Page 1

Supplementary instructions
Supplementary instructions
MFC 400
MFC 400
MFC 400MFC 400
Supplementary instructions Supplementary instructions
Signal converter for mass flowmeters
Description of Modbus interface
Description of Modbus interface
Description of Modbus interfaceDescription of Modbus interface
Electronic Revision: ER 1.0.3_
Modbus version 2.1.0_
© KROHNE 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 2

CONTENTS
MFC 400
1 General information 4
1.1 Scope of the document..................................................................................................... 4
1.2 Scope of delivery............................................................................................................... 4
1.3 Modbus protocol interface ............................................................................................... 4
2 Technical data 5
2.1 General technical data .....................................................................................................5
2.2 Technical data of the Modbus interface (acc. to EIA/TIA standards) .............................. 5
3 Electrical connections 6
3.1 Modbus connection........................................................................................................... 6
3.2 Connection to Modbus bus ............................................................................................... 6
4 Establish RS485 connection 7
5 Modbus protocol 8
5.1 RTU frame format............................................................................................................. 8
5.2 Data representation ......................................................................................................... 9
5.2.1 8-bit values.............................................................................................................................. 9
5.2.2 16-bit values............................................................................................................................ 9
5.2.3 32-bit values............................................................................................................................ 9
5.2.4 64-bit values.......................................................................................................................... 10
5.3 Modbus Register Addresses .......................................................................................... 11
5.4 Supported Function Codes............................................................................................. 11
5.5 Error messages.............................................................................................................. 11
5.6 Device identification ....................................................................................................... 12
5.7 Diagnostics ..................................................................................................................... 13
5.8 Parameters..................................................................................................................... 13
5.8.1 Device Control....................................................................................................................... 14
5.8.2 Device Status......................................................................................................................... 15
5.8.3 Measurement values ............................................................................................................ 16
5.8.4 Measurement Status compliant with NAMUR NE 107 ......................................................... 16
5.8.5 Auxiliary Values..................................................................................................................... 17
5.8.6 Totaliser ................................................................................................................................ 17
5.8.7 Zero Calibration .................................................................................................................... 20
5.8.8 Density Calibration Coefficients ........................................................................................... 21
5.8.9 Density Configuration ........................................................................................................... 21
5.8.10 Filters .................................................................................................................................. 22
5.8.11 System Control.................................................................................................................... 22
5.8.12 Calibration Coefficients ...................................................................................................... 23
5.8.13 Modbus RS485 Communication Settings ........................................................................... 24
5.8.14 NAMUR NE 107 Variable Event Group(s)............................................................................ 25
5.8.15 Concentration 1................................................................................................................... 26
5.8.16 Concentration 2................................................................................................................... 27
2
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 3
MFC 400
CONTENTS
6 Application sequences 28
6.1 Saving and restoring the configuration setting ............................................................. 28
6.2 Zero calibration .............................................................................................................. 29
7 Troubleshooting 30
7.1 No response to Modbus requests .................................................................................. 30
7.2 Communication errors ................................................................................................... 30
7.3 Responding with exception "Illegal Function"............................................................... 30
7.4 Responding with exception "Illegal Data Address" ....................................................... 31
7.5 Responding with exception "Illegal Data Value"............................................................ 31
8 Appendix 32
8.1 NAMUR NE 107 Event Group(s)...................................................................................... 32
8.2 NAMUR NE 107 status signals ....................................................................................... 33
8.3 Supported Modbus function codes................................................................................. 33
8.4 Number format............................................................................................................... 36
8.5 Glossary .......................................................................................................................... 36
9 Notes 37
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
3
Page 4

1 GENERAL INFORMATION
1.1 Scope of the document
These instructions are supplementary to the signal converter handbook. For all other data, use
the relevant chapters of the handbook. If you do not have this document, please contact the
nearest office or download them from the manufacturer's internet site.
1.2 Scope of delivery
The information in this supplementary manual only contains the data applicable to MODBUS
communication.
The technical data in the handbook shall be valid in its current version, provided that it is not
rendered invalid or replaced by this supplement.
1.3 Modbus protocol interface
The Modbus interface to the signal converter is implemented in the Modbus RTU
communications protocol and is done in accordance with the specification and requirements of
the "Modbus Protocol Specification V1.1b".
MFC 400
The physical electrical parameters of the Modbus specification are defined by the EIA/TIA-485
(RS485) standard and the "Modbus over Serial Line - Specification and Implementation Guide
V1.02".
Both specifications can be obtained on the official website of the Modbus organisation:
http://www.modbus.org
4
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 5

MFC 400
TECHNICAL DATA 2
2.1 General technical data
Interface RS485, galvanically isolated
Baud rate 1200, 2400, 3600, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600 or
Protocol Modbus RTU (available as a separate document on request)
Maximum participants on bus 32 per line, master included (may be extended by repeaters)
Coding NRZ bit coding
Address range 1...247
Transmission procedure Half duplex, asynchronous
Bus access Master / slave
Cable Screened twisted pair
Distances Maximum 1.2 km / 3937 ft without repeater (dependant on
115200 bps
baud rate and cable specifications)
2.2 Technical data of the Modbus interface (acc. to EIA/TIA standards)
Kind of signal transmission Differential, 2-wire topology
Maximum number of
transmitter/receivers
Voltage range on converter input -7...+12 V
Maximum voltage on converter output 5V
Minimum voltage on driver output, max.
load
Maximum input current (off state) -20...+20 μA
Receiver input voltage -7...+12 V
Sensitivity of the receiver -200...+200 mV
Receiver input resistance >12kΩ
Short circuit current < 250 mA
Termination / polarization resistors
(if activated by factory)
32
U
>1.5V
diff
120 Ω / 560 Ω
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
5
Page 6

3 ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
3.1 Modbus connection
The signal converter is hooked up onto the bus using terminals C and D:
Terminals Description
D- Signal A (D 0)
D Signal B (D 1)
C- Common 0 V
C Not connected
Terminals A and B of the signal converter are dependant on the options selected at order. Refer
to the standard handbook of the signal converter for connection details.
3.2 Connection to Modbus bus
The signal converter is designed to be connected as a slave device onto the 2-wire bus
implementation of the Modbus serial physical layer definition.
MFC 400
In addition to the D0 and D1 signal lines the bus MUST
ground reference point for the data signals.
For proper operation of Modbus in half duplex mode in single or multi-drop communication, it is
recommended that a termination resistor is applied to both ends of the data line. The simplest
form of termination is line-to-line resistor across the differential input.
In RTU mode the Modus protocol requires quiet periods on the communications bus for
synchronisation. It is therefore important that the Modbus is not allowed to "float", i.e.
unreferenced to 0 V, as this could lead to spurious signals due to noise pick-up. It is therefore
necessary to employ biasing resistors at one point on the bus network.
MUST include a "Common" signal line to act as a
MUSTMUST
6
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 7
MFC 400
ESTABLISH RS485 CONNECTION 4
To establish a RS485 connection with the signal converter, prepare the master device with the
appropriate default settings or use custom parameters specified via display of the signal
converter.
The Modbus RS485 settings can be found in the menu C6.8 of the display. The following
parameters can be configured:
Parameter Legal values Default values Display Fct. No.
Slave address 1...247 1 C6.8.1
"Baude rate" 1200, 2400, 3600, 4800, 9600,
Parity Even, Odd, No Even Parity C6.8.3
Data format Big Endian, Little Endian Big Endian C6.8.4
Transmission
delay
Stop Bits 1 Stop Bit, 2 Stop Bits 1 Stop Bit C6.8.6
19200, 38400, 57600, 115200
bps
0...0.04 [s] 0s C6.8.5
19200 bps C6.8.2
These settings can be changed via Modbus too. For further information refer to
Communication Settings
on page 24.
Modbus RS485
All devices connected to the bus, must have the same baud rate.
INFORMATION!
It is of great importance to ensure at the time of the procedure of devices addressing, that there
are not two devices with the same address. In such a case, an abnormal behaviour of the whole
serial bus can occur. It is then impossible for the master to communicate with all present slaves
on the bus.
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
7
Page 8
5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
5.1 RTU frame format
Using RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) format, data is transmitted as 8 bit binary characters. There
are no special characters to determine the start and end of a message frame. Synchronization is
achieved by a minimum silent period of at least 3.5 character times before the start of each
frame transmission and a maximum silent period of 1.5 character times between characters in
the same frame.
The format of the query and response frames vary slightly depending upon the function code.
The basic form is outlined below.
Command function Frame format Description
MFC 400
Silent period 3.5 x T All transmissions must be preceded by a minimum silent
Slave address 8bits This is a single byte slave address which is transmitted
Function code 8bits This is an eight bit code in the range of 1...255 although
Register start address or
byte count when required
Number of points or data
bytes when required
8 bit byte count
16 bit address
n×8bits Number of points:
period of 3.5 x T, where T is the transmission time of a
single character. This can be calculated from the baud
rate, e.g. T = 572 µs at 19.2 kbps.
first and must be in the range of 1...247. Address 0 is
reserved for a broadcast address which all slaves should
recognise, and therefore requires no response.
only 126 functions exist as the codes 129...255 represent
an error condition. An error condition occurs when the
addressed slave does not accept the command, in which
case it responds with the function code + 128, i.e. with its
msb set to 1.
Register start address:
Register start address: for a query command that requires
Register start address:Register start address:
data to be returned, this field will contain the 16 bit start
address of the register (or data) to be returned.
Note that the signal converter uses protocol addresses.
Therefore the register address listed is the actual number
required in the Modbus command.
E.g:
E.g: to access input register 30006, the register start
E.g:E.g:
address is 30006 = 0x7536.
Byte count:
Byte count: In general this is only present in frames that
Byte count:Byte count:
are transferring data, and has a value equal to the number
of bytes contained in the data field. The data field is limited
to a maximum of 250 bytes.
Number of points: for a query command that requires data
Number of points:Number of points:
to be returned, this field will contain the number of
registers to be returned regardless of their bit size.
Data bytes:
Data bytes: contains the data requested. The signal
Data bytes:Data bytes:
converter can use Big Endian format (MSB first) or Little
Endian format (LSB first).
CRC 16 bits This field contains a 16 bit CRC which is calculated on all
8
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
the data bits of the message bytes.
Page 9
MFC 400
5.2 Data representation
There are two data types used to transmit information on a Modbus data bus, the "Bit" and the
"Register". The "Bit" represents a single binary state, whether as an output or an input condition.
The "Register" is a 16-bit integer transmitted as two 8-bit characters. Using multiple "Registers"
the Modbus interface can transmit higher accuracy values such as "Floating Point" and "Double
Precision Floating Point" numbers.
"Bit" variables are packed into a byte containing 8 bit, so each character, sent or received, can
contain up to 8 "Bit" variables. The master and slave devices use only as many 8 bit data
characters as are required to transmit the information. Any unused bits in the data characters
are ignored. The bit that is requested by the start address is transmitted in the LSB at bit 0. The
next "Bit" value is transmitted in the next bit (bit 1). This continues until the last bit location (bit 7)
of the LSB is reached. The next "Bit" value is then transmitted in the next data byte (LSB+1/MSB)
at bit 0. This continues until all of the requested values have been transmitted. Any unused bits in
the MSB are filled out with "0"s.
For simple single register variables the MSB of the register is transmitted first, with the LSB
following immediately after. However, for variables that require multiple registers, i.e. the
"Floating Point" and "Double Precision Floating Point" variables, the transmission order can be
selected in the RS485 settings. By default, those values will be transmitted in Big Endian.
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
5.2.1 8-bit values
Register Hi Lo
N 0x00 Byte
5.2.2 16-bit values
Register Hi Lo
N MSB LSB
5.2.3 32-bit values
Little Endian
Register Hi Lo
N LSB + 1 LSB
N + 1 MSB LSB + 2
Big Endian
Register Hi Lo
N MSB LSB + 2
N + 1 LSB + 1 LSB
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
9
Page 10
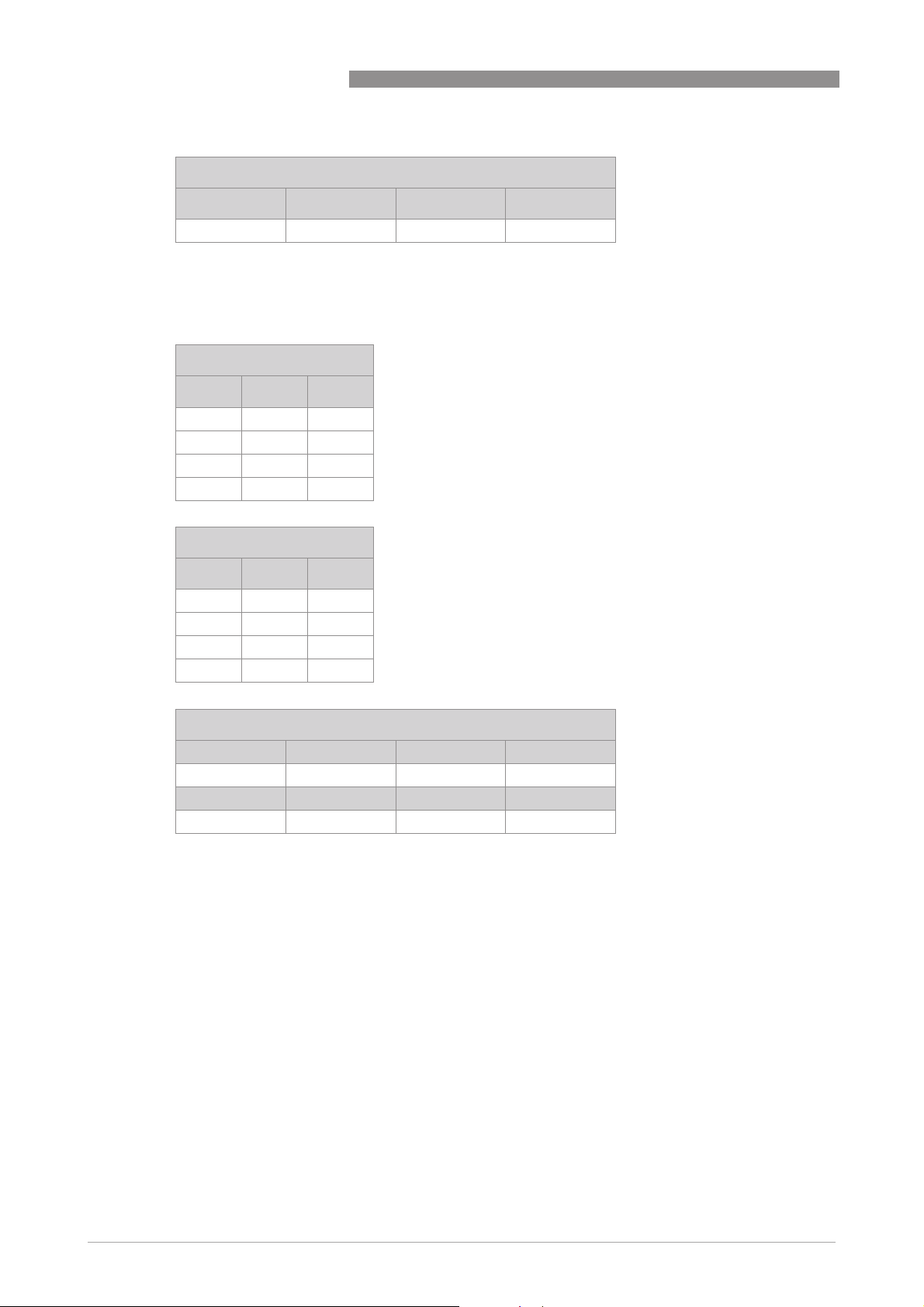
5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
Float (single precision, IEEE 754)
MSB LSB + 1 LSB + 1 LSB
SEEEEEEE EMMMMMMM MMMMMMMM MMMMMMMM
With S = sign, E = exponent, M = mantissa/fraction
5.2.4 64-bit values
Little Endian
Register Hi Lo
N LSB + 1 LSB
N + 1 LSB + 3 LSB + 2
N + 2 LSB + 5 LSB + 4
N + 3 MSB LSB + 6
MFC 400
Big Endian
Register Hi Lo
N MSB LSB + 6
N + 1 LSB + 5 LSB + 4
N + 2 LSB + 3 LSB + 2
N + 3 LSB + 1 LSB
Double (double precision, IEEE 754)
MSB
MSB LSB + 6
MSBMSB
SEEEEEEE EEEEMMMM MMMMMMMM MMMMMMMM
LSB + 3
LSB + 3 LSB + 2
LSB + 3LSB + 3
MMMMMMMM MMMMMMMM MMMMMMMM MMMMMMMM
LSB + 6 LSB + 5
LSB + 6LSB + 6
LSB + 2 LSB + 1
LSB + 2LSB + 2
LSB + 5 LSB + 4
LSB + 5LSB + 5
LSB + 1 LSB
LSB + 1LSB + 1
LSB + 4
LSB + 4LSB + 4
LSB
LSBLSB
With S = sign, E = exponent, M = mantissa/fraction
10
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 11
MFC 400
5.3 Modbus Register Addresses
The signal converter supports four types of data references, which are associated to a range of
Modbus registers.
Address range Primary tables Access rights
0...9999 Coils read + write
10000...19999 Discrete Inputs read
20000...39999 Input Registers read
40000...65535 Holding Registers read + write
INFORMATION!
•
Sometimes register numbers are asked for. The register numbers can be calculated by
adding a 1 to the register address.
•
Some systems cannot use addresses above 9999. For these systems there is the possibility to
use the listed addresses but
- for Input Registers omit the leading 3 of 3xxxx;
- for Holding Registers omit the leading 4 of 4xxxx.
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
5.4 Supported Function Codes
Function code Name
dec hex
01 01 Read Single Coil
02 02 Read Descrete Inputs
03 03 Read Holding Register
04 04 Read Input Register
05 05 Write Single Coil
08 08 Diagnostics
16 10 Write Multiple Register
43 2B Encapsulated Interface Transport
For detailed information about the telegrams structure of all function codes refer to
Modbus function codes
on page 33.
5.5 Error messages
When the signal converter detects an error in the requests, received in a properly formatted
telegram, it will respond with an error message. The error message response telegram is
formatted as follows:
Supported
Address Function Code Error Code CRC Lo CRC Hi
The msb (most significant bit) of the requested function code is set (add 0d128 / 0x80) in the
reponse telegram to indicate an error has been detected. For example, if an error were detected
in a function 1 request, then the returned function code would be 0x81 (0d129).
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
11
Page 12
5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
The single data character in the response telegram will indicate the type of error detected.
These are as follows:
MFC 400
Error
Name Meaning
Code
01 ILLEGAL FUNCTION The requested function code is not supported or not valid due to the
02 ILLEGAL DATA
03 ILLEGAL DATA VALUE The requested data is invalid for the register being written.
04 SLAVE DEVICE
06 SLAVE DEVICE BUSY The slave is unable to process the requested command because a
ADDRESS
FAILURE
Errors due to communications faults (CRC errors, Parity errors etc.) are logged but no response
is returned because the data in the received telegram is deemed unreliable. The master system
can read the error logs by using the diagnostics command (for details on Function Code 0x08
refer to
Diagnostics
on page 13).
5.6 Device identification
Retrieve all of the identification information from the signal converter.
Modbus Function Code "Encapsulated Interface Transport" (0x2B).
current settings of the device.
The register requested is not valid or the quantity of requested
registers hits invalid registers.
An unrecoverable error occurred while the slave was attempting to
perform the requested action.
long-duration command is in progress. The master should
retransmit the message later.
Modbus Encapsulated Interface (MEI) type (0x0E).
Category Object IdObject name Type Content
Basic 0x00 VendorName 16 byte ASCII String KROHNE
0x01 ProductCode 10 byte ASCII String CG number; order code for the
0x02 MajorMinorRevision 7 byte ASCII String Electronic Revision number
Regular 0x03 Vendor URL 32 byte ASCII String www.krohne.com
0x04 ProductName 16 byte ASCII String MFC400
0x05 ModelName 16 byte ASCII String Modbus
0x06 UserApplicationName 16 byte ASCII String User tag, displayed on the
signal converter assembly
header of the local screen
12
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 13

MFC 400
5.7 Diagnostics
This command function permits the user to perform one of several diagnostics operations, such
as retrieving the error and event logs. For further details on this command function, refer to the
Modbus Application Protocol Specification V1.1b.
Modbus Function Code "Diagnostics" (0x08)
Sub function code Name
dec hex
00 00 Return Query Data
01 01 Restart Communication Option
04 04 Force Listen Only Mode
10 0A Clear Counters
11 0B Return Bus Message Count
12 0C Return Bus Communication Error Count
13 0D Return Bus Exception Count
14 0E Return Slave Message Count
15 0F Return Slave No Response Count
18 12 Return Bus Character Overrun Count
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
5.8 Parameters
The functions of the Modbus interface are arranged in groups of thematically coherent
parameters.
Large gaps have been left between these groups of data types in order to permit expansion of the
signal converter interface and compatibility with further high performance signal converters.
Some registers are protected by a custody transfer lock for use when the signal converter is
used in custody transfer applications. These registers are indicated by the symbol.
The configuration of the signal converter can be changed via Modbus Holding Registers. Writing
data to those registers does not take effect immediately. In order to apply the new configuration
it is necessary to perform "Apply Changes". Parameters that require "Apply Changes" are
indicated by the symbol. Changes that are not applied can be discarded via "Discard Changes"
(details on page 14). For further information refer to
Application sequences
on page 28.
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
13
Page 14

5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
5.8.1 Device Control
The "Device Control" offers some basic functionality to operate with the signal converter.
Therefore, the Modbus interface provides five coils that can be accessed via Modbus Function
Code "Write Single Coil" (0x05).
MFC 400
Write a coil to value 1
value 1 (ON) to initiate the action.
value 1value 1
Modbus Function Code "Write Single Coil" (0x05)
Coil
Name Description Display
Address
1000
1000
10001000
(0x03E8)
1001
1001
10011001
(0x03E9)
1002
1002
10021002
(0x03EA)
1003
1003
10031003
(0x03EB)
1004
1004
10041004
(0x03EC)
Restart Device Restart entire signal converter D2.2.1
Reset Errors Clears the system error flags A3.1
Apply Changes Apply latest changes of configuration -
Discard Changes Discard all of the configuration changes made since the last "Apply
Reset to Factory
Data
Changes"
Resets the signal converter to factory configuration C6.6.3
The flow sensor can be switched between three modes. Use the following Modbus register to
request a change of the operation mode. The actual operation mode can be read via Modbus
register 39000 (details on page 15).
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
Fct. No.
-
Holding
Register
51000
51000
5100051000
(0XC738)
Name Description Type No. of
registers
Operation
Mode
Set the actual operation mode
of the flow sensor
Byte 1 1 = Stop Mode
Values Display
Fct. No.
A.9
3 = Measure Mode
5 = Standby Mode
14
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 15

MFC 400
5.8.2 Device Status
Modbus Function Codes "Read Discrete Inputs" (0x02)
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
Discrete
Name Description Type No. of
Inputs
10000
10000
1000010000
(0x2710)
10001
10001
1000110001
(0x2711)
Status of Custody
Transfer Lock
Are Changes
Made?
Indicates if custody transfer lock
is active or no
Indicates if there are unsaved
changes. "Apply Changes" to
save them, "Discard Changes" to
work with previous settings
Modbus Function Codes "Read Input Registers" (0x04)
Input
Name Type No. of
Register
39000
39000
3900039000
(0x9858)
39002
39002
3900239002
(0x985A)
39004
39004
3900439004
(0x985C)
39100
39100
3910039100
(0x98BC)
Actual Operation Mode Long 2 1 = Stop
Device Operation Time Float 2 [s] B2.1
NE 107 Status Groups Long 2 For further information refer to
NE 107 Device Status Byte 1 Bit 7 = Failure (F)
registers
Values
registers
Bit 1 0 = unlocked
Bit 1 0 = no changes made
1 = locked
1 = unsaved changes
detected
Values / Units Display
Fct. No.
2 = Startup
3 = Measuring
5 = Standby
NAMUR NE 107 Event Group(s)
on page 32.
Bit 6 = reserved
Bit 5 = Out of Specification (S)
Bit 4 = Function Check (C)
Bit 3 = reserved
Bit 2 = Maintenance required (M)
Bit 1 = reserved
Bit 0 = Information (I)
B2.16
-
-
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
15
Page 16

5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
5.8.3 Measurement values
Modbus Function Codes "Read Input Registers" (0x04)
MFC 400
Input
Register
30000
30000
3000030000
(0x7530)
30002
30002
3000230002
(0x7532)
30004
30004
3000430004
(0x7534)
30006
30006
3000630006
(0x7536)
30008
30008
3000830008
(0x7538)
30010
30010
3001030010
(0x753A)
30012
30012
3001230012
(0x753C)
30014
30014
3001430014
(0x753E)
30016
30016
3001630016
(0x7540)
1 Only available with option "concentration measurement"
Name Type No. of
Units Display
registers
Flow Velocity Float 2 [m/s] B2.5
Volume Flow Float 2 [m³/s] B2.4
Mass Flow Float 2 [kg/s] B2.3
Temperature Float 2 [K] B2.7
Density Float 2 [kg/m³] B2.6
Concentration 1 Value 1 Float 2 [Brix], [% Mass], [Baume 144],
Concentration 2 Value1 Float 2 -
Concentration 1 Flow 1 Float 2 [m³/s] or [kg/s] -
Concentration 2 Flow 1 Float 2 -
[Baume 145], [% NaOH], [Plato],
[% Volume], [API], [% Alcohol by
mass], [% Alcohol by volume]
5.8.4 Measurement Status compliant with NAMUR NE 107
Fct. No.
-
Modbus Function Codes "Read Input Registers" (0x04)
Input
Name Type No. of
Register
30500
30500
3050030500
(0x7724)
30501
30501
3050130501
(0x7725)
30502
30502
3050230502
(0x7726)
30503
30503
3050330503
(0x7727)
30504
30504
3050430504
(0x7728)
30505
30505
3050530505
(0x7729)
30506
30506
3050630506
(0x772A)
30507
30507
3050730507
(0x772B)
30508
30508
3050830508
(0x772C)
NE 107 Status of Flow Velocity Byte 1 Bit 7 = Failure (F)
NE 107 Status of Volume Flow Byte 1
NE 107 Status of Mass Flow Byte 1
NE 107 Status of Temperature Byte 1
NE 107 Status of Density Byte 1
NE 107 Status of Conc. 1 value Byte 1
NE 107 Status of Conc. 2 value Byte 1
NE 107 Status of Conc. 1 flow Byte 1
NE 107 Status of Conc. 2 flow Byte 1
Values
registers
Bit 6 = reserved
Bit 5 = Out of Specification (S)
Bit 4 = Function Check (C)
Bit 3 = Initial Value
Bit 2 = Maintenance required (M)
Bit 1 = Value is too large and limited
Bit 0 = Value is too small and limited
If none of these bits is set, there is no status
message.
16
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 17

MFC 400
5.8.5 Auxiliary Values
Modbus Function Codes "Read Input Registers" (0x04)
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
Input
Register
31000
31000
3100031000
(0x7918)
31002
31002
3100231002
(0x791A)
31004
31004
3100431004
(0x791C)
31006
31006
3100631006
(0x791E)
31008
31008
3100831008
(0x7920)
31010
31010
3101031010
(0x7922)
31012
31012
3101231012
(0x7924)
31014
31014
3101431014
(0x7926)
Name Type No. of
Units Display
registers
Drive Level Float 2 [%] B2.11
Sensor A Level Float 2 [%] B2.12
Sensor B Level Float 2 [%] B2.13
Strain 1 Float 2 [Ω] B2.8
Strain 2 Float 2 [Ω] B2.9
Tube Frequency Float 2 [Hz] B2.10
2 Phase Signal Float 2 - B2.14
SE PCB Temperature Float 2 [K] B2.15
5.8.6 Totaliser
Modbus Function Codes "Read Coils" (0x01) and "Write Single Coil" (0x05)
Coil
Address
Name Function Action Values Display
Fct. No.
Fct. No.
3000
3000
30003000
(0x0BB8)
3001
3001
30013001
(0x0BB9)
3002
3002
30023002
(0x0BBA)
3003
3003
30033003
(0x0BBB)
3004
3004
30043004
(0x0BBC)
3005
3005
30053005
(0x0BBD)
1 Only available in signal converters with "modular carrier"
Totaliser 1 Start / Stop Write 0 = stop totaliser
Status Read 0 = totaliser stopped
Totaliser 2 Start / Stop Write 0 = stop totaliser
Status Read 0 = totaliser stopped
Totaliser 3 1 Start / Stop Write 0 = stop totaliser
Status Read 0 = totaliser stopped
Totaliser 1 Reset set totaliser value
to zero
Totaliser 2 Reset set totaliser value
to zero
Totaliser 3 Reset 1set totaliser value
to zero
Write 1 = reset totaliser C4.1.6
Write 1 = reset totaliser C4.2.6
Write 1 = reset totaliser C4.3.6
1 = start totaliser
1 = totaliser running
1 = start totaliser
1 = totaliser running
1 = start totaliser
1 = totaliser running
C4.1.8 /
C4.1.9
-
C4.2.8 /
C4.2.9
-
C4.3.8 /
C4.3.9
-
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
17
Page 18

5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
Modbus Function Code "Read Input Registers" (0x04)
MFC 400
Input
Register
32000
32000
3200032000
(0x7D00)
32004
32004
3200432004
(0x7D04)
32008
32008
3200832008
(0x7D08)
32100
32100
3210032100
(0x7D64)
32102
32102
3210232102
(0x7D66)
32104
32104
3210432104
(0x7D68)
1 Only available in signal converters with "modular carrier"
Name Type No. of
Units
registers
Totaliser 1 value (double precision) Double 4 [m³] or [kg]
Totaliser 2 value (double precision) Double 4
Totaliser 3 value (double precision) 1 Double 4
Totaliser 1 value (single precision) Float 2
Totaliser 2 value (single precision) Float 2
Totaliser 3 value (single precision) 1 Float 2
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
Holding
Register
40000
40000
4000040000
(0x9C40)
40001
40001
4000140001
(0x9C41)
40002
40002
4000240002
(0x9C42)
40003
40003
4000340003
(0x9C43)
40004
40004
4000440004
(0x9C44)
40005
40005
4000540005
(0x9C45)
1 Only available in signal converters with "modular carrier"
2 Only available with option "concentration measurement"
Name Action Type No. of
Values Display
registers
Totaliser 1 Function Byte 1 0 = Off
Measurement Byte 1 1 = Volume Flow
Totaliser 2 Function Byte 1 0 = Off
Measurement Byte 1 1 = Volume Flow
Totaliser 3
1
Function Byte 1 0 = Off
Measurement Byte 1 1 = Volume Flow
1 = Absolute total
2 = Increment
3 = Decrement
2 = Mass Flow
14 = Conc. 1 Mass Flow 2
15 = Conc. 1 Volume Flow 2
16 = Conc. 2 Mass Flow 2
17 = Conc. 2 Volume Flow 2
1 = Absolute total
2 = Increment
3 = Decrement
2 = Mass Flow
14 = Conc. 1 Mass Flow 2
15 = Conc. 1 Volume Flow 2
16 = Conc. 2 Mass Flow 2
17 = Conc. 2 Volume Flow 2
1 = Absolute total
2 = Increment
3 = Decrement
2 = Mass Flow
14 = Conc. 1 Mass Flow 2
15 = Conc. 1 Volume Flow 2
16 = Conc. 2 Mass Flow 2
17 = Conc. 2 Volume Flow 2
Fct. No.
C4.1.1
C4.1.2
C4.2.1
C4.2.2
C4.3.1
C4.3.2
18
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 19

MFC 400
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
Holding
Name Action Type No. of
Register
40500
40500
4050040500
(0x9E34)
40502
40502
4050240502
(0x9E36)
40504
40504
4050440504
(0x9E38)
40506
40506
4050640506
(0x9E3A)
40508
40508
4050840508
(0x9E3C)
40510
40510
4051040510
(0x9E3E)
40512
40512
4051240512
(0x9E40)
40514
40514
4051440514
(0x9E42)
40516
40516
4051640516
(0x9E44)
40518
40518
4051840518
(0x9E46)
40520
40520
4052040520
(0x9E48)
40522
40522
4052240522
(0x9E4A)
1 Only available in signal converters with "modular carrier"
Totaliser 1 Low Flow Cut-Off
Totaliser 2 Low Flow Cut-Off
Totaliser 3
1
Value
Time Constant 0...100 [s] C4.1.4
Set or Read Value [m³] or [kg] C4.1.7
Preset [m³] or [kg] C4.1.5
Value
Time Constant 0...100 [s] C4.2.4
Set or Read Value [m³] or [kg] C4.2.7
Preset [m³] or [kg] C4.2.5
Low Flow Cut-Off
Value
Time Constant 0...100 [s] C4.3.4
Set or Read Value [m³] or [kg] C4.3.7
Preset [m³] or [kg] C4.3.5
Float 2 [m³/s] or [kg/s] C4.1.3
Float 2 [m³/s] or [kg/s] C4.2.3
Float 2 [m³/s] or [kg/s] C4.3.3
registers
Units Display
Fct. No.
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
19
Page 20

5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
5.8.7 Zero Calibration
Due to process and installation variations that cannot be accounted for by factory calibration, it is
always good practice to perform regular zero calibrations on the sensor to ensure the accuracy
of the results.
The Coils and Registers below are required to perform a zero calibration. For further
information refer to
Zero calibration
Modbus Function Codes "Read Coils" (0x01) and "Write Single Coil" (0x05)
on page 29.
MFC 400
Coil
Name Function Action Values Display
Address
2000
2000
20002000
(0x07D0)
Zero Calibration
Control
Start Write 1 = start zero calibration C1.1.1
Status Read 0 = zero calibration not running /
complete
1 = zero calibration in progress
Modbus Function Code "Read Input Registers" (0x04)
Input
Register
20000
20000
2000020000
(0x4E20)
20001
20001
2000120001
(0x4E21)
Name Type No. of
Values
registers
Zero Calibration Result Byte 1 0 = success
Zero Calibration new "Zero Flow
Offset"
Float 2 -
1 = fail – sensor not measuring
2 = fail – zero too high
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
Holding
Name Type No. of
Register
46000
46000
4600046000
(0xB3B0)
Zero Calibration Value Float 2
Fct. No.
-
registers
20
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 21

MFC 400
5.8.8 Density Calibration Coefficients
Modbus Function Code "Read Input Registers" (0x04)
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
Input
Name Type No. of registers Display
Register
33000
33000
3300033000
(0x80E8)
33002
33002
3300233002
(0x80EA)
33004
33004
3300433004
(0x80EC)
33006
33006
3300633006
(0x80EE)
33008
33008
3300833008
(0x80F0)
33010
33010
3301033010
(0x80F2)
33500
33500
3350033500
(0x82DC)
33501
33501
3350133501
(0x82DD)
DCF2 Float 2 C1.8.2
DCF3 Float 2 C1.8.3
DCF4 Float 2 C1.8.4
DCF6 Float 2 C1.8.6
DCF7 Float 2 C1.8.7
DCF8 Float 2 C1.8.8
DCF1 Byte 1 C1.8.1
DCF5 Byte 1 C1.8.5
5.8.9 Density Configuration
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
Holding
Register
Name Type No. of
registers
Values Display
Fct. No.
D1.2.2
D1.2.3
D1.2.4
D1.2.6
D1.2.7
D1.2.8
D1.2.1
D1.2.5
Fct. No.
43000
43000
4300043000
(0xA7F8)
43500
43500
4350043500
(0xA9EC)
43502
43502
4350243502
(0xA9EE)
43504
43504
4350443504
(0xA9F0)
43506
43506
4350643506
(0xA9F2)
43508
43508
4350843508
(0xA9F4)
43510
43510
4351043510
(0xA9F6)
43512
43512
4351243512
(0xA9F8)
1 Only if Density Mode = Fixed
2 Only if Density Mode = Referred
3 Only if Density Mode = Standard
Density Mode Byte 1 0 = Actual
Fixed Density Value
1
Density Referred Temperature
2
Referred Density Slope
2
Standard Density Temperature
3
Standard Density k0
3
Standard Density k1
3
Standard Density k2
3
1 = Fixed
C1.2.2
2 = Referred
3 = Standard
Float 2 0.08...5000 [kg/m³] C1.2.3
Float 2 28.15...773.15 [K] C1.2.3
Float 2 0...65 C1.2.4
Float 2 28.15...773.15 [K] C1.2.5
Float 2 0...5000 C1.2.6
Float 2 -100...100 C1.2.7
Float 2 -10...10 C1.2.8
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
21
Page 22

5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
5.8.10 Filters
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
MFC 400
Holding
Register
45000
45000
4500045000
(0xAFC8)
45500
45500
4550045500
(0xB1BC)
45502
45502
4550245502
(0xB1BE)
45504
45504
4550445504
(0xB1C0)
45506
45506
4550645506
(0xB1C2)
45508
45508
4550845508
(0xB1C4)
45510
45510
4551045510
(0xB1C6)
45512
45512
4551245512
(0xB1C8)
Name Type No. of
Values Display
registers
Flow Direction Byte 1 1 = Forwards
2 Phase Threshold Float 2 0...1000 C1.5.3
Pipe Diameter Float 2 0.001...0.5 [m] C1.3.1
User Flow Offset Float 2 -32...32 C1.1.2
Low Flow Cut-Off Float 2 0...10 [%] C1.3.4
Pressure Suppression Time Float 2 0...20 [s] C1.3.2
Pressure Suppression Cut-Off Float 2 0...10 [%] C1.3.3
Flow Correction Float 2 -10...10 [%] C1.1.4
2 = Backwards
5.8.11 System Control
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
Fct. No.
C1.3.1
Holding
Register
44000
44000
4400044000
(0xABE0)
44001
44001
4400144001
(0xABE1)
44500
44500
4450044500
(0xADD4)
44502
44502
4450244502
(0xADD6)
44504
44504
4450444504
(0xADD8)
44506
44506
4450644506
(0xADDA)
Name Type No. of
registers
Function Byte 1 1 = Off / No Action
Condition Byte 1 0 = Density
Density Min. Limit Float 2 0.08...5000 [kg/m³] C1.4.3
Density Max. Limit Float 2 0.08...5000 [kg/m³] C1.4.4
Temperature Min. Limit Float 2 73...773 [K] C1.4.3
Temperature Max. Limit Float 2 73...773 [K] C1.4.4
Values Display
Fct. No.
C1.4.1
2 = Flow=0
C1.4.2
1 = Temperature
22
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 23

MFC 400
5.8.12 Calibration Coefficients
Modbus Function Code "Read Input Registers" (0x04)
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
Input
Register
34000
34000
3400034000
(0x84D0)
34002
34002
3400234002
(0x84D2)
34004
34004
3400434004
(0x84D4)
34006
34006
3400634006
(0x84D6)
34008
34008
3400834008
(0x84D8)
34010
34010
3401034010
(0x84DA)
34012
34012
3401234012
(0x84DC)
34014
34014
3401434014
(0x84DE)
34016
34016
3401634016
(0x84E0)
34018
34018
3401834018
(0x84E2)
34020
34020
3402034020
(0x84E4)
34022
34022
3402234022
(0x84E6)
34024
34024
3402434024
(0x84E8)
34026
34026
3402634026
(0x84EA)
34028
34028
3402834028
(0x84EC)
34030
34030
3403034030
(0x84EE)
34032
34032
3403234032
(0x84F0)
34034
34034
3403434034
(0x84F2)
34036
34036
3403634036
(0x84F4)
34038
34038
3403834038
(0x84F6)
34040
34040
3404034040
(0x84F8)
34042
34042
3404234042
(0x84FA)
34044
34044
3404434044
(0x84FC)
Name Type No. of registers Display
Fct. No.
CF1 Float 2 D1.1.1
CF2 Float 2 D1.1.2
CF3 Float 2 D1.1.3
CF4 Float 2 D1.1.4
CF5 Float 2 D1.1.5
CF6 Float 2 D1.1.6
CF7 Float 2 D1.1.7
CF8 Float 2 D1.1.8
CF11 Float 2 D1.1.9
CF12 Float 2 D1.1.10
CF13 Float 2 D1.1.11
CF14 Float 2 D1.1.12
CF15 Float 2 D1.1.13
CF16 Float 2 D1.1.14
CF17 Float 2 D1.1.15
CF18 Float 2 D1.1.16
CF19 Float 2 D1.1.17
CF20 Float 2 D1.1.18
CF21 Float 2 D1.1.19
CF22 Float 2 D1.1.20
CF23 Float 2 D1.1.21
CF24 Float 2 D1.1.22
CF26 Float 2 D1.1.24
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
23
Page 24

5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
Modbus Function Code "Read Input Registers" (0x04)
MFC 400
Input
Name Type No. of registers Display
Register
34046
34046
3404634046
(0x84FE)
34500
34500
3450034500
(0x86C4)
CF27 Float 2 D1.1.25
CF25 Byte 1 D1.1.23
5.8.13 Modbus RS485 Communication Settings
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
Holding
Register
50000
50000
5000050000
(0xC350)
50002
50002
5000250002
(0xC352)
50004
50004
5000450004
(0xC354)
50005
50005
5000550005
(0xC355)
50006
50006
5000650006
(0xC356)
Name Description Type No. of
Values Display
registers
Baud rate Baud rate for the RS485
Transmission
Delay
Slave Address Modbus Slave Address Byte 1 1 (default)...247 C6.8.1
Parity Parity for the RS485 Modbus
Register
Format
Modbus Communication in
[bps]
Select transmission delay
between Modbus request and
Modbus response in [ms]
Communication
Switch Register Format Little
Endian or Big Endian
Long 2 1200, 2400, 3600,
4800, 9600, 19200
(default), 38400,
57600, 115200
Float 2 0 (default)...0.04 C6.8.5
Byte 1 0 = Even (default)
1 = Odd
3 = Off
Byte 1 0 = Little Endian
1 = Big Endian
(default)
Fct. No.
Fct. No.
C6.8.2
C6.8.3
C6.8.4
50007
50007
5000750007
(0xC357)
Stop Bits Number of Stop Bits Byte 1 1 = 1 Stop Bit
(default)
2 = 2 Stop Bits
C6.8.6
24
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 25

MFC 400
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
5.8.14 NAMUR NE 107 Variable Event Group(s)
The following eight event groups can be mapped to any status signal.
For further information refer to section "Status messages and diagnostic information" in the
signal converter standard manual.
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
Holding
Register
52016
52016
5201652016
(0xCB30)
52017
52017
5201752017
(0xCB31)
52018
52018
5201852018
(0xCB32)
52019
52019
5201952019
(0xCB33)
52020
52020
5202052020
(0xCB34)
52021
52021
5202152021
(0xCB35)
52022
52022
5202252022
(0xCB36)
52023
52023
5202352023
(0xCB37)
Description Status Group Type No. of
registers
Status Signal of
Event Group 15
Status Signal of
Event Group 14
Status Signal of
Event Group 13
Status Signal of
Event Group 12
Status Signal of
Event Group 11
Status Signal of
Event Group 10
Status Signal of
Event Group 9
Status Signal of
Event Group 8
Proc: Current Input Byte 1 128
Electr: IO Connection Byte 1 32
Proc: Signal Search Byte 1 128
Proc: 2 Phase Flow Byte 1 32
Proc: Signal Low Byte 1 32
Config: Totaliser Byte 1 32
Proc: System Control Byte 1 1
Electr: Power Failure Byte 1 32
Default Value Display
Fct. No.
C1.5.9
Failure (F)
C1.5.14
Out Of
Specification (S)
C1.5.8
Failure (F)
C1.5.10
Out Of
Specification (S)
C1.5.7
Out Of
Specification (S)
C1.5.12
Out Of
Specification (S)
C1.5.11
Information (I)
C1.5.13
Out Of
Specification (S)
Legal values for those registers:
• 128: Failure (F)
• 32: Out Of Specification (S)
• 16: Function Check (C)
• 4: Maintenance Request (M)
• 1: Information (I)
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
25
Page 26

5 MODBUS PROTOCOL
5.8.15 Concentration 1
INFORMATION!
Only available with option "concentration measurement".
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
MFC 400
Holding
Register
42000
42000
4200042000
(0xA410)
42001
42001
4200142001
(0xA411)
42002
42002
4200242002
(0xA412)
42003
42003
4200342003
(0xA413)
42050
42050
4205042050
(0xA442)
42052
42052
4205242052
(0xA444)
42054
42054
4205442054
(0xA446)
Name Type No. of
registers
Function Byte 1 0 = Off
Product Byte 1 0 = % of Product A
CCF01 Byte 1 0 = linear
CCF05 Byte 1 0 = pure water
Offset Float 2 -100...100 [%] C2.2.2
CCF02 Float 2 - C2.4.2
CCF03 Float 2 - C2.4.3
Values Display
Fct. No.
C2.2.1
2 = Brix
3 = % Mass
4 = Baume 144
5 = Baume 145
6 = % NaOH
7 = Plate
8 = % Volume
9 = API
10 = % Alcohol by mass
11 = % Alcohol by volume
C2.2.3
1 = % of Product B
C2.4.1
1 = non linear
C2.4.5
1 = town water
2 = other
42056
42056
4205642056
(0xA448)
42058
42058
4205842058
(0xA44A)
42060
42060
4206042060
(0xA44C)
42062
42062
4206242062
(0xA44E)
42064
42064
4206442064
(0xA450)
42066
42066
4206642066
(0xA452)
42068
42068
4206842068
(0xA454)
42070
42070
4207042070
(0xA456)
CCF04 Float 2 - C2.4.4
CCF06 Float 2 - C2.4.6
CCF07 Float 2 - C2.4.7
CCF08 Float 2 - C2.4.8
CCF09 Float 2 - C2.4.9
CCF10 Float 2 - C2.4.10
CCF11 Float 2 - C2.4.11
CCF12 Float 2 - C2.4.12
26
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 27

MFC 400
MODBUS PROTOCOL 5
5.8.16 Concentration 2
INFORMATION!
Only available with option "concentration measurement".
Modbus Function Codes "Read Holding Registers" (0x03) and "Write Multiple Registers" (0x10)
Holding
Register
42100
42100
4210042100
(0xA474)
42101
42101
4210142101
(0xA475)
42102
42102
4210242102
(0xA476)
42103
42103
4210342103
(0xA477)
42150
42150
4215042150
(0xA4A6)
42152
42152
4215242152
(0xA4A8)
42154
42154
4215442154
(0xA4AA)
Name Type No. of
registers
Function Byte 1 0 = Off
Product Byte 1 0 = % of Product A
CCF01 Byte 1 0 = linear
CCF05 Byte 1 0 = pure water
Offset Float 2 -100...100 [%] C2.3.2
CCF02 Float 2 - C2.5.2
CCF03 Float 2 - C2.5.3
Values Display
Fct. No.
C2.3.1
2 = Brix
3 = % Mass
4 = Baume 144
5 = Baume 145
6 = % NaOH
7 = Plate
8 = % Volume
9 = API
10 = % Alcohol by mass
11 = % Alcohol by volume
C2.3.3
1 = % of Product B
C2.5.1
1 = non linear
C2.5.5
1 = town water
2 = other
42156
42156
4215642156
(0xA4AC)
42158
42158
4215842158
(0xA4AE)
42160
42160
4216042160
(0xA4B0)
42162
42162
4216242162
(0xA4B2)
42164
42164
4216442164
(0xA4B4)
42166
42166
4216642166
(0xA4B6)
42168
42168
4216842168
(0xA4B8)
42170
42170
4217042170
(0xA4BA)
CCF04 Float 2 - C2.5.4
CCF06 Float 2 - C2.5.6
CCF07 Float 2 - C2.5.7
CCF08 Float 2 - C2.5.8
CCF09 Float 2 - C2.5.9
CCF10 Float 2 - C2.5.10
CCF11 Float 2 - C2.5.11
CCF12 Float 2 - C2.5.12
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
27
Page 28

6 APPLICATION SEQUENCES
6.1 Saving and restoring the configuration setting
MFC 400
1Start
2 Change Configuration
2a Write Holding Register(s)
2b [changes done]
3a [discard]
3b [apply]
4 Discard Changes
4a Set Coil 1003 (0x03EB)
MB-Telegram: 01 05 03 EB FF 00 + CRC
5 Previous configuration retained
6 Apply Changes
6a Set Coil 1002 (0x03EA)
MB-Telegram: 01 05 03 EA FF 00 + CRC
7 New configuration applied
The example assumes slave address 1 for Modbus telegram.
28
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 29

MFC 400
6.2 Zero calibration
APPLICATION SEQUENCES 6
1Start 6aFailed - Sensor not measuring
2 Start Zero Calibration 6b Failed - Zero too high
2a Set Coil 2000 (0x07D0)
MB-Telegram: 01 05 07 D0 FF 00 + CRC
3 Check Status Of Zero Calibration 7 Calibration Failure
3a Read Coil 2000 (0x07D0)
MB-Telegram: 01 01 07 D0 00 01 + CRC
4a running 8a Read Input Register 20001 (0x4E21)
4b ready 9 Write new Zero Flow Offset
5
Read Result
5a
Read Input Register 20000 (0x4E20)
MB-Telegram: 01 04 4E 20 00 01 + CRC
• The example assumes slave address 1 for Modbus telegram.
• Substitute "xx xx xx xx" with value read from Input Register 20001.
6c successful
8 Read new Zero Flow Offset
MB-Telegram: 01 04 4E 21 00 02 + CRC
9a Write Holding Register 46000 (0xB3B0)
MB-Telegram:
01 10 B3 B0 00 02 04 xx xx xx xx + CRC
10 Apply Changes
10a Set Coil 1002 (0x03EA)
MB-Telegram: 01 05 03 EA FF 00 + CRC
11 Calibration Done
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
29
Page 30

7 TROUBLESHOOTING
7.1 No response to Modbus requests
There are a number of possibilities why no response would be received from the signal
converter. Here is a list of some of the more obvious things to check:
• Check that there is an appropriate voltage input on the V+ and V- terminals of the signal
converter.
• Ensure that there is continuity between the A and B input terminals and their associated
terminals at the master device. Check that A and B are connected correctly (details on page
6). Ensure that there is a proper "Common" connection between the master device and the
signal converter.
• The signal converter will ignore messages that are not addressed to it, or any message that
contains fundamental formatting errors. So, check that the Address ID that is being
requested is correct, the default value is 1. Check that the transmission rate (default = 19200
Baud) and format (default = 8 data bits, even parity and 1 stop bit) are correct.
7.2 Communication errors
Intermittent communication errors can have a number of causes, almost all of which can be
attributed to the quality of the connection between the master device and the signal converter,
such as:
MFC 400
• Low quality connections at the terminals of the signal converter or master device. Ensure
that good contact is being made and that the connections are not frayed or corroded.
• Cable lengths and/or cable capacitance are too great for the data rates being used.
• Powerful sources of electromagnetic interference in close proximity to the path of the cable
route.
• It is common to use converter devices to connect the Modbus RS485 output of the signal
converter to the serial RS232 port or USB port of a host PC using off-the-shelf protocol
converters. Many of these, especially USB based converters will have problems operating the
Modbus interface as it is a timing critical protocol. Where possible, a dedicated RS485
interface PC card should be used.
7.3 Responding with exception "Illegal Function"
There can be two reasons why this error response will be returned by the signal converter in
answer to a request:
• The function being requested is not valid for the signal converter; check the list of valid
Modbus functions. For further information refer to
• An attempt is being made to write to a register that is protected by the Custody Transfer Lock.
Supported Function Codes
on page 11.
30
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 31

MFC 400
TROUBLESHOOTING 7
7.4 Responding with exception "Illegal Data Address"
There are four reasons why the signal converter will return an "Illegal Data Address" error
message when the master device makes a request.
a) The register address being requested is not supported by the signal conveter, check the
requested register against the registers specified in the section "Parameters".
b) Although the start address is valid, when accessing multiple registers the number of registers
requested may extend beyond the end of the valid address range for that group of variables.
Check the number of variables requested and ensure that the last register address is valid.
c) The number of registers requested is not correct for the data type being requested. For
example, if registers containing floating point variables are requested then the number of
requested registers must be a multiple of 2 as the floating point variables are held in two
consecutive registers. For double precision floating point variables the number of registers
requested must be a multiple of 4.
d) From c) above, the system will respond with an "Invalid Address" error when an attempt is
made to access the associated registers of a multi-register variable, for example when access to
the second register of a floating point variable is attempted. i.e. if an attempt is made to access
Input register 30001, which contains the second half of the variable accessed by Input register
30000.
7.5 Responding with exception "Illegal Data Value"
When the signal converter responds with an "Illegal Data Value", it is because the value being
written to a holding register in the signal converter is beyond the permitted limits for that
register. The limits for each holding register are indicated in the section "Parameters".
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
31
Page 32

8 APPENDIX
8.1 NAMUR NE 107 Event Group(s)
Modbus Input Register
39004 39005
Byte 0 Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3
MFC 400
Byte Bit Status
Event group
signal
3 7 - reserved
6 - reserved
5 - reserved
4 - reserved
3 - reserved
2 I Config: No Meas. Value
1 I Electr: Operation Info
0 - -
2 7 F Proc: Current Input 1
6 S Electr: IO Connection 1
5 F Proc: Signal Search 1
4 S Proc: 2 Phase Flow 1
3 S Proc: Signal Low 1
2 S Config: Totaliser 1
1 I Proc: System Control 1
0 I Electr: Power Failure 1
1 7 S Sensor
6 S Electronics
5 S Configuration
4 S Process
3 M Sensor
2 M Electronics
1 M Configuration
0 M Process
0 7 F Sensor
6 F Electronics
5 F Configuration
4 F Process
3 C Sensor
2 C Electronics
1 C Configuration
0 C Process
1 Those event groups can be mapped to any status signals.
32
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 33

MFC 400
8.2 NAMUR NE 107 status signals
APPENDIX 8
FFailure
Failure
FailureFailure
Output signal invalid due to malfunction in the signal converter.
C Function Check
Function Check
Function CheckFunction Check
Output signal temporarily invalid due to ongoing work on the signal converter.
S Out of specification
Out of specification
Out of specificationOut of specification
• Deviations from the permissible ambient or process conditions determined by
the signal converter itself through self-monitoring.
• Faults in the signal converter itself indicate that the measuring uncertainty of
flow sensors or deviations from the set value in actuators is probably greater
than expected under operating conditions.
M Maintenance required
Maintenance required
Maintenance requiredMaintenance required
Although the output signal is valid, the wear reserve is nearly exhausted or a
function will soon be restricted due to operational conditions.
8.3 Supported Modbus function codes
Function Code 0x01: Read Coils
Request Response Error
Function 0x01 Function 0x01 Function 0x81
Starting Address Hi0x00 to 0xFF Byte Count n Exception Code 0x01 / 0x02 /
Starting Address Lo0x00 to 0xFF Coil n Status
Quantity of Coils Hin (0x00 to 0x07) ... ...
Quantity of Coils Lon (0x01 to 0xFF)
max Quantity:
0x07D0
0x03 / 0x04
Function Code 0x02: Read Discrete Inputs
Request Response Error
Function 0x02 Function 0x02 Function 0x82
Starting Address Hi0x00 to 0xFF Byte Count n Exception Code 0x01 / 0x02 /
Starting Address Lo0x00 to 0xFF Input n Status
Quantity of
Registers Hi
Quantity of
Registers Lo
n (0x00 to 0x07) ... ...
n (0x01 to 0xFF)
max Quantity:
0x07D0
0x03 / 0x04
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
33
Page 34

8 APPENDIX
MFC 400
Function Code 0x03: Read Holding Registers
Request Response Error
Function 0x03 Function 0x03 Function 0x83
Starting Address Hi0x00 to 0xFF Byte Count 2 * n Exception Code 0x01 / 0x02 /
Starting Address Lo0x00 to 0xFF Register n Value
Quantity of
Registers Hi
Quantity of
Registers Lo
0x00 Register n Value
n (0x01 to 0x7D) ... ...
Hi
Lo
0x03 / 0x04
Function Code 0x04: Read Input Register
Request Response Error
Function 0x04 Function 0x04 Function 0x84
Starting Address Hi0x00 to 0xFF Byte Count 2 * n Exception Code 0x01 / 0x02 /
Starting Address Lo0x00 to 0xFF Input Register n
Quantity of Input
Registers Hi
Quantity of Input
Registers Lo
0x00 Input Register n
n (0x01 to 0x7D) ... ...
Hi
Lo
0x03 / 0x04
Function Code 0x05: Write Single Coil
Request Response Error
Function 0x05 Function 0x05 Function 0x85
Output Address Hi 0x00 to 0xFF Output Address Hi 0x00 to 0xFF Exception Code 0x01 / 0x02 /
Output Address Lo 0x00 to 0xFF Output Address Lo 0x00 to 0xFF
Output Value Hi 0x00 or 0xFF Output Value Hi 0x00 or 0xFF
Output Value Lo 0x00 Output Value Lo 0x00
0x03 / 0x04
Function Code 0x08: Diagnostics
Request Response Error
Function 0x08 Function 0x08 Function 0x88
Sub-function Hi 0x00 to 0xFF Sub-function Hi 0x00 to 0xFF Exception Code 0x01 / 0x03 /
Sub-function Lo 0x00 to 0xFF Sub-function Lo 0x00 to 0xFF
Data n Hi 0x00 to 0xFF Data n Hi 0x00 to 0xFF
Data n Lo 0x00 to 0xFF Data n Lo 0x00 to 0xFF
... ... ... ...
0x04
34
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 35

MFC 400
APPENDIX 8
Function Code 0x10: Write Multiple Registers
Request Response Error
Function 0x10 Function 0x10 Function 0x90
Starting Address Hi0x00 to 0xFF Starting Address Hi0x00 to 0xFF Exception Code 0x01 / 0x02 /
Starting Address Lo0x00 to 0xFF Starting Address Lo0x00 to 0xFF
0x03 / 0x04
Quantity of
Registers Hi
Quantity of
Registers Lo
Byte Count 2 * n (0x02 to
Register n Value Hi0x00 to 0xFF
Register n Value Lo0x00 to 0xFF
... ...
0x00 Quantity of
Registers Hi
0x01 to 0x7B Quantity of
Registers Lo
0xFF)
0x00
0x01 to 0x7B
Function Code 0x2B: Encapsulated Interface Transport 0x0E Read Device Identification
Request Response Error
Function 0x2B Function 0x2B Function 0xAB
MEI Type 0x0E MEI Type 0x0E Exception Code 0x01 / 0x02 /
Read Device ID
Code
Object ID 0x00 to 0xFF Conformity Level 0x02 (0x01 /
0x01 / 0x02
(0x03 / 0x04)
Read Device ID
Code
More Follows 0x00 (or 0xFF)
Next Object ID 0x00 to 0xFF
Number of
Objects
Object n ID 0x00 to 0xFF
Object n length 0x00 to 0xFF
Object n value n (1...254 bytes)
... ...
0x01 / 0x02
(0x03 / 0x04)
0x03 / 0x04)
0x01 to 0x07
(0xFF)
0x03 / 0x04
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
35
Page 36

8 APPENDIX
8.4 Number format
• Hexadecimal values are written in the format 0xNNNN, where NNNN is the hexadecimal
value.
• Decimal values are written in the format 0dNNNN or NNNN, where NNNN is the decimal
value.
8.5 Glossary
RTU Remote Terminal Unit mode is a Modbus serial transmission mode
RS232 TIA/EIA-232 Standard
RS485 TIA/EIA-485 Standard
Master/Client A device that polls one or more slave devices and always initiates
Slave/Server A device that responds to requests from a master and never initiates
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Checksum
Register A Modbus data object corresponding to a word (16 bits)
Coil A Modbus data object corresponding to a single bit
LSB Least Significant Byte
MSB Most Significant Byte
lsb least significant bit
msb most significant bit
MFC 400
communication
communication
36
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 37

MFC 400
NOTES 9
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
37
Page 38

9 NOTES
MFC 400
38
www.krohne.com 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
Page 39

MFC 400
NOTES 9
www.krohne.com05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en
39
Page 40

KROHNE product overview
• Electromagnetic flowmeters
• Variable area flowmeters
• Ultrasonic flowmeters
• Mass flowmeters
• Vortex flowmeters
• Flow controllers
• Level meters
• Temperature meters
• Pressure meters
• Analysis products
• Products and systems for the oil & gas industry
• Measuring systems for the marine industry
Head Office KROHNE Messtechnik GmbH
Ludwig-Krohne-Str. 5
47058 Duisburg (Germany)
Tel.:+49 (0)203 301 0
Fax:+49 (0)203 301 10389
info@krohne.de
© KROHNE 05/2013 - 4002525102 - AD Modbus MFC 400 R02 en - Subject to change without notice.
The current list of all KROHNE contacts and addresses can be found at:
www.krohne.com
 Loading...
Loading...