Mercedes-Benz Actros 963 Service Manual

Electronic systems, Actros, model 963
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Functional description

Mercedes>Benz Service
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963
Technical status
09.11
Daimler AG . Technical Information and Workshop Equipment(GSP/OI)
D$70546 Stuttgart

Information and copyright
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Product portfolio
You can also find comprehensive information about our
complete product portfolio on our Internet portal:
Link: http://aftersales.mercedes>benz.com
Questions and suggestions
If you have any questions or suggestions concerning this product, please write
to us.
E>Mail: customer.support@daimler.com
Telefax: +49>(0)18 05/0 10>79 78
or alternatively
Address: Daimler AG
GSP/OIS,
HPC R822, W002
D>70546 Stuttgart
(Germany)
©
2011 by Daimler AG
This document, including all its parts, is protected by copyright.
Any further processing or use requires the previous written consent of
Daimler AG, Department GSP/OIS, HPC R822, W002, D>70546 Stuttgart.
This applies in particular to reproduction, distribution, alteration, translation,
microfilming and storage and/or processing in electronic systems, including
databases and online services.
Image no. of title image: W00.01>1016>00
Order no. of this publication: 6517 1261 02 > HLI 000 000 02 89
09/11

SN00.00>W>0001>01HA Preface
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Preface
This brochure
Actros electronic systems, model 963
is intended for the technical personnel responsible for service and
maintenance of Mercedes>Benz trucks.
The content of this brochure is split up into:
•
function descriptions
•
component descriptions
•
Description of locations of electrical connectors, sockets and
ground points
All the data listed in this brochure correspond with the technical
status as per September 2011.
Any changes or supplements hereto will be published in the
Workshop Information System (WIS) only.
Additional documents for model 963, such as maintenance and
repair instructions or wiring diagrams are also available in the
Workshop Information System (WIS).
Mercedes>Benz
W‘rth plant, GSP/TTM
September 2011
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
1

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
SN00.00>W>0110H
MODEL 963
Overview of as>built configuration and function descriptions 2.8.11
Function descriptions
Overall network
Overall network, function
Maintenance system, function
Maintenance system, overall network
Data acquisition function
Data storage function
Normal mode displays function
Reset service item function
Forecast calculation, function
Life cycle consumption calculation,
function
Page 15
Page 16
Page 22
Page 23
Page 24
Page 29
Page 30
Page 32
Page 34
Page 35
Transmission automation, function
Transmission automation, overall network
Operation, function
Driver information, function
Transmission mode, function
Shifting the transmission, function
Controlling the clutch, function
Countershaft brake, function
Level control, function
Level control, overall network
Axle load measuring system, function
Monitoring/control of specified level,
function
Changeover from level 1 to level 2,
function
Raise/lower vehicle frame manually,
function
Store frame height, function
Constant frame height when
loading/unloading, function
Raise/lower lift axle, function
Page 37
Page 40
Page 41
Page 44
Page 45
Page 46
Page 52
Page 54
Page 56
Page 59
Page 60
Page 62
Page 64
Page 66
Page 68
Page 70
Page 73
2

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Starting>off aid, function
Load/relieve additional axles, function
Roll control, function
Roll control, overall network
Tire pressure monitor, function
Tire pressure monitor, overall network
Tire pressure monitor, driver information
Electronic Brake Control, function
Electronic Brake Control, overall network
Brake application on front axle with
Electronic Brake Control, function
Brake application on front axle without
Electronic Brake Control, function
Brake application on rear axle with
Electronic Brake Control, function
Brake application on rear axle without
Electronic Brake Control, function
Trailer control with Electronic Brake
Control, function
Trailer control without Electronic Brake
Control, function
Auxiliary braking effect, function
Page 76
Page 78
Page 81
Page 84
Page 85
Page 86
Page 87
Page 88
Page 92
Page 93
Page 95
Page 97
Page 99
Page 101
Page 104
Page 106
Electronic Stability Program, function
Electronic Stability Program, overall
network
Intervention of Electronic Stability Program
in the event of understeer or oversteer,
function
Intervention of Electronic Stability Program
upon risk of tipping, function
Compressed air supply system, function
Compressed air supply system, overall
network
Hydraulic retarder, function
Overall network of hydraulic retarder
Single>circuit power steering, function
Page 108
Page 111
Page 112
Page 114
Page 116
Page 122
Page 123
Page 129
Page 130
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
3
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Additional steering axle, function
Additional steering axle, overall network
Additional steering axle, hydraulics
diagram
Driving assistance systems, function
Driving assistance systems, overall network
Proximity Control Assist function
Active Brake Assist function
Lane Keeping Assist function
Battery sensor function
Overall network battery sensor
Modular switch panel function
Overall network modular switch panel
Instrument cluster, function
Instrument cluster, overall network
Instrument cluster operating notes
Display fuel quantity, function
Display outside temperature, function
Display engine speed, function
Display speed and travel distance, function
Display AdBlue level, function
Redundancy operation of Electronic Air>
Processing Unit (EAPU), function
Page 133
Page 137
Page 138
Page 139
Page 144
Page 145
Page 149
Page 154
Page 158
Page 159
Page 160
Page 162
Page 163
Page 166
Page 167
Page 168
Page 169
Page 170
Page 171
Page 173
Page 174
Signaling system, function
Overall network of signaling system
Power windows, function
Power windows, overall network
Electric power sliding roof, function
Electric power sliding rood, overall
network
Central locking, function
4
Page 175
Page 177
Page 178
Page 181
Page 182
Page 184
Page 185

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Central locking, overall network
Comfort locking system function
Comfort locking system overall network
Anti>theft alarm system, function
Anti>theft alarm system, overall network
Anti>theft alarm system, status messages
Activate antitheft alarm system, function
Deactivate anti>theft alarm system,
function
Triggering alarm by disconnecting trailer
or semitrailer, function
Alarm actuation by unlocking cab, function
Triggerring alarm with panic switch,
function
Alarm triggering with interior protection,
function
Alarm triggering by steeling fuel, function
Alarm triggering by unlocking/opening a
door/flap, function
Alarm triggering by alarm siren, function
Page 191
Page 192
Page 198
Page 199
Page 201
Page 202
Page 205
Page 210
Page 214
Page 217
Page 220
Page 223
Page 226
Page 229
Page 233
Drive authorization system, function
Drive authorization system overall network
Exterior lighting, function
Exterior lights, overall network
Headlamp control, function
Fog lamp actuation, function
Rear fog lamp actuation, function
Turn signal light actuation, function
Brake lights actuation, function
Backup light actuation, function
Emergency light actuation, function
Floodlight actuation, function
Interior illumination, function
Interior illumination, overall network
Ambient lighting actuation, function
Interior illumination actuation, function
Page 236
Page 238
Page 239
Page 241
Page 242
Page 246
Page 247
Page 248
Page 250
Page 252
Page 253
Page 255
Page 257
Page 259
Page 260
Page 261
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
5
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Reading light actuation, function
Night light actuation, function
Exit lamp actuation, function
Windshield wiper system, function With code (F8X) Rain and light sensor
With code (F8X) Rain and light sensor
Windshield wiper system overall network
Multifunction steering wheel, function
Multifunction steering wheel overall
network
Stationary air conditioning, function
Stationary air conditioner, overall network
Load cold reservoir, function
Discharge cold reservoir function
Automatic air conditioning, function
Automatic climate control, overall network
Ventilation function
Air supply in normal operation, function
Air supply in recirculated air mode,
function
Temperature control function
Refrigerant circuit, function
Heater circuit function
Temperature control during heater
operation, function
Temperature control during AC operation,
function
Page 264
Page 266
Page 267
Page 268
Page 270
Page 272
Page 273
Page 275
Page 276
Page 279
Page 280
Page 284
Page 286
Page 287
Page 288
Page 290
Page 292
Page 294
Page 295
Page 297
Page 299
Page 302
Auxiliary heater, function
Auxiliary heater, overall network
Heater operation, function
Terminate heater operation, function
Trigger heating mode, function
Triggering the permanent heater
operation, function
Triggering the preselection heater
operation, function
Automatic triggering of heat mode,
function
6
Page 306
Page 307
Page 308
Page 309
Page 315
Page 316
Page 318
Page 320

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Starting operation, function
Combustion mode, function
Control pause, function
Residual heat system, function
Residual heat system overall network
Component descriptions
Instrument cluster control unit (ICUC),
component description
Central gateway control unit (CGW),
component description
Component description drive control (CPC)
control unit
Component description for engine
management (MCM) control unit
Transmission control (TCM) control unit.
component description
Anti>theft alarm system control unit (ATA),
component description
Cab signal acquisition and actuation
module control unit (SCA), component
description
Signal acquisition and actuation module
control unit, frame (SCH), component
description
Electronic Brake Control control unit (EBS),
component description
Retarder control unit (RCM), component
description
Component description for automatic air
conditioning control unit
Auxiliary heater control unit, component
description
Stationary air conditioner control unit,
component description
Front radar sensor (RDF) control unit,
component description
Driver door control unit (DCMD),
component description
Passenger door module control unit
(DCMP), component description
Electronic Air>Processing Unit (EAPU),
component description
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A10b, A10c
A11
A12b
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18, 6.16, 6.17, 6.18
Page 322
Page 325
Page 327
Page 329
Page 330
Page 331
Page 333
Page 334
Page 335
Page 337
Page 338
Page 339
Page 340
Page 341
Page 342
Page 344
Page 346
Page 347
Page 348
Page 349
Page 350
Page 351
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
7
Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Front axle axle modulator, component
description
Rear axle axle modulator, component
description
Parameterizable special module (PSM)
control unit component description
Electronic Stability Program (ESP) control
unit, component description
Level control (CLCS) control unit,
component description
Driver switch group, component
description
Front passenger switch group, component
description
FleetBoard control unit, component
description
Battery disconnect switch control unit,
component description
Additional steering axle (ASA) control unit,
component description
Tire pressure monitor (TPM) control unit,
component description
Stationary air conditioner cold reservoir,
component description
Stationary air conditioner cold reservoir
temperature sensor, component
description
Stationary air conditioner cold reservoir
coolant pump, component description
Stationary air conditioner cold reservoir
solenoid valve, component description
Modular switch panel control unit (MSF),
component description
Instrument panel switch modules,
component description
Switch module special equipment,
component description
Roof switch modules, component
description
Bunk switch module, component
description
Driver assistance system (VRDU) control
unit, component description
EATU output NOx sensor, component
description
A20, A20a
A21, A21a
A22
A25, A25a
A26
A28
A29
A30
A33
A34
A35
A41
A41 b1
A41
A41 y1
A43
A44, A45, A46
A47
A48, A49
A50, A51
A53
A57
i The EATU output NOx sensor control
unit (A57) forms one unit with the EATU
output NOx sensor (A57 b1).
Page 509
Page 511
Page 356
Page 357
Page 358
Page 359
Page 360
Page 361
Page 362
Page 364
Page 365
Page 366
Page 367
Page 368
Page 369
Page 370
Page 372
Page 374
Page 375
Page 376
Page 378
8

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
Pump module, component description A58
i The SCR control unit (A58) forms one
unit with the pump module.
Exhaust aftertreatment (ACM) control unit,
component description
EATU input NOx sensor, component
description
Lane Assistant camera (SPA), component
description
Auxiliary heater heating unit, component
description
Exhaust temperature sensor, component
description
Component description for coolant
temperature sensor
Overheating protection, component
description
Glow plug, component description A901 E
Combustion air blower, component
description
Auxiliary heater coolant circulation pump,
component description
Brake wear sensor, component description B1, B2
Component description for the rpm sensor B13, B14
Brake value sensor, component description B17, B17a
Travel and speed sensor, component
description
Level control pressure sensor, component
description
A60
Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
A70
i The EATU input NOx sensor control unit
(A70) forms one unit with the EATU input
NOx sensor (A70 b1).
Vehicles with code (M5R) Engine version
EEV and vehicles with code (M5Y) Engine
version Euro V
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version
Euro VI
A72
A901
A901 B1
A901 B2
A901 B3
A901 M1
A901 M2
B18
B20, B21
Page 379
Page 381
Page 384
Page 386
Page 388
Page 390
Page 392
Page 395
Page 396
Page 398
Page 399
Page 400
Page 401
Page 402
Page 403
Page 404
Page 405
Page 406
Page 408
Page 409
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
9

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Travel sensor, component description B24, B25
Condensation sensor, component
description
Parking brake pressure switch, component
description
Vehicle interior temperature sensor,
component description
Air conditioning pressure sensor,
component description
Alarm siren, component description B42
Interior protection, component description B43
Component description for accelerator
pedal sensor
Outside air sensor, component description B49
Front axle steering angle sensor,
component description
Additional steering axle steering angle
sensor, component description
Steering wheel angle sensor (SAS),
component description
Rain/light sensor, component description B81
Outside temperature sensor, component
description
Main shaft rpm sensor, component
description
Countershaft rpm sensor, component
description
Clutch travel sensor, component
description
Range group travel sensor, component
description
Transmission oil temperature sensor,
component description
Component description for crankshaft
position sensor
Component description for camshaft
position sensor
Stationary air conditioning air outlet
temperature sensor, component
description
Stationary air conditioning air outlet
temperature sensor, component
description
Air quality sensor, component description B928
Evaporator temperature sensor,
component description
B26
B30
B32
B33
B44
B64
B65
B66
B92
B501
B502
B503
B504
B505
B600
B601
B908
B909
B929
Page 410
Page 412
Page 413
Page 414
Page 415
Page 418
Page 419
Page 420
Page 421
Page 422
Page 423
Page 424
Page 428
Page 430
Page 431
Page 432
Page 433
Page 434
Page 435
Page 436
Page 437
Page 439
Page 440
Page 441
Page 442
10

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Air outlet temperature sensor, component
description
Dual sun sensor, component description B931
Rear lamp unit, component description E3, E4
Headlamp, component description E5, E6
Component description for battery sensor G1a
Fuel metering pump, component
description
Power window motor, component
description
Door central locking motor, component
description
Sliding roof motor, component description M12
Blower motor, component description M13
Residual heat pump, component
description
Fresh air/air recirculation flap actuator
motor, component description
Temperature control actuator motor,
component description
Defroster flap actuator motor, component
description
Stationary air conditioner blower motor,
component description
Air distribution flap actuator motor,
component description
Tachograph (TCO) component description P1
Electronic ignition lock (EIS), component
description
Level control operating unit, component
description
Right multifunction control lever,
component description
EMERGENCY OFF switch, component
description
Frame EMERGENCY OFF switch,
component description
Cab unlock switch, component description S36, S37
Maintenance flap button, component
description
Stowage box switch, component
description
Multifunction steering wheel, component
description
B930
M2
M3
M7
M20
M900
M901
M902
M904
M905
S1
S22
S23
S30
S31
S81
S83
S110, S111
Page 443
Page 444
Page 445
Page 446
Page 447
Page 448
Page 449
Page 450
Page 451
Page 452
Page 453
Page 454
Page 455
Page 456
Page 457
Page 458
Page 459
Page 460
Page 461
Page 463
Page 464
Page 465
Page 466
Page 467
Page 468
Page 469
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
11

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Bunk auxiliary heating button, component
description
Bunk auxiliary heater and stationary air
conditioning button, component
description
Bunk stationary air conditioner button,
component description
Transmitter key, component description S953
Antenna, component description W3, W6, W7, W8, W9
Diagnostic socket, component description X100.16
Multifunction antenna, component
description
ABS solenoid valve, component description Y1, Y2
Proportional valve component description Y12, Y13, Y14, Y15, Y16, Y17, Y18, Y19
Stationary air conditioner solenoid valve,
component description
Front axle level control valve unit,
component description
Level control valve unit, 2>axle vehicles,
component description
Level control valve unit, 3>axle vehicles,
component description
Refrigerant compressor magnetic clutch,
component description
Heating shutoff valve, component
description
Additional steering axle valve unit,
component description
Transmission positioner, component
description
Overflow valve with return flow,
component description
Parking brake valve, component
description
Pressure limiting valve with ventilation,
component description
Coupling head for compressed air
supply/brake, component description
Pneumatic central clutch release bearing,
component description
Range group module, component
description
Wheel sensor, component description
Trailer control valve, component
description
S914, S915
S941, S942
S951, 952
W15
Y27
Y20
Y21
Y21a
Y40
Y49
Y39
Y900
7.01
14.01
30.03
35.02, 35.03
Page 470
Page 471
Page 472
Page 473
Page 476
Page 477
Page 478
Page 479
Page 480
Page 482
Page 483
Page 485
Page 487
Page 489
Page 490
Page 491
Page 492
Page 494
Page 495
Page 497
Page 498
Page 499
Page 501
Page 502
Page 503
12

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
3/2>way valve for auxiliary braking effect,
component description
Front axle axle modulator, component
description
Rear axle axle modulator, component
description
Retarder, component description
Steering gear, component description
Power steering fluid reservoir, component
description
Power steering pump, component
description
Additional steering axle steering cylinder,
component description
Additional steering axle flow dividing
valve, component description
Additional steering axle high pressure
filter, component description
Heating system heat exchanger,
component description
Stationary air conditioner heat exchanger,
component description
Stationary air conditioner check valve,
component description
Stationary air conditioner expansion valve,
component description
Condenser, component description
Evaporator, component description
Component description for expansion
valve
Fluid reservoir, component description
A/C compressor, component description
Auxiliary heater heat exchanger,
component description
Burner insert with burner tube, component
description
Page 507
Page 509
Page 511
Page 514
Page 520
Page 521
Page 522
Page 523
Page 524
Page 525
Page 526
Page 527
Page 528
Page 529
Page 530
Page 531
Page 532
Page 533
Page 534
Page 535
Page 536
Location of components
Arrangement of cable and plug
connections
Location of line connections and
connectors, interior compartment, left
Location of line connections and
connectors, interior compartment, right
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
Page 537
Page 541
Page 541
13

Contents
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Location of line connections and
connectors, instrument panel
Location of line connections and
connectors, frame
Location of line connections and
connectors, cab
Location of line connections and
connectors, doors
Location of line connections and
connectors, roof
Location of line connections and
connectors, footwell, left
Location of line connections and
connectors, footwell, right
Location of line connections and
connectors, engine compartment
Location of line connections and
connectors, electronics compartment
Location of line connections and
connectors, driver seat base
Location of line connections and
connectors, front passenger seat base
Location of sockets
Location of electrical sockets
Location of ground points
Location of left engine compartment
ground points
Location of right engine compartment
ground points
Location of left interior compartment
ground points
Location of ground points > frame
Location of ground points > instrument
panel
Page 542
Page 543
Page 544
Page 544
Page 545
Page 545
Page 546
Page 546
Page 547
Page 548
Page 548
Page 549
Page 550
Page 551
Page 552
Page 552
Page 552
Page 553
Page 553
14

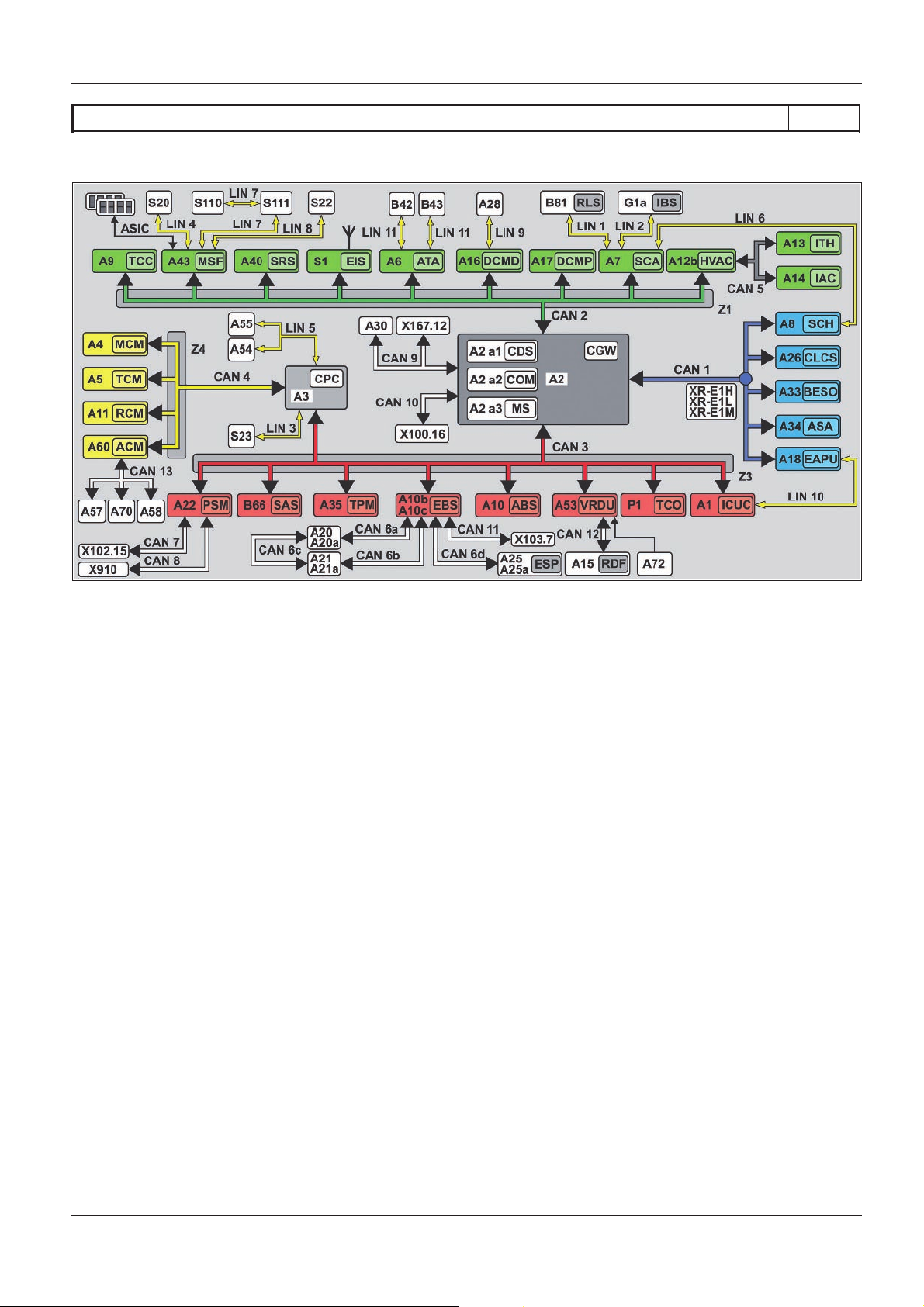
SN00.19>W>0001>02H Complete networking
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Illustrated on model 963.4
A1 Instrument cluster (ICUC) control
unit
A2 Central gateway control unit
(CGW)
A2 a1 Central data memory (CDS)
A2 a2 Communications interface (COM)
control unit
A2 a3 Maintenance system (MS) control
unit
A3 Drive control (CPC) control unit
A4 Engine management control unit
(MCM)
A5 Transmission control (TCM)
control unit
A6 Anti>theft alarm system (ATA)
control unit
A7 Cab signal acquisition and
actuation module control unit
(SCA)
Functions
A8 Frame signal acquisition and
actuation module control unit
(SCH)
A9
A10 Antilock brake system (ABS)
A10b Electronic brake control (EBS)
A10c Electronic brake control (EBS)
A11 Retarder control (RCM) control
A12b Heating, ventilation and air
A13 Truck auxiliary heater (ITH)
A14 Stationary air conditioning (IAC)
A15 Front radar sensor (RDF) control
A16 Driver door module (DCMD)
Truck Control Center (TCC)
control unit, 4>channel
control unit (Wabco)
control unit (Knorr)
unit
conditioning control unit (HVAC)
control unit
control unit
unit
control unit
A17 Front passenger door module
(DCMP) control unit
A18 Electronic Air Processing Unit
(EAPU) control unit
A20 Front axle axle modulator
(Wabco)
A20a Front axle axle modulator (Knorr)
A21 Rear axle axle modulator
(Wabco)
A21a Rear axle axle modulator (Knorr)
A22 Parameterizable special module
(PSM) control unit
A25 Electronic Stability Program
(ESP“) control unit (Wabco)
A25a Electronic Stability Program
(ESP“) control unit (Knorr)
A26 Level control (CLCS) control unit
W00.19>1065>76
A30 FleetBoard“ control unit
A35 Tire pressure monitor (TPM)
control unit
A40 Supplemental restraint system
(SRS) control unit
A43 Modular switch panel (MSF)
control unit
A53 Driver assistance system (VRDU)
control unit
A57 EATU output NOx sensor control
unit
A58 SCR control unit
A60 Exhaust aftertreatment (ACM)
control unit
A70 EATU input NOx sensor control
unit
A72 Lane Assistant camera
B66 Steering wheel angle sensor
(SAS)
P1 Tachograph (TCO)
S1 Electronic ignition lock (EIS)
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
15
Functions
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
GF00.19>W>0004H
MODEL 963
Overall network, function 2.8.11
A1 Instrument cluster (ICUC) control
unit
A2 Central gateway control unit (CGW)
A2 a1 Central data memory (CDS)
A2 a2 Communications interface (COM)
control unit
A2 a3 Maintenance system (MS) control
unit
A3 Drive control (CPC) control unit
A4 Engine management control unit
(MCM)
A5 Transmission control (TCM) control
unit
A6 Antitheft alarm system (ATA)
control unit
A7 Cab signal acquisition and
actuation module control unit
(SCA)
A8 Frame signal acquisition and
actuation module control unit
(SCH)
A9 Truck Control Center (TCC)
A10 Antilock brake system (ABS) control
unit, 4>channel
A10b Electronic Brake Control (EBS)
control unit (Wabco)
A10c Electronic Brake Control (EBS)
control unit (Knorr)
A11 Retarder control (RCM) control unit
A12b Heating, ventilation and air
conditioning control unit (HVAC)
A13 Truck auxiliary heater (ITH) control
unit
A14 Stationary air conditioning (IAC)
control unit
A15 Front radar sensor (RDF) control
unit
A16 Driver door module (DCMD) control
unit
A17 Front passenger door module
(DCMP) control unit
A18 Electronic Air Processing Unit
(EAPU) control unit
A20 Front axle axle modulator (Wabco)
A20a Front axle axle modulator (Knorr)
A21 Rear axle axle modulator (Wabco)
A21a Rear axle axle modulator (Knorr)
A22 Parameterizable special module
(PSM) control unit
A25 Electronic Stability Program (ESP“)
control unit (Wabco)
A25a Electronic Stability Program (ESP“)
control unit (Knorr)
A26 Level control (CLCS) control unit
A28 Driver switch group
A30 FleetBoard“ control unit
W00.19>1079>79
A33 Battery disconnect switch control
unit (BESO)
A34 Additional steering axle (ASA)
control unit
A35 Tire pressure monitor (TPM) control
unit
A40 Supplemental restraint system (SRS)
control unit
A43 Modular switch panel (MSF) control
unit
A53 Driver assistance system (VRDU)
control unit
A54 Lower radiator shutters controller
unit
A55 Upper radiator shutters controller
unit
A57 EATU output NOx sensor control
unit
A58 SCR control unit
A60 Exhaust aftertreatment (ACM)
control unit
A70 EATU input NOx sensor control unit
A72 Lane Assistant camera
B42 Alarm siren
B43 Interior protection sensor
B66 Steering wheel angle sensor (SAS)
B81 Rain and light sensor (RLS)
16

Functions
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
CAN 1 Exterior>CAN
CAN 2 Interior CAN
CAN 3 Frame CAN
CAN 4 Drive train CAN
CAN 5 Climate control CAN
CAN 6a Front axle brakes CAN
CAN 6b Rear axle brakes CAN
CAN 6c Redundant brakes CAN
CAN 6d ESP“ brakes CAN
CAN 7 Trailer CAN (PSM)
CAN 8 Body manufacturer CAN (PSM)
CAN 9 Telematics CAN
CAN 10 Diagnostic CAN
CAN 11 Trailer CAN (EBS)
CAN 12 Radar CAN
CAN 13 NOx>CAN
G1a Battery sensor (IBS)
LIN 1 Rain/light sensor LIN
LIN 2 Battery sensor LIN
1 General
The increase in electronic systems in the new Actros means that
more and more signals now have to be made available across all
the systems. This primarily has an impact on the networking,
which has also gained in complexity. Alongside the familiar CAN
and ASIC data bus systems the LIN data bus is now increasingly
being used. The new Actros alone has 11 LIN data buses, which
connect the various control units, switches or other electronic
components to each other. The number of CAN data buses by
contrast has only risen slightly.
LIN 3 Right multifunction control lever>
LIN
LIN 4 Left multifunction control lever LIN
LIN 5 Radiator shutters LIN
LIN 6 LIN SCA/SCH redundancy
LIN 7 Button group LIN
LIN 8 Level control LIN
LIN 9 Driver switch panel LIN
LIN 10 EAPU>LIN
LIN 11 ATA>LIN
P1 Tachograph (TCO)
S1 Electronic ignition lock (EIS)
S20 Left multifunction control lever
S22 Level control operating unit
S23 Right multifunction control lever
S110 Left multifunction steering wheel
button group
S111 Right multifunction steering wheel
button group
X100.16 Diagnostic socket
X102.15 Trailer socket , 15>pin
X103.7 ABS trailer socket 7>pin
X167.12 Fleet management system
electrical connector
X910 Electrical connector for body
manufacturers
XR>E1H CAN>H exterior cable weld point 1
XR>E1L CAN>L exterior cable weld point 1
XR>E1M CAN>ground exterior cable weld
point 1
Z1 Cab instrument panel CAN bus star
point
Z3 Frame CAN bus star point
Z4 Drive CAN bus star point
ASIC ASIC data bus (Application System
Integrated Circuit)
2 CAN data bus system
The CAN data bus system enables information to be exchanged
quickly and reliably between control units over only a few lines.
The information is sent or received successively (serial). The
exchange is bidirectional, i.e. each control unit operates as both a
transmitter and a receiver.
Transfer rates
2.1
In the new Actros up to 13 different CAN data buses are used. The
majority of these CAN data buses have a transfer rate of >250
kBaud and this classes them as high>speed CAN data buses. The
reasons for the increase in high>speed CAN data buses are:
•
Increase in data rate (number of messages that are sent)
•
Almost identical manufacturing costs as for low>speed CAN
data buses
•
Greater use of LIN data bus in non>critical safety areas
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
•
Shortening of flash or parameterization times, in particular
through increase in transfer rate for diagnostic CAN (CAN
10)
The following CAN data buses have a transfer rate of
500 kBaud:
•
Exterior CAN (CAN 1)
•
Interior CAN (CAN 2)
•
Frame CAN (CAN 3)
•
Climate control CAN (CAN 5)
•
Front axle brake CAN (CAN 6a)
•
Rear axle brake CAN (CAN 6b)
•
Redundancy brake CAN (CAN 6c)
•
Brake CAN ESP“ (CAN 6d)
•
Diagnostic CAN (CAN 10)
•
Radar CAN (CAN 12)
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
17

Functions
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
The transfer rate of the drive train CAN (CAN 4) was increased to
667 kBaud, because the high number of messages had
significantly increased the bus operating rate. If the data rate was
not increased, then there is the risk that some messages with low
priority could no longer be sent due to the bus operating rate.
To ensure that freight forwarders, for example for fleet
management, can continue to call up specific information on
vehicle location, current speed, etc. the transfer rate of the
telematics CAN (CAN 9) has been retained at 250 kBaud.
The transfer rates have also been retained on the trailer CAN
(PSM) (CAN 7), the body manufacturer CAN (PSM) (CAN 8) and the
trailer CAN (EBS) (CAN 11). They are 125 kBaud, whereby they are
still classified as low>speed CAN data buses.
The transfer rate for the NOx>CAN (CAN 13) has not been changed
either and is > as before > 250 kBaud.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
2.2 Gateways
To compensate for the different transfer speeds, some control units
also act as a gateway:
•
The central gateway control unit (CGW) (A2) routes the
respective messages from the exterior, interior, frame,
telematics and diagnostic CAN (CAN 1, 2, 3, 9 and 10).
•
The modular switch panel (MSF) control unit (A43) acts as a
gateway between the interior CAN (CAN 2), the ASIC data bus
(ASIC) and the three LIN data buses to the button groups on
the multifunction steering wheel, the left multifunction
control lever and the level control operating unit.
•
The Electronic Brake Control (EBS) control unit (A10b) or
(A10c), depending on the version, sends the messages from
the frame CAN (CAN 3) to the front axle brake CAN (CAN 6a),
the rear axle brake CAN (CAN 6b), the brake CAN ESP“ (CAN
6d) as well as, where applicable, the trailer CAN (EBS) (CAN
11) and vice versa.
•
The drive control (CPC) control unit (A3) acts as an interface
between the frame CAN (CAN 3) and the drive train CAN
(CAN 4).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
2.3 CAN neutral points and bus terminating resistors
Because of the high transfer rates on high>
there may be some reflections in the lines. Bus termination
resistors are used to avoid reflections that would lead to the
falsification of actual information. The characteristic impedance
of the electrical line is important for the bus termination resistor.
The total bus terminating resistor on a high>speed CAN data bus is
60 ].
In the neutral points for the cab instrument panel CAN bus (Z1)
and frame CAN bus (Z3) the bus terminating resistors are
integrated into the neutral points. The drive CAN bus neutral
point (Z4) only includes those ferrite elements that are also
installed in the neutral points for interference suppression of
high>frequency interference pulses.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
3 LIN data bus
The LIN data bus is an inexpensive serial subbus, which replaces
the CAN data bus in the area of uncritical data transfer. The
voltage supply for the LIN data bus is 12 V. This is realized
internally in the control units through voltage dividers. Signals are
transmitted through a single>
kBaud. Communication refers to ID>based communication. All
subscribers connected to the LIN data bus receive the message,
but only one subscriber responds to it.
A LIN data bus subscriber never sends information by itself, as is
the case, for example with a CAN data bus subscriber. Subscribers
of the LIN data bus only ever respond to a query.
wire line. The max. data rate is 20
speed CAN data buses,
The bus terminator on the exterior CAN (CAN 1) is realized by
using bus terminating resistors within the central gateway control
unit (CGW) (A2) and the Electronic Air>
control unit (A18). Located in both control units is a 120 ] resistor
each. The parallel connection then yields a total bus terminating
resistance of 60 ].
In the diagnostic CAN (CAN 10) the bus terminator is realized by a
60 ] resistor in the central gateway control unit (CGW) (A2).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Processing Unit (EAPU)
18

4 ASIC data bus system
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
The previously familiar ASIC data bus system is also used in the
new Actros.
The ASIC data bus (ASIC) belongs to the so>called subbuses. In
contrast to conventional switches which switch via their own
contacts and are connected to their components via separate
electrical lines (e.g. motors, solenoid valves, switch inputs, lighting
devices), the ASIC data bus performs these tasks.
The electronics installed in the ASIC signal switches notifies the
modular switch panel (MSF) control unit (A43) the following via
the ASIC data bus (ASIC):
f switch position (open, closed, operated, not operated)
f Functionality (normally closed contact, normally open
contact, changeover contact)
f System affiliation (e.g. headlamp cleaning system button,
power take>off 1 button, etc.)
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Functions
Each ASIC signal switch is connected over three contacts (pins) to
the ASIC data bus (ASIC), and it is evaluated by the modular switch
panel (MSF) control unit (A43). It is thus possible to install each
ASIC signal switch at any arbitrary point on the individual switch
modules.
For currents up to a maximum of 20 A there continues to be load
switches which as before switch via their own contacts and are
connected to their components through electrical lines.
These load switches are only connected to the switch panel via the
ASIC contacts for separate background lighting.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
5 Virtual control units
Virtual control units are not equipped with their own housing.
They are integrated into the hardware and software of other
control units. In Star Diagnosis and the instrument cluster control
unit (ICUC) (A1) they appear as independent control units.
Among the virtual control units are the central data memory
(CDS) (A2 a1), the communications interface (COM) control unit
(A2 a2) and the maintenance system (MS) control unit (A2 a3),
which are all integrated into the central gateway control unit
(CGW) (A2).
With the aid of the central data memory (CDS) (A2 a1) the
parameters for the electronic control units can be reset to
manufacturer default settings.
Instrument cluster control unit (ICUC),
component description
Central gateway control unit (CGW),
component description
Component description drive control (CPC)
control unit
Component description for engine
management (MCM) control unit
Transmission control (TCM) control unit.
component description
Antitheft alarm system control unit (ATA),
component description
Cab signal acquisition and actuation
module control unit (SCA), component
description
Signal acquisition and actuation module
control unit, frame (SCH), component
description
Electronic Brake Control (EBS) control unit,
component description
Retarder control unit (RCM), component
description
6 Safety strategy
Several control units have a redundant connection over LIN or
CAN data buses. The redundant connection serves as an
emergency communication, if the actual CAN connection
malfunctions. The use of redundant LIN or CAN data buses is
dependent on the safety relevance of each system.
The service brake system, for example has a redundant CAN data
bus connection between the axle modulators.
LIN data buses serve as redundancies between the sensor and
actuator module, cab (SCA) control unit (A7) and the sensor and
actuator module, chassis (SCH) control unit (A8) as well as
between the instrument cluster control unit (ICUC) (A1) and the
Electronic Air
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A10b, A10c
A11
i Only in vehicles with code (B3H)
Secondary water retarder.
>Processing Unit (EAPU) control unit (A18).
Page 331
Page 333
Page 334
Page 335
Page 337
Page 338
Page 339
Page 340
Page 341
Page 342
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
19

Functions
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Component description for automatic air
conditioning control unit
Auxiliary heater control unit, component
description
Stationary air conditioner control unit,
component description
Front radar sensor (RDF) control unit,
component description
Driver door control unit (DCMD),
component description
Passenger door module control unit
(DCMP), component description
Electronic Air>Processing Unit (EAPU),
component description
Front axle axle modulator, component
description
Rear axle axle modulator, component
description
Parameterizable special module (PSM)
control unit component description
Electronic Stability Program (ESP) control
unit, component description
Level control (CLCS) control unit,
component description
FleetBoard control unit, component
description
Battery disconnect switch control unit,
component description
Additional steering axle (ASA) control unit,
component description
Tire pressure monitor (TPM) control unit,
component description
A12b
A13
i Only in vehicles with code (D6M) Cab
auxiliary water heater or with code (D6N)
Cab and engine auxiliary water heater.
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
i The Electronic Air>Processing Unit
(EAPU) control unit (A18) forms a module
together with the Electronic Air>Processing
Unit (EAPU).
A20, A20a
A21, A21a
A22
A25, A25a
A26
A30
A33
i Only in vehicles with one of the
following codes:
•
Code (E5T) ADR model class EX/II,
including AT
•
Code (E5U) ADR model class EX/III,
including EX/II and AT
•
Code (E5V) ADR model class FL,
including EX/II, EX/III and AT
•
Code (E5X) ADR model class AT
•
Code (E5Z) Accessories, ADR
•
Code (E9D) Preinstallation, for bipolar
battery circuit breaker
•
Code (E9E) ADR preinstallation, without
chassis shielding
A34
A35
Page 344
Page 346
Page 347
Page 348
Page 349
Page 350
Page 351
Page 509
Page 511
Page 356
Page 357
Page 358
Page 361
Page 362
Page 364
Page 365
20

Functions
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Modular switch panel control unit (MSF),
component description
Driver assistance system control unit
(VRDU), component description
EATU output NOx sensor, component
description
Pump module, component description A58
Exhaust aftertreatment (ACM) control unit,
component description
EATU input NOx sensor, component
description
Lane Assistant (SPA) camera, component
description
Steering wheel angle sensor (SAS),
component description
Tachograph (TCO) component description P1
Electronic ignition lock (EIS), component
description
A43
A53
A57
i The EATU output NOx sensor control
unit (A57) together with the EATU output
NOx sensor (A57 b1) forms a unit.
Vehicles with code (M5R) EEV engine
version and vehicles with code (M5Y) Euro
V engine version
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Euro VI engine
version
i The SCR control unit (A58) together
with the pump module forms a unit.
A60
Vehicles with code (M5R) EEV engine
version and vehicles with code (M5Y) Euro
V engine version
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Euro VI engine
version
A70
i The EATU input NOx sensor control unit
(A70) together with the EATU input NOx
sensor (A70 b1) forms a unit.
Vehicles with code (M5R) EEV engine
version and vehicles with code (M5Y) Euro
V engine version
Vehicles with code (M5Z) Euro VI engine
version
A72
B66
S1
Page 370
Page 378
Page 379
Page 381
Page 384
Page 386
Page 388
Page 390
Page 392
Page 395
Page 424
Page 459
Page 460
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
21

Functions
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
GF00.20>W>0005H
Maintenance system, function 2.8.11
MODEL 963
1 CAN messages
2 "Maintenance" menu
A1 Instrument cluster (ICUC) control
unit
A1 p1 Multifunction display
A2 Central gateway control unit
(CGW)
A43 Modular switch panel (MSF)
control unit
CAN 2 Interior CAN
CAN 3 Frame CAN
CAN 10 Diagnostic CAN
LIN 7 Button group LIN
S110 Left multifunction steering wheel
button group
S111 Right multifunction steering wheel
button group
General information
The maintenance system (WS):
f Is a software which is integrated as a virtual control unit into
the central gateway control unit (CGW) (A2),
f records all the required measurement data as CAN messages
(1) using the CAN data bus system and
f calculates the load>
for each maintenance item in order to determine the service
dates.
i Load>dependent forecasting is used to carry out the
following:
f Individual determination of the service dates for each
maintenance item and they can be called up in the
"Maintenance" (2) menu of the instrument cluster control
unit (ICUC) (A1).
f Display of pending maintenance items as a message in the
multifunction display (A1 p1) when the ignition is switched
on.
dependent service life and forecast data
Maintenance system overall network
Data acquisition function
Data storage function
Life cycle consumption calculation,
function
Forecast calculation, function
Normal mode displays function
Reset service item function
Z1 Cab instrument panel CAN bus star
point
W00.20>1076>76
Z3 Frame CAN bus star point
X100.16
The menu is operated using the left multifunction steering wheel
button group (S110) and the right multifunction steering wheel
button group (S111).
Maintenance information is shown in the multifunction display
(A1 p1) of the instrument cluster control unit (ICUC) (A1). The
instrument cluster control unit (ICUC) (A1) acts as a display unit.
A maintenance item is reset using the left multifunction steering
wheel button group (S110) and the right multifunction steering
wheel button group (S111) or with the aid of Star Diagnosis
through the diagnostic socket (X100.16).
Diagnostic socket
Page 23
Page 24
Page 29
Page 35
Page 34
Page 30
Page 32
22

GF00.20>W>0005>02H Maintenance system overall network
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Functions
A1 Instrument cluster (ICUC) control
unit
A2 Central gateway control unit (CGW)
A2a3 Maintenance system (MS) control
unit
A3 Drive control (CPC) control unit
A4 Engine management control unit
(MCM)
A5 Transmission control (TCM) control
unit
A7 Cab signal acquisition and
actuation module control unit
(SCA)
A8 Frame signal acquisition and
actuation module control unit
(SCH)
A11 Retarder control (RCM) control
unit
A18 Electronic Air Processing Unit
(EAPU) control unit
A43 Modular switch panel (MSF)
control unit
A60 Exhaust aftertreatment (ACM)
control unit
CAN 1 Exterior>CAN
CAN 2 Interior CAN
CAN 3 Frame CAN
CAN 4 Drive train CAN
CAN 10 Diagnostic CAN
W00.20>1079>79
LIN 6 LIN SCA/SCH redundancy
LIN 7 Button group LIN
LIN 10 EAPU>LIN
P1 Tachograph (TCO)
S110 Left multifunction
steering wheel button group
S111 Right multifunction
steering wheel button group
X100.16 Diagnostic socket
Z1 Cab instrument panel CAN bus
star point
Z3 Frame CAN bus star point
Z4 Drive CAN bus star point
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
23

Functions
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
GF00.20>W>3000H
MODEL 963
Data acquisition function 2.8.11
A1 Instrument cluster (ICUC) control
unit
A1p1 Multifunction display
A2 Central gateway control unit (CGW)
A3 Drive control (CPC) control unit
A4 Engine management control unit
(MCM)
A5 Transmission control (TCM) control
unit
A7 Cab signal acquisition and
actuation module control unit
(SCA)
A8 Frame signal acquisition and
actuation module control unit
(SCH)
A11 Retarder control unit (RCM) (in
vehicle with code (B3H) Secondary
water retarder)
B48 Air filter sensor
B75
1st front axle temperature sensor
B77 1st rear axle temperature sensor
B92 Outside temperature sensor
B505 Transmission oil temperature
sensor
B600 Crankshaft position sensor
B605 Engine oil fill level sensor
B933 Coolant temperature sensor (in
vehicles with code (B3H) Secondary
water retarder)
A18 Electronic Air Processing Unit (EAPU)
control unit
A43 Modular switch panel (MSF) control
unit
A60 Exhaust aftertreatment (ACM)
control unit (in vehicles with code
(M5Z) Euro VI engine version)
B1 Left 1st front axle
brake wear sensor
B2 Right 1st front axle
brake wear sensor
B3 Left 2nd front axle
brake wear sensor
B4 Right 2nd front axle
brake wear sensor
CAN 1 Exterior>CAN
CAN 2 Interior CAN
CAN 3 Frame CAN
CAN 4 Drive train CAN
CAN 10 Diagnostic CAN
LIN 6 LIN SCA/SCH redundancy
LIN 7 Button group LIN
LIN 10 EAPU>LIN
P1 Tachograph (TCO)
W00.20>1078>79
B7 Left 1st rear axle
brake wear sensor
B8 Right 1st rear axle
brake wear sensor
B9 Left 2nd rear axle
brake wear sensor
B10 Right 2nd rear axle
brake wear sensor
B18 Travel and speed sensor
B26 Condensation sensor
B37 Exhaust pressure sensor upstream of
diesel oxidation catalytic converter (in
vehicles with code (M5Z) Euro VI
engine version)
B38 Exhaust pressure sensor downstream of
diesel particulate filter (in vehicles with
code (M5Z) Euro VI engine version)
S110 Left multifunction steering wheel
button group
S111 Right multifunction steering
wheel button group
Z1 Cab instrument panel CAN bus
star point
Z3 Frame CAN bus star point
Z4 Drive CAN bus star point
X100.16 Diagnostic socket
24

General information
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
The recording of data function enables the maintenance system
(WS) to receive two different types of input factors for calculating
the load>specific maintenance intervals:
f Basic data, which are determined unchangeable at first in
the form of a parameterization and
f measured values, which are sensed continuously.
Thus, two functions are differentiated:
f Acquiring the basic data
f Acquiring the measured values
Functions
Acquiring the basic data
The maintenance system (WS) requires certain basic data
(parameters), which:
f are a prerequisite for the general function and
f which are used to adapt the maintenance system (WS) to the
vehicle and the operating fluids.
The basic data are acquired in the form of the following
parameterizations:
f Basic parameterization
f Vehicle
f Subsequent parameterization
f Parameterization of operating fluids
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Subsequent parameterization
Subsequent parameterization:
f makes it possible to change parameters, which are
f may only be carried out in workshops authorized by
>specific parameterization
connected to constructional vehicle changes for instance or
special customer's requests, such as the "time>
servicing scheme grid" parameter and
Mercedes>Benz.
based
Basic parameterization
The basic parameterization (base parameterization):
f includes the pre>assignment of certain parameters with
values and is a prerequisite for the function of the
maintenance system (WS) and
f is made at the manufacturer of the central gateway control
unit (CGW) (A2).
Vehicle>specific parameterization
The vehicle>specific parameterization:
f is used to adapt the maintenance system (WS) to the vehicle
model and the vehicle equipment, or to the special features
of the individual maintenance items, such as
their cut>in or cutout and
f is carried out in the Mercedes>Benz production plant.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Parameterization of operating fluids
Parameterization of operating fluids:
f makes it possible to change parameters with regard to the
properties of fuels and lubricants, which can change during
the operation of the vehicle, such as engine oil quality,
engine oil viscosity, transmission oil quality, or sulfur content
of the fuel and
f may also be carried out by other workshops.
i Querying and operation are conducted using the left
multifunction steering wheel button group (S110) and right
multifunction steering wheel button group (S111) or using Star
Diagnosis through the diagnostic socket (X100.16).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
i The parameters can be checked and changed if necessary
through the "Fuels and Lubricants" submenu in the
"Adjustments" menu of the menu system. Querying and
operation are conducted using the left multifunction steering
wheel button group (S110) and right multifunction steering
wheel button group (S111) or using Star Diagnosis through the
diagnostic socket (X100.16).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
25

Functions
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Acquiring the measured values
The measurement values are recorded using different sensors,
which are connected to the system>specific control units or the
locally best suited modules, e.g. on the sensor and actuator
module, cab (SCA) control unit (A7).
The analog measured values are turned into corresponding CAN
messages by the particular control units or modules; these CAN
messages are transmitted with the aid of the CAN data bus system
to the maintenance system (WS).
The maintenance system (WS):
f processes the recorded measured values converting them to
input data for the life cycle consumption and forecast
calculation, whereby the quality of processed measured
values is of major significance in terms of the forecast
calculation result and
f monitors the acquired measured values for errors, exceeding
limit values, and plausibility.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Drive control (CPC) control unit (A3)
The drive control (CPC) control unit (A3):
f acquires the measured value for air filter contamination by
the air filter sensor (B48) and
f sends a corresponding CAN message over the frame CAN
(CAN 3) and over the frame CAN bus neutral point (Z3) to the
central gateway control unit (CGW) (A2).
Engine management (MCM) control unit (A4)
The engine management (MCM) control unit (A4):
f acquires the measured "crankshaft rpm" value from the
crankshaft position sensor (B600),
f acquires the measured "engine oil temperature" value from
the engine oil fill level sensor (B605),
f sends corresponding CAN messages over the drive train CAN
(CAN 4) and over the drive train CAN bus neutral point (Z4)
to the drive control (CPC) control unit (A3) and from there
over the frame CAN (CAN 3) and over the frame CAN bus
neutral point (Z3) to the central gateway control unit (CGW)
(A2).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Transmission (TCM) control unit (A5)
The transmission control unit (TCM) (A5):
f acquires the measured "transmission oil temperature" value
from the transmission oil temperature sensor (B505) and
f sends a corresponding CAN message over the drive train
CAN (CAN 4) and over the drive train CAN bus neutral point
(Z4) to the drive control (CPC) control unit (A3) and from
there over the frame CAN (CAN 3) and over the frame CAN
bus neutral point (Z3) to the central gateway control unit
(CGW) (A2).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Retarder control (RCM) control unit (A11)
i Only in vehicles with code (B3H) Secondary water retarder.
The retarder control unit (RCM) (A11):
f acquires the measured "coolant temperature" value from
the coolant temperature sensor (B933) and
f sends a corresponding CAN message over the drive train
CAN (CAN 4) and over the drive train CAN bus neutral point
(Z4) to the drive control (CPC) control unit (A3) and from
there over the frame CAN (CAN 3) and over the frame CAN
bus neutral point (Z3) to the central gateway control unit
(CGW) (A2).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
26

Functions
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 09 / 2011 –
Cab signal acquisition and actuation module (SCA) control unit
(A7)
The sensor and actuator module, cab (SCA) control unit (A7):
f acquires the measured "brake wear" value at the installed
front axles from the following brake wear sensors:
f Left 1st front axle brake wear sensor (B1)
f Right 1st front axle brake wear sensor (B2)
f Left 2nd front axle brake wear sensor (B3)
f Right 2nd front axle brake wear sensor (B4)
f acquires the measured "front axle oil temperature" value
from the front axle temperature sensor
(B75) at the first front axle,
f acquires the measured "outside temperature" value from
the outside temperature sensor (B92) and
f sends a corresponding CAN message over the interior CAN
(CAN 2) and over the cab instrument panel CAN bus neutral
point (Z1) to the central gateway control unit (CGW) (A2).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Electronic Air>Processing Unit (EAPU) control unit (A18)
i
Only in vehicles with code (B1C, B1D, B1E) Electronic Air>
Processing Unit (EAPU).
The Electronic Air>Processing Unit (EAPU) control unit (A18)
f records the measured "condensation water level" value
from the condensation sensor (B26),
f delivers the "reservoir pressure for brake circuit 1 and 2"
measurement value from the integrated reservoir pressure
sensors for brake circuit
1 and 2,
f sends corresponding CAN messages over the exterior CAN
(CAN 1) to the central gateway control unit (CGW) (A2),
f sends corresponding LIN messages over the redundant
EAPU>LIN (LIN 10) to the instrument cluster control unit
(ICUC) (A1).
Sensor and actuator module, chassis (SCH) control unit (A8)
The sensor and actuator module, chassis (SCH) control unit (A8):
f acquires the measured "brake wear" value at the installed
rear axles from the following brake wear sensors:
> Left 1st rear axle brake wear sensor (B7)
> Right 1st rear axle brake wear sensor (B8)
> Left 2nd rear axle brake wear sensor (B9)
> Right 2nd rear axle brake wear sensor (B10)
f records the "rear axle oil temperature" value at the first rear
axle from the 1st rear axle temperature sensor (B77),
f sends corresponding CAN messages over the exterior CAN
(CAN 1) to the central gateway control unit (CGW) (A2).
i In the event of any data transfer interference between the
central gateway control unit (CGW) (A2) and the sensor and
actuator module, cab (SCA) control unit (A7) or the sensor and
actuator module, chassis (SCH) control unit (A8) the data can be
sent as LIN messages redundantly over the redundancy LIN
SCA/SCH (LIN 6).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Exhaust aftertreatment (ACM) control unit (A60)
i Only for vehicles with code (M5Z) Engine version Euro VI.
The exhaust aftertreatment (ACM) control unit (A60)
f acquires the exhaust pressure measurement values on the
diesel oxidation catalytic converter/diesel particulate filter
from the following pressure sensors:
> exhaust pressure sensor upstream of diesel oxidation
catalytic converter (B37)
> exhaust pressure sensor downstream of diesel particulate
filter (B38)
f sends a corresponding CAN message over the drive train
CAN (CAN 4) and over the drive train CAN bus neutral point
(Z4) to the drive control (CPC) control unit (A3) and from
there over the frame CAN (CAN 3) and over the frame CAN
bus neutral point (Z3) to the central gateway control unit
(CGW) (A2).
Instrument cluster control unit (ICUC),
component description
Central gateway control unit (CGW),
component description
Component description drive control (CPC)
control unit
Component description for engine
management (MCM) control unit
Transmission control (TCM) control unit.
component description
Cab signal acquisition and actuation
module control unit (SCA), component
description
Signal acquisition and actuation module
control unit, frame (SCH), component
description
i
Electronic systems, Actros, model 963 > 09/2011 >
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A7
A8
Page 331
Page 333
Page 334
Page 335
Page 337
Page 339
Page 340
27
 Loading...
Loading...