Page 1

Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
R
Page 2

R
Xilinx is disclosing this Document and Intellectual Property (hereinafter “the Design”) to you for use in the development of designs to operate
on, or interface with Xilinx FPGAs. Except as stated herein, none of the Design may be copied, reproduced, distributed, republished,
downloaded, displayed, posted, or transmitted in any form or by any means including, but not limited to, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written consent of Xilinx. Any unauthorized use of the Design may violate copyright
laws, trademark laws, the laws of privacy and publicity, and communications regulations and statutes.
Xilinx does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of the Design; nor does Xilinx convey any license under its patents,
copyrights, or any rights of others. You are responsible for obtaining any rights you may require for your use or implementation of the Design.
Xilinx reserves the right to make changes, at any time, to the Design as deemed desirable in the sole discretion of Xilinx. Xilinx assumes no
obligation to correct any errors contained herein or to advise you of any correction if such be made. Xilinx will not assume any liability for the
accuracy or correctness of any engineering or technical support or assistance provided to you in connection with the Design.
THE DESIGN IS PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL FAULTS, AND THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO ITS FUNCTION AND IMPLEMENTATION IS
WITH YOU. YOU ACKNOWLEDGE AND AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NOT RELIED ON ANY ORAL OR WRITTEN INFORMATION OR
ADVICE, WHETHER GIVEN BY XILINX, OR ITS AGENTS OR EMPLOYEES. XILINX MAKES NO OTHER WARRANTIES, WHETHER
EXPRESS, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, REGARDING THE DESIGN, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, TITLE, AND NONINFRINGEMENT OF THIRD-PARTY RIGHTS.
IN NO EVENT WILL XILINX BE LIABLE FOR ANY CONSEQUENTIAL, INDIRECT, EXEMPLARY, SPECIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES,
INCLUDING ANY LOST DATA AND LOST PROFITS, ARISING FROM OR RELATING TO YOUR USE OF THE DESIGN, EVEN IF YOU
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. THE TOTAL CUMULATIVE LIABILITY OF XILINX IN CONNECTION
WITH YOUR USE OF THE DESIGN, WHETHER IN CONTRACT OR TORT OR OTHERWISE, WILL IN NO EVENT EXCEED THE
AMOUNT OF FEES PAID BY YOU TO XILINX HEREUNDER FOR USE OF THE DESIGN. YOU ACKNOWLEDGE THAT THE FEES, IF
ANY, REFLECT THE ALLOCATION OF RISK SET FORTH IN THIS AGREEMENT AND THAT XILINX WOULD NOT MAKE AVAILABLE
THE DESIGN TO YOU WITHOUT THESE LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY.
The Design is not designed or intended for use in the development of on-line control equipment in hazardous environments requiring failsafe controls, such as in the operation of nuclear facilities, aircraft navigation or communications systems, air traffic control, life support, or
weapons systems (“High-Risk Applications”). Xilinx specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of fitness for such High-Risk
Applications. You represent that use of the Design in such High-Risk Applications is fully at your risk.
© 2007 Xilinx, Inc. All rights reserved. XILINX, the Xilinx logo, and other designated brands included herein are trademarks of Xilinx,
Inc. PCI Express is a registered trademark of PCI-SIG. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Revision History
The following table shows the revision history for this document.
Date Version Revision
05/28/07 1.0 Initial Xilinx release.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 3
Table of Contents
Preface: About This Guide
Acknowledgments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Guide Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Additional Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Chapter 1: Introduction and Overview
Getting Started. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Operating the Default Demonstration Design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
VGA Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Rotary Knob/Push-Button Menu System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Select MultiBoot Configuration Image . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Scroll or Rotate Graphic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Scroll or Scale Graphic. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Restart AutoPilot, Speaker Volume Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
LCD Screen Control Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Power-Saving Suspend Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
RS-232 Serial Port Control Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Key Components and Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Design Trade-Offs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Configuration Methods Galore! . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Voltages for all Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Design Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Choose a Spartan-3 Generation Starter Kit Board for your Needs . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Spartan-3A/3AN FPGA Features and Embedded Processing Functions . . . . . . . . . . 22
Other Spartan-3 Generation Development Boards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Spartan-3A and Spartan-3AN FPGAs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Chapter 2: Switches, Buttons, and Rotary Knob
Slide Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Locations and Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
SUSPEND Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Push-Button Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Locations and Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
PROG_B Push-Button Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Rotary Push-Button Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Locations and Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Push-Button Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 3
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 4

Rotary Shaft Encoder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Discrete LEDs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Locations and Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Optional Discrete LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
AWAKE LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
INIT_B LED. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Chapter 3: Clock Sources
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Clock Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
50 MHz On-Board Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Auxiliary Clock Oscillator Socket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
SMA Clock Input or Output Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
UCF Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Clock Period Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
R
Chapter 4: FPGA Configuration Options
Configuration Mode Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Xilinx Platform Flash Configuration PROM(s) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
PROG Push-Button Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
DONE Pin LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Programming the FPGA or Platform Flash PROM via USB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Connecting the USB Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Platform Flash Programming Example in Spartan-3 Generation Configuration
User Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Chapter 5: Character LCD Screen
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Character LCD Interface Signals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Voltage Compatibility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
UCF Location Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
LCD Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
DD RAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
CG ROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
CG RAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Command Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Disabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Clear Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Return Cursor Home . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Entry Mode Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
4 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 5

R
Display On/Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Cursor and Display Shift . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Function Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Set CG RAM Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Set DD RAM Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Read Busy Flag and Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Write Data to CG RAM or DD RAM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Read Data from CG RAM or DD RAM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Four-Bit Data Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Transferring Eight-Bit Data over the Four-Bit Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Initializing the Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Power-On Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Display Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Writing Data to the Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Disabling the Unused LCD. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Chapter 6: VGA Display Port
Signal Timing for a 60 Hz, 640x480 VGA Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
VGA Signal Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
UCF Location Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Chapter 7: RS-232 Serial Ports
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
UCF Location Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Chapter 8: PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard Port
Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Mouse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Voltage Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Adding a Second PS/2 Port Using a Y-Splitter Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
UCF Location Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Chapter 9: Analog Capture Circuit
Digital Outputs from Analog Inputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Programmable Pre-Amplifier. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Programmable Gain. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
SPI Control Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
SPI Control Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 5
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 6

Connecting Analog Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Chapter 10: Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
SPI Communication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
SPI Communication Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Communication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Specifying the DAC Output Voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
UCF Location Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Chapter 11: Parallel NOR Flash PROM
Flash Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Shared SPI Flash and Platform Flash Data Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
UCF Location Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Setting the FPGA Mode Select Pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Creating and Programming Configuration Images for Parallel Flash . . . . . . . . . 89
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
R
Chapter 12: SPI Serial Flash
SPI Flash PROM Select Jumpers (J1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Shared SPI Flash and Platform Flash Data Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Jumper Settings to Configure FPGA from Selected SPI Flash PROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
UCF Location Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Creating and Programming Configuration Images for SPI Serial Flash . . . . . . . 95
SPI Flash PROM Programming Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Direct Programming Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Using Embedded USB JTAG Programmer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Using a Separate JTAG Parallel Programming Cable (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Direct SPI Flash Programming Using iMPACT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Indirect Programming Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Jumper Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Indirect SPI Flash Programming Using iMPACT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Chapter 13: DDR2 SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
UCF Location Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Reserve FPGA V
Special Layout Recommendations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
REF
6 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 7

R
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Chapter 14: 10/100 Ethernet Physical Layer Interface
Ethernet PHY Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
MicroBlaze Ethernet IP Cores . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
UCF Location Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Chapter 15: Expansion Connectors
Hirose 100-Pin FX2 Edge Connector (J17) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Expansion Connector Compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Voltage Supplies to the Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Connector Pinout and FPGA Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
FX2-Connector Compatible Boards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Mating Receptacle Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Differential I/O Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Using Differential Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Using Differential Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Differential Trace Layout Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
34-Conductor Cable Assemblies (2x17) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Six-Pin Accessory Headers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
J18 Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
J19 Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
J20 Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Digilent Peripheral Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Connectorless Debugging Port Landing Pads (J34) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Chapter 16: Miniature Stereo Audio Jack
Supported Audio Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
FPGA Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Chapter 17: Voltage Supplies
Measuring Power Across Voltage Supply Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
I2C Voltage Adjustment Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Possible Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Restoring Default Voltages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
UCF Location Constraints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Related Resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 7
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 8

R
8 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 9
R
About This Guide
This user guide provides basic information on the Spartan™-3A/3AN Starter Kit board
capabilities, functions, and design. It includes general information on how to use the
various peripheral functions included on the board. For detailed reference designs,
including VHDL or Verilog source code, please visit the following web link.
• Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board Web Page
http://www.xilinx.com/s3
There are multiple versions of the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit. This document describes
the three kits that include the “Revision D” Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board, which is an
updated version of the “Revision C” Spartan-3A Starter Kit Board. The following table
describes the different kits.
Preface
astarter and http://www.xilinx.com/s3anstarter
Feature
Part
Number
Device XC3S700AN XC3S700A
Board
Revision
DDR2
Memory
User
Guide
Web Pa g e www.xilinx.com/s3anstarter www.xilinx.com/s3addr2 www.xilinx.com/s3astarter
Spartan-3AN
Starter Kit
HW-SPAR3AN-SK-UNI-G
Supported with 133 MHz crystal oscillator in auxiliary socket
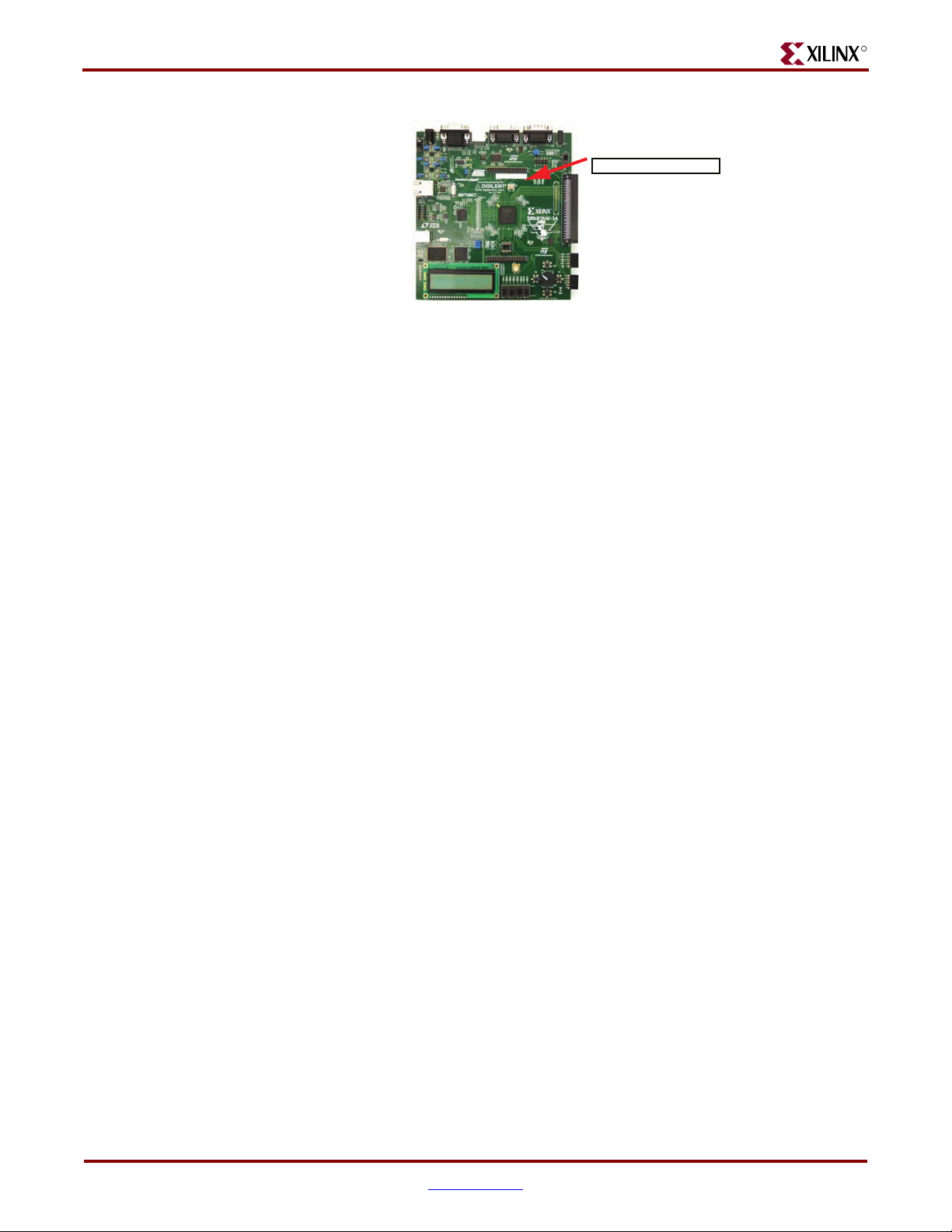
Almost all functionality is identical between the Revision C and Revision D boards,
although the silkscreen changes make the two boards look different. The pictures used in
this document are from the Revision D board. If you are using the original Revision C
version of the board, refer to
highlights where to find the board revision code on a Revision C board.
Spartan-3A DDR2 SDRAM
Interface Development Kit
HW-SPAR3ADDR2-DK-
UNI-G
Revision D Revision C
UG334 (this document) UG330
UG330 for pictures and documentation. The following figure
Spartan-3A Starter
Kit, Revision D
HW-SPAR3A-SK-UNI-G
Spartan-3A Starter Kit,
Revision C
Requires board
modification for
improved performance
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 9
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 10
Preface: About This Guide
Acknowledgments
Xilinx wishes to thank the following companies for their support of the Spartan-3A/3AN
Starter Kit board:
• STMicroelectronics for the 32 Mbit parallel NOR Flash and 16 Mbit SPI serial Flash
memories
• Atmel for the 16 Mbit SPI serial DataFlash memory
• Linear Technology for the SPI-compatible A/D and D/A converters and the
programmable pre-amplifier
• SMSC for the 10/100 Ethernet PHY
• National Semiconductor for the four-rail voltage regulators that power the FPGA and
and all peripheral components
• Xilinx, Inc. Configuration Solutions Division for the XCF04S Platform Flash PROM
and support for the embedded USB programmer
R
Board Revision Code
REV C
UG334_01_052707
Guide Contents
This manual contains the following chapters:
• Chapter 1, “Introduction and Overview,” provides an overview of the key features of
• Chapter 2, “Switches, Buttons, and Rotary Knob,” defines the switches, buttons, and
• Chapter 3, “Clock Sources,” describes the various clock sources available on the
• Chapter 4, “FPGA Configuration Options,” describes the configuration options for
• Chapter 5, “Character LCD Screen,” describes the functionality of the character LCD
• Chapter 6, “VGA Display Port,” describes the functionality of the VGA port.
• Chapter 7, “RS-232 Serial Ports,” describes the functionality of the RS-232 serial ports.
• Chapter 8, “PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard Port,” describes the functionality of the PS/2
• Chapter 10, “Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC),” describes the functionality of the
the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board.
knobs present on the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board.
the FPGA on the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board.
screen.
mouse and keyboard port.
D/A converter.
10 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 11
R
• Chapter 9, “Analog Capture Circuit,” describes the functionality of the A/D converter
with a programmable gain pre-amplifier.
• Chapter 11, “Parallel NOR Flash PROM,” describes the functionality of the
STMicroelectronics parallel NOR PROM.
• Chapter 12, “SPI Serial Flash,” describes the functionality of the SPI Serial Flash
memory interface.
• Chapter 13, “DDR2 SDRAM,” describes the functionality of the DDR2 SDRAM
memory interface.
• Chapter 14, “10/100 Ethernet Physical Layer Interface,” describes the functionality of
the 10/100Base-T Ethernet physical layer interface.
• Chapter 15, “Expansion Connectors,” describes the various connectors available on
the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board.
• Chapter 16, “Miniature Stereo Audio Jack,” describes the audio interface.
• Chapter 17, “Voltage Supplies,” describes the board’s power distribution system.
Additional Resources
To find additional documentation, see the Xilinx website at:
Additional Resources
http://www.xilinx.com/literature
.
To search the Answer Database of silicon, software, and IP questions and answers, or to
create a technical support WebCase, see the Xilinx website at:
h
ttp://www.xilinx.com/support.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 11
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 12

Preface: About This Guide
R
12 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 13
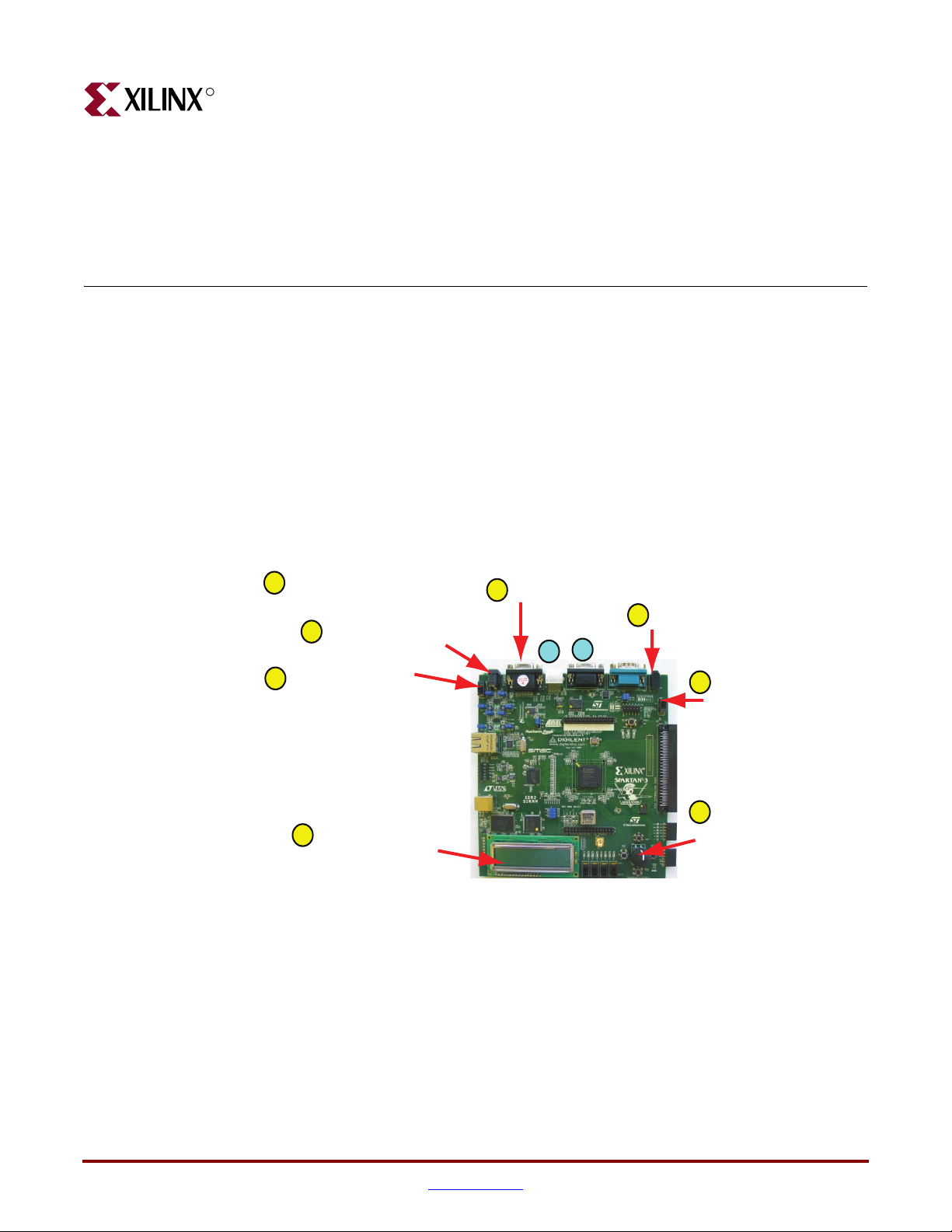
R
Introduction and Overview
Thank you for purchasing the Xilinx Spartan™-3A/3AN Starter Kit. The board is
invaluable to develop a Spartan-3A or Spartan-3AN FPGA application.
Getting Started
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board is ready for use, right out of the box. The design
stored in external Flash exercises the various I/O devices, such as the VGA display and
serial ports. In addition it demonstrates new FPGA features, such as selectable MultiBoot
and the power-saving Suspend mode.
To start using the board, follow the simple steps outlined in Figure 1-1.
Chapter 1
CHECK JUMPER SETTINGS!
1
Connect AC wall adapter.
5
Turn on power switch.
6
Optional: Connect VGA display.
2
3
RS-232
PS/2
10
9
Optional: Connect headphones
or amplified speakers
4
Set SUSPEND switch
to RUN position.
8
See messages and
7
instructions on LCD
character display.
Figure 1-1: Powering Up the Starter Kit Board
1. Double-check the position of the board jumpers, as shown in Figure 1-2, page 14.
These settings are required for the demonstration design to configure correctly.
2. Optionally connect a VGA display device. The display device can be a CRT, a flatpanel, or even a projector.
3. Optionally connect headphones or amplified speakers to the audio jack.
4. Set the SUSPEND switch to the “RUN” position.
5. Connect the included AC adapter to wall power and also to the board. The AC adapter
also includes attachments to support worldwide locals.
Control operation using
rotary / push-button switch.
UG334_c1_01_052407
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 13
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 14

Chapter 1: Introduction and Overview
6. Turn on the power switch.
7. The character LCD and VGA display, if connected, display various informational
messages and instructions. If an audio device is connected, the board offers words of
welcome in a variety of languages.
8. Use the rotary/push-button switch to control various board functions.
9. Optionally connect a PS/2-style keyboard to support one of the included
demonstrating designs.
10. Optionally connect a PC directly to the board using a standard 9-pin serial cable.
Power Supply Jumpers
(all jumpers installed)
Platform Flash Jumper
(jumper removed)
DONE
CE
PROM
GND
J46
R
SPI Flash Select Jumpers
(both jumpers installed, vertically)
J1
J4 2
J13
J12
J10 J9
J4 1
J40
J11
M0
M1
M2
J26
FPGA Mode Select Jumpers
(bottom two jumpers installed)
(SPI Mode)
UG334_c1_02_052707
Figure 1-2: Default Jumper Settings for Starter Kit Board
For more information on the demonstration design, visit the Design Examples web page:
• Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Demo Design Overview
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#demo
• Restoring the “Out of the Box” Flash Programming
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#out
14 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 15
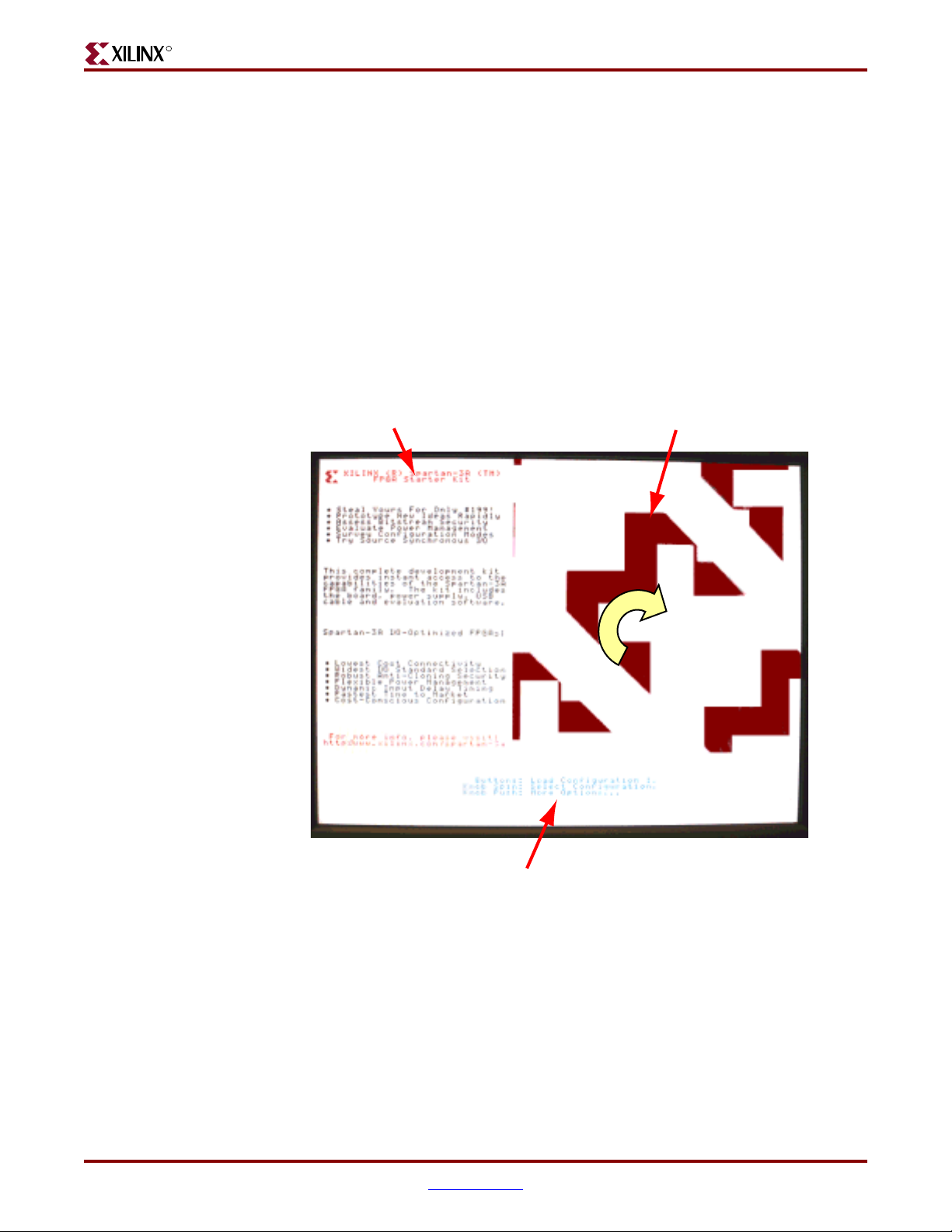
R
Operating the Default Demonstration Design
Operating the Default Demonstration Design
The demonstration design programmed onto the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board
provides various output information, depending on what I/O or display devices are
connected. The VGA and audio ports provide the richest experience.
VGA Display
If a VGA display is connected to the board, then the Starter Kit board displays graphics
similar to that shown in Figure 1-3.
Until one of the four push buttons around the rotary knob (Figure 2-5, page 27) is pressed,
the display automatically rotates a graphic image and zooms in and out around the image.
This is called “AutoPilot” mode. A brief text overview describing the board appears along
the left edge. Blue text at the bottom of the screen presents the menu system.
Rotating and Zooming GraphicsText Description
Rotary/Push-Button Menu System
UG330_c1_03_032207
Figure 1-3: Rotating/Zooming Graphics, Menu System Displayed on VGA Screen
Rotary Knob/Push-Button Menu System
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board demonstration design uses the rotary knob and
surrounding push-button switches, shown in Figure 2-5, page 27, to implement a menu
system. The menu display appears in blue text at the bottom of the VGA output. The menu
functions are highlighted in Tab le 1 -1 and Figure 1-4.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 15
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 16
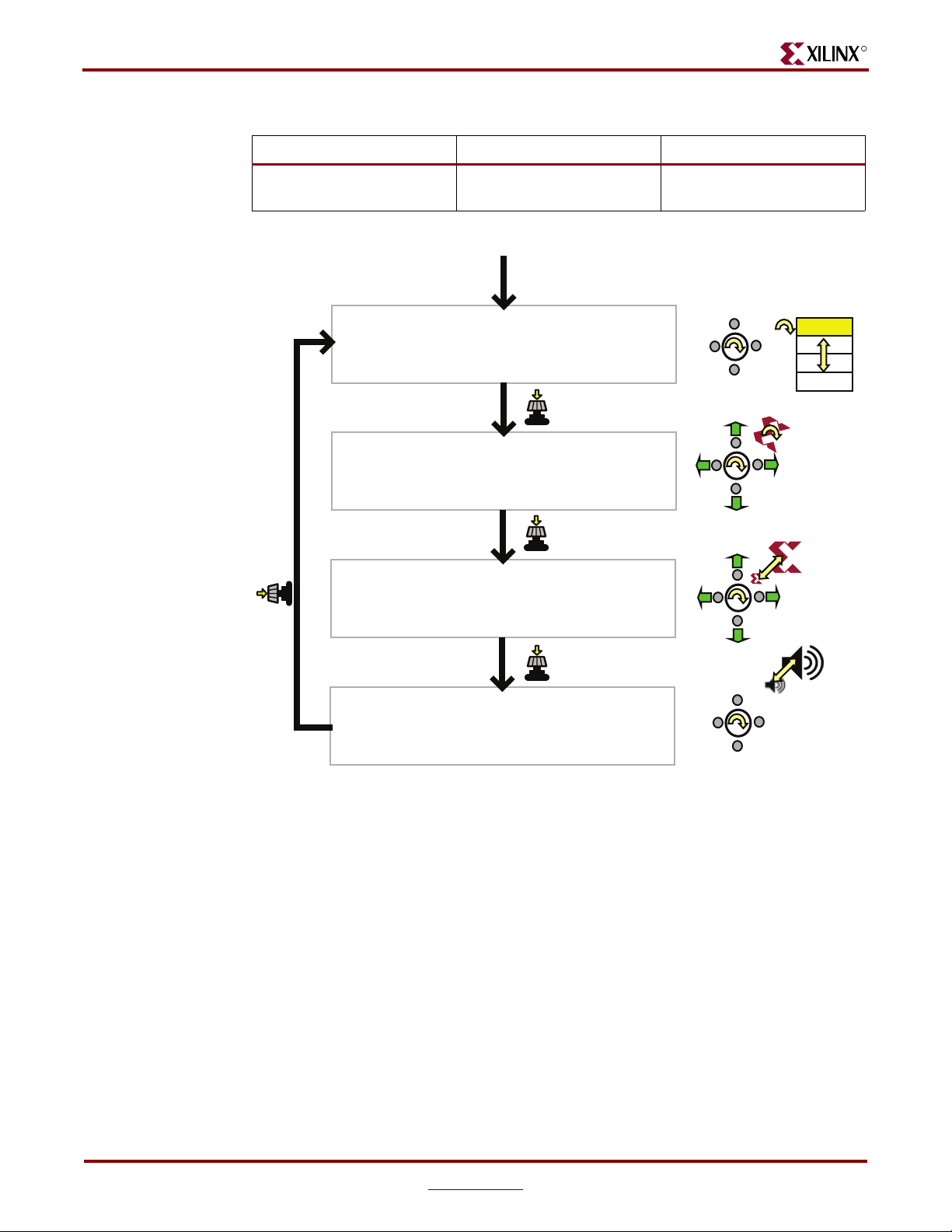
Chapter 1: Introduction and Overview
Table 1-1: Function of Each Menu Control
Press Knob Rotate Knob Press Push Button
R
Move to next menu selection,
next mode.
Start Demonstration Design
Select MultiBoot
Buttons: Load Configuration 1.
Knob Spin: Select Configuration.
Knob Push: More Options ...
Scroll/Rotate Graphic
Buttons: Scroll Image.
Knob Spin: Rotate Image.
Knob Push: More Options ...
Scroll/Scale Graphic
Press Knob
Buttons: Scroll Image.
Knob Spin: Scale Image.
Knob Push: More Options ...
Depends on current mode, as
shown in Figure 1-4.
Power-up board
Press PROG_B button
Press Knob
Press Knob
Depends on current mode, as
shown in Figure 1-4.
Select FPGA
MultiBoot
MultiBoot
MultiBoot
Configuration
MultiBoot
Config. 1
Config. 2
Config. 3
Config. 4
Rotate
Scale
AutoPilot/Volume
Buttons: Restart AutoPilot.
Knob Spin: Adjust Volume.
Knob Push: More Options ...
Figure 1-4: Rotary Knob/Push-Button Menu System
Select MultiBoot Configuration Image
Spartan-3A/3AN FPGAs support a selectable MultiBoot configuration interface. If the
FPGA configures in one of its Master configuration modes, then the FPGA always loads
the configuration image stored at address 0 in Flash at power-up, or whenever the
PROG_B button is pressed.
Spin the rotary knob to select a new FPGA configuration ima ge. The blue text at the bottom
of the display updates with each click of the rotary knob. For example, the application
displays “Buttons: Load Configuration x” where ‘x’ corresponds to the bitstream image
listed in Ta bl e 1- 2. Ta bl e 1 -2 describes the bitstreams preloaded on the board.
After selecting the desired image, press one of the four push-button switches that surround
the rotary knob. This action causes the FPGA to load the selected image from external
Flash memory.
To change to the “Scroll or Rotate Graphic” mode, press the rotary knob.
Press Knob
AutoPilot
AutoPilot
AutoPilot
Volume
AutoPilot
UG334_c1_04_052707
16 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 17

R
Operating the Default Demonstration Design
Table 1-2: FPGA Configuration Bitstreams Preprogrammed on the Starter Kit Board
FPGA
Configuration
Bitstream FPGA Application/Reference Design Example
0
(default)
1
2
3
4
Spartan-3AN
FPGA
Starter Kit board demonstration design. Loaded at power-up.
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#demo
Device DNA Reader: Reads the FPGA’s unique Device ID value and displays it on the character LCD
screen.
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#dna_reader
Fractal Generator: Computes fractal images in real time and displays on the VGA port. A usercontributed design by Matthias Alles. Rotate knob to zoom fractal image; press surrounding push
buttons to scroll the image.
www-user.rhrk.uni-kl.de/~alles/fpga/files.htm
ASCII Terminal: Implements a text terminal using an attached VGA display and PS/2 keyboard and
will communicate with HyperTerminal on a PC via an RS-232 serial connection.
Source included in www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#out
STMicro M29DW323DT Parallel Flash Programmer: Communicates to a PC using HyperTerminal via
an RS-232 serial connection. Programs, erases, and reads the STMicro M29DW323DT parallel Flash
PROM on the Starter Kit board.
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#parallel_flash_programmer
Internal Flash Paint Application: Use a mouse to create drawings and read or write them to In-System
Flash. Loaded from internal SPI Flash in Spartan-3AN Starter Kit Board. Requires setting Mode pins as
described in Tabl e 4 -1 , p ag e 3 9 for Internal Master SPI mode. For Spartan-3AN Starter Kit Board only.
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#paint
.
.
Scroll or Rotate Graphic
In this mode, rotate the knob to rotate the graphic image clockwise or counterclockwise.
Use the four push-button switches to scroll the graphic image up, down, left, or right.
Press the rotary knob to change to the “Scroll or Scale Graphic” mode.
Scroll or Scale Graphic
In this mode, rotate the knob to scale the size of the graphic image, zooming in and out.
Use the four push-button switches to scroll the resulting graphic image up, down, left, or
right.
Press the rotary knob to change to the “Restart AutoPilot, Speaker Volume Control” mode.
Restart AutoPilot, Speaker Volume Control
In this mode, rotate the knob to control the speaker output volume.
Press any of the four push-button switches to restart the AutoPilot function.
Press the rotary knob to change to the “Select MultiBoot Configuration Image” mode.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 17
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 18
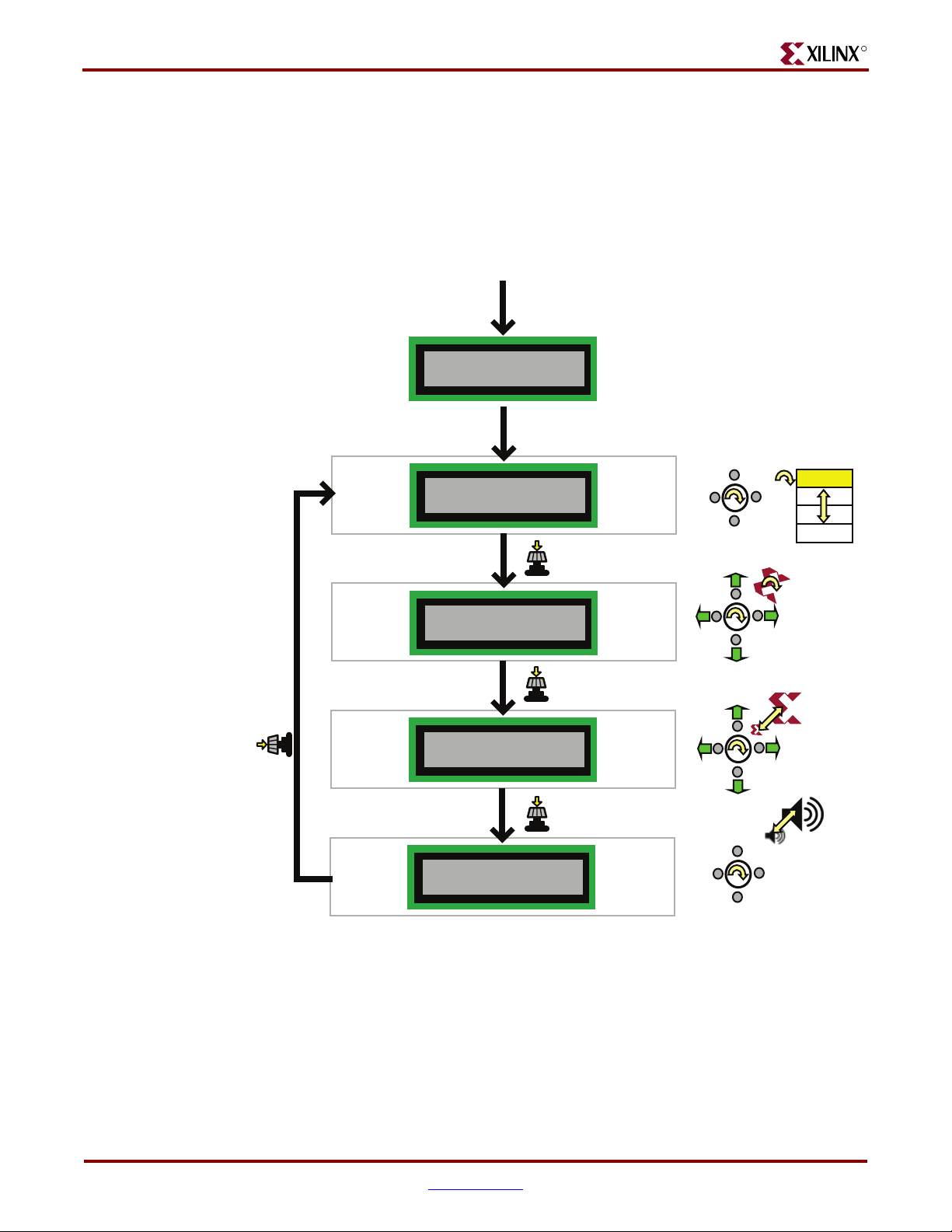
Chapter 1: Introduction and Overview
LCD Screen Control Option
While the demonstration design operates best with an attached VGA display, the on-board
LCD screen tracks similar functionality, as shown in Figure 1-5. If no VGA display is
attached, then the “Scroll or Rotate Graphic”, “Scroll or Scale Graphic”, and “Restart
AutoPilot, Speaker Volume Control” modes offer little to no functionality, the exception
being the volume control assuming that a speaker is attached to the audio jack.
Select MultiBoot
Start Demonstration Design
Power-up board
Press PROG_B button
Welcome to XLNX
S3A Starter Kit
Wait 1 second
Btns: Load Cfg 1
Spin: Select Cfg
MultiBoot
MultiBoot
MultiBoot
Select FPGA
Configuration
MultiBoot
Config. 1
Config. 2
Config. 3
Config. 4
R
Scroll/Rotate Graphic
Press Knob 3x
For Boot Menu
Scroll/Scale Graphic
Press Knob
Press Knob 2x
For Boot Menu
AutoPilot/Volume
Press Knob 1x
For Boot Menu
Figure 1-5: LCD Screen Output using Menu System
Power-Saving Suspend Mode
Press Knob
Press Knob
Press Knob
AutoPilot
AutoPilot
AutoPilot
Rotate
Scale
Volume
AutoPilot
UG334_c1_05_052707
All of the preloaded FPGA configuration bitstreams have the power-saving Suspend mode
enabled. Suspend mode reduces FPGA power consumption while preserving the present
state of the FPGA application and the FPGA’s configuration data. Set the SUSPEND switch
to RUN or SUSPEND as described in “SUSPEND Switch,” page 26.
18 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 19
R
Key Components and Features
Using one or two external multimeters, measure the corresponding difference in current
consumption, as described in “Measuring Power Across Voltage Supply Jumpers,” page
139.
Caution!
Flash PROM using configuration bitstream #4, as described in Ta b le 1 -2 .
Do not set the SUSPEND switch to “SUSPEND” while programming the parallel NOR
RS-232 Serial Port Control Option
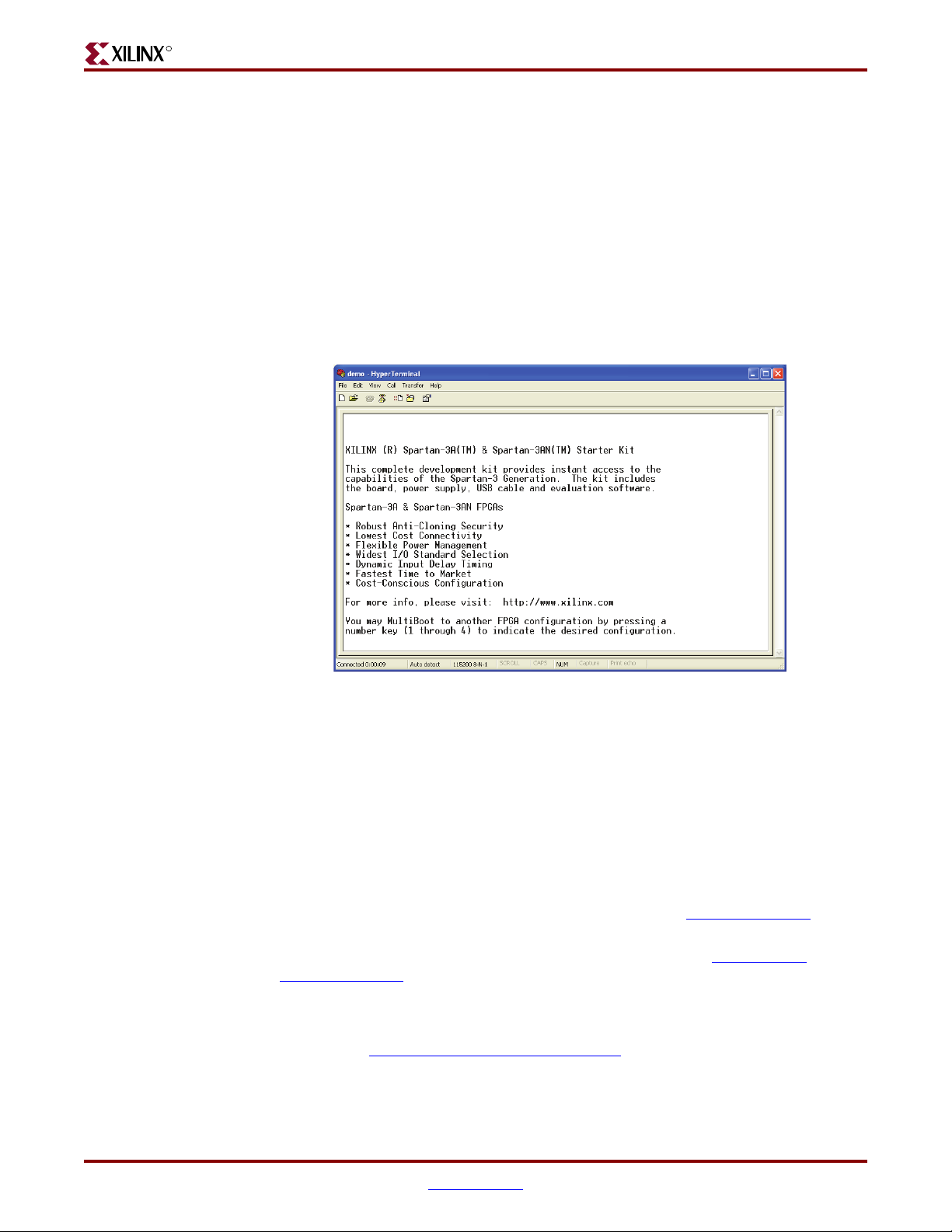
Optionally, control the demonstration design using a serial port connection to a PC or
workstation. On a PC, use the HyperTerminal program to communicate to the FPGA
application, as shown in Figure 1-6. Using a standard, straight-through 9-pin serial cable,
connect the PC’s 9-pin RS-232 port to the board’s DCE connector (see Figure 7-1, page 63).
Figure 1-6: Use HyperTerminal and a Standard Serial Cable to Connect to Board
When the demonstration design begins operating, it transmits a message using the serial
port.
Press a number key on the PC to load the associated MultiBoot bitstream listed in Tab le 1 -2.
Key Components and Features
The key features of the Spartan-3A Starter Kit board or the Spartan-3AN Starter Kit board
are:
• Spartan-3A Starter Kit Board: Xilinx 700K-gate XC3S700A Spartan-3A FPGA
Pb-free 484-ball BGA package (FGG484)
• Spartan-3AN Starter Kit Board: Xilinx 700K-gate XC3S700AN Spartan-3AN
nonvolatile FPGA in the Pb-free 484-ball BGA package (FGG484)
♦ Internal 8 Mbit In-System Flash memory
♦ Store FPGA configuration bitstream or nonvolatile data
• 4 Mbit Xilinx Platform Flash configuration PROM
• 64 MByte (512 Mbit) of DDR2 SDRAM, 32Mx16 data interface
• 4 MByte (32 Mbit) of parallel NOR Flash
UG334_c1_06_052707
in the
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 19
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 20

Chapter 1: Introduction and Overview
♦ FPGA configuration storage
♦ MicroBlaze™ code storage/shadowing
♦ x8 or x16 data interface after configuration
• Two 16 Mbit SPI serial Flash
♦ STMicroelectronics and Atmel DataFlash serial architectures
♦ FPGA configuration storage
- Supports single configuration bitstream or multiple MultiBoot configuration
bitstreams
♦ Nonvolatile data storage
♦ MicroBlaze code shadowing
• Two-line, 16-character LCD screen
• PS/2 port
♦ Supports PS/2-compatible mouse or keyboard
♦ Supports both mouse and keyboard using a Y-splitter cable (not included)
• VGA display port, 12-bit color
• 10/100 Ethernet PHY (requires Ethernet MAC in FPGA)
• Two nine-pin RS-232 ports (DTE- and DCE-style)
• On-board USB-based programming solution
♦ FPGA download/debug
♦ SPI serial Flash in-system direct programming
• 50 MHz clock oscillator
• 8-pin DIP socket for second oscillator
• SMA connector for clock inputs or outputs
• 100-pin Hirose FX2 expansion connector with up to 43 FPGA user I/Os
♦ Compatible with Digilent FX2 add-on cards
• High-speed differential I/O connectors
♦ Receiver: Six data channels or five data channels plus clock
♦ Transmitter: Six data channels or five data channels plus clock
♦ Supports multiple differential I/O standards, including LVDS, RSDS, mini-LVDS
♦ Also supports up to 24 single-ended I/O
♦ Uses widely available 34-conductor cables
• Two six-pin expansion connectors for Digilent Peripheral Modules
• Four-output, SPI-based Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
• Two-input, SPI-based Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) with programmable-gain
pre-amplifier
• Stereo audio jack using digital I/O pins
• ChipScope
• Rotary-encoder with push-button shaft
• Eight discrete LEDs
• Four slide switches
• Four push-button switches
R
™ SoftTouch debugging port
20 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 21

R
Design Trade-Offs
A few system-level design trade-offs were required in order to provide the Spartan3A/3AN Starter Kit board with the most functionality.
Configuration Methods Galore!
A typical FPGA application uses a single, nonvolatile memory to store configuration
images. A typical Spartan-3AN nonvolatile FPGA application would not require any
external memory. To demonstrate new Spartan-3A and Spartan-3AN FPGA capabilities,
the starter kit board has four different configuration memory sources that all must function
well together. The extra configuration functions make the starter kit board more complex
than typical FPGA applications.
The starter kit board also includes an on-board USB-based JTAG programming interface.
The on-chip circuitry simplifies the device programming experience. In typical
applications, the JTAG programming hardware resides off-board or in a separate
programming module, such as the Xilinx Platform USB cable.
Voltages for all Applications
Design Trade-Offs
The Spartan-3A/3AN FPGA typically operates with two supply rails, 1.2V and 3.3V. The
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board showcases a quadruple-output regulator developed by
National Semiconductor specifically to power Spartan-3 Generation FPGAs. This regulator
is sufficient for most standalone FPGA applications.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Design Examples
Visit the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Design Examples web page to download and use the
latest applications that specifically target the starter kit board:
• Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Design Examples Web Page
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm
The list of designs is ever growing and the applications are often updated to the latest
software releases. The following list provides a sample of design examples:
• Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Demo Design Overview
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#demo
This describes the out-of-the box demo design shipped with the board. Includes how
to set up and operate the demonstration, evaluate MultiBoot and Suspend, and
provides demo technical details.
• Restoring the “Out of the Box” Flash Programming
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#out
Provides a short overview of what the starter kit board does “out of the box” and
includes instructions on how to restore the board to the original “out of the box” state.
The ZIP file includes the “golden” MCS files that are pre-programmed into Flash
memory before the board is shipped. The PDF file contains instructions for restoring
the board to its original settings using these MCS files in case any of the configuration
memories were overwritten during normal use.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 21
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 22

Chapter 1: Introduction and Overview
• Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board Verification Design
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#test
This example includes the board test specification and the board test design. This
design was used during initial board verification and some functions are used during
production test. It is provided to test out a board if something is not working as
expected. The design files may also be of general interest. The ZIP file has the design
source, a script to run them, and the resulting compiled files.
• Programmer for the STMicroelectronics M29DW323DT Parallel NOR Flash
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#parallel_flash
_programmer
This design transforms the Spartan-3A or Spartan-3AN FPGA into a programmer for
the 32Mbit STMicroelectronics M29DW323DT parallel NOR Flash memory. This
memory optionally holds configuration images for the FPGA and provides general
non-volatile storage for other applications implemented within the FPGA. Using a
simple terminal program, this application provides the following capabilities:
♦ Erase the memory in part or in full
♦ Read the memory to verify contents
♦ Download complete configuration images using standard MCS files
♦ Manually program individual bytes
♦ Display the device identifier and 64-bit unique device numbers
• Spartan-3A/3AN “Device DNA” Reader
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#dna_reader
This design uses a PicoBlaze™ processor to read the unique “Device DNA” identifier
embedded in each Spartan-3A/3AN FPGA and then display it on the LCD screen.
R
Choose a Spartan-3 Generation Starter Kit Board for your Needs
The Spartan-3A and Spartan-3AN Starter Kit boards are best for prototyping
Spartan-3A/3AN FPGA applications. Depending on specific requirements, however,
Xilinx and third-party companies offer development boards that better suit other needs.
Spartan-3A/3AN FPGA Features and Embedded Processing Functions
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board highlights the unique features of the Spartan-3A
and Spartan-3AN FPGA families and provides a convenient development board for
embedded processing applications. The board highlights these features:
• Spartan-3AN specific features
♦ Nonvolatile configuration from internal SPI Flash
• Spartan-3A/3AN specific features
♦ Parallel NOR Flash configuration
♦ SPI serial Flash configuration using either the STMicroelectronics or Atmel
DataFlash architectures
♦ MultiBoot FPGA configuration from both Parallel NOR and SPI serial Flash
PROMs
• Embedded development
♦ MicroBlaze 32-bit embedded RISC processor
22 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 23
R
♦ PicoBlaze eight-bit embedded controller
Spartan-3A and Spartan-3AN FPGAs
• Power management using the Suspend mode feature
• DDR2 SDRAM memory interfaces
Other Spartan-3 Generation Development Boards
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board demonstrates the full capabilities of the
Spartan-3A and Spartan-3AN FPGA families and the Xilinx ISE™ development software.
For a development board specific to the Spartan-3E FPGA family, consider the Spartan-3E
Starter Kit board. There are multiple ordering codes, depending on the included power
supply.
• Spartan-3E Starter Kit Board (H
W-SPAR3E-SK_xx)
www.xilinx.com/s3estarter
For MicroBlaze development, consider the XC3S1600E Embedded Development board.
• XC3S1600E Embedded Development Board (DO-SP3E1600E-DK-UNI-G)
www.xilinx.com/sp3e1600e
For PCI Express® applications, consider the Spartan-3 PCI Express Starter Kit.
• Spartan-3 PCI Express Starter Kit (HW-S3PCIE-DK)
www.xilinx.com/s3pcie
For simple Spartan-3 FPGA applications, consider the fairly basic Spartan-3 Starter Kit
board.
• Spartan-3 Starter Kit (
HW-SPAR3-SK-UNI-G)
www.xilinx.com/s3starter
Also consider the capable boards offered by Xilinx partners:
• Spartan-3 and Spartan-3E Board Interactive Search
www.xilinx.com/products/devboards/index.htm
Spartan-3A and Spartan-3AN FPGAs
The Spartan-3AN FPGA platform offers nonvolatile pin-compatible versions of the
Spartan-3A FPGA platform. The Spartan-3AN FPGAs support the same external
programming sources as Spartan-3A FPGAs, but add an additional internal SPI Flash
programming mode. The internal SPI Flash can also be used for user data. The
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board supports both external and Spartan-3AN internal
configuration options.
Spartan-3AN FPGAs require V
to be either 2.5V or 3.3V. The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board uses a default V
to be 3.3V while Spartan-3A FPGAs allow V
CCAUX
CCAUX
CCAUX
of
3.3V.
Spartan-3A and Spartan-3AN FPGAs have different documentation and availability. Verify
the latest version of the appropriate documentation on xilinx.com.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 23
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 24

Chapter 1: Introduction and Overview
• Spartan-3A FPGAs
♦ Web pa ge
www.xilinx.com/spartan3a
♦ Data sheet
www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/publications/ds529.pdf
♦ Errata
www.xilinx.com/xlnx/xweb/xil_publications_display.jsp?category=-1212251
♦ Additional documentation
www.xilinx.com/xlnx/xweb/xil_publications_display.jsp?category=-1212246
• Spartan-3AN FPGAs
♦ Web pa ge
www.xilinx.com/spartan3an
♦ Data sheet
www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/publications/ds557.pdf
♦ Errata
www.xilinx.com/xlnx/xweb/xil_publications_display.jsp?category=-1212871
♦ Additional documentation
www.xilinx.com/xlnx/xweb/xil_publications_display.jsp?category=-1212828
R
Related Resources
Refer to the following links for additional information:
• Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit
www.xilinx.com/s3astarte
♦ Spartan-3A/3AN Rev D Starter Kit user guide
♦ Spartan-3A Rev C Starter Kit user guide
♦ Example User Constraints File (UCF)
♦ Board schematics (annotated)
♦ Bill of materials (BOM) list
♦ Link to design examples
• Xilinx MicroBlaze Soft Processor
www.xilinx.com/microblaze
• Xilinx PicoBlaze Soft Processor
www.xilinx.com/picoblaze
• Xilinx Embedded Development Kit
w
ww.xilinx.com/ise/embedded_design_prod/platform_studio.htm
• Xilinx Software Tutorials
ww.xilinx.com/support/techsup/tutorials/
w
• Xilinx Technical Support
www.xilinx.com/support
r and www.xilinx.com/s3anstarter
www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/userguides/ug33
4.pdf
www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/userguides/ug330.pdf
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/files/s3astarter.ucf
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/s3astarter_schematic.pdf
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/s3astarter_bom.xls
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.ht
m
24 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 25
R
Chapter 2
Switches, Buttons, and Rotary Knob
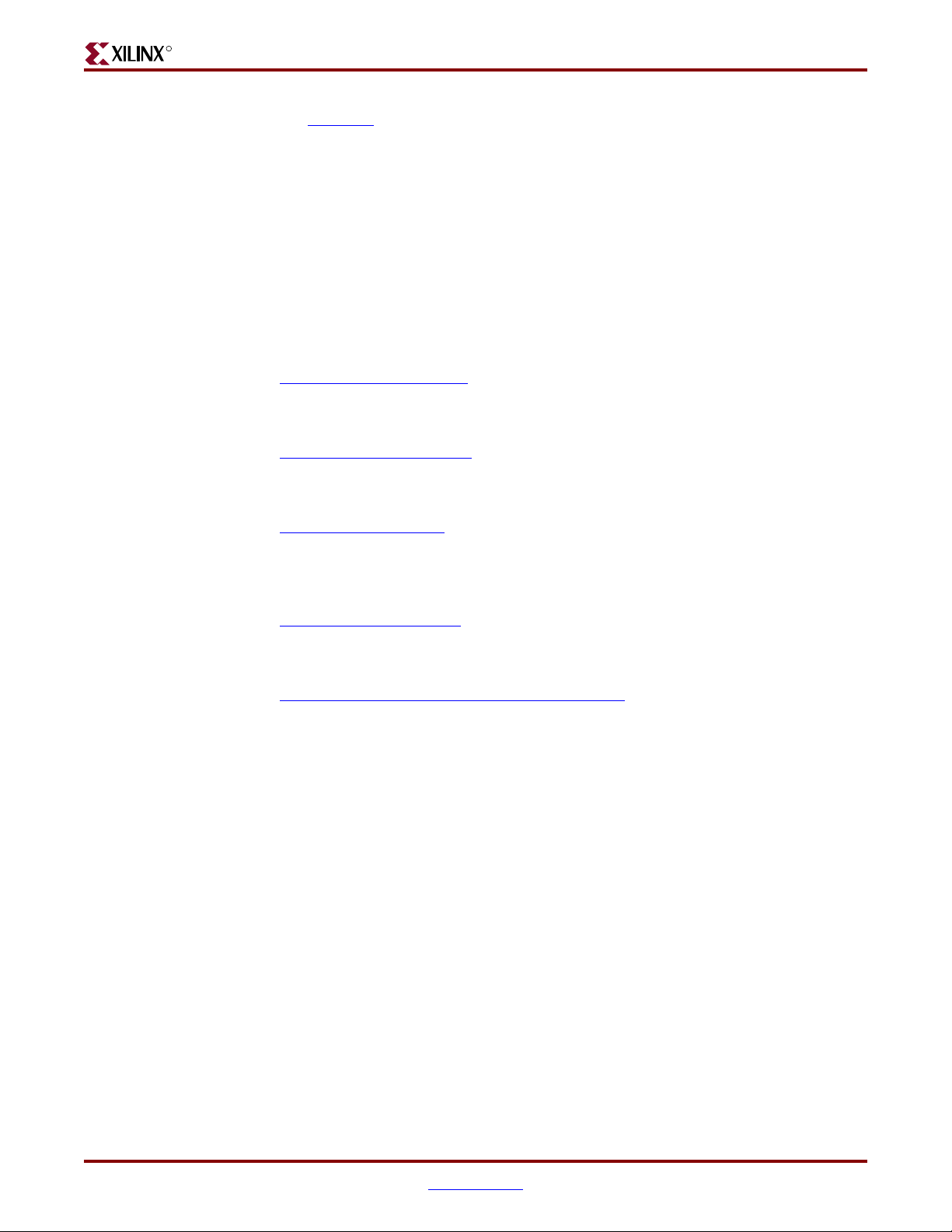
Slide Switches
Locations and Labels
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board has four slide switches, as shown in Figure 2-1. The
slide switches are located in the lower right corner of the board and are labeled SW3
through SW0. Switch SW3 is the left-most switch, and SW0 is the right-most switch.
SW3
(T9)
Operation
When in the UP or ON position, a switch connects the FPGA pin to 3.3V, a logic High.
When DOWN or in the OFF position, the switch connects the FPGA pin to ground, a logic
Low. The switches typically exhibit about 2 ms of mechanical bounce. There is no active
debouncing circuitry, although such circuitry could easily be added to the FPGA design
programmed on the board.
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 2-2 provides the UCF constraints for the four slide switches, including the I/O pin
assignment and the I/O standard used. The PULLUP resistor is not required, but it defines
the input value when the switch is in the middle of a transition.
SW2
(U8)
Figure 2-1: Four Slide Switches
SW1
(U10)
SW0
(V8)
HIGH, ‘1’
LOW, ‘0’
UG330_c2_01_021507
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 25
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 26

Chapter 2: Switches, Buttons, and Rotary Knob
NET "SW<0>" LOC = "V8" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLUP ;
NET "SW<1>" LOC = "U10"| IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLUP ;
NET "SW<2>" LOC = "U8" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLUP ;
NET "SW<3>" LOC = "T9" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL |
Figure 2-2: UCF Constraints for Slide Switches
SUSPEND Switch
The SUSPEND slide switch, shown in Figure 2-3, connects directly to the FPGA’s
SUSPEND input pin. If Suspend mode is enabled in the FPGA application, then the FPGA
enters Suspend mode whenever the switch is set to “SUSPEND.” If the switch is then
changed back to “RUN,” then the FPGA resumes operation from the state before it entered
Suspend mode. Likewise, if Suspend mode is enabled, then the AWAKE pin is reserved to
indicate when the FPGA is in Suspend mode. See “AWAKE LED,” page 32.
R
PULLUP ;
RUN
SUSPEND
UG334_c2_03_052407
Figure 2-3: Suspend Switch
To enable Suspend mode, add the configuration string shown in Figure 2-4 to the user
constraints file (UCF). If Suspend mode is not enabled in the application, then the
SUSPEND switch has no affect on the design and the AWAKE pin is available as a generalpurpose I/O.
CONFIG ENABLE_SUSPEND = “FILTERED” ;
Figure 2-4: UCF Constraints to Enable Suspend Mode
For more information on Suspend mode, see the following application note:
• XAPP480: Using Suspend Mode in Spartan-3 Generation FPGAs
www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/
appnotes/xapp480.pdf
26 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 27
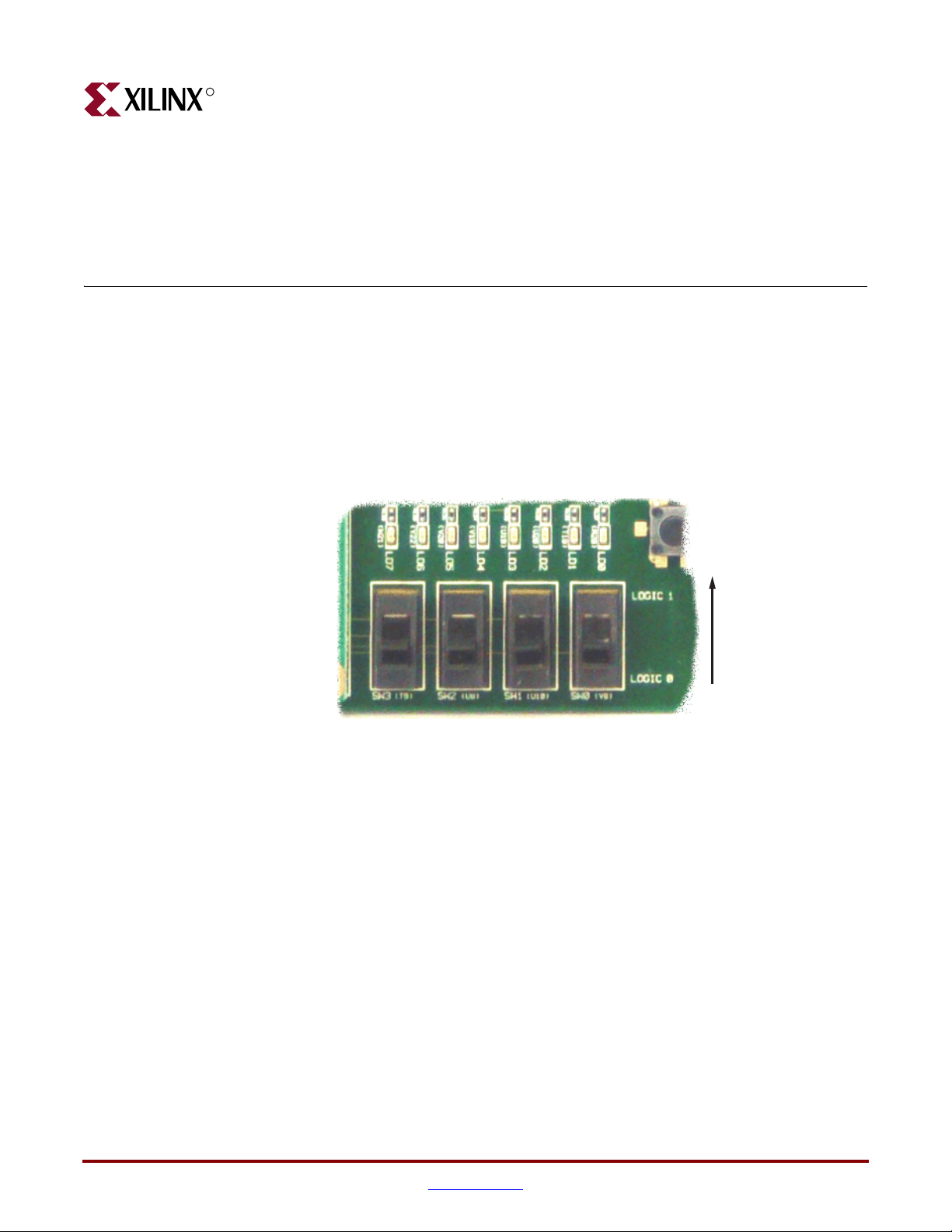
R
Push-Button Switches
Locations and Labels
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board has four momentary-contact push-button
switches, shown in Figure 2-5. The push buttons are located in the lower right corner of the
board and are labeled BTN_NORTH, BTN_EAST, BTN_SOUTH, and BTN_WEST. The
FPGA pins that connect to the push buttons appear in parentheses in Figure 2-5, and the
associated UCF is listed in Figure 2-7.
BTN_NORTH
(T14)
Rotary Push Button Switch
ROT_A: (T13)
ROT_B: (R14)
ROT_CENTER: (R13)
Push-Button Switches
Requires an internal pull-up
Requires an internal pull-up
Requires an internal pull-down
Operation
BTN_WEST
(U15)
BTN_SOUTH
(T15)
BTN_EAST
(T16)
UG334_c2_05_052407
Notes:
1. All BTN_* push-button inputs require an internal pull-down resistor.
Figure 2-5: Four Push-Button Switches Surround the Rotary Push-Button Switch
Pressing a push button connects the associated FPGA pin to 3.3V, as shown in Figure 2-6.
Use an internal pull-down resistor within the FPGA pin to generate a logic Low when the
button is not pressed. Figure 2-7 shows how to specify a pull-down resistor within the
UCF. There is no active debouncing circuitry on the push button.
3.3V
Push Button
FPGA I/O Pin
BTN_* Signal
UG230_c2_03_021206
Figure 2-6: Push-Button Switches Require an Internal Pull-Down Resistor in the
FPGA Input Pin
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 27
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 28

Chapter 2: Switches, Buttons, and Rotary Knob
PROG_B Push-Button Switch
The PROG_B push-button switch, shown in Figure 2-14, page 31, is part of the FPGA’s
configuration circuitry. See “PROG Push-Button Switch,” page 40.
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 2-7 provides the UCF constraints for the four push-button switches, including the
I/O pin assignment and the I/O standard used, and defines a pull-down resistor on each
input.
NET "BTN_EAST" LOC = "T16" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLDOWN ;
NET "BTN_NORTH" LOC = "T14" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLDOWN ;
NET "BTN_SOUTH" LOC = "T15" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLDOWN ;
NET "BTN_WEST" LOC = "U15" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLDOWN ;
Figure 2-7: UCF Constraints for Push-Button Switches
Rotary Push-Button Switch
R
Locations and Labels
The rotary push-button switch is located in the center of the four individual push-button
switches, as shown in Figure 2-5, page 27. The switch produces three outputs. The two
shaft encoder outputs are ROT_A and ROT_B. The center push-button switch is
ROT_CENTER.
Operation
The rotary push-button switch integrates two different functions. The switch shaft rotates
and outputs values whenever the shaft turns. The shaft can also be pressed, acting as a
push-button switch.
Push-Button Switch
Pressing the knob on the rotary/push-button switch connects the associated FPGA pin to
3.3V, as shown in Figure 2-8. Use an internal pull-down resistor within the FPGA pin to
generate a logic Low. Figure 2-11 shows how to specify a pull-down resistor within the
UCF. There is no active debouncing circuitry on the push button.
28 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 29

R
Rotary / Push Button
Rotary Push-Button Switch
3.3V
FPGA I/O Pin
ROT_CENTER Signal
UG230_c2_05_021206
Figure 2-8: Push-Button Switches Require an Internal Pull-up Resistor in the FPGA
Input Pin
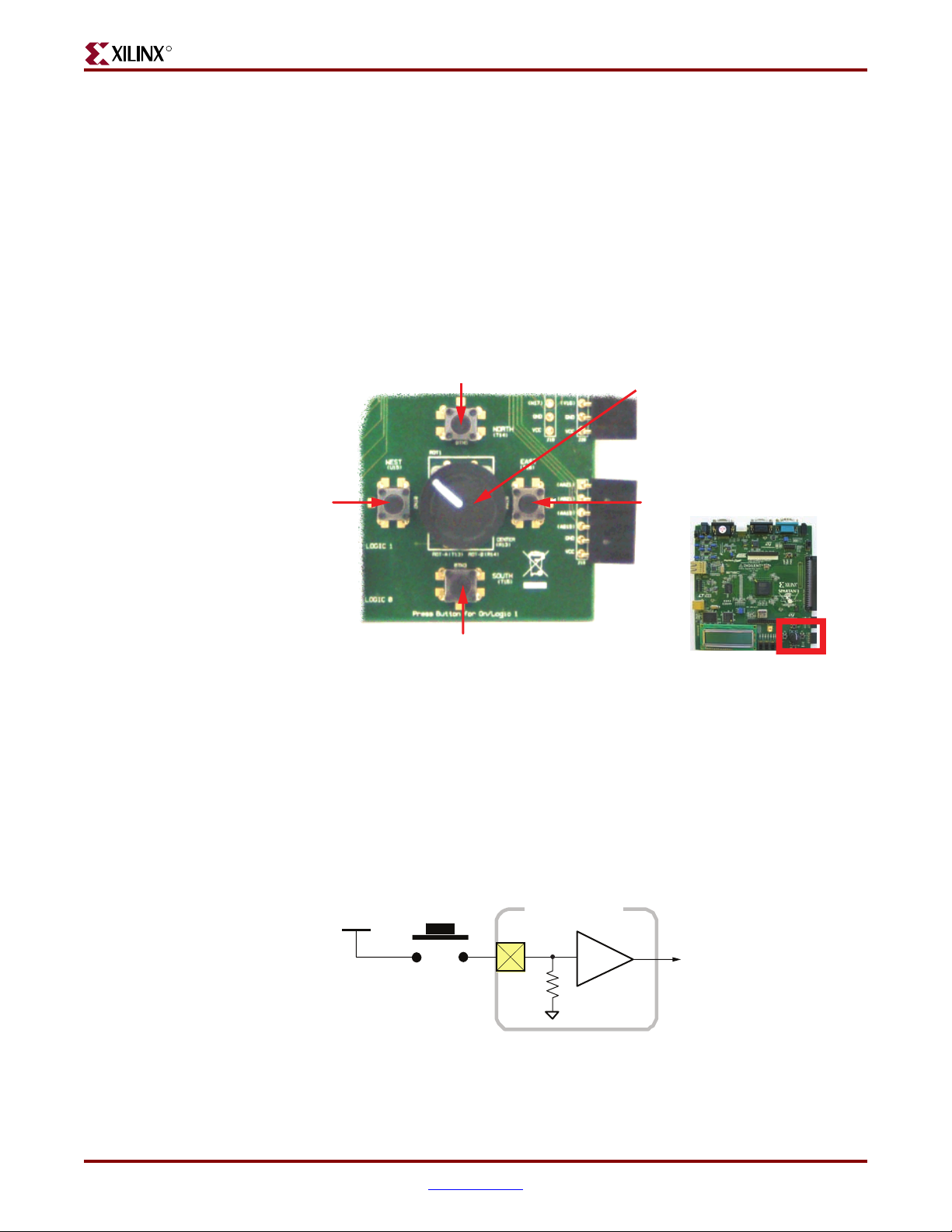
Rotary Shaft Encoder
In principal, the rotary shaft encoder behaves much like a cam connected to the central
shaft. Rotating the shaft then operates two push-button switches, as shown in Figure 2-9.
Depending on which way the shaft is rotated, one of the switches opens before the other.
Likewise, as the rotation continues, one switch closes before the other. However, when the
shaft is stationary, also called the detent position, both switches are closed.
A pull-up resistor in each input pin
generates a ‘1’ for an open switch.
See the UCF file for details on
specifying the pull-up resistor.
A=‘0’
FPGA
Vcco
Vcco
Rotary Shaft
Encoder
B=‘1’
GND
UG230_c2_06_030606
Figure 2-9: Basic Example of Rotary Shaft Encoder Circuitry
Closing a switch connects it to ground, generating a logic Low. When the switch is open, a
pull-up resistor within the FPGA pin pulls the signal to a logic High. The UCF constraints
in Figure 2-11 describe how to define the pull-up resistor.
The FPGA circuitry to decode the ‘A’ and ‘B’ inputs is simple but must consider the
mechanical switching noise on the inputs, also called chatter. As shown in Figure 2-10, the
chatter can falsely indicate extra rotation events or even indicate rotations in the opposite
direction!
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 29
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 30
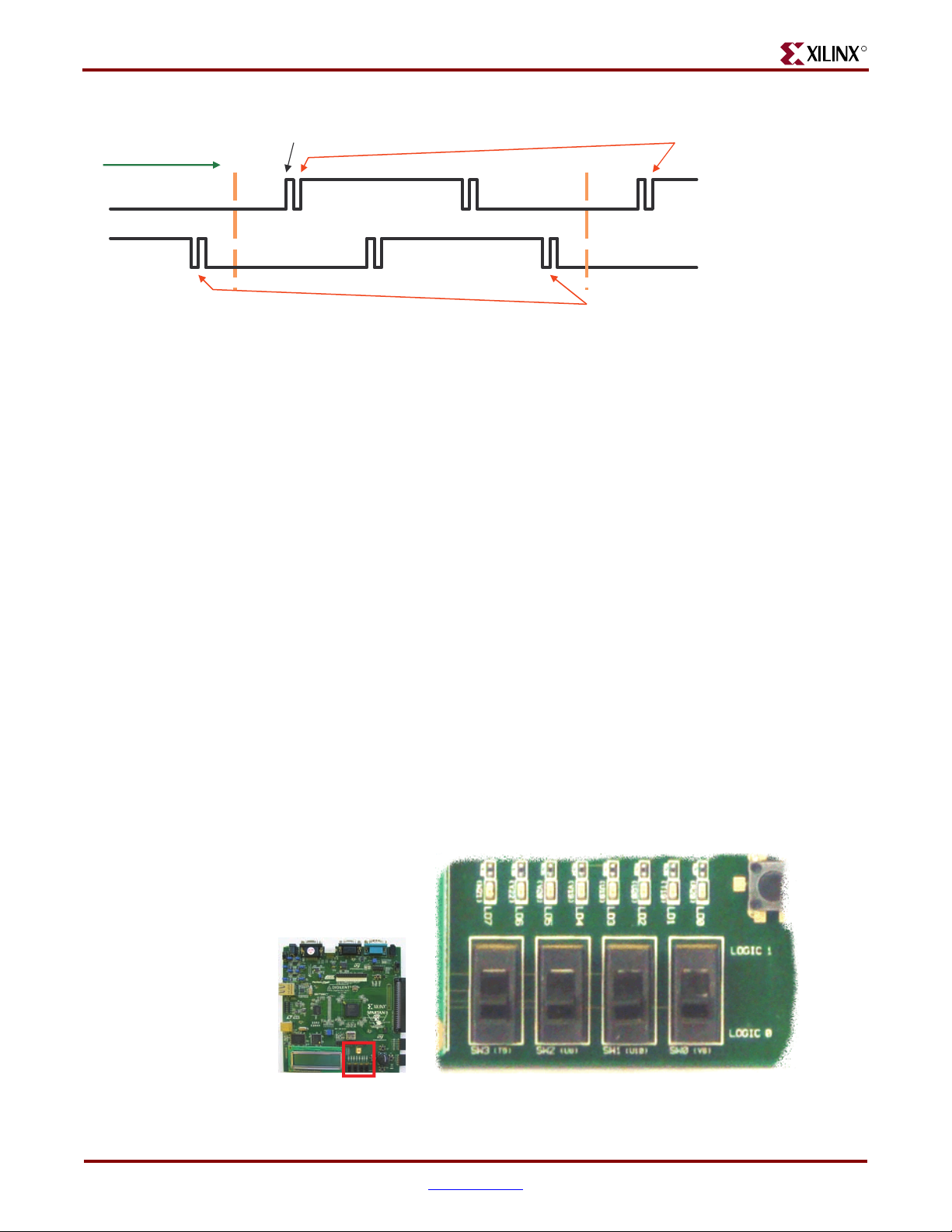
Chapter 2: Switches, Buttons, and Rotary Knob
R
Rotating RIGHT
A
B
UCF Location Constraints
Rising edge on ‘A’ when ‘B’ is Low indicates RIGHT (clockwise) rotation
Detent
Detent
Switch closing chatter on ‘B’
injects false “clicks” to the LEFT
(’B’ rising edge when ‘A’ is Low)
Switch opening chatter on ‘A’
injects false “clicks” to the RIGHT
UG230_c2_07_030606
Figure 2-10: Outputs from Rotary Shaft Encoder Might Include Mechanical Chatter
Figure 2-11 provides the UCF constraints for the rotary encoder/push-button switch,
including the I/O pin assignment and the I/O standard used, and defines a pull-up or
pull-down resistor for each FPGA input.
NET "ROT_A" LOC = "T13" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLUP ;
NET "ROT_B" LOC = "R14" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLUP ;
NET "ROT_CENTER" LOC = "R13" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | PULLDOWN ;
Figure 2-11: UCF Constraints for Rotary Push-Button Switch
Discrete LEDs
Locations and Labels
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board has eight individual surface-mount LEDs located
immediately above the slide switches as shown in Figure 2-12. The LEDs are labeled LED7
through LED0. LED7 is the left-most LED, LED0 the right-most LED.
LED6: (Y22)
LED7: (W21)
LED5: (V20)
LED4: (V19)
LED3: (U19)
LED2: (U20)
LED1: (T19)
LED0: (R20)
UG334_c2_12_052407
Figure 2-12: Eight Discrete LEDs
30 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 31

R
Operation
Each LED has one side connected to ground and the other side connected to a pin on the
device via a 390Ω current limiting resistor. To light an individual LED, drive the associated
FPGA control signal High.
If the FPGA is not yet configured, the LEDs may be dimly lit because pull-up resistors are
enabled during configuration. The FPGA’s PUDC_B pin is connected to GND on the
board.
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 2-13 provides the UCF constraints for the four push-button switches, including the
I/O pin assignment, the I/O standard used, the output slew rate, and the output drive
current.
NET "LED<7>" LOC = "W21" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "LED<6>" LOC = "Y22" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "LED<5>" LOC = "V20" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "LED<4>" LOC = "V19" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "LED<3>" LOC = "U19" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "LED<2>" LOC = "U20" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "LED<1>" LOC = "T19" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "LED<0>" LOC = "R20" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4
Optional Discrete LEDs
;
Optional Discrete LEDs
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board provides two optional LEDs, shown in Figure 2-14.
Depending on which features are used by an application, these LED connections may be
also used as user-I/O pins.
Figure 2-13: UCF Constraints for Eight Discrete LEDs
FPGA PROG_B Pin
(Press to reset/reprogram FPGA)
FPGA_INIT_B
(W21)
RED
FPGA_AWAKE
(AB15)
YELLOW
YELLOW
FPGA DONE Pin
(Lit when FPGA is configured)
GREEN
UG334_c2_14_052407
Figure 2-14: AWAKE and INIT_B LEDs
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 31
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 32

Chapter 2: Switches, Buttons, and Rotary Knob
AWAKE LED
The yellow-colored AWAKE LED connects to the FPGA’s AWAKE pin and is used if the
FPGA Suspend mode is enabled in the bitstream. If the Suspend mode is not used, then the
FPGA’s AWAKE pin is available as a full user-I/O pin.
If the FPGA is not yet configured, the FPGA’s AWAKE pin is dimly lit because pull-up
resistors are enabled during configuration. The FPGA’s PUDC_B pin is connected to GND
on the board.
To light the AWAKE LED in an application, drive the AWAKE pin High.
INIT_B LED
The red-colored INIT_B LED serves multiple purposes:
• At power-up or when the PROG_B button is pressed, the LED flashes momentarily
while the FPGA clears its configuration memory.
• If configuration fails for any reason, then the FPGA’s DONE LED will be unlit and the
INIT_B LED will light. This indicates that the FPGA could not successfully configure.
• After the FPGA successfully completes, the INIT_B pin is available as a generalpurpose user-I/O pin. If no signal drives INIT_B, then it is defined as an input pin
with a pull-down resistor. It might appear that the LED dimly glows. Drive the
INIT_B pin High to turn off the LED or Low to light the LED.
• If using the Readback CRC feature, the INIT_B pin is reserved and signals a CRC error
after configuration. If such an error occurs, the FPGA drives INIT_B Low, lighting the
LED.
R
If using the INIT_B pin as a user-I/O pin after configuration, drive the pin Low to light the
LED and High to shut it off. Jumper J46, shown in Table 4-2 , pa ge 40 , must be in either the
“Disabled” or “Enabled during Configuration” setting.
The “Always Enabled” setting for Jumper J46 allows the FPGA to read additional data
from the Platform Flash PROM after configuration, as described in Xilinx application note
XAPP694
.
Caution!
If the jumper controlling the Platform Flash PROM, jumper J46 in Table 4-2, page 40, is set to
“Always Enabled,” then the INIT_B signal controls the PROM’s active-Low output-enable (OE
input or active-High RESET input.
The FPGA’s INIT_B pin also connects to the Platform Flash PROM’s OE/RESET pin.
• XAPP694: Reading User Data from Configuration PROMs
www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/appnotes/xapp694.pdf
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 2-15 provides the UCF constraints for the optional LEDs, including the I/O pin
assignment, the I/O standard used, the output slew rate, and the output drive current. The
ENABLE_SUSPEND constraint must be set to NO in order to use FPGA_AWAKE LED.
NET "FPGA_INIT_B" LOC = "V13" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4 ;
# The AWAKE LED is only available if Suspend mode is disabled
CONFIG ENABLE_SUSPEND = NO ;
NET "FPGA_AWAKE" LOC = "AB15" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = QUIETIO | DRIVE = 4 ;
)
Figure 2-15: UCF Constraints for Optional Discrete LEDs
32 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 33

R
Clock Sources
Overview
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board supports three primary clock input sources, as
shown in Figure 3-1.
• The board includes an on-board 50 MHz clock oscillator.
• Clocks can be supplied off-board via an SMA-style connector. Alternatively, the FPGA
can generate clock signals or other high-speed signals on the SMA-style connector.
• A 133 MHz clock oscillator is installed in the CLK_AUX socket. Optionally substitute
a separate eight-pin DIP-style clock oscillator in the provided socket.
Chapter 3
CLK_50MHZ
(E12)
CLK_SMA
(U12)
Figure 3-1: Clock Sources on Starter Kit Board
CLK_AUX
(V12)
UG334_c3_01_052407
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 33
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 34

Chapter 3: Clock Sources
Clock Connections
Each of the clock inputs connect directly to a global buffer input. As shown in Ta bl e 3 -1 ,
each of the clock inputs also optimally connects to an associated DCM.
Only the CLK_AUX or the CLK_SMA input can use the associated DCM at any time.
However, both inputs are available as clock inputs.
Table 3-1: Clock Inputs and Associated Global Buffers and DCMs
Clock Input FPGA Pin I/O Bank Global Buffer Associated DCM LOC
CLK_50MHZ E12 0 GCLK5 Top Right DCM_X2Y3
CLK_AUX V12 2 GCLK2 Bottom Right DCM_X2Y0
CLK_SMA U12 2 GCLK3
50 MHz On-Board Oscillator
The board includes a 50 MHz oscillator with a 40% to 60% output duty cycle. The oscillator
is accurate to ±2500 Hz or ±50 ppm.
R
Auxiliary Clock Oscillator Socket
A 133 MHz clock oscillator is installed in the auxiliary clock oscillator socket. The provided
eight-pin socket accepts clock oscillators that fit the eight-pin DIP (8DIP) footprint.
Substitute the oscillator in this socket if the FPGA application requires a frequency other
than 50 MHz or 133 MHz. Alternatively, use the FPGA’s Digital Clock Manager (DCM) to
generate or synthesize other frequencies from the on-board 50 MHz or 133 MHz oscillator.
Caution!
associated socket.
Be aware of the pin 1 orientation on the crystal oscillator when installing it in the
SMA Clock Input or Output Connector
To provide a clock from an external source, connect the input clock signal to the SMA
connector. The FPGA can also generate a single-ended clock output or other high-speed
signal on the SMA clock connector for an external device.
UCF Constraints
The clock input sources require two different types of constraints. The location constraints
define the I/O pin assignments and I/O standards. The period constraints define the clock
period—and consequently the clock frequency—and the duty cycle of the incoming clock
signal.
Location
Figure 3-2 provides the UCF constraints for the three clock input sources, including the
I/O pin assignment and the I/O standard used.
34 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 35

R
NET "CLK_50MHZ" LOC = "E12"| IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 ;
NET "CLK_AUX" LOC = "V12"| IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 ;
NET "CLK_SMA" LOC = "U12"| IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 ;
Clock Period Constraints
The Xilinx ISE development software uses timing-driven logic placement and routing. Set
the clock PERIOD constraint as appropriate. An example constraint appears in Figure 3-3
for the on-board 50 MHz clock oscillator. The CLK_50MHZ frequency is 50 MHz, which
equates to a 20 ns period. The output duty cycle from the oscillator ranges between 40% to
60%.
# Define clock period for 50 MHz oscillator
NET "CLK_50MHZ" PERIOD = 20.0ns HIGH 40%;
Related Resources
Related Resources
Figure 3-2: UCF Location Constraints for Clock Sources
Figure 3-3: UCF Clock PERIOD Constraint
Refer to the following links for additional information:
• Epson SG-8002JF Series Oscillator Data Sheet (50 MHz Oscillator)
www.eea.epson.com/go/Prod_Admin/Categories/EEA/QD/Crystal_Oscillators/prog_oscillators/go/
Resources/TestC2/SG8002JF
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 35
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 36

Chapter 3: Clock Sources
R
36 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 37

R
FPGA Configuration Options
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board supports a variety of FPGA configuration options:
• Program the Spartan-3AN internal SPI Flash memory, then configure the FPGA at
power-up. This option is not available in the Spartan-3A Starter Kit.
• Download FPGA designs directly to the Spartan-3A/3AN FPGA via JTAG, using the
on-board USB interface. The on-board USB-JTAG logic also provides in-system
programming for the on-board Platform Flash PROM. SPI serial Flash and StrataFlash
programming are performed separately.
• Program the on-board 4 Mbit Xilinx XCF04S serial P
configure the FPGA from the image stored in the Platform Flash PROM using Master
Serial mode.
• Program the on-board 16 Mbit STMicroelectronics SPI serial Flash PROM or the
16 Mbit Atmel SPI-based DataFlash PROM, then configure the FPGA from the image
stored in the SPI serial Flash PROM using SPI mode. Further, an FPGA application
can dynamically load different FPGA configurations using the FPGA’s MultiBoot
mode. See U
on the MultiBoot feature. See Chapter 12, “SPI Serial Flash,” for more information on
using SPI serial Flash memory.
• Program the on-board 32 Mbit STMicroelectronics parallel NOR Flash PROM, then
configure the FPGA from the image stored in the Flash PROM using BPI Up
configuration mode. Further, an FPGA application can dynamically load different
FPGA configurations using the FPGA’s MultiBoot mode. See UG332
Generation Configuration User Guide for additional details on the MultiBoot feature. See
Chapter 11, “Parallel NOR Flash PROM,” for more information on using parallel
Flash memory.
G332: Spartan-3 Generation Configuration User Guide for additional details
latform Flash PROM, then
Chapter 4
: Spartan-3
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 37
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 38

Chapter 4: FPGA Configuration Options
Figure 4-1 indicates the position of the USB download/programming interface and the
on-board non-volatile memories that potentially store FPGA configuration images.
R
16 Mbit Atmel DataFlash SPI Serial Flash
4 Mbit Platform Flash
PROM
16 Mbit ST Micro SPI Serial Flash
PROGRAM Button
DONE LED
USB-based Download/
Debugging Port
Uses standard USB cable
FPGA Mode Select
Jumpers
In-System SPI Flash
(Spartan-3AN Starter Kit board only)
32 Mbit STMicro Flash
Parallel NOR Flash memory
Byte Peripheral Interface (BPI) mode
UG334_c4_01_052407
Figure 4-1: Starter Kit FPGA Configuration Options
The configuration mode jumpers determine which configuration mode the FPGA uses
when power is first applied, or whenever the PROG button is pressed.
The DONE pin LED lights when the FPGA successfully finishes configuration.
Pressing the PROG button forces the FPGA to restart its configuration process.
The Xilinx Platform Flash PROM provides easy, JTAG-programmable configuration
storage for the FPGA. The FPGA configures from the Platform Flash using Master Serial
mode.
38 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 39

R
Configuration Mode Jumpers
As shown in Tab le 4- 1, the J26 jumper block settings control the FPGA’s configuration
mode. Inserting a jumper grounds the associated mode pin. Insert or remove individual
jumpers to select the FPGA’s configuration mode and associated configuration memory
source. The J26 jumper block is shown in Figure 4-1.
Table 4-1: Configuration Mode Jumper Settings
Configuration Mode Jumpers
Mode Pins
Configuration Mode
M2:M1:M0
FPGA Configuration Image Source
Internal Master SPI 0:1:1 Spartan-3AN Starter Kit Board only! This
mode configures a Spartan-3AN FPGA
using the internal In-System Flash memory.
This mode is not supported on the
Spartan-3A Starter Kit board.
Master Serial 0:0:0 Platform Flash PROM
Set the J46 jumper per Tab le 4 -2
Master SPI
(see Chapter 12,
0:0:1 Select SPI Serial Flash PROM starting at
address 0
“SPI Serial Flash”)
Select specific SPI Flash PROM using
Jumper J1 (Table 12-2, page 93).
Disable the Platform Flash PROM via J46
jumper per Ta bl e 4 -2 .
Master BPI Up
(see Chapter 11,
“Parallel NOR Flash
0:1:0 Parallel NOR Flash PROM, starting at
address 0 and incrementing through address
space.
PROM”)
Disable the Platform Flash PROM via J46
jumper per Ta bl e 4 -2 .
J26 Jumper
Settings
M0
M1
M2
J26
M0
M1
M2
J26
M0
M1
M2
J26
M0
M1
M2
J26
J46 Jumper
Setting
DONE
CE
PROM
GND
J46
DISABLE
DONE
CE
PROM
GND
J46
JTAG 1:0:1 Downloaded from host via USB-JTAG port
M0
M1
M2
J26
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 39
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 40

Chapter 4: FPGA Configuration Options
Xilinx Platform Flash Configuration PROM(s)
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board includes a Xilinx Platform Flash configuration
interface. A single 4 Mbit XCF04S Platform Flash PROM appears in the JTAG chain with
the FPGA.
R
Caution!
PROM on the board. Be aware of potential data contention issues with the SPI serial Flash and
the D0 line of the parallel NOR Flash, depending on the current FPGA “Configuration Mode
Jumpers”, shown in Ta bl e 4 - 1.
The J46 jumper, shown in Table 4-2, page 40, enables or disables the Platform Flash
Caution! If the J46 jumper shown in Table 4-2, page 40 is set for “Always Enabled”, then the
FPGA’s INIT_B pin controls the Platform Flash PROM’s OE/RESET input. The INIT_B pin must
be High to read any data, other than from the Platform Flash PROM.
When using the Platform Flash PROM to configure the FPGA, the configuration mode
jumpers must be set for Master Serial mode, as shown in Tab le 4 -2 . If using any other
configuration mode, the Platform Flash PROM must be disabled.
Table 4-2: Platform Flash Enable Jumper (J46)
Platform Flash
Mode
Platform Flash
Enable (J46)
Allowed FPGA
Configuration Mode
Precautions/
Contention
None. Platform Flash disabled.
Disabled
(no jumper)
J46
DONE
CE
PROM
GND
Any
(see Ta bl e 4- 1)
The FPGA application has full
access to SPI serial Flash and
parallel NOR Flash PROMs after
configuration.
None. Platform Flash enabled
Enabled during
FPGA
Configuration
J46
DONE
CE
PROM
GND
Master Serial
or JTAG
during configuration and
disabled after configuration. The
FPGA application has full access
to SPI serial Flash and parallel
NOR Flash PROMs after
configuration.
Platform Flash continuously
Always
Enabled
J46
DONE
CE
PROM
GND
Master Serial
or JTAG
enabled. The FPGA application
can read additional data from
Platform Flash after
configuration as described in
application note XAPP694
:
Reading User Data from
Configuration PROMs. The FPGA
application has no read access to
SPI Flash or parallel NOR Flash.
PROG Push-Button Switch
The PROG push-button switch, labeled in Figure 4-1, forces the FPGA to reconfigure from
the configuration memory source selected by the “Configuration Mode Jumpers,” page 39.
Press and release this button to restart the FPGA configuration process at any time.
40 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 41

R
DONE Pin LED
The DONE pin LED, labeled in Figure 4-1, lights whenever the FPGA is successfully
configured. If this LED is not lit, then the FPGA is not configured.
Programming the FPGA or Platform Flash PROM via USB
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit includes embedded USB-based programming logic and a
USB endpoint with a Type B connector. Via a USB cable connection with the host PC, the
iMPACT programming software directly programs the FPGA, the Platform Flash PROM,
or the on-board CPLD. Direct programming of the parallel or serial Flash PROMs is not
presently supported.
Connecting the USB Cable
The kit includes a standard USB Type A/Type B cable, similar to the one shown in
Figure 4-2. The actual cable color might vary from the picture.
DONE Pin LED
USB Type B Connector
Connects to Starter Kit's USB connector
USB Type A Connector
Connects to computer's USB connector
UG230_c4_04_030306
Figure 4-2: Standard USB Type A/Type B Cable
The wider and narrower Type A connector fits the USB connector at the back of the
computer.
After installing the Xilinx software, connect the square Type B connector to the Spartan3A/3AN Starter Kit board, as shown in Figure 4-3. The USB connector is on the left side of
the board, immediately next to the Ethernet connector. When the board is powered on, the
Windows operating system automatically recognizes and installs the associated driver
software.
UG334_c4_03_052407
Figure 4-3: Connect the USB Type B Connector to the Starter Kit Board Connector
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 41
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 42

Chapter 4: FPGA Configuration Options
When the USB cable driver is successfully installed and the board is correctly connected to
the PC, a green LED lights up, indicating that the programming cable is ready. The USB
connection also has a red LED, which only lights if the Xilinx software is programming
firmware updates to the USB interface.
Platform Flash Programming Example in Spartan-3 Generation Configuration User Guide
The Spartan-3 Generation Configuration User Guide includes step-by-step instructions, some
including screen shots, on how to prepare the FPGA bitstream and download it to the
FPGA or PROM.
• UG332: Spartan-3 Generation Configuration User Guide
www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/userguides/ug332.pdf
For formatting and programming Platform Flash PROMs, please refer to the “Master Serial
Mode” chapter.
R
42 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 43

R
Character LCD Screen
Overview
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board prominently features a 2-line by 16-character
liquid crystal display (LCD). The FPGA controls the LCD via the eight-bit data interface
shown in Figure 5-1. The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board also supports the four-bit data
interface to remain compatible with other Xilinx development boards.
Chapter 5
Caution!
When using four-bit mode, the FPGA must drive the LCD_DB<3:0> signals High.
Character LCD
FPGA
(Y15)
(AB16)
(Y16)
(AA12)
(AB12)
(AB17)
(AA13)
(Y13)
(AB4)
(Y14)
(W13)
Figure 5-1: Character LCD Interface
LCD_DB<7>
LCD_DB<6>
LCD_DB<5>
LCD_DB<4>
LCD_DB<3>
LCD_DB<2>
LCD_DB<1>
LCD_DB<0>
LCD_E
LCD_R S
LCD_R W
390Ω
All
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
E
RS
R/W
Display
interface
Four-bit data
Eight-bit data interface
UG334_c5_01_052407
Once mastered, the LCD is a practical way to display a variety of information using
standard ASCII and custom characters. However, these displays are not fast. Scrolling the
display at half-second intervals tests the practical limit for clarity. Compared with the
50 MHz clock available on the board, the display is slow. A PicoBlaze processor efficiently
controls display timing plus the actual content of the display.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 43
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 44

Chapter 5: Character LCD Screen
Character LCD Interface Signals
Tab le 5- 1 shows the interface character LCD interface signals.
Table 5-1: Character LCD Interface
Signal Name FPGA Pin Function
LCD_DB<7> Y15 Data bit DB7
LCD_DB<6> AB16 Data bit DB6
LCD_DB<5> Y16 Data bit DB5
LCD_DB<4> AA12 Data bit DB4
LCD_DB<3> AB12 Data bit DB3 When using the four-bit
LCD_DB<2> AB17 Data bit DB2
LCD_DB<1> AB18 Data bit DB1
LCD_DB<0> Y13 Data bit DB0
LCD_E AB4 Read/Write Enable Pulse
LCD_RS Y14 Register Select
LCD_RW W13 Read/Write Control
R
interface, drive these signals
High.
0: Disabled
1: Read/Write operation enabled
0: Instruction register during write operations.
Busy Flash during read operations
1: Data for read or write operations
0: Write, LCD accepts data
1: Read, LCD presents data
Voltage Compatibility
The character LCD is power by +5V. The FPGA I/O signals are powered by 3.3V. However,
the FPGA’s output levels are recognized as valid Low or High logic levels by the LCD. The
LCD controller accepts 5V TTL signal levels and the 3.3V LVCMOS outputs provided by
the FPGA meet the 5V TTL voltage level requirements.
The 390Ω series resistors on the data lines prevent overstressing on the FPGA and
StrataFlash I/O pins when the character LCD drives a High logic value. The character LCD
drives the data lines when LCD_RW is High. Most applications treat the LCD as a writeonly peripheral and never read from the display.
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 5-2 provides the UCF constraints for the Character LCD, including the I/O pin
assignment and the I/O standard used.
44 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 45

R
LCD Controller
LCD Controller
NET "LCD_E" LOC = "AB4" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_RS" LOC = "Y14" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_RW" LOC = "W13" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_DB<7>" LOC = "Y15" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_DB<6>" LOC = "AB16" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_DB<5>" LOC = "Y16" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_DB<4>" LOC = "AA12" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_DB<3>" LOC = "AB12" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_DB<2>" LOC = "AB17" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_DB<1>" LOC = "AB18" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
NET "LCD_DB<0>" LOC = "Y13" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = QUIETIO ;
Figure 5-2: UCF Location Constraints for the Character LCD
The 2 x 16 character LCD has an internal Sitronix ST7066U graphics controller that is
functionally equivalent with the following devices.
• Samsung S6A0069X
or KS0066U
• Hitachi HD44780
• SMOS SED1278
Memory Map
The controller has three internal memory regions, each with a specific purpose: DD RAM,
CG ROM, and CG RAM. The display must be initialized before accessing any of these
memory regions.
DD RAM
The Display Data RAM (DD RAM) stores the character code to be displayed on the screen.
Most applications interact primarily with DD RAM. The character code stored in a DD
RAM location references a specific character bitmap stored either in the predefined CG
ROM character set or in the user-defined CG RAM character set.
Figure 5-3 shows the default address for the 32 character locations on the display. The
upper line of characters is stored between addresses 0x00 and 0x0F. The second line of
characters is stored between addresses 0x40 and 0x4F.
Character Display Addresses
1
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F 10 … 27
Undisplayed
Addresses
40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 4F 50 … 67
2
1234567891011121314151617…40
Figure 5-3: DD RAM Hexadecimal Addresses (No Display Shifting)
Physically, there are 80 total character locations in DD RAM with 40 characters available
per line. Locations 0x10 through 0x27 and 0x50 through 0x67 can be used to store other
non-display data. Alternatively, these locations can also store characters that can only be
displayed using controller’s display shifting functions.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 45
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 46

Chapter 5: Character LCD Screen
The Set DD RAM Address command initializes the address counter before reading or
writing to DD RAM. Write DD RAM data using the Write Data to CG RAM or DD RAM
command, and read DD RAM using the Read Data from CG RAM or DD RAM command.
The DD RAM address counter either remains constant after read or write operations, or
auto-increments or auto-decrements by one location, as defined by the I/D set by the Entry
Mode Set command.
CG ROM
The Character Generator ROM (CG ROM) contains the font bitmap for each of the
predefined characters that the LCD screen can display, shown in Figure 5-4. The character
code stored in DD RAM for each character location subsequently references a position with
the CG ROM. For example, a hexadecimal character code of 0x53 stored in a DD RAM
location displays the character ‘S’. The upper nibble of 0x53 equates to DB[7:4] = 0101
binary and the lower nibble equates to DB[3:0] = 0011 binary. As shown in Figure 5-4, the
character ‘S’ appears on the screen.
English/Roman characters are stored in CG ROM at their equivalent ASCII code
addresses.
R
46 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 47

R
LCD Controller
Lower Data Nibble
DB7
Upper Data Nibble
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
UG230_c5_02_030306
Figure 5-4: LCD Character Set
The character ROM contains the ASCII English character set and Japanese katakana
characters.
The controller also provides for eight custom character bitmaps, stored in CG RAM. These
eight custom characters are displayed by storing character codes 0x00 through 0x07 in a
DD RAM location.
CG RAM
The Character Generator RAM (CG RAM) provides space to create eight custom character
bitmaps. Each custom character location consists of a 5-dot by 8-line bitmap, as shown in
Figure 5-5.
The Set CG RAM Address command initializes the address counter before reading or
writing to CG RAM. Write CG RAM data using the Write Data to CG RAM or DD RAM
command, and read CG RAM using the Read Data from CG RAM or DD RAM command.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 47
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 48

Chapter 5: Character LCD Screen
The CG RAM address counter either remains constant after read or write operations, or
auto-increments or auto-decrements by one location, as defined by the I/D set by the Entry
Mode Set command.
Figure 5-5 provides an example that creates a special checkerboard character. The custom
character is stored in the fourth CG RAM character location, which is displayed when a
DD RAM location is 0x03. To write the custom character, the CG RAM address is first
initialized using the Set CG RAM Address command. The upper three address bits point to
the custom character location. The lower three address bits point to the row address for the
character bitmap. The Write Data to CG RAM or DD RAM command is used to write each
character bitmap row. A ‘1’ lights a bit on the display. A ‘0’ leaves the bit unlit. Only the
lower five data bits are used; the upper three data bits are don’t care positions. The eighth
row of bitmap data is usually left as all zeros to accommodate the cursor.
A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R
Upper Nibble Lower Nibble
Write Data to CG RAM or DD RAM
Character Address Row Address
011000
011001
011010
011011
011100
011101
011110
011111
Figure 5-5: Example Custom Checkerboard Character with Character Code 0x03
Command Set
Tab le 5- 2 summarizes the available LCD controller commands and bit definitions. Because
the display is set up for four-bit operation, each eight-bit command is sent as two four-bit
nibbles. The upper nibble is transferred first, followed by the lower nibble.
Table 5-2: LCD Character Display Command Set (4-bit mode)
Function
LCD_RS
LCD_RW
DB7
Don’t Care Character Bitmap
- - -01010
- - - 10101
- - -01010
- - - 10101
- - -01010
- - - 10101
- - -01010
- - -00000
Upper Nibble Lower Nibble
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
Clear Display 000000 0 0 0 1
Return Cursor Home 000000 0 0 1
Entry Mode Set 000000 0 1I/DS
Display On/Off 000000 1 D CB
Cursor and Display Shift 000001S/CR/L
48 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
-
- -
Page 49

R
LCD Controller
Table 5-2: LCD Character Display Command Set (4-bit mode) (Continued)
Upper Nibble Lower Nibble
Function
LCD_RS
Function Set 000010 1 0 - -
Set CG RAM Address 0001A5A4A3A2A1A0
Set DD RAM Address 0 0 1 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Read Busy Flag and Address 0 1 BF A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Write Data to CG RAM or DD RAM 1 0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Read Data from CG RAM or DD RAM 1 1 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
LCD_RW
DB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
Disabled
If the LCD_E enable signal is Low, all other inputs to the LCD are ignored.
Clear Display
Clears the display and returns the cursor to the home position, the top-left corner.
This command writes a blank space (ASCII/ANSI character code 0x20) into all DD RAM
addresses. The address counter is reset to 0, location 0x00 in DD RAM. Clears all option
settings. The I/D control bit is set to 1 (increment address counter mode) in the Entry Mode
Set command.
Execution Time: 82 μs – 1.64 ms
Return Cursor Home
Returns the cursor to the home position, the top-left corner. DD RAM contents are
unaffected. Also returns the display being shifted to the original position, shown in
Figure 5-3.
The address counter is reset to 0, location 0x00 in DD RAM. The display is returned to its
original status if it was shifted. The cursor or blink move to the top-left character location.
Execution Time: 40 μs – 1.6 ms
Entry Mode Set
Sets the cursor move direction and specifies whether or not to shift the display.
These operations are performed during data reads and writes.
Execution Time: 40 μs
Bit DB1: (I/D) Increment/Decrement
0 Auto-decrement address counter. Cursor/blink moves to left.
1 Auto-increment address counter. Cursor/blink moves to right.
This bit either auto-increments or auto-decrements the DD RAM and CG RAM address
counter by one location after each Write Data to CG RAM or DD RAM command or Read
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 49
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 50

Chapter 5: Character LCD Screen
Data from CG RAM or DD RAM command. The cursor or blink position moves
accordingly.
Bit DB0: (S) Shift
0 Shifting disabled
1 During a DD RAM write operation, shift the entire display value in the direction
controlled by Bit DB1 (I/D). It appears as though the cursor position remains constant
and the display moves.
Display On/Off
The display is turned on or off, controlling all characters. The cursor and cursor position
character (underscore) blink.
Execution Time: 40 μs
Bit DB2: (D) Display On/Off
0 No characters displayed. However, data stored in DD RAM is retained.
R
1 Display characters stored in DD RAM
Bit DB1: (C) Cursor On/Off
The cursor uses the five dots on the bottom line of the character. The cursor appears as a
line under the displayed character.
0 No cursor
1 Display cursor
Bit DB0: (B) Cursor Blink On/Off
0 No cursor blinking
1 Cursor blinks on and off approximately every half second
Cursor and Display Shift
Moves the cursor and shifts the display without changing DD RAM contents. Shift cursor
position or display to the right or left without writing or reading display data.
This function positions the cursor in order to modify an individual character, or to scroll
the display window left or right to reveal additional data stored in the DD RAM, beyond
the 16th character on a line. The cursor automatically moves to the second line when it
shifts beyond the 40th character location of the first line. The first and second line displays
shift at the same time.
When the displayed data is shifted repeatedly, both lines move horizontally. The second
display line does not shift into the first display line.
Execution Time: 40 μs
50 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 51

R
LCD Controller
Table 5-3: Shift Patterns According to S/C and R/L Bits
DB3
DB2
(S/C)
(R/L)
0 0 Shift the cursor position to the left. The address counter is decremented by one.
0 1 Shift the cursor position to the right. The address counter is incremented by one.
Operation
10
11
Shift the entire display to the left. The cursor follows the display shift. The
address counter is unchanged.
Shift the entire display to the right. The cursor follows the display shift. The
address counter is unchanged.
Function Set
Sets the interface data length, the number of display lines, and the character font.
The Starter Kit board supports a single function set with value 0x28.
Execution Time: 40 μs
Set CG RAM Address
Sets the initial CG RAM address.
After this command, all subsequent read or write operations to the display are to or from
CG RAM.
Execution Time: 40 μs
Set DD RAM Address
Sets the initial DD RAM address.
After this command, all subsequent read or write operations to the display are to or from
DD RAM. The addresses for displayed characters appear in Figure 5-3.
Execution Time: 40 μs
Read Busy Flag and Address
Reads the Busy flag (BF) to determine if an internal operation is in progress, and reads the
current address counter contents.
BF = 1 indicates that an internal operation is in progress. The next instruction is not
accepted until BF is cleared or until the current instruction is allowed the maximum time to
execute.
This command also returns the present value of the address counter. The address counter
is used for both CG RAM and DD RAM addresses. The specific context depends on the
most recent Set CG RAM Address or Set DD RAM Address command issued.
Execution Time: 1 μs
Write Data to CG RAM or DD RAM
Writes data into DD RAM if the command follows a previous Set DD RAM Address
command, or writes data into CG RAM if the command follows a previous Set CG RAM
Address command.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 51
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 52

Chapter 5: Character LCD Screen
After the write operation, the address is automatically incremented or decremented by 1
according to the Entry Mode Set command. The entry mode also determines display shift.
Execution Time: 40 μs
Read Data from CG RAM or DD RAM
Reads data from DD RAM if the command follows a previous Set DD RAM Address
command, or reads data from CG RAM if the command follows a previous Set CG RAM
Address command.
After the read operation, the address is automatically incremented or decremented by 1
according to the Entry Mode Set command. However, a display shift is not executed
during read operations.
Execution Time: 40 μs
Operation
The board has an eight-bit data interface to the character LCD. Other Xilinx boards use a
four-bit interface. As shown in Figure 5-1, the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board supports
both an eight-bit and a four-bit interface for compatibility reasons. Many existing reference
designs are already built around a four-bit interface.
R
Four-Bit Data Interface
Figure 5-6 illustrates a write operation to the LCD, showing the minimum times allowed
for setup, hold, and enable pulse length relative to the 50 MHz clock (20 ns period)
provided on the board.
52 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 53

R
CLOCK
Operation
LCD_RS
LCD_DB<7:4>
LCD_RW
LCD_E
Upper
4 bits
LCD_RS
LCD_DB<7:4>
LCD_RW
LCD_E
40 ns 10 ns
Lower
4 bits
1 μs40 μs
Figure 5-6: Character LCD Interface Timing
0 = Command, 1 = Data
Valid Data
230 ns
UG330_c5_03_072106
The data values on LCD_DB<7:4>, and the register select (LCD_RS) and the read/write
(LCD_RW) control signals must be set up and stable at least 40 ns before the enable LCD_E
goes High. The enable signal must remain High for 230 ns or longer—the equivalent of 12
or more clock cycles at 50 MHz.
In many applications, the LCD_RW signal can be tied Low permanently because the FPGA
generally has no reason to read information from the display.
Transferring Eight-Bit Data over the Four-Bit Interface
After initializing the display and establishing communication in four-bit mode, all
commands and data transfers to the character display are via eight bits, transferred using
two sequential four-bit operations. Each eight-bit transfer must be decomposed into two
four-bit transfers, spaced apart by at least 1 μs, as shown in Figure 5-6. The upper nibble is
transferred first, followed by the lower nibble. An eight-bit write operation must be spaced
least 40 μs before the next communication. This delay must be increased to 1.64 ms
following a Clear Display command.
Initializing the Display
After power-on, the display must be initialized to establish the required communication
protocol. The initialization sequence is simple and ideally suited to the highly-efficient
eight-bit P
available for more complex control or computation beyond simply driving the display.
icoBlaze embedded controller. After initialization, the PicoBlaze controller is
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 53
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 54

Chapter 5: Character LCD Screen
Power-On Initialization
The initialization sequence first establishes that the FPGA application wishes to use the
four-bit data interface to the LCD as follows:
1. Wait 15 ms or longer, although the display is generally ready when the FPGA finishes
configuration. The 15 ms interval is 750,000 clock cycles at 50 MHz.
2. Write LCD_DB<7:4> = 0x3, and pulse LCD_E High for 12 clock cycles.
3. Wait 4.1 ms or longer, which is 205,000 clock cycles at 50 MHz.
4. Write LCD_DB<7:4> = 0x3, and pulse LCD_E High for 12 clock cycles.
5. Wait 100 μs or longer, which is 5,000 clock cycles at 50 MHz.
6. Write LCD_DB<7:4> = 0x3, and pulse LCD_E High for 12 clock cycles.
7. Wait 40 μs or longer, which is 2,000 clock cycles at 50 MHz.
8. Write LCD_DB<7:4> = 0x2, and pulse LCD_E High for 12 clock cycles.
9. Wait 40 μs or longer, which is 2,000 clock cycles at 50 MHz.
Display Configuration
After the power-on initialization is completed, the four-bit interface is established. The
next part of the sequence configures the display:
R
1. Issue a Function Set command, 0x28, to configure the display for operation on the
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board.
2. Issue an Entry Mode Set command, 0x06, to set the display to automatically increment
the address pointer.
3. Issue a Display On/Off command, 0x0C to turn the display on and disable the cursor
and blinking.
4. Finally, issue a Clear Display command. Allow at least 1.64 ms (82,000 clock cycles)
after issuing this command.
Writing Data to the Display
To write data to the display, specify the start address, followed by one or more data values.
Before writing any data, issue a Set DD RAM Address command to specify the initial
seven-bit address in the DD RAM. See Figure 5-3 for DD RAM locations.
Write data to the display using a Write Data to CG RAM or DD RAM command. The eightbit data value represents the look-up address into the CG ROM or CG RAM, shown in
Figure 5-4. The stored bitmap in the CG ROM or CG RAM drives the 5 x 8 dot matrix to
represent the associated character.
If the address counter is configured to auto-increment, as described earlier, the application
can sequentially write multiple character codes, and each character is automatically stored
and displayed in the next available location.
Continuing to write characters, however, eventually falls off the end of the first display
line. The additional characters do not automatically appear on the second line because the
DD RAM map is not consecutive from the first line to the second.
54 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 55

R
Disabling the Unused LCD
If the FPGA application does not use the character LCD screen, drive the LCD_E pin Low
to disable it. Also drive the LCD_RW pin Low to prevent the LCD screen from presenting
data.
Related Resources
Refer to the following links for additional information:
• PowerTip PC1602-D Character LCD (Basic Electrical and Mechanical Data)
w
ww.powertipusa.com/pdf/pc1602d.pdf
• Sitronix ST7066U Character LCD Controller
w
ww.sitronix.com.tw/sitronix/product.nsf/Doc/ST7066U?OpenDocument
• Samsung S6A0069X Character LCD Controller
www.samsung.com/Products/Semiconductor/DisplayDriverIC/MobileDDI/
BWSTN/S6A0069X/S6A0069X.htm
• Design Example: Device DNA Reader and LCD Display Controller
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#dna_reader
Related Resources
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 55
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 56

Chapter 5: Character LCD Screen
R
56 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 57

R
VGA Display Port
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board includes a VGA display port via a standard highdensity HD-DB15 female connector. Connect this port directly to most PC monitors or flatpanel LCDs using a standard monitor cable. As shown in Figure 6-1, the VGA connector is
the left-most connector along the top of the board.
Chapter 6
FPGA
SYNC
(C8)
(B )
REDGREENBLUE
(B3 )
(A3
(D6)
(C6)
(D5)
(C5
(C9)
(B9 )
(D7)
(C7
(B11)
(C11)
VGA_R<3>
VGA_R<2>
8
VGA_R<1>
VGA_R<0>
)
VGA_G <3>
VGA_G <2>
VGA_G <1>
VGA_G <0>
)
VGA_B<3>
VGA_B<2>
VGA_B<1>
VGA_B<0>
)
VGA_VSYNC
VGA_HSYNC
510 Ω
1 kΩ
2 kΩ
4 k
Ω
510 Ω
1 kΩ
2 kΩ
Ω
4 k
510 Ω
1 kΩ
2 kΩ
4 k
Ω
82.5 Ω
82.5
Figure 6-1: VGA Connections from the Starter Kit Board
Red
Green
Blue
4
14
9
13
HD-DB15 VGA Connector
10
15 12 11
Vertical
Ω
Horizontal
1235
8 7 6
(front view)
(not VGA cable)
UG334_c6_01_052407
The FPGA directly drives the five VGA signals via resistors. Each red, green, and blue
signal has four outputs from the FPGA that feed a resistor-divider tree. This approach
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 57
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 58

Chapter 6: VGA Display Port
provides 4-bit resolution per color, generating 12-bit color, or 4,096 possible colors. The
series resistor, in combination with the 75Ω termination built into the VGA cable, ensures
that the color signals remain in the VGA-specified 0V to 0.7V range.
The VGA_HSYNC and VGA_VSYNC signals use LVTTL or LVCMOS33 I/O standard
drive levels.
Drive the VGA_R[3:0], VGA_G[3:0], and VGA_B[3:0] signals High or Low to generate the
desired colors. The scaled analog output is generated by a resistor-divider that converts the
FPGA’s digital outputs for an individual color. Each individual color output supports 16
possible values, as described by Equation 6-1. The three separate controls for red, green,
and blue support a maximum of 12-bit color, or 4,096 values.
For simplicity, the FPGA application can also treat the VGA port as a three-bit interface by
driving all four color outputs with the same digital value. The corresponding eight basic
color values are shown in Tab le 6 -1 .
Table 6-1: Example Display Color Codes
COLOR
OUT
VGA 3:0[]
-------------------------- -
15
R
COLOR×=
Equation 6-1
VGA_R[3:0] VGA_G[3:0] VGA_B[4:0] Resulting Color
0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 1111
0000 1111 0000 Green
0000 1111 1111
1111 0000 0000
1111 0000 1111
1111 1111 0000
1111 1111 1111
Signal Timing for a 60 Hz, 640x480 VGA Display
VGA signal timing is specified, published, copyrighted, and sold by the Video Electronics
Standards Association (VESA). The following VGA system and timing information is
provided as an example of how the FPGA might drive the VGA monitor in 640 by 480
mode. For more precise information or for information on higher VGA frequencies, refer to
documents available on the VESA website or other electronics websites (see “Related
Resources,” page 61). Standard VGA support is part of the factory demonstration designs,
but several extended VGA modes including SVGA are also achievable with faster timing
controllers.
Black
Blue
Cyan
Red
Magenta
Yellow
White
CRT-based VGA displays use amplitude-modulated, moving electron beams (or cathode
rays) to display information on a phosphor-coated screen. LCDs use an array of switches
that can impose a voltage across a small amount of liquid crystal, thereby changing light
permittivity through the crystal on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Although the following
description is limited to CRT displays, LCDs have evolved to use the same signal timings
as CRT displays. Consequently, the following discussion pertains to both CRTs and LCDs.
58 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 59

R
Signal Timing for a 60 Hz, 640x480 VGA Display
Within a CRT display, current waveforms pass through the coils to produce magnetic fields
that deflect electron beams to transverse the display surface in a raster pattern, horizontally
from left to right and vertically from top to bottom. As shown in Figure 6-2, information is
only displayed when the beam is moving in the forward direction—left to right and top to
bottom—and not during the time the beam returns back to the left or top edge of the
display. Much of the potential display time is therefore lost in blanking periods when the
beam is reset and stabilized to begin a new horizontal or vertical display pass.
Current
through the
horizontal
deflection
coil
pixel 0,0
pixel 0,639
640 pixels are displayed each
time the beam traverses the screen
VGA Display
pixel 479,0 pixel 479,639
Stable current ramp: Information is
displayed during this time
Retrace: No
information
is displayed
during
this time
Total horizontal time
Horizontal display time
retrace time
time
"front porch"
"front porch"
HS
Horizontal sync signal
"back porch"
sets the retrace frequency
UG230_c6_02_021706
Figure 6-2: CRT Display Timing Example
The display resolution defines the size of the beams, the frequency at which the beam
traces across the display, and the frequency at which the electron beam is modulated.
Modern VGA displays support multiple display resolutions, and the VGA controller
dictates the resolution by producing timing signals to control the raster patterns. The
controller produces TTL-level synchronizing pulses that set the frequency at which current
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 59
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 60

Chapter 6: VGA Display Port
flows through the deflection coils, and it ensures that pixel or video data is applied to the
electron guns at the correct time.
Video data typically comes from a video refresh memory with one or more bytes assigned
to each pixel location. The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board uses 12 bits per pixel,
producing one of the 4,096 possible colors. The controller indexes into the video data buffer
as the beams move across the display. The controller then retrieves and applies video data
to the display at precisely the time the electron beam is moving across a given pixel.
As shown in Figure 6-2, the VGA controller generates the horizontal sync (HS) and vertical
sync (VS) timing signals and coordinates the delivery of video data on each pixel clock. The
pixel clock defines the time available to display one pixel of information. The VS signal
defines the refresh frequency of the display, or the frequency at which all information on the
display is redrawn. The minimum refresh frequency is a function of the display’s phosphor
and electron beam intensity, with practical refresh frequencies in the 60 Hz to 120 Hz
range. The number of horizontal lines displayed at a given refresh frequency defines the
horizontal retrace frequency.
VGA Signal Timing
The signal timings in Tab le 6 -2 are derived for a 640-pixel by 480-row display using a
25 MHz pixel clock and 60 Hz ± 1 refresh. Figure 6-3 shows the relation between each of
the timing symbols. The timing for the sync pulse width (T
intervals (T
back porch intervals are the pre- and post-sync pulse times. Information cannot be
displayed during these times.
) and front and back porch
and TBP) is based on observations from various VGA displays. The front and
FP
PW
R
Table 6-2: 640x480 Mode VGA Timing
Vertical Sync Horizontal Sync
Symbol Parameter
Time Clocks Lines Time Clocks
T
Sync pulse time 16.7 ms 416,800 521 32 µs 800
S
T
Display time 15.36 ms 384,000 480 25.6 µs 640
DISP
T
Pulse width 64 µs 1,600 2 3.84 µs 96
PW
T
Front porch 320 µs 8,000 10 640 ns 16
FP
T
Back porch 928 µs 23,200 29 1.92 µs 48
BP
T
S
T
disp
T
pw
Figure 6-3: VGA Control Timing
T
fp
T
bp
UG230_c6_03_021706
Generally, a counter clocked by the pixel clock controls the horizontal timing. Decoded
counter values generate the HS signal. This counter tracks the current pixel display
location on a given row.
60 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 61

R
A separate counter tracks the vertical timing. The vertical-sync counter increments with
each HS pulse, and decoded values generate the VS signal. This counter tracks the current
display row. These two continuously running counters form the address into a video
display buffer. For example, the on-board DDR2 SDRAM provides an ideal display buffer.
No time relationship is specified between the onset of the HS pulse and the onset of the VS
pulse. Consequently, the counters can be arranged to easily form video RAM addresses or
to minimize decoding logic for sync pulse generation.
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 6-4 provides the UCF constraints for the VGA display port, including the I/O pin
assignment, the I/O standard used, the output slew rate, and the output drive current.
NET "VGA_R<3>" LOC = "C8" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_R<2>" LOC = "B8" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_R<1>" LOC = "B3" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_R<0>" LOC = "A3" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_G<3>" LOC = "D6" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_G<2>" LOC = "C6" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_G<1>" LOC = "D5" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_G<0>" LOC = "C5" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_B<3>" LOC = "C9" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_B<2>" LOC = "B9" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
"VGA_B<1>" LOC = "D7" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET
NET "VGA_B<0>" LOC = "C7" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_HSYNC" LOC = "C11" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
NET "VGA_VSYNC" LOC = "B11" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = FAST ;
UCF Location Constraints
Related Resources
Refer to the following links for additional information:
• VESA
w
ww.vesa.org
• VGA timing information
ww.epanorama.net/documents/pc/vga_timing.html
w
Figure 6-4: UCF Constraints for VGA Display Port
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 61
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 62

Chapter 6: VGA Display Port
R
62 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 63

R
RS-232 Serial Ports
Overview
As shown in Figure 7-1, the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board has two RS-232 serial ports:
a female DB9 DCE connector and a male DB9 DTE connector. The DCE-style port connects
directly to the serial port connector available on most personal computers and
workstations via a standard straight-through serial cable. For typical applications, the
board does not require null modem cables, gender changers, or crossover cables.
Use the DTE-style connector to control other RS-232 peripherals, such as modems or
printers, or perform simple loopback testing with the DCE connector.
Computer
Standard
9-pin serial cable
Standard
9-pin serial cable
Chapter 7
RS-232 Peripheral
TALK/DATA
RS CS TR RD TD CD
TALK
J36
GND
9
DCE
DCE
Female DB9
12345
678
GND
RS-232 Voltage Translator (IC3)
RS232_DCE_RXD
RS232_DCE_TXD
(F15)(E16)
FPGA
Figure 7-1: RS-232 Serial Ports
9
DTE
Male DB9
(F16)
DTE
678
RS232_DTE_RXD
RS232_DTE_TXD
(E15)
12345
J27
UG334_c7_01_052407
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 63
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 64

Chapter 7: RS-232 Serial Ports
Figure 7-1 shows the connection between the FPGA and the two DB9 connectors. The
FPGA supplies serial output data using LVTTL or LVCMOS levels to the Maxim device,
which in turn, converts the logic value to the appropriate RS-232 voltage level. Likewise,
the Maxim device converts the RS-232 serial input data to LVTTL levels for the FPGA. A
series resistor between the Maxim output pin and the FPGA’s RXD pin protects against
inadvertent logic conflicts such as accidentally connecting the board using a null-modem
cable. In this example, both the FPGA and the external serial device are driving data on the
transmit line.
Hardware flow control is not supported on the connector. The port’s DCD, DTR, and DSR
signals connect together, as shown in Figure 7-1. Similarly, the port’s RTS and CTS signals
connect together.
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 7-2 and Figure 7-3 provide the UCF constraints for the DTE and DCE RS-232 ports,
respectively, including the I/O pin assignment and the I/O standard used.
NET "RS232_DTE_RXD" LOC = "F16" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL ;
NET "RS232_DTE_TXD" LOC = "E15" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
R
Figure 7-2: UCF Location Constraints for DTE RS-232 Serial Port
NET "RS232_DCE_RXD" LOC = "E16" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL ;
NET "RS232_DCE_TXD" LOC = "F15" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
Figure 7-3: UCF Location Constraints for DCE RS-232 Serial Port
64 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 65

R
PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard Port
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board includes a PS/2 mouse/keyboard port and the
standard six-pin mini-DIN connector, labeled J28 on the board. Figure 8-1 shows the PS/2
connector, and Tab le 8- 1 shows the signals on the connector. Use the primary connections
indicated to connect a mouse or keyboard directly to the board. Also see “Adding a Second
PS/2 Port Using a Y-Splitter Cable,” page 69.
Chapter 8
Secondary Connection
(requires Y-splitter cable)
270Ω
PS2_DATA2: (Y12)
1
3
5
270
2
4
Ω
6
PS2_CLK2: (U11)
Figure 8-1: PS/2 Connector Location and Signals
Table 8-1: PS/2 Connector Pinout
PS/2 DIN Pin Signal FPGA Pin
1
2
3
Primary data connection
PS2_DATA1
Secondary data connection when using PS/2 splitter cable
PS2_DATA2
GND
Primary Connection
270Ω
PS2_DATA1: (V11)
Ω
270
PS2_CLK1: (W12)
UG334_c8_01_052407
V11
Y12
GND
4
5
6
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 65
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
+5V
Primary clock connection
PS2_CLK1
Secondary data connection with using PS/2 splitter cable
PS2_CLK2
No Connection
W12
U11
Page 66

Chapter 8: PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard Port
Both a PC mouse and keyboard use the two-wire PS/2 serial bus to communicate with a
host device, the FPGA in this case. The PS/2 bus includes both clock and data. Both a
mouse and keyboard drive the bus with identical signal timings, and both use 11-bit words
that include a start, a stop, and an odd parity bit. However, the data packets are organized
differently for a mouse and keyboard. Both the keyboard and mouse interfaces allows
bidirectional data transfers. For example, the FPGA host design can illuminate the state
LEDs on the keyboard or change the communicate rate with the mouse.
The PS/2 bus timing appears in Ta bl e 8- 2 and Figure 8-2. The clock and data signals are
only driven when data transfers occur; otherwise they are held in the idle state at a logic
High. The timing defines signal requirements for mouse-to-host communications and
bidirectional keyboard communications. As shown in Figure 8-2, the attached keyboard or
mouse writes a bit on the data line when the clock signal is High, and the host reads the
data line when the clock signal is Low.
Table 8-2: PS/2 Bus Timing
Symbol Parameter Min Max
R
Keyboard
T
T
T
HLD
Clock High or Low Time 30 μs 50 μs
CK
Data-to-clock Setup Time 5 μs 25 μs
SU
Clock-to-data Hold Time 5 μs 25 μs
T
T
CK
Edge 0 Edge 10
CK
CLK (PS2C)
T
T
SU
HLD
DATA (PS2D)
'0' start bit
'1' stop bit
UG230_c8_02_021806
Figure 8-2: PS/2 Bus Timing Waveforms
The keyboard uses open-collector drivers so that either the device or the host can drive the
two-wire bus. If the host never sends data, then the host can use simple input pins.
A PS/2-style keyboard uses scan codes to communicate key-press data. Each key has a
single, unique scan code that is sent whenever the corresponding key is pressed. The scan
codes for most keys appear in Figure 8-3.
If the key is pressed and held, the keyboard repeatedly sends the scan code every 100 ms or
so. When a key is released, the keyboard sends an “F0” key-up code, followed by the scan
code of the released key. The keyboard sends the same scan code, regardless if a key has
different shift and non-shift characters and regardless whether the Shift key is pressed or
not. The host determines which character is intended.
Some keys, called extended keys, send an “E0” ahead of the scan code, and furthermore,
they might send more than one scan code. When an extended key is released, an “E0 F0”
key-up code is sent, followed by the scan code.
66 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 67

R
Keyboard
ESC
76
` ~
0E
TA B
0D
Caps Lock
58
Shift
12
Ctrl
14
F105F206F304F4
0C
1 !162 @1E3 #264 $255 %
2E
Q15W
1DE24R2DT2C
A
1CS1BD23F2BG34
Z
1ZX22C21V2AB32
Alt
11
F503F60BF783F8
F901F1009F1178F12
0A
6 ^367 &3D8 *3E9 (460 )45- _4E= +
55
Y
[ {54] }
35U3CI43O44P4D
H
33J3BK42L4B
N31M
, <41> .49/ ?
3A
Space
29
; :
4C
4A
Alt
E0 11
' "
52
Back Space
66
5B
Enter
5A
Shift
59
E0 14
07
\ |
5D
Ctrl
UG230_c8_03_021806
Figure 8-3: PS/2 Keyboard Scan Codes
The host can also send commands and data to the keyboard. Tab le 8 -3 provides a short list
of some often-used commands.
Table 8-3: Common PS/2 Keyboard Commands
Command Description
ED Turn on/off Num Lock, Caps Lock, and Scroll Lock LEDs. The keyboard acknowledges receipt of an
“ED” command by replying with an “FA”, after which the host sends another byte to set LED status. The
bit positions for the keyboard LEDs are shown below. Write a ‘1’ to the specific bit to illuminate the
associated keyboard LED.
E0 75
E0 74
E0 6B
E0 72
765432 1 0
Ignored Caps Lock Num Lock Scroll Lock
EE Echo. Upon receiving an echo command, the keyboard replies with the same scan code “EE”.
F3 Set scan code repeat rate. The keyboard acknowledges receipt of an “F3” by returning an “FA”, after
which the host sends a second byte to set the repeat rate.
FE Resend. Upon receiving a resend command, the keyboard resends the last scan code.
FF Reset. Resets the keyboard.
The keyboard sends commands or data to the host only when both the data and clock lines
are High, the Idle state.
Because the host is the bus master, the keyboard checks whether the host is sending data
before driving the bus. The clock line can be used as a clear to send signal. If the host pulls
the clock line Low, the keyboard must not send any data until the clock is released.
The keyboard sends data to the host in 11-bit words that contain a ‘0’ start bit, followed by
eight bits of scan code (LSB first), followed by an odd parity bit and terminated with a ‘1’
stop bit. When the keyboard sends data, it generates 11 clock transitions at around 20 to
30 kHz, and data is valid on the falling edge of the clock as shown in Figure 8-2.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 67
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 68

Chapter 8: PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard Port
Mouse
PS/2-compatible mice potentially support two modes. In polled mode, the host controller
interrogates the mouse for activity. In streaming mode, the mouse reports any movement
or key presses. Streaming mode is the default operating mode.
To specifically enter streaming mode, the FPGA host must transmit a “Set Stream Mode”
command (0xEA) to the mouse. The mouse then generates a clock and data signal when
moved or when one or more keys are pressed; otherwise, these signals remain High,
indicating the Idle state. Each time the mouse is moved, the mouse sends three 11-bit
words to the host. Each of the 11-bit words contains a ‘0’ start bit, followed by 8 data bits
(LSB first), followed by an odd parity bit, and terminated with a ‘1’ stop bit. Each data
transmission contains 33 total bits, where bits 0, 11, and 22 are ‘0’ start bits, and bits 10, 21,
and 32 are ‘1’ stop bits. The three eight-bit data fields contain movement data as shown in
Figure 8-4. Data is valid at the falling edge of the clock, and the clock period is 20 to 30 kHz.
Mouse status byte X direction byte Y direction byte
R
L R C 1 XS YS XV YV P X0 X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 P Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 Y7 P
0 11
Idle state Idle state
Start bit
10 10
Stop bit Stop bit Stop bit
Start bit
Start bit
UG330_c8_04_032007
Figure 8-4: PS/2 Mouse Transaction
A PS/2-style mouse employs a relative coordinate system (see Figure 8-5), wherein
moving the mouse to the right generates a positive value in the X field, and moving to the
left generates a negative value. Likewise, moving the mouse up generates a positive value
in the Y field, and moving it down represents a negative value. The XS and YS bits in the
status byte define the sign of each value, where a ‘1’ indicates a negative value.
+Y values
(XS=1) (XS=0)
(YS=0)
+X values-X values
-Y values
(YS=1)
UG230_c8_05_021806
Figure 8-5: The Mouse Uses a Relative Coordinate System to Track Movement
The magnitude of the X and Y values represents the rate of mouse movement. The larger
the value, the faster the mouse is moving. The XV and YV bits in the status byte indicate
when the X or Y values exceed their maximum value, an overflow condition. A ‘1’
indicates when an overflow occurs. If the mouse moves continuously, the 33-bit
transmissions repeat every 50 ms or so.
68 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 69

R
The L, R, and C fields in the status byte correspond to Left, Right, and Center button
presses. A ‘1’ indicates that the associated mouse button is being pressed.
Voltage Supply
The PS/2 port on the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board is powered by 5V. Although the
Spartan-3A/3AN FPGA is not a 5V-tolerant device, it can communicate with a 5V device
using 270Ω series current-limiting resistors, as shown in Figure 8-1, page 65.
Adding a Second PS/2 Port Using a Y-Splitter Cable
Most applications that use the PS/2 port will connect a mouse or a keyboard directly to the
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board connector. These applications use the primary FPGA
connections to the PS/2 port, as shown in Figure 8-1, page 65.
However, it is possible to include a second PS/2 port by connecting a PS/2 Y-splitter cable
to the PS/2 connector on the board. Figure 8-6 shows an example of such a cable. The
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit does not include such a cable but one can be purchased from
a local electronics supply store or via the web. Some example vendors and part numbers
are listed below. Check various vendors and suppliers as prices vary greatly!
Voltage Supply
• StarTech PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Y-splitter Cable, KYC1MF
• American Power Conversion (APC) Mouse and Keyboard Splitter Cable, 62305-1
• Belkin Pro Series Notebook Y Cable, F3G117-01
• Tripp Lite, P230-001
• QVS CC321Y
• ComputerCableStore.com, 8-1718Y-00.5
• CablesToGo, 08017
UG330_c8_02_012507
Figure 8-6: Example PS/2 Y-Splitter Cable
When using the splitter cable, use both sets of FPGA connections listed in Figure 8-1,
page 65 and Table 8-1 , pa ge 65 . The primary connections appear at one side of the
Y-splitter while the secondary connections appear at the other side of the Y-splitter.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 69
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 70

Chapter 8: PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard Port
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 8-7 provides the UCF constraints for the PS/2 port connecting, including the I/O
pin assignment and the I/O standard used.
# Primary connection
NET "PS2_CLK1" LOC = "W12" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "PS2_DATA1" LOC = "V11" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = SLOW ;
# Secondary connection (requires Y-splitter cable)
NET "PS2_CLK2" LOC = "U11" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "PS2_DATA2" LOC = "Y12" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | DRIVE = 8 | SLEW = SLOW ;
Figure 8-7: UCF Location Constraints for PS/2 Port
Related Resources
Refer to the following links for additional information:
• PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard Protocol
w
ww.computer-engineering.org/ps2protocol
• PS/2 Keyboard Interface
ww.computer-engineering.org/ps2keyboard
w
• PS/2 Mouse Interface
ww.computer-engineering.org/ps2mouse
w
R
70 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 71

R
Analog Capture Circuit
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board includes a two-channel analog capture circuit,
consisting of a programmable scaling pre-amplifier and an analog-to-digital converter
(ADC), as shown in Figure 9-1.
Linear Tech LTC1407A-1 Dual A/D
Chapter 9
SPI_SCK: (AA20)
AD_CONV: (Y6)
AD_DOUT: (D16)
Linear Tech LTC6912-1 Dual Amp
SPI_MOSI: (AB14)
AMP_CS: (W6)
SPI_SCK: (AA20)
AMP_SHDN: (W15)
AMP_DOUT: (T7)
6-pin ADC Header (J22)
UG334_c9_01_052407
Figure 9-1: Analog Capture Circuit and Associated Stake Pin Header (J22)
The analog capture circuit consists of a Linear Technology LTC6912-1 programmable preamplifier that scales the incoming analog signal on the J22 header. The output of the preamplifier connects to a Linear Technology LTC1407A-1 ADC. Both the pre-amplifier and
the ADC are serially programmed or controlled by the FPGA.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 71
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 72

Chapter 9: Analog Capture Circuit
Header J22
R
DAC_REF_AB
DAC_REF_CD
(3.3V)
(3.3V)
VINA
VINB
GND
VCC
(3.3V)
(D16) (AB14)
(T7)
DAC_REF_CD reference voltage is nominally 3.3V.
The reference is supplied by the LP3906 adjustable regulator, IC18.
The voltage is adjustable using the regulator’s I C interface.
LTC 6912-1 AMP
2
A
B
REF = 1.65V
FPGA
(W6)
(AA20)
(W15)
SPI_MOSI
AMP_CS
SPI_SCK
AMP_SHDN
DIN
A GAIN B GAIN
CS/LD
SCK
SPI Control Interface
SHDN
LTC 1407A-1 ADC
A/D
Channel 0
A/D
Channel 1
DOUT
32103210 130... 130 ...
CHANNEL 1 CHANNEL 0
SCK
SPI Control Interface
CONV
14
14
SDO
AD_CONV
(Y6)
AMP_DOUT
AD_DOUT
Figure 9-2: Detailed View of Analog Capture Circuit
Digital Outputs from Analog Inputs
The analog capture circuit converts the analog voltage on VINA or VINB and converts it to
a 14-bit digital representation, D[13:0], as expressed by Equation 9-1.
D 13:0[]GAIN
The GAIN is the current setting loaded into the programmable pre-amplifier. The various
allowable settings for GAIN and allowable voltages applied to the VINA and VINB inputs
appear in Tab le 9- 2.
The reference voltage for the amplifier and the ADC is 1.65V, generated via a voltage
divider shown in Figure 9-2. Consequently, 1.65V is subtracted from the input voltage on
VINA or VINB.
The maximum range of the ADC is ±1.25V, centered around the reference voltage, 1.65V.
Hence, 1.25V appears in the denominator to scale the analog input accordingly.
V
1.65V–()
IN
----------------------------------- -
× 8192×=
1.25V
UG334_c9_02_052407
Equation 9-1
72 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 73

R
Programmable Pre-Amplifier
Finally, the ADC presents a 14-bit, two’s complement digital output. A 14-bit, two’s
complement number represents values between -2
13
scaled by 8192, or 2
.
See “Programmable Pre-Amplifier” to control the GAIN settings on the programmable
pre-amplifier.
The reference design files provide more information on converting the voltage applied on
VINA or VINB to a digital representation (see “Related Resources,” page 77).
Programmable Pre-Amplifier
The LTC6912-1 provides two independent, inverting amplifiers with programmable gain.
The purpose of the amplifier is to scale the incoming voltage on VINA or VINB so that it
maximizes the conversion range of the DAC, namely 1.65 ± 1.25V.
Interface
Tab le 9- 1 lists the interface signals between the FPGA and the amplifier. The SPI_MOSI
and SPI_SCK signals are shared with other devices on the SPI bus. The AMP_CS signal is
the active-Low slave select input to the amplifier.
Table 9-1: AMP Interface Signals
Signal FPGA Pin Direction Description
13
and 213-1. Therefore, the quantity is
SPI_MOSI AB14 FPGAÆAMP Serial data: Master Output, Slave Input.
AMP_CS W6 FPGAÆAMP Active-Low chip select. The amplifier gain is
SPI_SCK AA20 FPGAÆAMP Clock
AMP_SHDN W15 FPGAÆAMP Active-High shutdown, reset
AMP_DOUT T7 FPGAÅAMP Serial data. Echoes previous amplifier gain
Programmable Gain
Each analog channel has an associated programmable gain amplifier (see Figure 9-2).
Analog signals presented on the VINA or VINB inputs on the J7 header are amplified
relative to 1.65V. The 1.65V reference is generated using a voltage divider of the 3.3V
voltage supply.
The gain of each amplifier is programmable from -1 to -100, as shown in Ta bl e 9- 2.
Table 9-2: Programmable Gain Settings for Pre-Amplifier
Gain
Presents eight-bit programmable gain
settings, as defined in Ta bl e 9 -2 .
set when the signal returns High.
settings. Can be ignored in most applications.
A3 A2 A1 A0 Input Voltage Range
B3 B2 B1 B0 Minimum Maximum
00000
-100010.42.9
-2 0 0 1 0 1.025 2.275
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 73
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 74

Chapter 9: Analog Capture Circuit
Table 9-2: Programmable Gain Settings for Pre-Amplifier (Continued)
R
Gain
-500111.41.9
-10 0 1 0 0 1.525 1.775
-20 0 1 0 1 1.5875 1.7125
-50 0 1 1 0 1.625 1.675
-100 0 1 1 1 1.6375 1.6625
SPI Control Interface
Figure 9-3 highlights the SPI-based communications interface with the amplifier. The gain
for each amplifier is sent as an eight-bit command word, consisting of two four-bit fields.
The most-significant bit, B3, is sent first.
A3 A2 A1 A0 Input Voltage Range
B3 B2 B1 B0 Minimum Maximum
AMP_DOUT
FPGA
Master
SPI_MOSI
AMP_CS
SPI_SCK
0
A
Slave: LTC2624-1
A1A2A
0
3
A Gain B Gain
B
0
B1B2B
7
3
AMP_CS
SPI_SCK
SPI_MOSI
(from FPGA)
AMP_DOUT
(from AMP)
UG334_c9_03_052407
Figure 9-3: SPI Serial Interface to Amplifier
The AMP_DOUT output from the amplifier echoes the previous gain settings. These
values can be ignored for most applications.
The SPI bus transaction starts when the FPGA asserts AMP_CS Low (see Figure 9-4). The
amplifier captures serial data on SPI_MOSI on the rising edge of the SPI_SCK clock signal.
The amplifier presents serial data on AMP_DOUT on the falling edge of SPI_SCK.
30
30
765432
85 max
Previous 7
65432
All timing is minimum in nanoseconds unless otherwise noted.
5050
UG230_c10_04_022306
Figure 9-4: SPI Timing When Communicating with Amplifier
The amplifier interface is relatively slow, supporting only about a 10 MHz clock frequency.
74 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 75

R
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 9-5 provides the User Constraint File (UCF) constraints for the amplifier interface,
including the I/O pin assignment and I/O standard used.
NET "SPI_MOSI" LOC = "AB14"| IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 8 ;
NET "AMP_CS" LOC = "W6" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "SPI_SCK" LOC = "AA20"| IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 12 ;
NET "AMP_SHDN" LOC = "W15" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "AMP_DOUT" LOC = "T7" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL ;
Figure 9-5: UCF Location Constraints for the Pre-amplifier Interface (AMP)
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
The LTC1407A-1 provides two ADCs. Both analog inputs are sampled simultaneously
when the AD_CONV signal is applied.
Interface
Tab le 9- 3 lists the interface signals between the FPGA and the ADC. The SPI_SCK signal is
shared with other devices on the SPI bus. The active-High AD_CONV signal is the activeLow slave select input to the DAC. The DAC_CLR signal is the active-Low, asynchronous
reset input to the DAC.
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
Table 9-3: ADC Interface Signals
Signal FPGA Pin Direction Description
SPI_SCK AA20 FPGAÆADC Clock
AD_CONV Y6 FPGAÆADC Active-High, initiates conversion process.
ADC_OUT D16 FPGAÅADC Serial data. Presents the digital representation of the
SPI Control Interface
Figure 9-6 provides an example SPI bus transaction to the ADC.
When the AD_CONV signal goes High, the ADC simultaneously samples both analog
channels. The results of this conversion are not presented until the next time AD_CONV is
asserted, a latency of one sample. The maximum sample rate is approximately 1.5 MHz.
The ADC presents the digital representation of the sampled analog values as a 14-bit, two’s
complement binary value.
sample analog values as two 14-bit two’s
complement binary values.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 75
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 76

Chapter 9: Analog Capture Circuit
ADC_OUT
D1D2D
D
0
Z
Converted data is presented with a latency of one sample.
The sampled analog value is converted to digital data 32 SPI_SCK cycles after asserting AD_CONV.
The converted values is then presented after the next AD_CONV pulse.
FPGA
Master
AD_CONV
AD_CONV
SPI_SCK
Sample
point
Slave: LTC1407A-1 A/D Converter
D5D6D
D
3
4
Channel 1 Channel 0
7
D
8
D9D10D
D13D
11
12
D
0
D1D2D
3
Z
D
4
D5D6D
7
D
8
D9D10D
Sample
point
R
D13D
11
12
Z
SPI_SCK
ADC_OUT
AD_CONV
SPI_SCK
ADC_OUT
4ns min
3ns
Channel 0 Channel 0Channel 1
1313
00
13
UG334_c9_06_052407
Figure 9-6: Analog-to-Digital Conversion Interface
Figure 9-7 shows detailed transaction timing. The AD_CONV signal is not a traditional SPI
slave select enable. Be sure to provide enough SPI_SCK clock cycles so that the ADC leaves
the ADC_OUT signal in the high-impedance state. As shown in Figure 9-6, use a 34-cycle
communications sequence. The ADC 3-states its data output for two clock cycles before
and after each 14-bit data transfer.
19.6ns min
12
High-Z
AD_CONV
3
Channel 0
13
4
8ns
5
12 11
6
45ns min
SPI_SCK
ADC_OUT
Channel 1
3
32
333130
6ns
2 10
34
High-Z
The A/D converter sets its SDO output line to high impedance after 33 SPI_SCK clock cycles
UG330_c10_06_032007
Figure 9-7: Detailed SPI Timing to ADC
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 9-8 provides the User Constraint File (UCF) constraints for the amplifier interface,
including the I/O pin assignment and I/O standard used.
NET "AD_CONV" LOC = "Y6" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "SPI_SCK" LOC = "AA20" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 12 ;
NET "AD_DOUT" LOC = "D16" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL ;
Figure 9-8: UCF Location Constraints for the ADC Interface
76 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 77

R
Connecting Analog Inputs
Connect AC signals to VINA or VINB via a DC blocking capacitor.
Related Resources
Refer to the following links for additional information:
• Xilinx PicoBlaze Soft Processor
http://www.xilinx.com/picoblaze
• LTC6912 Dual Programmable Gain Amplifiers with Serial Digital Interface
http://www.linear.com/pc/downloadDocument.do?navId=H0,C1,C1154,C1009,C1121,P7596,D5359
• LTC1407A-1 Serial 14-bit Simultaneous Sampling ADCs with Shutdown
http://www.linear.com/pc/downloadDocument.do?navId=H0,C1,C1155,C1001,C1158,P2420,D1295
Connecting Analog Inputs
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 77
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 78

Chapter 9: Analog Capture Circuit
R
78 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 79

R
Chapter 10
Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board includes an SPI-compatible, four-channel, serial
Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC). The DAC device is a Linear Technology LTC2624
quad DAC with 12-bit unsigned resolution. The four outputs from the DAC appear on the
J21 header, which uses the Digilent six-pin Peripheral Module
header are located immediately below the Ethernet RJ-45 connector, as shown in
Figure 10-1.
Linear Tech LTC2624 Quad DAC
SPI_MOSI: (AB14)
SPI_SCK: (AA20)
DAC_CS: (W7)
DAC_CLR: (AB13)
DAC_OUT: (V7)
format. The DAC and the
6-pin DAC Header (J21)
Figure 10-1: DAC and Associated Stake Pin Header (J21)
UG334_c10_01_052407
SPI Communication
As shown in Figure 10-2, the FPGA uses a Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) to communicate
digital values to each of the four DAC channels. The SPI bus is a full-duplex, synchronous,
character-oriented channel employing a simple four-wire interface. A bus master—the
FPGA in this example—drives the bus clock signal (SPI_SCK) and transmits serial data
(SPI_MOSI) to the selected bus slave—the DAC in this example. At the same time, the bus
slave provides serial data (SPI_MISO) back to the bus master.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 79
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 80

Chapter 10: Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
R
3.3V by default.
Programmable reference
supplied by adjustable
LP3906 regulator, IC18.
(V7) (AB14)
Interface Signals
LTC 2624 DAC
REF A
3.3V
REF B
DAC A
12
DAC B
REF C
12
DAC C
REF D
12
DAC D
FPGA
(W7)
(AA20)
(AB13)
SPI_MOSI
DAC_CS
SPI_SCK
DAC_CLR
SDI
CS/LD
SCK
CLR
12
SPI Control Interface
DAC_OUT
Figure 10-2: Digital-to-Analog Connection Schematics
VOUTA
VOUTB
VOUTC
VOUTD
SDO
Header J5
A
B
C
D
GND
VCC
(3.3V)
UG334_c10_02_052407
Tab le 10 -1 lists the interface signals between the FPGA and the DAC. The SPI_MOSI,
DAC_OUT, and SPI_SCK signals are shared with other devices on the SPI bus. The
DAC_CS signal is the active-Low slave select input to the DAC. The DAC_CLR signal is
the active-Low, asynchronous reset input to the DAC.
Table 10-1: DAC Interface Signals
Signal FPGA Pin Direction Description
SPI_MOSI AB14 FPGAÆDAC Serial data: Master Output, Slave Input
DAC_CS W7 FPGAÆDAC Active-Low chip-select. Digital-to-analog
SPI_SCK AA20 FPGAÆDAC Clock
DAC_CLR AB13 FPGAÆDAC Asynchronous, active-Low reset input
DAC_OUT V7 FPGAÅDAC Serial data from the DAC
The serial data output from the DAC is primarily used to cascade multiple DACs. This
signal can be ignored in most applications although it does demonstrate full-duplex
communication over the SPI bus.
SPI Communication Details
Figure 10-3 shows a detailed example of the SPI bus timing. Each bit is transmitted or
received relative to the SPI_SCK clock signal. The bus is fully static and supports clock
rates up to the maximum of 50 MHz. However, check all timing parameters using the
LTC2624 data sheet if operating at or close to the maximum speed.
conversion starts when this signal returns
High.
80 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 81

R
SPI Communication
DAC_CS
SPI_MOSI
SPI_SCK
DAC_OUT Previous 31
After driving the DAC_CS slave select signal Low, the FPGA transmits data on the
SPI_MOSI signal, MSB first. The LTC2624 captures input data (SPI_MOSI) on the rising
edge of SPI_SCK; the data must be valid for at least 4 ns relative to the rising clock edge.
The LTC2624 DAC transmits its data on the DAC_OUT signal on the falling edge of
SPI_SCK. The FPGA captures this data on the next rising SPI_SCK edge. The FPGA must
read the first DAC_OUT value on the first rising SPI_SCK edge after DAC_CS goes Low.
Otherwise, bit 31 is missed.
After transmitting all 32 data bits, the FPGA completes the SPI bus transaction by
returning the DAC_CS slave select signal High. The High-going edge starts the actual
digital-to-analog conversion process within the DAC.
Communication Protocol
Figure 10-4 shows the communications protocol required to interface with the LTC2624
DAC. The DAC supports both 24-bit and 32-bit protocol. The 32-bit protocol is shown.
31 30 29
Previous 30 Previous 29
UG330_c9_03_071906
Figure 10-3: SPI Communication Waveforms
Master
FPGA
Inside the DAC, the SPI interface is formed by a 32-bit shift register. Each 32-bit command
word consists of a command and an address, followed by a data value. As a new command
enters the DAC, the previous 32-bit command word is echoed back to the master. The
response from the DAC can be ignored although it is a useful to confirm correct
communication.
DAC_OUT
SPI_MOSI
DAC_CS
SPI_SCK
xxxx
Don’t Care
Slave: LTC2624 DAC
12-bit Unsigned
DATA
a3a2a1a
0000
0001
0010
0011
1111
0
910
a
11876543210
msblsb
ADDRESS
DAC A
DAC B
DAC C
DAC D
All
0a1a2a3c0
COMMAND
c
c2c
1
3
Don’t Care
Figure 10-4: SPI Communications Protocol to LTC2624 DAC
3
10
xxxxxxxx
UG334_c10_04_052407
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 81
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 82

Chapter 10: Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
The FPGA first sends eight dummy or don’t care bits, followed by a four-bit command. The
most commonly used command with the board is COMMAND[3:0] = 0011 binary, which
immediately updates the selected DAC output with the specified data value. Following the
command, the FPGA selects one or all the DAC output channels via a four-bit address
field. Following the address field, the FPGA sends a 12-bit unsigned data value that the
DAC converts to an analog value on the selected output(s). Finally, four additional dummy
or don’t care bits pad the 32-bit command word.
Specifying the DAC Output Voltage
As shown in Figure 10-2, each DAC output level is the analog equivalent of a 12-bit
unsigned digital value, D[11:0], written by the FPGA to the DAC via the SPI interface.
The voltage on a specific output is generally described in Equation 10-1. The reference
voltage, V
REFERENCE
3.3V reference voltage. Channels C and D have a separate reference voltage, nominally also
3.3V, supplied by the LP3906 regulator designated as IC18. The reference voltage for
Channels C and D can be modified, as described in “I
page 140.
The reference voltages themselves have a ±5% tolerance, so there are slight corresponding
variances in the output voltage.
, is different between the four DAC outputs. Channels A and B use a
2
C Voltage Adjustment Interface,”
R
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 10-5 provides the UCF constraints for the DAC interface, including the I/O pin
assignment and the I/O standard used.
NET "SPI_MOSI" LOC = "AB14" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "SPI_SCK" LOC = "AA20" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "DAC_CS" LOC = "W7" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "DAC_CLR" LOC = "AB13" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "DAC_OUT" LOC = "V7" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL ;
Figure 10-5: UCF Location Constraints for the DAC Interface
Related Resources
Refer to the following links for additional information:
• LTC2624 Quad DAC Data Sheet
http://www.linear.com/pc/downloadDocument.do?navId=H0,C1,C1155,C1005,C1156,P2048,D2170
• Xilinx PicoBlaze Soft Processor
http://www.xilinx.com/picoblaze
• Digilent, Inc. Peripheral Modules
http://www.digilentinc.com/Products/Catalog.cfm?Nav1=Products&Nav2=Peripheral&Cat=Peripheral
V
OUT
D 11: 0[]
-------------------- -
4 096,
×=
V
REFERENCE
Equation 10-1
82 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 83

R
Parallel NOR Flash PROM
As shown in Figure 11-1, the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board includes a 32 Mbit
(4 Mbyte) parallel NOR Flash PROM.
FPGA
LDC0
LDC1
HDC
LDC2
User-I/O
User-I/O WP
User-I/O
D[7:1] DQ[7:1]
D[0]
A[21:1]
A[0]
NF_CE
NF_OE
NF_WE
NF_BYTE
NF_STS
NF_RP
NF_WP
NF_D<14:8>
NF_D<7:1>
SPI_MISO
NF_A<21:1>
NF_A<0>
Chapter 11
STMicro
M29DW323DT
E
G
W
BYTE
RB
RPUser-I/O
DQ[14:8]
DQ[0]
A[20:0]
D15/A-1
32 Mbit
A[25:22]
UG334_c11_01_052407
Figure 11-1: Connections to 32 Mbit Parallel NOR Flash Memory
The parallel NOR Flash PROM provides various functions:
• Stores a single FPGA configuration in the Flash memory.
• Stores various, different FPGA configurations in the Flash memory and dynamically
switches between the various images using the FPGA’s MultiBoot feature.
• Stores and executes MicroBlaze processor code directly from the Flash memory.
• Stores MicroBlaze processor code in the Flash memory and shadows the code into the
DDR2 SDRAM memory before executing the code.
• Stores non-volatile user data from the FPGA application.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 83
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 84

Chapter 11: Parallel NOR Flash PROM
Flash Connections
Table 11-1 shows the connections between the FPGA and the Flash memory device.
Although the XC3S700A/AN FPGA only requires just slightly over 2.6 Mbits per
uncompressed configuration image, the FPGA-to-Flash interface on the board supports up
to a 256 Mbit Flash. The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board ships with a 32 Mbit device.
Address lines SF_A<25:22> are not used.
In general, the Flash memory device connects to the FPGA to support Byte Peripheral
Interface (BPI) configuration, as described in Table 11-1.
Table 11-1: FPGA-to-Flash Connections
Category
Signal Name
NOR Flash
FPGA Pin
Number
Function
NF_A25 G17 The upper four Flash addresses are not used
NF_A24 G18
on the board. The board only has a 32 Mbit
parallel NOR Flash PROM.
NF_A23 B21
NF_A22 B22
R
Address
NF_A21 C21 Connects to FPGA pins A[21:0] to support
NF_A20 C22
the BPI configuration.
NF_A19 F21
NF_A18 F22
NF_A17 H20
NF_A16 H21
NF_A15 G22
NF_A14 H22
NF_A13 J20
NF_A12 J21
NF_A11 J22
NF_A10 K22
NF_A9 N17
NF_A8 N18
NF_A7 N19
NF_A6 N20
NF_A5 N21
NF_A4 N22
NF_A3 P18
NF_A2 R19
NF_A1
NF_A0
84 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
T18
T17
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 85

R
Flash Connections
Table 11-1: FPGA-to-Flash Connections (Continued)
Category
NOR Flash
Signal Name
FPGA Pin
Number
Function
NF_D15
(NF_A0)
NF_D14
NF_D13
NF_D12
NF_D11
NF_D10
NF_D9
NF_D8
NF_D7
Data
NF_D6
NF_D5
NF_D4
NF_D3
NF_D2
NF_D1
NF_D0
(SPI_MISO)
T17
R21
T22
U22
U21
V22
W22
T20
Y9
AB9
Y11
AB11
U13
AA17
Y17
AB20
Upper 8 bits of a 16-bit halfword when Flash is
configured for x16 data (NF_BYTE=High). The
Flash does not have a dedicated D15 pin.
Instead, this function is shared with the leastsignificant address pin. On the Flash memory
component, this pin is named D15/A-1, which
connects to the FPGA’s A0 address pin. After
configuration, if the FPGA application asserts
NF_BYTE-High, use NF_A0 to carry the D15
signal. Connect the other higher-order data
lines to FPGA user I/Os.
Upper 7 bits of a data byte or lower 8 bits of a
16-bit halfword. Connects to FPGA pins D[7:1]
to support the BPI configuration.
Bit 0 of a data byte and a 16-bit halfword.
Connects to FPGA pin D0/DIN to support the
BPI configuration. Shared with other SPI
peripherals and Platform Flash PROM.
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 85
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 86

Chapter 11: Parallel NOR Flash PROM
Table 11-1: FPGA-to-Flash Connections (Continued)
Category
Signal Name
NOR Flash
FPGA Pin
Number
R
Function
NF_BYTE
NF_CE
NF_OE
NF_RP
Control
NF_STS
NF_WE
NF_WP
Y21
W20
W19
R22
P22
AA22
E14
Active-Low Flash Byte Enable. Connects to
FPGA pin LDC2 to support the BPI
configuration.
0: x8 data
1: x16 data
Active-Low Flash Chip Enable. Connects to
FPGA pin LDC0 to support the BPI
configuration.
0: Enabled
1: Disabled
Active-Low Flash Chip Enable. Connects to
FPGA pin LDC1 to support the BPI
configuration.
0: Enable data outputs to read Flash data
1: Disabled
Active-Low Flash Reset. Connects to FPGA
user-I/O pin.
0: Reset
1: Flash active
Flash Status signal. Optional input to FPGA
open-drain output from Flash.
Active-Low Flash Write Enable. Connects to
FPGA pin HDC to support the BPI
configuration.
0: Enable Flash data write operations
1: Disabled
Active-Low Hardware Write Protect. Connects
to FPGA user-I/O pin.
0: Protect two outermost Flash boot blocks
against all program and erase operations.
1: Hardware protection disabled.
Shared SPI Flash and Platform Flash Data Line
The least-significant Flash data line, NF_D<0>, is shared with data output signals from the
serial SPI serial Flash PROMs and the serial output from the Platform Flash PROM as
shown in Table 11-2, page 87. To avoid contention, the FPGA application must ensure that
only one data source is active at any time.
86 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 87

R
Table 11-2: Possible Potential Competing Devices on SPI_MISO (NF_D<0>) Data
Signal or
Jumper
Jumper J46
Platform Flash PROM. Set to “Disabled” or “Enable
FPGA_INIT_B
SPI_SS_B SPI Flash PROM selected by
Jumper J1, as shown in
Table 12-2, page 93.
ALT_SS_B SPI Flash PROM selected by
Jumper J1, as shown in
Table 12-2, page 93.
UCF Location Constraints
UCF Location Constraints
Disabled Device Disable Value
during Configuration” as
shown in Table 4 - 2, p ag e 40.
FPGA_INIT_B has no effect.
If set to “Always Enabled,” then
FPGA_INIT_B must be 1
1
1
Address
Figure 11-2 provides the UCF constraints for the Flash address pins, including the I/O pin
assignment and the I/O standard used.
NET "NF_A<24>" LOC = "A11" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<23>" LOC = "N11" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<22>" LOC = "V12" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<21>" LOC = "C21" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<20>" LOC = "C22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<19>" LOC = "F21" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<18>" LOC = "F22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<17>" LOC = "H20" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<16>" LOC = "H21" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<15>" LOC = "G22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
"NF_A<14>" LOC = "H22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET
NET "NF_A<13>" LOC = "J20" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<12>" LOC = "J21" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<11>" LOC = "J22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<10>" LOC = "K22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<9>" LOC = "N17" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<8>" LOC = "N18" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<7>" LOC = "N19" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<6>" LOC = "N20" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<5>" LOC = "N21" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<4>"
NET "NF_A<3>" LOC = "P18" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<2>" LOC = "R19" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<1>" LOC = "T18" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_A<0>" LOC = "T17" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
# Upper four address lines, NF_A<25:22>, are unconnected using a 32Mbit Flash
# They are available as user I/Os but do not connect to anything on the board
CONFIG PROHIBIT = B22;
CONFIG PROHIBIT = B21;
CONFIG PROHIBIT = G18;
CONFIG PROHIBIT = G17;
LOC = "N22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
Figure 11-2: UCF Location Constraints for Flash Address Signals
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 87
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 88

Chapter 11: Parallel NOR Flash PROM
Data
Figure 11-3 provides the UCF constraints for the Flash data pins, including the I/O pin
assignment and the I/O standard used.
# NET "NF_D<15>" --> use NF_A<0> on pin T17 when NF_BYTE = High
NET "NF_D<14>" LOC = "R21" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<13>" LOC = "T22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<12>" LOC = "U22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<11>" LOC = "U21" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<10>" LOC = "V22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<9>" LOC = "W22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<8>" LOC = "T20" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<7>" LOC = "Y9" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<6>" LOC = "AB9" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<5>" LOC = "Y11" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<4>" LOC = "AB11" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<3>" LOC = "U13" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<2>" LOC = "AA17" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_D<1>" LOC = "Y17" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "SPI_MISO" LOC = "AB20" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 6 | SLEW = SLOW ;
Figure 11-3: UCF Location Constraints for Flash Data I/O Pins
R
Control
Figure 11-4 provides the UCF constraints for the Flash control pins, including the I/O pin
assignment and the I/O standard used.
NET "NF_BYTE" LOC = "Y21" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_CE" LOC = "W20" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_OE" LOC = "W19" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_RP" LOC = "R22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_STS" LOC = "P22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | PULLUP ;
NET "NF_WE" LOC = "AA22" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
NET "NF_WP" LOC = "E14" | IOSTANDARD = LVCMOS33 | DRIVE = 4 | SLEW = SLOW ;
Figure 11-4: UCF Location Constraints for Flash Control Pins
Setting the FPGA Mode Select Pins
To configure the FPGA from NOR Flash, set the FPGA configuration mode pins for BPI Up
mode, as shown in Tab le 11 -3 . The Spartan-3A/3AN FPGA families do not support the BPI
Down mode that is available in the Spartan-3E FPGA family.
Also be sure to disable the Platform Flash PROM by removing jumper J46, as shown in
Table 11-3.
Table 11-3: Selecting BPI-Up Configuration Mode (J26)
Configuration
Mode
Mode Pins
M2:M1:M0
FPGA Configuration Image in
Flash
Mode Select Jumper
Settings (J26)
Platform Flash
Enable (J46)
BPI Up 0:1:0 FPGA starts at address 0 and
J46
DONE
CE
PROM
GND
increments through address space.
88 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
M0
M1
M2
J26
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 89

R
Creating and Programming Configuration Images for Parallel Flash
Creating and Programming Configuration Images for Parallel
Flash
Refer to the “Master BPI Mode” chapter in the Spartan-3 Generation Configuration User Guide
for information on how to create and format FPGA configuration images for parallel Flash.
To program the parallel Flash memory, see the associated design example.
• UG332: Spartan-3 Generation Configuration User Guide
www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/userguides/ug332.pdf
• Design Example: Programmer for the STMicroelectronics M29DW323DT Parallel
NOR Flash
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#parallel_flash
_programmer
Related Resources
Refer to the following links for additional information:
• STMicroelectronics M29DW323DT 32 Mbit Parallel NOR Flash PROM
w
ww.st.com/stonline/products/literature/ds/8516.pdf
• Design Example: Programmer for the STMicroelectronics M29DW323DT Parallel
NOR Flash
www.xilinx.com/products/boards/s3astarter/reference_designs.htm#parallel_flash
_programmer
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 89
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 90

Chapter 11: Parallel NOR Flash PROM
R
90 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 91

R
SPI Serial Flash
The Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board includes two different styles of SPI serial Flash, as
shown in Figure 12-1. Only one style is available to configure the FPGA. After
configuration, however, the FPGA application has full access to both PROMs for data
storage or Flash update purposes.
Chapter 12
• STMicroelectronics M25P16
• Atmel AT45DB161D
Platform Flash
Jumper (J46)
FPGA Mode Select
Jumpers (J26)
Figure 12-1: SPI Serial Flash PROMs and Associated Jumpers
The SPI serial Flash is useful in a variety of applications. The SPI Flash provides a possible
means to configure the FPGA—a new feature in Spartan-3E and Spartan-3A/3AN FPGAs.
The SPI Flash is also available to the FPGA after configuration for a variety of purposes,
such as:
• Simple non-volatile data storage
• Storage for identifier codes, serial numbers, IP addresses, etc.
• Storage of MicroBlaze processor code that can be shadowed into DDR SDRAM.
16 Mbit SPI serial DataFlash PROM
Atmel AT45DB161D
16 Mbit SPI serial Flash PROM
STMicro M25P16
SPI Flash Select
Jumpers (J1)
JTAG and SPI
Programming
Blocks (J23, J25)
UG334_c12_01_052407
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 91
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 92

Chapter 12: SPI Serial Flash
FPGA
(AB20)
(AB14)
(AA20)
SPI_MISO
SPI_MOSI
SPI_SCK
16Mbit
AT45DB161 D
16Mbit
10Ω 10Ω
M25P16
R
DATAFLASH_WP
(C14)
DATAFLASH_RST
(C15)
(C13)
(Y5)
(Y4)
ST_SPI_WP
ALT_SS_B
SPI_SS_B
Table 12-1: SPI Flash PROM Interface Signals
Signal
FPGA
Pin
SPI_MISO AB20
SPI_MOSI AB14
Direction Description
FPGAÅPROM
FPGAÆPROM
Serial data: Master Input, Slave Output
Serial data: Master Output, Slave Input
SO
SI
SCK
WP
RST
‘1’
CS
ROM-CS0
CSO-B
CSO-SEL
ROM-CS1
SPI Flash Select
Jumpers (J1)
Figure 12-2: SPI Serial Flash Interface
D
Q
C
W
HLD
S
= 4.7kΩ to 3.3V
UG334_c12_02_052407
SPI_SCK AA20
FPGAÆPROM
Clock. Actively toggles during configuration. User I/O pin after
configuration.
SPI_SS_B Y4
FPGAÆPROM
Asynchronous, active-Low slave select signal. Actively drives Low during
SPI Flash configuration mode. User I/O pin after configuration. Drive High
if unused. Steered to selected “SPI Flash PROM Select Jumpers (J1),” page
93.
ALT_SS_B Y5
FPGAÆPROM
Second, asynchronous, active-Low slave select signal. Pulled High during
configuration. User I/O pin after configuration. Drive High if unused.
Steered to selected “SPI Flash PROM Select Jumpers (J1),” page 93.
DATAFLASH_WP
C14
FPGAÆPROM
Write-protect input to Atmel AT45DB161D PROM. Must be High to
program the PROM. Has external 4.7kΩ pull-up resistor.
DATAFLASH_RST
C15
FPGAÆPROM
Reset input to Atmel AT45DB161D PROM. Must be High to read, program,
or erase the PROM. Has external 4.7kΩ pull-up resistor.
ST_SPI_WP C13
FPGAÆPROM
Write-protect input to ST M25P16 PROM. Must be High to program the
PROM. Has external 4.7kΩ pull-up resistor.
92 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 93

R
SPI Flash PROM Select Jumpers (J1)
The J1 jumper block, shown in Figure 12-1, defines which SPI Flash PROM is connected to
the FPGA for Master SPI mode configuration and which is optionally available via a
separate, second SPI slave select signal.
Tab le 12 -2 indicates how the FPGA’s CSO_B signal is steered to one of the SPI Flash
PROMs during Master SPI configuration mode. The jumpers are designed so that there can
be no conflict.
• If both jumpers are inserted and oriented vertically, then the FPGA configures from
the Atmel SPI Flash PROM. After configuration, the FPGA application selects the
Atmel PROM using the SPI_SS_B signal and the STMicro PROM using the ALT_SS_B
signal.
• If both jumpers are inserted and oriented horizontally, then the FPGA configures from
the STMicro SPI Flash PROM. After configuration, the FPGA application selects the
STMicro PROM using SPI_SS_B signal and the Atmel PROM using the ALT_SS_B
signal.
Table 12-2: SPI Flash PROM Select Jumper Settings
SPI Flash PROM Select Jumpers (J1)
After Configuration
Jumper J1
Setting
J1
J1
J1
J1
SPI Mode
Configuration Source
Atmel
AT45DB161D
STMicro
M25P16
Atmel
AT45DB161D
STMicro
M25P16
Atmel AT45DB161D
Slave Select Signal
SPI_SS_B
(Y4)
N/A
SPI_SS_B
(Y4)
ALT_SS_B
(Y5)
STMicro M25P16
Slave Select Signal
N/A
SPI_SS_B
(Y4)
ALT_SS_B
(Y5)
SPI_SS_B
(Y4)
J1
None None None
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 93
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 94

Chapter 12: SPI Serial Flash
Shared SPI Flash and Platform Flash Data Line
The SPI_MISO signal from the two SPI Flash PROMs is shared with data output signals
from the parallel NOR Flash PROM and the serial output from the Platform Flash PROM
as shown in Table 12-3. To avoid contention, the FPGA application must ensure that only
one data source is active at any time.
Table 12-3: Possible Potential Competing Devices on SPI_MISO (NF_D<0>) Data
Signal or
Jumper
R
Disabled Device Disable Value
Jumper J46
FPGA_INIT_B
SPI_SS_B SPI Flash PROM selected by
ALT_SS_B SPI Flash PROM selected by
NF_CE
NF_OE
Platform Flash PROM. Set to “Disabled” or “Enable
during Configuration” as
shown in Table 4 - 2, p ag e 40.
FPGA_INIT_B has no effect.
If set to “Always Enabled,” then
FPGA_INIT_B must be 1
1
Jumper J1, as shown in
Table 12-2, page 93.
1
Jumper J1, as shown in
Table 12-2, page 93.
Parallel Flash PROM NF_CE = 1 or NF_OE = 1
Jumper Settings to Configure FPGA from Selected SPI Flash PROM
To successfully configure the FPGA from the selected external SPI Flash PROM, set the
following jumpers as described below.
• Set the FPGA configure mode, using the Jumper J26 jumper header, shown in
Tab le 12 -4 .
• Disable the Platform Flash PROM using Jumper J46, shown in Tab le 1 2- 4.
Table 12-4: Configuration Mode Jumper Settings for Master SPI Mode (J26, J46)
Configuration Mode
Master SPI 0:0:1
Mode Pins
M2:M1:M0
Jumper J26 Settings
M0
M1
M2
J26
Platform Flash
Enable (J46)
DONE
CE
PROM
GND
J46
• Select one of the SPI serial Flash PROMs as the SPI configuration source, as shown in
Tab le 12 -2 .
94 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 95

R
UCF Location Constraints
UCF Location Constraints
Figure 12-3 provides the UCF constraints for the SPI serial Flash PROM, including the I/O
pin assignment and the I/O standard used.
# some connections shared with SPI Flash, DAC, ADC, and AMP
NET "SPI_MISO" LOC = "AB20" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL ;
NET "SPI_MOSI" LOC = "AB14" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "SPI_SCK" LOC = "AA20" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 12 ;
NET "SPI_SS_B" LOC = "Y4" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "ALT_SS_B" LOC = "Y5" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
# write-protect and reset controls for Atmel AT45DB161D PROM
NET "DATAFLASH_WP" LOC = "C14" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
NET "DATAFLASH_RST" LOC = "C15" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
# write-protect control for ST M25P16 PROM
NET "ST_SPI_WP" LOC = "C13" | IOSTANDARD = LVTTL | SLEW = SLOW | DRIVE = 4 ;
Figure 12-3: UCF Location Constraints for SPI Flash Connections
Creating and Programming Configuration Images for SPI Serial Flash
Refer to the “Master SPI Mode” chapter in the Spartan-3 Generation Configuration User Guide
for information on how to create and format FPGA configuration images for SPI serial
Flash and how to program SPI Flash using the Xilinx iMPACT software.
• UG332: Spartan-3 Generation Configuration User Guide
www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/userguides/ug332.pdf
SPI Flash PROM Programming Options
Starting with ISE 9.1i, Service Pack 2 and later, the iMPACT programming software
supports two different methods to program an attached SPI Flash PROM, as summarized
in Tab le 12 -5 .
Using the Direct Programming Method, the programming cable communicates directly to
the SPI Flash PROM. The FPGA is not involved in the programming process and the FPGA
I/O pins that connect to the PROM must be in their high-impedance state (Hi-Z) during
programming. Hold the FPGA’s PROG_B input Low using jumper J16 to place the I/Os in
Hi-Z; the FPGA’s DONE pin remains Low.
Using the Indirect Programming Method, the programming cable connects to the FPGA’s
JTAG port. The iMPACT software first programs the FPGA with a special design that
performs the SPI PROM programming and uses the JTAG interface as a serial
communications port. During the process, the FPGA’s DONE output is High and the
DONE LED is lit because the FPGA is configured with the programming logic. All pins
that are not connected to the SPI Flash PROM or the JTAG interface have an internal
pull-up resistor to the V
voltage supply associated with the pin.
CCO
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 95
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 96

Chapter 12: SPI Serial Flash
Table 12-5: Summary of SPI Flash PROM Programming Options
R
Direct Method Indirect Method
ISE Version Required ISE 9.1i or later
Interface/Cable Connection Directly to SPI PROM FPGA’s JTAG Port
DONE Pin Status during
Programming
Required PROG_B Control PROG_B = Low
Status of non-SPI Pins
during Programming
Direct Programming Method
The iMPACT software supports direct programming of select SPI serial Flash. The Spartan3A/3AN Starter Kit board primarily supports direct programming using the embedded
USB JTAG programmer included on the board. Optionally, the SPI Flash can be
programmed using a separate programming cable, as well.
Using Embedded USB JTAG Programmer
Follow these steps to prepare the board for direct SPI Flash programming using the
embedded USB JTAG programmer included on the board.
Low
High-impedance because
PROG_B = Low
ISE 9.1i, Service Pack 2 or
later
High
(FPGA is configured with
special programming design)
N/A
Pulled High using internal
pull-up resistor to associated
V
supply input
CCO
1. Disconnect power to the board.
2. Connect either a USB cable between the board and the PC, or connect a separate JTAG
cable as described in “Using a Separate JTAG Parallel Programming Cable (Optional),”
page 97.
3. Locate the J1, J23, and J25 jumpers in the upper right corner of the board, using
Figure 12-1 as a guide. Figure 12-4 also provides a reference diagram.
STMicro PROM Atmel PROM
J1
CSO-SEL
ROM-CS1
PROG_B
GND
UG330_c15_05_032907
ROM-CS0
CSO-B
JTAG Header
SPI Header
J1
TMS
CSO-B
CSO-SEL
ROM-CS1
TDI
TDO
SDI
SDO
TCK
SCK
PROG_B
ROM-CS0
GND
VCC
VCC
GND
CSO-B
J25
J23
J16
Figure 12-4: Jumper Settings for Direct SPI Flash Programming
96 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 97

R
Creating and Programming Configuration Images for SPI Serial Flash
4. Insert a jumper in jumper block J1, as shown in Figure 12-4. The figure shows the
setting to program the STMicro M25P16 PROM. Alternatively, set the jumper to
program the Atmel AT45DB161D DataFlash PROM.
5. Insert four jumpers between jumper blocks J25 and J23, as shown in Figure 12-4. These
jumpers connect the embedded USB JTAG programmer on the J25 jumper pins to the
SPI PROM via the J23 jumper pins.
6. Set the FPGA mode select pins for Master SPI mode using jumper J26, as shown in
Tab le 12 -4 . The location of the J26 jumper appears in Figure 12-1.
7. Disable the Platform Flash PROM by removing jumper J46, shown in Figure 12-1 and
Tab le 12 -4 .
8. For direct programming, the FPGA’s PROG_B pin must be held Low. Insert a jumper
in jumper J16, as shown in Figure 12-4. This holds all the FPGA’s I/O in three-state to
allow the JTAG programmer full access to the SPI PROM pins.
9. Re-apply power to the board.
Using a Separate JTAG Parallel Programming Cable (Optional)
Using Embedded USB JTAG Programmer is the preferred programming method. With the
jumpers installed between the J23 and J25 headers, the embedded USB programmer
communicates directly to the SPI Flash PROM. However, it is possible to communicate
directly to the SPI Flash PROM using another a programming cable, such as:
• Xilinx Parallel Cable IV
• Digilent JTAG3 or JTAG-USB
with flying leads
programming cable
Connect the cable directly to the J23 header block, as illustrated in Figure 12-5. These cables
are not provided with the Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit board but can be purchased
separately.
a) JTAG3 Parallel Connector b) Parallel Cable III or Parallel Cable IV
with Flying Leads
UG334_c12_05_052407
Figure 12-5: Attaching a JTAG Parallel Programming Cable to the Board
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 97
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 98

Chapter 12: SPI Serial Flash
First, turn off the power on the Starter Kit board.
If the USB cable is attached to the board, disconnect it. Simultaneously connecting both the
USB cable and the parallel cable to the PC confuses the iMPACT software.
Connect one end of the JTAG parallel programming cable to the parallel printer port of the
PC.
Connect the JTAG end of the cable to Header J23, as shown in Figure 12-5a. The J23 header
connects directly to the SPI Flash pins; it is not connected to the JTAG chain.
The JTAG3 cable directly mounts to Header J23. The labels on the JTAG3 cable face toward
the J11 jumpers. If using flying leads, they must be connected as shown in Figure 12-5b and
Tab le 12 -6 . Note the color coding for the leads. The gray INIT lead is left unconnected.
Table 12-6: Cable Connections to J23 Header
J23 Header Label SEL SDI SDO SCK GND VCC
JTAG3 Cable Label TMS TDI TDO TCK GND VCC
R
Cable and Labels Connections
Flying Leads Label
TMS/
PROG
TDI/
DIN
TDO/
DONE
TCK/
CCLK
GND/
GND
Direct SPI Flash Programming Using iMPACT
The following steps describe how to program the SPI PROM using the iMPACT software
and a Xilinx programming cable.
1. Click Direct SPI Configuration from within iMPACT, as shown in Figure 12-6.
3
1
UG332_c4_03_101006
Figure 12-6: iMPACT Supports Direct Programming for SPI Serial Flash Memories
VREF/
VREF
2
2. Right-click in the area indicated.
3. Select Add SPI Device.
98 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 99

R
Creating and Programming Configuration Images for SPI Serial Flash
4. Select a previously formatted PROM file, as shown in Figure 12-7.
4
5
UG332_c4_04_101006
Figure 12-7: Select a Previously Formatted PROM File
5. Click Open.
6. Select the Part Name for a supported SPI serial Flash, as shown in Figure 12-8.
7. Click OK.
6
7
UG332_c4_05_101006
Figure 12-8: Select a Supported SPI Flash Memory Device
Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide www.xilinx.com 99
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
Page 100

Chapter 12: SPI Serial Flash
8. The iMPACT software displays the selected SPI Flash PROM, as shown in Figure 12-9.
R
8
9
14
UG332_c4_06_101006
Figure 12-9: Directly Program Supported SPI Flash PROM
9. Click Program.
Note:
10. Click the Programming Properties option under Category, as shown in Figure 12-10.
Step 14 occurs later.
10
11
12
13
UG332_c4_07_101006
Figure 12-10: SPI PROM Programming Options
11. Check Ve r i fy. Unchecking Verify reduces programming time but the iMPACT
software can only guarantee correct programming for a verified PROM.
100 www.xilinx.com Spartan-3A/3AN Starter Kit Board User Guide
UG334 (v1.0) May 28, 2007
 Loading...
Loading...