Page 1

OperOper
Oper
OperOper
ManualManual
Manual
ManualManual
aa
tor’tor’
a
tor’
aa
tor’tor’
ss
s
ss
Part Number 0075239EE
July, 2005
Page 2

The aerial platform is not electrically insulated. Death or serious injury will result from contact with, or inadequate clearance from, an energized conductor.
Do not go closer than the minimum safe approach distance as defined by the Minimum Safe
Approach Distance section in Chapter 3 – Safety.
Regard all conductors as energized.
Allow for electrical wire sag and aerial platform sway.
If the platform, booms, or any part of the aerial platform contacts a high-voltage electrical conductor,
the entire machine can become electrically charged.
If that happens, remain on the machine and do not contact any other structure or object. This includes
the ground, adjacent buildings, poles, and any other objects that are not part of the aerial platform.
Such contact could make your body a conductor to the other object, creating an electrical shock
hazard resulting in death or serious injury.
If an aerial platform is in contact with an energized conductor the platform operator must warn ground
personnel in the vicinity to stay away. Their bodies can conduct electricity creating an electrical shock
hazard resulting in death or serious injury.
Do not approach or leave the aerial platform until the electricity has been turned off.
Do not attempt to operate the lower controls when the platform, booms, or any part of the aerial
platform is in contact with a high-voltage electrical conductor or if there is an immediate danger of such
contact.
Personnel on or near an aerial platform must be continuously aware of electrical hazards, recognizing
that death or serious injury can result from contact with an energized conductor.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 – Introduction
Aerial Platform Features ............................................ 1
Options ..................................................................... 1
Operator’s Manual ..................................................... 1
Safety Alerts ............................................................. 1
Operation .................................................................. 1
Maintenance ............................................................. 2
Owner and User Responsibilities ............................... 2
Additional Information ................................................ 2
Chapter 2 – Specifications
Component Identification ........................................... 3
Working Envelope ..................................................... 4
General Specifications............................................... 5
Aerial Platform ........................................................ 5
Platform .................................................................. 5
Function Speed .......................................................5
Drive System .......................................................... 5
Tires ....................................................................... 5
Electrical System ................................................... 5
Hydraulic System ................................................... 5
Engine .................................................................... 5
Fuel Tank Capacity ................................................. 5
Ambient Air Temperature Operating Range .............. 5
Maximum Wind Speed ............................................5
Engine Specifications ................................................ 6
Engine Oil Viscosity.................................................. 7
Cummins B3.3 ........................................................ 7
Deutz F3L-2011F .................................................... 7
Chapter 3 – Safety
Electrocution Hazards ............................................... 9
Minimum Safe Approach Distance ............................. 9
Prestart Inspection ................................................... 10
Work Place Inspection and Practices ....................... 10
Operation .................................................................10
Tip-Over and Falling Hazards ....................................10
Electrical System ..................................................... 11
Hydraulic System ..................................................... 11
Engine and Fuel Handling Precautions ..................... 11
Placards and Decals ................................................ 12
Chapter 4 – Safety Devices
Emergency Stop Controls ........................................ 13
Emergency Power System .......................................13
Emergency Lowering Knob .......................................13
Ground Operation Switch .........................................14
Platform Foot Switch ................................................14
Guardrails ................................................................14
Lanyard Anchors ...................................................... 14
Tilt Alarm .................................................................. 14
Platform Overload Sensing System ..........................15
Engine Protection Systems ...................................... 15
High Engine Temperature Alarm ............................ 15
Low Oil Pressure Alarm ........................................ 15
Horn ......................................................................... 16
Drive Motion Alarm ................................................... 16
Flashing Light .......................................................... 16
Driving Lights............................................................ 16
Platform Work Lights ............................................... 16
Chapter 5 – Gauges and Displays
Hour Meter ............................................................... 17
Engine Temperature Gauge ...................................... 17
Ammeter ..................................................................17
Engine Air Filter Gauge ............................................ 17
Fuel ......................................................................... 17
Engine Oil ................................................................18
Hydraulic Fluid Filter Gauge .....................................18
Fluid Level and Temperature Gauge .......................... 18
Chapter 6 – Controls
Battery Disconnect Switch .......................................19
Lower Controls ......................................................... 19
Emergency Stop Button ........................................ 19
Control Selector Switch ........................................ 19
Start Switch .......................................................... 19
Ground Operation Switch ...................................... 20
Rotation Switch .....................................................20
Boom Elevation Switch ......................................... 20
Boom Extend/Retract Switch ................................ 20
Jib Articulation Switch ........................................... 20
Platform Level Switch ............................................ 20
Platform Rotation Switch .......................................20
Engine/Emergency Power Switch ......................... 20
Throttle Switch ...................................................... 20
Circuit Breaker Reset Buttons ............................... 20
Upper Controls ......................................................... 21
Start Switch .......................................................... 21
Emergency Stop Button ........................................ 21
Speed Knob .......................................................... 21
Drive/Boom Selector Switch .................................. 22
Boom Joystick ...................................................... 22
Drive Joystick ....................................................... 22
Drive Range Switch ............................................... 22
Jib Articulation Switch ........................................... 22
Boom Extend/Retract Switch ................................ 22
Platform Rotate Switch ......................................... 22
Platform Level Switch ............................................ 22
Engine/Emergency Power Switch ......................... 22
Throttle Switch ...................................................... 22
Horn Button .......................................................... 23
Platform Foot Switch ............................................. 23
Machine/Generator Switch ....................................... 23
Driving and Platform Work Lights.............................. 23
TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Operator’s Manual ....................................................25
Engine ..................................................................... 25
Oil Level ................................................................ 25
Coolant ................................................................. 25
Radiator ................................................................ 26
Fuel Tank .............................................................. 26
Fuel Line ............................................................... 26
Air Filter ................................................................26
Charging System .................................................. 26
Cold Weather Start Kit—Block Heater................... 26
Electrical System ..................................................... 26
Emergency Power Battery .................................... 27
Battery Fluid Level ................................................ 27
Battery Terminals .................................................. 27
Cables and Wiring Harness ......................................27
Hydraulic System ..................................................... 27
Fluid Level............................................................. 27
Fluid Filter............................................................. 28
Hoses, Tubes, and Fittings ................................... 28
Tires and Wheels ..................................................... 28
Lower Control Station ............................................... 28
Operating Controls ................................................ 29
Emergency Stop ................................................... 29
Emergency Power................................................. 29
Emergency Lowering ................................................29
Level Sensor ............................................................29
Flashing Light .......................................................... 30
Sandblast Protection Kit .......................................... 30
Structures ................................................................ 30
Weldments ........................................................... 30
Slide Pads ............................................................ 30
Wire Ropes ........................................................... 30
Fasteners ............................................................. 31
Upper Control Station ............................................... 31
Guardrail System .................................................. 31
Lanyard Anchors ................................................... 32
Operating Controls ................................................ 32
Emergency Stop ................................................... 32
Emergency Power................................................. 32
Horn ...................................................................... 32
Electrical Power Outlet ......................................... 32
Drive Motion Alarm ................................................ 32
Driving and Work Lights ........................................ 32
Platform Control Cover .......................................... 32
Tow Kit ..................................................................... 32
Placards and Decals ................................................ 33
Prestart Inspection Checklist ...................................37
Chapter 8 – Operation
Cold Weather Start-Up ............................................. 39
Engine Cold Weather Start Kit.................................. 39
Cummins — Block Heater .................................... 39
Deutz — Manifold Preheater ................................. 39
Hydraulic System Cold Weather Warm-Up............... 39
Preparing for Operation............................................. 40
Lower Controls ......................................................... 40
Upper Controls ......................................................... 40
Boom Operation .................................................... 41
Platform Overload Sensing System ....................... 41
Driving and Steering .............................................. 42
Drive Speeds ......................................................... 42
Motion Warning Alarm ........................................... 43
Four Wheel Drive ......................................................43
AC Generator ........................................................... 43
Air Line .................................................................... 43
Driving Lights............................................................ 43
Platform Work Lights ............................................... 43
Chapter 9 – Stowing and Transporting
Stowing ....................................................................45
Tucked Stow ......................................................... 45
Transporting ............................................................. 45
Driving ................................................................... 46
Winching .............................................................. 46
Hoisting ................................................................ 47
Securing for Transport ........................................... 48
Chapter 10 – Emergency Operation
Emergency Power System .......................................49
Lower Controls ...................................................... 49
Upper Controls ...................................................... 49
Emergency Lowering ................................................50
Towing ......................................................................50
Chapter 11 – Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Chart ..............................................53
Appendix A – Glossary
Limited Warranty
TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 5

Chapter 1 – Introduction
Aerial Platform Features
The aerial platform is a boom-supported elevating work
platform used to raise personnel, their tools, and material to the workstation. The booms are raised and lowered with hydraulic cylinders. Hydraulic motors on the
drive wheels provide power to move the aerial platform.
The standard machine includes the following features.
• Proportional boom lift, swing, and drive control
• 170 degree hydraulic platform rotation
• Two safety lanyard attachments
• Manual lowering valve at chassis
• Hydraulic oil level and temperature gauges
• Lifting lugs
• Tie-down lugs
• Horn
• 3.5 degree tilt alarm
• Electronic ignition
• Hour meter
• Ammeter
• Coolant temperature gauge
• High engine temperature shut down
• Low oil pressure shut down
• Foam filled tires
• Battery operated emergency power system
• 360 degree continuous turntable rotation
• 76 cm x 152 cm (30″ x 60″) steel platform
• Platform gravity gate
• Platform overload sensing system
• Five year limited warranty
The machine may be powered with one of the following
engines.
• Cummins B3.3 – Diesel
• Deutz F3L-2011F – Diesel
• 76 cm x 234 cm (30″ x 92″) aluminum 226 kg (500 lb)
capacity platform
• 76 cm x 152 cm (30″ x 60″) aluminum 272 kg (600 lb)
capacity platform
Operator’s Manual
This manual provides information for safe and proper operation of the aerial platform. Read and understand the
information in this Operator’s Manual before operating
the aerial platform on the job.
Additional copies of this manual may be ordered from
Snorkel. Supply the model and manual part number from
the front cover to assure that the correct manual will be
supplied.
All information in this manual is based on the latest product information at the time of publication. Snorkel reserves
the right to make product changes at any time without
obligation.
Safety Alerts
A safety alert symbol is used throughout this manual to
indicate danger, warning, and caution instructions. Follow these instructions to reduce the likelihood of personal injury and property damage. The terms danger,
warning, and caution indicate varying degrees of personal
injury or property damage that can result if the instruction is not followed.
ADanger
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
This signal word is to be used in the most extreme
situations.
The aerial platform has been manufactured to conform to
European Directive 98/37/EC and European Standard
EN280.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Options
The following options may be provided on the machine.
• Platform control cover
• Platform work lights – flood lights
• Flashing light – amber
• Platform swinging gate
• Sandblast protection kit
• Driving lights – two headlights and two rear lights
• Spark arrestor muffler – Deutz engines
• Cold weather start kit Cummins – block heater
• Cold weather start kit Deutz – manifold preheater
• AC generator – hydraulic powered, 220 VAC
• Drive motion alarm
• Road tread tires
• Flotation tires
• Airline to platform
• Tow kit
TB47J – 0075239EE 1
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury. It may also be used to alert against unsafe
practices.
Notes
Notes are used to provide special information or helpful
hints to assist in aerial platform operation, but do not
indicate a hazardous situation.
Operation
The aerial platform has built-in safety features and has
been factory tested for compliance with Snorkel specifications and industry standards. However, any personnel
lifting aerial platform can be potentially dangerous in the
hands of untrained or careless operators.
AWarning
ACaution
Page 6

Chapter 1 – Introduction
AWarning
The potential for an accident increases when the
aerial platform is operated by personnel who are
not trained and authorized. Death or serious injury
can result from such accidents. Read and understand the information in this manual and on the placards and decals on the machine before operating
the aerial platform on the job.
Training is essential and must be performed by a qualified person. Become proficient in knowledge and actual
operation before using the aerial platform on the job. You
must be trained and authorized to perform any functions
of the aerial platform. Operation of the aerial platform must
be within the scope of the machine specifications.
The operator bears ultimate responsibility for following all
manufacturer’s instructions and warnings, regulations and
safety rules of their employer and/or any state or federal
law.
Maintenance
Every person who maintains, inspects, tests, or repairs
the aerial platform must be qualified to do so. Following
the daily prestart inspection in this Operator’s Manual
will help keep the aerial platform in optimum working con-
dition. Other maintenance functions must be performed
by maintenance personnel who are qualified to work on
the aerial platform.
Do not modify this aerial platform without prior written
consent of the Snorkel Engineering Department. Modification may void the warranty, adversely affect stability,
or affect the operational characteristics of the aerial platform.
Owner and User Responsibilities
All owners and users of the aerial platform must read,
understand, and comply with all applicable regulations.
Ultimate compliance to national safety regulations is the
responsibility of the user and their employer.
Additional Information
For additional information contact your local dealer or
Snorkel at:
Snorkel International
P.O. Box 1160
St. Joseph, MO 64502-1160 USA
785-989-3000
http://www.snorkelusa.com
2 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 7
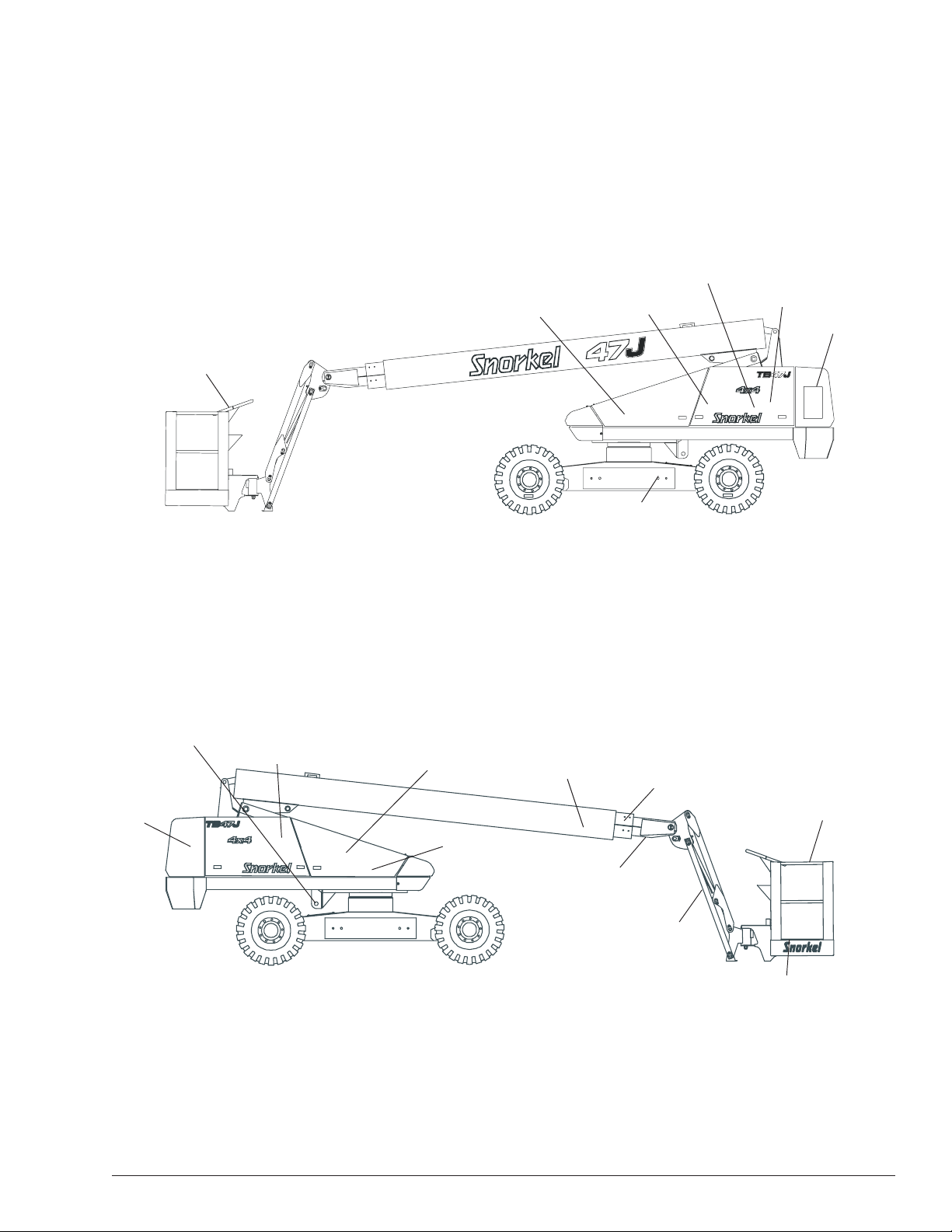
Component Identification
Chapter 2 – Specifications
Upper Controls
Emergency
Lowering
Valve
Engine
Hydraulic Fluid Tank
And Filter
LP Fuel Tank
Right Side
Battery Disconnect Switch
Main Boom
Fuel Tank
Chassis
Intermediate
Boom
Wiring Box
Steer Wheels
Operator’s
Manual
Lower Controls
Platform
Batteries
Tip Boom
Jib
Steer Wheels
Platform
Foot Switch
Left Side
TB47J – 0075239EE 3
Page 8
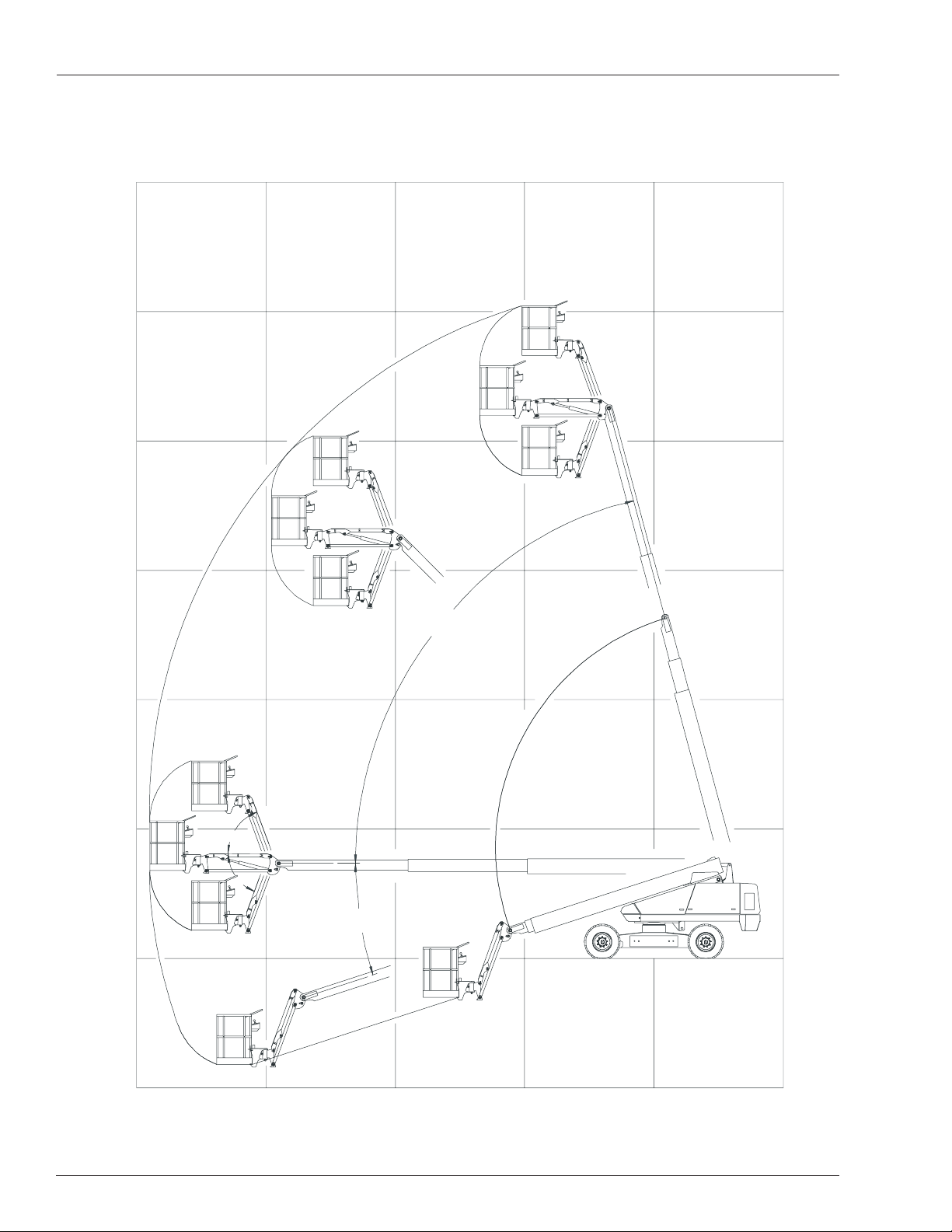
Chapter 2 – Specifications
Working Envelope
Meters
(Feet)
15.2
(50)
12.2
(40)
9.1
(30)
6.1
(20)
3.0
(10)
0
75°
70°
70°
18°
12.2
(40)
4 TB47J – 0075239EE
9.1
(30)
6.1
(20)
3.0
(10) 0
3.0
(10)
Page 9

General Specifications
Chapter 2 – Specifications
Aerial Platform
Working height 16 m (52′ 6″)
Maximum platform height 14.2 m (46′ 6″)
Horizontal reach 11.9 m (39′)
Main boom
Articulation -18° to +75°
Extension 2.5 m (8′ 4.75″)
Turntable rotation 360° continuous
Turning radius, inside
Two wheel drive 1.6 m (5′ 2″)
Four wheel drive 1.7 m (5′ 6″)
Wheelbase 2.4 m (8′)
Ground clearance 25 cm (10″)
Maximum wheel load 2,495 kg (5,500 lbs)
Maximum ground pressure 3.8 kg/cm² (54 psi)
Weight, GVW
Approximate 6,123 kg (13,500 lbs)
Stowed width 2.4 m (7′ 11.5″)
With flotation tires 2.6 m (8′ 7.5″)
Stowed length 8.1 m (26′ 9″)
Stowed length, tucked stow 6.5 m (21′ 3.5″)
Stowed height 2.3 m (7′ 9″)
Stowed height, tucked stow 2.4 m (7′ 11.5″)
Platform
Dimensions
Standard steel 76 cm x 152 cm (30″ x 60″)
Rated work load 227 kg (500 lb)
Optional aluminum 76 cm x 234 cm (30″ x 92″)
Rated work load 227 kg (500 lb)
Optional aluminum 76 cm x 152 cm (30″ x 60″)
Rated work load 227 kg (600 lb)
Rotation 90° CW to 80° CCW
Maximum number of occupants 2 people
Optional AC generator 220 VAC
Function Speed
Turntable rotation, 360 degrees 108 to 113 seconds
Main boom
Up 65 to 70 seconds
Down 65 to 70 seconds
Extend 40 to 45 seconds
Retract 25 to 30 seconds
Jib
Up 25 to 35 seconds
Down 25 to 35 seconds
Platform rotation, 170 degrees 8 to 15 seconds
Drive
High, booms stowed 4.8 km/h (3.0 mph)
Low, booms elevated 1.6 km/h (1.0 mph)
Drive System
Standard Four wheel drive
Optional Two wheel drive
Gradeability 25%
Tires
Street tread, 10 ply 30 cm x 42 cm (12″ x 16.5″)
Bar lug, 10 ply 30 cm x 42 cm (12″ x 16.5″)
Flotation, 10 ply 33/16LL-16.1
Foam filled, 10 ply Street tread or bar lug
Electrical System
Voltage 12 V DC negative chassis ground
Source Two - 12 V 600 CCA batteries
Fluid recommended distilled water
Hydraulic System
Maximum pressure 20,684 kPa (3,000 psi)
Reservoir capacity 62.4 l (16.5 US gal)
System capacity 94.6 l (25 US gal)
Maximum operating temperature 93°C (200°F)
Hydraulic fluid recommended
Above -13°C (10°F) Mobil DTE-13M
(ISO VG32)
Below -13°C (10°F) Mobil DTE-11M
(ISO VG15)
Engine
Diesel Cummins B3.3
Diesel Deutz F3L-2011F
Fuel Tank Capacity
Diesel 75.7 l (20 US gal)
Ambient Air Temperature Operating Range
Celsius -18°C to 43°C
Fahrenheit 0°F to 110°F
Maximum Wind Speed
Gust or steady 45 km/h (28 mph)
TB47J – 0075239EE 5
Page 10
Chapter 2 – Specifications
Engine Specifications
Engine
Cummins
B3.3
Diesel
CID Fuel Grade Coolant
ASTM No. 2D fuel with a
3.26 liter
(199 cu. in.)
minimum Cetane number of
1
40.
For operating tempera-
tures below 0°C (32°F) use
winterized No. 2D.
• DIN 51 601 (February 1986).
50% water
50% Antifreeze
1
Operating
Temperature
60°C to 100°C
2
140°F to 212°F
Oil
Capacity
7.5 liter (2 gal)
total
1.5 liter (1.6 qt)
Low to High
Grade
15W-40
CH4/SG
• BS 2869: A1 and A2 (with A2
Deutz
F3L-2011F
Diesel
2.0 liter
(125 cu. in.)
refer to Deutz manual about
sulfur content)
• ASTM D 975-88: 1-D and 2-D
• CEN EN 590 or DIN EN 590
• NATO Code F-54 and F-75
1
Air
78°C to 95°C
172°F to 203°F
6.0 liter
(1.59 US gal)
API: CD
or higher
• For operating temperatures
below 0°C (32°F) use winter
grade diesel.
Note 1: Refer to the engine manufacturers manual for specific fuel recommendations and specifications.
Note 2: Ethylene glycol or Propylene glycol may be used. Refer to the Cummins® Operation and Maintenance Manual B3.3 Series
Note 3: Refer to the engine manufacturers manual for specific lubricating oil recommendations and specifications.
Engines for specific coolant recommendations and specifications.
Oil
SAE
API:
3
3
6 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 11
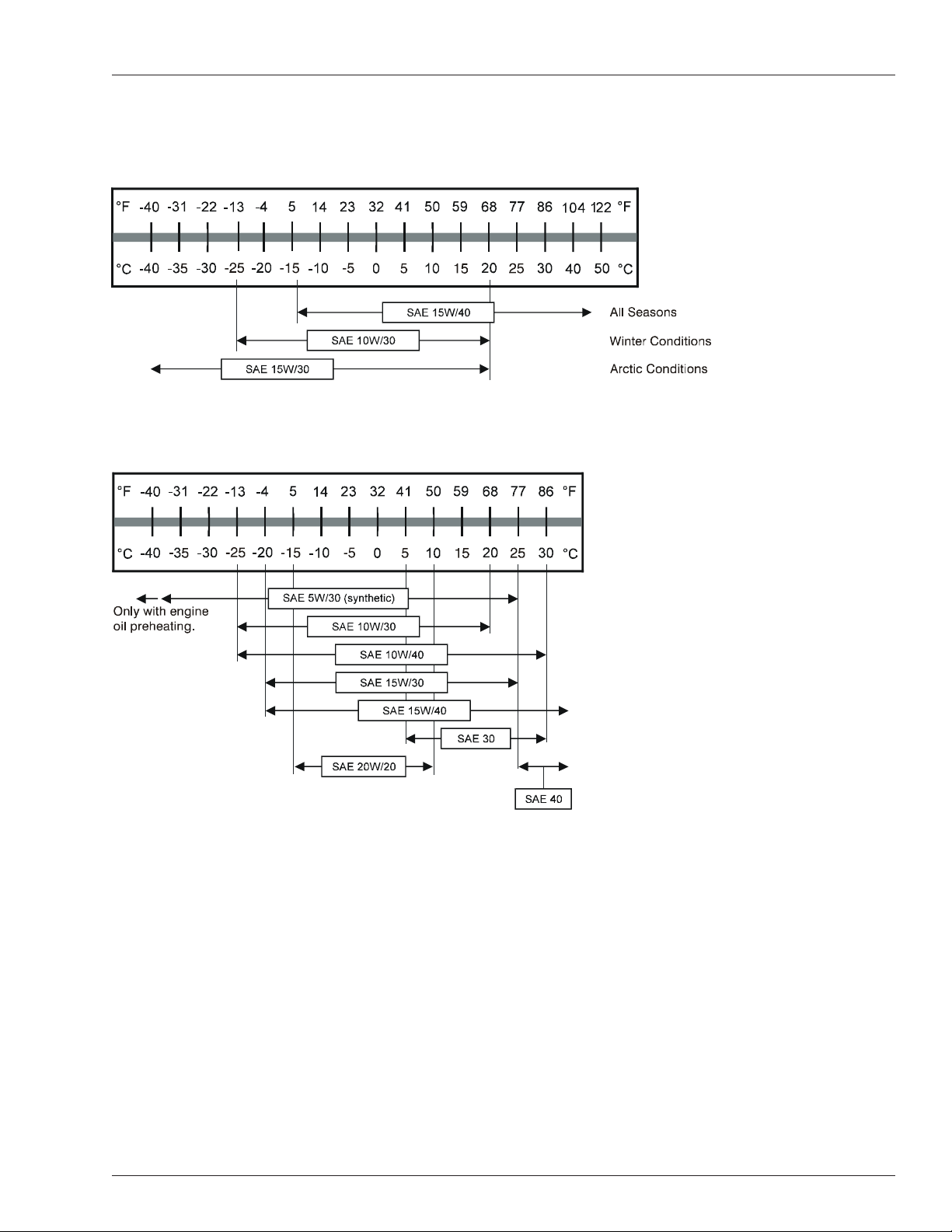
Engine Oil Viscosity
Cummins B3.3
Deutz F3L-2011F
Chapter 2 – Specifications
TB47J – 0075239EE 7
Page 12

Chapter 2 – Specifications
8 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 13
Chapter 3 – Safety
Knowledge of the information in this manual, and proper
training, provide a basis for safely operating the aerial
platform. Know the location of all controls and how they
operate to act quickly and responsibly in an emergency.
Safety devices reduce the likelihood of an accident. Never
disable, modify, or ignore any safety device. Safety alerts
in this manual indicate situations where accidents may
occur.
If any malfunction, hazard or potentially unsafe condition
relating to capacity, intended use, or safe operation is
suspected, stop aerial platform operation and seek assistance.
The operator bears ultimate responsibility for following all
manufacturer’s instructions and warnings, regulations and
safety rules of their employer and/or any state or federal
law.
Electrocution Hazards
The aerial platform is made of metal components and is
not insulated. Regard all conductors as energized. Do
not operate outside during a thunderstorm.
Minimum Safe Approach Distance
Minimum safe approach distances to energized power
lines and their associated parts must be observed while
operating the aerial platform.
ADanger
The aerial platform is not electrically insulated.
Death or serious injury will result from contact with,
or inadequate clearance from, an energized conductor. Do not go closer than the minimum safe approach distance as defined by ANSI.
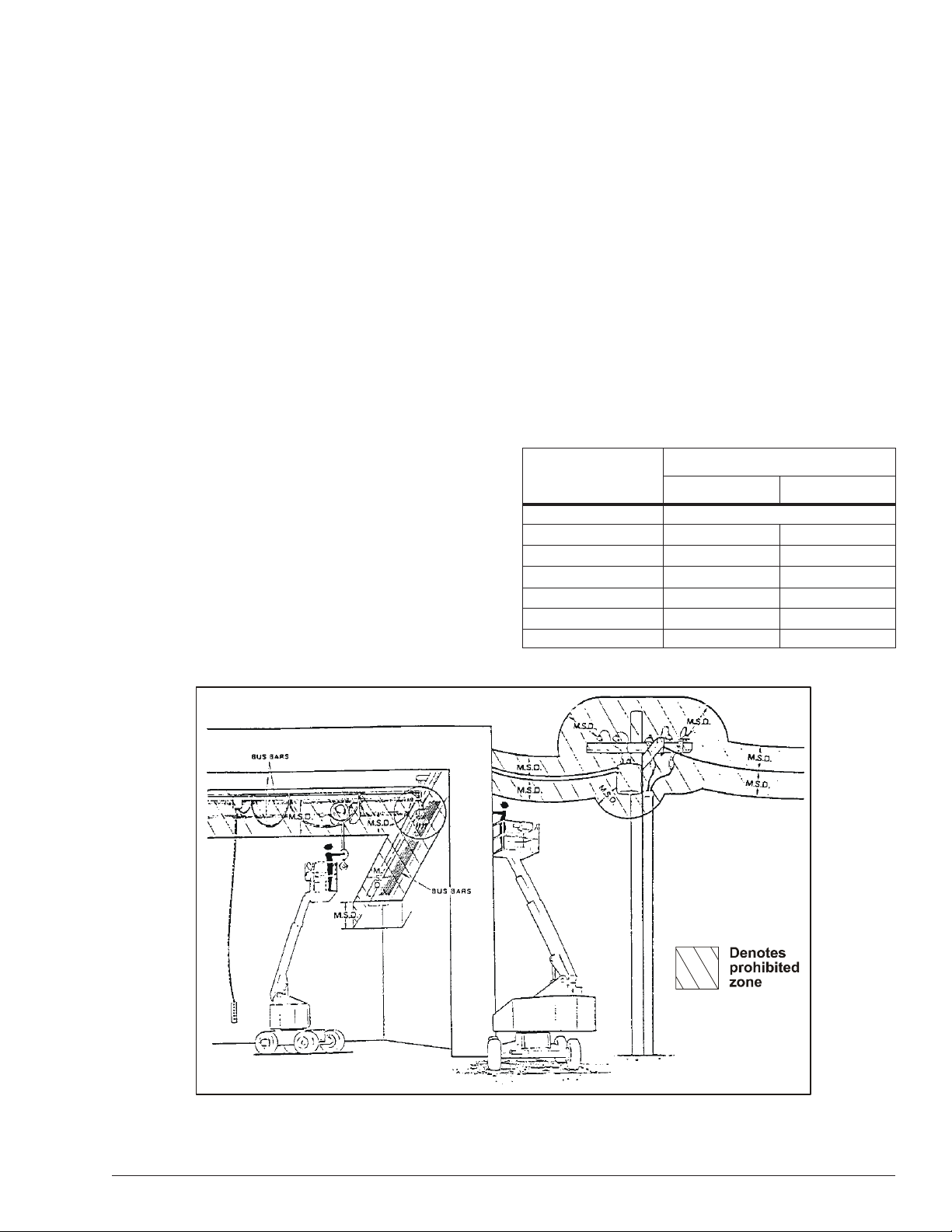
ANSI publications define minimum distances that must
be observed when working near bus bars and energized
power lines. Table 1 and Figure 3 are reprinted courtesy
of Scaffold Industry Association, ANSI/SIA A92.5
Voltage Range
(Phase to Phase)
0 to 300V
Over 300V to 50kV
Over 50kV to 200kV
Over 200kV to 350kV
Over 350kV to 500kV
Over 500kV to 750kV
Over 750kV to 1000kV
Minimum Safe Approach Distance
Feet Meters
Avoid Contact
10
15
20
25
35
45
3.05
4.60
6.10
7.62
10.67
13.72
Table 1 – Minimum Safe Approach Distance
Figure 3 – Minimum Safe Approach Distance
TB47J – 0075239EE 9
Page 14

Chapter 3 – Safety
Prestart Inspection
Perform a prestart inspection before each shift as described in Chapter 7. Do not use the aerial platform on
the job unless you are trained and authorized to do so.
Work Place Inspection and Practices
Do not use the aerial platform as a ground connection
when welding. The welding ground clamp must be attached to the same structure that is being welded. Electrical current flow can be very intense, causing serious
internal damage to some components.
Inspect the area before and during aerial platform use.
The following are some potential hazards that may be in
the work place.
• Debris
• Slopes
• Drop-offs or holes
• Bumps and floor obstructions
• Overhead obstructions
• Unauthorized persons
• High voltage conductors
• Wind and weather conditions
• Inadequate surface and support to withstand load
forces applied by the aerial platform in all operating
configurations
Always look in the direction of movement. Drive with care
and at speeds compatible with the work place conditions.
Use caution when driving over rough ground, on slopes,
and when turning. Do not engage in any form of horseplay or permit riders any place other than in the platform.
Secure all accessories, containers, tools, and other materials in the platform to prevent them from accidentally
falling or being kicked off the platform. Remove all objects that do not belong in or on the aerial platform.
Never steady the platform by positioning it against another platform.
Do not operate the aerial platform if it is damaged or not
functioning properly. Qualified maintenance personnel
must correct the problem before putting the aerial platform back into service.
Operation
Use three points of support when entering or exiting the
platform. For example, use two hands and one foot when
climbing into the platform.
Never cover the platform floor grating or otherwise obstruct your view below. Make sure the area below the
platform is free of personnel before lowering.
Before using the aerial platform in any hazardous (classified) location, make certain it is approved and of the type
required by ANSI/NFPA 505 for use in that particular location.
Know and understand the job site traffic-flow patterns and
obey the flagmen, road signs, and signals.
While operating the aerial platform, a good safety practice is to have qualified personnel in the immediate work
area to:
• Help in case of an emergency.
• Operate emergency controls as required.
• Watch for loss of control by platform operator.
• Warn the operator of any obstructions or hazards
that may not be obvious to them.
• Watch for soft terrain, sloping surfaces, drop-offs,
etc. where stability could be jeopardized.
• Watch for bystanders and never allow anyone to be
under, or to reach through the booms while operating
the aerial platform.
ADanger
Pinch points may exist between moving components. Death or serious injury will result from becoming trapped between components, buildings,
structures, or other obstacles. Make sure there is
sufficient clearance around the machine before
moving the chassis, booms, or platform. Allow sufficient room and time to stop movement to avoid contact with structures or other hazards.
Keep both feet positioned firmly on the platform floor.
Operate the controls slowly and deliberately to avoid jerky
and erratic operation. Always stop the controls in neutral
before going in the opposite direction.
Do not dismount while the aerial platform is in motion or
jump off the platform.
Properly stow the aerial platform and secure it against
unauthorized operation at the end of each work day, before transporting, or if it is left unattended.
Tip-Over and Falling Hazards
Operate the aerial platform only on a firm, flat, level surface capable of withstanding all load forces imposed by
the aerial platform in all operating conditions. Refer to the
General Specifications chart for the maximum wheel load
and ground pressure. Raise the booms only when the
aerial platform is on level ground.
ADanger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tipover accident. Do not drive or position the aerial
platform for elevated use near any drop-off, hole,
slope, soft or uneven ground, or other tip-over hazard. Do not raise the boom in winds above 45 km/h
(28 mph).
All platform occupants must wear a fall restraint device
connected to a lanyard anchor point.
10 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 15

Chapter 3 – Safety
It is best not to transfer from the platform to another structure or from the structure to the platform, unless that is
the safest way to do the job. Judge each situation separately taking the work environment into account. If it is
necessary to transfer from the platform to another structure the following guidelines apply:
1. Where possible, place the platform over a roof or
walking structure to do the transfer.
2. Transfer your anchorage from one structure to the
other before stepping across.
3. Remember that you might be transferring to a structure where personal fall arrest is required.
4. Use the platform entrance, do not climb over or
through the guardrails.
Do not operate the aerial platform in windy or gusty conditions. Do not add anything to the aerial platform that
will increase the wind loading such as billboards, banners, flags, etc.
Never operate the aerial platform without all parts of the
guardrail system in place and the gate closed. Make sure
that all protective guards, cowlings, and doors are securely fastened.
Do not exceed the platform capacity as indicated on the
platform rating placard on the platform. Do not carry loads
that extend beyond the platform guardrails without prior
written consent from Snorkel.
Do not operate the aerial platform from trucks, trailers,
railway cars, floating vessels, scaffolds, or similar equipment unless the application is approved in writing by
Snorkel.
Do not operate any of the aerial platform functions while
the battery charger is plugged in.
AWarning
Batteries give off hydrogen and oxygen that can
combine explosively. Death or serious injury could
result from a chemical explosion. Do not smoke or
permit open flames or sparks when checking the
batteries.
Battery acid can damage the skin and eyes. Serious infection or reaction can result if medical treatment is not given immediately. Wear face and eye
protection when working near the batteries.
Batteries contain sulfuric acid that can damage your eyes
or skin on contact. Wear a face shield, rubber gloves,
and protective clothing when working around batteries. If
acid contacts your eyes, flush immediately with clear
water and get medical attention. If acid contacts your
skin, wash off immediately with clear water.
Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system contains hoses with hydraulic fluid
under pressure.
ADanger
Hydraulic fluid escaping under pressure can have
enough force to inject fluid into the flesh. Serious
infection or reaction will result if medical treatment
is not given immediately. In case of injury by escaping hydraulic fluid, seek medical attention at once.
Do not place your hand or any part of your body in front of
escaping hydraulic fluid. Use a piece of cardboard or wood
to search for hydraulic leaks.
Do not use the aerial platform as a crane, hoist, jack, or
for any purpose other than to position personnel, tools,
and materials.
Do not climb on the guardrails or use ladders, planks, or
other devices to extend or increase the work position
from the platform.
Take care to prevent rope, electrical cords, and hoses,
etc., from becoming caught in or on the aerial platform. If
the platform or booms becomes caught on an adjacent
structure or other obstacle and is prevented from normal
motion, reverse the control to free the platform. If control
reversal does not free the platform, evacuate the platform
before attempting to free it.
Electrical System
Charge the batteries in a well-ventilated area free of flame,
sparks, or other hazards that might cause fire or explosion.
TB47J – 0075239EE 11
Engine and Fuel Handling Precautions
Refer to the engine manufacturer’s Operator’s Manual for
complete information on safe engine operation, maintenance, and specifications.
ADanger
Engine exhaust contains carbon monoxide, a poisonous gas that is invisible and odorless. Breathing
engine exhaust fumes will cause death or serious
illness. Do not run the engine in an enclosed area
or indoors without adequate ventilation.
Be careful not to run the diesel fuel tank empty. Bleed
the fuel system if air enters the lines between the tank
and the injection pump.
Allow the engine to return to idle before shutting the engine off.
Do not smoke or permit open flames while fueling or near
fueling operations.
Page 16

Chapter 3 – Safety
Never remove the fuel cap or fill the fuel tank while the
engine is running or hot. Never allow fuel to spill on hot
machine components.
Maintain control of the fuel filler nozzle when filling the
tank. Spilled fuel is a potential fire hazard.
Do not overfill the fuel tank. Allow room for expansion.
Clean up spilled fuel immediately.
Tighten the fuel tank cap securely. If the fuel cap is lost,
replace it with an approved cap from Snorkel. Use of a
non-approved cap without proper venting may result in
pressurization of the tank.
Never use fuel for cleaning purposes.
For diesel engines, use the correct fuel grade for the
operating season.
ACaution
Engine coolant escaping under pressure can cause
serious burns. Shut the engine off and let it cool
before removing the radiator cap.
Let the engine and radiator cool before adding coolant.
Placards and Decals
The aerial platform is equipped with placards and decals
that provide instruction for operation and accident prevention. Do not operate the aerial platform if any placards or decals are missing or not legible.
12 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 17
Chapter 4 – Safety Devices
This aerial work platform is manufactured with safety devices, placards, and decals to reduce the likelihood of an
accident. For the safety of all personnel, do not disable,
modify, or ignore any safety device. Safety devices are
included in the daily prestart inspection.
AWarning
The potential for an accident increases when safety
devices do not function properly. Death or serious
injury can result from such accidents. Do not alter,
disable, or override any safety device.
If any safety devices are defective, remove the aerial platform from service until qualified maintenance personnel
can make repairs.
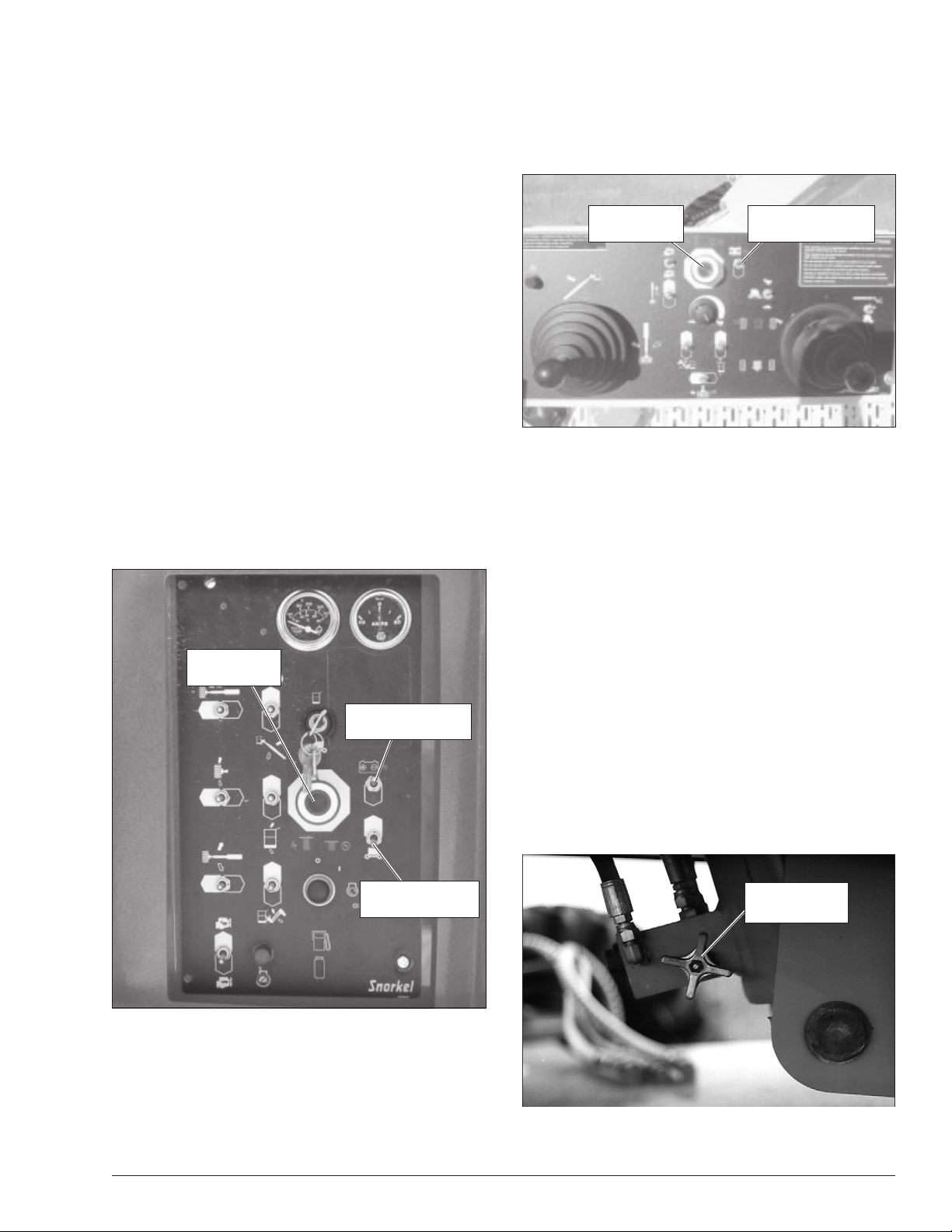
Emergency Stop Controls
There is an emergency stop control at the lower and upper controls.
At the lower controls, the emergency stop is a two-position push button (refer to Figure 4.1). Push the emergency stop button in to disconnect power to all control
circuits. Pull the button out to restore power.
Emergency
Stop Button
Engine/Emergency
Power Switch
At the upper controls, the emergency stop is a two-position push button (refer to Figure 4.2).
Emergency
Stop Button
Figure 4.2 – Upper Controls
Push the emergency stop button in to disconnect power
to the upper control circuits. Pull the button out to restore power.
Engine/Emergency
Power Switch
Emergency Power System
The emergency power system includes a back-up pump,
motor, and battery. Use this system to operate the boom
and turntable functions to lower the platform if the main
power system fails due to engine or pump failure. Hold
the engine/emergency power switch (refer to Figure 4.1
and 4.2) down to activate the emergency power system.
The length of time the pump can be operated depends on
the capacity of the battery.
Emergency Lowering Knob
The emergency lowering knob may be used to lower the
booms if the engine will not start and the emergency
power system will not work. The knob is on the base end
of the main boom lift cylinder (refer to Figure 4.3) under
the left side of the turntable.
Ground Operation
Switch
Figure 4.1 – Lower Controls
Note
The lower controls override the upper controls. If the upper control emergency stop button is engaged, the lower
controls can still be used to operate the aerial platform.
TB47J – 0075239EE 13
Figure 4.3 – Emergency Lowering Knob
Emergency
Lowering Knob
Page 18

Chapter 4 – Safety Devices
Ground Operation Switch
The ground operation switch (refer to Figure 4.1) prevents
boom and platform movement if a control switch on the
lower control panel is accidentally moved.
Hold the switch up to operate the machine from the lower
controls.
Platform Foot Switch
Stepping down on the platform foot switch (refer to Figure
4.4) activates the upper controls.
Top Rail
Gravity
Lanyard
Anchors
Platform Foot
Switch
Gate
Mid Rail
Toeboard
The gates close automatically after entering or exiting
the platform. The gate is part of the guardrail system and
must be securely fastened after entering the platform.
Lanyard Anchors
Two lanyard anchors for fall restraint anchorage are provided below the upper controls at the front of the platform
(refer to Figure 4.4).
Note
The lanyard anchors are not for lifting or tying the machine down.
All personnel in the platform must connect their fall restraint device to a lanyard anchor before raising the platform. Do not use the aerial platform for personal fall ar-
rest anchorage.
Tilt Alarm
If the aerial platform chassis is out of level more than 3.5
degrees when the main boom is raised or extended, an
alarm will sound. The tilt alarm is located under the upper
control box (refer to Figure 4.6).
Figure 4.4 – Platform
The foot switch must be engaged and a control must be
moved to operate the boom, drive, and/or platform from
the upper controls.
Guardrails
The guardrail system includes a top rail, mid rail, and
toeboards around the sides of the platform (refer to Figure 4.4).
A gravity gate (refer to Figure 4.4) or an optional swinging
gate (refer to Figure 4.5) allows for access to the platform.
Swinging
Gate
Tilt Alarm
Figure 4.6 – Tilt Alarm
ADanger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tipover accident. Do not drive or position the aerial
platform for elevated use near any drop-off, hole,
slope, soft or uneven ground, or other tip-over hazard.
Retract and lower the main boom and then drive to a level
surface when the tilt alarm sounds.
The tilt alarm is for added protection and does not justify
operating on anything other than firm, flat, level surfaces.
Figure 4.5 – Platform
14 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 19
Chapter 4 – Safety Devices
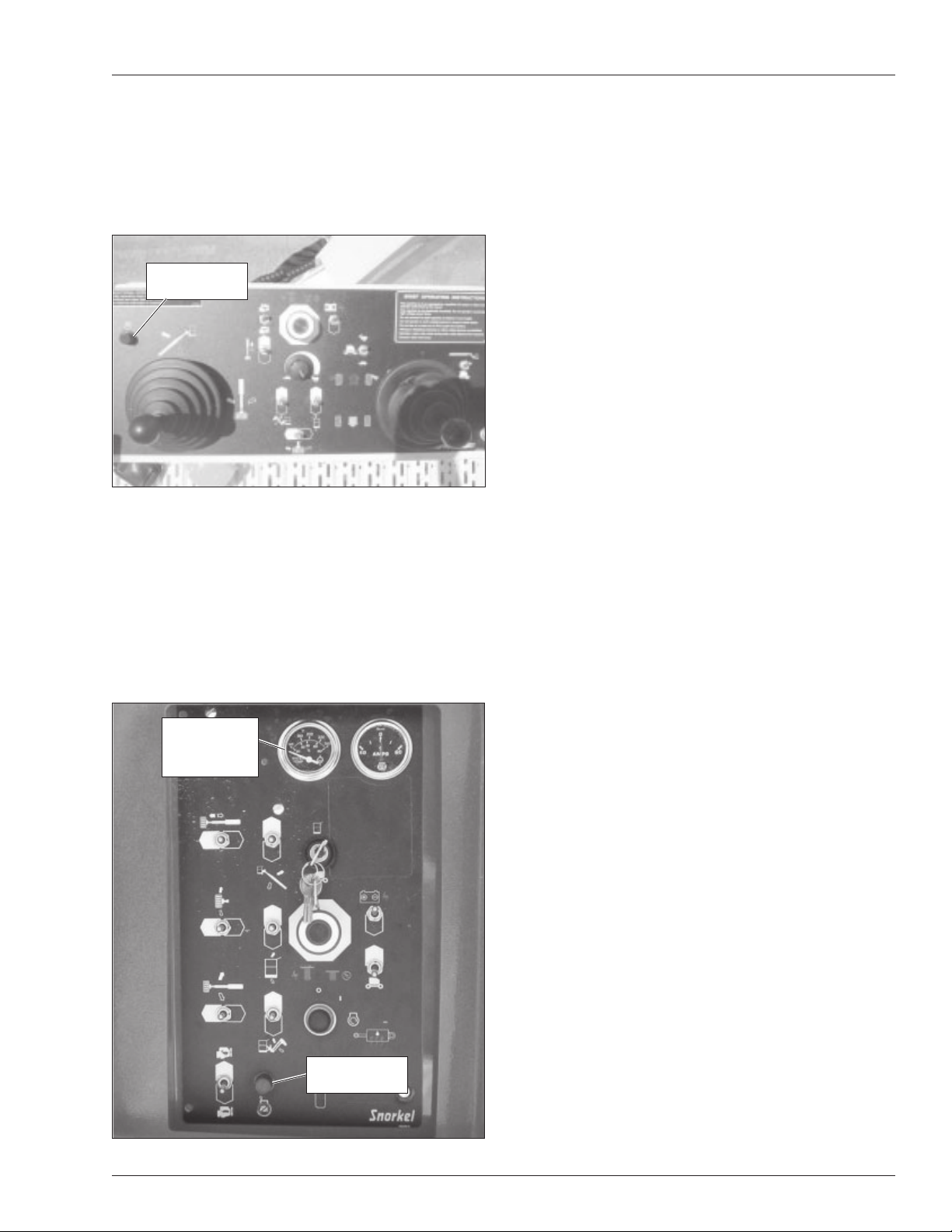
Platform Overload Sensing System
Boom and drive functions are stopped when the platform
load reaches or exceeds rated capacity. The horn will
sound intermittently and the red light (refer to Figure 4.7)
will illuminate when the platform rated work load is exceeded.
Platform
Overload Light
Figure 4.7 – Upper Controls
The horn will sound and the light will flash until the excess load is removed from the platform. At that time, the
boom and drive functions are again operational.
If the overload exceeds rated platform capacity by more
than 20 percent, the system will error out, stopping all
boom and drive functions. The horn will then sound continuously and the red light will stay illuminated at the
upper and lower controls (refer to Figure 4.8).
The horn will sound and the light will stay on until the
excess load is removed from the platform and the start
switch is turned off and back on, resetting the system. At
that time, the boom and drive functions are operational.
ADanger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tipover accident. Do not exceed the capacity values
indicated on the platform rating placard.
The overload sensing system is not active when the machine is being driven with the main boom below horizontal and fully retracted. This allows the machine to be driven
without the system sensing an overload due to rough
ground conditions.
To eliminate repeated tripping of the system during machine operation, there is a five second delay in machine
functions following:
• starting the engine.
• placing the drive/boom selector switch in the boom
position when the main boom is below horizontal and
fully retracted.
• removing excess load from the platform.
Engine Protection Systems
A constant tone alarm will sound to warn against high
engine temperature or low oil pressure.
Engine
Temperature
Gauge
Platform
Overload Light
Figure 4.8 – Lower Control Panel
The engine will shut-down if the operating temperature
exceeds a preset level or if the oil pressure is too low for
safe operation. An engine temperature gauge is on the
lower control panel (refer to Figure 4.8).
High Engine Temperature Alarm
If the coolant in a Cummins engine exceeds the engine
operating temperature an alarm will sound and the engine will shut off.
If the oil in a Deutz engine exceeds 110°C (230°F) an
alarm will sound and the engine will shut off. Any time
there is no alternator current being produced, an alarm
will sound and the engine will shut off. This prevents high
engine temperature if the fan belt breaks.
Do not restart the engine until the condition that caused
the overheating has been corrected.
Low Oil Pressure Alarm
The low oil pressure alarm sounds when the engine oil
pressure is near the lower limit for safe engine operation.
If the alarm sounds, lower the platform to the ground and
then turn the engine off. Do not restart the engine until
the condition that caused the low oil pressure has been
corrected.
TB47J – 0075239EE 15
Page 20

Chapter 4 – Safety Devices
If the engine oil pressure falls below a safe operating value
the engine will shut off. The engine can be restarted with
low oil pressure, but it will only run a few seconds before
it shuts off again.
Horn
The horn may be used to warn personnel on the ground.
The horn button is on the right side of the upper control
box. The horn is operational when the machine is set up
for operation from the upper controls.
Drive Motion Alarm
An optional drive motion alarm may be provided on the
machine. When the drive/steer control is moved out of
neutral the alarm sounds, in short beeps, to warn personnel in the work area to stand clear.
Flashing Light
An optional amber flashing light may be located on the
top of the boom near the base end (refer to Figure 4.9).
The flashing light warns personnel that the aerial platform
is in the area.
Flashing Light
The light flashes at about one flash per second when the
engine is running.
Driving Lights
Optional headlights and blinking tail lights may be installed on the machine. The headlights are located on
the top of the front cowling. The tail lights are mounted on
the sides of the rear cowling.
Driving lights help improve visibility while driving the aerial
platform and help others see it too. Driving lights are not
for driving on public roadways.
Platform Work Lights
Optional platform work lights may be located on the top
rail of the platform, one on each side of the upper control
panel.
Use the platform lights to improve visibility while working
aloft in dimly lit areas. Do not use the platform work lights
to drive on public roadways.
Figure 4.9 – Flashing Light
Figure 4.10 – Platform Work Lights
16 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 21

Chapter 5 – Gauges and Displays
The aerial platform is equipped with several gauges to
monitor the condition of the machine before and during
operation.
Hour Meter
The hour meter is located on the wiring box on the left
side of the lower controls (refer to Figure 5.1). It measures the accumulated engine operating time.
Hour
Meter
On liquid cooled engines it shows the temperature of the
water and antifreeze mixture in the engine block. The
gauge on air cooled engines shows the temperature of
the engine oil as the oil leaves the filter.
Ammeter
The ammeter is located on the lower control panel (refer
to Figure 5.2). The ammeter displays the level of current
flow from the alternator to the batteries.
After the engine has been running for a few minutes under normal operating conditions, the ammeter gauge indicator should read “0.”
Engine Air Filter Gauge
The air filter gauge (refer to Figure 5.3) is located above
the lower control panel. The gauge measures the air pressure between the intake manifold and the air filter.
Air Filter
Gauge
Figure 5.1 – Wiring Box
Engine Temperature Gauge
The temperature gauge is located on the lower control
panel (refer to Figure 5.2).
Engine
Temperature
Gauge
Ammeter
Reset Button
Figure 5.3 – Air Filter Gauge
The yellow indicator disk inside the sight glass stays at
its highest level when the engine is turned off.
When the yellow indicator disk reaches the red area, it’s
time to change the filter element. After changing the filter,
press the reset button to reset the indicator disk to the
bottom of the sight glass.
Fuel
The fuel tank is translucent (refer to Figure 5.4). The amount
of fuel in the tank can be gauged by raising the doors on
the right side of the machine and looking at the tank.
Note
Do not run a diesel fuel tank empty. Air in the fuel line
makes the engine hard to start.
Figure 5.2 – Lower Controls
TB47J – 0075239EE 17
Page 22

Chapter 5 – Gauges and Displays
Fluid Level and Temperature Gauge
A gauge on the right end of the reservoir displays the
level and temperature of the hydraulic fluid (refer to Figure 5.6).
Fuel Level
Figure 5.4 – Fuel Tank
Engine Oil
The engine oil level is measured with a dipstick. The dipstick is the only way to accurately determine the engine
oil level. The engine oil level should always be between
the add and full marks on the dipstick.
Hydraulic Fluid Filter Gauge
The fluid filter gauge (refer to Figure 5.5) is located on the
return line filter on the left side of the reservoir. The reservoir is behind the door on the left side of the turntable.
During high pump flow situations, the gauge indicates
the condition of the filter. When the needle on the gauge
is in the red zone, it is time to change the filter.
Fluid Level and
Temperature Gauge
Figure 5.6 – Hydraulic Fluid Gauge
If the temperature rises above 93°C (200°F) stop machine
operation and let the fluid cool before resuming operation.
Filter Gauge
Figure 5.5 – Hydraulic Fluid Filter Gauge
18 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 23

Chapter 6 – Controls
ADanger
Pinch points may exist between moving components. Death or serious injury can result from being
trapped between components, buildings, structures,
or other obstacles. Make sure all personnel stand
clear while operating the aerial platform.
Controls to position the platform are located on the lower
control panel on the turntable and on the upper control
panel in the platform. Drive controls are located on the
upper control panel only.
Battery Disconnect Switch
The battery disconnect is located behind the door on the
left side of the turntable above the batteries (refer to Figure 6.1).
Battery Disconnect Switch
• Ground operation switch
• Rotation switch
• Boom elevation switch
• Boom extend/retract switch
• Jib articulation switch
• Platform level switch
• Platform rotation switch
• Engine/emergency power switch
• Throttle switch
Figure 6.1 – Battery Disconnect Switch
The battery disconnect removes electrical power from all
electrically controlled functions when in the off position.
Place the switch in the on position to electrically connect the battery to the electrical system.
ACaution
Only authorized personnel should operate the aerial
platform. Unqualified personnel may cause injury
to coworkers or property damage. Lock the battery
disconnect switch in the off position before leaving
the aerial platform unattended.
Turn the battery disconnect switch off to prevent unauthorized use of the aerial platform.
Lower Controls
The lower controls (refer to Figure 6.2) are located on the
right side of the turntable. Boom and platform functions
can be operated from the lower controls. The following
are located on the lower control panel.
• Emergency stop button
• Control selector switch
• Start switch
Figure 6.2 – Lower Controls
Emergency Stop Button
The emergency stop is a two-position, red push button.
Push the button in to disconnect power to all control circuits. Pull the button out to restore power.
Control Selector Switch
Use the control switch to select between off, lower control, and upper control operation. Insert the key in the
switch and turn the switch to the upper controls position
to operate the aerial platform from the upper controls and
in the lower controls position for lower controls operation.
Start Switch
The start switch works like an automobile ignition switch.
Push the start button until the engine starts, then release it to on. If the engine dies, the control switch must
be turned to off before the engine can be restarted.
An alarm sounds when the switch is turned on to warn
others that the machine engine is being started.
TB47J – 0075239EE 19
Page 24

Chapter 6 – Controls
Ground Operation Switch
Hold the switch upward continually to operate the machine from the lower controls. This switch is spring returned to the off position.
Rotation Switch
The rotation switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used to rotate
the turntable in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. The switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch to the right to rotate the turntable counterclockwise. Hold the switch to the left to rotate the turntable clockwise.
Boom Elevation Switch
The boom elevation switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used to
raise or lower the main boom. The switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch up to raise the main boom. Hold the
switch down to lower the main boom.
Boom Extend/Retract Switch
The boom extend/retract switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is
used to extend or retract the booms. The switch is spring
returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch to the left to extend the tip boom. Hold
the switch to the right to retract the tip boom.
Hold the switch to the right to rotate the platform counterclockwise. Hold the switch to the left to rotate the platform clockwise.
Engine/Emergency Power Switch
Hold the engine/emergency power switch (refer to Figure
6.2) down to operate aerial platform functions using the
emergency power system. Release the switch to disengage the emergency power system.
Note
The emergency power system is for lowering the platform
during an emergency and is not intended for normal machine operation.
If the engine is running, it will stop when the switch is
placed in the emergency power position.
Throttle Switch
The throttle switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used to set the
engine throttle speed to either low or high idle.
Place the switch in the low position before starting the
engine and in the high position for machine operation and
for engine and/or hydraulic system warm-up.
The engine has a two speed throttle operation from the
lower controls. When the throttle switch is in the low
position the engine is at idle. Placing the switch in the
high position increases the engine speed to mid-range.
Jib Articulation Switch
The jib switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used to raise or
lower the jib. The switch is spring returned to the center
off position.
Hold the switch up to raise the jib. Hold the switch down
to lower the jib.
Note
The jib and platform rotate functions can not be operated at the same time. The platform rotate function will
override the jib function.
Platform Level Switch
The platform level switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used to
level the platform floor with respect to the ground. The
switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch up to tilt the platform floor upward or
away from the ground. Hold the switch down to tilt the
platform floor downward or toward the ground.
Platform Rotation Switch
The platform rotation switch (refer to Figure 6.2) is used
to rotate the platform relative to the end of the tip boom.
The switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Placing the ground controls switch in the on position also
increase the engine speed to mid-range.
Circuit Breaker Reset Buttons
The wiring box next to the lower control panel has a circuit breaker for the main, run, and throttle control circuits. There is a reset button for each circuit breaker on
the front of the wiring box (refer to Figure 6.3).
Circuit Breaker Reset Buttons
Figure 6.3 – Wiring Box
20 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 25

Chapter 6 – Controls
The upper control panel has a circuit breaker for the swing
(turntable rotation), lift, drive and main control circuits.
The circuit breakers are on the front of the upper control
panel (refer to Figure 6.4).
Circuit Breaker Reset Buttons
Start Switch
Figure 6.4 – Upper Control Panel Front
The circuit breakers protect the electrical wiring and components from electrical overload in case of a short circuit
or other fault.
Engine/Emergency
Power
Drive Range
Drive/Boom
Selector
Platform
Level
Drive Joystick
Engine
Throttle
Boom Extend/
Retract Switch
Jib Switch
Boom Joystick
Emergency Stop
Speed
Knob
Platform Rotate
Figure 6.5 – Upper Control Panel Top
Start Switch
The engine can be started from the platform using the
anti-restart master switch on the front of the upper control panel (refer to Figure 6.4).
This switch is similar to an automobile ignition switch.
Turn the switch to start until the engine starts, then release it to on. If the engine dies, the switch must be
turned to off before it can be turned back to start.
ACaution
A tripped circuit breaker indicates a malfunction in
the electrical system. Component damage can result if the cause of the malfunction is not corrected.
Do not operate the aerial platform if the circuit
breaker trips repeatedly.
Push the button to reset the circuit breaker.
Upper Controls
The upper controls (refer to Figure 6.5) are located on the
control panel at the platform. Boom, platform, and drive
functions can be operated from the upper controls. The
following controls are located on the upper control panel.
• Start switch
• Emergency stop button
• Speed knob
• Drive/boom selector switch
• Boom joystick
• Drive joystick
• Drive range switch
• Jib articulation switch
• Platform level switch
• Boom extend/retract switch
• Engine/emergency power switch
• Throttle switch
• Platform rotate switch
An alarm sounds when the switch is turned on to warn
others that the machine engine is being started.
Note
On some machines it may be necessary to pause about
three seconds in the on position before going to start so
the starter can engage.
Turn the switch to off to turn the engine off and save fuel
if the platform is to stay in a particular position for a long
time.
Emergency Stop Button
The emergency stop is a two-position, red push button
on the top of the upper control panel (refer to Figure 6.5).
Push the button in to disconnect power to all control circuits at the upper controls. Pull the button out to restore
power.
Note
The lower controls override the upper controls. If the upper control emergency stop button is engaged the lower
controls can still be used to operate the aerial platform.
Push the emergency stop button in when the upper controls are not in use to protect against unintentional operation.
Speed Knob
Use the boom speed control knob (refer to Figure 6.5) to
control the speed of the following boom functions.
• Boom extend/retract
• Jib up/down
• Platform rotate clockwise/counterclockwise
TB47J – 0075239EE 21
Page 26

Chapter 6 – Controls
Set the knob to slow when beginning a boom movement.
The speed may be increased by slowly rotating the knob
toward fast. For smooth operation, rotate the knob to
slow when ending boom movement.
Drive/Boom Selector Switch
Place the drive/boom selector switch (refer to Figure 6.5)
in the drive position to drive the aerial platform.
Place the drive/boom selector switch in the boom position to operate the boom functions.
Note
Boom and drive functions can not be operated at the
same time.
Boom Joystick
The boom joystick (refer to Figure 6.5) is used to raise
and lower the main boom and to rotate the turntable. The
boom and turntable functions may be operated simultaneously.
Note
The distance the joystick is moved is proportional to the
speed of the function.
Hold the joystick forward to raise the main boom and
backward to lower the boom.
Hold the joystick to the right to rotate the turntable counterclockwise and to the left to rotate the turntable clockwise.
Drive Joystick
The drive joystick (refer to Figure 6.5) is used to control
forward and reverse motion of the aerial platform. It is
also used to steer the machine. The steering and drive
functions may be operated simultaneously.
Jib Articulation Switch
The jib switch (refer to Figure 6.5) is used to raise or
lower the jib. The switch is spring returned to the center
off position.
Hold the switch up to raise the jib. Hold the switch down
to lower the jib.
Note
The jib and platform rotate functions can not be operated at the same time. The platform rotate function will
override the jib function.
Boom Extend/Retract Switch
The boom extend/retract switch (refer to Figure 6.5) is
used to extend or retract the tip and intermediate booms.
The switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch down to extend the booms. Hold the
switch up to retract the booms.
Platform Rotate Switch
The platform rotate switch (refer to Figure 6.5) is used to
rotate the platform relative to the end of the tip boom. The
switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch to the left to rotate the platform clockwise. Hold the switch to the right to rotate the platform
counterclockwise.
Platform Level Switch
The platform level switch (refer to Figure 6.5) is used to
level the platform floor with respect to the ground. The
switch is spring returned to the center off position.
Hold the switch up to tilt the platform floor upward or
away from the ground. Hold the switch down to tilt the
platform floor downward or toward the ground.
Note
The distance the joystick is moved is proportional to the
speed of the function.
Engine/Emergency Power Switch
The engine/emergency power switch (refer to Figure 6.5)
is spring returned to the engine position for aerial plat-
form engine operation.
Hold the joystick forward to move the aerial platform forward and backward to move in reverse as indicated by
the directional arrows on the chassis.
Place the switch in the emergency power position and
hold to operate aerial platform functions using the emer-
gency power system. Release the switch to disengage
Hold the joystick to the right to steer the aerial platform
the emergency power system.
to the right and to the left to steer to the left as indicated
by the directional arrows on the chassis.
Note
The emergency power system is for lowering the platNote
The steering wheels are not self-centering. Set the steer-
form during an emergency and is not intended for normal
machine operation.
ing wheels straight ahead after completing a turn.
If the engine is running, it will stop when the switch is
Drive Range Switch
placed in the emergency power position.
The drive range switch (refer to Figure 6.5) has two positions to select drive wheel operation:
Throttle Switch
The throttle switch (refer to Figure 6.5) is used to set the
• HI – high speed and low torque operation.
engine throttle speed to either low or high idle.
• LO – low speed and high torque operation.
22 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 27

Chapter 6 – Controls
Place the switch in the low position for normal machine
operation and in high to drive at maximum speed.
The engine has a three speed throttle operation from the
upper controls. Independent of the throttle switch, the
platform foot switch, when depressed, increases the engine speed from low to mid-range.
High engine speed is obtained when the main boom is
horizontal, the foot switch is depressed, the throttle switch
is in the high position, and the drive joystick is moved out
of neutral into the forward or reverse position.
The machine can be driven in mid-range engine speed
with the throttle switch place in the low position.
Horn Button
The horn button is on the right side of the upper control
panel. Press the button to sound the horn.
Platform Foot Switch
The upper controls are interlocked through the platform
foot switch (refer to Figure 6.6). Step down on and hold
the platform foot switch to activate the drive and boom
functions from the upper controls.
Machine/Generator Switch
The switch for the optional AC generator is located on the
front of the upper control panel.
With the engine running, place the switch in the generator position to provide electrical power to the electrical
outlet at the platform. Place the switch in the machine
position to turn off the generator and resume machine
operation.
Machine functions will not operate while the switch is in
the generator position.
Driving and Platform Work Lights
The control for the optional driving lights is on the back of
each light. Place the switch in the on position to operate
the driving lights.
The control for the optional platform work lights is on the
back of each light (refer to Figure 6.7).
Platform Foot
Switch
Figure 6.6 – Platform
Figure 6.7 – Platform Work Lights
TB47J – 0075239EE 23
Page 28

Chapter 6 – Controls
24 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 29

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Potential service and safety problems may be detected
by inspecting the aerial platform. This chapter includes
information on properly inspecting the aerial platform and
includes a prestart inspection check list at the end of the
chapter to ensure that no areas are overlooked.
AWarning
The potential for an accident increases when operating an aerial platform that is damaged or malfunctioning. Death or serious injury can result from
such accidents. Do not operate the aerial platform
if it is damaged or malfunctioning.
Perform a prestart inspection at the beginning of each
shift, before using the aerial platform on the job. The inspection site must have a smooth and level surface.
Operator’s Manual
The manual holder is located behind the front cowling
door (refer to Figure 7.1) on the right side of the machine.
Operator’s Manual Holder
Coolant
Cummins engines are liquid cooled. The coolant reservoir is behind the front cowling door on the left side of the
machine (refer to Figure 7.2). When the engine is cold,
there should be about 2.5 cm (1″) of coolant in the bottom of the reservoir.
Coolant
Reservoir
Figure 7.2 – Coolant Reservoir
ACaution
Engine coolant escaping under pressure can cause
serious burns. Shut the engine off and let it cool
before removing the radiator cap.
Figure 7.1 – Operator’s Manual Holder
Check to see that the proper Operator’s Manual is in the
holder. The manual should be complete with all pages
intact and in readable condition.
Engine
Open the engine compartment doors on both sides of the
machine and visually inspect the engine and its components with the engine off.
Oil Level
Check the engine oil level before starting the engine so
the oil has drained to the pan. The proper oil level is between the add and full marks on the dipstick.
The distance between the top and bottom dipstick marks
corresponds to about 1 l (1 quart US). Add oil, if necessary, before starting the engine.
Add coolant, if necessary, when the engine is cold and
not running. When running at operating temperature the
coolant should be at the hot level.
Deutz engines are air cooled. Visually inspect the air
intake and fan (refer to Figure 7.3) to be sure they are
free of obstructions that could stop or slow the flow of air.
Inspect the fan belt to see that it is in place and not
cracked.
Fan
Fan Belt
Figure 7.3 – Deutz Air Intake
TB47J – 0075239EE 25
Page 30

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Radiator
Inspect the radiator hoses and clamps for wear, leakage,
or damage. Make sure the hoses are not hardened,
cracked, or feel spongy. Make sure the cap is in place
and tight.
Coolant leaks are easily visible on the ground. Check
under the chassis for coolant that has leaked.
Make sure the radiator core and ventilation openings on
the cover are free of bugs, dirt, or foreign material that
might restrict airflow.
Fuel Tank
Check the fuel level (refer to Figure 7.4) and add fuel if
necessary. Make sure the cap is securely fastened on
gasoline or diesel tanks.
Air Filter
Gauge
Ammeter
Reset Button
Figure 7.5 – Gauges at Lower Controls
To inspect the air filter:
1. Turn the battery disconnect switch on and close the
cowling door.
Fuel Level
Figure 7.4 – Fuel Tank
Fuel Line
Visually inspect the entire length of the fuel line for leaks
and damage. Start at the fuel tank and trace the line to
the engine inspecting.
Air Filter
The air filter gauge (refer to Figure 7.5) has an indicator
to show when the filter needs replaced.
2. At the lower controls, pull the emergency stop button outward.
3. Insert the key into the control switch and press the
start button to turn the engine on.
4. Check the clear zone after running the engine for 30
seconds.
• If the indicator is in the red area, replace the filter.
• If the indicator is in the clear area, the filter is OK.
5. Shut off the engine.
Charging System
When the engine is running, the ammeter needle (refer to
Figure 7.6) should be to the right of “0.” Left of the “0” is
discharging.
Cold Weather Start Kit—Block Heater
If the machine engine is a Cummins that is equipped with
an optional engine block heater, visually inspect the heater
and power cord. Inspect for leaks around the heater and
for damage to the power cord.
Electrical System
Electrical power is supplied from either one or two, 600
CCA, 12 volt batteries. These batteries supply 12 volt DC
electrical power to operate the aerial platform electrical
and electrohydraulic components.
26 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 31

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Machines with gasoline engines have one battery and
machines with diesel engines have two batteries.
AWarning
Batteries give off hydrogen and oxygen that can
combine explosively. Death or serious injury can
result from a chemical explosion. Do not smoke or
permit open flames or sparks when checking the
batteries.
ACaution
Even with low voltage electrical systems, severe
arcing can occur. Electrical shock or component
damage can result from contact with energized conductors. Use caution when working with any electrical device.
The batteries are behind the door on the left side of the
turntable.
Emergency Power Battery
The emergency power battery (refer to Figure 7.6) is behind the door on the right side of the chassis. The battery
is automatically charged when the engine is running.
Clean the terminals and cable ends with a wire brush or
terminal cleaning tool. All cable ends must be securely
fastened to the terminals.
Cables and Wiring Harness
Inspect all cables and wiring for wear and/or physical
damage such as loose connections, broken wires, and
frayed insulation. Check the wiring in areas where a change
in routing direction may cause them to become pinched.
Make sure the cables and wires are properly routed to
avoid sharp edges, pinching, and scuffing.
Hydraulic System
Hydraulic power is supplied from an engine driven variable displacement piston pump.
ADanger
Hydraulic fluid escaping under pressure can have
enough force to inject fluid into the flesh. Serious
infection or reaction will result if medical treatment
is not given immediately. In case of injury by escaping hydraulic fluid, seek medical attention at once.
The hydraulic reservoir is behind the door on the left side
of the turntable. The pump is mounted on the engine.
Terminals
Figure 7.6 – Emergency Power Battery
Include the emergency power battery when inspecting
and servicing the electrical system.
Battery Fluid Level
Remove the caps from each battery (refer to Figure 7.6).
Visually check the battery fluid level. If the level is not
within 6 mm (1/4″) of the bottom of the filler neck inside
each hole, add distilled water.
Replace the caps on the batteries. The caps must be in
place and tight during machine operation.
Battery Terminals
Check the top of the batteries, the terminals, and cable
ends (refer to Figure 7.6). They should be clean and free
of corrosion. Clean the top of the batteries if necessary.
Caps
Fluid Level
Check the hydraulic reservoir fluid level with the aerial
platform stowed on a level surface. The fluid level must
be between the full and add marks as viewed on the sight
glass (refer to Figure 7.7).
Fluid Level and
Temperature Gauge
Figure 7.7 – Fluid Level Indicator
ACaution
Not all hydraulic fluid is suitable to use in the hydraulic system. Some have poor lubricating characteristics and can increase component wear. Only
use hydraulic fluid as recommended.
TB47J – 0075239EE 27
Page 32

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
If necessary, remove the filler cap and add fluid of the
proper type. Refer to Chapter 2 for the proper type and
grade of hydraulic fluid to use. The need to regularly add
fluid indicates a leak that should be corrected.
The sight glass on the reservoir has an internal thermometer to measure the fluid temperature. The temperature
should be less than 93°C (200°F).
Fluid Filter
Checking the condition of the hydraulic fluid filter is part
of the machine maintenance schedule and should not be
performed by the operator.
Hoses, Tubes, and Fittings
Inspect all hydraulic hoses, tubes, and fittings for wear,
leakage, or damage (refer to Figure 7.8). Make sure the
hoses are properly routed to avoid sharp edges, kinking,
and scuffing. Inspect the tubes for dents or other damage
that may restrict fluid flow. Make sure all hoses and tubes
are held firmly in their support brackets.
Figure 7.9 – Tires and Wheels
The aerial platform has foam filled tires. Foam filled tires
do not have a pressure decal or a valve core.
Inspect for large holes or cuts where foam is coming out
of the tire. Look for large imbedded objects, such as angle
iron, that can rip a tire open.
Figure 7.8 – Hoses, Tubes, and Fittings
Hydraulic fluid leaks are easily visible on the ground.
Check under the chassis for fluid that has leaked.
Tires and Wheels
Visually inspect the tires and wheels (refer to Figure 7.9)
to make sure they are suitable for service. Check the
wheel lug nuts to see that none are missing, damaged,
or loose.
Punctures caused by bolts, screws, or nails are not a
problem for foam filled tires.
Lower Control Station
With no personnel in the platform, test the operation of
each control from the lower controls (refer to Figure 7.10).
Control Selector
Switch
Emergency
Stop Button
Engine/Emergency
Power Switch
Ground Operation
Switch
Start Switch
Figure 7.10 – Lower Controls
28 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 33

Operating Controls
Use the following procedure to operate the machine from
the lower controls.
1. Turn the battery disconnect switch on.
2. At the lower controls, pull the emergency stop button outward. Insert the key in the control selector
switch and turn the switch to the lower control position.
3. Press the start button until the engine starts, then
release.
4. Let the engine warm to operating temperature.
5. Hold the ground operation switch upward.
ADanger
Pinch points may exist between moving components. Death or serious injury will result from becoming trapped between components, buildings,
structures, or other obstacles. Make sure all personnel stand clear of the aerial platform while performing the prestart inspection.
Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Emergency
Lowering Knob
Figure 7.11 – Emergency Lowering Knob
2. Turn the engine off.
ADanger
Pinch points may exist between moving components. Death or serious injury will result from becoming trapped between components. Stand clear
of moving components while test operating the machine.
6. Test the operation of each function in both directions.
Note
When checking the turntable rotation function in the
clockwise direction, the turntable will rotate toward you.
Emergency Stop
Push the emergency stop button in to turn off the engine.
The lower control functions should not operate with the
emergency stop in this position.
Emergency Power
Place the battery disconnect switch, the emergency stop
button, and the master switch in the on position.
Hold the engine/emergency power switch in the emergency power position and the ground operation switch in
the on position to operate the aerial platform from the
lower controls using the emergency power system.
Emergency Lowering
The main boom can be lowered in an emergency using
the emergency lowering knob. The emergency lowering
knob is at the base of the main boom lift cylinder (refer to
Figure 7.11).
Use the following procedure to test the emergency lowering system.
3. Slowly turn the knob to open the bleed down valve.
The boom should slowly lower by gravity.
AWarning
The potential for an accident increases when safety
devices do not function properly. Death or serious
injury can result from such accidents. Fully close
the emergency lowering knob before operating the
aerial platform.
4. Turn the knob to close the cylinder bleed down valve.
Level Sensor
Use the following procedure to test the level sensor.
1. Position the aerial platform on a smooth, flat, level
surface.
2. Remove all persons and materials from the platform.
3. Start the engine and raise the main boom to just
above horizontal.
4. Open the rear door on the left side of the machine to
access the level sensor (refer to Figure 7.12).
1. Use the lower controls to raise the main boom.
TB47J – 0075239EE 29
Page 34

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Inspect the welds on the structural components. Pay
particular attention to boom welds. The area to be inspected should be clean and free of dirt and grease. Look
for visible cracks in the weld and at the weld to parent
material joint. A bright light may be used to provide adequate visibility of the inspection area.
Slide Pads
The main boom has slide pads (refer to Figure 7.13) between the boom sections.
Figure 7.12 – Level Sensor
5. Pull the level sensor to the side as far as possible to
activate the tilt alarm.
AWarning
The potential for an accident increases when safety
devices do not function properly. Death or serious
injury can result from such accidents. Do not alter,
disable, or override any safety device.
6. If the alarm does not sound, remove the machine
from service until the problem is corrected.
7. Lower the main boom.
Flashing Light
If the machine is equipped with an optional flashing light,
visually check to see that it flashes. The light should
flash when the engine is running.
Sandblast Protection Kit
The optional sandblast protection kit protects the cylinders from abrasion while sandblasting or from paint
overspray. Rubber covers protect each cylinder rod as it
extends and retracts. The covers prevent sand and paint
from damaging the cylinder seals and rod.
Slide Pads
Slide Pads
Figure 7.13 – Boom Sections
Use the lower controls to raise the main boom to horizontal. Extend the tip boom about 30 cm (1′). Visually
inspect the slide pads to make sure they are in place
and are not obviously loose.
Inspect the surface where the pads contact the intermediate and tip booms. The paint must be in place with no
signs of bare metal.
Wire Ropes
Visually inspect the wire ropes where they are connected
to the outside of the main boom. There is a wire rope
connection on the bottom of the tip end of the main boom
(refer to Figure 7.14) and also one on the top of the base
end of the boom (refer to Figure 7.15).
Inspect the covers while operating the machine to ensure
they are securely fastened and completely cover the cylinder rod. Make sure there are no holes in the covers.
Structures
Visually inspect all weldments and related components.
It is important to inspect the fasteners that connect the
components.
Weldments
Visually inspect all weldments for abnormal wear, abrasion, or deformation that could cause interference between moving parts.
Figure 7.14 – Bottom of Main Boom at Tip End
30 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 35

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Rotation Bearing Bolts
Figure 7.17 – Inside Turntable
Figure 7.15 – Top of Main Boom at Base End
Also inspect the wire ropes just inside the base end of
the main boom (refer to Figure 7.16).
Figure 7.16 – Base End of Main Boom
Fasteners
Visually inspect all fasteners to see that none are missing or loose.
Pay particular attention to all of the bolts, nuts, rollpins,
collars, and snap rings that connect the booms and cylinders. They should all be present, tight, and not damaged in any way.
Raise the main boom to access the rotation bearing bolts
in the turntable (refer to Figure 7.17).
Inspect the rotation bearing bolts to ensure that none are
missing, damaged, or loose.
Upper Control Station
Inspect the platform and upper controls only if all functions operated properly from the lower controls.
Guardrail System
The guardrail system (refer to Figure 7.18) includes the
top rail, mid rail, toeboards and a gravity gate or optional
swinging gate.
Top Rail
Gravity
Lanyard
Anchors
Platform Foot
Switch
Figure 7.18 – Guardrail System
Inspect all components of the guardrail system. The rails
and toeboards must all be in place and free of any damage or deformation. Visually check the rail and toeboard
welds for cracks. All bolts and nuts fastening the platform in place must be present and not show any signs of
looseness.
Inspect the gravity gate to be sure it is present, is not
damaged, and moves freely.
Inspect the optional swinging gate to see that it swings
freely, closes firmly, and is not deformed in any way. Make
sure the spring closes and secures the gate when the
gate is closed.
Gate
Mid Rail
Toeboard
TB47J – 0075239EE 31
Page 36

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Lanyard Anchors
There are two lanyard anchors below the upper control
panel (refer to Figure 7.18).
Visually inspect the lanyard anchors to make sure they
are in place, are not deformed and are securely fastened
to the platform.
Operating Controls
Use the following procedure to operate the machine from
the upper controls.
1. Turn the battery disconnect switch on.
2. At the lower controls, pull the emergency stop button outward. Insert the key in the control selector
and turn the switch to the upper control position.
3. At the upper controls (refer to Figure 7.19), pull the
emergency stop button outward.
Engine/Emergency
Power
Drive Range
Drive/Boom
Selector
Platform
Level
Engine
Throttle
Boom Extend/
Retract Switch
Jib Switch
Emergency Stop
Speed
Knob
8. Test the operation of each control in both directions
from the upper controls.
9. The drive range switch and maximum travel speeds
are interlocked through a limit switch on the turntable that senses the main boom position. When the
main boom is raised to just below horizontal the machine should travel in low speed only. To operate in
high speed the booms must be stowed.
Emergency Stop
Push the emergency stop button in to turn off the engine.
The upper control functions should not operate with the
emergency stop in this position.
Emergency Power
Pull the emergency stop button up and place the antirestart master switch in the on position.
Hold the engine/emergency power switch in the emergency power position and step on the platform foot switch
to operate the aerial platform from the upper controls using the emergency power system.
Horn
Press the horn button to ensure that it sounds to warn
personnel in the area.
Electrical Power Outlet
With the engine running, place the machine/generator
control (refer to Figure 7.20) in the generator position to
provide electrical power to the outlet at the platform and
to the outlet on the end of the generator housing.
Boom Joystick
Platform Rotate
Drive Joystick
Figure 7.19 – Upper Control Panel Top
4. Turn the master start switch on the front of the upper
control panel to start until the engine starts, then
release it.
5. Let the engine warm to operating temperature.
ADanger
Pinch points may exist between moving components. Death or serious injury will result from becoming trapped between components, buildings,
structures, or other obstacles. Make sure all personnel stand clear of the aerial platform while performing the prestart inspection.
6. Place the drive/boom selector switch in the boom
position.
7. Test the platform foot switch by moving a boom function switch without stepping on the foot switch. If
movement occurs the interlock is not functioning properly. Do not operate the machine until the problem is
corrected.
Machine/
Generator Switch
Figure 7.20 – Upper Control Panel Front
Plug an electrical tool into the receptacle at the platform
and at the generator and try to operate the tool to verify
proper operation of the outlet.
Drive Motion Alarm
The machine may be equipped with an optional drive
motion alarm. Drive in both the forward and reverse directions to ensure that the alarm sounds to warn personnel
in the area that the aerial platform is in motion.
32 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 37

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Driving and Work Lights
The machine may be equipped with driving lights and/or
platform working lights. Turn the engine on and use the
switch on the back of each light to momentarily turn it on
to see that it works.
Platform Control Cover
The machine may be equipped with an optional platform
control cover. Inspect the cover to ensure it fits properly
over the control panel.
Tow Kit
The machine may be equipped with an optional tow kit.
Inspect the tow bar and steering arm to verify the components are present and in working condition.
Placards and Decals
Inspect all safety and operational placards and decals.
Make certain they are in place, in good condition, and
are legible.
The placards and decals may be cleaned with soap and
water, and a soft cloth if the words or pictures cannot be
seen.
ACaution
Solvents may contain hazardous ingredients. Follow the manufacturer’s label for proper use and disposal. Wear protective gloves and splash-proof
safety glasses when using solvents.
Wet paint overspray may be removed using a natural biodegradable solvent and a soft cloth.
Replace any missing or illegible placards or decals before operating the aerial platform. Placard and decal kits
are available from Snorkel dealers.
The safety related placards and decals are illustrated on
the following pages.
0190989E
Right Side
0190989E
0190989E
0074311
(One per Cylinder)
0074210
0074311
0074210
TB47J – 0075239EE 33
Page 38

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
0162366
0162336E
0162366
0162366
This machine is not electrically insulated.
Do not operate in proximity to high
voltage power lines and parts!
0162336E
0162336E
0070901
Right Side
0323897
0162366
0162336E
0070901
0323897
34 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 39

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
0082164
0082164
(Tow Option Only)
0162366
0162336E
0073298
Right Side
Front
0082160
(Tow Option Only)
0082203
(Tow Option Only)
0073298
0082160
0162366
0162366
This machine is not electrically insulated.
Do not operate in proximity to high
voltage power lines and parts!
0162336E
0162336E
0082203
TB47J – 0075239EE 35
Page 40

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
0151410E
(Cummins Engines Only)
Radiator
0162366
0162336E
KEEP CLEAR
Rotatin g Engine Part s
Serious Injury Can Result
0151410E
0162366
This machine is not electrically insulated.
Do not operate in proximity to high
voltage power lines and parts!
0162336E
0151410E
0162366
0162336E
0073298
Left Side
0072531
Platform
0073298
0072531
0072530
Upper Control Panel Front
0072530
36 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 41

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
Prestart Inspection Checklist
Item Inspect For Ok
Operator’s Manual In manual holder
Engine
Oil level Between full and add marks
Coolant Liquid cooled engines – proper fluid level
Radiator Cap tight, good condition and clean
Air cooled engines Air intake and fan free of obstructions. Belt
in good condition
Fuel tank and line Tank full, cap in place and tight/no leaks
Air filter Clear indicator
Charging system Proper operation
Cold weather start kit No damage or deformation
Electrical System
Emergency power battery Condition and charged for proper operation
Battery fluid level and terminals Proper level/clean, connectors tight
Cables and wiring harness No wear or physical damage
Hydraulic System
Fluid level Between full and add marks
Fluid filter Verify operation in the green zone
Hoses, tubes, and fittings No leaks
Cold weather warm-up kit Proper operation
Tires and Wheels
Foam filled Good condition
Lower Control Station
Operating controls Proper operation
Emergency stop and emergency power Shuts off lower controls/proper operation
Emergency Lowering Proper operation
Level Sensor Sounds tilt alarm
Flashing Light Proper operation
Sandblast Protection Kit In place and proper operation
Structures
Weldments Welds intact, no damage or deformation
Slide pads In place, no damage or deformation
Fasteners In place and tight
Wire ropes No deformation or broken strands
Upper Control Station
Guardrail system and lanyard anchors Welds intact, no damage or deformation
Operating controls Proper operation
Emergency stop and emergency power Shuts off upper controls/proper operation
Horn Sounds when activated
Electrical power outlet Proper operation of outlet and GFCI
Drive motion alarm Sounds when aerial platform moves
Driving and work lights Proper operation
Platform control cover In place and proper operation
Tow Kit In place, no damage or deformation
Placards and Decals In place and readable
TB47J – 0075239EE 37
Page 42

Chapter 7 – Prestart Inspection
38 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 43

Chapter 8 – Operation
The aerial platform may be operated from either the lower
or upper controls.
ADanger
The aerial platform is not electrically insulated.
Death or serious injury will result from contact with,
or inadequate clearance from, an energized conductor. Do not go closer than the minimum safe approach distance as defined by ANSI or national
safety regulations.
Pinch points may exist between moving components. Death or serious injury will result from becoming trapped between components, buildings,
structures, or other obstacles. Make sure there is
sufficient clearance around the machine before
moving the chassis, booms, or platform. Allow sufficient room and time to stop movement to avoid contact with structures or other hazards.
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tipover accident. Operate the aerial platform on a firm,
flat, level surface. Avoid travel speeds and/or rough
terrain that could cause sudden changes in platform
position. Do not drive or position the aerial platform
for elevated use near any drop-off, hole, slope, soft
or uneven ground, or other tip-over hazard.
The platform rated work load is the total weight of the
personnel and equipment that may be lifted in the platform. The work loads are stated on the platform rating
placard mounted at the rear of the platform.
ADanger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tipover accident. Do not exceed the capacity values
indicated on the platform rating placard.
Capacity values indicate the rated lifting capacity and do
not indicate aerial platform stability.
Engine Cold Weather Start Kit
The optional engine cold weather start kit may be an
engine block heater or a manifold air pre-heater. The type
of starting assist system depends on the engine manufacturer.
The last two letters of the model number stamped on the
serial number placard indicates the engine manufacturer
(refer to Figure 8.1). The serial number placard is mounted
on the right rear of the chassis.
Last Two Letters
of Model Number
CU
DZ
Figure 8.1 – Engine Manufacturer/Start System
Refer to the engine manufacturer below for specific cold
weather start-up information for that particular engine type
and cold weather start system.
Cummins — Block Heater
Plug the heater cord in eight hours before starting the
engine. The heater will warm the engine block to make
cold weather starting easier.
Unplug the power cord before starting the engine.
Deutz — Manifold Preheater
At the lower controls, hold the manifold heater switch on
for about a minute before turning the master switch to
start the engine. A glow plug in the manifold preheats the
air to help start the engine. Continue to hold the switch
while starting the engine. Do not release the switch until
the engine starts.
If the engine does not start within 20 seconds, continue
to hold the manifold heater switch and turn the master
switch off. Wait for one minute before trying to start the
engine again.
Engine
Manufacturer
Cummins
Deutz
Cold Weather
Start System
Engine block heater
Manifold air pre-heater
The operator bears ultimate responsibility for ensuring
that the aerial platform is properly set up for the particular
conditions encountered.
Cold Weather Start-Up
If the ambient temperature is 0°C (32°F) or below, the
engine and hydraulic system oil may need to be warmed
before operation. Do not operate the engine at more than
a fast idle until the engine and hydraulic oil has had a
chance to warm. The engine may be equipped with an
optional cold weather start kit.
Cold, thick hydraulic oil does not flow well and may cause
delay in response to control movement and improper voltage output of the AC generator. Cold oil may also cause
cavitation and pump damage. The hydraulic system may
be equipped with an optional cold weather warm-up kit.
TB47J – 0075239EE 39
Hydraulic System Cold Weather Warm-Up
The hydraulic oil may be warmed by bottoming out the
boom extension cylinder. Raise the main boom so it is
horizontal and operate the boom retract function while
the machine is stowed. With the cylinder bottomed out
the oil flow will produce heat to warm the hydraulic oil.
ACaution
Not all hydraulic fluid is suitable to use in the hydraulic system. Some have poor lubricating characteristics and can increase component wear. Only
use hydraulic fluid as recommended.
Use cold weather hydraulic oil as recommended in the
machine General Specifications in temperatures of 0°C
(10°F) or below.
Page 44

Chapter 8 – Operation
Preparing for Operation
Use the following procedure to prepare the aerial platform
for operation.
1. Perform a prestart inspection as described in Chapter 7.
2. Place the battery disconnect switch in the on position.
3. Close and latch the doors.
4. Before painting or sandblasting make sure the sandblast protection kit and the platform control cover are
properly installed. These options, when used properly will protect the control placards and cylinder rods
from paint overspray and abrasion while sandblasting.
Lower Controls
The lower controls override the upper controls. This means
that the lower controls can always be used to operate
the platform regardless of the position of the upper control emergency stop button.
Emergency
Stop Button
Platform
Overload Light
Control Selector
Switch
Engine/Emergency
Power Switch
Start Switch
Ground Operation
Switch
Boom, turntable, and platform functions may be operated from the lower controls. The lower controls may be
used for initial set up of the aerial platform, and for testing
and inspection.
Use the following procedure to operate boom, turntable,
or platform functions using the lower controls. Refer to
Figure 8.2.
1. Pull the emergency stop button (refer to Figure 8.2)
outward. Insert the key in the control selector and
turn the switch to the lower control position.
2. Press the start button until the engine starts, then
release. The engine will not start if the control selector switch is left in the lower control position for 30
seconds or longer before starting the engine. The
control selector switch must be turned back to off
before the engine will start.
3. Let the engine warm to operating temperature.
4. Hold the ground operation switch up while operating
the control toggle switches.
5. Hold the appropriate toggle switch in the desired direction.
6. Release the function toggle switch to stop movement.
Figure 8.2 – Lower Controls
Upper Controls
The upper controls may be used for driving the aerial platform and positioning the booms and platform while on the
job.
Use the following procedure to operate machine functions using the upper controls.
1. At the lower controls, pull the emergency stop button outward. Insert the key in the control selector
and turn the switch to the upper control position.
2. Enter the platform and securely close the gate.
3. Attach the fall restraint lanyard to one of the anchor
points.
4. Pull the emergency stop outward (refer to Figure 8.3).
5. Turn the anti-restart master switch to on and pause
a few seconds while the alarm sounds to alert others
that the machine is about to start. Turn the switch to
start, then release it to on. The engine will not start if
the switch is left in the on position for 30 seconds or
longer before turning it to start. The switch must be
turned back to off before the engine will start.
7. Place the ground operation switch in the off position
6. Let the engine warm to operating temperature.
when no functions are being operated.
40 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 45

Chapter 8 – Operation
Platform
Overload Light
Emergency Stop
Top
Figure 8.3 – Upper Controls
Boom Operation
Use the following procedure to operate the turntable,
boom, or platform functions.
1. Turn the boom speed knob to slow.
2. Step down on the platform foot switch. This switch
must be held down to operate the upper controls.
Start Switch
Front
The horn will sound and the light will flash until the excess load is removed from the platform. At that time, the
boom and drive functions are again operational.
If the overload exceeds rated platform capacity by more
than 20 percent, the system will error out, stopping all
boom and drive functions. The horn will then sound continuously and the red light will stay illuminated at the
upper and lower controls (refer to Figure 8.2).
Lanyard
Anchors
Platform Foot Switch
Figure 8.4 – Platform
3. Hold the appropriate control in the desired direction.
Always look in the direction of movement.
4. Gradually turn the boom speed knob to control the
boom extend, jib, and platform rotate function speed.
5. Releasing the control to its neutral position, or releasing the foot switch will stop movement.
Platform Overload Sensing System
Boom and drive functions are stopped when the platform
load reaches or exceeds rated capacity. The horn will
sound intermittently and the red light (refer to Figure 8.3)
will illuminate when the platform rated work load is exceeded.
The horn will sound and the light will stay on until the
excess load is removed from the platform and the start
switch is turned off and back on, resetting the system. At
that time, the boom and drive functions are operational.
ADanger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tipover accident. Do not exceed the capacity values
indicated on the platform rating placard.
The overload sensing system is not active when the machine is being driven with the main boom below horizontal and fully retracted. This allows the machine to be driven
without the system sensing an overload due to rough
ground conditions.
To eliminate repeated tripping of the system during machine operation, there is a five second delay in machine
functions following:
• starting the engine.
• placing the drive/boom selector switch in the boom
position when the main boom is below horizontal and
fully retracted.
• removing excess load from the platform.
TB47J – 0075239EE 41
Page 46

Chapter 8 – Operation
Driving and Steering
ADanger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tipover accident. Do not drive an elevated aerial platform on soft, uneven, or sloping surfaces. Do not
drive the machine on grades that exceed 25 percent.
For operation on grades up to 25 percent, it is recommended that the main boom be near horizontal and the
jib elevated just enough to provide adequate ground clearance. A 25 percent grade is a 0.76 m (30″) vertical rise in
3.05 m (10′) horizontal length.
Avoid driving with the platform over the front (steer) end of
the chassis. In this position the machine is difficult to
control because:
• drive and steer control movements and their resulting machine movements are reversed.
• when driving fast, sudden turns or stops produce more
severe reactions to platform occupants.
Use the following procedure to operate the drive and steer
functions.
1. Determine the desired drive range for the specific driving conditions.
• Use high range when traveling across firm, flat,
level surfaces. High range can only be activated
when the booms are stowed. High range is for high
speed, low torque operation.
• Use low range for driving on loading ramps or other
steep grades and when safety considerations demand slow deliberate machine movement. Low
range is for low speed, high torque operation.
2. Place the drive/boom selector switch in the drive position.
3. Step down on the platform foot switch.
4. Push the drive joystick forward to move the chassis
forward, the direction of the blue arrow. Pull the joystick backward to move the chassis backward, the
direction of the yellow arrow. The drive speed is proportional to the joystick position.
• more turning space is required to prevent the platform from colliding with obstacles several feet beyond the path of the tires.
AWarning
Death or serious injury can result from improperly
driving or steering the aerial platform. Read and
understand the information in this manual and on
the placards and decals on the machine before operating the aerial platform on the job.
The blue and yellow arrows on the chassis indicate the
direction the chassis will move when the drive or steer
control is moved toward the corresponding color.
When the machine is in the stowed position, with the
booms centered between the rear wheels, the direction
of drive and steer control movement corresponds with the
direction of chassis movement.
When the turntable is rotated from the stowed position,
with the booms to either side of or in front of the chassis,
the direction of control movement does not correspond
with the direction of chassis movement.
To avoid confusion, always drive to the work area or move
between work areas with the turntable and booms in the
stowed position. After arriving at the work area, the booms
may be positioned to the side or the front of the chassis
for final positioning. Always look in the direction of movement as indicated by the directional arrows on the chassis.
5. To stop drive motion, return the joystick to neutral.
6. Push the drive joystick to the right to steer to the
right, the direction of the yellow arrow. Push the joystick to the left to steer to the left, the direction of the
blue arrow.
Note
The steering wheels are not self-centering. Set the steering wheels straight ahead after completing a turn.
7. After driving to the desired location, release the foot
switch, or push the emergency stop button to apply
the parking brakes.
Drive Speeds
The drive speed is proportional to the joystick position.
The farther the joystick is moved, the faster the travel
speed.
Always slow down and shift the drive system to low range
before traveling over rough terrain or any sloped surface.
Drive speed ranges are interlocked through a limit switch
that senses the main boom position. When the boom is
elevated, only the slowest drive speed will work regardless of the drive range switch position.
AWarning
The potential for an accident increases when safety
devices do not function properly. Death or serious
injury can result from such accidents. Do not alter,
disable, or override any safety device.
42 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 47

Chapter 8 – Operation
Do not use the aerial platform if it drives faster than 1.6
km/h (1.0 mile per hour) [13.4 m (44 feet) in 30 seconds]
when the booms are elevated from the stowed position.
Motion Warning Alarm
The motion warning alarm sounds loud intermittent beeps
when the drive joystick is in the forward or reverse position.
Four Wheel Drive
The machine may be equipped with a four wheel drive
system. This system operates full time and requires no
action by the operator.
Four wheel drive machines have a “4x4” decal on each
side of the chassis and all four of the wheel hubs are
drive hubs and look the same.
AC Generator
The generator supplies power to the electrical outlet only
when the engine is running and the machine is stationary. The machine functions will not operate when the
machine/generator selector switch is in the generator
position.
ACaution
Cold hydraulic oil does not flow well and may produce improper generator output voltage. Improper
outlet voltage can damage some electrical power
tools and equipment. Warm the hydraulic oil before operating the generator.
Do not operate the generator unless the hydraulic oil temperature is at least 38°C (100°F). Refer to Cold Weather
Start-Up for a hydraulic oil warm-up procedure.
Air Line
The optional air line may be used to conduct air for tool
operation at the platform. The input connector is at the
rear of the chassis and the output connector is at the
platform on the rotator guard. The maximum working pressure of the line is 1,723 kPa (250 psi).
The air line may be used to conduct fluids such as water
or antifreeze. Contact Snorkel for compatibility information before using the air line to conduct other fluids.
ACaution
Fluid in the air line can damage some air tools or
freeze and damage the line. Drain and blow out the
air line after using it to conduct fluids.
Use the following procedure to drain the air line.
1. Close the input connector on the chassis.
2. Open the output connector at the platform.
3. Raise the boom slightly above horizontal.
4. Open the input connector on the chassis.
5. Allow the fluid to drain from the line.
6. Lower the boom and close both connections.
Driving Lights
The optional driving lights are for use in dimly lit areas
and are not intended for driving on public roadways. There
are two headlights at the front of the chassis and two
blinking taillights at the rear of the chassis.
Start the engine and place the machine/generator selector switch (refer to Figure 8.5) in the generator position.
Machine/
Generator Switch
The lights are operational when the battery disconnect
switch and the master switch are turned on.
Note
Working with the driving or platform work lights on, while
the engine is off, can discharge the batteries enough
that the engine will not start or the emergency power system will not operate. If the engine cannot be left running
while the lights are on, start and run the engine for at
least 15 minutes each hour.
Platform Work Lights
The optional platform work lights (refer to Figure 8.6) are
located on the top rail of the platform. The direction a
light points can be adjusted by using two 1/2″ wrenches
to loosen the clamp below the light.
The lights are operational when the upper controls emer-
Figure 8.5 – Upper Control Panel Front
The engine will run at high idle while the generator is
operating. The generator will continue to operate as long
as the engine is running and the switch is in the generator position.
TB47J – 0075239EE 43
gency stop button is pulled up and the anti-restart master switch is turned on.
The engine speed increases to high idle when the platform work lights are turned on.
Page 48

Chapter 8 – Operation
Figure 8.6 – Platform Work Lights
44 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 49

Chapter 9 – Stowing and Transporting
To prevent unauthorized use and damage, properly stow
the aerial platform at the end of each work day. It must
also be properly stowed while transporting.
Stowing
The properly stowed position is shown in Figure 9.1.
Figure 9.1 – Stowed Position
Use the following procedure to properly stow the aerial
platform.
1. Rotate the platform so it is perpendicular to the end
of the boom.
2. Fully retract the booms and then lower the main boom
until the foot on the jib is near the ground to allow for
exiting the platform.
3. Center the booms between the rear wheels.
4. If the engine has just been under load and is hot, set
the throttle switch to low and let the engine idle for
five minutes.
5. Turn the start switch off and place the platform control box cover over the upper controls if the machine
is equipped with that option.
6. Push the lower controls emergency stop button inward. Turn the control selector switch off and remove
the key.
7. Turn the battery disconnect switch off.
8. Close and latch the cowling doors.
Tucked Stow
The platform may be tucked underneath the main boom
to reduce the overall length of the machine when it is
stowed for an extended period of time or for transporting.
Figure 9.2 – Tucked Stowed Position
Use the following procedure to stow the platform in the
tucked position using the lower controls.
1. Rotate the platform so it is perpendicular to the end
of the boom.
2. Fully retract the tip boom and then raise the main
boom slightly above horizontal.
3. Operate the platform level switch in the down position to tuck the platform beneath the main boom.
Watch the position of the platform to make sure it
does not contact the ground surface. It may be necessary to slightly raise the main boom to prevent the
platform from contacting the ground
4. Center the booms between the rear wheels.
5. If the engine has just been under load and is hot, set
the throttle switch to low and let the engine idle for
five minutes.
6. Turn the start switch off and place the platform control box cover over the upper controls if the machine
is equipped with that option.
7. Push the lower controls emergency stop button inward. Turn the control selector switch off and remove
the key.
8. Turn the battery disconnect switch off.
9. Close and latch the cowling doors.
Transporting
The aerial platform may be moved on a transport vehicle.
Depending on the particular situation, the aerial platform
may be driven, winched, or hoisted onto a vehicle such
as a truck or trailer. Driving is the preferred method.
The tucked stow position is shown in Figure 9.2.
TB47J – 0075239EE 45
Page 50

Chapter 9 – Stowing and Transporting
ADanger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tipover accident. Do not drive on ramps that exceed
25 percent grade, or where conditions of the ramp
could cause driving to be hazardous.
Drive the aerial platform onto the transport vehicle if the
ramp incline is within the 25 percent grade capability of
the aerial platform.
A 25 percent grade is a 0.76 m (30″) vertical rise in 3.05
m (10′) horizontal length.
Use a winch to load and unload the aerial platform on
ramps that exceed 25 percent grade. A winch may also
be used when conditions of the ramp could cause driving
to be hazardous.
The equipment used to load, unload, and transport the
aerial platform must have adequate capacity. Refer to
Chapter 2 to determine the approximate weight of the
aerial platform.
The user assumes all responsibility for choosing the proper
method of transportation, and the proper selection and
use of transportation and tie-down devices, making sure
the equipment used is capable of supporting the weight
of the aerial platform and that all manufacturer’s instructions and warnings, regulations and safety rules of their
employer, the DOT and/or any other state or federal law
are followed.
ADanger
The aerial platform can tip over if it becomes unstable. Death or serious injury will result from a tipover accident. Set the drive range to low before
driving up or down a grade.
9. Place the drive range switch in the low position.
10. Drive the aerial platform onto the transport vehicle in
a straight line through the grade transitions with minimal turning.
11. Rotate the turntable to align the main boom between
the rear wheels.
12. When driving down the ramp, always back the machine with the platform on the downhill side only.
Winching
Use the following procedure to winch the aerial platform
onto the transport vehicle.
1. Locate the transport vehicle so the aerial platform
will not roll forward after it is loaded.
2. Remove any unnecessary tools, materials, or other
loose objects from the platform.
3. Drive the machine to the foot of the loading ramp with
the front wheels nearest the ramp. Make sure the
machine is centered with the ramps and that the steering wheels are straight.
Driving
Use the following procedure to drive the aerial platform
onto the transport vehicle.
1. Locate the transport vehicle so it is in a straight line
with the loading ramp.
2. Chock the vehicle wheels so it cannot roll away from
the ramp while the machine is loaded.
3. Remove any unnecessary tools, materials, or other
loose objects from the platform.
4. Drive the machine to the foot of the loading ramp with
the front wheels nearest the ramp. Make sure the
machine is centered with the ramps and that the steering wheels are straight.
5. Rotate the platform so it is perpendicular to the boom.
6. Retract the tip boom and raise the main boom so it
is horizontal.
7. Rotate the turntable slightly to the side so you can
see the front wheels.
8. Verify that the machine wheels, loading ramps, and
transport vehicle are aligned.
4. Properly stow the aerial platform.
5. Attach the winch to the tie-down lugs (refer to Figure
9.3) on the front of the chassis.
Tie-Down
Lugs
Figure 9.3 – Front Tie-Down Lugs
6. At each drive wheel, remove the two bolts from the
disconnect plate (refer to Figure 9.4). Turn the plate
over so the nipple points inward. Reinstall the two
bolts.
46 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 51

Chapter 9 – Stowing and Transporting
Use the following procedure to hoist the aerial platform
onto the transport vehicle.
1. Properly stow the aerial platform.
Bolt
Disconnect Plate
Figure 9.4 – Drive Wheel
7. Use the winch to position the aerial platform on the
transport vehicle.
AWarning
The aerial platform is free to move when the drive
hubs are disabled. Death or serious injury can result. Re-enable the drive hubs before operating the
aerial platform.
8. At each drive wheel, remove the two bolts and return
the plate to its original position as shown in Figure
9.4.
9. Start the engine and operate the drive control in forward and reverse several times to engage the drive
hubs.
Note
The lifting lugs at the rear of the chassis are farther apart
than those at the front. Rotating the turntable 180° will
place the counterweight at the rear of the chassis. This
will reduce the number of spreader bars needed by one
and sometimes two.
2. Inspect the lifting lugs (refer to Figure 9.5) to make
sure they are free of cracks, rust, and are in good
condition. Have any damage repaired by a qualified
service technician before attempting to hoist the
machine.
Lifting Lugs
Figure 9.5 – Lifting Lugs
Hoisting
Use a four point sling arrangement attached to the lifting
lugs when hoisting the aerial platform. Machine damage
can occur if the sling is attached to the booms, turntable,
or platform.
AWarning
The potential for an accident increases when the
aerial platform is lifted using improper equipment
and/or lifting techniques. Death or serious injury can
result from such accidents. Use proper equipment
and lifting techniques when lifting the aerial platform.
Know the weight of the aerial platform and the capacity of
the lifting devices before hoisting. Lifting devices include
the hoist or crane, chains, straps, cables, hooks, sheaves,
shackles, slings, and other hardware used to support the
machine. The gross vehicle weight is stamped on the
serial number placard and is listed in Chapter 2.
The user assumes all responsibility for making sure the
equipment used is capable of supporting the weight of
the aerial platform and that all manufacturer’s instructions and warnings, regulations and safety rules of their
employer and/or any state or federal law are followed.
3. Remove all personnel, tools, materials, or other loose
objects from the platform.
4. Connect the chains or straps to the lifting lugs using
bolted shackles. Hooks that fit properly in the lugs
and that have latching mechanisms to prevent them
from falling out under a slack line condition may also
be used.
Do not run the sling cable through the lifting lugs.
Cable damage and/or failure can result from the cable
contacting the sharp corners of the lug. There is no
effective way of putting a corner protector in the hole
of the lifting lug.
5. Use spreader bars of sufficient length to keep the
chains, straps, or cables from contacting the turntable or booms. When using cables, use rigid corner
protectors at any point where the cable contacts sharp
corners to prevent damaging the cable. Careful rigging of the spreaders is required to prevent machine
damage.
6. Adjust the length of each chain or strap so the aerial
platform remains level when raised off the ground.
TB47J – 0075239EE 47
Page 52

Chapter 9 – Stowing and Transporting
7. Use the hoist or crane to carefully raise and position
the aerial platform onto the transport vehicle.
Securing for Transport
Use the following procedure to secure the aerial platform
on the transport vehicle.
1. Chock the wheels.
2. Raise the main boom about 0.3 m (1′).
3. Place a wood block under the jib foot. Lower the platform so the foot rests on the wood block.
4. Remove all personnel, tools, materials, or other loose
objects from the platform.
5. Turn the start switch off and place the platform control box cover over the upper controls if the machine
is equipped with that option.
6. Push the lower controls emergency stop button inward. Turn the control selector switch off and remove
the key.
7. Turn the battery disconnect switch off.
8. Close and latch the cowling doors.
9. Use wire-ties to fasten the platform gate to the guardrails to prevent the gate from bouncing. Also, use
wire-ties to fasten the platform foot switch to the platform floor.
10. Use a nylon strap to securely fasten the platform
against the wood block. Thread the strap over the
toeboard as shown in Figure 9.6.
Figure 9.6 – Platform
ACaution
Ratchets, winches, and come-alongs can produce
enough force to damage machine components. Do
not over tighten the straps or chains when securing
the aerial platform to the transport vehicle.
11. Use chains or straps to securely fasten the aerial
platform to the transport vehicle using the tie-down
lugs as attachment points. Proper tie-down and hauling are the responsibility of the carrier.
48 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 53

Chapter 10 – Emergency Operation
If the main hydraulic system fails, the aerial platform may
be lowered and stowed using the emergency power system. The main boom may be lowered using the emergency lowering knob. The machine may be towed if the
drive system fails. Refer to Emergency Power System,
Emergency Lowering, or Towing for the appropriate procedure.
Emergency Power System
The emergency power system can be used to operate
the machine from the lower or upper controls.
ACaution
The emergency power system is for emergency lowering and stowing only. The length of time the pump
can be operated depends on the capacity of the
battery. Do not use this system for normal operation.
Only use the emergency power system if the main power
system fails.
Lower Controls
Use the following procedure to operate the machine using the emergency power system from the lower controls.
Control Selector
Switch
Emergency
Stop Button
Start Switch
Figure 10.2 – Lower Controls
Engine/Emergency
Power Switch
Ground Operation
Switch
1. Place the battery disconnect switch in the on position (refer to Figure 10.1).
Battery Disconnect Switch
Figure 10.1 – Battery Disconnect Switch
2. Place the key in the control selector switch (refer to
Figure 10.2) and turn the control switch to the lower
control position.
3. Pull the emergency stop button outward.
4. Hold the ground operation switch in the on position
while holding the engine/emergency power switch
down in the emergency power position.
5. Hold the appropriate function toggle switch in the
desired direction.
Upper Controls
For the upper controls to be operational:
• the battery disconnect switch must be in the on position.
• the emergency stop button at the lower controls must
be in the on position.
• the controls selector switch at the lower controls must
be in the upper controls position.
Use the following procedure to operate the machine using the emergency power system from the upper controls.
1. Pull the emergency stop button outward (refer to Figure 10.3).
2. Turn the start switch on.
3. Place the drive/boom selector switch in the appropriate position.
4. Step down on the platform foot switch (refer to Figure
10.4).
TB47J – 0075239EE 49
Page 54

Chapter 10 – Emergency Operation
Emergency Stop Engine/Emergency
Top Front
Power Switch
Start Switch
Drive/Boom
Selector
Figure 10.3 – Upper Controls
1. Slowly turn the knob (refer to Figure 10.5) to open
the bleed down valve. Control the rate of descent by
turning the knob.
Platform Foot
Switch
Figure 10.4 – Platform Foot Switch
5. Hold the engine/emergency power switch in the emergency power position.
6. Hold the appropriate function toggle switch in the
desired direction.
Emergency Lowering
The main boom can be lowered in an emergency using
the emergency lowering knob at the base of the lift cylinder. The emergency lowering knob allows the main boom
to be lowered only. Only use this method if the engine
will not start and the emergency power system will not
work.
ADanger
Pinch points exist between boom components and
between the booms and turntable. Death or serious
injury will result if the booms or platform lowers
onto personnel. Make sure all personnel stand clear
while lowering the booms.
Emergency
Lowering Knob
Figure 10.5 – Emergency Lowering Knob
AWarning
The potential for an accident increases when safety
devices do not function properly. Death or serious
injury can result from such accidents. Fully close
the emergency lowering knob before operating the
aerial platform.
2. Turn the knob to close the cylinder bleed down valve.
Towing
The aerial platform may be towed at slow speeds using
the optional tow kit. The tow vehicle must have sufficient
capacity to safely tow and stop itself and the aerial platform on the steepest grade and type of surface that may
be encountered. Refer to Chapter 2 for the gross vehicle
weight of the aerial platform.
Use the following procedure to manually lower the main
boom.
50 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 55

AWarning
The aerial platform is free to move when the drive
hubs are disabled. Death or serious injury can result. Securely fasten the tow vehicle to the aerial
platform before disabling the drive hubs.
Chapter 10 – Emergency Operation
Bolt
Use the following procedure to manually disengage the
drive hubs and tow the machine.
1. With the machine in the stowed position, remove the
tow bar from the storage cradles at the rear of the
chassis and lay the tow bar near the front of the chassis.
ADanger
Pinch points may exist between machine components. Death or serious injury will result from becoming trapped between components. Do not attach the tow bar to the tow vehicle until the counterweight is to the side of the chassis.
2. Rotate the turntable, until the counterweight is to the
side of the chassis, to allow room to attach the tow
bar.
3. Attach the tow bar to the front steering arm with the
tow pin and snap pin.
4. Attach the tow bar to the tow vehicle.
5. Rotate the turntable so the counterweight is back at
the front of the chassis. Raise the platform about 1 m
(3′) above the ground.
Disconnect Plate
Figure 10.6 – Drive Wheel
8. Pull the steering float valve knob out. The knob is
located behind the rear door on the right side of the
turntable next to the fuel tank.
9. Do not exceed 16 km/h (10 mph) when towing. Use
caution when traveling around a curve or when turning a corner. If the tow bar contacts the chassis the
steering mechanism might be damaged or the tow
vehicle and the aerial platform could jackknife.
AWarning
The aerial platform is free to move when the drive
hubs are disabled. Death or serious injury can result. Re-enable the drive hubs before operating the
aerial platform.
10. Push the steering float valve knob in.
6. Shut the engine off and turn the battery disconnect
switch off.
7. At each drive wheel, remove the two bolts from the
disconnect plate (refer to Figure 10.6). Turn the plate
over so the nipple points inward. Reinstall the two
bolts.
11. At each drive wheel, remove the two bolts and return
the plate to its original position as shown in Figure
10.6.
12. Unfasten the tow vehicle from the machine and replace the tow bar on the storage cradles.
13. Verify that the drive system operates properly.
TB47J – 0075239EE 51
Page 56

Chapter 10 – Emergency Operation
52 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 57

Chapter 11 – Troubleshooting
The troubleshooting chart may be used to locate and
eliminate situations where machine operation may be
interrupted. If the problem cannot be corrected with the
Troubleshooting Chart
Symptom
Engine will not start from lower or
upper controls.
Possible Cause
Out of fuel. The engine will crank,
but will not start.
Engine is cold.
High engine temperature.
action listed, stow the machine and remove it from service. Repairs must be made by qualified maintenance
personnel.
Corrective Action
Add correct type of fuel. Try starting
the engine for 20 seconds and then
let the starter motor cool for 60 seconds. Repeat as necessary.
Cummins engine – plug the block
heater in eight hours before starting
the engine.
Deutz engine – hold the manifold
heater switch on for about a minute
before starting the engine. Hold the
switch on until the engine starts.
Let engine cool. Do not restart the
engine until the cause of overheating has been corrected.
Engine will not start from lower
controls.
Low oil pressure.
Switches are set wrong. The engine
will not crank.
The control selector switch was left
in the lower control position for 30
seconds or longer before starting the
engine.
Do not try to start the engine until
the cause of low oil pressure has
been corrected. The engine can be
restarted with low oil pressure, but
it will only run a few seconds before
it shuts off again.
Turn the battery disconnect switch
on and then at the lower controls:
• Turn the control selector switch
off.
• Pull the emergency stop button
outward.
• Place the control selector
switch in the lower control position.
• Wait for 5 seconds and then
press the start switch to start.
Press the start button within 30 seconds of placing the control selector
in the lower controls position.
The main system circuit breaker on
the wiring box has tripped. The engine will not crank.
TB47J – 0075239EE 53
Push the main system circuit breaker
button back in. If the button pops
back out, refer the problem to a
qualified service technician.
Page 58

Chapter 11 – Troubleshooting
Symptom
Engine will not start from upper
controls.
Possible Cause
Switches are set wrong. The engine
will not crank.
Platform foot switch is activated.
Corrective Action
Turn the battery disconnect switch on
and then at the lower controls:
• Turn the control selector switch
off.
• Pull the emergency stop button
outward.
• Place the control selector switch
in the upper control position.
From the upper controls:
• Turn the start switch off.
• Pull the emergency stop button
outward.
• Place the start switch in the on
position for 5 seconds and the
then turn the switch to start.
Do not step on foot switch while starting the engine.
Engine dies when the control selector switch at the lower controls
is placed in the platform position.
Constant tone alarm sounds while
the engine is running.
The start switch was left in the on
position for 30 seconds or longer before turning it to start.
The main system circuit breaker on
the upper control panel or wiring box
has tripped. The engine will not crank.
Upper controls are not set-up properly.
High engine temperature.
Low oil pressure.
No alternator current/broken fan belt.
Turn the start switch back to off, then
to start within 30 seconds.
Push the main system circuit breaker
button back in. If the button pops back
out, refer the problem to a qualified
service technician.
At the upper controls, pull the emergency stop button upward and turn
the anti-restart master switch on.
Lower the platform and reduce the
engine speed to idle for five minutes.
Turn the engine off and let it cool. Do
not restart the engine until the cause
of overheating has been corrected.
Lower the platform and turn the engine off. Do not restart the engine until
the cause of low oil pressure has been
corrected.
Turn the engine off. Do not restart the
engine until the cause of no alternator current has been corrected or the
fan belt is replaced.
54 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 59

Chapter 11 – Troubleshooting
Symptom
Constant tone alarm sounds and
engine shuts off.
Horn is sounding intermittently
and the overload light is flashing.
Horn is sounding constantly and
the overload light is on.
Platform overload sense system
does not work while operating the
upper controls.
Possible Cause
High engine temperature.
Low oil pressure.
The load in the platform is greater
than the rated capacity.
The platform overload system has an
error.
Drive/boom selector switch is in the
drive position and the main boom is
below horizontal.
Corrective Action
Let the engine cool. Do not restart
the engine until the cause of overheating has been corrected.
Do not restart the engine until the
cause of low oil pressure has been
corrected. The engine can be restarted with low oil pressure, but it
will only run a few seconds before it
shuts off again.
Remove load from the platform until
the alarms stop.
Remove load until at or below rated
capacity. Cycle machine power off,
then on. If alarm continues, system
may need recalibration.
Normal operation. The platform overload system is inactive while driving
with the boom below horizontal to
prevent accidental activation due to
rough terrain.
Boom functions do not immediately return when switching from
drive to boom. There is a delay in
boom functions after switching the
drive/boom switch to the boom
position after driving the machine
with the boom below horizontal.
All functions stop working.
System needs calibration.
Platform overload system delay.
Low fluid level in reservoir.
Engine or pump failure.
Circuit breaker is tripped.
Electrical system malfunction.
Platform overload sensor is tripped.
Refer the problem to a qualified service technician.
Normal operation. The system includes a 5 second delay to eliminate
rapid stop and restart of movements
if the overload system trips during
operation.
Check fluid level. Add correct type of
fluid if necessary.
Manually stow the machine using the
emergency power system or the
emergency lowering knob.
Push circuit breaker button in to reset.
Manually lower the boom using the
emergency lowering knob.
If horn is sounding and red overload
light is on or blinking, remove weight
from the platform until the load is at
or below rated capacity.
Lower controls do
Battery disconnect switch turned off.
Place switch in the on position.
not work.
Emergency stop switch at lower controls is pushed in to the off position.
TB47J – 0075239EE 55
Pull the emergency stop button out
to the on position.
Page 60

Chapter 11 – Troubleshooting
Symptom
Lower controls do not work.
Upper controls do not work.
Possible Cause
Control selector switch is in the platform position.
Ground operation switch not held in
the on position.
Platform overload sensor is tripped.
Battery disconnect switch turned off.
Emergency stop switch at lower and
upper controls is in the off position.
Control selector switch at lower controls is in the lower control position.
Platform foot switch not engaged.
Platform overload sensor is tripped.
Corrective Action
Place the switch in the lower control
position.
Hold the ground operation switch in
the on position while operating the
control toggle switches.
If horn is sounding and red overload
light is on or blinking, remove weight
from the platform until the load is at
or below rated capacity.
Place switch in the on position.
Place the emergency stop in the on
position.
Place switch in the upper control position.
Step down on platform foot switch
while operating controls.
If horn is sounding and red overload
light is on or blinking, remove weight
from the platform until the load is at
or below rated capacity.
Boom functions do not work.
Boom and drive functions seem
sluggish.
Boom jerks while it is extended.
Tip boom extend/retract, jib, and
platform rotate functions do not
work from the upper controls.
Booms drift down.
The drive/boom switch is in the drive
position.
Hydraulic oil is cold and thick.
Wire ropes are loose.
Boom speed knob set too slow.
The emergency lowering valve is open.
Hydraulic system malfunction.
Place the switch in the boom position.
Use cold weather hydraulic oil as recommended for weather conditions.
Warm oil before operating the machine.
Refer the problem to a qualified service technician.
Turn knob toward fast.
Turn the emergency lowering knob to
close the valve.
Stow the machine and do not operate until repairs are made.
56 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 61

Chapter 11 – Troubleshooting
Symptom
Drive functions do
not work.
Wheels will not turn when
winching.
Only slow drive speed works.
Steer wheels do not turn right or
left on machines with tow option.
Possible Cause
The drive/boom switch is in the boom
position.
Machine on too steep a grade.
Drive hubs are disengaged.
Low hydraulic system pressure.
Platform overload sensor is tripped.
Drive hubs are engaged.
The booms are elevated. High range
not selected.
Tow kit steering float valve is open.
Corrective Action
Place the switch in the drive position.
Lower the booms and drive to a level
surface.
Turn drive wheel disconnect plates
around so nipples point outward.
Stow the machine and do not operate until repairs are made.
If horn is sounding and red overload
light is on or blinking, remove weight
from the platform until the load is at
or below rated capacity.
Turn drive wheel disconnect plates
around so nipples point inward.
Completely lower the booms. Place
the drive range switch in the high position.
Close the steering float valve.
Tilt alarm does not work.
Circuit breaker will not reset.
Electrical outlet does not work.
Improper AC generator output
voltage.
Hydraulic fluid temperature 93°C
(200°F ) or more.
Booms are stowed.
Electrical circuit has not had time to
cool.
Electrical system malfunction.
Power supply not plugged in.
Machine/generator switch not in the
generator position.
Hydraulic oil is cold and thick.
Prolonged boom operation or driving.
High pressure fluid return to reservoir caused by kinked or twisted
hose.
Normal operation. The tilt alarm is not
active until the booms are elevated.
Wait a minute or two for circuit to
cool, then push circuit breaker button in to reset.
Do not operate machine until repairs
are made.
Plug the power cord into the powerinput connector on the generator.
With engine running, place the machine/generator switch in the generator position.
Use cold weather hydraulic oil as recommended. Warm oil before operating the machine.
Stop operation until fluid cools.
Remove the kink or twist from the
hose. Let fluid cool before resuming
operation.
Hydraulic system component failure.
Stow the machine and do not operate until repairs are made.
Severe hydraulic leak.
Failure of hose, tube, fitting, seal,
etc.
TB47J – 0075239EE 57
Do not operate machine until repairs
are made.
Page 62

Chapter 11 – Troubleshooting
58 TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 63

Appendix A – Glossary
aerial platform – a mobile device that has an adjustable position
platform, supported from ground level by a structure.
ambient temperature – the air temperature of the immediate environment.
ammeter – an instrument for measuring the strength of an electric
current in amperes.
authorized personnel – personnel approved as assigned to perform
specific duties at a specific location.
base – the relevant contact points of the aerial platform that form the
stability support (e.g. wheels, casters, outriggers, stabilizers).
boom – a movable cantilever beam which supports the platform.
center of gravity – the point in the aerial platform around which its
weight is evenly balanced.
chassis – the integral part of the aerial platform that provides mobility and support for the booms.
fall restraint – a system that is used while working on a boom lift within
the boundaries of platform guardrails to provide restraint from being
projected upward from the platform. This system includes a harness or
belt, lanyard, and a lanyard anchor. Federal OSHA, ANSI, and Snorkel
require the use of additional fall protection beyond the platform guardrails on boom supported aerial platforms.
floor or ground pressure – the maximum pressure, expressed in pounds
per square inch, a single wheel concentrates on the floor or ground.
gradeability – the maximum slope that the aerial platform is capable
of travel.
guardrail system – a vertical barrier around the platform to prevent
personnel from falling.
hazardous location – any location that contains, or has the potential
to contain, an explosive or flammable atmosphere as defined by
ANSI/NFPA 505.
maximum wheel load – the load or weight that can be transmitted
through a single wheel to the floor or ground.
Minimum Safe Approach Distance – the minimum safe distance that
electrical conductors may be approached when using the aerial platform. Also called M.S.A.D.
operation – the performance of any aerial platform functions within
the scope of its specifications and in accordance with the manufacturer’s
instructions, the users work rules, and all applicable governmental
regulations.
operator – a qualified person who controls the movement of an aerial
platform.
personal fall arrest system – a fall protection system that is used
while working on an unprotected edge (such as a roof top with no
guardrail). This system includes a harness, lanyard or other connecting
device, a fall arrestor, an energy absorber or decelerator, an anchorage connector, and a secure anchorage such as a building beam,
girders or columns. An aerial platform is not a fall arrest anchorage.
platform – the portion of an aerial platform intended to be occupied
by personnel with their tools and materials.
platform height – the vertical distance measured from the floor of the
platform to the surface upon which the chassis is being supported.
prestart inspection – a required safety inspection routine that is
performed daily before operating the aerial platform.
qualified person – a person, who by reason of knowledge, experience,
or training is familiar with the operation to be performed and the
hazards involved.
rated work load – the designed carrying capacity of the aerial platform as specified by the manufacturer.
stow – to place a component, such as the platform, in its rest position.
tip boom – a telescopic boom section that extends and retracts from
within the main boom. The tip boom is nearest the platform.
intermediate boom – a telescopic boom section that extends and
retracts from within the main boom. The intermediate boom is between the base, or lower most section of the main boom, and the tip
boom.
jib – an articulating boom attached to the tip boom which increases
the overall boom reach.
level sensor – a device that detects a preset degree of variation from
perfect level. The level sensor is used to sound an alarm if operating
on a slope greater than the preset value.
lower controls – the controls located at ground level for operating
some or all of the functions of the aerial platform.
main boom – a boom assembly located between the turntable and the
platform.
manufacturer – a person or entity who makes, builds or produces an
aerial platform.
maximum travel height – the maximum platform height or the most
adverse configuration(s) with respect to stability in which travel is permitted by the manufacturer.
TB47J – 0075239EE
turning radius – the radius of the circle created by the wheel during a
360° turn with the steering wheels turned to maximum. Inside turning
radius is the wheel closest to the center and outside turning radius is
the wheel farthest from the center.
turntable – the structure above the rotation bearing which supports the
main boom. The turntable rotates about the centerline of rotation.
unrestricted rated work load – the maximum designed carrying capacity of the aerial platform allowed by the manufacturer in all operating configurations.
upper controls – the controls located on or beside the platform used
for operating some or all of the functions of the aerial platform.
wheelbase – the distance from the center of the rear wheel to the
center of the front wheel.
working envelope – the area defined by the horizontal and vertical
limits of boom travel that the platform may be positioned in.
working height – platform height plus six feet.
Page 64

Appendix A – Glossary
TB47J – 0075239EE
Page 65

LIMITED WARRANTY
Snorkel warrants each new machine manufactured and sold by it to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a
period of one (1) year from date of delivery to a Customer or for one year after the machine has been placed in first service in
a Dealer rental fleet, whichever comes first. Any part or parts which, upon examination by the Snorkel Service Department, are
found to be defective, will be replaced or repaired, at the sole discretion of Snorkel, through its local Authorized Dealer at no
charge.
Snorkel further warrants the structural components; specifically, the mainframe chassis, turntable, booms and scissor arms, of
each new machine manufactured by it to be free from defects in material and workmanship for an additional period of four (4)
years. Any such part or parts which, upon examination by the Snorkel Service Department, are found to be defective will be
replaced or repaired by Snorkel through its local Authorized Dealer at no charge; however, any labor charges incurred as a result
of such replacement or repair will be the responsibility of the Customer or Dealer.
The Snorkel Service Department must be notified within forty-eight (48) hours of any possible warranty situation during the
applicable warranty period. Personnel performing warranty repair or replacement must obtain specific approval by Snorkel
Service Department prior to performing any warranty repair or replacement.
Customer and Dealer shall not be entitled to the benefits of this warranty and Snorkel shall have no obligations hereunder unless
the “Pre-Delivery and Inspection Report” has been properly completed and returned to the Snorkel Service Department within ten
(10) days after delivery of the Snorkel product to Customer or Dealer’s rental fleet. Snorkel must be notified, in writing, within ten
(10) days, of any machine sold to a Customer from a Dealer’s rental fleet during the warranty period.
At the direction of the Snorkel Service Department, any component part(s) of Snorkel products to be replaced or repaired under
this warranty program must be returned freight prepaid to the Snorkel Service Department for inspection. All warranty replacement parts will be shipped freight prepaid (standard ground) from the Snorkel Service Department or from Snorkel’s Vendor to
Dealer or Customer.
REPLACEMENT PARTS WARRANTY
Any replacement or service part made or sold by Snorkel is not subject to the preceding Limited Warranty beyond the normal
warranty period of the machine upon which the part was installed.
THIS WARRANTY EXCLUDES AND SNORKEL DOES NOT WARRANT:
1. Engines, motors, tires and batteries which are manufactured by suppliers to Snorkel, who furnish their own warranty.
Snorkel will, however, to the extent permitted, pass through any such warranty protection to the Customer or Dealer.
2. Any Snorkel product which has been modified or altered outside Snorkel’s factory without Snorkel’s written approval, if
such modification or alteration, in the sole judgment of Snorkel’s Engineering and/or Service Departments, adversely affects
the stability, reliability or service life of the Snorkel product or any component thereof.
3. Any Snorkel product which has been subject to misuse, improper maintenance or accident. “Misuse” includes but is not
limited to operation beyond the factory-rated load capacity and speeds. “Improper maintenance” includes but is not limited
to failure to follow the recommendations contained in the Snorkel Operation, Maintenance, Repair Parts Manuals. Snorkel is
not responsible for normal maintenance, service adjustments and replacements, including but not limited to hydraulic fluid,
filters and lubrication.
4. Normal wear of any Snorkel component part(s). Normal wear of component parts may vary with the type application or type
of environment in which the machine may be used; such as, but not limited to sandblasting applications.
5. Any Snorkel product that has come in direct contact with any chemical or abrasive material.
6. Incidental or consequential expenses, losses, or damages related to any part or equipment failure, including but not limited
to freight cost to transport the machine to a repair facility, downtime of the machine, lost time for workers, lost orders, lost
rental revenue, lost profits or increased cost.
This warranty is expressly in lieu of all other warranties, representations or liabilities of Snorkel, either expressed or implied,
unless otherwise amended in writing by Snorkel’s President, Vice President-Engineering, Vice President-Sales or Vice President-Marketing.
SNORKEL MAKES NO WARRANTIES WHICH EXTEND BEYOND THE DESCRIPTION OF THIS LIMITED WARRANTY. SNORKEL
MAKES NO IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND DISCLAIMS
ALL LIABILITY FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO INJURY TO PERSONS
OR PROPERTY.
The Customer shall make all warranty claims through its local Authorized Dealer and should contact the Dealer from whom the
Snorkel product was purchased for warranty service. Or, if unable to contact the Dealer, contact the Snorkel Service Department
for further assistance.
Effective July 1995
© Snorkel International, Inc. – all rights reserved Printed in the U.S.A.
Page 66

 Loading...
Loading...