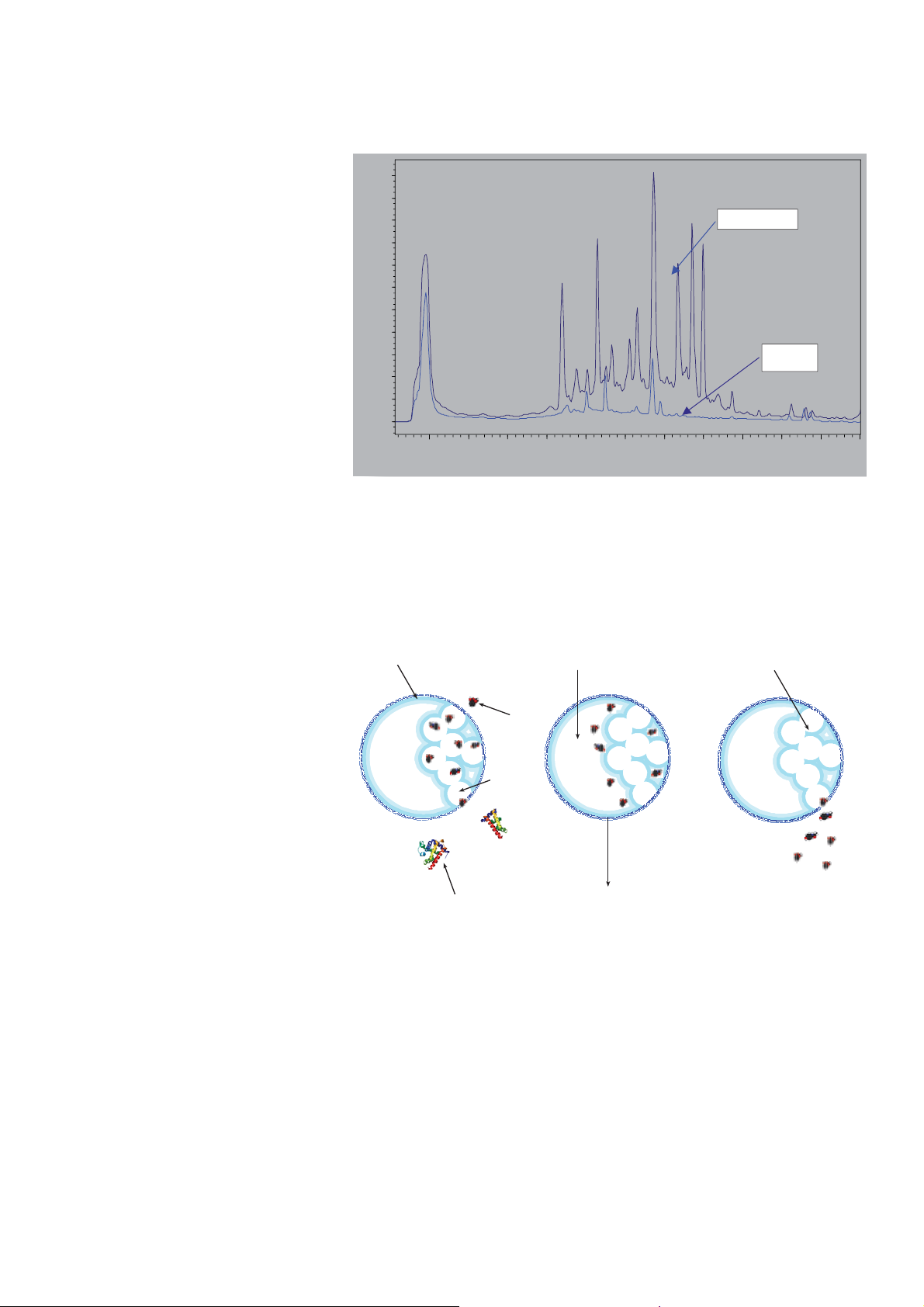
chromatographic analysis (Figure 1).
The composed fermentation products
vary greatly in molecule size and
polarity and require an effective
fractionation prior to identifi cation
and bioassay. For example, the
macromolecules have to be removed
before the compounds of interest can
be selectively collected according
to their polarities. Preparative
chromatography is one technique,
which can be used to clean-up and
fractionate. However, the high price
and the long analysis time make this
technique ineffi cient for our work.
2.20
2.00
1.80
1.60
1.40
1.20
AU
1.00
0.80
0.60
0.40
0.20
0.00
1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 9.00 10.00 11.00 12.0
Figure 1. Chromatogram showing comparison of compound production using Hypha fermentation and
conventional fermentation. Hypha’s fermentation provides increased titres and expression of new
molecules
LOAD
Water-rich, hydrophilic
surface allows excellent
phase transfer of analytes into
the polymer core.
WASH
Analytes that have crossed
the hydrophilic layers will
remain tightly bound in the
hydrophobic core.
Mi nutes
Hypha Fermentation
Conventional
Fermentation
ELUTE
Specially engineered pore
structure allows excellent
mass transfer out of the
polymer.
A very effi cient method is the clean-up
and fractionation on a new polymerbased, solid phase extraction (SPE)
product, Bond Elut Plexa. The primary
extracts generated from the proprietary
method are processed through the
SPE cartridges to remove proteins,
enzymes, oligosaccharides and other
biopolymers, which are known to cause
interference in target-based screening.
Analyte
Hydrophobic
Pores
Large endogenous proteins do
not bind to the surface of the
polymer and cannot access
pore structure
Figure 2. The water-wettable, hydroxylated exterior allows excellent fl ow of bio-fl uid samples. A
gradient of polarity on the polymer surface shunts small analytes to the more hydrophobic center
of the polymer bead where they are retained. As the surface is highly polar and entirely amide-free,
binding of proteins on the polymer surface is minimized, resulting in cleaner samples and reduced ion
suppression
core
Interferences washed away
without leaching the analytes
of interest
Clean extract with high
recovery
2
SPE Sorbent
Bond Elut Plexa is a new type of
polymeric SPE product, designed for
improved analytical performance and
ease of use. The base material is a
macroporous styrene divinylbenzene
co-polymer. The monodisperse
polymer particles are functionalized
with hydrophilic substituents. These
hydroxyl-containing moieties create a
‘water-rich’ environment on the surface
of the polymeric bead and a polar
gradient into the hydrophobic pores
(Figure 2).
Large molecules cannot access
the pore structure of the core. This
facilitates a highly effi cient sample
throughput by allowing quick removal
of unwanted assay interferences. The
polarity gradient in the pore helps to
fractionate some samples into different
polarity groups.
Elution in one step with
100% MeOH. Rich and
complex mixture which
includes smaller, more
drug-like compounds
0 12min
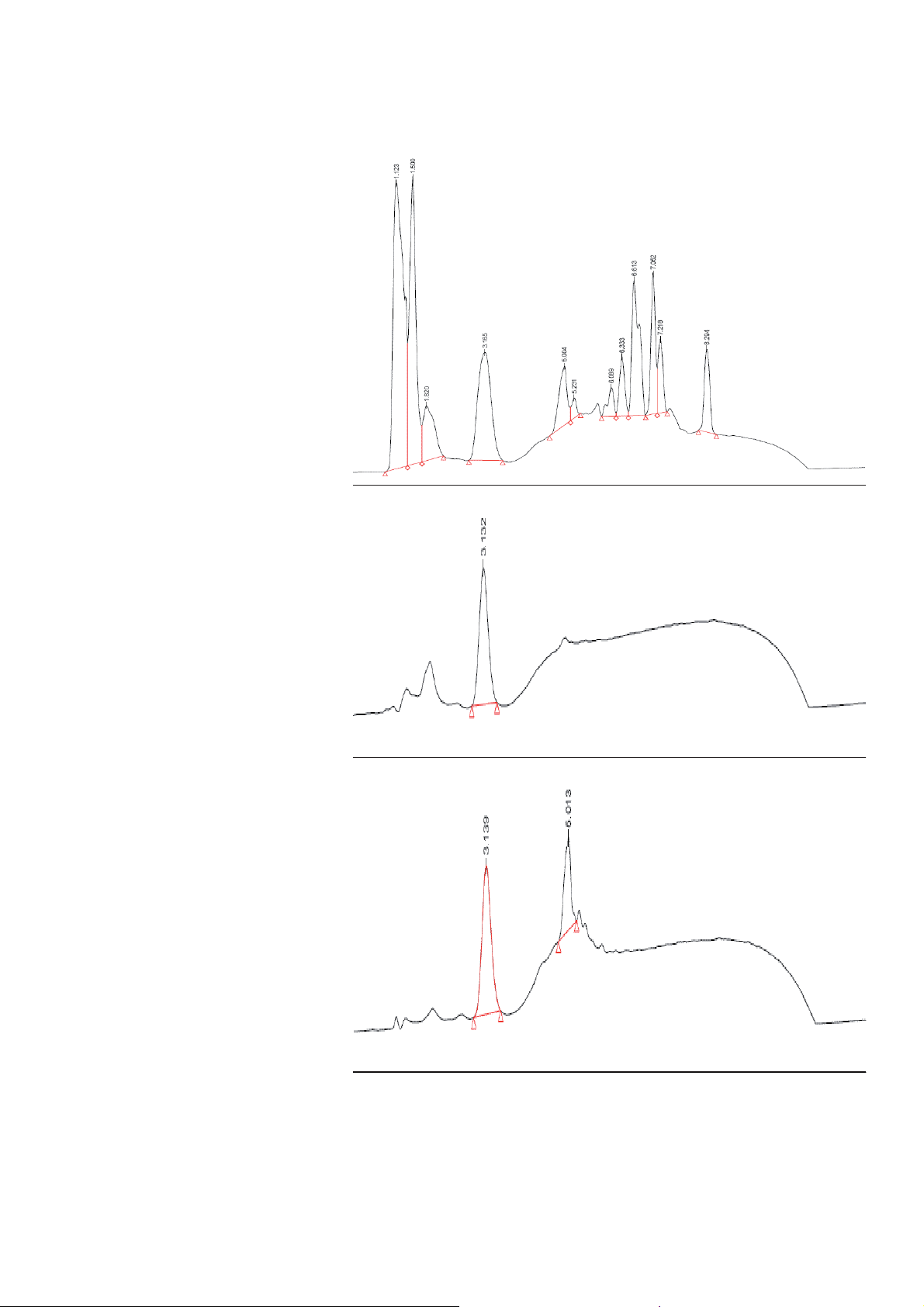
Fraction 1 contains
polar metabolites (85%
buffer, 15% MeOH)
Method
The fermented sample is loaded onto
the 500 mg Bond Elut Plexa cartridge
in the presence of ion-pair reagent
enabling retention of very polar
compounds, even those of similar
retention to aminoglycoside antibiotics.
Drug-like molecules are retained
within the porous particles at the
hydrophobic core. Macromolecules are
washed away in a buffer-wash step.
With the macromolecules removed,
the compounds of interest can then
be selectively eluted according to their
polarities. Component molecules are
fractionated into four groups of polarity,
allowing the operator to select subsets
with different ranges of hydrophobicity
(Figure 3).
0 12min
Fraction 2 contains
metabolites seen in
Fraction 1 and more
retained compounds
(55% buffer, 45%
MeOH)
0 12min
Figure 3. Fractionated SPE of basidiomycetes fermentation with Bond Elut Plexa sample loading is
performed in the presence of ion-pair reagent enabling retention of very polar N-compounds, even
those of similar retention to aminoglycoside antibiotics (continued on page 4)
3
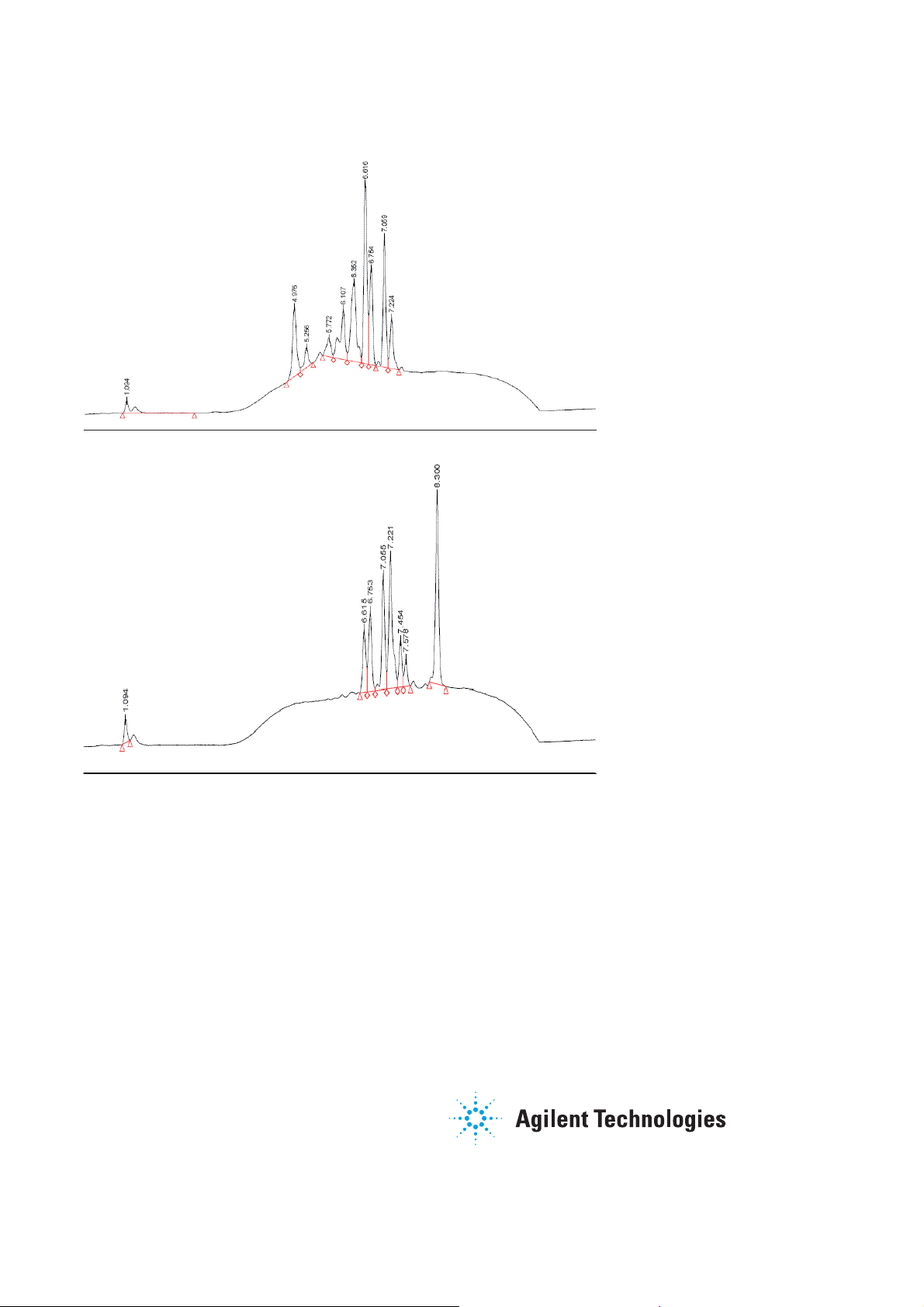
0 12min
Fraction 3 contains
mid-range polarity
components, perhaps
with the most favorable
pharmacokinetic
properties (25% buffer,
75% MeOH)
Fraction 4 contains
the highly retained
components from the
broth sample (100%
MeOH)
Conclusion
SPE on Bond Elut Plexa works
with a combination of mechanics.
When compared to other polymeric
materials that we have used at Hypha,
this material greatly increases the
precision and speed of our research.
The advanced design of the pore
facilitates a highly effi cient sample
throughput by allowing us to quickly
remove unwanted sources of assay
interferences such as proteins and
oligosaccharides, while the polarity
gradient in the pore enables us to
fractionate samples into more precise
groups of polarity. This results in more
effi cient targeting of small molecules of
interest.
0 12min
www.agilent.com/chem
This information is subject to change without notice.
© Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2010
Published in UK, August 17, 2010
SI-00969
 Loading...
Loading...