Siemens SAB80C517A-M18, SAB80C517A-N18, SAB80C517A-N18-T3, SAB83C517A-N18-T4, SAB83C517A-5N18 Datasheet
...
Microcomputer Components
8-Bit CMOS Single-Chip Microcontroller
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Data Sheet 05.94

High-Performance SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
8-Bit CMOS Single-Chip Microcontroller
Preliminary
SAB 83C517A-5 Microcontroller with factory mask-programmable ROM
SAB 80C517A Microcontroller for external ROM
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5,
l
Eight data pointers for external memory
l
up to 18 MHz operation addressing
l
32 K
8 ROM (SAB 83C517A-5 only,
×
Seventeen interrupt vectors, four priority
l
ROM-Protection available) levels selectable
256
l
l
l
8 on-chip RAM
×
×
2 K
8 on-chip RAM (XRAM) 12 multiplexed inputs
Superset of SAB 80C51 architecture:
µ
– 1
s instruction cycle time at 12 MHz programmable Baudrate-Generators
– 666 ns instruction cycle time at 18 MHz
Genuine 10-bit A/D converter with
l
l
Two full duplex serial interfaces with
Fully upward compatible with SAB 80C515,
l
– 256 directly addressable bits SAB 80C517, SAB 80C515A
– Boolean processor
– 64 Kbyte external data and
program memory addressing
Four 16-bit timer/counters
l
Powerful 16-bit compare/capture unit 0 to 70
l
(CCU) with up to 21 high-speed or PWM – 40 to 85
output channels and 5 capture inputs – 40 to 110
l
Versatile "fail-safe" provisions
Fast 32-bit division, 16-bit multiplication, P-MQFP-100-2
l
l
Extended power saving mode
Fast Power-On Reset
l
l
Nine ports: 56 I/O lines, 12 input lines
Three temperature ranges available:
l
o
C (T1)
o
C (T3)
o
C (T4)
l
Plastic packages: P-LCC-84,
32-bit normalize and shift by peripheral
MUL/DIV unit (MDU)
The SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5 is a high-end member of the Siemens SAB 8051 family of
microcontrollers. It is designed in Siemens ACMOS technology and based on SAB 8051
architecture. ACMOS is a technology which combines high-speed and density characteristics
with low-power consumption or dissipation.
While maintaining all the SAB 80C517 features and operating characteristics the
SAB 80C517A is expanded in its "fail-safe" characteristics and timer capabilities.The
SAB 80C517A is identical with the SAB 83C517A-5 except that it lacks the on-chip program
memory. The SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5 is supplied in a 84-pin plastic leaded chip carrier
package (P-LCC-84) and in a 100-pin plastic quad flat package (P-MQFP-100-2).
Semiconductor Group 1 1994-05-01

,
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Revision History 05.94
Previous Releases 01.94/08.93/11.92/10.91/04.91
Page Subjects (changes since last revision 04.91)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
6
4
7-15
several
3
26, 27, 31
– Pin configuration P-MQFP-100-2 added
– Pin differences updated
– Pin numbers for P-MQFP-100-2 package added
– Correction of P-MRFP-100 into P-MQFP-100-2
°
– Ordering information for -40 to +110
C versions
– Correction of register names S0RELL, SCON, ADCON, ICRON,
and SBUF
34
41
49
60
62
65
several
66
66
– Figure 4 corrected
– Figure 8 corrected
/SWD function description completed
– PE
– Correct ordering numbers
V
– Test condition for V
– t
t
name corrected
PXIZ
AVIV,
t
values corrected
AZPL
OH
OH1
corrected
– Minimum clock frequence is now 3.5 MHz
– t
– t
(data setup before WR
QVWH
LLAX2
corrected
) corrected and added
Page Subjects (changes since last revision 08.93)
26
51
– Corrected SFR name S0RELL
– Below "Termination of HWPD Mode": 4th paragraph with ident
corrected
65
65
74
– Description of t
– Program Memory Read Cycle: t
– Oscillator circuit drawings: MQFP-100-2 pin numbers added.
LLIV
corrected
PXAV
added
Page Subjects (changes since last revision 01.94)
– Minor changes on several pages
47
– Table 6 corrected
Semiconductor Group 2 1994-05-01

SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Ordering Information
Type Ordering
Code
Package Description
8-bit CMOS Microcontroller
SAB 80C517A-N18 Q67120-C583 P-LCC-84
for external memory,18 MHz
SAB 80C517A-M18 TBD P-MQFP-100-2
SAB 83C517A-5N18 Q67120-C582 P-LCC-84 with mask-programmable ROM,
18 MHz
SAB 80C517A-N18-T3 Q67120-C769 P-LCC-84 for external memory,18 MHz
o
ext. temperature – 40 to 85
C
SAB 83C517A-5N18-T3Q67120-C771 P-LCC-84 with mask-programmable ROM,
18 MHz
ext. temperature – 40 to 85
o
C
SAB 83C517A-N18-T4 TBD P-LCC-84 for external memory, 18 MHz
ext. temperature -40 to +110
o
C
SAB 83C517A-5N18-T4TBD P-LCC-84 with mask-programmable ROM,
18 MHz
ext. temperature -40 to +110
o
C
Semiconductor Group 3 1994-05-01

SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Logic Symbol
Semiconductor Group 4 1994-05-01

Pin Configuration
(P-LCC-84)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
The pin functions of the SAB 80C517A are identical with those of the SAB 80C517/80C537 with
one exception:
Typ SAB 80C517A SAB 80C517/80C537
P-LCC-84, Pin 60
HWPD
P-MQFP-100-2, Pin 36
N.C.
Semiconductor Group 5 1994-05-01

SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Pin Configuration
(P-MQFP-100-2)
Semiconductor Group 6 1994-05-01

Pin Definitions and Functions
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Symbol Pin Number I/O
P-LCC-84 P-MQFP-100-2
P4.0 – P4.7 1– 3, 5 – 9 64 - 66,
I/O
68 - 72
*)
Function
Port 4
is a bidirectional I/O port with internal
pull-up resistors. Port 4 pins that have 1
s written to them are pulled high by the
internal pull-up resistors, and in that
state can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 4 pins being externally pulled low
will source current ( I
in the DC char-
IL,
acteristics) because of the internal pullup resistors.
This port also serves alternate compare
functions. The secondary functions are
assigned to the pins of port 4 as follows:
– CM0 (P4.0): Compare Channel 0
– CM1 (P4.1): Compare Channel 1
– CM2 (P4.2): Compare Channel 2
– CM3 (P4.3): Compare Channel 3
– CM4 (P4.4): Compare Channel 4
– CM5 (P4.5): Compare Channel 5
– CM6 (P4.6): Compare Channel 6
– CM7 (P4.7): Compare Channel 7
/SWD 4 67 I
PE
*
I = Input
O = Output
Power saving modes enable Start
Watchdog Timer
A low level on this pin allows the software to enter the power down, idle and
slow down mode. In case the low level
is also seen during reset, the watchdog
timer function is off on default.
Use of the software controlled power
saving modes is blocked, when this pin
is held on high level. A high level during
reset performs an automatic start of the
watchdog timer immediately after reset.
When left unconnected this pin is pulled
high by a weak internal pull-up resistor.
Semiconductor Group 7 1994-05-01

Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Symbol Pin Number
P-LCC-84 P-MQFP-100-2
RESET
V
AREF
V
AGND
10 73 I RESET
11 78
12 79
P7.7 -P7.0 13 - 20 80 - 87 I
I/O
*)
Function
A low level on this pin for the duration of
one machine cycle while the oscillator is
running resets the SAB 80C517A. A
small internal pull-up resistor permits
power-on reset using only a capacitor
connected to V
SS
.
Reference voltage for the A/D con-
verter.
Reference ground for the A/D
converter.
Port 7
is an 8-bit unidirectional input port. Port
pins can be used for digital input, if
voltage levels meet the specified input
high/low voltages, and for the lower 8bit of the multiplexed analog inputs of
the A/D converter, simultaneously.
*
I = Input
O = Output
Semiconductor Group 8 1994-05-01

Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Symbol Pin Number
I/O
*)
Function
P-LCC-84 P-MQFP-100-2
P3.0 - P3.7 21 - 28 90 - 97 I/O Port 3
is a bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup resistors. Port 3 pins that have 1 s
written to them are pulled high by the
internal pull-up resistors, and in that state
can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 3
pins being externally pulled low will source
current ( I
because of the internal pull-up resistors.
Port 3 also contains the interrupt, timer,
serial port 0 and external memory strobe
pins that are used by various options. The
output latch corresponding to a secondary
function must be programmed to a one (1)
for that function to operate.
The secondary functions are assigned to
the pins of port 3, as follows:
in the DC characteristics)
IL,
× D0 (P3.0): receiver data input
– R
(asynchronous) or data input/output
(synchronous) of serial interface
× D0 (P3.1): transmitter data output
–T
(asynchronous) or clock output
(synchronous) of serial interface 0
– INT0
(P3.2): interrupt 0 input/timer 0
gate control
– INT1
(P3.3): interrupt 1 input/timer 1
gate control
– T0 (P3.4): counter 0 input
– T1 (P3.5): counter 1 input
–WR
(P3.6): the write control signal
latches the data byte from port 0 into the
external data memory
– RD
(P3.7): the read control signal
enables the external data memory to
port 0
*
I = Input
O = Output
Semiconductor Group 9 1994-05-01

Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Symbol Pin Number
P-LCC-84 P-MQFP-100-2
P1.7 - P1.0 29 - 36 98 - 100,
1, 6 - 9
*)
I/O
Function
I/O Port 1
is a bidirectional I/O port with internal
pull-up resistors. Port 1 pins that have
1 s written to them are pulled high by the
internal pull-up resistors, and in that state
can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 1
pins being externally pulled low will source
current (I
because of the internal pull-up resistors. It
is used for the low order address byte
during program verification. It also contains
the interrupt, timer, clock, capture and
compare pins that are used by various
options. The output latch must be
programmed to a one (1) for that function to
operate (except when used for the compare
functions).
The secondary functions are assigned to
the port 1 pins as follows:
, in the DC characteristics)
IL
*
I = Input
O = Output
– INT3
/CC0 (P1.0): interrupt 3 input/
compare 0 output /capture 0 input
– INT4/CC1 (P1.1): interrupt 4 input /
compare 1 output /capture 1 input
– INT5/CC2 (P1.2): interrupt 5 input /
compare 2 output /capture 2 input
– INT6/CC3 (P1.3): interrupt 6 input /
compare 3 output /capture 3 input
– INT2
/CC4 (P1.4): interrupt 2 input /
compare 4 output /capture 4 input
– T2EX (P1.5): timer 2 external
reload trigger input
– CLKOUT (P1.6): system clock output
– T2 (P1.7): counter 2 input
Semiconductor Group 10 1994-05-01
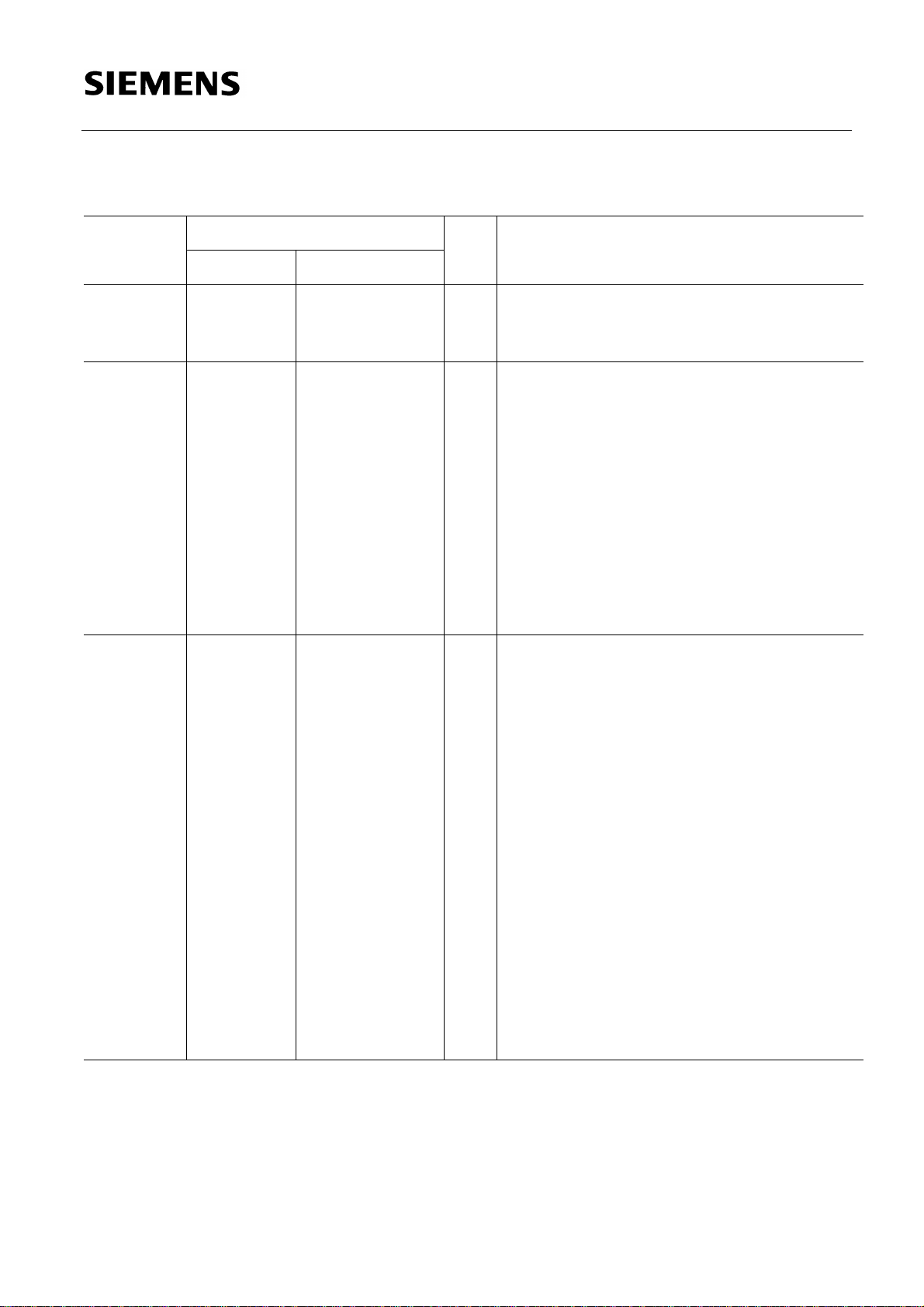
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Symbol Pin Number
I/O
*)
Function
P-LCC-84 P-MQFP-100-2
XTAL2 39 12 – XTAL2
Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and
input to the internal clock generator circuits.
XTAL1 40 13 – XTAL1
Output of the inverting oscillator amplifier.
To drive the device from an external clock
source, XTAL2 should be driven, while
XTAL1 is left unconnected. There are no
requirements on the duty cycle of the
external clock signal, since the input to the
internal clocking circuitry is devided down
by a divide-by-two flip-flop. Minimum and
maximum high and low times as well as
rise/fall times specified in the AC
characteristics must be observed.
P2.0 - P2.7 41 - 48 14 - 21 I/O Port 2
is a bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup resistors. Port 2 pins that have 1 s
written to them are pulled high by the
internal pull-up resistors, and in that state
can be used as in-puts. As inputs, port 2
pins being externally pulled low will source
current (I
because of the internal pull-up resistors.
Port 2 emits the high-order address byte
during fetches from external program
memory and during accesses to external
data memory that use 16-bit addresses
(MOVX @DPTR). In this application it uses
strong internal pull-up resistors when
issuing1 s. During accesses to external
data memory that use 8-bit addresses
(MOVX @Ri), port 2 issues the contents of
the P2 special function register.
, in the DC characteristics)
IL
*
I = Input
O = Output
Semiconductor Group 11 1994-05-01

Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Symbol Pin Number
I/O
*)
Function
P-LCC-84 P-MQFP-100-2
PSEN 49 22 O The Program Store Enable
output is a control signal that enables the
external program memory to the bus during
external fetch operations. It is activated
every six oscillator periodes except during
external data memory accesses. Remains
high during internal program execution.
ALE 50 23 O The Address Latch Enable
output is used for latching the address into
external memory during normal operation.
It is activated every six oscillator periodes
except during an external data memory
access
EA
51 24 I External Access Enable
When held at high level, instructions are
fetched from the internal ROM (SAB
83C517A-5 only) when the PC is less than
8000H. When held at low level, the SAB
80C517A fetches all instructions from external program memory. For the SAB
80C517A this pin must be tied low
P0.0 - P0.7 52 - 59 26 - 27,
30 - 35
*
I = Input
O = Output
I/O Port 0
is an 8-bit open-drain bidirectional I/O port.
Port 0 pins that have 1 s written to them
float, and in that state can be used as highimpe-dance inputs. Port 0 is also the
multiplexed low-order address and data
bus during accesses to external program or
data memory. In this application it uses
strong internal pull-up resistors when
issuing 1 s. Port 0 also out-puts the code
bytes during program verification in the
SAB 83C517A if ROM-Protection was not
enabled. External pull-up resistors are
required during program verification.
Semiconductor Group 12 1994-05-01

Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Symbol Pin Number
I/O
*)
Function
P-LCC-84 P-MQFP-100-2
HWPD 60 36 I Hardware Power Down
A low level on this pin for the duration of
one machine cycle while the oscillator is
running resets the SAB 80C517A. A low
level for a longer period will force the part to
Power Down Mode with the pins floating.
(see table 7)
P5.7 - P5.0 61 - 68 37 - 44 I/OIPort 5
is a bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup resistors. Port 5 pins that have 1 s
written to them are pulled high by the
internal pull-up resistors, and in that state
can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 5
pins being externally pulled low will source
current (I
, in the DC characteristics)
IL
because of the internal pull-up resistors.
This port also serves the alternate function
"Concurrent Compare" and "Set/Reset
Compare". The secondary functions are
assigned to the port 5 pins as follows:
– CCM0 to CCM7 (P5.0 to P5.7):
concurrent compare or Set/Reset
OWE 69 45 I/O Oscillator Watchdog Enable
A high level on this pin enables the
oscillator watchdog. When left
unconnected this pin is pulled high by a
weak internal pull-up resistor. When held at
low level the oscillator watchdog function is
off.
*
I = Input
O = Output
Semiconductor Group 13 1994-05-01

Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Symbol Pin Number
P-LCC-84 P-MQFP-100-2
P6.0 - P6.7 70 - 77 46 - 50,
54 - 56
*)
I/O
Function
I/O Port 6
is a bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup resistors. Port 6 pins that have 1 s
written to them are pulled high by the
internal pull-up resistors, and in that state
can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 6
pins being externally pulled low will source
current (I
because of the internal pull-up resistors.
Port 6 also contains the external A/D
converter control pin and the transmit and
receive pins for serial channel 1. The
output latch corresponding to a secondary
function must be programmed to a one (1)
for that function to operate.
The secondary functions are assigned to
the pins of port 6, as follows:
, in the DC characteristics)
IL
– ADST
start pin
× D1 (P6.1): receiver data input
– R
of serial interface 1
× D1 (P6.2): transmitter data output
–T
of serial interface 1
P8.0 - P8.3 78 - 81 57 - 60 I Port 8
is a 4-bit unidirectional input port. Port pins
can be used for digital input, if voltage
levels meet the specified input high/low
voltages, and for the higher 4-bit of the
multiplexed analog inputs of the A/D
converter, simultaneously
*
I = Input
O = Output
(P6.0): external A/D converter
Semiconductor Group 14 1994-05-01

Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Symbol Pin Number
I/O
*)
Function
P-LCC-84 P-MQFP-100-2
R
O 82 61 O Reset Output
This pin outputs the internally
synchronized reset request signal. This
signal may be generated by an external
hardware reset, a watchdog timer reset
or an oscillator watch-dog reset. The
reset output is active low.
V
S S
V
CC
37, 83 10, 62 – Circuit ground potential
38, 84 11, 63 – Supply Terminal for all operating
modes
N.C. – 2 - 5, 25,
– Not connected
28 - 29,
51 - 53,
74 - 77,
88 - 89
*
I = Input
O = Output
Semiconductor Group 15 1994-05-01

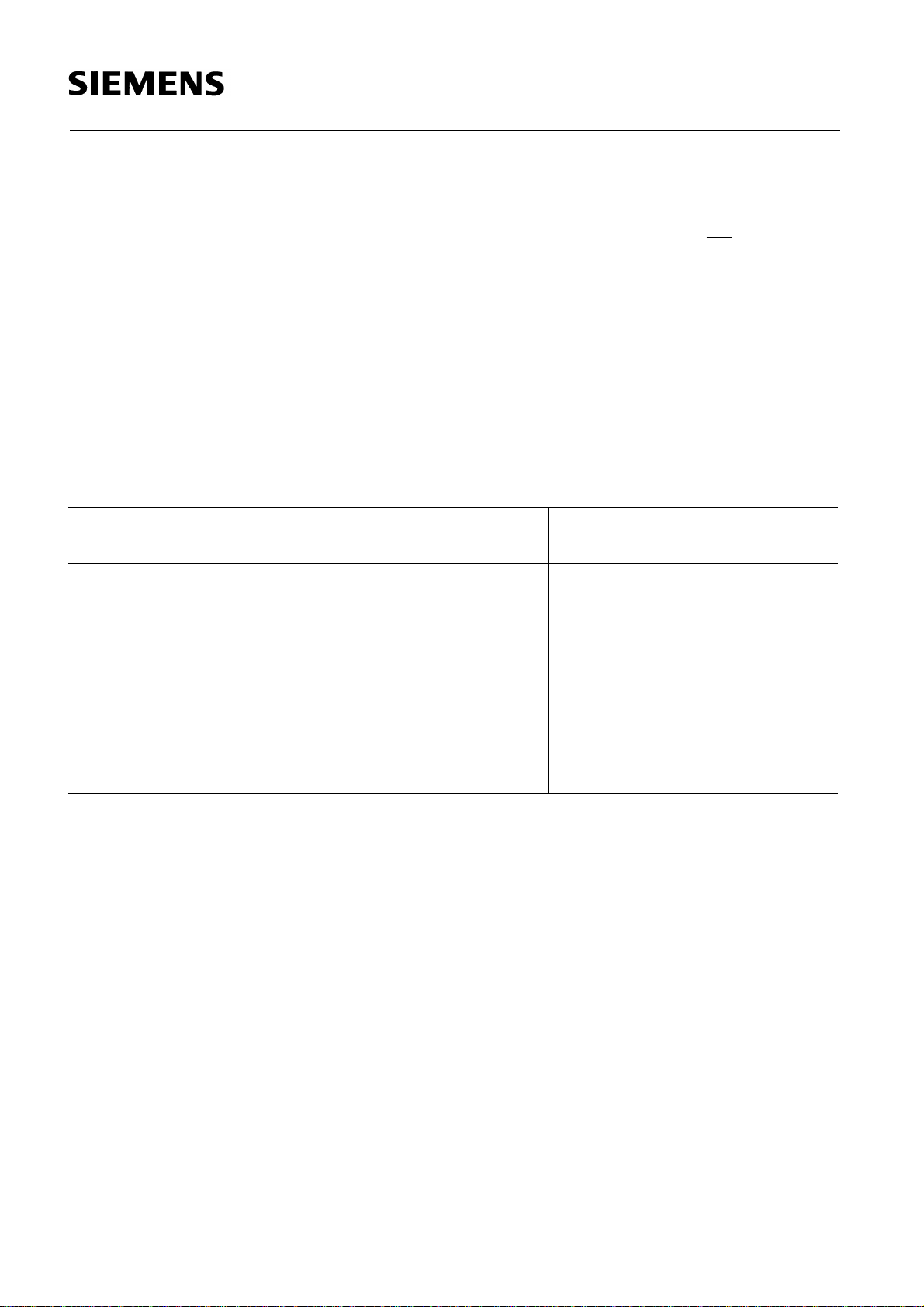
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Figure 1
Block Diagram
Semiconductor Group 16 1994-05-01

SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Functional Description
The SAB 80C517A is based on 8051 architecture. It is a fully compatible member of the
Siemens SAB 8051/80C51 microcontroller family being an significantly enhanced
SAB 80C517. The SAB 80C517A is therefore compatible with code written for the
SAB 80C517.
Having an 8-bit CPU with extensive facilities for bit-handling and binary BCD arithmetics the
SAB 80C517A is optimized for control applications. With a 18 MHz crystal, 58 % of the
instructions are executed in 666.67 ns.
Being designed to close the performance gap to the 16-bit microcontroller world, the
SAB 80C517A’s CPU is supported by a powerful 32-/16-bit arithmetic unit and a more flexible
addressing of external memory by eight 16-bit datapointers.
Memory Organisation
According to the SAB 8051 architecture, the SAB 80C517A has separate address spaces for
program and data memory. Figure 2 illustrates the mapping of address spaces.
Figure 2
Memory Map
Semiconductor Group 17 1994-05-01
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Program Memory ('Code Space')
The SAB 83C517A-5 has 32 Kbyte of on-chip ROM, while the SAB 80C517A has no internal
ROM. The program memory can externally be expanded up to 64 Kbyte. Pin EA
whether program fetches below address 8000H are done from internal or external memory.
As a new feature the SAB 83C517A-5 offers the possibility of protecting the internal ROM
against unauthorized access. This protection is implemented in the ROM-Mask.Therefore, the
decision ROM-Protection 'yes' or 'no' has to be made when delivering the ROM-Code. Once
enabled, there is no way of disabling the ROM-Protection.
Effect: The access to internal ROM done by an externally fetched MOVC instruction
is disabled. Nevertheless, an access from internal ROM to external ROM is possible.
To verify the read protected ROM-Code a special ROM-Verify-Mode is implemented. This
mode also can be used to verify unprotected internal ROM.
controls
ROM -Protection ROM-Verification Mode
(see 'AC Characteristics')
no ROM-Verification Mode 1
(standard 8051 Verification Mode)
ROM-Verification Mode 2
yes ROM-Verification Mode 2 – standard 8051
Restrictions
–
Verification Mode is
disabled
– externally applied MOVC
accessing internal ROM
is disabled
Semiconductor Group 18 1994-05-01

SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Data Memory ('Code Space')
The data memory space consists of an internal and an external memory space. The
SAB 80C517A contains another 2 Kbyte on On-Chip RAM above the 256-bytes internal RAM
of the base type SAB 80C517. This RAM is called XRAM in this document.
External Data Memory
Up to 64 Kbyte external data memory can be addressed by instructions that use 8-bit or 16-bit
indirect addressing. For 8-bit addressing MOVX instructions in combination with registers R0
and R1 can be used. A 16-bit external memory addressing is supported by eight 16-bit
datapointers. Registers XPAGE and SYSCON are controlling whether data fetches at
addresses F800
Internal Data Memory
The internal data memory is divided into four physically distinct blocks:
to FFFFH are done from internal XRAM or from external data memory.
H
– the lower 128 bytes of RAM including four banks containing eight registers each
– the upper 128 byte of RAM
– the 128 byte special function register area.
– a 2 K
chip at the address range from F800
× 8 area which is accessed like external RAM (MOVX-instructions), implemented on
to FFFFH. Special Function Register SYSCON
H
controls whether data is read or written to XRAM or external RAM.
A mapping of the internal data memory is also shown in figure 2. The overlapping address
spaces are accessed by different addressing modes (see User's Manual SAB 80C517). The
stack can be located anywhere in the internal data memory.
Architecture for the XRAM
The contents of the XRAM is not affected by a reset or HW Power Down. After power-up the
contents is undefined, while it remains unchanged during and after a reset or HW Power Down
if the power supply is not turned off.
The additional On-Chip RAM is logically located in the "external data memory" range at the
upper end of the 64 Kbyte address range (F800
-FFFFH). It is possible to enable and disable
H
(only by reset) the XRAM. If it is disabled the device shows the same behaviour as the parts
without XRAM, i.e. all MOVX accesses use the external bus to physically external data
memory.
Semiconductor Group 19 1994-05-01

SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Accesses to XRAM
Because the XRAM is used in the same way as external data memory the same instruction
types must be used for accessing the XRAM.
Note:
If a reset occurs during a write operation to XRAM, the effect on XRAM depends on the
cycle which the reset is detected at (MOVX is a 2-cycle instruction):
Reset detection at cycle 1: The new value will not be written to XRAM. The old value
is not affected.
Reset detection at cycle 2: The old value in XRAM is overwritten by the new value.
Accesses to XRAM using the DPTR
There are a Read and a Write instruction from and to XRAM which use one of the 16-bit DPTR
for indirect addressing. The instructions are:
MOVX A, @DPTR (Read)
MOVX @DPTR, A (Write)
Normally the use of these instructions would use a physically external memory. However, in the
SAB 80C517A the XRAM is accessed if it is enabled and if the DPTR points to the XRAM
address space (DPTR F800
Accesses to XRAM using the Registers R0/R1
The 8051 architecture provides also instructions for accesses to external data memory range
which use only an 8-bit address (indirect addressing with registers R0 or R1). The instructions
are:
H
).
MOVX A, @Ri (Read)
MOVX @Ri, A (Write)
In application systems, either a real 8-bit bus (with 8-bit address) is used or Port 2 serves as
page register which selects pages of 256-byte. However, the distinction, whether Port 2 is
used as general purpose I/O or as "page address" is made by the external system design. From
the device’s point of view it cannot be decided whether the Port 2 data is used externally as
address or as I/O data!
Hence, a special page register is implemented into the SAB 80C517A to provide the possibility
of accessing the XRAM also with the MOVX @Ri instructions, i.e. XPAGE serves the same
function for the XRAM as Port 2 for external data memory.
Semiconductor Group 20 1994-05-01

Special Function Register XPAGE
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Addr. 91
The reset value of XPAGE is 00
XPAGE can be set and read by software.
The register XPAGE provides the upper address byte for accesses to XRAM with MOVX @Ri
instructions. If the address formed from XPAGE and Ri is less than the XRAM address range,
then an external access is performed. For the SAB 80C517A the contents of XPAGE must be
greater or equal than F8H in order to use the XRAM. Of course, the XRAM must be enabled if
it shall be used with MOVX @Ri instructions.
Thus, the register XPAGE is used for addressing of the XRAM; additionally its contents are
used for generating the internal XRAM select. If the contents of XPAGE is less than the XRAM
address range then an external bus access is performed where the upper address byte is
provided by P2 and not by XPAGE!
Therefore, the software has to distinguish two cases, if the MOVX @Ri instructions with paging
shall be used:
a) Access to XRAM: The upper address byte must be written to XPAGE
H
.
H
or P2; both writes selects the XRAM address range.
XPAGE
b) Access to external memory: The upper address byte must be written to P2; XPAGE
will be loaded with the same address in order to deselect
the XRAM.
Semiconductor Group 21 1994-05-01
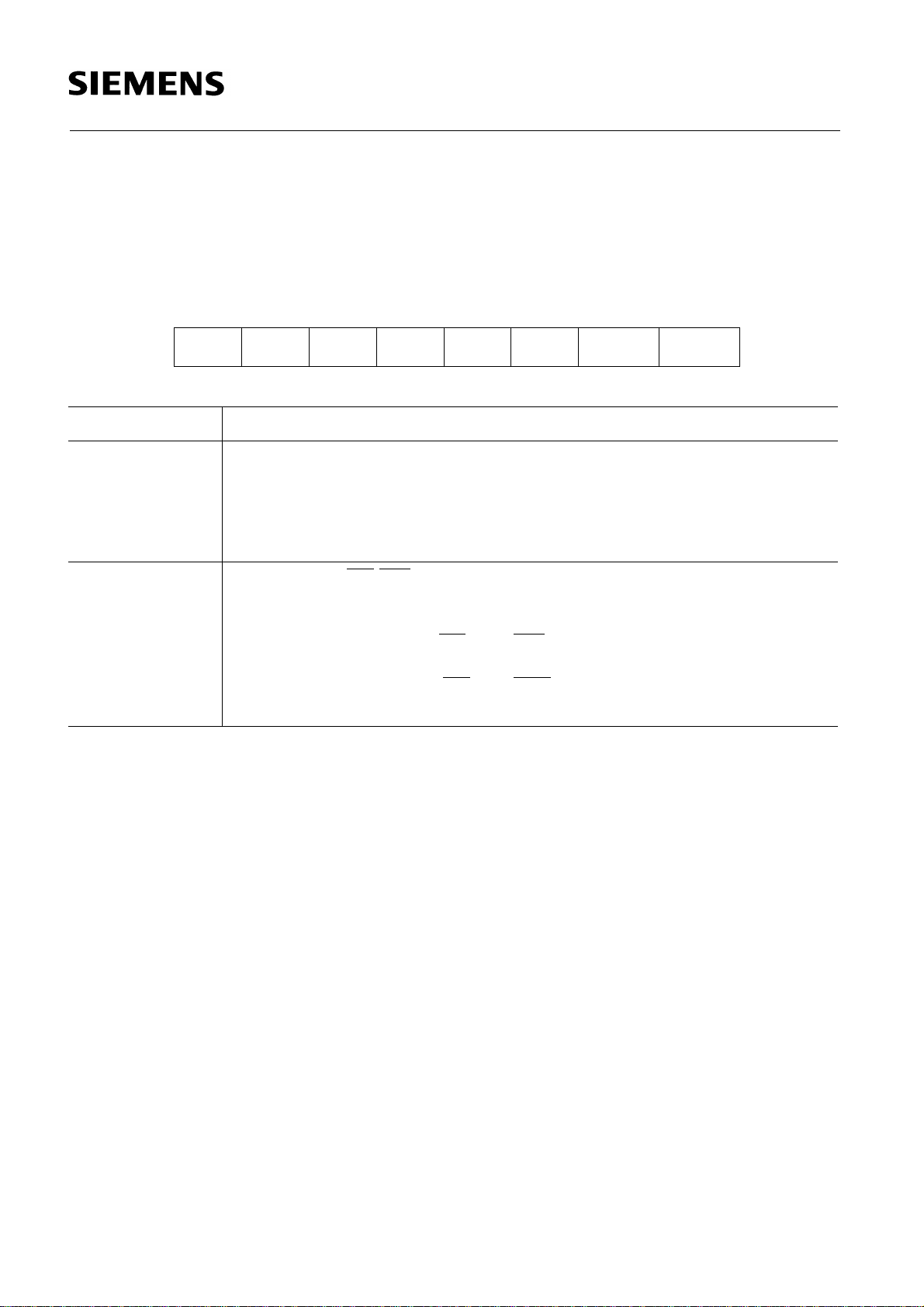
SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
Control of XRAM in the SAB 80C517A
There are two control bits in register SYSCON which control the use and the bus operation
during accesses to the additional On-Chip RAM (XRAM).
Special Function Register SYSCON
Addr. 0B1
Bit Function
XMAP0 Global enable/disable bit for XRAM memory.
XMAP1 Control bit for RD
Reset value of SYSCON is xxxx xx01B.
The control bit XMAP0 is a global enable/disable bit for the additional On-Chip RAM (XRAM).
If this bit is set, the XRAM is disabled, all MOVX accesses use external memory via the external
bus. In this case the SAB 80C517A does not use the additional On-Chip RAM and is compatible
with the types without XRAM.
——————XMAP1 XMAP0 SYSCON
H
XMAP0 = 0: The access to XRAM (= On-Chip XDATA memory) is enabled.
XMAP0 = 1: The access to XRAM is disabled. All MOVX accesses are performed by the external bus (reset state).
/WR signals during accesses to XRAM; this bit has no
effect if XRAM is disabled (XMAP0 = 1) or if addresses exceeding the
XRAM address range are used for MOVX accesses.
XMAP1 = 0: The signals RD
to XRAM.
XMAP1 = 1: The signals RD
XRAM.
and WR are not activated during accesses
and WR are activated during accesses to
Semiconductor Group 22 1994-05-01

SAB 80C517A/83C517A-5
XMAP0 is hardware protected by an unsymmetric latch. An unintentional disabling of XRAM
could be dangerous since indeterminate values would be read from external bus. To avoid this
the XMAP-bit is forced to '1' only by reset. Additionally, during reset an internal capacitor is
loaded. So after reset state XRAM is disabled. Because of the load time of the capacitor
XMAP0-bit once written to '0' (that is, discharging capacitor) cannot be set to '1' again by
software. On the other hand any distortion (software hang up, noise, ...) is not able to load this
capacitor, too. That is, the stable status is XRAM enabled. The only way to disable XRAM after
it was enabled is a reset.
The clear instruction for XMAP0 should be integrated in the program initialization routine before
XRAM is used. In extremely noisy systems the user may have redundant clear instructions.
The control bit XMAP1 is relevant only if the XRAM is accessed. In this case the externa RD
and WR
debug purposes it might be useful to have these signals and the addresses at Ports 0.2
available. This is performed if XMAP1 is set.
The behaviour of Port 0 and P2 during a MOVX access depends on the control bits in register
SYSCON and on the state of pin EA
the following characteristics:
a) Use of P0 and P2 pins during the MOVX access.
b) Activation of the RD
c) Use of internal or external XDATA memory.
The shaded areas describe the standard operation as each 80C51 device without on-chip
XRAM behaves.
signals at P3.6 and P3.7 are not activated during the access, if XMAP1 is cleared. For
. The table 1 lists the various operating conditions. It shows
Bus: The pins work as external address/data bus. If (internal) XRAM is accessed, the
data written to the XRAM can be seen on the bus in debug mode.
I/0: The pins work as Input/Output lines under control of their latch.
and WR pin during the access.
Semiconductor Group 23 1994-05-01
 Loading...
Loading...