Page 1

MVI94-DNP
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet
Communication Module
December 17, 2010
USER MANUAL
Page 2

Your Feedback Please
We always want you to feel that you made the right decision to use our products. If you have suggestions, comments,
compliments or complaints about our products, documentation, or support, please write or call us.
How to Contact Us
ProSoft Technology
5201 Truxtun Ave., 3rd Floor
Bakersfield, CA 93309
+1 (661) 716-5100
+1 (661) 716-5101 (Fax)
www.prosoft-technology.com
support@prosoft-technology.com
Copyright © 2010 ProSoft Technology, Inc., all rights reserved.
MVI94-DNP User Manual
December 17, 2010
ProSoft Technology ®, ProLinx ®, inRAx ®, ProTalk ®, and RadioLinx ® are Registered Trademarks of ProSoft
Technology, Inc. All other brand or product names are or may be trademarks of, and are used to identify products
and services of, their respective owners.
ProSoft Technology® Product Documentation
In an effort to conserve paper, ProSoft Technology no longer includes printed manuals with our product shipments.
User Manuals, Datasheets, Sample Ladder Files, and Configuration Files are provided on the enclosed CD-ROM,
and are available at no charge from our web site: www.prosoft-technology.com
Printed documentation is available for purchase. Contact ProSoft Technology for pricing and availability.
North America: +1.661.716.5100
Asia Pacific: +603.7724.2080
Europe, Middle East, Africa: +33 (0) 5.3436.87.20
Latin America: +1.281.298.9109
Page 3

Important Installation Instructions
Power, Input, and Output (I/O) wiring must be in accordance with Class I, Division 2 wiring methods, Article 501-4 (b)
of the National Electrical Code, NFPA 70 for installation in the U.S., or as specified in Section 18-1J2 of the Canadian
Electrical Code for installations in Canada, and in accordance with the authority having jurisdiction. The following
warnings must be heeded:
A WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - SUBSTITUTION OF COMPONENTS MAY IMPAIR SUITABILITY FOR
CLASS I, DIV. 2;
B WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - WHEN IN HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS, TURN OFF POWER BEFORE
REPLACING OR WIRING MODULES
C WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - DO NOT DISCONNECT EQUIPMENT UNLESS POWER HAS BEEN
SWITCHED OFF OR THE AREA IS KNOWN TO BE NON-HAZARDOUS.
D THIS DEVICE SHALL BE POWERED BY CLASS 2 OUTPUTS ONLY.
MVI (Multi Vendor Interface) Modules
WARNING - EXPLOSION HAZARD - DO NOT DISCONNECT EQUIPMENT UNLESS POWER HAS BEEN
SWITCHED OFF OR THE AREA IS KNOWN TO BE NON-HAZARDOUS.
AVERTISSEMENT - RISQUE D'EXPLOSION - AVANT DE DÉCONNECTER L'ÉQUIPEMENT, COUPER LE
COURANT OU S'ASSURER QUE L'EMPLACEMENT EST DÉSIGNÉ NON DANGEREUX.
Warnings
North America Warnings
A Warning - Explosion Hazard - Substitution of components may impair suitability for Class I, Division 2.
B Warning - Explosion Hazard - When in Hazardous Locations, turn off power before replacing or rewiring
modules.
Warning - Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect equipment unless power has been switched off or the area is
known to be nonhazardous.
C Suitable for use in Class I, division 2 Groups A, B, C and D Hazardous Locations or Non-Hazardous Locations.
MVI94 Markings
Electrical Ratings
Backplane Current Load: 800 mA @ 5 Vdc
Operating Temperature: 0°C to 60°C (32°F to 140°F)
Storage Temperature: -40°C to 85°C (-40°F to 185°F)
Shock: 30g Operational; 50g non-operational; Vibration: 5 g from 10 Hz to 150 Hz
Relative Humidity 5% to 95% without condensation)
All phase conductor sizes must be at least 1.3 mm(squared) and all earth ground conductors must be at least
4mm(squared).
Label Markings
Agency Approvals and Certifications
cUL C22.2 No. 213-1987
Page 4

Page 5
MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Contents
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Contents
Your Feedback Please ........................................................................................................................ 2
How to Contact Us .............................................................................................................................. 2
ProSoft Technology® Product Documentation .................................................................................... 2
Important Installation Instructions ....................................................................................................... 3
MVI (Multi Vendor Interface) Modules ................................................................................................ 3
Warnings ............................................................................................................................................. 3
MVI94 Markings .................................................................................................................................. 3
1 Quick Start 9
2 Hardware Installation 11
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
Verify Package Contents ......................................................................................... 12
Mounting the MVI 94 Flex I/O Base ........................................................................ 13
Setting Jumpers ...................................................................................................... 14
Installing the Module onto the Base ........................................................................ 15
Installing the Serial Adapter Cables ........................................................................ 16
Wiring the Power Connections ................................................................................ 17
3 Configuration 19
3.1
3.2
3.3
3.4
3.5
3.6
3.7
3.8
3.9
3.1.1
3.4.1
3.7.1
3.9.1
3.9.2
Configuration File .................................................................................................... 20
Editing the Configuration File .................................................................................. 21
[Module] ................................................................................................................... 23
[DNP Slave] ............................................................................................................. 24
[DNP Slave Database] ............................................................................................ 25
Slave Class/Deadband Overrides ........................................................................... 25
[DNP Master] ........................................................................................................... 26
[IED Database] ........................................................................................................ 27
[DNP Master Slave List] .......................................................................................... 28
Command List ......................................................................................................... 30
[DNP Master Commands] ....................................................................................... 33
Uploading and Downloading the Configuration File ................................................ 34
Transferring the Configuration File to Your PC ....................................................... 34
Transferring the Configuration File to the Module ................................................... 36
4 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting 41
4.1
4.1.1
4.1.2
4.1.3
4.1.4
4.1.5
4.2
4.2.1
4.2.2
4.3
LED Status Indicators .............................................................................................. 42
PRT1 ....................................................................................................................... 42
U1 ............................................................................................................................ 42
U2 ............................................................................................................................ 42
STS .......................................................................................................................... 42
PRT2 ....................................................................................................................... 42
The Configuration/Debug Menu .............................................................................. 43
Navigation ............................................................................................................... 43
Keystrokes ............................................................................................................... 43
Required Software ................................................................................................... 45
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 5 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 6

Contents MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
4.4
4.5
4.6
4.7
4.4.1
4.4.2
4.4.3
4.4.4
4.4.5
4.6.1
4.6.2
4.6.3
4.7.1
4.7.2
Using the Configuration/Debug Port ....................................................................... 46
Main Menu .............................................................................................................. 46
DNP Database View Menu ..................................................................................... 50
The Class Assignment Menu .................................................................................. 53
Master Command List Menu ................................................................................... 54
Master Command Error List Menu.......................................................................... 55
Reading Status Data from the Module ................................................................... 56
Error Status Data .................................................................................................... 57
Error Status Data .................................................................................................... 57
Command Error List ................................................................................................ 61
Slave Status Data ................................................................................................... 61
Error Codes ............................................................................................................. 62
Module Error Codes ................................................................................................ 62
Command Error Codes ........................................................................................... 65
5 Reference 67
5.1
5.2
5.3
5.4
5.5
5.6
5.7
5.8
5.1.1
5.1.2
5.1.3
5.2.1
5.2.2
5.2.3
5.2.4
5.2.5
5.4.1
5.4.2
5.4.3
5.4.4
5.4.5
5.5.1
5.5.2
Product Specifications ............................................................................................ 68
General Specifications ............................................................................................ 68
FLEX I/O Interfaces ................................................................................................ 68
Functional Specifications ........................................................................................ 69
Cable Connections ................................................................................................. 71
RS-232 Application Port(s) .................................................................................... 71
RS-232 Configuration/Debug Port .......................................................................... 73
RS-485 Application Port(s) ..................................................................................... 73
RS-422 .................................................................................................................... 74
DB9 to Mini-DIN Adaptor (Cable 09) ...................................................................... 74
Collision Avoidance (DNP modules only) ............................................................... 75
Functional Overview ............................................................................................... 76
Database Information ............................................................................................. 77
Data Transfer .......................................................................................................... 80
Slave Driver ............................................................................................................ 92
Master Driver .......................................................................................................... 93
IIN Bits .................................................................................................................... 94
MVI94-DNP Configuration Forms ........................................................................... 95
Slave Configuration ................................................................................................ 95
Master Configuration ............................................................................................ 101
DNP Master Subset Definition .............................................................................. 105
DNP Slave Subset Definition ................................................................................ 111
Device Profile ........................................................................................................ 118
6 Support, Service & Warranty 121
Contacting Technical Support ........................................................................................................ 121
6.1
6.1.1
6.1.2
6.1.3
6.2
6.2.1
6.2.2
6.2.3
6.2.4
Return Material Authorization (RMA) Policies and Conditions ............................. 123
Returning Any Product .......................................................................................... 123
Returning Units Under Warranty ........................................................................... 124
Returning Units Out of Warranty ........................................................................... 124
LIMITED WARRANTY .......................................................................................... 125
What Is Covered By This Warranty ...................................................................... 125
What Is Not Covered By This Warranty ................................................................ 126
Disclaimer Regarding High Risk Activities ............................................................ 126
Intellectual Property Indemnity ............................................................................. 127
Page 6 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 7

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Contents
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
6.2.5
6.2.6
6.2.7
6.2.8
6.2.9
6.2.10
Disclaimer of all Other Warranties ........................................................................ 127
Limitation of Remedies ** ...................................................................................... 128
Time Limit for Bringing Suit ................................................................................... 128
No Other Warranties ............................................................................................. 128
Allocation of Risks ................................................................................................. 128
Controlling Law and Severability ........................................................................... 128
Index 129
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 7 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 8

Contents MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Page 8 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 9

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Quick Start
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
1 Quick Start
This section describes the procedure for installing and configuring the module for
communication. These steps should be followed for successful implementation of
a module in a user application.
1 Define the communication characteristics of the DNP master or slave port.
2 If a master device will be simulated, define the command lists to be used on
the DNP master port.
3 Fill in the blank configuration form for application using the data sets defined
in steps one and two.
4 Edit the configuration text file
data from the configuration form and save the file under a different name.
These text files are provided as a starting point to ease application
development.
5 Connect the MVI94-DNP module’s Configuration/Debug Port to a computer
containing HyperTerminal with a null-modem cable.
6 Connect the module to a 24 Vdc power source.
7 Select the directory containing the correct configuration file on the computer.
8 Start the terminal emulation program on the computer.
9 Press [?] to verify that the module is communicating with the computer and
that the main menu mode is current.
10 Press [>] on the terminal emulator to begin receiving the configuration file.
Press [Y] to confirm the request.
11 Press [ALT-F3] key (DOS Version) or open the Transfer menu and choose
S
END
(Windows Version) on the terminal emulator and enter the name of the
configuration file to be loaded into the module. The configuration will be
downloaded, and the module will restart using the new configuration.
12 Connect the module’s DNP port to the DNP network. If everything is
configured correctly and the cable connections are correct, communications
should be present on the port.
13 Monitor the communication statistics for the port to verify that everything is
working correctly.
14 View the database in the module using the terminal emulator.
15 Edit the ladder logic provided with the module for your system. The ladder
logic is responsible for transferring the data between the module and
processor.
16 Connect the module to the Flex I/O processor or ControlNet processor. If all
is configured correctly, the data in the module should be visible in the
processor.
17 Use the Configuration/Debug port to view the backplane transfer statistics.
Master.Cfg
or
Slave.Cfg
to reflect the desired
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 9 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 10

Quick Start MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Page 10 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 11

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Hardware Installation
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
2 Hardware Installation
In This Chapter
Verify Package Contents ....................................................................... 12
Mounting the MVI 94 Flex I/O Base ....................................................... 13
Setting Jumpers .................................................................................... 14
Installing the Module onto the Base ...................................................... 15
Installing the Serial Adapter Cables ...................................................... 16
Wiring the Power Connections .............................................................. 17
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 11 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 12

Hardware Installation MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
2.1 Verify Package Contents
Make sure that you verify the contents of the product before you discard the
packing material. The following components should be included with the product:
1 A MVI94 Flex I/O Base
2 A MVI94 Module with 3 jumpers installed
3 One Serial Adapter Cable
Page 12 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 13
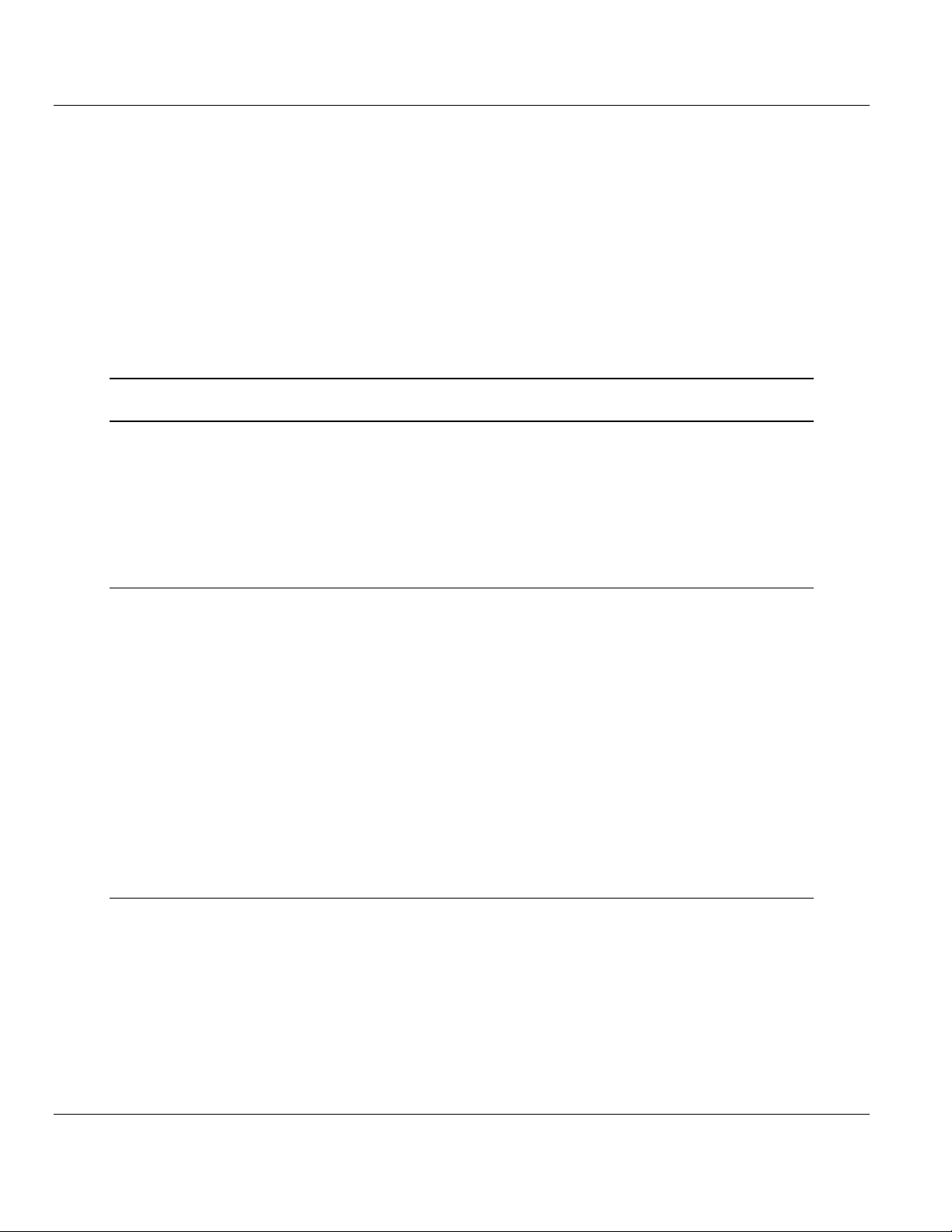
MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Hardware Installation
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
2.2 Mounting the MVI 94 Flex I/O Base
1 Remove the cover plug (if used) in the male connector of the unit to which
you are connecting this Base.
2 Check to make sure that the 16 pins in the male connector on the adjacent
device are straight and in line so that the mating female connector on this
Base will mate correctly.
3 Make certain that the female flexbus connector C is fully retracted into the
Base.
4 Position the Base on a 35 x 7.5mm DIN-rail A at a slight angle with the hook
B on the left side of the Base hooked into the right side of the unit on the left.
5 Rotate the Base onto the DIN-rail with the top of the rail hooked under the lip
on the rear of the Base. Use caution to make sure that the female flexbus
connector does not strike any of the pins in the mating male connector.
6 Press the terminal base down onto the DIN-rail until flush. The locking tab D
snaps into position and locks the terminal base to the DIN-rail.
7 If the Base does not lock in place, use a screwdriver or similar device to
move the locking tab down, press the Base flush with the DIN-rail and release
the locking tab to lock the base in place.
8 Gently push the female flexbus C connector into the adjacent base or
adapter male connector to complete the flexbus connections.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 13 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 14
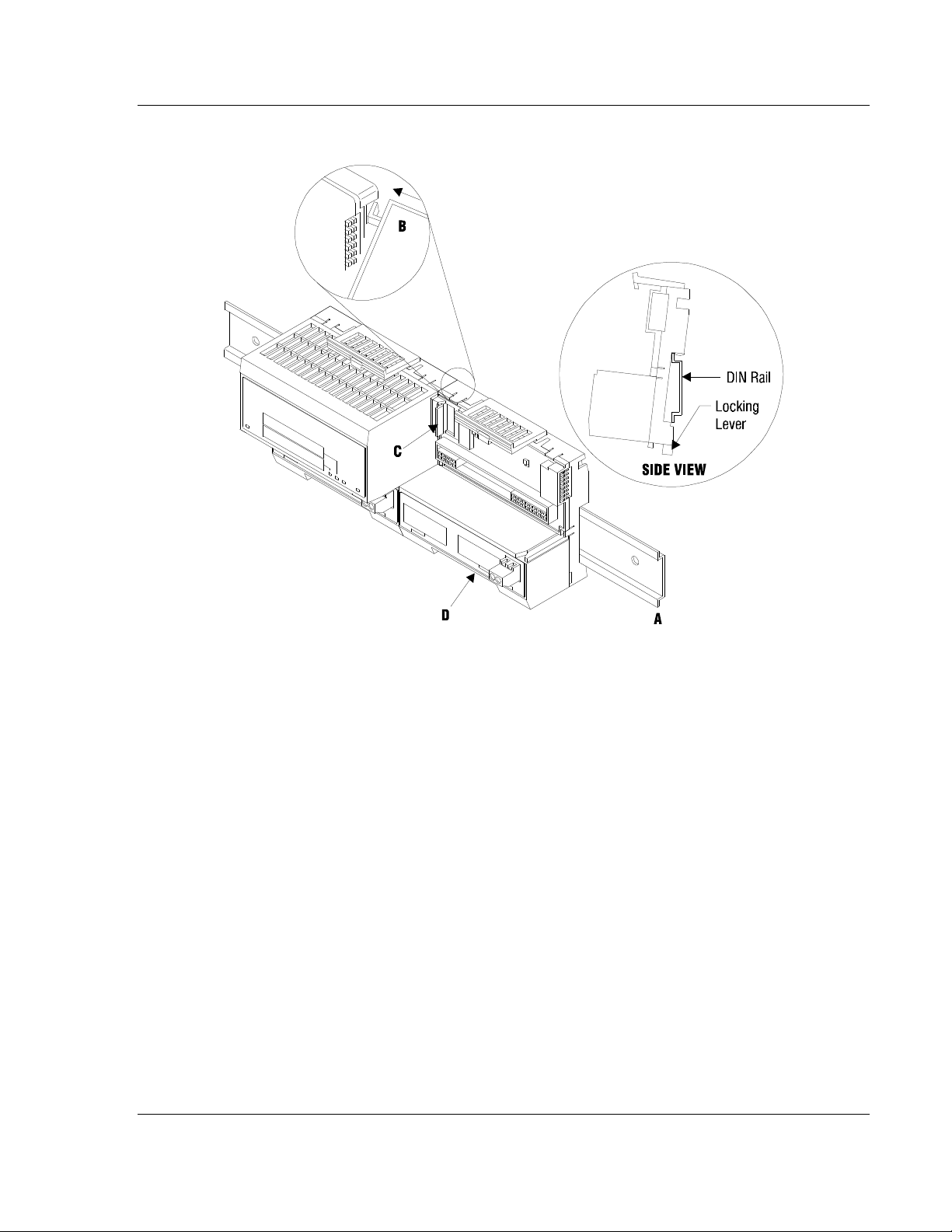
Hardware Installation MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
2.3 Setting Jumpers
Before installing the MVI94 module onto its base, the module’s configuration can
be set using the jumpers on the bottom of the module as shown in this figure.
Port 2 RS-232/422/485: Select with jumper (shipped in 232).
BP Reset: If the MVI94 module is to be reset when the Flex Bus is reset, install
the BP RESET jumper in the Enabled position.
ATTENTION: Do not remove or replace a base unit when power is applied. Interruption of the
flexbus can result in unintended operation or machine motion.
SETUP: To place the module in SETUP mode, install the jumper in the Selected
position (DOS default). To prevent the module from being in Setup mode, leave
the jumper in the disabled position.
Page 14 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 15
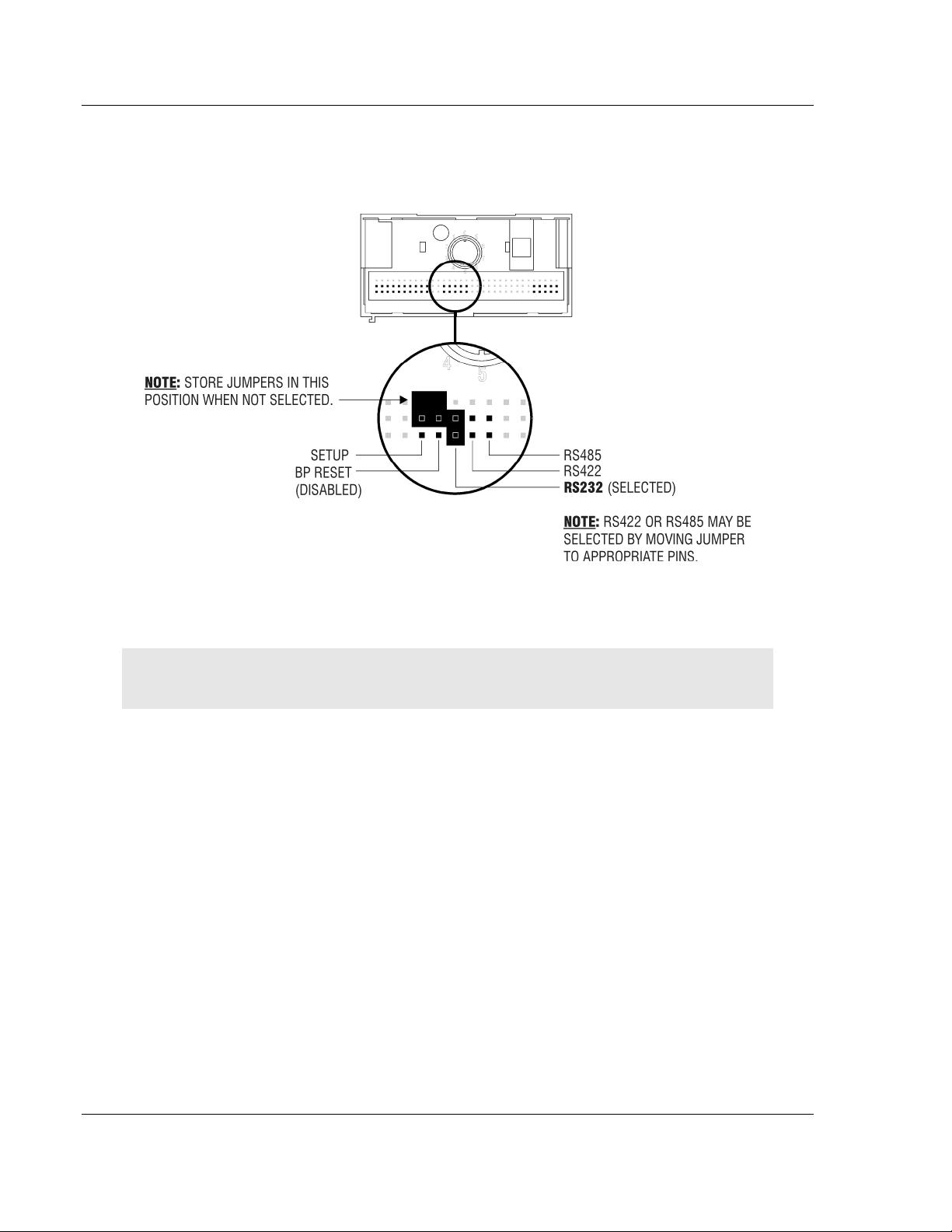
MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Hardware Installation
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
2.4 Installing the Module onto the Base
1 Rotate the keyswitch 1 on the Base clockwise to position #1.
2 Make certain the flexbus connector 3 on the Base is pushed all the way to the
left to connect with the neighboring base or adapter. The Module cannot be
installed unless the flexbus connector is fully extended.
3 Make sure that the pins on the bottom of the Module are straight so they will
align properly with the connector socket on the Base.
4 Position the Module with its alignment bar 5 aligned with the groove 6 on the
Base.
5 Press firmly and evenly to seat the Module in the Base. The Module is seated
when the latch 7 on the Base is locked into the Module.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 15 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 16
Hardware Installation MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
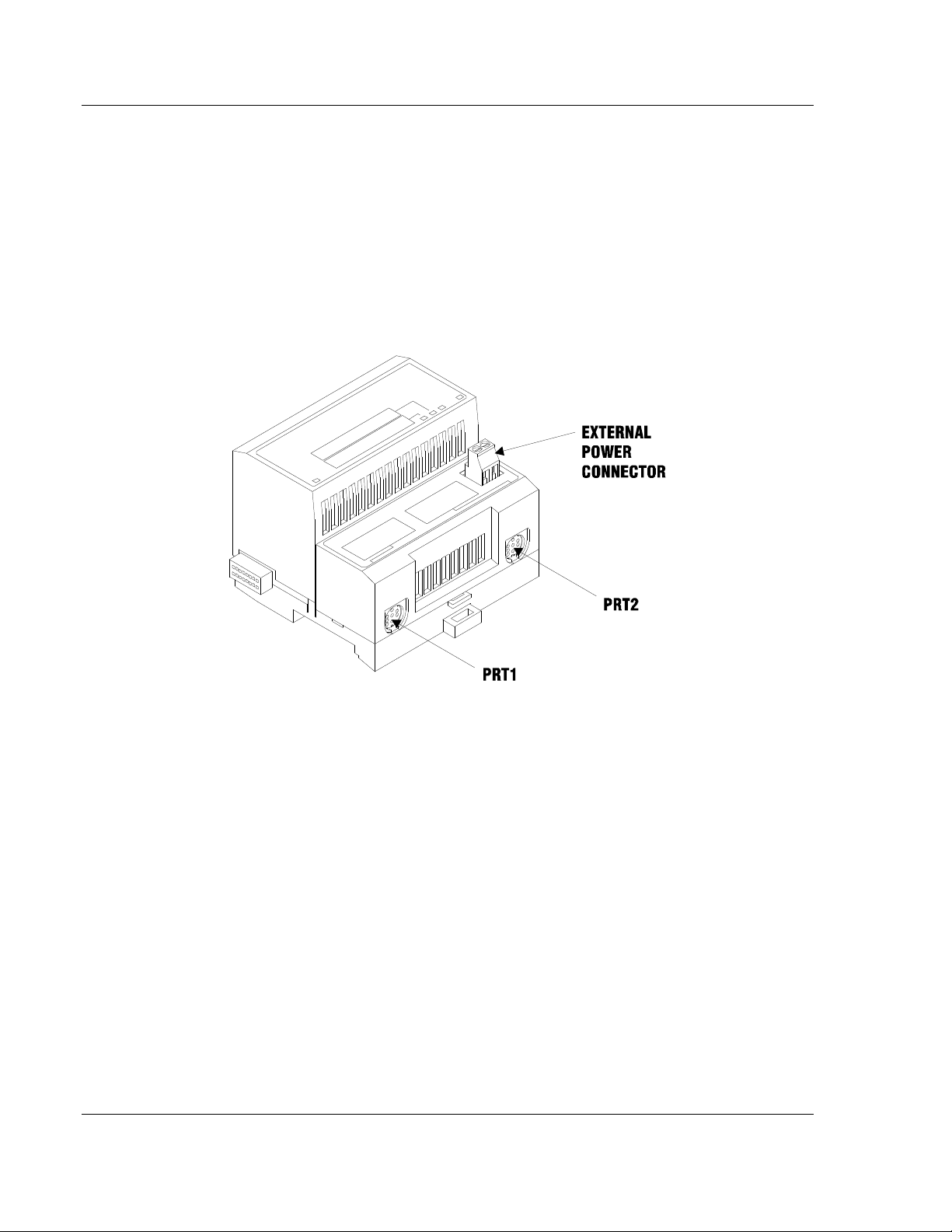
2.5 Installing the Serial Adapter Cables
Two identical serial adapter cables are supplied. Each cable has a locking-type 8
pin Mini-DIN plug on one end and a DB-9 male connector on the other end. The
Mini-DIN connector on each cable is inserted into the Mini-DIN receptacles
marked PRT1 and PRT2 on the Base.
To install the locking-type Mini-DIN connector, slide the spring-loaded sleeve
back while inserting the plug into the receptacle on the Base, and then release
the sleeve when fully seated. The locking mechanism prevents the cable from
being removed during normal operation. To remove the cable, slide the sleeve
back and remove the plug.
Page 16 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 17

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Hardware Installation
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
2.6 Wiring the Power Connections
External power is supplied to the Base on the 2 pin screw terminal block. The
power supply can be either 24Vdc or 12Vdc, and should be located in close
proximity of the base.
Connect dc common to the COM terminal
Connect +24V dc or +12V dc to the 24VDC terminal
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 17 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 18

Hardware Installation MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Page 18 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 19

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
3 Configuration
In This Chapter
Configuration File .................................................................................. 20
[Module]................................................................................................. 23
[DNP Slave] ........................................................................................... 24
[DNP Slave Database]........................................................................... 25
[DNP Master] ......................................................................................... 26
[IED Database] ...................................................................................... 27
[DNP Master Slave List] ........................................................................ 28
[DNP Master Commands] ...................................................................... 33
Uploading and Downloading the Configuration File ............................... 34
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 19 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 20

Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
3.1 Configuration File
The MVI94-DNP module stores its configuration in a text file called Master.Cfg or
Slave.Cfg, located in the module's flash memory. When the module starts up, it
reads the configuration file and uses the information to control how the
Distributed Network Protocol protocol interacts with the module's application
port(s).
The configuration file is arranged in Sections, with a heading in [ ] characters at
the beginning of each section. Each Section contains a list of Parameters and
Values, followed by an optional Comment that explains the parameter.
The following illustration shows an example of a Section, a Parameter, a Value,
and a Comment.
The Parameter must be followed by a [:] (colon) character. The text following the
[:] is a Value.
The module ignores "comment" text following the [#] character. Use comments to
document your configuration settings.
You can get a sample configuration file for the module in the following places:
Copy the Master.Cfg or Slave.Cfg from the module's flash memory to your
PC
Copy the Master.Cfg or Slave.Cfg from the ProSoft Solutions CD-ROM
supplied with the module
Download the Master.Cfg or Slave.Cfg from the ProSoft Technology web site
at www.prosoft-technology.com
Page 20 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 21

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
3.1.1 Editing the Configuration File
The DNPSNET_Q.CFG file consists of the following sections:
[Module]
[Backplane Configuration]
[DNP ENET Slave]
[DNP ENET IP Addresses]
[DNP Slave Binary Inputs]
[DNP Slave Analog Inputs]
[DNP Slave Float Inputs]
Important notes to consider when editing the sample configuration file:
Comments within the file are preceded by the pound (#) sign. Any text on a
line that occurs after the # character will be ignored.
Do not use tabs or other non-printing characters instead of spaces to
separate parameters (spacebar).
Parameter names must begin in the first column of a line, and may not be
preceded with a space (spacebar) or other non-printing character.
The Master.Cfg or Slave.Cfg file is a plain ASCII text file. Use a text editor such
as Notepad.exe (included with Microsoft Windows) to open and edit the file.
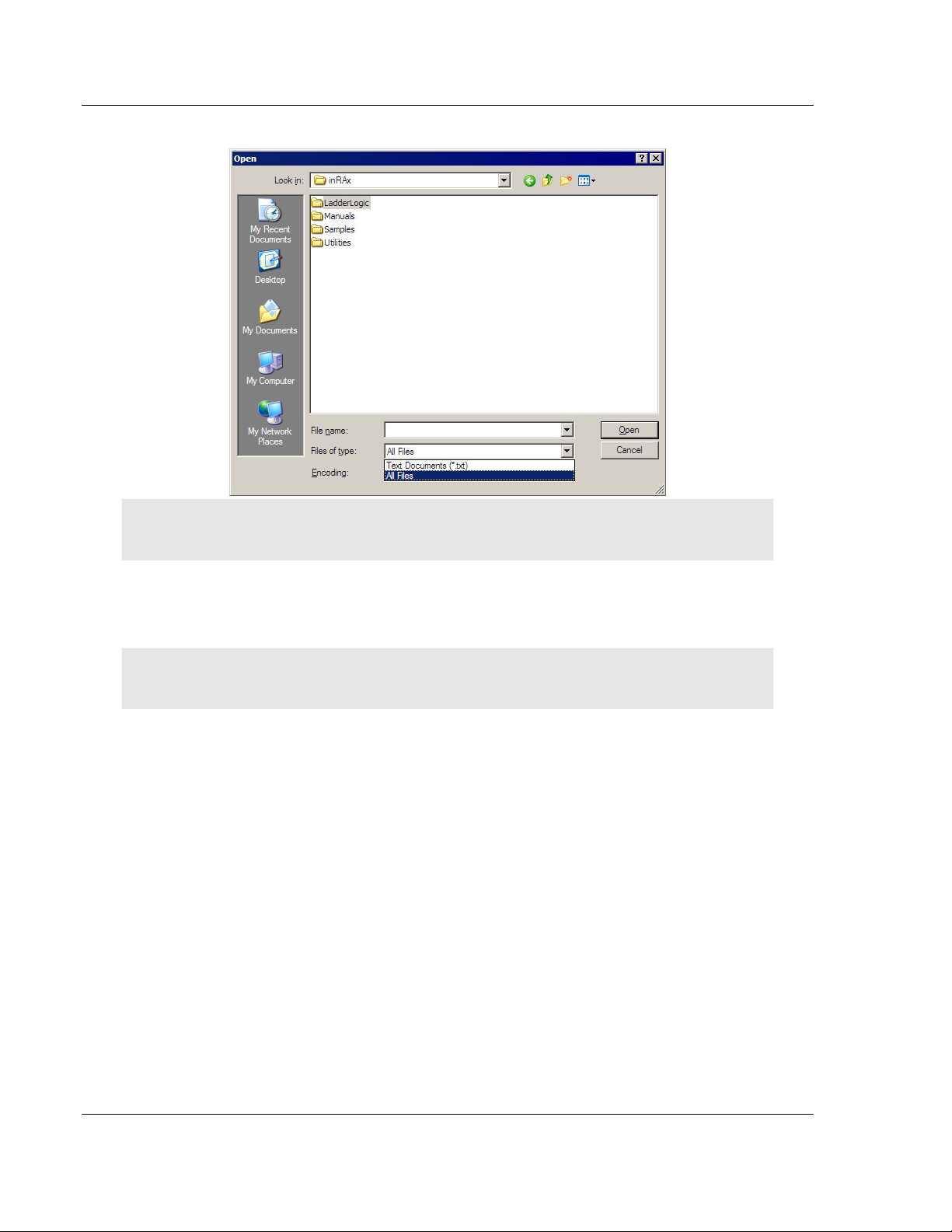
To open the configuration file in Notepad
1 Click the S
2 Expand the Programs menu, and then choose A
3 On the Accessories menu, choose N
TART
button, and then choose P
OTEPAD
ROGRAMS
CCESSORIES
.
.
4 In Notepad, open the F
ILE
menu, and then choose O
PEN
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 21 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 22
Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
5 In the Open dialog box, select A
LL FILES
in the Files of Type: dropdown list.
Tip: Sample configuration files are stored under the LadderLogic folder on the ProSoft Solutions
CD-ROM.
6 Navigate to the folder containing the configuration file, and then select the file
to edit.
7 Click O
8 When you have finished editing,
PEN
to open the file.
SAVE
the file and close Notepad.
Important: Changes to the configuration file will not take effect until you download the file to the
module, and then reboot the module.
Page 22 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 23

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
3.2 [Module]
The [MODULE] section defines if the module will emulate a DNP master or slave
device.
The following table describes the parameters in this section.
Variable Name Data Range Description IF Error
[Module] This section header indicates the start of
Module Name: 80 Characters This parameter sets the name or
Type: M=Master or
S=Slave
the module specific parameter set.
description of the module's application
This parameter must be set to M for the
DNP port to use as a master port. If the
parameter is set to any other value, the
port will be used as a slave port.
"Not Configured"
S
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 23 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 24

Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
3.3 [DNP Slave]
The [DNP SLAVE] section is only required if the module is emulating a slave
device. This section contains the information required to configure the
communication port and set the protocol specific parameters. Refer to the
configuration form (page 95) for a complete list of the parameters set in this
section.
Page 24 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 25

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
3.4 [DNP Slave Database]
The [DNP SLAVE DATABASE] section is only used if the module is simulating a
slave device. This section contains the information to size the database to be
used to interface with the remote master. The values entered in this section
define the blocks to be transferred between the module and the processor over
the backplane and the data to be interfaced with the remote DNP master device.
The parameters defined in this section are shown in the configuration form (page
95).
3.4.1 Slave Class/Deadband Overrides
The [DNP SLAVE x INPUTS] sections are only used if the module is simulating a
slave device. These sections contain the class and deadband information to
override the default values stated under the [DNP Slave] section for each point in
the input data sets. If no overrides are to be specified for a data type, its section
can be omitted. The parameters defined in these sections are shown in the
configuration form displayed in the Reference chapter.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 25 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 26

Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
3.5 [DNP Master]
The [DNP MASTER] section is only used if the module is simulating a DNP
master device. This section contains information required to configure the
communication port and set the protocol specific parameters. The parameters set
in this section are shown in the configuration form (page 95).
Page 26 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 27

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
3.6 [IED Database]
The [IED DATABASE] section is only used if the module is simulating a DNP
master device. The size of each point type in the database is specified in the
section. These data areas are transferred between the module and the processor
using the module's I/O image. These data areas also interface to attached IED
units connected to the port. Commands present in the master port command list
use the database to control and monitor the attached devices. The parameters
set in this section are described in the configuration form (page 95).
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 27 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 28
Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
3.7 [DNP Master Slave List]
The [DNP MASTER SLAVE LIST] section is only used if the module is simulating
a DNP master device. This list defines the protocol specific information for each
IED unit to be interfaced with on the master port.
The slave list is formatted differently than the other sections of the configuration
file. Each IED unit is present on a separate line in the section between the labels
START and END. These labels inform the program where the lists starts and
stops. The module's program will parse each IED unit's information from each
line and place the data in the module and will continue reading records until the
END label is reached or the maximum number of slave are processed.
The following table describes the format of each record.
Column Variable
Name
1 DNP Slave
Address
2 Data Link
Confirm Mode
3 Data Link
Confirm Timeout
4 Maximum
Retries for
Data Link
Confirm
5 Application
Layer
Response
Time-out
6 Slave Mode Coded Value
Data Range Description IF Error Config. Value
0 to 65534 This is the slave address for the unit to
Coded Value
(0=Never,
1=Sometimes,
2=Always).
1 to 65535
milliseconds
0 to 255 retries Maximum number of retries at the Data
1 to 65535
milliseconds
(Bit 0=Enable,
Bit 1=Unsol
Msg, Bit 2=Use
DM, Bit 3=Auto
Time Sync).
override the default values.
This value specifies if data link frames
sent to the remote device require a data
link confirm. This value should always be
set to zero for almost all applications.
This parameter specifies the time to wait
for a data link confirm from the remote
device before a retry is attempted.
Link level to obtain a confirmation. If this
value is set to 0, retries are disabled at
the data link level of the protocol. This
parameter is only used if the frame is sent
with confirmation requested.
Time-out period the master will wait for
each response message fragment. If data
link confirms are enabled, make sure the
time-out period is set long enough to
permit all data confirm retries.
This word contains bits that define the
slave mode. The slave mode defines the
functionality of the slave device and can
be combined in any combination. The
fields have the following definition:
Enable: determines if this slave will be
used. Unsol Msg: causes an enabled
unsolicited response message to be sent
to the slave when its RESTART IIN bit is
set. This parameter is also required for
unsolicited message reporting by the IED
unit. Use DM: uses delay measurement.
Auto Time Sync: time synchronization
used when NEED TIME IIN bit set.
Ignore
0
300
3
5000
5
An example of the [DNP Master Slave List] section is as follows:
[DNP Master Slave List] This section header defines the location of
the DNP master slave definition list.
# DL Conf Mode ==> 0=Never, 1=Sometimes and 2=Always (select 0).
Page 28 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 29
MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
# Flag parameter is bit coded as follows:
# Bit 0 (decimal 1) ==> Enable the slave
# Bit 1 (decimal 2) ==> Use Unsolicited messaging with this slave
# Bit 2 (decimal 4) ==> Use delay measurement with this slave
# Bit 3 (decimal 8) ==> Auto time synchronization enabled
#
START This string signals the start of the slave
definition list.
# Node DL Conf Conf Conf App Rsp
# Address Mode Timeout Retry Timeout Flags
2 0 1000 0 5000 9
END This string signals the end of the slave
definition list.
A record is required for each IED unit on the master port. As the program reads
in the information, it generates a list of slaves as shown in the following example:
When the commands are read in from the configuration, a link between the IED
point and the module's database is generated and stored in this link list. This
data is used by the module to handle event data transferred from the IED units to
the module. When the master port receives an event from an IED unit, the data in
the link list places the received data into the module's database.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 29 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 30

Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
3.7.1 Command List
The command list stores the command list used by the DNP master port. This list
only must be defined if the DNP master port is used. Up to 300 commands can
be defined for the master port. The structure of each row in the list is shown in
the following table.
Word Offset Definitions
0 Port/Flags
1 Slave Address
2 Object
3 Variation
4 Function
5 Address in Slave
6 Point Count
7 DNP DB Address
8 IED DB Address
9 Poll Interval
The definition of each parameter required for each command is provided in the
following table.
Bits in the Port/Flags parameter are dependent on the data type. The following
table defines the Port/Flags bits for binary input, analog input and counter data
points.
Port/Flags Bits Description Decimal Equivalent
0 to 1 Communication port (0=Internal, 2=Port 2) 0 or 2
2 Enable/Disable Command (1=Enable, 0=Disable) 4
3 RBE Flag(0=Events from IED, 1=Events by module) 8
4 to 7 Not Used
For these data types the qualifier used in the data request depends on the Point
Count and Address in Slave fields in the command as follows:
If Point Count < 0, then use Qualifier 06h (All points, packed & -Point Count = #
of points to consider)
If Address in Slave = 0 & Point Count > 0, then use Qualifier 00h or 01h (points 0
to Point Count -1)
If Address in Slave > 0 & Point Count > 0, then use Qualifier 00h or 01h (Address
in Slave to Address in Slave + Point Count -1)
Page 30 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 31

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
The following table defines the Port/Flags bits for binary output and analog output
points.
Port/Flags Bits Description Decimal Equivalent
0 to 1 Communication port (0=Internal, 2=Port 2) 0 or 2
2 Enable/Disable Command (1=Enable, 0=Disable) 4
3 Poll Type (0=Poll, 1=Exception) 8
4 Data Source(0=DNP Database, 1=IED Database) 16
5 to 7 Not Used
For these data types the qualifier used in the data request depends on the Point
Count and Address in Slave fields in the command as follows:
If Address in Slave = 0 & Point Count > 0, then use Qualifier 17h or 28h (Point
Count specified starting at point 0)
If Address in Slave > 0 & Point Count > 0, then use Qualifier 17h or28h (points
from Address in Slave to Address in Slave + Point Count -1)
If Point Count <= 0, then ignore because this is illegal for outputs.
Slave Address
This parameter specifies the IED unit address on the DNP network to consider
with the command. The parameter has a range of 0 to 65535. The value of
65535 is reserved for broadcast messages. Verify that the slave configuration
information is set up in the module for each slave defined in the command list.
Object
This parameter specifies the DNP object type in the command. Valid objects for
the module are 1, 2, 12, 20, 21, 30, 32, 41, 50, 60 and 80. A value of 0 is
permitted in this field for a set of special commands.
Variation
This parameter is specific to the object type selected.
Function
This parameter specifies the DNP function for the command list object. The
object type determines the value of the functions permitted. For example, the
only function permitted for binary input data points is the read function (Function
Code 1). For counter and output objects, more functions are available.
Address In Slave
This value must be greater-than or equal to zero. If it is set to a value less-than
zero, the command will be ignored. This parameter specifies the starting point
address to consider in the IED unit.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 31 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 32

Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Point Count
This parameter defines the number of points in the IED unit. Refer to the
discussion above for the interpretation of this parameter’s values for the different
object types.
DNP DB Address
This parameter defines the starting location in the DNP database for the
command. If the parameter has a value of -1, the DNP database is not used with
the point.
IED DB Address
This parameter defines the starting location in the IED database for the
command. If the parameter has a value of -1, the IED database is not used with
the point.
Poll Interval
This parameter specifies the minimum frequency at which the module should
execute the command. The value is entered in units of seconds. For example, to
execute a command every 10 seconds, enter a value of 10 in the field. A value of
0 for the parameter implies that the command should be executed every scan of
the list.
Page 32 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 33

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
3.8 [DNP Master Commands]
The [DNP MASTER COMMANDS] section of the configuration file sets the DNP
master port command list. This list polls DNP slave devices attached to a
simulated master port. The module supports numerous commands. This permits
the module to interface with a wide variety of DNP protocol devices.
The command list is formatted differently than the other sections of the
configuration file. Commands are present in a block between the labels START
and END. These labels inform the program where the list resides. The module's
program will parse all commands after the START label until it reaches the END
label or maximum number of commands are processed.
The following table describes the structure of a single command.
[DNP Master Commands] This section header defines the location of
the DNP master command list.
START This string signals the start of the command
list.
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
#Flags/ Node Data Data Cmd Device Point DNP DB IED DB Poll
#Enable Address Object Variation Func Address Count Address Address Interval
6 2 1 0 1 0 -20 -1 0 0
END This string signals the end of the command
list.
Function codes used for each command are specific to the module and are
defined to permit the module to interface with a wide variety of DNP
communication devices.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 33 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 34

Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
3.9 Uploading and Downloading the Configuration File
ProSoft modules are shipped with a pre-loaded configuration file. In order to edit
this file, you may transfer the file from the module to your PC or locate and load
the file from the distribution CD-ROM supplied with the module. After editing, you
must transfer the file back to the module for your changes to take effect.
This section describes these procedures.
Important: The illustrations of configuration/debug menus in this section are intended as a general
guide and may not exactly match the configuration/debug menus in your own module. For specific
information about the configuration/debug menus in your module, refer to The Configuration/Debug
Menu (page 43).
3.9.1 Transferring the Configuration File to Your PC
1 Connect your PC to the Configuration/Debug port of the module using a
terminal program such as HyperTerminal. Press [?] to display the main
menu.
2 Press [>] key (Send Module Configuration). The message "Press Y to
confirm configuration send!" is displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Page 34 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 35

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
3 Press [Y]. The module will automatically start a Zmodem file transfer. The
configuration file will be stored in the default file transfer folder on your PC.
Note: ProSoft Technology suggests that you download the configuration file pre-loaded on
your module. However, configuration files are also available on the ProSoft CD as well as the
ProSoft Technology web site at www.prosoft-technology.com.
When the configuration file has been transferred to your PC, the dialog box
will indicate that the transfer is complete.
The configuration file is now in a folder on your PC. To view the location of
this folder, open the Transfer menu in HyperTerminal and choose Receive
File.
4 You can now open and edit the file in a text editor such as Notepad. When
you have finished editing the file, save it and close Notepad.
Important: You must name this file DNP.CFG before you transfer it to the module. The module will
not recognize configuration files with any other name or extension.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 35 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 36

Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
3.9.2 Transferring the Configuration File to the Module
Perform the following steps to transfer a configuration file from your PC to the
module.
1 Connect your PC to the Configuration/Debug port of the module using a
terminal program such as HyperTerminal. Press [?] to display the main
menu.
2 Press [<] (Receive Module Configuration). The message "Press Y key to
confirm configuration receive!" is displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Page 36 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 37

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
3 Press [Y]. The screen now indicates that the PC is ready to send.
4 From the Transfer menu in HyperTerminal, select Send File.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 37 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 38

Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
The Send File dialog appears.
5 Use the Browse button to locate the configuration file your computer.
Note: This procedure assumes that you are uploading a newly edited configuration file from your
PC to the module. However, configuration files are also available on the ProSoft CD as well as the
ProSoft Technology web site.
6 Select Zmodem as the protocol.
7 Click the Send button. This action opens the Zmodem File Send dialog box.
Page 38 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 39

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Configuration
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
When the upload is complete, the screen indicates that the module has
reloaded program values and displays information about the module.
8 Your module now contains the new configuration. Press [?] to see the
module’s main menu.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 39 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 40

Configuration MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Page 40 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 41

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
4 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
In This Chapter
LED Status Indicators ............................................................................ 42
The Configuration/Debug Menu ............................................................ 43
Required Software ................................................................................. 45
Using the Configuration/Debug Port ...................................................... 46
Reading Status Data from the Module .................................................. 56
Error Status Data ................................................................................... 57
Error Codes ........................................................................................... 62
The module provides information on diagnostics and troubleshooting in the
following forms:
LED status indicators on the front of the module provide general information
on the module's status.
Status data contained in the module can be viewed through the
Configuration/Debug port, using the troubleshooting and diagnostic
capabilities of Microsoft Windows HyperTerminal.
Status data values can be transferred from the module to processor memory
and can be monitored there manually or by customer-created logic.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 41 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 42

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
4.1 LED Status Indicators
This section defines the indications provided on the MVI94-DNP module through
LEDs.
4.1.1 PRT1
This LED indicates data transmit and receive activity on the configuration port.
When the TXD or RXD pin is active on the port, the LED will be illuminated
green. When the port is not active, the LED will be in the off state.
4.1.2 U1
This LED indicates backplane data transfer operation. When the module is
successfully writing data to the FLEX I/O backplane, the LED will be in the off
state. When the module is reading a new block of data from the FLEX I/O
backplane, the LED will be in the on state (amber). During normal operation of
the module, this LED should turn on and off at a very rapid rate. If the LED never
turns on, check your ladder logic to verify that the data transfer is set up
correctly.
4.1.3 U2
This LED indicates communication errors on the DNP application port. The LED
is off when no error exists on the port. If a communication error is recognized on
the port, the LED will be illuminated. If the LED is turned on, check for errors in
the command list to determine the error condition recognized by the module.
4.1.4 STS
This LED indicates the "health" of the module. When power is applied to the
module, the LED will be illuminated. If the LED is green, the program is working
correctly and the user configuration is being used. If the LED is red, the program
is halted. Try restarting the module by cycling power. This should cause the
module to return to its normal state.The module should return to its normal state.
4.1.5 PRT2
This LED indicates data transmit and receive activity on the DNP master/slave
port. When the TXD or RXD pin is active on the port, the LED will be illuminated
green. When the port is not active, the LED will be in the off state.
Page 42 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 43

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
4.2 The Configuration/Debug Menu
The Configuration and Debug menu for this module is arranged as a tree
structure, with the Main Menu at the top of the tree, and one or more sub-menus
for each menu command. The first menu you see when you connect to the
module is the Main menu.
Because this is a text-based menu system, you enter commands by typing the
command letter from your computer keyboard in Prosoft Configuration Builder
(PCB). The module does not respond to mouse movements or clicks. The
command executes as soon as you press the command letter — you do not need
to press [Enter]. When you type a command letter, a new screen will be
displayed in your terminal application.
4.2.1 Navigation
All of the submenus for this module contain commands to redisplay the menu or
return to the previous menu. You can always return from a submenu to the next
higher menu by pressing [M] on your keyboard.
The organization of the menu structure is represented in simplified form in the
following illustration:
The remainder of this section shows the menus available for this module, and
briefly discusses the commands available to you.
4.2.2 Keystrokes
The keyboard commands on these menus are usually not case sensitive. You
can enter most commands in lowercase or uppercase letters.
The menus use a few special characters (?, -, +, @) that must be entered exactly
as shown. Some of these characters will require you to use the SHIFT, CTRL, or
ALT keys to enter them correctly. For example, on US English keyboards, enter
the ? command as SHIFT and /.
Also, take care to distinguish the different uses for uppercase letter "eye" (I),
lowercase letter "el" (L), and the number one (1). Likewise, uppercase letter "oh"
(O) and the number zero (0) are not interchangeable. Although these characters
look alike on the screen, they perform different actions on the module and may
not be used interchangeably.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 43 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 44

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Page 44 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 45

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
4.3 Required Software
In order to send and receive data over the serial port (COM port) on your
computer to the module, you must use a communication program (terminal
emulator).
A simple communication program called HyperTerminal is pre-installed with
recent versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems. If you are connecting
from a machine running DOS, you must obtain and install a compatible
communication program. The following table lists communication programs that
have been tested by ProSoft Technology.
DOS ProComm, as well as several other terminal emulation programs
Windows 3.1 Terminal
Windows 95/98 HyperTerminal
Windows NT/2000/XP HyperTerminal
The module uses the Ymodem file transfer protocol to send and receive
configuration files from your module. If you use a communication program that is
not on the list above, please be sure that it supports Ymodem file transfers.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 45 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 46

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
4.4 Using the Configuration/Debug Port
To connect to the module’s Configuration/Debug port:
1 Connect your computer to the module’s port using a null modem cable.
2 Start the communication program on your computer and configure the
communication parameters with the following settings:
Baud Rate 57,600
Parity None
Data Bits 8
Stop Bits 1
Software Handshaking None
3 Open the connection. When you are connected, press the [?] key on your
keyboard. If the system is set up properly, you will see a menu with the
module name followed by a list of letters and the commands associated with
them.
If there is no response from the module, follow these steps:
1 Verify that the null modem cable is connected properly between your
computer’s serial port and the module. A regular serial cable will not work.
2 Verify that RSLinx is not controlling the COM port. Refer to Disabling the
RSLinx Driver for the Com Port on the PC.
3 Verify that your communication software is using the correct settings for baud
rate, parity and handshaking.
4 On computers with more than one serial port, verify that your communication
program is connected to the same port that is connected to the module.
If you are still not able to establish a connection, you can contact ProSoft
Technology Technical Support for further assistance.
4.4.1 Main Menu
When you first connect to the module from your computer, your terminal screen
will be blank. To activate the main menu, press the [?] key on your computer’s
keyboard. If the module is connected properly, the following menu will appear.
Page 46 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 47

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Setting the Debug Level
You can increase or decrease the level of debug messages sent from the module
to the Debug Menu. The following table shows the type of debugging information
for each key [0] to [9], [A] to [F]
Key None DNP Statistics Data Link Layer
Messages
0 X
1 X
2 X
3 X X
4
5 X
6 X
7 X X
8 X
9 X X
A X X
B X X X
C X
D X X
E X X
F X X X
DPA Level
Messages
Viewing the Error List
Press [L] to display the last 60 errors for the DNP slave port. Refer to the error
list section of the user manual to interpret each error recorded by the module.
If there are no errors present for the module, the message "NO ERRORS FOR
SYSTEM!" is displayed.
Viewing DNP Set Up & Pointers
Press [P] to display the memory allocation and the database setup parameters.
Viewing Operating Parameters
Press [O] to view the DNP Protocol setup information (Operating Parameters) for
the module.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 47 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 48

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Warm Booting the Module
Caution: Some of the commands available to you from this menu are designed for advanced
debugging and system testing only, and can cause the module to stop communicating with the
processor or with other devices, resulting in potential data loss or other failures. Only use these
commands if you are specifically directed to do so by ProSoft Technology Technical Support staff.
Some of these command keys are not listed on the menu, but are active nevertheless. Please be
careful when pressing keys so that you do not accidentally execute an unwanted command.
Press [R] from the Main Menu to warm boot (restart) the module. This command
will cause the program to exit and reload, refreshing configuration parameters
that must be set on program initialization. Only use this command if you must
cause the module to re-boot.
Viewing Comm Status
Press [S] to view the communication status for the DNP port.
Clearing the Error List
Press [W] to clear the error list. Use this command after viewing the error list
(page 47) to delete the current list of errors and start a new list.
Viewing COM States
Press [V] to view the current state of the DNP application port and the port
configuration information.
Viewing Master Port Slave Setup
Press [T] to view configuration information for the Master Port Slave.
Viewing Version Information
Press [G] to view Version information for the module.
Use this command to view the current version of the software for the module, as
well as other important values. You may be asked to provide this information
when calling for technical support on the product.
Values at the bottom of the display are important in determining module
operation. The Program Scan Counter value is incremented each time a
module’s program cycle is complete.
Tip: Repeat this command at one-second intervals to determine the frequency of program
execution.
Opening the Class/Deadband Assignment Menu
Press [Y] to view the class and deadband override values for the binary, analog,
float and double input DNP database.
Page 48 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 49

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Opening the DNP Database View Menu
Press [U] to open the DNP Database View Menu. This menu allows you to view
all data associated with the DNP Server driver. For more information about the
commands on this menu, refer to DNP Database View Menu (page 50).
Receiving the Configuration File
Press [<] (S
HIFT COMMA
) to download (receive) the current configuration file from
the module. For more information on receiving and sending configuration files,
please see Uploading and Downloading the Configuration File (page 34).
Sending the Configuration File
Press [>] (S
HIFT PERIOD
) to upload (send) an updated configuration file to the
module. For more information on receiving and sending configuration files,
please see Uploading and Downloading the Configuration File (page 34).
Viewing Block Transfer Statistics
Press [N] from the Main Menu to view the Block Transfer Statistics screen.
Use this command to display the configuration and statistics of the backplane
data transfer operations between the module and the processor. The information
on this screen can help determine if there are communication problems between
the processor and the module.
Tip: Repeat this command at one-second intervals to determine the number of blocks transferred
each second.
Opening the Command List Menu
Press [X] to open the Command List menu. Use this command to view the
configured command list for the module.
Opening the Command Error List Menu
Press [Z] to open the Command Error List. This list consists of multiple pages of
command list error/status data. Press [?] to view a list of commands available on
this menu.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 49 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 50

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
4.4.2 DNP Database View Menu
Use this menu command to view the current contents of the selected database.
Press [D] to view a list of commands available on this menu.
Viewing Data Type Databases
Press [D] from the DNP menu, then hold down the [S
HIFT
] key and press the [/]
key.
Use the number keys 1 to 6 to select the display of the data type you wish to
view. For example, if the [1] key is pressed, the following is displayed:
Viewing Register Pages
To view sets of register pages, use the keys described below:
Command Description
[0]
[1]
[2]
Display registers 0 to 99
Display registers 1000 to 1099
Display registers 2000 to 2099
And so on. The total number of register pages available to view depends on your
module’s configuration.
Page 50 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 51

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Displaying the Current Page of Registers Again
Press [S] from the Database View menu to show the current page of registers
again.
This screen displays the current page of 100 registers in the database.
Moving Back Through 5 Pages of Registers
Press [-] from the Database View menu to skip five pages back in the database
to see the 100 registers of data starting 500 registers before the currently
displayed page.
Viewing the Previous Page of Registers
Press [P] from the Database View menu to display the previous page of data.
Moving Forward Through 5 Pages of Registers
Press [+] from the Database View menu to skip five pages ahead in the database
to see 100 registers of data 500 registers ahead of the currently displayed page.
Viewing the Next Page of Registers
Press [N] from the Database View menu to display the next page of data.
Viewing Data in Decimal Format
Press [D] from the Database View menu to display the data on the current page
in decimal format.
Viewing Data in Hexadecimal Format
Press [H] from the Database View menu to display the data on the current page
in hexadecimal format.
Viewing Data in Floating-Point Format
Press [F] from the Database View menu to display the data on the current page
in floating-point format. The program assumes that the values are aligned on
even register boundaries. If floating-point values are not aligned as such, they
are not displayed properly.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 51 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 52

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Viewing Data in ASCII (Text) Format
Press [A] from the Database View menu to display the data on the current page
in ASCII format. This is useful for regions of the database that contain ASCII
data.
Viewing Data in Double Word Decimal Format
Press [L] to display the data on the current page in Double Word Decimal format.
This is useful for regions of the database that contain Double Word Decimal data.
Viewing Data in Double Word Decimal Format
Press [X] to display the data on the current page in Double Word Hexadecimal
format. This is useful for regions of the database that contain Double Word
Hexadecimal data.
Viewing DNP Binary Inputs
Press [1] to view a list of DNP Binary Inputs.
Viewing DNP Binary Outputs
Press [2] to view a list of DNP Binary Outputs.
Viewing DNP Counters
Press [3] to view a list of DNP Counters.
Viewing DNP Analog Inputs
Press [4] to view a list of DNP Analog Inputs.
Viewing DNP Analog Outputs
Press [5] to view a list of DNP Analog Outputs.
Viewing DNP Frozen Counters
Press [6] to view a list of DNP Frozen Counters.
Viewing DNP Float Inputs
Press [7] to view a list of DNP Float Inputs.
Viewing DNP Float Outputs
Press [9] to view a list of DNP Float Outputs.
Returning to the Main Menu
Press [M] to return to the Main menu.
Page 52 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 53

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
4.4.3 The Class Assignment Menu
This menu allows you to view the class and deadband override values for the
binary, analog, float and double input DNP database. Press [?] to display the
commands available on this menu.
The following illustration shows the output for the Analog data set (menu key [1])
Viewing Binary Inputs
Press [0] to view the override values for Binary Input Data.
Viewing Analog Inputs
Press [1] to view the override values for Analog Input Data.
Viewing Float Inputs
Press [2] to view the override values for Float Input Data.
Viewing Double Inputs
Press [3] to view the override values for Double Input Data.
Redisplaying the Current Page
Press [S] to display the current page of data.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 53 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 54

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Viewing the Previous Page of Data
Press [P] to display the previous page of data.
Viewing the Next Page of Data
Press [N] to display the next page of data.
Returning to the Main Menu
Press [M] to return to the Main menu.
4.4.4 Master Command List Menu
Use this menu to view the command list for the module. Press [?] to view a list of
commands available on this menu.
Redisplaying the Current Page
Press [S] to display the current page of data.
Viewing the Previous 50 Commands
Press [-] to view the previous 50 commands.
Viewing the Previous Page of Commands
Press [P] to display the previous page of commands.
Viewing the Next 50 Commands
Press [+] to view the next 50 commands from the master command list.
Viewing the Next Page of Commands
Press [N] to display the next page of commands.
Returning to the Main Menu
Press [M] to return to the Main menu.
Page 54 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 55

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
4.4.5 Master Command Error List Menu
Use this menu to view the command error list for the module. Press [?] to view a
list of commands available on this menu.
Redisplaying the Current Page
Press [S] to display the current page of data.
Moving Back Through 5 Pages of Commands
Press [-] to display data for last 5 page commands.
Viewing the Previous Page of Commands
Press [P] to display the previous page of commands.
Moving Forward (Skipping) Through 5 Pages of Commands
Press [+] to display data for the next page of commands.
Viewing the Next Page of Commands
Press [N] to display the next page of commands.
Returning to the Main Menu
Press [M] to return to the Main menu.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 55 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 56

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
4.5 Reading Status Data from the Module
The module provides three sets of error/status data areas. The data sets are
Error/Status Data, Slave Status Data, and Command Error List Data. This data is
available for viewing through the Config/Debug port.
Page 56 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 57

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
4.6 Error Status Data
The module error/status data areas are discussed in this section. Three sets of
data are available with this type of data: Error/Status Data, Slave Status Data
and Command Error List Data. Each of these datasets are discussed in the
following topics:
4.6.1 Error Status Data
This data is provided to the processor using blocks 200 to 210 and is available
for viewing using the configuration/debug port option. The module transfers this
data to the processor at the end of each scan of normal data-block transfer. Each
block contains 6-words of data. Ladder logic should be written to place the data
received into a user data file. The following table describes the block numbers
and data received in each block:
Word Block
Number
0 200 2 Current DNP Slave Port
1 200 3 DNP Slave Port last
2 200 4 DNP Slave Port total
3 200 5 DNP Slave Port total
4 200 6 DNP Slave Port total
5 200 7 DNP Slave
6 201 2 DNP Slave overrun error
Block
Offset
Variable Name Description
This value represents the current value
status
transmitted error code
number of message
frames received by slave
number of response
message frames sent
from slave
number of message
frames seen by slave
synchronization error
count (Physical Layer
Error)
count (Physical Layer
Error)
of the error code for the port. This value
will only be valid if the port is
configured as a slave. The possible
values are described in the application
documentation.
This value represents the last error
code transmitted to the master by this
slave port.
This value represents the total number
of message frames that have matched
this slaves address on this port. This
count includes message frames which
the slave may or may not be able to
parse and respond.
This value represents the number of
good (non-error) responses that the
slave has sent to the master on this
port. The presumption is that if the
slave is responding, the message was
good. Note: This is a frame count.
This value represents the total number
of message frames received by the
slave, regardless of the slave address.
This value counts the number of times
a sync error occurs. The error occurs
when extra bytes are received before
the start bytes (0x05 and 0x64) are
received.
This value counts the number of times
the overrun error occurs. This error
occurs when the mainline Data Link
Layer routine cannot read the data
received on the communication port
before it is overwritten.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 57 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 58

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Word Block
Number
7 201 3 DNP Slave length error
8 201 4 DNP Slave bad CRC
9 201 5 DNP Slave user data
10 201 6 DNP Slave sequence
11 201 7 DNP Slave address error
12 202 2 DNP Slave Binary Input
13 202 3 DNP Slave Binary Input
14 202 4 DNP Slave Analog Input
15 202 5 DNP Slave Analog Input
16 202 6 DNP Slave bad function
17 202 7 DNP Slave object
18 203 2 DNP Slave out of range
19 203 3 DNP Slave message
20 203 4 DNP Slave multi-frame
Block
Offset
Variable Name Description
This value counts the number of times
count (Physical Layer
Error)
error (Data Link Layer
Error)
overflow error (Transport
Layer Error)
error (Transport Layer
Error)
(Transport Layer Error)
Event count
Event count in buffer
Event count
Event count in buffer
code error (Application
Layer Error)
unknown error
(Application Layer Error)
error (Application Layer
Error)
overflow error
(Application Layer Error)
message from DNP
Master error (Application
Layer Error)
an invalid length byte is received. If the
length of the message does not match
the length value in the message, this
error occurs.
This value counts the number of times
a bad CRC value is received in a
message.
This value counts the number of times
the application layer receives a
message fragment buffer which is too
small.
This value counts the number of times
the sequence numbers of multi-frame
request fragments do not increment
correctly.
This value counts the number of times
the source addresses contained in a
multi-frame request fragments do not
match.
This value contains the total number of
binary input events which have
occurred.
This value represents the number of
binary input events which are waiting to
be sent to the master.
This value contains the total number of
analog input events which have
occurred.
This value represents the number of
analog input events which are waiting
to be sent to the master.
This value counts the number of times
a bad function code for a selected
object/variation is received by the slave
device.
This value counts the number of times
a request for an unsupported object is
received by the slave device.
This value counts the number of times
a parameter in the qualifier, range or
data field is not valid or out of range.
This value counts the number of times
an application response message from
the slave is too long to transmit.
This value counts the number of times
the slave receives a multi-frame
message from the master. The
application does not support multi-
frame master messages.
Page 58 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 59

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Word Block
Number
21 203 5 Total blocks transferred Total BTR/BTW or side-connect
22 203 6 Successful blocks
23 203 7 Total errors in block
24 204 2 Total BTR or write errors Total number of BTR or write transfers
25 204 3 Total BTW or read errors Total number of BTW or read transfers
26 204 4 Block number error Number of BTW requests that resulted
27 204 5 Continuous block error
28 204 6 Block transfer error flag This flag indicates that data is not being
29 204 7 Configuration Type This is a coded field that defines the
30 to 31 205 2 to 3 Product Name (ASCII) These two words contain the product
32 to 33 205 4 to 5 Revision (ASCII) These two words contain the product
34 to 35 205 6 to 7 Operating System
36 to 37 206 2 to 3 Production Run Number
38 206 4 DNP Master Port Slave
39 206 5 DNP Master Port
Block
Offset
Variable Name Description
interface transfers attempted by the
module.
This value represents the total number
transferred
transfer
counter
Revision (ASCII)
(ASCII)
Count
Command Count
of transfer operations between the PLC
and module that are successful.
Total number of transfers that resulted
in an error condition.
that resulted in an error.
that resulted in an error.
in an incorrect BTW identification code.
Count of sequential data transfer
errors. When this value exceeds that
specified for the data transfer
operation, the error flag below will be
set.
successfully transferred between the
PLC and the module. This flag
corresponds to the Device Trouble IIN
bit.
configuration of the module. The codes
are as follows: 1=Slave Configuration,
2=Master Configuration
name of the module in ASCII format.
revision level of the firmware in ASCII
format.
These two words contain the module’s
internal operating system revision level
in ASCII format.
These two words contain the
production "batch" number for the
particular chip in the module in ASCII
format.
This is the total number of slaves
configured for the DNP Master port.
This may not represent the number of
active slaves as it includes slaves that
are not enabled.
This is the total number of commands
configured for the DNP Master port.
This may not represent the number of
active commands as it includes
commands that are disabled.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 59 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 60

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Word Block
Number
40 206 6 DNP Master Port Device
41 206 7 DNP Master Port Frame
42 207 2 DNP Master Port Data
43 207 3 DNP Master Port Data
44 207 4 DNP Master Port
45 207 5 DNP Master Port
46 207 6 DNP Master Port Device
47 207 7 DNP Master Port
48 208 2 DNP Master Port Data
49 208 3 DNP Master Port Data
50 208 4 DNP Master Port
51 208 5 DNP Master Port
52 208 6 DNP Master
Block
Offset
Variable Name Description
This value represents the number of
Memory Block Count
Block Count
Link Receive Block
Count
Link Transmit Block
Count
Application Layer
Receive Block Count
Application Layer
Receive Block Count
Memory Allocation Error
Count
Physical Layer Memory
Allocation Error Count
Link Layer Receive
Memory Allocation Error
Count
Link Layer Transmit
Memory Allocation Error
Count
Application Layer
Receive Memory
Allocation Error Count
Application Layer
Transmit Memory
Allocation Error Count
Synchronization Error
Count (Physical Layer
Error)
memory allocation blocks for slave
devices. This number should be one
greater than the number of slave
devices. The extra device is held for
the broadcast device.
This value represents the number of
physical layer frame memory allocation
blocks used by the program.
This value represents the number of
receive data link layer memory blocks
allocated.
This value represents the number of
transmit data link layer memory blocks
allocated.
This value represents the number of
application layer receive memory
blocks allocated.
This value represents the number of
application layer transmit memory
blocks allocated.
This value represents the number of
memory allocation errors for device
blocks.
This value represents the number of
memory allocation errors for physical
layer frame blocks.
This value represents the number of
memory allocation errors for data link
layer receive blocks.
This value represents the number of
memory allocation errors for data link
layer transmit blocks.
This value represents the number of
memory allocation errors for application
layer receive blocks.
This value represents the number of
memory allocation errors for application
layer transmit blocks.
This value counts the number of times
a sync error occurs. The error occurs
when extra bytes are received before
the start bytes (0x05 and 0x64) are
received.
Page 60 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 61

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Word Block
Number
53 208 7 DNP Master Length Error
54 209 2 DNP Master Bad CRC
55 209 3 Scan Counter LSB Program scan counter
56 209 4 Scan Counter MSB
57 209 5 Free Memory LSB Free memory in module
58 209 6 Free Memory MSB
59 209 7 Reserved Future Use
60 210 2 DNP Slave Float Input
61 210 3 DNP Slave Double Float
62 210 4 Reserved Future Use
63 210 5 Reserved Future Use
64 210 6 Reserved Future Use
65 210 7 Reserved Future Use
Block
Offset
Variable Name Description
This value counts the number of times
Count (Physical Layer
Error)
Error Count (Physical
Layer Error)
Event count
Input Event count
an invalid length byte is received. If the
length of the message does not match
the length value in the message, this
error occurs.
This value counts the number of times
a bad CRC value is received in a
message.
This value contains the total number of
floating-point input events which have
occurred.
This value contains the total number of
double floating-point input events which
have occurred.
4.6.2 Command Error List
Each command in the command list has a reserved word value for a status/error
code. This error data list can be read using the Configuration/Debug Port.
Additionally, can be retrieved from the module by the processor using command
block 9950.
The first word in the register location defined contains the status/error code for
the first command in the port's command list. Each successive word in the
command error list is associated with the next command in the list. Therefore, the
size of the data area is dependent upon the number of commands defined.
Refer to the following Error Codes section to interpret the status/error codes
present in the data area.
4.6.3 Slave Status Data
The slave status data contains the communication statistics for each IED unit
interfaced with by the master port. This information is available for viewing using
the configuration/debug port or by using command block 9949 requests from the
processor.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 61 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 62

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
4.7 Error Codes
The module error codes are listed in this section. Error codes are separated into
module errors and command errors. The following two sections present the
errors associated with each set of errors.
4.7.1 Module Error Codes
These error codes are generated by the module in response to communication
problems on an emulated slave port or configuration errors. Review the error list
to view the last set of 60 errors generated by the module. The error codes are
listed in the following tables:
Slave Port Communication Errors
Error Code Name Description
0 OK The module is operating correctly and there are no
errors.
10 DNP synchronization error
(Physical Layer Error)
11 DNP overrun error (Physical
Layer Error)
12 DNP length error (Physical
Layer Error)
13 DNP bad CRC error (Data
Link Layer Error)
14 DNP user data overflow
error (Transport Layer
Error)
15 DNP sequence error
(Transport Layer Error)
16 DNP address error
(Transport Layer Error)
17 DNP bad function code
error (Application Layer
Error)
18 DNP object unknown error
(Application Layer Error)
19 DNP out of range error
(Application Layer Error)
20 DNP message overflow
error (Application Layer
Error)
21 DNP master multi-frame
message error (Application
Layer Error)
Extra bytes are received before the start bytes (0x05
and 0x64).
Mainline Data Link Layer routine could not read data
received on DNP port before it was overwritten.
Length of message does not match length value in
message.
Computed CRC value for message does not match
that received in message.
Application layer received a message fragment buffer
which is too small.
Sequence numbers of multi-frame request fragments
do not increment correctly.
Source addresses contained in multi-frame request
fragments do not match.
Function code received from DNP master is not
supported for selected object/variation.
Slave does not have the specified objects or there are
no objects assigned to the requested class.
Qualifier, range or data fields are not valid or out of
range for the selected object/variation.
Application response buffer overflow condition. The
response message from the slave is too long to
transmit.
Received a multi-frame message from the DNP
master. This application does not support multi-frame
messages from the master.
Page 62 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 63

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
System Configuration Errors
Error Code Name Description
100 Too many binary input
points
101 Too many binary output
points
102 Too many counter points Too many counter points are configured for the
103 Too many analog input
points
104 Too many analog input
points
105 Too many binary input
events
106 Too many analog input
events
107 Invalid analog input
deadband
108 Not enough memory There is not enough memory in the module to
109 Invalid block transfer delay
for blocks 251 and 252
(error/status blocks)
110 File count invalid The file count must be in the range of 0 to 6.
111 Invalid file record size The file record size must be in the range of 1 to 120.
112 Invalid block identification
code for file
Too many binary input points are configured for the
module. Maximum value is 15360.
Too many binary output points are configured for the
module. Maximum value is 15360.
module. Maximum value is 480.
Too many analog input points are configured for the
module. Maximum value is 960.
Too many analog output points are configured for the
module. Maximum value is 960.
Too many binary input events are configured for the
module. Maximum value is 400.
Too many analog input events are configured for the
module. Maximum value is 400.
Deadband value for analog input events is out of
range. Value must be in the range of 0 to 32767.
configure the module as specified.
Block transfer delay value specified is too low.
The file block transfer code must be in the range of
100 to 120.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 63 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 64

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
DNP Port Configuration Errors
Error Code Name Description
212 Invalid DNP address The DNP address specified in the configuration is not
valid (0 to 65534).
213 Invalid DNP port baud rate The baud rate code specified in the configuration is
not valid.
219 Invalid DNP data link layer
confirm mode
220 Invalid DNP data link
confirm time-out
The data link confirmation mode code is not valid in
the configuration.
The data link time-out period specified in the
configuration is 0. It must be an integer in the range of
1 to 65535.
222 Invalid DNP select/operate
arm time duration
223 Invalid DNP application
layer confirm time-out
224 Invalid DNP write time
interval
The select/operate arm timer is set to 0. It must be an
integer in the range of 1 to 65535.
The application layer confirm time-out value is set to 0.
It must be an integer in the range of 1 to 65535.
The write time interval is not in the data range in the
configuration. The value must be in the range of 0 to
1440.
225 Invalid DNP unsolicited
response mode
226 Invalid DNP unsolicited
response minimum quantity
for Class 1
227 Invalid DNP unsolicited
response minimum quantity
for Class 2
228 Invalid DNP unsolicited
response minimum quantity
for Class 3
230 Invalid DNP unsolicited
response destination
address
The unsolicited response mode code is not valid in the
configuration.
The unsolicited response minimum quantity for Class
1 is not valid in the configuration. Value must be an
integer in the range of 1 to 255.
The unsolicited response minimum quantity for Class
2 is not valid in the configuration. Value must be an
integer in the range of 1 to 255.
The unsolicited response minimum quantity for Class
3 is not valid in the configuration. Value must be an
integer in the range of 1 to 255.
The unsolicited response destination address is not
valid in the configuration. Value must be in the range
of 1 to 65534.
Page 64 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 65

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
4.7.2 Command Error Codes
Command error codes are generated by the module's program. These errors are
generated when an error occurs when issuing a request or processing a
response of a command list function. The following tables list the command error
codes used in the module:
General Command Errors
Error Code Name Description
1 Device not defined The IED slave address referenced in the command is
not defined in the module. Check to make sure there
is an entry in the slave table for each slave device
referenced in the command list.
2 Invalid command This command is not valid. Check to make sure the
slave address parameter is greater than or equal to
zero and that the point count is not set to zero.
3 Object not supported The data object in the command is not supported by
the module. Refer to the DNP subset for the Master
Port.
4 Command function not
supported
10 Invalid binary input poll
command
11 Invalid binary input event
poll command
20 Invalid binary output
command function
30 Invalid counter poll
command function
31 Invalid counter poll
command
40 Invalid frozen counter poll
command
50 Invalid analog input poll
command
51 Invalid analog input event
poll command
60 Invalid analog output poll
command function
61 Invalid analog output poll
command
70 Invalid time/date poll
command
80 Invalid event poll command This event poll command is not valid.
The function specified in the command is not
supported for the object type selected. Refer to the
DNP subset for the Master Port.
This binary input object command is not valid.
This binary input event object poll command is not
valid.
This binary output command function is not valid.
The counter object poll command contains an invalid
function code.
This counter object poll command is not valid.
This frozen counter object poll command is not valid.
This analog input poll command is not valid.
This analog input event poll command is not valid.
This analog output poll command contains an invalid
function code.
This analog output poll command is not valid.
This time/date object poll command is not valid.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 65 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 66

Diagnostics and Troubleshooting MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Application Layer Errors
Error Code Name Description
1000 Device index invalid The device index in the request or response message
is not found in the slave list.
1001 Duplicate request in
application layer queue
1002 COM port device removed
from system
1003 Sequence number error The application sequence number in the response
1004 Response to select before
operate does not match
1005 Response does not contain
date/time object
1006 Time-out condition on
response
1007 Function code in application
layer message not
supported
1008 Read operation not
supported for
object/variation
1009 Operate function not
supported for the
object/variation
1010 Write operation not
supported for the
object/variation
The newly submitted message to the application layer
already exists in the queue. The message is ignored.
The communication port for the message has been
uninstalled on the system. This error should never
occur as the communication ports are only uninstalled
when the module's program is terminated.
message does not match that based on the last
request message. This indicates application layer
messages are received out of order.
The select response message received from the slave
module is not that expected from the last select
request. This indicates a synchronization problem
between the master and slave devices.
The response message from the slave device does
not contain a date/time object. The master expects
this object for the response message.
The slave device did not respond to the last request
message from the master within the time-out set for
the IED device. The application layer time-out value is
specified for each IED unit in the slave configuration
table in the module. This table is established each
time the module performs the restart operation.
The function code returned in the response message
is not valid for the application layer or not supported
by the module.
The application layer response message contains an
object that does not support the read function.
The application layer response message contains an
object that does not support the operate function.
The application layer response message contains an
object that does not support the write function.
Use the error codes returned for each command in the list to determine the
success or failure of the command. If the command fails, use the error code to
determine the cause of failure.
Page 66 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 67

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5 Reference
In This Chapter
Product Specifications ........................................................................... 68
Cable Connections ................................................................................ 71
Collision Avoidance (DNP modules only) .............................................. 75
Functional Overview .............................................................................. 76
MVI94-DNP Configuration Forms .......................................................... 95
DNP Master Subset Definition ............................................................. 105
DNP Slave Subset Definition ............................................................... 111
Device Profile ...................................................................................... 118
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 67 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 68

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
5.1 Product Specifications
The MVI94 DNP 3.0 Master/Slave Communication Module is a single slot, backplane compatible
DNP 3.0 interface solution for the FLEX platform. This module provides highly configurable support
of both DNP 3.0 Master and Slave implementations (level 2 minimum), allowing the many SCADA
and field devices supporting the DNP protocol to be integrated into the powerful FLEX platform.
The module supports DNP Subset Level 2 features and some of the Level 3 features allowing the
many SCADA and field devices supporting the DNP protocol to be integrated into the FLEX
platform. The module acts as an input/output module between the DNP network and the FLEX
backplane. The data transfer from the FLEX processor is asynchronous from the actions on the
DNP network. Databases are user defined and stored in the module to hold the data required by
the protocol.
5.1.1 General Specifications
Some of the general specifications include:
Operation via simple ladder logic
Complete setup and monitoring of module through Debug port and user
configuration file
Flex backplane interface via I/O access
5.1.2 FLEX I/O Interfaces
Specification Description
Form Factor Single Slot 1794 Backplane compatible
Backplane current load 20 mA @ 5 V
External power supply 12 Vdc to 24 Vdc
Operating temperature 0°C to 55°C (32°F to 131°F)
Storage temperature -40°C to 85°C (-40°F to 185°F)
Shock 30 g operational
Relative humidity 5% to 95% (without condensation)
LED indicators Module status
Configuration Serial port (PRT1) Mini-DIN
Application serial Port (PRT2) Mini-DIN
Dimensions (with Module
installed in Base)
Locate in any slot of Backplane
340 mA to 170 mA
50 g non-operational
5 g from 10150 Hz
Backplane transfer status
Application status
Serial activity and error LED status
RS-232
Hardware handshaking
RS-232/422/485 jumper selectable
500V optical isolation from backplane
3.7H x 3.7W x 2.7D inches
94H x 94W x 69D mm
Page 68 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 69

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5.1.3 Functional Specifications
The module has two DNP protocol ports that can be user configured to operate in
a Master/Slave or in a Slave/Slave redundant port configuration.
User defined internal register space is accessible to the protocol driver and to the
FLEX processor memory.
DNP 3.0 Slave Protocol Specifications
The DNP Slave port(s) accepts DNP commands to control and monitor data
stored in the module’s DNP Slave databases. If a DNP Master port is also
configured, a portion of these slave databases can be derived from or can control
IED devices connected to the DNP master port.
Report-by-Exception data is logged to the module’s database
Supports unsolicited messaging
Each DNP point type is user configurable by point
Class assignments are completely user-definable on a Type and point basis
(BI, AI, FI, DI point types)
Supports clock synchronization from a master or from the processor
Up to 400 events are stored for Floats, Binary In, Analog In and Double
Inputs
Collision avoidance algorithm per DNP organization for redundant port
switching (redundant slave mode)
Special modem AT command string and timing support for dialing out on
redundant port (redundant slave mode)
DNP 3.0 Master Protocol Specifications
The DNP 3.0 Master port can be configured as a virtual DNP Master device that
actively issues user-defined DNP commands to nodes on the network.
The Master port supports 300 user defined commands, each one containing
its own set of data link and application layer characteristics
Master port logically supports up to 40 slave devices
Individual command configuration includes conditional or continuous polling
and Poll Delay Time
Slave status and Command status available for transfer to the processor
Event data received from the slave devices updates the module database
(Date and Time stamping is not stored or used by module)
Special command handling for Digital Output CROB under processor control
for pulse output control
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 69 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 70

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
DNP 3.0 port (PRT2)
User-definable module memory usage
Full radio, modem and multi-drop support
Support for the storage and transfer of all DNP data types across the
backplane
Communication parameters
o
Address: 0 to 65534 (slave mode)
o
Baud rate: 110 to 115K
o
Parity: none, data bits: 8, Stop bit: 1
o
RTS on delay: 0 to 65535 milliseconds
o
RTS off delay: 0 to 65535 milliseconds
Page 70 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 71

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5.2 Cable Connections
The application ports on the MVI94-DNP module support RS-232, RS-422, and
RS-485 interfaces. Please inspect the module to ensure that the jumpers are set
correctly to correspond with the type of interface you are using.
Note: When using RS-232 with radio modem applications, some radios or modems require
hardware handshaking (control and monitoring of modem signal lines). Enable this in the
configuration of the module by setting the UseCTS parameter to 1.
5.2.1 RS-232 Application Port(s)
When the RS-232 interface is selected, the use of hardware handshaking
(control and monitoring of modem signal lines) is user definable. If no hardware
handshaking will be used, here are the cable pinouts to connect to the port.
RS-232: Modem Connection (Hardware Handshaking Required)
This type of connection is required between the module and a modem or other
communication device.
The "Use CTS Line" parameter for the port configuration should be set to 'Y' for
most modem applications.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 71 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 72

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
RS-232: Null Modem Connection (Hardware Handshaking)
This type of connection is used when the device connected to the module
requires hardware handshaking (control and monitoring of modem signal lines).
RS-232: Null Modem Connection (No Hardware Handshaking)
This type of connection can be used to connect the module to a computer or field
device communication port.
Note: For most null modem connections where hardware handshaking is not required, the Use
CTS Line parameter should be set to N and no jumper will be required between Pins 7 (RTS) and 8
(CTS) on the connector. If the port is configured with the Use CTS Line set to Y, then a jumper is
required between the RTS and the CTS lines on the port connection.
Page 72 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 73

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5.2.2 RS-232 Configuration/Debug Port
This port is physically an eight-pin, Mini-DIN8F connection. A Mini-DIN8M to
DB9M adapter cable is included with the module. This port permits a PC-based
terminal emulation program to view configuration and status data in the module
and to control the module. Here are the cable pinouts for RS-232 communication
on this port.
5.2.3 RS-485 Application Port(s)
The RS-485 interface requires a single two or three wire cable. The Common
connection is optional, depending on the RS-485 network devices used. The
cable required for this interface is shown below:
Note: Terminating resistors are generally not required on the RS-485 network, unless you are
experiencing communication problems that can be attributed to signal echoes or reflections. In
these cases, installing a 120-ohm terminating resistor between pins 1 and 8 on the module
connector end of the RS-485 line may improve communication quality.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 73 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 74

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
5.2.4 RS-422
The RS-422 interface requires a single four or five wire cable. The Common
connection is optional, depending on the RS-422 network devices used. The
cable required for this interface is shown below:
RS-485 and RS-422 Tip
If communication in the RS-422 or RS-485 mode does not work at first, despite
all attempts, try switching termination polarities. Some manufacturers interpret +
and -, or A and B, polarities differently.
5.2.5 DB9 to Mini-DIN Adaptor (Cable 09)
Page 74 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 75

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5.3 Collision Avoidance (DNP modules only)
The RTS line is controlled by the RTS on and off parameters set for the port. If
the CTS line is used (usually only required for half-duplex modems and not
defined for use in the DNPS specification), the RTS and CTS lines must either be
connected together or connected to the modem. The following illustration shows
the cable required when connecting the port to a modem.
If collision avoidance is used in a point-to-point connection on the RS-232
interface, the following cable should be used.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 75 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 76
Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
5.4 Functional Overview
The MVI94-DNP communication module interfaces DNP slave or master devices
with the Flex I/O system. The module contains a database defined by the user.
This database is used for the request and command messages sent from the
DNP master port to DNP slave devices. If the module is used as a virtual DNP
slave device, the database is used to source read requests and is the destination
of remote master write requests. The following illustration shows the data flow
within the module and between the DNP network and backplane.
Processor
User Data Files
Read Data
Write Data
Special Control
Blocks
Processor
Ladder Logic
Transfers data
from module’s
Input image
to data
areas in the
processor
Ladder Logic
transfers
data from
processor
data areas
to Out put image
Ladder Logic
processes
special control
command
MVI94-DNP Module
Module’s
Internal
Database
Input
Image
Master
Master
Driver
Backplane Driver
Output
Image
Special
Special
Block
Block
Handling
Handling
Driver
Logic
Logic
Slave
Slave
Driver
Driver
Logic
Logic
DNP
Port
Drivers
To DNP
Network
The database also interfaces with the Flex I/O system using the Flex I/O bus
(backplane). Data is made available to the PLC or any processor on a ControlNet
network using this backplane interface. Input and output image tables in the
module present the data in the database to the backplane.
If the module is used as a DNP master device on the application port, it can
continuously poll DNP slave devices. Up to 100 user-defined commands can be
defined for the port. Data read from the slave devices are placed in the database.
Any write requests for the slave devices are sourced with data from the
database.
Commands can be activated in the module under processor control. When a
command is activated, it is placed in the command queue for immediate
execution. Normal command polling will begin after the command queue is
completely processed.
Page 76 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 77

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
If the module is used as a DNP slave device, it responds to requests from a
remote DNP master device. All data in the module's database is available to the
remote master device for read and write requests.
The module provides a Configuration/Debug port for use with an external
computer executing a terminal emulation program. The terminal emulation
program provided with the module permits uploading and downloading of the
configuration information required by the module. Additionally, the
Configuration/Debug port provides a view into the virtual database,
communication statistics, and the configuration. Refer to Diagnostics and
Troubleshooting for a full discussion of this port's functionality.
5.4.1 Database Information
Central to the functionality of the module is the database. This database is used
as the interface between remote DNP devices and the Flex I/O bus. The content
and structure of the user data area of the database is completely user defined.
The following illustration shows the general format of the module’s database.
DATA AREA BLOCKS
DNP DATA BINARY INPUTS PLC DATA 0 to 9
BINARY OUTPUTS PLC DATA 20 to 29
COUNTER DATA PLC DATA 40 to 49
ANALOG INPUTS PLC DATA 60 to 79
ANALOG OUTPUTS PLC DATA 80 to 89
FLOAT INPUTS PLC DATA 300 to 319
DOUBLE INPUTS PLC DATA 320 to 349
FLOAT OUTPUTS PLC DATA 400 to 419
DOUBLE OUTPUTS PLC DATA 420 to 449
FROZEN COUNTER DATA
BINARY INPUT EVENTS
ANALOG INPUT EVENTS
LAST VALUE DATA BINARY INPUTS
ANALOG INPUTS
DNP BINARY OUTPUTS
DNP ANALOG OUTPUTS
IED BINARY OUTPUTS
IED ANALOG OUTPUTS
IED DATA BINARY INPUTS 100 to 109
BINARY OUTPUTS 120 to 129
COUNTER DATA 140 to 149
ANALOG INPUTS 160 to 179
ANALOG OUTPUTS 180 to 189
RBE FLAGS BINARY INPUT
ANALOG INPUT
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 77 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 78

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
The Flex I/O bus reads data from and write data to the user data area using the
backplane interface. The module interfaces data contained in remote DNP slave
devices to the database using the DNP application port. User commands are
issued out the master port from a command list. These commands gather or
control data in the slave devices. The following illustration shows the
relationships discussed above for a simulated master device:
The database defined in the module depends on the DNP device type emulated.
If the module emulates a DNP slave device, the database will be as shown in the
following example:
BTR/BTW ID'S DNP MEMORY
BLOCK 0 (DIGITAL
INPUT DATA)
BLOCK 20 (DIGITAL
OUTPUT DATA)
BLOCK 40 (COUNTER
DATA)
BLOCK 41 (COUNTER
DATA)
BLOCK 60 (ANALOG
INPUT DATA)
BLOCK 61 (ANALOG
INPUT DATA)
BLOCK 62 (ANALOG
INPUT DATA)
DIGITAL INPUT DATA
DIGITAL OUTPUT DATA
COUNTER DATA
ANALOG INPUT DATA
ANALOG OUTPUT DATA
BLOCK 80 (ANALOG
OUTPUT DATA)
FROZEN COUNTER,
LAST VALUE AND
EVENT DATA
BLOCK 81 (ANALOG
OUTPUT DATA)
Page 78 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 79

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
BLOCK 140 (COUNTER
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Binary and analog input and counter data is transferred from the processor to the
module. The remote DNP master device reads this data. Binary and analog
output data is transferred from the remote DNP master device to the module.
This data is then passed to the processor.
If the module emulates a DNP master device, the database will be as shown in
the following example:
IED MEMORY
BLOCK 100 (DIGITAL
INPUT DATA)
IED BINARY INPUT DATA
BLOCK 120 (DIGITAL
OUTPUT DATA)
IED BINARY OUTPUT
DATA
IED COUNTER DATA
DATA)
BLOCK 160 (ANALOG
INPUT DATA)
BLOCK 180 (ANALOG
OUTPUT DATA)
IED ANALOG INPUT
DATA
IED ANALOG OUTPUT
DATA
Binary and analog input and counter data is read by the DNP master port and
placed in the internal database. This data is transferred to the processor. Binary
and analog output data is received from the processor and placed in the
database. This data is then used to control IED devices on the DNP network by
the master command list.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 79 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 80
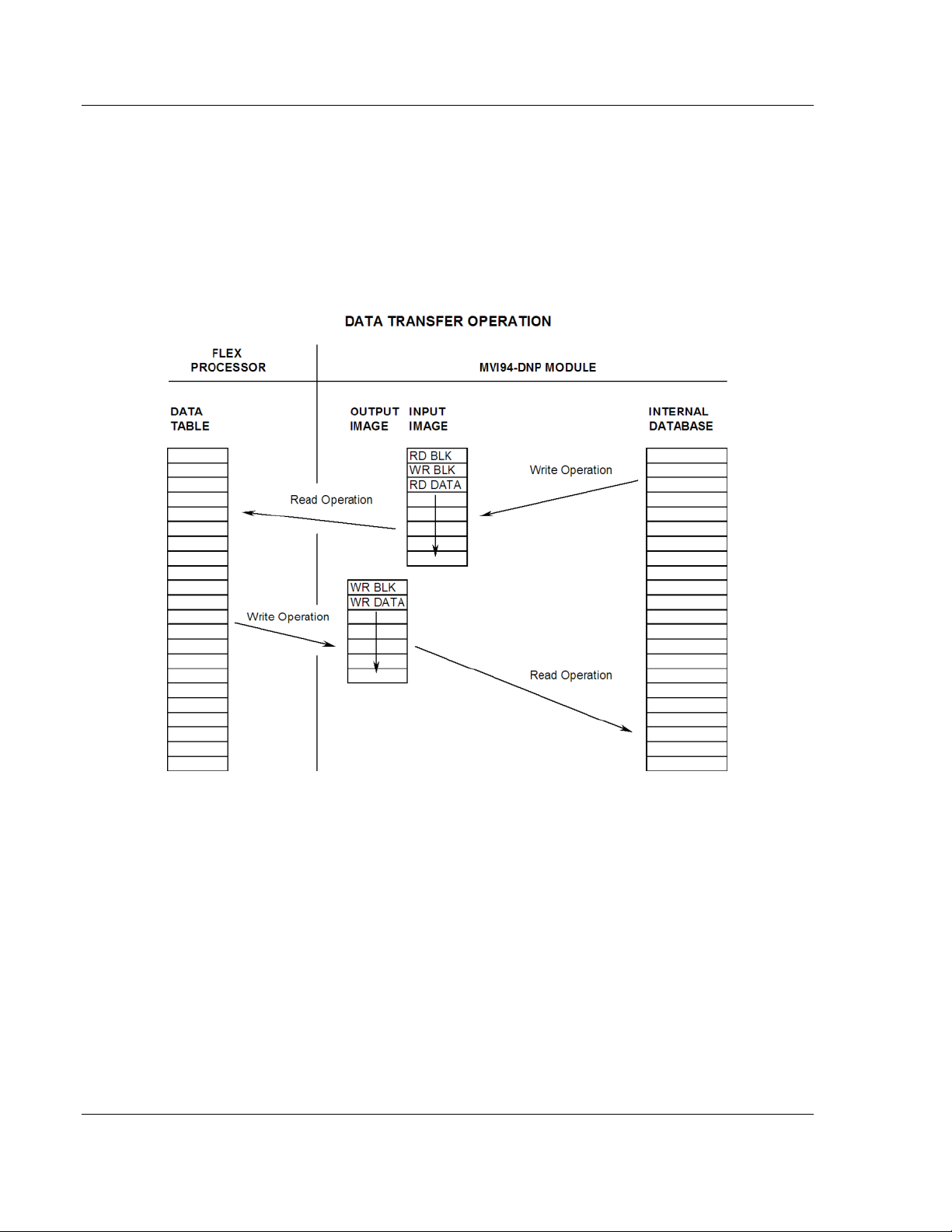
Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
5.4.2 Data Transfer
Data is transferred over the backplane using the module’s input and output
images. The module is configured with an eight-word input image and a sevenword output image. The module and the Flex processor use these images to
page data and commands. The input image is set (written) by the module and is
read by the Flex processor. The output image is set (written) by the Flex
processor and read by the module. The following illustration shows this
relationship:
The module’s program is responsible for setting the block identification code
used to identify the data block written and the block identification code of the
block it wants to read from the processor. User definition of the database to use
with the module defines the blocks to be transferred between the module and the
processor.
Each read and write operation transfers a six-word data area. The processor
read operation contains a two-word header that defines the block identification
code of the read data and the block identification code of the write block
requested. These identification codes are in the range of 0 to 189, 300 to 349
and 400 to 449.
Page 80 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 81
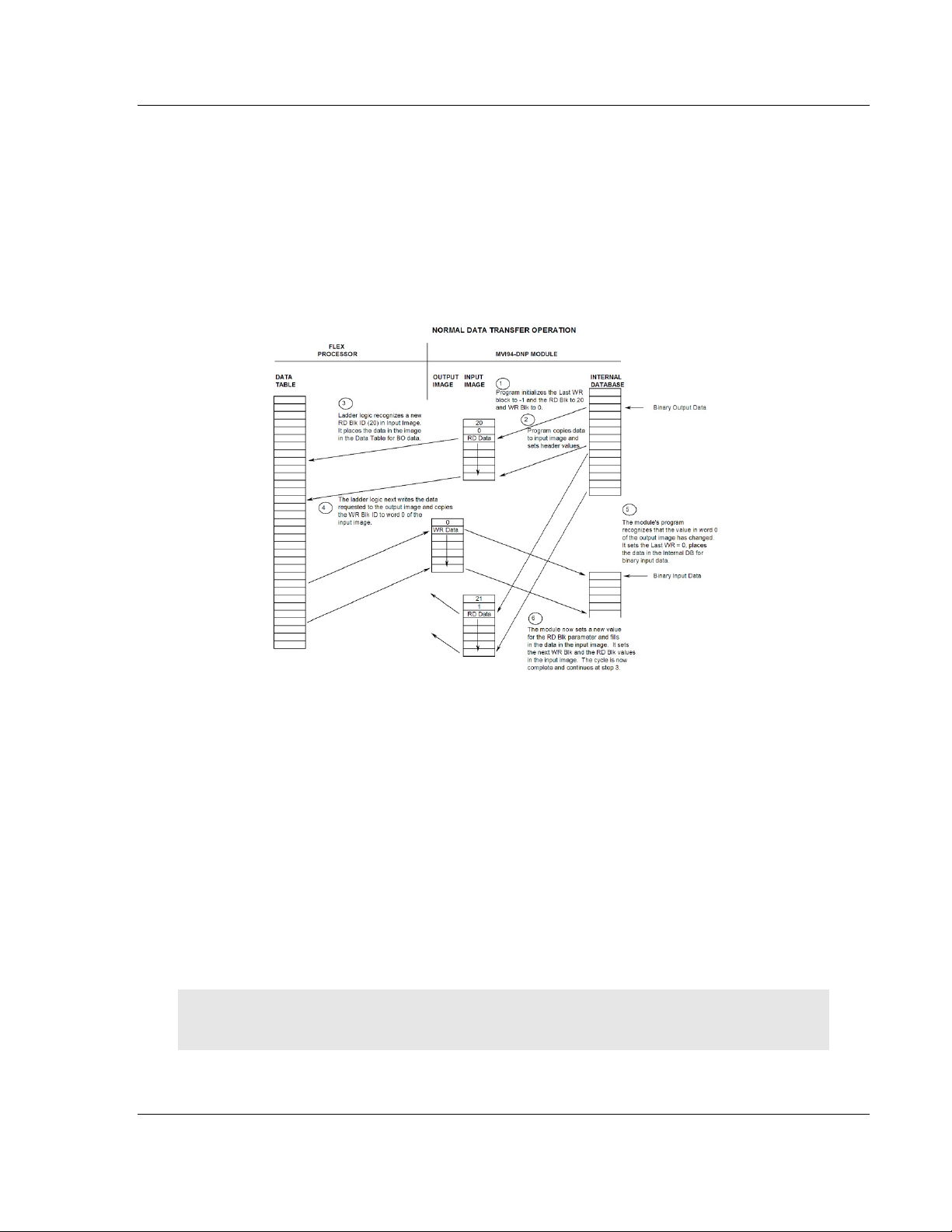
MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
The module and the processor constantly monitor input and output images. How
does either one know when a new block of data is available? Recognizing a
change in the header information of the image (word 0) solves the problem. For
example, when the module recognizes a different value in the first word of the
output image, new processor write data is available. When the processor
recognizes a new value in the first word of the input image, new processor read
data is available. This technique requires the storage of the previously processed
data block identification code.
The following illustration shows the normal sequence of events for data transfer:
1 The steps outlined in the diagram above are discussed below:
2 During program initialization, the write block identification code is set to 0
(binary input data) and read block identification codes are set to 20 (binary
output data). The last block write variable is set to -1.
3 The program copies the first six-word block of the binary output database to
the input image (words 2 to 7). It then sets the current write block code in
word 1 of the input image. To "trigger" the write operation, the program
places the current read block code into word 0 of the input image.
4 The Flex processor recognizes a new value in word 0 of the input image
(based on the last_read_block_code not equal to read_block_code) in its
ladder logic. The ladder logic computes the offset into the file based on the
data block number (defines the data type and offset of block for data type).
5 The new data contained in the input image (words 2 to 7) is copied to the
offset in the processor’s user data file. The last_read_block_code storage
register in the processor is updated with the new read_block_code.
Note: If the data area transferred from the module exceeds the size of a single user file in the Flex
processor, logic will be required to handle multiple files.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 81 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 82

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
6 Next the ladder logic examines the value of the write_block_code and
determines the data type and offset into the data type data table where the
data will be sourced.
7 The required six-word, write data is copied to the module’s output image
(words 1 to 6). To "trigger" the transfer operation, the ladder logic moves the
write_block_code into word 0 of the output image.
8 The module’s program recognizes the new write_block_code. It transfers the
data to the correct offset in the database using the block number provided.
9 The module sets the last_write_block_code to the value of write_block_code.
10 The module now selects the next read and write blocks. The data for the
processor read operation is placed in the input image and the
write_block_code is set in word 1. The module "triggers" the transfer
operation by setting the new read_block_code in word 0 of the input image.
11 The sequence continues at step 3.
The previous discussion is for normal data transfer operation. The following table
lists the block identification codes used by the module for data transfer.
Data Type Start Block # Max Block # Max # Of Points Type
Digital Input 0 9 960 Slave
Digital Output 20 29 960
Counters 40 49 30
Analog Input 60 79 120
Float Input 300 319 60
Double Input 320 349 30
Analog Output 80 89 60
Float Output 400 419 60
Double Output 420 449 30
IED Digital Input 100 109 960 Master
IED Digital Output 120 129 960
IED Counters 140 149 30
IED Analog Input 160 179 120
IED Analog Output 180 189 60
Data is transferred between the processor and the module using the block
identification codes of 0 to 189, 300 to 349 and 400 to 449. Other block codes
control the module from the processor’s ladder logic. They are implemented
when the ladder logic needs to control the module. In order to use one of the
blocks, the ladder logic inserts the data and code in the output image of the
module. The data should be set before the code is placed in the block. This
operation should be performed after the receipt of a new write block from the
module.
Page 82 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 83

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
The full list of block codes supported by the module are listed in the following
table.
Block Number Function/Description
-1 or -2 Dummy Blocks: Used by module when no data is to be transferred
0 to 89 DNP Data blocks
100 to 189 IED Data blocks
200 to 210 Error/Status List Blocks
300 to 349 DNP Data blocks for float and double input data
400 to 449 DNP Data blocks for float and double output data
9901 CROB Control Block for Digital Outputs
9902 Command Control Block (Add command to Command List Queue)
9949 Slave IED unit errors on master port
9950 Command List Error data
9958 PLC Binary Input Event data
9959 PLC Analog Input Event Data
9970 Set PLC time using module’s DNP time
9971 Set module’s time using PLC time
9998 Warm Boot Request from PLC (Block contains no data)
9999 Cold Boot Request from PLC (Block contains no data)
Each of the special control blocks is discussed in the following topics.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 83 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 84

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
CROB Control Block for Digital Outputs (Block 9901)
The CROB (Control Relay Output Block) controls a digital output on an IED unit
connected to a master port under program control. This block provides more
control than the binary output control offered in the command list. The selected
point can use the pulse on/off feature of the DNP protocol using this block. Refer
to the Basic 4 documentation for a full discussion of the CROB object and its
functionality. The structure of the block sent from the processor to the module is
shown in the following table.
Word Offset in Block Data Field(s) Description
0 Block ID This field contains the block identification code of
9901 for the block.
1 Slave Address This is the IED node address for the slave to
consider on the network.
2 Function Function codes 3, 5 and 6 supported. Function
code 4 is automatically sent after a successful
function 3.
3 Address in Slave Point in IED to consider with the CROB.
4 Control Code This is a standard DNP protocol control code
byte (see description below).
5 Pulse Count This parameter specifies the number of pulses to
generate for pulse output control. This parameter
has a range of 0 to 255 as the value is a byte
parameter in the CROB. If a value of zero is
entered, the operation will not execute.
6 Pulse On/Off Time This parameter specifies the on-time and off-time
intervals for pulse control. The same time value is
used for both parameters in the constructed
CROB message.
The Control Code field of the block defines the method of output control. This bitmapped value has the following definition:
Bits Definitions Description
0 to 3 Code These bits determine the control operation to be
performed by the command: 0=No operation,
1=Pulse on, 2=Pulse off, 3=Latch on and 4=Latch
off. All other values are undefined in the DNP
protocol.
4 Queue 0=Normal (execute once), 1=Requeue (place at
end of queue after operation).
5 Clear This parameter clears the queue. If the value is
set to zero, the queue is not affected. If the value
is set to 1, the queue will be cleared.
6 to 7 Trip/Close These two bits select the trip or close relay. For
close relay control, set the bits to 01. For trip
relay control, set the bits to 10. A value of 00 for
the bits is used for single point control of normal
digital output points.
When the module receives this block, it will place the request in the command
queue as long as there is room in the queue for the command. This will cause
the command to be executed at a high priority. The module does not send a
response message back to the processor for this block.
Page 84 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 85

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Command Control Block (Block 9902)
The Command Control Block places commands in the command list in the
command queue. Commands in the command list need not have their enable bit
set and can be executed using this block. The structure of the block built by the
processor for the module is shown in the following table.
Word Offset in
Block
0 Block ID This field contains the value of 9902 identifying the
1 Command count This field contains the number of commands to enable in
2 to 6 Command Numbers
Data Field(s) Description
enable command to the module.
the command list. Valid values for this field are 1 to 5.
These 5 words of data contain the command numbers in
to enable
the command list to enable. The commands in the list will
be placed in the command queue for immediate
processing by the module. The first command in the list
has an index of 0.
When the module receives the block, it places the commands represented in the
block in the command queue until it is full. These commands will execute at a
high priority. The module does not send a response block back to the processor
for this command block.
Slave IED Unit Errors (Block 9949)
This command block is used by the processor to request slave status information
for a specific IED unit. The format of the block constructed by the processor is
shown in the following table.
Word Offset in
Block
0 Block ID This field contains the value of 9949 identifying the block
2 Slave Index This parameter sets the index in the slave array to
3 to 6 Spare Not Used
Data Field(s) Description
type to the module.
consider. The first slave in the array has a value of 0. The
last index in the array has a value of MaxSlaves -1.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 85 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 86

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
When the module receives this block, it searches the slave list for the slave index
contained in the block. If the index is valid for the module, it constructs a
response block containing the status data for the indicated IED unit. The format
of the response block is shown in the following table.
Word Offset in
Block
0 Block ID This field contains the value of 9949 identifying the block
1 Block ID This is the next block requested by the module.
2 Bad CRC This value represents the number of bad CRC values
3 Buff Ovrflw This value represents the number of buffer overflow
4 Tran Seq# This value represents the number of incorrect transport
5 Conf Retry This value represents the number of data link layer
6 Conf Fail This value represents the number of data link layer
7 No App Rsp This value represents the number of application layer no
Data Field(s) Description
type to the PLC.
received from the slave device.
messages received from the slave device.
layer sequence number errors.
confirm request retries.
confirm request failures.
responses to requests.
Ladder logic must handle this response block and to place the data in a user data
file.
Command List Error Data
This block is used by the processor to request the command list error data from
the module. The format of the block constructed by the processor is shown in the
following table.
Word Offset in
Block
0 Block ID This field contains the value of 9950 identifying the block
1 Number of
2 Start Index of First
3 to 6 Spare Not Used
Data Field(s) Description
type to the module.
This field contains the number of commands to report in
Commands to report
Command
the response message. The value has a range of 1 to 4.
This parameter sets the index in the command list where
to start. The first command in the list has a value of 0.
The last index in the list has a value of MaxCommands -
1.
Page 86 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 87

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
When the module receives this block, it searches the command list to validate
the request. If the request is validated, the module constructs a response block
containing the last error code for each command requested. The format of the
response block is shown in the following table.
Word Offset in
Block
0 Block ID This field contains the value of 9950 identifying the block
1 Block ID This is the next block requested by the module.
2 Number of
3 Start Index of First
4 to 7 Command List
Data Field(s) Description
type to the PLC.
This field contains the number of commands contained in
Commands reported
Command
Errors
the block that must be processed by the PLC. This field
will have a value of 0 to 4.
This field contains the index in the command list for the
first value in the file. This field will have a value of 0 to
MaxCommands-1.
Each word of this area contains the last error value
recorded for the command. The command index of the
first value (offset 4) is specified in word 3 of the block.
The number of valid command errors in the block is set in
word 2 of the block. Refer to the command error list to
interpret the error codes reported.
PLC Binary Input Event Data (Block 9958)
This block is used by the processor to send binary input event data from the
processor to the module. This event is generated by the processor and not the
module and only has validity when a slave device is emulated on the application
port. When the processor recognizes a binary input event, it constructs a request
block with the following format:
Word Offset in
Block
0 Block ID This field contains the value of 9958 identifying the event
1 Sequence Counter This field holds the sequence counter for each 9958
2 DNP Binary Input
3 Month/Day/State Formatted: bits 0 to 4 = Day, bits 8 to 11 = Month, bit 15
4 Hour/Minute Formatted: bits 0 to 5 = Minutes, bits 8 to 12 = Hour. All
5 Sec/Millisecond Formatted: bits 0 to 9 = Milliseconds, bits 10 to 15 =
6 Year This is the four digit year for the event. Bits 12 and 13
Data Field(s) Description
block to the module.
block transfer. This synchronizes and confirms receipt of
the block by the module.
This is the data point in the DNP binary input database
Data point
represented by the event.
= digital state for point. All other bits are ignored.
other bits are ignored.
Seconds.
can contain the class override values of 1 to 3.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 87 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 88

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
When the processor receives the block, it places the information in the module’s
binary input event queue. This information is then made available to the remote
DNP master unit on binary event object or class poll requests. The module
informs the processor that the event has been processed by generating a
response block with the following format:
Word Offset in
Block
0 Block ID Identification code for block set to 9958.
1 Block ID Block identification code for request from PLC by the
2 Event Count This field contains the number of events processed by
3 Sequence Counter This field contains the sequence counter of the last
4 to 7 Spare Not used
Data Field(s) Description
module.
the module.
successful block 9958 received.
The Sequence Counter and the Event Count fields in the response block can be
utilized to insure that the module has processed the event. If the event buffer in
the module is full, the event is not processed and the processor should resend
the event to the module. If the module processes the event, the processor can
remove the event from its buffer.
PLC Analog Input Event Data (Block 9959)
This block is used by the processor to send analog input event data from the
processor to the module. This event is generated by the processor; not the
module, and only has validity when a slave device is emulated on the application
port. When the processor recognizes an analog input event, it constructs a
request block with the following format:
Word Offset in
Block
0 Block ID This field contains the value of 9959 identifying the event
1 DNP Analog Input
2 Analog Input Value This is the new analog input value represented in the
3 Month/Day Formatted: bits 0 to 4 = Day, bits 8 to 11 = Month. All
4 Hour/Minute Formatted: bits 0 to 5 = Minutes, bits 8 to 12 = Hour. All
5 Sec/Millisecond Formatted: bits 0 to 9 = Milliseconds, bits 10 to 15 =
6 Year This is the four digit year for the event (0-4095). Bits 12
Data Field(s) Description
block to the module.
This is the data point in the DNP analog input database
Data point
represented by the event.
event.
other bits are ignored.
other bits are ignored.
Seconds.
and 13 can contain the class override values of 1 to 3.
Page 88 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 89

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
When the processor receives the block, it places the information in the module’s
analog input event queue. This information is then made available to the remote
DNP master unit on analog event object or class poll requests. The module
informs the processor that the event has been processed by generating a
response block with the following format:
Word Offset in
Block
0 Block ID Identification code for block set to 9959.
1 Block ID Block identification code for request from PLC by the
2 Event Count This field contains the number of events processed by the
3 DNP Analog Input
4 to 7 Spare Not used
Data Field(s) Description
module.
module.
This field contains the analog input point of the last
Data point
successful block 9959 received.
The Sequence Counter and the Event Count fields in the response block can be
utilized to insure that the module has processed the event. If the event buffer in
the module is full, the event is not processed and the processor should resend
the event to the module. If the module processes the event, the processor can
remove the event from its buffer.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 89 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 90

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Set Processor Time Block (9970)
This block is constructed by the processor to request the module’s time. The
following table describes the format of this block.
Word Offset in Block Data Field(s) Description
0 Block ID This field contains the value of 9970 identifying
the block type to the module.
1 to 6 Not Used Not Used
When the module receives this block, it immediately constructs a response block
containing the modules current time. The following table describes the format of
this block.
Word Offset in Block Data Field(s) Description
0 Block Read ID This field contains the block identification code of
9970 for the block.
1 Block Write ID This is the next block requested by the module.
2 Year This field contains the four-digit year for the new
time value.
3 Month This field contains the month value for the new
time. Valid entry for this field is in the range of 1
to 12.
4 Day This field contains the day value for the new time.
Valid entry for this field is in the range of 1 to 31.
5 Hour This field contains the hour value for the new
time. Valid entry for this field is in the range of 0
to 23.
6 Minute This field contains the minute value for the new
time. Valid entry for this field is in the range of 0
to 59.
7 Seconds This field contains the second value for the new
time. Valid entry for this field is in the range of 0
to 59.
Page 90 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 91

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Set Module Time Block (9971)
This block is constructed by the processor to send its time to the module. The
following table describes the format of this block.
Word Offset in Block Data Field(s) Description
0 Block ID This field contains the block identification code of
9971 for the block.
1 Year This field contains the four-digit year for the new
time value.
2 Month This field contains the month value for the new
time. Valid entry for this field is in the range of 1
to 12.
3 Day This field contains the day value for the new time.
Valid entry for this field is in the range of 1 to 31.
4 Hour This field contains the hour value for the new
time. Valid entry for this field is in the range of 0
to 23.
5 Minute This field contains the minute value for the new
time. Valid entry for this field is in the range of 0
to 59.
6 Seconds This field contains the second value for the new
time. Valid entry for this field is in the range of 0
to 59.
When the module receives the block, it immediately sets its time using the
information contained in the block.
Warm Boot Block (9998)
This block does not contain any data. When the processor places a value of
9998 in word 0 of the output image, the module performs a warm-start. This
involves clearing the configuration and all program status data. Finally, the
program loads the configuration information from the flash disk and begin
running. There is no positive response to this message other than the status data
being set to zero and the block polling starting over. The format of this block is
shown in the following table.
Word Description Length
0 9998 1
1 to 6 Not used 6
Cold Boot Block (9999)
This block does not contain any data. When the processor places a value of
9999 in word 0 of the output image, the module performs a hardware restart. This
causes the module to reboot and reload the program. There is no positive
response to this message other than the status data being set to zero and the
block polling starting over. The format of this block is shown in the following
table.
Word Description Length
0 9999 1
1 to 6 Not used 6
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 91 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 92
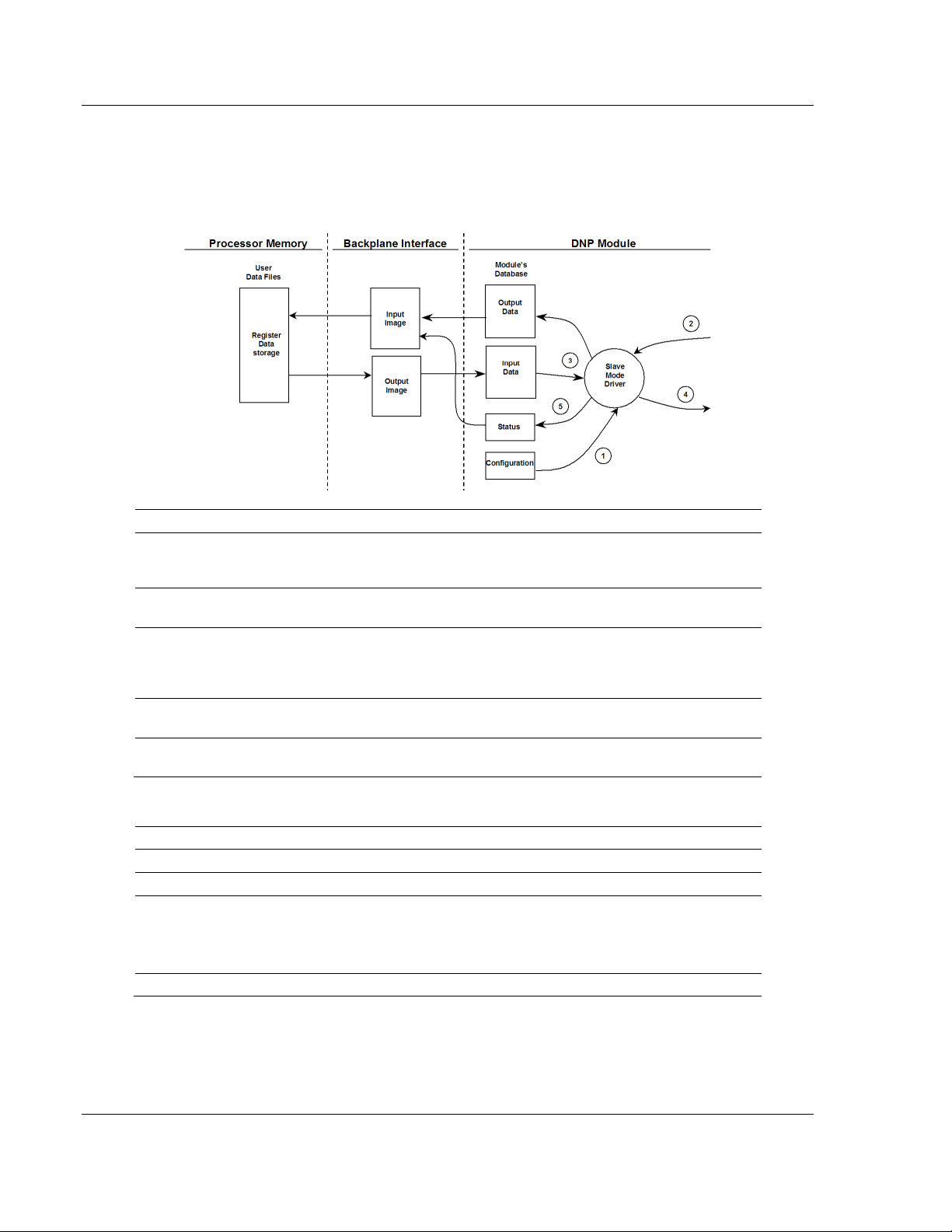
Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
5.4.3 Slave Driver
The Slave Driver Mode allows the MVI94-DNP module to respond to data read
and write commands issued by a master on the DNP network. The following flow
chart and associated table describe the flow of data into and out of the module:
Step Description
1 The DNP slave port driver receives the configuration information from the Flash data
area in the module. This information configures the serial port and define the slave node
characteristics.
2 A Host device issues read or write commands to the module’s node address. The port
driver qualifies the message before accepting it into the module.
3 After the module accepts the command, the data is immediately transferred to or from
the internal database in the module. If the command is a read command, the data is read
out of the database and a response message is built. If the command is a write
command, the data is written directly into the database and a response message is built.
4 After the data processing has been completed in Step 3, the response is issued to the
originating master node.
5 Counters are available in the Status Block that permit the ladder logic program to
determine the level of activity of the Slave Driver.
The slave driver supports object 110 (octet string data). Four points are preassigned values as defined in the following table.
Point # Description
0 Module Name as assigned in configuration file.
1 Product Name
2 Version Information in format:
wwww xxxx yyyy zzzz
Where wwww is product code, xxxx is the revision, yyyy is the operating system
number and zzzz is the run number.
3 Manufacturer name for module.
The variation used in the request message determines the length of the string
returned for each point. The maximum string length used by the module is 100.
Page 92 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 93

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5.4.4 Master Driver
In the Master mode, the MVI94-DNP module is responsible for issuing read or
write commands to slave devices on the DNP network. These commands are
user-configured in the module via the Master Command List read from the
module’s Flash. Command status is returned to the processor for each individual
command in the command list status block. The location of this status block in
the module’s internal database is user-defined. The following flow chart and
associated table describe the flow of data into and out of the module:
Step Description
1
2 After configuration, the Master driver begins transmitting read and/or write commands to
3 Presuming successful processing by the node specified in the command, a response
4 Data received from the node on the network is passed into the module’s internal
5 Status is returned to the processor for each command in the Master Command List.
The Master driver obtains configuration data from the Flash area of the module. The
configuration data obtained includes the number of commands and the Master Command
List. These values are used by the Master driver to determine the type of commands to
be issued to the other nodes on the DNP network.
the other nodes on the network. If writing data to another node, the data for the write
command is obtained from the module’s internal database to build the command.
message is received into the Master driver for processing.
database, assuming a read command.
Care must be taken in constructing each command in the list for predictable
operation of the module. If two commands write to the same internal database
address of the module, the results will not be as desired. All commands
containing invalid data are ignored by the module.
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 93 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 94

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
5.4.5 IIN Bits
MVI94-DNP Module Internal Indication Bits (IIN Bits) for DNP Slave Port
The internal indication bits are stored in a word that follows the function code in
all response messages. These bits report status and error information to the
master DNP device. Below is a description of the word:
First Byte
Bit Description
0 All stations message received. Set when a request is received with the destination address
set to 0xffff. Cleared after next response. Used to let master station know broadcast
received.
1 Class 1 data available. Set when class 1 data is ready to be sent from the slave to the
master. Master should request class 1 data when this bit is set.
2 Class 2 data available. Set when class 2 data is ready to be sent from the slave to the
master. Master should request class 2 data when this bit is set.
3 Class 3 data available. Set when class 3 data is ready to be sent from the slave to the
master. Master should request class 3 data when this bit is set.
4 Time synchronization required from master. The master should write the date and time when
this bit is set. After receiving the write command the bit will be cleared.
5 Slave digital outputs are in local control. This bit is not used in this application.
6 Not used.
7 Device restart. This bit is set when the slave either warm or cold boots. It is cleared after a
master writes a 0 to the bit.
Second Byte
Bit Description
0 Bad function code. The function code contained in the master request is not supported for
the specified object/variation.
1 Requested object(s) unknown. Object requested by master is not supported by the
application.
2 Parameters in the qualifier, range or data fields are not valid or out of range for the slave.
3 Event buffer(s) or other application buffers have overflowed. This bit is also set if the slave
receives a multi-frame message from the master.
4 Request understood but requested operation is already executing. The slave will never set
this bit.
5 Bad configuration. The slave configuration is invalid and should be re-configured. If the
configuration is invalid, the slave will set the invalid parameters to default values and
continue to run. Check error log using debug port.
6 Reserved, always 0.
7 Reserved, always 0.
Page 94 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 95

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
5.5 MVI94-DNP Configuration Forms
This section contains configuration forms that will aid in the configuration of the
module. If you design your system before trying to directly implement it, you will
have a greater chance of success. Fill in the configuration forms for your
application, and then edit the configuration text file. This section contains forms
for both master and slave configuration:
5.5.1 Slave Configuration
Variable
Name
[Module] This section header indicates the start of the module specific
Module Name: 80
Type: M=Master
Variable
Name
[DNP Slave] This section header defines the start of the DNP slave parameter set.
Internal Slave
ID:
Baud Rate: Baud Rate
RTS On: 0 to 65535 This value represents the number of 1 ms
RTS Off: 0 to 65535 This value represents the number of 1 ms
Min Response
Delay:
Modem: Y or N This parameter defines if a dial-up modem
Connect
Timeout:
Data
Range
Characters
or S=Slave
Data
Range
0 to 65534 This is the DNP address for the module. All
from Table
0 to 65535 Minimum time between receiving a request
0 to 65535 Defines the number of milliseconds to wait
Description IF Error Config.
parameter set.
This parameter sets the name or description
of the module’s application
This parameter must be set to M for the
DNP port to be used as a master port. If the
parameter is set to any other value, the port
will be used as a slave port.
Description IF Error Config.
messages with this address from the master
will be processed by the module.
Port Baud Rate: 300, 600, 1200, 2400,
4800, 9600, 19200, 384 (38400), 576
(57600), 115 (115200)
increments to be inserted between
asserting the RTS modem line and the
actual transmission of the data.
increments to be inserted after the last
character of data is transmitted before the
RTS modem line is dropped.
and transmitting a response. Allows master
time to disable transmitter on an RS-485
network.
is used on the DNP slave port. If the value
is set to N, no modem is used. If the
parameter is set to Y, a modem is used.
for the CD signal to be set high. The CD
signal indicates a connection is made using
a dial-up modem.
Value
"Not
Configured
"
S Slave
65534
9600
NA
NA
NA
N
NA
Value
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 95 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 96

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Variable
Name
First
Character
Delay:
Redial Delay
Time:
Redial
Random
Delay:
Idle Timeout: 0 to 65535 Defines the number of milliseconds the
Phone
Number:
Collision
Avoidance:
CD Idle Time: 0 to 32000 Defines the minimum number of
CD Random
Time:
CD Time
Before
Receive:
BI Class: 0 to 3 This parameter sets the default class
AI Class: 0 to 3 This parameter sets the default class
Float Class: 0 to 3 This parameter sets the default class
Data
Range
0 to 65535 Defines the number of milliseconds to wait
0 to 65535 Defines the minimum number of
0 to 65535 Defines a random millisecond time range to
ASCII
String Data
Y or N This parameter defines if the collision
0 to 32000 Defines the range of random time to be
0 to 65535 Defines the number of milliseconds to wait
Description IF Error Config.
before sending the first message after the
connection is first made. This delay only
applies to the first packet sent to the
modem.
milliseconds to wait before a redial attempt
is made by the slave.
be added to the redial delay time before the
modem is accessed.
modem is inactive before it will disconnect.
These fields contain a null-terminated,
ASCII character string used by the dial-up
modem. The string must contain all
characters required by the modem. An
example string is ATDT1800222333.
Maximum length is 34 bytes including the
terminating 0.
avoidance functionality is to be applied to
the port. If the parameter is set to N,
collision avoidance is not used. It will be
used if set to Y. If collision avoidance is
used, it requires a special cable.
milliseconds to wait before transmitting a
message after the CD signal is recognized
as low.
added to the CD Idle Time before a
message will be transmitted from the slave.
before receiving characters after the CD
signal is recognized as high.
assignment for points in the binary input
dataset. All points not specified in the
override section of the configuration will be
assigned to this class. For class 0, no
events will be generated for the points.
assignment for points in the analog input
dataset. All points not specified in the
override section of the configuration will be
assigned to this class. For class 0, no
events will be generated for the points.
assignment for points in the float input
dataset. All points not specified in the
override section of the configuration will be
assigned to this class. For class 0, no
events will be generated for the points.
Value
NA
NA
NA
NA
NA
N
32000
32000
NA
0
0
0
Page 96 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 97

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Variable
Name
Double Class: 0 to 3 This parameter sets the default class
AI Deadband: 0 to 32767 This value sets the global deadband for all
Float
Deadband:
Double
Deadband:
Select/Operat
e Arm Time:
Write Time
Interval:
Data Link
Confirm
Mode:
Data Link
Confirm Tout:
Data Link Max
Retry:
App Layer
Confirm Tout:
Data
Range
Any valid
floatingpoint value
Any valid
double
floatingpoint value
1 to 65535 Time period after select command received
0 to 1440
minutes
N, S or A IED can request acknowledgement from
1 to 65535 Time period to wait for Master Data Link
0 to 255 Maximum number of retries at the Data Link
1 to 65535 Event data contained in the last response
Description IF Error Config.
assignment for points in the double input
dataset. All points not specified in the
override section of the configuration will be
assigned to this class. For class 0, no
events will be generated for the points.
analog input points not specified in the
override section. Events will be generated
when the last saved value exceeds the limit
of this parameter.
This value sets the global deadband for all
float input points not specified in the
override section. Events will be generated
when the last saved value exceeds the limit
of this parameter.
This value sets the global deadband for all
double input points not specified in the
override section. Events will be generated
when the last saved value exceeds the limit
of this parameter.
in which operate command will be
performed. After the select command is
received, the operate command will only be
honored if it arrives within this period of
time.
Time interval to set the need time IIN bit
(0=never), which will cause the master to
write the time. Stored in milliseconds in the
module memory.
master station when sending data. The
codes are as follows: N=Never,
S=Sometimes, A=Always
confirmation of last frame sent. This time is
in milliseconds. This parameter is only used
if the frame is sent with confirmation
requested.
level to obtain a confirmation. If this value is
set to 0, retries are disabled at the data link
level of the protocol. This parameter is only
used if the frame is sent with confirmation
requested.
may be sent again if not confirmed within
the millisecond time period set. If
application layer confirms are used with
data link confirms, ensure that the
application layer confirm timeout is set long
enough.
Value
0
32767
0
0
2000
1440
N
1
255
2000
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 97 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 98

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
Variable
Name
Unsolicited
Response:
Class 1 Unsol
Resp Min:
Class 2 Unsol
Resp Min:
Class 3 Unsol
Resp Min:
Unsol Resp
Delay:
Uresp Master
Address:
AI Events with
time:
Time Sync
Before
Events:
Initialize DNP
BO/AO:
Data
Range
Y or N Set if the slave unit will send unsolicited
1 to 255
events
1 to 255
events
1 to 255
events
0 to 65535
millisecond
s
0 to 65534 DNP destination address where unsolicited
Y or N This parameter determines if the analog
Y or N This parameter defines if the remote DNP
Y or N This parameter defines if the binary and
Description IF Error Config.
response messages. If set to N, the slave
will not send unsolicited responses. If set to
Y, the slave will send unsolicited responses.
This feature requires collision avoidance on
a multi-drop network.
Minimum number of events in Class 1
required before an unsolicited response will
be generated (not implemented).
Minimum number of events in Class 2
required before an unsolicited response will
be generated (binary input events).
Minimum number of events in Class 3
required before an unsolicited response will
be generated (analog input events).
Maximum number of 1 millisecond intervals
to wait after an event occurs before sending
an unsolicited response message. If set to
0, only use minimum number of events.
response messages are sent.
input events are to be returned with a time
value. If the parameter is set to N, no time
will be returned with the event. If the
parameter is set to Y, a time will be
returned.
master must synchronize the time before
events are generated by the slave. If the
parameter is set to N, this synchronization
is not required. If set to Y, the
synchronization is required.
analog outputs are to be read from the
processor before the program starts its
normal data transfer. If the parameter is set
to N, this feature is not implemented. If the
parameter is set to Y, the feature is used
and special ladder logic must be
implemented to transfer the data from the
processor to the module.
Value
N
10
25
25
NA
65534
N
N
N
Variable
Name
[DNP Slave
Database]
Binary Inputs: 0 TO 960 Number of digital input points to configure in
Data
Range
This section header defines the start of the DNP slave database
Description IF Error Config.
Value
definition parameter set.
0
the DNP slave device. Each point will be
stored as a single bit in the module
memory.
Page 98 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
Page 99

MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O Reference
DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module User Manual
Variable
Name
Analog Inputs: 0 TO 120 Number of analog input points to configure
Float Inputs: 0 TO 60 Number of float input points to configure in
Double Inputs: 0 TO 30 Number of double input points to configure
Counters: 0 TO 30 Number of counter points to configure in the
Binary
Outputs:
Analog
Outputs:
Float Outputs: 0 TO 60 Number of float output points to configure in
Double
Outputs:
Data
Range
0 TO 960 Number of digital output points to configure
0 TO 60 Number of analog output points to configure
0 TO 30 Number of double output points to configure
Description IF Error Config.
in the DNP slave device. Each point will
occupy a one word area in the module
memory.
the DNP slave device. Each point will
occupy a double-word area in the module
memory.
in the DNP slave device. Each point will
occupy a four-word area in the module
memory.
DNP slave device. Each point will occupy a
two word area in the module memory. This
number corresponds to the number of
frozen counters. The application maps the
counters to the frozen counters directly.
in the DNP slave device. Each point will be
stored as a single bit in the module
memory.
in the DNP slave device. Each point will
occupy a one word area in the module
memory.
the DNP slave device. Each point will
occupy a double-word area in the module
memory.
in the DNP slave device. Each point will
occupy a four-word area in the module
memory.
Value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Variable
Name
[DNP Slave
Binary Inputs]
START This string signals the start of the point definition list.
END This string signals the end of the point definition list.
Description
This section is used to override the default values of the class
assignment for the binary input points.
Variable
Name
Description
ProSoft Technology, Inc. Page 99 of 131
December 17, 2010
Page 100

Reference MVI94-DNP ♦ Flex I/O
User Manual DNP 3.0 Server over Ethernet Communication Module
[DNP Slave
Analog
Inputs]
START This string signals the start of the point definition list.
END This string signals the end of the point definition list.
This section is used to override the default values of the class and
deadband assignments for the analog input points.
-5=class 1, deadband = 1000
Variable
Name
[DNP Slave
Float Inputs]
START This string signals the start of the point definition list.
END This string signals the end of the point definition list.
Description
This section is used to override the default values of the class and
deadband assignments for the float input points.
Variable
Name
[DNP Slave
Double
Inputs]
START This string signals the start of the point definition list.
END This string signals the end of the point definition list.
Description
This section is used to override the default values of the class and
deadband assignments for the double input points.
Page 100 of 131 ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 17, 2010
 Loading...
Loading...