Page 1
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
IM010
Models 3656 / 3756
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
Page 2

Owner’s Information
Please fill in information and give this booklet to homeowner.
Warranty information is on page 14.
Model Number:
Serial Number:
Dealer:
Dealer’s Phone No.
Date of Purchase: Installation Date:
Table of Contents
SUBJECT PAGE
Safety Instructions ......................................................................2
Description and Specifications ................................................... 2
Engineering Data ........................................................................ 2
Installation ..................................................................................2
Location .................................................................................. 2
Close-Coupled Units .............................................................. 2
Frame-Mounted Units ............................................................ 3
SAE Engine Driven Pumps .........................................................3
Coupling Alignment ................................................................... 6
Frame-Mounted Units Only ..................................................6
Piping .......................................................................................... 6
Suction .................................................................................... 6
Discharge ................................................................................ 6
Wiring and Grounding ...............................................................7
Rotation ......................................................................................7
Operation....................................................................................7
Maintenance ............................................................................... 7
Disassembly ................................................................................8
Reassembly..................................................................................8
Packed Box Instructions .............................................................9
Troubleshooting ........................................................................10
Repair Parts ...............................................................................11
Limited Warranty .....................................................................14
2
Page 3
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
WARNING
Hazardous fluids
can cause fire,
burns or death.
NOTICE: INSPECT UNIT FOR DAMAGE AND
REPORT ALL DAMAGE TO CARRIER
IMMEDIATELY.
DESCRIPTION and SPECIFICATIONS
The series 3656/3756 are single stage, end suction, centrifugal
pumps for general liquid transfer, booster applications, irrigation and general service pumping. Pumps are available in three
different materials of construction: all iron, bronze-fitted and
all bronze (“S” group only).
Pump impellers are fully enclosed, key driven and held in
position by an impeller bolt and washer. Casings are full volute
in design with replaceable wear rings.
Dependant on the pump size, the suction and discharge
connections will be threaded or flanged. Shafts are protected
with stainless steel shaft sleeves.
Close-coupled units have NEMA standard JM or JP motors
with C-face mounting and key driven shaft extension. SAE
drive units bolt directly to the engine flywheel housing for SAE
sizes 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5. Optional elastomer element couplings
are available for 6½, 7½, 8, 10, 11½ and 14 inch flywheels.
Frame mounted units can be coupled to motors through a
spacer coupling, or belt driven.
TO AVOID SERIOUS OR FATAL PERSONAL INJURY
OR MAJOR PROPERTY DAMAGE, READ AND
FOLLOW ALL SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS IN THE
MANUAL AND ON THE PUMP.
This is a SAFETY ALERT SYMBOL.
When you see this symbol on the pump or
in the manual, look for one of the following
signal words and be alert to the potential for
personal injury or property damage.
Warns of hazards that WILL cause serious
personal injury, death or major property
damage.
Warns of hazards that CAN cause serious
personal injury, death or major property
damage.
Warns of hazards that CAN cause personal
injury or property damage.
NOTICE: INDICATES SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS
WHICH ARE VERY IMPORTANT AND
MUST BE FOLLOWED.
THIS MANUAL IS INTENDED TO ASSIST IN THE
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION OF THIS UNIT.
THOROUGHLY REVIEW ALL INSTRUCTIONS AND
WARNINGS PRIOR TO PERFORMING ANY WORK
ON THIS PUMP.
MAINTAIN ALL SAFETY DECALS.
UNIT NOT DESIGNED FOR USE
WITH HAZARDOUS LIQUIDS OR
FLAMMABLE GASES.
Engineering Data
Maximum Liquid Temperature:
212º F (100º C) – standard seal or packing
250º F (120º C) – Optional high temp. seal
Maximum Working Pressure (Fluid temperature dependant):
– NPT connections, 200 PSI (1379 kPa)
– 125# ANSI flanged connections, 200 PSI (1379 kPa)
Maximum Suction Pressure: 100 PSI (689.5 kPa)
Starts per Hour: 20, evenly distributed
Group Size Suction Discharge
1½ x 2-6 (H) 2" NPT 1½" NPT
1 x 2-7 2" NPT 1" NPT
2½ x 3-7 3" NPT 2½" NPT
S
1 x 2-8 2" NPT 1" NPT
1½ x 2-8 2" NPT 1½" NPT
2 x 2-5 2" NPT 2" NPT
2½ x 2½-5 2½" NPT 2½" NPT
LH 3 x 3-5 3" NPT 3" NPT
4 x 4-5 4" Flange 4" Flange
5 x 5-6 5" Flange 5" Flange
2½ x 3-8 3" NPT 2½" NPT
3 x 4-8 4" Flange 3" Flange
4 x 5-8 5" Flange 4" Flange
1½ x 2-10 2" NPT 1½" NPT
2½ x 3-10 3" Flange 2½" Flange
4 x 6-10 6" Flange 4" Flange
2½ x 3-13 3" Flange 2½ " Flange
3 x 4-13 4" Flange 3" Flange
4 x 6-13 6" Flange 4" Flange
6 x 8-13 8" Flange 6" Flange
L 8 x 10-13 10" Flange 8" Flange
4 x 6-16 6" Flange 4" Flange
3 x 4-7 4" Flange 3" Flange
M
3 x 4-10 4" Flange 3" Flange
Installation
LOCATION
• Locate the pump as near liquid source as practical; below
level of liquid for automatic repriming capability.
• Allow adequate space for servicing and ventilation. Protect
the unit from weather and water damage due to rain,
flooding or freezing temperatures.
• Protect the pump and piping from freezing temperatures.
• Allow adequate space around the unit for service and
ventilation.
CLOSE-COUPLED UNITS
• Units may be installed horizontally, inclined or vertically with
the motor above the pump.
• The motor feet MUST be bolted to a substantial surface
(horizontal or vertical) that is capable of complete and rigid
support for the pump and motor. For L-Group pumps, the
motor adapter feet must also be bolted to the supportive
surface.
• For vertical operation, the motor should be tted with a drip
cover or otherwise protected against liquid entering the motor (rain, spray, condensation, etc.)
NOTICE: DO NOT INSTALL WITH MOTOR
BELOW PUMP. ANY LEAKAGE OR
CONDENSATION WILL AFFECT
THE MOTOR.
3
Page 4
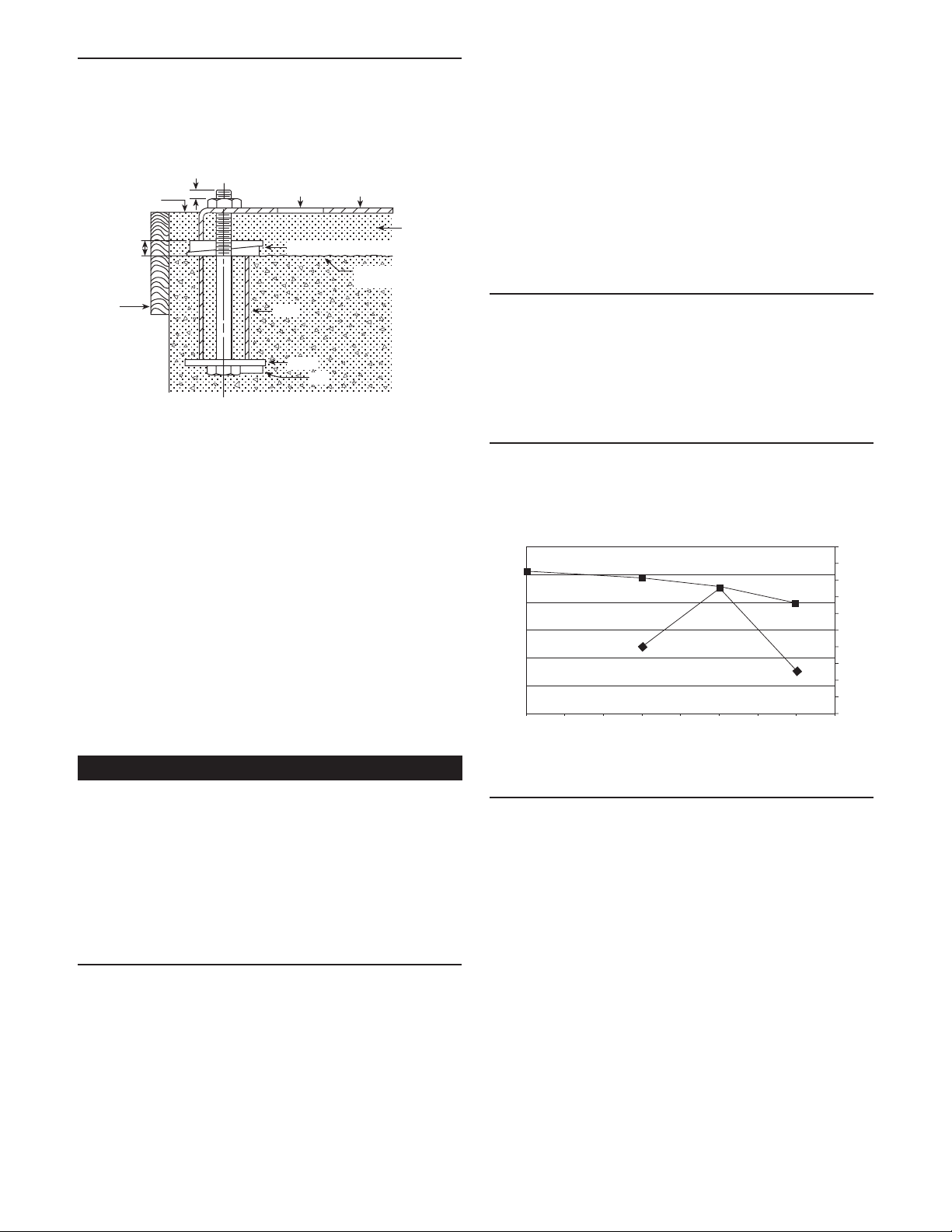
FRAME-MOUNTED UNITS
• A at substantial foundation surface MUST be provided to
avoid distortion and/or strain when tightening the foundation bolts. A rubber mounting is acceptable to reduce noise
or excessive vibration.
• Tighten motor hold-down bolts BEFORE connecting piping
to pump.
Finished grouting
(1/2 to 3/4”)
Allowance
for leveling
Wood
frame
(
Leveling wedges or shims – left in place
Sleeve
Washer
Lug
BaseGrout hole
Grout
Top of foundation –
clean and wet down
1
/4”)
Figure 1
• It is recommended that the baseplate be grouted to a
foundation with solid footing. Refer to Figure 1.
• Place unit in position on wedges located at four points, two
below approximate center of driver and two below
approximate center of pump. Adjust wedges to level unit.
Level or plumb suction and discharge connections.
• Make sure bedplate is not distorted and nal coupling
alignment can be made within the limits of movement of
motor and by shimming, if necessary.
• Tighten foundation bolts nger tight and build dam around
foundation. Pour grout under bedplate making sure the areas
under the pump and motor feet are filled solid. Allow grout
to harden 48 hours before fully tightening foundation bolts.
• Tighten pump and motor hold-down bolts before aligning
shaft or connecting the piping to pump.
• Allow grout to harden for 48 hours before tightening 4
foundation bolts.
SAE – Engine Driven Pumps
The SAE engine drive bearing frame is designed to bolt directly
to the flywheel housing for engines with an SAE no. 1, 2,
3, 4 or 5 mount. The pump shaft extension is sized for use
with couplings bolted directly to the flywheel. Goulds Water
Systems optional couplings are sized for 6½", 7½", 8", 10", and
14" flywheels. Although other flywheel mount couplings may
be used, it is recommended that the Goulds Water Systems
coupling be used to ensure long and trouble-free operation
from your Goulds Pump.
REQUIREMENTS FOR PROPER OPERATION
Pump End:
When delivering the required capacity (GPM) to the system
piping, the pump must add the amount of Head required
by the system at the capacity. The operating head-capacity
point should be as close as possible to the highest efficiency
line shown on the performance curve, and must be below the
head-capacity line labeled “maximum” RPM. The maximum
operaton RPM for the pump is determined by bearing life, or
in some cases, by the pressure limits of the pump. Suction and
discharge openings are NPT tapped for standard pipe, or faced
and drilled per ANSI B16.1, class 125 for standard flanges as
indicated. Maximum working pressure for class 30 cast iron,
per ANSI B16.1, is 175 PSI.
Internal combustion engines are variable speed and variable
power machines. The power output depends on the engine
speed (RPM) and will be reduced when operating altitude,
and/or the air temperature increases. When driving the pump
at the RPM required to deliver water into the system piping,
the engine must operate within the Engine Manufacturers
minimum and maximum RPM limits. The power output to
supply the pump power demand must not exceed the continuous power rating of the engine, after derating for all power
consuming engine accessories, and adjustmaner for installation
site altitude and air temperature.
DRIVE-TRAIN SIZING (BHP)
The BHP Equation is: (Flow x TDH) / 3960 x Eff.)
Note: For internal combustion units the BHP calculation must
be de-rated for the following conditions:
• 20% for continuous duty
• 5% for right-angle drive
• 3% for each 1,000 feet above sea level
• 1% for each 10º F above 60º F.
DRIVE-TRAIN SIZING (TORQUE)
Other than sizing an engine for BHP, torque calculations also
are required for proper sizing. Typically the horsepower and
torque rating do not follow the same relationship throughout
the usable range of a diesel engine (Figure 2). The equation for
torque (lbs/ft) is (5250 x BHP) / RPM.
600
500
400
300
200
TORQUE (LBS/FT)
100
0
1500 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 2100 2200 2300
RPM
180
178
176
174
172
170
168
166
164
162
160
Figure 2: HP (◆) vs. Torque (■)
VERIFY MATCH OF PUMP END TO ENGINE
SAE Bracket Size:
Engine drive pumps are available to fit engines having a standard SAE 5 through SAE 1 flywheel housing.
For a new engine, the engine supplier can provide the SAE
housing number.
For an existing engine, the flywheel housing bore and bolt
circle can be measured and compared against the standard SAE
housing dimensions listed in Table 1, to identify the housing
SAE number.
• Measure the ywheel housing bore (A), and the bolt circle
(B), as accurately as possible with a tape measure (to the
nearest 1/32 inch).
• Count the number of threaded holes in the ywheel housing
(C). Test the threaded holes with a bolt, to determine the
thread series.
• Compare the measured dimensions (A), (B), and (C) against
Table 1, to determine the SAE number of the flywheel housing, to be sure it matches the SAE number of your pump.
HP
4
Page 5
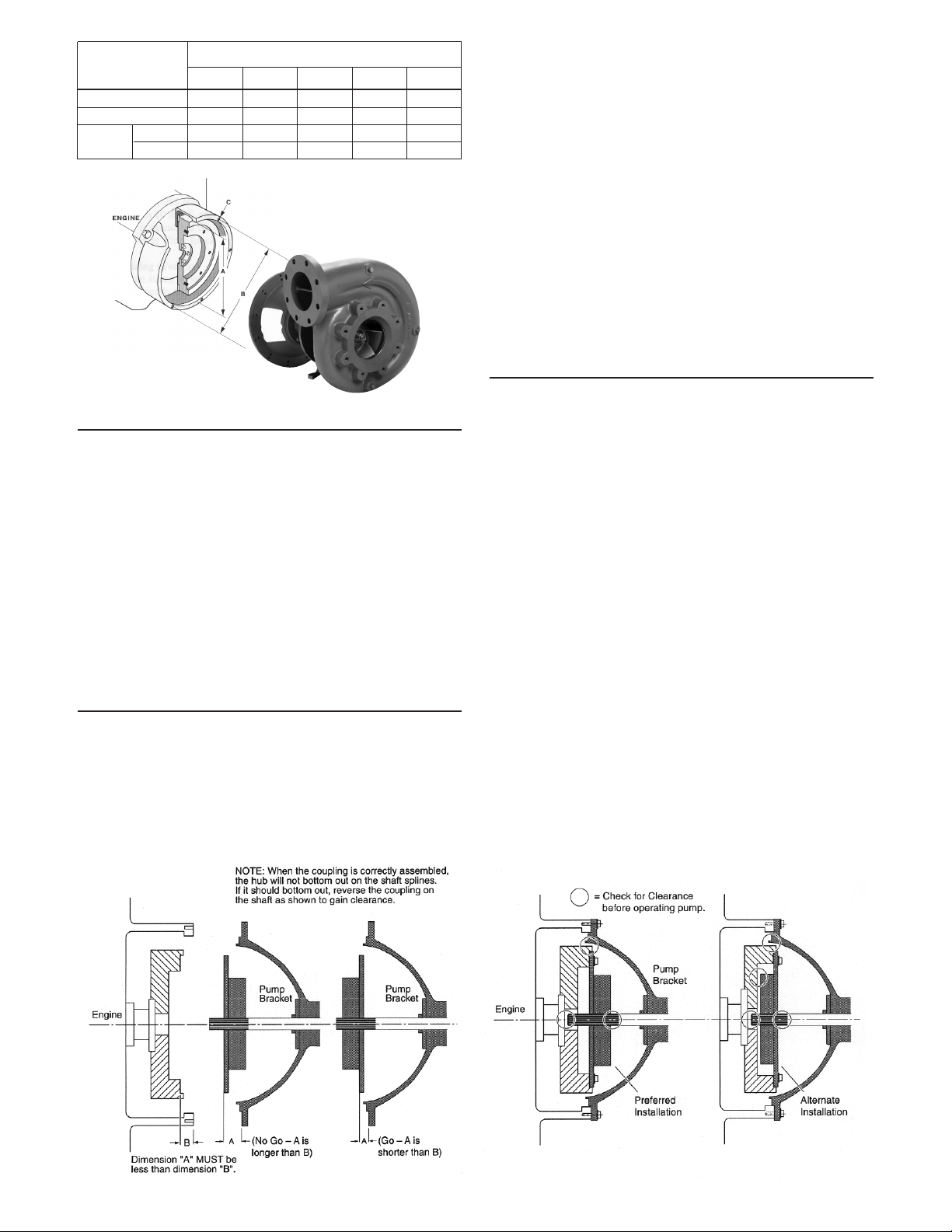
Flywheel
SAE Flywheel Housing Size
Housing
1 2 3 4 5
Dimensions
A 201⁄8 175⁄8 161⁄8 141⁄4 123⁄8
B 207⁄8 183⁄8 167⁄8 15 131⁄8
C No. 12 12 12 12 8
Size 7⁄16-14
3
⁄8-16
3
⁄8-16
3
⁄8-16
3
⁄8-16
Table 1
Figure 3
INSTALLATION
• The pump may be installed horizontally, with the discharge
rotated to any position allowed by the casing bolt pattern
(13). It is recommended that the discharge be located horizontally, above the suction.
• The casing must be supported on all pumps by a rigid support which is anchored to the unit base or foundation.
• For M-Group pumps it is recommended that this support
is bolted to the motor adapter ring using 2 or more of the
casing bolts (13). It is likely that longer bolts will be required
for the additional support thickness. Use SAE grade 5 bolts,
torqued as indicated in this manual.
• For L-Group pumps it is recommended that the pump is
supported beneath the two feet cast into the motor adapter
(3). These feet must be bolted to the support.
PUMP TO ENGINE ASSEMBLY (SPLINE COUPLING)
Preparation for Assembly of Pump on Engine
• Clean face and register t of ywheel housing and ywheel
as necessary to remove all grease, dirt, or rust (and all traces
of rust preventative) which would interfere with installation
of pump and/or prevent correct alignment. If flywheel is fitted with a pilot bearing for a transmission shaft, remove and
discard. The pilot bearing is not required for installation of
the pump end, and could interfere with the pump shaft.
• Examine shaft spline closely. Use a le, if necessary, to
remove any burrs that would prevent coupling from sliding
freely onto the shaft.
• Lubricate pump shaft spline sparingly with light grease.
Don’t lubricate straight keyed shaft.
• Slide the coupling onto shaft until it is stopped against the
shaft (refer to page 5 for straight shaft installation).
• Measure the distance from the engine side of the ywheel
coupling adapter ring to the mounting face of the pump
bracket. Refer to Figure 4 below, Dimension “A”.
• Next, measure depth from face of ywheel housing on
engine, to face on flywheel against which coupling will be
bolted. Refer to Figure 4 below, Dimension “B”.
• Pump measurement must be less than engine measurement
or axial interference will result in thrust force on engine
crank shaft bearings. Simply stated, Dimension “A” must be
less than Dimension “B”.
FLYWHEEL COUPLING
• The ywheel coupling transmits power from the engine
flywheel to the pump shaft. The maximum power that a
coupling can safely handle is shown by a rating number, “R”,
which is listed in the coupling dimensions tables.
• When selecting a ywheel coupling for a pump and engine,
first determine the power rating that the pump will demand.
On the pump performance curve, find the RPM and BHP
values required to produce the spplication head-capacity
point.
• Divide the BHP by the RPM, then multiply the result times
100. The result will be the demand number for the pump.
For example, a 20BFSAE1AO can deliver 800 GPM at 270
feet Total Head when running at 1800 RPM. The power
required by the pump will be 75 BHP. The demand number
will be: (75 / 1800) x 100 = 4.16
• Next, select a coupling that can safely transmit the power,
and which will fit the flywheel dimensions. For a coupling to
be suitable, it must have an “R” rating number GREATER
THAN the pump demand number. In the above example,
the minimum coupling “R” number whould be 5.
• Torsional compatibility of the engine, pump, and coupling
is the responsibility of the assembler. Goulds Water Systems
will supply data for the pump and coupling for use by the
assembler for a torsional analysis.
NOTE: If the flywheel is fitted with a pilot bearing pressed
into a bore at the center, remove it to avoid interference with
the pump shaft.
Figure 4 Figure 5
5
Page 6
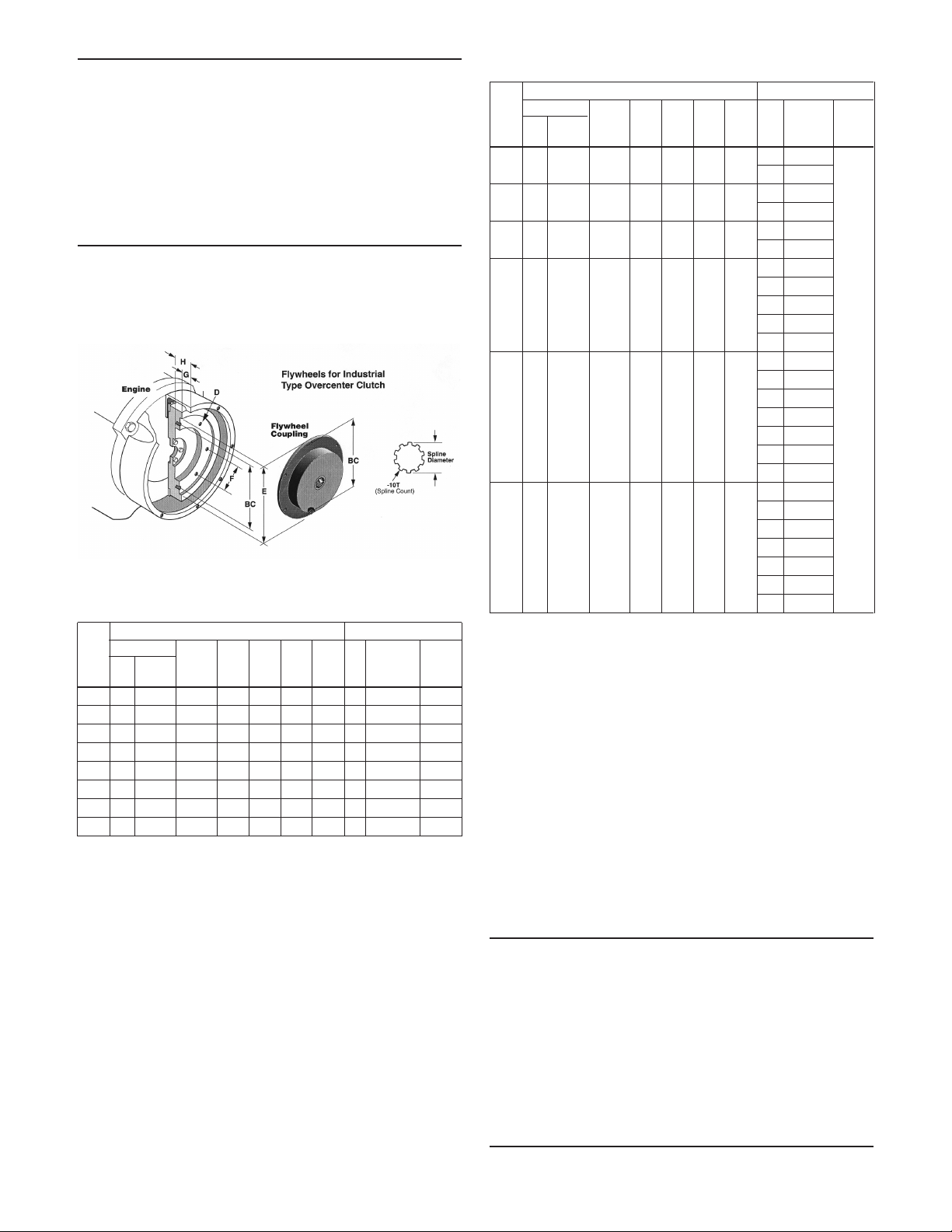
FLYWHEEL FOR INDUSTRIAL TYPE OVERCENTER CLUTCHES
• Figure 6 shows the hollowed-out appearance of the ywheels made for use with overcenter type clutch power
take-off assemblies.
• These ywheels will have a recessed bore machined into the
face, and a set of tapped holes, which will be used to attach
the coupling to the flywheel. Dimensions are governed by
an SAE standard and are listed in Tables 1A and 1B, Figure
3. The “clutch size” shown in the table is the nominal clutch
facing diameter for Drive Ring Type Overcenter Clutches.
OTHER FLYWHEELS
• Some engines are tted with ywheels especially machined
for coupling to other kinds of machinery (electrical generators, torque converters, etc.), and require nonstandard
flywheel couplings. These may be purchased from third party
vendors or suppliers.
Figure 6
Table IA –
Wide RPM Range, Elastomer Mounted Hub – Spline Shaft
Flywheel Dimensions Flywheel Coupling (Spline)
Clutch D Shaft
Size
(UNC) Number Dia.
6½" 6 5⁄16-18 8½ OD 7.88 3.94 1.19 1.69 7 A00569C 1 1½" 10T
7½" 8 5⁄16-18 9½" OD 8.75 3.69 1.19 1.69 7 A00569C 2 1½" 10T
8" 6 3⁄8-16 103⁄8" OD 9.62 4.81 2.44 2.94 7 A00569C 3 1½" 10T
10" 8 3⁄8-16 123⁄8" OD 11.62 4.47 2.13 2.75 7 A00569C 4 1½" 10T
10" 8 3⁄8-16 123⁄8" OD 11.62 4.47 2.13 2.75 9 A00569C 6 1½" 10T
11½" 8 3⁄8-16 137⁄8" OD 13.12 5.06 1.56 2.69 7 A00569C 5 1½" 10T
11½" 8 3⁄8-16 137⁄8" OD 13.12 5.06 1.56 2.69 9 A00569C 7 1½" 10T
14" 8 ½-13 183⁄8" OD 17.25 6.63 1.00 2.13 9 A00569C 8 1½" 10T
* R = Coupling Rating Max.
Coupling Rating = (Rated horsepower x 100) / Rated RPM
Size E BC F G H R* Catalog Spline
Qty.
6
Table IB –
Wide RPM Range, Elastomer Mounted Hub – Straight Shaft
Flywheel Dimensions Flywheel Coupling
Clutch D Shaft
Size
(UNC) Number Dia.
6½" 6 5⁄16-18 8½ OD 7.88 3.94 1.19 1.69
3.51 CD625
7½" 8 5⁄16-18 9½" OD 8.75 3.69 1.19 1.69
3.51 CD725
8" 6 3⁄8-16 103⁄8" OD 9.62 4.81 2.44 2.94
3.51 CD825
2.28 CD1016
3.51 CD1025
10" 8 3⁄8-16 123⁄8" OD 11.62 4.47 2.13 2.75 5.71 CD1030
8.57 CD1050
11.23 CD1080
2.28 CD1116
3.51 CD1125
5.71 CD1130
11½" 8 3⁄8-16 137⁄8" OD 13.12 5.06 1.56 2.69 8.57 CD1150
11.23 CD1180
12.62 CD1190
16.85 CD11110H
2.28 CD1416
3.51 CD1425
5.71 CD1430
14" 8 3⁄8-16 183⁄8" OD 17.25 6.63 1.00 2.13 8.57 CD1450
11.23 CD1480
12.62 CD1490
16.85 CD14110H
Dimensions in inches
* R = Coupling Rating Max.
Coupling Rating = (Rated horsepower x 100) / Rated RPM
Size E BC F G H R* Catalog Spline
Qty.
2.28 CD616
2.28 CD716
2.28 CD816
1.625-
1.624Ø
3
⁄8 x 3⁄
Keyway
16
• For Goulds Water Systems straight shaft keyed couplings –
Ensure that the coupling hub set screw is backed out enough
to ensure clearance for the shaft key during assembly.
• Mount the coupling assembly to the engine ywheel using
the bolts provided torqued as follows in a crossing sequence:
6½" or 7½" Flywheel – 11 lbs.-ft. (15 N.m)
8", 10" or 11½" Flywheel – 20 lbs.-ft. (27 N.m)
14" Flywheel – 50 lbs.-ft. (68 N.m)
(For other couplings follow manufacturers
recommended installation procedure.)
• Place the pump shaft key into the pump shaft (122) and align
the shaft to the coupling. Slide the pump into the coupling
until the engine adapter ring (340) contacts the engine
flywheel housing.
INSTALLATION OF COUPLING ON FLYWHEEL
Flywheel Coupling Overcenter Type:
• These couplings are aligned concentrically with the ywheel
by register fit on the flywheel.
• Be sure to remove all preservatives from the engine’s y-
wheel.
• Fit the coupling into the ywheel. Align the bolt holes and
engage coupling with register fit on flywheel. Tap coupling
with a soft heavy hammer, if necessary, to be sure that it is
seated flat against flywheel. Secure coupling tightly to fly-
wheel with capscrews and lockwasher.
INSTALLATION OF PUMP ON ENGINE
• Lift pump with suitable lifting apparatus and align pump shaft
with coupling. End of pump shaft has a pilot diameter which
epermits wasy engagement of pump shaft into coupling.
Page 7
• Reach into pump suction opening and rotate impeller slightly
Hazardous machinery
can cause personal
injury or death.
WARNING
until the shaft will engage the coupling. Verify that there is
no gap between bracket and flywheel housing faces. Rotate
pump as necessary to align bracket holes with engine. Install
capscrews and bolt pump end securely to engine.
NOTE: If any interference, or incompatibility of parts is
detected during installation, DO NOT proceed with
assembly. Direct the problem to your nearest Goulds
Pumps distributor.
• Mount the pump to the engine using the bolts and lock-
washers provided, torqued as follows in a crossing sequence:
SAE #2, #3, #4, #5 – 20 lbs.-ft. (27 N.m)
SAE #1 – 50 lbs.-ft. (68 N.m)
• Install coupling guards (501N).
• Bolt motor adapter (3) to the rigid support described above.
Coupling Alignment
FAILURE TO DISCONNECT AND
LOCKOUT ELECTRICAL POWER
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
MAINTENANCE CAN CAUSE
SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY.
FRAME-MOUNTED UNITS ONLY
• Alignment MUST be checked prior to running. See Figure 7.
Parallel
• All piping MUST be independently supported and MUST
NOT place any piping loads on the pump
NOTICE: DO NOT FORCE PIPING INTO PLACE
AT PUMP SUCTION AND DISCHARGE
CONNECTIONS.
• All pipe joints MUST be airtight.
PIPING – SUCTION
• For suction lifts over 10 ft. (3 m) and liquid temperatures
over 120° F (49° C), consult pump performance curve for
net positive suction head required (NPSHR).
• If a pipe size larger than pump suction is required, an ec-
centric pipe reducer, with the straight side up, MUST be
installed at the pump suction.
• If pump is installed below the liquid source, install a gate
valve in the suction for pump inspection and maintenance.
NOTICE: DO NOT USE THE GATE VALVE TO
THROTTLE PUMP. THIS MAY CAUSE LOSS
OF PRIME, EXCESSIVE TEMPERATURES
AND DAMAGE TO PUMP, VOIDING
WARRANTY.
• If the pump is installed above the liquid source, the following
MUST be provided:
• To avoid air pockets, no part of the piping should be above
the pump suction connection.
• Slope the piping upward from liquid source.
• Use a foot valve or check valve ONLY if necessary for
priming or to hold prime during intermittent duty.
• The suction strainer or suction bell MUST be at least
3 times the suction pipe diameter area.
• Insure that the size and minimum submergence over suction inlet is sufficient to prevent air from entering pump
through a suction vortex. See Figures 8 through 11.
Angular
Figure 7
• Tighten all hold-down bolts before checking alignment.
• If realignment is necessary, always move the motor. Shim
as required.
• Parallel misalignment, shafts with axis parallel but not
concentric. Place dial indicator on one hub and rotate this
hub 360° while taking readings on the outside diameter of
the other hub. Parallel alignment is achieved when reading is
0.010" (0.254 mm) TIR, or less.
• Angular misalignment, shaft with axis concentric but not parallel. Place dial indicator on one hub and rotate this hub 360°
while taking readings on the face of the other hub. Angular
alignment is achieved when reading is 0.020" (0.508
mm) TIR, or less.
• Final alignment is achieved when parallel and angular requirements are satisfied with motor hold-down bolts tight.
NOTICE: ALWAYS RECHECK BOTH ALIGNMENTS
AFTER MAKING ANY MECHANICAL
ADJUSTMENTS.
Piping
• Piping should be no smaller than pump’s discharge and
suction connections and kept as short as possible, avoiding
unnecessary fittings to minimize friction losses. See Table 1.
H min.
D
Figure 8 Figure 9
3.0D
min.
1.5D
min.
H min.
D min.
D D
2
H min.
H
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
H = Min. Submergence in feet
1
12345678910 11121314 1516
V = Velocity in feet per second
= GPM x 0.321
Area
GPM x 0.4085
D
V
2
D
Figure 10 Figure 11
PIPING – DISCHARGE
• Install a check valve suitable to handle the ow, liquids and
to prevent backflow. After the check valve, install an appropriately sized gate valve to be used to regulate the pump
capacity, pump inspection and for maintenance.
• When required, pipe increaser should be installed between
the check valve and the pump discharge.
7
Page 8
Wiring and Grounding
WARNING
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
WARNING
Hazardous
voltage
Hazardous machinery
can cause personal
injury or death.
WARNING
WARNING
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
Extreme heat can
cause personal injury
or property damage.
WARNING
Hazardous fluids can
cause personal injury
or property damage.
WARNING
WARNING
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
Hazardous pressure
can cause personal
injury or property
damage.
CAUTION
Install, ground and wire according
to local and National Electrical Code
Requirements.
Install an all leg electrical power
disconnect switch near the pump.
Disconnect and lockout electrical
power before installing or servicing
the pump.
Electrical supply MUST match
pump’s nameplate specifications. Incorrect voltage can cause fire, damage
motor and void the warranty.
Motors without built-in protection MUST be provided
with contactors and thermal overloads for single phase
motors, or starters with heaters for three phase motors.
See motor nameplate.
• Use only copper wire to motor and ground. The ground
wire MUST be at least as large as the wire to the motor.
Wires should be color coded for ease of maintenance.
• Follow motor manufacturer’s wiring diagram on the motor
nameplate or terminal cover carefully.
FAILURE TO PERMANENTLY
GROUND THE PUMP, MOTOR AND
CONTROLS BEFORE CONNECTING
TO ELECTRICAL POWER CAN CAUSE
SHOCK, BURNS OR DEATH.
OPERATION AT OR NEAR ZERO
FLOW CAN CAUSE EXTREME HEAT,
PERSONAL INJURY OR PROPERTY
DAMAGE.
NOTICE: NO NOT RUN PUMP DRY OR SEAL
DAMAGE WILL RESULT.
• After stabilizing the system at normal operating conditions,
check the piping. If necessary, adjust the pipe supports.
• On frame-mounted units, coupling alignment may have
changed due to the temperature differential between pump
and motor. Recheck alignment following procedures and
hazard warnings in “COUPLING ALIGNMENT” section
of this manual.
Maintenance
FAILURE TO DISCONNECT AND
LOCKOUT ELECTRICAL POWER
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
MAINTENANCE CAN CAUSE SHOCK,
BURNS OR DEATH.
NOTICE: INCORRECT ROTATION MAY CAUSE
DAMAGE TO THE PUMP AND VOIDS
THE WARRANTY.
• Correct rotation is right-hand, CLOCKWISE when viewed
• To reverse three phase motor rotation, interchange any two
8
Rotation
from the motor end. For frame mounted units, switch power
on and off quickly to observe rotation. On close coupled
units, remove motor end plug or cover to observe rotation.
power supply leads.
Operation
DO NOT OPERATE FRAME
MOUNTED OR SAE UNITS WITHOUT
SAFETY GUARDS IN PLACE OR
SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY MAY
RESULT.
SPLASHING OR IMMERSING OPEN
DRIP PROOF MOTORS IN FLUID
CAN CAUSE FIRE, SHOCK, BURNS OR
DEATH.
FAILURE TO RELIEVE SYSTEM
PRESSURE AND DRAIN SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
MAINTENANCE CAN CAUSE
PROPERTY DAMAGE, PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH.
IF PIPING HAZARDOUS OR TOXIC
FLUIDS, SYSTEM MUST BE FLUSHED
PRIOR TO PERFORMING SERVICE.
CLOSE-COUPLED UNITS
• Bearings are located in and are part of the motor. For lubrication information, refer to motor manufacturer’s instructions.
FRAME-MOUNTED UNITS
• Model 3756 S-group has greased for life bearings.
No regreasing is possible or necessary.
• Model 3756 M or L-group bearing frame and SAE drive
bearing frame should be regreased every 2,000 hours or
at a three month interval, whichever occurs first. Use a #2
sodium or lithium based grease. Fill until grease comes out of
relief fittings, or lip seals, then wipe off excess.
• Follow motor or engine and coupling manufacturer’s lubrication instructions.
• Recheck alignment.
Page 9

SEASONAL SERVICE
• To REMOVE pump from service, remove drain plug and
drain all unprotected piping.
• To RETURN pump to service, replace drain plug using
Teflon™ tape or equivalent on male threads.
• Reconnect suction line if removed, examine union and repair
if necessary.
• Refer to OPERATION section of manual.
Disassembly
• Follow ALL warnings and instructions in the “MAINTE-
NANCE” section of this manual.
• Close-coupled units: Remove motor hold-down bolts.
• Frame-mounted units: Remove coupling guard, spacer, cou-
pling and frame hold-down bolts.
LIQUID END
1. Remove casing bolts (13).
2. Remove back pull-out assembly from casing (1).
3. Remove casing wear ring (4) if excessively worn.
NOTICE: DO NOT INSERT SCREWDRIVER BETWEEN
IMPELLER VANES TO PREVENT ROTATION.
4. On close-coupled units, remove motor end plug or cover
to expose screwdriver slot or flats on end of motor shaft.
5. While restraining shaft with an appropriate tool (close-
coupled units) or with a strap wrench (frame-mounted
units) remove impeller bolt (6). Impeller bolt may need
to be heated with torch to remove. Discard.
NOTICE: EXERCISE CAUTION WHEN HANDLING
HOT IMPELLER BOLT.
NOTICE: FOR SAE DRIVE UNITS, REMOVE IMPELLER
NUT SET SCREW (22A) PRIOR TO
REMOVING IMPELLER NUT (22). IMPELLER
SET SCREW AND IMPELLER NUT MAY NEED
TO BE HEATED TO BE REMOVED.
6. Remove impeller washer (7).
7. Insert two pry bars, 180° apart, between impeller (2) and
seal housing (3). CAREFULLY pry off impeller.
8. Remove impeller key (8).
9. Remove seal housing bolts (14) and seal housing (3)
pulling with it the mechanical seal assembly. Discard seal
assembly and seal housing o-ring (9). For packed box
pumps see “PACKED BOX INSTRUCTIONS”.
10. Remove adapter (108).
11. Inspect shaft sleeve (11). If badly scored, remove by
heating with torch. Discard.
12. Push out the mechanical seal stationary seat from the
seal housing. Discard.
13. On units equipped, remove seal housing wear ring (5)
if excessively worn.
DISASSEMBLY OF BEARING FRAME OR
SAE BEARING FRAME
1. Remove deflector (123) from shaft.
2. Remove bearing cover (134).
3. Remove shaft assembly from frame.
4. Remove lip seals (138, 139) from bearing frame (228) and
bearing cover (134) if worn. Discard.
5. Remove retaining ring (361).
6. Use bearing puller or arbor press to remove ball
bearings (112, 168).
Reassembly
• All parts should be cleaned before assembly.
NOTICE: O-RING SHOULD BE REPLACED AFTER ANY
DISASSEMBLY OF UNIT.
BEARING FRAME
1. Replace lip seals if removed.
2. Replace ball bearings if loose, rough or noisy when rotated.
3. Check shaft (122) for runout. Maximum permissible is
0.002" (0.05 mm) TIR.
4. Refer to the “MAINTENANCE” section of this manual
for M-group bearing frame regreasing instructions.
LIQUID END
1. Inspect shaft removing any debris or burrs.
2. Treat shaft with LOCQUIC® Primer “T”, or equivalent,
following manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
3. When replacing shaft sleeve, spray new shaft sleeve’s bore
with LOCQUIC® Primer “T”, or equivalent. Let parts dry
and then apply LOCTITE® #262 on the same surfaces.
Slide new sleeve over shaft with a twisting motion, wipe
off excess. Let cure according to instructions.
NOTICE: MECHANICAL SEAL MUST BE REPLACED
WHENEVER SEAL HAS BEEN REMOVED.
FOLLOW SEAL MANUFACTURER’S
INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. FOR PACKED
BOX PUMPS SEE “PACKED BOX
INSTRUCTIONS”.
4. Replace seal housing wear ring, if removed.
5. For mechanical seal pumps, stationary seal seat may be
dipped in water to ease installation. Place stationary seal
seat squarely into seal housing bore. Cover the polished
face of the seat with a thin piece of cardboard or paper
towel. Press seat firmly into bore using a round piece of
plastic or wood that disperses the force over the entire
seal face. NOTE: If mechanical seal is supplied with a
spring retainer, remove and discard the retainer.
6. Place adapter, concave face pointing up, over motor
shaft and lower it onto the motor.
7. Replace seal housing o-ring. This o-ring may be lubricated
with water or glycerin to ease in installation. Install seal
housing on adapter. Exercise care in that the motor shaft
does not dislodge or damage seal seat.
8. Fully and squarely install the rotary assembly of seal
against the stationary seat.
NOTICE: REPLACE IMPELLER BOLT AND WASHER
WHENEVER IMPELLER IS REMOVED.
9. Install impeller key in shaft keyway. Mount impeller on
shaft and push until it bottoms. Hold in place. For SAE
units, apply LOCTITE 271 to the impeller bore, keyway
and shaft. Mount impeller on shaft and push until it
bottoms. Hold in place.
10. Install new impeller washer. Impeller washer not used for
SAE units..
9
Page 10

11. Apply LOCTITE® #271 or equivalent, to new impeller bolt
CORRECT WRONG
threads and tighten to:
3⁄8"-16 bolts 20 lbs.-ft. (27 N.m)
½"-13 bolts 38 lbs.-ft. (51 N.m)
Impeller bolt not used for SAE units.
12. For SAE units apply LOCTITE® #271 to the external
threads of the shaft and internal threads of the impeller
nut (22). Tighten impeller nut to the following:
½"-Impeller Nut (SAE M-Group) 80 lbs.-ft. (107 N.m)
¾"-Impeller Nut (SAE L-Group) 100 lbs.-ft. (134 N.m)
13. For SAE units, after impeller nut (22) has been installed,
apply
LOCTITE® #271 to set screw (22A). Install impeller
set screw into face of impeller nut (22) and tighten
hand-tight.
14. Replace casing wear ring, if removed.
15. Replace casing bolts and tighten, in a crossing sequence,
to torque values indicated below:
3⁄8"-16 bolts (bronze casing) 25 lbs.-ft. (34 N.m)
½"-16 bolts (cast iron casing) 37 lbs.-ft. (50 N.m)
½"-13 bolts (cast iron casing) 90 lbs.-ft. (122 N.m)
¾"-10 bolts (cast iron casing) 175 lbs.-ft. (237 N.m)
16. Check reassembled unit for binding by rotating shaft with
appropriate tool from motor end.
17. If rubbing exists, loosen casing bolts and proceed with
tightening sequence again.
18. Replace motor hold-down bolts and motor end plug or
cover on close-coupled units.
19. Replace coupling, spacer, coupling guard and frame
hold-down bolts on frame-mounted units.
NOTICE: ALWAYS RECHECK BOTH ALIGNMENTS
AFTER MAKING ANY ADJUSTMENTS.
20. Refer to the “COUPLING ALIGNMENT” section of
this manual to realign shaft.
21. Assembly is complete.
Packed Box
1. Make sure stuffing box is free of foreign materials and
clean before beginning packing of packed box. Refer to
Sectional Assembly in the repair parts section.
2. Take special care during installation of packing rings
because they are die-formed. To install, twist the ring
sideways just enough to fit it around the shaft sleeve.
DO NOT ATTEMPT TO PULL RINGS STRAIGHT
OUT. See Figure 12.
Figure 12
3. Install the two piece Teflon lantern ring supplied as shown
in figure 13. Note: two pieces make one ring. Notches on
ring must face each other, but alignment is not necessary.
Teflon Lantern Ring
Figure 13
4. Install the packing rings and lantern ring in the following
sequence to pack the packed box. Install two rings of
packing, then the lantern ring, followed by the final three
rings of packing. Install each ring separately and firmly
seat. The use of a wooden split bushing is recommended
to accomplish this. See Figure 14. Use gland to jack the
bushing and ring into the box. Stagger joints in each ring
90°. Make sure the flush tap in the packed box lines up
with the center of the lantern ring. Any extra rings are
spares.
WOODEN “SPLIT BUSHING”
GLAND
STUFFING
BOX
SHAFT
Figure 14
5. Tighten gland nuts evenly, but not tight. When the pump
is started, slowly tighten the gland nuts until the leak rate
is between 40 and 60 drops per minute. A grease lubricant
can be used when the pumpage contains abrasive particles
or for a suction lift condition.
REMOVAL OF PACKED BOX
• Follow these steps to remove the packing from the
packed box.
1. Remove gland assembly.
2. With a “packing hook” remove packing.
3. Insert a wire hook into the ring on the outer edge to
remove the lantern ring.
4. Clean the packed box.
PRIME SAFE ARRANGEMENT (Optional – M & L Group Only)
• The Prime Safe arrangement can be provided with grease or
an oiler feed lubrication.
1. The grease gland (24) will have the letters "G" and "O"
stamped on the outside diameter and have two 1⁄8" NPT
connections for mounting a grease feeder or oiler.
10
Page 11
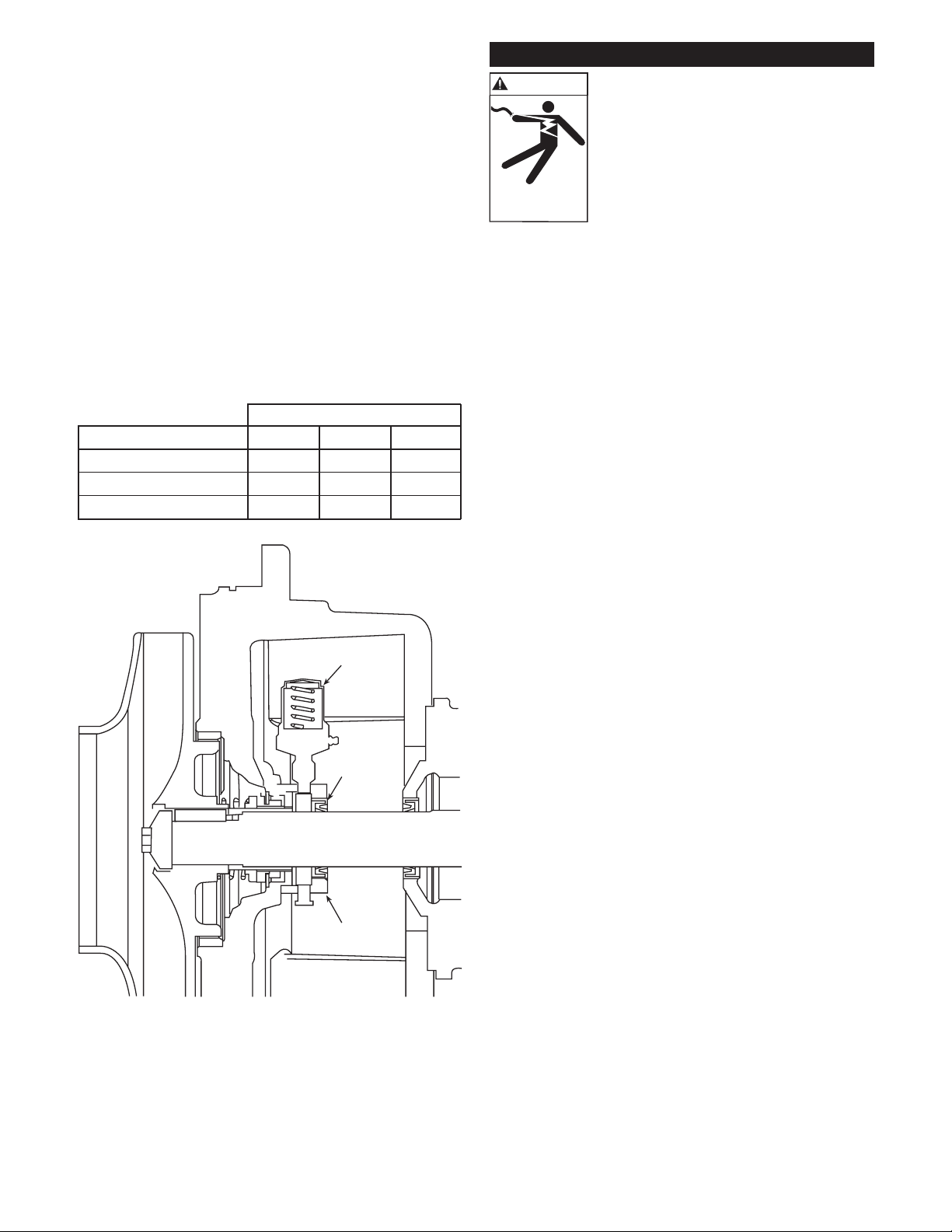
2. For grease feed applications, the grease gland is assembled
23
26
24
WARNING
Hazardous voltage
can shock, burn or
cause death.
with the “G” stamp in the 12 o' clock position. The grease
feeder (23) will mount in the grease gland at a 30 degree
angle from the horizontal. This is done to gain access to the
grease fitting located on the grease feeder. The lip seal (26)
mounted in the grease gland will be assembled as shown in
Figure 15.
3. For oiler feed applications, the grease gland is assembled
with the “O” stamp in the 12 o' clock position. The two
1
⁄8" NPT connections on the grease gland will be located on
the horizontal, which is to ensure proper function of the
oiler. The lip seal (26) is to be mounted in the reverse or
opposite direction as shown in Figure 10.
4. The mounting of a grease feeder or oiler may require
additional pipe extensions and/or fittings that will be
provided from the factory as needed.
5. The grease feeder (23) will come with three springs (blue,
red and silver). The use of the different springs will be
varied depending on the operating temperature and the
lubricant (grease) to be used.
Grease Feeder Spring Size
Operating Temperature No. 1 Grease No. 2 Grease No. 3 Grease
-10ºF (-23ºC) to 40ºF (4ºC) SILVER RED —
-40ºF (-40ºC) to 110ºF (43ºC) SILVER SILVER RED
-110ºF (-79ºC) to 200ºF (93ºC) BLUE SILVER SILVER
Use SAE 30W oil for oiler application.
Troubleshooting Guide
DISCONNECT AND LOCKOUT
ELECTRICAL POWER BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY MAINTENANCE.
FAILURE TO DO SO CAN CAUSE A
SHOCK, BURN OR DEATH.
SYMPTOM
MOTOR NOT RUNNING
See Probable Cause – 1 through 5
LITTLE OR NO LIQUID DELIVERED
See Probable Cause – 6 through 13
EXCESSIVE POWER CONSUMPTION
See Probable Cause – 3, 13, 14, 15
EXCESSIVE NOISE and VIBRATION
See Probable Cause – 3, 6, 7, 10, 12, 14, 16, 17
PROBABLE CAUSE
1. Motor thermal protector tripped
2. Open circuit breaker or blown fuse
3. Impeller binding
4. Motor improperly wired
5. Defective motor
6. Pump is not primed, air or gases in pumpage
7. Discharge, suction plugged or valve closed
8. Incorrect rotation (3 phase only)
9. Low voltage or phase loss
10. Impeller worn or plugged
11. System head too high
12. NPSHA too low – Excessive Suction lift or losses
13. Incorrect impeller diameter
14. Discharge head too low – excessive flow rate
15. Fluid viscosity, specific gravity too high
16. Worn bearing
17. Pump, motor or piping loose
Figure 15
11
Page 12
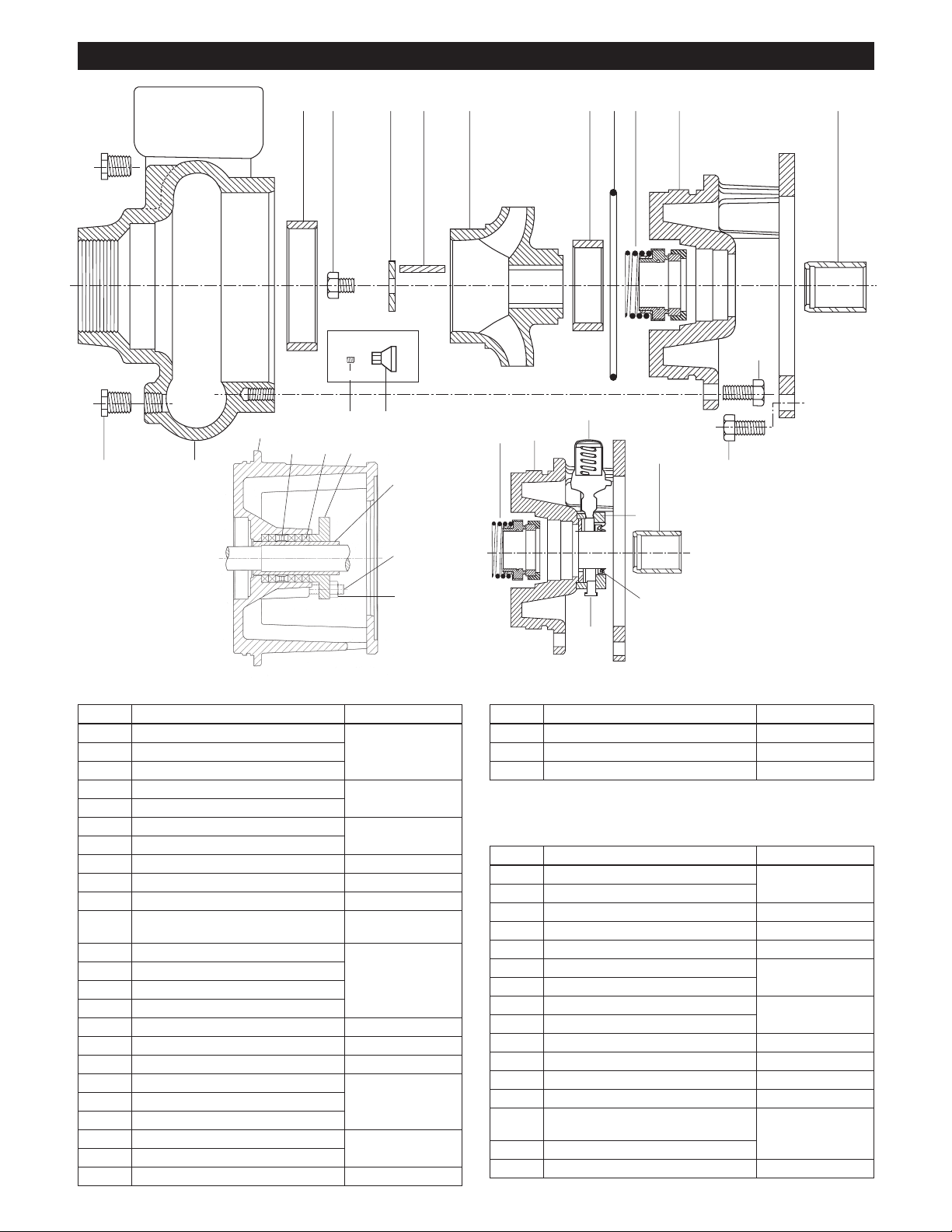
Repair Parts Series 3656/3756
SAE M & L
Replaces 6 & 7
4 6 7 8 2 5 9 10 3 11
13
3
2222A
16 17 18
12 1
19
20
21
Packed Box Arrangement
LIQUID END COMPONENTS
Item No. Description Material
1 Casing
2 Impeller Cast iron or Sil-brass*
3 Adapter
4 Wear ring (casing) Cast iron or bronze*
5** Wear ring (seal housing)
6 Impeller bolt
7 Impeller washer
AISI Type 300
stainless steel
8 Impeller key Steel
9 Seal housing o-ring (optional materials) BUNA-N/EPR/Viton
10 Mechanical seal Consult factory
11 Shaft sleeve AISI Type 300
stainless steel
12 Drain plug – ¼ or 3⁄8 NPT
13 Hex head cap screw (casing to adapter) Zinc plated steel
14 Hex head cap screw (adapter to motor/frame)
15 Hex head cap screw (Adapter to seal housing)
16 Lantern ring Teflon™
17 Packing, 5 rings Teflon™ impregnated
18 Gland AISI 300SS
19 Shaft sleeve
20 Gland stud
AISI Type 300
stainless steel
21 Gland nut
22 Impeller nut (SAE only) 304 SS
22A Set screw, impeller nut (SAE only)
23 Grease feeder (oiler optional) Polycarbonate
12
23
3
10
11
14
24
26
25
Prime Safe Arrangement (optional – M & L group only)
LIQUID END COMPONENTS
Item No. Description Material
24 Grease gland Aluminum
25 Pipe plug Zinc plated steel
26 Lip seal Buna
* Lead free
** Item #5 supplied on S-group model 2½ x 3-7 (7½, 10 and 15 HP) and
M-group (except 3 x 4-10).
POWER END COMPONENTS (shown on next page)
Item No. Description Material
112 Ball bearing (outboard) Steel
122 Pump shaft
122A Pump shaft (SAE) AISI 4140 steel
123 V-ring, deflector BUNA-N
134 Bearing cover Cast iron
138 Lip seal (outboard) BUNA-N
139 Lip seal (inboard)
168 Ball bearing (inboard) Steel
193 Grease fitting (M & L group)
327C Screw (cover to adapter) (SAE only) Zinc plated steel
340 Adapter/engine (SAE only) Cast iron
361 Retaining ring Steel
370C Hex head cap screw (frame to cover) Zinc plated steel
371C Hex head cap screw (adapter to frame)
(SAE only)
NOT SHOWN
Steel
399 Key, coupling
501N Cover/adapter (SAE only) Galvanized steel
Page 13
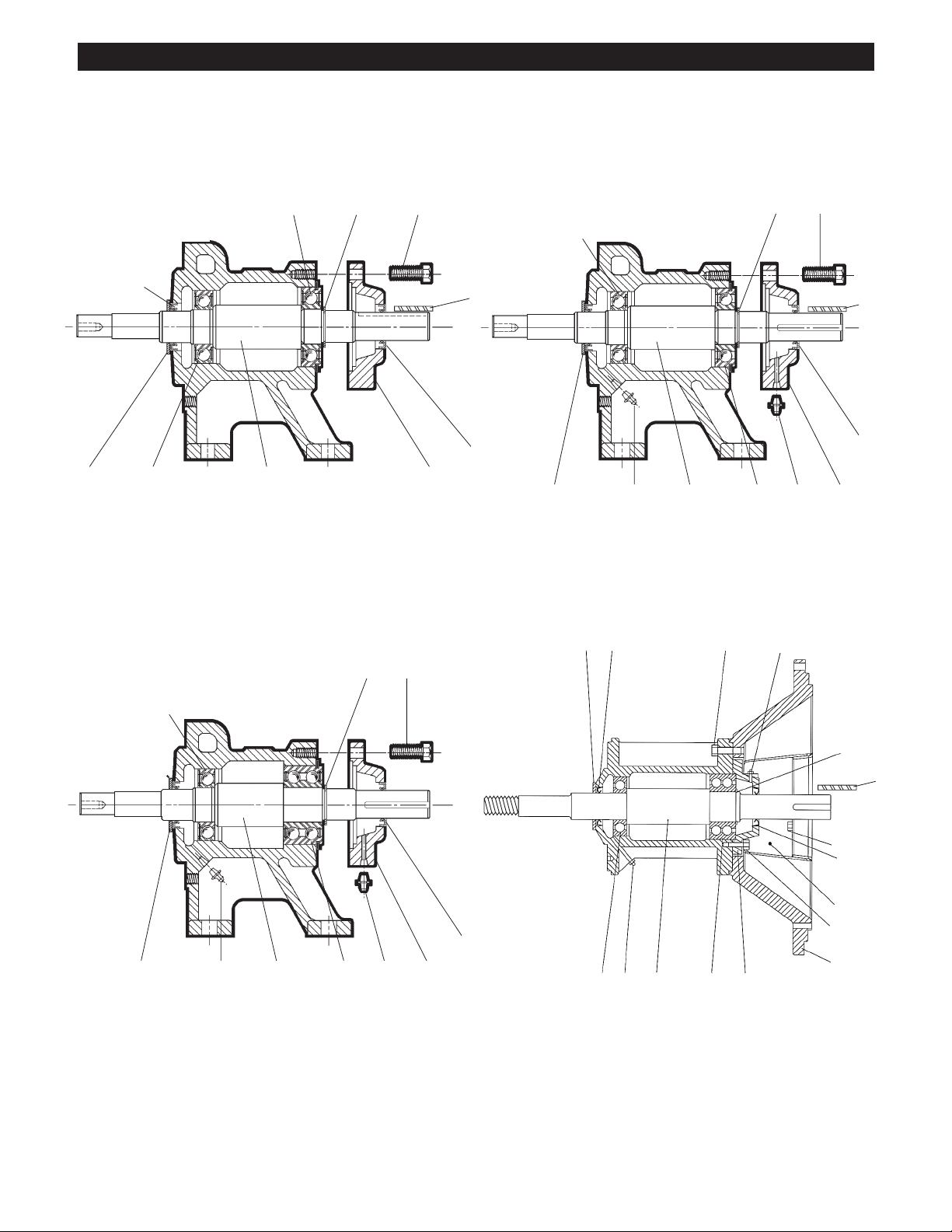
3656/3756 Power Frames
370C
361 370C112
168
361
139
123 168 122 134
S-Group Power Frame M-Group Power Frame
370C
361
168
399
138
123
139
371L
112122193123
399
138
193 134
193
139
399
138
193 134
112122193123
122A
112193168
L-Group Power Frame SAE Power Frame
361
399
327C
138
501N
370C
340
134
13
Page 14
GOULDS WATER TECHNOLOGY LIMITED WARRANTY
This warranty applies to all water systems pumps manufactured by Goulds Water Technology.
Any part or parts found to be defective within the warranty period shall be replaced at no charge to the dealer during the warranty period. The warranty period shall exist for a
period of twelve (12) months from date of installation or eighteen (18) months from date of manufacture, whichever period is shorter.
A dealer who believes that a warranty claim exists must contact the authorized Goulds Water Technology distributor from whom the pump was purchased and furnish complete
details regarding the claim. The distributor is authorized to adjust any warranty claims utilizing the Goulds Water Technology Customer Service Department.
The warranty excludes:
(a) Labor, transportation and related costs incurred by the dealer;
(b) Reinstallation costs of repaired equipment;
(c) Reinstallation costs of replacement equipment;
(d) Consequential damages of any kind; and,
(e) Reimbursement for loss caused by interruption of service.
For purposes of this warranty, the following terms have these definitions:
(1) “Distributor” means any individual, partnership, corporation, association, or other legal relationship that stands between Goulds Water Technology and the dealer in
purchases, consignments or contracts for sale of the subject pumps.
(2) “Dealer” means any individual, partnership, corporation, association, or other legal relationship which engages in the business of selling or leasing pumps to customers.
(3) “Customer” means any entity who buys or leases the subject pumps from a dealer. The “customer” may mean an individual, partnership, corporation, limited liability
company, association or other legal entity which may engage in any type of business.
THIS WARRANTY EXTENDS TO THE DEALER ONLY.
Xylem, Inc.
2881 East Bayard Street Ext., Suite A
Seneca Falls, NY 13148
Phone: (800) 453-6777
Fax: (888) 322-5877
www.xyleminc.com/brands/gouldswatertechnology
Goulds is a registered trademark of Goulds Pumps, Inc. and is used under license.
© 2012 Xylem Inc. IM010 Revision Number 8 July 2012
Page 15
MANUAL DE INSTRUCCIÓN
IM010
Modelos 3656 y 3756
INSTRUCCIONES DE INSTALACIÓN, FUNCIONAMIENTO Y MANTENIMIENTO
Page 16

Información del propietario
Por favor anote los siguientes datos y entregue el manual al
dueño de casa. Encontrará información sobre garantía en
la página 28.
Número de modelo:
Número de serie:
Comercio donde se adquirió:
Teléfono del comercio:
Fecha de compra: Fecha de instalación:
Índice
TÓPICO PÁGINA
Instrucciones de seguridad ........................................... 16
Descripción y especificaciones ..................................... 16
Datos de ingeniería ...................................................... 16
Instalación ................................................................... 16
Ubicación ................................................................. 16
Bombas de acoplamiento corto ................................ 16
Bombas de montaje en bastidor ................................ 17
Bombas accionadas por motor SAE.............................. 17
Alineación del acoplamiento ........................................ 20
Bombas de montaje en bastidor únicamente ............. 20
Tuberías ....................................................................... 20
Succión .................................................................... 20
Descarga .................................................................. 21
Cableado y puesta a tierra ........................................... 21
Rotación ...................................................................... 21
Operación ................................................................... 21
Mantenimiento ............................................................ 22
Desarmado .................................................................. 22
Reensamblaje ............................................................... 23
Instrucciones para la caja prensaestopas ....................... 24
Guía de identificación y resolución de problemas ........ 25
Partes de repuesto........................................................ 26
Garantía limitada ......................................................... 28
16
Page 17

INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD
PELIGRO
ADVERTENCIA
PRECAUCIÓN
ADVERTENCIA
Los fluidos peligrosos
pueden causar
incendios, quemaduras
o la muerte.
ATENCIÓN: INSPECCIONE LA UNIDAD E INFORME
INMEDIATAMENTE AL TRANSPORTISTA
DE CUALQUIER DAÑO QUE ENCUENTRE.
DESCRIPCIÓN Y ESPECIFICACIONES
Las bombas de la serie 3656/3756 son bombas centrífugas
de una etapa con succión en el extremo, para la transferencia
general de líquidos, aplicaciones de refuerzo, riego y servicios
generales de bombeo. Están disponibles en tres materiales
distintos: todo hierro, con accesorios de bronce o todo bronce
(grupo “S” únicamente).
Los impulsores de la bomba están completamente encerrados,
son accionados por chaveta y se mantienen en posición con
un perno y una arandela. Las carcasas tienen diseño de voluta
completa con anillos de desgaste reemplazables.
Dependiendo del tamaño de la bomba, las conexiones de
succión y descarga son roscadas o con bridas. Los ejes están
protegidos por camisas de acero inoxidable.
Las unidades de acoplamiento corto tienen motores NEMA
JM o JP estándar con montaje en cara C y extensión del eje
accionado por chaveta. Las unidades con accionamiento SAE
se sujetan con pernos directamente a la cubierta del volante del
motor en los modelos de tamaño SAE 1, 2, 3, 4 y 5. Para los
volantes de 6½, 7½, 8, 10, 11½ y 14 pulgadas, hay disponibles elementos
PARA EVITAR LESIONES PERSONALES GRAVES O
FATALES Y SERIOS DAÑOS MATERIALES, LEA Y SIGA
TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD EN EL
MANUAL Y EN LA BOMBA.
Este es un SÍMBOLO DE ALERTA
relacionado con la seguridad. Cuando
encuentre este símbolo en la bomba o en el
manual, busque una de las siguientes palabras
de advertencia y esté alerta a las potenciales
lesiones personales o daños materiales.
Advierte sobre peligros que CAUSARÁN
lesiones personales graves, muerte o daños
materiales mayores.
Advierte sobre peligros que PUEDEN causar
lesiones personales graves, muerte o daños
materiales mayores.
Advierte sobre peligros que PUEDEN causar
lesiones personales o daños materiales.
ATENCIÓN: INDICA QUE A CONTINUACIÓN
ENCONTRARÁ INSTRUCCIONES
ESPECIALES MUY IMPORTANTES,
LAS CUALES DEBE OBSERVAR.
ESTE MANUAL HA SIDO CREADO COMO UNA GUÍA
PARA LA INSTALACIÓN Y OPERACIÓN DE
LA UNIDAD. REPASE EN DETALLE TODAS
LAS INSTRUCCIONES Y ADVERTENCIAS ANTES
DE REALIZAR CUALQUIER TRABAJO EN ESTA
BOMBA.
CONSERVE TODAS LAS CALCOMANÍAS DE
SEGURIDAD.
ESTA UNIDAD NO HA SIDO DISEÑADA PARA OPERAR CON LÍQUIDOS
PELIGROSOS O GASES INFLAMABLES.
elastómeros para acoplamiento. Las unidades
para montaje en bastidor se pueden acoplar a motores a
través de un acoplamiento espaciador, o pueden ser accionadas por correa.
Datos de ingeniería
Temperatura máxima del líquido:
212ºF (100ºC) - sello o empaque estándar
250ºF (120ºC) - sello de alta temperatura opcional
Presión máxima de trabajo (dependiendo de la temperatura
del fluido):
- conexiones NPT, 200 PSI (1379 kPa)
- conexiones con brida ANSI de 125 lbs., 200 PSI (1379 kPa)
Presión máxima de succión: 100 PSI (689.5 kPa)
Arranques por hora: 20, distribuidos uniformemente
Grupo Tamaño Succión Descarga
1½ x 2-6 (H) 2" NPT 1½" NPT
1 x 2-7 2" NPT 1" NPT
2½ x 3-7 3" NPT 2½" NPT
S
1 x 2-8 2" NPT 1" NPT
1½ x 2-8 2" NPT 1½" NPT
2 x 2-5 2" NPT 2" NPT
2½ x 2½-5 2½" NPT 2½" NPT
LH 3 x 3-5 3" NPT 3" NPT
4 x 4-5 4" Brida 4" Brida
5 x 5-6 5" Brida 5" Brida
2½ x 3-8 3" NPT 2½" NPT
3 x 4-8 4" Brida 3" Brida
4 x 5-8 5" Brida 4" Brida
1½ x 2-10 2" NPT 1½" NPT
2½ x 3-10 3" Brida 2½" Brida
4 x 6-10 6" Brida 4" Brida
2½ x 3-13 3" Brida 2½ " Brida
3 x 4-13 4" Brida 3" Brida
4 x 6-13 6" Brida 4" Brida
6 x 8-13 8" Brida 6" Brida
L 8 x 10-13 10" Brida 8" Brida
4 x 6-16 6" Brida 4" Brida
3 x 4-7 4" Brida 3" Brida
M
3 x 4-10 4" Brida 3" Brida
Instalación
UBICACIÓN
• Ubique la bomba tan cerca de la fuente de líquido como
resulte práctico y por debajo del nivel del líquido para
permitir el cebado automático.
• Deje suciente espacio para ventilación y tareas de
manteni-miento. Proteja la unidad de las inclemencias del
tiempo y daños causados por lluvias, inundaciones o
temperaturas bajo cero.
• Proteja la bomba y las cañerías de temperaturas bajo cero.
• Deje suciente espacio alrededor de la unidad para
ventilación y tareas de mantenimiento.
BOMBAS DE ACOPLAMIENTO CORTO
• Estas unidades se pueden instalar en forma horizontal,
inclinada o vertical con el motor sobre la bomba.
• Los pies del motor DEBEN abulonarse a una superficie
resistente (horizontal o vertical) que sea capaz de brindar un
soporte completo y rígido para la bomba y el motor. Para
las bombas del grupo L, los pies del adaptador del motor
también deben estar abulonados a la superficie de apoyo.
• Para la operación vertical, el motor debe equiparse con una
cubierta antigoteo o protegerse de alguna otra manera para
evitar que entre líquido (lluvia, rociado, condensación, etc.).
ATENCIÓN: NO INSTALE EL MOTOR POR DEBAJO DE
LA BOMBA. CUALQUIER PÉRDIDA O
CONDENSACIÓN AFECTARÁ AL MOTOR.
17
Page 18

BOMBAS DE MONTAJE EN BASTIDOR
• Se DEBE proveer una superficie de base substancial para
evitar la distorsión o la tensión al ajustar los bulones de la
base de montaje. Se puede utilizar un montaje de caucho
para reducir el ruido y la vibración excesiva.
• Ajuste los pernos de sujeción del motor ANTES de conectar
la tubería a la bomba.
Lechada completa
1
/2 a 3/4 pulg.)
(
Espacio para
nivelar
Marco de
madera
(
Cuñas o planchas de relleno para nivelar - quedan en su lugar
Manga
Arandela
Lengüeta
BaseOrificio para lechada
Parte superior de la base
- limpiar y mojar
Lechada
1
/4”)
Figura 1
• Se recomienda enlechar la placa de base a un cimiento con
zapata sólida. Consulte la figura 1.
• Coloque la unidad en posición sobre cuñas ubicadas en las
cuatro puntas, dos debajo del centro aproximado del motor
accionador y dos debajo del centro aproximado de la bomba.
Ajuste las cuñas para nivelar la unidad. Nivele o verifique con
plomada las conexiones de succión y descarga.
• Asegúrese de que la placa de base no está distorsionada y que
la alineación final del acoplamiento se puede efectuar dentro
de los límites de movimiento del motor, con la ayuda de cuñas
si fuera necesario.
• Ajuste los pernos de la base con la mano y construya una presa
alrededor de la base. Vierta la lechada debajo de la placa de base
asegurándose de llenar completamente las áreas debajo de los
pies del motor y de la bomba. Deje endurecer la lechada por 48
horas antes de ajustar completamente los pernos de la base.
• Ajuste los bulones de sujeción de la bomba y el motor antes de
alinear el eje o conectar la cañería a la bomba.
• Deje endurecer la lechada por 48 horas antes de ajustar los 4
pernos de la base.
Bombas accionadas por motor SAE
La caja de cojinetes del motor de accionamiento SAE está diseñada para sujetarla directamente a la cubierta del motor para
los montajes SAE tamaño 1, 2, 3, 4 y 5. La extensión del eje de
la bomba es del tamaño apropiado para acoplamientos abulonados directamente al volante. Goulds Water Systems ofrece
acoplamientos opcionales para los volantes de 6½, 7½, 8, 10
y 14 pulgadas. Si bien se pueden utilizar otros acoplamientos
de montaje en el volante, recomendamos el uso de los acoplamientos de Goulds Water Systems para asegurar la operación
prolongada y sin inconvenientes de la bomba.
REQUISITOS PARA UNA CORRECTA OPERACIÓN
Extremo de la bomba
Cuando se libere la capacidad requerida (GPM) a la tubería
del sistema, la bomba deberá añadir la cantidad de Altura
requerida por el sistema a tal capacidad. El punto de capacidad
de altura de operación debe encontrarse lo más cerca posible
a la mayor línea de rendimiento que se muestra en la curva
de desempeño, y debe encontrarse por debajo de la línea de
capacidad de altura indicada como “máxima” RPM. La máxima velocidad de operación RPM para la bomba se encuentra
determinada por la antigüedad del cojinete o, en ciertos casos,
18
por los límites de presión de la bomba. Las aberturas de succión y descarga tienen roscas NPT para tuberías estándar, o
recubiertas y taladradas según norma ANSI B16.1, clase 125
para bridas estándar de acuerdo con lo indicado. La presión
máxima de trabajo para el hierro fundido clase 30, según la
norma ANSI B16.1, es 175 PSI.
Los motores de combustión interna son de velocidad variable
y de potencia variable. La salida de potencia depende de la
velocidad del motor (RPM) y se reducirá al operar la altitud
y/o los aumentos de la temperatura aérea. Cuando se acciona
la bomba a las RPM requeridas para distribuir el agua en la
tubería del sistema, el motor debe operar dentro de los límites
mínimos y máximos de RPM establecidos por el fabricante
del motor. Luego de la reducción de la potencia nominal de
todos los accesorios del motor que consumen energía y el
ajuste de la altitud y la temperatura aérea del sitio de instalación, la salida de potencia que suministra la potencia demandada por la bomba no debe exceder la potencia nominal
continua del motor.
CALIBRACIÓN DEL GRUPO DE ENGRANAJES CONDUCTORES (BHP)
La ecuación para obtener el BHP es: (Flujo x TDH) / 3960 x
Rendimiento).
Nota: Para las unidades de combustión interna el cálculo del
BHP debe disminuirse de acuerdo con las siguientes
condiciones:
• 20% por servicio continuo
• 5% por accionamiento de ángulo recto
• 3% por cada 1.000 pies sobre el nivel del mar
• 1% por cada 10º F sobre 60º F.
CALIBRACIÓN DEL GRUPO DE ENGRANAJES CONDUCTORES (TORQUE)
Además de la calibración de un motor por BHP, también se
requieren cálculos de torque para una correcta calibración.
Generalmente, la potencia y el torque nominal no mantienen
la misma relación durante el rango utilizable de un motor
diesel (Figura 2). La ecuación para obtener el torque (libras/
pies) es (5250 x BHP) / RPM.
600
500
400
300
200
Torque (libras/pies)
100
0
1500 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 2100 2200 2300
RPM
180
178
176
174
172
170
168
166
164
162
160
Figura 2: HP (◆) vs. Torque (■)
VERIFIQUE LA COINCIDENCIA DEL EXTREMO DE LA BOMBA Y EL
MOTOR
Tamaño de la abrazadera SAE
A las bombas accionadas por motor se les pueden colocar
motores que poseen desde una cubierta del volante estándar
SAE 5 hasta una SAE 1.
En el caso de un motor nuevo, el proveedor del motor puede
suministrar el número de cubierta SAE.
En el caso de un motor existente, puede medir el orificio de
la cubierta del volante y la circunferencia de los agujeros de
los pernos y luego compararlos con las dimensiones estándar
de cubierta SAE detalladas en la Tabla 1, para identificar el
número de cubierta SAE.
HP
Page 19

Mida el orificio de la cubierta del volante (A) y la circunferencia de los agujeros de los pernos (B), con la mayor precisión
posible, con una cinta métrica (a la medida más cercana a
1/32 pulgada).
• Cuente la cantidad de oricios roscados en la cubierta del
volante (C). Pruebe los orificios roscados con un perno,
para determinar la serie de rosca.
• Compare las dimensiones tomadas (A), (B), (C) con la Tabla
1 para determinar el número SAE de la cubierta del volante,
para asegurarse de que coincida con el número SAE de su
bomba.
Dimensiones
Tamaño de la cubierta del volante SAE
de la cubierta
1 2 3 4 5
del volante
A 201⁄8 175⁄8 161⁄8 141⁄4 123⁄8
B 207⁄8 183⁄8 167⁄8 15 131⁄8
C Nº 12 12 12 12 8
Tamaño 7⁄16-14
3
⁄8-16
3
⁄8-16
3
⁄8-16
3
⁄8-16
Tabla 1
Motor
Figura 3
INSTALACIÓN
• La bomba se puede instalar en posición horizontal, con la
descarga girada hacia cualquier posición permitida por el
patrón de los pernos de la carcasa (13). Se recomienda que
la descarga se encuentre en posición horizontal, por encima
de la succión.
• En todas las bombas la carcasa debe estar sostenida por un
soporte rígido sujeto al cimiento o base de la unidad.
• Para las bombas del grupo M, se recomienda que dicho
soporte se sujete con 2 o más pernos de la carcasa (13) al
anillo adaptador del motor. Probablemente se requieran
pernos más largos para el grosor adicional del soporte.
Utilice pernos SAE grado 5, torsionados según se indica en
este manual.
NOTA: Cuando el acoplamiento se encuentre correctamente montado, el
buje no llegará al fondo en las ranuras del eje. Si tocara fondo, retraiga el
acoplamiento en el eje según se muestra, para ganar espacio.
• Para las bombas del grupo L, se recomienda que la bomba
se apoye debajo de los dos pies fundidos en el adaptador
del motor (3). Dichos pies deben sujetarse con pernos al
soporte.
MONTAJE DE LA BOMBA SOBRE EL MOTOR (ACOPLAMIENTO RANURADO)
Preparación para el montaje de la bomba sobre el motor
• Limpie la supercie y controle que coincidan la cubierta del
volante y el volante según sea necesario para quitar toda
la grasa, suciedad o polvo (y todos los rastros de antioxidante), que interferirían en la instalación de la bomba y/o
impedirían la correcta alineación. Si el volante se coloca
mediante un cojinete piloto para un eje de transmisión,
quítelo y deséchelo. No se necesita el cojinete piloto para la
instalación del extremo de la bomba, y puede interferir con
el eje de la bomba.
• Examine detenidamente la ranura del eje. Utilice una lima,
si es necesario, para quitar toda la rebaba que impediría el
libre desplazamiento del acoplamiento sobre el eje.
• Lubrique moderadamente la ranura del eje de la bomba con
grasa liviana. No lubrique el eje recto con chaveta.
• Deslice el acoplamiento sobre el eje hasta que se detenga
contra el eje (remítase a la página 5 para la instalación del
eje recto).
• Mida la distancia existente desde el lado del motor del anillo adaptador de acoplamiento del volante hasta la superficie de montaje de la abrazadera de la bomba. Remítase a la
Figura 4 debajo, Dimensión “A”.
• Luego, mida la profundidad existente desde la supercie de
la cubierta del volante sobre el motor hasta la superficie del
volante contra la cual se colocará con pernos el acoplamiento. Remítase a la Figura 4 debajo, Dimensión “B”.
• La medición de la bomba debe ser inferior a la medición
del motor porque sino la interferencia axial producirá una
fuerza de empuje sobre los cojinetes de cigüeñal del motor.
Dicho de manera simple, la Dimensión “A” debe ser inferior
a la Dimensión “B”.
ACOPLAMIENTO DEL VOLANTE
• El acoplamiento del volante transmite la potencia desde el
volante del motor hasta el eje de la bomba. El máximo de
potencia que un acoplamiento puede manejar sin peligros
se demuestra en un número nominal, “R”, que se detalla en
las tablas de dimensiones de acoplamiento.
• Al escoger un acoplamiento del volante para una bomba y
un motor, primero determine la potencia nominal que la
Controle la distancia antes
de operar la bomba
Motor
La dimensión “A” DEBE ser inferior a
la dimensión “B”.
Abrazadera
Abrazadera
de la bomba
Imposible – (A es
mayor que B)
Abrazadera
de la bomba
Posible – (A es
menor que B)
Motor
de la bomba
Instalación
preferida
Figura 4 Figura 5
Instalación
alternativa
19
Page 20

bomba demandará. En la curva de desempeño de la bomba,
obtenga los valores de RPM y BHP necesarios para producir el punto de aplicación de la capacidad de altura.
• Divida el BHP por EL RPM, luego multiplique el resultado
por 100. El resultado será el número de demanda de la
bomba. Por ejemplo, una 20BFSAE1AO puede liberar 800
GPM a 270 pies de Altura total mientras funciona a 1800
RPM. La potencia requerida por la bomba será de 75 BHP.
El número de demanda será: (75 / 1800) x 100 = 4.16
• Luego, seleccione un acoplamiento que pueda transmitir sin
peligros la potencia y que se adecuará a las dimensiones del
volante. Para que un acoplamiento resulte adecuado debe
poseer un número nominal “R” MAYOR QUE el número
de demanda de la bomba. En el ejemplo anterior, el mínimo
número “R” de acoplamiento sería 5.
• La compatibilidad de torsión del motor, la bomba y el
acoplamiento es responsabilidad de quien realiza el montaje. Goulds Water Systems suministrará los datos necesarios
sobre la bomba y el acoplamiento para ser utilizados por
quien realiza el montaje en una análisis torsional.
NOTA: Si el volante se coloca con un cojinete piloto pre-
sionado en un orificio en el centro, quítelo para evitar la
interferencia con el eje de la bomba.
VOLANTE PARA EMBRAGUES DE SOBRECENTRO DE TIPO INDUSTRIAL
• La Figura 3 muestra la apariencia ahuecada de los
volantes fabricados para ser utilizados en montajes de
despegue propulsados con embragues de sobrecentro.
• Dichos volantes poseerán un oricio empotrado
mecanizado en la superficie, y un conjunto de agujeros
de colada, que serán utilizados para conectar el acoplamiento al volante. Las dimensiones se encuentran
determinadas por el estándar SAE y se detallan en las
Tabla 1A y 1B, Figura 3. El “tamaño del embrague”
que se muestra en la tabla es el diámetro nominal del
recubrimiento del embrague para Embragues de sobrecentro con anillo de accionamiento.
OTROS VOLANTES
• Ciertos motores están equipados con volantes especialmente mecanizados para acoplarse a otros tipos de
maquinaria (generadores eléctricos, convertidores de
torque, etc.) y necesitan de acoplamientos de volante
que no sean estándar. Estos pueden adquirirse por
medio de vendedores o proveedores.
Volantes para embrague de
Motor
sobrecentro de tipo industrial
Acoplamiento
del volante
-10T
(número de ranura)
Diámetro
de la ranura
Figura 6
Tabla IA –
Rango amplio de RPM, Buje montado elastomérico –
Eje ranurado
Tamaño Dimensiones del volante Acoplamiento del volante (Ranurado)
del D diám. de
emb rague (UNC) Catálago del eje
6½" 6 5⁄16-18 8½ OD 7.88 3.94 1.19 1.69 7 A00569C 1 1½" 10T
7½" 8 5⁄16-18 9½" OD 8.75 3.69 1.19 1.69 7 A00569C 2 1½" 10T
8" 6 3⁄8-16 103⁄8" OD 9.62 4.81 2.44 2.94 7 A00569C 3 1½" 10T
10" 8 3⁄8-16 123⁄8" OD 11.62 4.47 2.13 2.75 7 A00569C 4 1½" 10T
10" 8 3⁄8-16 123⁄8" OD 11.62 4.47 2.13 2.75 9 A00569C 6 1½" 10T
11½" 8 3⁄8-16 137⁄8" OD 13.12 5.06 1.56 2.69 7 A00569C 5 1½" 10T
11½" 8 3⁄8-16 137⁄8" OD 13.12 5.06 1.56 2.69 9 A00569C 7 1½" 10T
14" 8 ½-13 183⁄8" OD 17.25 6.63 1.00 2.13 9 A00569C 8 1½" 10T
OD = Diámetro exterior
*R = Máxima potencia nominal del acoplamiento
Potencia nominal del acoplamiento = (Potencia Nominal x 100) / RPM nominal
Tamaño E BC F G H R* Nº del la ranura
Cant.
Table IB –
Rango amplio de RPM, Buje montado elastomérico –
Eje recto
Tamaño Dimensiones del volante Acoplamiento del volante (Ranurado)
del D diám. de
emb rague (UNC) Catálago del eje
6½" 6 5⁄16-18 8½ OD 7.88 3.94 1.19 1.69
3.51 CD625
7½" 8 5⁄16-18 9½" OD 8.75 3.69 1.19 1.69
3.51 CD725
8" 6 3⁄8-16 103⁄8" OD 9.62 4.81 2.44 2.94
3.51 CD825
2.28 CD1016
3.51 CD1025
10" 8 3⁄8-16 123⁄8" OD 11.62 4.47 2.13 2.75 5.71 CD1030
8.57 CD1050
11.23 CD1080
2.28 CD1116
3.51 CD1125
5.71 CD1130
11½" 8 3⁄8-16 137⁄8" OD 13.12 5.06 1.56 2.69 8.57 CD1150
11.23 CD1180
12.62 CD1190
16.85 CD11110H
2.28 CD1416
3.51 CD1425
5.71 CD1430
14" 8 3⁄8-16 183⁄8" OD 17.25 6.63 1.00 2.13 8.57 CD1450
11.23 CD1480
12.62 CD1490
16.85 CD14110H
OD = Diámetro exterior
Dimensiones en pulgadas
*R = Máxima potencia nominal del acoplamiento
Potencia nominal del acoplamiento = (Potencia Nominal x 100) / RPM nominal
Tamaño E BC F G H R* Nº del la ranura
Cant.
2.28 CD616
2.28 CD716
2.28 CD816
1.625-
1.624 Ø
Ranura de
3
⁄8 x 3⁄
16
• Para los acoplamientos Goulds Water Systems con chaveta
de eje recto – Asegúrese de que el tornillo de fijación del
rodete de acoplamiento se encuentre lo suficientemente
retraído como para asegurar espacio para la chaveta del eje
durante el montaje.
20
Page 21

Las maquinarias
peligrosas pueden
causar lesiones
personales o la muerte.
ADVERTENCIA
• Monte el ensamblaje de acoplamiento en el volante del
motor utilizando los pernos suministrados, ajustándolos en
zigzag de la siguiente manera:
Volante de 6½ ó 7½ " – 11 libras-pie (15 N·m)
Volante de 8, 10 o 11½ ” – 20 libras-pie (27 N·m)
Volante de 14” - 50 libras-pie (68 N·m)
(Para otros acoplamientos, respete el procedimiento de
instalación recomendado por sus fabricantes.)
• Coloque la chaveta del eje de la bomba en el eje (122) y
alinee el eje con el acoplamiento. Deslice la bomba dentro
del acoplamiento hasta que el anillo adaptador del motor
(340) esté en contacto con la cubierta del volante del motor.
INSTALACIÓN DEL ACOPLAMIENTO EN EL VOLANTE
Acoplamiento del volante de sobrecentro:
• Estos acoplamientos se encuentran alineados en forma
concéntrica con el volante mediante el montaje de registro
del volante.
• Asegúrese de quitar todos los protectores del volante del
motor.
• Coloque el acoplamiento dentro del volante. Alinee los
agujeros de los pernos y conecte el acoplamiento con el
montaje de registro en el volante. Golpee ligeramente el
acoplamiento con un martillo pesado dúctil, si es necesario,
para asegurarse que se encuentra aplastado contra el
volante. Asegure fuertemente el acoplamiento al volante
con tornillos tipo “capscrew” y arandela de presión.
INSTALACIÓN DE LA BOMBA EN EL MOTOR
• Eleve la bomba utilizando un aparato de elevación adecuado y alinee el eje de la bomba con el acoplamiento. El
extremo del eje de la bomba posee un diámetro piloto que
facilita el encaje del eje de la bomba en el acoplamiento.
• Introdúzcalo en la abertura de succión de la bomba y gire
el impulsor ligeramente hasta que el eje se conecte con el
acoplamiento. Verifique que no existan espacios entre las
superficies de la abrazadera y la cubierta del volante. Gire la
bomba lo necesario para alinear los agujeros de la abrazadera con el motor. Instale los tornillos tipo “capscrew” y
sujete con pernos el extremo de la bomba al motor.
NOTA: Si se detectara alguna interferencia o
incompatibilidad de las partes durante
la instalación, NO prosiga con el montaje. Notifique
el problema al distribuidor de Goulds Water Systems
más cercano.
• Monte la bomba en el motor utilizando los pernos y
arandelas de seguridad provistos y ajústelos en zigzag
como sigue:
SAE No. 2, 3, 4, 5 – 20 libras-pie (27 N . m)
SAE No. 1 - 50 libras-pie (68 N . m)
• Instale los protectores de acoplamiento (501N).
• Sujete con pernos el adaptador del motor (3) al soporte
rígido descripto anteriormente.
Alineación del acoplamiento
EL NO DESCONECTAR Y BLOQUEAR
LA ALIMENTACIÓN ELÉCTRICA
ANTES DE INTENTAR TAREAS DE
MANTENIMIENTO PUEDE CAUSAR
LESIONES PERSONALES GRAVES.
BOMBAS DE MONTAJE EN BASTIDOR ÚNICAMENTE
• Se DEBE controlar la alineación antes de operar la bomba.
Observe la figura 7.
Paralelo
Angular
Figura 7
• Ajuste todos los bulones de sujeción antes de vericar
la alineación.
• Si fuera necesario realinear, mueva siempre el motor.
Coloque planchas de relleno según sea necesario.
• Desalineación paralela, ejes con línea de centro paralela pero
no concéntrica. Coloque el indicador de dial en un rodete y
haga girar el rodete 360° mientras registra las lecturas en el diámetro exterior del otro rodete. La alineación paralela se logra
cuando la lectura es 0.010 pulg. (0.254 mm) TIR o menos.
• Desalineación angular, ejes con línea de centro concéntrica
pero no paralela. Coloque el indicador de dial en un rodete
y haga girar el rodete 360º mientras registra las lecturas
en la cara del otro rodete. La alineación angular se alcanza
cuando la lectura es 0.020 pulg. (0.508 mm) TIR o menos.
• La alineación nal se alcanza cuando se satisfacen los requisitos paralelos y angulares con los bulones de sujeción del
motor completamente ajustados.
ATENCIÓN: SIEMPRE VUELVA A VERIFICAR AMBAS
ALINEACIONES LUEGO DE EFECTUAR
CUALQUIER AJUSTE MECÁNICO.
Tuberías
• La tubería no debe ser menor que las conexiones de
succión y descarga de la bomba, y debe ser lo más corta
posible. Evite conexiones innecesarias para minimizar las
pérdidas por fricción. Observe la tabla 1.
• Toda la tubería DEBE estar soportada en forma indepen-
diente y NO DEBE existir ninguna carga de la tubería sobre
la bomba.
ATENCIÓN: NO FUERCE LA TUBERÍA EN LAS
CONEXIONES DE SUCCIÓN O
DESCARGA.
• Todas las juntas de la tubería DEBEN ser herméticas.
TUBERÍA – SUCCIÓN
• Para elevaciones de succión de más de 10 pies (3 m) y líquidos con temperaturas de más de 120º F (49° C), consulte la
curva de desempeño de la bomba para la carga de succión
positiva neta requerida (NPSHR).
• Si es necesario utilizar un tamaño de tubería mayor que
el tamaño de la succión de la bomba, se DEBE instalar un
reductor de caño excéntrico (con el lado recto hacia arriba)
en la succión de la bomba.
• Si la bomba se instala por debajo de la fuente de líquido,
instale una válvula de aislamiento total de flujo en la succión
de la bomba para tareas de inspección y mantenimiento.
ATENCIÓN: NO USE LA VÁLVULA DE AISLAMIENTO
DE SUCCIÓN PARA AHOGAR LA BOMBA.
DE HACERLO, PODRÍA OCASIONAR LA
PÉRDIDA DE CEBADO, TEMPERATURAS
EXCESIVAS O DAÑOS A LA BOMBA, Y
ADEMÁS ANULARÁ LA GARANTÍA.
21
Page 22

• Si la bomba se instala por encima de la fuente de líquido, se
ADVERTENCIA
Un voltaje peligroso puede
producir golpes el ctricos,
quemaduras o la muerte.
Las maquinarias
peligrosas pueden
causar lesiones
personales o la muerte.
ADVERTENCIA
ADVERTENCIA
Un voltaje peligroso puede
producir golpes el ctricos,
quemaduras o la muerte.
ADVERTENCIA
El calor extremo puede
causar lesiones
personales o daños
materiales.
DEBEN seguir los siguientes pasos:
• Para evitar baches de aire, ninguna sección de la tubería
• Incline la tubería hacia arriba desde la fuente de líquido.
• Utilice una válvula de pie o una válvula de retención
• La pantalla o campana de succión DEBE ser al menos 3
• Asegúrese de que el tamaño de la succión de entrada y la
Figura 8 Figura 9
Figura 10 Figura 11
TUBERÍA – DESCARGA
• Instale una válvula de retención capaz de manejar el ujo,
los líquidos y evitar el retroflujo. Después de la válvula de
retención, instale una válvula de compuerta del tamaño
apropiado para regular la capacidad de la bomba y realizar
inspecciones y tareas de mantenimiento.
• Cuando sea necesario, se debe instalar un aumentador del
caño entre la válvula de retención y la descarga de la bomba.
22
debe estar más elevada que la conexión de succión de la
bomba.
SÓLO si fuera necesario para cebar la bomba o mantener
el cebado durante el servicio intermitente.
veces más grande que el diámetro de la tubería de succión.
inmersión mínima de la succión de entrada sean suficientes para que no se produzca la entrada de aire a la bomba
a causa de un arremolinamiento de succión. Consulte las
figuras 8 a 11.
1.5D
mín.
D D
3.0D
mín.
H mín.
D mín.
2
H mín.
D
H mín.
H
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
H = Sumersión mín. en pies
1
12345678910 11121314 1516
V = Velocidad en pies por segundo
= GPM x 0.321
Área
GPM x 0.4085
D
2
D
Cableado y puesta a tierra
Instale el cableado y la puesta a
tierra de acuerdo con los requisitos
locales y al Código Eléctrico Nacional Requisitos.
Instale un interruptor de desconexión
de todos los circuitos de alimentación
eléctrica cerca de la bomba.
Desconecte y bloquee el suministro
eléctrico antes de instalar la bomba o
realizar tareas de mantenimiento.
El suministro eléctrico DEBE ser el que se especifica en
la placa nominal de la bomba. Un voltaje incorrecto
puede provocar un incendio, dañar el motor y anular
la garantía.
Los motores sin protección incorporada DEBEN equiparse con contactores y protectores contra sobrecarga
térmica si son monofásicos, o con arrancadores con
calentadores si son trifásicos. Consulte la placa nominal del motor.
• Use únicamente cable de cobre para la conexión al motor y
a tierra. El cable a tierra DEBE ser por lo menos del mismo
tamaño que el cable al motor. Los cables deben estar codificados con colores para facilitar el mantenimiento.
• Siga cuidadosamente el diagrama de cableado indicado por
el fabricante del motor en la placa nominal o en la tapa de
la terminal.
ADVERTENCIA
Tensión
p
eligrosa
SI LA BOMBA, EL MOTOR O LOS
CONTROLES NO SE CONECTAN A
TIERRA EN FORMA PERMANENTE
ANTES DE CONECTAR LA ALIMENTACIÓN ELÉCTRICA, SE PUEDEN
PRODUCIR DESCARGAS ELÉCTRICAS,
QUEMADURAS Y HASTA LA MUERTE.
Rotación
ATENCIÓN: LA ROTACIÓN INCORRECTA PUEDE
DAÑAR LA BOMBA Y ANULA
LA GARANTÍA.
• La rotación correcta es hacia la derecha, en el SENTIDO
DE LAS AGUJAS DEL RELOJ cuando se mira desde el
extremo del motor. En las unidades montadas en bastidor,
encienda y apague la bomba rápidamente para observar la
rotación. En las unidades de acoplamiento corto, retire el
motor y el tapón o la cubierta para observar la rotación.
• Para invertir la rotación de un motor trifásico, intercambie
dos conductores eléctricos cualesquiera.
Operación
NO HAGA FUNCIONAR LAS UNI-
V
ATENCIÓN: NO HAGA FUNCIONAR LA BOMBA EN
SECO. DE HACERLO, SE DAÑARÁ
EL SELLO.
• Luego de estabilizar el sistema en las condiciones normales
de operación, verifique la tubería. Si fuera necesario, ajuste
los soportes de la tubería.
• En las unidades de montaje en bastidor, la alineación del
acoplamiento puede haber variado debido a las diferencias de
DADES SAE O LAS UNIDADES
MONTADAS EN BASTIDOR SIN LAS
PROTECCIONES DE SEGURIDAD
CORRESPONDIENTES. DE HACERLO,
PODRÍA SUFRIR GRAVES LESIONES
PERSONALES.
SALPICAR O SUMERGIR EN FLUIDOS
UN MOTOR ABIERTO A PRUEBA DE
FILTRACIONES PUEDE PROVOCAR
UN INCENDIO, UNA DESCARGA
ELÉCTRICA, QUEMADURAS, O INCLUSO LA MUERTE.
EL FUNCIONAMIENTO SIN FLUJO O
CON FLUJO MÍNIMO PUEDE CAUSAR
TEMPERATURAS EXCESIVAS, LESIONES PERSONALES O DAÑOS MATERIALES.
Page 23

BOMBAS DE ACOPLAMIENTO CORTO
ADVERTENCIA
Un voltaje peligroso puede
producir golpes el ctricos,
quemaduras o la muerte.
PRECAUCI N
Niveles de presi n
peligrosos pueden causar
lesiones personales o
da os materiales.
Los fluidos peligrosos
pueden causar lesiones
personales o daños
materiales.
ADVERTENCIA
• Los cojinetes están ubicados en el motor y forman parte del
BOMBAS DE MONTAJE EN BASTIDOR
• El modelo 3756 del grupo S cuenta con cojinetes engrasados
• La caja de cojinetes del modelo 3756 de los grupos M y L y
• Siga las instrucciones de lubricación del fabricante del motor y
• Verique nuevamente la alineación.
SERVICIO REGULAR
• Para RETIRAR la bomba del servicio, saque el tapón de
• Para VOLVER A PONER la bomba en servicio, vuelva a
• Reconecte la línea de succión si ha sido desconectada,
• Consulte la sección “OPERACIÓN” del manual.
• Observe TODAS las instrucciones y advertencias de la
temperatura entre la bomba y el motor. Vuelva a controlar la
alineación siguiendo los procedimientos y advertencias de la
sección “ALINEACIÓN DEL ACOPLAMIENTO” de este
manual.
Mantenimiento
EL NO DESCONECTAR Y BLOQUEAR
LA ALIMENTACIÓN ELÉCTRICA
ANTES DE INTENTAR TAREAS DE
MANTENIMIENTO PUEDE CAUSAR
DESCARGAS ELÉCTRICAS,
QUEMADURAS E INCLUSO
LA MUERTE.
SI NO SE LIBERA LA PRESIÓN Y SE
DRENA EL SISTEMA ANTES DE
INTENTAR TAREAS DE
MANTENIMIENTO, SE PUEDEN
PRODUCIR DAÑOS MATERIALES Y
LESIONES PERSONALES,
INCLUYENDO LA MUERTE.
SI SE BOMBEAN FLUIDOS TÓXICOS
O PELIGROSOS, EL SISTEMA DEBE
LAVARSE COMPLETAMENTE CON
UNA DESCARGA DE AGUA ANTES
DE REALIZAR TAREAS DE
MANTENIMIENTO.
mismo. Para obtener información sobre lubricación, consulte
las instrucciones del fabricante del motor.
de por vida. No es posible lubricarlos, y tampoco es necesario.
de accionamiento SAE debe ser lubricada cada 2000 horas o
cada 3 meses, lo que se presente primero. Use grasa con base
de litio o sodio No. 2. Llene hasta que la grasa salga por los
accesorios de alivio o los sellos, luego limpie la grasa excesiva.
el acoplamiento.
drenaje y drene toda la tubería no protegida.
colocar el tapón de drenaje utilizando cinta de Teflon™ o
equivalente en las roscas macho.
inspeccione la unión y repare si fuera necesario.
Desarmado
sección “MANTENIMIENTO” de este manual.
• Unidades de acoplamiento corto: Retire los bulones de
sujeción del motor.
• Unidades montadas en bastidor: Retire los bulones de
sujeción del protector de acoplamiento, espaciador, acoplamiento y bastidor.
EXTREMO DEL LÍQUIDO
1. Retire los bulones de la carcasa (13).
2. Retire de la carcasa el conjunto posterior retractable (1).
3. Retire el anillo de desgaste de la carcasa (4) si se
encuentra muy gastado.
ATENCIÓN: NO INSERTE UN DESTORNILLADOR
ENTRE LAS ALETAS DEL IMPULSOR
PARA EVITAR LA ROTACIÓN.
4. En las unidades de acoplamiento corto, retire el tapón o
cubierta del extremo del motor para dejar a la vista
las partes planas o ranuras para el destornillador en
el extremo del eje del motor.
5. Mientras inmoviliza el eje con una herramienta apropiada
(unidades de acoplamiento corto) o con una llave de
lengüeta (unidades de montaje en bastidor), retire el perno
del impulsor (6). Puede ser necesario tener que calentar
el perno del impulsor con una antorcha para poder
retirarlo. Deséchelo.
ATENCIÓN: TENGA CUIDADO AL MANIPULAR EL
PERNO CALIENTE DEL IMPULSOR.
AVISO: PARA UNIDADES DE IMPULSIÓN SAE, QUITE
EL TORNILLO DE FIJACIÓN DE LA TUERCA
DEL IMPULSOR (22A) ANTES DE CALENTAR
CON EL SOPLETE.
6. Retire la arandela del impulsor (7).
7. Inserte dos barras de palanca a 180° de distancia entre sí,
entre el impulsor (2) y el compartimiento del sello (3).
CON SUMO CUIDADO, haga palanca y retire
el impulsor.
8. Retire la chaveta del impulsor (8).
9. Retire los tornillos del compartimiento de sellos (14) y
el compartimiento (3), sacando con él el conjunto del
sello mecánico. Deseche el conjunto del sello y el anillo en
O del compartimiento del sello (9). Para las bombas con
caja prensaestopas, consulte las “INSTRUCCIONES
PARA CAJA PRENSAESTOPAS”.
10. Retire el adaptador (108).
11. Inspeccione la camisa del eje (11). Si tiene muchas muescas,
retírela calentándola con una antorcha. Deséchela.
ATENCIÓN: TENGA CUIDADO AL MANIPULAR
LA CAMISA DEL EJE CALIENTE.
12. Empuje y saque del compartimiento de sellos el asiento
del sello mecánico estacionario. Deséchelo.
13. En las unidades equipadas con anillo de desgaste (5) en
el compartimiento de sellos, retírelo si se encuentra muy
gastado.
DESMONTAJE DE LA CAJA DE COJINETES O CAJA DE
COJINETES SAE
1. Retire el deflector (123) del eje.
2. Retire la cubierta de cojinetes (134).
3. Retire del bastidor el conjunto del eje.
4. Retire los sellos de reborde (138, 139) de la caja de
cojinetes (228) y la cubierta de cojinetes (134) si se
encuentran gastados. Deséchelos.
5. Retire el anillo de retención (361).
6. Use un jalador de cojinetes o una prensa de eje para retirar
los cojinetes de bola (112, 168).
23
Page 24

Reensamblaje
• Antes de volver a armar la bomba se deben limpiar todas las
piezas.
ATENCIÓN: EL ANILLO EN O SE DEBE REEMPLAZAR
CADA VEZ QUE SE DESARMA
LA UNIDAD.
CAJA DE COJINETES
1. Reemplace los sellos de reborde si han sido retirados.
2. Reemplace los cojinetes de bola si están sueltos o hacen
ruido al rotar.
3. Controle el descentramiento del eje (122). El valor máximo
permitido es 0.002 pulgadas (0.05 mm) TIR.
4. Consulte la sección “MANTENIMIENTO” de este
manual para las instrucciones de lubricación de la caja de
cojinetes en las bombas del grupo M.
EXTREMO DEL LÍQUIDO
1. Inspeccione el eje y limpie toda basura o rebaba.
2. Aplique LOCQUIC® Primer “T” o equivalente al eje,
siguiendo cuidadosamente las instrucciones del fabricante.
3. Al colocar la nueva camisa del eje, rocíe el diámetro
interior de la camisa con LOCQUIC® Primer “T” o
equivalente. Deje secar las piezas y aplique LOCTITE®
#262 a las mismas superficies. Deslice la nueva camisa
sobre el eje con un movimiento de torsión y limpie el
excedente. Deje curar de acuerdo con las instrucciones.
ATENCIÓN: EL SELLO MECÁNICO DEBE SER
REEMPLAZADO CADA VEZ QUE SE
RETIRA EL SELLO. SIGA ATENTAMENTE
LAS INSTRUCCIONES DEL FABRICANTE
DEL SELLO. PARA BOMBAS CON CAJA
PRENSAESTOPAS, CONSULTE
LAS “INSTRUCCIONES PARA CAJA
PRENSAESTOPAS”.
4. Reemplace el anillo de desgaste del compartimiento
de sellos si es que ha sido retirado.
5. En el caso de bombas de sello mecánico, el asiento del sello
estacionario puede sumergirse en agua para facilitar la instalación. Coloque el asiento del sello estacionario encuadrado
en el agujero de la caja del sello. Cubra la cara pulida del
asiento con una sección delgada de cartón o toalla de papel.
Oprima firmemente el asiento en el agujero usando una
sección de plástico o madera que disperse la fuerza sobre
la cara completa del sello. NOTA: Si el sello mecánico está
equipado con un retén a resorte, retire y descarte el retén.
6. Coloque el adaptador, con la cara cóncava hacia arriba,
sobre el eje del motor y hágalo descender hasta el motor.
7. Reemplace el anillo en O del compartimiento de sellos. Este
anillo en O puede ser lubricado con agua o glicerina para
facilitar la instalación. Instale el compartimiento del sello
sobre el adaptador. Tenga cuidado para que el eje del motor
no dañe o desaloje el asiento del sello.
8. Instale de frente y completamente el conjunto rotativo del
sello contra el asiento estacionario.
AVISO: REEMPLACE EL PERNO Y LA ARANDELA DEL
IMPULSOR CADA VEZ QUE SE RETIRE ESTE
ÚLTIMO.
9. Instale la chaveta del impulsor en la ranura de
posicionamiento. Monte el impulsor sobre el eje y
empújelo hasta que llegue al fondo. Sosténgalo en su lugar.
Para las unidades del SAE, aplique el loctite 271 al alesaje, a
la chavetera y al eje del impeledor. Monte el impeledor en
el eje y empuje hasta que él bottome. Sostenga en lugar.
10. Instale una nueva arandela del impulsor. Para unidades
SAE, aplique Loctite 271 al diámetro interior, chavetero y
eje del impulsor. Después de haber ajustado la tuerca del
impulsor SAE, aplique 271 al tornillo de fijación y apriete
con la mano hacia la cara del perno del impulsor.
11. Aplique LOCTITE® #271 o su equivalente a las roscas del
perno nuevo del impulsor y apriete a:
Pernos de 3⁄8 pulg.-16 20 lbs.-pie (27 N.m)
Pernos de ½ pulg.-13 38 lbs.-pie (51 N.m)
Perno del impeledor no usado para las unidades del SAE.
12. Para el SAE las unidades aplican el loctite 271 a los hilos
de rosca externos del eje y a los hilos de rosca internos del
impeledor (22). Apriete la tuerca del impeledor al siguiente:
½ pulg. – Tuerca Del Impeledor 80 lbs.-pie (107 N.m)
(SAE grupo M)
¾ pulg. – Tuerca Del Impeledor 100 lbs.-pie (134 N.m)
(SAE Grupo L)
13. Para las unidades del SAE, después de que la tuerca del
impeledor (22) haya estado instalada, aplique el loctite 271
al tornillo de presión (2À). Instale el tornillo de presión del
impeledor en la cara de la tuerca del impeledor (22) y
apriete hand-tight.
14. Reemplace el anillo de desgaste de la carcasa si es que
ha sido retirado.
15. Coloque y ajuste los pernos de la carcasa en una secuencia
de zigzag hasta los valores indicados a continuación:
3⁄8"-16 pernos (carcasa de bronce) 25 lbs.-pie (34 N . m)
3⁄8"-16 pernos (carcasa de hierro fundido) 37 lbs.-pie (50 N
½"-13 pernos (carcasa de hierro fundido) 90 lbs.-pie (122 N
¾"-10 pernos (carcasa de hierro fundido) 175 lbs.-pie (237 N
16. Verifique que la unidad reensamblada no experimente
agarrotamiento. Haga rotar el eje con la herramienta
apropiada desde el extremo del motor.
17. Si hubiera rozamiento, afloje los pernos de la carcasa y
realice la secuencia de ajuste otra vez.
18. Vuelva a colocar los pernos de sujeción del motor y el
tapón o la cubierta del extremo del motor en las unidades
de acoplamiento corto.
19. Vuelva a colocar los pernos de sujeción del acoplamiento,
el espaciador, el protector de acoplamiento y el bastidor en
las unidades montadas en bastidor.
ATENCIÓN: SIEMPRE VUELVA A VERIFICAR AMBAS
ALINEACIONES LUEGO DE EFECTUAR
ALGÚN AJUSTE.
20. Para realinear el eje, consulte la sección “ALINEACIÓN
DEL ACOPLAMIENTO” en este manual.
21. El reensamblaje está ahora completo.
.
m)
.
m)
.
m)
24
Page 25

Instrucciones para la caja prensaestopas
CORRECTO INCORRECTO
1. Asegúrese de que la caja prensaestopas esté limpia y libre
de materias extrañas antes de comenzar la empaquetadura.
Consulte el título Ensamblaje por Secciones en la sección
de repuestos.
2. Sea especialmente cuidadoso durante la instalación de
los anillos de empaque porque están formados con matriz.
Para instalarlos, retuerza el anillo hacia el costado lo
suficiente como para poder colocarlo alrededor de la
camisa del eje. NO INTENTE RETIRAR LOS ANILLOS
JALANDO DIRECTAMENTE. Observe la figura 12.
Figura 12
3. Instale el aro de linterna de Teflon de dos piezas provisto
según se muestra en la figura 13. Nota: dos piezas conforman un aro. Las muescas del anillo deben enfrentarse, pero el alineamiento no es necesario.
Aro de linterna de Teflon
Figura 13
4. Para empacar la caja prensaestopas, instale los anillos de
empaque y el aro de linterna en la secuencia siguiente.
Instale dos anillos de empaquetadura, luego el aro de
linterna, y luego los tres anillos de empaquetadura restantes.
Instale cada anillo por separado y asiéntelo firmemente. Se
recomienda el uso de un manguito dividido de madera para
esta operación. Vea la figura 14. Use el casquillo para mover
el manguito y el anillo dentro de la caja. Alterne las juntas en
cada aro 90º. Asegúrese de que la toma embutida en la caja
prensaestopas se alinea con el centro del aro de linterna.
Los anillos extra son de repuesto.
5. Ajuste las tuercas del casquillo en forma pareja pero sin
ajustar mucho. Cuando se arranca la bomba, lentamente
ajuste las tuercas del casquillo hasta que la pérdida llegue a
entre 40 y 60 gotas por minuto. Se puede utilizar un
lubricante a base de grasa cuando el líquido bombeado
contiene partículas abrasivas o para mejorar la carga de
succión.
PARA RETIRAR LA CAJA PRENSAESTOPAS
• Para retirar las empaquetaduras de la caja prensaestopas
siga estos pasos.
1. Retire el conjunto del casquillo.
2. Retire la empaquetadura con un “gancho de empaque”.
3. Inserte un gancho de alambre en el anillo en el borde
exterior para retirar el aro de linterna.
4. Limpie la caja prensaestopas.
DISPOSICIÓN DE CEBADO SEGURO
(Opcional – Grupo M y L únicamente)
• La disposición Prime Safe puede lubricarse con grasa o por
alimentación de aceitador.
1. El casquillo para grasa (24) tendrá las letras “G” y “O”
estampadas en el diámetro exterior y dos conexiones NPT
de 1⁄8 pulg. para montar una grasera o aceitador.
2. Para las aplicaciones de alimentación de grasa, el casquillo
para grasa se instala con la marca “G” en la posición de
las 12:00. El alimentador de grasa (23) se montará en
el casquillo para grasa en un ángulo de 30 grados con
respecto a la horizontal. Esto se hace para ganar acceso a
la grasera situada en el alimentador de grasa. El sello de
reborde (26) montado en el casquillo para grasa se instalar· en la forma mostrada en la Figura 10.
3. Para las aplicaciones de alimentación con aceitador, el
casquillo para grasa se instala con la marca “O” en la
posición de las 12:00. Las dos conexiones NPT de 1⁄8
pulg. sobre el casquillo para grasa estarán situadas sobre la
horizontal, lo cual asegurará el funcionamiento apropiado
del aceitador. El sello de reborde (26) debe montarse en
la dirección inversa u opuesta, tal como se muestra en la
Figura 15.
4. El montaje del alimentador de grasa o aceitador podría requerir extensiones de tubos y/o accesorios adicionales que
serán suministrados por la fábrica según sea necesario.
5. El alimentador de grasa (23) incluirá tres resortes (azul, rojo
y plateado). El uso de resortes diferentes variará dependiendo de la temperatura de operación y del lubricante (grasa) a
utilizarse.
“MANGUITO DIVIDIDO” DE MADERA
CAJA
PRENSAESTOPAS
EJE
Figura 14
CASQUILLO
25
Page 26

23
26
24
ADVERTENCIA
Un voltaje peligroso puede
producir golpes el ctricos,
quemaduras o la muerte.
Temperatura de operación Grasa Nº 1 Grasa Nº 2 Grasa Nº 3
Tamaño del resorte del alimentador de grasa
-10ºF (-23ºC) a 40ºF (4ºC) PLATEADO ROJO —
-40ºF (-40ºC) a 110ºF (43ºC) PLATEADO PLATEADO ROJO
-110ºF (-79ºC) a 200ºF (93ºC) AZUL PLATEADO PLATEADO
Utilice aceite SAE 30W para la aplicación del engrasador.
Figura 15
Guía de resolución de problemas
DESCONECTE Y BLOQUEE
LA ALIMENTACIÓN ELÉCTRICA
ANTES DE INTENTAR TAREAS DE
MANTENIMIENTO. EL NO HACERLO PUEDE OCASIONAR DESCARGAS
ELÉCTRICAS, QUEMADURAS O INCLUSO LA MUERTE.
SÍNTOMA
EL MOTOR NO FUNCIONA
Vea las causas probables N° 1 a 5
SE ENTREGA POCO O NADA DE LÍQUIDO
Vea las causas probables N° 6 a 13
CONSUMO EXCESIVO DE ELECTRICIDAD
Vea las causas probables N° 3, 13, 14 y 15
RUIDO O VIBRACIÓN EXCESIVOS
Vea las causas probables N° 3, 6, 7 10, 12, 14, 16 y 17
CAUSA PROBABLE
1. Se disparó el protector térmico del motor
2. Interruptor de circuito abierto o fusible quemado
3. Agarrotamiento del impulsor
4. El cableado del motor es incorrecto
5. El motor es defectuoso
6. La bomba no está cebada, hay aire o gases en el bombeo
7. Descarga o succión bloqueadas o válvula cerrada
8. Rotación incorrecta (motor trifásico solamente)
9. Bajo voltaje o pérdida de fase
10. Impulsor gastado o tapado
11. Altura del sistema muy alta
12. NPSHA muy baja – Elevación excesiva de succión o pérdidas
13. Diámetro incorrecto del impulsor
14. Altura de descarga muy baja — velocidad excesiva del flujo
15. Viscosidad o gravedad específica del fluido muy altas
16. Cojinete gastado
17. Bomba, motor o tubería flojos
26
Page 27

Partes de repuesto de la Serie 3656/3756
SAE M y L
Substituye 6 y 7
4 6 7 8 2 5 9 10 3 11
13
3
2222A
16 17 18
12 1
19
20
21
Conjunto de la caja prensaestopas
COMPONENTES DEL EXTREMO DEL LÍQUIDO
No. Ítem Descripción Material
1 Carcasa
2 Impulsor
3 Adaptador
4 Anillo de desgaste (carcasa)
5** Anillo de desgaste (compartimiento de sellos)
6 Perno del impulsor
7 Arandela del impulsor
8 Chaveta del impulsor
Hierro fundido o
silicio-latón*
Hierro fundido o bronce*
Acero inoxidable
tipo AISI 300
9 Anillo en O de la caja del sello (materiales opcionales) BUNA-N/EPR/Viton
10 Sello mecánico Consulte la tabla
11 Camisa del eje
tipo AISI 300
Acero inoxidable
12 Tapón de drenaje – 1⁄4 ó 3⁄8 NPT Acero zincado
13 Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal (de la carcasa al adaptador)
14 Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal
(del adaptador al motor/bastidor) Acero zincado
15 Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal
(del adaptador al compartimiento de sellos)
16 Aro de linterna Teflon™
17 Empaque, 5 anillos Impregnado de Teflon
18 Casquillo Acero inoxidable AISI 316
19 Camisa del eje
20 Perno del casquillo
21 Tuerca del casquillo
22 Tuerca del impulsor (SAE únicamente) 304 SS Acero inoxidable 304
Acero inoxidable
tipo AISI 300
22A Tornillo de fijación, tuerca del impulsor (SAE únicamente)
23 Engrasador (aceitador opcional) Policarbonato
23
3
10
11
14
24
26
25
Disposición de cebado seguro (opcional – grupo M y L únicamente)
COMPONENTES DEL EXTREMO DEL LÍQUIDO
No. Ítem Descripción Material
24 Casquillo para grasa Aluminum
25 Tapón de tubería Acero zincado
26 Sello del reborde Buna
* Sin plomo
** El ítem No. 5 se provee con los modelos 21⁄2 x 3-7 (71⁄2 , 10 y 15 HP) del grupo S y con
el grupo M (excepto 3 x 4-10).
COMPONENTES DEL EXTREMO DE POTENCIA (ilustrados en la página siguiente)
No. Ítem Descripción Material
112 Cojinete de bolas (exterior) Acero
122 Eje de la bomba
122A Eje de la bomba (SAE) Acero AISI 4140
123 Anillo en V (Deflector) BUNA-N
134 Cubierta del cojinete Hierro fundido
138 Sello de reborde (exterior) BUNA-N
139 Sello de reborde (interior)
168 Cojinete de bolas (interior) Acero
193 Grasera (grupo M y L)
327C Tornillo (cubierta a adaptador) (SAE únicamente) Acero zincado
340 Adaptador/motor (SAE únicamente) Hierro fundido
361 Anillo de retención Acero
370C Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal (del marco a la cubierta) Acero zincado
371C Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal (del adaptador al marco)
(SAE únicamente)
NO SE MUESTRA
Acero
399 Chaveta, acoplamiento
501N Cubierta/adaptador (SAE únicamente) Acero galvanizado
27
Page 28

Cuadros de fuerza, 3656/3756
361 370C112
139
123 168 122 134
Cuadro de fuerza, Grupo S Cuadro de fuerza, Grupo M
370C
361
399
138
168
123
139
371L
112122193123
361
193 134
193
370C
399
138
168
139
112122193123
193 134
399
138
122A
Cuadro de fuerza, Grupo L Cuadro de fuerza, SAE
361
399
327C
138
501N
370C
340
134
112193168
28
Page 29

Notes
29
Page 30

GARANTÍA LIMITADA DE GOULDS WATER TECHNOLOGY
Esta garantía es aplicable a todas las bombas para sistemas de agua fabricadas por Goulds Water Technology.
Toda parte o partes que resulten defectuosas dentro del período de garantía serán reemplazadas sin cargo para el comerciante durante dicho período de garantía. Tal período de
garantía se extiende por doce (12) meses a partir de la fecha de instalación, o dieciocho (18) meses a partir de la fecha de fabricación, cualquiera se cumpla primero.
Todo comerciante que considere que existe lugar a un reclamo de garantía deberá ponerse en contacto con el distribuidor autorizado de Goulds Water Technology del
cual adquiriera la bomba, y ofrecer información detallada con respecto al reclamo. El distribuidor está autorizado a liquidar todos los reclamos por garantía a través del
Departamento de Servicios a Clientes de Goulds Water Technology.
La presente garantía excluye:
(a) La mano de obra, el transporte y los costos relacionados en los que incurra el comerciante;
(b) los costos de reinstalación del equipo reparado;
(c) los costos de reinstalación del equipo reemplazado;
(d) daños emergentes de cualquier naturaleza; y
(e) el reembolso de cualquier pérdida causada por la interrupción del servicio.
A los fines de esta garantía, los términos “Distribuidor”, “Comerciante” y “Cliente” se definen como sigue:
(1) “Distribuidor” es aquel individuo, sociedad, corporación, asociación u otra entidad jurídica que opera entre Goulds Water Technology y el comerciante para la compra,
consignación o contratos de venta de las bombas en cuestión.
(2) “Comerciante” es todo individuo, sociedad, corporación, asociación u otra entidad jurídica que realiza negocios de venta o alquiler-venta (leasing) de bombas a clientes.
(3) “Cliente” es toda entidad que compra o que adquiere bajo la modalidad de leasing las bombas en cuestión de un comerciante. El término “cliente” puede significar un
individuo, una sociedad, una corporación, una sociedad de responsabilidad limitada, una asociación o cualquier otra entidad jurídica con actividades en cualquier tipo de
negocios.
LA PRESENTE GARANTÍA SE EXTIENDE AL COMERCIANTE ÚNICAMENTE
Xylem, Inc.
2881 East Bayard Street Ext., Suite A
Seneca Falls, NY 13148
Teléfono: (800) 453-6777
Fax: (888) 322-5877
www.xyleminc.com/brands/gouldswatertechnology
Goulds es una marca registrada de Goulds Pumps, Inc. y se utiliza bajo licencia.
© 2012 Xylem Inc. IM010 Revisión Número 8 Julio 2012
Page 31

MANUEL D'UTILISATION
IM010
Modèles 3656 et 3756
DIRECTIVES D’INSTALLATION, D’UTILISATION ET D’ENTRETIEN
Page 32

Informations pour le propriétaire
Noter les informations pertinentes ci-dessous et remettre le livret à
la ou au propriétaire. La garantie est présentée en page 44.
Numéro de modèle :
Numéro de série :
Détaillant :
No de téléphone du détaillant :
Date d’achat : Date d’installation :
Table des matières
SUJET PAGE
Consignes de sécurité .................................................. 30
Description et caractéristiques ..................................... 30
Données techniques ..................................................... 30
Installation .................................................................. 30
Emplacement ........................................................... 30
Groupes monobloc (pompes sur moteur) ................. 30
Pompes sur palier ..................................................... 31
Pompes sur palier SAE (moteur thermique) .............. 31
Alignement de l’accouplement ..................................... 34
Pompes sur palier seulement .................................... 34
Tuyauterie ................................................................... 34
Aspiration ................................................................ 34
Refoulement ............................................................ 35
Câblage et mise à la terre ............................................. 35
Sens de rotation ........................................................... 35
Utilisation .................................................................... 35
Entretien ..................................................................... 35
Démontage .................................................................. 36
Remontage .................................................................. 36
Presse-garniture ........................................................... 37
Diagnostic des anomalies ............................................. 39
Pièces de rechange – séries 3656 et 3756 ..................... 40
Garantie limitée ........................................................... 44
32
Page 33

CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ
DANGER
AVERTISSEMENT
ATTENTION
AVERTISSEMENT
Les fluides dangereux
peuvent causer un
incendie, des brûlures
et la mort.
AVIS : INSPECTER L’APPAREIL ET SIGNALER
IMMÉDIATEMENT TOUT DOMMAGE AU
TRANSPORTEUR OU AU DÉTAILLANT.
DESCRIPTION et CARACTÉRISTIQUES
Les pompes de séries 3656 et 3756 sont des pompes
centrifuges à un étage, à aspiration en bout, servant au
transfert de liquides et au pompage de nature générale, ainsi
qu’à l’augmentation de pression et à l’irrigation. Elles sont
offertes en trois versions : tout fonte, avec composants en
bronze ou tout bronze (groupe S seulement).
Les pompes sont munies d’une roue fermée, clavetée sur
l’arbre et retenue par une rondelle et une vis. Le corps de
pompe est du type à volute, à bagues d’usure remplaçables.
Selon les dimensions de la pompe, les raccords d’aspiration
et de refoulement sont filetés ou à brides. Des chemises
d’arbre en inox protègent l’arbre.
AFIN DE PRÉVENIR LES BLESSURES GRAVES OU
MORTELLES ET LES DOMMAGES MATÉRIELS
IMPORTANTS, LIRE ET SUIVRE TOUTES LES
CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ FIGURANT DANS
LE PRÉSENT MANUEL ET SUR LA POMPE.
Le symbole ci-contre est un SYMBOLE DE
SÉCURITÉ employé pour signaler les
mots-indicateurs dont on trouvera la
description ci-dessous. Sa présence sert à
attirer l’attention afin d’éviter les blessures
et les dommages matériels.
Prévient des risques qui VONT causer des
blessures graves, la mort ou des dommages
matériels importants.
Prévient des risques qui PEUVENT causer
des blessures graves, la mort ou des
dommages matériels importants.
Prévient des risques qui PEUVENT causer
des blessures ou des dommages matériels.
AVIS : SERT À ÉNONCER LES DIRECTIVES
SPÉCIALES DE GRANDE IMPORTANCE
QUE L’ON DOIT SUIVRE.
LE PRÉSENT MANUEL A POUR BUT DE FACILITER
L’INSTALLATION ET L’UTILISATION DE LA POMPE.
LIRE SOIGNEUSEMENT CHAQUE DIRECTIVE ET
AVERTISSEMENT AVANT D’EFFECTUER TOUT
TRAVAIL SUR LA POMPE.
N’ENLEVER AUCUNE DÉCALCOMANIE DE SÉCURITÉ.
APPAREIL NON CONÇU POUR LES
LIQUIDES DANGEREUX NI POUR LES
GAZ INFLAMMABLES.
Les groupes monobloc (pompes sur moteur) sont dotés de
moteurs JM ou JP conformes aux normes NEMA, d’un
adaptateur en C et d’un arbre-rallonge claveté. Les paliers
SAE sont vissés au carter de volant du moteur thermique
par l’intermédiaire d’un support SAE de format no 1, 2, 3,
4 ou 5. Des accouplements en élastomère sont offerts en
option pour les diamètres de volant de 6½ po, 7½ po, 8
po, 10 po, 11½ po et 14 po. Les pompes montées sur palier
peuvent être entraînées par accouplement ou par courroie.
Données techniques
Température maximale du liquide :
100 °C (212 °F), avec garniture mécanique ou
d’étanchéité standard ;
120 °C (250 °F), avec garniture mécanique pour
hautes températures, en option.
Pression de service maximale (selon la température du
liquide) :
1,379 MPa (200 lbf/po2), avec raccords NPT ;
1,379 MPa (200 lbf/po2), avec raccords à bride
ANSI 125.
Pression d’aspiration maximale : 689,5 kPa (100 lbf/po2)
Démarrages par heure : 20, répartis uniformément
Groupe Dimensions Aspiration Refoulement
1½ x 2-6 (H) 2 po, NPT 1½ po, NPT
1 x 2-7 2 po, NPT 1 po, NPT
2½ x 3-7 3 po, NPT 2½ po, NPT
S
1 x 2-8 2 po, NPT 1 po, NPT
1½ x 2-8 2 po, NPT 1½ po, NPT
2 x 2-5 2 po, NPT 2 po, NPT
2½ x 2½-5 2½ po, NPT 2½ po, NPT
LH 3 x 3-5 3 po, NPT 3 po, NPT
4 x 4-5 4 po, à bride 4 po, à bride
5 x 5-6 5 po, à bride 5 po, à bride
2½ x 3-8 3 po, NPT 2½ po, NPT
3 x 4-8 4 po, à bride 3 po, à bride
4 x 5-8 5 po, à bride 4 po, à bride
1½ x 2-10 2 po, NPT 1½ po, NPT
2½ x 3-10 3 po, à bride 2½ po, à bride
4 x 6-10 6 po, à bride 4 po, à bride
2½ x 3-13 3 po, à bride 2½ po, à bride
3 x 4-13 4 po, à bride 3 po, à bride
4 x 6-13 6 po, à bride 4 po, à bride
6 x 8-13 8 po, à bride 6 po, à bride
L 8 x 10-13 10 po, à bride 8 po, à bride
4 x 6-16 6 po, à bride 4 po, à bride
3 x 4-7 4 po, à bride 3 po, à bride
M
3 x 4-10 4 po, à bride 3 po, à bride
Installation
EMPLACEMENT
• Placer la pompe aussi près de la source de liquide que
possible, plus bas que celle-ci pour assurer l’amorçage
automatique.
• Le dégagement autour du groupe de pompage doit être
suffisant pour faciliter l’entretien et l’aération.
• Protéger l’appareil contre les intempéries, les inondations
et le gel.
• Protéger la tuyauterie contre le gel.
GROUPES MONOBLOC (POMPES SUR MOTEUR)
• Le groupe monobloc peut être installé à l’horizontale,
à la verticale ou sur une surface inclinée, le moteur plus
haut que la pompe.
33
Page 34

• Les pattes de xation du moteur DOIVENT être ancrées
à une surface solide et rigide pouvant supporter tout le
poids du groupe monobloc. Dans le cas du groupe L, les
pattes de l’adaptateur de moteur doivent aussi être ancrées
à cette surface.
• S’il s’agit d’une installation verticale, protéger le moteur contre les intempéries, les éclaboussures, la condensation, etc.
AVIS : NE PAS PLACER LE MOTEUR PLUS BAS QUE
LA POMPE AFIN DE LE PROTÉGER CONTRE
LES FUITES ET L’EAU DE CONDENSATION.
POMPES SUR PALIER
• On DOIT fixer le groupe de pompage à une surface plane
et solide pour prévenir toute déformation ou contrainte
due au serrage des boulons d’ancrage. Le montage sur
support en caoutchouc est permis pour réduire les
vibrations et le bruit excessifs.
• Serrer les boulons de xation du moteur AVANT de
raccorder la tuyauterie à la pompe.
Plaque de
base
Dessus de la dalle (massif),
nettoyé et humecté
Patte de blocage
Coulis
Coulis arasé
Espace de
nivellement :
1
/2 à 3/4 po)
(
Coffrage
en bois
1
/4 po)
Trou de remplissage
(coulis)6,36 mm (
Coins ou cales de nivellement, laissés en place
Manchon
Rondelle
Figure 1
• Il est recommandé de remplir de coulis le vide entre la
plaque de base et le massif de béton. Le massif doit reposer
sur une semelle de fondations solide. (Voir la figure 1.)
• Placer des coins de nivellement sous le groupe de pompage :
en deux endroits distincts sous le centre approximatif du
moteur et en deux autres sous celui de la pompe. Régler la
hauteur des coins pour que les raccords d’aspiration et de
refoulement soient de niveau (employer un fil à plomb ou
un niveau).
• S’assurer que la plaque de base n’est pas déformée et que
l’alignement final de l’accouplement est possible dans les
limites de déplacement du moteur ou en calant celui-ci au
besoin.
• Serrer les boulons d’ancrage à la main et construire un
coffrage autour de la plaque de base. Remplir entièrement
le coffrage et le dessous de la plaque de coulis : s’assurer
qu’il n’y a aucun creux sous les pattes de fixation de la
pompe et du moteur.
• Laisser le coulis durcir pendant 48 heures avant de visser
les boulons d’ancrage à fond.
• Serrer les boulons de xation de la pompe et du moteur
avant d’aligner les arbres ou de raccorder la tuyauterie à la
pompe.
Pompes sur palier SAE (moteur thermique)
• Le palier SAE est xé au carter de volant du moteur
thermique par le biais d’un support SAE de format no 1,
2, 3, 4 ou 5. L’arbre-rallonge de la pompe est conçu pour
être accouplé directement au volant. Goulds offre des
accouplements en option pour les diamètres de volant de
6½ po, 7½ po, 8 po, 10 po, 11½ po et 14 po. Bien que l’on
34
puisse employer d’autres accouplements, il est recommandé
d’utiliser les accouplements Goulds, conçus pour assurer un
fonctionnement fiable et de longue durée.
EXIGENCES VISANT LE BON FONCTIONNEMENT
Pompe
Outre le débit requis (en gal US/min) fourni par la pompe, la
hauteur manométrique totale à pareil débit doit être prise en
compte. Le point de fonctionnement débit-hauteur manométrique totale devrait être aussi près que possible du point de
rendement le plus haut de la courbe de performances, mais
doit être sous la vitesse de rotation « maximale » (en r/min),
déterminée selon la durée de vie des roulements et, parfois, la
limite de pression de la pompe.
Les orifices d’aspiration et de refoulement sont soit taraudés
(NPT) pour les tuyaux ordinaires, soit à bride standard à trous
de vis ANSI B16.1, classe 125. Suivant la norme ANSI B16.1,
la pression de service maximale pour la fonte de classe 30 est
de 175 lbf/po².
Les moteurs à combustion interne ont une vitesse et une
puissance utile variables. La puissance est fonction de la vitesse
et diminue quand il y a hausse de la température de l’air ou de
l’altitude d’utilisation du moteur. Lorsqu’il entraîne la pompe à
la vitesse requise pour fournir l’eau au système, le moteur doit
tourner dans les limites de vitesse minimale et maximale stipulées par le constructeur du moteur. La puissance nécessaire à la
pompe ne doit pas dépasser la puissance continue nominale du
moteur, une fois incluse toute réduction de puissance due aux
accessoires de moteur et à la hausse de la température de l’air
ou de l’altitude de service du moteur.
Pe DU GROUPE MOTOPROPULSEUR
On choisit le groupe motopropulseur à combustion interne
selon la Pe, la puissance effective (au frein), égale au débit
multiplié par la hauteur manométrique totale, divisés par
3 960 fois le rendement ([gal US/min x hmt] ÷ [3 960 x rend.]).
Nota : on doit cependant réduire la Pe comme suit :
• 20 % pour le service continu ;
• 5 % pour la transmission à angle droit ;
• 3 % aux 1 000 pi au-dessus du niveau de la mer ;
• 1 % aux 10 °F passé 60 °F.
COUPLE DU GROUPE MOTOPROPULSEUR
Il faut aussi tenir compte du couple pour choisir le groupe
motopropulseur. En général, la relation entre la Pe et le couple
varie dans la plage utile d’un diesel (v. fig. 2). Le couple (en
lbf·pi) égale 5 250 fois la puissance effective, divisée par la
vitesse de rotation ([5 250 x Pe] ÷ r/min).
600
500
400
300
lbf·pi
200
100
0
1500 1 600 1 700 1 800 1900 2000 2100 2 200 2300
r/min
180
178
176
174
172
170
168
166
164
162
160
Figure 2 — Courbes puissance (◆)-couple (■)
hp
Page 35

VÉRIFICATION DE LA CORRESPONDANCE POMPE-MOTEUR
Format de la ferrure SAE
Les pompes pour moteurs à combustion sont prévues pour les
carters de volant (moteur) de formats SAE 1 à 5.
S’il s’agit d’un nouveau moteur, on peut s’adresser au
fournisseur pour savoir le format SAE du carter de volant.
Si le moteur est déjà en place, on peut en mesurer comme suit
le diamètre d’alésage du carter de volant et le diamètre du
cercle de vissage et les comparer avec ceux de la table 1 pour
trouver le format SAE :
• Prendre au 1/32 po le plus proche la mesure diamétrale
de l'alésage (A) et du cercle (B) avec un ruban à mesurer
(v. fig. 3).
• Compter le nombre de trous taraudés sur le carter de volant
(C). Utiliser des vis de séries de filetages différentes pour
déterminer la série des trous.
• Comparer les données de A, B et C avec celles de la table 1
pour connaître le format SAE du carter de volant et s'assurer
qu'il convient à la pompe.
Dimensions
Format SAE du carter de volant
du carter de
1 2 3 4 5
volant (en po)
A 201⁄8 175⁄8 161⁄8 141⁄4 123⁄8
B 207⁄8 183⁄8 167⁄8 15 131⁄8
C Nombre 12 12 12 12 8
Cotation 7⁄16 — 14 3⁄8 — 16 3⁄8 — 16 3⁄8 — 16 3⁄8 — 16
Table 1
Moteur
Figure 3
INSTALLATION
• S'il s'agit d'une installation horizontale, on peut placer
l'orifice de refoulement dans n'importe laquelle des positions
permises par l'emplacement des vis de fixation (13) du corps
de pompe. Il est toutefois recommandé de mettre l'orifice
de refoulement à l'horizontale et plus haut que l'orifice
d'aspiration.
• Chaque corps de pompe doit être soutenu par un support
rigide assujetti à la plaque de base ou au massif de béton.
• Dans le cas du groupe M, xer le support rigide à l'anneau-
adaptateur du moteur avec au moins deux (2) des vis de
fixation (13) du corps de pompe. L'épaisseur accrue du
support pourrait requérir des vis plus longues. Employer des
vis SAE 5, serrées au couple indiqué ci-après.
• Pour le groupe L, supporter la pompe à l'aide des deux pattes
moulées de l'adaptateur de moteur (3). Les pattes doivent être
vissées au support.
ACCOUPLEMENT CANNELÉ
Préparatifs
• Au besoin, nettoyer les faces d'emboîtement et de xation
du carter de volant et du volant pour les débarrasser de la
graisse, des saletés, de la rouille et des résidus d'antirouille,
pouvant nuire à la pose et à l'alignement de la pompe. Si
le volant est muni d'un roulement-guide pour arbre de
transmission, enlever et jeter le roulement, non requis pour
l'installation de la pompe et pouvant gêner l'introduction de
l'arbre de pompe.
• Examiner les cannelures de l'arbre de près. Au besoin, en
limer les bavures pour faciliter le glissement de l'arbre dans le
moyeu de l'accouplement.
• Avec modération, appliquer de la graisse sur les cannelures de
l'arbre. Ne pas en mettre sur les arbres clavetés.
• Enler l'accouplement sur l'arbre et le pousser à fond (v. en
page suivante pour les arbres clavetés).
• Mesurer l'écart A entre la face de xation de l'accouplement
et la face de fixation de la ferrure de pompe (v. A, fig. 4).
• Mesurer l'écart B entre la face du volant servant à xer
l'accouplement et la face du carter de volant utilisée pour
fixer la ferrure de pompe (v. B, fig. 4).
NOTA : l’écart A (côté moteur de la pompe) doit être moindre
que l’écart B (côté pompe du moteur), sinon le vilebrequin du
moteur subira une poussée axiale nuisible. Donc, A doit être
plus petit que B.
ACCOUPLEMENT DE VOLANT
• L'accouplement de volant transmet l'énergie du moteur à
l'arbre de pompe. La limite de puissance maximale que peut
supporter sans risque l'accouplement est exprimée par un
chiffre dans la colonne R des tables 1A et 1B.
Moteur
A DOIT être
plus petit que B.
NOTA : quand l’accouplement est posé correctement, il n’atteint
pas la partie lisse de l’arbre. S’il l’atteint, inverser l’accouplement (v.
fig. ci-dessous) pour en augmenter le jeu.
Ferrure
de pompe
Non — A est
plus grand que B.
Ferrure
de pompe
Moteur
Oui — A est
plus petit que B.
= dégagement à vérifier
avant la mise en service
Ferrure
de pompe
Position de
premier choix
Figure 4 Figure 5
Position de
second choix
35
Page 36

• Pour choisir l'accouplement de volant, déterminer d'abord
la puissance nominale requise par la pompe en repérant, sur
sa courbe de performances, le point de rencontre des valeurs
r/min et Pe nécessaires pour obtenir le point débit-hauteur
manométrique totale approprié.
• Diviser ensuite Pe par r/min, puis multiplier le quotient par
100. Le résultat constituera la limite de puissance pour la
pompe. Par exemple, pour une 20BFSAE1AO fournissant
800 gal US/min à une hmt de 270 pi, à 1 800 r/min, la Pe serait
de 75 hp, et la limite de puissance pour la pompe, de 4,16
([75 ÷ 1 800] x 100).
• Choisir l'accouplement convenant au volant (limite de puissance et dimensions). En pareil cas, l'accouplement doit avoir
une limite de puissance (R) SUPÉRIEURE à celle qui a été
calculée pour la pompe. Dans l'exemple ci-dessus, la limite de
puissance R pour l'accouplement serait au moins de 5.
• L'ajusteur-monteur est responsable de l'analyse de compatibilité du moteur, de la pompe et de l'accouplement quant
à leur rigidité en torsion. Goulds Water Systems fournira à
l'ajusteur- monteur les données pour la pompe et
l'accouplement.
NOTA : si le moyeu du volant est muni d’un roulement-guide,
enlever le roulement pour ne pas qu’il gêne l’insertion de
l’arbre de pompe.
VOLANT POUR EMBRAYAGES CONCENTRIQUES INDUSTRIELS
• La g. 6 montre le volant évidé conçu pour les embrayages
concentriques des prises de force.
• On y notera aussi la partie alésée renfoncée du volant, dotée
de trous taraudés servant à fixer l'accouplement. Les dimensions sont conformes aux normes SAE et figurent dans les
tables 1A et 1B. Le diamètre d'embrayage mentionné est le
diamètre nominal de la garniture du disque d'embrayage
concentrique de type couronne.
Volant pour embrayage
Moteur
concentrique industriel
Accouplement
de volant
10 cannelures
extérieures
Diam. extér.
des cannelures
Figure 6
Table 1A — Accouplement cannelé à moyeu
en élastomère pour plage r/min étendue
Diam.
Dimensions du volant (en pouces) Accoupl. cannelé (po)
d’embr.
D E Diam.
(po)
UNC extér.)
6½ 6 5⁄16 — 18 8½ 7,88 3,94 1,19 1,69 7 A00569C 1 1½
7½ 8 5⁄16 — 18 9½ 8,75 3,69 1,19 1,69 7 A00569C 2 1½
8 6 3⁄8 — 16 103⁄8 9,62 4,81 2,44 2,94 7 A00569C 3 1½
10 8 3⁄8 — 16 123⁄8 11,62 4,47 2,13 2,75 7 A00569C 4 1½
10 8 3⁄8 — 16 123⁄8 11,62 4,47 2,13 2,75 9 A00569C 6 1½
11½ 8 3⁄8 — 16 137⁄8 13,12 5,06 1,56 2,69 7 A00569C 5 1½
11½ 8 3⁄8 — 16 137⁄8 13,12 5,06 1,56 2,69 9 A00569C 7 1½
14 8 ½ — 13 183⁄8 17,25 6,63 1,00 2,13 9 A00569C 8 1½
* R = limite de puissance maximale pour l’accouplement = (hp nomin. x 100) ÷ r/min nomin.
Filet. (diam. BC F G H R*
bre
N
Numéro
d’article
extér.,
cannel.
Table 1B — Accouplement claveté à moyeu
en élastomère pour plage r/min étendue
Dimensions du volant (en pouces) Accoupl. claveté (po)
Diam.
D E Diam.
d’embr.
(po)
UNC extér.)
6½ 6 5⁄16 — 18 8½ 7,88 3,94 1,19 1,69
3,51 CD625
7½ 8 5⁄16 — 18 9½ 8,75 3,69 1,19 1,69
3,51 CD725
8 6 3⁄8 — 16 103⁄8 9,62 4,81 2,44 2,94
3,51 CD825
2,28 CD1016
3,51 CD1025
10 8 3⁄8 — 16 123⁄8 11,62 4,47 2,13 2,75 5,71 CD1030
8,57 CD1050
11,23 CD1080
2,28 CD1116
3,51 CD1125
5,71 CD1130
11½ 8 3⁄8 — 16 137⁄8 13,12 5,06 1,56 2,69 8,57 CD1150
11,23 CD1180
12,62 CD1190
16,85 CD11110H
2,28 CD1416
3,51 CD1425
5,71 CD1430
14 8 3⁄8 — 16 183⁄8 17,25 6,63 1,00 2,13 8,57 CD1450
11,23 CD1480
12,62 CD1490
16,85 CD14110H
* R = limite de puissance max. pour l’accouplement = (hp nomin. x 100) ÷ r/min nomin.
Filet. (diam. BC F G H R*
bre
N
Numéro
d’article
2,28 CD616
2,28 CD716
2,28 CD816
de
l’arbre
1,625 à
1,624
Rainure
de cla-
vette :
3
⁄8 x 3⁄
AUTRES TYPES DE VOLANTS
• Le volant de certains moteurs est usiné spécialement pour diverses machines (génératrices, convertisseurs de couple, etc.)
et nécessite donc un accouplement de volant spécial, que l'on
obtiendra d'un vendeur ou d'un fournisseur indépendants.
• S'il s'agit d'un accouplement claveté Goulds Water Systems,
s'assurer que la vis de pression du moyeu de l'accouplement
est suffisamment dévissée pour permettre l'insertion de la
clavette cours du montage.
• Fixer l'accouplement au volant du moteur avec les vis fournies, serrées en croix au couple approprié ci-après : 15 N·m
(11 lbf·pi) pour les volants de 6½ po et de 7½ po, 27 N·m
(20 lbf·pi) pour les volants de 8 po, de 10 po et de 11½ po
et 68 N·m (50 lbf·pi) pour ceux de 14 po. (Pour tout autre
accouplement, suivre les directives d’installation recommandées par le fabricant.)
• Placer la clavette dans la rainure de l'arbre de pompe (122)
et aligner l'arbre sur l'accouplement. Introduire l'arbre de
pompe dans l'accouplement jusqu'à ce que la ferrure ou
l'adaptateur de pompe (340) touche le carter de volant.
FIXATION DE L’ACCOUPLEMENT AU VOLANT
Accouplement de volant du type concentrique
• Ce type d'accouplement est concentrique par rapport au
volant et est aligné sur celui-ci par emboîtement.
• S'assurer d'enlever tout enduit protecteur du volant du
moteur.
16
36
Page 37

Parallèlle
Angulaire
L’équipement
dangereux peut causer
des blessures ou la mort.
AVERTISSEMENT
• Emboîter l'accouplement dans le volant en prenant soin
d'aligner les trous de vis. Au besoin, frapper l'accouplement
avec une massette à panne douce pour s'assurer qu'il est bien
appuyé contre le volant. Fixer l'accouplement solidement
en place avec des vis d'assemblage et des rondelles-freins à
ressort.
FIXATION DE LA POMPE AU MOTEUR
• Lever la pompe avec un appareil approprié et aligner
l'arbre de pompe sur le moyeu d'accouplement. Le bout
de l'arbre est biseauté pour en faciliter l'introduction
dans l'accouplement.
• Par l'orice d'aspiration de la pompe, faire tourner la roue
légèrement jusqu'à ce que l'arbre pénètre dans le moyeu d'accouplement. S'assurer qu'il n'y aucun espace entre la face de
fixation de la ferrure de pompe et celle du carter de volant.
Au besoin, faire tourner le corps de pompe pour aligner les
trous de vis de la ferrure sur ceux du carter. Avec des vis
d'assemblage, fixer la pompe solidement au carter.
NOTA : si l’on découvre des pièces incompatibles, impossibles
à poser, etc. au cours de l’installation, NE PAS poursuivre le
travail. S’en référer au distributeur Goulds Water Systems.
• Assujettir la pompe au moteur avec les rondelles-freins et les
vis fournies, serrées en croix au couple approprié ci-dessous :
indices SAE nos 2, 3, 4, et 5 – 27 N·m (20 lbf·pi) ;
indice SAE no 1 – 68 N·m (50 lbf·pi).
• Poser le carter d’accouplement (501N).
• Visser l’adaptateur de moteur (3) au support rigide précité.
Alignement de l’accouplement
OMETTRE LE VERROUILLAGE
DU CIRCUIT D’ALIMENTATION
ÉLECTRIQUE EN POSITION OUVERTE (HORS CIRCUIT) AVANT
D’EFFECTUER TOUT TRAVAIL
D’ENTRETIEN SUR LA POMPE PEUT
CAUSER DES BLESSURES GRAVES.
POMPES SUR PALIER SEULEMENT
• On DOIT vérifier l’alignement avant la mise en service de
la pompe (fig. 7).
Figure 7
• Serrer tous les boulons de xation avant de vérier
l’alignement.
• Lorsqu’un alignement est nécessaire, on doit toujours déplacer
uniquement le moteur. Employer des cales au besoin.
• Désalignement parallèle (arbres parallèles mais non
concentriques) – Fixer au moyeu d’un demi-accouplement
un comparateur à cadran, dont on déplace le curseur de
360° le long de la jante de l’autre demi-accouplement tout en
notant l’écart indiqué par l’aiguille. L’alignement est correct
si le faux-rond total est de 0,254 mm (0,010 po) ou moins.
• Désalignement angulaire (arbres concentriques mais non
parallèles) – Fixer au moyeu d’un demi-accouplement un
comparateur à cadran et déplacer le curseur de celui-ci de
360° le long du plateau de l’autre demi-accouplement tout en
notant l’écart indiqué par l’aiguille. L’alignement est correct si
le faux-rond total est de 0,508 mm (0,020 po) ou moins.
• L’alignement nal est correct quand il est conforme aux
exigences sur l’alignement parallèle et angulaire après le
serrage à fond des boulons de fixation du moteur.
AVIS : IL FAUT TOUJOURS VÉRIFIER LES DEUX
TYPES D’ALIGNEMENT APRÈS CHAQUE
RÉGLAGE MÉCANIQUE.
Tuyauterie
• An de réduire les pertes de charge (par frottement) au
minimum, maintenir la tuyauterie aussi courte que possible, ne pas employer un calibre de tuyau inférieur à celui
des raccords d’aspiration et de refoulement de la pompe ni
utiliser d’accessoires ou de raccords de tuyauterie superflus.
• La tuyauterie DOIT posséder ses propres supports et
N’appliquer AUCUNE contrainte sur la pompe.
AVIS : LA TUYAUTERIE NE DOIT APPLIQUER
AUCUNE CONTRAINTE SUR LES RACCORDS
D’ASPIRATION ET DE REFOULEMENT DE
LA POMPE.
• Chaque joint DOIT être étanche.
ASPIRATION
• Si la hauteur d’aspiration dépasse 3 m (10 pi), et la
température du liquide, 49 °C (120 °F), consulter la courbe
de performances de la pompe pour obtenir la hauteur nette
d’aspiration requise (NPSHR).
• Lorsqu’il faut un tuyau d’aspiration plus gros que l’orice
d’aspiration de la pompe, on DOIT poser un raccord
réducteur excentré (la partie droite en haut) près de l’orifice.
• Si la pompe est plus basse que la source de liquide, poser
un robinet-vanne sur le tuyau d’aspiration pour pouvoir
effectuer l’inspection et l’entretien de la pompe.
AVIS : NE PAS EMPLOYER LE ROBINET-VANNE
POUR RÉDUIRE L’ÉCOULEMENT DU
LIQUIDE VERS LA POMPE, CAR CELA
POURRAIT DÉSAMORCER CELLE-CI, EN
CAUSER LA SURCHAUFFE ET
L’ENDOMMAGER, ANNULANT AINSI
LA GARANTIE.
• Lorsque la pompe est plus haute que la source de liquide,
on DOIT suivre les directives suivantes :
• Prévenir les poches d’air en ne posant aucun élément
de la tuyauterie d’aspiration plus haut que le raccord
d’aspiration de la pompe.
• Incliner la tuyauterie vers le haut à partir de la source de
liquide.
• Employer un clapet de pied SEULEMENT s’il est néces-
saire pour amorcer la pompe ou la maintenir amorcée au
cours des interruptions de service.
• La section de passage de la crépine ou de la tulipe
d’aspiration doit être au moins le triple de celle du tuyau
d’aspiration.
• S’assurer que le diamètre (d) et la hauteur d’immersion (h)
de l’orifice d’entrée du tuyau d’aspiration sont suffisants
pour empêcher l’aspiration d’air par vortex (fig. 8 à 11).
37
Page 38

Figure 8 Figure 9
AVERTISSEMENT
Tension
dangereuse
AVERTISSEMENT
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures et
la mort.
La machinerie dangereuse peut causer des
blessures mortelles.
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures et
la mort.
AVERTISSEMENT
Les hautes
températures peuvent
causer blessures et
dommages matériels.
AVERTISSEMENT
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures et
la mort.
Figure 10 Figure 11
REFOULEMENT
• Poser un clapet de non-retour convenant au débit et aux
• Lorsqu’un raccord agrandisseur est nécessaire, le poser
• N’utiliser que du l de cuivre pour la mise à la terre et
• Suivre soigneusement le schéma de câblage sur la plaque
38
1,5d
min.
d d
3,0d
min.
h min.
d min.
2
h min.
d
h min.
d
h
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
h = hauteur d’immersion minimale (pi)
12345678910 11121314 1516
v = vitesse d’écoulement (pi/s)
gal US/min x 0,321
=
section de passage
gal US/min x 0,408 5
2
d
v
liquides pompés. En aval du clapet, installer un robinet-vanne
de section de passage appropriée pour la régularisation du
débit ainsi que l’inspection et l’entretien de la pompe.
entre le clapet de non-retour et l’orifice de refoulement de la
pompe.
Câblage et mise à la terre
Installer la pompe, la mettre à la
terre et la brancher suivant les
prescriptions du code provincial ou
national de l’électricité pertinent et
les règlements locaux.
Poser un sectionneur tout
conducteur près de la pompe.
Verrouiller le circuit d’alimentation
électrique de la pompe en
position ouverte (hors circuit)
avant de procéder à l’installation
ou à l’entretien de la pompe.
L’alimentation électrique DOIT être conforme aux
spécifications de la plaque signalétique. Une tension
inappropriée peut causer un incendie ou des
dommages au moteur et annule la garantie.
Les moteurs monophasés non protégés DOIVENT
être munis de contacteurs et de protections contre
les surcharges thermiques, et les moteurs triphasés,
de démarreurs à protection contre la surcharge.
Consulter la plaque signalétique du moteur.
l’alimentation du moteur. Le calibre du fil de terre DOIT
être au moins égal à celui des fils d’alimentation, et les fils
devraient tous être chromocodés pour faciliter l’entretien.
signalétique ou le cache-bornes du moteur.
OMETTRE LA MISE À LA TERRE
PERMANENTE DE LA POMPE, DU
MOTEUR ET DES COMMANDES
AVANT LE BRANCHEMENT À LA
SOURCE DE COURANT PEUT
CAUSER UN CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE,
DES BRÛLURES OU LA MORT.
Sens de rotation
AVIS : LA ROTATION DANS LE MAUVAIS SENS
PEUT ENDOMMAGER LA POMPE ET
ANNULE LA GARANTIE.
• La rotation appropriée est EN SENS HORAIRE (vers
la droite), vue de l’extrémité du moteur. S’il s’agit d’une
pompe sur palier, la mettre en marche, puis l’arrêter
rapidement tout en vérifiant son sens de rotation. Dans le
cas des pompes sur moteur, enlever l’obturateur ou le couvercle d’extrémité du moteur et vérifier le sens de rotation.
• Pour inverser la rotation des moteurs triphasés, en intervertir deux des conducteurs.
Utilisation
NE PAS FAIRE FONCTIONNER
LES POMPES SUR PALIER (ORDINAIRE OU SAE) SANS CARTER
D’ACCOUPLEMENT, CAR CELA
POURRAIT CAUSER DES BLESSURES
GRAVES.
ÉCLABOUSSER OU PLONGER UN
MOTEUR ABRITÉ DANS UN LIQUIDE
PEUT CAUSER UN INCENDIE, UN
CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE, DES BRÛLURES
OU LA MORT.
NE PAS FAIRE FONCTIONNER LA
POMPE SI SON DÉBIT EST NUL OU
PRESQUE, SINON IL POURRAIT EN
RÉSULTER UN ÉCHAUFFEMENT
EXCESSIF, DES BLESSURES OU DES
DOMMAGES MATÉRIELS.
AVIS : NE PAS FAIRE FONCTIONNER LA POMPE À
SEC POUR NE PAS ENDOMMAGER
LA GARNITURE MÉCANIQUE.
• Faire fonctionner la pompe dans des conditions de service
normales, attendre que le système se stabilise, puis vérifier la
tuyauterie et en régler la position des supports au besoin.
• La différence de température entre la pompe sur palier et le
moteur peut provoquer le désalignement de l’accouplement.
Par conséquent, vérifier l’alignement de nouveau en
respectant les directives et les avertissements de la section
« Alignement de l’accouplement » ci-dessus.
Entretien
OMETTRE LE VERROUILLAGE
DU CIRCUIT D’ALIMENTATION
ÉLECTRIQUE EN POSITION OUVERTE (HORS CIRCUIT) AVANT
D’EFFECTUER TOUT TRAVAIL
D’ENTRETIEN SUR LA POMPE PEUT
CAUSER UN CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE,
DES BRÛLURES OU LA MORT.
Page 39

GROUPES MONOBLOC
ATTENTION
Les pressions dangereuses
peuvent causer des
blessures et des
dommages matériels.
Les fluides dangereux
peuvent causer des
blessures et des
dommages matériels.
AVERTISSEMENT
• Les roulements sont situés à l’intérieur du moteur. Suivre
POMPES SUR PALIER
• Les roulements de palier du modèle 3756, groupe S, sont
• Les roulements de palier SAE et de palier modèle 3756,
• Suivre les directives du fabricant du moteur et de
• Vérier l’alignement de nouveau.
ENTRETIEN SAISONNIER
• Avant la MISE HORS SERVICE de la pompe, enlever le
• Avant la REMISE EN SERVICE de la pompe, garnir les filets
• Si le tuyau d’aspiration a été séparé de la pompe, en examiner
• Consulter la section « Utilisation » ci-dessus.
• Suivre CHAQUE avertissement et directive de la section
• Groupes monobloc : enlever les boulons de xation
• Pompes sur palier : déposer le carter d’accouplement, la
POMPE
1. Enlever les vis (13) du corps de pompe.
2. Écarter l’ensemble d’entraînement d’avec le corps
de pompe (1).
3. Retirer la bague d’usure (4) du corps de pompe si elle
est trop usée.
OMETTRE DE RÉDUIRE LA PRESSION DU SYSTÈME OU DE VIDANGER CELUI-CI AVANT DE PROCÉDER
À L’ENTRETIEN PEUT CAUSER DES
DOMMAGES MATÉRIELS ET DES
BLESSURES, VOIRE LA MORT.
LORSQUE LES LIQUIDES POMPÉS
SONT DANGEREUX OU TOXIQUES, ON DOIT RINCER LE SYSTÈME AVANT D’EN EFFECTUER
L’ENTRETIEN.
les directives du fabricant du moteur pour leur graissage.
graissés à vie. Il est donc impossible et inutile de les graisser.
groupes M et L, devraient être graissés à la fin de la
période suivante arrivant la première : 2 000 heures de
fonctionnement ou trois mois de temps écoulé. Employer
une graisse au lithium ou au sodium no 2. Injecter la graisse
dans le roulement jusqu’à ce qu’elle sorte par les garnitures
ou les joints à lèvre(s), puis essuyer le surplus.
l’accouplement pour le graissage.
bouchon de vidange et vidanger tous les tuyaux non protégés
du gel.
du bouchon de vidange de ruban de TéflonMC ou l’équivalent
et reposer le bouchon.
le raccord union, le réparer au besoin, puis raccorder le tuyau.
Démontage
« Entretien » ci-dessus.
du moteur.
pièce d’écartement de l’accouplement, l’accouplement et les
boulons de fixation du palier.
AVIS : NE PAS INSÉRER DE TOURNEVIS ENTRE LES
AUBES DE LA ROUE POUR EMPÊCHER
CELLE-CI DE TOURNER.
4. Dans le cas des groupes monobloc (pompes sur moteur),
enlever l’obturateur ou le couvercle d’extrémité du moteur
pour accéder à la fente ou aux méplats de blocage du
bout d’arbre.
5. Bloquer l’arbre de la pompe sur moteur avec l’outil
approprié et celui de la pompe sur palier avec un serre-tubes
à sangle, puis enlever et jeter la vis (6) de la roue : on
devra peut-être chauffer la vis au chalumeau d’abord.
AVIS : MANIPULER LA VIS DE LA ROUE AVEC
PRÉCAUTION QUAND ELLE EST CHAUDE.
AVIS : POUR LES POMPES SUR PALIER SAE,
ENLEVER LA VIS D’ARRÊT (22A), PUIS
L’ÉCROU DE ROUE (22). ON DEVRA
PEUT- ÊTRE CHAUFFER LA VIS ET
L’ÉCROU D’ABORD.
6. Ôter la rondelle de roue (7).
7. Enlever la roue (2) DÉLICATEMENT au moyen de
deux leviers placés entre celle-ci et le logement de garniture
mécanique (3), dans un angle de 180°.
8. Ôter la clavette (8).
9. Déposer les vis (14) du logement de garniture
mécanique (3), puis tirer le logement pour l’enlever avec
la garniture. Jeter cette dernière ainsi que le joint torique
(9) du logement. Pour les directives portant sur le presse garniture, voir la section « Presse-garniture ».
10. Enlever l’adaptateur (108).
11. Inspecter la chemise d’arbre (11). Si elle trop rayée,
la chauffer au chalumeau, l’enlever et la jeter.
12. Pousser l’élément fixe de la garniture mécanique hors du
logement et le jeter.
13. Dans le cas des logements de garniture munis d’une bague
d’usure (5), enlever la bague si elle est trop usée.
DÉMONTAGE DU PALIER (ORDINAIRE OU SAE)
1. Ôter le déflecteur (123) de l’arbre.
2. Enlever le couvercle de palier (134).
3. Sortir l’ensemble arbre du palier.
4. Si les joints à lèvre(s) 138 et 139 sont usés, les enlever du
couvercle de palier (134) et du corps de palier (228) et
les jeter.
5. Déposer la bague de retenue (361).
6. Avec un arrache-roulement ou une presse à mandriner,
ôter les roulements (112 et 168).
Remontage
• Chaque pièce devrait être nettoyée avant le remontage.
AVIS : ON DEVRAIT REMPLACER LE JOINT
TORIQUE CHAQUE FOIS QUE LA POMPE
EST DÉMONTÉE.
PALIER
1. Remplacer les joints à lèvre(s) s’ils ont été enlevés.
2. Remplacer les roulements à billes s’ils ont du jeu, s’ils
ne tournent pas rond ou s’ils sont bruyants.
3. Vérifier si l’arbre (122) comporte un faux-rond : le faux-
rond maximal admissible est de 0,05 mm (0,002 po).
4. Voir les directives de graissage des pompes du groupe M
dans la section « Entretien ».
39
Page 40

POMPE
1. Inspecter l’arbre et en enlever les aspérités et les résidus.
2. Appliquer de l’apprêt Primer T de LOCQUICMD ou
l’équivalent sur l’arbre : suivre les directives du fabricant
avec soin.
3. Lorsque l’on pose une chemise d’arbre neuve, en enduire
la paroi intérieure d’apprêt Primer T de LOCQUICMD ou
l’équivalent. Laisser l’apprêt sécher, puis le recouvrir de
LOCTITEMD no 262. Poser ensuite la chemise sur l’arbre
dans un mouvement de rotation, puis essuyer l’arbre.
Laisser le produit durcir suivant les directives pertinentes.
AVIS : LA GARNITURE MÉCANIQUE DOIT ÊTRE
REMPLACÉE CHAQUE FOIS QU’ON
L’ENLÈVE. SUIVRE LES DIRECTIVES DU
FABRICANT DE LA GARNITURE AVEC SOIN.
POUR LES PRESSE-GARNITURE, VOIR
LA SECTION « Presse-garniture ».
4. Si l’on a retiré la bague d’usure du logement de garniture
mécanique, la remplacer.
5. On peut tremper l’élément fixe de la garniture mécanique
dans l’eau pour en faciliter la pose. L’aligner ensuite avec
soin sur son logement. En recouvrir la surface polie avec un
morceau de carton mince ou d’essuie-tout. Pousser
l’élément jusqu’au fond avec un morceau de plastique ou de
bois rond pour répartir uniformément la force appliquée.
NOTA : si la garniture mécanique est munie d’un anneau
élastique, enlever et jeter celui-ci.
6. Poser l’adaptateur sur le moteur, la face plate de
l’adaptateur contre le moteur.
7. Mettre le joint torique sur le logement de garniture. On peut
glycériner ou tremper le joint dans l’eau pour en faciliter la
pose. Poser le logement de garniture sur l’adaptateur.
Prendre garde que l’arbre ne déloge l’élément fixe de
la garniture ni n’en endommage le siège.
8. Poser l’élément mobile de la garniture sur l’arbre en
l’alignant avec soin et en le poussant à fond contre
l’élément fixe.
AVIS : REMPLACER LA VIS ET LA RONDELLE DE
ROUE CHAQUE FOIS QUE L’ON DÉPOSE
LA ROUE.
9. Insérer la clavette de la roue dans sa rainure, poser la
roue sur l’arbre, la pousser à fond et la maintenir en
place. Dans le cas des pompes sur palier SAE, enduire
d’abord de Loctite 271 la rainure de clavetage, la paroi
intérieure alésée de la roue et la surface correspondante
de l’arbre, puis poser la roue sur l’arbre, la pousser
à fond et la maintenir en place.
10. Poser une rondelle de roue neuve. Il n’y a pas de
rondelle de roue dans les pompes sur palier SAE.
11. Enduire de Loctite 271 (ou l’équivalent) les filets de la
vis de roue neuve, puis poser la vis et la serrer au couple
approprié ci-dessous :
vis 3⁄8 - 16 — 27 N·m (20 lbf·pi) ;
vis ½ - 13 — 51 N·m (38 lbf·pi) ;
(aucune vis de roue dans les pompes sur palier SAE).
12. S’il s’agit d’une pompe sur palier SAE, enduire de
Loctite 271 les filets du bout d’arbre et ceux de l’écrou
de roue (22), poser l’écrou et le serrer au couple
approprié suivant :
écrou de ½ po (SAE, groupe M) — 107 N·m (80 lbf·pi) ;
écrou de ¾ po (SAE, groupe L) — 134 N·m (100 lbf·pi).
13. Une fois l’écrou de roue (pompe sur palier SAE) en
place, mettre du Loctite 271 sur la vis d’arrêt (22A),
poser la vis sur l’écrou et la serrer à la main.
14. Si l’on a retiré la bague d’usure du corps de pompe,
la remplacer.
15. Poser les vis du corps de pompe et les serrer en croix au
couple approprié ci-dessous :
vis 3⁄8 - 16 (corps en bronze) – 34 N·m (25 lbf·pi) ;
vis 3⁄8 - 16 (corps en fonte) – 50 N·m (37 lbf·pi) ;
vis ½ - 13 (corps en fonte) – 122 N·m (90 lbf·pi) ;
vis ¾ - 10 po (corps en fonte) – 237 N·m (175 lbf·pi).
16. Une fois la pompe remontée, faire tourner l’arbre par
l’extrémité du moteur avec l’outil approprié pour vérifier
s’il y a grippage.
17. En cas de grippage ou de frottement, desserrer les vis du
corps de pompe, puis les serrer de nouveau.
18. Dans le cas des groupes monobloc, reposer les boulons de
fixation, puis l’obturateur ou le couvercle d’extrémité du
moteur.
19. S’il s’agit d’une pompe sur palier, reposer l’accouplement,
la pièce d’écartement, le carter d’accouplement et les
boulons de fixation du palier.
AVIS : IL FAUT TOUJOURS VÉRIFIER LES DEUX
TYPES D’ALIGNEMENT APRÈS CHAQUE
RÉGLAGE MÉCANIQUE.
20. Voir la section « Alignement de l’accouplement » pour
aligner celui-ci de nouveau.
21. Le remontage est maintenant terminé.
Presse-garniture
1. S’assurer que le presse-garniture est propre et exempt de
corps étrangers avant d’y placer la garniture. Voir le
presse-garniture illustré dans la section « Pièces de
rechange – séries 3656 et 3756 ».
2. Poser les anneaux de garniture avec précaution parce qu’ils
sont matricés. Mettre chaque anneau en place en en
écartant les extrémités par torsion juste assez pour y
introduire la chemise d’arbre. NE PAS ESSAYER
D’ÉCARTER LES EXTRÉMITÉS EN LIGNE DROITE.
Voir la figure 12.
CORRECT INCORRECT
Figure 12
3. Placer les deux pièces en Téflon (fournies) de la lanterne
d’arrosage comme le montre la figure 13. Les encoches
doivent être l’une en face de l’autre, sans être
obligatoirement alignées.
Lanterne d'arrosage en Téflon (2 pièces)
Figure 13
40
Page 41

4. On pose les éléments de garniture dans l’ordre suivant :
23
26
24
deux anneaux de garniture, deux pièces de lanterne
d’arrosage, trois anneaux de garniture. Placer le joint de
chaque anneau à 90° par rapport à celui de l’anneau
précédent. Introduire et pousser chaque élément séparément
et à fond. Pour ce faire, il est recommandé d’employer une
douille de bois en deux pièces (fig. 14), enfoncée à l’aide du
fouloir. S’assurer que la lanterne d’arrosage est bien en face
de l’orifice d’admission du liquide de rinçage. Les anneaux
de garniture supplémentaires servent de rechanges.
DOUILLE DE BOIS EN DEUX PIÈCES
FOULOIR
BOÎTE À
GARNITURE
ARBRE
Figure 14
5. Poser les écrous sur les goujons du fouloir et les serrer
légèrement et uniformément. Après la mise en marche de
la pompe, les serrer davantage et lentement jusqu’à ce que
le débit de suintement soit de 40-60 gouttes par minute.
On peut utiliser une graisse lubrifiante quand le liquide
pompé contient des particules abrasives ou que la pression
à l’entrée de la pompe est inférieure à la pression
atmosphérique.
ENLÈVEMENT DE LA GARNITURE
• Suivre les étapes ci-dessous pour retirer la garniture du
presse-garniture.
1. Enlever le fouloir.
2. Extraire la garniture avec un « crochet à garniture ».
3. Introduire un crochet en métal dans un des orifices du
pourtour des pièces de lanterne d’arrosage, puis retirer
ces dernières.
4. Nettoyer le presse-garniture.
GRAISSEUR PRIME SAFE
(en option — groupes M et L seulement)
• Le graisseur Prime Safe peut être fourni avec un lubricateur
à graisse ou à huile.
1. La boîte de lubrification (24) est marquée de la lettre G ou
O et possède deux orifices de 1⁄8 po, NPT, pour la pose du
lubrificateur.
2. Si l’on choisit le lubrificateur à graisse (23), la boîte de lubrification portera la lettre G, placée en haut, et le lubrificateur
sera monté dans un angle de 30º par rapport à l’horizontale
pour permettre l’accès à son téton de graissage. Le joint à
lèvre(s) 26 sera posé sur la boîte de lubrification comme le
montre la figure 10.
3. Dans le cas du lubrificateur à huile, la boîte de lubrification portera la lettre O, placée en haut, et les deux orifices
de 1⁄8 po, NPT, seront montés à l’horizontale pour assurer
une bonne lubrification. Le joint à lèvre(s) 26 sera toutefois
posé sur la boîte de lubrification en sens inverse par rapport
à celui de la figure 15.
4. La pose du lubrificateur peut nécessiter l’emploi de tubes et
de raccords, qui seront fournis par l’usine selon le cas.
5. Le lubrificateur à graisse (23) vient avec trois ressorts
(argent, rouge et bleu). Le choix du ressort est fonction de
la température de service et de la graisse utilisée :
Ressort de lubrificateur à graisse
Température de service
– 23 ºC (– 10 ºF) à 4 ºC (40 ºF)
– 40 ºC (– 40 ºF) à 43 ºC (110 ºF)
– 79 ºC (– 110 ºF) à 93 ºC (200 ºF)
Graisse no 1 Graisse no 2 Graisse no 3
ARGENT ROUGE
ARGENT ARGENT ROUGE
BLEU ARGENT ARGENT
Employer de l’huile SAE 30W pour le lubrificateur à huile.
Figure 15
41
Page 42

AVERTISSEMENT
Les tensions dangereuses
peuvent causer un choc
électrique, des brûlures et
la mort.
Diagnostic des anomalies
VERROUILLER LE CIRCUIT
D’ALIMENTATION ÉLECTRIQUE
EN POSITION OUVERTE (HORS
CIRCUIT) AVANT D’EFFECTUER
TOUT TRAVAIL D’ENTRETIEN SUR
LA POMPE. OMETTRE CE POINT
PEUT CAUSER UN CHOC
ÉLECTRIQUE, DES BRÛLURES
OU LA MORT.
ANOMALIE
LE MOTEUR NE FONCTIONNE PAS.
(V. causes probables 1 à 5.)
LE DÉBIT DE REFOULEMENT EST FAIBLE OU NUL.
(V. causes probables 6 à 13.)
LA POMPE CONSOMME TROP D’ÉNERGIE.
(V. causes probables 3, 13, 14 et 15.)
LA VIBRATION ET LE BRUIT SONT EXCESSIFS.
(V. causes probables 3, 6, 7, 10, 12, 14, 16, et 17.)
CAUSES PROBABLES
1. Protecteur thermique du moteur déclenché
2. Disjoncteur ouvert ou fusible sauté
3. Roue grippée
4. Câblage incorrect
5. Moteur défectueux
6. Pompe non amorcée, air ou gaz présent dans le liquide
pompé
7. Tuyau d’aspiration ou de refoulement obstrué ou
robinet(s) fermé(s)
8. Mauvais sens de rotation (moteurs triphasés seulement)
9. Basse tension électrique ou perte de phase
10. Roue usée ou engorgée
11. Hauteur de charge trop élevée du système
12. Hauteur nette d’aspiration disponible (NPSHA) :
hauteur ou perte d’aspiration excessives
13. Diamètre de roue inapproprié
14. Hauteur de refoulement trop faible – débit excessif
15. Viscosité ou densité trop élevée du liquide
16. Roulement usé
17. Pompe, moteur ou tuyauterie mal assujettis
42
Page 43

Pièces de rechange – séries 3656 et 3756
SAE, M et L
À la place de 6 et 7
4 6 7 8 2 5 9 10 3 11
13
3
2222A
16 17 18
12 1
19
20
21
Composants du presse-garniture
COMPOSANTS DE LA POMPE
No d’article Description Matériau
1 Corps de pompe
2 Roue
Fonte ou laiton au
silicium*
3 Adaptateur
4 Bague d’usure (corps de pompe)
5** Bague d’usure (logement de garniture méc.)
6 Vis (roue)
7 Rondelle (roue)
Fonte ou bronze*
Inox AISI, type 300
8 Clavette de roue Acier
9 Joint torique (logem. de garn. méc.. — matér. opt.) Buna-N, E-P➀, Viton
10 Garniture mécanique
(communiquer avec l’usine)
11 Chemise d’arbre Inox AISI, type 300
12 Bouchon de vidange, 1⁄4 et 3⁄8 po NPT
13 Vis à tête hex. (adaptateur-corps de pompe)
14 Vis à tête hex. (adapt.-moteur, adapt.-palier)
Acier zingué
15 Vis à tête hex. (adaptateur-logem. de garn.)
16 Lanterne d’arrosage Téflon
MC
17 Anneaux de garniture (cinq) TéflonMC imprégné
18 Fouloir Inox AISI 300
19 Chemise d’arbre
20 Goujon de fouloir Inox AISI, type 300
21 Écrou de fouloir
22 Écrou de roue (SAE seulement)
22A Vis d’arrêt de l’écrou de roue (SAE seulement)
23
Lubrificateur à graisse (lubrific. à huile en option)
Inox 304
Polycarbonate
23
3
10
11
14
24
26
25
Graisseur Prime Safe (en option — M et L seulement)
COMPOSANTS DE LA POMPE
(suite)
No d’article Description Matériau
24 Boîte de lubrification Aluminium
25 Bouchon de tuyau Acier zingué
26 Joint à lèvre(s) Buna
* Sans plomb ; ➀ E-P = éthylène-propylène.
** L’article 5 est fourni pour le groupe S, dimensions 2½x3-7 (7½, 10 et 15 hp),
et le groupe M (sauf les dimensions 3x4-10).
COMPOSANTS DES PALIERS (v. page suivante)
No d’article Description Matériau
112 Roulement à billes externe
122 Arbre de pompe
Acier
122A Arbre de pompe (SAE) Acier AISI 4140
123 Déflecteur annulaire en V Buna-N
134 Couvercle de palier Fonte
138 Joint à lèvre(s) externe
139 Joint à lèvre(s) interne
168 Roulement à billes interne
193 Graisseur (groupes M et L)
Buna-N
Acier
327C Vis (couvercle de l’adaptateur) – SAE seulement Acier zingué
340 Adaptateur de moteur thermique SAE Fonte
361 Bague de retenue Acier
370C Vis à tête hex. (couvercle-palier)
Vis à tête hex. (adaptateur-palier) –
371C
SAE seulement – (non montrée) Acier
Acier zingué
399 Clavette (accouplement)
501N Couvercle de l’adaptateur – SAE seulement Acier galvanisé
43
Page 44

Paliers – séries 3656 et 3756
361 370C112
139
123 168 122 134
Palier du groupe S Palier du groupe M
370C
361
399
138
168
123
139
371L
112122193123
361
193 134
193
370C
399
138
139
168
399
138
193 134
112122193123
122A
112193168
Palier du groupe L Palier SAE
361
399
327C
138
501N
370C
340
134
44
Page 45

Notes
45
Page 46

Notes
46
Page 47

Declaration of Conformity
Declaration of Conformity
We at,
Goulds Water Technology/Xylem Inc.
1 Goulds Drive
Auburn, NY 13021
Declare that the following products: NPE, MCS, MCC, 3656, 3656 SP, GB, e-SV, SVI, NPO, Prime Line
SP, HB, HMS, LC, NPV, LB, LBS comply with Machine Directive 06/42/EC. This equipment is intended
to be incorporated with machinery covered by this directive, but must not be put into service until the
machinery into which it is to be incorporated has been declared in conformity with the actual provisions
of the directive.
Declaración de Conformidad
Declaración de Conformidad
Nosotros en
Goulds Water Technology/Xylem Inc.
1 Goulds Drive
Auburn, NY 13021
Declaramos que los siguientes productos: NPE, MCS, MCC, 3656, 3656 SP, GB, e-SV, SVI, NPO, Prime
Line SP, HB, HMS, LC, NPV, LB, LBS cumplen con las Directivas para Maquinarias 06/42/EC. Este
equipo ha sido diseñado para ser incorporado a la maquinaria cubierta por esta directiva pero no debe
ponerse en funcionamiento hasta que se declare que la maquinaria en la que será incorporado cumple
con las disposiciones reales de la directiva.
Déclaration de Conformité
Déclaration de Conformité
Nous, à
Goulds Water Technology/Xylem Inc.
1 Goulds Drive
Auburn, NY, U.S.A. 13021,
déclarons que les produits NPE, MCS, MCC, 3656, 3656 SP, GB, e-SV, SVI, NPO, Prime Line SP, HB,
HMS, LC, NPV, LB et LBS sont conformes à la directive 06/42/EC (législation relative aux machines). Ils
sont destinés à être intégrés dans la machinerie faisant l’objet de ladite directive, mais ne doivent pas être
mis en service tant que la machinerie en question ne sera pas déclarée conforme aux stipulations de la
directive.
47
Page 48

GARANTIE LIMITÉE DE GOULDS WATER TECHNOLOGY
La présente garantie s’applique à chaque pompe de système d’alimentation en eau fabriquée par Goulds Water Technology.
Toute pièce se révélant défectueuse durant la période de garantie sera remplacée sans frais pour le détaillant durant ladite période, qui dure douze (12) mois à compter de la
date d’installation ou dix-huit (18) mois à partir de la date de fabrication, soit la période qui expirera la première.
Le détaillant qui, aux termes de cette garantie, désire effectuer une demande de règlement doit s’adresser au distributeur Goulds Water Technology agréé chez lequel la pompe
a été achetée et fournir tous les détails à l’appui de sa demande. Le distributeur est autorisé à régler toute demande par le biais du service à la clientèle de Goulds Water
Technology.
La garantie ne couvre pas :
a) les frais de main-d’oeuvre ou de transport ni les frais connexes encourus par le détaillant ;
b) les frais de réinstallation de l’équipement réparé ;
c) les frais de réinstallation de l’équipement de remplacement ;
d) les dommages indirects de quelque nature que ce soit ;
e) ni les pertes découlant de la panne.
Aux fins de la présente garantie, les termes ci-dessous sont définis comme suit :
1) «Distributeur» signifie une personne, une société de personnes, une société de capitaux, une association ou autre entité juridique servant d’intermédiaire entre Goulds
Water Technology et le détaillant pour les achats, les consignations ou les contrats de vente des pompes en question.
2) «Détaillant» veut dire une personne, une société de personnes, une société de capitaux, une association ou autre entité juridique dont les activités commerciales sont la
vente ou la location de pompes à des clients.
3) «Client» signifie une entité qui achète ou loue les pompes en question chez un détaillant. Un «client» peut être une personne, une société de personnes, une société de
capitaux, une société à responsabilité limitée, une association ou autre entité juridique se livrant à quelque activité que ce soit.
CETTE GARANTIE SE RAPPORTE AU DÉTAILLANT SEULEMENT.
Xylem, Inc.
2881 East Bayard Street Ext., Suite A
Seneca Falls, NY 13148
Téléphone: (800) 453-6777
Télécopie: (888) 322-5877
www.xyleminc.com/brands/gouldswatertechnology
Goulds est une marque déposée de Goulds Pumps, Inc. et est utilisé sous le permis.
© 2012, Xylem Inc. IM010 Révision numéro 8 Juillet 2012
 Loading...
Loading...