Page 1

User Manual
Bulletin 193 E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module
Catalog Number
193-ETN
Page 2
Important User Information
IMPORTANT
Solid-state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of electromechanical equipment. Safety
Guidelines for the Application, Installation and Maintenance of Solid State Controls (publication SGI-1.1
your local Rockwell Automation sales office or online at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/literature/
important differences between solid-state equipment and hard-wired electromechanical devices. Because of this difference,
and also because of the wide variety of uses for solid-state equipment, all persons responsible for applying this equipment
must satisfy themselves that each intended application of this equipment is acceptable.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or consequential damages resulting from
the use or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many variables and
requirements associated with any particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or
liability for actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or
software described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation,
Inc., is prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary, we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
WARNING: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can cause an explosion in a hazardous
environment, which may lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
available from
) describes some
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death,
property damage, or economic loss. Attentions help you identify a hazard, avoid a hazard, and recognize the
consequence
SHOCK HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that
dangerous voltage may be present.
BURN HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that
surfaces may reach dangerous temperatures.
Identifies information that is critical for successful application and understanding of the product.
Allen-Bradley, Rockwell Software, Rockwell Automation, and TechConnect are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Trademarks not belonging to Rockwell Automation are property of their respective companies.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Installation and Wiring
Protection Functions
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Network Design. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Trip Status / Identification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Trip Resetting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Trip and Warning Enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Overload and Phase Loss Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Overload Warning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Jam Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Jam Trip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Jam Warning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Underload Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Underload Warning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Communication Fault Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Comm Fault Warning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Communication Idle Protection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Comm Idle Warning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Configure an E1 Plus EtherNet/
IP Module To Operate on the
Network
Automation Controller and
Software Communications
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Determining Network Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Setting the IP Network Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Assign Network Parameters via the BOOTP/DHCP Utility. . . . . . . . . 20
Assign Network Parameters Via a Web Browser and MAC Scanner
Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Other Factors to Consider When Assigning Network Parameters . . . . 24
Duplicate IP Address Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Behavior of Modules With Duplicate IP Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
DNS Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Install EDS File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Download EDS File Embedded in the Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Download EDS File from Allen-Bradley EDS File Download Site 27
Register the EDS File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
I/O Messaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
ControlLogix Configuration with Add-On Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
EtherNet/IP Network Configuration with Add-On Profiles . . . . . 35
Accessing Module Data with Add-On Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
ControlLogix Generic Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
EtherNet/IP Network Generic Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Downloading the Generic Configuration to the PLC . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 3
Page 4

Accessing Generic Module Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Logix Explicit Messaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
MicroLogix 1100 and 1400 Explicit Messaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
FactoryTalk View with Predefined Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Email Notifications
Device Parameters and Tags
Troubleshooting
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Notification Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Email Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Email Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Configure Device Identity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Parameter and Tag Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Program Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Resetting to the Factory Default Values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Parameter Group Listing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Monitor Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Advanced Setup Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Reset/Lock Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
I/O Setup Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Trip History Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
EtherNet/IP Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Power-Up Reset Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Run Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Recoverable Error Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Unrecoverable Error Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
EtherNet/IP Troubleshooting Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Input and Output Troubleshooting Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Specifications
EtherNet/IP Information
4 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Electronic Data Sheets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
EtherNet/IP Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Identity Object — CLASS CODE 0x01. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Message Router Object — CLASS CODE 0x02. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Assembly Object — CLASS CODE 0x04 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Connection Manager Object — CLASS CODE 0x06 . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Discrete Input Point Object — CLASS CODE 0x08 . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Discrete Output Point Object — CLASS CODE 0x09 . . . . . . . . . . 86
Parameter Object — CLASS CODE 0x0F. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Parameter Group Object — CLASS CODE 0x10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Page 5

Control Supervisor Object — CLASS CODE 0x29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Overload Object — CLASS CODE 0x2C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
PCP Object — CLASS CODE 0xC2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
TCP/IP Interface Object — CLASS CODE 0xF5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Ethernet Link Object — CLASS CODE 0xF6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Rockwell Automation Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Installation Assistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
New Product Satisfaction Return . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 5
Page 6

6 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 7

Installation and Wiring
Chapter
1
Introduction
The purpose of this chapter is to provide the necessary instructions to successfully
install an E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module to an E1 Plus Overload Relay and
properly connect to a EtherNet/IP network.
ATTENTION: To prevent electrical shock, disconnect from power
source before installing or servicing. Install in suitable enclosure.
Keep free from contaminants.
ATTENTION: The side mount module contains ESD (electrostatic
discharge) sensitive parts and assemblies. Static control
precautions are required when installing, testing, servicing, or
repairing this assembly. Component damage may result if ESD
control procedures are not followed. If you are not familiar with
static control procedures, refer to Rockwell Automation publication
8000-4.5.2, “Guarding Against Electrostatic Damage”, or any other
applicable ESD protection handbook.
ATTENTION: The purpose of this document is to serve as a guide
for proper installation. The National Electrical Code and any other
governing regional or local code will take precedence. Rockwell
Automation cannot assume responsibility for the compliance or
proper installation of the side mount module or associated
equipment. A hazard of personal injury and/or equipment damage
exists if codes are ignored during installation.
ATTENTION: An incorrectly applied or installed side mount
module can result in damage to the components or reduction in
product life. Wiring or application errors such as supplying
incorrect or inadequate supply voltage, or operating/storing in
excessive ambient temperatures may result in malfunction of the
product.
ATTENTION: Only personnel familiar with the side mount module
and associated machinery should plan to install, set up, and
maintain the system. Failure to comply may result in personal
injury and/or equipment damage.
ATTENTION: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment,
this product may cause radio interference, in which case, the user
may be required to take adequate measures.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 7
Page 8
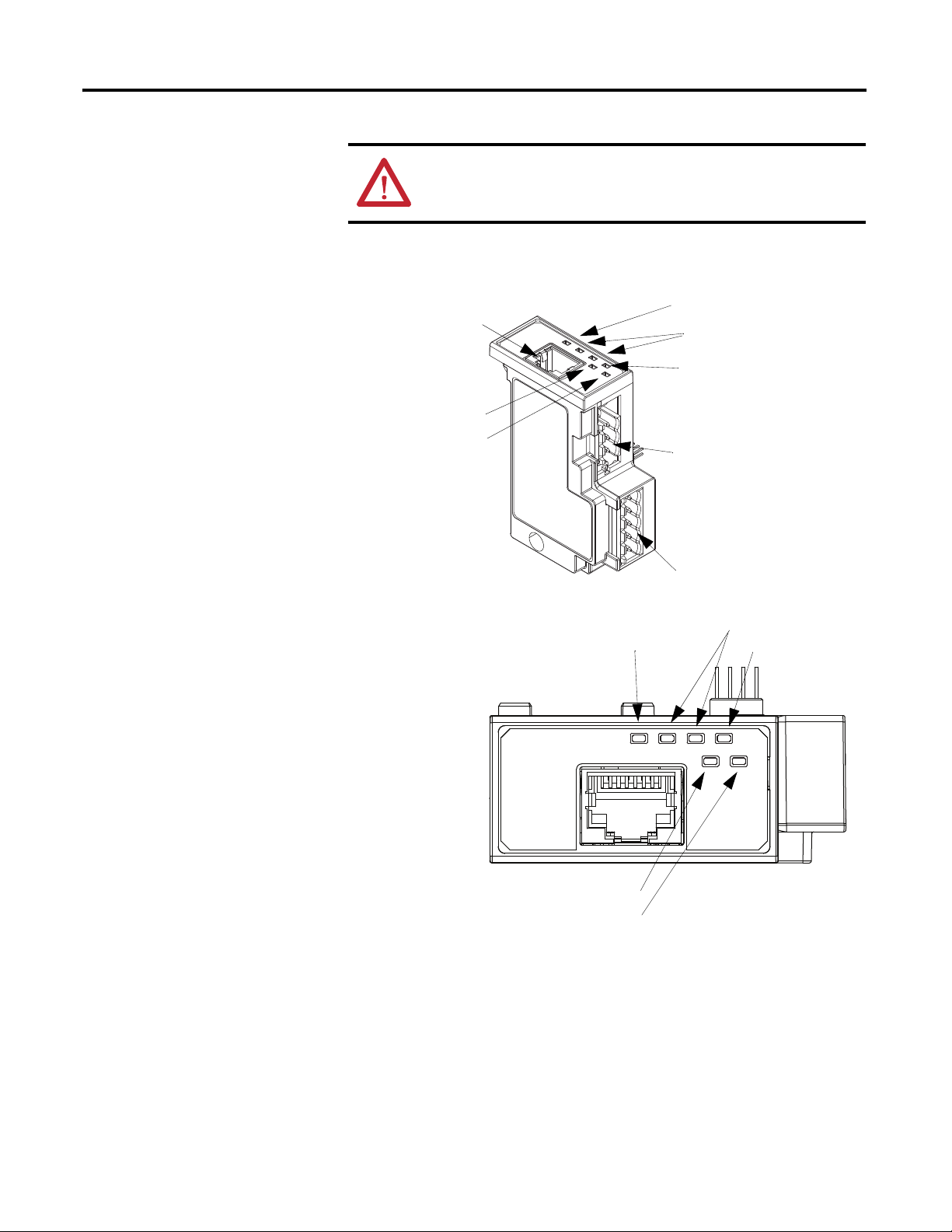
Chapter 1
Network Status LED
Output Status LED
Input Status LED
Power Connector
I/O Connector
Module Status LED
Link/Activity LED
Ethernet Connector
Module Status LED
Input Status LED
Output Status LED
Network Status LED
Link/Activity LED
ATTENTION: To remain compliant with UL/CSA Certifications, the
EtherNet/IP power supply must meet NEC Class 2 requirements.
Features
Figure 1 - Features
8 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 9
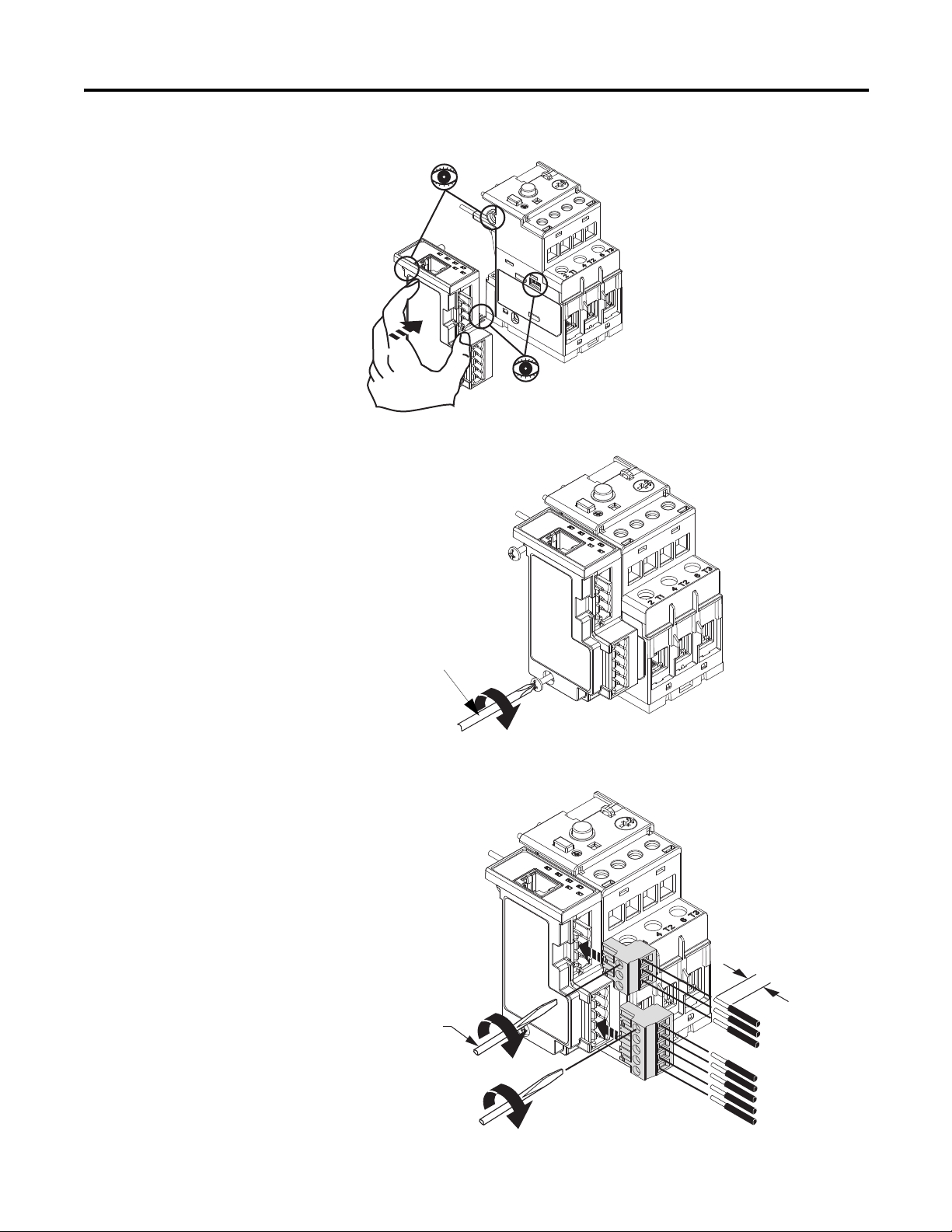
Chapter 1
#2 Driver
0.7…1.1 N•m
(6…10 lb.-in)
0.6 mm X 3.5 mm Blade
(0.02 in X 0.14 in Blade
)
0.5…0.6 N•m
(4.4…5.3 lb.-in)
7 mm
(0.28 in)
Installation
Figure 2 - Installation [1]
Figure 3 - Installation [2]
Figure 4 - Installation [3]
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 9
Page 10
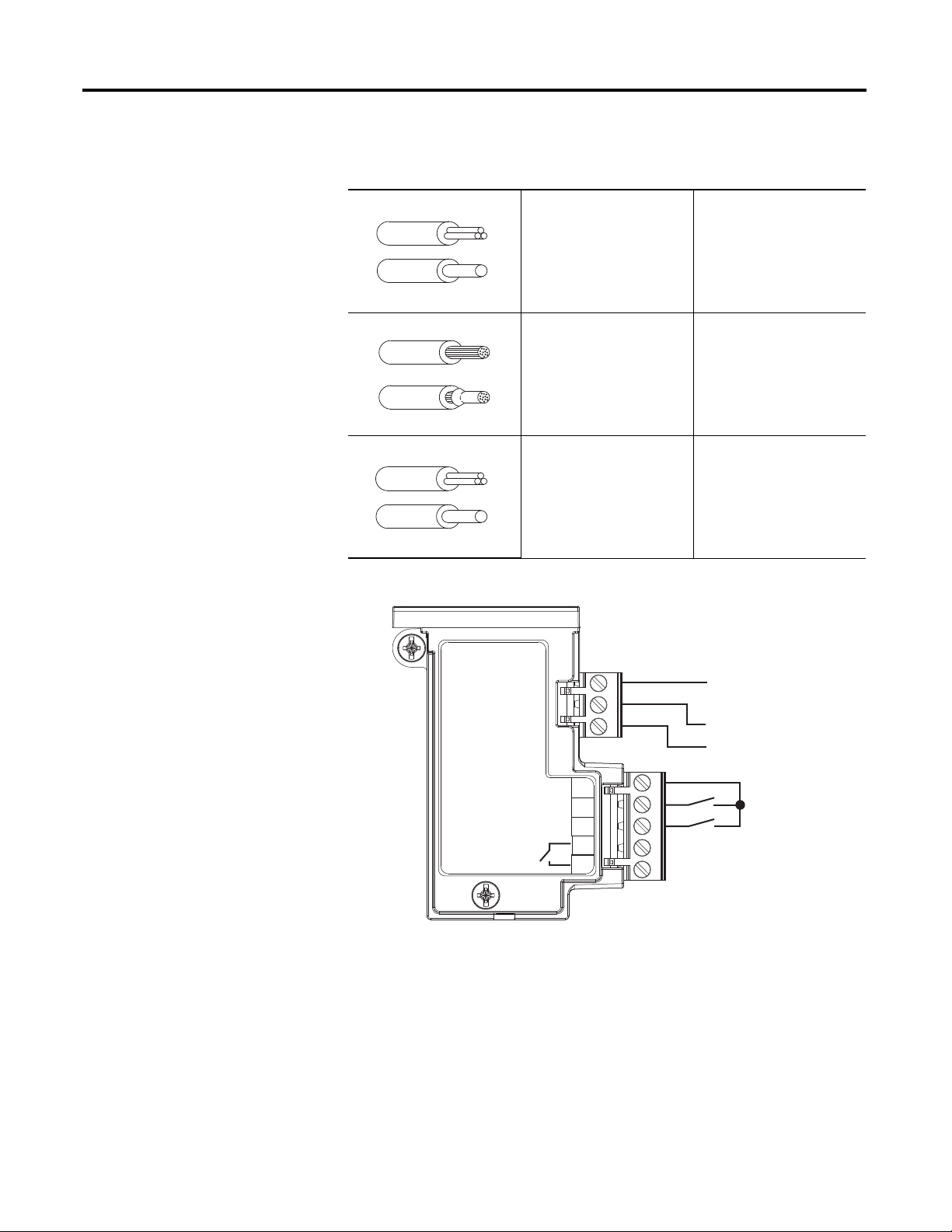
Chapter 1
OUTA
(B300)
13
14
1
2
3
A1 (+)
SSV
IN2
IN1
GND
A2 (-)
(20.4…26.4V DC)
Wiring
Table 1 - Wire and Size Torque Specifications
Figure 5 - Wiring Diagram
1X
2X
1X
2X
1X
2X
24…12 AWG
24…16 AWG
5 lb.-in
0.2…2.5 mm
0.25…1 mm
0.56 N•m
0.2…2.5 mm
0.2…1 mm
0.56 N•m
2
2
2
2
10 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 11
Chapter 1
A
F
G
B
D
E
K
L
H
C
J
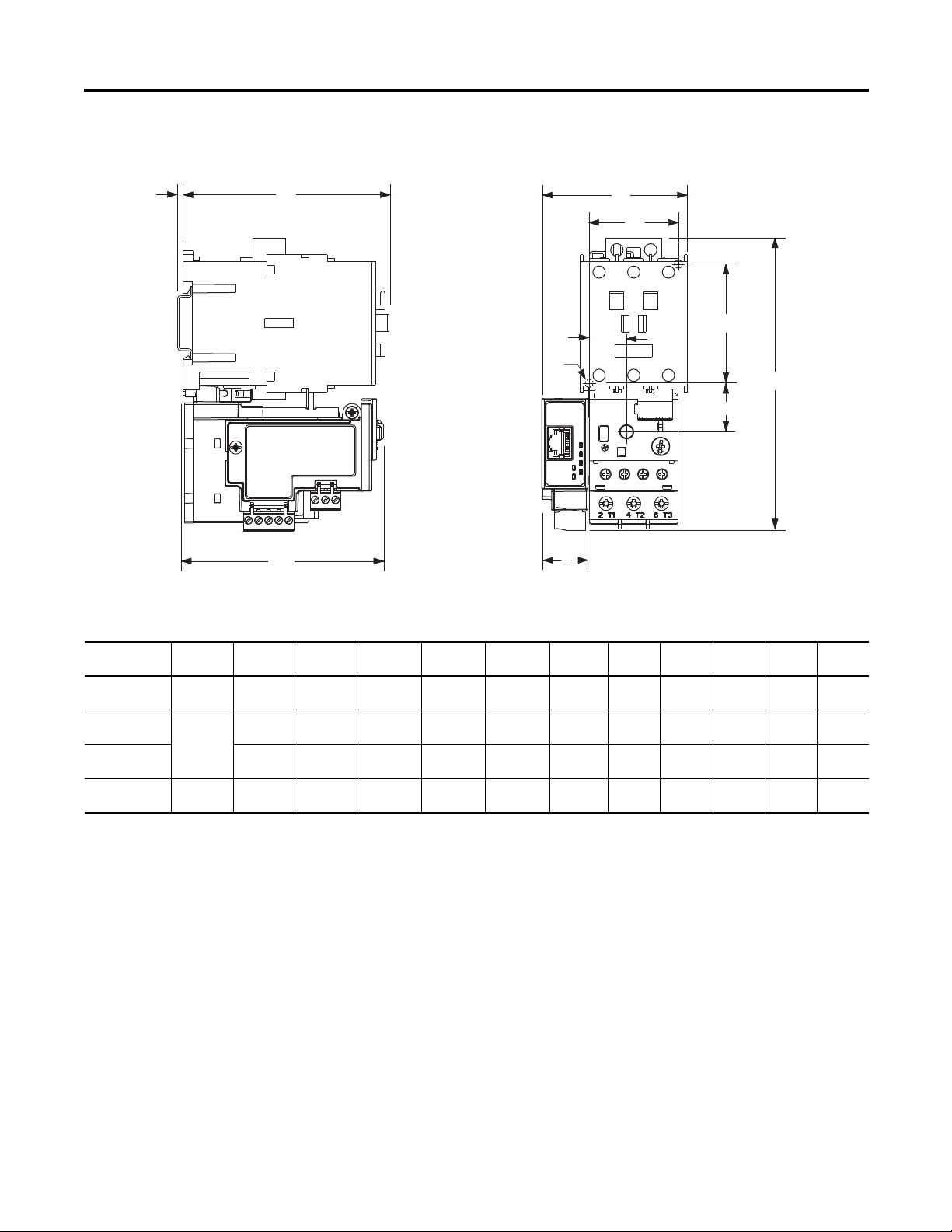
Dimensions
Figure 6 - Dimension Diagram
Table 2 - Dimension Specifications
Contactor Cat.
No.
100-C09, -C12,
-C16, -C23
100-C30, -C37
100-C43
100-C60, -C72,
-C85
Network Design
E1 Plus
Cat. No.
193*-EE_B
193*EE_D
193*-EE_E
ABC D E FGHJKL
67,3 mm
(2.65 in)
67,3 mm
(2.65 in)
71.8 mm
(2.83 in)
94,3 mm
(3.71 in)
148 mm
(4.83 in)
148 mm
(5.83 in)
148 mm
(5.83 in)
191.6 mm
(7.54 in)
85.2 mm
(3.35 in)
101.2 mm
(3.98 in)
101.2 mm
(3.98 in)
120.4 mm
(4.74 in)
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module has one RJ45 port to connect a CAT5 type or
better Ethernet cable. Rockwell Automation offers a wide variety of
24.5 mm
(0.96 in)
24.5 mm
(0.96 in)
24.5 mm
(0.96 in)
29 mm
(1.14 in)
13.9 mm
(0.55 in)
13.9 mm
(0.56 in)
18.4 mm
(0.74 in)
23.8 mm
(0.94 in)
35 mm
(1.38 in)
35 mm
(0.55 in)
45 mm
(1.77 in)
55 mm
(2.16 in)
60 mm
(2.36 in)
60 mm
(2.36 in)
60 mm
(2.36 in)
100 mm
(3.94 in)
86.5 mm
(3.40 in)
104 mm
(4.09 in)
104 mm
(4.09 in)
126 mm
(4.94 in)
2 mm
(0.08 in)
2 mm
(0.08 in)
2 mm
(0.08 in)
2 mm
(0.08 in)
4.5 mm
(0.17 in)
4.5 mm
(0.17 in)
4.5 mm
(0.17 in)
5.4 mm
(0.21 in)
22,3 mm
(0.88 in)
22,3 mm
(0.88 in)
22,3 mm
(0.88 in)
22,3 mm
(0.88 in)
Allen-Bradley Ethernet patch cables with its Bulletin 1585 line of Ethernet cables
(http://www.ab.com/sensors/ethernet/incabinet.html).
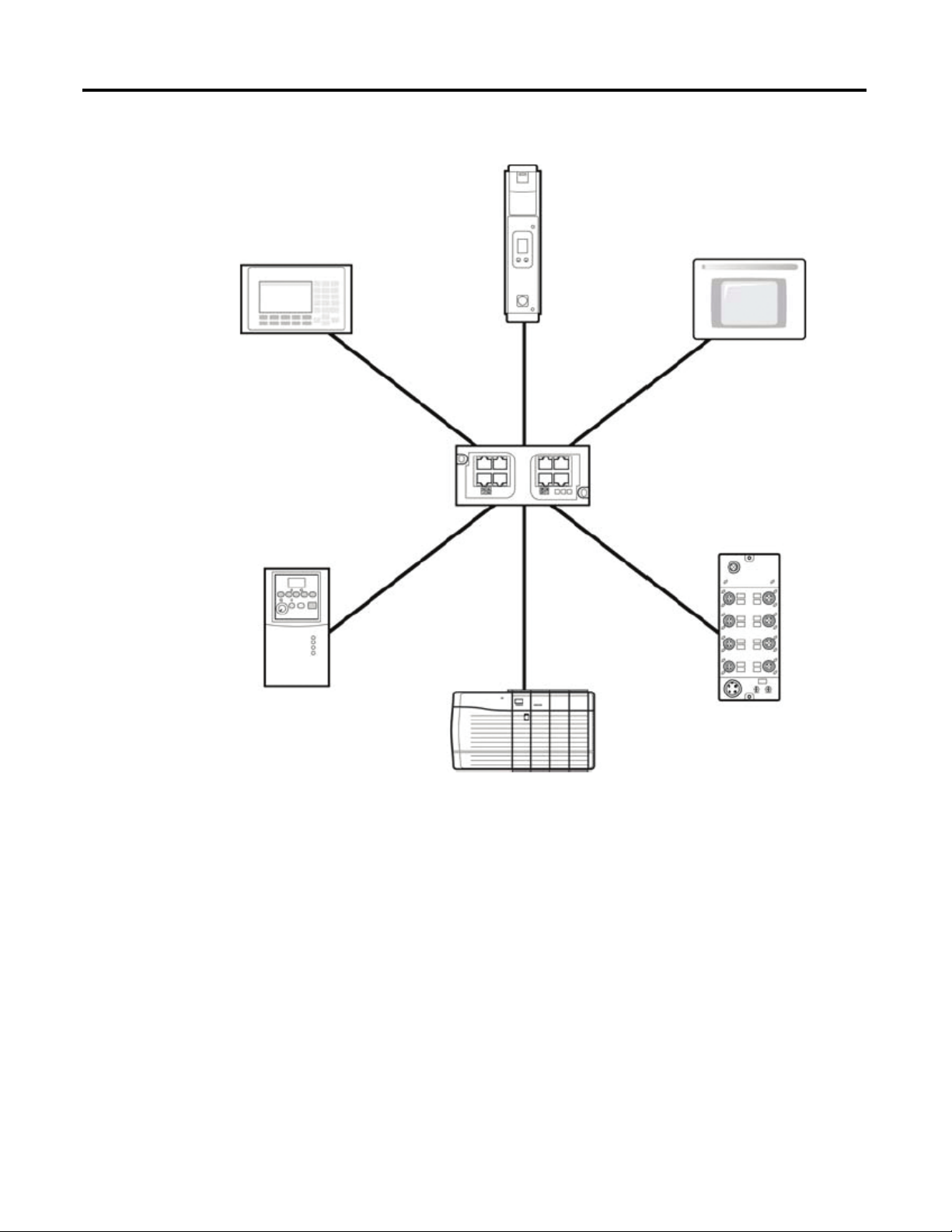
The E1 Plus supports a Star Ethernet topology in which all Ethernet nodes wire
back to a central Ethernet switch, hub, or router as shown below:
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 11
Page 12
Chapter 1
Rockwell Automation offers a line of Allen-Bradley managed and unmanaged
Ethernet Switches with its Stratix family of Ethernet Switches (http://
www.ab.com/networks/switches/).
12 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 13

Protection Functions
IMPORTANT
Chapter
2
Introduction
Trip Status / Identification
Trip Resetting
The purpose of this chapter is to provide detailed information regarding the
protective trip and warning functions that the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module adds
to the E1 Plus Overload Relay. In this chapter, you will find considerable mention
given to parameters as they relate to these functions. For complete descriptions of
the programming parameters, refer to Chapter 6- Device Parameters and Tags.
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module determines trip status and identification
through monitoring of reference signals inside the E1 Plus Overload Relay. On
power-up, it assumes that the E1 Plus Overload Relay is in a non-tripped
condition. For definitive feedback on trip status of the E1 Plus Overload Relay,
one of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module inputs may be wired to the N.O. auxiliary
contact (terminals 97 and 98) of the E1 Plus Overload Relay. Parameters 40 and
41 are used to configure the assignment of the inputs. For this function, use the
“OL Contact” configuration.
The following options are available for resetting a tripped E1 Plus Overload Relay
with an E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module:
• Blue mechanical reset button located on the front of the E1 Plus Overload
Relay
• Setting Parameter 14, Tri p Re set , to “Reset trip”
• Setting the trip reset bit in an output assembly from a logic controller
• Using a push button (N.O. contact configuration) wired to one of the
EtherNet/IP module inputs, programming the corresponding input
assignment parameter (40 or 41) to “Trip Reset”
• Setting the CIP Tag, Trip_Reset, to 1
Trip and Warning Enable
Setting parameter 16, Reset Mode, to “Automatic” does not result in
other reset commands being ignored.
Parameter 12, Trip E na bl e, allows the installer to enable or disable the jam trip
protective function.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 13
Page 14

Chapter 2
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
Parameter 13, War n in g En a bl e , allows the installer to enable or disable the
overload, jam, underload, and communication warning protective functions.
ATTENTION: The Trip Enable settings should not be altered during
machine operation, as unexpected behavior could occur. This may
result in an unintended actuation of controlled industrial
equipment, with the potential for machine damage or serious
injury to personnel.
Overload and Phase Loss Protection
Thermal overload and phase loss trip protection is provided exclusively by the E1
Plus Overload Relay. The E1 Plus Overload Relay provides uninterrupted
protection to the motor, even in the event of an E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module
failure. Settings for FLA and trip class are found directly on the E1 Plus Overload
Relay.
The reset mode DIP switch adjustment is overridden by the E1 Plus
EtherNet/IP module parameter 16, OL Reset Mode, while the E1 Plus
EtherNet/IP module is powered.
Overload Warning
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module continuously monitors the E1 Plus Overload
Relay's percentage of thermal utilization signal. Parameter 2,%Therm Utilized,
provides this value.
Parameter 17, OL Warn Level, is used to adjust the setpoint to alert for an
impending overload trip and is adjustable from 0…100% TCU.
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module will indicate an overload warning if all the
following conditions are met:
• No warning currently exists
• Overload warning is enabled
• %Therm Utilized is equal to or greater than OL Warn Level
When the overload warning conditions are satisfied, the following will occur:
• Bit 0 in Parameter 4, Wa r n in g S t at us , will go to “1”
• Bit 1 of Parameter 10, Device Status, will go to “1”
%Therm Utilized will stabilize at a value of approximately 88% with
the motor operating continuously at rated current.
14 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 15

Chapter 2
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
Jam Protection
Motor current greater than the motor's nameplate rating can indicate a high
overload or stall condition, such as an overloaded conveyor or jammed gear.
These conditions can result in overheating of the motor, and equipment damage.
Rapid jam fault detection helps to minimize damage and loss of production.
By continuously monitoring the motor current level signal as a percentage of the
E1 Plus Overload Relay's dial FLA setting, the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module
allows jam trip and warning capability.
Jam Trip
The following parameters are available for configuring the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP
Module's jam trip performance:
• Parameter 18, Jam Inhibit Time, allows the installer to inhibit a jam trip
from occurring during the motor starting sequence. It is adjustable from
0…250 seconds.
• Parameter 19, Jam Trip Delay, allows the installer to define the time period
a jam condition must be present before a trip occurs. It is adjustable from
5…250 seconds.
• Parameter 20, Jam Trip Level, allows the installer to define the current at
which the E1 Plus Overload Relay will trip on a jam. It is user-adjustable
from 150…600% of the FLA dial setting.
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module will command the E1 Plus Overload Relay to
trip if all the following conditions are met:
• No trip currently exists
• Jam Protection is enabled
• Jam Inhibit Time has expired
• The motor current is greater than the Jam Trip Level for a time period
greater than the Jam Trip Delay
When the conditions for a jam trip are satisfied, the following will occur:
• Bit 2 in Parameter 3, Trip Sta tus , will go to “1”
• Bit 0 in Parameter 10, Device Status, will go to “1”
• The E1 Plus Overload Relay's trip relay contacts (95 and 96) will open
• Out A will be placed in their Protection Fault State (if so programmed)
The Protection Fault State of OUT A is defined by parameter 34 (OUTA
Pr FltState) and parameter 35 (OUTA Pr FltValue).
The jam inhibit timer starts after the load current transitions from 0 A
to 30% FLA. The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module does not begin
monitoring for a jam condition until the Jam Inhibit Time expires.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 15
Page 16

Chapter 2
IMPORTANT
Jam Warning
Parameter 21, Jam Warn Level, allows the installer to define the current at which
the EtherNet Module will indicate a warning. It is user-adjustable from
100…600% FLA.
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module will indicate a Jam warning if:
• No warning currently exists
• Jam Warning is enabled
• Jam Inhibit Time has expired
• The motor current is equal to or greater than the Jam Warn Level
When the Jam Warning conditions are satisfied, the following will occur:
• Bit 2 in Parameter 4, Warning Status, will go to “1”
• Bit 1 in Parameter 10, Device Status, will go to “1”
The Jam Warning function does not include a time delay feature.
Once the Jam Inhibit Time has expired, the Jam Warning indication is
instantaneous.
Underload Protection
Motor current less than a specific level may indicate a mechanical malfunction in
the installation, such as a torn conveyor belt, damaged fan blade, broken shaft, or
worn tool. Such conditions may not harm the motor, however, rapid detection
may help to minimize equipment damage and loss of production.
Underload Warning
The following parameters are available for configuring the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP
Module's underload warning performance:
• Parameter 22, UL Inhibit Time, allows the installer to inhibit an underload
indication from occurring during the motor starting sequence. It is
adjustable from 0…250 seconds.
• Parameter 23, UL Warn Level, allows the installer to define the current at
which the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module will indicate a warning. It is useradjustable from 30…100% of the FLA dial setting.
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module will immediately indicate an Underload
warning if:
• No warning currently exists
• Underload Warning is enabled
• UL Inhibit Time has expired
• The motor current is less than the UL Warn Level
16 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 17

Chapter 2
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
When the Underload Warning conditions are satisfied, the following will occur:
• Bit 3 in Parameter 4, War n in g S ta tu s , will go to “1”
• Bit 1 of Parameter 10, Device Status, will go to “1”
The Underload Warning function does not include a time delay
feature. Once the UL Inhibit Time has expired, the Underload warning
indication is instantaneous.
Communication Fault Protection
A disruption of the communication link between the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP
Module and a EtherNet/IP network can result in the loss of application control
and/or critical process diagnostic data. Rapid communication fault detection
helps minimize potential damage due to uncontrolled or unmonitored
applications.
Comm Fault Warning
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module will indicate a Comm Fault warning if:
• No warning currently exists
• Comm Fault Warning is enabled
• The EtherNet/IP Module experiences a loss of communication
When the Comm Fault warning conditions are satisfied, the following will occur:
• The Network Status LED will blink red or become solid red
• Bit 5 in Parameter 4, War n in g S ta tu s , will go to “1”
• Bit 1 of Parameter 10, Device Status, will go to “1”
The Comm Fault State of OUT A is defined by Parameter 36 (OUTA En
FltState) and parameter 37 (OUTA En FltValue).
Communication Idle Protection
When a programmable controller is placed into the program mode, the execution
of its ladder program is suspended, and any connected networks go to an idle
state. If inadvertent, this can result in the loss of application control and/or
critical process diagnostic data. Rapid communication idle detection helps
minimize the potential damage due to uncontrolled or unmonitored
applications.
Comm Idle Warning
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module will indicate a Comm Idle warning if:
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 17
Page 18

Chapter 2
IMPORTANT
• No warning currently exists
• Comm Idle Warning is enabled
• The network controller that is communicating to the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP
Module is placed in idle mode
When the Comm Idle warning conditions are satisfied, the following will occur:
• Bit 6 in Parameter 4, Wa r n in g S t at us , will go to “1”
• Bit 1 in Parameter 10, Device Status, will go to “1”
The Comm Idle State of OUT A is defined by Parameter 38 (OUTA En
IdlState) and parameter 39 (OUTA En IdlValue).
18 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 19
Chapter
3
Configure an E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module To Operate on the Network
Introduction
Determining Network
This chapter describes how to configure an E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module to
operate on an EtherNet/IP network.
When you first install an E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module, the module is Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) enabled.
To operate an EtherNet/IP network, you must define these parameters.
Parameters
Table 3 - EtherNet/IP Network Parameters
EtherNet/IP Network Parameter Description
IP address The IP address uniquely identifies the module. The IP address is in the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx where
Subnet mask Subnet addressing is an extension of the IP address scheme that allows a site to use a single
Gateway A gateway connects individual physical networks into a system of networks. When a node needs to
each xxx is a number from 0...255. These are reserved values you cannot use:
• 0.0.0.1...0.255.255.255
• 127.0.0.0...127.255.255.255
• 224.255.255.255...255.255.255.255
network ID for multiple physical networks. Routing outside of the site continues by dividing the IP
address into a net ID and a host ID via the class. Inside a site, the subnet mask is used to redivide
the IP address into a custom network ID portion and host ID portion.
If you change the subnet mask of an already-configured module, you must cycle power to
the module for the change to take effect.
communicate with a node on another network, a gateway transfers the data between the two
networks.
If you use DNS addressing, or reference the module via a host name in an MSG
instruction, then define these parameters.
Table 4 - EtherNet/IP Network Parameters for DNS Addressing
EtherNet/IP Network Parameter Description
Host name A host name is part of a text address that identifies the module. The full text address of a module is
Domain name A domain name is part of a text address that identifies the domain in which the module resides. The
Primary DNS server address This identifies any DNS servers used in the network. You must have a DNS server configured if you
Secondary DNS server address
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 19
host_name.domain_name.
full text address of a module is host_name.domain_name. The domain name has a 48-character
limit.
specify an SMTP server with a name. The DNS server converts the domain name or host name to an
IP address that can be used by the network.
For more information on DNS addressing, see page 26.
Page 20

Chapter 3
IMPORTANT
Check with your Ethernet network administrator to determine if you need to
specify these parameters.
Setting the IP Network Address
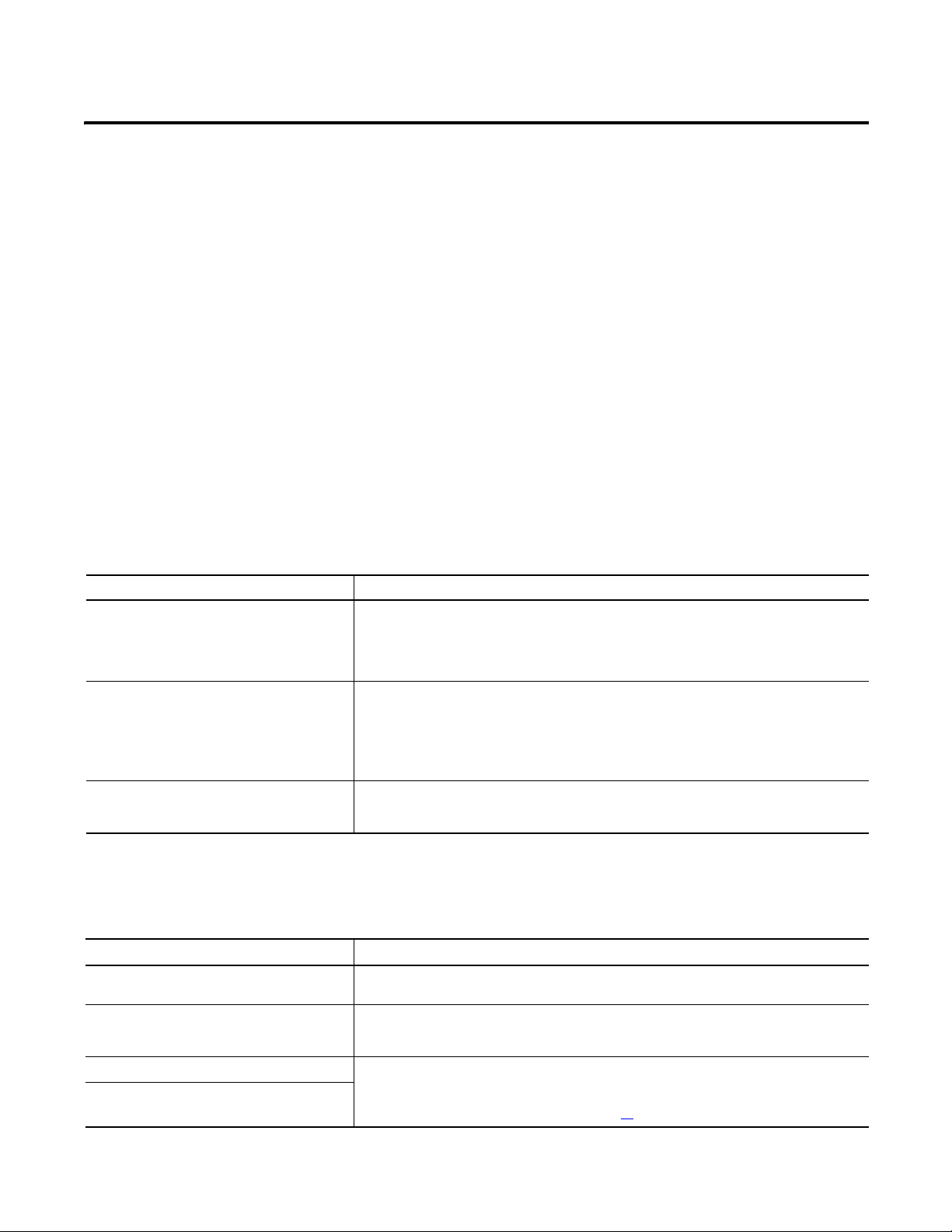
Assign Network Parameters via the BOOTP/ DHCP Utility
E1 Plus EtherNet/IP modules ship with DHCP enabled. You can set the network
Internet Protocol (IP) address by:
• Using a Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP)/Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) server, such as the Rockwell Automation BOOTPDHCP Server Utility, which is included with Rockwell Software’s
RSLinx™ Classic software
• Using a web browser and MAC Scanner software
By default, the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module is DHCP enabled. The BOOTP/
DHCP utility is a standalone program that is located in the:
• BOOTP-DHCP Server folder accessed from the Start menu.
Before you start the BOOTP/DHCP utility, make sure you have the
hardware MAC ID of the module, which is printed on the side of the
E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module. The MAC ID has a format similar to: 000b-db-14-55-35.
This utility recognizes DHCP-enabled devices and provides an interface to
configure a static IP address for each device.
To assign network parameters via the BOOTP/DHCP utility, perform this
procedure.
1. Start the BOOTP/DHCP software.
2. Select Tool → Network Settings.
3. If appropriate for the network, enter the subnet mask, gateway address,
primary/secondary server addresses, and domain name.
4. Click OK.
The Request History panel displays the hardware addresses of modules
issuing BOOTP or DHCP requests.
20 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 21
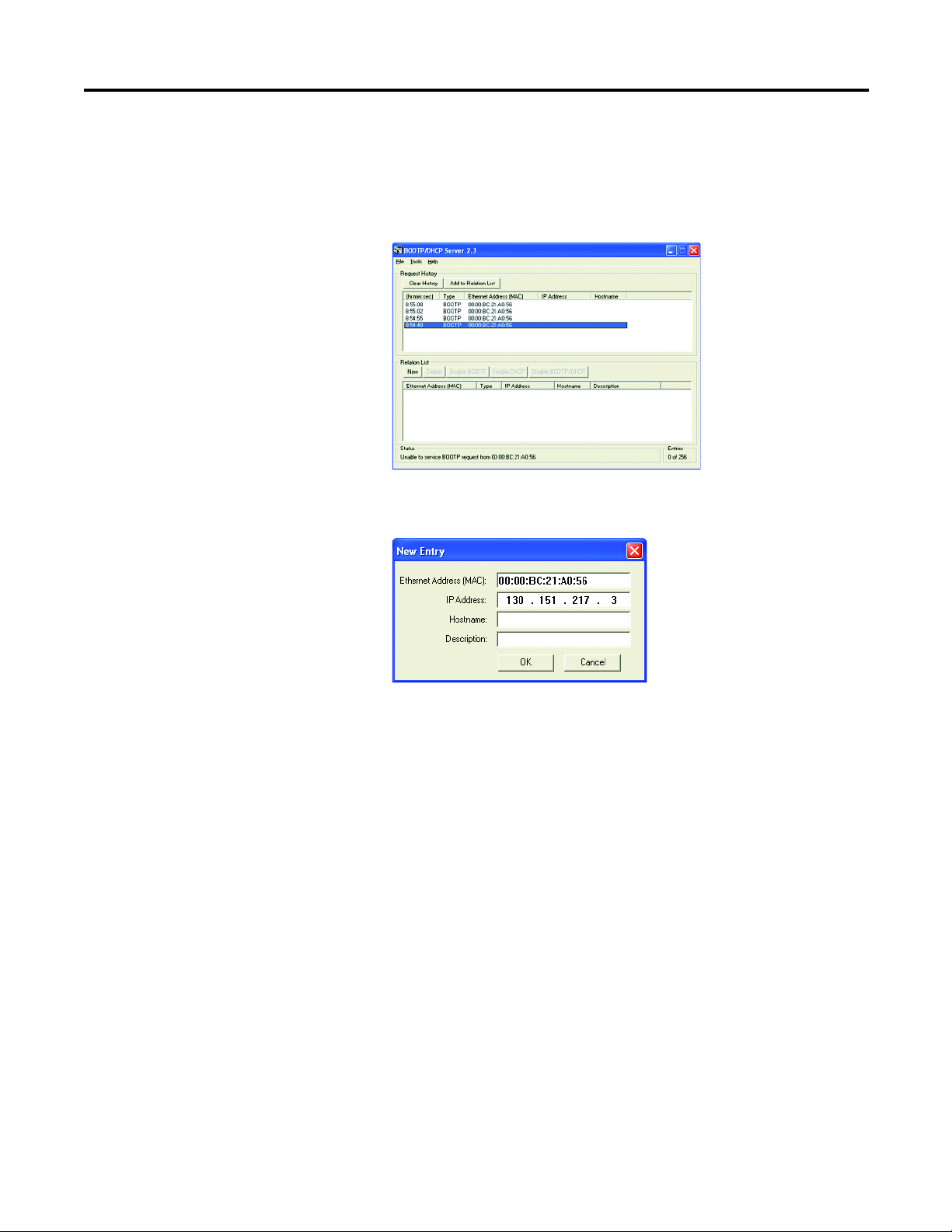
5. Double-click the MAC address of the module to be configured.
The MAC address is printed on the side of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP
module. The format of the hardware address resembles
00-0b-db-14-55-35.
The New Entry window appears with the module’s Ethernet Address
(MAC).
Chapter 3
6. Enter the IP address, host name, and a module description.
7. Click OK.
8. Re-cycle power to the module. To recycle power, remove and reapply the
control power terminals A1 and A2.
9. To permanently assign this configuration to the module, highlight the module in the Relation List panel and click the Disable BOOTP/DHCP button.
When module power is recycled, it uses the assigned configuration and
does not issue a DHCP request.
If you do not select the Disable BOOTP/DHCP button, on a power cycle,
the module clears the current IP configuration and will again begin
sending DHCP requests.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 21
Page 22
Chapter 3
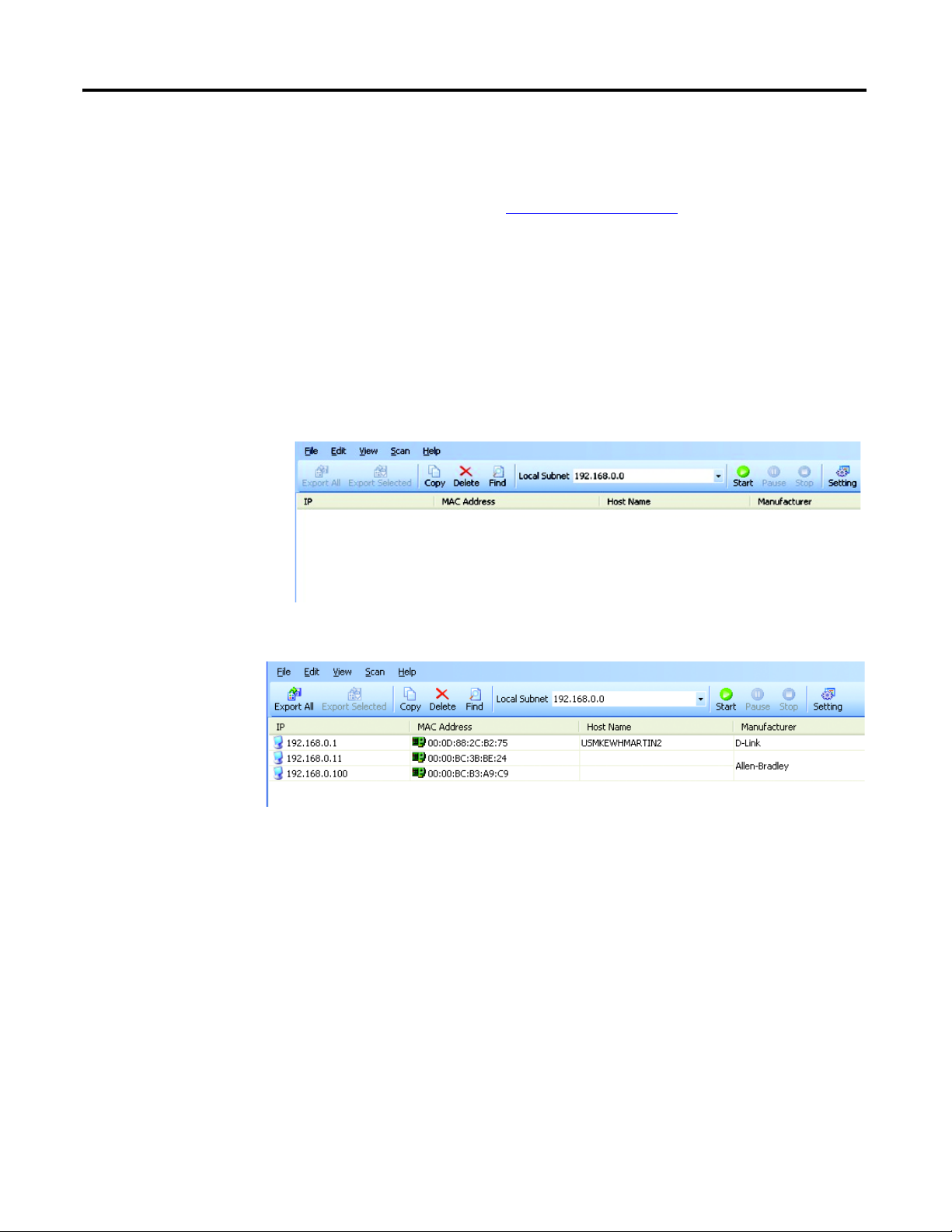
Assign Network Parameters Via a Web Browser and MAC Scanner Software
In the event that a user does not have access to a DHCP software utility, a user
can assign network parameters via a web browser, such as Microsoft’s Internet
Explorer, and Media Access Control (MAC) scanner software, such as MAC
Scanner from Colasoft - http://www.colasoft.com/
configure the module using this method.
. Follow these steps to
1. Locate and identify the MAC ID printed on the label of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module. This address has a format that is similar to: 00-0b-db-14-55-35
2. Connect the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module to the same Wide Area Network (WAN) as your personal computer.
3. Start the MAC scanner software
4. Select the appropriate subnet to scan for available MAC addresses.
5. Scan the Subnet for all available MAC addresses.
6. Identify the IP address assigned to the MAC ID of the E1 Plus EtherNet/
IP Side Mount Module. The IP address will have a format that is similar to
192.168.0.100.
22 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 23
Chapter 3
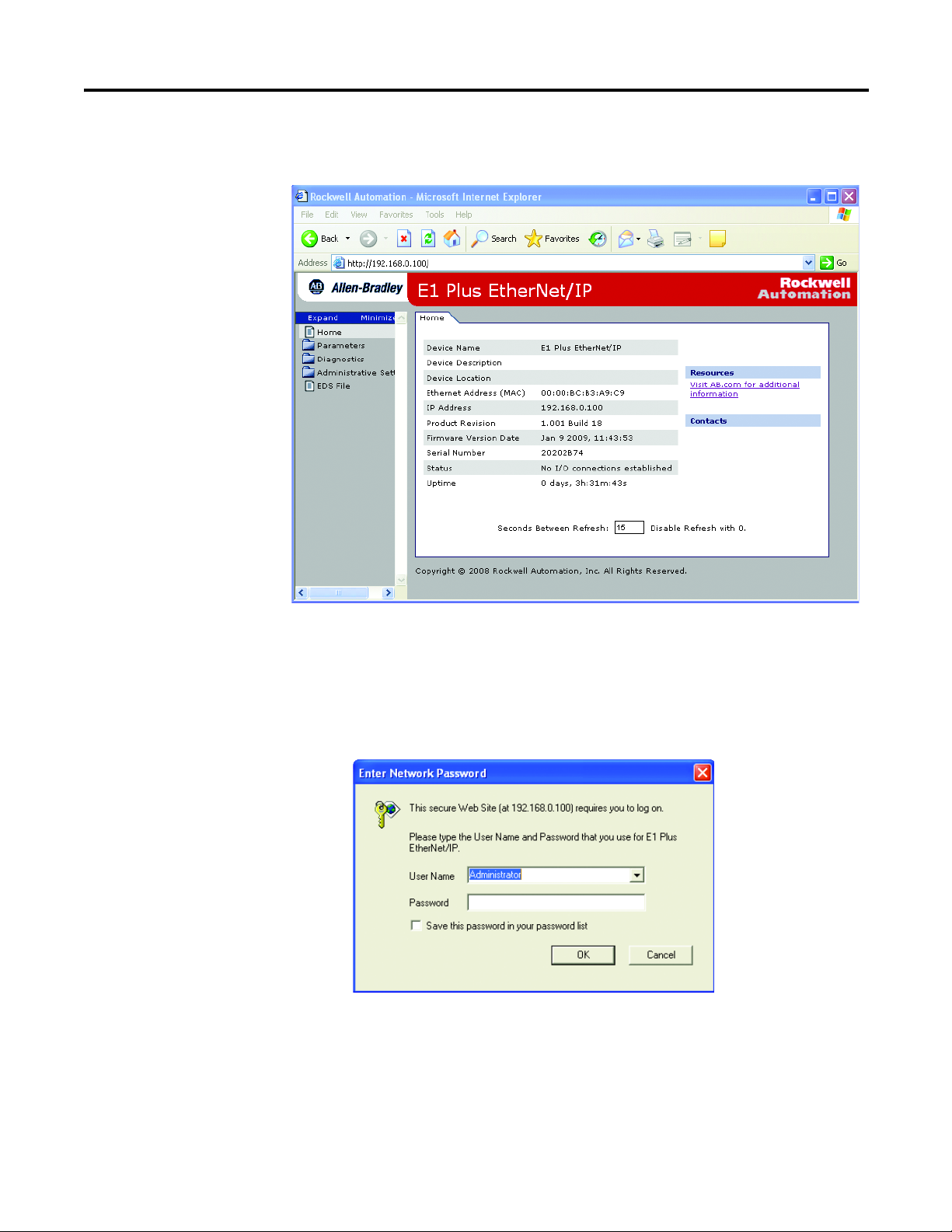
7. Open a web browser and type the IP address on the address line to view the internal web server of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module.
8. Select Administration Settings->Network Configuration to change the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module to a static IP address.
9. The module will prompt the user for a User Name and Password. Use “Administrator” for the user name, leave the password field blank, and select OK.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 23
Page 24
Chapter 3
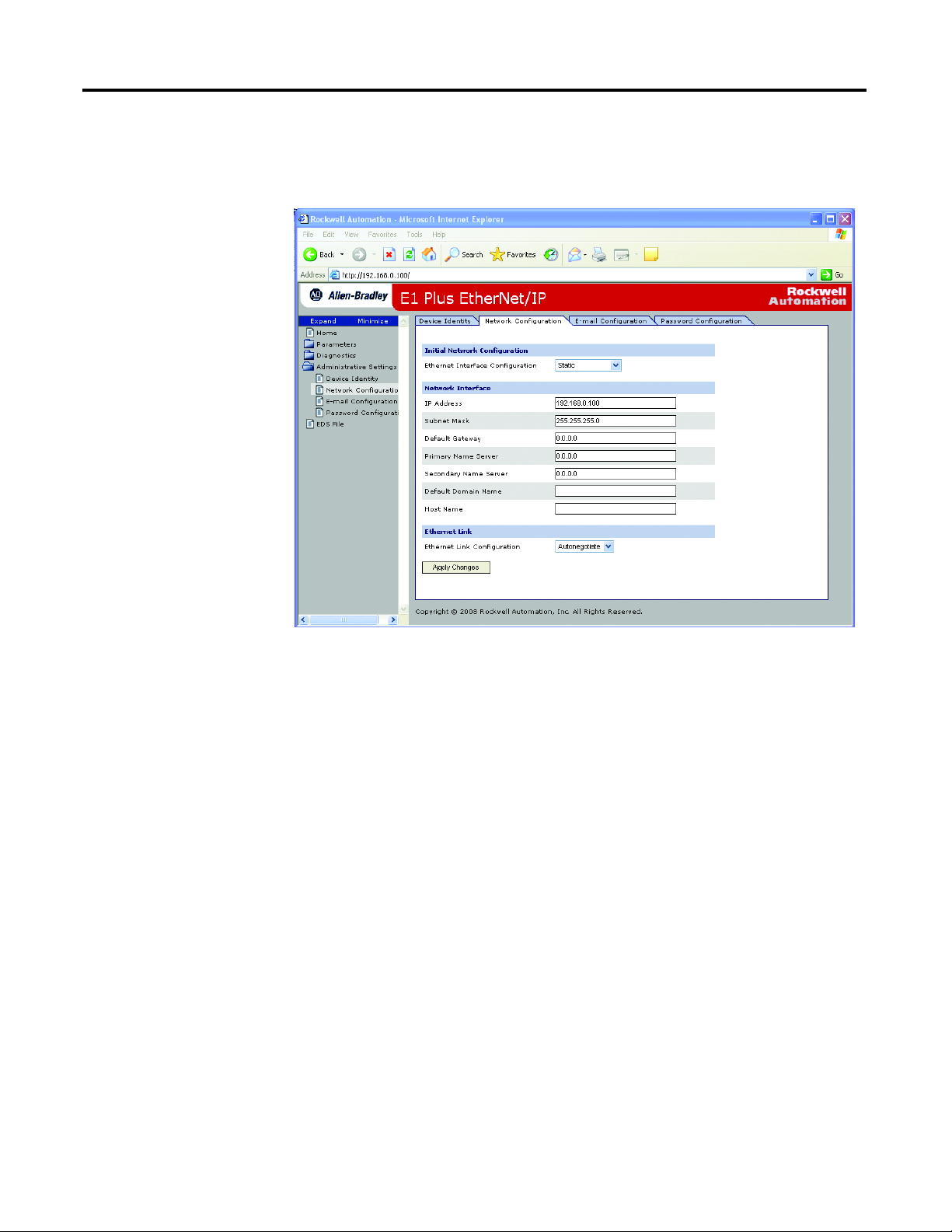
10. Assign the appropriate network settings per the recommendation of the network administrator for the network that this module will be communicating on and select Apply.
Other Factors to Consider When Assigning Network Parameters
11. Recycle the power on the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module for the communications changes to take affect. To recycle power, remove and reapply the control power terminals A1 and A2.
There are other factors to consider when assigning networks parameters, which
include:
• Network isolation from or integration into the plant/enterprise network
• Network size
For large networks, even isolated networks, it might be more convenient
and safer to use a BOOTP/DHCP server rather than RSLinx software.
The BOOTP/DHCP server also limits the possibility of assigning
duplicate IP addresses.
• Company policies and procedures dealing with plant floor network
installation and maintenance
• Level of involvement by IT personnel in plant floor network installation
and maintenance
• Type of training offered to control engineers and maintenance personnel
If you use the Rockwell Automation BOOTP or DHCP server in an uplinked
subnet where an enterprise DHCP server exists, a module may get an address
from the enterprise server before the Rockwell Automation utility even sees the
24 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 25

Chapter 3
module. You might have to disconnect from the uplink to set the address and
configure the module to retain its static address before reconnecting to the
uplink. This is not a problem if you have node names configured in the module
and leave DHCP enabled.
ATTENTION: The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module must be assigned a
fixed network address. The IP address of this module must not be
dynamically provided.
Failure to observe this precaution may result in unintended
machine motion or loss of process control.
Duplicate IP Address Detection
When you change the IP address or connect the module to an EtherNet/IP
network, the module checks to make sure that the IP address assigned to this
module does not match the address of any other network device. If the module
determines that another device on the network with a matching IP address, the
EtherNet/IP port of the module goes into conflict mode.
• NETWORK STATUS LED indicator is solid red.
To resolve this conflict, use the instructions in this chapter to change the IP
address of the module. Then cycle power to the module or reset the modules by
disconnecting and then reconnecting the EtherNet cable.
Two modules could possibly detect a conflict simultaneously. If this occurs,
perform this procedure.
1. Remove the module with the incorrect IP address and correct its conflict.
2. Cycle power or disconnect the EtherNet cable from the second module
and reconnect it.
Behavior of Modules With Duplicate IP Addresses
Devices in conflict over an IP address behave differently depending on whether
connections have been established to either of the modules and whether both
modules support duplicate IP address detection.
Table 5 - Device Conflict Over Duplicate IP Addresses
If Then
Both modules support duplicate IP address detection The first started module uses and retains its IP address.
The other module will detect a conflict, give up the IP address and enter conflict mode.
Both modules support duplicate IP address detection
and are started at roughly the same time
One module supports duplicate IP address detection
and a second module does not
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 25
One of them surrenders the IP address and enters conflict mode.
The second module generally keeps its IP address, regardless of which module first obtains the
IP address.
The module that supports duplicate IP address detection will detect the conflict and give up the
IP address.
Page 26

Chapter 3
DNS Addressing
Install EDS File
To further qualify a module’s address, use DNS addressing to specify a host name
for a module, which also includes specifying a domain name and DNS servers.
DNS addressing makes it possible to set up similar network structures and IP
address sequences under different domains.
DNS addressing is only necessary if you refer to the module by host name, such as
in path descriptions in MSG instructions.
To use DNS addressing, perform this procedure.
1. Assign a host name to the module.
A network administrator should be able to assign a host name. Valid host
names should be IEC-1131-3 compliant.
2. Configure the module's parameters.
3. In addition to the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address, configure
a host name for the module, domain name, and primary/secondary DNS
server addresses.
Before the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module is configured to
communicate on an EtherNet/IP network, it must be registered to the software
that configures the network such as Rockwell Software’s RSLinx Classic and
RSNetWorx for EtherNet/IP software. A user registers the module by installing
an Electronic Data Sheet (EDS file). The EDS file for the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP
Side Mount Module can be obtained from one of two locations:
• Embedded in the module
• Allen-Bradley EDS file download website
Download EDS File Embedded in the Module
The EDS file for the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module is embedded
within the module. After the IP address for the module has been configured,
connect the module to same Ethernet network as a personal computer. Using a
web browser on the personal computer, a user can download the EDS file using a
web browser by following these steps:
26 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 27
Chapter 3
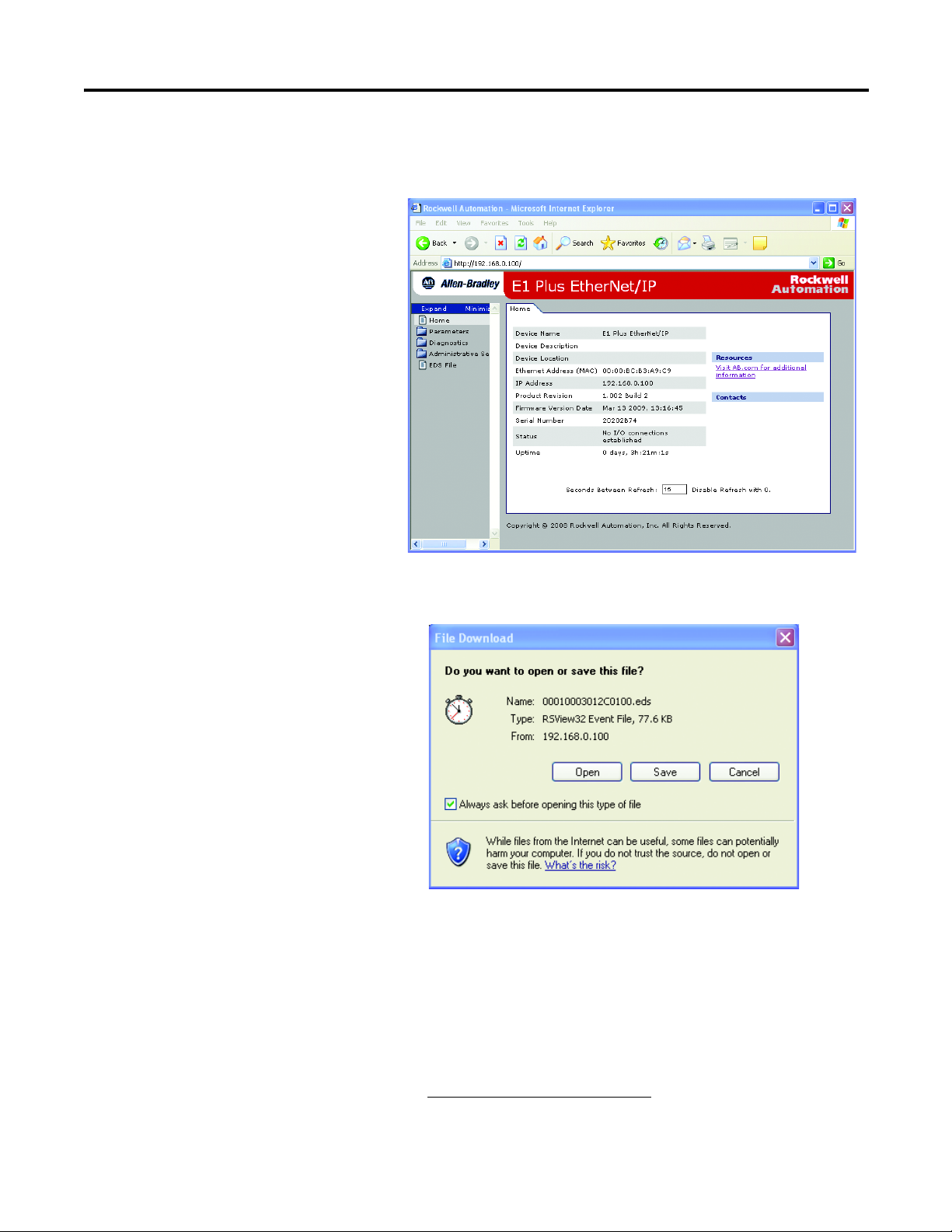
1. Type the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module on
the address line of the web browser.
2. Right click on the EDS File link
3. Select Save to save the EDS file to the personal computer.
Download EDS File from Allen-Bradley EDS File Download Site
The EDS file for the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module can also be
downloaded from the Allen-Bradley EDS File download site. Using a web
browser on the personal computer that is connected to the Internet, a user can
download the EDS file by following these steps:
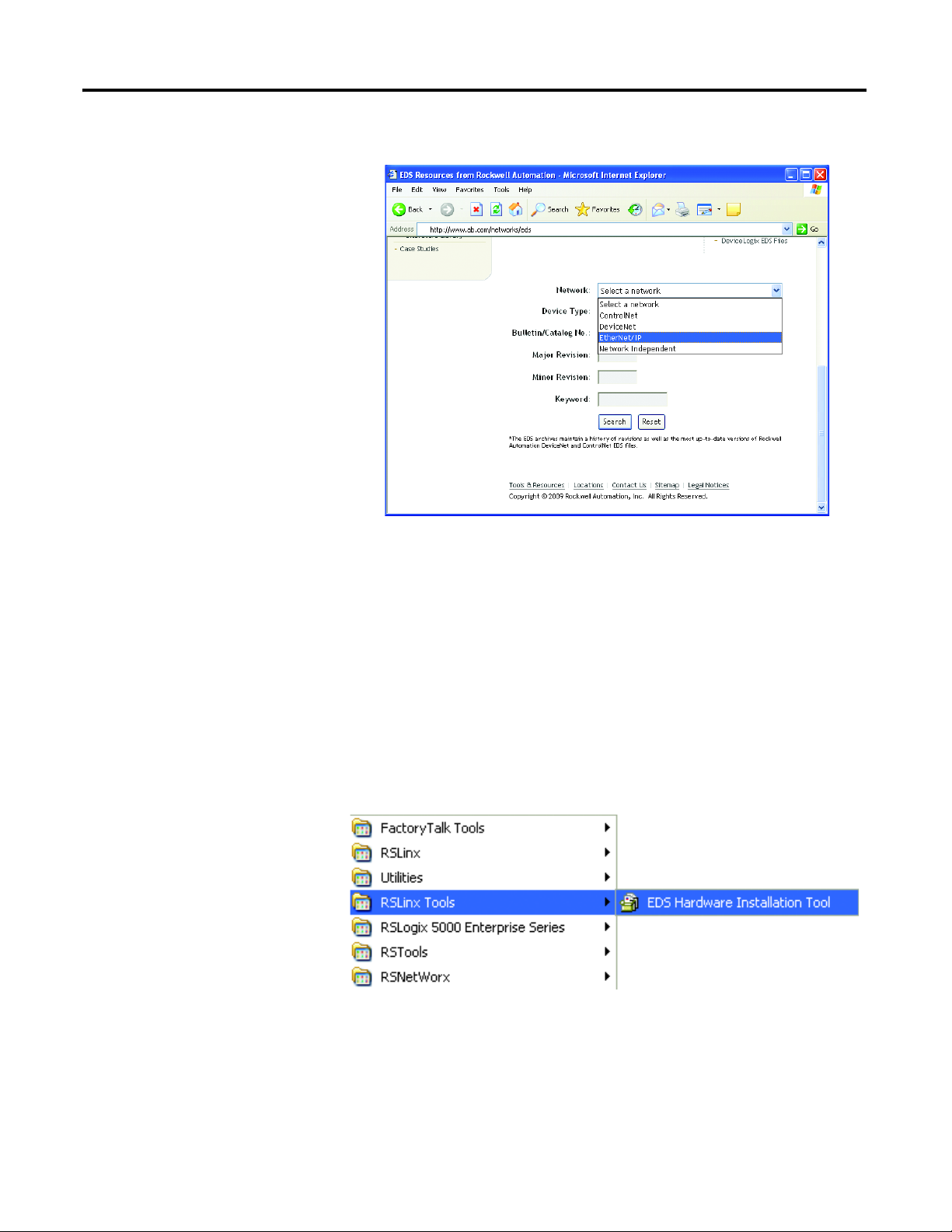
1. Type http://www.ab.com/networks/eds
on the address line of the web
browser.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 27
Page 28
Chapter 3
2. Select the network type as EtherNet/IP and select Search.
3. Locate the EDS file for the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module and
download it to the personal computer.
Register the EDS File
After the EDS file has been downloaded, a user will need to register the EDS file
with the software that configures the EtherNet/IP network. The following
example lists the steps needed to register an EDS file with Rockwell Software’s
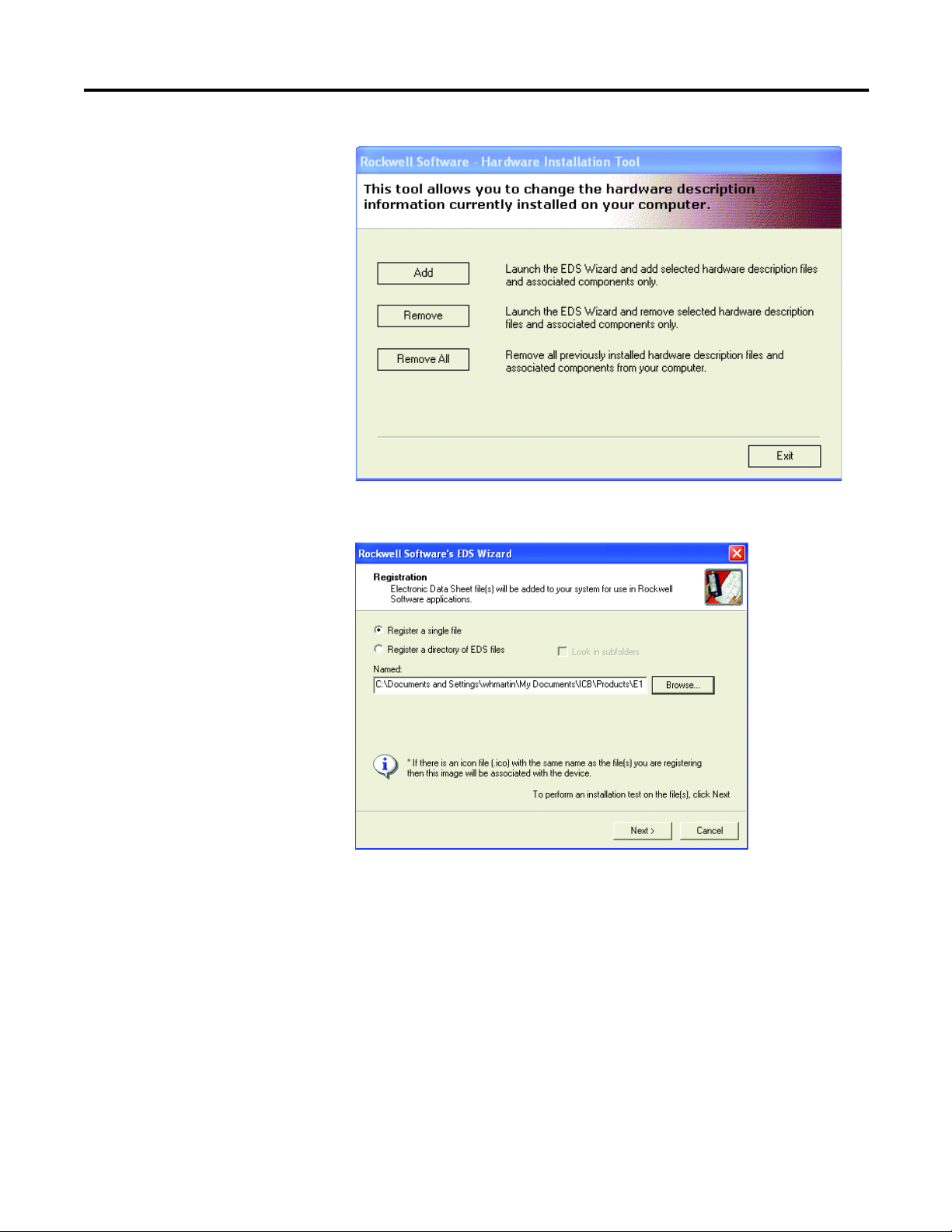
RSLinx Classic software.
1. Start the EDS Hardware Installation Tool, located at Start->Programs>Rockwell Software->RSLinx Tools.
2. Select Add to register a new device.
28 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 29
Chapter 3
3. Register a single file, browse to the location where the EDS file is located, and select Next.
4. Select Next to accept the installation test results.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 29
Page 30
Chapter 3
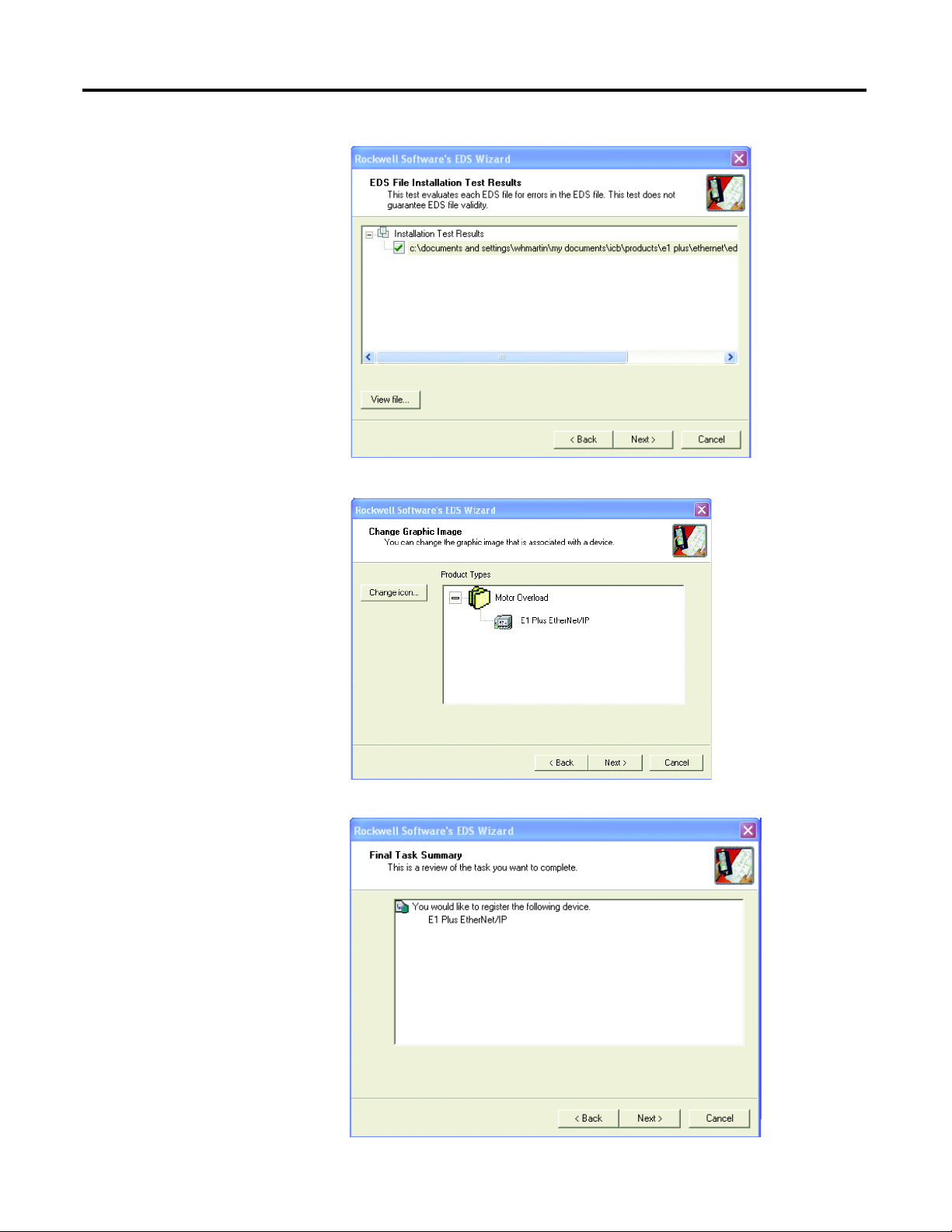
5. Accept the Graphic Image by selecting Next.
6. Select Next to register the device.
30 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 31

7. Select Finish to successfully register the module.
Chapter 3
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 31
Page 32

Chapter 3
32 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 33

Chapter
Automation Controller and Software Communications
4
Introduction
I/O Messaging
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module supports three types of EtherNet/
IP messaging:
• I/O Messaging — Used for deterministic Ethernet communications with
ControlLogix™, CompactLogix™, SoftLogix™, and EtherNet/IP scanners.
Its primary use is to read and write I/O data for control purposes.
• Explicit Messaging — Used for non-deterministic communications in
which the data is not critical for control. Explicit messages have a lower
priority compared to I/O messages, and they are used to read and write
non-critical data. Logix controllers, MicroLogix 1100 and 1400 controllers
support Explicit Messaging using a MSG instruction.
• ControlLogix Style Tags — Used for non-deterministic communications
in which the data will is used in an HMI, SCADA, or historical data
logging software system. Software packages can read and write data
directly from the device.
This chapter describes and shows examples of how each type of messaging is used.
RSLogix 5000™ software is used to configure I/O messaging between an
automation controller and an E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module on an
EtherNet/IP Network. This example will show the steps necessary to configure a
ControlLogix controller for this type of messaging.
Note: If you are not using Add-on
profiles, please turn to page 38
.
ControlLogix Configuration with Add-On Profiles
If you have RSLogix 5000 v. 20.0, the E1 Plus add-on profile (AOP) is included.
Proceed with the following instructions. If you do have v. 19 or earlier, download
the AOP before proceeding.
An existing project can be used or a new project can be created to configure
EtherNet/IP I/O messaging. To create a new configuration in RSLogix 5000,
select File → New.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 33
Page 34

Chapter 4
1. Select the controller type, chassis type, slot number, and project path. Enter a name for the controller and click OK.
2. Right-click on I/O Configuration and select New Module to open the Select Module Type window.
34 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 35

3. Select the desired EtherNet/IP scanner module and click OK.
4. Enter the desired communication settings and click Finish.
Chapter 4
EtherNet/IP Network Configuration with Add-On Profiles
After the controller configuration, the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module
has to be added to the I/O configuration.
1. Place the program in Offline mode.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 35
Page 36

Chapter 4
2. Right-click on the Ethernet/IP scanner in I/O Configuration and select New Module to open the Select Module Type window.
3. Select E1 Plus Ethernet Module and click OK.
4. Enter a name for the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module. The name
will create a tag in RSLogix 5000 that can be used to read and write data
from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module.
36 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 37

Chapter 4
5. Enter the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module.
6. Click Next.
7. The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module is now shown as a module
in the I/O configuration.
Accessing Module Data with Add-On Profiles
With both the controller and EtherNet/IP network configured, the
ControlLogix controller can exchange data with the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side
Mount Module.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 37
Page 38

Chapter 4
1. Open the Controller Tags window.
2. Select the Monitor Tags tab.
Three tags, "E1Plus:C", "E1Plus:I" and "E1Plus:O", have been added to
represent the three I/O Instances: Configuration, input and output. The
Configuration Instance was created even though its size was configured as
zero. The E1Plus:I tag represents input data, which is data coming from
the E1Plus into the controller (%FLA, %TCU, Trip Status, Warning
Status, etc.). The E1 Plus:O tag represents output data, which is data going
from the controller out to the E1 Plus (Enable Output A, Trip Reset, etc.).
ControlLogix Generic Configuration
An existing project can be used or a new project can be created to configure
EtherNet/IP I/O messaging. To create a new configuration in RSLogix 5000,
select File → New.
38 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 39

Chapter 4
1. Select the controller type, chassis type, slot number, and project path. Enter a name for the controller and click OK.
2. Right-click on I/O Configuration and select New Module to open the Select Module Type window.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 39
Page 40

Chapter 4
3. Select the desired EtherNet/IP scanner module and click OK.
4. Enter the desired communication settings and click Finish.
EtherNet/IP Network Generic Configuration
After the controller configuration, the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module
has to be added to the I/O configuration.
1. Place the program in Offline mode.
40 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 41

Chapter 4
2. Right-click on the Ethernet/IP scanner in I/O Configuration and select New Module to open the Select Module Type window.
3. Select Generic Ethernet Module and click OK.
4. Enter a name for the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module. The name
will create a tag in RSLogix 5000 that can be used to read and write data
from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module.
5. Select Data-SINT for the Comm Format. The Comm Format tells RSLogix 5000 the format of the data. The Data-SINT format will represent the data from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module as a field of 8-bit values.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 41
Page 42

Chapter 4
6. Set the Connection Parameters. I/O data is accessed using Input Instances
50, 51, 106, 110 or 111 and Output Instances 2, 101 or 103. The size of
the input connection and the output connection shall correspond to the
size of the chosen instance. The E1 Plus configuration assembly instance is
120. In this example configuration data is not used, so the data size is set to
0.
7. Enter the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module.
8. Click Next.
9. Enter a value for the time between each scan of the module. Make sure
Inhibit Module is not checked.
10. Click Finish to add the E1 Plus to the I/O Configuration in RSLogix 5000.
42 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 43

Chapter 4
Downloading the Generic Configuration to the PLC
1. In the RSLogix 5000 program, select Communications → Who Active.
2. Select the desired communication path and click Set Project Path.
3. Select Communications → Go Online.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 43
Page 44

Chapter 4
4. In the Connected To Go Online window, click Download.
5. In the Download confirmation window, click Download to download the
configuration to the PLC.
If there are any errors, a warning triangle will be present on the E1 Plus in
the I/O configuration listing.
Double-click the module to view any error that is reported.
Accessing Generic Module Data
With both the controller and EtherNet/IP network configured, the
ControlLogix controller can exchange data with the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side
Mount Module.
1. Go online and switch the controller to Remote Run mode.
44 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 45
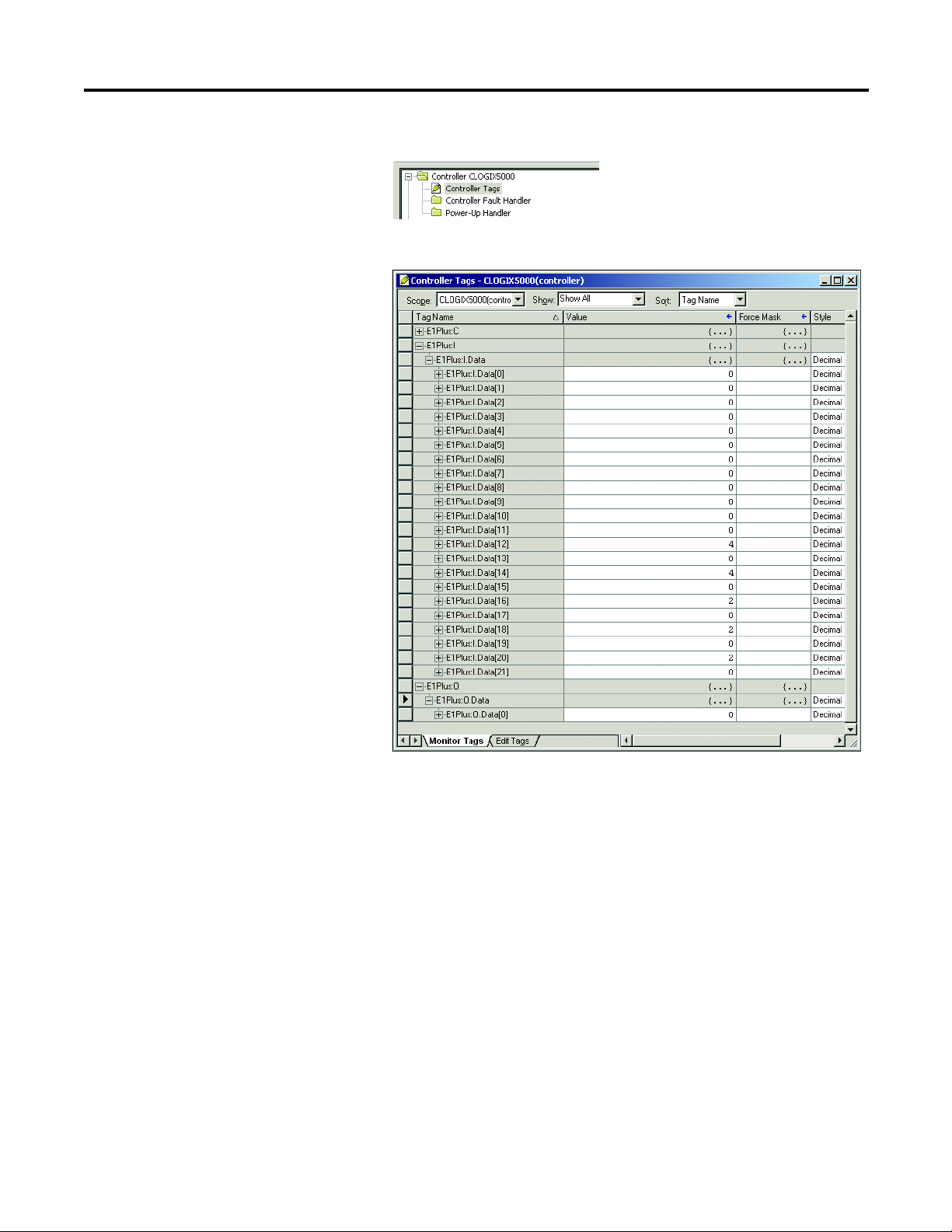
2. Open the Controller Tags window.
3. Select the Monitor Tags tab.
Chapter 4
Logix Explicit Messaging
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 45
Three tags, "E1Plus:C", "E1Plus:I" and "E1Plus:O", have been added to
represent the three I/O Instances: Configuration, input and output. The
Configuration Instance was created even though its size was configured as
zero. The E1Plus:I tag represents input data, which is data coming from
the E1Plus into the controller (%FLA, %TCU, Trip Status, Warning
Status, etc.). The E1 Plus:O tag represents output data, which is data going
from the controller out to the E1 Plus (Enable Output A, Trip Reset, etc.).
CompactLogix, ControlLogix, and SoftLogix controllers can read and write
specific information to and from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module
using Explicit Messaging and the Parameter Object. An example of configuring a
ControlLogix explicit message using the MSG instruction to read the Device
Status parameter data from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module is
shown below.
Page 46

Chapter 4
1. Configure the configuration tab for the message instruction with the follow settings:
• Message type: CIP Generic
• Service type: Parameter Read
• Instance: 10: The parameter you want to read back (e.g., 10 represents
device status)
• Destination: The controller tag to write the data to.
2. Configure the path field in the communications tab to point to the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module.
Path: 1, 2, 2, 192.168.0.100
For this example, 1 represents the processor slot, 2 represents the
EtherNet/IP scanner slot, 2 represents the EtherNet/IP port, and
192.168.0.100 represents the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side
Mount Module.
46 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 47

Chapter 4
Users can read all of the motor diagnostic data back in one MSG instruction by
using Assembly Instance 111. An example of configuring a ControlLogix explicit
message using the MSG instruction to read all of the motor diagnostic data from
the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module is shown below.
1. Configure the configuration tab for the message instruction with the follow settings:
• Message type: CIP Generic
• Service type: Get Attribute Single
• Class: 4 – the Assembly Object
• Instance: 111 - the Complete Motor Starter assembly
• Destination: The controller tag to write the data to.
• Attribute: 3 – get/set data instance attribute
2. Configure the path field in the communications tab to point to the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module.
Path: 1, 2, 2, 192.168.0.100
For this example, 1 represents the processor slot, 2 represents the
EtherNet/IP scanner slot, 2 represents the EtherNet/IP port, and
192.168.0.100 represents the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side
Mount Module.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 47
Page 48

Chapter 4
MicroLogix 1100 and 1400 Explicit Messaging
MicroLogix 1100 and 1400 controllers can read and write information to and
from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module using Explicit Messaging and
the Assembly Object. RSLogix 500 Version 8.10 or higher is required to
configure EtherNet/IP explicit messaging with these controllers.
An example of a MicroLogix 1100 using the MSG instruction to read all of the
motor diagnostic data from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module is
shown below.
1. Write the appropriate ladder logic to periodically execute a MSG instruction for the MicroLogix controller.
2. Configure General tab in the MSG instruction with the following parameters:
• Channel: 1 (Integral) - the Ethernet port on the processor
• Communication Command: CIP Generic
• Data Table Address: the location to store the information
• Size in Bytes: 22 – assembly 111 consists of 22 bytes of information
• MultiHop: Yes
• Service: Read Assembly – to read an input assembly
48 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 49

• Class: 4 – the Assembly Object
• Instance: 111 – the Complete Motor Starter assembly
• Attribute: 3 – get/set data instance attribute
Chapter 4
3. Configure MultiHop tab in the MSG instruction with the following parameters:
To Address: the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount
Module.
An example of a MicroLogix 1100 using the MSG instruction to write data to
energize an output relay on the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module is
shown below.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 49
Page 50

Chapter 4
1. Write the appropriate ladder logic to execute a MSG instruction for the MicroLogix controller (an EEM instruction for the SLC-5/05) to control the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module.
2. Configure General tab in the MSG instruction with the following parameters:
• Channel: 1 (Integral) - the Ethernet port on the processor
• Communication Command: CIP Generic
• Data Table Address: the location to write the information from
• Size in Bytes: 1 – assembly 101 consists of 1 byte of information
• MultiHop: Yes
• Service: Write Assembly – to write an output assembly
• Class: 4 – the Assembly Object
• Instance: 101 – the Basic Contact output assembly
• Attribute: 3 – get/set data instance attribute
50 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 51

Chapter 4
3. Configure the MultiHop tab in the MSG instruction with the following parameters:
To Address: the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount
Module.
FactoryTalk View with Predefined Tags
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module embedded predefined CIP tags
within the module. This allows software packages, such as FactoryTalk View
Supervisory Edition (SE), to read and write data directly from the E1 Plus
EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module. An example of using RSLinx Classic as an
OPC (OLE for Process Control) server to serve data to FactoryTalk View SE is
show below. Follow these steps to read data directly from the E1 Plus EtherNet/
IP Side Mount Module using its predefined tags.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 51
Page 52

Chapter 4
1. Configure an OPC topic within RSLinx Classic to communicate to the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module. In the Data Source tab, select New to create a new OPC topic name, high light the device to establish communications with, and press Apply.
2. In the Data Collection tab, select the process type Logix5000 and select Apply
52 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 53

Chapter 4
3. Start FactoryTalk View Studio and create a new application. Draw a numeric display. Right click on the display and select Connections.
4. Select the Tag selector tool to select a tag from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module.
5. Right click on the project name and select Refresh All Folders to get an updated list of topics to read data from.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 53
Page 54

Chapter 4
6. Expand the OPC topic name that you created in RSLinx Classic, select the
Online folder, choose the tag you would like to display in the numeric
display, and press OK.
7. Select OK to select the tag to display in the numeric display.
54 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 55

Chapter 4
8. Test the display by pressing the Test Run button to view data directly from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module on the display.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 55
Page 56

Chapter 4
56 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 57

Email Notifications
IMPORTANT
Chapter
5
Introduction
Notification Events
This chapter describes email notifications and how to configure an E1 Plus
EtherNet/IP module to send email notifications for different events.
There are several events that can trigger an email notification; the events are listed
below.
• Overload trip
• Phase loss trip
• Jam trip
• Tri p c le ar
• Overload warning
• Jam warning
• Underload warning
• Communication fault warning
• Communication idle warning
• EEPROM fault warning
• Warning clear
If an event has been disabled within the Control Supervisor Attribute
108 or 109 (see page 90
emails generated.
), it is not possible to override this and have
Email Contents
The subject and body contents in the email message will be created from the type
of trip or warning that is detected, the Device Name, Device Description, Device
Location and Contact Info. Sample email messages are shown here:
Email Subject
E1Plus module has detected a trip
Email Body
Trip status: Overload
Device Name: E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module
Device Description: Module under development
Device Location: The Location
Contact Info: Contact Person
contact.person@thecontact.com
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 57
Page 58

Chapter 5
The first word in the subject is the Device Name. If a Device Name is not
configured, then the product name attribute from the identity object will be used.
Email Configuration
To be able to send an email, the IP address or the hostname of a Simple Mail
Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server must be configured and notifications must be
selected. Follow these steps to configure an email notification.
1. In a web browser, enter the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module in the address bar and press Enter.
2. Select Administrative Settings → email Configuration, and a login
window will appear.
3. Log in with the username "Administrator" and no password. If desired, a password can be set within the Administrative Settings tab Password Configuration.
58 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 59

Chapter 5
Email Recipient The email address of the person who will receive the notifications.
Email Sender The email address from which the notification will be sent.
SMTP Server The SMTP server address. Ask your network administration what address
to use.
SMTP Username The username for the SMTP server. Ask your network administration what
username to use.
SMTP Password The password for the SMTP server. Ask your network administration what
password to use.
SMTP Port The SMTP Server Port. Ask your network administration what port number
to use (Port 25 is a common SMTP port).
4. Enter the information into the email notification fields as described below.
5. Select the specific fault and warning notifications to send to the email
recipient. These can be changed after the initial configuration.
6. Click "Apply Changes" to save the configuration.
Configure Device Identity
The Device Identity properties populate the notification email subject and body.
To configure the Device Identity, perform these steps:
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 59
Page 60

Chapter 5
1. In a web browser, enter the IP address of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module in the address bar and press Enter.
2. Select Administrative Settings → Device Identity and a login window will
appear.
3. Log in with the username "Administrator" and no password. If desired, a password can be set within the Administrative Settings tab Password Configuration.
60 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 61

Chapter 5
Device Name The name of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module.
Device Description The description of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module.
Device Location The location of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module.
Contact Info Contact information for the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module.
4. Enter the Device Identity information into the fields as described below.
Limitations
5. Click "Apply Changes" to save the configuration.
Based on the functionality of the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP module there are some
limitations on when emails can be triggered.
• If two events occur at the same time, an email will only be sent for the most
significant event.
• If the module has been configured to send an email for a lower prioritized
event and this event occurs at the same time as a higher prioritized event
for which the module has not been programmed to send an email, no email
will be sent for either event.
• The Clear email will only be sent when all events have been cleared and an
event email has previously been sent. For example: if the module is
configured to send an email when a jam trip is detected and it detects an
overload trip for which no email notification is configured , no email will be
sent when the overload event is cleared.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 61
Page 62

Chapter 5
62 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 63

Device Parameters and Tags
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
Chapter
6
Introduction
Parameter and Tag Programming
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module allows the Parameter Object to
respond to explicit messages using the MSG instruction from Logix Controllers
and SLC-500/MicroLogix controllers. The module also supports the Symbolic
Object, which allows software packages such FactoryTalk View to communicate
directly to the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Side Mount Module as if it were a Logix
Controller with predefined tags. This chapter describes each parameter and tag.
Refer to Chapter 3, Configure an E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module To Operate on the
Network, for instructions to modify EtherNet/IP parameter settings.
Parameter setting changes to the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module take
effect immediately even during a “running” status.
Program Lock
Parameter 24, Program Lock, provides a degree of security from having parameter
settings unintentionally altered when programmed to the “locked” setting.
Resetting to the Factory Default Values
Parameter 25, Set to Default, allows the installer to reset all parameter settings
(including trip logs) to the factory default values.
Resetting to factory default values also resets the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP
Module’s IP and DHCP settings.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 63
Page 64

Chapter 6
Parameter Group Listing
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module contains five parameter groups
Table 6 - Parameter Groups
Monitor parameters Advanced Setup Reset/Lock I/O Setup Trip History
1 Average %FLA 12 Trip Enable 14 Trip Reset 34 OutA Pr FltState 5 Trip Log 0
2%Therm Utilized 13 Warning Enable 24 Program Lock 35 OutA Pr FltValue 6 Trip Log 1
3 Trip Status 15 Single/Three Ph 25 Set to Default 36 OutA En FltState 7 Trip Log 2
4 Warning Status 16 OL Reset Mode 37 OutA En FltValue 8 Trip Log 3
10 Device Status 17 OL Warning Level 38 OutA En IdlState 9 Trip Log 4
18 Jam Inhibit Time 39 OutA En IdlValue
19 Jam Trip Delay 40 IN1 Assignment
20 Jam Trip Level 41 IN2 Assignment
21 Jam Warn Level
22 UL Inhibit Time
23 UL Warn Level
Monitor Group
Average %FLA Parameter No. 1
This parameter reports the average motor current.
The value is reported as a percentage of motor
rated current (dial setting on the E1 Plus Overload
Relay), and is reported in increments of 5.
% Therm Utilized Parameter No. 2
This parameter reports the percent thermal
utilization of the connected motor.
Access Rule Get
Data Type UINT
Units %
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1275
Default Value 0
Tag Name Average_%FLA
Access Rule Get
Data Type USINT
Units %
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 100
Default Value None
Tag Name %_Therm_Utilized
64 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 65

Trip Status Parameter No. 3
This parameter provides trip identification.
1 = Trip
0 = No Trip
Bit 0: Overload — Tag Name: Trip_Status: Overload
Bit 1: Phase Loss — Tag Name: Trip_Status: Phase_Loss
Bit 2: Jam — Tag Name: Trip_Status: Jam
Access Rule Get
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x0007
Default Value 0x0000
Chapter 6
Warning Status Parameter
This parameter provides warning identification
1 = Warning
0 = No Warning
Bit 0: Overload — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Overload
Bit 2: Jam — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Jam
Bit 3: Underload — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Underload
Bit 5: Comm Fault — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Comm_Fault
Bit 6: Comm Idle — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Comm_Idle
Bit 7: Non Vol Mem Fault — Tag Name: NV_Mem_Fault
Device Status Parameter
This parameter provides status information related to the E1 Plus
Overload Relay and the SMM.
1 = On or Present
0 = Off or Not Present
Bit 0: Trip — Tag Name: Device_Status: Trip
Bit 1: Warning — Tag Name: Device_Status: Warning
Bit 2: Output A — Tag Name: Device_Status: Out_A
Bit 3: Input #1 — Tag Name: Device_Status: In_1
Bit 4: Input #2 — Tag Name: Device_Status: In_2
Bit 5: Motor Current — Tag Name: Device_Status: Motor_Current
No.
Access Rule Get
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x00FF
Default Value 0x0000
No.
Access Rule Get
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x003F
Default
Value
Advanced Setup Group
4
10
0x0000
Trip Enable Parameter No. 12
This parameter allows the installer to enable or
disable the Jam Trip function
1 = Enabled
0 = Disabled
Bit 2: Jam— Tag Name: Trip_Enable: Jam
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 65
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x0007
Default Value 0x0000
Page 66

Chapter 6
Warning Enable Parameter
This parameter allows the installer to enable or disable the warning
functions separately. All warning functions are disabled from the
factory.
1 = Enabled
0 = Disabled
Bit 0: Overload — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Overload
Bit 2: Jam — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Jam
Bit 3: Underload — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Underload
Bit 5: Comm Fault — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Comm_Fault
Bit 6: Comm Idle — Tag Name: Warning_Status: Comm_Idle
Single/Three Ph Parameter No. 15
This parameter configures the EtherNet/IP
Module for single- or three-phase application.
This parameter should be set to “Single Phase"
when Bulletin 193S or 592S devices are
employed.
0 = Single Phase
1 = Three Phase
OL Reset Mode Parameter No. 16
This parameter defines whether a trip can be
automatically or manually reset. This setting
overrides the E1 Plus DIP switch adjustment while
the SMM is powered. Note, however, that the E1
Plus manual reset button, accessible at the front,
is always active.
0 = Manual
1 = Automatic
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 1
Tag Name Single_Three_Ph
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name OL_Reset_Mode
No.
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x007F
Default Value 0x0000
13
OL Warning Level Parameter No. 17
This parameter sets the overload warning level. Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type USINT
Units % TCU
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 100
Default Value 90
Tag Name OL_Warning_Level
66 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 67

Jam Inhibit Time Parameter No. 18
This parameter defines the amount of time for
which jam detection is inhibited during a motor
starting sequence.
Jam Trip Delay Parameter No. 19
This parameter allows the installer to program a
time duration for which a jam condition must exist
at the programmed level prior to the device
tripping.
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type USINT
Units Seconds
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 250
Default Value 10
Tag Name Jam_Inhibit_Time
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type USINT
Units Seconds
Min. Value 5
Max. Value 250
Default Value 50
Tag Name Jam_Trip_Delay
Chapter 6
Jam Trip Level Parameter No. 20
This parameter sets the jam trip level. Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type UINT
Units % FLA
Min. Value 150
Max. Value 600
Default Value 250
Tag Name Jam_Trip_Level
Jam Warn Level Parameter No. 21
This parameter sets the jam warning level. Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type UINT
Units % FLA
Min. Value 100
Max. Value 600
Default Value 150
Tag Name Jam_Warn_Level
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 67
Page 68

Chapter 6
UL Inhibit Time Parameter No. 22
This parameter defines the amount of time for
which underload detection is inhibited during a
motor starting sequence.
UL Warn Level Parameter No. 23
This parameter sets the underload warning level. Access Rule Get/Set
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type USINT
Units Seconds
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 250
Default Value 10
Tag Name UL_Inhibit_Time
Data Type USINT
Units % FLA
Min. Value 30
Max. Value 100
Default Value 70
Tag Name UL_Warn_Level
Reset/Lock Group
Trip Reset Parameter No. 14
This parameter provides the user with the
capability of resetting a trip over the EtherNet/IP
network. After a trip is reset, the parameter
automatically returns to a “Ready” state.
0 = Ready
1 = Reset Trip
Note: A transition from 0 to 1 is necessary to
trigger a trip reset when mapped on the cyclic
data.
Program Lock Parameter No. 24
This parameter prohibits the device parameters
from being altered when set to “Locked”. It must
be set to “Unlocked” to allow parameter
modification.
It doesn’t affect parameters when they’re
accessed through the assembly object.
0 = Unlocked
1 = Locked
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name Trip_Reset
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name Program_Lock
68 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 69

Set To Defaults Parameter No. 25
This parameter allows the user to reset the
parameter settings to the factory default values.
After parameter values have been reset to the
factory default settings, the parameter
automatically returns to a “Ready” state.
0 = Ready
1 = Reset Defaults
Note: A transition from 0 to 1 is necessary to
trigger a set to default when mapped on the cyclic
data.
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name Set_To_Default
I/O Setup Group
OutA Pr FltState Parameter No. 34
This parameter, in conjunction with the Pr
FltValue, defines how Output A will respond when
a trip occurs. When set to “1”, Output A will
continue to operate as commanded via the
network. When set to “0”, Output A will open or
close as determined by the setting of the Pr
FltValue.
0 = Go to FltValue
1 = Ignore Fault
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name OutA_Pr_FLTState
Chapter 6
OutA Pr FltValue Parameter No. 35
This parameter determines the state that Output A
assumes when a trip occurs and the Pr FltState is
set to “0”.
0 = Open
1 = Closed
OutA En FltState Parameter No. 36
This parameter, in conjunction with the FltValue,
defines how Output A will respond when a
EtherNet/IP network fault occurs. When set to
“1”, Output A will hold the state prior to trip
occurrence. When set to “0”, Output A will open
or close as determined by the setting of the
FltValue.
0 = Go to FltValue
1 = Hold Last State
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name OutA_Pr_FLTValue
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name OutA_En_FLTState
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 69
Page 70

Chapter 6
OutA En FltValue Parameter No. 37
This parameter determines the state that Output A
assumes when a EtherNet/IP network fault occurs
and the FltState is set to “0”.
0 = Open
1 = Closed
OutA En IdlState Parameter No. 38
This parameter, in conjunction with the IdlState,
defines how Output A will respond when the
EtherNet/IP network is idle (clear mode). When
set to “1”, Output A will hold the state prior to trip
occurrence. When set to “0”, Output A will open
or close. The En Flt parameters supersede the En
Idl parameters.
0 = Go to IdlValue
1 = Hold Last State
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name OutA_En_FLTValue
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name OutA_En_IdlState
OutA En IdlValue Parameter No. 39
This parameter determines the state that Output A
assumes when the network is idle and instructed
by the IdlState parameter.
0 = Open
1 = Closed
IN1 Assignment Parameter No. 40
This parameter allows the user to assign a
specific function to the discrete IN1 input.
0 = Normal
1 = Trip Reset
2 = OL Contact
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type BOOL
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 1
Default Value 0
Tag Name OutA_En_IdlValue
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type USINT
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 2
Default Value 0
Tag Name IN1_Assignment
70 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 71

IN2 Assignment Parameter No. 41
This parameter allows the user to assign a
specific function to the discrete IN2 input.
0 = Normal
1 = Trip Reset
2 = OL Contact
Access Rule Get/Set
Data Type USINT
Units —
Min. Value 0
Max. Value 2
Default Value 0
Tag Name IN2_Assignment
Trip History Group
Trip Log 0 Parameter No. 5
This parameter records the latest trip. Access Rule Get
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x0007
Default Value 0x0000
Tag Name Trip_Log_0
Chapter 6
Trip Log 1 Parameter No. 6
This parameter records the trip previous to Trip
Log 0.
Trip Log 2 Parameter No. 7
This parameter records the trip previous to Trip
Log 1.
Access Rule Get
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x0007
Default Value 0x0000
Tag Name Trip_Log_1
Access Rule Get
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x0007
Default Value 0x0000
Tag Name Trip_Log_2
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 71
Page 72

Chapter 6
Trip Log 3 Parameter No. 8
This parameter records the trip previous to Trip
Log 2.
Trip Log 4 Parameter No. 9
This parameter records the trip previous to Trip
Log 3.
Access Rule Get
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x0007
Default Value 0x0000
Tag Name Trip_Log_3
Access Rule Get
Data Type WORD
Units —
Min. Value 0x0000
Max. Value 0x0007
Default Value 0x0000
Tag Name Trip_Log_4
72 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 73

Troubleshooting
Chapter
7
Introduction
The purpose of this chapter is to assist in troubleshooting the E1 Plus EtherNet/
IP module.
ATTENTION: Servicing energized industrial control equipment can
be hazardous. Electrical shock, burns, or unintentional actuation of
controlled industrial equipment may cause death or serious injury.
For safety of maintenance personnel, as well as other who may be
exposed to electrical hazards associated with the maintenance
activities, follow the local safety-related work practices (for
example, the NFPS 70W, Part II, Electrical Safety for Employee
Workplaces, in the United States) when working on or near
energized equipment. maintenance personnel must be trained in
the safety practices, procedures, and requirements that pertain to
their respective job assignments. Do not work alone on energized
equipment.
ATTENTION: Do not attempt to defeat or override fault circuits.
The cause of a fault indication must be determined and corrected
before attempting operation. Failure to correct a control system or
mechanical malfunction may result in personal injury and/or
equipment damage due to uncontrolled machine system operation.
EtherNet/IP Modes of Operation
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module has four EtherNet/IP modes of operation:
Power-Up Reset Mode, Run Mode, Recoverable Error Mode, and Unrecoverable
Error Mode.
Power-Up Reset Mode
During Power-Up Reset Mode, the following occurs:
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 73
Page 74

Chapter 7
IMPORTANT
1. The MODULE STATUS LED should flash green for approximately 1/4
second, then red for 1/4 second. The MODULE STATUS LED will then
stay lit green and the NETWORK STATUS LED should flash green for
approximately 1/4 second, then red for 1/4 second before turning off. The
NETWORK STATUS LED and the MODULE STATUS LED will now
return to their standard indication.
The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module protection functions are still
operational even without an established network connection.
2. The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module performs a duplicate IP address check to
verify another module is not assigned to the same IP address. If a duplicate
IP address is detected on the network, the NETWORK STATUS LED
turns solid red, the MODULE STATUS LED turns flashing red, and the
E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module enters the Recoverable Error Mode.
If the power-up or reset is successful, the overload relay will enter Run Mode.
Run Mode
In Run Mode, the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module will operate as a slave device to a
master device. The NETWORK STATUS LED will blink green if there are no
network connections established with a network master. When one or more
connections are in the “established” state, the NETWORK STATUS LED will
turn solid green. When one or more connections are in the “timed-out” state, the
NETWORK STATUS LED will blink red. In the Run Mode, the E1 Plus
EtherNet/IP Module will:
• Accept messages from a master on the EtherNet/IP network.
• Send response messages, COS messages, or CYCLIC messages to a master.
If a communication error is detected, the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module will either
enter the Recoverable Error or Unrecoverable Error Mode.
Recoverable Error Mode
In Recoverable Error Mode, the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module’s MODULE
STATUS LED turns flashing red. The overload relays will respond to messages
that are specified in offline node recovery message protocol.
Error Type Description LED State
Recoverable Duplicate IP address detected Flashing Red
74 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 75

Chapter 7
Unrecoverable Error Mode
In Unrecoverable Error Mode, the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module’s MODULE
STATUS LED turns solid red. The overload relay continues in this state as long as
the device is powered.
Error Type Description LED State
Unrecoverable Power-up initialization failure Solid Red
Fatal communication error
EtherNet/IP
Troubleshooting
The following table identifies possible causes and corrective actions when
troubleshooting EtherNet/IP-related failures using the NETWORK STATUS
LED.
Procedures
Table 7 - EtherNet/IP Troubleshooting Procedures
Color State Possible Cause Corrective Action
None The E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module is not receiving power
Green
Red
Off
Green Flashing E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module is online but with no
Green Solid Normal operating state, and the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP
Red Flashing One or more connections timed-out. Reset EtherNet/IP master device.
Red Solid 1. Diagnostics test failed on power-up/reset. Internal
Flashing (once) Normal The Network Status LED flashes green, red, and off once
at the EtherNet/IP connector.
connections established.
Module is allocated to a master.
fault exists.
2. Duplicate EtherNet/IP module address exists (two EtherNet/IP modules cannot have the same address).
3. A fatal communication error occurred.
Check EtherNet/IP power and cable connections and the
power connection on the EtherNet/IP connector.
during a normal power-up sequence.
Check EtherNet/IP master and its scan list for correct
scanner configuration.
No action required.
1. Cycle power to the unit and network. If the fault still exists, replace unit.
2. Change the IP address to a valid setting and reset the device.
3. Check EtherNet/IP media for proper installation.
Input and Output Troubleshooting Procedures
ATTENTION: If the outputs are to be commanded via an explicit
message, ensure that there can never be an established I/O
connection that can actively control them, and that the explicit
message connection has a non-zero expected packet rate (EPR)
setting.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 75
Page 76

Chapter 7
Table 8 - Input and Output Troubleshooting Procedures
Failure Type Failure Description Corrective Action
Input 1, 2 Input 1 or 2 does not appear
to recognize a contact
closure
1. Check the supply voltage on the power connector.
2. If the applicable contact closed but the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module Input does not recognize the closure, check the continuity and wiring to the connected contact.
3. Check the IN 1 and 2 status LEDs. If the appropriate LED does not illuminate, measure the voltage
across and current through the applicable input. Verify they are within the ratings of the E1 Plus
EtherNet/IP Module (See Appendix A).
4. If the appropriate Input LED does illuminate, but the input status is not reported properly over the EtherNet/IP network, check the programmable controller ladder logic and I/O mapping.
Input 1, 2 Trip reset operation Check the programming of Parameter 40, IN1 Assignment or Parameter 41, IN2 Assignment.
OUT A Output A does not appear to
turn on (close) when
commanded to do so.
OUT A Output A does not appear to
turn off (open) when
commanded to do so.
OUT A The contactor connected to
Output A appears to
“chatter”
1. Check the supply voltage on the
2. Check the OUTA status LED. If the appropriate LED does not illuminate, check the programmable controller ladder logic and I/O mapping.
3. If the appropriate Output LED is illuminated, remove the control circuit power and check for
continuity across the appropriate output terminals (13/14). If the continuity test indicates the
output is open, replace the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module. Check the supply voltage against
the ratings of the contactor and the relay output before installing a new unit.
4. Remove control circuit power and check the control circuit fuse and the control wiring to the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module output terminals.
5. Check the control circuit power supply. Verify the voltage is within the contactor and overload relay ratings.
6. Check the DEVICE STATUS and TRIP STATUS parameters. If a Protection Fault exists, refer to the TRIP STATUS parameters. If a EtherNet/IP-related fault exists, refer to the EtherNet/IP troubleshooting procedure.
7. Check the OUTA Pr FltState, Pr FltValue, En FltState, En FltValue, En IdlState, and En IdlValue programmable parameters. The Pr FltState and Pr FltValue parameter supersede the En Flt or En Idle parameters.
1. Check the OUTA status LED. If the appropriate LED remains illuminated, check the programmable controller ladder logic and I/O mapping.
2. If the appropriate Output LED is not illuminated, remove the control circuit power and check for
continuity across the appropriate output terminals (13/14). If the continuity test indicates the
output is closed, replace the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module. Check the supply voltage against
ratings of the contactor and the relay output before installing a new unit.
3. Remove control circuit power and check the control circuit fuse and the control wiring to the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module output terminals.
4. Check the OUTA Pr FltState, Pr FltValue, En FltState, En FltValue, En IdlState, and En IdlValue
programmable parameters. Then check the DEVICE STATUS and TRIP STATUS parameters. If a
Protection Fault exists, refer to the TRIP STATUS parameters. If a
exists, refer to the EtherNet troubleshooting procedure.
1. Verify the OUT A LED remains in the appropriate On or Off state. If the LED is flickering, check the programmable controller’s ladder logic program.
2. Check the control circuit supply voltage. Verify it is within the ratings of the contactor coil and the overload relay’s outputs.
3. Remove the control circuit power. Verify all control wiring is properly secured.
power connector.
EtherNet/IP-related fault
76 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 77

Specifications
Appendix
Specifications
Terminal Ratings:
Terminal Screw M3
Wire Cross Section See wiring diagram section
Torque 0.56…0.79 N•m (5…7 lb.-in)
Degree of Protection IP20
Power Supply Ratings:
Rated Supply Voltage U
Rated Operating Range U
Rated Supply Current I
Maximum Surge Current at Power-Up 2.5 A
Maximum Power Consumption 2.7 W
Output Relay Ratings:
Te rm in al s
OUT A: 13/14
Type of Contacts Form A
Rated Thermal Current I
Rated Insulation Voltage U
Rated Operating Voltage U
Rated Operating Current I
Minimum Operating Current 10 mA at 5V DC
Rating Designation B300
Utilization Category AC-15
Resistive Load Rating
(p.f.=1.0)
Inductive Load Rating
(p.f.=0.4), (L/R=7 ms)
Short Circuit Current Rating 1,000 A
Recommended Control Circuit Fuse KTK-R-6
Rated Number of Operations
Out A:
W/100-C-09…100-C43
W/100-C-60…100-C85
W/NEMA Size 0…2
W/NEMA Size 3
Input Ratings:
s
e
e
the
i
e
e
24V DC
24V -15%, +10% DC
110 mA at 24V DC
SPST - NO
5 A
300V AC
240V AC
3 A (at 120V AC), 1.5 A (at 240V AC)
0.25 A (at 110V DC), 0.1 A (at 220V DC)
5 A, 250V DC
5 A, 30V DC
2 A, 250V AC
2 A, 30V DC
(6 A, 600V)
5,000,000
2,500,000
1,000,000
300,000
A
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 77
Page 78

Appendix A
Te rm in al s
IN 1:
IN 2:
SSV (Sensor Supply Voltage)
1
2
3
Supply Voltage (provided by module) 24V DC±10%
Type of Inputs Current Sinking
ON-State Voltage 15V DC
On-State Current (turn-on) 2 mA
Steady State Current 5 mA
Off-State Voltage 5V DC
Off-State Current 0.5 mA
Transition Voltage 5…15V DC
Transition Current 0.5…2.0 mA
Environmental Ratings:
Ambient Temperature T
Storage
amb
-40…+85°C (-40…+185°F)
Operating
(Open)
(Enclosed)
-20…+60°C (-4…+140°F)
-20…+40°C (-4…+104°F)
Humidity
Operating
Damp Heat - Steady State
Damp Heat - Cyclic
5…95% non-condensing
per IEC 68-2-3
per IEC 68-2-30
Cooling Method Natural Convection
Vibration (per IEC 68-2-6) 3 G
Shock (per IEC 68-2-27) 30 G
Maximum Altitude 2000 m
Pollution Environment Pollution Degree 2
Terminal Marking EN 50012
Degree of Protection IP20
Electromagnetic Compatibility
Electrostatic Discharge Immunity
Test Level
Performance Criteria
8 kV Air Discharge; 4 kV Contact Discharge
1➊➋
RF Immunity
Test Level
Performance Criteria
10V/m
1➊➋
Electrical Fast Transient/Burst Immunity
Test Level
Performance Criteria
2 kV (Power); 1 kV (control)
1➊➋
Surge Immunity
Test Level
Performance Criteria
2 kV L-E; 1 kV L-L
1➊➋
Radiated Emissions Class A
Conducted Emissions Not tested
➊
Performance Criteria 1 requires the DUT (device under test) not to experience degradation or loss of
performance.
➋ Environment 2 - Heavy Industrial.
78 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 79

Appendix A
WARNING: This is a class A product. In domestic environment, this product may
cause radio interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate
measures.
EtherNet/IP Communications:
Connections
TCP
CIP
CIP Unconnected Messages 128
Packet Rates (packets/second)
I/O
HIM/MSG
Media Support
Twisted Pair
Fiber
Speed Duplex (Half/Full) 10/100
Duplicate IP Detection Yes
Jam Protection:
Trip Level 150…600% FLA
Trip Delay 0.1…25.0 sec.
Inhibit 0…250 sec.
Standards and Certifications
UL 508
CSA 22.2, No. 14
EN 60947-4-1
150
48
500
500
Yes
No
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 79
Page 80

Appendix A
80 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 81

EtherNet/IP Information
Appendix
B
Electronic Data Sheets
EtherNet/IP Objects
Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) files are specially formatted ASCII files that provide
all of the information necessary for a configuration tool (e.g., RSNetWorx for
EtherNet/IP) to access and alter the parameters of a device. The EDS file
contains all the parameter information of a device: number of parameters,
groupings, parameter name, min., max, and default values, units, data format and
scaling. The EDS file for the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module is available from the
Internet at www.ab.com/networks/eds/index/html
automatically by some configuration tools since all of the information necessary
for an EDS file may be extracted from the E1 Plus EtherNet/IP Module.
The following object classes are supported.
Table 9 - EtherNet object Classes
Class Object
0x01 Identity
0x02 Message Router
0x04 Assembly
0x06 Connection Manager
0x08 Discrete Input Point
0x09 Discrete Output Point
0x0F Parameter
0x10 Parameter Group
0x29 Control Supervisor
0x2C Overload
0xC2 PCP
0xF5 TCP/IP Interface
0xF6 Ethernet Link
. It can also be built
Identity Object — CLASS CODE 0x01
The following class attributes are supported for the Identity Object:
Table 10 - Identity Object Class Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0001
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 81
Page 82

Appendix B
Identity Object instances contain the following instance attributes:
Table 11 - Identity Object Instance Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Vendor ID UINT Programmable via test object
2 Get Device Type UINT 0x0003
3 Get Product Code UINT 300
4 Get Revision Structure of:
Major Revision USINT 1
Minor Revision USINT N/A
5 Get Status WORD Bit 0: Owned, shall be set when at least one connection i
6 Get Serial Number UDINT Unique number assigned for each device
7 Get Product Name SHORT_STRING Product name
8 Get State USINT 3=Operational
configured
Bit 1: Reserved, set to 0
Bit 2: Configured
Bit 3: Reserved, set to 0
Bit 4-7: See extended device status
Bit 8: Minor Recoverable fault
BIt 9: Minor Unrecoverable fault
Bit 10: Major Recoverable fault
Bit 11: Major Unrecoverable fault
Bit 12-15: Reserved, set to 0
Extended device status (Bit 4-7)
0000=Unknown
0001=Firmware updated in progress
0010=Faulted I/O connection
0011=No I/O connection established
0100=Non volatile configuration bad
0101=Major fault
0110=Connection in run mode
0111=Connection in idle mode
The following common services are implemented for the Identity Object:
Table 12 - Identity Object Common Services
Service Code Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
0x01 No Yes Get Attribute All
0x0E Yes Yes Get Attribute Single
0x05 No Yes Reset
Message Router Object — CLASS CODE 0x02
No class or instance attributes are supported. The message router object exists
only to rout explicit messages to other objects.
82 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 83

Assembly Object — CLASS CODE 0x04
The following class attributes are supported for the Assembly Object:
Table 13 - Assembly Object Class Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0002
2 Get Max Instance UINT 120
Instance Attributes
Instances/Connection points implements the following data attributes:
Table 14 - Instance Attributes
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get Number of members in
list
2 Get Member list Array of N/A Array of CIP paths
3 Get/Set Data Array of UINT — Data produced/consumed by the module
4 Get Size UINT N/A No. of USINTs in attribute #3
100 Get Name SHORT_STRING N/A Name of the assembly instance
UINT N/A No. of members to follow in the list in attribute #2
Appendix B
Output Assemblies
The following output assembly instances are implemented:
Table 15 - Instance 2 — Basic Overload Output Assembly from ODVA Profile
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Trip Reset
Table 16 - Instance 101 — Similar to Basic Contact Output Assembly from ODVA Contact Profile
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Output A
Table 17 - Instance 103 — Similar to Basic Starter Output Assembly from ODVA Starter Profile
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Trip Reset Output A
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 83
Page 84

Appendix B
Input Assemblies
Table 18 - Instance 50 — Trip Status Input Assembly from ODVA Overload Profile
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Tripped
Table 19 - Instance 51 —Basic Status Input Assembly from ODVA Overload Profile
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Warning Tripped
Table 20 - Instance 106 —Motor Starter Input Assembly
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Motor
Current
Table 21 - Instance 110 —Extended Motor Starter Input Assembly
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Motor
Current
1Unused
2 Average % FLA (low byte)
3 Average % FLA (high byte)
4 %Therm Utilized (low byte)
5 %Therm Utilized (high byte)
Table 22 - Instance 111 —Complete Motor Starter Input Assembly
Input 2 Input 1 Out A Stat Warning Tripped
Input 2 Input 1 Out A Stat Warning Tripped
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Motor
Current
1Unused
2 Average % FLA (low byte)
3 Average % FLA (high byte)
4 %Therm Utilized (low byte)
5 %Therm Utilized (high byte)
6 Trip Status (low byte)
7 Trip Status (high byte)
8 Warning Status (low byte)
9 Warning Status (high byte)
10 Device Status (low byte)
11 Device Status (high byte)
12 Trip Log 0 (low byte)
13 Trip Log 0 (high byte)
14 Trip Log 1 (low byte)
15 Trip Log 1 (high byte)
Input 2 Input 1 Out A Stat Warning Tripped
84 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 85

Appendix B
Table 22 - Instance 111 —Complete Motor Starter Input Assembly
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
16 Trip Log 2 (low byte)
17 Trip Log 2 (high byte)
18 Trip Log 3 (low byte)
19 Trip Log 3 (high byte)
20 Trip Log 4 (low byte)
21 Trip Log 4 (high byte)
The following services are implemented for the Assembly Object:
Table 23 - EtherNet Object Common Services
Service
Code
0x0E Yes Yes Yes Get Attribute Single
0x10 No Yes No Set Attribute Single
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
Consuming
Instance
Producing
Connection Manager Object — CLASS CODE 0x06
No class or instance attributes are supported.
The following common service are implemented for the Connection Manager
Object:
Table 24 - Connection Manager Object Common Services
Service Code Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
0x54 No Yes Forward Open
0x4E No Yes Forward Close
Discrete Input Point Object — CLASS CODE 0x08
The following class attributes are supported for the Discrete Input Point Object:
Table 25 - Discrete Input Point Object Class Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0002
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0x0002
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 85
Page 86

Appendix B
Two instances of the Discrete Input Point Object are supported as follows:
Table 26 - Discrete Input Point Object Instances
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
3 Get Value BOOL 0=OFF
1=ON
The following common services are implemented for the Discrete Input Point
Object:
Table 27 - Discrete Input Object Common Services
Service
Code
0x0E Yes Yes Get Attribute Single
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
Discrete Output Point Object — CLASS CODE 0x09
The following class attributes are supported for the Discrete Output point
Object:
Table 28 - Discrete Output Point Object Class Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0001
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0x0001
A single instance is implemented and contains the following attributes:
Table 29 - Discrete Output Point Object Instance 1 - Output A
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
3 Get Value BOOL 0=OFF
5 Get/Set Fault Action BOOL 0=Fault Value
6 Get/Set Fault Value BOOL 0=OFF
7 Get/Set Idle Action BOOL 0=Fault Value
8 Get/Set Idle Value BOOL 0=OFF
113 Get/Set Pr Fault Action BOOL 0=Pr Fault Value
114 Get/Set Pr Fault Value BOOL 0=OFF
1=ON
Attribute
1=Hold Last State
1=ON
Attribute
1=Hold Last State
1=ON
Attribute
1=Ignore
1=ON
86 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 87

Appendix B
The following common services are implemented for the Discrete Output Point
Object:
Table 30 - Discrete Output Object Common Services
Service
Code
0x0E Yes Yes Get Attribute Single
0x10 No Yes Set Attribute Single
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
Parameter Object — CLASS CODE 0x0F
The following class attributes are supported for the Parameter Object:
Table 31 - Parameter Object Class Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0001
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0x0029
8 Get Parameter Class Descriptor WORD 0x000B
9 Get Configuration Assembly Instance UINT 0x0078
10 Get Native Language UINT 0x01=English
The following instance attributes are implemented for all parameter attributes:
Table 32 - Parameter Object Instance Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get/Set Value Specified in Descriptor N/A
2 Get Link Path Size USINT N/A
3 Get Link Path Packed EPATH: Path to specified object attribute
4 Get Descriptor WORD Parameter Dependent
5 Get Data Type EPATH Parameter Dependent
6 Get Data Size USINT Parameter Dependent
7 Get Parameter Name String SHORT_STRING Parameter Dependent
8 Get Units String SHORT_STRING Parameter Dependent
9 Get Help String SHORT_STRING Parameter Dependent
10 Get Minimum Value Specified in Descriptor Parameter Dependent
11 Get Maximum Value Specified in Descriptor Parameter Dependent
12 Get Default Value Specified in Descriptor Parameter Dependent
13 Get Scaling Multiplier UINT 1
14 Get Scaling Divisor UINT 1
15 Get Scaling Base UINT 1
16 Get Scaling Offset INT 0
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 87
Page 88

Appendix B
Table 32 - Parameter Object Instance Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
17 Get Multiplier Link UINT 0
18 Get Divisor Link UINT 0
19 Get Base Link UINT 0
20 Get Offset Link UINT 0
21 Get Decimal Precision USINT Parameter Dependent
The following commons services are implemented for the Parameter Object:
Table 33 - Parameter Object Common Services
Service
Code
0x01 No Yes Get Attribute All
0x0E Yes Yes Get Attribute Single
0x10 No Yes Set Attribute Single
0x4B No Yes Get Enum String
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
Parameter Group Object — CLASS CODE 0x10
The following class attributes are supported for the Parameter Group Object:
Table 34 - Parameter Group Object Class Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0001
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0x0005
8 Get Native Language USINT 0x01=English
The following parameter group objects are supported:
• Instance 1 = Monitor Parameters
• Instance 2 = Trip History
• Instance 3 = Reset/Lock
• Instance 4 = Advanced Setup
• Instance 5 = I/O Setup
88 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 89

Appendix B
The following instance attributes are supported for all parameter group instances:
Table 35 - Parameter Group Object Instance Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Group Name String SHORT_STRING N/A
2 Get Number of Members UINT N/A
3 Get 1st Parameter UINT N/A
4 Get 2nd parameter UINT N/A
n Get Nth Parameter UINT N/A
The following common services are implemented for the Parameter Group
Object:
Table 36 - Parameter Group Object Common Services
Service
Code
0x0E Yes Yes Get Attribute Single
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
Control Supervisor Object — CLASS CODE 0x29
No class attributes are supported for the Control Supervisor Object. A single
instance (instance 1) of the Control Supervisor Object is supported. The
following instance attributes are supported.
Table 37 - Control Supervisor Object Instance 1 Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
10 Get Faulted BOOL 0=No Fault present
11 Get Warning BOOL 0=No Warnings present
12 Get/Set Fault Rst BOOL 0=No action
13 Get FaultCode UINT If in Faulted state, FaultCode indicates the fault that caused the transition to
14 Get Warning Code UINT Code word indicating warning present. If multiple warnings are present, the
100 Get Trip Status WORD Bit 0=Overload
1= Fault Latched
1=Warning present (not latched)
0->1=Fault reset
Faulted state. If not in Faulted state, FaultCode indicates the fault that
caused the last transition to the Faulted state.
lowest code value is displayed.
Bit 1=Phase Loss
Bit 2=Jam
Bit 3-Bit 15=Not used
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 89
Page 90

Appendix B
Table 37 - Control Supervisor Object Instance 1 Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
101 Get Warning Status WORD Bit 0=Overload
102 Get Trip Log 0 WORD Last trip condition. Bit definitions of the value are the same as attribute 101
103 Get Trip Log 1 WORD Last trip condition. Bit definitions of the value are the same as attribute 101
104 Get Trip Log 2 WORD Last trip condition. Bit definitions of the value are the same as attribute 101
105 Get Trip Log 3 WORD Last trip condition. Bit definitions of the value are the same as attribute 101
106 Get Trip Log 4 WORD Last trip condition. Bit definitions of the value are the same as attribute 101
107 Get Device Status WORD Bit 0=Trip
108 Get/Set Trip Enable WORD Bit 0=Not Used
109 Get/Set Warning Enable WORD Bit 0=Overload
110 Get/Set OL Reset Mode BOOL 0=Manual
111 Get/Set IN1 Assignment USINT 0=Normal
112 Get/Set IN2 Assignment USINT 0=Normal
Bit 1=Not Used
Bit 2=Jam
Bit 3=Underload
Bit 4=Not Used
BIt 5=Comm Fault
Bit 6=Comm Idle
Bit 7=Non Vol Mem Fault
Bit 8-Bit 15=Not used
Bit 1=Warning
Bit 2=OutputA
Bit 3=Input 1
Bit 4=Input 2
Bit 5=Motor Current
Bit 6-Bit 15=Not used
Bit 1=Not Used
Bit 2=Jam
Bit 3-Bit 15=Not Used
Bit 1=Not Used
Bit 2=Jam
Bit 3=Underload
Bit 4=Not Used
BIt 5=Comm Fault
Bit 6=Comm Idle
Bit 7-Bit 15=Not Used
1=Automatic
1=Trip Reset
2=OL Contact
1=Trip Reset
2=OL Contact
The following common services are implemented for the Control Supervisor
Object:
Table 38 - Control Supervisor Object Common Services
Service
Code
0x0E No Yes Get Attribute Single
0x10 No Yes Set Attribute Single
0x05 No Yes Reset
90 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
Page 91

Appendix B
Overload Object — CLASS CODE 0x2C
No class attributes are supported for the Overload Object. A single instance
(instance 1) of the Overload Object is supported:
Table 39 - Overload Object Instance Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
7 Get % Thermal Utilized USINT xxx% FLA
108 Get Average % FLA UINT 0…1000%FLA
109 Get % Thermal Utilized USINT 0…100%
127 Get/Set Single/Three Phase BOOL 0=Single Phase
132 Get/Set OL Warn Level USINT 0…100% TCU
141 Get/Set Jam Inhibit Time USINT 0…250 s
142 Get/Set Jam Trip Delay USINT 0.5…25.0 s
143 Get/Set Jam Trip Level UINT 150…600%FLA
144 Get/Set Jam Warn Level UINT 100…600%FLA
145 Get/Set UL Inhibit Time USINT 0…250 s
148 Get/Set UL Warn Level USINT 30…100%FLA
1=Three Phase
The following common services are implemented for the Overload Object:
Table 40 - Overload Object Common Services
Service
Code
0x0E No Yes Get Attribute Single
0x10 No Yes Set Attribute Single
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
PCP Object — CLASS CODE 0xC2
The following class attributes are supported for the PCP Object:
Table B.1 PCP Object Class Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Revision UINT 1
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 91
Page 92

Appendix B
The following instance attributes are implemented for all parameter attributes:
Table 41 - PCP Object Instance Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get/Set MCC Number USINT 0-255
2 Get/Set Vertical Section Number USINT 0-255
3 Get/Set Starting Section Letter USINT 0-255
4 Get/Set Space Factors USINT 0-0x3F
5 Get/Set Cabinet Width USINT 0-255
6 Get/Set Controlled Device USINT 0-255
7 Get Number of Device Inputs USINT 2
8 Get/Set Devices Connected at Inputs Array of USINT
9 Get Number of Device Outputs USINT 1
10 Get/Set Devices Connected at Outputs Array of USINT
The following common services are implemented for the PCP Object:
Table 42 - PCP Object Common Services
Service
Code
0x01 No Yes Get Attribute All
0x02 No Yes Set Attribute All
0x0E Yes Yes Get Attribute Single
0x10 No Yes Set Attribute Single
TCP/IP Interface Object — CLASS CODE 0xF5
The following class attributes are supported for the TCP/IP Interface Object:
Table 43 - TCP/IP Interface Object Class Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Revision UINT 1
The following instance attributes are implemented for all parameter attributes:
Table 44 - TCP/IP Interface Object Instance Attributes
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Status DWORD N/A
2 Get Configuration capability DWORD 0x00000014
3 Get/Set Configuration control DWORD N/A
92 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 93

Table 44 - TCP/IP Interface Object Instance Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
4 Get Physical Link Object Struct of:
Path size UINT 0x0002
Path Padded EPATH 20 F6 24 01
5 Get/Set Interface configuration Structure of:
IP Address UDINT
Network Mask UDINT
Gateway Address UDINT
Name Server UDINT
Name Server 2 UDINT
Domain Name STRING
6 Get/Set Host Name STRING
8 Get/Set TTL Value USINT 1
9 Get/Set Mcast Config Structure of:
Alloc Control USINT 0
Reserved USINT
Num Mcast UINT 4
Mcast Start Addr UDINT
Appendix B
The following common services are implemented for the TCP/IP Interface
Object:
Table 45 - TCP/IP Interface Common Services
Service
Code
0x01 No Yes Get Attribute All
0x0E Yes Yes Get Attribute Single
0x10 No Yes Set Attribute Single
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
Ethernet Link Object — CLASS CODE 0xF6
The following class attributes are supported for the Ethernet Link Object:
Table 46 - Ethernet Link Object Class Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Revision UINT 3
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 93
Page 94

Appendix B
The following instance attributes are implemented for all parameter attributes:
Table 47 - Ethernet Link Object Instance Attributes
Attribute ID Access Rule Name Data Type Value
1 Get Interface Speed UDINT 10 or 100
2 Get Interface Flags DWORD
3 Get Physical Address ARRAY of 6 USINTs MAC Address
4 Get Interface Counters Structure of:
In Octets UDINT N/A
In Ucast Packets UDINT N/A
In NUcast Packets UDINT N/A
In Discards UDINT N/A
In Errors UDINT N/A
In Unknown Protos UDINT N/A
Out Octets UDINT N/A
Out Ucast Packets UDINT N/A
Out NUcast Packets UDINT N/A
Out Discards UDINT N/A
Out Errors UDINT N/A
5 Get Media Counters Structure of:
Alignment Errors UDINT N/A
FCS Errors UDINT N/A
Single Collisions UDINT N/A
Multiple Collisions UDINT N/A
SQE Test Errors UDINT 0
Deferred Transmission UDINT N/A
Late Collisions UDINT N/A
Excessive Collisions UDINT N/A
MAC Transmit Errors UDINT N/A
Carrier Sense Errors UDINT N/A
Frame Too Long UDINT N/A
MAC Receive Errors UDINT N/A
6 Get/Set Interface Control Structure of:
Control Bits WORD N/A
Forces Interface Speed UINT N/A
94 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 95

Appendix B
The following common services are implemented for the Ethernet Link Object:
Table 48 - Ethernet Link Common Services
Rockwell Automation Support
Service
Code
0x01 Yes Yes Get Attribute All
0x0E No Yes Get Attribute Single
0x10 No Yes Set Attribute Single
0x4C No Yes Get And Clear
Implemented for: Service Name
Class Instance
Rockwell Automation provides technical information on the web to assist you in
using its products. At http://support.rockwellautomation.com, you can find
technical manuals, a knowledge base of FAQs, technical and application notes,
sample code and links to software service packs, and a MySupport feature that
you can customize to make the best use of these tools.
For an additional level of technical phone support for installation, configuration
and troubleshooting, we offer TechConnect Support programs. For more
information, contact your local distributor or Rockwell Automation
representative, or visit http://support.rockwellautomation.com.
Installation Assistance
If you experience a problem with a hardware module within the first 24 hours of
installation, please review the information that's contained in this manual. You
can also contact a special Customer Support number for initial help in getting
your module up and running:
United States 1.440.646.3223
Monday – Friday, 8am – 5pm EST
Outside United
States
Please contact your local Rockwell Automation representative for any
technical support issues.
New Product Satisfaction Return
Rockwell tests all of its products to ensure that they are fully operational when
shipped from the manufacturing facility. However, if your product is not
functioning and needs to be returned:
United States Contact your distributor. You must provide a Customer Support case number
Outside United
States
(see phone number above to obtain one) to your distributor in order to
complete the return process.
Please contact your local Rockwell Automation representative for return
procedure.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 95
Page 96

Appendix B
96 Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011
Page 97

Page 98

Rockwell Otomasyon Ticaret A.Ş., Kar Plaza İş Merkezi E Blok Kat:6 34752 İçerenköy, İstanbul, Tel: +90 (216) 5698400
Rockwell Automation Support
Rockwell Automation provides technical information on the Web to assist you in using its products.
At http://www.rockwellautomation.com/support/
application notes, sample code and links to software service packs, and a MySupport feature that you can customize to make the
best use of these tools.
For an additional level of technical phone support for installation, configuration, and troubleshooting, we offer TechConnect
support programs. For more information, contact your local distributor or Rockwell Automation representative,
or visit http://www.rockwellautomation.com/support/
Installation Assistance
If you experience a problem within the first 24 hours of installation, review the information that is contained in this manual.
You can contact Customer Support for initial help in getting your product up and running.
United States or Canada 1.440.646.3434
Outside United States or
Canada
Use the Worldwide Locator
your local Rockwell Automation representative.
, you can find technical manuals, a knowledge base of FAQs, technical and
.
at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/support/americas/phone_en.html, or contact
New Product Satisfaction Return
Rockwell Automation tests all of its products to ensure that they are fully operational when shipped from the manufacturing facility.
However, if your product is not functioning and needs to be returned, follow these procedures.
United States Contact your distributor. You must provide a Customer Support case number (call the phone number above to obtain
Outside United States Please contact your local Rockwell Automation representative for the return procedure.
one) to your distributor to complete the return process.
Documentation Feedback
Your comments will help us serve your documentation needs better. If you have any suggestions on how to improve this document,
complete this form, publication RA-DU002
, available at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/literature/.
Rockwell Automation Publication 193-UM012B-EN-P - June 2011 98
Supersedes Publication 193-UM012A-EN-P - March 2009 Copyright © 2011 Rockwell Automation, In c. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...