Page 1

1391-DES Digital
AC Servo Drive
User Manual
Page 2
Important User Information Because of the variety of uses for this equipment and because of the
differences between this solid-state equipment and electromechanical
equipment, the user of and those responsible for applying this equipment
must satisfy themselves as to the acceptability of each application and use
of the equipment. In no event will Allen-Bradley Company be responsible
or liable for indirect or consequential damages resulting from the use or
application of this equipment.
The illustrations shown in this manual are intended solely to illustrate the
text of this manual. Because of the many variables and requirements
associated with any particular installation, the Allen-Bradley Company
cannot assume responsibility or liability for actual use based upon the
illustrative uses and applications.
No patent liability is assumed by Allen-Bradley Company with respect to
use of information, circuits or equipment described in this text.
Reproduction of the content of this manual, in whole or in part, without
written permission of the Allen-Bradley Company is prohibited.
This information in this manual is organized in numbered chapters. Read
each chapter in sequence and perform procedures when you are instructed
to do so. Do not proceed to the next chapter until you have completed all
procedures.
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or
circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death, property
!
damage or economic loss.
Attentions help you:
• identify a hazard
• avoid the hazard
• recognize the consequences
IMPORTANT: Identifies information that is especially important for
successful application and understanding of the product.
Page 3

Summary of Changes
Summary of Changes
Summary of Manual Changes This release of the 1391-DES User Manual contains some new and updated
information. The new and updated information is summarized in the table
below. For further information, refer to the page numbers provided.
Description of New or Updated Information Page Type
Linear Accel/Decel information added 1-4 New
Speed Regulation specification added 2-1 New
Torque Plus Motor, Gearbox & Cable info 3-4, 7, 8 New
Important statement added to TB1 5-1 New
Bus voltage info added to shunt resistor 5-4 New
Important statement added 5-7 Clarification
Parameter 69 name change 6-14 Update
Parameter 170 maximum value updated 6-18 Update
Parameter 199 updated 6-20 Update
Encoder Wiring 7-5 Clarification
Torque Plus info added to step 11 8-3 New
Torque Plus info added (steps 30, 31) 8-7 New
Figure 8.1 updated 8-10 Update
Linear Accel/Decel information added 8-11 New
Torque Plus data added 9-3 New
#4 added to Auto Tune Fault 11-7 Update
TP50 description updated 11-10 Update
Enclosure items list A-3 New
Interconnect drawings updated & added App. B Update
1-4
Page 4

Chapter
Introduction
Manual Objectives This manual is meant to guide the interface, installation, programming and
troubleshooting of a 1391-DES Digital AC Servo Drive. The contents are
arranged in order from a general description of the drive to troubleshooting
and maintenance. To assure successful installation and operation, the
material presented must be thoroughly read and understood before
proceeding. Particular attention must be directed to the Attention and
Important statements contained within.
Important Information about this Manual
This manual has been prepared primarily to support this product in a single
drive application. It is a standard document that is intended to help the user
understand the individual operating characteristics and limitations of this
equipment including hazards associated with installation, programming and
maintenance procedures. Note the following points:
• This equipment has been designed to meet the requirements of a
component drive in an integrated drive system.
• While the potential hazards associated with the drive remain the same
when used in a system environment, it must be noted that special
considerations are to be given to characteristics of other peripheral
solid-state control equipment and the cumulative impact on safety.
• Manufacturers and engineering groups responsible for specification or
design of electrical control equipment must refer to applicable industry
standards and codes for specific safety guidelines and interface
requirements.
• In the actual factory environment, the user is responsible to ensure
compliance with applicable machine and operator safety codes or
regulations which are beyond the scope and purpose of this document.
1-5
Page 5
Chapter 1
Introduction
General Precautions In addition to the precautions listed throughout this manual, the following
statements which are general to the drive must be read and understood.
ATTENTION: Only personnel familiar with the 1391-DES
!
!
!
Digital Servo Drive and associated machinery should plan or
implement the installation, start-up and subsequent maintenance
of the drive. Failure to comply may result in personal injury
and/or equipment damage.
ATTENTION: An incorrectly applied or installed drive can
result in component damage or a reduction in product life.
Wiring or application errors, such as, undersizing the motor,
incorrect or inadequate AC supply, or excessive ambient
temperatures may result in malfunction of the drive.
ATTENTION: This drive contains ESD (Electrostatic
Discharge) sensitive parts and assemblies. Static control
precautions are required when installing, testing, servicing or
repairing this assembly. Component damage may result if ESD
control procedures are not followed. If you are not familiar with
static control procedures, reference Allen-Bradley publication
8000-4.5.2, Guarding Against Electrostatic Damage or any
other applicable ESD Protection Handbook.
Certification Notice: In order to maintain UL listing on Allen-Bradley
1391-DES Digital Servo Drives, the user must
Isolation Transformer. Use of any other transformer voids the UL listing.
The user is responsible for providing motor overload protection in
accordance with the National Electrical Code (NEC), and any other local
codes that may apply.
provide power from a 1391
Drive Description The 1391-DES Pulse Width Modulated Digital Servo Drive is a digital and
programmable single axis, AC servo drive. It has been packaged to require
a minimum amount of panel space while containing, as standard, a number
of features required by the machine tool and automated equipment
industries.
The 1391-DES allows Allen-Bradley 1326 AC servomotors to be operated
from 33% to 50% over their rated speed. This can help achieve greater
precision, a finer finished product and increased production from existing
machinery.
1-6
Page 6

Chapter 1
Introduction
The 1391-DES is generally used with computer aided, closed loop
positioning systems such as Allen-Bradley “S” Class or IMC products.
These systems control the position and linear or rotary motion of various
machine members on an automated machine. To enhance system reliability,
the 1391-DES has an encoder output (AQB) that produces four channels of
2048, 1024, 512 or 256 lines and two marker pulses per motor revolution
which feeds position information to the position controller.
All components are mounted in an open framed package with a slide-on
front cover. The drive is intended to be panel mounted in an enclosure and
ventilated with filtered and/or cooled air. An internal fan is included to
circulate air over the power heat sink.
The 1391-DES converts a three-phase, 50/60 Hz input, to a variable AC
voltage with controlled phase, amplitude and frequency. The output which
is proportional to a user supplied analog command, regulates the speed
and/or current (torque) of a 1326 permanent magnet AC servomotor. The
drive is available in ratings of 15, 22.5 and 45A RMS with all package
sizes being identical. A 1391 Transformer, 1326 AC Servomotor and 1326
Cables complete the servo system.
Standard Features The 1391-DES contains a number of standard features required in a typical
automated machine servo system.
• Input protected against transient voltage.
• A power line/DB contactor which opens the AC line to the drive and
inserts a shunt regulator resistor across the DC bus whenever the
contactor is de-energized.
• An integral circuit breaker which will open all three AC line leads in the
event of a short circuit condition in the power circuitry.
• A standard 300V DC power bus supply that includes an integral shunt
regulator.
• A shunt regulator resistor to dissipate the energy generated by the motor
during regenerative braking.
• Prompted startup procedure to shorten setup time.
• Two line LCD display and programming panel.
• Patented current control implementation.
• Torque feedforward differential input.
• Microprocessor based logic boards that can be quickly removed and
easily interchanged for troubleshooting and diagnostics.
• Three drive ratings that are in the same physical package and have
identical mounting dimensions.
• True vector control.
• Up to 600 feet (183 meters) between drive and motor.
1-7
Page 7

Chapter 1
Introduction
Options/Modifications The 1391-DES contains most functions needed in a servo system.
The following are selectable at the user’s option:
• Contactor Auxiliary Switch
Two N.O. (normally open) contacts are mounted on the main power
contactor and wired to the power terminal block. These contacts can be
used in a motor brake control circuit or as an indicator that the contactor
has closed.
• Current or Torque Amplifier Operation
When the velocity loop is being closed as part of the position control
system, the drive can be configured to operate as a current or torque
amplifier by selection on the programming panel.
• External Shunt Regulator Resistor
On 15 and 22.5A drives an internal power resistor that is part of the DC
bus voltage shunt regulator can dissipate 162 watts continuous power.
Some applications such as an overhauling load have excessive
regenerative energy to dissipate. For these applications, an external
shunt regulator resistor rated at 386 watts continuous can be supplied for
user mounting on 22.5A drives. This is selectable by removing the
jumper on TB5 and using an external resistor. The shunt has integral
fusing accessible from the outside of 15 and 22.5A drives. The 45A
drive has an externally mounted resistor and fuse.
Important: An external shunt regulator resistor is included as standard
equipment on 45A units. An additional unit is not required.
• Tach Output
A voltage equal to 1.2V DC/1000 RPM is available at TB2.
• Torque or Current Monitor
A voltage equal to 3.0V DC=100% scaled current is available at TB2.
• Anti-Backlash
Anti-backlash control can be implemented with several software
parameters and an additional instruction manual. Contact your local
Allen-Bradley Sales Office for details.
• Linear Accel/Decel
Linear accel/decel can be set using the CR-APG-001 Control Module.
This module provides a manually generated trapezoidal velocity profile
for up to four preset speeds.
Important: The 1391-DES contains one accel/decel rate which can be
used if accel/decel times will be the same.
Drive Layout Figure 1.1 provides an exterior view of the 1391-DES AC Servo Drive,
showing accessibility of various components.
1-8
Page 8

Figure 1.1
1391-DES Digital AC Servo Drive
Duty Cycle Selector Switch
TB5 – Power Connections
TB4 – Control Signals
Chapter 1
Introduction
Ground Stud
2 Line, 16 Character
LCD Display
5 Button Keypad used
for Programming
Status LED
- Flashes green when no faults are
present and the bus is low.
- Steady green when no faults are
present and bus voltage is OK.
- Flashes red when a fault has
occurred.
Enable LED
- Steady green when Enable input is
closed at TB2-9 & 10.
- Not illuminated when Enable input
is open.
Circuit Breaker
Fuses
TB2 – Interface Signals
TB3 – A Quad B Encoder Output Signals
1-9
Page 9

Chapter 1
Introduction
End of Chapter
1-10
Page 10

Chapter
Specifications
Chapter Objectives Chapter two contains the electrical and environmental specifications for the
1391-DES. Dimensions are provided in Appendix A.
Drive Specifications The general specifications of the 1391-DES are provided in the listing
below. The specifications are divided when necessary for the various drive
ratings.
Specific Drive Ratings 1391-DES15 1391-DES22 1391-DES45
Nominal Bus Voltage 300V DC 300V DC 300V DC
Continuous Current (RMS) 15A 22.5A 45A
Peak Current (RMS) 30A 45A 90A
Continuous Power Output 5.0 kW 7.5 kW 15.0 kW
Peak Power Output 10.0 kW 15.0 kW 30.0 kW
Input Circuit Breaker Rating 17A RMS 26A RMS 38A RMS
Circuit Breaker Interrupt Rating
(Symmetrical Amperes) 1300A 1300A 1300A
Unit Weight in lbs. (kg) 22 (9.97) 28 (12.69) 34 (15.40)
All Drive Ratings
Static Gain (A/RMS) 1.5 x Rated Motor Current / rpm (typical)
Form Factor 1.03 or less
Peak Current Limit Adjust 20 to 300% of Rated Motor Current or 2 x Continuous Rating of
Drive (max.), whichever achieves Drive Peak Current Rating first
Drive Efficiency 85% (Minimum at Rated Load)
Power Factor 95% Minimum
Modulation Frequency 2500 Hz ±10%
Drift (Referred to Tach) 0.07 rpm /Degrees C. Maximum
Speed Regulation 0 to 0.05% of Maximum Motor Speed with 95% Load Change
Ambient Temperature 0 to 60° C (32 to 140° F)
Storage Temperature 0 to 65° C (32 to 149° F)
Input Voltage (from Transformer) Power: 230V AC +10%/–15%, Three-Phase, 50/60 Hz ±3 Hz
Control: 36V AC, Single-Phase
Transformer Input Tolerance +10%, –15%
Relative Humidity 5 to 95% Non-Condensing
Deadband Zero
Altitude 1000 meters (3300 feet)
Integral Fan Output 50 CFM (Unloaded)
Max. RMS Short Circuit Current 1300A (Symmetrical Amperes)
Certifications UL Listed - File No. E59272, CSA Certified - File No. LR32334-548,
Specifications are for reference only and are subject to change without notice.
2-1
Page 11

Chapter 2
Specifications
Environmental Specifications The 1391-DES must be mounted in an enclosure that is clean, dry and
ventilated by filtered or cooled air. Enclosures vented with ambient air
must have appropriate filtering to protect against contamination caused by
oils, coolants, dust, condensation etc. The ambient air temperature must be
kept between 0 to 60° C (32 to 140° F) and the humidity between 5 and
95%, non-condensing.
The 1391-DES is equipped with an integral cooling fan. The general flow
of air through the unit must be maintained by following the recommended
spacing guidelines found in Chapter 7. The 1391-DES can operate at
elevations to 3300 feet (1000 meters) without derating, however, the
current rating must be derated by 3% for each additional 1000 feet (305
meters) up to 10,000 feet (3050 meters). Consult with your local
Allen-Bradley Sales Representative prior to operation over 10,000 feet
(3050 meters).
Drive Power Dissipation The 1391-DES dissipation characteristics are approximated in Table 2.A.
Table 2.A
Drive Power Dissipation
Rated Power Output
(%)
20
40
60
80
100
1391-DES15
(watts)
38
76
114
152
190
1391-DES22
(watts)
55
110
165
220
275
1391-DES45
(watts)
104
208
312
416
520
Transformer Power Dissipation The power dissipation characteristics of the 1391 Isolation Transformer are
shown in Table 2.B.
Table 2.B
1391 Isolation Transformer Power Dissipation
Rated Power Output
(%)
20
40
60
80
100
1.5kVA
(watts)
13
25
38
50
60
3.5kVA
(watts)
35
70
105
140
175
5.0kVA
(watts)
50
100
150
200
250
10.0kVA
(watts)
100
200
300
400
500
12.5kVA
(watts)
125
250
375
500
625
15.0kVA
(watts)
150
300
450
600
750
2-2
Important: Power Dissipation figures shown are for use in calculating
cumulative system heat dissipation to ensure ambient temperature inside
enclosure does not exceed 60° C (140° F).
Page 12

Chapter
Receiving, Unpacking and Inspection
Chapter Objectives Chapter 3 provides the information needed to unpack, properly inspect and
if necessary, store the 1391-DES and related equipment. The section entitled Inspection provides a complete explanation of the 1391-DES catalog numbering system.
Receiving It is the responsibility of the user to thoroughly inspect the equipment
before accepting the shipment from the freight company. Check the item(s)
received against the purchase order. If any items are obviously damaged, it
is the responsibility of the user not to accept delivery until the freight agent
has noted the damage on the freight bill. Should any concealed damage be
found during unpacking, it is again the responsibility of the user to notify
the freight agent. The shipping container must be left intact and the freight
agent should be requested to make a visual inspection of the equipment.
Unpacking Remove all packing material, wedges, or braces from within and around
the drive. Remove all packing material from the cooling fans, heat sink etc.
Important: Before the installation and start-up of the drive, a general
inspection of mechanical integrity (i.e. loose parts, wires, connections,
packing materials, etc.) must be made.
Inspection After unpacking, check the item(s) nameplate catalog number against the
purchase order. An explanation of the catalog numbering system is
included on the following pages as an aid for nameplate interpretation.
Storing The drive should remain in its shipping container prior to installation. If the
equipment is not to be used for a period of time, it must be stored
according to the following instructions:
• Store in a clean, dry location.
• Store within an ambient temperature range of 0 to 65° C (32 to 149° F).
• Store within a relative humidity range of 5% to 95%, non-condensing.
• Do not store equipment where it could be exposed to a corrosive
atmosphere.
• Do not store equipment in a construction area.
3-1
Page 13
Chapter 3
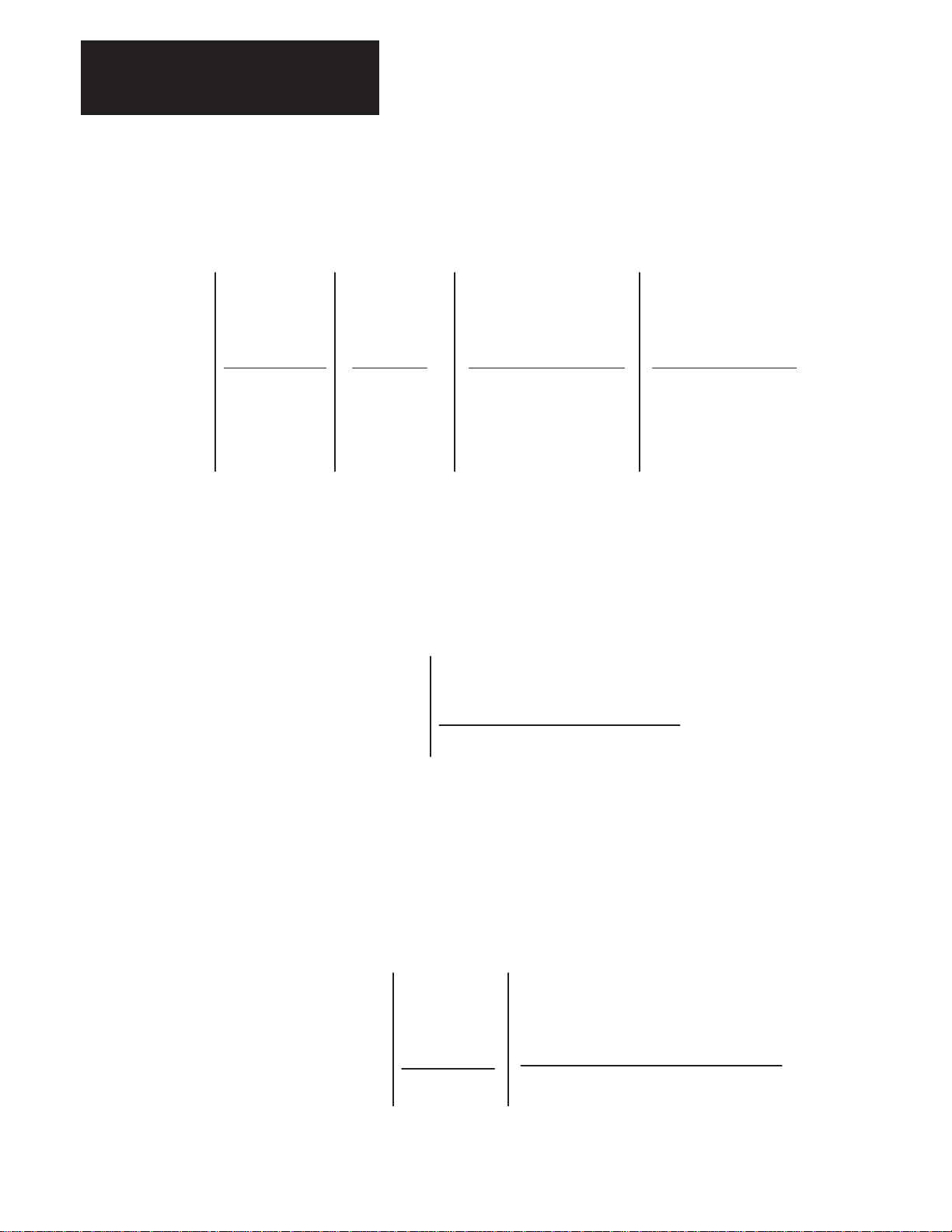
Receiving, Unpacking and Inspection
Isolation Transformer
1391 T
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
–
Type
Description
Letter
Transformer
T
Open Core
and Coil
015
kVA Rating
Number
015
035
050
100
125
150
kVA
1.5
3.5
5.0
10.0
12.5
15.0
NEMA Type 1 Transformer Enclosure Kit
1391
Bulletin
Number
Fourth Position
Primary Voltage
& Frequency
Letter
D
E
N
TA2–
Accessory
Module
D
Description
240/480V AC, ThreePhase, 60 Hz
240/380/415/480V AC,
Three-Phase, 50/60 Hz
208/230/460/575V AC,
Three-Phase, 60 Hz
T
Fifth Position
Secondary
Voltage
Description
Letter
230V AC, three-phase
T
and four 36V AC,
single-phase
C.T.windings
3-2
Description
Letter
Fits all kVA ratings on 1386, 1388,
TA2
1389 and 1391 Isolation Transformers.
External Shunt Regulator Resistor
1391 MOD SR22A
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
1
Drive comes equipped with this resistor as standard. Catalog number is provided if spare or replacement is required,
–
Type
Code
MOD
Description
Modification Kit
–
Description
Code
SR22A
SR45A
Description
Shunt Regulator Resistor for 22.5A Drive
Shunt Regulator Resistor for 45A Drive
1
Page 14
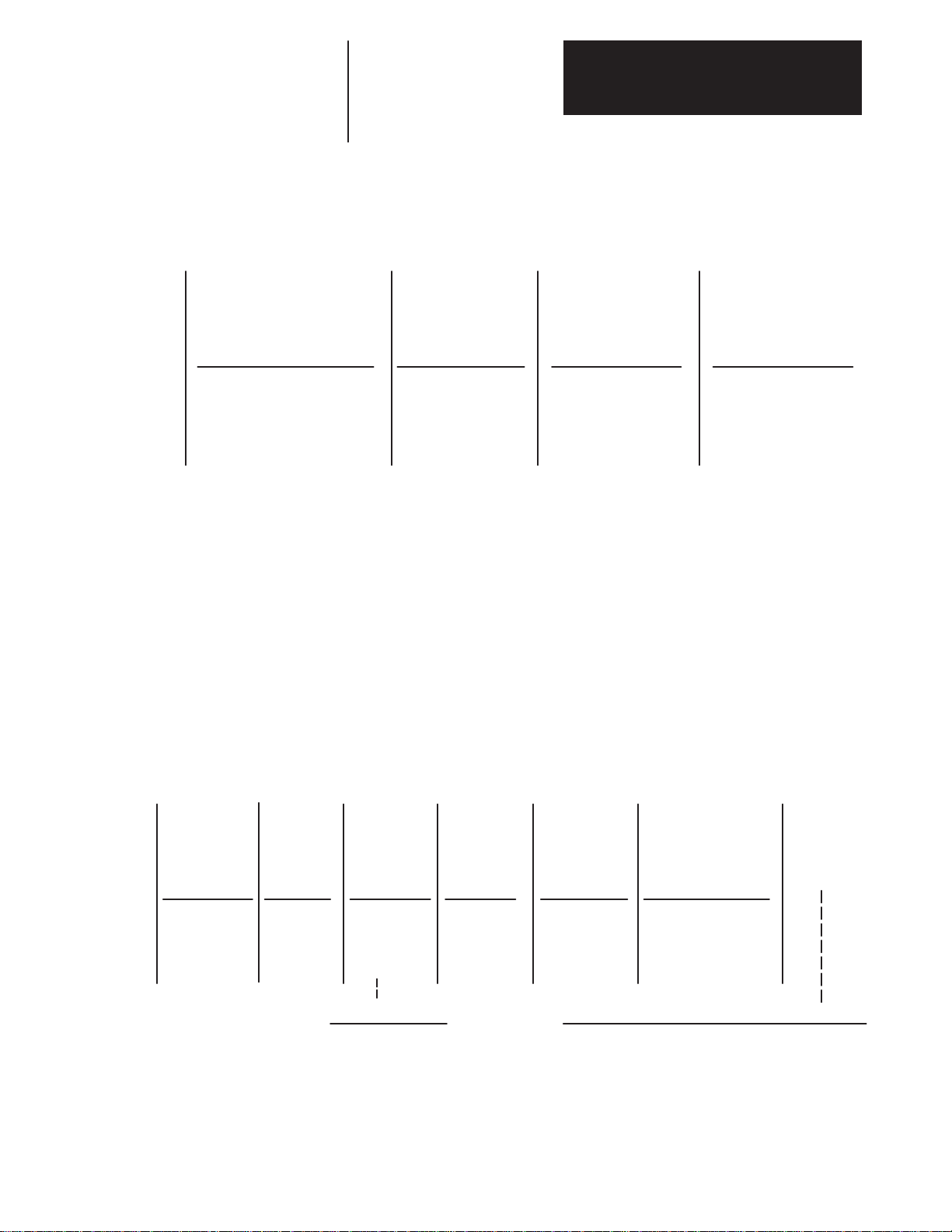
Bulletin 1391-DES Drive
Chapter 3
Receiving, Unpacking and Inspection
1391 DES15
First Position Second Position
Bulletin
Number
Configuration/
Current Rating
Code
DES15
DES22
DES45
Description
15A Continuous Current
22.5A Continuous Current
45A Continuous Current
–
Third Position
User
Interface
Code
DI
DI
Description
Includes Integral
Display
AQB–
Fourth Position
Output
Configuration
Description
Code
Encoder Output –
AQB
2048, 1024, 512,
256 selectable
pulses/motor
revolution
A––
Fifth Position
Options
Description
Letter
24V DC M contactor
A
coil voltage instead of
115V AC (available
on 22A drives only)
Blank
115V AC M contactor
coil voltage
1326AB Servomotor
1326 A 3
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
Type
Letter
A
Description
AC
Servomotor
PM Type
Design
Description
Factory
use only
–
Fourth Position
Series
Description
Sequentially
lettered to
designate frame
diameters.
Description
Code
4.25” (108 mm)
A
5.88” (149 mm)
B
7.63” (194 mm)
C
Fifth Position
Motor
Length
Description
Sequentially
numbered to
indicate stack
length within a
given frame size.
E
Sixth Position
Max. Op.
2
Speed
RPM
Letter
1600/2000
B
2000/3000
C
3000/4000
E
5000/6000
G
Code
A4
A5
A7
K4
K5
K7
–
Description
72 lb.-in. (8.1 N-m) Holding Brake w/90V DC Coil.
120 lb.-in. (13.6 N-m) Holding Brake w/90V DC Coil.
360 lb.-in. (40.7 N-m) Holding Brake w/90V DC Coil.
72 lb.-in. (8.1 N-m) Holding Brake w/24V DC Coil.
120 lb.-in. (13.6 N-m) Holding Brake w/24V DC Coil.
360 lb.-in. (40.7 N-m) Holding Brake w/24V DC Coil.
11
Seventh Position
Mounting & Shaft
Description
Description
Code
NEMA Inch Combina-
11
tion Face/Flange with
Keyway
21
IEC Metric Flange
with Keyway
–BA
A4
Eighth Position
Standard
Options
2
Ratings shown indicate the rated speed and speed capability of the motor with the 1391-DES (rated/w 1391-DES).
3-3
Page 15
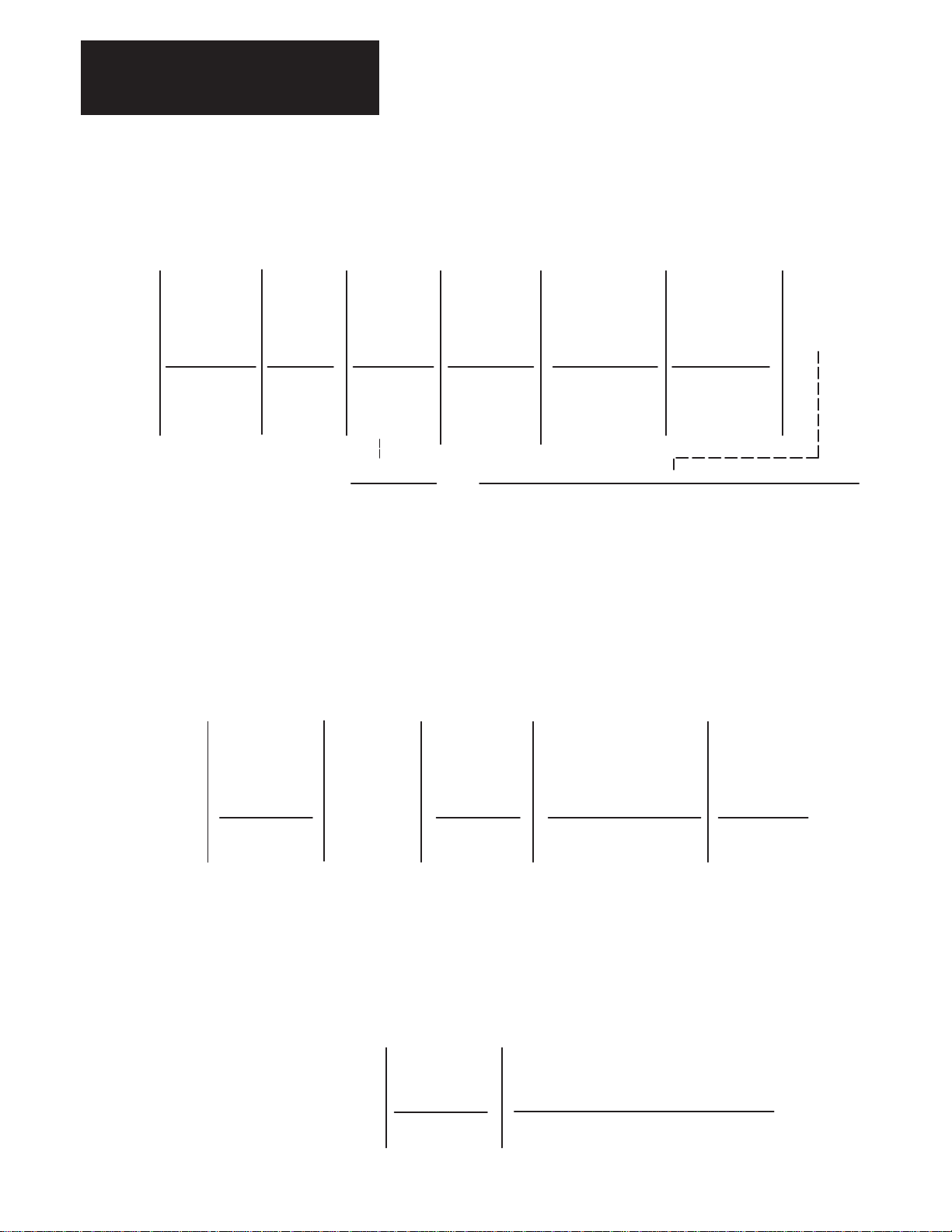
Chapter 3
Receiving, Unpacking and Inspection
1326AB Torque Plus Series Servomotor
1326 AB 30
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
Type
Letter
AB
Description
Ferrite AC
Servomotor
–
Voltage
Code
A
Rating
230V AC
Fourth Position
Series
Description
Sequentially
lettered to
designate frame
diameters.
Description
Code
115 mm
4
166 mm
5
215 mm
7
Fifth Position
Motor
Length
Description
Sequentially
numbered to
indicate stack
length within a
given frame size.
Shaft Oil Seal Kit
E
Sixth Position
Max. Operating
Speed
Rated/1391-DES
Letter
1600/2000 rpm
B
2000/3000 rpm
C
3000/4000 rpm
E
5000/6000 rpm
G
Code
Description
A4
72 lb.-in. (8.1 N-m) Holding Brake w/90V DC Coil for 1326AB-A4
A5
120 lb.-in. (13.6 N-m) Holding Brake w/90V DC Coil for 1326AB-A5
A7
360 lb.-in. (40.7 N-m) Holding Brake w/90V DC Coil for 1326AB-A7
K4
72 lb.-in. (8.1 N-m) Holding Brake w/24V DC Coil for 1326AB-A4
K5
120 lb.-in. (13.6 N-m) Holding Brake w/24V DC Coil for 1326AB-A5
K7
360 lb.-in. (40.7 N-m) Holding Brake w/24V DC Coil for 1326AB-A7
–
21
Seventh Position
Mounting & Shaft
Description
Description
Code
IEC Metric
21
Flange with
Keyway
–A4
A4
Eighth Position
Standard
Options
3-4
1326AB MOD
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
Type
Code
MOD
Description
Modification Kit
3
“A” Series motors with brake must use 1326AB-MOD-SSV-A2.
Bulletin
Number
SS V
–
Shaft
Seal
Brake Power Supply Rectifier
1326 MOD BPS
–
4
Up to 4 brakes per rectifier can be used.
Type
Code
MOD
Fourth Position
Material
Description
Letter
Viton
V
–
Description
Modification Kit
–
Description
Code
BPS
A
Fifth Position
Motor
Series
Letter
Standard
A
Series A
B
Series B
C
Series C
Description
Single-phase, full-wave, screw mount
rectifier. 115V AC input, for use with 90V DC
4
brakes.
Torque Plus
-A4
-A5
-A7
Use
Metric
Only
1–
Sixth Position
Motor
Mounting
Number
1
2
3
Description
Std. Inch
Metric
Page 16
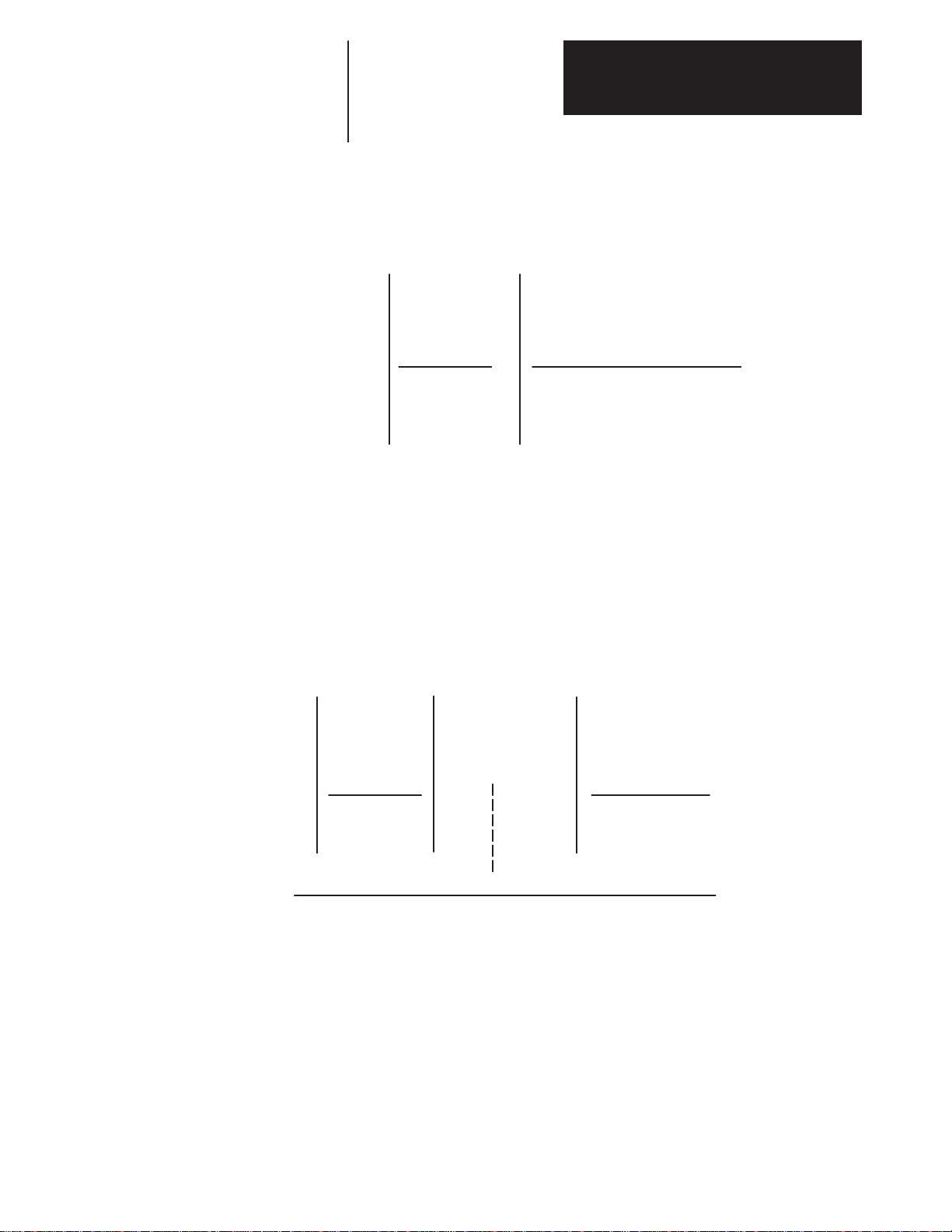
Chapter 3
Receiving, Unpacking and Inspection
Motor Junction Box Kit
1326AB MOD RJAB
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
5
The motor comes standard with IP65 plug style connectors mounted radially to the motor. This kit allows the
connectors to be brought out axially to the motor without further wiring. Kit includes Motor Junction Box and
Mounting Hardware.
–
Type Description
Description
Code
Modifica-
MOD
tion Kit
Feedback Mounting Adapter Kit
5
–
Code
Description
RJAB
For all AB-A & B Series Motors
(A4 & A5 Torque Plus Motors)
RJB
For all AB-B4 & Cx Series Motors
C
(A7 Torque Plus Motors)
6
1326AB MOD
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
–
Type
Description
Code
Modifica-
MOD
tion Kit
Description
Code
A-B 845H/T Encoder for AB-A series motor (A4 Torque Plus)
M4
A-B 845H/T Encoder for AB-B series motor (A5 Torque Plus)
M5
A-B 845H/T Encoder for AB-C series motor (A7 Torque Plus)
M6
Type VC/VD 4.25” (108mm) Resolver for AB-B series motor (A5 Torque Plus)
M22
Type VC/VD 4.25” (108mm) Resolver for AB-C series motor (A7 Torque Plus)
M23
0.375” (9.5 mm) diameter heavy duty shaft extension adapter
M24
0.625” (15.9 mm) diameter heavy duty shaft extension for type VC/VD 4.25”
M25
(108 mm) resolver
Foot mounting kit for M25
M26
–
M4 C1
Mounting Adapter
Kit for . . .
–
Fourth Position
Coupling Size
for . . .
Code
C1
Blank
Motor Series
A, B, C (A4, A5, A7 Torque Plus)
For M22, M23, M24, M25, M26
6
All kits contain a feedback device mounting adapter and mounting hardware. M4, M5 and M6 include a
motor to encoder coupling. M22 and M23 do not include a coupling since it is included with the resolver
feedback device.
3-5
Page 17
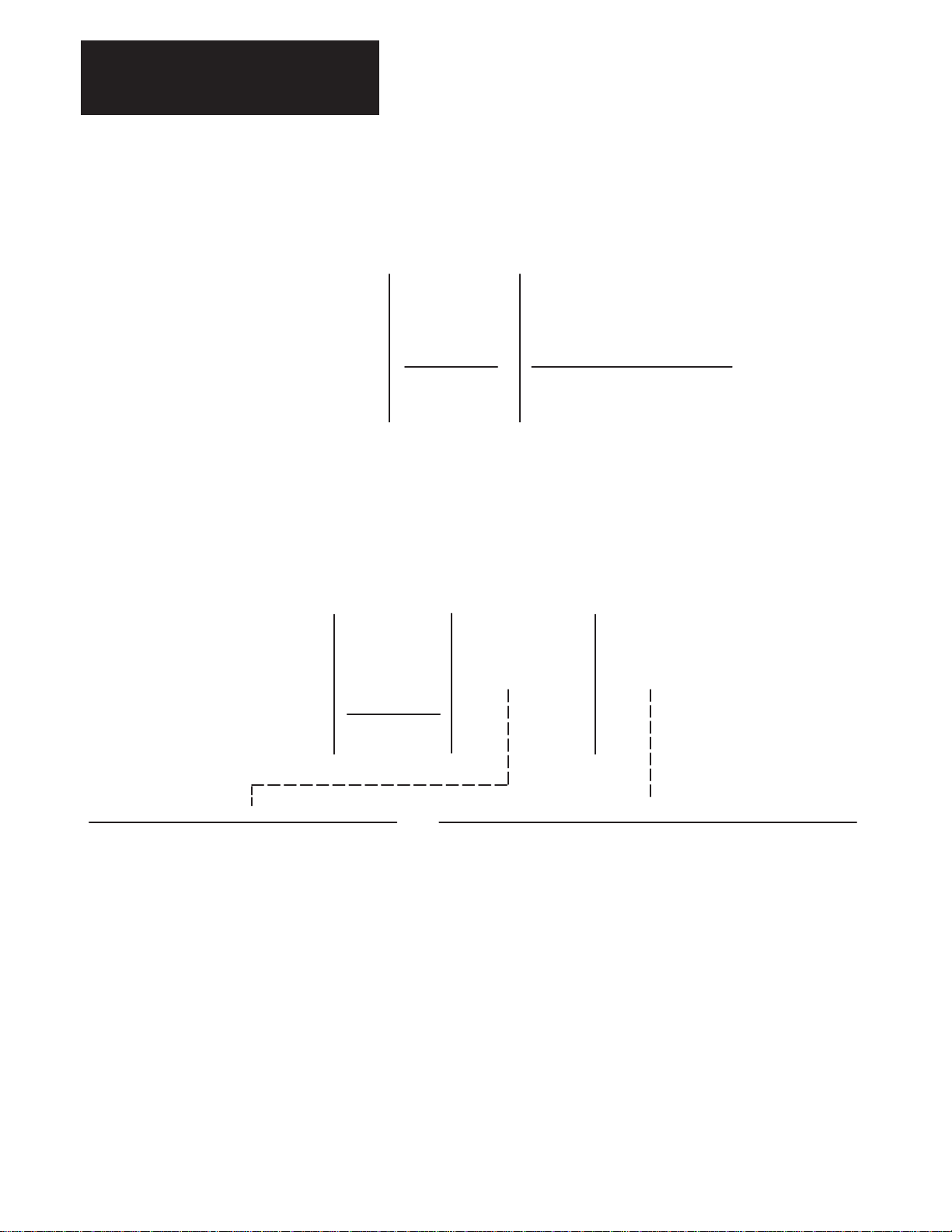
Chapter 3
Receiving, Unpacking and Inspection
–
VC
7
Coupling
Size
–
Size
Code
C1
C2
Motor Shaft to Encoder Shaft
3/8” to 3/8” (9.5 mm to 9.5 mm) –
Standard on all 1326AB Motors
1/4” to 3/8” (6.4 mm to 9.5 mm)
Feedback Coupling
1326 MOD C1
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
7
The feedback coupling is included as standard with all Feedback Mounting Adapter Kits.
1326AB MOD
First Position Second Position Third Position
–
–
Type
Description
Code
Modifica-
MOD
tion Kit
Resolver Feedback Package
–
1:1
Fourth Position
Bulletin
Number
Code
Description
VC
4.25” (108 mm) feedback package with cast
housing and single or vernier (dual) format with
receiver (Harowe 11BRW-300-F-58A or equivalent)
type resolver(s) for use with A-B series 8200 CNC
]
120, 121, 123.
and IMC
4.25” (108 mm) feedback package with cast
VD
housing and single or vernier (dual) format with
transmitter (Harowe 11BRCX-300-C10/6 or
equivalent) type resolver(s) for use with A-B series
8600, MAX and IMC S Class controllers with a
REC 4096 Board.
Type
Code
MOD
Description
Modification Kit
Resolver Feedback
Package
8
Code
Description
1:1
Single device format – 1 turn of the motor shaft to 1 turn of the resolver.
1:2
Single device format – 1 turn of the motor shaft to 2 turns of the resolver.
1:2.5
Single device format – 1 turn of the motor shaft to 2.5 turns of the resolver.
1:5
Single device format – 1 turn of the motor shaft to 5 turns of the resolver.
255
Absolute master/vernier format – 1:1 input/master, 255:256 master/vernier
for IMC 120, 121, 123 only.
256
Absolute master/vernier format – 1:1 input/master, 256:255 master/vernier
for 8600 series and MAX, IMC S class controls with a REC 4096 Board.
424
Absolute master/vernier format – 1:1 input/master, 424:425 master/vernier
for IMC 120, 121, 123 only.
425
Absolute master/vernier format – 1:1 input/master, 425:424 master/vernier
for 8600 series and MAX, IMC S class controls with a REC 4096 Board.
800
Absolute master/vernier format – 1:1 input/master, 800:801 master/vernier
for IMC 120, 121, 123 only.
801
Absolute master/vernier format – 1:1 input/master, 801:800 master/vernier
for 8600 series controllers (is not applicable for use with MAX and IMC S
Class controls)
Gear Ratio
Input:Resolver
3-6
8
Kit includes Resolver Feedback Package, mounting hardware and 3/8” to 3/8” (9.5 mm to 9.5mm) resolver to motor mounting coupling.
Page 18
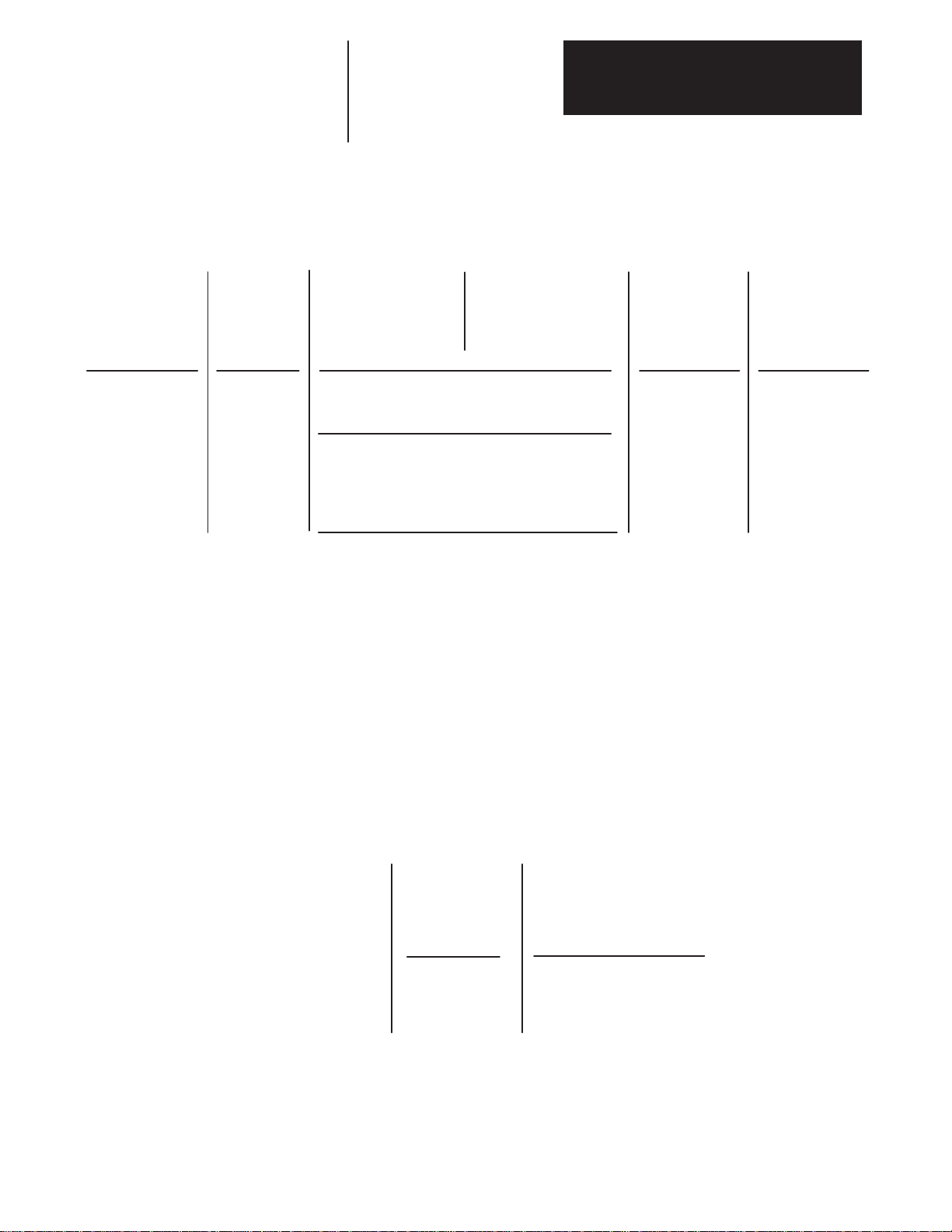
Power and Feedback Cables
Chapter 3
Receiving, Unpacking and Inspection
1326 C
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
Code
1326
1326ES
Description
Standard
Cable
9
Extended
length cable
used with
1391B-ES
&
1391-DES
Only
9
The extended length option is only available for 1326-CFUxx, CPABxx and CPCxx cables and can only be used with 1391B-ES and 1391-DES drives.
–
Type
Code
C
CC
Description
Connector
& Cable
Assembly
Connector
on both
ends (for
use with
1391C-HB)
PAB
Function
Description
Letter
Power Connection
P
Commutation &
F
Feedback Connection
845H/T Encoder
E
All 4.25” (108 mm)
V
Resolver Packages
Fourth Position
Motor Size
Used On
Type
Code
Series A & B (except
AB
1326AB-B4)
Series C & 1326AB-B4
C
All SeriesU
T
Fifth Position
Power Track
Cable
Description
Letter
All Series,
T
used for
high flex
applications
Blank
Standard
Cable
15
Sixth Position
Cable
Length
Code
Description
K
Connector Kit
(No Cable)
15
15’ (4.6 m)
30
30’ (9.1 m)
50
50’ (15.2 m)
100
100’ (30.4 m)
9
150
150’ (45.7 m)
9
200
200’ (61 m)
9
250
250’ (76.2 m)
9
300
300’ (91.4 m)
Blower Mod Kit
1326AB MOD G3
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
–
Type Description
Description
Code
Modifica-
MOD
tion Kit
–
Code
G3
G4
Motor Series
Rear mounted blower for C
series motors
“Saddle” type blower for C
series motors with rear
mounted encoders
3-7
Page 19

Chapter 3
Receiving, Unpacking and Inspection
Planetary Gearbox
1326AB PG
–A05
First Position Second Position Third Position
Bulletin
Number
Type
Code
Description
PG
Straight
Planetary Gearbox
RP
Right Angle
Planetary Gearbox
Used on 1326AB
Motor Series
Code
Standard
A
Series A
B
Series B
C
Series C
10
Use only -21 (Metric) style adapter gearboxes for -A4, -A5 Torque Plus Motors.
Torque Plus
10
-A4
10
-A5
10
-A7
–
Fourth Position
Gear Ratio
(Motor Shaft:Output Shaft)
Code
Description
03
3:1
05
5:1
10
10:1
15
15:1
20
20:1
30
30:1
50
50:1
100
100:1
LB 21–
Fifth Position
Options
Code
Description
Blank
No Options
LB
Low Backlash Option
Sixth Position
Adapter
Code
Description
21
Metric
11
English
3-8
Page 20

Introduction Chapter 1
Manual Objectives 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Precautions 1-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Drive Description 1-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Standard Features 1-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Options/Modifications 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Drive Layout 1-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Specifications Chapter 2
Chapter Objectives 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Drive Specifications 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Environmental Specifications 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Drive Power Dissipation 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transformer Power Dissipation 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table of Contents
Receiving, Unpacking & Inspection Chapter 3
Chapter Objectives 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiving 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Unpacking 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storing 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Description of Operation Chapter 4
Chapter Objectives 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
300V DC Power Bus Supply 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PWM Operation 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shunt Regulator Operation 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Logic Power Supply 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Logic Control Boards 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fault Monitoring and Detection 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Microprocessor Control 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Isolated Current Sensing 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Integral Circuit Breaker 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Line/DB Contactor 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Driver Board 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A Quad B Board 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Starting and Stopping 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power-Up/Down Sequence 4-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inputs, Outputs and Switch SettingsChapter 5
Chapter Objectives 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inputs/Outputs 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Switch Settings 5-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
i
Page 21

Table of Contents
Programming Chapter 6
Chapter Objectives 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Display Description 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Keypad Description 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parameter Levels 6-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accessing Parameter Levels 6-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Programming 6-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parameter Descriptions 6-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Chapter 7
Chapter Objectives 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mounting 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wiring Recommendations 7-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wiring 7-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Start-Up Chapter 8
Chapter Objectives 8-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Start-Up Procedure 8-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear Accel/Decel Control Module 8-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1326AB AC Servomotor Chapter 9
Chapter Objectives 9-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction 9-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Motor Options/Accessories 9-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transformers and Shunt RegulatorsChapter 10
Chapter Objectives 10-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1391 Transformers 10-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shunt Regulator Operation 10-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shunt Regulator Installation 10-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Troubleshooting Chapter 11
Chapter Objectives 11-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Troubleshooting 11-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dimensions Appendix A
Interconnect Drawings Appendix B
Cable Information Appendix C
Block Diagrams Appendix D
Parameter Record Appendix E
ii
Page 22

Chapter
Description of Operation
Chapter Objectives Chapter 4 is intended to familiarize the reader with the circuitry of the
1391-DES in terms of function and operation.
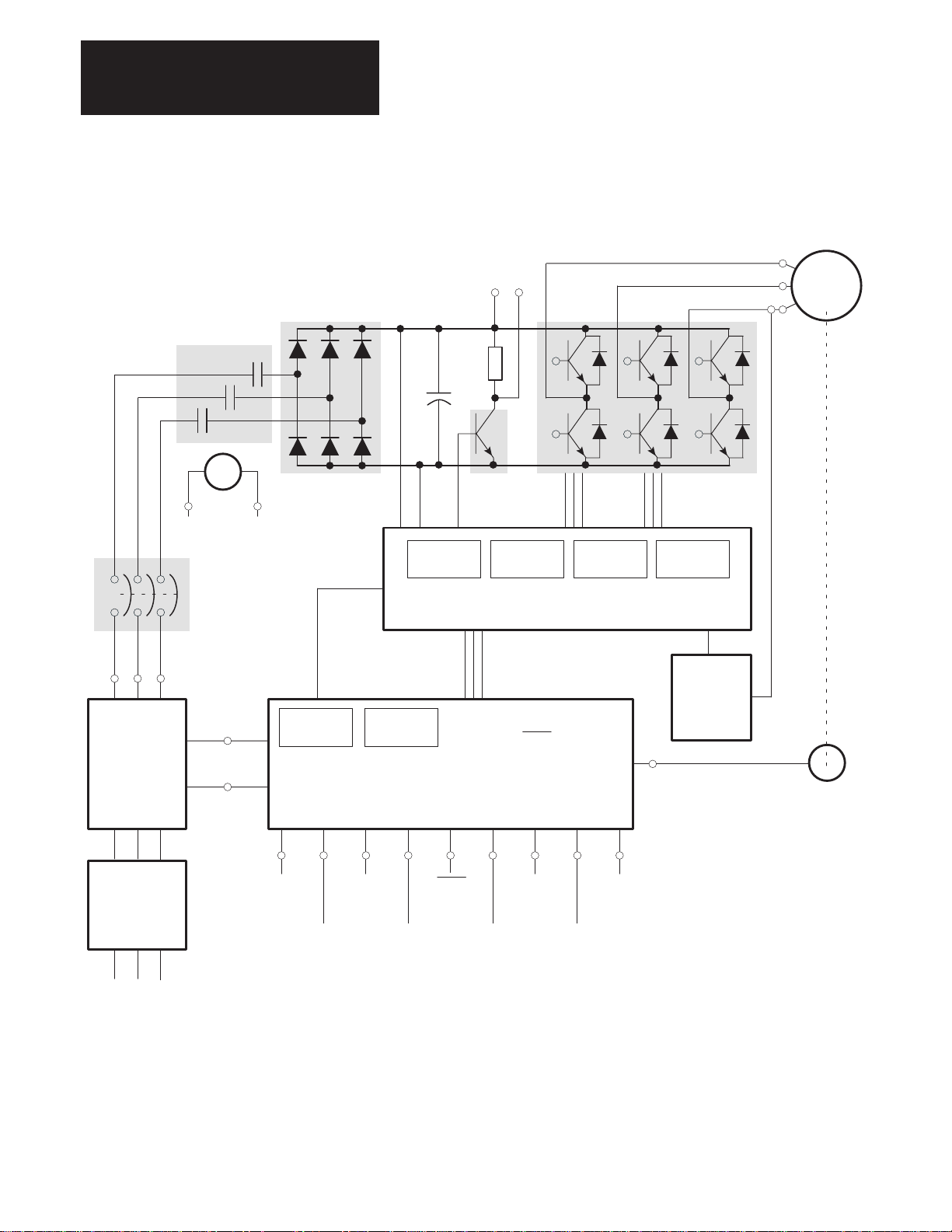
General The intended use of the 1391-DES is to control the speed and torque of an
AC servomotor in a closed loop position system. A complete servo system
can be configured with a 1391-DES Servo Drive, 1326 AC Servomotor
and 1391 Isolation Transformer. Refer to the 1391-DES Block Diagram
presented in Figure 4.4 for general layout.
The 1391-DES PWM Servo Drive is made up of the following: 300V DC
power supply, power transistor output modules, shunt regulator circuit,
logic power supply, microprocessor based logic boards, isolated current
sensing, circuit breaker and line contactor.
300V DC Power Bus Supply The drive contains an integral, unregulated, 300V DC nominal, full load
power supply. It consists of the power transformer input (230V AC,
three-phase, 50 or 60 Hz), a three-phase input bridge rectifier and one
power supply filter capacitor (C1).
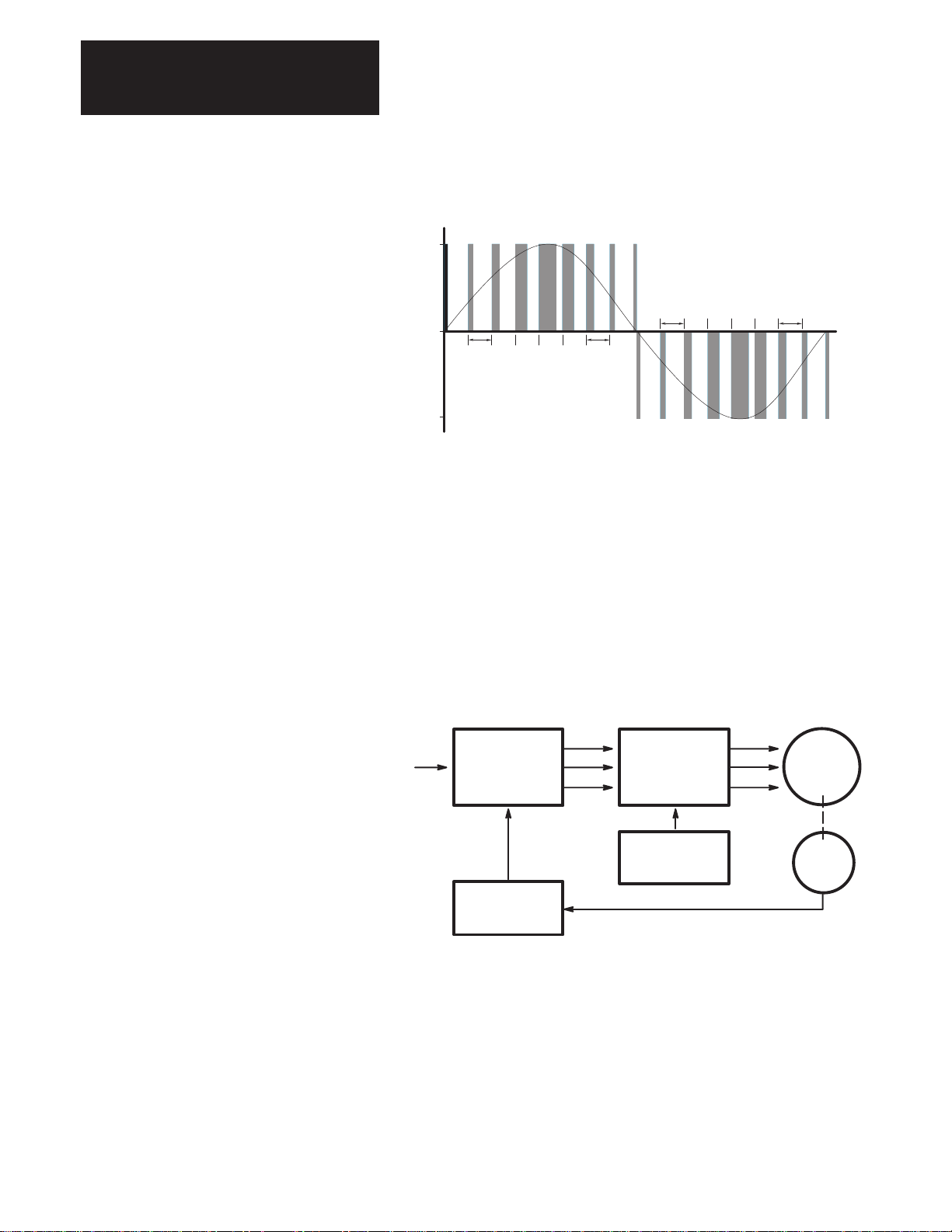
PWM Operation The 1391-DES incorporates a fixed timing wave (V
drive generates a three-phase sine wave by varying the width of the fixed
timing pulses (see Figure 4.1). This frequency corresponds to the velocity
command. The 0 to 10V DC velocity command is scaled to provide an
output frequency (dotted line) that varies from 0 to 200 Hz, depending on
the maximum velocity of the motor. This variable frequency output drives
a permanent magnet AC servomotor whose speed varies as a function of
the frequency.
) of 2500 Hz. The
T
4-1
Page 23
Chapter 4
Description of Operation
Figure 4.1
PWM Waveform
300V DC
Bus
400µs
Typical
0
400µs
Typical
400µs
Typical
400µs
Typical
Time
The three-phase relationship between the reference signal and the timing
wave provide PWM pulses to the power transistor base drive. This base
drive switches the power transistors across the 300V DC bus, providing
current to the motor windings, thus causing the motor to turn. A resolver
attached to the motor provides a signal corresponding to the actual rotor
position of the motor. This signal is decoded to a signal representing rotor
position and is fed to the commutation logic along with the torque
command. In this way, the drive combines the desired position signal and
current reference with the decoded resolver signal to produce a reference
signal commanding the motor to speed up or slow down. See Figure 4.2.
Figure 4.2
Operation
4-2
Current
Reference
Commutation
Logic & Current
Loop Integrator
Position Decoder
PWM Generator
& Base Drive
Timing Signal
Generator
Motor
Resolver
Page 24

Chapter 4
Description of Operation
Shunt Regulator Operation The 1391-DES shunt regulator provides power dissipation for regenerative
conditions when the energy returned to the drive by the motor exceeds that
which can be stored in the bus capacitors. The shunt regulator monitors the
bus voltage and at a predetermined “ON” point activates the shunt
regulator transistor, allowing current to flow through the shunt resistor and
dissipating power in the form of heat. A fuse is placed in series with the
resistor to protect it against short circuit conditions. When the shunt
transistor is activated and power is being dissipated at the resistor, the bus
voltage will quickly decrease, turning the transistor off when the voltage
reaches the “OFF” point. This cycle repeats, provided the bus voltage
continues to increase to the “ON” point. If too much regenerative energy is
present, the bus voltage will continue to increase even with the shunt
regulator on. At a predetermined bus voltage level, the 1391-DES will
determine that an overvoltage condition exists, and trip out on an
Overvoltage Fault.
The shunt regulator behavior is further modified by an adjustable duty
cycle timer. The timer is used to model the shunt resistor temperature.
SW1, a selector switch located on the top of the drive (see Figure 1.1)
determines the temperature level and therefore the average power level at
which the drive will trip out. When this level is reached, the drive will be
forced to trip out on an Overvoltage Fault. This action would be equivalent
to turning the shunt regulator off. Refer to Chapter 10 for further shunt
regulator information.
Logic Power Supply The 1391-DES control logic voltage is ±12V DC and +5V DC. The
voltages are generated on the Power Driver Board, which receives its 36V
AC input from a tertiary winding on the isolation transformer.
Logic Control Boards The Logic Control Boards are the printed circuit boards that are readily
accessible behind the front cover of the drive. They contain all circuits
necessary to control the 1391-DES. These circuits include: the velocity and
current loop, programming panel, A Quad B Board, fault detection and
annunciation circuits, power-up/power-down logic, PWM generation and
forward/reverse controlling circuits.
Fault Monitoring and Detection A number of fault monitor and detection functions exist on the 1391-DES
that guard the drive and help to minimize motor and system faults. The
occurrence of a fault will cause the drive to trip out. In this condition, the
Drive OK (DROK) contact will open and remain open until the fault is
cleared. If the DROK contact is wired into the user’s stop circuit, the
line/DB contactor (M) will also de-energize. This will place the shunt
resistor across the bus causing the motor to dynamic brake to a stop.
These fault conditions are annunciated through the front panel display. The
conditions displayed include:
4-3
Page 25

Chapter 4
Description of Operation
Overtemperature
The drive contains a thermal switch on the heat sink which indirectly
senses transistor module temperature. If the temperature rating of the
switch is exceeded, the DROK contact opens and the drive is disabled.
Power Fault
A fault related to the power bridge section of the drive will cause the drive
to be disabled and open the DROK contact.
Control Voltage Fault
If the control voltage varies more than ±10% of the nominal 12V DC, this
fault will occur. When a fault is detected, the DROK contact opens and the
drive is disabled.
Resolver Loss Fault
If the resolver wiring is grounded or missing, this fault will occur. When a
fault is detected, the DROK contact opens and the drive is disabled.
Overvoltage
The DC power bus voltage is continuously monitored. If it exceeds a preset
level of 405V DC, the DROK contact opens and the drive is disabled
Undervoltage
If the DC power bus voltage drops below 50% of its nominal operating
value an undervoltage fault occurs. Parameter 130 selects the reaction of
the DROK contacts to an undervoltage detection. Two options are possible:
1) DROK opens, but closes when the bus voltage is restored; 2) DROK is
not affected by an undervoltage.
Important: Regardless of interaction with the DROK contacts, the
transistor bridge is disabled upon an undervoltage condition. This is done
to protect the output transistors against voltage transients.
Current Foldback
The drive contains a fixed time versus current overload circuit which
monitors the current through each leg of the output bridge. If the overload
is sustained for a period, resulting in the drive rating being exceeded, the
circuitry will reduce (foldback) the peak output current of the drive. A
continuous overload will fold the available peak current down to its
continuous rating. This condition will reduce the current limit or torque
available to the motor.
Enable LED
The application of an enable signal by the machine position drive will
cause the front panel ENABLE LED to illuminate.
Status LED
The status of the power supplies and fault conditions are monitored
continuously. If a fault is present, the front panel FAULT/DRIVE READY
LED will flash red and the DROK contact will be open. If the drive is
operational, this LED will be green.
4-4
Page 26

Chapter 4
Description of Operation
Microprocessor Control The 1391-DES is controlled by an 80C196KB microprocessor. Velocity
control, sequencing, fault logic, programming and option control is
performed by the processor. Current control is analog, as is the input
velocity command. The input command is fed through a 14 bit digital to
analog converter (13 bits/8192 resolution and a +/– sign bit).
Isolated Current Sensing The Logic Control Boards receive current feedback from the Isolated
Current Sense Board. This circuitry provides the data used for current loop
closure.
Integral Circuit Breaker The DC bus supply, input rectifier and power circuitry are protected against
overcurrents by an integral three pole magnetic circuit breaker. This is not
designed nor intended to meet NEC branch circuit requirements.
Line/DB Contactor The three-phase incoming AC line is opened by the contactor whenever the
voltage on the contactor coil is removed. This operation in conjunction
with the shunt regulator reduces the bus voltage when the contactor is
disabled. The Logic Control Board remains energized except when voltage
is removed from the incoming isolation transformer.
Important: The 1391-DES contains a definite purpose contactor that is not
to be energized/de-energized more than twice an hour on a continuous
basis. The life of the contactor may be reduced considerably if the cycle is
exceeded. Contact your local Allen-Bradley Sales Representative for
additional information.
Power Driver Board The Power Driver Board contains the circuitry needed to switch the power
transistor modules.
A Quad B Board The A Quad B Board changes the resolver signal from a 1326AB or AD
motor into an encoder signal for use by a position controller (such as an
IMC S Class or 12x family controller).
Starting and Stopping
ATTENTION: The Enable control circuitry in the 1391-DES
!
includes solid-state components. If hazards due to accidental
contact with moving machinery or unintentional flow of liquid,
gas or solids exist, an additional hardwired stop circuit may be
required. Refer to the codes and standards applicable to your
particular system for specific requirements and additional
information. A device that removes AC input power when a
stop is initiated is an integral part of this drive. Refer to the
following individual stop mode explanations.
4-5
Page 27

Chapter 4
Description of Operation
ATTENTION: The user has the ultimate responsibility to
!
determine which stopping method is best suited to the application and will meet applicable standards for operator safety.
Starting and Stopping must be accomplished by hardwired user supplied
elements as shown in Appendix B. Stopping modes for the 1391-DES are
outlined below. Refer to the paragraphs that follow for detailed
information. The effects described below assume that the 36V AC control
voltage has not been de-energized.
Cause Effect on Motor
De-energize Line/DB Contactor (M) Coil Dynamic Brake
Speed Command brought to Zero Regenerative Brake
Open Enable Input Regenerative Brake
DROK Opens (Fault) Coast to Stop
Dynamic Braking
When the line/DB contactor (M) is de-energized by the control circuitry, an
inherent dynamic braking effect will occur during the DC bus decay,
provided the 36V AC logic voltage is not de-energized. The dynamic
braking effect depends on the value of the shunt regulator resistor and total
load inertia.
Important: Frequent cycling of the line/DB contactor to start/stop the
motor will reduce the life of the contactor.
Regenerative Braking
Normal run commands to the drive are performed through the Enable input
and any additional customer supplied control circuitry. Refer to Appendix
B. With input power applied, a mechanical contact closure (or solid-state
contact closure rated +15 to +30V DC, 30 mA) between TB2-9 & 10 will
cause the drive to run, provided the line/DB contactor (M) has been
energized by the control circuitry. When the Enable input is de-energized,
the maximum available reverse torque is applied to the motor in a
regenerative stopping mode, which will occur for approximately 450ms.
Coast
4-6
An internal drive fault opens the DROK contact. Coasting will only occur
if the DROK contact is not wired to the line/DB contactor coil (M) or the
Enable input circuits.
Page 28
Chapter 4
Description of Operation
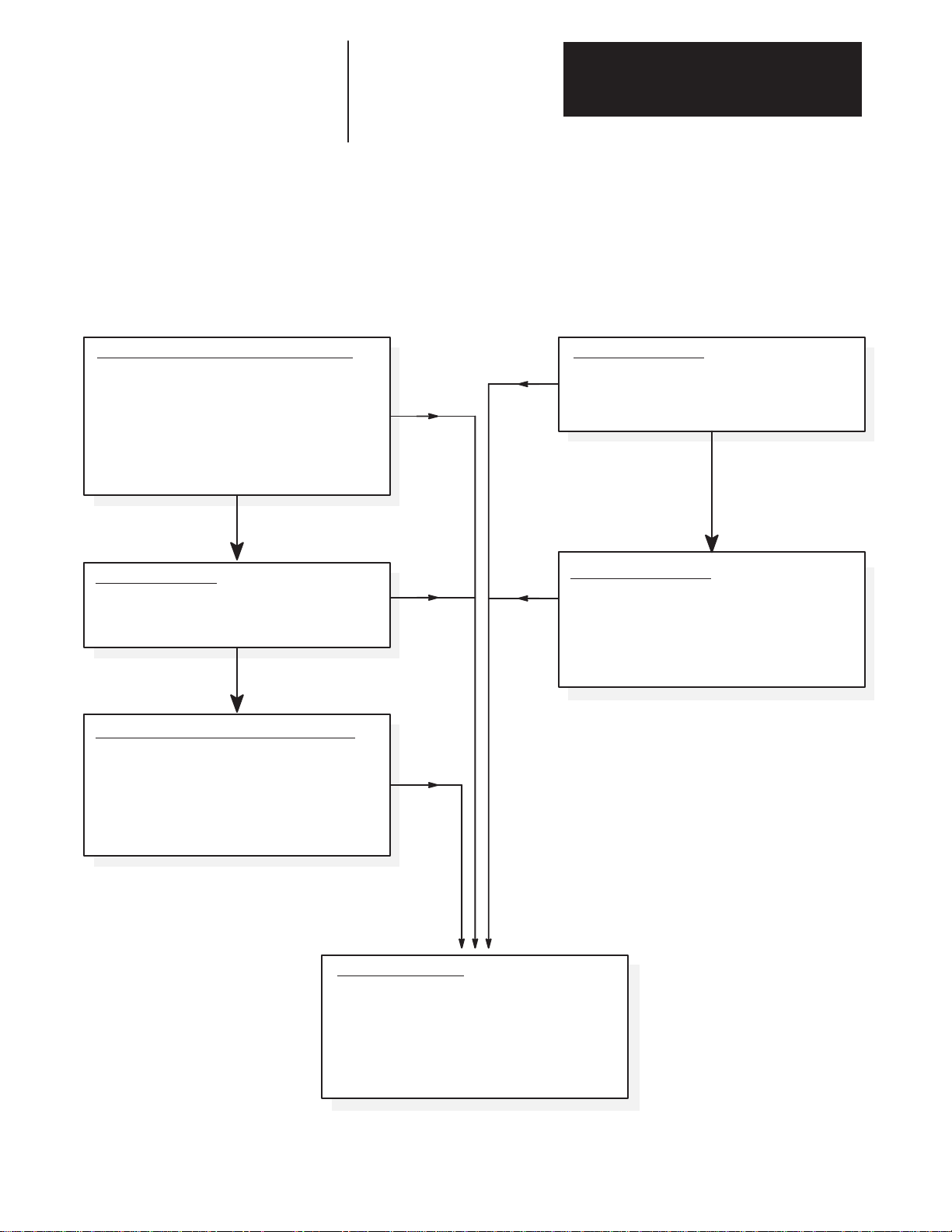
Power-Up/Down Sequence Figure 4.3 describes the various steps involved in the power-up/down
sequence of the 1391-DES Drive.
Figure 4.3
Drive Power-Up / Down Sequence
POWER-UP SEQUENCE
Apply AC Input Power to Isolation Transformer
a) Logic power supplies and base drive circuits
power-up.
b) Apply 115V AC to contactor.
c) Power bus charges.
d) If no faults are encountered, the DROK relay
energizes. Drive is ready to receive customer
enable signal.
Enable Signal Applied
Minimum of 100 ms after Contactor is Closed
a) Base drive enabled and will respond to velocity
command inputs.
Enable Signal is Applied Prior to 36V AC Power
a) When 36V AC power is applied, fault circuits detect
that the enable signal is already applied. Random
fault conditions occur.
b) Re-application of enable after resetting the drive
and with 36V AC power still present, will energize
the drive.
Fault
Fault
Fault
Fault
Fault
POWER-DOWN SEQUENCE
Enable Signal Removed
a) Motor will regenerate to a stop.
b) Output power stage is disabled.
c) DROK relay maintains a no fault status.
AC Input Power Removed
a) Logic and DC link power supplies begin decaying to
zero volts.
b) Undervoltage (fault) condition occurs.
c) DROK relay de-energizes based on setting of
parameter 130.
Fault Condition Occurs
a) Drive output stage disabled.
b) DROK relay is de-energized and a fault is
displayed.
c) If contactor (M) is wired to the DROK relay in a
stop string, contactor will open and the shunt
regulator will discharge the power bus supply.
4-7
Page 29
Chapter 4
Description of Operation
Contactor
Rectifier D1
Figure 4.4
1391-DES Block Diagram
External Shunt
Regulator
Resistor
TB5–1
TB5–2
TB5–3
1326A AC
Servomotor
Isolation
Transformer
(MPT)
M
M
M
TB4–11
Contactor Coil
Circuit Breaker
(MCB)
TB5–4
TB5–5
TB5–6
TB4–19
TB4–21
36V AC
1–Phase
M
TB4–12
Protection
Circuitry
Digital Control Boards
Shunt
Regulator
Power Driver Board
Control
Logic
R1
C1
Shunt
Regulator
Transistor
Transistor
Base Drive
LEDs
Status
Enable
Logic
Suppy
Power Transistor
Output Modules
Power Fault
Protection
TB1–1
through
TB1–10
Isolated
Current
Sense
Board
Brushless
Resolver
User Supplied
Branch Circuit
Protection &
Disconnect
AC Line Input
4-8
TB2–1
TB2–2
TB2–3
Velocity
Command
TB2–4
TB2–5
Velocity
Output
TB2–6
TB2–7
Current
Output
TB2–9
TB2–10
Reset Torque
Enable
TB2–11
TB2–12
Adjustable
Current
Limit
TB2–13
TB2–14
Command
Input
TB2–15
TB2–16
Encoder
Output
TB3–1
through
TB3–10
TB4–17
TB4–18
DROK
Contact
Page 30

Chapter
Inputs, Outputs and Switch Settings
Chapter Objectives Chapter 5 contains descriptions of the various inputs and outputs available
on the 1391-DES Digital Servo Drive. Additionally, information for
properly setting the drive switches is provided for reference when you
perform start-up. For information on shunt regulator adjustments, refer to
Chapter 10.
Inputs/Outputs The following paragraphs provide detailed descriptions of the various
inputs and outputs available for the 1391-DES. See Figure 5.2 for terminal
block locations.
Terminal Block - TB1
Resolver Signals (TB1, Terminals 1-10)
These terminals are used for connecting the commutation resolver from the
motor to the drive. Refer to Appendix B for connection details.
Important: Terminal 1 of TB1 must be connected to chassis ground at the
Ground Stud (see Figure 5.2 for Ground Stud location).
Terminal Block - TB2
Please note that there are no connections to TB2-18, 19 & 20.
Velocity Command Input (TB2, Terminals 1, 2)
The drive will accept up to a ±10V DC velocity command signal to achieve
maximum motor speed. Voltages lower than ±10V DC can be used by
reprogramming parameter 211 (Analog Velocity Gain). The plus (+) and
minus (–) reference are at terminals 2 and 1, respectively. Shield must be
terminated at one end only. The differential impedance of the velocity
command input is 80k ohms (40k ohms for single ended inputs).
Signal Common (TB2, Terminals 3, 5, 7, 8, 12, 17)
Signal input reference point.
Analog Out 1 (Velocity) (TB2, Terminal 4)
A voltage corresponding to the motor velocity and direction of rotation will
be present between this terminal and signal common (Terminal 5). +1.2V
DC for each 1000 rpm is available. Minimum impedance that can be
placed across this output is 10k ohm.
5-1
Page 31

Chapter 5
Inputs, Outputs and Switch Settings
Analog Out 2 (Current) (TB2, Terminal 6)
A voltage corresponding to positive and negative current will be present at
this terminal and signal common (Terminal 7). +3V DC equals 100% of the
continuous rating of the motor with +6V DC equaling 200%. Minimum
impedance that can be placed across this output is 10k ohm.
Enable Input (TB2, Terminals 9, 10)
Normal Run commands to the drive are performed through the Enable
input and any additional user supplied run control circuitry. With input
power applied and the line contactor energized, a mechanical contact
closure (or a solid-state contact closure rated +15 to +30V DC, 30 mA)
between TB2-9 & 10 will cause the drive to run. When this input is
de-energized, the control will cause a regenerative braking action in the
motor.
Reset (TB2, Terminal 11)
Removing the Enable signal and momentarily connecting this terminal to
signal common (TB2-12) will reset the drive after a drive fault occurs.
Important: A Reset must
not be initiated until the cause is determined and
corrected.
Adjustable Current Limit (TB2, Terminal 13, 14)
The current limit of the drive is set to 300% of motor continuous rating or
twice the continuous rating of the drive, whichever is lower. Applying a
voltage between 0 and +10V DC to terminals 13 & 14 will limit the peak
current of the drive. The range of this input is the lower of the following:
- Value set by parameters 156 and 157,
- Twice the continuous rating of the drive.
For each volt applied, 30% reduction of current limit is achieved, based on
300% of motor rating being available. If only 200% current (drive peak) is
available, a voltage of less than 3.33 volts will have no effect on current
limit. On TB2, pin 14 must be positive with respect to pin 13 for this input
to operate. Refer to the following information.
Percent of Percent of
Voltage
10V 10% 4V 180%
9V 30% 3V 210%
8V 60% 2V 240%
7V 90% 1V 270%
6V 120% 0V (open) 300%
5V 150%
Peak Rating Voltage Peak Rating
5-2
Torque Command Input (TB2, Terminals 15, 16)
Terminals 15 and 16 provide a small amount of input filtering for operating
the drive as a torque block (with IMC S Class, MAX, IMC 121 and 123) or
velocity feedforward mode. A ±3V DC command equals 100% of the
motor current setting (as set by parameter 155).
Page 32

Chapter 5
Inputs, Outputs and Switch Settings
Terminal Block - TB3 (A Quad B Board)
Figure 5.1 provides interconnect information between the position
controller and TB3 on the A Quad B Board.
ATTENTION: To guard against possible damage to the A
!
Figure 5.1
A Quad B Board Wiring
Quad B Board, assure that wiring between TB3 and the position
controller is correct. Refer to Figure 5.1.
A Quad B Board
1 TB2 20
1 TB3 10
To Position
Controller
Important: Note terminal orientation prior to wiring.
1
Recommended Wire – Belden #9728 or equivalent. Maximum distance between the A Quad B Board and
the position controller is 40 feet (12.2 meters) using a 5 volt signal. For distances up to 300 feet (91 meters),
18 AWG (0.8 mm
2
For proper operation when interconnecting to IMC classic products (IMC 110, 12x), the B and B (NOT)
signals must be reversed.
3
When interfacing to IMC 121 or 123 controllers, use the 1391-CAQB cable. When interfacing to the
integrated packages of the MAX or S Class controls, use the 1391-SAQB or 1391 SAQBK cable.
1
2
) wire (Belden 9388 or equivalent) and an 8 to 15V DC power supply must be used.
Top Logic Control Board
21S1
987654321
Power Supply
1
Input
TB3
Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Description
A
A (NOT)
2
B
2
B (NOT)
Z
Z (NOT)
+5V DC (
Signal Common
+8 to +15V DC In
No Connection
±5%)
The A Quad B option operates in the same manner as the Allen-Bradley
845H Line Driver Encoder (26LS31 line driver output). The option
requires either a regulated +5V DC at terminal 7 or an unregulated +8 to
+15V DC input at terminal 9 (board draws 125mA maximum). The pulse
train output is selectable to 256, 512, 1024 or 2048 lines per revolution via
the Encoder Output switch, S1 (see page 5-6).
Terminal Block - TB4
Please note that there are no connections to TB4-20 & 22.
Contactor Coil (TB4, Terminals 11, 12)
Connections to the coil of the integral contactor are performed at these
terminals. The coil voltage is 115V AC, 50/60 Hz.
Important: Drives with a catalog number of 1391-DESxx-DI-AQB-A will
have a 24V DC coil. Drives with a catalog number of 1391-DESxx-DIAQB-B will have a 240V AC coil.
5-3
Page 33

Chapter 5
Inputs, Outputs and Switch Settings
“M” Contactor Auxiliary Contacts (TB4, Terminals 13, 14, 15, 16)
The auxiliary contacts of the integral contactor are accessed through these
terminals. Refer to Table 5.A for contact ratings.
Table 5.A
“M” Contact Ratings (minimum 50 mA at all voltages)
AC Ratings
Volts
)
(U
e
12-120
220-240
380-480
500-600
Amperes
)
(I
e
6
3
1.5
1.2
DC Ratings
Volts
)
(U
e
28
110
220
440
660
Amperes
)
(I
e
5.0
1.25
0.62
0.27
0.20
Drive OK (DROK) Contacts (TB4, Terminals 17, 18)
Application of power to the transformer energizes the logic supply of the
drive. When 50% of rated DC Bus voltage is achieved and no drive faults
are detected, this relay contact is closed. The contact remains closed until a
drive fault occurs or power is removed from the transformer. Contact
rating: 115V AC, 1A or 24V DC, 0.3A.
36V AC Logic Supply Voltage (TB4, Terminals 19, 21)
The isolation transformer contains four separate windings. Each winding
supplies 36V AC. The 36V AC leads are brought out to terminals 19 and
21 of TB4. See Chapter 10 for transformer details.
Terminal Block - TB5
Motor Power Terminals (TB5, Terminals 1, 2, 3)
Motor power is provided at these terminals. Refer to Chapter 7 and
Appendix B for connection details.
5-4
Input Power Terminals (TB5, Terminals 4, 5, 6)
The drive requires a 230V AC, three-phase, 50 or 60 Hz input supplied by
the transformer secondary. Refer to Chapters 7, 10 and Appendix B for
wiring and transformer information.
External Shunt Regulator Resistor (TB5, Terminals 8, 9, 10)
The 22.5A drives have provisions to accept an external shunt resistor to
supplement the integral unit. This is available for applications that require
the dissipation of more regenerative energy to the DC Bus. To use an
external shunt resistor, first remove the jumper at terminals 8 and 10 of
TB5. Consult your Allen-Bradley sales office for application assistance.
Additionally, the bus voltage can be monitored at terminals 9 (+) and 7 (–)
of TB5.
The shunt regulator resistor supplied with the 1391-DES45 must be
externally mounted and connected to terminals 8 and 9 of TB5 prior to
operation. Refer to Chapter 10 and Appendix B for details.
Page 34

Chapter 5
Inputs, Outputs and Switch Settings
Figure 5.2
Terminal Block, Circuit Board and Switch Locations
TB1
1
A Quad B Board
1
TB3
Ground Stud
Top View of Controller
Main Logic Control Board
Display Board
Memory Board
1
2
S1
1
TB2
1
1
TB5
10
SW1
MCB
22
F3
1
F2
11
TB4
F3 provided on 15 & 22.5A units only
15A = Bussmann KLM10 or equivalent
22.5A = Bussmann FNQ6 1/4 or equivalent
F1
A Quad B Board
Main Logic Control Board
Display, Memory and Adapter Boards
5-5
Page 35

Chapter 5
Inputs, Outputs and Switch Settings
Switch Settings This section provides information on setting the Duty Cycle Selector
switch (SW1) and the A Quad B Encoder Output switch (S1). Note that the
settings for 1326AP motors are the same as 1326AB motors. Refer to
Figure 5.2 for switch locations.
Duty Cycle Selector Switch - SW1
The Duty Cycle Selector Switch (SW1) which is located on top of the
drive, modifies the behavior of the shunt regulator. The switch determines
the temperature level and therefore the average power level at which the
drive will fault. Refer to Chapter 10 for detailed switch setting information.
A Quad B Encoder Output Switch - S1
S1 selects the line count that will be output from the A Quad B Board.
ATTENTION: Incorrect setting of S1 can cause erratic and/or
!
improper machine motion which may result in personal injury
or equipment damage. Assure that switch S1 has been properly
set as shown in Figure 5.3.
Figure 5.3
A Quad B Board Switch (S1) Settings
– ON –
S1
12
2 Marker Pulses per Revolution
CCW Rotation of Motor Shaft
(similar to Allen-Bradley 845H)
Line Count/
Revolution
2048
1024
512
256
A (NOT)
B (NOT)
Z (NOT)
S1-1
Switch Setting
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
A
B
Z
S1-2
Switch Setting
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
5-6
Page 36

Chapter 5
Inputs, Outputs and Switch Settings
When using the A Quad B option with Allen-Bradley IMC motion
controllers, the AMP parameters will be set according to the line count
selected. In general, one parameter must be justified when using this
device.
Important: For all IMC classic products (IMC 110, 12x) the normal line
counts per cycle of the encoder must be divided by two since the drive will
see two markers per cycle.
Example (using an IMC 12x Controller)
With switch S1 set to 1024 lines per revolution (S1-2 OFF, S1-1 ON), the
lines per cycle of the position feedback device (located in the Feedback
Parameters File) must be 2048.
1024 x 4 = 4096 / 2 = 2048
(Quadrature)
Lines/Revolution 2 Markers/Revolution
5-7
Page 37

Chapter 5
Inputs, Outputs and Switch Settings
End of Chapter
5-8
Page 38

Chapter
Programming
Chapter Objectives This chapter explains the programming/setup system of the 1391-DES
Digital AC Servo Drive. Included is an explanation of the display, general
programming procedure and description of the programmable parameters.
You will need to read this chapter before performing the start-up procedure
provided in Chapter 8.
Display Description The 1391-DES display is used for programming, as well as status and
diagnostic messages. The display consists of a 16 character, 2 line,
“Super-Twist” LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) that allows a wide viewing
area. The display can be divided into several different sections as shown in
Figure 6.1.
Figure 6.1
LCD Display
Level Indicator
Parameter Number
Parameter Name
Parameter Value
When power is applied to the 1391-DES the Basic Display (see Figure 6.4)
will be shown. The Basic Display alternates (every 2 seconds) between the
two displays shown. The alternating display indicates that the drive is
functioning normally.
Keypad Description The 1391-DES display panel utilizes five keys (pushbuttons) which allow
the various parameters to be accessed. Once a parameter is accessed, status
information of the drive can be viewed. In addition, certain parameters can
also be modified.
Each of the keys has several functions depending on the view/modify
mode. Refer Figure 6.2 and the paragraphs that follow for a description of
the display panel controls.
6-1
Page 39

Chapter 6
Programming
Figure 6.2
1391-DES Display Panel
Display
Keypad
Up Arrow Key
This key is used to increase values when modifying
parameters. Other uses will be described when applicable.
Down Arrow Key
The Down Arrow key is used to activate modifiable
parameters or decrease values. Other uses will be described
as required.
Left Arrow Key
This key is used to scroll through parameters or move the
cursor when modifying parameters. Other key functions will
be described as needed.
Right Arrow Key
The Right Arrow key can be used to scroll through
parameters or move the cursor when modifying. Other key
functions will be described when required.
6-2
Enter
Enter Key
The Enter key is used to make a selection or store a changed
parameter value in memory. Other key functions will be
described as needed.
Page 40

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter Levels For ease of use, the various parameters of the 1391-DES are numbered and
arranged in three different levels. The levels range from viewing simple
drive status parameters to more complex setup information. The three
levels are as follows:
View Level
The View level allows viewing only of the drive operating conditions (see
below). The View level is denoted on the display by a single dot (
the upper left corner (see Figure 6.1).
03 Drive Size
19 Final Velocity Command
20 Velocity Feedback
45 Iq (Torque) Current Reference
50 Current Feedback Rated
51 Current Limit
57 Analog Velocity Command
154 Motor Type
253 Display Software Version
254 Drive Software Version
) in
Modify Level
The Modify level allows access to the View level parameters in addition to
the system configuration parameters listed below. This level of
programming allows parameter modification to some of the View level
parameters and the other parameters listed. The Modify level is denoted by
two dots (
68 Bandwidth Maximum
69 Auto Tune Friction Compensation
128 EEprom Functions
130 Drive OK Mode
131 Language Select
132 Velocity Mode Select
133 Torque Mode Select
144 Clockwise Velocity Limit
145 Counterclockwise Velocity Limit
146 Accel/Decel Ramp
156 Positive Current Limit
157 Negative Current Limit
159 Current Preload
168 Kp Velocity Loop
169 Ki Velocity Loop
170 Feed Forward Gain
171 Static Gain
182 Desired Velocity Bandwidth
183 Velocity Damping Selection
184 Velocity Low Pass Filter Bandwidth
185 Lead/Lag Velocity Feedback Filter Gain
186 Lead/Lag Velocity Feedback Filter Bandwidth
187 Auto Tune Velocity
188 Auto Tune Current Limit
189 Auto Tune Inertia
190 Auto Tune Select
210 A/D Converter Offset
211 Analog Velocity Gain
) in the upper left corner of the display (see Figure 6.1).
6-3
Page 41

Chapter 6
Programming
212 D/A #1 Gain
233 Cable Compensation
Maintenance Level
The Maintenance level allows access to all of the parameters listed in the
View and Modify levels in addition to the parameters listed below. Two
squares (
denote that this level is active (see Figure 6.1).
04 Adapter Type
05 Logic Command
06 Drive Faults
07 Drive Status
08 Auto Tune Status
17 Velocity Reference Whole
18 Velocity Reference Fraction
21 Filtered Velocity Feedback
22 Average Motor Velocity
23 Resolver Turns
24 Resolver Position Feedback
25 Pre Ramp Velocity
33 Proportional Velocity Error
34 Velocity Loop PI Output
35 Integral Velocity Error
44 External Torque Reference
46 Id (Flux) Current Reference
47 IT Protection Limit
48 Bridge Current Limit
49 Current Feedback Scale
58 D/A #1 Command Value
59 D/A #2 Command Value
129 Units Select
135 Up to Speed Tolerance
136 Drive Address
155 Rated Motor Current
158 Current Rate Limit
172 Velocity Loop Integrator Preset Value
181 Motor Inertia
199 Friction Compensation
200 Friction Hysteresis
201 Friction Bit
213 D/A #2 Gain
222 Id RPM Start
223 Id RPM End
224 Id Percent Limit
234 Transport Compensation
243 Indirect Sink Parameter 1
244 Indirect Source Parameter 1
245 Indirect Sink Parameter 2
246 Indirect Source Parameter 2
251 Access Timeout
252 Drive Init Stats
) will be present in the upper left corner of the display to
6-4
In addition to the three levels described, each level has additional auxiliary
menus. These menus allow quick access to important parameters such as
fault status and setup data. Refer to Figure 6.3 for further information.
Page 42

Figure 6.3
1391-DES Programming Levels
Chapter 6
Programming
Digital Servo
1391-DESxx
View/modify
parameters
View Level
Parameters
View/modify
parameters
Allen-Bradley Co
Copyright 1992
View Level
View current
drive status
Status
Messages
Use Up & Down
Arrow Keys to
View Status
Enter
Modify Level
View current
drive status
Basic Display (alternating)
View current
fault status
Fault
Messages
Use Up & Down
Arrow Keys to
View Faults
View current
fault status
Use Left & Right
Arrow Keys to Move
through Selections
or Parameters
Save/retrieve
drive parameters
Auto tune the
servo drive
= Down Arrow Key
= Up Arrow Key
= Left Arrow Key
= Right Arrow Key
Setup drive
with motor data
Modify Level
Parameters
within 4 seconds, simultaneously press
View/modify
parameters
Maintenance Lev-
el Parameters
Use Left & Right
Arrow keys to View
Parameters – Use
the Down Arrow
key to Modify
Parameters
Status
Messages
Enter
Enter
Maintenance Level
View current
drive status
Status
Messages
Use Up & Down
Arrow Keys to
View Status
Fault
Messages
Use Up & Down
Arrow Keys to
View Faults
View current
fault status
Fault
Messages
Use Up & Down
Arrow Keys to
View Faults
EEprom func
parameter 128
Use Up & Down
Arrow Keys to
Modify, Enter to
Select and Right
Arrow + Enter to
Cancel
Save/retrieve
drive parameters
EEprom func
parameter 128
Use Up & Down
Arrow Keys to
Modify, Enter to
Select and Right
Arrow + Enter to
Cancel
Auto Tune
Procedure
Follow Auto Tune
Procedure
Auto tune the
servo drive
Auto tune the
servo drive
Follow Auto Tune
Procedure
Motor type
parameter 154
Use Up & Down
Arrow Keys to
Modify, Enter to
Select and Right
Arrow + Enter to
Cancel
Setup drive
with motor data
Motor type
parameter 154
Use Up & Down
Arrow Keys to
Modify, Enter to
Select and Right
Arrow + Enter to
Cancel
6-5
Page 43

Chapter 6
Programming
Accessing Parameter Levels To help guard against access to advanced programming levels by untrained
personnel, special key combinations must be pressed to gain access.
When power is first applied to the 1391-DES the Basic Display (see
Figure 6.4) will be shown. The Basic Display alternates (every 2 seconds)
between the two displays shown. The alternating display indicates that the
drive is functioning normally. If for some reason the display does not
alternate or is not shown, refer to Chapter 11, Troubleshooting.
Figure 6.4
1391-DES Basic Display
The three parameter levels can be accessed by using the key combinations
described below. The parameter level can be confirmed by observing the
number of dots in the upper left corner of the display.
■ To Access the View Level
Press the Down Arrow key once, the View Level will be active.
Enter
■ To Access the Modify Level
Press the up, down and left arrow keys simultaneously and release.
Enter
■ To Access the Maintenance Level
a) Press the up, down and left arrow keys simultaneously,
then within 4 seconds . . .
b) simultaneously press the up, left arrow and Enter keys and release.
Enter
within 4 seconds, simultaneously press
6-6
Enter
■ To Return to the Basic Display
Press the Up Arrow and Enter keys simultaneously to return to the Basic
Display.
Page 44

Chapter 6
Programming
Programming Important: Programming of most 1391-DES parameters is not required.
When power is initially applied to the drive, a prompted start-up procedure
will occur (first time only). The display will guide the user through this
procedure, which will set all of the main parameters for machine operation.
Parameters listed in this chapter are essentially for reference only. Follow
the Start-Up Procedure in Chapter 8 before attempting to change any
parameters.
Pressing the Down Arrow key from the Basic Display (see Figure 6.4) will
cause the “View/Modify parameters” menu to be displayed. Pressing the
Down Arrow key a second time allows the View level parameters to be
viewed. From this point any of the other levels can be selected using the
preceding procedures.
After a level has been selected, the Left and Right Arrow keys will be used
to locate the desired parameter.
Parameter Types
Two types of parameters are used in the 1391-DES programming system;
Numeric and Selection.
Numeric Parameter
A Numeric parameter contains a numeric value. When this type of
parameter is displayed in the Modify or Maintenance levels, pressing the
Down Arrow key will cause the cursor to flash. Pressing the right or left
arrow keys will then move the cursor one digit to the right or left. The Up
and Down Arrow keys can then be used to scroll to the desired value.
When the parameter is set to the desired value, press the Enter key. The
cursor will stop flashing to indicate that the change has been loaded into
memory. To cancel the modification (before pressing Enter), press the
Right Arrow and Enter keys simultaneously.
Selection Parameter
When viewing a Selection parameter, multiple choices will be displayed
for the parameter. Pressing the Up and Down Arrow keys will scroll
through the possible choices. When the desired choice is displayed, press
the Enter key to make the selection. To cancel the selection (before
pressing Enter), press the Right Arrow and Enter keys simultaneously.
Important: Parameter values or selections will not be stored in EEprom
until parameter 128 (EEprom Functions) is accessed, and item 3 (Save) is
selected. Parameter 128 can be accessed at any time by pressing the Left
and Right Arrow keys simultaneously.
6-7
Page 45

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter Descriptions This section lists and describes the various parameters currently available
(software version 2.01). Not all parameters will be available in every
parameter level. Refer to the “Parameter Type” classification in each
description for further information. In addition to the Parameter Type, each
description (when applicable) will also provide Minimum, Maximum and
Default Values. Please note that parameter numbers not listed are reserved
for future software enhancements.
Important: Parameter names followed by an asterisk (*) should not be
modified. These parameters are provided for information purposes only.
ATTENTION: To guard against personnel injury and/or
!
machine damage caused by improper programming, parameter
names followed by an asterisk (*) should only be modified by
qualified personnel.
Parameter 00 – Reset Display Faults (Rst Disp Flts)
This parameter clears display faults.
Parameter Type: View/Modify in Maintenance level only
Parameter 03 – Drive Size *
The current drive size in amperes (as read from the drive on power-up) is
contained in this parameter.
Parameter Type: View only, all levels
Parameter 04 – Adapter Type *
This parameter is not active at this time.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Parameter 05 – Logic Command (Logic Comd) *
This parameter contains a 16 bit, bit encoded, binary word that represents
the logic commands from an adapter board. A bit set to “1” indicates that a
condition exists. If a “0” is displayed that condition does not exist.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
6-8
Page 46

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 06 – Drive Faults (Drv Faults) *
Parameter 06 is a 16 bit, binary word that represents the drive faults. A “1”
indicates that a fault has occurred. If a “0” is displayed, a fault has not
occurred. Refer to the list below for an explanation of the individual bits.
Bit 15 Bit 0
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
bit 0 Not Used
bit 1 Drive Overtemperature
bit 2 Power Up Enable
bit 3 Not Used
bit 4 Control Voltage Fault
bit 5 Resolver Loss
bit 6 Not Used
bit 7 Power Fault
bit 8 Bus Overvoltage
bit 9 Not Used
bit 10 External A/D Conversion Fault
bit 11 Internal A/D Conversion Fault
bit 12 Not Used
bit 13 Not Used
bit 14 EEprom Fault
bit 15 Auto Tune Fault
Parameter 07 – Drive Status (Drv Status) *
A 16 bit, binary word represents the drive status. A “1” indicates that a
particular state exists. If a “0” is displayed, that state does not exist. Refer
to the list below for an explanation of the individual bits.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
bit 0 Class 1 Fault
bit 1 At Zero Speed
bit 2 At Speed
bit 3 IT Active
bit 4 EEprom Write Enabled
bit 5 Drive State
bit 6 Drive State
bit 7 Drive State
bit 8 At Current Limit.
bit 9 Not Used
bit 10 Not Used
bit 11 Not Used
bit 12 Not Used
bit 13 Not Used
bit 14 Not Used
bit 15 Not Used.
6-9
Page 47

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 08 – Auto Tune Status (ATn Status) *
A 16 bit, binary word represents the auto tune status. A “1” indicates that a
particular state exists. If a “0” is displayed, that state does not exist. Refer
to the list below for an explanation of the individual bits.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
bit 0 Ready
bit 1 Active
bit 2 Enable Drive
bit 3 Not Used
bit 4 Accel
bit 5 Decel
bit 6 Abort
bit 7 Complete
bit 8 Enable Time Limit
bit 9 Execution Time Limit
bit 10 Accel Fault
bit 11 Decel Fault
bit 12 Gain Calculation Fault
bit 13 Gains Updated
bit 14 Not Used
bit 15 Not Used
Parameter 17 – Velocity Reference Whole (Vel Ref Whole) *
This parameter supplies the whole number part of an internal digital
velocity reference, when internal digital velocity control has been selected
in parameter 132. The data contained in this parameter represents the
whole number of the velocity reference.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –8000 rpm
Maximum Value: +8000 rpm
Parameter 18 – Velocity Reference Fraction (Vel Ref Fract) *
The fractional part of an external velocity reference when internal digital
velocity control has been selected in parameter 132 is contained in this
parameter. The data contained represents the low order, fractional part of
the internal digital velocity reference.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rpm
Maximum Value: 65535 rpm
Parameter 19 – Final Velocity Command (Vel Command) *
Parameter 19 indicates the value of the velocity reference into the velocity
PI regulator, after the Velocity Mode Select (parameter 132) and the
Velocity Limiter.
Parameter Type: View only, all levels
Minimum Value: –8000 rpm
Maximum Value: +8000 rpm
6-10
Page 48

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 20 – Velocity Feedback (Vel Feedback) *
The unfiltered motor velocity is displayed through this parameter.
Parameter Type: View only, all levels
Minimum Value: –8000 rpm
Maximum Value: +8000 rpm
Parameter 21 – Filtered Velocity Feedback (Filtrd Vel Fb) *
The filtered velocity feedback which is output by the lead/lag filter is
supplied by this parameter. The bandwidth of the filter is specified by
parameter 186 and the filter gain is specified by parameter 185.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –8000 rpm
Maximum Value: +8000 rpm
Parameter 22 – Average Motor Velocity (Average Mtr Vel) *
This parameter supplies the average velocity feedback which is output by
the single pole low pass filter. The bandwidth of the filter is specified by
parameter 184.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –8000 rpm
Maximum Value: +8000 rpm
Parameter 23 – Resolver Turns *
The number of resolver electrical turns is supplied by this parameter. When
these values reach maximum, the value drops to zero and begins to again
count up and down.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –32768
Maximum Value: +32767
Parameter 24 – Resolver Position Feedback (Resolver Posn) *
This parameter supplies the position feedback count. 65,535 represents the
counts per 1/2 motor revolution.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 65535
Parameter 25 – Pre Ramp Velocity (Pre Ramp Vel) *
This is the velocity before the velocity rate limiter.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –8000 rpm
Maximum Value: +8000 rpm
Parameter 33 – Proportional Velocity Error (Prop Vel Error) *
This is the error between the Final Velocity Command (parameter 19) and
the Filtered Velocity Command (parameter 21).
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –8000 rpm
Maximum Value: +8000 rpm
6-11
Page 49

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 34 – Velocity Loop PI Output (Vel PI Output) *
Indicates the latest output of the velocity PI regulator.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –8000 rpm
Maximum Value: +8000 rpm
Parameter 35 – Integral Velocity Error (Intg Vel Error) *
The error between the Final Velocity Command (parameter 19) and the
Velocity Feedback (parameter 20) is supplied by this parameter.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –8000 rpm
Maximum Value: +8000 rpm
Parameter 44 – External Torque Reference (Ext Torque Ref) *
A digital motor torque reference to the drive is supplied by this parameter
from an adapter board (not available at this time). This reference can be
selected by setting the Torque Mode (parameter 133).
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –300% rated motor current or 2 times drive rating (whichever is less)
Maximum Value: +300% rated motor current
Parameter 45 – Iq (Torque) Current Reference (Iq Current Ref) *
This parameter displays the torque producing current reference.
Parameter Type: View only in all levels
Minimum Value: –300% rated motor current or 2 times drive rating (whichever is less)
Maximum Value: +300% rated motor current
Parameter 46 – Id (Flux) Current Reference (Id Current Ref) *
The flux producing current reference is displayed by this parameter.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 70% rated motor current
Parameter 47 – IT Protection Limit (IT Protect Lim) *
This parameter displays the amount that the bridge current limit is reduced,
based on the output of an analog circuit which models the thermal
characteristic of the inverter power transistors.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: Drive current rating
Parameter 48 – Bridge Current Limit (Bridge Cur Lim) *
The bridge current limit which is calculated by the drive based on motor
current and drive size (parameters 155 & 3) is displayed by this parameter.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 Amperes
Maximum Value: 200% drive rating or 3 times motor rating
6-12
Page 50

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 49 – Current Feedback Scale (Cur Fdbk Scale) *
The current feedback scaling is displayed based on motor current rating
and drive size (parameters 155 & 3). See Table 6.A.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 15
Table 6.A
Typical Current Feedback Scaling
Motor Rated Current
1391-DES15
15.0
14.1
13.1
12.2
11.3
10.3
9.4
8.4
7.5
6.6
5.6
4.7
3.8
2.8
1.9
0.9
1391-DES22
22.5
21.1
19.7
18.3
16.9
15.5
14.0
12.6
11.3
9.8
8.5
7.0
5.7
4.2
2.8
1.4
1391-DES45
45.0
42.2
39.4
36.6
33.8
30.9
28.1
25.3
22.5
19.7
16.9
14.1
11.3
8.4
5.6
2.8
Parameter 49 Value
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Parameter 50 – Current Feedback Rated (Cur Fdbk Rated) *
This parameter displays the actual motor current scaling based on current
feedback scale and drive size (parameters 49 & 3).
Parameter Type: View only in all levels
Minimum Value: Drive size/16
Maximum Value: Drive size
Parameter 51 – Current Limit *
The real time current limit is displayed by this parameter.
Parameter Type: View only in all levels
Min/Max Value: Whichever is less: 200% drive rating, +/– current limit, 3 times motor current,
ext limit or IT limit
Parameter 57 – Analog Velocity Command (Analog Vel Cmd) *
This parameter displays the analog velocity command value.
Parameter Type: View only in all levels
Minimum Value: –7000 rpm
Maximum Value: +7000 rpm
6-13
Page 51

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 58 – D/A #1 Command Value (D/A 1 Cmd Val) *
This parameter displays the actual value input to D/A Converter 1.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –2047
Maximum Value: +2047
Parameter 59 – D/A #2 Command Value (D/A 2 Cmd Val) *
This parameter displays the actual value input to D/A Converter 2.
Parameter Type: View only in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –2047
Maximum Value: +2047
Parameter 68 – Bandwidth Maximum (Bandwidth Max.) *
After an auto tune, this parameter displays the maximum system bandwidth
that can be achieved with the machine mechanics.
Parameter Type: View only in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rads/second
Maximum Value: 250 rads/second
To convert rads/second to Hertz, divide by 6.28.
Parameter 69 – Auto Tune Friction (Auto Tune Friction)*
The system friction as measured by the auto tune cycle is represented
through this parameter.
Parameter Type: View only in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0%
Maximum Value: 100% = rated motor current
Parameter 128 – EEprom Functions (EEprom Func)
This parameter allows the user to initialize, recall or save the parameters
stored in the EEprom. Entering the number listed will cause the drive to
perform the designated action.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
0 Exit – exit EEprom functions
1 Initialize* – load the default parameters into EEprom
2 Recall – load the drive with the current EEprom values
3 Save – save the current drive parameters to EEprom
*Important: initializing the EEprom will convert all parameters to default values – all previous
values will be lost.
Parameter 129 – Units Select
Allows selection of “User Units” or “Per Unit Values.”
Important: All values shown in this manual are “User Units.” Changing
this parameter is not recommended.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Default Value: 0 User Units
0 User Units
1 Per Unit
6-14
Page 52

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 130 – Drive OK Mode
This parameter specifies how the Drive OK (DROK) relay is controlled. If
the parameter is set to “0,” the relay will be opened when a fault occurs. If
the parameter is set to “1,” the relay will open when a fault occurs and
there is not sufficient DC bus voltage.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Default Value: 0 Fault only
0 Fault only
1 Fault and undervoltage
Parameter 131 – Language Select (Language Selct)
This parameter allows selection of available languages.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Default Value: 0 English
0 English
Parameter 132 – Velocity Mode Select (Vel Mode Selct)
Parameter 132 selects the velocity command source(s) within the drive.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Default Value: 0 A/D Input
0 A/D Input – analog reference from the 14 bit A/D converter (parameter 57) which is fed from
user input command voltage (typically 0 to ±10V DC).
1 Digital Inp – internal digital reference (parameters 17, 18)
2 A/D+Digt1 – analog and digital reference (parameters 57 + 17, 18)
3 Zero Input – zero velocity reference
Parameter 133 – Torque Select
This parameter selects the torque command source within the drive. When
operating the drive in velocity mode, set to Velocity Mode 1. When
operating in torque mode, (using S Class, MAX, IMC 121 & 123) set to
A/D Torque Block (#4).
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Default Value: 0 Vel Mode 1
0 Vel Mode 1 – velocity regulator PI output (parameter 34)
1 Vel Mode 2 – PI output + current preload + external torque reference (parameters 34, 159, 44)
2 Torq Block – Digital torque reference (parameter 44)
3 Vel Mode 3 – PI output + A/D value (3V = 4096) + current preload
(parameters 34 + A/D + 159)
4 A/D Tq Blk – current preload + A/D value (159 + A/D)
5 Zero Ref. – zero torque command
Parameter 135 – Up To Speed Tolerance (Up To Spd Tol)
This parameter establishes a band around the velocity command that is
used to determine when to update the At Speed bit in parameter 7.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rpm
Maximum Value: 7812 rpm
Default Value: 19.5 rpm
6-15
Page 53

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 136 – Drive Address *
This parameter is not active at this time.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 1
Maximum Value: 14
Default Value: 1
Parameter 144 – Clockwise Velocity Limit (CW Vel Limit)
Specifies maximum velocity reference in the clockwise (positive)
direction.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rpm
Maximum Value: 7000 rpm
Default Value: Set by “Setup drive with motor data” routine
Parameter 145 – Counterclockwise Velocity Limit (CCW Vel Limit)
The maximum counterclockwise (negative) velocity reference is specified
by this parameter.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 7000 rpm
Default Value: Set by “Setup drive with motor data” routine
Parameter 146 – Accel/Decel Ramp (Acc/Dec Ramp)
This parameter specifies the largest change in the velocity command per
velocity loop sample that will be allowed except when an immediate stop
causes the velocity limit block to be bypassed.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 5 revs per sec/sec
Maximum Value: 22216 revs per sec/sec
Default Value: 22216 revs per sec/sec
Parameter 154 – Motor Type
The catalog number of the 1326 servomotor currently installed is contained
in this parameter.
Important: Changing this parameter doesn’t change any motor related
parameters. Motor changes must be made through the “Setup drive with
motor data” menu.
Parameter Type: Can be viewed in all levels – modified in Maintenance level
Default Value: Set by “Setup drive with motor data” routine
Parameter 155 – Rated Motor Current (Mtr Rated Cur) *
This parameter scales the current feedback in the drive to match the
servomotors continuous current rating.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: Drive/motor dependent
Maximum Value: Drive/motor dependent
6-16
Page 54

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 156 – Positive Current Limit (Pos. Cur Limit)
Parameter 156 specifies the maximum allowable positive motor current
that can be commanded. If greater than parameter 48, parameter 48 will
then set the limits.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 10% rated motor current
Maximum Value: 300% rated motor current or 2 times drive rating (whichever is less)
Default Value: Set by “Setup drive with motor data” routine
Parameter 157 – Negative Current Limit (Neg. Cur Limit)
The maximum allowable negative motor current that can be commanded is
specified through this parameter. If greater than parameter 48, parameter 48
will then set the limits.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 10% rated motor current
Maximum Value: 300% rated motor current or 2 times drive rating (whichever is less)
Default Value: Set by “Setup drive with motor data” routine
Parameter 158 – Current Rate Limit (Cur Rate Limit) *
The largest change in the current reference per velocity loop sample that
will be allowed is specified through this parameter. Value shown on the
display is in amperes/second. Description is based on percentage of motor
rating to allow interpretation of value.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 130% rated motor current per second
Maximum Value: 80% rated motor current per millisecond
Default Value: 36% of motor rated current/ms, but will change according to motor selection
Parameter 159 – Current Preload (Cur Preload)
This parameter specifies the amount of preload added to the velocity loop
Pl output.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –200% rated motor current
Maximum Value: +200% rated motor current
Default Value: 0
Parameter 168 – KP Velocity Loop (Prop Gain kp)
This parameter controls the proportional error gain of the velocity
regulator. For example, if KP = 8, then velocity (1000 rpm) error will
produce a (rated motor) current torque reference.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 560
Default Value: 100
6-17
Page 55

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 169 – Kl Velocity Loop (Intg Gain ki)
This parameter controls the integral error gain of the velocity regulator. For
example, if KI = 8, then velocity (1000 rpm) error for 1 second will
produce a (rated motor) current torque reference.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 24000
Default Value: 6667
Parameter 170 – Feed Forward Gain (Feed Frwd Gain)
Controls the feedforward gain of the velocity regulator. Setting this to a
value greater than zero reduces the velocity feedback overshoot in response
to a step change in the velocity reference. The velocity loop response to a
load disturbance is unaffected by the Feed Forward Gain.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 0.39
Default Value: 0
Parameter 171 – Static Gain/Droop
Specifies the velocity regulation tolerance in rpm.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rpm
Maximum Value: 15.6 rpm
Default Value: 1 rpm
Parameter 172 – Velocity Loop Integrator Preset (Intg Prest Val)
The velocity loop integrator will be set to the value in this parameter when
the drive transitions into the run state.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –200% rated motor current
Maximum Value: +200% rated motor current
Default Value: 0
Parameter 181 – Motor Inertia
Displays the time it will take for the selected motor to reach 1000 rpm at
100% of rated torque. This assumes that the motor has 0.2 times the motor
inertia connected to it, representing typical system inertia (couplings, etc.)
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 ms
Maximum Value: 500 ms
Default Value: Set by “Setup drive with motor data” routine
6-18
Parameter 182 – Desired Velocity Bandwidth (Desired Vel BW)
This is associated with the Auto Tune Calculate function and allows the
user to enter a desired velocity bandwidth less than or equal to the
Maximum Bandwidth (parameter 68) as calculated by the auto tune cycle.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 1 rads/second
Maximum Value: 250 rads/second
Default Value: 200 rads/second – To convert rads/second to Hertz, divide by 6.28.
Page 56

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 183 – Velocity Damping Selection (Vel Damp Selct)
This parameter is associated with the auto tune function and specifies the
velocity damping desired by the user. The auto tuning procedure calculates
a new set of Velocity Loop Gains (parameters 168 & 169) and a new
Current Rate Limit (parameter 158) when the user initiates the Auto Tune
Calculate function. Refer to Figure 8.1 for further information.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 3
Default Value: 0
0 zeta = 0.87
1 zeta = 1.0
2 zeta = 0.7
3 zeta = 1.4
Parameter 184 – Velocity Low Pass Filter Bandwidth (Vel Low Pas BW)
Specifies the single pole low pass velocity feedback filter bandwidth. A
value of 30000 disables the filter.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rads/second
Maximum Value: 30000 rads/second
Default Value: 30000 rads/second
Parameter 185 – Lead/Lag Velocity Fdbk. Filter Gain (Lead/Lag Gain)
Specifies the gain of the velocity feedback filter. A value of 1.00 disables
the filter.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –10.00 (lag)
Maximum Value: +10.00 (lead)
Default Value: 1.00
Parameter 186 – Lead/Lag Velocity Fdbk. Filter BW. (Lead/Lag BW)
Specifies the bandwidth of the velocity feedback filter.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rads/second
Maximum Value: 2700 rads/second
Default Value: 250 rads/second
Parameter 187 – Auto Tune Velocity (Auto Tune Vel)
This parameter specifies the maximum velocity attained during an auto
tune cycle.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –2000 rpm
Maximum Value: +2000 rpm
Default Value: +1000 rpm
6-19
Page 57

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 188 – Auto Tune Current Limit (Auto Tune Cur)
The motor current used while an auto tune cycle is executing is specified
with this parameter.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 200% rated motor current in amperes
Default Value: 50% rated motor current in amps
Parameter 189 – Auto Tune Inertia (Auto Tun Inert)
This parameter is calculated during auto tune and is the time that the motor
or motor and system takes to reach Auto Tune Velocity (parameter 187) at
Auto Tune Current Limit (parameter 188) and back to zero rpm. To
determine the inertia of the machine system, use the following formula:
J
system
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 ms
Maximum Value: 10000 ms
Default Value: 100 ms
Parameter 189
=
Parameter 181 x 0.83
x Motor
(from Motor Data Sheet in lb.-in.-sec2)
actual
Parameter 190 – Auto Tune Select (Auto Tune Sel)
This parameter initiates an auto tune cycle which measures the Auto Tune
Inertia (parameter 189) and Auto Tune Friction (parameter 69) by
accelerating the motor up to the Auto Tune Velocity (parameter 187) at the
Auto Tune Current Limit (parameter 188). The parameter also calculates
the gains based on auto tune information.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
0 Exit
1 Clr Status
2 Systm Tune
3 Calculate
Parameter 199 – Friction Compensation (Friction Comp)
This value represents the machine friction torque as a percentage of the
measured friction torque (or parameter 69) as measured by auto tuning.
This will be compensated for in the velocity loop.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0% (No Friction Compensation)
Maximum Value: 100%
Default Value: 50%
6-20
Parameter 200 – Friction Hysteresis (Frictn Hystrs)
This parameter defines the number of bits of velocity command before a
switch is made by Friction Bit (parameter 201).
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 2.4 rpm
Default Value: 0.5 rpm
Page 58

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 201 – Friction Bit (Frictn Bit)
The number of bits surrounding Friction Hysteresis (parameter 200).
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 50
Default Value: 10
Parameter 210 – Analog to Digital Converter Offset (Anlg Vel Offst)
This parameter adds an offset to the A/D converter value to correct for
input A/D offset and user input command D/A output offset.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –61 mV
Maximum Value: +61 mV
Default Value: 0 mV
Parameter 211 – Analog Velocity Gain (Anlg Vel Gain)
This parameter determines how the A/D converter value is scaled. It is set
to the number of motor rpm that is to represent 1 volt of input command.
The desired input velocity command voltage to motor rpm scaling is
accomplished with the Analog Velocity Gain parameter (211). The default
setting is 500 rpm/volt. Use the following formula if the maximum motor
speed (rpm) and maximum velocity command (volts) are known.
Maximum Desired Motor RPM
Maximum Velocity Command
for example:
3000 RPM Maximum
8V DC Maximum Command
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –790 rpm per volt
Maximum Value: +790 rpm per volt
Default Value: +500 rpm per volt
=
=
RPM
Volts
375 RPM
Volts
Parameter 212 – Digital to Analog #1 Gain (D/A 1 Gain)
This parameter scales the D/A #1 Command Value (parameter 58) before it
is output to D/A Converter 1.
To change output voltage scaling: Desired Voltage per 1000 rpm x 0.05553.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: gain of –14.6
Maximum Value: gain of +14.6
Default Value: gain of +0.067
6-21
Page 59

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 213 – Digital to Analog #2 Gain (D/A 2 Gain)
This parameter scales the D/A #2 Command Value (parameter 59) before it
is output to D/A Converter 2.
To change scaling: Desired Voltage /Rated Current x 0.05553.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: gain of –14.6
Maximum Value: gain of +14.6
Default Value: gain of +0.167
Parameter 222 – Id RPM Start *
This parameter is associated with the field weakening function.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rpm
Maximum Value: 6000 rpm
Default Value: Set by “Setup drive with motor data” routine
Parameter 223 – Id RPM End *
This parameter is associated with the field weakening function.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rpm
Maximum Value: 8000 rpm
Default Value: Set by “Setup drive with motor data” routine
Parameter 224 – Id Percent Limit (Id Percnt Lim) *
This parameter is associated with the field weakening function.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0 rpm
Maximum Value: 100%
Default Value: 70%
Parameter 233 – Cable Compensation (Cable Comp)
This parameter is set based on the distance between the motor and drive. It
optimizes drive for resolver cable length variations based on installation.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Modify level and Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 5 feet
Maximum Value: 600 feet (183 m)
Default Value: 50 feet (15.2 m)
Parameter 234 – Transport Compensation (Transport Comp) *
This parameter specifies the amount of linear transport lag compensation
due to the sample time of the control loops.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: –200
Maximum Value: +200
Default Value: 81
6-22
Page 60

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 243 – Indirect Sink Parameter 1 (Indirect Sink1) *
This parameter specifies the sink parameter for Indirect Link 1. Parameters
243 and 244 define a link between two other parameters. The value of the
parameter specified by parameter 244 is written to the parameter specified
by parameter 243 once every velocity loop update.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 245
Default Value: 59
Parameter 244 – Indirect Source Parameter 1 (Indirect Sorc1) *
This parameter specifies the source parameter for Indirect Link 1.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 254
Default Value: 20
Parameter 245 – Indirect Sink Parameter 2 (Indirect Sink2) *
This parameter specifies the sink parameter for Indirect 2. Parameters 245
and 246 define a link between two other parameters. The value of the
parameter specified by parameter 246 is written to the parameter specified
by parameter 245 once every velocity loop update.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 254
Default Value: 59
Parameter 246 – Indirect Source Parameter 2 (Indirect Sorc2) *
This parameter specifies the source parameter for Indirect Link 2.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 254
Default Value: 45
Parameter 251 – Access Timeout
This parameter specifies the length of time in minutes that the display will
spend unattended before going back to the View level from a higher level.
A value of zero disables this function.
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Minimum Value: 0
Maximum Value: 32767
Default Value: 0
6-23
Page 61

Chapter 6
Programming
Parameter 252 – Drive Initialization Status (Drv Init Stats)
This parameter specifies if the drive has gone through an out-of-the-box
start-up procedure (defined in Chapter 8).
Parameter Type: View/modify in Maintenance level
Default Value: 1 No
1 No – has not been setup
0 Yes – has been setup
Parameter 253 – Display Software Version (Display SW Ver) *
This parameter displays the current display software version number.
Parameter Type: View only in all levels
Parameter 254 – Drive Software Version (Drive SW Ver.) *
This parameter displays the current drive software version number.
Parameter Type: View only in all levels
6-24
Page 62

Chapter
Chapter
7
Installation
Chapter Objectives Chapter 7 provides the information needed to help properly mount and
wire the 1391-DES Servo Drive for operation. Since most start-up
difficulties are the result of incorrect wiring, every precaution must be
taken to assure that the wiring is done as instructed. All items must be
read and thoroughly understood before the actual installation begins.
ATTENTION: The following information is merely a guide for
!
proper installation. The National Electrical Code and any other
governing regional or local code will overrule this information.
The Allen-Bradley Company cannot assume responsibility for
the compliance or the noncompliance to any code, national,
local or otherwise for the proper installation of this drive or
associated equipment. A hazard of personal injury and/or
equipment damage exists if codes are ignored during
installation.
Mounting Mounting dimensions for the 1391-DES Servo Drive can be found in
Appendix A. Chapter 2 provides information on power dissipation and
environmental specifications. The drive must be located on a flat, rigid,
vertical surface and must not be subjected to shock, vibration, moisture, oil
mist, dust, corrosive vapors, etc. or temperatures that exceed 60° C (140°
F) ambient.
Drives can be mounted adjacent to each other with a minimum clearance of
0.312” (7.9 mm) between units and/or surrounding cabinetry and
non-current carrying surfaces. However, it is recommended that a space of
approximately 1.0” (25.4 mm) be left between adjacent units to allow easy
access and removal of the front cover. To allow for proper airflow, a
minimum clearance of 3.0” (76.2 mm) is required along the top and bottom
of the unit and any adjacent components.
The transformer that supplies 230V AC, three-phase and 36V AC to each
servo drive must have 3” (76.2 mm) of clearance around it and any
adjacent components. This will allow for proper airflow and wiring access.
The transformer can be mounted in either a horizontal or vertical position.
7-1
Page 63

Chapter 7
Installation
ATTENTION: The installation of the drive must be planned
!
such that all cutting, drilling, tapping and welding can be
accomplished with the drive removed from the enclosure. The
drive is of the open type construction and any metal debris must
be kept from falling into it. Metal debris or other foreign matter
may become lodged in the circuitry resulting in component
damage.
7-2
Page 64

Wiring Recommendations General Information
The information supplied in this manual on wire sizes, practices, layouts,
system configurations and grounding/shielding techniques for the
1391-DES Servo Drive are presented as guidelines. Due to the diversity of
applications and systems, no single method of wiring is completely
applicable.
Important: This information represents common PWM servo system
wiring configurations, size and practices that have proven satisfactory in a
majority of applications. The National Electrical Code, local electrical
codes, special operating temperatures, duty cycles or system configurations
will take precedence over the values and methods listed. Refer to Chapter 5
for detailed descriptions of input and output terminations before beginning
the task of wiring.
Wire Sizes
Unless noted, the wire sizes in this manual are recommended minimums
and assume type MTW wire (machine tool wire, 75° C, minimum) per
NFPA 79. Since ambient conditions vary widely, on certain applications, a
derating factor has to be taken into account. Also, wiring to drives or
motors exceeding 50 feet (15.2 meters) in length (total includes to and
from device) may cause excessive voltage drops. Consult the National
Electrical (or local) Code for factors on ambient conditions, length etc. or
the Allen-Bradley Sales Representative in your area for further
information.
Chapter 7
Installation
Shielding
Reasonable care must be taken when connecting and routing power and
signal wiring on a machine or system. Radiated noise from nearby relays
(relay coils should have surge suppressors), transformers, other electronic
drives, etc. may be induced into the velocity command signal lines causing
undesired movement of the servomotor.
To help alleviate the problem, machine power and signal lines must be
routed separately. The 1391-DES power and signal lines must be shielded,
twisted and routed in separate ferrous metal conduit or harnesses spaced at
least 12” (304.8 mm) apart. Power leads are defined here as the transformer
primary and secondary leads, motor leads and any 115V AC or above
control wiring for relays, fans, thermal protectors etc. Signal wiring is
defined as velocity command, resolver feedback, enable lines and low level
logic signal lines.
Feedback, command signal and other shields must be insulated from each
other and connected at a common machine or system earth ground in a
“star” fashion (i.e. all shields connected to a single earth ground point).
This helps to minimize radiated and induced noise problems and ground
loops. Refer to the paragraph entitled “Grounding” and Appendix B.
7-3
Page 65

Chapter 7
Installation
Open ended shields (resolver feedback cable at the resolver and velocity
command cable at the servo drive) must be insulated so that they do not
accidentally cause ground loops.
EMI Shielding
The 1391-DES has an inverter carrier frequency of 2500 Hz. Therefore, the
system may induce noise into sensitive equipment lines adjacent to it.
ATTENTION: This drive can produce electromagnetic
!
radiation that may cause industrial or radio controlled
equipment to operate erratically and cause possible injury to
personnel.
The 1391-DES system is designed to be interconnected with
Allen-Bradley EMI shielded motor cables only. Do
substitute cables. The EMI shield of the motor cable only, must
be grounded at both ends to function properly.
Not
Wiring
Important: The thermal switch and brake wires are routed near motor
power and can pickup PWM radiation. Isolation from control devices may
be required.
Grounding
All equipment and components of a machine or process system shall have
their chassis connected to a common earth ground point. This ground
system provides a low impedance path that helps minimize shock hazards
to personnel and damage to equipment caused by short circuits, transient
overvoltages and accidental connection of energized conductors to the
equipment chassis.
Grounding requirements, conventions and definitions are contained in the
National Electrical Code. Local codes will usually dictate what particular
rules and regulations are to be followed concerning system safety grounds.
See Appendix B.
ATTENTION: The National Electrical Code (NEC) and local
!
codes outline provisions for safely installing electrical
equipment. Installation must comply with specifications
regarding wire types, conductor sizes, branch circuit protection,
and disconnect devices. Failure to do so may result in personal
injury and/or equipment damage.
7-4
Page 66

Chapter 7
Installation
The Interconnect Drawing presented in Appendix B provides typical
interconnection wiring for the 1391-DES AC Servo Drive. Typical control
logic circuitry (starting and stopping), motor interconnections and
grounding techniques are shown.
Please note that the drive circuit breaker (MCB) is not designed or intended
to meet branch circuit protection requirements. The circuit breaker protects
the DC bus supply, input rectifier and power circuitry against overcurrents.
Motor Wiring
The motor wiring size is determined by the continuous and overload
current requirements (RMS Duty Cycle), NEC and local codes. In general,
motors operated from the following drives would not require wire sizes
larger than those accepted by TB5, but codes must be followed. In
addition, the motor leads must be twisted throughout their entire length to
minimize radiated electrical noise. Allen-Bradley 1326 cables (or
equivalent type) must be used. The maximum motor wire sizes that the
1391-DES drive will accept are shown in Table 7.A.
Table 7.A
Maximum Motor Wire Sizes – TB5
Drive Catalog Number
1391-DES15
1391-DES22
1391-DES45
Max. Wire Size Accepted
#8 AWG (6 mm
#8 AWG (6 mm
#8 AWG (6 mm
2
) – MTW
2
) – MTW
2
) – MTW
7-5
Page 67

Chapter 7
Installation
Motor Feedback Wiring
Connections to the integral commutation resolver must be made using an
Allen-Bradley 1326-CFUxx shielded cable.
ATTENTION: To guard against hazard of personal injury or
!
damage to equipment, the interconnections to the motor and
resolver must be made exactly as shown in Appendix B. Failure
to do so could cause loss of motor control and/or severe
oscillation of the motor shaft.
Encoder (A Quad B Board) Wiring
Recommended Wire – Belden #9728 or equivalent. Maximum distance
between the A Quad B Board and the position controller is 40 feet (12.2
meters) using a 5 volt signal. For distances up to 300 feet (91 meters), 18
AWG wire (0.75 mm
15V DC power supply must be used.
2
), such as Belden #9388 (or equivalent) and an 8 to
For proper operation when interconnecting to IMC products, the B and
B (NOT) signals must be reversed.
Applications that interface the 1391-DES with an IMC Classic Controller
(IMC 110, 120, 121, 123) require a relay to sequence the encoder power
supply during a drive shutdown.
Without this power supply relay, erroneous counts could be received by the
IMC Classic Controller when AC power is cycled to the drive, but not the
controller. When power is removed to the drive, the AQB Board will not
have control voltage. However, the board will still receive the encoder
voltage (+5V DC or +8-15V DC) from the IMC Classic Controller. As the
drive power is cycled, it will briefly output a stream of encoder pulses
which will be interpreted as movement of the servomotor by the IMC
Classic Controller.
It is recommended that a normally open (N.O.) contact from an external
relay be wired in series with the encoder voltage going to the drive from
the IMC Classic Controller. The relay coil must be wired into the control
circuit. When power is not applied to the drive, a Quadrature Fault will
occur in the controller, forcing a re-homing and calibration of the
controller.
7-6
Transformer Wiring
The transformer secondary (230V AC, three-phase) connection to the drive
is phase insensitive and is shown in Appendix B. The maximum wire size
TB5 will accept is 8 AWG (6 mm
transformer wiring diagrams.
The minimum recommended wire sizes for the transformer secondary are
shown in Table 7.B.
2
). Refer to Chapter 10 for the
Page 68

Chapter 7
Installation
Table 7.B
Minimum Transformer Wire Sizes – AWG (mm2)
kVA
Input Voltage
208V AC
240V AC
380V AC
415V AC
480V AC
575V AC
1.5
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
3.5
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
5.0
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
10.0
#8 (6)
#8 (6)
#10 (4)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
#12 (2.5)
12.5
#8 (6)
#8 (6)
#10 (4)
#10 (4)
#10 (4)
#12 (2.5)
15.0
#6 (10)
#8 (6)
#8 (6)
#10 (4)
#10 (4)
#10 (4)
Important: The transformer primary requires protection by means of a
customer supplied branch circuit disconnect device. Refer to Appendix B.
Fusing (Transformer Primary)
Time delay fusing similar to Bussman Fusetron FRS Series or equivalent
must be used if the primary circuit is fused. Circuit breakers must provide
protection equivalent to fuses.
Fuse ratings shown in Table 7.C are the highest ratings allowed in a 25° C
(77° F) ambient temperature. Higher electrical enclosure ambient
temperatures will require fuses with higher current ratings. Consult fuse
manufacturer’s derating data. Fuses larger than those listed below may
result in transformer damage.
Table 7.C
Fuse Current Rating – Amperes
kVA
15.0
12.5
Primary Voltage
208V AC
240V AC
380V AC
415V AC
480V AC
575V AC
1.5
8
7
4.5
4
3.5
3
3.5
17.5
15
9
8
7
6
5.0
20
20
12
12
10
8
10.0
40
35
25
20
17.5
15
50
45
30
25
25
20
60
50
35
30
30
25
External Shunt Regulator Resistor
The external Shunt Regulator Resistor and fuse for the 45A 1391-DES
must be connected to TB5-8 and TB5-9 as described in Chapter 10.
22.5A drives must be converted for use with an external shunt resistor and
fuse. Refer to Chapter 10 and Appendix B for detailed instructions.
Interface Connections
Refer to Chapter 5 and Appendix B for connection information.
7-7
Page 69

Chapter
8
Start-Up
Chapter Objectives Chapter 8 provides the steps needed to help properly start-up the
1391-DES Digital AC Servo Drive. Included in the procedure are typical
adjustments and voltage checks to assure proper operation. The
information contained in Chapters 5, 6 and 7 must be read and understood
before proceeding.
Start-Up Procedure The following procedure provides the required steps to start-up the
1391-DES AC Servo Drive in velocity and position mode.
ATTENTION: Power must be applied to the drive to perform
!
!
many of the adjustments specified in the following paragraphs.
Voltages behind the front panel are at incoming line potential.
To avoid injury to personnel and/or damage to equipment, only
qualified service personnel should perform the following
start-up procedures. Thoroughly read and understand the
following procedure before beginning the Start-Up Procedure.
If an event does not occur while performing this start-up, Do
Not Proceed. Remove Power by opening the branch circuit
disconnect device and correct the malfunction before
continuing.
ATTENTION: This product contains stored energy devices. To
avoid hazard of electrical shock, verify that all voltage on the
capacitors has been discharged before attempting to service,
repair or remove this unit.
Voltage at terminals 9 (+) and 7 (–) of TB5 must be “0.00” as
measured with a standard digital voltmeter or multimeter.
Only qualified personnel familiar with solid-state control
equipment and safety procedures in publication NFPA 70E
should attempt this procedure.
1. Assure that all power to the drive branch circuit is off. Most start-up
difficulties are the result of wiring errors. Therefore, prior to
applying power to the first device in the branch circuit, primary of
the transformer or system, check all of the system interconnection
wiring.
8-1
Page 70

Chapter 8
Start-Up
2. Check terminal block connections as described in Chapter 5 and
Appendix B.
3. Set switches S1 (A Quad B Board) and SW1 (top of drive) as
explained in Switch Settings in Chapter 5
4. Assure that the drive circuit breaker (MCB), contactor (M) and
Enable input are OFF (de-energized).
5. Apply power to the input transformer primary, but Do
Not Enable
the drive or energize the contactor (M). The Enable LED should be
Off.
6. Using a voltmeter, verify that the voltages listed below are present at
the locations shown. The tolerance for all voltages is ±10%. Clear
faults before replacing any blown fuses. Refer to Chapter 11 for test
point locations.
Location Voltage
TB5-4 to TB5-5 230V AC
TB5-4 to TB5-6 230V AC
TB5-5 to TB5-6 230V AC
TB4-21 to TB4-19 36V AC
TP13 to TP12 +12V DC
TP14 to TP12 –12V DC
7. Remove all power to the transformer.
8. The wires connected to terminals 9 and 10 of TB2 must be marked
and removed to allow for local operation of the enable circuit.
Connect a suitable temporary switch between these terminals and
insulate the switch connections.
8-2
9. Once control connections are made:
a) Open the enable switch – the ENABLE LED will be Off.
b) Apply power to the transformer primary.
c) Place the circuit breaker (MCB) to the On position.
d) Energize the contactor (M). The STATUS LED should illuminate
to a steady green.
Important: If power is applied while the drive is enabled, the
STATUS LED will flash red and disable the drive. The drive may be
reset by removing the Enable signal and momentarily grounding the
Reset terminal (TB2-11). An alternate method would be to remove
and reapply the branch circuit or drive power (36V) with the Enable
input removed.
Page 71

Chapter 8
Start-Up
10. The drive will now prompt you through a start-up procedure. Read
the following important points before continuing.
• From time to time the drive will display the message “EEprom
Fnction in progress.” This message alerts the user that an
EEprom function is in progress and that operation will return to
normal momentarily. If the message “drive can’t be running for
EE” is displayed, verify that the drive is disabled.
• If the drive faults during start-up (i.e. feedback miswired, etc.) the
procedure will be continued from the point where you left off,
after the cause of the fault has been resolved.
• To stop the start-up procedure at any time and restart from this
step: press the first 4 keys on the keypad (Up, Down, Left and
Right Arrow keys ) simultaneously and release.
• To cancel the procedure and return to the Basic Display at any
time: disable the drive and simultaneously press the last 4 keys of
the keypad (Down, Left, Right and Enter keys) and release.
• If you wish to repeat the start-up procedure: access the
Maintenance programming level by pressing the Up, Down and
Left Arrow keys, simultaneously – then within 4 seconds –
press the Up, Left and Enter keys. Access parameter 252 and
enter a value of 1, press Enter. Then press the Left or Right
Arrow keys to access parameter 128. Select “Save” to save the
parameters to EEprom, press Enter. Cycle all power and proceed.
11. The display will now read, “START UP PROCEDURE” – press the
Enter key to continue.
Display: “setup drive with motor data.” Press Enter to continue. If a
custom motor is being used, consult Allen-Bradley for special
instructions before proceeding.
The drive will now allow you to select the catalog number of the
motor being used. Use the Up and Down Arrow keys to select the
appropriate motor catalog number – press Enter to select.
Torque Plus catalog numbers will not be displayed. Use the
following cross reference to select a motor catalog number.
Torque Plus Use this Torque Plus Use this
Catalog Number
1326AB-A410G-21 1326AB-A1G 1326AB-A520E-21 1326AB-B2E
1326AB-A420E-21 1326AB-A2E 1326AB-A530E-21 1326AB-B3E
1326AB-A430E-21 1326AB-A3E 1326AB-A740B-21 1326AB-C4B
1326AB-A515E-21 1326AB-B2E
Catalog Number Catalog Number Catalog Number
The drive will respond by displaying “writing data to servo drive.”
12. The display will show “execute motor rotation test.” This test
assures that the motor cables have been connected correctly – press
Enter to continue.
8-3
Page 72

Chapter 8
Start-Up
ATTENTION: In the following steps, reverse rotation or
!
13. The drive will display the message “DANGER, MOTOR MAY
14. The display will now read “enable to strt rotation test.”
uncontrolled rotation at high speed can occur. Be prepared to
remove drive power by opening (MCB) or the branch circuit
disconnect device if this occurs. This movement may be due to
a wiring error or system component malfunction and must be
corrected before proceeding. Damage to machine system
components can occur due to uncontrolled machine movements.
RUNAWAY!!” Be prepared to open MCB on the drive if the motor
does not run correctly (under this condition the motor current limit is
set to 25% of rated current to minimize motor speed) – press Enter
to continue.
Energize the contactor (M) and enable the drive.
A correctly wired drive will rotate the motor clockwise at 30 rpm for
5 seconds – stop for 2 seconds – then rotate the motor
counterclockwise for 5 seconds – then stop.
If the motor runs away or does not rotate, verify all power and
resolver wiring.
15. The display will now read “disable drive to continue.” Disable the
drive by opening the Enable input, leaving the contactor energized.
Display: “press enter to exit motor test” – press Enter.
16. The display will now read “zero analog velocity offset” – press
Enter.
In this mode the drive will automatically adjust out any offset, while
the motor remains at zero speed. When the display reads: “enable to
strt zero vel offset,” apply the Enable input to the drive.
The display will now read “jumper analog velocity inputs.” Jumper
TB2-1 to TB2-2. This applies zero volts to the velocity inputs. Press
Enter to continue.
The display will now read “now zeroing velocity offset.” The drive
can take up to 60 seconds to zero the offset. If zeroing was
successful, the display will show “velocity zero complete.” Remove
the jumper and press Enter.
8-4
Important: If for some reason the offset cannot be adjusted, the
message “cannot zero velocity offset” will be displayed. If this
occurs, verify that the jumper connections are correct and continue
on with the procedure. After completion, do a manual zero speed
adjustment as explained in step 32.
The display will now read “disable drive to continue” – Remove
enable, leaving the contactor (M) energized.
Page 73

Chapter 8
Start-Up
17. The display will now read “enter parameter information” – press the
Enter key to continue.
The drive will allow you to enter a value for the Analog Velocity
Gain.
The desired input velocity command voltage to motor rpm scaling is
accomplished with the Analog Velocity Gain parameter (211). The
default setting is 500 rpm/volt. Use the following formula if the
maximum motor speed (rpm) and maximum velocity command
(volts) are known.
Maximum Desired Motor RPM
Maximum Velocity Command
for example:
3000 RPM Maximum
8V DC Maximum Command
=
=
RPM
Volts
375 RPM
Volts
Enter the desired value followed by the Enter key.
18. The drive will prompt for CW and CCW velocity limits (parameters
144 and 145, Clockwise/Counterclockwise Velocity Limits). Enter
the maximum speed limit of the motor plus 10% at maximum
velocity command. If the maximum command voltage exceeds the
normal maximum level, these values will limit the speed of the
motor. If unknown, leave setting at the default value.
Important: Factory default values are set +10% over the maximum
rated speed of the motor as shown in Table 9.A.
Press the Enter key to continue.
19. The drive will prompt for the resolver cable length being used,
(parameter 233, Cable Compensation). Use the Up or Down Arrow
key to select the cable length value closest to the length of the
feedback cable being used.
When the desired value is displayed, press the Enter key to make the
selection.
20. To continue with this start-up procedure, go to step 22.
Auto Tune Procedure
21. This step only needs to be performed when repeating the auto tune
cycle. Access the Modify programming level (from the View level)
by pressing the Up, Down and Left Arrow keys simultaneously.
Press the Down Arrow key and use the Left or Right Arrow keys to
select “autotune the servo drive.” Press the Down Arrow key.
8-5
Page 74

Chapter 8
Start-Up
22. Display: “autotune the servo drive” – press Enter to continue.
Assure that the drive Enable input is de-energized and the contactor
(M) is energized. The drive will display the message “drive not
ready to tune” if this has not been done.
The drive will prompt you for Auto Tune Current Limit. This
current is used for auto tuning only. The default value displayed is
sufficient, however, a different value of up to 100% of motor rating
can be entered if desired. Press the Enter key to accept the value.
23. The drive will prompt you for Auto Tune Velocity. This velocity is
used for auto tune only. To accept the default value, press Enter. If
clockwise motor rotation (looking at the motor shaft) is desired, this
parameter value should be positive. If counterclockwise rotation is
desired, set this parameter value negative.
ATTENTION: A portion of the following auto tune cycle will
!
24. The drive will display the message “DANGER ## MTR REVS
cause the motor to accelerate to a desired velocity and
decelerate to zero velocity. Be prepared for this movement and
take precautions to guard against personnel injury or machine
damage. Depending on the inertia of the system, several
revolutions of the motor may occur. Axis movement must take
place for the drive to complete the auto tune cycle.
POSSIBLE.” This means that the motor may make ## revolutions
during auto tune, causing machine movement.
Important: If the number of motor revolutions displayed is
acceptable, press Enter and proceed to step 25. If the number of
motor revolutions displayed could cause damage to your equipment,
Do
Not Continue! – Press The Up Arrow Key to end the auto tune
procedure.
Repeat the auto tune procedure by returning to step 21. During the
procedure the value for Auto Tune Current Limit can be increased,
or the Auto Tune Velocity can be decreased. Either value will lower
the number of motor revolutions. For example, twice the current will
halve the number of revolutions to do auto tune.
8-6
25. The display will now read “enable drive to execute autotune.”
Important: When you enable the drive the motor will ramp up to
the auto tune velocity and back to zero again.
The display will now read “disable drv to continue” – Disable the
drive.
Page 75

Chapter 8
Start-Up
26. The drive will display the Bandwidth Max. parameter (68). The
value displayed is the maximum bandwidth, in rads/sec. your system
can achieve. Record this value for future reference and press Enter.
Bandwidth Maximum = rads/sec.
(rads/sec. can be converted to Hertz (Hz) by dividing by 6.28)
27. The drive will display the Desired Velocity BW (182). Enter any
value of bandwidth up to the value of Bandwidth Max. from above.
Values greater than Bandwidth Max. will be ignored. Press Enter.
28. The auto tune and startup procedure is now complete. Press Enter.
Now press the Up Arrow and Enter keys simultaneously to return to
the Basic Display – values have now been stored in EEprom.
If it is desired to repeat the auto tune procedure, return to step 21.
Important: Do Not initialize the EEprom unless you wish to return
all parameters to their default state.
Remove power. Reconnect user command wiring (if previously
disconnected), apply power and check operation. If motor rotation is
incorrect, reverse the Velocity Command Input leads at TB2-1 & 2.
29. If the drive is to be run in torque control (with S Class, IMC 123
Controllers etc.) set parameter 133, (Torque Select) to “A/D Torque
Block.”
30. Enter the Maintenance programming level by pressing the up, down
and left arrow keys simultaneously – then within 4 seconds–
simultaneously press the up, left arrow and Enter keys.
Access parameters 155 (Rated Motor Current) and 181 (Motor
Inertia) – enter the appropriate values shown below.
Motor Parameter 155 Parameter 181
Catalog Number
1326AB-A410G-21 (1326AB-A1G) 7.1 A 21 ms
1326AB-A420E-21 (1326AB-A2E) 7.0 A 22 ms
1326AB-A430E-21 (1326AB-A3E) 9.5 A 22 ms
1326AB-A515E-21 (1326AB-B2E) 15.2 A 62ms
1326AB-A520E-21 (1326AB-B2E) 19.2 A 62ms
1326AB-A530E-21 (1326AB-B3E) 28.4 A 62ms
1326AB-A740B-21 (1326AB-C4B) 38.2A 73ms
Value Value
31. Access parameter 128 (EEprom Functions) and select “Save,”
followed by the Enter key. This will load the parameter values into
memory.
If further tuning is not required, record parameter settings in
Appendix E. Proceed to step 39.
8-7
Page 76

Chapter 8
Start-Up
Manual Tuning Procedure
If manual tuning of certain parameters is required, the following procedure
can be followed after
Parameters referenced in the following steps are located in the Modify
programming level. This level can be reached from the View level by
pressing the Up, Down and Left Arrow keys, simultaneously.
32. Zero Speed Adjust
a) Remove all power from the drive.
b) Install a jumper between TB2-1 & 2 or leave the velocity
command wiring in place if the system offset adjust is being
performed.
c) Apply power, energize the contactor (M) and enable the drive.
d) Access the Offset parameter (210, Modify level) and increase or
decrease the value until the motor shaft does not rotate.
all of the previous steps have been performed.
e) Perform step 36.
f) De-energize the Enable input, remove power and reconnect all
wiring, if applicable.
33. Analog Velocity Gain
a) Apply power to the drive.
b) Energize the contactor (M), but Do
Not Enable the drive.
c) Access the Analog Velocity Gain parameter (211, Modify level).
d) The drive will allow you to enter a value for the Analog Velocity
Gain.
The desired input velocity voltage to motor rpm scaling is
accomplished with the Analog Velocity Gain parameter (211).
The default setting is 500 rpm/volt. Use the following formula if
the maximum motor speed (rpm) and maximum velocity
command (volts) are known.
Maximum Desired Motor RPM
Maximum Velocity Command
for example:
RPM
=
Volts
8-8
3000 RPM Maximum
8V DC Maximum Command
=
375 RPM
Volts
Enter the desired value followed by the Enter key.
e) Perform step 36.
f) Remove power and reconnect all wiring, if applicable.
Page 77

Chapter 8
Start-Up
34. Clockwise/Counterclockwise Velocity Limits
a) Apply power to the drive.
b) Energize the contactor (M), but Do
Not Enable the drive.
c) Access parameters 144 and 145 (Clockwise/Counterclockwise
Velocity Limits) to enter the maximum speed limit of the motor at
maximum velocity command. If the maximum command voltage
exceeds the normal maximum level, these values will limit the
speed of the motor.
d) Perform step 36.
e) Remove power and reconnect all wiring, if applicable.
35. Current Limit Adjustment
a) Apply power to the drive.
b) Energize the contactor (M), but Do
Not Enable the drive.
c) Access parameters 156 and 157 (Positive and Negative Current
Limits) to enter the desired positive and negative current limits.
d) Perform step 36.
e) Remove power and reconnect all wiring, if applicable.
36. Saving Current Parameters to EEprom
If this step was just performed, proceed to the System Compensation
Procedure or step 39.
a) Access parameter 128 (EEprom Functions) and select “Save,”
followed by the Enter key. This will load the parameter values
into memory.
If no additional changes are required, press the Up Arrow key and
Enter keys simultaneously to show the Basic Display.
System Compensation Procedure
The auto tune feature of the 1391-DES drive should provide sufficient
system velocity loop compensation for the majority of applications.
Additional tuning is usually not required. However, the following manual
procedure for system velocity loop compensation can be followed, if
desired.
37. Enable the drive and monitor the velocity feedback signal at
terminals 5 (common) and 4 of TB2 with an oscilloscope or chart
recorder. Default scaling is 1.2V/krpm.
8-9
Page 78

Chapter 8
Start-Up
ATTENTION: If an oscilloscope (or chart recorder) is used
!
during Start-Up or Troubleshooting, it must be properly
grounded. The oscilloscope chassis may be at a potentially fatal
voltage if not properly grounded. Always connect the
oscilloscope chassis to earth ground.
When using an oscilloscope (or chart recorder) it is
recommended that the test probe ground be connected to TB2-5.
38. Adjust parameter 168 (Kp Velocity Loop) and observe the velocity
response (at TB2-4) profile at various levels of step input speed
commands. The “Underdamped” response curve in Figure 8.1 with a
single velocity overshoot of 20-30% on accel and decel is optimal
on a point to point positioning or velocity controlled system. The
“Critically Damped” curve is desirable on a contouring or metal
removing system.
Commanded Velocity
Parameter 169 (Ki Velocity Loop) should be adjusted so that the
motor achieves the commanded speed or final position as quickly as
possible with little or no overshoot. In addition to the dynamic
response, the motor shaft should not oscillate or exhibit any erratic
motion at zero speed.
39. Remove power with the branch circuit disconnect.
40. Remove the local Enable switch and reconnect external wiring.
41. Apply power and check system operation.
Figure 8.1
Velocity Response Profiles
Parameter 169 Controls Amount of Overshoot
Z = 0.7
Z = 1.0
Z = 0.87
Z = 1.4
8-10
Underdamped
Critically Damped
Overdamped
Time
Page 79

Chapter 8
Start-Up
Linear Accel/Decel Control Module The following information explains manual controller operation with the
Linear Accel/Decel Control Module (CR-APG-001). This module provides
adjustable acceleration/deceleration control for the 1391-DES. Up to four
remote or local preset speeds are available.
Important: The 1391-DES Accel/Decel Ramp parameter (146) locally
controls the velocity command per time rate. The default value is set to a
maximum of 22216 revs per sec/sec. This parameter must be kept at
maximum to allow the Linear Accel/Decel Control Module to set the
accel/decel rate within the minimum/maximum values.
1. Perform the Start-Up Procedure presented earlier in this chapter.
2. Remove all system power.
3. Install and interconnect the Linear Accel/Decel Control Module as
shown in Figure 8.2. Refer to Figure 8.3 for dimension information.
4. Set all of the Speed pots (SPD 1-SPD 4 or remote pots) to the
maximum clockwise position (speed minimum). Set the front panel
Accel and Decel pots to the maximum counterclockwise position
(minimum accel/decel time).
Important: All potentiometers on the module are 15 turn,
bi-directional. The Local Speed pots are setup such that
counterclockwise rotation will increase output and clockwise
rotation will decrease output. Counterclockwise rotation of the
Accel/Decel pots will decrease time, while clockwise rotation will
increase time.
5. Apply 115V AC to terminals 1 & 2 of J3. Using a voltmeter, verify
that this voltage is present. Also verify that +10V DC is present
between terminals 9 (+) and 2 (–) of J1. The “ON/OFF” LED
located on the front of the module will be illuminated.
6. Select Remote or Local speed control.
To select Remote Speed
a) Connect an external, 1k ohm, 1/2 watt speed potentiometer as
shown in Figure 8.2.
b) Energize the R/L 1 input (terminals 3 & 4 of J2) with either
24V DC or 115V AC.
c) Energize the speed select input, SEL 1 (terminals 1 & 2 of J2)
with the same voltage used in the previous step. The front panel
“R/L 1” LED will illuminate.
d) Repeat steps a through c for any of the other three preset speeds.
Important: If more than one speed is selected at the same time,
the resulting speed for the velocity profile will not be predictable.
8-11
Page 80

Chapter 8
Start-Up
To select Local Speed
a) Energize the speed select input, SEL 1 (terminals 1 & 2 of J2)
with either 24V DC or 115V AC. The front panel “SEL 1” LED
will illuminate.
b) Repeat the above step for any of the other three preset speeds.
Important: If more than one speed is selected at the same time,
the resulting speed for the velocity profile will not be predictable.
Important: In the following steps, the local speed control (SPD 1)
will be used. If your application utilizes remote speed pots, the
remote pot should be substituted for SPD 1.
7. Connect a voltmeter between terminals 11 (+) and 10 (–) of J1.
While monitoring the meter, turn the speed pot (SPD 1 or remote)
counterclockwise until the output voltage is approximately +10V
DC. Toggle the FWD/REV switch. The voltage measured should
change in polarity.
If the polarity does not change, recheck the wiring and connections
of the FWD/REV relay and switch.
Important: Changing direction with the speed input follows the
accel/decel times set on the module.
8. Move the meter leads to drive terminals 1 (–) & 2 (+) of TB2. The
meter should indicate a voltage of approximately +10V DC.
9. Rotate the Accel and Decel pots (located on the module front panel)
approximately 7 turns.
10. De-energize the SEL 1 input (terminals 1 & 2 of J2) and note the
time needed for the meter voltage to reach zero (minimum) volts.
Energize the SEL 1 input and note the time needed for the voltage to
reach +10V DC (maximum).
11. Adjust the Accel/Decel pots for desired ramp times (approximate
range is 0.25 to 6.5 seconds) by repeating step 10. The final ramp
time will be set during final system calibration. Rotate the speed pot
fully clockwise for minimum speed. Remove the SEL1 input.
ATTENTION: To protect against rapid accel/decel commands
!
from the module and possible machine damage or personal
injury, the “Bypass” input (terminals 19 & 20 of J2) must
energized. Applying 24V DC or 115V AC to this input will
remove the Accel/Decel pot settings from the circuit, causing
the output to immediately ramp to +10V DC or zero volts.
not be
8-12
Page 81

Chapter 8
Start-Up
12. The output of the module is controlled by the “Deadman” input at
terminals 10 & 11 of J1. Applying 24V DC or 115V AC to this input
will cause the module to operate. The front panel “Dedman” LED
will be off. When this input is de-energized, the module output will
be connected to logic ground, thus disabling output. At this point the
“Dedman” LED will illuminate.
Energize the “Deadman” input with 24V DC or 115V AC.
ATTENTION: During subsequent steps, the servomotor may
!
begin to rotate and cause incorrect machine movement when the
drive is enabled. Be prepared to remove drive power by opening
(MCB) or the branch circuit disconnect device if this occurs.
This movement may be due to a wiring error or system
component malfunction and must be corrected before
proceeding with this procedure. Damage to machine system
components can occur due to uncontrolled machine movements.
13. Apply power to the drive and module. Initiate a Start command by
selecting speed input, SEL1. Command a speed through the speed
pot, SPD 1 that represents approximately 10% of maximum speed
(i.e. 1V DC).
The motor should rotate slowly under control (following the speed
pot). If the motor is uncontrollable or rotates incorrectly, de-energize
SEL 1. Remove all power and check wiring.
If the application requires reverse direction, use the FWD/REV
toggle switch to check operation in the reverse direction.
14. With a zero velocity command from the module, use the drive
parameter 210 (Analog to Digital Converter Offset) to set zero
motor speed. Refer to Chapter 6 for more information on this
parameter.
Important: The motor may begin to move slowly after a period of
time (several minutes) even though parameter 210 is set to zero.
15. Rotate the speed pot (SPD 1) fully counterclockwise. Adjust the
Analog Velocity Gain parameter (211) if necessary to give the
desired motor speed.
16. Check the accel/decel rate settings at speeds selected for the
application. Refer to steps 10 & 11.
17. If applicable, repeat steps 6-16 for any of the other three preset
speeds
8-13
Page 82

Chapter 8
Start-Up
Remote
Speed 1
Remote
Speed 2
Remote
Speed 3
Figure 8.2
Linear Accel/Decel Control Module Wiring
J1
+10V DC
9
1
2
Speed 1
3
4
Speed 2
5
6
Speed 3
SPD 1
Local
J1
SPD 2
Local
J1
SPD 3
Local
Local
Remote
Select 1
Local
Remote
Select 2
Local
Remote
Select 3
Speed
Select 1
Speed
Select 2
Speed
Select 3
Direction
Change
Ramp
Generator
Decel
Direction
Change Select
Accel
Ramp
Select
24V DC or
115V AC
J2
FWD./REV.
+
17
–
18
Invert
J2
+
Bypass
19
–
Bypass
20
J1
7
8
Remote
Speed 4
24V DC or
115V AC
R/L 1 (+)
R/L 1 (–)
R/L 2 (+)
R/L 2 (–)
R/L 3 (+)
R/L 3 (–)
R/L 4 (+)
R/L 4 (–)
SEL 1 (+)
SEL 1 (–)
SEL 2 (+)
SEL 2 (–)
SEL 3 (+)
SEL 3 (–)
SEL 4 (+)
SEL 4 (–)
* Indicates component located in controller
1
Required only with IMC 110, 120, 121 AND 123 controllers
Speed 4
3
4
7
8
11
12
15
16
1
2
5
6
9
10
13
14
Local
J2
SPD 4
STOP
TB4–17
Local
Remote
Select 4
DROK*
Speed
Select 4
TYPICAL CONTROL CIRCUIT
115V AC, 50/60 HZ.
CR
TB4–18
LS
Transformer
ReverseForward
Start
M*
TB4–13 TB4–14
Motor
TB4–11
M*
CR2
CR
F/R
Enable
Select
TB4–12
1
J2
M
+
21
–
22
Deadman
J1
11
10
to TB2–1
to TB2–2
J3
1
115V AC
Power Supply
2
8-14
Page 83

Chapter 8
Start-Up
Figure 8.3
Linear Accel/Decel Control Module Dimensions
4.25 (108.0)
0.41 (10.3)
3.44 (87.3)
0.50 (12.7)
8.12
(206.2)
0.75 (19.1)
7.25
(184.2)
Dimensions are in inches (mm)
2.75 (69.9)
0.75
(19.1)
0.5
(12.7)
8-15
Page 84

Chapter 8
Start-Up
End of Chapter
8-16
Page 85

Chapter
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
Ç
9
1326 AC Servomotors
Chapter Objectives Chapter 9 describes the operation of a standard 1326 AC Servomotor with
the enhanced capabilities of a Bulletin 1391-DES Digital AC Servo Drive.
Refer to the 1326 AC Servomotor Product Data for further information on
Allen-Bradley AC Servomotors.
Introduction The 1391-DES provides additional energy to the 1326 motor, allowing it to
operate at higher speeds without a reduction of torque.
In general, the 1326 motor will follow the speed–torque curve shown in
Figure 9.1
Figure 9.1
Typical Bulletin 1326 Speed–Torque Curve
Standard Peak Torque
with Nominal 15% Low
Input Line Voltage
1391-DES Peak Torque
with Nominal 15% Low
Input Line Voltage
75%
Intermittent OperationRated Operation
1391B Rated Speed
Speed
(% rated rpm)
1391-DES Rated Operation 1391-DES Intermittent Operation
1391-DES Rated Speed
Peak Torque with
Nominal Input
Line Voltage
120
xx
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
100
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
80
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
60
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
40
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
20
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
ÇÇÇÇ
ÇÇ
0
0 40 80 120 160 200 240 280
70%
70%
100 300
(Tc) (Tp)
Torque (% rated)
9-1
Page 86

Chapter 9
1326 AC Servomotors
Tc – rated torque of motor with windings at rated temperature and an
ambient of 40°C. The drive is operating in a rated ambient of 60°C.
Tp – the peak torque that can be produced by the motor/drive combination
with both at rated temperature and the motor in a 40°C ambient and the
drive in a 60°C ambient. Higher peak torques are permissible where RMS
torque is less than or equal to the rated torque (Tc). 1391-DES operation is
shown in the outer envelope and will show higher speed and 300% torque
capability.
Rated Speed – the operating speed of the drive and motor combination at
which a minimum of 70% of continuous rated torque (Tc) can be
developed. This point is defined with the motor at 25°C and drive
operating in a 60°C ambient.
Rated Operation Area – boundary of speed-torque curve where the motor
and drive combination may operate on a servo basis without exceeding the
RMS rating of either.
Duty Cycle Profile
RPM
4
Decelerate
(Tpd)
t
3
Rest
(Tr)
4
Repeat
t
4
Accelerate
(Tpa)
Total Cycle Time t
2
Tpa
Trms =
where:
Trms The motors RMS or average torque over the duty cycle. (Expressed in lb.-in. or
lb.-ft. The same units must be used throughout the formula.)
Tpa Motor peak torque to accelerate to maximum speed. (Expressed in lb.-in. or lb.-ft.
The same units must be used throughout the formula.)
Tss Motor torque present at the motor shaft during constant speed segment.
(Expressed in lb.-in. or lb.-ft. The same units must be used throughout the
formula.)
Tpd Motor peak torque to decelerate to zero speed. (Expressed in lb.-in. or lb.-ft. The
same units must be used throughout the formula.)
Tr Torque when motor is at zero speed.
, t2, t3, t4 Time for each portion of the duty cycle in seconds.
t
1
x t1 + Tss2 x t2 + Tpd2 x t3 + Tr2 x t
1
t1 + t2 + t3 + t
Steady
Speed
(Tss)
t
2
Move Cycle
9-2
Intermittent Operation Area – Boundary of speed-torque curve where
the motor and drive combination may operate in acceleration-deceleration
mode without exceeding peak rating of either, provided that the duty cycle
RMS continuous torque limit is not exceeded.
Page 87

Chapter 9
1326 AC Servomotors
Table 9.A provides a comparison of the resultant speed obtained from
standard 1326 servomotors using 1391 and 1391-DES Servo Drives. Table
9.B provides performance data for the 1326AB Torque Plus Series Motors.
Table 9.A
1391/1391-DES Speed Comparison
Continuous
Stall Torque
(lb.-in./N-m)
16/1.8
32/3.6
48/5.4
93.3/10.53
102/11.5
140/15.8
153/17.3
210/23.7
310/35.0
420/47.4
420/47.4
1
All ratings are for 40° C motor ambient,110° C case and 60° C amplifier ambient. For extended ratings at lower ambients contact Allen-Bradley.
2
The motor contains two thermal switches wired in series that will open on an overtemperature condition. They are set to open at 150° C (typical) and close at 90-100° C
(typical). Contacts are rated for 1A at 115V AC, 1A at 24V DC.
3
–10% line voltage maximum.
Peak Stall
Torque
(lb.-in./N-m)
48/5.4
96/10.84
144/16.3
170.7/19.3
279/31.5
280/31.6
459/51.9
569/64.3
568/64.1
811/91.7
989/111.8
Mtr. Rated
Speed
(rpm)
5000
3000
3000
3000
3000
3000
3000
3000
3000
2000
1600
1391-DES
Speed
(rpm)
6000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
3000
2000
Motor
Catalog
Number
1326AB-A1G
1326AB-A2E
1326AB-A3E
1326AB-B2E
1326AB-B2E
1326AB-B3E
1326AB-B3E
1326AB-C2E
1326AB-C3E
1326AB-C4C
1326AB-C4B
Servo
Amplifier
Catalog Number
1391-DES15
1391-DES15
1391-DES15
1391-DES15
1391-DES22
1391-DES22
1391-DES45
1391-DES45
1391-DES45
1391-DES45
1391-DES45
1, 2
Amperes at
Continuous
Stall Torque
4.5
5.2
7.8
15.0
16.8
22.5
24.6
33.2
49.1
46.6
38.2
Rotor
Inertia
2
/kg-m2)
(lb.-in.-s
0.004/0.0005
0.007/0.0008
0.010/0.001
0.05/0.006
0.05/0.006
0.08/0.009
0.08/0.009
0.14/0.015
0.22/0.024
0.29/0.032
0.29/0.032
Rated/DES
Output
(kW)
0.7/0.9
0.8/1.1
1.2/1.6
2.28/3.0
2.5/3.3
3.5/4.7
3.8/5.1
5.2/6.9
7.5/10.0
7.0/9.3
5.6/7.5
3
Table 9.B
Torque Plus Performance Data and Selection List
Continuous
Stall Torque
(lb.-in./N-m)
24/2.7
40/4.5
58/6.6
92/10.4
92/10.4
106/11.98
165/18.6
500/56.5
1
All ratings are for 40° C motor ambient, 110° C case and 60° C amplifier ambient. For extended ratings at lower ambients contact Allen-Bradley.
2
The motor contains two thermal switches wired in series that will open on an overtemperature condition. They are set to open at 150° C (typical) and close at 90-100° C
(typical). Contacts are rated for 1A at 115V AC, 1A at 24V DC.
Peak Stall
Torque
(lb.-in./N-m)
72/8.1
120/13.6
174/19.7
181.5/20.5
272.4/30.8
248/28.0
489/55.2
1178/133
Rated
Speed
(rpm)
6000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
4000
2000
Rotor
Inertia
2
/kg-m2)
(lb.-in.-s
0.004/0.0005
0.007/0.0008
0.010/0.001
0.038/0.0043
0.038/0.0043
0.050/0.006
0.080/0.009
0.29/0.32
Motor
Catalog Number
1326AB-A410G
1326AB-A420E
1326AB-A430G
1326AB-A515E
1326AB-A515E
1326AB-A520E
1326AB-A530E
1326AB-A740B
1, 2
Servo Drive
Catalog Number
1391-DESAA15
1391-DESAA15
1391-DESAA15
1391-DESAA15
1391-DESAA22
1391-DESAA22
1391-DESAA45
1391-DESAA45
Amperes at
Continuous
Torque
7.1
7.0
9.5
15.2
15.2
21.0
29.5
38.2
Rated
Output
(kW)
1.2
1.3
1.9
3.0
3.0
3.5
5.5
8.3
Motor Options/Accessories For detailed motor option/accessory information, refer to the individual
instruction sheets shipped with the option/accessory.
9-3
Page 88

Chapter 9
1326 AC Servomotors
End of Chapter
9-4
Page 89

Chapter
10
Transformers and Shunt Regulators
Chapter Objectives Chapter 10 provides general information about the 1391 Isolation
Transformer. In addition, shunt regulator information is also provided.
1391 Transformers The 1391-DES must operate from an isolation transformer having a
three-phase, 230V AC output and a single-phase, 36V AC output.
Transformers supplied with the 1391-DES can provide power for up to four
drives. Standard three-phase input voltages for the 60 Hz units are
available. The kVA values specified are the continuous outputs of the units
in a 60° C ambient.
Important: The maximum rating that can be connected to the 1391-DES is
15 kVA.
Important: The 1391-DES drive uses a 36V AC transformer tap to
provide power to the Logic Control Board. It is recommended that a 1391
Isolation Transformer be used. Contact your local Allen-Bradley Sales
Representative if a transformer of a different type must be used. Refer to
Figure 10.1 and Appendix B for connection information.
60 Hz Transformers
Two 60 Hz transformers are available and have input ratings of:
1. 240/480V AC , three-phase
2. 208/230/460/575V AC, three-phase
50/60 Hz Transformers
The 50/60 Hz transformer that is available has an input rating of
240/380/415/480V AC, three-phase.
NEMA Type 1 Enclosure
Dimensions for the NEMA Type 1 enclosures are shown in Appendix A.
Important: The NEMA Type 1 enclosure is shipped as a kit for customer
assembly.
If other input voltages or special enclosures are required, consult your local
Allen-Bradley Sales Representative. Refer to Figure 10.1 for connection
information and Appendix A for dimensions.
10-1
Page 90

Chapter 10
Transformers and Shunt Regulators
Faraday
Shield
G2
Figure 10.1
1391 Transformer Wiring Diagrams
1
1391–TxxxDT (60 Hz.)
Primary
Voltage
240V AC
480V AC
H1 H3 H2 H4 P1 P2 G0
G1
X1 X2 X3
X0
H6 H5 H7 H9 H8
230V AC
230V AC230V AC
Connect
H1 to H3 to H8
H2 to H4 to H6
H5 to H7 to H9
H2 to H3
H5 to H6
H8 to H9
Lines On
H1
H4
H7
H1
H4
H7
Y2
Y1
Y3 Y4
36V AC
CT 200VA
Thermal switch for transformer protection
(rated 115V AC/1A, 24V DC/0.25A min.,
185_C ±5_C
Y5
Y6 Y7
36V AC
CT 200VA
Y8
Y9 Y10
36V AC
CT 200VA
CT 200VA
36V AC
Y11
Y12
Faraday
Shield
X0
1391–TxxxET (50/60 Hz.)
Primary
Voltage
240V AC
380V AC
415V AC
480V AC
X1 X2 X3
Connect
H2 to H6
H7 to H11
H12 to H1
H3 to H6
H8 to H11
H13 to H1
H4 to H6
H9 to H11
H14 to H1
H5 to H6
H10 to H11
H15 to H1
H6 H7 H8 H9 H10H1 H2 H3 H4 H5 H11 H12 H13 H14 H15 P1 P2 G1 G0
230V AC
Lines On
H1
H6
H11
230V AC230V AC
Primary
Voltage
208V AC
240V AC
480V AC
575V AC
1391–TxxxNT (60 Hz.)
Connect
H2 to H6
H7 to H11
H12 to H1
H3 to H6
H8 to H11
H13 to H1
H4 to H6
H9 to H11
H14 to H1
H5 to H6
H10 to H11
H15 to H1
Thermal switch for transformer protection
(rated 115V AC, 1A, 24V DC/0.25A min.,
185_C ±5_C)
Y2
Y1
Y3 Y4
36V AC
CT 200VA
36V AC
CT 200VA
Lines On
H1
H6
H11
Y5
Y6 Y7
Y8
Y9 Y10
36V AC
CT 200VA
Y11
Y12
36V AC
CT 200VA
10-2
1
The Y2, Y5,Y8 and Y11 center taps are available but not used with the 1391-DES.
Page 91

Chapter 10
Transformers and Shunt Regulators
Shunt Regulator Operation Refer to Chapter 4 for an explanation of the shunt regulator circuitry. The
nominal data for the shunt regulator is as follows:.
Overvoltage Trip Point = 405V DC±2.5%
DC Bus Shunt “ON” Point = 386.4V DC
DC Bus Shunt “OFF” Point = 366.9V DC
Nominal DC Bus Voltage = 300V DC
DC Bus Undervoltage Detect = 145V DC±20%
The shunt regulator behavior is modified by an adjustable duty cycle timer.
The timer is used to model the shunt resistor temperature. A selector switch
(SW1) determines the temperature level and therefore the average power
level at which the drive will fault. When this level is reached, the drive will
be forced to fault on an overvoltage. This action would be equivalent to
turning the shunt regulator off.
The Duty Cycle Selector Switch is located on top of the drive near terminal
Block, TB5 (see Figure 1.1). The switch has 16 positions designated “0 to
F,” with “0” being the lowest value and “F” the highest. The higher the
setting, the higher the average power seen by the shunt resistor. The Duty
Cycle Selector Switch settings for various drive/shunt combinations are
shown in Tables 10.A and B.
Important: Accurate operation of the Duty Cycle Timer is dependent on
the shunt resistor value. Do Not substitute alternate values.
Important: Setting SW1 higher than the rating of the shunt resistor may
cause a blown fuse, resulting in repeated overvoltage faults. This will occur
until the fuse is replaced and/or the switch is set correctly (see Table 10.B).
Table 10.A provides the required Duty Cycle Selector Switch settings and
resistor power trip points for factory supplied configurations. An optional
external resistor assembly (catalog number 1391-MOD-SR22A) is
available for the 22.5A 1391-DES.
Table 10.A
Maximum Switch Settings and Trip Points for Factory Supplied Configurations
Configuration
1391-DES15 w/ standard 16 ohm internal resistor
1391-DES22 w/ standard 12 ohm internal resistor
1391-DES22 w/ 9 ohm external resistor (1391-MOD-SR22A)
1391-DES45 w/ standard 5 ohm external resistor
* Denotes SW1 setting at time of shipment. User must reconfigure drive when using optional
1391-MOD-SR22A.
SW1 Switch
Setting
B*
B*
F
D*
Nominal Trip
Point
164w, ±10%
162w, ±10%
386w, ±10%
715w, ±10%
ATTENTION: The designated settings for the factory supplied
!
configurations must be used or damage to the drive may result.
10-3
Page 92

Chapter 10
Transformers and Shunt Regulators
Table 10.B shows the nominal resistor power trip levels in watts for the
various switch settings. When shunt requirements exceed the selector
setting, the excess power will cause the bus voltage to rise, resulting in an
overvoltage fault condition and loss of braking.
Table 10.B
Nominal Power Trip Level Reference Data (continuous watts,±10%)*
SW1 Switch
Setting
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
* Denotes the maximum allowable settings for factory supplied configurations.
15A
W/ Int. 16 Ohm
Resistor
67
71
75
80
85
91
99
107
118
130
145
164*
189
223
272
347
22.5A
W/ Int. 12 Ohm
Resistor
73
77
82
86
92
98
105
113
122
133
146
162*
183
208
242
290
22.5A
W/ Ext. 9 Ohm
Resistor
98
103
109
115
122
130
139
150
163
177
195
216
243
277
323
386*
45A
W/ Ext. 5 Ohm
Resistor
215
227
241
256
274
294
317
344
378
417
466
527
607
715*
872
1115
10-4
ATTENTION: To guard against personal injury and/or
!
equipment damage from an overheated resistor, the designated
duty cycle settings for factory supplied shunt resistor
configurations must not be exceeded. Check the Duty Cycle
Selector Switch (SW1) to ensure that it is set properly before
operation.
ATTENTION: When using a customer supplied external shunt
!
resistor assembly, the Duty Cycle Selector Switch (SW1) must
be set to an appropriate level for that resistor assembly. Consult
the resistor manufacturer for the appropriate derating
guidelines. Failure to comply could result in personal injury
and/or equipment damage from an overheated resistor.
Page 93

Frequent overvoltage trips and blown fuse on high inertia systems during
regenerative states (deceleration) may be an indication that an external
shunt resistor having increased power dissipation capacity is required.
Based on the data supplied, Allen-Bradley will specify a shunt resistor with
the proper resistance value for the drive being used.
Shunt Regulator Installation External Shunt Resistors
The 1391-DES is designed to allow the use of an external shunt resistor on
the 22.5 and 45A units. To use an external shunt resistor with the 22.5A
units, the user must reconfigure the drive at terminal block TB5.
The following steps provide the information needed to properly convert
22.5A drives for use with an external shunt resistor and fuse. Refer to the
resistor and fuse mounting dimensions provided in Appendix A and the
Interconnect Diagram in Appendix B, as required. A minimum wire size of
12 AWG (2.5 mm
2
) must be used when connecting an external resistor.
Chapter 10
Transformers and Shunt Regulators
ATTENTION: To guard against an electrical shock hazard,
!
1. Remove and discard the jumper present between terminals 8 and 10 of
!
2. Connect one end of the new external shunt fuse to terminal 9 of TB5.
ensure that all power to the drive has been removed prior to
performing the following procedure and the bus voltage at
terminal 9 (+) and 7 (–) of TB5 measures 0.00 volts.
TB5. This disconnects the internal shunt resistor and fuse from the
shunt regulator circuit.
ATTENTION: When using an external shunt resistor assembly
with the 22.5A 1391-DES, ensure that the internal resistor
assembly has been disconnected per the above instructions.
Personal injury and/or equipment damage could result from an
overheated resistor if the internal resistor is not disconnected.
Connect the other end of the fuse to one end of the shunt resistor.
Important: The external shunt resistor must have a fuse in series with
the shunt resistor. Refer to the paragraph entitled “Shunt Fusing” for
more information.
3. Connect the remaining end of the shunt resistor to terminal 8 of TB5.
4. Using Table 10.B, set the Duty Cycle Selector Switch to the
appropriate setting for the resistor being used.
5. Install the appropriate shunt fuse in its holder.
10-5
Page 94

Chapter 10
Transformers and Shunt Regulators
ATTENTION: Proper derating must be applied to the
!
manufacturers nominal resistor power ratings when using these
in external shunt configurations. Consult the resistor
manufacturer for recommended derating. Failure to comply
could result in personal injury and/or equipment damage from
an overheated resistor.
Shunt Fusing
Shunt regulator fusing is provided with all of the 1391-DES drives. The
fuse is in series with the resistor and used to protect the resistor against
short circuits. The shunt fuse is located on top of the drive near the circuit
breaker for 15 and 22.5A drives. External resistors for 22.5A and 45A
drives are supplied with a fuse which must be mounted external to the
drive (see Appendix A for mounting dimensions). Refer to Table 10.C for
further shunt fuse information.
Table 10.C
Shunt Fuse Information
Drive Rating
15A
22.5A
22.5A
45A
Fuse Location
Top Panel
Top Panel
External
External
Fuse Type
Bussmann KLM-10 or equivalent
Bussmann FNM-6.25 or equivalent
Bussmann KTK-15 or equivalent
Bussmann KLM-20 or equivalent
Important: Repeated overvoltage tripping can be an indication that the
shunt fuse has malfunctioned.
10-6
Page 95

Chapter
11
Troubleshooting
Chapter Objectives Chapter 11 provides information to guide the user in troubleshooting the
1391-DES. Included in the chapter are board and drive substitution
procedures, fault indications, general system faults and test point
descriptions.
System Troubleshooting Most drive faults are annunciated by fault messages on the front panel
display. Many system malfunctions manifest themselves through a drive
fault. The troubleshooting information provided will take advantage of the
fault messages and list a number of potential system problems related to
each. In addition, a number of common system and motor malfunctions are
described.
ATTENTION: This product contains stored energy devices. To
!
!
!
avoid hazard of electrical shock, verify that all voltage on the
capacitors has been discharged before attempting to service,
repair or remove this unit.
Voltage at terminals 9 (+) and 7 (–) of TB5 must be “0.00” as
measured with a standard digital voltmeter or multimeter.
Only qualified personnel familiar with solid-state control
equipment and safety procedures in publication NFPA 70E
should attempt this procedure.
ATTENTION: Do not attempt to defeat or override the drive
fault circuits. The cause of a fault indication must be determined
and corrected before attempting operation. Failure to correct a
drive or system malfunction may result in personal injury and/or
equipment damage due to uncontrolled machine system
operation.
ATTENTION: If an oscilloscope (or chart recorder) is used for
troubleshooting, it must be properly grounded. The oscilloscope
chassis may be at a potentially fatal voltage if not properly
grounded. Always connect the oscilloscope chassis to earth
ground.
11-1
Page 96

Chapter 11
Troubleshooting
The majority of faults cause the DROK contact to operate. The use of fault
messages may aid in identifying drive and motor malfunctions. If a drive
fault occurs, the fault detection circuitry can be reset by removing and
reapplying power to the transformer supplying the servo drive or
connecting the Reset input (TB2-11) to ground (TB2-12) with the enable
removed.
This material along with the diagnostic/troubleshooting information included with the position controller, will help identify most common system
malfunctions to an assembly level. The position controller is considered to
be a; computer numerical control (such as an Allen-Bradley 9/240), programmable controller (IMC 120, 121, 123) or stand-alone control (S Class,
MAX), controlling a closed loop position or velocity system.
Substituting or interchanging complete servo drives or major board
assemblies is a common technique used in troubleshooting closed loop
position systems. The 1391-DES has been designed to facilitate this
technique. The procedures provided must be followed when substituting or
interchanging drives or board assemblies. Refer to Figure 11.1 for board
and connector locations.
ATTENTION: This drive contains ESD (Electrostatic
Discharge) sensitive parts and assemblies. Static control
!
precautions are required when installing, testing, servicing or
repairing this drive. Component damage may result if ESD
control procedures are not followed. If you are not familiar
with static control procedures, reference A-B publication
8000-4.5.2, Guarding Against Electrostatic Damage or any
other applicable ESD protection handbook.
Drive Substitution
1. Remove all power to the drive branch circuit.
2. Remove connectors TB1, TB2 and TB3.
3. Label and remove the motor leads and three-phase input at TB4. Also
remove the drive ground wire.
4. Remove the Memory Board. Refer to Figure 11.1 and the following
page for further information.
5. Remove the drive and insert replacement unit.
6. Reconnect the ground wire, motor leads, three-phase input and signal
connectors previously removed.
11-2
7. Replace the Memory Board previously removed.
8. Apply power to the system and check for proper operation – tuning
should not be required.
Page 97

Chapter 11
Troubleshooting
Display Board Substitution
1. Remove all power to the drive branch circuit.
2. Remove the front cover from the drive.
3. Loosen the 4 thumb screws and remove the cable between the Display
and Logic Control Boards. Remove the Display Board.
4. Install the new Display Board. Reconnect cable.
5. Apply power to the system and check for proper operation – tuning is
not be required.
Memory Board Substitution
1. Remove all power to the drive branch circuit.
2. Remove the front cover from the drive.
3. Remove the Memory Board by squeezing the nylon latches.
4. Install the new Memory Board.
5. Apply power to the system – tuning will be required.
Logic Control Board Substitution
1. Remove all power to the drive branch circuit.
2. Remove the front cover from the drive. Label and remove the ribbon
cables and signal connectors (TB1 and TB2) from the Logic Control
Board.
3. Remove the Memory and Display Boards.
4. Insert the replacement Logic Control Board.
5. Replace the Memory and Display Boards and reconnect the signal
connectors/cables previously removed.
6. Apply power to the system and check for proper operation – tuning
should not be required.
11-3
Page 98

Chapter 11
Troubleshooting
A Quad B Board Substitution
1. Remove all power to the drive branch circuit.
2. Remove the front cover from the drive. Label and remove the ribbon
cables and signal connectors (TB1, TB2 and TB3) from the A Quad B
and Logic Control Boards.
3. Remove the Display and Logic Control Boards.
4. Remove the A Quad B Board.
5. Install the new A Quad B Board to the Logic Control Board with the 8
thumb screws.
6. Install the Logic Control Board (w/AQB Board) verifying that the
connectors between the boards mate. Tighten the 8 screws.
7. Install the Display Board and cable.
8. Reconnect the signal connectors/cables previously removed.
9. Apply power to the system and check for proper operation – tuning
should not be required.
LED Indications
The 1391-DES has two LEDs visible from the front of the drive. The top
LED, labeled “STATUS,” flashes green when no faults are detected by the
drive and a bus undervoltage condition exists. The LED will be a steady
green when no faults exist and bus voltage is present. If a fault is detected,
the LED will turn red and flash.
The lower green LED, labeled “ENABLE,” will be lit when the drive is
enabled (on and in control of the servomotor). An enable signal must be
applied to terminals TB2-9 & 10 for the LED to be lit. Refer to Table 11.A
for further information.
11-4
Page 99

Table 11.A
LED Fault Diagnostics
Chapter 11
Troubleshooting
Enable Enable LED is NOT Illuminated
Status Status LED is flashing red.
The application of an Enable signal
by the machine position controller
will cause the ENABLE LED to
illuminate.
This LED is green until a system
fault occurs. The LED will flash
green when bus voltage is not
present (DROK open).
If the DC Power Bus drops
below a preset level the DROK
contact will open if parameter
130 is set to 1.
1. The position controller has not enabled the drive.
2. The Enable wiring to the drive is open.
3. The position controller Enable relay/switch has malfunctioned.
4. The position controller has detected a machine system malfunction that will not
allow the drives to be Enabled.
5. Power has not been applied to input transformer.
6. The logic supply (±12V DC) circuits have malfunctioned (fuse blown etc.) or the
AC input at TB4-19, 21 is incorrectly wired or missing.
Enable LED is Illuminated, but drive does not Enable
1. A drive malfunction has occurred but is not annunciated by the LED indicators.
Check the status of the Drive OK output (DROK) relay.
2. A component malfunction exists in the Enable circuit.
3. The circuit breaker (MCB) is tripped.
4. The power contactor has not been energized or has malfunctioned.
5. Motor cables removed.
The drive logic supplies are not operational
1. The logic supply fuses are blown
2. Logic supply AC voltage is missing
3. A drive malfunction has occurred but is not annunciated by the LED indicators
(check the status of the Drive OK contacts).
1. System fault has occurred.
2. Power was applied while the drive was enabled. Remove enable and reapply
power.
1. The power contactor (M) has not energized or has dropped out.
2. The input line voltage is low.
3. The shunt regulator circuit has malfunctioned and is placing the shunt resistor
across the power bus.
4. The power bus capacitor has malfunctioned.
5. The circuit breaker (MCB) has tripped.
6. The three-phase input line is open.
7. Transformer is supplying the wrong line voltage or has malfunctioned.
11-5
Page 100

Chapter 11
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Tables
Table 11.B provides a listing and description of the faults shown through
the front panel display. Also included are possible solutions to the faults.
Table 11.C provides a listing of common system malfunctions and their
possible causes. Table 11.D lists servomotor malfunctions and their
possible causes. Table 11.E provides a listing and description of the
available test points. Refer to Figure 11.1 for board, connector and test
point locations.
Fault Codes
Parameter 06 is a 16 bit, binary word that represents the drive faults. A “1”
indicates that a fault has occurred. If a “0” is displayed, a fault has not
occurred. Refer to the following table for an explanation of the individual
codes.
Fault/Message
“No Active Faults”
Drive
Overtemperature
“amp overtemp”
(Bit 1)
Control Voltage Fault
“cntrl voltage”
(Bit 4)
Resolver Loss
“resolver loss”
(Bit 5)
Power Fault
“power fault”
(Bit 7)
Bit 15 Bit 0
Table 11.B
Fault Descriptions and Diagnostics
Fault Description
None
The drive contains a thermal switch on
the heat sink which senses the power
transistor temperature. If the
temperature is exceeded the LED will
illuminate.
A fault will occur if the logic supply
rises or drops 10% from its nominal
value.
The resolver wiring is open or
shorted or missing.
The current through the power
output transistors is monitored. If the
current exceeds a fixed level
(greater than 300% of drive rating)
the LED will illuminate.
Potential Cause
All circuits are functional.
The logic supply (±12V DC, +5V DC) circuits have malfunctioned (fuse blown
etc.) or the AC input at TB4-19, 20, 21 is incorrectly wired.
The heat sink thermal overload has tripped. One or more of the following may
have occurred:
1. The cabinet ambient temperature is above rating.
2. The machine duty cycle requires an RMS current exceeding the continuous
rating of the drive.
3. The integral fan is not functioning.
4. The airflow access to the drive is limited or blocked.
1. The input line voltage is out of tolerance.
2. The transformer auxiliary logic supply winding is open.
3. The logic supply (±12V DC, +5V DC) circuits have malfunctioned (fuse
blown etc.) or the AC input at TB4-19, 20, 21 is incorrectly wired.
1. Open or short circuit on resolver wiring.
2. Incorrect resolver wiring.
1. The current through any one of the power transistors has exceeded 300%
of the drive’s current rating.
2. Malfunctioning power transistor.
3. Shorted Lead.
4. Motor malfunction.
11-6
 Loading...
Loading...