Page 1

www.3com.com
Baseline Switch
2226 Plus
User Guide
Bedienungsanleitung
3C16475CS
Part No. 10015240 Rev. BA
Published February 2008
Page 2

3Com Corporation • 350 Campus Drive • Marlborough • MA USA 01752-3064
Copyright © 2007, 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this
documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to
make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation)
without written permission from 3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make
changes in content from time to time without obligation on the part of 3Com
Corporation to provide notification of such revision or change.
3Com Corporation provides this documentation without warranty, term, or
condition of any kind, either implied or expressed, including, but not limited to,
the implied warranties, terms or conditions of merchantability, satisfactory
quality, and fitness for a particular purpose. 3Com may make improvements or
changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this documentation
at any time.
If there is any software on removable media described in this documentation, it
is furnished under a license agreement included with the product as a separate
document, in the hard copy documentation, or on the removable media in a
directory file named LICENSE.TXT or !LICENSE.TXT. If you are unable to locate a
copy, please contact 3Com and a copy will be provided to you.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
If you are a United States government agency, then this documentation and the
software described herein are provided to you subject to the following:
All technical data and computer software are commercial in nature and
developed solely at private expense. Software is delivered as “Commercial
Computer Software” as defined in DFARS 252.227-7014 (June 1995) or as a
“commercial item” as defined in FAR 2.101(a) and as such is provided with only
such rights as are provided in 3Com’s standard commercial license for the
Software. Technical data is provided with limited rights only as provided in DFAR
252.227-7015 (Nov 1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987), whichever is
applicable. You agree not to remove or deface any portion of any legend
provided on any licensed program or documentation contained in, or delivered
to you in conjunction with, this User Guide.
Unless otherwise indicated, 3Com registered trademarks are registered in the
United States and may or may not be registered in other countries.
3Com, 3Com Express, 3Com Guardian and the 3Com logo are registered
trademarks of 3Com Corporation.
IEEE and 802 are registered trademarks of the Institute of Electrical and
Electronics Engineers, Inc. Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Xerox is a registered trademark of Xerox Corporation. UNIX is a registered
trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively through
X/Open Company, Ltd.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective
companies with which they are associated.
ENVIRONMENTAL STATEMENT
It is the policy of 3Com Corporation to be environmentally-friendly in all
operations. To uphold our policy, we are committed to:
■ Establishing environmental performance standards that comply with national
legislation and regulations.
■ Conserving energy, materials and natural resources in all operations.
■ Reducing the waste generated by all operations. Ensuring that all waste
conforms to recognized environmental standards. Maximizing the recyclable
and reusable content of all products.
■ Ensuring that all products can be recycled, reused and disposed of safely.
■ Ensuring that all products are labelled according to recognized
environmental standards.
■ Improving our environmental record on a continual basis.
End of Life Statement
3Com processes allow for the recovery, reclamation and safe disposal of all
end-of-life electronic components.
Regulated Materials Statement
3Com products do not contain any hazardous or ozone-depleting material.
Environmental Statement about the Documentation
The documentation for this product is printed on paper that comes from
sustainable, managed forests; it is fully biodegradable and recyclable, and is
completely chlorine-free. The varnish is environmentally-friendly, and the inks are
vegetable-based with a low heavy-metal content.
Page 3

CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions 7
Documentation Comments 8
Product Registration 8
1 INTRODUCING THE BASELINE SWITCH
Overview of the Baseline Switch 9
Features and Capabilities 9
Autosensing of MDI/MDIX Connections 9
Autonegotiating 10/100 Mbps Ports 9
Gigabit Combo Ports (RJ-45/SFP) 9
Physical Features 10
Front Panel 10
Rear Panel 13
Package Contents 14
2 INSTALLING THE SWITCH
Before You Begin 15
Positioning the Switch 15
Rack-Mounting or Free-Standing 16
Using the Mounting Kit 16
Montagesatz Anweisungen 17
Placing Units On Top of Each Other 17
Supplying Power to the Switch 18
Checking for Correct Operation 18
Using SFP Tranceivers 19
Approved SFP Transceivers 19
Inserting an SFP Transceiver 19
Removing an SFP Transceiver 20
Performing Spot Checks 21
3 CONNECTING TO THE WEB INTERFACE
Requirements for Accessing the Web Interface 23
Running the Discovery Application 23
Logging On to the Web Interface 25
Navigating the Web Interface 25
Menu 25
Buttons 28
Port Status 28
Accessing the Interface Without Using Discovery 28
DHCP Assigned IP Address 29
Manually Assigned (Static) IP Address 29
4 CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Configuration Overview 31
Device Summary Information 31
Administration Settings 33
Modifying the IP Address Settings 33
Automatic IP Configuration 33
Page 4

IP Setup 34
Backup Configuration 35
Restore Configuration 35
Firmware Upgrade 35
Initialize 36
Reboot 36
System Access 37
System Time 39
SNMP 39
Configuring VLANs 41
VLAN 42
Forwarding Tagged/Untagged Frames 46
Sample VLAN Configurations 46
Spanning Tree 48
IGMP Snooping 50
IGMP Query 50
Broadcast Storm 51
Configuring Port Settings 51
Administration 51
Speed/Duplex for 1000 Mbps Connections 53
Link Aggregation 54
Spanning Tree per Port 56
Port Mirroring 58
Statistics 60
QoS VoIP Traffic Settings 60
Security 64
RADIUS Client 64
802.1X Settings 66
Monitoring 68
Address Table 68
Cable Diagnostics 68
5 TROUBLESHOOTING
Resetting to Factory Defaults 71
Forgotten Password 71
Forgotten Static IP Address 72
Solving LED Issues 72
If the Problem Persists 73
A OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR PRODUCT
Register Your Product 75
Purchase Value-Added Services 75
Troubleshoot Online 75
Access Software Downloads 75
Telephone Technical Support and Repair 76
Contact Us 76
B TECHNICAL INFORMATION
Related Standards 79
Environmental 79
Physical 79
Electrical 79
C SAFETY INFORMATION
Important Safety Information 81
Page 5

GLOSSARY
REGULATORY NOTICES
INDEX
Page 6

Page 7
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide describes how to install your 3Com Switch
and perform initial management configurations.
This guide is intended for use by those responsible for
installing and setting up network equipment;
consequently, it assumes a basic working knowledge of
LANs (Local Area Networks).
Diese Anleitung ist fur die Benutzung durch
Netzwerkadministratoren vorgesehen, die fur die
Installation und das einstellen von
Netzwerkkomponenten verantwortlich sind; sie setzt
Erfahrung bei der Arbeit mit LANs (Local Area Networks)
voraus.
If release notes are shipped with your product and the
information there differs from the information in this
guide, follow the instructions in the release notes.
Most user guides and release notes are available in
Adobe Acrobat Reader Portable Document Format (PDF)
or HTML on the 3Com World Wide Web site:
www.3com.com
Conventions
Table 1 and Table 2 list conventions that are used
throughout this guide.
Ta b l e 1 Notice Icons
Icon Notice Type Description
Information note Information that describes
Caution Information that alerts you to
Warning Information that alerts you to
important features or instructions
potential loss of data or potential
damage to an application, system,
or device
potential personal injury
Page 8

8 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Tabl e 2 Text Conventions
Convention Description
The words “enter”
and “type”
Keyboard key names If you must press two or more keys
Words in italics Italics are used to:
When you see the word “enter” in this
guide, you must type something, and then
press Return or Enter. Do not press Return
or Enter when an instruction simply says
“type.”
simultaneously, the key names are linked
with a plus sign (+). Example:
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del
■ Emphasize a point.
■ Denote a new term at the place where it
is defined in the text.
■ Identify menu names, menu commands,
and software button names. Examples:
From the Help menu, select Contents.
Click OK.
Documentation Comments
Your suggestions are very important to us. They will
help make our documentation more useful to you.
Please e-mail comments about this document to 3Com
at:
pddtechpubs_comments@3com.com
Please include the following information when
contacting us:
■ Document title
■ Document part number (on the title page)
■ Page number (if appropriate)
Example:
■ Baseline Switch 2226 Plus User Guide
■ Part number: 10015240
■ Page 25
Please note that we can only respond to comments and
questions about 3Com product documentation at this
e-mail address. Questions related to technical support or
sales should be directed in the first instance to your
network supplier.
Product Registration
You can now register your Baseline Switch on the 3Com
Web site to receive up-to-date information on your
product:
http://esupport.3com.com
Page 9

1
INTRODUCING THE BASELINE SWITCH
This chapter provides an overview of the features and
capabilities of the 3Com Baseline Switch 2226 Plus. It
also identifies the contents of the Switch package and
helps you get to know the physical features of the
device.
Overview of the Baseline Switch
The 3Com® Baseline Switch 2226 Plus is a versatile,
easy-to-use unmanaged switch. It is ideal for users who
want the high-speed performance of 10/100 switching
with the added functionality of Gigabit fiber links, but
do not need sophisticated management capabilities. The
Switch is shipped ready for use. No configuration is
necessary.
Features and Capabilities
The Switch has 24 shielded RJ-45, 10/100 Mbps
auto-negotiating ports and 2 Gigabit combo ports
(which comprised of a RJ-45 port and a Small Form
Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceiver slot) on the front
panel for easy, flexible connection to fiber-based Gigabit
media.
Autosensing of MDI/MDIX Connections
All ports on the Switch can autosense both medium
dependent interface (MDI) and medium dependent
interface crossover (MDIX) connections. This allows you
to connect network devices to each port using either a
normal straight-through TP (twisted pair) cable or a
‘crossover’ TP cable.
Any port can therefore be used to connect to another
switch port, server, or workstation without additional
configuration.
Autonegotiating 10/100 Mbps Ports
Each 10/100 Mbps port automatically determines the
speed and duplex mode of the connected equipment
and provides a suitable switched connection. The
10/100 Mbps ports can operate in either half-duplex or
full-duplex mode.
Gigabit Combo Ports (RJ-45/SFP)
The 2 Gigabit combo ports support fiber Gigabit
Ethernet short-wave (SX) and long-wave (LX) SFP
transceivers in any combination. This offers you the
flexibility of using SFP transceivers to provide
connectivity between the Switch and a 1000 Mbps core
network.
Page 10
10 INTRODUCING THE BASELINE SWITCH
When an SFP port is in operation, the corresponding
1000BASE-T port is disabled. The 1000 Mbps
connections can only operate in full duplex mode.
Physical Features
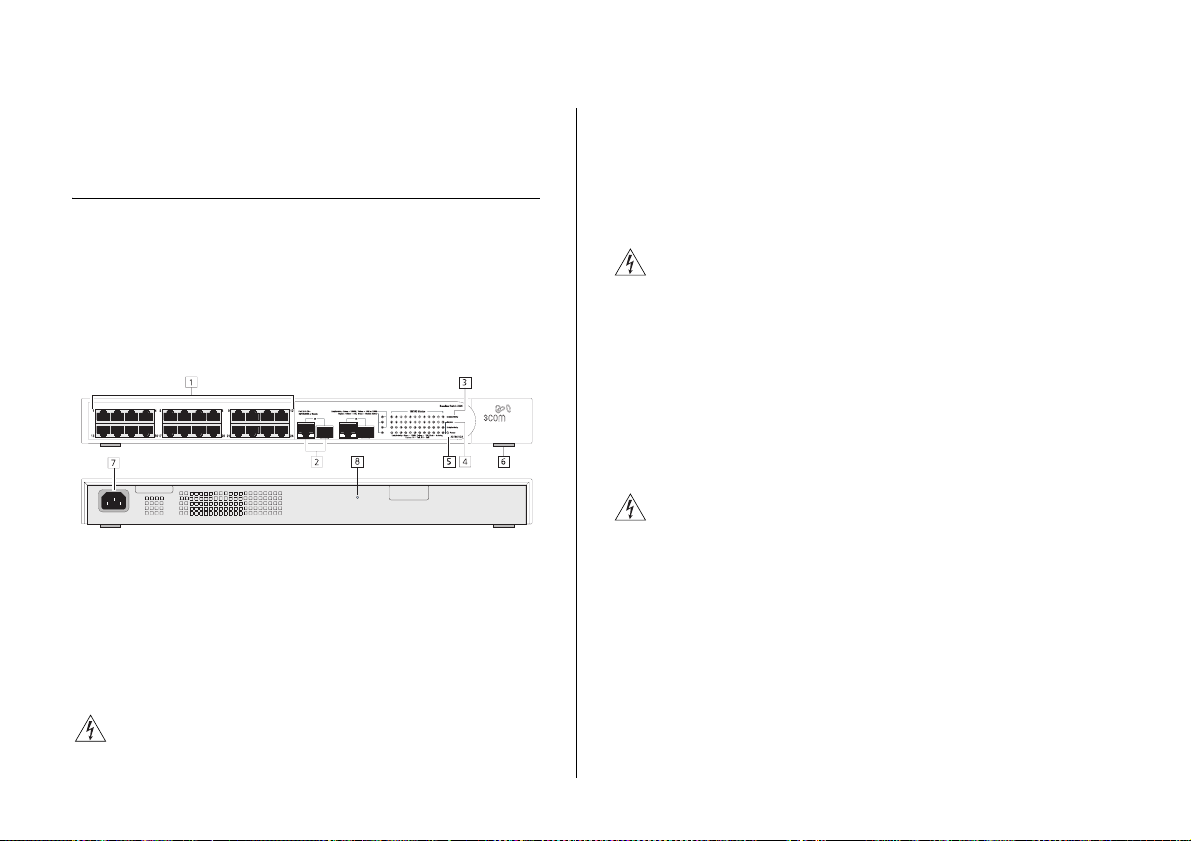
Figure 1 shows the front and rear panels of the Switch.
The numbers in this diagram refer to numbered sections
in “Front Panel” on page 10 and “Rear Panel” on
page 13.
Figure 1 Front and Rear Panels
Front Panel
The front panel of the Switch contains a series of
indicator lights (LEDs) that help describe the state of
various networking and connection operations.
(1) RJ-45 10/100 Ports
WARNING: RJ-45 Ports. These are shielded RJ-45 data
sockets. They cannot be used as standard traditional
telephone sockets, or to connect the unit to a
traditional PBX or public telephone network. Only
connect RJ-45 data connectors, network telephony
systems, or network telephones to these sockets.
Either shielded or unshielded data cables with shielded
or unshielded jacks can be connected to these data
sockets.
AVERTISSEMENT: Points d’accès RJ-45. Ceux-ci sont
protégés par des prises de données. Ils ne peuvent pas
être utilisés comme prises de téléphone conventionnelles
standard, ni pour la connection de l’unité à un réseau
téléphonique central privé ou public. Raccorder
seulement connecteurs de données RJ-45, systèmes de
réseaux de téléphonie ou téléphones de réseaux à ces
prises.
Il est possible de raccorder des câbles protégés ou non
protégés avec des jacks protégés ou non protégés à ces
prises de données.
WARNHINWEIS: RJ-45-Porte. Diese Porte sind
geschützte Datensteckdosen. Sie dürfen weder wie
normale traditionelle Telefonsteckdosen noch für die
Verbindung der Einheit mit einem traditionellem
privatem oder öffentlichem Telefonnetzwerk gebraucht
werden. Nur RJ-45-Datenanscluße, Telefonnetzsysteme
or Netztelefone an diese Steckdosen anschließen.
Entweder geschützte oder ungeschützte Buchsen dürfen
an diese Datensteckdosen angeschlossen werden.
The Switch has 24 10/100 Mbps auto-negotiating ports.
Each port supports automatic MDI/MDI-X detection and
Page 11
Physical Features 11
can be connected to either a 10BASE-T, or 100BASE-TX
device.
For each port, the speed and duplex mode (half duplex
or full duplex for 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX) are
automatically determined by the capabilities of the
connected device.
CAUTION: The Switch supports full duplex
auto-negotiation. If auto-negotiation is disabled for
1000BASE-T, then the Switch uses the forced-mode
default of 100 full duplex mode. If the connected device
does not support auto-negotiation, the Switch will
operate in half duplex mode (even if the attached device
is operating in full duplex mode). In such a
configuration, you may notice some degradation of
network performance. 3Com recommends that you use
devices that are capable of auto-negotiation (and that
you ensure that auto-negotiation is enabled, if it is a
configurable option).
(2) Gigabit Combo Ports (RJ-45/SFP)
The Gigabit combo ports (RJ-45/Small Form Factor
Pluggable (SFP) ports) are numbered 25 and 26. If the
link connections on the SFP ports are active, the
associated RJ-45 port of the same number is disabled.
The two SFP ports support fiber Gigabit Ethernet
short-wave (SX) and long-wave (LX) SFP transceivers in
any combination. This offers you the flexibility of using
SFP transceivers to provide connectivity between the
Switch and remote 1000 Mbps workgroups or to create
a high-capacity aggregated link backbone connection.
The default active port is the SFP port. The selection of
active ports can be configured via the Web interface.
The SFP port supports full duplex mode only.
SFP ports are numbered 25 and 26 on the Switch.
When an SFP port is active it has priority over the
10/100/1000 port of the same number. The
corresponding 10/100/1000 port is disabled when an
SFP link connection is active.
(3) Link/Activity Status LEDs
The first (top) and third row of LEDs, which are colored
yellow or green, show the link, activity and speed status
of the related ports:
10/100/1000BASE-T Ports
Status Meaning
Green The link is operating at 1000 Mbps.
Yellow The link is operating at 10 or 100 Mbps.
Flashing
Green
Flashing
Yellow
Packets are being received or transmitted on the
port at 1000 Mbps.
Packets are being received or transmitted on the
port at 10 or 100 Mbps.
Page 12
12 INTRODUCING THE BASELINE SWITCH
Off The link has not been established, either nothing
is connected to the port, or there is a problem:
■ Check that the attached device is powered
on.
■ Check that the cable or fiber is the correct
type and is not faulty.
■ For fiber connections, ensure that the receive
(RX) and transmit (TX) cable connectors are
not swapped.
If these checks do not identify the cause of the
problem, it may be that the unit or the device
connected to the port is faulty. Contact your
supplier for further advice.
10/100BASE-TX Ports
Status Meaning
Green The link is operating at 100 Mbps.
Yel lo w The link is operating at 10 Mbps.
Flashing
Green
Flashing
Yel lo w
Packets are being received or transmitted on the
port at 100 Mbps.
Packets are being received or transmitted on the
port at 10 Mbps.
Off The link has not been established, either nothing
is connected to the port, or there is a problem:
■ Check that the attached device is powered
on.
■ Check that the cable or fiber is the correct
type and is not faulty.
■ For fiber connections, ensure that the receive
(RX) and transmit (TX) cable connectors are
not swapped.
If these checks do not identify the cause of the
problem, it may be that the unit or the device
connected to the port is faulty. Contact your
supplier for further advice.
(4) Duplex Status LEDs
The second and fourth (bottom) row of Status LEDs,
which are colored yellow (for duplex) or green (for
module active), show the duplex status of the related
ports:
10/100/1000BASE-T Ports
Status Meaning
Yellow The port is operating in full duplex mode.
Off The port is operating in half duplex mode.
1000BASE-T only operates in full duplex mode.
10/100BASE-TX can be in half or full duplex mode.
Page 13

Physical Features 13
Gigabit Combo Ports
Status Meaning
Green SFP is inserted in the slot.
Off No SFP in the slot.
(5) Power LED
The Power LED shows the power status of the Switch.
Status Meaning
Green The unit is powered on and ready for use.
Yellow Internal power, POST, or loopback test has
Off The unit is not receiving power.
failed. Switch is in fail-safe mode.
■ Check that the power cord is connected cor-
rectly.
■ If the unit still does not operate, contact your
supplier.
(6) Self-adhesive Pads
The unit is supplied with four self-adhesive rubber pads.
Do not apply the pads if you intend to rack mount the
unit.
If the unit is to be part of a free-standing stack, apply
the pads to each marked corner area on the underside
of the unit. Place the unit on top of the lower unit,
ensuring that the pads locate with the recesses of the
lower unit.
Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Switch contains a power supply
socket and a recovery button.
(7) Power Supply
The Switch automatically adjusts to the supply voltage.
Only use the power cord that is supplied with the unit.
(8) Recovery Button
The recovery button reinitializes the Switch. This returns
the Switch to the factory default settings if, for
example, you have forgotten the default IP address, or
forgotten your user name or password.
CAUTION: 3Com recommends that you back up your
configuration settings before you recover the Switch,
otherwise your configuration may be lost. Refer to
“Resetting to Factory Defaults” on page 71 for details.
Page 14
14 INTRODUCING THE BASELINE SWITCH
Package Contents
Before installing and using the Switch, verify that your
Switch package is complete. The Switch comes with:
■ One power cord
■ Four standard height, self-adhesive rubber pads
■ One mounting kit
■ Installation CD
■ This User Guide
■ Warranty flyer
The Switch is powered from the AC supply.
If any of the above items are damaged or missing,
contact your 3Com network supplier immediately.
Page 15
2
INSTALLING THE SWITCH
This chapter contains information that you need to
install and set up the Switch. It covers the following
topics:
■ Before You Begin
■ Positioning the Switch
■ Rack-Mounting or Free-Standing
■ Supplying Power to the Switch
■ Using SFP Transceivers
■ Performing Spot Checks
Before You Begin
WARNING: Safety Information. Before installing or
removing any components from the Switch or carrying
out any maintenance procedures, read the safety
information provided in Appendix C of this guide.
AVERTISSEMENT: Consignes de Sécurité. Avant
d'installer ou d'enlever tout composant du Switch ou
d'entamer une procédure de maintenance, lisez les
informations relatives à la sécurité qui se trouvent dans
l'Appendice C (Appendix C) de ce guide.
WARNHINWEIS: Sicherheitsinformationen. Bevor Sie
Komponenten aus dem Switch entfernen oder dem
Switch hinzufuegen oder Instandhaltungsarbeiten
verrichten, lesen Sie die Sicherheitsanweisungen, die in
Anhang C (Appendix C) in diesem Handbuch
aufgefuehrt sind.
ADVERTENCIA: Información de Seguridad. Antes de
instalar o extraer cualquier componente del product o
de realizar tareas de mantenimiento, debe leer la
información de seguridad facilitada en el Apéndice C
(Appendix C) de esta guía del usuario.
AVVERTENZA: Informazioni di Sicurezza. Prima di
installare o rimuovere qualsiasi componente dal product
o di eseguire qualsiasi procedura di manutenzione,
leggere le informazioni di sicurezza riportate
nell'Appendice C (Appendix C) della presente guida per
l'utente.
Positioning the Switch
The Switch is suitable for use in an office environment
where it can be free-standing or mounted in a standard
19-inch equipment rack.
Page 16
16 INSTALLING THE SWITCH
Alternatively, the Switch can be rack-mounted in a
wiring closet or equipment room. A mounting kit,
containing two mounting brackets and four screws, is
supplied with the Switch.
When deciding where to position the Switch, ensure
that:
■ It is accessible and cables can be connected easily.
■ Cabling is away from sources of electrical noise.
These include lift shafts, microwave ovens, and air
conditioning units. Electromagnetic fields can
interfere with the signals on copper cabling and
introduce errors, therefore slowing down your
network.
■ Water or moisture cannot enter the case of the unit.
■ Air flow around the unit and through the vents on
the side of the case is not restricted (3Com
recommends that you provide a minimum of 25 mm
(1 in.) clearance).
■ The air is as free from dust as possible.
■ Temperature operating limits are not likely to be
exceeded. It is recommended that the unit is installed
in a clean, air conditioned environment.
Rack-Mounting or Free-Standing
The unit can be mounted in a 19-inch equipment rack
using the mounting kit or it can be free standing. Do
not place objects on top of the unit or stack.
CAUTION: If installing the Switch in a free-standing
stack of different size Baseline or Superstack 3 units, the
smaller units must be installed above the larger ones.
Do not have a free-standing stack of more than six
units.
Using the Mounting Kit
The Switch is supplied with two mounting brackets and
four screws. These are used for rack mounting the unit.
When mounting the unit, you should take note of the
guidelines given in “Positioning the Switch” on
page 15.
The Switch is 1U (1.7 inches) high and will fit in a
standard 19-inch rack.
CAUTION: Disconnect all cables from the unit before
continuing. Remove the self-adhesive pads from the
underside of unit, if already fitted.
It is always good practice to wear an anti-static wrist
strap when installing network equipment, connected to
a ground point. If one is not available, try to keep in
contact with a grounded rack and avoid touching the
unit's ports and connectors, if possible. Static discharge
can cause reliability problems in your equipment.
To rack-mount the Switch:
1 Place the unit the right way up on a hard, flat surface
with the front facing towards you.
2 Locate a mounting bracket over the mounting holes on
one side of the unit.
Page 17
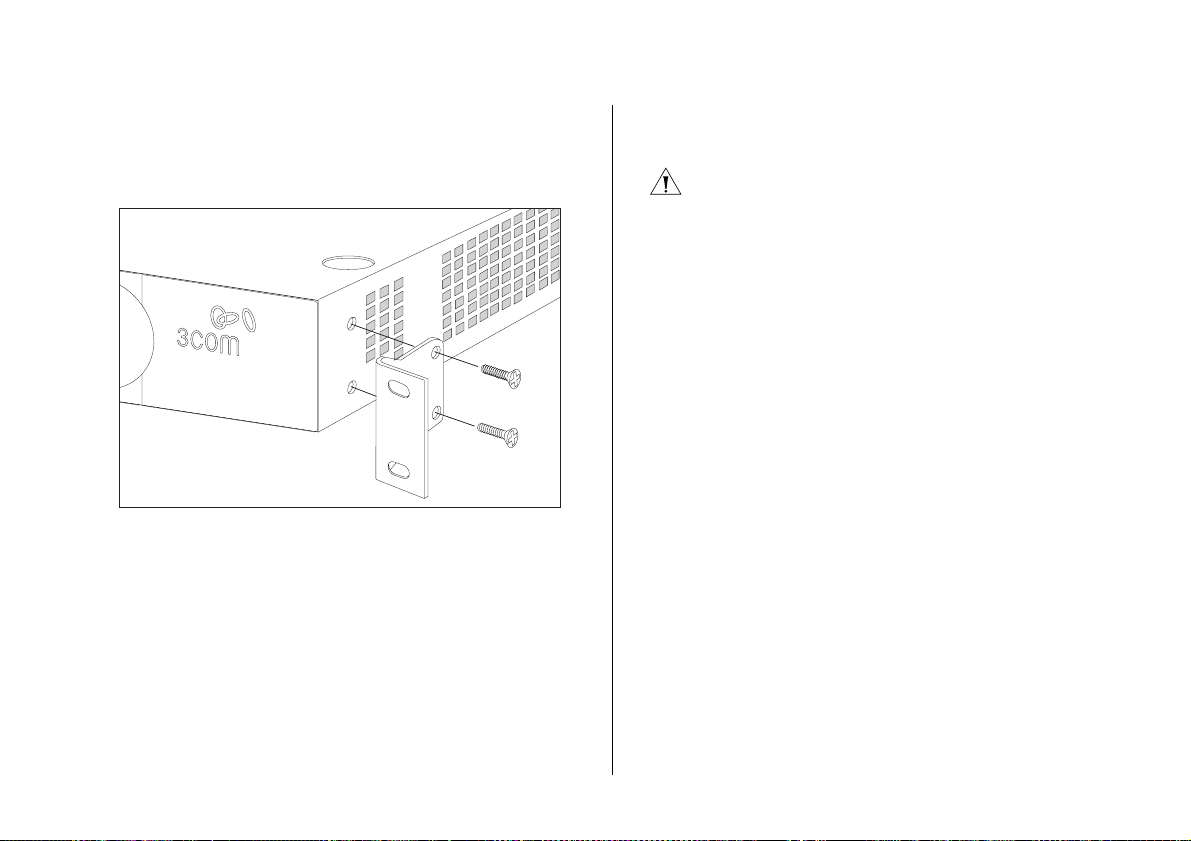
Rack-Mounting or Free-Standing 17
3 Insert the two screws supplied in the mounting kit and
fully tighten with a suitable screwdriver.
Figure 2 Rack Mounting the Unit
4 Repeat steps 2 and 3 for the other side of the unit.
5 Insert the unit into the 19-inch rack and secure with
suitable screws (not provided).
6 Reconnect the cables.
Montagesatz Anweisungen
Der Switch wird mit zwei Halterungen und vier
Schrauben geliefert. Diese werde für den Einbau in
einen Baugruppenträger benutzt. Bei der Montage der
Baugruppe beachten Sie die Anweisungen aus
“Positioning the Switch” on page 15.
Der Switch ist eine Baueinheit hoch und passt in einen
Standard 19'' (Zoll) Baugruppenträger.
ACHTUNG: Entfernen Sie alle Kabel, bevor Sie
fortfahren. Entfernen Sie die selbstklebenden Polster
(Füße) von der Unterseite der Baugruppe, falls diese
bereits angebracht sind.
1 Platzieren Sie die Baugruppe aufrecht auf einer harten,
ebenen Fläche mit der Vorderseite zu Ihnen.
2 Ordnen Sie eine der Halterungen über den Löchern an
der Seite der Baugruppe an.
3 Stecken Sie zwei der mitgelieferten Schrauben in die
Löcher und drehen Sie diese mit einem geeigneten
Schraubendreher fest.
4 Widerholen Sie letzten beiden Schritte auf der anderen
Seite der Baugruppe.
5 Führen Sie die Baugruppe in den 19" (Zoll)
Baugruppenträger ein und sichern sie die Baugruppe mit
geeigneten Schrauben. (Nicht im Lieferumfang
enthalten).
6 Schließen Sie alle Kabel wieder an.
Placing Units On Top of Each Other
If the Switch units are free-standing, up to six units can
be placed one on top of the other. If you are mixing a
variety of Baseline and SuperStack units, the smaller
units must be positioned at the top.
Page 18
18 INSTALLING THE SWITCH
If you are placing Switch units one on top of the other,
you must use the self-adhesive rubber pads supplied.
Apply the pads to the underside of each Switch, sticking
one in the marked area at each corner.
Place the Switch units on top of each other, ensuring
that the pads of the upper unit line up with the recesses
of the lower unit.
Supplying Power to the Switch
Power problems can be the cause of serious failures and
downtime in your network. Ensure that the power input
to your system is clean and free from sags and surges to
avoid unforeseen network outages. 3Com recommends
that you install power conditioning, especially in areas
prone to blackout, power dips and electrical storms.
The unit is intended to be grounded. Ensure it is
connected to earth ground during normal use. Installing
proper grounding helps to avoid damage from lightning
and power surges.
Before powering on the Switch, verify that the network
cables and the power cable are securely connected.
CAUTION: The Switch has no ON/OFF switch. The only
way to power on and power off the Switch is by
connecting and disconnecting the power cord. This is
called “power cycling”.
To power on the Switch:
1 Plug the power cord into the power socket on the rear
panel of the Switch. Refer to “(7) Power Supply” on
page 13 for more information.
2 Plug the other end of the power cord into a power
outlet.
When the Switch is powered on, the Power LED lights
up. If the Power LED does not light up, refer to “(5)
Power LED” on page 13 for more information.
Checking for Correct Operation
After you power on the Switch, it automatically
performs a power-on self-test (POST). During POST, the
Power LED on the front panel of the Switch flashes
green.
When POST is complete, the Power LED turns green. If
the Power LED turns yellow after POST, it means that
POST failed and the Switch has entered fail-safe mode.
The following summarizes the possible colors for the
Power LED after POST.
Status Meaning
Green The unit is powered on and ready to use.
Yellow Power-on self-test or loopback test failed. The
Switch is in fail-safe mode. This can happen if a
port or ports fail when the Switch was powered
on.
Page 19

Using SFP Tranceivers 19
Off The unit is not receiving power:
■ Verify that the power cord is connected cor-
rectly, and then try powering on the Switch
again
■ If the Switch still does not operate, contact
your 3Com network supplier
If POST fails, try the following:
■ Power off the Switch, and then power it on again.
Check the Power LED and see if POST was
successfully completed.
■ Reset the Switch. See “Resetting to Factory Defaults”
on page 71.
CAUTION: Resetting the Switch to its factory defaults
erases all your settings. You will need to reconfigure the
Switch after you reset it.
If these do not resolve the issue:
■ Check the 3Com Knowledgebase for a solution. To
visit the 3Com Knowledgebase Web site, start your
Web browser, and then enter
http://knowledgebase.3com.com.
■ Contact your 3Com network supplier for assistance.
Using SFP Tranceivers
The following sections describe how to insert an SFP
transceiver into an SFP slot.
SFP transceivers are hot-insertable and hot-swappable.
You can remove them from and insert them into any
SFP port without having to power down the Switch.
Approved SFP Transceivers
The following list of approved SFP transceivers is correct
at the time of publication:
■ 3CSFP91 SFP (SX)
■ 3CSFP92 SFP (LX)
To access the latest list of approved SFP transceivers for
the Switch on the 3Com Web site, enter this URL into
your Internet browser:
http://www.3com.com
3Com recommends using 3Com SFPs on the Switch. If
you insert an SFP transceiver that is not supported, the
Switch will not recognize it.
Inserting an SFP Transceiver
To be recognized as valid, the SFP transceiver must have
the following characteristics:
■ 1000BASE-SX or 1000BASE-LX media type:
■ 1000BASE-SX SFP transceiver
Use this transceiver to connect the Switch directly
to a multimode fiber-optic cable.
Page 20
20 INSTALLING THE SWITCH
■ 1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver
Use this transceiver to connect the Switch directly
to a single mode fiber-optic cable or to multimode fiber using a conditioned launch cable.
If the SFP transceiver is faulty, it will not operate within
the Switch. See “Troubleshooting” on page 71.
To activate the SFP port:
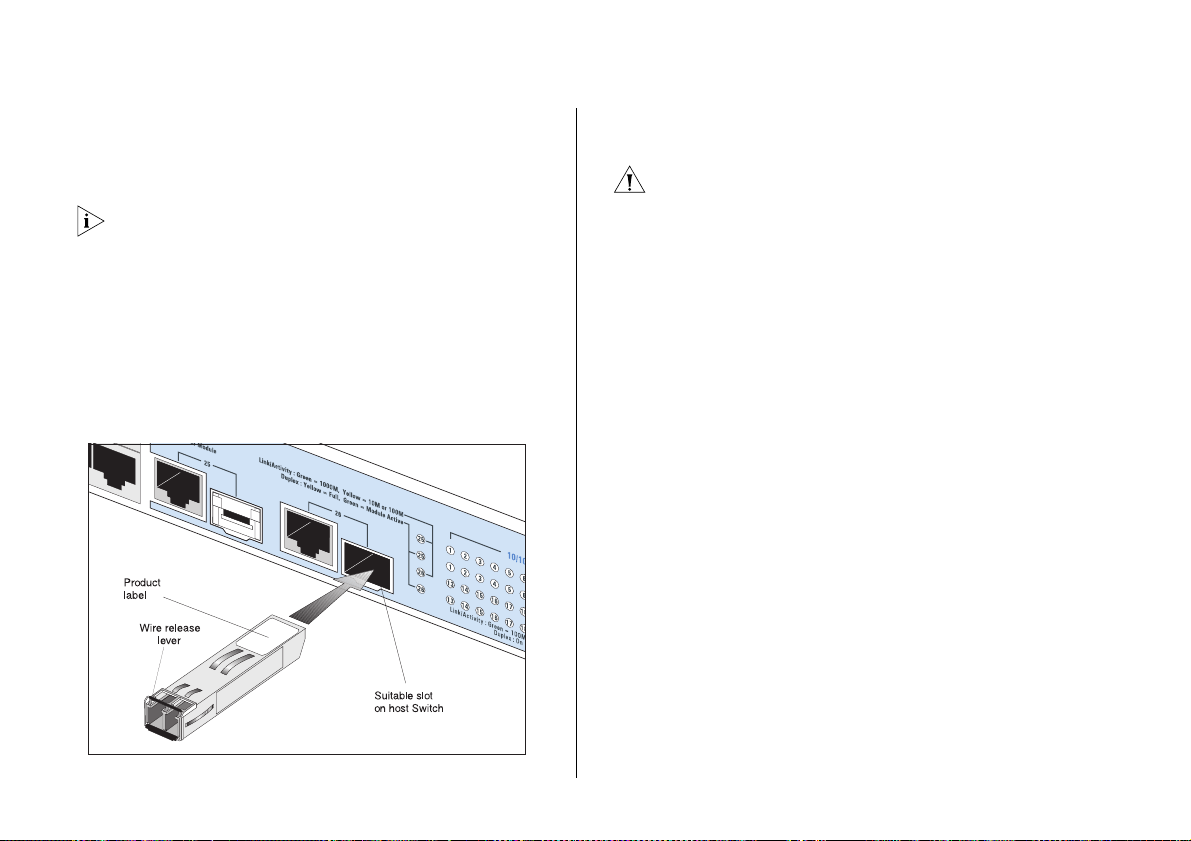
1 Hold the transceiver so that the fiber connector is
toward you and the product label is visible, as shown in
Figure 3. Ensure the wire release lever is closed (in the
upright position).
Figure 3 Inserting an SFP Transceiver
2 Gently slide the transceiver into the SFP slot until it
clicks into place.
CAUTION: SFP transceivers are keyed and can be
properly inserted only one way. If the transceiver does
not click when you insert it, remove it, turn it over, and
reinsert it.
3 Remove the plastic protective cover, if fitted.
4 Connect the fiber cable.
5 Attach a male duplex LC connector on the network
cable into the duplex LC connector on the transceiver.
6 Connect the other end of the cable to a device fitted
with an appropriate Gigabit Ethernet connection.
7 Check the Module Active LEDs on the front of the
Switch to ensure that the SFP transceiver is operating
correctly.
Removing an SFP Transceiver
Removing an SFP transceiver does not require powering
off the Switch.
To remove an SFP transceiver:
1 Disconnect the cable from the transceiver.
2 Move the wire release lever downwards until it is
pointing toward you.
3 Pull the wire release lever toward you to release the
catch mechanism.
The SFP transceiver should slide out easily.
Page 21

Performing Spot Checks
At frequent intervals, you should visually check the
Switch. Regular checks can give you an early warning of
a possible failure; any problems can then be attended to
when there will be least effect on users.
3Com recommends periodically checking the items listed
in Table 1.
Tabl e 1 Items to Check
Performing Spot Checks 21
Cabling Check that all external cabling connections
Cooling fan Where possible, check that the cooling fan
are secure and that no cables are pulled
taut.
is operating by listening to the unit. The fan
is fitted near to the front right hand side of
the unit (when viewed from the front).
If you experience any problems operating the Switch,
refer to “Troubleshooting” on page 71.
Page 22
22 INSTALLING THE SWITCH
Page 23
3
CONNECTING TO THE WEB INTERFACE
The Switch has a built-in Web interface that you can
use to set the admin password, change the IP address
that is assigned to the Switch, and configure its
advanced settings.
If you only want the Switch to function as a basic layer
2 switch, you do not need to access the Web interface
and configure the Switch.
This chapter provides information on how the gain
access to the Web interface using the Discovery
application. It also introduces the menu items and
buttons that are available on the Web interface.
The following topics are covered:
■ Requirements for Accessing the Web Interface
■ Running the Discovery Application
■ Logging On to the Web Interface
■ Navigating the Web Interface
■ Accessing the Interface Without Using Discovery
Requirements for Accessing the Web Interface
To connect to the Web interface, you need the
following:
■ The Discovery application, which is included on
3Com Baseline Switch 2226 Plus CD-ROM that is
supplied with your Switch
■ A computer that is connected to the Switch and that
has a Web browser
Running the Discovery Application
The 3Com Baseline Switch 2226 Plus CD-ROM contains,
among others, the Discovery application.
The Discovery application can be used for detecting and
connecting to the Switch on the network. The
application will launch a Web interface that provides the
user with options to configure, modify, and upgrade the
Switch.
Page 24
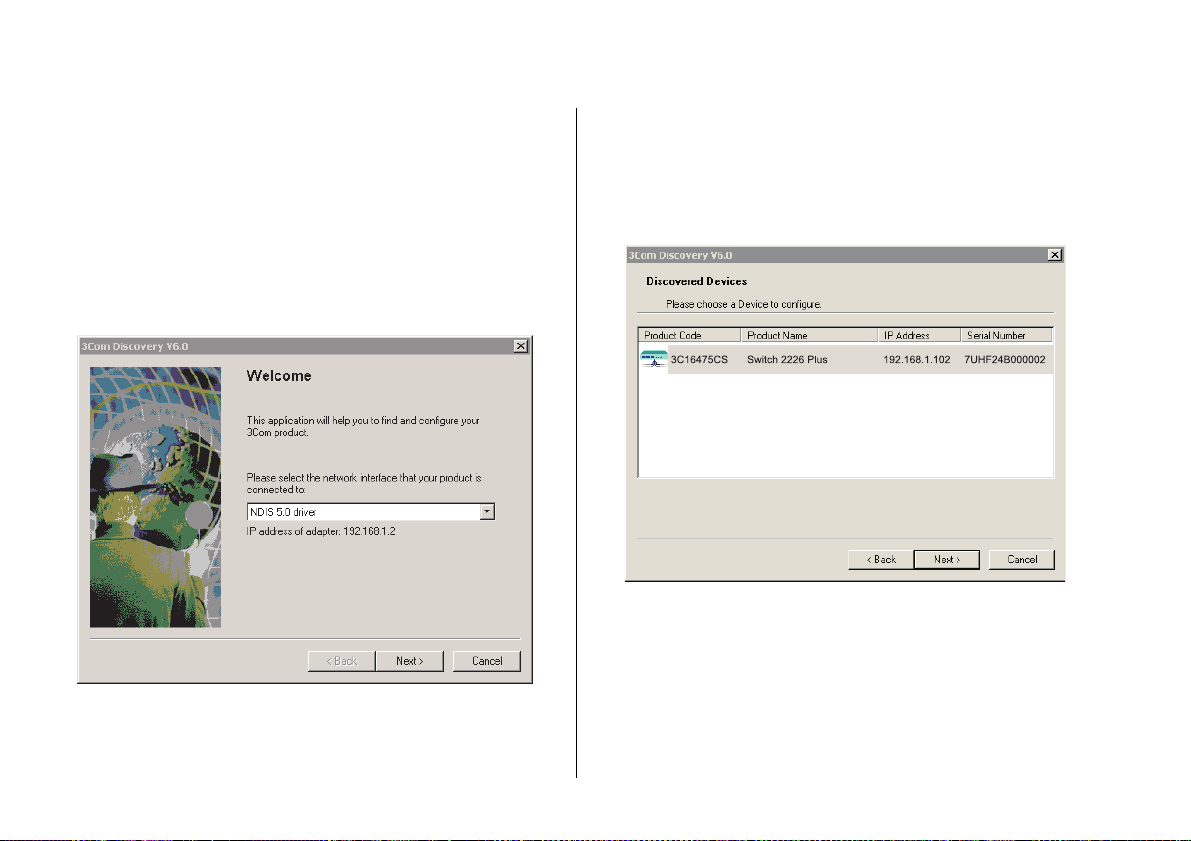
24 CHAPTER 3: CONNECTING TO THE WEB INTERFACE
To use Discovery to connect to the Web interface, do
the following:
1 On a computer that is connected to the Switch, insert
the CD-ROM into its CD drive.
Discovery should start automatically. If it does not start
automatically, go to the
CD-ROM, and then double-click
\Discovery folder on the
discovery.exe.
The Welcome screen of Discovery appears.
Figure 4 Welcome Screen of Discovery
2 If the computer has multiple network adapters, select
the adapter that connects the computer to the Switch,
and then click Next.
If the computer has only one adapter, click Next.
Discovery searches the network for 3Com devices.
When detection is complete, the Discovered Devices
screen displays detected network devices.
Figure 5 Discovered Devices Screen
3 On the Discovered Devices screen, click Baseline Switch
2226 Plus, and then click Next.
The Completing the 3Com Discovery Application screen
appears.
4 Click Finish.
The logon dialog box for the Web interface appears.
Page 25
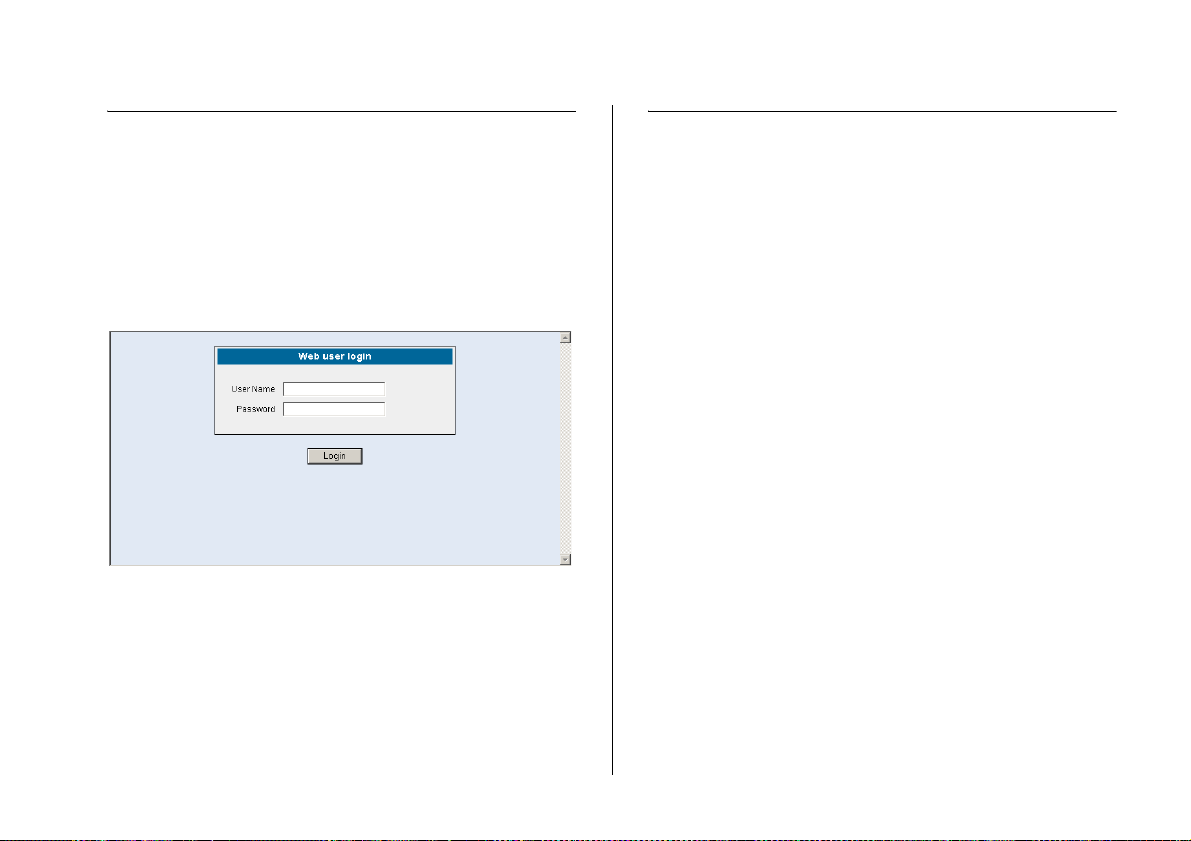
Logging On to the Web Interface 25
Logging On to the Web Interface
After the Web interface loads in your Web browser, the
first page that appears is the logon screen. On this
screen, you need to enter the administration user name
and password to gain access to the Web interface.
The browser’s address bar also displays the IP address
that the Switch is currently using.
Figure 6 Logon Dialog Box
To log on to the Web interface:
1 In User name, type admin.
2 Leave the Password field blank.
3 Click OK.
If your switch administration browser session remains
inactive for more than 10 minutes, the Switch will
automatically log you out.
Navigating the Web Interface
The Web interface has been designed to enable you to
easily perform advanced configuration tasks and view
information about the Switch.
Menu
The menu is located on the left side of the Web
interface. When you click an item on the menu, the
related screen appears in the main part of the interface.
Some menu items will give you sub-menu tabs to
choose from.
Page 26
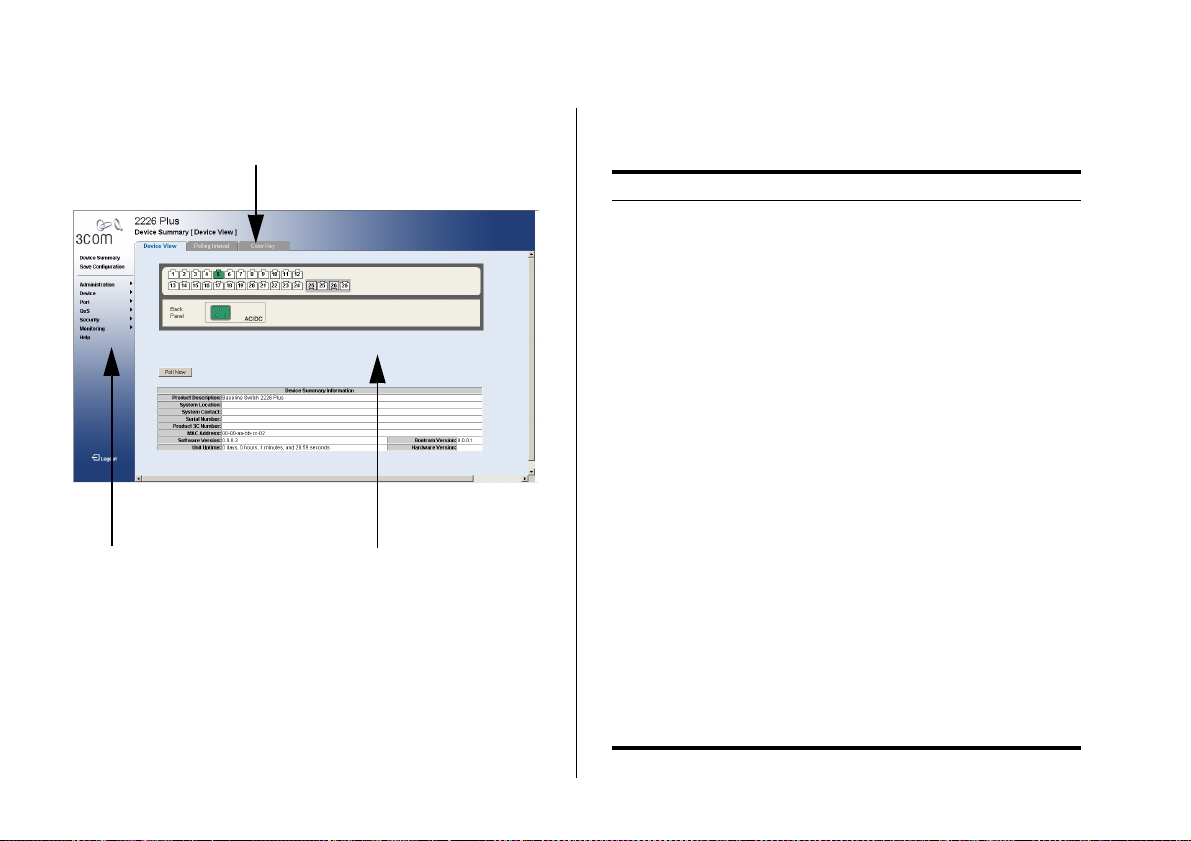
26 CHAPTER 3: CONNECTING TO THE WEB INTERFACE
Figure 7 Switch Screen Layout
Sub-Menu Tabs
Menu
System Information
Table 2 lists the available items on the menu.
Tabl e 2 Available Menu Items
Menu Item Description
Device Summary Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Provide a summary of the Switch’s basic
settings and versions of current components.
■ Set the polling interval in seconds.
■ Display the description for each color
coded port.
Save Configuration Saves the Switch’s configuration.
Administration Manages the device.
IP Setup Allows you to setup, modify, or view the IP
Backup Configuration Allows you to backup the Switch’s
Restore Configuration Allows you to restore a saved
Firmware Upgrade Allows you to upgrade the current
Initialize Allows you to reset the Switch to factory
Reboot Allows you to perform system reboot.
System Access Contains tabs that allow you to:
configuration parameters.
configuration.
configuration.
firmware via HTTP.
default settings.
■ Display user summary information.
■ Create a new user.
■ Modify existing users.
■ Remove existing users.
Page 27

Navigating the Web Interface 27
Menu Item Description
System Time Allows you to set the system time.
SNMP Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Set the SNMP Agent status.
■ Add community strings.
■ Remove community strings.
Device Configures the device.
VLAN Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Create a VLAN.
■ Modify a VLAN.
■ Modify VLAN membership for a port.
■ Rename a VLAN.
■ Remove a VLAN.
■ Display VLAN membership for a port.
■ Display VLAN information.
Spanning Tree Allows you to configure a Spanning Tree
IGMP Snooping Allows you to enable or disable IGMP
IGMP Query Allows you to enable or disable IGMP query
Broadcast Storm Allows you to enable and configure, or
Protocol.
snooping.
mode.
disable rate limiting.
Port Configures the ports.
Administration Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Display selected port information for the
entire Switch.
■ Display individual port information.
■ Modify the port settings.
Menu Item Description
Link Aggregation Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Display link aggregation summary.
■ Create an aggregation group.
■ Modify the port memberships.
■ Remove an aggregation group.
Spanning Tree per
Port
Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Display selected spanning tree informa-
tion for every port.
■ Display individual port spanning tree
information.
■ Modify the spanning tree settings for a
port.
Port Mirroring Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Display the current Port Traffic Monitor-
ing configuration.
■ Modify Port Traffic Monitoring settings.
Statistics Display statistics for a selected port.
QoS Configures QoS settings.
VoIP Traffic Setting Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Display Voice VLAN summary.
■ Configure Voice VLAN global settings.
■ Configure Voice VLAN port settings.
■ Display port information for Voice VLAN
and Trunk details.
■ Display OUI summary.
■ Add or remove OUI.
Security Configures security settings.
Page 28

28 CHAPTER 3: CONNECTING TO THE WEB INTERFACE
Menu Item Description
Radius Client Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Display Radius Client information.
■ Configure Radius Client settings and set
authentication parameters.
802.1X Settings Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Display system authentication summary.
■ Display detailed information per port.
■ Configure system authentication set-
tings.
Monitoring Display Switch monitoring information.
Address Table Displays MAC address table information for
ports and VLANs.
Cable Diagnostics Contains tabs that allow you to:
■ Display selected cable diagnostics infor-
mation for all ports.
■ Display all cable diagnostics information
for a single port.
Help Displays 3Com contact information and
Log Out Allows you to securely log off the Web
describes how to use the online help
system.
interface.
Buttons
Depending on the screen that is currently displayed, the
following buttons may appear:
■ Apply – Click to save and apply any changes that
you have made
■ Cancel – Click to discard any unsaved changes
■ Help – Click to display the context-sensitive help
information for the screen that is currently displayed.
The help pages provide information on the tasks that
you can perform on each screen.
Port Status
There is an image of the Switch’s front panel in the
Device View page, which indicates ports that are
currently in use.
To configure a port, click the port on the image for the
these following configuration options:
■ View detailed port information
■ Configure the port settings
■ View port statistics
Accessing the Interface Without Using Discovery
The Discovery application works by automatically
detecting the IP address that is assigned to the Switch,
and then using that address to connect to the Web
Page 29

Accessing the Interface Without Using Discovery 29
interface. If you know the Switch’s IP address, you can
access the Web interface without using Discovery.
This section describes how to access the interface
directly, without using Discovery.
If you do not configure the Switch’s IP address settings,
it will perform auto IP configuration to assign an IP
address to itself. For more information, refer to
“Automatic IP Configuration” on page 33.
To determine the IP address that the Switch will assign
to itself during auto IP configuration, check the sticker
on the base of the Switch. This sticker contains the
MAC address and default IP address of the Switch.
DHCP Assigned IP Address
If you set the IP address mode to DHCP, check the
DHCP server for the IP address that is assigned to the
Switch, and then use that IP address to access the Web
interface.
For example, if the DHCP server assigned the IP address
192.168.0.123 to the Switch, start your Web browser,
and then type
http://192.168.0.123.
Manually Assigned (Static) IP Address
If you assigned a static IP address to the Switch, you
need to use that IP address to access the Web interface
the next time you want to configure the Switch.
For example, if you assigned the Switch the IP address
192.168.0.123, start your Web browser, and then type
http://192.168.0.123.
Page 30

30 CHAPTER 3: CONNECTING TO THE WEB INTERFACE
Page 31

4
CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
This chapter provides information on how to configure
the Switch’s advanced features. Topics include:
■ Device Summary Information
■ Administration Settings
■ Configuring VLANs
■ Configuring Port Settings
■ QoS VoIP Traffic Settings
■ Security
■ Monitoring
Configuration Overview
The Switch is shipped ready for use. If you only want
the Switch to function as a basic layer 2 switch, you do
not need to access the Web interface and configure the
Switch.
You only need to access the Web interface if you want
to:
■ Set the administration password to the Web
interface
■ Assign an IP address to the Switch
■ Configure the Switch’s advanced features
■ Upgrade the firmware
If your switch administration browser session remains
inactive for more than 10 minutes, the Switch will
automatically log you out.
Device Summary Information
The Device Summary screen, which automatically loads
after you log on to the Web interface, provides a
snapshot of the Switch’s basic settings and versions of
current components.
Click Device Summary on the menu. A screen appears
with three tabs that include:
■ Device View
■ Polling Interval
■ Color Key
Device View
Contains fields that display the system, switch, and
management information to identify the Switch. The
fields include Product Description, System Location,
System Contact, Serial Number, Product 3C Number,
Page 32

32 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
MAC Address, Software Version, Unit Uptime, Bootroom
Version, and Hardware Version.
Figure 8 Device View
If you request for technical assistance from 3Com
Support, you may be asked to print out the information
on this screen.
Polling Interval
Enter the interval in seconds you would like the Switch
to refresh. (Range: 10 to 180 seconds; 0 to disable
polling).
Figure 9 Polling Interval
To set the polling interval:
1 Click the Device Summary menu, click Polling Interval
tab.
2 Enter a number between 10 to 180 seconds for the
polling interval. Enter a 0 to disable polling.
Page 33

Administration Settings 33
Color Key
Description of the color coding.
Figure 10 Color Key
Administration Settings
The Administration menu includes eight administration
items:
■ IP Setup
■ Backup Configuration
■ Restore Configuration
■ Firmware Upgrade
■ Initialize
■ Reboot
■ System Access
■ System Time
■ SNMP
Modifying the IP Address Settings
To enable devices on the network to communicate with
the Switch, you need to assign an IP address to it —
either by DHCP or by assigning a static IP address.
By default, the Switch performs automatic IP
configuration and assigns an IP address to itself. This is
necessary for the Discovery application to be able to
connect to the Web interface.
Automatic IP Configuration
When you power on the Switch for the first time, it
automatically uses the default IP address
x and y are the last two bytes of its MAC
where
address.
To determine the exact IP address that the Switch
assigns to itself during auto IP configuration, check the
sticker on the base of the Switch. This sticker contains
the MAC address and default IP address of the Switch.
169.254.x.y,
Page 34

34 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
To detect its IP information using the automatic configuration process, the Switch goes through the following
sequence of steps:
1 The Switch tries to configure itself with the default IP
address
169.254.x.y, where x and y are converted
from the last two bytes of its MAC address.
For example, if the MAC address is
IP address would be
169.254.1.2. This address is used
08004E000102, the
if the Switch is operating in a standalone mode, or no
other switches on the network have this IP address.
The Switch also assigns the subnet mask 255.255.0.0
(default class B mask) to itself.
2 If this default IP address is already in use on the
network, then the Switch detects this, and increments
the last byte of the MAC address by one to generate its
IP address.
The IP address would therefore become
3 The Switch repeats step 2 until an unused IP address is
169.254.1.3.
found.
3Com recommends using automatic IP configuration
only for the initial setup. Once you gain access to the
console, you should assign an IP address to the Switch
(either by using DHCP or assigning a static IP address) to
ensure successful communication between the Switch
and other network devices.
IP Setup
To set the IP address for the Switch:
1 Click Administration, then IP Setting on the menu. The
IP Settings screen appears. Follow the IP Setup Wizard
to complete the setup.
This wizard can also be used to set system name,
location and contact information.
Figure 11 IP Settings Screen
Page 35

Administration Settings 35
Backup Configuration
To save the Switch configuration settings:
1 Click Administration, then Backup Configuration on the
menu. The Backup Configuration screen appears.
Figure 12 Backup Configuration
2 Click OK. You will be prompted to provide a location
where the configuration file will be saved.
Restore Configuration
To reload configuration settings that you previously
saved to a file:
1 Click Administration, then Restore Configuration on the
menu. The Restore Configuration screen appears.
Figure 13 Restore Configuration
2 Click Browse to locate the backup file on your computer
to restore the configuration settings.
3 Click Restore to copy the configuration back to the
Switch.
For security purposes, restoring the configuration does
not change the password.
Firmware Upgrade
The Upgrade facility allows you to install on the Switch
any new releases of system firmware that 3Com may
make available.
Newer versions of firmware can be downloaded via
HTTP and copied to the Switch; the Switch will restart
and apply the newer system firmware version.
Figure 14 Upgrade Screen
1 Click Administration, then Firmware Upgrade on the
menu. The Firmware Upgrade screen appears.
Page 36

36 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
2 Once you have downloaded the firmware, use the
Browse button to locate the file on your computer, and
then click OK.
You may need to change the file type in the dialog box
displayed by your Web browser to *.* to be able to see
the file.
The file will be copied to the Switch, and once this has
completed, the Switch will restart. Although the
upgrade process has been designed to preserve your
configuration settings, 3Com recommends that you
make a backup of the configuration beforehand, in case
the upgrade process fails for any reason (for example,
the connection between the computer and the Switch is
lost while the new firmware is being copied to the
Switch).
A progress screen displays while the upgrade is taking
place.
The upgrade procedure can take a few minutes, and is
complete when the progress bar has finished running
and the Power LED has stopped flashing and is
permanently green.
CAUTION: Do not interrupt power to the Switch
during the upgrade procedure. If you do, the firmware
may be corrupted and the Switch may not start up
properly afterwards.
Initialize
To reset the Switch to factory default settings:
1 Click Administration, then Initialize on the menu.
You will lose all your configuration changes. The Switch
LAN IP address will revert to the default IP address
169.254.x.y. (see “Automatic IP Configuration” on
page 33). You may need to restart your computer to
re-establish communication with the Switch.
Reboot
Clicking on Administration, then Reboot on the menu
has the same effect as power cycling the unit. No
configuration information will be lost. Reboot the
Switch if you are experiencing problems and you want
to re-establish your Internet connection.
Any network users that are currently accessing the
Internet will have their access interrupted while the
reboot takes place, and they may need to restart their
computers when the reboot has completed and the
Switch is operational again.
Page 37

Administration Settings 37
System Access
Click Administration, then System Access on the menu.
A screen appears with four system access tabs:
■ User Summary
■ Create User
■ Modify User
■ Remove User
To prevent unauthorized users from accessing the Web
interface and modifying the Switch’s settings, the
interface is password-protected.
The default admin account settings are:
■ User name – admin
■ Password – blank (no password)
To ensure that unauthorized users do not access the
Web interface, 3Com recommends that you set an
admin password when you first configure the Switch.
Even if you do not intend to actively manage the
switch, 3Com recommends that you change the
password to prevent unauthorized access to your
network.
The password can be up to 8 characters long and is
case-sensitive.
If you forget the administration password after you set
it, refer to “Forgotten Password” on page 71 for
information on how to regain access to the Web
interface.
User Summary
Displays the list of user names and their access level.
Figure 15 User Summary Screen
Page 38

38 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Create User
This page allows you to create a user and define the
access level and password for that user.
Figure 16 Create User Screen
Modify User
This page allows you to modify a user’s access level and
password.
Figure 17 Modify User Screen
Page 39

Administration Settings 39
Remove User
To remove a user from the Switch, click on the user
name, then click Remove.
Figure 18 Remove User Screen
System Time
Click Administration, then System Time on the menu.
This screen allows you to set the system time. You can
set the Year, Month, Day, Hours, Minutes, and Seconds.
Figure 19 System Time Screen
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a communication protocol designed specifically for managing
devices on a network. Equipment commonly managed
with SNMP includes switches, routers and host computers. SNMP is typically used to configure these devices for
proper operation in a network environment, as well as
to monitor them to evaluate performance or detect
potential problems.
Click Administration, then SNMP on the menu. A screen
appears with three tabs:
■ Setup
■ SNMP Add
■ SNMP Remove
Page 40

40 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Setup
Enable or disable the SNMP Agent Status for the
Switch.
If you do not want to use SNMP management in your
network, it is recommended to disable the SNMP Agent.
Figure 20 SNMP Setup Screen
SNMP Add
This page allows you to create community strings for
management access and specify management station IP
addresses to receive SNMP trap messages. A community
string’s access level, and an SNMP destination’s
community string and version information can also be
modified via this page.
Community strings are limited to 32 characters and are
case sensitive (String is not the same as string). A
maximum of five community strings and five SNMP
destinations can be defined. For security reasons, you
should consider removing the default community strings
(“public” and “private”). Community strings and SNMP
destination IP addresses cannot be modified, but must
first be removed and re-added with the correct name or
IP address, respectively.
Traps indicating status changes are issued by the switch
to specified SNMP destinations (trap managers). You
must specify trap managers so that key events are
reported by this switch to your management station
(using network management platforms such as HP
OpenView). You can specify up to five management
stations that will receive authentication failure messages
and other trap messages from the switch.
Page 41

Configuring VLANs 41
Figure 21 SNMP Add Screen
SNMP Remove
This page allows you to remove community strings and
SNMP destinations.
Figure 22 SNMP Remove Screen
Configuring VLANs
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a collection of network nodes
that share the same collision domain, regardless of their
physical location or connection point in the network. A
VLAN serves as a logical workgroup with no physical
barriers, and allows users to share information and
resources as though located on the same LAN.
Page 42

42 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
You can use the Switch to create VLANs to organize any
group of ports into separate broadcast domains. VLANs
confine broadcast traffic to the originating group and
help eliminate broadcast storms in large networks. This
also provides for a more secure and cleaner network
environment.
You can create up to 64 VLANs, add specific ports to a
chosen VLAN (so that the port can only communicate
with other ports on the VLAN), or configure a port
make it a member of multiple or even all VLANs.
Communication between different VLANs can only take
place if they are all connected to a router or layer 3
switch.
The Device menu includes five items:
■ VLAN
■ Spanning Tree
■ IGMP Snooping
■ IGMP Query
■ Broadcast Storm
VLAN
Click Device, then VLAN on the menu. A screen appears
with seven tabs that include:
■ Setup
■ Modify VLAN
■ Modify Port
■ Rename
■ Remove
■ Port Detail
■ VLAN Detail
Setup
Use the Setup screen to create VLANs on the Switch. To
propagate information about VLAN groups used on this
Switch to external devices, you must specify a VLAN ID
for each VLAN.
Figure 23 Setup Screen
Available options on the Setup screen include:
■ VLAN ID – ID of configured VLAN (1-4094, no
leading zeroes)
For examples on setting up VLANs, refer to “Sample
VLAN Configurations”.
Page 43

Configuring VLANs 43
CAUTION: At least one port must always be an
untagged member of VLAN 1 (the management VLAN).
If you choose to connect all ports to VLANs other than
VLAN 1, you will no longer be able to access the Web
interface. If this happens, you will need to reset the
Switch to factory settings.
By default, all ports belong to VLAN 1 as untagged
members. However, they can belong to multiple VLANs
as tagged members. Also, newly created VLANs will
initially have no ports associated with them.
Modify VLAN
Use the Modify VLAN screen to change the VLAN to
which a port belongs, and configure the port to
communicate with all other VLANs, or a selected VLAN.
Figure 24 Modify VLAN Screen
1 Enter a set of VLANs or select all VLANs to configure,
then click Select.
2 From the drop down menu, select a VLAN to modify.
Page 44

44 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
3 Select a membership use. Available options for each
port include (only one option can be associated with a
single port):
■ Ta gg ed
■ Untagged
4 Select ports to associate with the membership, then
click Apply.
Modify Port
Use the Modify Port screen to modify the VLAN
membership of a port.
Figure 25 Modify Port Screen
1 Select a membership use. Available options for each
port include (only one option can be associated with a
single port):
■ Not a member
■ Ta gg ed
■ Untagged
2 Select a port to associate with the membership.
3 Enter a VLAN to apply these changes to, then click
Apply.
Rename
Use the Rename screen to change the name of a VLAN.
Figure 26 Rename Screen
1 Enter a set of VLANs or select all VLANs to add to the
rename list, then click Select.
2 From the list of selected VLANs, choose a VLAN to
rename. Enter a new VLAN name and click Apply.
Page 45

Configuring VLANs 45
Remove
Use the Remove screen to remove a VLAN.
Figure 27 Remove Screen
1 Enter a set of VLANs or select all VLANs to add to the
remove list, then click Select.
2 From the list of selected VLANs choose a VLAN to
remove, or click the Select All button to select all the
VLANs. Click Remove to remove the VLAN.
Port Detail
Choose a port to display the tagged and untagged
VLAN memberships it is associated with.
Figure 28 Port Detail Screen
Page 46

46 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
VLAN Detail
Use this screen to display detailed VLAN information.
1 Enter a set of VLANs or select all VLANs to add to the
details list, then click Select.
2 From the drop down menu, choose a VLAN to display
the associated tagged and untagged member ports.
Figure 29 VLAN Detail Screen
Forwarding Tagged/Untagged Frames
Each port on the Switch is capable of passing tagged or
untagged frames.
The following describes how the Switch will handle
tagged and untagged frames.
■ When a port receives a tagged frame with a VLAN
ID and the port is a member (untagged or tagged)
of that VLAN, the frame is accepted. If the port is
not a member of that VLAN, the frame is discarded.
■ When a port receives an untagged frame and the
port is an untagged member of a VLAN, the frame is
accepted and assigned to that VLAN ID. If the port is
not an untagged member of any VLAN, the frame is
discarded.
The Switch will only forward a frame to ports that are
members (tagged or untagged) of the VLAN to which
the frame is assigned. If the port is an untagged
member, the egress frame will be stripped of the VLAN
tag and forwarded as untagged. However, if the port is
a tagged member, the egress frame is forwarded as
tagged.
Sample VLAN Configurations
To illustrate how you can segment network devices that
are connected to the Switch, the following sample
configurations are provided.
Page 47

Configuring VLANs 47
Setting Up Two VLANs on the Same Switch
Figure 30 illustrates how you can set up a simple VLAN
on the Switch using desktop connections.
Figure 30 Desktop VLAN Configuration
If you want to add ports 1, 3, and 26 to VLAN2 (as
shown in Figure 30), so that the ports on the default
VLAN1 and the ports on VLAN2 cannot communicate
with each other, do the following:
1 Create a new VLAN and set the VLAN ID to 2. Refer to
“Setup” for instructions. VLAN1 is the default VLAN and
already exists.
2 Set ports 1, 3, and 26 to associate with the Untagged
membership in VLAN2.
3 Click Apply.
Ports 1, 3, and 26 now belong to VLAN2, and will not
communicate with any other ports, unless you add
other ports to the VLAN or change the port
configuration.
Setting Up VLAN Across Two Switches
This example explains how you can set up a VLAN
across two Switches using Ta gg ed ports. This enables
ports that are members of the same VLAN (but are on
different switches) to communicate, provided that a port
on each Switch is set to Tagged, and that these ports
are connected.
Page 48

48 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Figure 31 Tagged VLAN Configuration
To set up the configuration shown in Figure 31, do the
following:
1 Create VLAN2 on both Switch 1 and Switch 2. You
need not create VLAN1 since it exists by default.
2 On Switch 1, set the ports that you want to be part of
VLAN2 to Untagged. Set one port (for example, port
16) to Ta gg ed .
Click Apply.
3 On Switch 2, set the ports that you want to be part of
VLAN2 to Untagged. Set one port (for example, port 8)
to Ta gg ed .
Click Apply.
4 Connect the Ta gg ed port on Switch 1 (in this example,
port 16) to the Tagged port on Switch 2 (in this
example, port 8).
Those ports on Switch 1 that are members of VLAN2
can now communicate with those ports on Switch 2
that are members of VLAN2.
Spanning Tree
Spanning tree is a bridge-based system for providing
fault tolerance on networks and can be used to detect
and disable network loops. The spanning tree ensures
that the optimal path is maintained between spanning
tree-compliant networked devices by:
■ Disabling redundant paths when the main paths are
operational.
■ Enabling redundant paths if the main paths fail.
Spanning tree uses a distributed algorithm to select a
bridging device that serves as the root of the spanning
tree network. The bridging device, known as the Root
Page 49

Configuring VLANs 49
Bridge, generates bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) on
all ports at a regular interval, known as the Hello Time.
All other spanning tree-compliant devices on the
network have a designated Root Port. This is the Port
nearest the Root Bridge and it is used for receiving the
BPDUs initiated by the Root Bridge. If a bridge does not
get a Hello BPDU after a predetermined interval, the
bridge assumes that the link to the Root Bridge is down.
This bridge will then initiate negotiations with other
bridges to reconfigure the network to reestablish a valid
network topology.
After all the bridges on the network have determined
the configuration of their ports, each bridge only
forwards traffic between the Root Port and the ports
that are the Designated Bridge Ports for each network
segment. All other ports are blocked, which means that
they are prevented from forwarding traffic.
To use spanning tree, choose Enabled from the State
drop down menu, fill in the setup parameters, and click
Apply.
Figure 32 Spanning Tree Screen
Page 50

50 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
IGMP Snooping
This switch uses IGMP (Internet Group Management
Protocol) to query for any attached hosts that want to
receive a specific multicast service. It identifies the ports
containing hosts requesting to join the service and sends
data out to those ports only. It then propagates the
service request up to any neighboring multicast
switch/router to ensure that it will continue to receive
the multicast service. This procedure is called multicast
filtering.
The purpose of IP multicast filtering is to optimize a
switched network’s performance, so multicast packets
will only be forwarded to those ports containing
multicast group hosts or multicast routers/switches,
instead of flooding traffic to all ports in the subnet
(VLAN).
Choose Enabled or Disabled from the IGMP Snooping
Mode drop down menu.
Figure 33 IGMP Snooping Setup Screen
IGMP Query
Choose Enabled or Disabled from the IGMP Query
Mode drop down menu.
Figure 34 IGMP Query Setup Screen
Page 51

Configuring Port Settings 51
Broadcast Storm
Use the Broadcast Storm page to set the Switch’s
broadcast storm control and threshold limits.
A broadcast storm occurs when an incorrect packet is
sent out on a network, causing most hosts to respond
all at once and typically with wrong answers that start
the process over again. Broadcast storms use substantial
network bandwidth and may cause network time-outs.
The settings include:
■ Status – Enables and disables broadcast storm
control.
■ Packet Rate Threshold – Sets the broadcast storm
threshold (64 to 1000000 kilobits per second).
Figure 35 Broadcast Storm Setup Screen
Configuring Port Settings
Using the Web interface, you can configure the
speed/duplex, flow control, link aggregation, and port
mirroring settings of each port. You can also view the
current connection status of each port or shut down or
disable ports.
The Port menu includes five items:
■ Administration
■ Link Aggregation
■ Spanning Tree per Port
■ Port Mirroring
■ Statistics
Administration
Three tabs are available on the Port Administration
page:
■ Summary
■ Detail
■ Setup
Page 52

52 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Summary
Use the Summary tab to display Port State, Flow
Control, Speed, Default VLAN ID, Link Type, or Duplex
for all the ports.
Figure 36 Port Administration Summary Screen
Detail
Use the Detail tab to display detailed port setting
information for a port.
Figure 37 Port Administration Detail Screen
Page 53

Configuring Port Settings 53
Setup
Use the Setup tab to configure the port settings. The
following options are available:
■ Port State – Enables and disables the port.
■ Flow Control – Enables and disables flow control on
the port. When flow control is enabled for the port,
the Switch regulates the packet flow so that a
sending device does not transmit more packets than
a receiving device can process. If flow control is
disabled, packets may be dropped under certain
periods of high traffic.
Flow control is disabled by default.
■ Speed – Sets the speed mode of the port. Available
options include auto, 10, 100, and 1000. For 1000
Mbps connections, see “Speed/Duplex for 1000
Mbps Connections” below.
Auto (or autonegotiation) sets the optimum combination of speed and duplex that can be supported
by both ends of the link.
■ Duplex – Sets the duplex mode of the port. Available
options include auto, half, and full.
CAUTION: It is advised not to enable Flow Control on
ports that will be connected to telephony and other
time sensitive traffic as it may hamper the QoS
performance.
If you modify any of these settings, click Apply to save
your changes.
Figure 38 Port Administration Setup Screen
Speed/Duplex for 1000 Mbps Connections
You cannot preset the speed to 1000 Mbps. To r u n a
port at 1000 Mbps, you must enable autonegotiation
for the port. When autonegotiation is enabled, the
Switch will automatically connect at 1000 Mbps,
providing the connected device also supports this speed.
1000 Mbps connections are always full-duplex.
Half-duplex connections are only available for 10 Mbps
and 100 Mbps settings.
Page 54

54 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
CAUTION: Before manually setting a port to
full-duplex, verify that the device connected to the port
is also manually set to the same speed and duplex
setting. If connecting link partners are left to
autonegotiate for a link manually set on this switch to
full-duplex, they will always negotiate to half-duplex,
resulting in a duplex mismatch. This can result in a
significant reduction in network performance. If you are
unsure of how to configure the speed/duplex setting,
simply enable autonegotiation for the port.
You cannot modify the speed/duplex settings of ports
that are members of a trunk or aggregated link.
Supported SFP transceivers only operate at 1000 Mbps
full-duplex. Inserting an SFP transceiver into a gigabit
port disables the corresponding RJ-45 port, even if no
fiber cable is inserted.
Link Aggregation
Link aggregation, also called “trunking”, refers to
bonding multiple ports into a single group to effectively
combine the bandwidth into a single connection or a
“trunk”. If you are connecting the Switch to another
switch or to an Internet backbone, you can aggregate
links on the Switch to increase throughput and prevent
packet loopback between switches.
For link aggregation to work, the trunks must be
configured on both ends (switches).
Guidelines for Creating Trunks
■ Any port on the Switch can be used for creating a
trunk.
■ This switch supports a maximum of four trunks.
■ Each trunk may contain up to four members.
■ A port may only be a member of one trunk at any
one time.
■ All ports in a trunk must be configured in an
identical manner, including communication mode
(that is, speed, duplex mode and flow control).
Page 55

Configuring Port Settings 55
Four tabs are available on the Port Link Aggregation
page:
■ Summary
■ Create
■ Modify
■ Remove
Summary
Use the Summary tab to display a list of configured link
aggregation Group IDs and the associated member
Ports.
Figure 39 Link Aggregation Summary Screen
Create
Use the Create tab to add ports to a group membership.
Figure 40 Link Aggregation Create Screen
To create a new link aggregation group:
1 Enter a link aggregation group ID in the text box.
2 Select the ports to add to the goup.
3 Click Apply.
Page 56

56 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Modify
Use the Modify tab to reassign member ports of a link
aggregation group.
Figure 41 Link Aggregation Modify Screen
To modify a link aggregation group:
1 Select the aggregation group to modify, then click
Select.
2 Select the ports to add to, and/or remove from, the
goup.
3 Click Apply.
Remove
Use the Remove tab to delete a link aggregation group.
Figure 42 Link Aggregation Remove Screen
To remove a link aggregation group:
1 From the link aggregation group list, select the
aggregated group to remove.
2 Click Remove.
Spanning Tree per Port
This administrative tool supports the configuration of
the Switch to forward, or block and discard 802.1D
spanning tree BPDU packets.
Spanning tree is a bridge-based system for providing
fault tolerance on networks and can be used to detect
and disable network loops. The spanning tree ensures
that the optimal path is maintained between spanning
tree-compliant networked devices by:
Page 57

Configuring Port Settings 57
■ Disabling redundant paths when the main paths are
operational.
■ Enabling redundant paths if the main paths fail.
Spanning tree uses a distributed algorithm to select a
bridging device that serves as the root of the spanning
tree network. The bridging device, known as the Root
Bridge, generates BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units) on
all ports at a regular interval, known as the Hello Time.
All other spanning tree-compliant devices on the
network have a designated Root Port. This is the Port
nearest the Root Bridge and it is used for receiving the
BPDUs initiated by the Root Bridge. If a bridge does not
get a Hello BPDU after a predetermined interval, the
bridge assumes that the link to the Root Bridge is down.
This bridge will then initiate negotiations with other
bridges to reconfigure the network to re-establish a
valid network topology.
After all the bridges on the network have determined
the configuration of their ports, each bridge only
forwards traffic between the Root Port and the ports
that are the Designated Bridge Ports for each network
segment. All other ports are blocked, which means that
they are prevented from forwarding traffic.
Three tabs are available on the Spanning Tree per Port
page:
■ Summary
■ Detail
■ Setup
Summary
Use the Summary tab to display Status, Edged Port, Link
Type, Path Cost, State, or Port Priority for all the ports.
Figure 43 Spanning Tree Summary Screen
Page 58

58 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Detail
Use the Detail tab to display detailed spanning tree
information for a port.
Figure 44 Spanning Tree Detail Screen
Setup
Use the Setup tab to configure the spanning tree
settings for each port. The following options are
available:
■ Status – Enables and disables spanning tree for the
port.
■ Edged Port – Enables and disables edged port for
the port.
■ Link Type – Choose between Point-to-Point, Shared,
or Auto for the link type.
■ Path Cost – The path cost is used to determine the
best path between devices. The path cost method is
used to determine the range of values that can be
assigned to each interface.
■ Port Priority – Used in selecting the root device, root
port, and designated port. The device with the
highest priority becomes the STA root device.
However, if all devices have the same priority, the
device with the lowest MAC address will then
become the root device.
If you modify any of these settings, click Apply to save
your changes.
Figure 45 Spanning Tree Setup Screen
Port Mirroring
The Switch allows you to monitor traffic going in and
out of a particular port. For traffic monitoring to work,
you need to attach a network analyzer to one port and
use it to monitor the traffic of other ports in the stack.
To set up traffic monitoring, you need to set an analysis
port (the port that is connected to the analyzer), and a
monitor port (the port that is to be monitored). Once
Page 59

Configuring Port Settings 59
the pair is defined, and you enable traffic monitoring,
the Switch takes all the traffic going in and out of the
monitor port and copies it to the analysis port.
CAUTION: The analyzer port should have a higher
bandwidth than the mirror port. Otherwise, the Switch
may not be able to copy all traffic effectively during
periods of high traffic.
Two tabs are available on the Port Mirroring page:
■ Summary
■ Setup
Summary
Use the Summary tab to display information about the
current Port Mirroring configuration.
Figure 46 Port Mirroring Summary Screen
Setup
Use the Setup tab to configure Port Mirroring on the
switch. The following options are available:
■ Monitor Port - The port you want to monitor.
■ Analyser Port - The port to which you have
connected your network analyzer.
■ Mirror Type - Select to monitor incoming traffic,
outgoing traffic, or both.
If you modify any of these settings, click Apply to save
your changes.
Figure 47 Port Mirroring Setup Screen
Page 60

60 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Statistics
The Switch allows you to display detailed statistics of
one, several, or all ports.
Figure 48 Port Statistics Screen
To display statistics for a port:
1 Access the Web interface. Click Port, then Statistics on
the menu. The Port Statistics Screen appears.
2 Select one port, multiple ports, or choose Select All, and
enter a refresh interval.
3 Click Apply.
4 Click Reset to clear all counters for the selected port(s).
QoS VoIP Traffic Settings
Using the Web interface, you can configure the Voice
over Internet Protocol (VoIP) settings.
The QoS VoIP Traffic Setting menu includes six tabs:
■ Summary
■ Setup
■ Port Setup
■ Port Detail
■ OUI Summary
■ OUI Modify
Page 61

QoS VoIP Traffic Settings 61
Summary
Use the Summary tab to display the global settings for
the Voice VLAN.
Figure 49 QoS VoIP Summary Screen
Setup
Use the Setup tab to configure the global settings for
the Voice VLAN. The following options are available:
■ Voice VLAN Status – Enable or disable Voice VLAN
for the switch.
■ Voice VLAN ID – Input the Voice VLAN ID for the
switch.
■ Voice VLAN Aging Time – Input the aging time.
You must first create a VLAN from the VLAN Setup
page before you can assign and configure a Voice
VLAN.
Figure 50 QoS VoIP Setup Screen
Page 62

62 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Port Setup
Use the Port Setup tab to configure the port or trunk
setting for Voice VLAN. The following options are
available:
■ Voice VLAN Port Mode– Select between None,
Manual, or Auto.
■ Voice VLAN Port Security – Enable or disable the
security.
To configure the Voice VLAN settings for ports:
1 Select Voice VLAN Mode, and Security settings.
2 Select the ports you would like to apply these settings
to.
3 Click Apply.
Figure 51 QoS Port Setup Screen
Page 63

QoS VoIP Traffic Settings 63
Port Detail
Use the Port Detail tab to display the Voice VLAN
information for selected ports.
Figure 52 QoS Port Detail Screen
OUI Summary
Use the OUI Summary tab to display the list of
Organizational Unique Identifier for a company and their
description.
Figure 53 QoS OUI Summary Screen
OUI Modify
Use the OUI Modify tab to add to the list of
Organizational Unique Identifier. The following options
are available:
■ Telephony OUI – Input a new company identifier to
add to the list.
■ Description – Input a description for the new
company identifier.
Page 64

64 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
To add to the OUI list:
1 Enter a Telephony OUI and description.
2 Click Add.
To remove an OUI from the list:
1 Select a Telephony OUI from the list.
2 Click Remove.
Figure 54 QoS OUI Modify Screen
Security
Using the Web interface, you can configure the RADIUS
Client and 802.1X settings.
The Security menu includes two items:
■ RADIUS Client
■ 802.1X Settings
RADIUS Client
Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) is a
logon authentication protocol that uses software
running on a central server to control access to
RADIUS-aware devices on the network. An
authentication server contains a database of multiple
user name/password pairs with associated privilege
levels for each user or group that require management
access to a switch.
The RADIUS Client menu includes two tabs:
■ Detail
■ Configure
Page 65

Security 65
Detail
Use the Detail tab to display the RADIUS Client settings.
Figure 55 RADIUS Client Detail Screen
Configure
Use the Configure tab to configure the RADIUS settings.
The following parameters are available:
■ Max Retries – Sets the number of retries of sending
authentication requests.
■ Timeout – Sets the interval between sending
authentication requests.
■ IP Address – The IP address of the RADIUS server.
■ UDP port – The RADIUS server UDP port used for
authentication messages.
■ Key – Sets the RADIUS encryption key.
After you have filled in the parameters, click Apply to
save your changes.
Figure 56 RADIUS Client Configure Screen
Page 66

66 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
802.1X Settings
The IEEE 802.1X (dot1x) standard defines a port-based
access control procedure that prevents unauthorized
access to a network by requiring users to first submit
credentials for authentication.
The 802.1X settings menu includes three tabs:
■ Summary
■ Detail
■ Setup
Summary
Use the Summary tab to display the 802.1X
authentication settings.
Figure 57 802.1X Summary Screen
Page 67

Security 67
Detail
Use the Detail tab to display detailed 802.1X
authentication information for a port.
Figure 58 802.1X Detail Screen
Setup
Use the Setup tab to configure the 802.1X
authenticaion settings. The following fields are available:
■ System Authentication – Sets the global setting for
802.1X. (Default: Disabled)
■ Operation Mode – Allows single or multiple hosts
(clients) to connect to an 802.1X-authorized port.
(Options: Single-Host, Multi-Host; Default:
Single-Host)
■ Mode – Sets the authentication mode to one of the
following options:
■ Auto – Requires a dot1x-aware client to be
authorized by the authentication server. Clients
that are not dot1x-aware will be denied access.
■ Force-Authorized – Forces the port to grant
access to all clients, either dot1x-aware or
otherwise.
■ Force-Unauthorized – Forces the port to deny
access to all clients, either dot1x-aware or
otherwise.
■ Maximum Request – Sets the maximum number of
times the switch port will retransmit an EAP request
packet to the client before it times out the
authentication session. (Range: 1-10; Default 2)
■ Mode Reauthentication – Sets the client to be
re-authenticated after the interval specified by the
Re-authentication Period. Re-authentication can be
used to detect if a new device is plugged into a
switch port. (Default: Disabled)
■ Max Count – The maximum number of hosts that
can connect to a port when the Multi-Host operation
mode is selected. (Range: 1-1024; Default: 5)
■ Reauthentication Period – Sets the time period after
which a connected client must be re-authenticated.
(Range: 1-65535 seconds; Default: 3600 seconds)
■ Quiet Period – Sets the time that a switch port waits
after the Max Request Count has been exceeded
Page 68

68 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
before attempting to acquire a new client. (Range:
1-65535 seconds; Default: 60 seconds)
■ Transmit Period – Sets the time period during an
authentication session that the switch waits before
re-transmitting an EAP packet. (Range: 1-65535
seconds; Default: 30 seconds)
After you have filled in the parameters, click Apply to
save your changes.
Figure 59 802.1X Setup Screen
Monitoring
Using the Web interface, you can display address table
information and cable diagnostics.
The Monitoring menu includes two items:
■ Address Table
■ Cable Diagnostics
Address Table
Use the Address Table Summary screen to display the
Address Table information. You can query by selecting a
port, choosing a VLAN, or entering in a MAC Address,
then click Select.
Figure 60 Address Table Screen
Cable Diagnostics
The Switch provides a cable diagnostics utility, which
helps you detect and resolve issues with the attached
cables.
The Cable Diagnostics menu includes two tabs:
■ Summary
■ Diagnostics
Page 69

Monitoring 69
Summary
Use the Summary tab to display information on Test
Result, Cable Fault Distance, or Last Update for every
port on the switch.
Figure 61 Cable Diagnostic Summary Screen
Diagnostics
Use the Diagnostics tab to display individual port
information on Test Result, Cable Fault Distance, and
Last Update.
Figure 62 Cable Diagnostic Screen
Page 70

70 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Page 71

5
TROUBLESHOOTING
This chapter lists some issues that you may encounter
while installing, using, and managing the Switch, with
suggested courses of corrective action to take.
If you encounter an issue that is not listed here and you
cannot solve it, check the 3Com Knowledgebase at
http://knowledgebase.3com.com before contacting
your local technical support representative.
For more information on how to obtain support for your
Switch, refer to Appendix A.
Resetting to Factory Defaults
If the Switch does not operate normally or if the
firmware becomes corrupted, you can reset the Switch
to factory defaults.
CAUTION: Resetting the Switch to factory defaults
erases all your settings. You will need to reconfigure
the Switch after you reset it.
To reset the Switch to its factory defaults:
1 Using the tip of a pen (or a similar object), press the
Recovery button on the rear panel of the Switch. See
Figure 1 for illustration.
2 Power off the Switch, and then power it back on, while
keeping the Recovery button pressed.
3 Release the Recovery button.
4 Reset the Switch either by:
■ Accessing the Web interface using Discovery, and
then pressing the RESET button on the Initialize tab
of the Administration menu. After you click RESET, a
confirmation message appears. Click OK to confirm.
■ Powering off the Switch, and then powering it back
on.
The Switch will perform automatic IP configuration
after you reset it. See “Automatic IP Configuration” on
page 33 for more information.
Forgotten Password
If you forget the password to the Web interface after
you set it, you will need to reset the Switch to regain
access. See “Resetting to Factory Defaults” on page 71
for instructions.
Page 72

72 CHAPTER 5: TROUBLESHOOTING
After resetting the Switch, log on to the Web interface
using the default admin account settings:
■ User name – admin
■ Password – blank (no password)
Forgotten Static IP Address
If you forget the static IP address that you assigned to
the Switch and you need to access the Web interface,
use the Discovery application to automatically detect the
IP address and connect to the interface.
For information on using the Discovery application, refer
to “Running the Discovery Application” on page 23.
Solving LED Issues
This section lists some issues that are related to the LEDs
on the front panel of the Switch. For information on
basic LED checks, refer to the following topics in
Chapter 1:
■ (2) Gigabit Combo Ports (RJ-45/SFP)
■ (3) Link/Activity Status LEDs
■ (5) Power LED
A link is connected, but the Link/Activity
LED for the port is off.
There is a problem with this connection. Verify that:
■ The device being connected to is powered on and
operating correctly.
■ The cable is connected at both ends.
■ The cable is not damaged.
■ If the connection is to a workstation, that the
workstation's network interface is installed and
configured correctly.
■ The correct category of cable is being used for the
required link speed. Category 3 cables can be used
for 10BASE-T operation only. Category 5 cable is
required for 100BASE-TX or 1000BASE-T. 3Com
recommends Category 5e or 6 cables for
1000BASE-T operation.
A fiber cable is connected, but the Module
Active LED is off.
Verify that:
■ The fiber cable is in good condition.
■ The SFP module is correctly inserted.
■ A 3Com SFP module is being used. Refer to
“Approved SFP Transceivers” on page 19 for details.
■ The equipment at the far end is installed and
correctly configured.
Page 73

If the Problem Persists 73
The Link/Activity LED is on, but network
performance is poor
The Switch supports full-duplex autonegotiation. If the
connected device does not support autonegotiation,
ensure that it is configured for half-duplex operation
only. If the connected device has autonegotiation
disabled or overridden, and is configured as full-duplex,
the Switch will configure the link as half-duplex, causing
a mismatch that will reduce network performance when
data is transmitting and receiving simultaneously on the
same link.
Ensure that the connected device has either:
■ Autonegotiation enabled, or
■ The ports are configured for half-duplex operation
All ports appear to show continual activity.
There may be broadcast storms on the network. Remove
port connections one at a time, waiting a few seconds
between each port. If the LEDs go off after removing a
port connection, the device that was connected to that
port is introducing an excessive amount of broadcast
frames to the network. Some pieces of network
equipment operate by sending out broadcast frames
regularly.
Refer to the documentation that accompanies the
device for information on disabling the broadcast
operation.
If the Problem Persists
If the problem persists and the unit still does not
operate successfully, contact your 3Com network
supplier with the following information before returning
the unit:
■ Product number and serial number (printed on a
label supplied with the unit).
■ A brief description of the issue
Page 74

74 CHAPTER 5: TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 75

A
OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR PRODUCT
Register Your Product
Warranty and other service benefits start from the date
of purchase, so it is important to register your product
quickly to ensure you get full use of the warranty and
other service benefits available to you.
Warranty and other service benefits are enabled through
product registration. Register your product at
http://eSupport.3com.com/. 3Com eSupport
services are based on accounts that you create or have
authorization to access. First time users must apply for a
user name and password that provides access to a
number of eSupport features including Product
Registration, Repair Services, and Service Request. If you
have trouble registering your product, please contact
3Com Global Services for assistance.
Purchase Value-Added Services
To enhance response times or extend warranty benefits,
contact 3Com or your authorized 3Com reseller.
Value-added services like 3Com ExpressSM and
Guardian
support, software upgrades, onsite assistance or
advance hardware replacement. Experienced engineers
SM
can include 24x7 telephone technical
are available to manage your installation with minimal
disruption to your network. Expert assessment and
implementation services are offered to fill resource gaps
and ensure the success of your networking projects.
More information on 3Com maintenance and
Professional Services is available at www.3com.com.
Contact your authorized 3Com reseller or 3Com for a
complete list of the value-added services available in
your area.
Troubleshoot Online
You will find support tools posted on the 3Com Web
www.3com.com/
site at
3Com Knowledgebase helps you troubleshoot 3Com
products. This query-based interactive tool is located at
http://knowledgebase.3com.com and
contains thousands of technical solutions written by
3Com support engineers.
Access Software Downloads
Software Updates are the bug fix/maintenance
releases for the version of software initially purchased
with the product. In order to access these Software
Page 76

76 APPENDIX A: OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR PRODUCT
Updates you must first register your product on the
3Com Web site at
http://eSupport.3com.com/.
First time users will need to apply for a user name and
password. A link to software downloads can be found
at http://eSupport.3com.com/, or under the
Product Support heading at
www.3com.com/
Software Upgrades are the feature releases that
follow the software version included with your original
product. In order to access upgrades and related
documentation you must first purchase a service
contract from 3Com or your reseller.
Telephone Technical Support and Repair
To obtain telephone support as part of your warranty
and other service benefits, you must first register your
product at http://eSupport.3com.com/
Warranty and other service benefits start from the date
of purchase, so it is important to register your product
quickly to ensure you get full use of the warranty and
other service benefits available to you.
When you contact 3Com for assistance, please have the
following information ready:
■ Product model name, part number, and serial
number
■ Proof of purchase, if you have not pre-registered
your product
■ A list of system hardware and software, including
revision level
■ Diagnostic error messages
■ Details about recent configuration changes, if
applicable
To send a product directly to 3Com for repair, you must
first obtain a return authorization number (RMA).
Products sent to 3Com, without authorization numbers
clearly marked on the outside of the package, will be
returned to the sender unopened, at the sender’s
expense. If your product is registered and under
warranty, you can obtain an RMA number online at
http://eSupport.3com.com/. First time users
will need to apply for a user name and password.
Contact Us
3Com offers telephone, e-mail and Internet access to
technical support and repair services. To access these
services for your region, use the appropriate telephone
number, URL or e-mail address from the list below.
Telephone numbers are correct at the time of
publication. Find a current directory of support
telephone numbers posted on the 3Com Web site at
http://csoweb4.3com.com/contactus/
Page 77

Contact Us 77
.
Country Telephone Number
Asia, Pacific Rim Telephone Technical Support and Repair
Australia
Hong Kong
India
Indonesia
Japan
Malaysia
New Zealand
Pakistan
Philippines
P.R. of China
Singapore
S. Korea
Ta iw an
Thailand
You can also obtain support in this region using the following
e-mail: apr_technical_support@3com.com
Or request a repair authorization number (RMA) by fax using
this number: +65 543 6348
Europe, Middle East, and Africa Telephone Technical
Support and Repair
From anywhere in these
regions, call:
From the following countries, you may use the numbers
shown:
1 800 678 515
800 933 486
+61 2 9424 5179 or
000800 6501111
001 803 61 009
00531 616 439 or
03 3507 5984
1800 801 777
0800 446 398
+61 2 9937 5083
1235 61 266 2602 or
1800 1 888 9469
800 810 3033
800 6161 463
080 333 3308
00801 611 261
001 800 611 2000
+44 (0)1442 435529
Country Telephone Number
Austria
Belgium
Denmark
Finland
France
Germany
Hungary
Ireland
Israel
Italy
Luxembourg
Netherlands
Norway
Poland
Portugal
South Africa
Spain
Sweden
Switzerland
U.K.
You can also obtain support in this region using the following
URL: http://emea .3com.com/sup port/email.ht ml
0800 297 468
0800 71429
800 17309
0800 113153
0800 917959
0800 182 1502
06800 12813
1 800 553 117
1800 945 3794
800 879489
800 23625
0800 0227788
800 11376
00800 4411 357
800 831416
0800 995 014
900 938 919
020 795 482
0800 553 072
0800 096 3266
Page 78

78 APPENDIX A: OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR PRODUCT
Country Telephone Number
Latin America Telephone Technical Support and Repair
Antigua Barbuda
Argentina Local Number
Argentina
Argentina
Aruba
Bahamas
Barbados
Belize
Bermuda
Bolivia
Brazil Local Number
Brazil
British Virgin Islands
Cayman Islands
Chile
Columbia Local Number
Colombia
Costa Rica
Curacao
Dominica
Dominique
Equador
El Salvador
French Guiana
Grenada
Guadalupe
Guatemala
Guyana
Haiti
Honduras
Jamaica
Mexico Local Number
Mexico
Mexico
Monserrat
Nicaragua
Panama
Paraguay
Peru
AT&T +800 988 2112
54 11 5556 3200
0 810 444 3COM
810 44 32 66
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
55 11 5643 2700
800 133 266
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
57 1 592 5000
800 011 3266
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
52 55 52 01 00 04
01 800 849CARE
01 800 849 2273
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
Country Telephone Number
Puerto Rico
Saba Anquila
St. Kitts Neives
St. Lucia
St. Vincent
Suriname
Trinidad and Tobago
Turks and Caycos
Uruguay - Montevideo
Venezuela
Virgin Islands
You can also obtain support in this region using the following:
Spanish speakers, enter the URL:
http://lat.3com.com/lat/support/form.html
Portuguese speakers, enter the URL:
http://lat.3com.com/br/support/form.html
English speakers in Latin America should send e-mail to:
lat_support_anc@3com.com
US and Canada Telephone Technical Support and Repair
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
1 800 876 3266
Page 79

B
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
Related Standards
The Baseline Switch 2226 Plus has been designed to the
following standards:
Functional
MAC
Address
Safety
EMC Emissions
Immunity
Environmental
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Humidity
Standard
IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet), IEEE 802.3u (Fast
Ethernet), IEEE 802.3ab and IEEE 802.3z
(Gigabit Ethernet), IEEE 802.3x (Flow Control),
IEEE 802.1D 1993 (Bridging), IEEE D802.1Q
1998 (Virtual LAN)
4096
UL/CUL (UL 60950-1, CSA 22.2 No 60950-1),
TÜV/GS (EN 60950-1), IEC 60950-1, CB
EN50081-1, EN 55022 Class A, EN50082-1,
IEC 1000-4-2/3/4/6, EN60555-2 Class A, EN
60555-3, FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class A,
EN 55024
0-45 °C (32–113 °F)
-40-70 °C (-40-158 °F)
0-95% (non-condensing)
EN 60068 (IEC 68)—various parts
Physical
Width
Depth
Height
Weight
Mounting
Electrical
Power Inlet
AC Line Frequency
Input Voltage
Current Rating
Maximum Power
Consumption
Maximum Power
Dissipation
44 cm (17.3 in.)
23.8 cm (9.4 in.)
4.4 cm (1.7 in.) or 1U
3.2 kg (7.05 lb)
Free standing, or 19 in. rack mounted using
the mounting kit supplied
IEC 320
47-63 Hz (+/- 3 Hz)
100–240 VAC (auto range)
2 Amp (maximum)
60 W
286.7 BTU/hr
Page 80

80 APPENDIX B: TECHNICAL INFORMATION
Page 81

C
Important Safety Information
Please refer to the safety information found in the
3Com Switch Family Safety and Regulatory Information
manual included with this product.
SAFETY INFORMATION
You can find the 3Com Switch Family Safety and
Regulatory Information manual on the product CD-ROM
that was included with your switch. You can also
download the safety manual from the 3Com Web site:
www.3Com.com
Page 82

82 APPENDIX C: SAFETY INFORMATION
Page 83

GLOSSARY
10BASE-T
The IEEE specification for 10 Mbps Ethernet over
Category 3, 4 or 5 twisted pair cable.
100BASE-TX
The IEEE specification for 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet over
Category 5 twisted-pair cable.
1000BASE-LX
IEEE 802.3z specification for Gigabit Ethernet over 9/125
micron core single-mode fiber cable.
1000BASE-SX
IEEE 802.3z specification for Gigabit Ethernet over two
strands of 50/125 or 62.5/125 micron core multimode
fiber cable.
1000BASE-T
IEEE 802.3ab specification for Gigabit Ethernet over
100-ohm Category 5, 5e or 6 twisted-pair cable (using all
four wire pairs).
Auto-negotiation
Auto-negotiation is where two devices sharing a link,
automatically configure to use the best common speed.
The order of preference (best first) is: 1000BASE-T full
duplex, 100BASE-TX full duplex, 100BASE-TX half
duplex, 10BASE-T full duplex, and 10BASE-T half duplex.
Auto-negotiation is defined in the IEEE 802.3 standard
for Ethernet and is an operation that takes place in a
few milliseconds. Auto-negotiation must be enabled for
the 1000BASE-T ports to operate at 1000 Mbps, full
duplex.
Bandwidth
The information capacity, measured in bits per second,
that a channel can transmit. The bandwidth of Ethernet
is 10 Mbps, the bandwidth of Fast Ethernet is 100
Mbps and Gigabit Ethernet is 1000 Mbps.
BPDU
Bridge Protocol Data Unit. A type of information packet
that ensures that data is efficiently exchanged between
Switches in a LAN. BPDU messages detect loops in a
network, and remove them by shutting down the bridge
causing the loop.
Page 84

84 GLOSSARY
Category 3 Cables
One of five grades of Twisted Pair (TP) cabling defined
by the EIA/TIA-568 standard. Category 3 is voice grade
cable and can only be used in Ethernet networks
(10BASE-T) to transmit data at speeds of up to 10
Mbps.
Category 5 Cables
One of five grades of Twisted Pair (TP) cabling defined
by the EIA/TIA-568 standard. Category 5 can be used in
Ethernet (10BASE-T) and Fast Ethernet networks
(100BASE-TX) and can transmit data at speeds of up to
100 Mbps. Category 5 cabling is better to use for
network cabling than Category 3, because it supports
both Ethernet (10 Mbps) and Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps)
speeds.
Category 5e Cables
One of five grades of Twisted Pair (TP) cabling defined
by the EIA/TIA-568 standard. Category 5e can be used
in Ethernet (10BASE-T), Fast Ethernet (100BASE-TX) and
Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T) networks, and can
transmit data at speeds of up to 1000 Mbps.
Category 6 Cables
One of five grades of Twisted Pair (TP) cabling defined
by the EIA/TIA-568-B standard. Category 6 can be used
in Ethernet (10BASE-T), Fast Ethernet (100BASE-TX) and
Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T) networks, and can
transmit data at speeds of up to 1000 Mbps.
Client
The term used to describe the desktop PC that is
connected to your network.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. This protocol
automatically assigns an IP address for every computer
on your network. Windows 95, Windows 98 and
Windows NT 4.0 contain software that assigns IP
addresses to workstations on a network. These
assignments are made by the DHCP server software that
runs on Windows NT Server.
Ethernet
A LAN specification developed jointly by Xerox, Intel and
Digital Equipment Corporation. Ethernet networks use
CSMA/CD to transmit packets at a rate of 10 Mbps and
100 Mbps over a variety of cables.
Ethernet Address
See MAC address.
Fast Ethernet
An Ethernet system that is designed to operate at 100
Mbps.
Gigabit Ethernet
An Ethernet system that is designed to operate at 1000
Mbps.
Page 85

85
Full Duplex
A system that allows packets to be transmitted and
received at the same time and, in effect, doubles the
potential throughput of a link.
Half Duplex
A system that allows packets to be transmitted and
received, but not at the same time. Half duplex is not
supported for 1000 Mbps. Contrast with full duplex.
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. This
American organization was founded in 1963 and sets
standards for computers and communications.
IEEE 802.1D
Specifies a general method for the operation of MAC
bridges, including the Spanning Tree Protocol.
IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN Tagging - Defines Ethernet frame tags which carry
VLAN information. It allows switches to assign
endstations to different virtual LANs, and defines a
standard way for VLANs to communicate across
switched networks.
IEEE 802.3ad
A standard that defines link aggregation. 802.3ad is
now incorporated into the relevant sections of the IEEE
Std. 802.3-2002.
IETF
Internet Engineering Task Force. An organization
responsible for providing engineering solutions for
TCP/IP networks. In the network management area, this
group is responsible for the development of the SNMP
protocol.
IP
Internet Protocol. IP is a layer 3 network protocol that
is the standard for sending data through a network. IP
is part of the TCP/IP set of protocols that describe the
routing of packets to addressed devices. An IP address
consists of 32 bits divided into two or three fields: a
network number and a host number or a network
number, a subnet number, and a host number.
IP Address
Internet Protocol Address. A unique identifier for a
device attached to a network using TCP/IP. The address
is written as four octets separated with periods
(full-stops), and is made up of a network section, an
optional subnet section and a host section.
ISP
Internet Service Provider. An ISP is a business that
provides connectivity to the Internet for individuals and
other businesses or organizations.
LAN
Local Area Network. A network of end stations (such
as PCs, printers, servers) and network devices (hubs and
Page 86

86 GLOSSARY
switches) that cover a relatively small geographic area
(usually not larger than a floor or building). LANs are
characterized by high transmission speeds over short
distances (up to 1000 metres).
Layer 2
Data Link layer in the ISO 7-Layer Data Communications
Protocol. This is related directly to the hardware
interface for the network devices and passes on traffic
based on MAC addresses.
Link Aggregation
See Trunking.
MAC
Media Access Control. A protocol specified by the IEEE
for determining which devices have access to a network
at any one time.
MAC Address
Media Access Control Address. Also called the
hardware, physical or Ethernet address. A layer 2
address associated with a particular network device.
Most devices that connect to a LAN have a MAC
address assigned to them as they are used to identify
other devices in a network. MAC addresses are 6 bytes
long.
purpose of exchanging information or sharing resources.
Networks vary in size, some are within a single room,
others span continents.
Ping
Packet Internet Groper. An Internet utility used to
determine whether a particular IP address is online. It is
used to test and debug a network by sending out a
packet and waiting for a response.
Protocol
A set of rules for communication between devices on a
network. The rules dictate format, timing, sequencing
and error control.
RJ-45
A standard connector used to connect Ethernet
networks. The "RJ" stands for "registered jack."
Network
A Network is a collection of computers and other
computer equipment that are connected for the
Page 87

87
Server
A computer in a network that is shared by multiple end
stations. Servers provide end stations with access to
shared network services such as computer files and
printer queues.
SFP
Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP) Connectors are based
on an open standard that enables hot swapping of
various type of fiber optic and copper-based transceivers
into the host equipment.
Subnet Address
An extension of the IP addressing scheme that allows a
site to use a single IP network address for multiple
physical networks.
Subnet Mask
A subnet mask, which may be a part of the TCP/IP
information provided by your ISP, is a set of four
numbers configured like an IP address. It is used to
create IP address numbers used only within a particular
network (as opposed to valid IP address numbers
recognized by the Internet, which must assigned by
InterNIC).
Subnets
A network that is a component of a larger network.
Switch
A device that interconnects several LANs to form a
single logical LAN that comprises of several LAN
segments. Switches are similar to bridges, in that they
connect LANs of a different type; however they connect
more LANs than a bridge and are generally more
sophisticated.
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol.
This is the name for two of the most well-known
protocols developed for the interconnection of
networks. Originally a UNIX standard, TCP/IP is now
supported on almost all platforms, and is the protocol
of the Internet.
TCP relates to the content of the data travelling through
a network — ensuring that the information sent arrives
in one piece when it reaches its destination. IP relates to
the address of the end station to which data is being
sent, as well as the address of the destination network.
Traffic Monitoring
Enables the monitoring of port traffic by attaching a
network analyzer to one switch port, in order to
monitor the traffic of other ports on the Switch.
Trunking
A method which specifies how to create a single
high-speed logical link that combines several
lower-speed physical links.
Page 88

88 GLOSSARY
VLAN
A Virtual LAN is a collection of network nodes that
share the same collision domain regardless of their
physical location or connection point in the network. A
VLAN serves as a logical workgroup with no physical
barriers, and allows users to share information and
resources as though located on the same LAN.
Page 89

REGULATORY NOTICES
FCC Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a commerical environment. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
harmful interference to radio communications, in which case the user will be required to
correct the interference at their own expense.
Information to the User
If this equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
■ Reorient the receiving antenna.
■ Relocate the equipment with respect to the receiver.
■ Move the equipment away from the receiver.
■ Plug the equipment into a different outlet so that equipment and receiver are
on different branch circuits.
If necessary the user should consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television
technician for additional suggestions. The user may find the following booklet prepared
by the Federal Communications Commission helpful:
How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems
This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
20402, Stock No. 004-000-00345-4. In order to meet FCC emissions limits, this
equipment must be used only with cables which comply with IEEE 802.3.
CE Statement (Europe)
This product complies with the European Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC and EMC
Directive 89/336/EEC as amended by European Directive 93/68/EEC.
CSA Statement
This Class A digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian
Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le
matériel brouilleur du Canada.
89
Page 90

90
Page 91

INDEX
Numbers
1000BASE-LX 83
1000BASE-SX 83
1000BASE-T 83
100BASE-TX 83
10BASE-T 83
A
auto IP configuration 33
default IP address 34
default mask 34
B
bandwidth 83
Baseline Switch 2848-SFP 79
C
category 3 cables 84
category 5 cables 84
category 5e cables 84
category 6 cables 84
client 84
configuration
overview 31
conventions
text, About This Guide 8
CSA statement 89
D
DHCP 84
diagram
front panel 10
Discovery 23
dynamic host control protocol 84
E
Ethernet 84
F
Fast Ethernet 84
FCC statement 89
Feedback about this User Guide 8
forgotten IP address 71
forgotten password 71
front panel diagram 10
full duplex 85
G
Gigabit Ethernet 84
Glossary 83
H
half duplex 85
I
IEEE 85
IETF 85
IP address
auto configuration 33
modifying 33
IP defined 85
ISP defined 85
L
LAN defined 85
LED issues 72
link aggregation 54
local area network 85
M
MAC address 86
media access control 86
monitoring traffic 58, 60
Page 92

92 INDEX
N
network analyzer 58, 60
network defined 86
P
password
changing 37
default (blank) 37
setting 32
port settings
configuring 51, 60, 64
positioning the Switch 15
POST 18
protocol defined 86
R
resetting to factory defaults 71
RJ-45 defined 86
S
server defined 87
SFP transceivers
approved (supported) 19
inserting 19
removing 20
spot checks 21
subnet mask 87
Switch
positioning 15
switch defined 87
T
TCP/IP 85
defined 87
technical specifications 79
traffic 87
monitoring 58, 60
troubleshooting 71
forgotten IP address 71
forgotten password 71
LED-related issues 72
POST failed 19
trunking See link aggregation
U
user name
default 37
V
viewing
status information 31
VLANs 41
creating 48
maximum supported 42
sample configurations 46
W
Web interface
accessing directly 28
accessing using Discovery 23
buttons 28
connecting 23
logging on 25
menu 25
navigating 25
requirements for accessing 23
 Loading...
Loading...