MACK MRU, LEU Operator's Manual

Mack® Natural Gas
(LEU / MRU)
® Gas Natural Mack
Mack® Natural Gas
(LEU / MRU)
21607699 © Mack Trucks, Inc. 2010
Printed in U.S.A.
21607699
21607699
September 2010
Foreword
The information in this manual applies to vehicles built January 2010 and later. Please keep this manual in the vehicle at all times.
This Handbook only applies to LEU and MRU models equipped with natural gas engines. For models equipped with diesel engines, please refer to Mack Terra Pro Series Operator’s Handbook.
Note: Illustrations in this manual are used for reference only and may differ slightly from the actual vehicle. However, key components addressed in this document are represented as accurately as possible.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and MACK Trucks, Inc. should be informed immediately if you believe that the vehicle has a defect that could cause a crash, injury or death.
Contact NHTSA by calling the Auto Safety Hotline at 1 (888) 327-4236, by writing to NHTSA, U.S. Department of Transportation, Washington, DC 20590, by TTY at 1 (800) 424-9153, or visit their website at www.nhtsa.dot.gov.
Mack Trucks, Inc.
Greensboro, NC USA
Order number: PV776-21607699
©2010 Mack Trucks, Inc., Greensboro, NC USA
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system, or transmitted in any forms by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Mack Trucks, Inc.

Contents |
|
OPERATOR’S HANDBOOK CUMMINS-WESPORT ISL-G NATURAL GAS |
|
ENGINE....................................................................................................................... |
1 |
INTRODUCTION.......................................................................................................... |
1 |
TO THE OWNER........................................................................................................ |
1 |
About This Handbook.............................................................................................. |
1 |
Safety Information......................................................................................................... |
2 |
INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS........................................................................... |
15 |
CAB INTERIOR.......................................................................................................... |
15 |
Methane Detector/Alarm System............................................................................. |
19 |
OPERATION.................................................................................................................. |
20 |
LIQUID NATURAL GAS SYSTEM.......................................................................... |
20 |
LNG Tank................................................................................................................ |
20 |
LNG Fueling............................................................................................................ |
23 |
COMPRESSED NATURAL GAS SYSTEM.............................................................. |
26 |
CNG Fueling............................................................................................................ |
26 |
MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION.................................................................... |
27 |
MAINTENANCE INTRODUCTION......................................................................... |
27 |
DAILY LNG/CNG FUEL SYSTEM CHECKS.......................................................... |
27 |
BEFORE PERFORMING MAINTENANCE ON THE LNG OR CNG TANKS |
|
OR FUEL SYSTEM.................................................................................................... |
29 |
Removing Pressure Before Working on the Engine Fuel System ........................... |
29 |
Removing Pressure Before Working on the Tanks.................................................. |
30 |
Moving a Vehicle Using Auxiliary Fuel.................................................................. |
30 |
ENGINE MAINTENANCE........................................................................................ |
32 |
Air Filter................................................................................................................... |
32 |
Air Inlet System Ducts, Hoses and Clamps............................................................. |
34 |
Chassis-Mounted Charge Air Cooling (CMCAC)....................................................... |
34 |
Fuel System.............................................................................................................. |
35 |
COOLING SYSTEM................................................................................................... |
36 |
Radiator Pressure Cap.............................................................................................. |
37 |
Thermostat............................................................................................................... |
37 |
Federal Emissions.......................................................................................................... |
39 |
FEDERAL EMISSION REQUIREMENTS................................................................ |
39 |
Tampering with Gaseous Emission Control Systems Prohibited ............................ |
39 |
Gaseous Emission Control Systems Warranty......................................................... |
40 |
GASEOUS EMISSIONS CONTROL SYSTEM WARRANTY FEDERAL |
|
EMISSION REQUIREMENTS................................................................................... |
41 |
Items Not Covered by the Emission Control Systems Warranty............................. |
41 |
Emission Control Systems Warranty — California................................................. |
42 |
EMISSIONS CONTROL SYSTEM WARRANTY — CALIFORNIA...................... |
44 |
Procedures for Handling Emissions Control System Warranty............................... |
44 |
ELECTRICAL............................................................................................................... |
46 |

..................................................................................................................................... |
46 |
Circuit Breaker and Relay Panel .............................................................................. |
46 |

INTRODUCTION 1
TO THE OWNER
About This Handbook
This handbook is referred to as the Cummins-Wesport ISL-G™ Natural Gas Engine Handbook. It covers all Natural Gas Engine models. Keep this handbook with the vehicle at all times to ensure that each owner and/or operator will have access to all pertinent information relating to the operation and handling of this vehicle.
This supplement was prepared to provide the driver with all relevant information concerning the natural gas engine, its characteristics and its potential hazards if not maintained properly. Please read it thoroughly; pay particular attention to advisory labels that have been included to draw attention to important issues of operator safety and overall performance.
Information and illustrations in this handbook are based on the latest production usage at the time of printing and are subject to change without prior notice.
Refer to your vehicle’s Operator’s Handbook for additional vehicle information.

2 Safety Information
Important Safety Information for All Operators of Natural Gas Vehicles
 DANGER
DANGER
Do not operate, occupy or refuel an LNG/CNG vehicle if you are unsure of your qualifications for operating, refuelingorrecognizingandresponding to potentially dangerous emergency situations that could arise related to LNG/CNG vehicles and equipment.
Although formal certification is not currently required - from an operational, safety and liability perspective - it may be desirable for personnel handling LNG/CNG equipmenttocarryawrittencertificateattestingtosuchtraining. Itistheresponsibility of the owner and operator of any LNG/CNG facility or equipment to have proper safety training before operating LNG/CNG equipment. Information concerning proper LNG/CNG safety training is available through the manufacturer of LNG/CNG vehicles and equipment. If you are unsure about your qualifications for operating, refueling or recognizing and responding to potentially dangerous emergency situations that could arise related to the operating of an LNG/CNG vehicle, contact your immediate supervisor or call MACK OneCall™ Customer Support System
at 1-800-866-1177.
The scope of this handbook is not to cover all situations related to LNG/CNG safety. Effective safety training programs are required at all LNG/CNG vehicle facilities to ensure the safety of personnel, protect property and maintain facility performance requirements. Familiarizing all personnel with basic LNG/CNG information will allow them to make well-informed safety judgments. A safety program at the facility should include:
1Scheduled equipment inspections
2Operational safety procedures
3Personnel training and certification
4Emergency response procedures and periodic practice drills
5Emergency response community interaction

Safety Information 3
Although this handbook contains safety information that may be used in conjunction with a safety training program, it is not to be viewed as a safety-training manual. The safety information contained in this manual is for reference and recall of information already covered in an ongoing safety program. Only safety training and periodic practice drills can adequately train operators and local emergency personnel (such as firedepartments, medicalemergencyunitsandpolicedepartments)forsafelyhandling potentially dangerous situations in the community proximate to LNG/CNG facilities and LNG/CNG vehicle operation.
 DANGER
DANGER
It is recommended that personnel never enteravaporcloud. Ifthevaporignites, they could be severely burned. Inhaling the vapor can cause breathing problems or asphyxiation.

4 Safety Information
Properties of LNG:
Liquefied Natural Gas/Methane (LNG) is a colorless, odorless gas or liquid. At ambient temperatures, the product is a gas, but at cryogenic (super-cooled)
temperatures it is a liquid or heavy gas that may travel along the ground, rise as it warms and vaporizes, and become trapped under any closed-in space.
Properties of CNG:
Compressed Natural Gas/Methane (CNG) is a colorless, odorless (sulfur) gas. It is compressed at 2400 to 3600 pounds per square inch and stored/used in specially designed cylinders.
Normal Methane Venting
The methane fuel tanks automatically vent to release pressure when the vehicle is parked for some time. During venting a hissing sound may be heard. The frequency and duration of this venting will vary depending on tank pressure and ambient temperature. Itwillcontinuetoventuntilthetruckisoperatedagain,therebydropping the pressure, or until the tank(s) is empty.
Primary LNG Tank Vent Piping
From the factory, the vent piping from the primary LNG tank vents is attached to the intake stack by disposable plastic straps. The piping should be removed from the intake stack and plumbed up and over the body by the body installers as shown in the following illustration. For more information, see the section titled "LNG Tank Pressure Vents" in the OPERATION section of this manual.
 CAUTION
CAUTION
It is important to keep the primary pressure vent free of blockage due to ice, snow or debris.
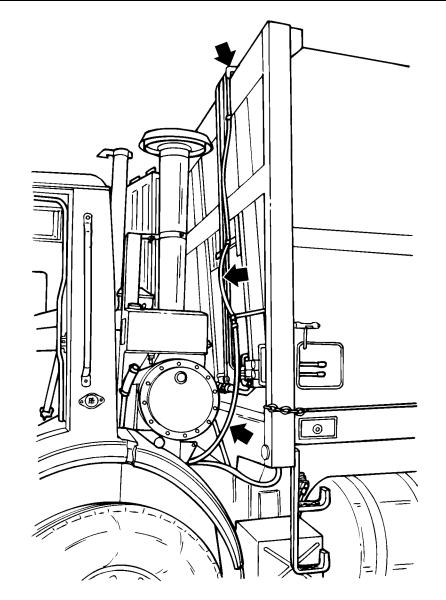
Safety Information 5
C0032249

6 Safety Information
Methane Leaks
During the daily walk around, inspect the outside of the LNG fuel tank for frost. Frosted LNG tank(s), other than at the shroud area*, indicates that the inner tank is leaking into the outer tank. The appearance of a vapor cloud accompanied by a
hissing noise may also indicate a methane leak. A leak requires service on the tank(s) before the vehicle can be operated.
*Rear fuel tank door and plumbing fixtures.
 WARNING
WARNING
Do not operate a vehicle which has a methane leak.
Rapid Pressure Rise
There are three main causes of rapid pressure rise on LNG systems; overfilling, fuel system leaks or malfunctions and loss of vacuum. A properly functioning, properly filled LNG fuel system should build less than 15 psig/ day. Any system building more than 40 psig/ day needs troubleshooting to find the cause.
Vacuum Loss
Total vacuum loss is an unusual event for an LNG tank (resulting in frosting the entire shell), however the vacuum will slowly decay with time as gasses diffuse out of the tank materials. This will show up over time as a more rapid pressure rise time, eventually exceeding 40 psig/ day. Once the vacuum has decayed to this point, the tank will need to be re-evacuated by a competent maintenance facility.

Safety Information 7
METHANE DETECTOR/ALARM SYSTEM
Note: The following information applies to equipment located on the vehicle only. Separate methane detector/alarm systems should be installed in facilities that frequently house natural gas vehicles. In addition, hand-held methane detector/alarm devices should be used when working on natural gas vehicles with non-functioning or disconnected methane detector/alarm systems and where no auxiliary methane detector/alarm system is installed.
Note: Consult your local fire code and/or |
detection and prevention measures are in |
fire inspector to make sue that adequate |
place. |
The methane vapor detection system utilizes two sensors to identify methane vapors; one located in the cab compartment and one located in the engine compartment of the vehicle. The system operates with both a visual and an audible alarm to warn the operator of potential danger. The alarms are triggered at trace levels (20% LEL [Lower Explosive Limit]) and at significant levels (50% LEL) of vapor concentration. The system and sensor operation is constantly monitored. An internal relay controls two indicator lamps (1 green and 1 red) that can be seen through the windshield. The green lamp will go out and the red lamp will illuminate 15 seconds after a significant level of methane has been detected. The methane detector also has a passtotest button that can be used to test the indicator lamps and the audible alarm.

8 Safety Information
Before Entering the Vehicle
Green and red methane detector remote indicator lamps are easily viewed through the windshield and should always be checked before entering the vehicle. (See illustration.)
W0059509

Safety Information 9
 DANGER
DANGER
WHEN APPROACHING THE CAB TO ENTER: Do not open the vehicle doors if the RED LAMP IS ON! Do not open the vehicle doors if the ALARM IS SOUNDING! Do not open the vehicle doors if the GREEN LAMP is NOT ON! If the indicator lamp is red, if the alarm is sounding or if the green lamp is NOT ON, it is unsafe to open the vehicle doors because even static electricity can ignite concentrated methane fumes in an enclosed area. Immediately implement the following procedure:* Remove all personnel from the area. Turn off electrical circuits and sources of ignition in the immediate area. Manually turn off the Fuel ShutOff Valve on each fuel tank to prevent further gas leakage. Wait until the gas has dissipated and the alarm situation has cleared. It is now safe to open the vehicle doors and windows to vent the vehicle. Donotoperatethevehicleuntil the source of the leak has been repaired.
Note: When the battery is disconnected, the methane detector/alarm system will not operate so the green lights will not be on. The methane detector/alarm system is powered by the battery and is active at all times unless the battery is disconnected or the fuse is blown.
Hand-held methane detector/alarm devices should be used when working on natural gas vehicles with a nonfunctional or disconnected methane detector/alarm system and where no auxiliary methane detector/ alarm system is installed.

10 Safety Information
 DANGER
DANGER
In the event of an alarm while operating the vehicle, immediately open the cab windows, safely stop the vehicle, shut down the engine and turn off the ignition. Exit the cab and leave the doors and windows open to vent the vehicle. Manually turn off the Fuel Shut-Off Valve on each fuel tank to prevent further gas leakage.Wait until the gas has dissipated and the alarm situation has cleared. Do not operate the vehicle until the source of the leak has been repaired.
 CAUTION
CAUTION
AMGaDS III Plus is a propane, CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) and LNG (Liquid Natural Gas) detector only. However, because the sensors detect all hydrocarbon vapors, an alarm may be triggered by the use of chemicals such as cleaners, paint, polish, lacquer, etc. Do not expose sensors to liquids or chemicals unnecessarily. When using such substances, keep the vehicle well ventilated and do not allow direct contact with the sensors. For cleaning and maintenance of the Gas Detection System, refer to the AMGaDS III Plus Owner’s Manual supplied with the vehicle.
Note: For additional information, refer to and in the INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS section of this handbook.

Safety Information 11
Potential Hazard Associates with LNG/CNG:
Skin/Eyes
LNG is stored at cryogenic temperatures (low-temperature state, starts at or below -240 °F (about -150 °C) and CNG is stored in specially designed tanks under extremely high pressure. Therefore, properly insulated safety gloves and eye protection such as goggles or a face shield should be worn when working with or around LNG/CNG as when refueling. If super-cooled liquid or gas comes into contact with the skin or eyes, see a physician immediately.
WARNING
COVER EYES AND EXPOSED SKIN. Accidental contact of the eyes or skin with LNG may cause a freezing injury similar to a burn. Protect the eyes and cover the skin whenever the possibility of contact with super-cold metals, liquids or gas exists.

12 Safety Information
Inhalation
LNG/CNG is not toxic, but can cause asphyxiation in concentration or in enclosed areas because it reduces the oxygen available for breathing. For this reason, methane detectors are located in the engine compartment and inside the cab. These detectors will trigger an alarm inside the cab if methane concentration goes above a safe level. Thesedetectorsarealwaysactivewhetherthevehicleisonoroff,aslongasthebattery is connected and the fuse is in place and not blown. If overcome by vapor, remove the individual from exposure and call a physician immediately. If breathing is irregular or has stopped, start resuscitation (if trained in CPR) and administer oxygen if available.
 DANGER
DANGER
KEEP THE EQUIPMENT AREA WELL VENTILATED. Although LNG/CNG is non-toxic, it can cause asphyxiation in a confined area without ventilation. Any atmosphere that does notcontainenoughoxygenforbreathing can cause dizziness, unconsciousness, or even death. LNG, being colorless, odorless and tasteless, cannot be detected by human senses. Even though CNG is sulfurized, the smell may
go unnoticed on some vehicles, such as a refuse truck. Without adequate ventilation, natural gas will displace the oxygen and give no warning that a non-life supporting atmosphere is present. Store LNG/CNG in a well ventilated area.
If vehicles equipped with an LNG engine must be parked or worked on indoors for short periods of time, piping from the primary LNG tank vent pipe to the outside of the building should be provided. See "Primary LNG Tank Vent Piping" at the end of the SAFETY section. De-fueling or removal of the LNG tank(s) is recommended for vehicles stored indoors for long periods of time.
Separate methane detector/alarm systems should be installed in facilities that frequently house LNG/CNG vehicles, consult local codes and ordinances to ensure compliance. In addition, handheld methane detector/alarm devices should be used when working on LNG/CNG vehicles with non-functioning or disconnected methane detector/alarm system and where no auxiliary methane detector/alarm system is installed.
Note: Due to the cryogenic state of LNG fuel, it cannot be odorized, therefore, it will not smell like CNG or pipeline gas in a home.

Safety Information 13
Flammability
Since LNG is extremely flammable, the tank(s) should be grounded when fueling, to avoid creating sparks from static electricity. Keep any source of ignition, such as a lit cigarette, far away from LNG/CNG tanks and fueling areas.
 WARNING
WARNING
KEEP AWAY FROM FLAME OR SPARK.
Natural gas is flammable. Smoking, open flames, and general purpose electrical equipment shall be prohibited where natural gas is stored or handled.
Pressure
The LNG/CNG fuel systems are pressurized systems. Therefore, automatic and manual safety vents, relief valves and shutoff points are installed throughout the system to prevent excess pressure from building.
 WARNING
WARNING
REMOVE PRESSURE. Always empty the LNG/CNG fuel tank(s) and remove any pressure on the system prior to removing parts or components of the tank for repair.
Releases or Spills
During a release or spill, shut off and eliminate all ignition sources. If desired, stop the source of the release or spill. Keep people away. Minimize breathing vapors. Absolutely avoid skin contact. Ventilate confined spaces. No disposal method is necessary, nor should it be attempted, because extremely rapid evaporation of the natural gas will take place. If a spill is in danger of igniting, use a water spray (do not use solid streams of water) to direct gas-air mixtures away from ignition sources
If a spill has ignited, use water to keep fire-exposed containers and equipment cool and to protect personnel who may have to stop the source of the leak. If it is desirable to extinguish the fire, use dry chemical, carbon dioxide or halogenated extinguishing agents.

14 Safety Information
SPECIFIC SAFETY INFORMATION REGARDING THE INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS, THE OPERATION, AND THE MAINTENANCE OF THE CHASSIS WILL BE COVERED IN YOUR OPERATOR’S HANDBOOK.
Cab Entry/Exit
As described in your Operator’s Handbook, follow the Three-Limb Contact Rule to enter and exit your vehicle.
 DANGER
DANGER
Before opening either vehicle door, always look through the driver side window at the methane alarm box located on instrument panel (MRU and LEU). Do NOT open the door if a red alarm light is on or if you hear the audible alarm sounding. Do NOT open the door if the green light is not ON.
 Loading...
Loading...