Page 1

LanciaKappa2.0Sedan
1995,107Kw,Petr ol
Page 2

Technical
data
Page 3
Notes Specified value Measured value
Vehicle identification
No. of cylinders Type 5/DOHC
Capacity (Fiscal) cc 1998
Compression ratio :1 10,0
Suitable for unleaded petrol Yes
Minimum octane rating RON 95
Ignition system Type Motronic
Ignition system Description Map-DI
Trigger location Cam/ Crankshaft
Fuel system Make Bosch
Fuel System Type Motronic M2.10
Fuel System Description MFI-s
Air metering Type Mass
Combined ignition and fuel ECM Yes
Diagnostic socket Yes
Ignition system
Ignition coil Make Bosch
Ignition coil Type 0 221 152 067
Ignition coil supply voltage + with ballast V 11,0
Primary resistance Ohm 0,4
Secondary resistance Ohm 8500
Firing order 1-2-4-5-3
Tuning and emissions
Ignition timing - basic BTDC °Engine/rpm Not adjustable
Ignition advance checks °Engine/rpm ECM Controlled
Idle speed rpm Not adjustable
Oil temperature for CO test °C 60
CO level at idle speed - tailpipe (Cat) Vol. % CO 0,35 Max Not adjustable
CO level at idle speed - sample pipe Vol. % CO 0,4±0,1
HC level at idle speed ppm 90 Max
CO2 level at idle speed Vol. % CO2 13 Min
O2 level at idle speed Vol. % O2 0,1-0,5
Increased idle speed for CO test rpm 2500-2900
CO content at increased idle speed Vol. % 0,3
Lambda at increased idle λ 0,97-1,03
Spark plugs
Spark plugs Original equipment Champion
Spark plug Type RC7BMC
Electrode gap mm 0,5
Spark plugs Make Autolite
Spark plug Type APP3922
Electrode gap mm 0,9
Spark plugs Make Beru
Spark plug Type 14FR-6LDU
Electrode gap mm 0,8
Spark plugs Make Champion
Spark plug Type RC7BMC
Electrode gap mm 0,5
Spark plugs Make NGK
Spark plug Type BKR6EKC
Electrode gap mm 0,9
Fuel system
System pressure without vacuum bar 3,0
RPM/TDC sensor Ohm 774-946
Oxygen sensor heater Ohm 2,5-4,5
Service checks and adjustments
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 4
Valve clearance -INLET mm 0,38±0,04 cold
Valve clearance -EXHAUST mm 0,43±0,04 cold
Oil pressure bar/rpm 4,0/4000
Lubricants and capacities
Engine oil grade - moderate climate SAE 15W/40
Engine oil classification API/ACEA SG/A2-96
Engine oil grade - alternative - moderate climate SAE 10W/30 Semi-Synth.
Engine oil classification - alternative - moderate climate API/ACEA SG/A3-96
Engine with filter litres 5,4
Gearbox oil grade SAE 75W/90
Gearbox 4/5 speed litres 2,0
Cooling system litres 8,3
Brake fluid Type DOT 3/4
Tightening torques
Cylinder head instructions
Cylinder head
Renew bolts No
Stage 1 Tighten 40 Nm
Stage 2 Tighten 90°
Stage 3 Tighten 90°
Stage 4 Tighten 90°
Other tightening torques
Main bearings Renew bolts/nuts No
Main bearings Stage 1 25 Nm
Main bearings Stage 2 100°
Big end bearings Renew bolts/nuts No
Big end bearings Stage 1 25 Nm+60°
Oil pump to cylinder block 9 Nm
39 Sump bolts
Sump drain bolt 20 Nm
Flywheel/driveplate 160 Nm
Crankshaft pulley/damper 360 Nm
Camshaft sprocket/gear 118 Nm
Camshaft/rocker cover 8 Nm
Inlet manifold to cylinder head 25 Nm
Exhaust manifold to cylinder head 25 Nm
Spark plugs 27 Nm
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor 20 Nm
Oxygen sensor (Lambda) 50-60 Nm
Knock sensor (KS) 25 Nm
Engine oil pressure switch 22 Nm
Front hub 60 Nm+52°
Rear hub 320 Nm
Steering track rod end 38 Nm
Brake disc to hub Front 20 Nm
Brake caliper carrier to hub Front 160 Nm
Brake disc to hub Rear 12 Nm
Brake caliper carrier to hub Rear 55 Nm
ABS sensor Front 10 Nm
ABS sensor Rear 10 Nm
Road wheels 98 Nm
Starting and charging
Battery V/RC(Ah) 12/90 (60)
Starter motor Make Marelli
Starter motor Type E70R-12v-1,4kW
Minimum starting voltage V 8,1
Maximum cranking amps A 162-198
Alternator/Regulator Make Marelli
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 5

Alternator/Regulator Type A127I
Alternator output at engine speed A/V/rpm 100/14/3500
Voltage regulator Type 24TR/B
Regulated voltage V 14,3-14,6
Brake disc and drum dimensions
Minimum disc thickness - ventilated Front 20,2 mm
Minimum disc thickness Rear 9,2 mm
Disc runout Front 0,15 mm
Disc runout Rear 0,15 mm
Minimum pad thickness Front 1,5 mm
Minimum pad thickness Rear 1,5 mm
Handbrake travel No. of notches 5-6
Air conditioning
Air conditioning refrigerant Type R134a
32 Air conditioning refrigerant quantity grams
33 Air conditioning oil Type
38 Air conditioning oil quantity cmł
Cylinder layout Tightening sequence
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 6

Wheelalignment
Page 7

Kappa 1995-02
Rim size Tyre size Model Front bar(psi) Rear bar(psi)
4x15 125/90 R 15 96M 4,2 (60) 4,2 (60)
6,5x15 195/65 R 15 91V 2,2 (31) 2,2 (31)
6,5x15 205/60 R 15 91V 2,2 (31) 2,2 (31)
6,5x15 205/60 R 15 91W 2,2 (31) 2,2 (31)
6,5x16 205/55 R 16 89W 2,2 (31) 2,2 (31)
7,5x16 205/55 R 16 91W 2,2 (31) 2,2 (31)
7,5x16 215/55 R 16 91W 2,2 (31) 2,2 (31)
Telephone:
Fax:
VAT Registration No.:
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.12.02.
V5.500-
Page 8
Dimensions
Notes Specified value Measured value
Wheelbase mm 2700
Track - front/rear mm 1546/1527
Tightening torques
Notes Specified value Measured value
Tightening torque - steel wheels 98 Nm
Tightening torque - alloy wheels 98 Nm
Checking range - Front wheels
Notes Specified value Measured value
Load positioning unladen
Toe-in (N = negative, toe-out) mm 0 - 2
Toe-in deg 0° - 0°20'
Toe-in deg-1/100 0 - 0,33
Camber deg 0°35'N - 1°15'N
Camber deg-1/100 0,58N - 1,25N
Castor deg 2°50' - 3°30'
Castor deg-1/100 2,83 - 3,50
Setting data - Four wheels
Notes Specified value Measured value
Load positioning unladen
Toe-in (N = negative, toe-out) mm 1±1
Toe-in deg 0°10'±10'
Toe-in deg-1/100 0,17±0,17
Camber deg 0°55'N±20'
Camber deg-1/100 0,92N±0,33
Camber adjustment Not adjustable
Castor deg 3°10'±20'
Castor deg-1/100 3,17±0,33
Castor adjustment Not adjustable
Lock angles - max. inner deg 37°±30'
Lock angles - max. inner deg-1/100 37±0,50
Lock angles - max. outer deg 32°40'
Lock angles - max. outer deg-1/100 32,67
Rear toe-in mm 2,5±1
Rear toe-in deg 0°23'±10'
Rear toe-in deg-1/100 0,38±0,17
Rear toe-in adjustment $ADJ
Rear camber deg 0°45'N±20'
Rear camber deg-1/100 0,75N±0,33
Rear camber adjustment Not adjustable
Rear toe-in adjustment
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
Lancia
838A1.000
R-Cat
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 9

Timingbelt
replacement
intervals
Page 10

Important note
Important note
The intervals and procedures given are subject to alteration by the manufacturer at any time.
Check the regularly updated Timing Belts section on our website to ensure that you are kept
informed of any changes that may occur between issues of the Autodata CD.
http://www.autodata-cd.com
Timing belt replacement intervals
The information relating to timing belt replacement intervals is additional to the main purpose of this CD, but is included to
provide guidance to garages and for customer advice.
Where possible the recommended intervals have been compiled from vehicle manufacturers' information. In a few instances no
recommendation has been made by the manufacturer and the decision to replace the belt must be made from the evidence of
a thorough examination of the condition of the existing belt.
Apart from the visible condition of the belt, which is explained fully later in this section, there are several other factors which
must be considered when checking a timing belt:
Is the belt an original or a replacement.1.
When was the belt last replaced and was it at the correct mileage.2.
Is the service history of the vehicle known.3.
Has the vehicle been operated under arduous conditions which might warrant a shorter replacement interval.4.
Is the general condition of other components in the camshaft drive, such as the tensioner, pulleys, and other ancillary
5.
components driven by the timing belt, typically the water pump, sound enough to ensure that the life of the replacement
belt will not be affected.
If the condition of the existing belt appears good, can you be satisfied that the belt will not fail before the next check or
6.
service is due.
If the belt does fail, have you considered the consequences. If the engine is an INTERFERENCE type then considerable
7.
expensive damage may well be the result.
The cost of replacing a belt as part of a routine service could be as little as 5 to 10% of the repair cost following a belt
8.
failure. Make sure your customer is aware of the consequences.
If in doubt about the condition of the belt - RENEW it.9.
Replacement Interval Guide
Replacement Interval Guide
Lancia recommend check & replace if necessary every 60,000 km and replacement every 105,000 km.
The previous use and service history of the vehicle must always be taken into account.
Check For Engine Damage
Check For Engine Damage
CAUTION: This engine has been identified as an INTERFERENCE engine in which the possibility of valve-to-piston
damage in the event of a timing belt failure is MOST LIKELY to occur.
A compression check of all cylinders should be performed before removing the cylinder head.
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
1994-02
© Autodata Limited 2004
V5.500-
2006.10.21.
Page 11

Repair Times - hrs
Repair Times - hrs
Kappa 2,0/2,4 5 Cyl. 1995-04
Remove and install 2,45
Remove and install - AC 2,65
Special Tools
Special Tools
Tensioner pulley locking pin - Lancia No.1860830000.
Camshaft locking tools - Lancia No.1860819000.
Special Precautions
Special Precautions
Disconnect battery earth lead.
DO NOT turn crankshaft or camshaft when timing belt removed.
Remove spark plugs to ease turning engine.
Turn engine in normal direction of rotation (unless otherwise stated).
DO NOT turn engine via camshaft or other sprockets.
Observe all tightening torques.
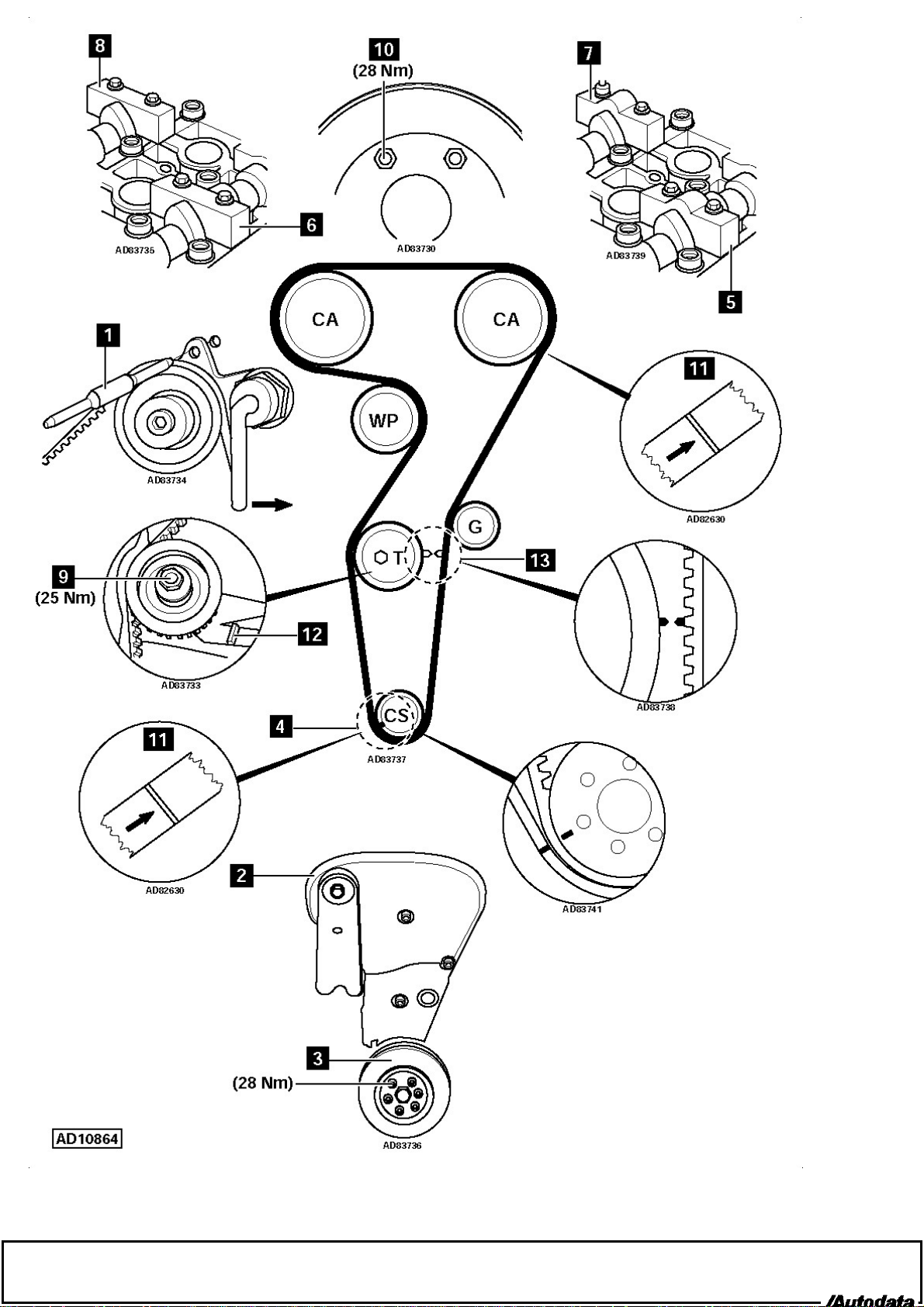
Removal
Removal
Raise and support front of vehicle.1.
2.
Remove:
RH front wheel.
Wheel arch liner.
Turn auxiliary drive belt tensioner pulley anti-clockwise. Use suitable spanner.3.
Lock tensioner pulley. Use tool No.1860830000 [1] .4.
5.
Remove:
Auxiliary drive belt.
Engine upper torque link.
Spark plug cover.
Cylinder head covers.
Timing belt cover [2] .
Crankshaft pulley (6 bolts) [3] .
Turn crankshaft to TDC on No.1 cylinder [4] .6.
Ensure both camshafts at TDC on No.1 cylinder. If not: Turn crankshaft one turn clockwise.7.
Remove third bearing cap from exhaust camshaft [5] .8.
Remove fourth bearing cap from inlet camshaft [7] .
9.
NOTE: Mark bearing caps before removal for identification.
Fit locking tools in place of bearing caps [6] & [8] . Tool No.1860819000.
10.
NOTE: Locking tools are marked 'exhaust' and 'inlet'. Ensure locking tools aligned with respective cam profiles
to prevent damage.
Slacken tensioner sprocket nut [9] . Turn tensioner sprocket anti-clockwise to release tension on belt. Lightly tighten nut.11.
Remove timing belt.12.
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 12

Installation
Installation
Ensure crankshaft at TDC on No.1 cylinder. Ensure timing marks aligned [4] .1.
Ensure locking tools located correctly in camshafts [6] & [8] .2.
Slacken bolts of each camshaft sprocket [10] .3.
4.
Fit timing belt in following order:
Crankshaft sprocket.
Guide pulley.
Exhaust camshaft sprocket.
Inlet camshaft sprocket.
Water pump sprocket.
Tensioner sprocket.
Ensure marks on belt aligned with marks on sprockets [11] .5.
Slacken tensioner sprocket nut [9] .6.
Push on tensioner sprocket to pre-tension belt [12] . Lightly tighten nut.7.
Tighten bolts of each camshaft sprocket [10] . Tightening torque: 28 Nm.8.
Remove locking tools from camshafts [6] & [8] .9.
Fit bearing caps in correct locations. Tighten bolts to 15 Nm.10.
Turn crankshaft two turns in normal direction of rotation.11.
Ensure timing marks aligned [4] .12.
Slacken tensioner sprocket nut [9] .13.
Tensioner sprocket should operate and marks align [13] .14.
Tighten tensioner sprocket nut [9] . Tightening torque: 25 Nm.15.
Install components in reverse order of removal.16.
Fit auxiliary drive belt. Remove locking pin from tensioner pulley.17.
Tighten crankshaft pulley bolts. Tightening torque: 28 Nm.18.
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 13
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 14

Service
indicator
Page 15
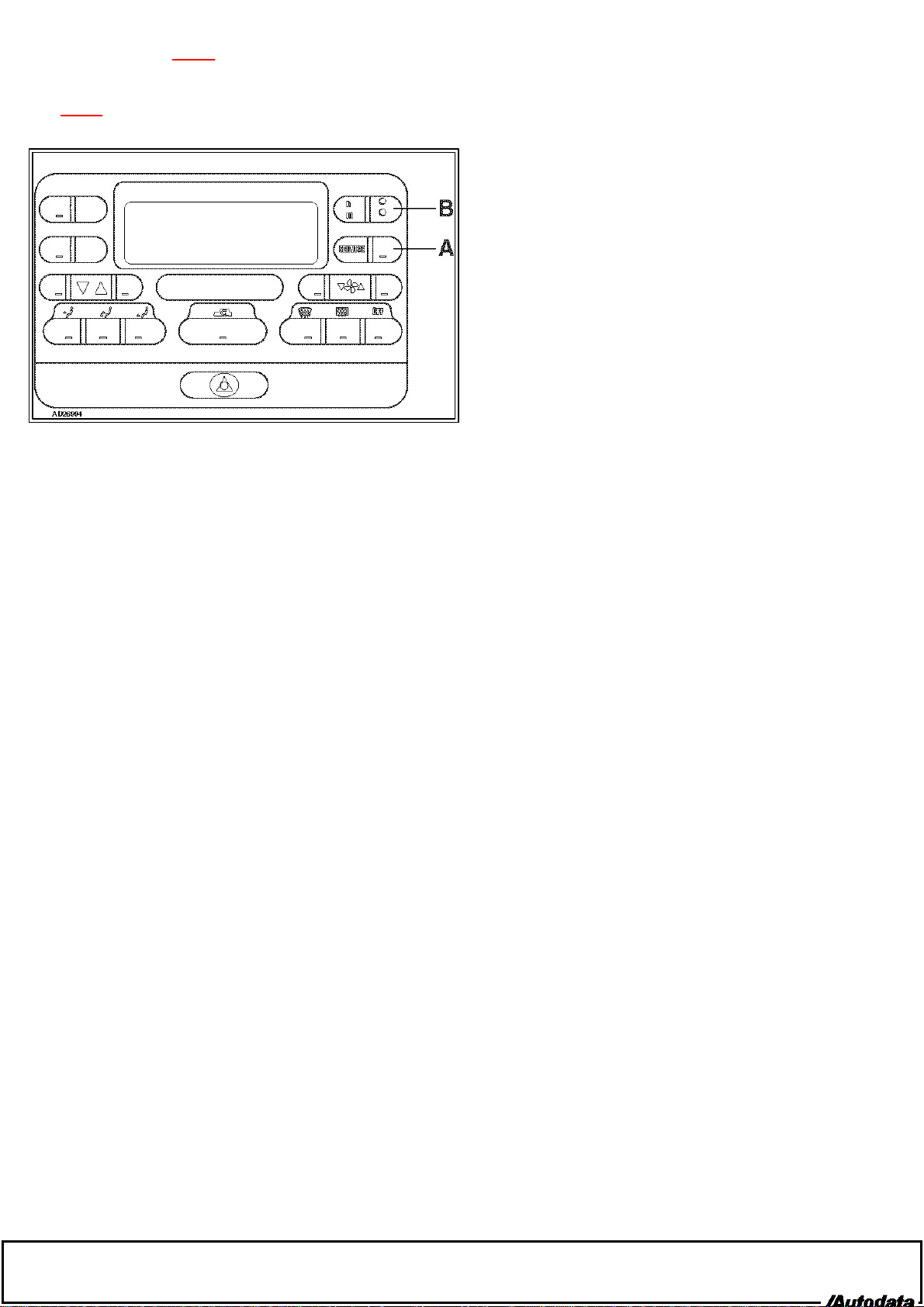
Switch ignition ON.
Press button [A] Fig. 26994
.
Press button [B] to reset the display.
Switch ignition OFF.
Fig. 26994
26994
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 16

Engine
management
pindata
Page 17
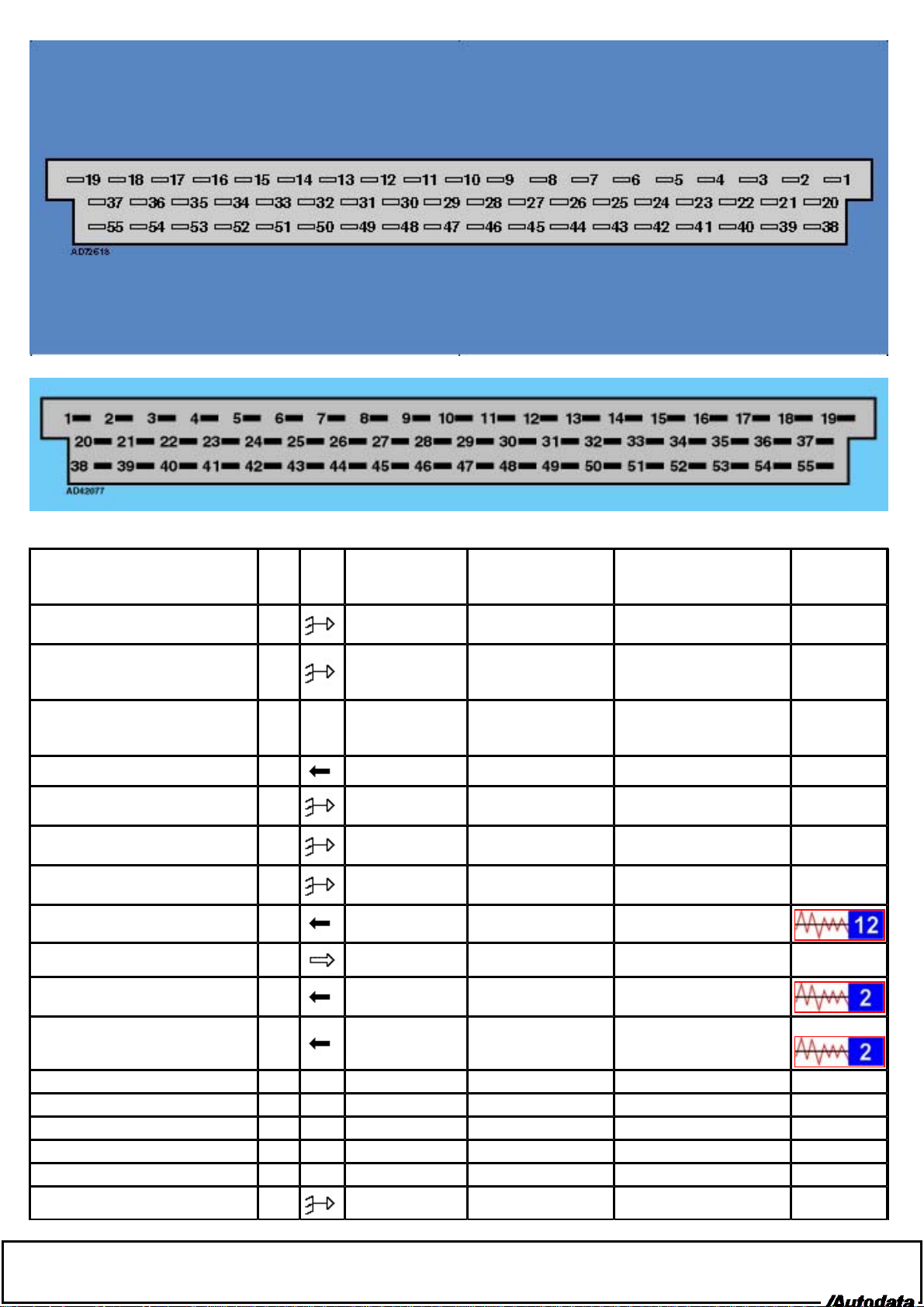
Terminal side
Wire side
Component/circuit description
AC compressor clutch relay 32
AC compressor clutch relay 32
AC refrigerant pressure switch 40
Battery 18 Ignition OFF 11-14 V
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator
relay
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator
relay
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator
relay
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor 8 Engine idling 2 V/50 ms
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor 12 Ignition ON 5 V
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
ECM
Signal Condition Typical value
pin
Engine idling - AC
OFF
Engine idling - AC
ON - AC
compressor ON
52 Ignition ON 11-14 V
52 Engine idling 11-14 V
52
48
(49)
49
(48)
Engine idling accelerate briefly
Engine idling 5 V/2 ms
Engine idling 5 V/2 ms
11-14 V
0-1 V
Connected pin - no test
data available or
random digital signal
0-1 V briefly
Oscilloscope setting
(Suggested settings -
Voltage/time per division)
Wave form
Reversed
Earth 2 Ignition ON 0 V
Earth 14 Ignition ON 0 V
Earth 19 Ignition ON 0 V
Earth 24 Ignition ON 0 V
Earth 42 Ignition ON 0 V
Engine control relay 36 Ignition OFF 11-14 V
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
1994-02
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 18
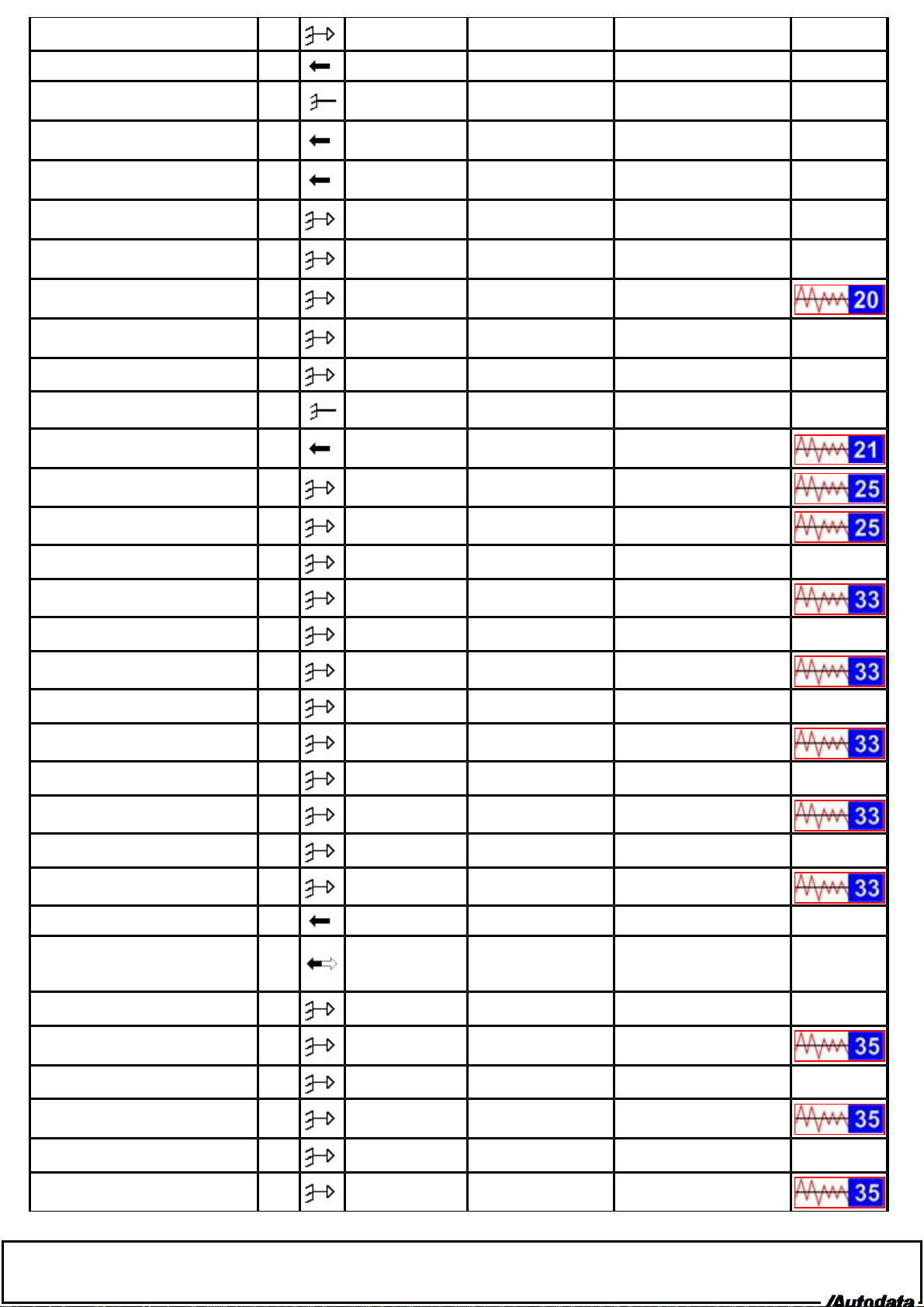
Engine control relay 36 Ignition ON 0 V
Engine control relay 37 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor
Engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor
Engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister
purge valve
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister
purge valve
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister
purge valve
Fuel pump relay 3 Ignition ON
Fuel pump relay 3 Engine cranking 0-1 V
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 10 Engine idling 0 V
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 28
Idle air control (IAC) valve 4 Engine idling 5 V/5 ms
Idle air control (IAC) valve 22 Engine idling 5 V/5 ms
30 Ignition ON 0 V
45
45
5 Ignition ON 11-14 V
5 Engine idling 11-14 V
5
Ignition ON coolant temp. 10°C
Ignition ON coolant temp. 80°C
Engine hot - valve
operating
Engine idling engine hot
3,5 V
0,6 V
0-1 V briefly then 11-14
V
0,1-1 V fluctuating 0,2 V/1 sec.
10 V/20 ms
Ignition coil - cylinder 1 1 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Ignition coil 1 Engine idling 5 V/2 ms
Ignition coil - cylinder 2 20 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Ignition coil 20 Engine idling 5 V/2 ms
Ignition coil - cylinder 3 39 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Ignition coil 39 Engine idling 5 V/2 ms
Ignition coil - cylinder 4 21 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Ignition coil 21 Engine idling 5 V/2 ms
Ignition coil - cylinder 5 38 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Ignition coil 38 Engine idling 5 V/2 ms
Ignition switch 27 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Immobilizer control module diagnostic link
Injector 1 17 Ignition ON 11-14 V
55
Connected pin - no test
data available or
random digital signal
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Engine idling engine hot
Engine idling engine hot
Engine idling engine hot
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
Injector 1 17
Injector 2 16 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Injector 2 16
Injector 3 15 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Injector 3 15
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
Lancia
838A1.000
R-Cat
2,5-3,5 ms 10 V/2 ms
2,5-3,5 ms 10 V/2 ms
2,5-3,5 ms 10 V/2 ms
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 19
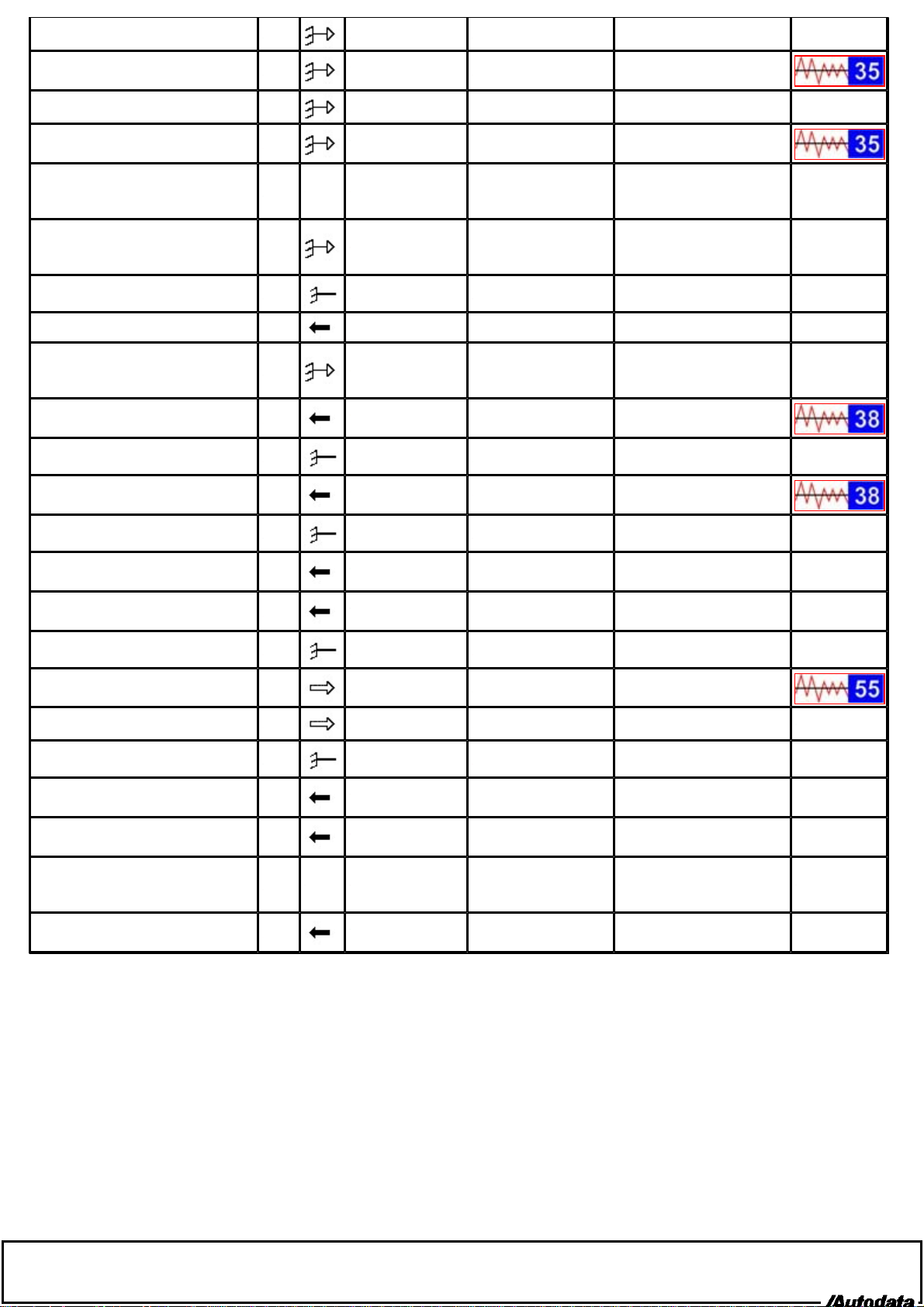
Injector 4 35 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Injector 4 35
Injector 5 34 Ignition ON 11-14 V
Injector 5 34
Instrumentation control module/heater
function control module
Instrumentation control module/heater
function control module - malfunction
indicator signal
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor 30 Ignition ON 0 V
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor 54 Ignition ON - 20°C 3 V
Intake manifold air control relay - 2,4 23
Knock sensor (KS) 1 11
Knock sensor (KS) 1 30 Engine running 0 V
Knock sensor (KS) 2 29
41
51
Engine idling engine hot
Engine idling engine hot
Engine idling accelerate briefly
Engine idling accelerate briefly
2,5-3,5 ms 10 V/2 ms
2,5-3,5 ms 10 V/2 ms
Connected pin - no test
data available or
random digital signal
Connected pin - no test
data available or
random digital signal
Connected pin - no test
data available or
random digital signal
50 mV/1 ms
50 mV/1 ms
Knock sensor (KS) 2 30 Engine running 0 V
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor 7
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor 7
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor 26 Ignition ON 0 V
Tachometer 6 Engine idling 30 Hz 2 V/20 ms
Throttle position (TP) sensor 12 Ignition ON 5 V
Throttle position (TP) sensor 30 Ignition ON 0 V
Throttle position (TP) sensor 53
Throttle position (TP) sensor 53
Transmission control module (TCM) 43
Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) 9
Engine idling engine hot
Engine idling accelerate briefly
Ignition ON throttle closed
Ignition ON throttle fully open
Ignition ON vehicle pushed
0,7-1,3 V
4,2 V briefly
0,1-0,7 V
4-4,8 V
Connected pin - no test
data available or
random digital signal
0 V or 11-14 V
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 20
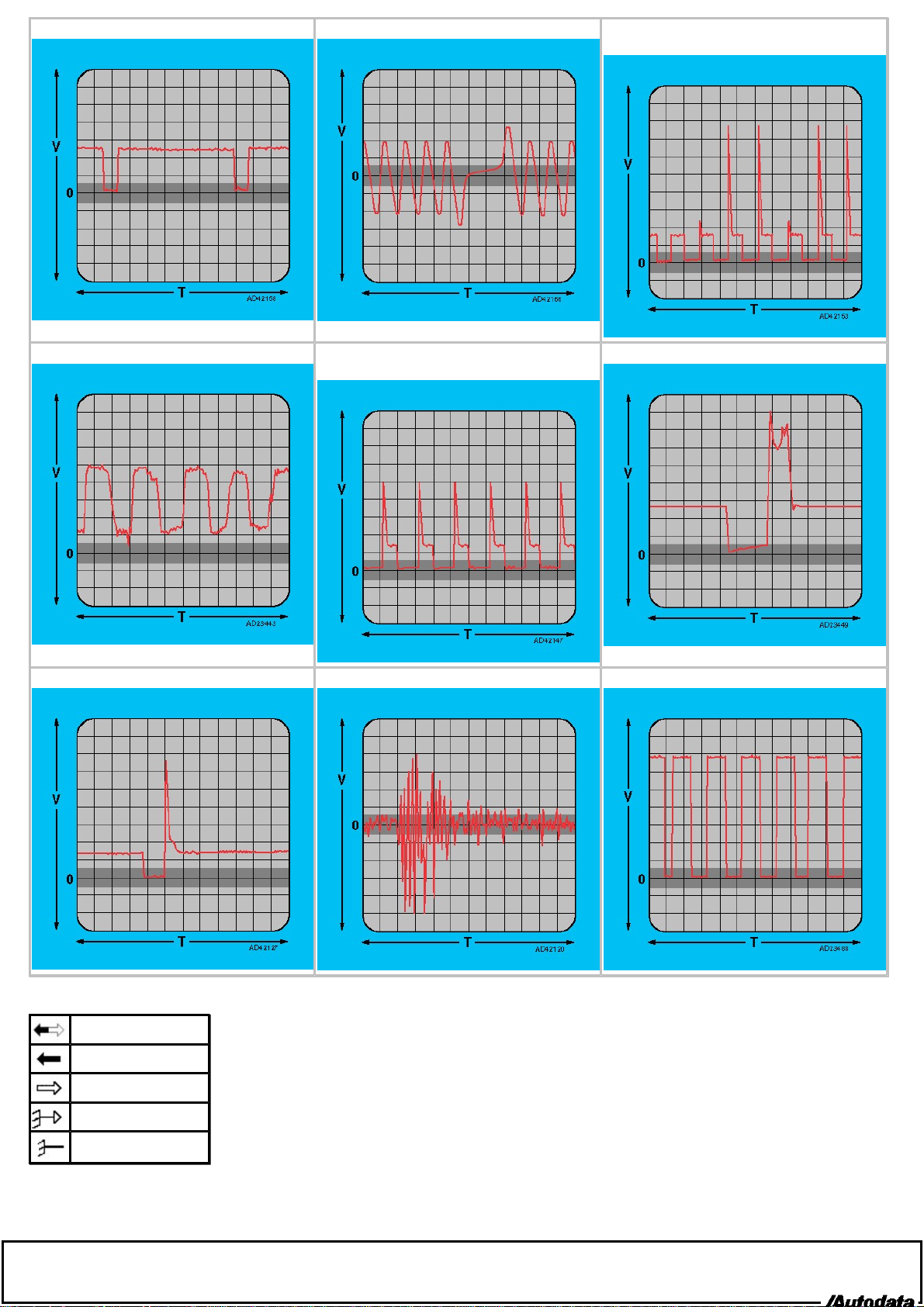
12. Digital, DC, frequency modulated 2. Analogue, AC, frequency modulated
20. Digital, DC, pulse width modulated or
digital, DC, frequency modulated
21. Analogue, DC
35. Digital, DC, pulse width modulated 38. Analogue, AC 55. Digital, DC, frequency modulated
25. Digital, DC, pulse width modulated or
digital, DC, frequency modulated
33. Digital, DC, frequency modulated
input/output signal
input signal
output signal
ECM switched earth
ECM earth circuit
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 21

Battery
replacement
Page 22

Fig. 3
3
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 23

Immobilizer
Page 24

System operation
Arms automatically when ignition key is removed.
Programming
When
Key remote control added or replaced.
System malfunction.
How
NOTE: A maximum of 8 keys can be programmed. NOTE: Immobilizer LED located in centre console.
Obtain all keys.
Insert master key into ignition switch.
Switch ignition ON.
Wait for LED to extinguish.
Switch ignition OFF.
Carry out the following within 10 seconds:
Remove master key.
Insert non programmed key into ignition switch.
Switch ignition ON.
Wait for LED to extinguish.
Switch ignition OFF.
Remove key.
Repeat above procedure to program remaining keys.
After programming last key proceed as follows:
Insert master key into ignition switch.
Switch ignition ON.
Wait for LED to extinguish.
Switch ignition OFF.
Switch ignition ON. Wait approximately 3 seconds.
Ensure immobilizer LED illuminates for approximately 0,7 second and then goes out to indicate correct programming.
3
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 25

Remote alarm
Page 26
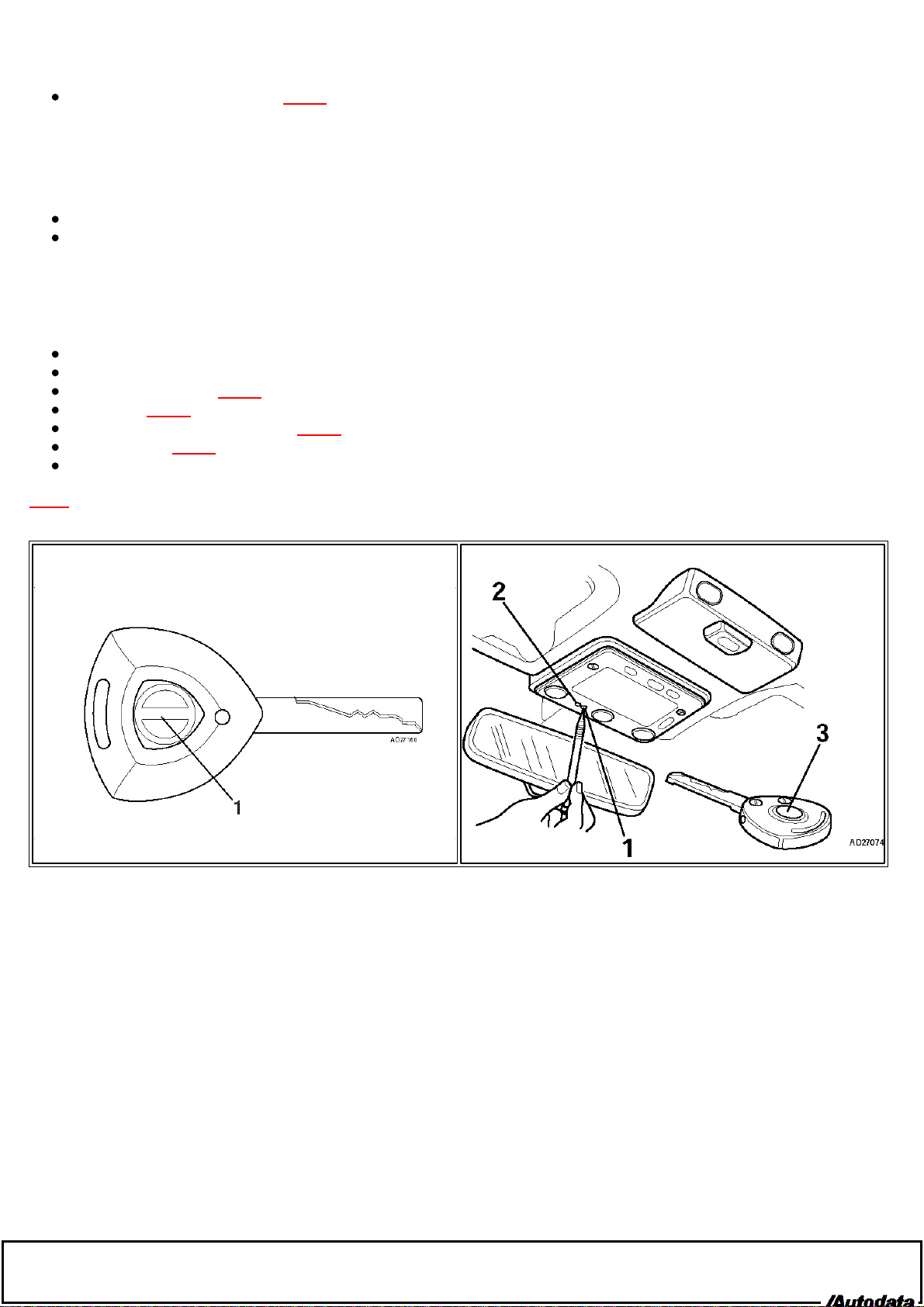
System operation
Pressing key lock/unlock button Fig. 1
[1] activates alarm and central locking.
Programming
When
Key added or replaced.
System malfunction.
How
NOTE: A maximum of 8 keys can be programmed.
Obtain all keys.
Distance from receiver: At least 20 cm.
Press and hold button Fig. 2 [1].
Check LED Fig. 2 [2] flashes.
Press and hold lock/unlock button Fig. 2 [3] until LED [2] illuminates.
Release button Fig. 2 [1].
Repeat above procedure to program remaining keys.
Fig. 2
2
1
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 27

Diagnostic
Page 28

Accessing and erasing
The engine control module (ECM) fault memory can be accessed and erased using diagnostic equipment connected to
the data link connector (DLC).
Trouble code identification
P type
Fault location Probable cause
P0
Refer to EOBD trouble code table -
1
EOBD codes
All EOBD codes starting with P zero have standard meanings irrespective of vehicle make or model.
For EOBD codes, other than those starting P zero, refer to model specific chapters.
The following list covers all P0 codes allocated at the time of publication.
Trouble
code
Fault location Probable cause
P0000 No fault found P0001 Fuel volume regulator control - circuit open Wiring, regulator control solenoid
P0002 Fuel volume regulator control - circuit range/performance Wiring, regulator control solenoid
P0003 Fuel volume regulator control - circuit low Wiring short to earth, regulator control solenoid
P0004 Fuel volume regulator control - circuit high
Wiring open circuit/short to positive, regulator control
solenoid
P0005 Fuel shut-off valve - circuit open Wiring open circuit, fuel shut-off valve
P0006 Fuel shut-off valve - circuit low Wiring short to earth, fuel shut-off valve
P0007 Fuel shut-off valve - circuit high Wiring short to positive, fuel shut-off valve
P0008 Engine position system, bank 1 - engine performance Mechanical fault
P0009 Engine position system, bank 2 - engine performance Mechanical fault
P0010
P0011
P0012
P0013
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator, intake/left/front, bank
1 - circuit malfunction
Camshaft position (CMP), intake/left/front, bank 1 - timing
over-advanced/system performance
Camshaft position (CMP), intake/left/front, bank 1 - timing
over-retarded
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator, intake/left/front, bank
1 - circuit malfunction
Wiring, CMP actuator, ECM
Valve timing, engine mechanical fault, CMP actuator
Valve timing, engine mechanical fault, CMP actuator
Wiring, CMP actuator, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 29
P0014
P0015
P0016
P0017
P0018
P0019
P0020
P0021
P0022
P0023
P0024
P0025
P0026
P0027
P0028
P0029
P0030
P0031
P0032
P0033
P0034
P0035
P0036
P0037
P0038
P0039
P0040
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator, exhaust/right/rear,
bank 1 - timing over-advanced/system performance
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator, exhaust/right/rear,
bank 1 - timing over-retarded
Crankshaft position/camshaft position, bank 1 sensor A correlation
Crankshaft position/camshaft position, bank 1 sensor B correlation
Crankshaft position/camshaft position, bank 2 sensor A correlation
Crankshaft position/camshaft position, bank 2 sensor B correlation
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator, intake/left/front, bank
2 - circuit malfunction
Camshaft position (CMP), intake/left/front, bank 2 - timing
over-advanced/system performance
Camshaft position (CMP), intake/left/front, bank 2 - timing
over-retarded
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator, exhaust/right/rear,
bank 2 - circuit malfunction
Camshaft position (CMP), exhaust/right/rear, bank 2 timing over-advanced/system performance
Camshaft position (CMP), exhaust/right/rear, bank 2 timing over-retarded
Intake valve control solenoid circuit, bank 1 range/performance
Exhaust valve control solenoid circuit, bank 1 range/performance
Intake valve control solenoid circuit, bank 2 range/performance
Exhaust valve control solenoid circuit, bank 2 range/performance
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 1, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 1, heater control circuit low
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 1, heater control circuit high
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve - circuit
malfunction
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve - circuit
low
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve - circuit
high
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 1, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 1, heater control circuit low
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 1, heater control circuit high
Turbo/super charger bypass valve, control circuit range/performance
Oxygen sensor signals swapped, bank 1 sensor 1/bank 2
sensor 1
Valve timing, engine mechanical fault, CMP actuator
Valve timing, engine mechanical fault, CMP actuator
Wiring, CKP sensor, CMP sensor, mechanical fault
Wiring, CKP sensor, CMP sensor, mechanical fault
Wiring, CKP sensor, CMP sensor, mechanical fault
Wiring, CKP sensor, CMP sensor, mechanical fault
Wiring, CMP actuator, ECM
Valve timing, engine mechanical fault, CMP actuator
Valve timing, engine mechanical fault, CMP actuator
Wiring, CMP actuator, ECM
Valve timing, engine mechanical fault, CMP actuator
Valve timing, engine mechanical fault, CMP actuator
Wiring, intake valve control solenoid
Wiring, exhaust valve control solenoid
Wiring, intake valve control solenoid
Wiring, exhaust valve control solenoid
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
Wiring, TC wastegate regulating valve, ECM
Wiring short to earth, TC wastegate regulating valve,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, TC wastegate regulating valve,
ECM
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
Wiring, bypass valve
Wiring
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 30
P0041
P0042
P0043
P0044
Oxygen sensor signals swapped, bank 1 sensor 2/bank 2
sensor 2
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 1, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 1, heater control circuit low
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 1, heater control circuit high
Wiring
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
P0045 Turbo/super charger boost control solenoid - circuit open Wiring, boost control solenoid
P0046
Turbo/super charger boost control solenoid - circuit
range/performance
Wiring, boost control solenoid, mechanical fault
P0047 Turbo/super charger boost control solenoid - circuit low Wiring short to earth, boost control solenoid
P0048 Turbo/super charger boost control solenoid - circuit high Wiring short to positive, boost control solenoid
P0049 Turbo/super charger turbine - over-speed Mechanical fault
P0050
P0051
P0052
P0053
P0054
P0055
P0056
P0057
P0058
P0059
P0060
P0061
P0062
P0063
P0064
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 2, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 2, heater control circuit low
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 2, heater control circuit high
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), bank 1, sensor 1 - heater
resistance
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), bank 1, sensor 2 - heater
resistance
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), bank 1, sensor 3 - heater
resistance
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 2, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 2, heater control heater circuit low
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 2, heater control circuit high
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), bank 2, sensor 1 - heater
resistance
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), bank 2, sensor 2 - heater
resistance
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), bank 2, sensor 3 - heater
resistance
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 2, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 2, heater control circuit low
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 2, heater control circuit high
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
Wiring, HO2S
Wiring, HO2S
Wiring, HO2S
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
Wiring, HO2S
Wiring, HO2S
Wiring, HO2S
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
P0065 Air assisted injector - range/performance problem Air assisted injector
P0066 Air assisted injector - circuit malfunction/circuit low Wiring short to earth, air assisted injector, ECM
P0067 Air assisted injector - circuit high Wiring short to positive, air assisted injector, ECM
P0068
P0069
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor/mass air flow
(MAF) sensor/throttle position correlation
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor/barometric
pressure (BARO) sensor correlation
Wiring, MAP sensor, MAF sensor, mechanical fault
MAP sensor, mechanical fault
P0070 Outside air temperature sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, outside air temperature sensor, ECM
P0071
Outside air temperature sensor - range/performance
problem
Outside air temperature sensor
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 31

P0072 Outside air temperature sensor - low input
P0073 Outside air temperature sensor - high input
P0074 Outside air temperature sensor - circuit intermittent
Wiring short to earth, outside air temperature sensor,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, outside air temperature sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, outside air temperature
sensor, ECM
P0075 Intake valve control solenoid, bank 1 - circuit malfunction Wiring, intake valve control solenoid, ECM
P0076 Intake valve control solenoid, bank 1 - circuit low
P0077 Intake valve control solenoid, bank 1 - circuit high
P0078
Exhaust valve control solenoid, bank 1 - circuit
malfunction
P0079 Exhaust valve control solenoid, bank 1 - circuit low
P0080 Exhaust valve control solenoid, bank 1 - circuit high
Wiring short to earth, intake valve control solenoid,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, intake valve control solenoid,
ECM
Wiring, exhaust valve control solenoid, ECM
Wiring short to earth, exhaust valve control solenoid,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, exhaust valve control solenoid,
ECM
P0081 Intake valve control solenoid, bank 2 - circuit malfunction Wiring, intake valve control solenoid, ECM
P0082 Intake valve control solenoid, bank 2 - circuit low
P0083 Intake valve control solenoid, bank 2 - circuit high
P0084
Exhaust valve control solenoid, bank 2 - circuit
malfunction
P0085 Exhaust valve control solenoid, bank 2 - circuit low
P0086 Exhaust valve control solenoid, bank 2 - circuit high
P0087 Fuel rail/system pressure too low
P0088 Fuel rail/system pressure too high
Wiring short to earth, intake valve control solenoid,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, intake valve control solenoid,
ECM
Wiring, exhaust valve control solenoid, ECM
Wiring short to earth, exhaust valve control solenoid,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, exhaust valve control solenoid,
ECM
Fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, fuel supply pipe
blockage, mechanical fault
Fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, fuel return pipe
blockage, mechanical fault
P0089 Fuel pressure regulator - performance problem Fuel pressure regulator, mechanical fault
P0090 Fuel metering solenoid - open circuit Wiring open circuit, fuel metering solenoid, ECM
P0091 Fuel metering solenoid - short to earth Wiring short to earth, fuel metering solenoid, ECM
P0092 Fuel metering solenoid - short to positive Wiring short to positive, fuel metering solenoid, ECM
P0093 Fuel system leak - large leak detected Wiring, fuel pressure sensor, mechanical fault
P0094 Fuel system leak - small leak detected Wiring, fuel pressure sensor, mechanical fault
P0095 Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor 2 - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, IAT sensor, ECM
P0096
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor 2 - circuit
range/performance
Wiring, poor connection, IAT sensor, ECM
P0097 Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor 2 - circuit low input Wiring short to earth, IAT sensor, ECM
P0098 Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor 2 - circuit high input Wiring short to positive, IAT sensor, ECM
P0099
P0100
P0101
P0102
P0103
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor 2 - circuit
intermittent/erratic
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor/volume air flow (VAF) sensor
- circuit malfunction
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor/volume air flow (VAF) sensor
- range/performance problem
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor/volume air flow (VAF) sensor
- low input
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor/volume air flow (VAF) sensor
- high input
Wiring, poor connection, IAT sensor, ECM
Wiring, MAF/VAF sensor, ECM
Intake leak/blockage, MAF/VAF sensor
Wiring short to earth, MAF/VAF sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, MAF/VAF sensor, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 32

P0104
P0105
P0106
P0107
P0108
P0109
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor/volume air flow (VAF) sensor
- circuit intermittent
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor/barometric
pressure (BARO) sensor - circuit malfunction
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor/barometric
pressure (BARO) sensor - range/performance problem
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor/barometric
pressure (BARO) sensor - low input
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor/barometric
pressure (BARO) sensor - high input
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor/barometric
pressure (BARO) sensor - circuit intermittent
Wiring, poor connection, MAF/VAF sensor, ECM
Wiring, MAP sensor, BARO sensor, ECM
Intake/exhaust leak, wiring, MAP sensor, BARO sensor
Wiring short to earth, MAP sensor, BARO sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, MAP sensor, BARO sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, MAP sensor, BARO sensor,
ECM
P0110 Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, IAT sensor, ECM
P0111
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor - range/performance
problem
IAT sensor
P0112 Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor - low input Wiring short to earth, IAT sensor, ECM
P0113 Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor - high input
Wiring open circuit/short to positive, earth wire
defective, IAT sensor, ECM
P0114 Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, IAT sensor, ECM
P0115
P0116
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor - circuit
malfunction
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor range/performance problem
Wiring, ECT sensor, ECM
Coolant thermostat, poor connection, wiring, ECT
sensor
P0117 Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor - low input Coolant thermostat, wiring short to earth, ECT sensor
P0118 Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor - high input
P0119
P0120
P0120
P0121
P0121
P0122
P0122
P0123
P0123
P0124
P0124
P0125
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor - circuit
intermittent
Throttle position (TP) sensor A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor A - circuit malfunction
Throttle position (TP) switch A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch A - circuit malfunction
Throttle position (TP) sensor A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor A - range/performance problem
Throttle position (TP) switch A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch A - range/performance problem
Throttle position (TP) sensor A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor A - low input
Throttle position (TP) switch A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch A - low input
Throttle position (TP) sensor A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor A - high input
Throttle position (TP) switch A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch A - high input
Throttle position (TP) sensor A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor A - circuit intermittent
Throttle position (TP) switch A/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch A - circuit intermittent
Insufficient coolant temperature for closed loop fuel
control
Coolant thermostat, wiring open circuit/short to positive,
earth wire defective, ECT sensor
Wiring, poor connection, ECT sensor, ECM
Wiring, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring, TP/APP switch, ECM
Accelerator cable adjustment, TP/APP sensor
Accelerator cable adjustment, TP/APP switch
Wiring short to earth, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to earth, TP/APP switch, ECM
Wiring short to positive, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, TP/APP switch, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, TP/APP switch, ECM
Wiring, cooling system, coolant thermostat, ECT sensor
P0126 Insufficient coolant temperature for stable operation Wiring, cooling system, coolant thermostat, ECT sensor
P0127 Intake air temperature too high
Wiring short to earth, IAT sensor 2, mechanical fault,
ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 33

P0128
Coolant thermostat - coolant temperature below
thermostat regulating temperature
Mechanical fault
P0129 Barometric pressure too low Wiring, BARO sensor, mechanical fault
P0130
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 1 - circuit
malfunction
Heating inoperative, poor connection, wiring, HO2S
P0130 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 1 - circuit malfunction Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0131 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 1 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
P0131 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 1 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, O2S, ECM
P0132 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 1 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
P0132 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 1 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, O2S, ECM
P0133 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 1 - slow response Heating inoperative, wiring, HO2S
P0133 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 1 - slow response Wiring, O2S
P0134
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 1 - no activity
detected
Wiring open circuit, heating inoperative, HO2S
P0134 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 1 - no activity detected Wiring, O2S
P0135
P0136
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 1, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 1 - circuit
malfunction
Fuse, wiring, HO2S, ECM
Heating inoperative, wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0136 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 1 - circuit malfunction Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0137 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 1 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
P0137 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 1 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, O2S, ECM
P0138 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 1 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
P0138 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 1 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, O2S, ECM
P0139 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 1 - slow response Heating inoperative, wiring, HO2S
P0139 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 1 - slow response Wiring, O2S
P0140
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 1 - no activity
detected
Wiring, heating inoperative, HO2S, ECM
P0140 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 1 - no activity detected Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0141
P0142
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 1, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 1 - circuit
malfunction
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0143 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 1 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
P0143 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 3, bank 1 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, O2S, ECM
P0144 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 1 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
P0144 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 3, bank 1 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, O2S, ECM
P0145 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 1 - slow response Heating inoperative, wiring, HO2S
P0145 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 3, bank 1 - slow response Wiring, O2S
P0146
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 1 - no activity
detected
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0146 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 3, bank 1 - no activity detected Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0147
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 1, heater control circuit malfunction
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0148 Fuel delivery error Fuel pump/fuel injection pump
P0149 Fuel timing error Fuel pump/fuel injection pump
P0150
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 2 - circuit
malfunction
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0150 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 2 - circuit malfunction Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0151 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 2 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 34

P0151 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 2 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, O2S, ECM
P0152 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 2 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
P0152 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 2 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, O2S, ECM
P0153 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 2 - slow response Heating inoperative, wiring, HO2S
P0153 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 2 - slow response Wiring, O2S
P0154
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 2 - no activity
detected
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0154 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 1, bank 2 - no activity detected Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0155
P0156
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1, bank 2, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 2 - circuit
malfunction
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
Heating inoperative, wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0156 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 2 - circuit malfunction Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0157 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 2 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
P0157 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 2 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, O2S, ECM
P0158 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 2 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
P0158 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 2 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, O2S, ECM
P0159 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 2 - slow response Heating inoperative, wiring, HO2S
P0159 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 2 - slow response Wiring, O2S
P0160
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 2 - no activity
detected
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0160 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 2, bank 2 - no activity detected Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0161
P0162
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 2, bank 2, heater control circuit malfunction
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 2 - circuit
malfunction
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0162 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 3, bank 2 - circuit malfunction Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0163 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 2 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, HO2S, ECM
P0163 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 3, bank 2 - low voltage Exhaust leak, wiring short to earth, O2S, ECM
P0164 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 2 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, HO2S, ECM
P0164 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 3, bank 2 - high voltage Wiring short to positive, O2S, ECM
P0165 Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 2 - slow response Heating inoperative, wiring, HO2S
P0165 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 3, bank 2 - slow response Wiring, O2S
P0166
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 2 - no activity
detected
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0166 Oxygen sensor (O2S) 3, bank 2 - no activity detected Wiring, O2S, ECM
P0167
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 3, bank 2, heater control circuit malfunction
Wiring, HO2S, ECM
P0168 Fuel temperature too high Wiring, fuel temperature sensor, mechanical fault
P0169 Incorrect fuel composition Wiring, fuel composition sensor, mechanical fault
P0170 Fuel trim (FT), bank 1 - malfunction
P0171 System too lean, bank 1
P0172 System too rich, bank 1
P0173 Fuel trim (FT), bank 2 - malfunction
P0174 System too lean, bank 2
Intake leak, AIR system, fuel pressure/pump,
injector(s), EVAP canister purge valve, HO2S
Intake/exhaust leak, AIR system, MAF/VAF sensor, fuel
pressure/pump, injector(s), HO2S
Intake blocked, EVAP canister purge valve, fuel
pressure, EGR system, injector(s), HO2S
Intake leak, AIR system, fuel pressure/pump,
injector(s), EVAP canister purge valve, HO2S
Intake/exhaust leak, fuel pressure/pump, injector(s),
AIR system, hose connection(s)
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 35

P0175 System too rich, bank 2
Intake blocked, EVAP canister purge valve, fuel
pressure, EGR system, injector(s), HO2S
P0176 Fuel composition sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, fuel composition sensor, ECM
P0177 Fuel composition sensor - range/performance problem Fuel composition sensor
P0178 Fuel composition sensor - low input Wiring short to earth, fuel composition sensor, ECM
P0179 Fuel composition sensor - high input Wiring short to positive, fuel composition sensor, ECM
P0180 Fuel temperature sensor A - circuit malfunction Wiring, fuel temperature sensor, ECM
P0181 Fuel temperature sensor A - range/performance problem Fuel temperature sensor
P0182 Fuel temperature sensor A - low input Wiring short to earth, fuel temperature sensor, ECM
P0183 Fuel temperature sensor A - high input Wiring short to positive, fuel temperature sensor, ECM
P0184 Fuel temperature sensor A - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, fuel temperature sensor, ECM
P0185 Fuel temperature sensor B - circuit malfunction Wiring, fuel temperature sensor, ECM
P0186 Fuel temperature sensor B - range/performance problem Fuel temperature sensor
P0187 Fuel temperature sensor B - low input Wiring short to earth, fuel temperature sensor, ECM
P0188 Fuel temperature sensor B - high input Wiring short to positive, fuel temperature sensor, ECM
P0189 Fuel temperature sensor B - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, fuel temperature sensor, ECM
P0190 Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, fuel rail pressure sensor, ECM
P0191
Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor - range/performance
problem
Wiring, FRP sensor
P0192 Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor - low input Wiring short to earth, FRP sensor
P0193 Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor - high input Wiring short to positive, FRP sensor
P0194 Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, FRP sensor
P0195 Engine oil temperature (EOT) sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, EOT sensor, ECM
P0196
Engine oil temperature (EOT) sensor range/performance problem
EOT sensor
P0197 Engine oil temperature (EOT) sensor - low input Wiring short to earth, EOT sensor
P0198 Engine oil temperature (EOT) sensor - high input Wiring short to positive, EOT sensor
P0199 Engine oil temperature (EOT) sensor - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, EOT sensor, ECM
P0200 Injector - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0201 Injector 1 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0202 Injector 2 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0203 Injector 3 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0204 Injector 4 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0205 Injector 5 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0206 Injector 6 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0207 Injector 7 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0208 Injector 8 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0209 Injector 9 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0210 Injector 10 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0211 Injector 11 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0212 Injector 12 - circuit malfunction Wiring, injector, ECM
P0213 Cold start injector 1 - circuit malfunction Wiring, cold start injector, ECM
P0214 Cold start injector 2 - circuit malfunction Wiring, cold start injector, ECM
P0215 Fuel shut-off solenoid - circuit malfunction Wiring, fuel shut-off solenoid, ECM
P0216 Fuel injection timing control - circuit malfunction Wiring, fuel injection timing control solenoid, ECM
P0217 Engine over temperature condition Wiring, cooling system, coolant thermostat, ECT sensor
P0218 Transmission over temperature condition Wiring, TFT sensor, ECM
P0219 Engine over speed condition Incorrect gear change
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 36

P0220
P0220
P0221
P0221
P0222
P0222
P0223
P0223
P0224
P0224
P0225
P0225
P0226
P0226
P0227
P0227
P0228
P0228
P0229
P0229
Throttle position (TP) sensor B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor B - circuit malfunction
Throttle position (TP) switch B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch B - circuit malfunction
Throttle position (TP) sensor B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor B - range/performance problem
Throttle position (TP) switch B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch B - range/performance problem
Throttle position (TP) sensor B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor B - low input
Throttle position (TP) switch B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch B - low input
Throttle position (TP) sensor B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor B - high input
Throttle position (TP) switch B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch B - high input
Throttle position (TP) sensor B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor B - circuit intermittent
Throttle position (TP) switch B/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch B - circuit intermittent
Throttle position (TP) sensor C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor C - circuit malfunction
Throttle position (TP) switch C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch C - circuit malfunction
Throttle position (TP) sensor C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor C - range/performance problem
Throttle position (TP) switch C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch C - range/performance problem
Throttle position (TP) sensor C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor C - low input
Throttle position (TP) switch C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch C - low input
Throttle position (TP) sensor C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor C - high input
Throttle position (TP) switch C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch C - high input
Throttle position (TP) sensor C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor C - circuit intermittent
Throttle position (TP) switch C/accelerator pedal position
(APP) switch C - circuit intermittent
Wiring, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring, TP/APP switch, ECM
Accelerator cable adjustment, TP/APP sensor
Accelerator cable adjustment, TP/APP switch
Wiring short to earth, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to earth, TP/APP switch, ECM
Wiring short to positive, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, TP/APP switch, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, TP/APP switch, ECM
Wiring, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring, TP/APP switch, ECM
Accelerator cable adjustment, TP/APP sensor
Accelerator cable adjustment, TP/APP switch
Wiring short to earth, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to earth, TP/APP switch, ECM
Wiring short to positive, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, TP/APP switch, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, TP/APP sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, TP/APP switch, ECM
P0230 Fuel pump relay - circuit malfunction Wiring, fuel pump relay, ECM
P0231 Fuel pump relay - circuit low Wiring short to earth, fuel pump relay, ECM
P0232 Fuel pump relay - circuit high Wiring short to positive, fuel pump relay, ECM
P0233 Fuel pump relay - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, fuel pump relay, ECM
P0234 Engine boost condition - limit exceeded
P0235 Engine boost condition - limit not reached
P0236
P0237
P0238
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor A, TC system range/performance problem
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor A, TC system low input
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor A, TC system high input
Hose connection(s), wiring, TC wastegate regulating
valve, TC wastegate
Hose connection(s), wiring, TC wastegate regulating
valve, TC wastegate, TC
Intake/exhaust leak, hose connection(s), MAP sensor
Wiring short to earth, MAP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, MAP sensor, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 37

P0239
P0240
P0241
P0242
P0243
P0244
P0245
P0246
P0247
P0248
P0249
P0250
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor B, TC system circuit malfunction
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor B, TC system range/performance problem
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor B, TC system low input
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor B, TC system high input
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve A - circuit
malfunction
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve A range/performance problem
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve A - circuit
low
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve A - circuit
high
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve B - circuit
malfunction
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve B range/performance problem
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve B - circuit
low
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve B - circuit
high
Wiring, MAP sensor, ECM
Intake/exhaust leak, hose connection(s), MAP sensor
Wiring short to earth, MAP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, MAP sensor, ECM
Wiring, TC wastegate regulating valve, ECM
TC wastegate regulating valve
Wiring short to earth, TC wastegate regulating valve,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, TC wastegate regulating valve,
ECM
Wiring, TC wastegate regulating valve, ECM
TC wastegate regulating valve
Wiring short to earth, TC wastegate regulating valve,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, TC wastegate regulating valve,
ECM
P0251 Injection pump A, rotor/cam - circuit malfunction Wiring, injection pump, ECM
P0252 Injection pump A, rotor/cam - range/performance problem Injection pump
P0253 Injection pump A, rotor/cam - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injection pump, ECM
P0254 Injection pump A, rotor/cam - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injection pump, ECM
P0255 Injection pump A, rotor/cam - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, injection pump, ECM
P0256 Injection pump B, rotor/cam - circuit malfunction Wiring, injection pump, ECM
P0257 Injection pump B, rotor/cam - range/performance problem Injection pump
P0258 Injection pump B, rotor/cam - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injection pump, ECM
P0259 Injection pump B, rotor/cam - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injection pump, ECM
P0260 Injection pump B, rotor/cam - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, injection pump, ECM
P0261 Injector 1 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0262 Injector 1 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0263 Cylinder 1 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0264 Injector 2 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0265 Injector 2 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0266 Cylinder 2 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0267 Injector 3 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0268 Injector 3 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0269 Cylinder 3 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0270 Injector 4 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0271 Injector 4 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0272 Cylinder 4 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0273 Injector 5 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0274 Injector 5 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0275 Cylinder 5 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0276 Injector 6 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0277 Injector 6 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 38

P0278 Cylinder 6 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0279 Injector 7 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0280 Injector 7 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0281 Cylinder 7 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0282 Injector 8 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0283 Injector 8 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0284 Cylinder 8 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0285 Injector 9 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0286 Injector 9 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0287 Cylinder 9 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0288 Injector 10 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0289 Injector 10 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0290 Cylinder 10 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0291 Injector 11 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0292 Injector 11 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0293 Cylinder 11 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0294 Injector 12 - circuit low Wiring short to earth, injector, ECM
P0295 Injector 12 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, injector, ECM
P0296 Cylinder 12 - contribution/balance fault Wiring, fuel system, ECM
P0297 Vehicle over-speed condition Wiring, VSS, mechanical fault
P0298 Engine oil temperature too high Wiring, EOT sensor, mechanical fault
P0299 Turbo/super charger - low boost Mechanical fault
P0300 Random/multiple cylinder(s) - misfire detected
P0301 Cylinder 1 - misfire detected
P0302 Cylinder 2 - misfire detected
P0303 Cylinder 3 - misfire detected
P0304 Cylinder 4 - misfire detected
P0305 Cylinder 5 - misfire detected
P0306 Cylinder 6 - misfire detected
P0307 Cylinder 7 - misfire detected
P0308 Cylinder 8 - misfire detected
P0309 Cylinder 9 - misfire detected
P0310 Cylinder 10 - misfire detected
P0311 Cylinder 11 - misfire detected
P0312 Cylinder 12 - misfire detected
Spark plug(s), HT lead(s), injector(s), ignition coil(s),
low compression, wiring
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector, ECT/MAF sensor, ECM
P0313 Misfire detected - low fuel level Fuel system, mechanical fault
P0314 Single cylinder misfire - cylinder not specified
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 39

P0315 Crankshaft position system - variation not learned Engine mechanical fault, wiring
P0316 Misfire detected during start-up - first 1000 revolutions
Engine mechanical fault, wiring, ignition/fuel system,
injector
P0317 Rough road hardware not present Wiring, ECM
P0318 Rough road sensor signal A - circuit malfunction Wiring, rough road sensor A, mechanical fault
P0319 Rough road sensor signal B - circuit malfunction Wiring, rough road sensor B, mechanical fault
P0320
P0321
P0322
P0323
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor/engine speed (RPM)
sensor - circuit malfunction
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor/engine speed (RPM)
sensor - range/performance problem
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor/engine speed (RPM)
sensor - no signal
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor/engine speed (RPM)
sensor - circuit intermittent
Wiring, CKP/RPM sensor, ECM
Air gap, metal particle contamination, insecure
sensor/rotor, wiring, CKP/RPM sensor
Wiring, CKP/RPM sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, CKP/RPM sensor, ECM
P0324 Knock control system error Wiring, poor connection, KS, ECM
P0325 Knock sensor (KS) 1, bank 1 - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, KS
P0326
P0327 Knock sensor (KS) 1, bank 1 - low input
P0328 Knock sensor (KS) 1, bank 1 - high input
Knock sensor (KS) 1, bank 1 - range/performance
problem
Wiring, KS incorrectly tightened, KS
Insecure KS, poor connection, wiring short to earth,
incorrectly tightened, KS, ECM
Wiring short to positive, KS incorrectly tightened, KS,
ECM
P0329 Knock sensor (KS) 1, bank 1 - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, KS, ECM
P0330 Knock sensor (KS) 2, bank 2 - circuit malfunction Wiring, KS, ECM
P0331
P0332 Knock sensor (KS) 2, bank 2 - low input
P0333 Knock sensor (KS) 2, bank 2 - high input
Knock sensor (KS) 2, bank 2 - range/performance
problem
Wiring, KS incorrectly tightened, KS
Insecure KS, poor connection, wiring short to earth, KS
incorrectly tightened, KS, ECM
Wiring short to positive, KS incorrectly tightened, KS,
ECM
P0334 Knock sensor (KS) 2, bank 2 - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, KS, ECM
P0335 Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, CKP sensor, ECM
P0336
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor - range/performance
problem
Insecure sensor/rotor, air gap, wiring, CKP sensor
P0337 Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor - low input Wiring short to earth, CKP sensor, ECM
P0338 Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor - high input Wiring short to positive, CKP sensor, ECM
P0339 Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, CKP sensor, ECM
P0340
P0341
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 1 - circuit
malfunction
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 1 range/performance problem
Wiring, CMP sensor, ECM
Insecure sensor/rotor, air gap, wiring, CMP sensor
P0342 Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 1 - low input Wiring short to earth, CMP sensor, ECM
P0343 Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 1 - high input Wiring short to positive, CMP sensor, ECM
P0344
P0345
P0346
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 1 - circuit
intermittent
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 2 - circuit
malfunction
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 2 range/performance problem
Wiring, poor connection, CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring, CMP sensor, ECM
Insecure sensor/rotor, air gap, wiring, CMP sensor
P0347 Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 2 - low input Wiring short to earth, CMP sensor, ECM
P0348 Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 2 - high input Wiring short to positive, CMP sensor, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 40

P0349
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor A, bank 2 - circuit
intermittent
Wiring, poor connection, CMP sensor, ECM
P0350 Ignition coil, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0351 Ignition coil A, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0352 Ignition coil B, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0353 Ignition coil C, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0354 Ignition coil D, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0355 Ignition coil E, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0356 Ignition coil F, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0357 Ignition coil G, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0358 Ignition coil H, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0359 Ignition coil I, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0360 Ignition coil J, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0361 Ignition coil K, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0362 Ignition coil L, primary/secondary - circuit malfunction Wiring, ignition coil, ECM
P0363 Misfire detected - fuelling disabled Fuel system, mechanical fault
P0365
P0366
P0367
P0368
P0369
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 1 - circuit
malfunction
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 1 - circuit
range/performance
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 1 - circuit low
input
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 1 - circuit high
input
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 1 - circuit
intermittent
Wiring, poor connection, CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, CMP sensor
Wiring short to earth, CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, ECM
P0370 Timing reference, high resolution signal A - malfunction Wiring, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
P0371
P0372
P0373
Timing reference, high resolution signal A - too many
pulses
Timing reference, high resolution signal A - too few
pulses
Timing reference, high resolution signal A - intermittent
erratic pulses
Wiring, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
P0374 Timing reference, high resolution signal A - no pulses Wiring, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
P0375 Timing reference, high resolution signal B - malfunction Wiring, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
P0376
P0377
P0378
Timing reference, high resolution signal B - too many
pulses
Timing reference, high resolution signal B - too few
pulses
Timing reference, high resolution signal B - intermittent
erratic pulses
Wiring, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
P0379 Timing reference, high resolution signal B - no pulses Wiring, CKP/RPM/CMP sensor, ECM
P0380 Glow plugs, circuit A - malfunction Wiring, glow plug relay, fuse, glow plugs, ECM
P0381 Glow plug warning lamp - circuit malfunction Wiring, glow plug warning lamp, ECM
P0382 Glow plugs, circuit B - malfunction Wiring, glow plug relay, glow plugs, ECM
P0385 Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor B - circuit malfunction Wiring, CKP sensor, ECM
P0386
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor B - range/performance
problem
Insecure sensor/rotor, air gap, wiring, CKP sensor
P0387 Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor B - low input Wiring short to earth, CKP sensor, ECM
P0388 Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor B - high input Wiring short to positive, CKP sensor, ECM
P0389 Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor B - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, CKP sensor, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 41

P0390
P0391
P0392
P0393
P0394
P0400
P0401
P0402
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 2 - circuit
malfunction
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 2 - circuit
range/performance
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 2 - circuit low
input
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 2 - circuit high
input
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor B, bank 2 - circuit
intermittent
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system - flow
malfunction
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system - insufficient flow
detected
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system - excessive flow
detected
Wiring, poor connection, CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, CMP sensor
Wiring short to earth, CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, CMP sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, ECM
Hose leak/blockage, basic setting not carried out (if
applicable), wiring, EGR valve, EGR solenoid, ECM
Hose leak/blockage, basic setting not carried out (if
applicable), wiring, EGR valve, EGR solenoid, ECM
Hose leak/blockage, basic setting not carried out (if
applicable), wiring, EGR valve, EGR solenoid, ECM
P0403 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) - circuit malfunction Wiring, EGR solenoid, ECM
P0404
P0405
P0406
P0407
P0408
P0409
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system range/performance problem
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve position sensor A low input
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve position sensor A high input
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve position sensor B low input
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve position sensor B high input
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) sensor A - circuit
malfunction
Hose leak/blockage, wiring, EGR valve/solenoid
Wiring short to earth, EGR valve position sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, EGR valve position sensor,
ECM
Wiring short to earth, EGR valve position sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, EGR valve position sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, EGR sensor, ECM
P0410 Secondary air injection (AIR) system - malfunction Wiring, AIR valve, AIR solenoid, ECM
P0411
P0412
Secondary air injection (AIR) system - incorrect flow
detected
Secondary air injection (AIR) solenoid A - circuit
malfunction
AIR pump, AIR valve, AIR hose(s)
Wiring, AIR solenoid, ECM
P0413 Secondary air injection (AIR) solenoid A - open circuit Wiring open circuit, AIR solenoid, ECM
P0414 Secondary air injection (AIR) solenoid A - short circuit Wiring short circuit, AIR solenoid, ECM
P0415
Secondary air injection (AIR) solenoid B - circuit
malfunction
Wiring, AIR solenoid, ECM
P0416 Secondary air injection (AIR) solenoid B - open circuit Wiring open circuit, AIR solenoid, ECM
P0417 Secondary air injection (AIR) solenoid B - short circuit Wiring short circuit, AIR solenoid, ECM
P0418
P0419
P0420
P0421
P0422
P0423
P0424
Secondary air injection (AIR) pump relay A - circuit
malfunction
Secondary air injection (AIR) pump relay B - circuit
malfunction
Catalytic converter system, bank 1 - efficiency below
threshold
Warm up catalytic converter, bank 1 - efficiency below
threshold
Main catalytic converter, bank 1 - efficiency below
threshold
Heated catalytic converter, bank 1 - efficiency below
threshold
Heated catalytic converter, bank 1 - temperature below
threshold
Wiring, AIR pump relay, ECM
Wiring, AIR pump relay, ECM
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 42

P0425 Catalytic converter temperature sensor, bank 1
P0426
Catalytic converter temperature sensor, bank 1 range/performance
P0427 Catalytic converter temperature sensor, bank 1 - low input
P0428
P0429
P0430
P0431
P0432
P0433
P0434
Catalytic converter temperature sensor, bank 1 - high
input
Catalytic converter heater, bank 1 - control circuit
malfunction
Catalytic converter system, bank 2 - efficiency below
threshold
Warm up catalytic converter, bank 2 - efficiency below
threshold
Main catalytic converter, bank 2 - efficiency below
threshold
Heated catalytic converter, bank 2 - efficiency below
threshold
Heated catalytic converter, bank 2 - temperature below
threshold
P0435 Catalytic converter temperature sensor, bank 2
P0436
Catalytic converter temperature sensor, bank 2 range/performance
P0437 Catalytic converter temperature sensor, bank 2 - low input
P0438
P0439
Catalytic converter temperature sensor, bank 2 - high
input
Catalytic converter heater, bank 2 - control circuit
malfunction
P0440 Evaporative emission (EVAP) system - malfunction
P0441
P0442
P0443
P0444
P0445
P0446
P0447
P0448
P0449
P0450
P0451
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system - incorrect flow
detected
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system - small leak
detected
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge valve circuit malfunction
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge valve - open
circuit
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge valve - short
circuit
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system, vent control circuit malfunction
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system, vent control - open
circuit
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system, vent control - short
circuit
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system, vent valve - circuit
malfunction
Evaporative emission (EVAP) pressure sensor - circuit
malfunction
Evaporative emission (EVAP) pressure sensor range/performance problem
Wiring, poor connection, catalytic converter
temperature sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, catalytic converter
temperature sensor
Wiring short to earth, catalytic converter temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, catalytic converter temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring, relay, ECM
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Catalytic converter, wiring, HO2S 2
Wiring, poor connection, catalytic converter
temperature sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, catalytic converter
temperature sensor
Wiring short to earth, catalytic converter temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, catalytic converter temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring, relay, ECM
Hose connection(s), intake leak, EVAP canister purge
valve
Hose connection(s), intake leak, EVAP canister purge
valve
Hose connection(s), intake leak, EVAP canister, EVAP
canister purge valve
Wiring, EVAP canister purge valve, ECM
Wiring open circuit, EVAP canister purge valve, ECM
Wiring short circuit, EVAP canister purge valve, ECM
Wiring, EVAP canister purge valve, ECM
Wiring open circuit, EVAP canister purge valve, ECM
Wiring short circuit, EVAP canister purge valve, ECM
Wiring, EVAP canister purge valve, ECM
Wiring, EVAP pressure sensor, ECM
EVAP pressure sensor
P0452 Evaporative emission (EVAP) pressure sensor - low input Wiring short to earth, EVAP pressure sensor, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 43

P0453
P0454
P0455
P0456
P0457
P0458
P0459
Evaporative emission (EVAP) pressure sensor - high
input
Evaporative emission (EVAP) pressure sensor - circuit
intermittent
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system - large leak
detected
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system - very small leak
detected
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system - leak detected
(filler cap loose/off)
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system, EVAP valve circuit low
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system, EVAP valve circuit high
Wiring short to positive, EVAP pressure sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, EVAP pressure sensor, ECM
Hose connection(s), intake leak, EVAP canister, EVAP
canister purge valve
Mechanical fault, hose connection(s), EVAP pressure
sensor
Mechanical fault, hose connection(s), EVAP pressure
sensor
Wiring short to earth, EVAP valve
Wiring short to positive, EVAP valve
P0460 Fuel tank level sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, fuel tank level sensor, ECM
P0461 Fuel tank level sensor - range/performance problem Wiring, fuel tank level sensor
P0462 Fuel tank level sensor - low input Wiring short to earth, fuel tank level sensor, ECM
P0463 Fuel tank level sensor - high input Wiring short to positive, fuel tank level sensor, ECM
P0464 Fuel tank level sensor - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, fuel tank level sensor, ECM
P0465
P0466
P0467
P0468
P0469
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge flow sensor
- circuit malfunction
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge flow sensor
- range/performance problem
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge flow sensor
- low input
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge flow sensor
- high input
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge flow sensor
- circuit intermittent
Wiring, EVAP canister purge flow sensor, ECM
EVAP canister purge flow sensor
Wiring short to earth, EVAP canister purge flow sensor,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, EVAP canister purge flow
sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, EVAP canister purge flow
sensor, ECM
P0470 Exhaust gas pressure sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, exhaust gas pressure sensor, ECM
P0471
P0472 Exhaust gas pressure sensor - low input
P0473 Exhaust gas pressure sensor - high input
P0474 Exhaust gas pressure sensor - circuit intermittent
Exhaust gas pressure sensor - range/performance
problem
Exhaust gas pressure sensor
Wiring short to earth, exhaust gas pressure sensor,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, exhaust gas pressure sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, exhaust gas pressure sensor,
ECM
P0475 Exhaust gas pressure control valve - circuit malfunction Wiring, exhaust gas pressure control valve, ECM
P0476
P0477 Exhaust gas pressure control valve - low input
P0478 Exhaust gas pressure control valve - high input
P0479 Exhaust gas pressure control valve - circuit intermittent
Exhaust gas pressure control valve - range/performance
problem
Exhaust gas pressure control valve
Wiring short to earth, exhaust gas pressure control
valve, ECM
Wiring short to positive, exhaust gas pressure control
valve, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, exhaust gas pressure control
valve, ECM
P0480 Engine coolant blower motor 1 - circuit malfunction Wiring, engine coolant blower motor, ECM
P0481 Engine coolant blower motor 2 - circuit malfunction Wiring, engine coolant blower motor, ECM
P0482 Engine coolant blower motor 3 - circuit malfunction Wiring, engine coolant blower motor, ECM
P0483
Engine coolant blower motor, rationality check malfunction
Wiring, engine coolant blower motor, ECM
P0484 Engine coolant blower motor - circuit over current Wiring, engine coolant blower motor, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 44

P0485
P0486
P0487
P0488
Engine coolant blower motor, power/earth - circuit
malfunction
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve position sensor B circuit malfunction
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system, throttle position
control - circuit malfunction
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system, throttle position
control - range/performance
Wiring, engine coolant blower motor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, EGR valve position sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, ECM
P0489 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system - circuit low Wiring short to earth, EGR valve
P0490 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system - circuit high Wiring short to positive, EGR valve
P0491
P0492
Secondary air injection (AIR) system, bank 1 malfunction
Secondary air injection (AIR) system, bank 2 malfunction
Wiring, AIR solenoid, hose connections, mechanical
fault
Wiring, AIR solenoid, hose connections, mechanical
fault
P0493 Engine coolant blower motor over-speed (clutch locked) Blower motor clutch, mechanical fault
P0494 Engine coolant blower motor speed - low Wiring, relay, blower motor, mechanical fault
P0495 Engine coolant blower motor speed - high Wiring, relay, blower motor, mechanical fault
P0496 Evaporative emission (EVAP) system - high purge flow Wiring, EVAP valve, mechanical fault
P0497 Evaporative emission (EVAP) system - low purge flow Wiring, EVAP valve, hoses blocked, mechanical fault
P0498
P0499
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system, vent control circuit low
Evaporative emission (EVAP) system, vent control circuit high
Wiring short to earth, EVAP valve
Wiring short to positive, EVAP valve
P0500 Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - circuit malfunction Wiring, VSS, ECM
P0501
Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - range/performance
problem
Wiring, speedometer, VSS, CAN data bus
P0502 Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - low input Wiring short to earth, VSS, ECM
P0503
Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - intermittent/erratic/high
input
Wiring, poor connection, other connected system,
instrument panel, VSS
P0504 Brake switch - A/B correlation Wiring, mechanical fault
P0505 Idle speed control (ISC) system - malfunction
P0506
P0507
Idle speed control (ISC) system - rpm lower than
expected
Idle speed control (ISC) system - rpm higher than
expected
Wiring, ISC actuator/IAC valve, throttle motor, throttle
valve tight/sticking, ECM
Wiring, ISC actuator/IAC valve, throttle motor, throttle
valve tight/sticking, ECM
Wiring, ISC actuator/IAC valve, throttle motor, throttle
valve tight/sticking, ECM
P0508 Idle air control (IAC) - circuit low Wiring short to earth, IAC valve, ECM
P0509 Idle air control (IAC) - circuit high Wiring short to positive, IAC valve, ECM
P0510 Closed throttle position (CTP) switch - circuit malfunction Wiring, CTP switch, ECM
P0511 Idle air control (IAC) - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, IAC valve, ECM
P0512 Starter request circuit - malfunction Wiring, immobilizer system, relay
P0513 Incorrect immobilizer key Immobilizer system
P0514 Battery temperature sensor - circuit range/performance Wiring, poor connection, battery temperature sensor
P0515 Battery temperature sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, battery temperature sensor
P0516 Battery temperature sensor - circuit low Wiring short to earth, battery temperature sensor, ECM
P0517 Battery temperature sensor - circuit high
Wiring short to positive, battery temperature sensor,
ECM
P0518 Idle air control (IAC) - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, IAC valve, ECM
P0519 Idle air control (IAC) - circuit performance Wiring, poor connection, IAC valve, ECM
P0520 Engine oil pressure sensor/switch - circuit malfunction Wiring, engine oil pressure sensor/switch, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 45

P0521
P0522 Engine oil pressure sensor/switch - low voltage
P0523 Engine oil pressure sensor/switch - high voltage
Engine oil pressure sensor/switch - range/performance
problem
Engine oil pressure sensor/switch
Wiring short to earth, engine oil pressure sensor/switch,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, engine oil pressure
sensor/switch, ECM
P0524 Engine oil pressure too low Mechanical fault
P0525
P0526
P0527
P0528 Engine coolant blower motor speed sensor - no signal
P0529
Cruise control system, actuator control - circuit
range/performance
Engine coolant blower motor speed sensor - circuit
malfunction
Engine coolant blower motor speed sensor - circuit
range/performance
Engine coolant blower motor speed sensor - circuit
intermittent
Wiring, poor connection, cruise control actuator
Wiring, poor connection, blower motor speed sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, blower motor speed sensor
Wiring, poor connection, blower motor speed sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, ECM
P0530 AC refrigerant pressure sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, AC refrigerant pressure sensor, ECM
P0531
P0532 AC refrigerant pressure sensor - low input
AC refrigerant pressure sensor - range/performance
problem
AC refrigerant pressure sensor
AC refrigerant pressure too low (incorrectly charged),
wiring, AC refrigerant pressure sensor, ECM
AC refrigerant pressure too high (cooling
P0533 AC refrigerant pressure sensor - high input
fault/incorrectly charged), wiring, AC refrigerant
pressure sensor, ECM
P0534 AC refrigerant charge loss AC leak, wiring, AC refrigerant pressure sensor
P0535 AC evaporator temperature sensor - circuit malfunction
P0536
AC evaporator temperature sensor - circuit
range/performance
P0537 AC evaporator temperature sensor - circuit low
P0538 AC evaporator temperature sensor - circuit high
P0539 AC evaporator temperature sensor - circuit intermittent
Wiring, poor connection, AC evaporator temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, AC evaporator temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring short to earth, AC evaporator temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, AC evaporator temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, AC evaporator temperature
sensor, ECM
P0540 Intake air heater A - circuit malfunction Wiring, relay, intake air heater
P0541 Intake air heater A - circuit low Wiring short to earth, intake air heater
P0542 Intake air heater A - circuit high Wiring short to positive, intake air heater
P0543 Intake air heater A - circuit open Wiring, intake air heater
P0544
P0545
P0546
P0547
P0548
P0549
P0550
Exhaust gas recirculation temperature (EGRT) sensor,
bank 1 - circuit malfunction
Exhaust gas recirculation temperature (EGRT) sensor,
bank 1 - low input
Exhaust gas recirculation temperature (EGRT) sensor,
bank 1 - high input
Exhaust gas temperature sensor, bank 2 sensor 1 circuit malfunction
Exhaust gas temperature sensor, bank 2 sensor 1 circuit low
Exhaust gas temperature sensor, bank 2 sensor 1 circuit high
Power steering pressure (PSP) sensor/switch - circuit
malfunction
Wiring, EGRT sensor, ECM
Wiring short to earth, EGRT sensor, ECM
Wiring short to positive, EGRT sensor, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, exhaust gas temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring short to earth, exhaust gas temperature sensor,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, exhaust gas temperature
sensor, ECM
Wiring, PSP sensor/switch, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 46

P0551
Power steering pressure (PSP) sensor/switch range/performance problem
PAS system, PSP sensor/switch
P0552 Power steering pressure (PSP) sensor/switch - low input Wiring short to earth, PSP sensor/switch, ECM
P0553 Power steering pressure (PSP) sensor/switch - high input Wiring short to positive, PSP sensor/switch, ECM
P0554
P0555 Brake servo pressure sensor - circuit malfunction
P0556 Brake servo pressure sensor - circuit range/performance
P0557 Brake servo pressure sensor - circuit low input
P0558 Brake servo pressure sensor - circuit high input
P0559 Brake servo pressure sensor - circuit intermittent
Power steering pressure (PSP) sensor/switch - circuit
intermittent
Wiring, poor connection, PSP sensor/switch, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, brake servo pressure sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, brake servo pressure sensor,
ECM
Wiring short to earth, brake servo pressure sensor,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, brake servo pressure sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, brake servo pressure sensor,
ECM
P0560 System voltage - malfunction Wiring, poor connection, battery, alternator
P0561 System voltage - unstable Wiring, poor connection, battery, alternator
P0562 System voltage - low Wiring, poor connection, battery, alternator
P0563 System voltage - high Alternator
P0564
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input A circuit malfunction
Wiring, poor connection, multi-function switch,
mechanical fault
P0565 Cruise control master switch, ON signal - malfunction Wiring, cruise control master switch, ECM
P0566 Cruise control master switch, OFF signal - malfunction Wiring, cruise control master switch, ECM
P0567
Cruise control selector switch, RESUME signal malfunction
Wiring, cruise control selector switch, ECM
P0568 Cruise control master switch, SET signal - malfunction Wiring, cruise control master switch, ECM
P0569
Cruise control selector switch, COAST signal malfunction
Wiring, cruise control selector switch, ECM
P0570 Cruise control system, APP sensor signal - malfunction Wiring, APP sensor, ECM
P0571 Cruise/brake switch A - circuit malfunction Wiring, cruise/brake switch, ECM
P0572 Cruise/brake switch A - circuit low Wiring short to earth, cruise/brake switch, ECM
P0573 Cruise/brake switch A - circuit high Wiring short to positive, cruise/brake switch, ECM
P0574 Cruise control system - vehicle speed too high Mechanical fault
P0575 Cruise control system - input circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, mechanical fault, ECM
P0576 Cruise control system - input circuit low Wiring short to earth
P0577 Cruise control system - input circuit high Wiring short to positive
P0578
P0579
P0580
P0581
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input A circuit stuck
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input A circuit range/performance
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input A circuit low
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input A circuit high
Wiring, poor connection, multi-function switch,
mechanical fault
Wiring, poor connection, multi-function switch,
mechanical fault
Wiring short to earth, multi-function switch, mechanical
fault
Wiring short to positive, multi-function switch,
mechanical fault
P0582 Cruise control system, vacuum control - circuit open Wiring, vacuum control solenoid
P0583 Cruise control system, vacuum control - circuit low Wiring short to earth, vacuum control solenoid
P0584 Cruise control system, vacuum control - circuit high Wiring short to positive, vacuum control solenoid
P0585
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input A/B correlation
Mechanical fault
P0586 Cruise control system, vent control - circuit open Wiring, vent control solenoid
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 47

P0587 Cruise control system, vent control - circuit low Wiring short to earth, vent control solenoid
P0588 Cruise control system, vent control - circuit high Wiring short to positive, vent control solenoid
P0589
P0590
P0591
P0592
P0593
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input B circuit malfunction
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input B circuit stuck
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input B circuit range/performance
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input B circuit low
Cruise control system, multi-function switch input B circuit high
Wiring, poor connection, multi-function switch,
mechanical fault
Wiring, poor connection, multi-function switch,
mechanical fault
Wiring, poor connection, multi-function switch,
mechanical fault
Wiring short to earth, multi-function switch, mechanical
fault
Wiring short to positive, multi-function switch,
mechanical fault
P0594 Cruise control system, actuator control - circuit open Wiring, actuator
P0595 Cruise control system, actuator control - circuit low Wiring short to earth, actuator
P0596 Cruise control system, actuator control - circuit high Wiring short to positive, actuator
P0597 Thermostat heater control system - circuit open Wiring, relay, thermostat heater
P0598 Thermostat heater control system - circuit low Wiring short to earth, relay, thermostat heater
P0599 Thermostat heater control system - circuit high Wiring short to positive, relay, thermostat heater
P0600 CAN data bus - malfunction Wiring, connected system, ECM
P0601 Engine control module (ECM) - memory check sum error ECM
P0602 Engine control module (ECM) - programming error ECM
P0603 Engine control module (ECM) - KAM error ECM
P0604 Engine control module (ECM) - RAM error ECM
P0605 Engine control module (ECM) - ROM error ECM
P0606
Engine control module (ECM)/powertrain control module
(PCM) - processor fault
ECM/PCM
P0607 Control module - performance problem Control module
P0608
P0609
Engine control module (ECM), VSS output A malfunction
Engine control module (ECM), VSS output B malfunction
ECM
ECM
P0610 Control module - vehicle options error Control module
P0611 Fuel injector control module - performance problem Fuel injector control module
P0612 Fuel injector control module - control relay circuit Wiring, relay, fuel injector control module
P0613 Transmission control module (TCM) - processor error TCM
P0614
Engine control module (ECM)/transmission control
module (TCM) - mismatch
ECM/TCM
P0615 Starter motor relay - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, starter motor relay, ECM
P0616 Starter motor relay - circuit low Wiring short to earth, starter motor relay, ECM
P0617 Starter motor relay - circuit high Wiring short to positive, starter motor relay, ECM
P0618 Alternative fuel control module - KAM error Alternative fuel control module
P0619 Alternative fuel control module - RAM/ROM error Alternative fuel control module
P0620 Alternator, control - circuit malfunction Wiring, alternator, battery, ECM
P0621 Alternator warning lamp - circuit malfunction Wiring, alternator warning lamp, ECM
P0622 Alternator, field control - circuit malfunction Wiring, alternator, battery, ECM
P0623 Generator control lamp - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, bulb, ECM
P0624 Filler cap control lamp - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, bulb, ECM
P0625 Generator field terminal - circuit low Wiring short to earth, generator
P0626 Generator field terminal - circuit high Wiring short to positive, generator
P0627 Fuel pump control - circuit open Wiring, relay, fuel pump
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 48

P0628 Fuel pump control - circuit low Wiring short to earth, relay, fuel pump
P0629 Fuel pump control - circuit high Wiring short to positive, relay, fuel pump
P0630 VIN not programmed or mismatch - ECM/PCM ECM/PCM
P0631 VIN not programmed or mismatch - TCM TCM
P0632 Odometer not programmed - ECM/PCM ECM/PCM
P0633 Immobilizer key not programmed - ECM/PCM ECM/PCM
P0634 PCM/ECM/TCM - internal temperature too high Mechanical fault, PCM/ECM/TCM
P0635 Power steering control - circuit malfunction
P0636 Power steering control - circuit low
P0637 Power steering control - circuit high
P0638
Throttle actuator control, bank 1 - range/performance
problem
Wiring, poor connection, power steering pressure
(PSP) switch, ECM
Wiring short to earth, power steering pressure
(PSP)switch, ECM
Wiring short to positive, power steering pressure
(PSP)switch, ECM
Basic setting not carried out (if applicable), ISC
actuator/throttle motor, APP sensor
P0639 Throttle actuator control, bank 2 - range/performance Wiring, throttle control unit
P0640 Intake air heater control - circuit malfunction Wiring, relay, intake air heater
P0641 Sensor reference voltage A - circuit open Wiring short to positive
P0642 Engine control module (ECM), knock control - defective ECM
P0643 Sensor reference voltage A - circuit high Wiring short to positive
P0644 Driver display, serial communication - circuit malfunction Wiring, CAN data bus, ECM
P0645 Air conditioning (AC) Wiring, AC system
P0646 AC compressor clutch relay - circuit low Wiring short to earth, AC compressor clutch relay
P0647 AC compressor clutch relay - circuit high Wiring short to positive, AC compressor clutch relay
P0648 Immobilizer control lamp - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, bulb, ECM
P0649 Cruise control lamp - circuit Wiring, poor connection, bulb, ECM
P0650 Malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) - circuit malfunction Wiring, MIL, ECM
P0651 Sensor reference voltage B - circuit open Wiring short to positive
P0652 Sensor reference voltage B - circuit low Wiring short to earth
P0653 Sensor reference voltage B - circuit high Wiring short to positive
P0654 Engine rpm, output - circuit malfunction Wiring, ECM
P0655 Engine hot lamp output - circuit malfunction Wiring, engine hot lamp, ECM
P0656 Fuel level output - circuit malfunction Wiring, ECM
P0657 Actuator supply voltage - circuit open Wiring
P0658 Actuator supply voltage - circuit low Wiring short to earth, actuator
P0659 Actuator supply voltage - circuit high Wiring short to positive, actuator
P0660 Intake manifold air control solenoid, bank 1 - circuit open Wiring, intake manifold air control solenoid
P0661 Intake manifold air control solenoid, bank 1 - circuit low
P0662 Intake manifold air control solenoid, bank 1 - circuit high
Wiring short to earth, intake manifold air control
solenoid
Wiring short to positive, intake manifold air control
solenoid
P0663 Intake manifold air control solenoid, bank 2 - circuit open Wiring, intake manifold air control solenoid
P0664 Intake manifold air control solenoid, bank 2 - circuit low
Wiring short to earth, intake manifold air control
solenoid
P0665 Intake manifold air control solenoid, bank 2 - circuit high Wiring short to positive, intake manifold
P0666
P0667
PCM/ECM/TCM internal temperature sensor - circuit
malfunction
PCM/ECM/TCM internal temperature sensor range/performance
Wiring, poor connection, internal temperature sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, internal temperature sensor,
ECM
P0668 PCM/ECM/TCM internal temperature sensor - circuit low Wiring short to earth, internal temperature sensor, ECM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 49

P0669 PCM/ECM/TCM internal temperature sensor - circuit high
P0670 Glow plug control module - circuit malfunction
P0671 Glow plug, cylinder 1 - circuit malfunction
P0672 Glow plug, cylinder 2 - circuit malfunction
P0673 Glow plug, cylinder 3 - circuit malfunction
P0674 Glow plug, cylinder 4 - circuit malfunction
P0675 Glow plug, cylinder 5 - circuit malfunction
P0676 Glow plug, cylinder 6 - circuit malfunction
P0677 Glow plug, cylinder 7 - circuit malfunction
P0678 Glow plug, cylinder 8 - circuit malfunction
P0679 Glow plug, cylinder 9 - circuit malfunction
P0680 Glow plug, cylinder 10 - circuit malfunction
P0681 Glow plug, cylinder 11 - circuit malfunction
P0682 Glow plug, cylinder 12 - circuit malfunction
P0683
P0684
Glow plug control module/ECM/PCM communication malfunction
Glow plug control module/ECM/PCM communication range/performance
Wiring short to positive, internal temperature sensor,
ECM
Wiring, poor connection, glow plug control module,
glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, relay, glow plug control
module, glow plug, ECM
Wiring, poor connection, glow plug control module,
ECM/PCM
Wiring, poor connection, glow plug control module,
ECM/PCM
P0685 ECM/PCM power relay - circuit open Wiring, ECM/PCM power relay
P0686 ECM/PCM power relay - circuit low Wiring short to earth, ECM/PCM power relay, ECM
P0687 Engine control relay - short to earth Wiring short to earth, engine control relay, ECM
P0688 Engine control relay - short to positive Wiring short to positive, engine control relay, ECM
P0689 ECM/PCM power relay - sense circuit low Wiring short to earth, ECM/PCM power relay, ECM
P0690 ECM/PCM power relay - sense circuit high Wiring short to positive, ECM/PCM power relay, ECM
P0691 Engine coolant blower motor 1 - short to earth
P0692 Engine coolant blower motor 1 - short to positive
P0693 Engine coolant blower motor 2 - short to earth
P0694 Engine coolant blower motor 2 - short to positive
Wiring short to earth, engine coolant blower motor,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, engine coolant blower motor,
ECM
Wiring short to earth, engine coolant blower motor,
ECM
Wiring short to positive, engine coolant blower motor,
ECM
P0695 Engine coolant blower motor 3 - control circuit low Wiring short to earth, blower motor
P0696 Engine coolant blower motor 3 - control circuit high Wiring short to positive, blower motor
P0697 Sensor reference voltage C - circuit open Wiring short to positive
P0698 Sensor reference voltage C - circuit low Wiring short to earth
P0699 Sensor reference voltage C - circuit high Wiring short to positive
P0700 Transmission control system - malfunction Wiring, ECM/PCM/TCM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 50

P0701
Transmission control system - range/performance
problem
Wiring, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0702 Transmission control system - electrical Wiring, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0703 Torque converter/brake switch B - circuit malfunction Wiring, torque converter/brake switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0704 Clutch pedal position (CPP) switch - circuit malfunction Wiring, CPP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0705
P0706
P0707 Transmission range (TR) sensor/switch - low input
P0708 Transmission range (TR) sensor/switch - high input
P0709
P0710
P0711
Transmission range (TR) sensor/switch, PRNDL input circuit malfunction
Transmission range (TR) sensor/switch range/performance problem
Transmission range (TR) sensor/switch - circuit
intermittent
Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor range/performance problem
Wiring, TR sensor/switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, TR sensor/switch
Wiring short to earth, TR sensor/switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring short to positive, TR sensor/switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TR sensor/switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, TFT sensor, ECM, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, TFT sensor
P0712 Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor - low input Wiring short to earth, TFT sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0713 Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor - high input Wiring short to positive, TFT sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0714
Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor - circuit
intermittent
Wiring, poor connection, TFT sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0715 Turbine shaft speed (TSS) sensor - circuit malfunction Wiring, TSS sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0716
Turbine shaft speed (TSS) sensor - range/performance
problem
Wiring, TSS sensor
P0717 Turbine shaft speed (TSS) sensor - no signal Wiring, TSS sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0718 Turbine shaft speed (TSS) sensor - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, TSS sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0719 Torque converter/brake switch B - circuit low
Wiring short to earth, torque converter/brake switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0720 Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - circuit malfunction Wiring, VSS, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0721
Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - range/performance
problem
Wiring, VSS
P0722 Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - no signal Wiring, VSS, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0723 Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, VSS, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0724 Torque converter/brake switch B - circuit high
Wiring short to positive, torque converter/brake switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0725 Engine RPM input - circuit malfunction Wiring, CKP/RPM sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0726 Engine RPM input - range/performance problem Wiring, CKP/RPM sensor
P0727 Engine RPM input - no signal Wiring, CKP/RPM sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0728 Engine RPM input - circuit intermittent
P0730 Incorrect gear ratio
P0731 Gear 1 - incorrect ratio
P0732 Gear 2 - incorrect ratio
P0733 Gear 3 - incorrect ratio
P0734 Gear 4 - incorrect ratio
Wiring, poor connection, CKP/RPM sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, TR sensor/switch, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Wiring, TR sensor/switch, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Wiring, TR sensor/switch, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Wiring, TR sensor/switch, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Wiring, TR sensor/switch, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 51

P0735 Gear 5 - incorrect ratio
P0736 Reverse - incorrect ratio
Wiring, TR sensor/switch, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Wiring, TR sensor/switch, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
P0737 TCM engine speed - output circuit Wiring, TCM
P0738 TCM engine speed - output circuit low Wiring, TCM
P0739 TCM engine speed - output circuit high Wiring, TCM
P0740
P0741
Torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid - circuit
malfunction
Torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid - performance or
stuck off
Wiring, TCC solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, TCC solenoid
P0742 Torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid - stuck on Wiring, TCC solenoid
P0743 Torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid - electrical Wiring, TCC solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0744
P0745
P0746
Torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid - circuit
intermittent
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid - performance
or stuck off
Wiring, poor connection, TCC solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, TFP solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, TFP solenoid
P0747 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid - stuck on Wiring, TFP solenoid
P0748 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid - electrical Wiring, TFP solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0749
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid - circuit
intermittent
Wiring, poor connection, TFP solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0750 Shift solenoid (SS) A - circuit malfunction Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0751 Shift solenoid (SS) A - performance or stuck off Wiring, shift solenoid
P0752 Shift solenoid (SS) A - stuck on Wiring, shift solenoid
P0753 Shift solenoid (SS) A - electrical Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0754 Shift solenoid (SS) A - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0755 Shift solenoid (SS) B - circuit malfunction Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0756 Shift solenoid (SS) B - performance or stuck off Wiring, shift solenoid
P0757 Shift solenoid (SS) B - stuck on Wiring, shift solenoid
P0758 Shift solenoid (SS) B - electrical Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0759 Shift solenoid (SS) B - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0760 Shift solenoid (SS) C - circuit malfunction Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0761 Shift solenoid (SS) C - performance or stuck off Wiring, shift solenoid
P0762 Shift solenoid (SS) C - stuck on Wiring, shift solenoid
P0763 Shift solenoid (SS) C - electrical Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0764 Shift solenoid (SS) C - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0765 Shift solenoid (SS) D - circuit malfunction Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0766 Shift solenoid (SS) D - performance or stuck off Wiring, shift solenoid
P0767 Shift solenoid (SS) D - stuck on Wiring, shift solenoid
P0768 Shift solenoid (SS) D - electrical Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0769 Shift solenoid (SS) D - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0770 Shift solenoid (SS) E - circuit malfunction Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0771 Shift solenoid (SS) E - performance or stuck off Wiring, shift solenoid
P0772 Shift solenoid (SS) E - stuck on Wiring, shift solenoid
P0773 Shift solenoid (SS) E - electrical Wiring, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0774 Shift solenoid (SS) E - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0775 Pressure control solenoid B - malfunction Pressure control solenoid
P0776 Pressure control solenoid B - performance or stuck off Wiring, pressure control solenoid
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 52

P0777 Pressure control solenoid B - stuck on Wiring, pressure control solenoid
P0778 Pressure control solenoid B - electrical malfunction Wiring, pressure control solenoid
P0779 Pressure control solenoid B - circuit intermittent Wiring, poor connection, pressure control solenoid
P0780 Gear selection - shift malfunction
P0781 Gear selection, 1-2 - shift malfunction
P0782 Gear selection, 2-3 - shift malfunction
P0783 Gear selection, 3-4 - shift malfunction
P0784 Gear selection, 4-5 - shift malfunction
Wiring, TR sensor, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Wiring, TR sensor, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Wiring, TR sensor, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Wiring, TR sensor, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
Wiring, TR sensor, shift solenoids, transmission
mechanical fault
P0785 Shift/timing solenoid - circuit malfunction Wiring, shift/timing solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0786 Shift/timing solenoid - range/performance problem Wiring, shift/timing solenoid
P0787 Shift/timing solenoid - low
P0788 Shift/timing solenoid - high
P0789 Shift/timing solenoid - intermittent
P0790 Transmission mode selection switch - circuit malfunction
P0791 Intermediate shaft speed sensor - circuit malfunction
P0792
Intermediate shaft speed sensor - range/performance
problem
P0793 Intermediate shaft speed sensor - no signal
P0794
P0795
P0796
Intermediate shaft speed sensor - intermittent circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid C - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid C performance or stuck off
P0797 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid C - stuck on
P0798
P0799
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid C - electrical
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) solenoid C intermittent circuit malfunction
Wiring short to earth, shift/timing solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring short to positive, shift/timing solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, shift/timing solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, transmission mode selection switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, intermediate shaft speed
sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, intermediate shaft speed
sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, short to earth, intermediate
shaft speed sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, intermediate shaft speed
sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0800 Transfer box control system, MIL request - malfunction Wiring, mechanical fault
P0801 Reverse inhibit circuit - malfunction Wiring, poor connection
P0802 Transmission control system, MIL request - circuit open Wiring, mechanical fault
P0803 1-4 Upshift (Skip shift) solenoid - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, upshift solenoid
P0804 1-4 Upshift (Skip shift) warning lamp - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection
P0805 Clutch position sensor - circuit malfunction
P0806 Clutch position sensor - range/performance problem
P0807 Clutch position sensor - low input
Wiring, poor connection, clutch position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, clutch position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, clutch position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 53

P0808 Clutch position sensor - high input
P0809 Clutch position sensor - intermittent circuit malfunction
Wiring, short to positive, clutch position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, clutch position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0810 Clutch position control error Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0811 Excessive clutch slip
Wiring, poor connection, mechanical fault,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0812 Reverse gear - input circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0813 Reverse gear - output circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0814 Transmission range (TR) display - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, TR sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0815 Upshift switch - circuit malfunction
P0816 Downshift switch - circuit malfunction
Wiring, poor connection, upshift switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, downshift switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0817 Starter disable circuit - malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0818 Driveline disconnect switch - circuit malfunction
Wiring, poor connection, upshift switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0819 Up/down shift switch to transmission range correlation Wiring, poor connection, TR sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0820 Gear lever X-Y position sensor - circuit malfunction
P0821 Gear lever X position sensor - circuit malfunction
P0822 Gear lever Y position sensor - circuit malfunction
P0823 Gear lever X position sensor - circuit intermittent
P0824 Gear lever Y position sensor - circuit intermittent
P0825 Gear lever push-pull switch - circuit malfunction
Wiring, poor connection, gear lever position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, gear lever position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, gear lever position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, gear lever position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, gear lever position sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, gear lever push-pull switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0826 Up/down shift switch - input circuit Wiring, up/down shift switch
P0827 Up/down shift switch - input circuit low Wiring short to earth, up/down shift switch
P0828 Up/down shift switch - input circuit high Wiring short to positive, up/down shift switch
P0829 5-6 Upshift Mechanical fault
P0830 Clutch pedal position (CPP) switch A - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, CPP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0831 Clutch pedal position (CPP) switch A - low input Wiring, short to earth, CPP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0832 Clutch pedal position (CPP) switch A - high input Wiring, short to positive, CPP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0833 Clutch pedal position (CPP) switch B - circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, CPP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0834 Clutch pedal position (CPP) switch B - low input Wiring, short to earth, CPP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0835 Clutch pedal position (CPP) switch B - high input Wiring, short to positive, CPP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0836 Four wheel drive switch - circuit malfunction
P0837 Four wheel drive switch - range/performance problem
P0838 Four wheel drive switch - low input
P0839 Four wheel drive switch - high input
P0840
P0840
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor A - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch A - circuit
malfunction
Wiring, poor connection, four wheel drive switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, four wheel drive switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, four wheel drive switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, four wheel drive switch,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 54

P0841
P0841
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor A range/performance problem
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch A range/performance problem
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0842 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor A - low input Wiring, short to earth, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0842 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch A - low input Wiring, short to earth, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0843 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor A - high input Wiring, short to positive, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0843 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch A - high input Wiring, short to positive, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0844
P0844
P0845
P0845
P0846
P0846
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor A - intermittent
circuit malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch A - intermittent
circuit malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor B - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch B - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor B range/performance problem
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch B range/performance problem
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0847 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor B - low input Wiring, short to earth, TFP sensor ,ECM/PCM/TCM
P0847 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch B - low input Wiring, short to earth, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0848 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor B - high input Wiring, short to positive, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0848 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch B - high input Wiring, short to positive, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0849
P0849
P0850
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor B - intermittent
circuit malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch B - intermittent
circuit malfunction
Park/neutral position (PNP) switch - input circuit
malfunction
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, PNP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0851 Park/neutral position (PNP) switch - input circuit low Wiring, short to earth, PNP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0852 Park/neutral position (PNP) switch - input circuit high Wiring, short to positive, PNP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0853 Drive switch - input circuit malfunction Wiring, drive switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0854 Drive switch - input circuit low Wiring, short to earth, drive switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0855 Drive switch - input circuit high Wiring, short to positive, drive switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0856 Traction control input signal - malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0857 Traction control input signal - range/performance problem Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0858 Traction control input signal - low Wiring, short to earth, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0859 Traction control input signal - high Wiring, short to positive, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0860 Gear shift module communication circuit - malfunction
P0861 Gear shift module communication circuit - low input
P0862 Gear shift module communication circuit - high input
P0863
P0864
P0865
Transmission control module (TCM) communication
circuit - malfunction
Transmission control module (TCM) communication
circuit - range/performance problem
Transmission control module (TCM) communication
circuit - low input
Wiring, poor connection, gear shift module,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, gear shift module,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, gear shift module,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TCM
Wiring, short to earth, TCM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 55

P0866
Transmission control module (TCM) communication
circuit - high input
Wiring, short to positive, TCM
P0867 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0868 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor - low Wiring, short to earth, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0869 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor - high Wiring, short to positive, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0870
P0870
P0871
P0871
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor C - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch C - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor C range/performance
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch C range/performance
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0872 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor C - circuit low Wiring, short to earth, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0872 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch C - circuit low Wiring, short to earth, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0873 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor C - circuit high Wiring, short to positive, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0873 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch C - circuit high Wiring, short to positive, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0874
P0874
P0875
P0875
P0876
P0876
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor C - intermittent
circuit malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch C - intermittent
circuit malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor D - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch D - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor D range/performance
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch D range/performance
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0877 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor D - circuit low Wiring, short to earth, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0877 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch D - circuit low Wiring, short to earth, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0878 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor D - circuit high Wiring, short to positive, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0878 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch D - circuit high Wiring, short to positive, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0879
P0879
P0880
P0881
P0882
P0883
P0884
P0885
P0886
P0887
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor D - intermittent
circuit malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch D - intermittent
circuit malfunction
Transmission control module (TCM) - power input signal
malfunction
Transmission control module (TCM) - power input signal
range/performance
Transmission control module (TCM) - power input signal
low
Transmission control module (TCM) - power input signal
high
Transmission control module (TCM) - power input signal
intermittent malfunction
Transmission control module (TCM) power relay - control
circuit open
Transmission control module (TCM) power relay - control
circuit low
Transmission control module (TCM) power relay - control
circuit high
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TCM
Wiring, short to earth, TCM
Wiring, short to positive, TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TCM power relay, TCM
Wiring, short to earth, TCM power relay, TCM
Wiring, short to positive, TCM power relay, TCM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 56

P0888
P0889
P0890
P0891
P0892
Transmission control module (TCM) power relay - sense
circuit malfunction
Transmission control module (TCM) power relay - sense
circuit range/performance
Transmission control module (TCM) power relay - sense
circuit low
Transmission control module (TCM) power relay - sense
circuit high
Transmission control module (TCM) power relay - sense
circuit intermittent malfunction
Wiring, poor connection, TCM power relay, TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TCM power relay, TCM
Wiring, short to earth, TCM power relay, TCM
Wiring, short to positive, TCM power relay, TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TCM power relay, TCM
P0893 Multiple gears engaged Mechanical fault
P0894 Transmission component slipping Mechanical fault
P0895 Shift time too short Mechanical fault
P0896 Shift time too long Mechanical fault
P0897 Transmission fluid deteriorated Mechanical fault
P0898 Transmission control system - MIL request - circuit low Wiring, poor connection, short to earth
P0899 Transmission control system - MIL request - circuit high Wiring, poor connection, short to positive
P0900 Clutch actuator - circuit open Wiring, clutch actuator, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0901 Clutch actuator - circuit range/performance
Wiring, poor connection, clutch actuator,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0902 Clutch actuator - circuit low Wiring, short to earth, clutch actuator, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0903 Clutch actuator - circuit high
Wiring, short to positive, clutch actuator,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0904 Transmission gate select position circuit - malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0905
Transmission gate select position circuit range/performance
Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0906 Transmission gate select position circuit - low Wiring, short to earth, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0907 Transmission gate select position circuit - high Wiring, short to positive, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0908
Transmission gate select position circuit - intermittent
circuit malfunction
Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0909 Transmission gate select control error Mechanical fault
P0910 Transmission gate select actuator - circuit open
P0911
Transmission gate select actuator - circuit
range/performance
P0912 Transmission gate select actuator - circuit low
P0913 Transmission gate select actuator - circuit high
Wiring, transmission gate select actuator,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, transmission gate select
actuator, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, transmission gate select
actuator, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, transmission gate select
actuator, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0914 Gear shift position circuit - malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0915 Gear shift position circuit - range/performance Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0916 Gear shift position circuit - low Wiring, short to earth, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0917 Gear shift position circuit - high Wiring, short to positive, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0918 Gear shift position circuit - intermittent malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0919 Gear shift position control - error Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0920 Gear shift forward actuator - circuit open Wiring, gear shift forward actuator, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0921 Gear shift forward actuator - circuit range/performance
P0922 Gear shift forward actuator - circuit low
P0923 Gear shift forward actuator - circuit high
Wiring, poor connection, gear shift forward actuator,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, gear shift forward actuator,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, gear shift forward actuator,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 57

P0924 Gear shift reverse actuator - circuit open Wiring, gear shift reverse actuator, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0925 Gear shift reverse actuator - circuit range/performance
P0926 Gear shift reverse actuator - circuit low
P0927 Gear shift reverse actuator - circuit high
Wiring, poor connection, gear shift reverse actuator,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, gear shift reverse actuator,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, gear shift reverse actuator,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0928 Gear shift lock solenoid - circuit open Wiring, gear shift lock solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0929 Gear shift lock solenoid - circuit range/performance Wiring, gear shift lock solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0930 Gear shift lock solenoid - circuit low
P0931 Gear shift lock solenoid - circuit high
P0932 Hydraulic pressure sensor - circuit malfunction
Wiring, short to earth, gear shift lock solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, gear shift lock solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, hydraulic pressure sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0933 Hydraulic pressure sensor - range/performance Wiring, hydraulic pressure sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0934 Hydraulic pressure sensor - circuit low input
P0935 Hydraulic pressure sensor - circuit high input
P0936 Hydraulic pressure sensor - circuit intermittent
P0937 Hydraulic oil temperature sensor - circuit malfunction
P0938 Hydraulic oil temperature sensor - range/performance
P0939 Hydraulic oil temperature sensor - circuit low input
P0940 Hydraulic oil temperature sensor - circuit high input
P0941 Hydraulic oil temperature sensor - circuit intermittent
Wiring, short to earth, hydraulic pressure sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, hydraulic pressure sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, hydraulic pressure sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, hydraulic oil temperature
sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, hydraulic oil temperature sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, hydraulic oil temperature sensor,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, hydraulic oil temperature
sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, hydraulic oil temperature
sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0942 Hydraulic pressure unit Mechanical fault
P0943 Hydraulic pressure unit - cycling period too short Mechanical fault
P0944 Hydraulic pressure unit - loss of pressure Mechanical fault
P0945 Hydraulic pump relay - circuit open Wiring, hydraulic pump relay, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0946 Hydraulic pump relay - circuit range/performance Wiring, hydraulic pump relay, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0947 Hydraulic pump relay - circuit low
P0948 Hydraulic pump relay - circuit high
Wiring, short to earth, hydraulic pump relay,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, hydraulic pump relay,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0949 ASM - adaptive learning not done ECM/PCM/TCM
P0950 ASM control circuit Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0951 ASM control circuit - range/performance Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0952 ASM control circuit - low
P0953 ASM control circuit - high
Wiring, poor connection, short to earth,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, short to positive,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0954 ASM - intermittent circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0955 ASM mode circuit - malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0956 ASM mode circuit - range/performance Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0957 ASM mode circuit - low
Wiring, poor connection, short to earth,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 58

P0958 ASM mode circuit - high
Wiring, poor connection, short to positive,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0959 ASM mode circuit - intermittent circuit malfunction Wiring, poor connection, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0960 Pressure control (PC) solenoid A - control circuit open
P0961
Pressure control (PC) solenoid A - control circuit
range/performance
P0962 Pressure control (PC) solenoid A - control circuit low
P0963 Pressure control (PC) solenoid A - control circuit high
P0964 Pressure control (PC) solenoid B - control circuit open
P0965
Pressure control (PC) solenoid B - control circuit
range/performance
P0966 Pressure control (PC) solenoid B - control circuit low
P0967 Pressure control (PC) solenoid B - control circuit high
P0968 Pressure control (PC) solenoid C - control circuit open
P0969
Pressure control (PC) solenoid C - control circuit
range/performance
P0970 Pressure control (PC) solenoid C - control circuit low
P0971 Pressure control (PC) solenoid C - control circuit high
Wiring, poor connection, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to earth, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, short to positive, pressure control solenoid,
ECM/PCM/TCM
P0972 Shift solenoid (SS) A - control circuit range/performance Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0973 Shift solenoid (SS) A - control circuit low Wiring, short to earth, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0974 Shift solenoid (SS) A - control circuit high Wiring, short to positive, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0975 Shift solenoid (SS) B - control circuit range/performance Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0976 Shift solenoid (SS) B - control circuit low Wiring, short to earth, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0977 Shift solenoid (SS) B - control circuit high Wiring, short to positive, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0978 Shift solenoid (SS) C - control circuit range/performance Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0979 Shift solenoid (SS) C - control circuit low Wiring, short to earth, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0980 Shift solenoid (SS) C - control circuit high Wiring, short to positive, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0981 Shift solenoid (SS) D - control circuit range/performance Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0982 Shift solenoid (SS) D - control circuit low Wiring, short to earth, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0983 Shift solenoid (SS) D - control circuit high Wiring, short to positive, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0984 Shift solenoid (SS) E - control circuit range/performance Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0985 Shift solenoid (SS) E - control circuit low Wiring, short to earth, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0986 Shift solenoid (SS) E - control circuit high Wiring, short to positive, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0987
P0987
P0988
P0988
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor E - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch E - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor E - circuit
range/performance
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch E - circuit
range/performance
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0989 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor E - circuit low Wiring, short to earth, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0989 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch E - circuit low Wiring, short to earth, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 59

P0990 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor E - circuit high Wiring, short to positive, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0990 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch E - circuit high Wiring, short to positive, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0991
P0991
P0992
P0992
P0993
P0993
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor E - circuit
intermittent
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch E - circuit
intermittent
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor F - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch F - circuit
malfunction
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor F - circuit
range/performance
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch F - circuit
range/performance
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0994 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor F - circuit low Wiring, short to earth, TFP sensor , ECM/PCM/TCM
P0994 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch F - circuit low Wiring, short to earth, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0995 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor F - circuit high Wiring, short to positive, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0995 Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch F - circuit high Wiring, short to positive, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0996
P0996
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) sensor F - circuit
intermittent
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch F - circuit
intermittent
Wiring, poor connection, TFP sensor, ECM/PCM/TCM
Wiring, poor connection, TFP switch, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0997 Shift solenoid (SS) F - control circuit range/performance Wiring, poor connection, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0998 Shift solenoid (SS) F - control circuit low Wiring short to earth, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
P0999 Shift solenoid (SS) F - control circuit high Wiring short to positive, shift solenoid, ECM/PCM/TCM
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 60

Airbag
Page 61

System description
Driver's and front passenger's airbags fitted as standard.
1999 : Front passenger's airbag seat pressure sensor fitted as standard.
1999 : Front side airbags fitted as standard.
Airbag locations identified by the inscription 'Airbag'.
Airbag warning label located in glove compartment.
Airbag warning label located on spiral cable.
Airbag warning label located on slam panel, under bonnet.
Airbag warning label located on SRS control module.
SRS control module mounted separately.
Pyrotechnic pretensioners fitted as standard on front seat belts.
Special attention
To prevent personal injury, expansion area of all airbags MUST remain clear.
Steering wheel spiral cable has limited rotary movement.
Centralise steering before disconnecting steering column. To prevent damage, ensure steering wheel and spiral cable DO
NOT rotate before or during reassembly.
Manufacturer recommends airbag replacement every 10 years. For further information refer to label in glove
compartment.
Pyrotechnic pretensioners are electrically triggered by SRS control module.
SRS warning lamp
Operation
Switch ignition ON.
SRS warning lamp illuminates.
Lamp extinguishes after approximately 4 seconds.
If not: Refer to Self-diagnosis section.
SRS control module fault memory can only be checked using diagnostic equipment connected to the data link connector
(DLC).
Disarm the system
When
Fascia/instrument panel removal or replacement.
Front passenger's seat repair or replacement, if seat pressure sensor fitted.
Front seat belt removal or replacement.
Front seat repair or replacement, if side airbags fitted.
Repair work around SRS components, especially airbags and pretensioners.
SRS component removal or replacement.
Steering wheel/column repair or replacement.
Welding operations.
How
Ensure ignition switched OFF.
Remove ignition key.
Disconnect all battery leads. Make sure accidental reconnection is not possible.
Wait 10 minutes before commencing work.
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 62

Additional procedures
Disconnect SRS control module when repairing bodywork.
Disconnect airbag(s) and pyrotechnic pretensioners when repairing or welding bodywork.
Remove airbag(s), pyrotechnic pretensioners and SRS control module, if temperature is likely to be more than 85°C.
Remove SRS control module when welding near component.
Remove pyrotechnic pretensioner when repairing or welding bodywork near component.
Arm the system
How
Ensure ignition switched OFF.
Reconnect all battery leads.
Switch ignition ON.
Check SRS warning lamp operation.
After deployment
Check
All mounting brackets for SRS components.
All SRS components including undeployed airbag(s)/pretensioner(s).
Fascia/instrument panel.
Seat assemblies.
Seat belts, including buckles and anchorage points.
Steering wheel and column.
Surrounding components and trims.
SRS control module and bracket.
SRS wiring harness and multi-plugs for charred or damaged areas.
Renew
All deployed or damaged airbags.
Fascia/instrument panel, if damaged.
Mounting brackets, if damaged.
Seat belt(s), if damaged or pretensioner(s) deployed.
Seat components, if damaged.
Side crash sensor, if damaged or side airbag deployed.
Spiral cable.
Steering column, if damaged.
Steering wheel, if damaged.
Surrounding components and trims, if damaged.
SRS control module, if damaged or front airbag(s) deployed.
SRS control module, if pyrotechnic pretensioner(s) deployed 3 times.
SRS wiring harness and multi-plugs, if charred or damaged areas found.
Disposal
Vehicle manufacturer suggests that deployed SRS components are sealed in a plastic bag and disposed of in accordance
with local regulations.
Steering wheel removal and installation
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
Lancia
838A1.000
R-Cat
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 63

Special attention
Disarm system and remove driver's airbag.
Centralise steering and disconnect spiral cable multi-plug(s) before removing steering wheel.
Before removing steering wheel, mark its position on steering column.
Remove screws securing steering wheel to spiral cable Fig. 1 [1].
Spiral cable should not be allowed to rotate once steering wheel removed.
Once rotated renew spiral cable.
Ensure spiral cable remains centralised during reassembly.
Replacement spiral cable held in central position by cable ties Fig. 2 [1]. Remove during installation.
Steering wheel and airbag assembly Fig. 1
Spiral cable Fig. 2
Tightening torques
Driver's airbag
6 Nm
Front passenger's airbag 7 Nm
Front seat belt inertia reel 40-50 Nm
Front seat belt buckle 50 Nm
Front seat belt lower anchorage point Not specified
Front seat belt upper anchorage point 50 Nm
Front side airbag Not specified
Side crash sensor Not specified
Steering wheel 50 Nm
SRS control module Not specified
1 2
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 64

2
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 65

Airbagself
diagnosis
Page 66

SRS control module incorporates self-diagnosis function.
¶¶
SRS warning lamp will illuminate if certain faults are recorded.
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 67

SRS diagnostic connector location Fig. 2
48934
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 68

NOTE: On vehicles with a 30-pin SRS control module, fault memory can only be checked using diagnostic equipment
connected to the data link connector (DLC).
Switch ignition ON.
Bridge SRS diagnostic connector terminal 1 (light blue/white wire) and earth with a switched lead. Contacts normally open
.
Fig. 1
Operate switch for 1-5 seconds.
Count SRS warning lamp flashes.
Note trouble code.
Compare with trouble code table.
Switch ignition OFF.
If another trouble code is stored:
Repeat checking procedure.
SRS control module fault memory can also be checked using diagnostic equipment connected to the SRS diagnostic
connector.
NOTE: SRS control module fault memory can only display one trouble code at a time.
48931
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 69

Switch ignition ON.
Operate switch for 5-10 seconds to erase trouble code.
Repeat checking procedure to ensure no data remains in SRS control module fault memory.
If another trouble code is displayed:
Repeat erasing procedure.
Diagnostic equipment can also be used to erase data from SRS control module fault memory.
NOTE: SRS control module fault memory can only be erased if specified fault is repaired.
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 70

Trouble code Fault location Probable cause
1 No fault found 2 SRS control module SRS control module
3 SRS wiring harness Wiring, short circuit to positive
4 SRS wiring harness Wiring, short circuit to earth
5 Driver's airbag, igniter circuit Wiring, driver's airbag, resistance
6 Passenger's airbag, igniter circuit Wiring, passenger's airbag, resistance
7 Supply voltage too low Battery
8 SRS warning lamp Warning lamp circuit, bulb, wiring
9 Crash data stored Renew recommended components
10 Pretensioner wiring Wiring, short circuit to positive
11 Pretensioner wiring Wiring, short circuit to earth
12 Front seat belt pretensioner, driver's side Seat belt pretensioner
13 Front seat belt pretensioner, passenger's side Seat belt pretensioner
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 71

Service
intervals
Page 72

Service: 9 000 miles/12 months
Service time (hrs): 1,10
Total service time: 1,10
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0320
Body work/paint
Check
condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090
Front brake pad wear sensors
Check
operation
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040
Battery electrolyte level
Check/top-up
4.0070
4.0080
4.0090
4.0110
Washer bottle(s)
Brake fluid reservoir
Clutch fluid reservoir
Power steering fluid
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
1994-02
© Autodata Limited 2004
V5.500-
2006.10.21.
Page 73

Service: 18 000 miles/24 months
Service time (hrs): 1,70
Total service time: 1,70
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0100 Fault diagnosis codes Check
1.0320 Body work/paint Check condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0230 Auto transmission linkage Check/lubricate
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090 Front brake pad wear sensors Check operation
3.0190 Rear brake pads Check/report
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040 Battery electrolyte level Check/top-up
4.0070 Washer bottle(s) Check/top-up
4.0080 Brake fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0090 Clutch fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0110 Power steering fluid Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0240 Air filter Renew
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.0760 Auxiliary drive belt/s Check/adjust
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
FINAL ITEMS CHECK
5.0040 Engine self-diagnosis system Check/report
Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
1994-02
© Autodata Limited 2004
V5.500-
2006.10.21.
Page 74

Service: 27 000 miles/36 months
Service time (hrs): 1,50
Total service time: 1,50
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0320 Body work/paint Check condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0110 Gearbox oil Check/top-up
2.0190 Auto transmission oil Drain/refill
2.0200 Auto transmission oil filter Renew
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090 Front brake pad wear sensors Check operation
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040 Battery electrolyte level Check/top-up
4.0070 Washer bottle(s) Check/top-up
4.0080 Brake fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0090 Clutch fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0110 Power steering fluid Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.0830 Spark plugs Renew
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
4.1260 Oxygen sensor Check/report
Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
1994-02
© Autodata Limited 2004
V5.500-
2006.10.21.
Page 75

Service: 36 000 miles/48 months
Service time (hrs): 2,20
Total service time: 2,20
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0100 Fault diagnosis codes Check
1.0320 Body work/paint Check condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0230 Auto transmission linkage Check/lubricate
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090 Front brake pad wear sensors Check operation
3.0190 Rear brake pads Check/report
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040 Battery electrolyte level Check/top-up
4.0070 Washer bottle(s) Check/top-up
4.0080 Brake fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0090 Clutch fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0110 Power steering fluid Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0240 Air filter Renew
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.0460 Petrol fuel filter - injection Renew
4.0760 Auxiliary drive belt/s Check/adjust
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
FINAL ITEMS CHECK
5.0040 Engine self-diagnosis system Check/report
Continued over page ......
Page 76

Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 77

Service: 45 000 miles/60 months
Service time (hrs): 1,10
Total service time: 1,10
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0320
Body work/paint
Check
condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090
Front brake pad wear sensors
Check
operation
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040
Battery electrolyte level
Check/top-up
4.0070
4.0080
4.0090
4.0110
Washer bottle(s)
Brake fluid reservoir
Clutch fluid reservoir
Power steering fluid
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
1994-02
© Autodata Limited 2004
V5.500-
2006.10.21.
Page 78

Service: 54 000 miles/72 months
Service time (hrs): 2,15
Total service time: 2,15
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0100 Fault diagnosis codes Check
1.0320 Body work/paint Check condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0110 Gearbox oil Check/top-up
2.0190 Auto transmission oil Drain/refill
2.0200 Auto transmission oil filter Renew
2.0230 Auto transmission linkage Check/lubricate
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090 Front brake pad wear sensors Check operation
3.0190 Rear brake pads Check/report
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040 Battery electrolyte level Check/top-up
4.0070 Washer bottle(s) Check/top-up
4.0080 Brake fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0090 Clutch fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0110 Power steering fluid Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0240 Air filter Renew
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.0640 Crankcase ventilation Check/clean
4.0760 Auxiliary drive belt/s Check/adjust
4.0830 Spark plugs Renew
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
4.1260 Oxygen sensor Check/report
FINAL ITEMS CHECK
5.0040 Engine self-diagnosis system Check/report
Continued over page ......
Page 79

Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 80

Service: 63 000 miles/84 months
Service time (hrs): 3,35
Total service time: 3,35
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0320
Body work/paint
Check
condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090
Front brake pad wear sensors
Check
operation
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040
Battery electrolyte level
Check/top-up
4.0070
4.0080
4.0090
4.0110
Washer bottle(s)
Brake fluid reservoir
Clutch fluid reservoir
Power steering fluid
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.0722 Timing belt Renew
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 81

Service: 72 000 miles/96 months
Service time (hrs): 2,50
Total service time: 2,50
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0100 Fault diagnosis codes Check
1.0320 Body work/paint Check condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0120 Gearbox oil Drain/refill
2.0230 Auto transmission linkage Check/lubricate
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090 Front brake pad wear sensors Check operation
3.0190 Rear brake pads Check/report
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040 Battery electrolyte level Check/top-up
4.0070 Washer bottle(s) Check/top-up
4.0080 Brake fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0090 Clutch fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0110 Power steering fluid Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0240 Air filter Renew
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.0460 Petrol fuel filter - injection Renew
4.0760 Auxiliary drive belt/s Check/adjust
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
FINAL ITEMS CHECK
5.0040 Engine self-diagnosis system Check/report
Continued over page ......
Page 82

Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 83

Service: 81 000 miles/108 months
Service time (hrs): 1,45
Total service time: 1,45
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0320 Body work/paint Check condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0110 Gearbox oil Check/top-up
2.0190 Auto transmission oil Drain/refill
2.0200 Auto transmission oil filter Renew
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090 Front brake pad wear sensors Check operation
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040 Battery electrolyte level Check/top-up
4.0070 Washer bottle(s) Check/top-up
4.0080 Brake fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0090 Clutch fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0110 Power steering fluid Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.0830 Spark plugs Renew
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
4.1260 Oxygen sensor Check/report
Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
1994-02
© Autodata Limited 2004
V5.500-
2006.10.21.
Page 84

Service: 90 000 miles/120 months
Service time (hrs): 1,70
Total service time: 1,70
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0100 Fault diagnosis codes Check
1.0320 Body work/paint Check condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0230 Auto transmission linkage Check/lubricate
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090 Front brake pad wear sensors Check operation
3.0190 Rear brake pads Check/report
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040 Battery electrolyte level Check/top-up
4.0070 Washer bottle(s) Check/top-up
4.0080 Brake fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0090 Clutch fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0110 Power steering fluid Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0240 Air filter Renew
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.0760 Auxiliary drive belt/s Check/adjust
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
FINAL ITEMS CHECK
5.0040 Engine self-diagnosis system Check/report
Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
1994-02
© Autodata Limited 2004
V5.500-
2006.10.21.
Page 85

Service: 99 000 miles/132 months
Service time (hrs): 1,15
Total service time: 1,15
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0320
Body work/paint
Check
condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090
Front brake pad wear sensors
Check
operation
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040
Battery electrolyte level
Check/top-up
4.0070
4.0080
4.0090
4.0110
Washer bottle(s)
Brake fluid reservoir
Clutch fluid reservoir
Power steering fluid
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
1994-02
© Autodata Limited 2004
V5.500-
2006.10.21.
Page 86

Service: 108 000 miles/144 months
Service time (hrs): 2,60
Total service time: 2,60
OK - Checked/Completed
Needs attention - see notes
VEHICLE ON FLOOR
1.0100 Fault diagnosis codes Check
1.0320 Body work/paint Check condition
VEHICLE FULLY RAISED
2.0020 Engine oil Drain/refill
2.0030 Engine oil filter Renew
2.0080 Clutch hydraulic system Check/report
2.0110 Gearbox oil Check/top-up
2.0190 Auto transmission oil Drain/refill
2.0200 Auto transmission oil filter Renew
2.0230 Auto transmission linkage Check/lubricate
2.0430 Steering rack/box Check/report
2.0450 PAS hoses Check
2.0500 Suspension joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0560 Drive shaft joints/seals/gaiters Check/report
2.0670 Exhaust system/mountings Check/report
2.0700 Brake pipe corrosion Check/report
2.0720 Fuel system leakage Check/report
2.0750 Underbody condition/sealant Check/report
VEHICLE HALF RAISED
3.0090 Front brake pad wear sensors Check operation
3.0190 Rear brake pads Check/report
3.0310 Brake hydraulic system Check/report
3.0380 Tyre condition Check/report
3.0410 Tyre pressures Check/adjust
UNDER BONNET OPERATIONS
4.0040 Battery electrolyte level Check/top-up
4.0070 Washer bottle(s) Check/top-up
4.0080 Brake fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0090 Clutch fluid reservoir Check/top-up
4.0110 Power steering fluid Check/top-up
4.0140 Coolant level/anti-freeze strength Check/adjust
4.0160 Coolant hoses Check/report
4.0240 Air filter Renew
4.0350 Pollen filter, if fitted Renew
4.0460 Petrol fuel filter - injection Renew
4.0640 Crankcase ventilation Check/clean
4.0760 Auxiliary drive belt/s Check/adjust
4.0830 Spark plugs Renew
4.1232 CO content Cat Check
4.1260 Oxygen sensor Check/report
FINAL ITEMS CHECK
5.0040 Engine self-diagnosis system Check/report
Continued over page ......
Page 87

Notes/Comments:
Technician's signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 88

Troubleshooter
Enginewill
notstart
Page 89

Component check sequence
Immobilizer
Starter/battery/circuits
Electrical connections - engine
Engine compression
Ignition system
Air intake system/vacuum system - leaks
Fuel tank/fuel level
Fuel pump/fuse
Fuel pressure/delivery rate/fuel pressure regulator
Condition of fuel/fuel filter
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor/engine speed (RPM) sensor
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
Injectors
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor
Engine management system - connections/wiring/relays
Exhaust system/catalytic converter
Engine control module (ECM)
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 90

Troubleshooter
Enginedifficult
tostartcold
Page 91

Component check sequence
Electrical connections - engine/battery
Engine compression
Air intake system/vacuum system - leaks
Fuel tank/fuel level
Fuel pressure/delivery rate/fuel pressure regulator
Condition of fuel/fuel filter
Ignition system
Fuel pump
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
Throttle position (TP) sensor
Injectors
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
Barometric pressure (BARO) sensor
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor/engine speed (RPM) sensor
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor
Engine management system - connections/wiring
Exhaust system/catalytic converter
Engine control module (ECM)
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 92

Engine
difficultto
startengine
warm
Page 93

Component check sequence
Electrical connections - engine/battery
Air intake system/vacuum system - leaks
Engine compression
Fuel tank/fuel level
Ignition system
Fuel pressure/delivery rate/fuel pressure regulator
Condition of fuel/fuel filter
Fuel pump/non-return valve
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge valve
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
Injectors
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor/engine speed (RPM) sensor
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor
Barometric pressure (BARO) sensor
Engine management system - connections/wiring
Engine control module (ECM)
Exhaust system/catalytic converter
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 94

Engine
starts
thenstops
Page 95

Component check sequence
Immobilizer
Engine control module (ECM) - basic setting
Air intake system/vacuum system - leaks
Fuel pressure/delivery rate/fuel pressure regulator
Fuel tank/fuel level
Evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge valve
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve
Idle air control (IAC) valve
Idle speed control (ISC) actuator
Idle speed control (ISC) actuator position sensor
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
Throttle position (TP) sensor
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
Engine management system - connections/wiring
Engine control module (ECM)
Exhaust system/catalytic converter
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 96

Misfire
Page 97

Component check sequence
Ignition system
Air intake system/vacuum system - leaks
Fuel tank/fuel level
Fuel pressure/delivery rate/fuel pressure regulator
Condition of fuel/fuel filter
Fuel pump
Engine compression
Engine management system - connections/wiring
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 98

Lackofpower
Page 99

Component check sequence
Accelerator cable/adjustment
Air filter
Air intake system/vacuum system - leaks/blockage
Fuel tank/fuel level
Fuel pressure/delivery rate/fuel pressure regulator
Condition of fuel/fuel filter
Fuel pump
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S)
Camshaft position (CMP) actuator
Turbocharger (TC) wastegate regulating valve
Intake manifold air control solenoid
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
Injectors
Ignition system/control
Knock sensor(s) (KS)
Throttle position (TP) sensor
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
Barometric pressure (BARO) sensor
Exhaust system/catalytic converter
Engine management system - connections/wiring
Engine control module (ECM)
Telephone:
Fax:
VAT Registration No.:
Manufacturer:
Engine code:
Tuned for:
R-Cat
Lancia
838A1.000
Model:
Output:
1994-02
Year:
Kappa 2,0
107 (145) 6100
© Autodata Limited 2004
2006.10.21.
V5.500-
Page 100

Excessivefuel
consumption
 Loading...
Loading...