Page 1

UHF FM TRANSCEIVER
TK-8180
SERVICE MANUAL
© 2004-7 PRINTED IN JAPAN
B51-8692-00 (N) 1007
Microphone
(T91-0639-05)
Cabinet
(A01-2194-11)
CONTENTS
GENERAL .................................................................. 2
SYSTEM SET-UP ...................................................... 3
REALIGNMENT ......................................................... 4
INSTALLATION ......................................................... 7
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR ................................. 13
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION .......................................... 16
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA ...................................... 20
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION .............................. 22
PARTS LIST ............................................................. 24
EXPLODED VIEW.................................................... 33
PACKING ................................................................. 34
ADJUSTMENT ........................................................ 35
TERMINAL FUNCTION ........................................... 46
PC BOARD
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) ............................ 50
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (A/3, C/3) ............... 52
Key top
(K29-9312-21)
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3) ....................... 54
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) ............................ 58
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) ................................ 60
INTERCONNECTION DIAGRAM ............................ 69
BLOCK DIAGRAM ................................................... 70
LEVEL DIAGRAM .................................................... 72
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
KRK-10
KAP-2 (Horn Alert/P.A. Relay unit) ................... 79
KCT-40 (Radio Interface Cable).......................... 79
KCT-46 (Ignition Sense Cable) ........................... 79
KMC-35 (Microphone) ........................................ 79
KMC-36 (Keypad Microphone) .......................... 79
SPECIFICATIONS ................................. BACK COVER
(Control Head Remote Kit: 23ft/7m) ......
Panel assy
(A62-1094-23)
74
Page 2

TK-8180
GENERAL
INTRODUCTION
SCOPE OF THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended for use by experienced technicians familiar with similar types of commercial grade communications equipment. It contains all required service information for the equipment and is current as of this publication
date. Changes which may occur after publication are covered
by either Service Bulletins or Manual Revisions, which are
issued as required.
ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
When ordering replacement parts or equipment information, the full part identification number should be included.
This applies to all parts : components, kits, and chassis. If the
part number is not known, include the chassis or kit number
of which it is a part and a sufficient description of the required
component for proper identification.
PERSONAL SAFETY
The following precautions are recommended for personal
safety :
•DONOT transmit if someone is within two feet (0.6
meter) of the antenna.
•DONOT transmit until all RF connectors are secure and
any open connectors are properly terminated.
• SHUT OFF this equipment when near electrical blasting
caps or while in an explosive atmosphere.
• All equipment should be properly grounded before power-
up for safe operation.
• This equipment should be serviced by only qualified tech-
nicians.
PRE-INSTALLATION CONSIDERATIONS
1. UNPACKING
Unpack the radio from its shipping container and check for
accessory items. If any item is missing, please contact
KENWOOD immediately.
2. LICENSING REQUIREMENTS
Federal regulations require a station license for each radio
installation (mobile or base) be obtained by the equipment
owner. The licensee is responsible for ensuring transmitter
power, frequency, and deviation are within the limits permitted by the station license.
Transmitter adjustments may be performed only by a licensed technician holding an FCC first, second or general
class commercial radiotelephone operator’s license. There is
no license required to install or operate the radio.
3. PRE-INSTALLATION CHECKOUT
3-1. Introduction
Each radio is adjusted and tested before shipment. However, it is recommended that receiver and transmitter operation be checked for proper operation before installation.
3-2. Testing
The radio should be tested complete with all cabling and
accessories as they will be connected in the final installation.
Transmitter frequency, deviation, and power output should
be checked, as should receiver sensitivity, squelch operation,
and audio output. Signalling equipment operation should be
verified.
4. PLANNING THE INSTALLATION
4-1. General
Inspect the vehicle and determine how and where the radio antenna and accessories will be mounted.
Plan cable runs for protection against pinching or crushing
wiring, and radio installation to prevent overheating.
4-2. Antenna
The favored location for an antenna is in the center of a
large, flat conductive area, usually at the roof center. The
trunk lid is preferred, bond the trunk lid and vehicle chassis
using ground straps to ensure the lid is at chassis ground.
4-3. Radio
The universal mount bracket allows the radio to be
mounted in a variety of ways. Be sure the mounting surface
is adequate to support the radio’s weight. Allow sufficient
space around the radio for air cooling. Position the radio close
enough to the vehicle operator to permit easy access to the
controls when driving.
4-4. DC Power and wiring
1. This radio may be installed in negative ground electrical
systems only. Reverse polarity will cause the cable fuse to
blow. Check the vehicle ground polarity before installation
to prevent wasted time and effort.
2. Connect the positive power lead directly to the vehicle
battery positive terminal. Connecting the Positive lead to
any other positive voltage source in the vehicle is not rec-
ommended.
3. Connect the ground lead directly to the battery negative
terminal.
4. The cable provided with the radio is sufficient to handle
the maximum radio current demand. If the cable must be
extended, be sure the additional wire is sufficient for the
current to be carried and length of the added lead.
5. INSTALLATION PLANNING – CONTROL STATIONS
5-1. Antenna system
Control station. The antenna system selection depends on
many factors and is beyond the scope of this manual. Your
KENWOOD dealer can help you select an antenna system
that will best serve your particular needs.
5-2. Radio location
Select a convenient location for your control station radio
which is as close as practical to the antenna cable entry point.
Secondly, use your system’s power supply (which supplies
the voltage and current required for your system). Make sure
sufficient air can flow around the radio and power supply to
allow adequate cooling.
2
Page 3
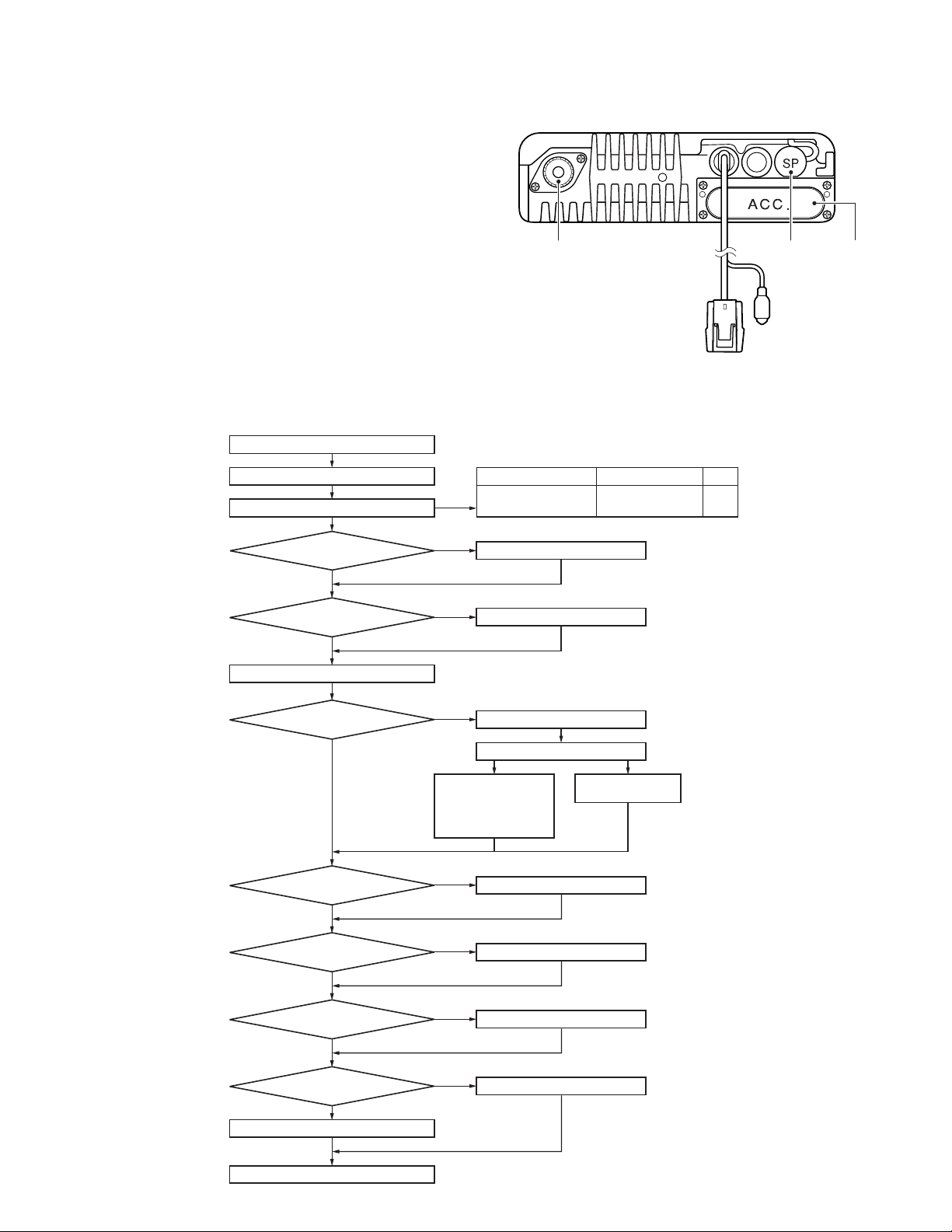
GENERAL / SYSTEM SET-UP
SERVICE
This radio is designed for easy servicing. Refer to the
schematic diagrams, printed circuit board views, and alignment procedures contained in this manual.
TK-8180
NOTE
• If you do not intend to use the speaker 3.5-mm jack and
the D-sub 25-pin connector, fit the supplied speaker-jack
cap and D-sub cap to stop dust and sand from getting in.
• If the transceiver is turned ON or OFF when the power-on/
off status message is enabled, the transceiver sends the
status.
SYSTEM SET-UP
Merchandise received
License and frequency allocated by FCC
Choose the type of transceiver
Are you using
the remote kit?
NO
Are you using
the ignition sense cable?
NO
Transceiver programming
Are you using
the radio interface cable?
NO
YES
YES
See page 4.
A personal computer (IBM PC or compatible), programming
interface (KPG-46), and programming software (KPG-89D)
are required for programming.
YES
Antenna
connector
Power input
connector
Frequency range RF power Type
450~520MHz
KRK-10
KCT-46
KCT-40
KCT-36 Extension cable
30W
(490~520MHz : 25W)
See page 9.
(Option)
See page 7.
(Option)
See page 7.
(Option)
(Option)
K
Speaker
jack cap
Ignition
sense cable
D-sub
cap
Are you using
the public address?
NO
Are you using
the voice guide & storage
unit?
NO
Are you using
the external speaker?
NO
Are you using
the keypad microphone?
NO
Supplied microphone
Delivery
KGP-2A
Modem GPS receiver
or
KGP-2B
Modem GPS controller
(Option)
YES
YES
YES
YES
KES-3 or KES-5 External speaker
KMC-32 or KMC-36
or
KAP-2
VGS-1
KDS-100
Mobile data terminal
Desk top microphone KMC-9C
(Option)
See page 8.
(Option)
See page 10.
(Option)
(Option)
(Option)
3
Page 4
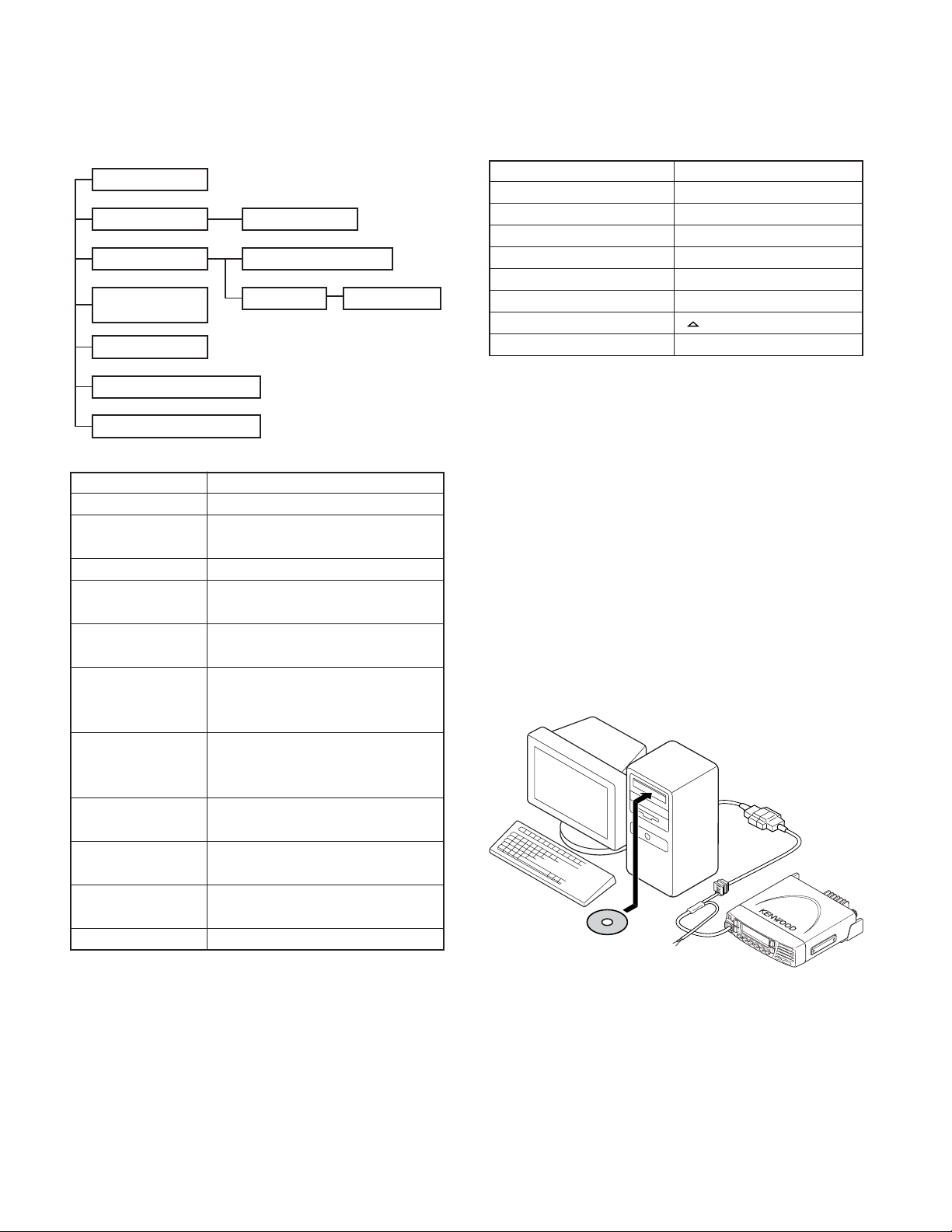
TK-8180
KPG-89D
IBM PC
KPG-46 or
KPG-46 +
Tuning cable
(E30-3383-05)
REALIGNMENT
1. Modes
User mode
Panel test mode
PC mode
Firmware
programming mode
Clone mode
Firmware version information
Clock adjustment mode
Mode Function
User mode For normal use.
Panel test mode Used by the dealer to check the funda-
Panel tuning mode Used by the dealer to tune the radio.
PC mode Used for communication between the
Data programming Used to read and write frequency data
mode and other features to and from the radio.
PC test mode Used to check the radio using the PC.
PC tuning mode Used to tune the radio using the PC.
Firmware Used when changing the main program
programming mode of the flash memory.
Clone mode Used to transfer programming data from
Firmware version Used to confirm the internal firmware
information version.
Clock adjustment mode
Panel tuning mode
Data programming mode
PC test mode
mental characteristics.
radio and PC (IBM compatible).
This feature is included in the FPU.
See panel test.
This feature is included in the FPU.
See panel tuning.
one radio to another.
Used to adjust date and time.
PC tuning mode
2. How to Enter Each Mode
Mode Operation
User mode Power ON
Panel test mode [A] + Power ON
PC mode Received commands from PC
Panel tuning mode [Panel test mode] + [S]
Firmware programming mode [S] + Power ON
Clone mode [B] + Power ON
Firmware version information [ ] + Power ON
Clock adjustment mode [C] + Power ON
3. Panel Test Mode
Setting method refer to ADJUSTMENT.
4. Panel Tuning Mode
Setting method refer to ADJUSTMENT.
5. PC Mode
5-1. Preface
The transceiver is programmed by using a personal computer, programming interface (KPG-46) and programming
software (KPG-89D).
The programming software can be used with an IBM PC
or compatible. Figure 1 shows the setup of an IBM PC for
programming.
Fig. 1
4
Page 5

REALIGNMENT
TK-8180
5-2. Connection procedure
1. Connect the transceiver to the personal computer with
the interface cable.
2. When the POWER switch on, user mode can be entered
immediately. When PC sends command the radio enter
PC mode, and “PROGRAM” is displayed on the LCD.
When data transmitting from transceiver, the red LED is
lights.
When data receiving to transceiver, the green LED is
lights.
Note:
• The data stored in the personal computer must match
model type, when it is written into the flash memory.
5-3. KPG-46 description
(PC programming interface cable: Option)
The KPG-46 is required to interface the transceiver to the
computer. It has a circuit in its D-subconnector (25-pin) case
that converts the RS-232C logic level to the TTL level.
The KPG-46 connects the modular microphone jack of the
transceiver to the computers RS-232C serial port.
5-4. Programming software KPG-89D description
The KPG-89D is the programming software for the trans-
ceiver supplied on a CD-ROM. This software runs under MSWindows 98, ME, Windows 2000 or XP on an IBM-PC or
compatible machine.
The data can be input to or read from the transceiver and
edited on the screen. The programmed or edited data can be
printed out. It is also possible to tune the transceiver.
6. Firmware Programming Mode
6-1. Preface
Flash memory is mounted on the transceiver. This allows
the transceiver to be upgraded when new features are released in the future. (For details on how to obtain the firmware, contact Customer Service.)
6-2. Connection procedure
Connect the transceiver to the personal computer (IBM
PC or compatible) with the interface cable (KPG-46). (Connection is the same as in the PC Mode.)
Note :
You can only program firmware from the 8-pin micro-
phone connector on the front panel. Using the 25-pin logic
interface on the rear panel will not work.
6-3. Programming
1. Start up the firmware programming software (Fpro.exe).
2. Set the communications speed (normally, 115200 bps)
and communications port in the configuration item.
3. Set the firmware to be updated by File name item.
4. Turn the transceiver power ON with the [S] key held
down. Then, the orange LED on the transceiver lights and
“PROG 115200” is displayed.
5. Check the connection between the transceiver and the
personal computer, and make sure that the transceiver is
in the Program mode.
6. Press write button in the window. When the transceiver
starts to receive data, the [PG] display is blinking.
7. If writing ends successfully, the checksum is calculated
and a result is displayed.
8. If you want to continue programming other transceivers,
repeat steps 4 to 7.
Notes:
• This mode cannot be entered if the Firmware Programming mode is set to Disable in the Programming software.
• When programming the firmware, it is recommend to
copy the data from the floppy disk to your hard disk before
update the radio firmware.
Directly copying from the floppy disk to the radio may not
work because the access speed is too slow.
6-4. Function
1. If you press the [■ ] key while “PROG 115200” is displayed, the display changes to “PROG 19200” (The LED
blinks green) to indicate that the write speed is low speed
(19200 bps). If you press the [■] key again while “PROG
19200” is displayed, the display changes to “PROG
38400” (The LED lights red and orange alternatively). If
you press the [■] key again while “PROG 38400” is displayed, the display changes to “PROG 57600” (The LED
blinks orange). If you press the [■ ] key again while
“PROG 57600” is displayed, the display returns to “PROG
115200” (The LED lights orange).
2. If you press the [
played, the checksum is calculated, and a result is displayed. If you press the [
checksum is displayed, “PROG 115200” is redisplayed.
] key while “PROG 115200” is dis-
] key again while the
Note:
Normally, write in the high-speed mode.
7. Clone Mode
Programming data can be transferred from one radio to
another by connecting them via their 8-pin microphone connectors. The operation is as follows (the transmit radio is the
master and the receive radio is a slave).
1. Turn the master transceiver power ON with the [B] key
held down. If the read authorization password is set to the
transceiver, the transceiver displays “CLONE LOCK”. If
the password is not set, the transceiver displays “CLONE
MODE”.
2. When you enter the correct password, and “CLONE
MODE” is displayed, the transceiver can be used as the
cloning master. The following describes how to enter the
password.
5
Page 6

TK-8180
REALIGNMENT
3. How to enter the password with the microphone keypad;
If you press a key while “CLONE LOCK” is displayed, the
number that was pressed is displayed on the transceiver.
Each press of the key shifts the display in order to the left.
When you enter the password and press the [✳] key,
“CLONE MODE” is displayed if the entered password is
correct. If the password is incorrect, “CLONE LOCK” is
redisplayed.
How to enter the password with the [
If the [
displayed, numbers (0 to 9) are displayed flashing. When
you press the [C] key, the currently selected number is
determined. If you press the [S] key after entering the
password in this procedure, “CLONE MODE” is displayed
if the entered password is correct. If the password is incorrect, “CLONE LOCK” is redisplayed.
4. Power on the slave transceiver.
5. Connect the cloning cable (Part No. E30-3382-05) to the
modular microphone jacks on the master and slave.
6. Press the [S] key on the master while the master displays
“CLONE MODE”. The data of the master is sent to the
slave. While the slave is receiving the data, “PROGRAM”
is displayed. When cloning of data is completed, the master displays “END”, and the slave automatically operates
in the User mode. The slave can then be operated by the
same program as the master.
7. The other slave can be continuously cloned. When the [S]
key on the master is pressed while the master displays
“END”, the master displays “CLONE MODE”. Carry out
the operation in step 4 to 6. Can not be cloned if the overwrite password is programmed to the slave.
] and [ ] keys is pressed while “CLONE LOCK” is
] and [ ] keys;
8. Firmware Version Information
Turn the transceiver ON with the [ ] key held down.
Then, the version is displayed during holding the [
] key.
9. Clock Adjustment Mode
9-1. Flow chart of operation
[C] + Power ON
YEAR
[S]
MONTH
[S]
DAY
[S]
HOUR
[S]
MINUTE
[S]
[ ] and [ ] keys
[ ] and [ ] keys
[ ] and [ ] keys
[ ] and [ ] keys
[ ] and [ ] keys
Completion
Note:
Only the same models can be cloned together.
Cloning cable
(E30-3382-05)
Fig. 2
6
Page 7

KDS-100, KGP-2A,
KGP-2B or through
KCT-36 extension cable
q
e
w
INSTALLATION
1. Ignition Sense Cable (KCT-46 : Option)
The KCT-46 is an optional cable for enabling the ignition
function. The ignition function lets you turn the power to the
transceiver on and off with the car ignition key.
1-1. Connecting the KCT-46 cable to the transceiver
1. Open the KCT-46 fuse holder and insert a mini blade fuse
(3A). ( q )
2. While holding a clear protective cover, remove the black
cap at the end of the yellow cable (ignition sense cable) of
the transceiver. ( w )
3. Connect the plug of the KCT-46 to the yellow cable termi-
nal of the transceiver. ( e )
4. Connect the other end of the KCT-46 to the ignition line of
the car. ( r )
Note : You must setup using the KPG-89D.
TK-8180
Fig. 2
w
e
F52-0019-05
q
r
Iginition line
of the car
Fig. 1
2. Radio Interface Cable (KCT-40 : Option)
The KCT-40 connection cable kit is used to connect the
TK-8180 transceiver to the KDS-100 (Mobile data terminal),
KGP-2A (Modem GPS receiver), KGP-2B (Modem GPS controller) or through the KCT-36 extension cable.
2-1. Connecting the KCT-40 cable to the transceiver
1. Remove the D-sub cap on the rear of the transceiver. ( q )
2. Connect the D-sub connector of the KCT-40 to the D-sub
25-pin terminal of the transceiver. ( w )
3. Connect the 15-pin connector of the KCT-40 to a KDS-100,
KGP-2A, KGP-2B or through a KCT-36 extension cable.
( e )
Note : You must setup using the KPG-89D.
2-2. Terminal function
D-sub 25-pin
Pin No. Function Pin No. Function Function
1- ---
2- ---
3- ---
4- ---
5DI5DO DO
6- ---
7 GND 3 GND GND
8 AIO8 9 TXS/LOK TXS/LOK
9 TXD2 15 RXD RXD
10 RXD2 14 TXD TXD
11 - ---
12 AIO7 11 MM MM
13 AIO6 6 PTT PTT
14 SB 1 SB SB
15 - ---
16 - ---
17 - ---
18 - ---
19 DEO 4 DI DI
20 AIO5 8 SQ SQ
21 AIO4 10 AM AM
22 AIO3 13 - DISP OFF
23 AIO2 12 - -
24 AIO1 7 DTC DTC
25 - ---
TK-7180
Molex 15-pin
KDS-100 KGP-2A/2B
7
Page 8
TK-8180
INSTALLATION
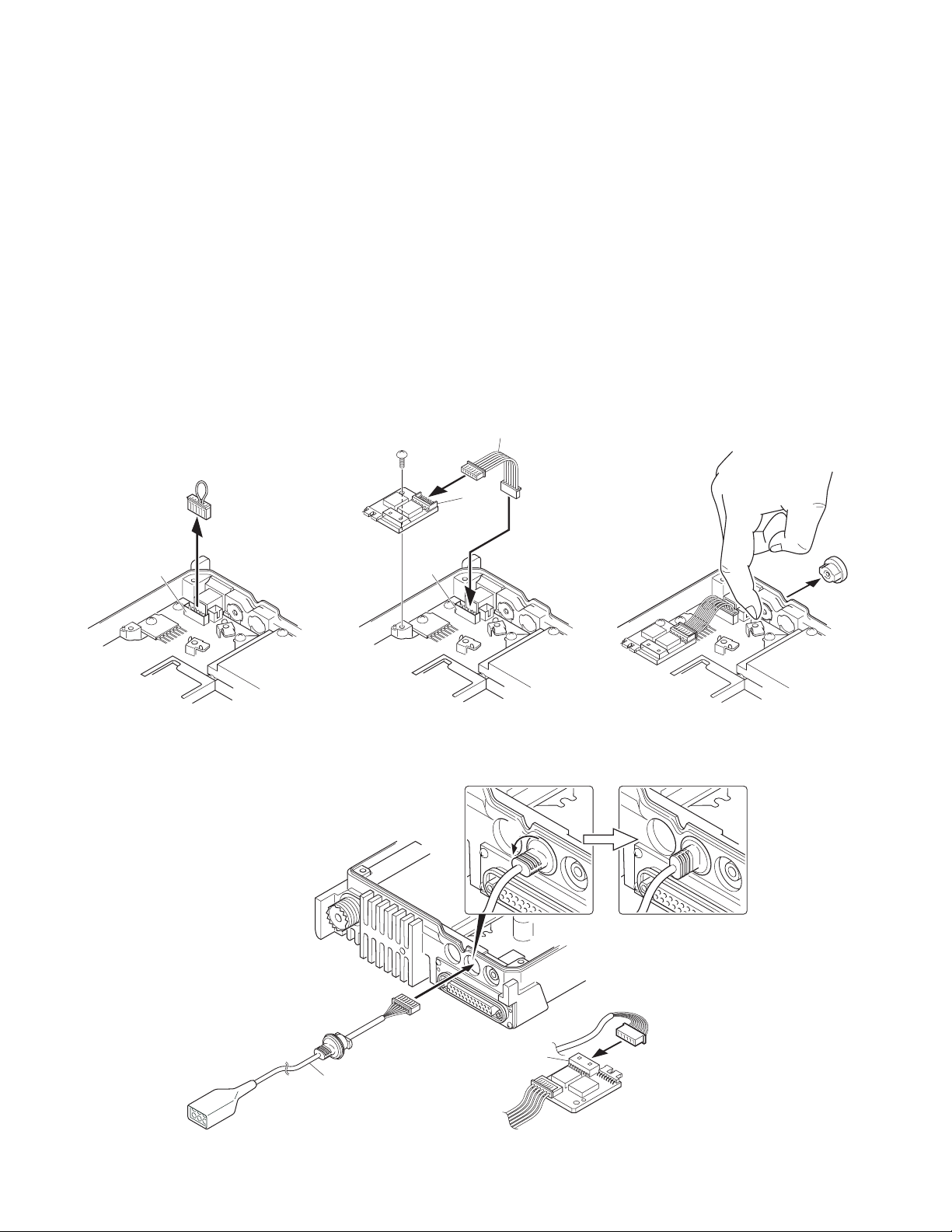
3. Horn Alert/P.A. Relay Unit (KAP-2 : Option)
The Horn alert (max. 2A drive), Public address and External
speaker function are enabled by installing the KAP-2 in the
TK-8180 transceiver.
3-1. Installing the KAP-2 unit in the transceiver
1. Remove the cabinet, top packing and shielding plate of the
transceiver.
2. Set the KAP-2 relay unit jumper pins according to the purpose of use.
3. Remove the 6-pin jumper connector inserted in the TX-RX
unit (B/3) connector (CN428). ( q )
4. Insert one side of the lead wire with connector (E37-1114-
05) into the relay unit connector (CN3) ( w ) and the other
side into the TX-RX unit (B/3) connector (CN428) ( e ).
5. Place the relay unit at the position shown in Figure 3-2 and
secure it to the chassis with a screw.
6. Remove the cap on the rear of the chassis by pushing it
from the inside with your finger. ( r )
7. Pass the 6-pin connector of the cable (E37-1113-05)
through the chassis hole ( t ) and insert the bush into the
chassis hole.
8. Rotate the bush of the cable 90 degrees counterclockwise
as viewed from the rear of the chassis. ( y )
9. Insert the 6-pin connector of the cable into the connector
(CN2) of the KAP-2 relay unit. ( u )
Note : You must setup using the KPG-89D.
E37-1114-05
w
CN3
e
q
CN428
CN428
Fig. 3-1 Fig. 3-2 Fig. 3-3
y
r
t
CN2
E37-1113-05
u
Fig. 3-4
8
Page 9
CN1
KRK-10 main panel
u
i
INSTALLATION
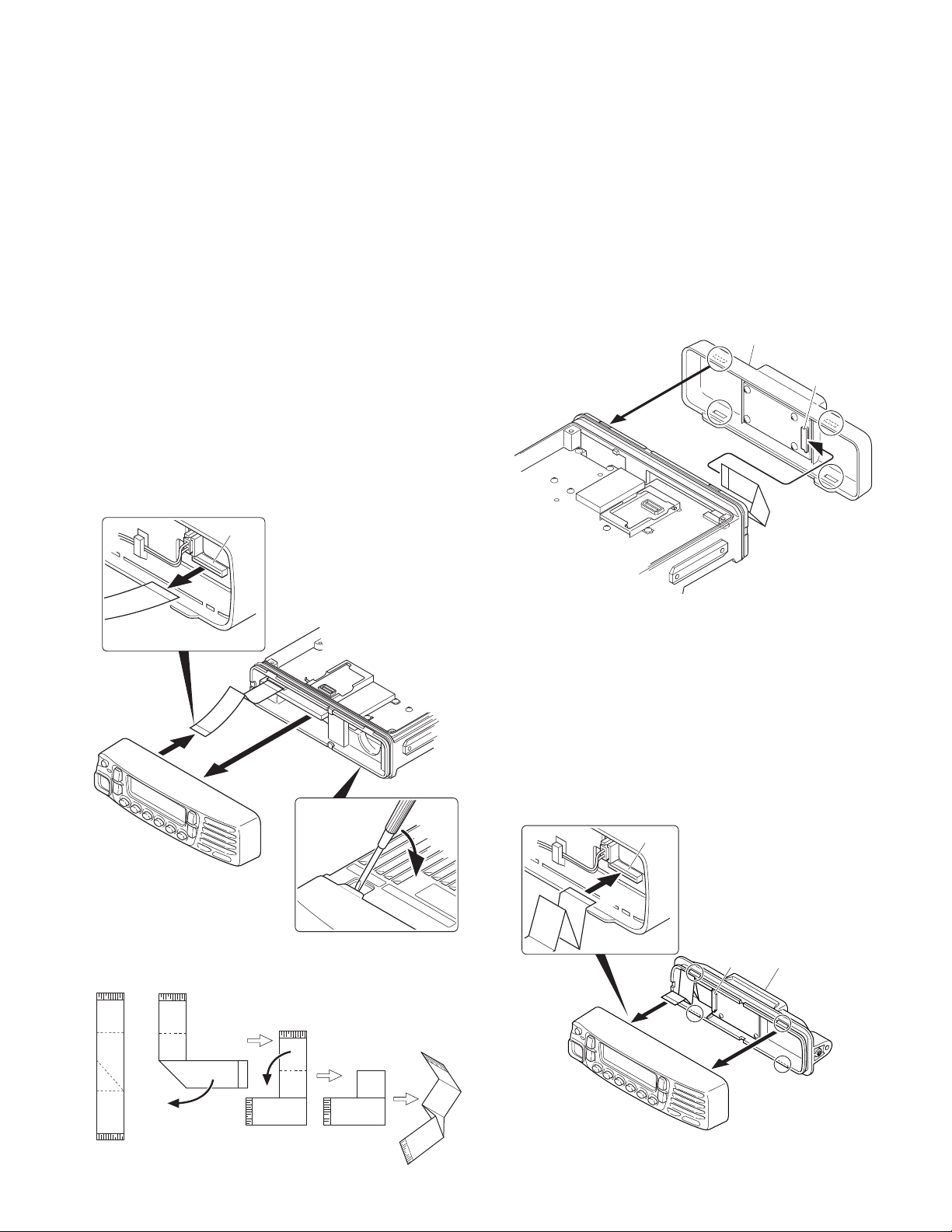
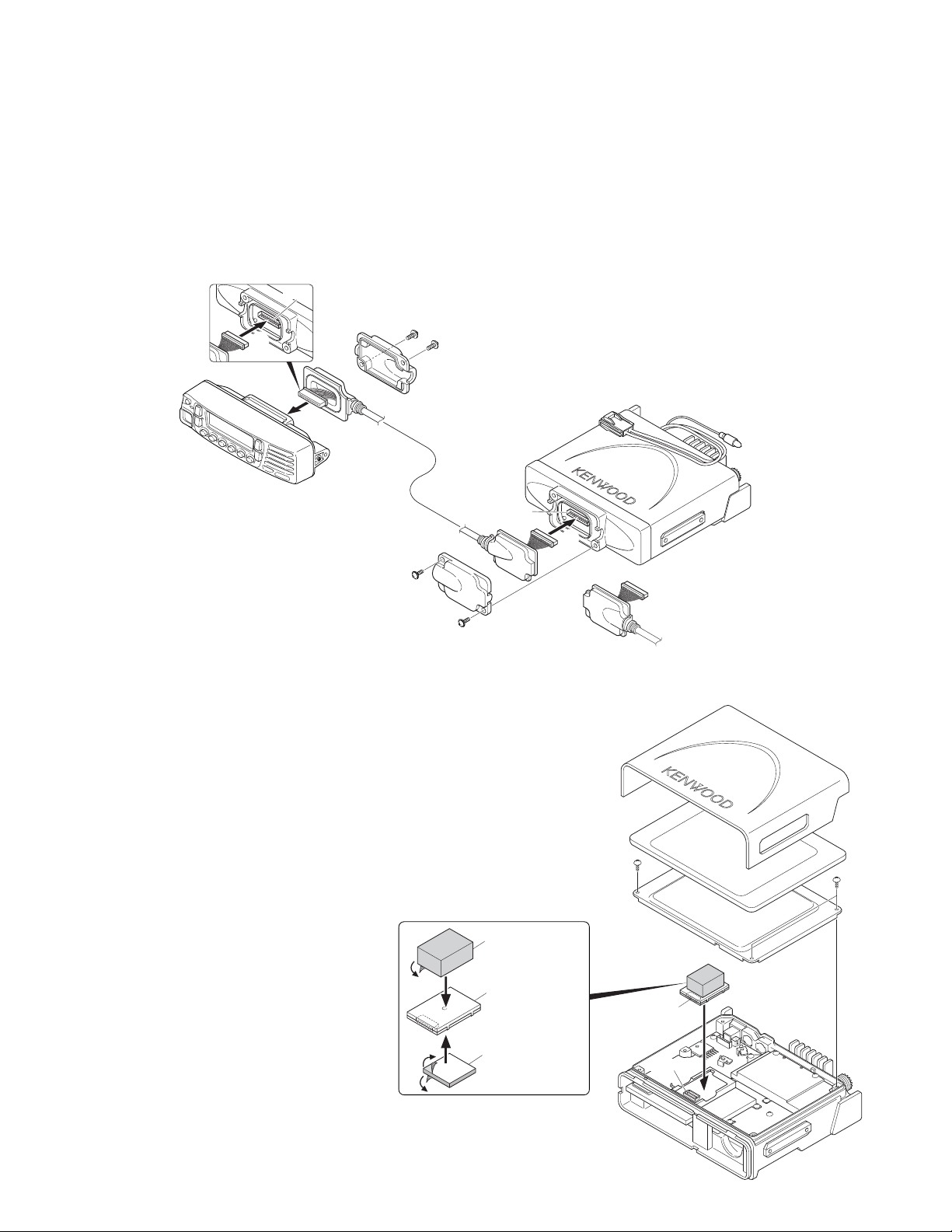
4. Control Head Remote Kit (KRK-10 : Option)
The KRK-10 remote kit is used to remotely operate a TK-
8180 transceiver.
4-1. Installing the KRK-10 kit to the transceiver
1. Remove the front panel from the transceiver.
2. Install the KRK-10 main panel onto the transceiver.
3. Install the KRK-10 rear panel onto the front panel.
4. Connect the KRK-10 main panel to the rear panel with the
cable.
■ Remove the front panel from the transceiver
1. Lift the two tabs of the panel on the bottom of the transceiver with a flat-head screwdriver ( q ) and remove the
panel from the chassis ( w ).
Note : Confirm that the tabs of the speaker hardware fixture and holder is securely fitted in the front panel.
2. Remove the flat cable from the connector (CN902) of the
display unit of the panel. ( e )
3. Fold the black line of the flat cable (in three parts) as
shown in Figure 4-2. ( r, t, y )
TK-8180
■
Install the KRK-10 main panel onto the transceiver
4. Insert the flat cable that was removed in step 2 above into
the connector (CN1) of the interface unit (A/2) of the KRK10 main panel (A62-1101-01). ( u )
Note : The terminal side of the flat cable must face down
when inserting the flat cable into the connector.
5. Fit the main panel with four tabs onto the front of the
chassis. ( i )
Note : When installing the main panel onto the front of the
chassis, hold down the flat cable with your fingers to prevent it from being caught.
Chassis
side
r
CN902
e
w
Fig. 4-1
q
Fig. 4-3
■ Install the KRK-10 rear panel onto the front panel
6. Insert the flat cable attached to the interface unit (B/2) of
the KRK-10 rear panel (A82-0056-01) into the connector
(CN902) of the display unit of the panel ( o ). (The flat
cable has been pre-inserted in the connector (CN2) of the
rear panel at the time of shipping.)
Note : The terminal side of the flat cable must face down
when inserting the flat cable into the connector.
7. Fit the four tabs of the rear panel into the front panel. ( !0 )
CN902
o
CN2
KRK-10 rear panel
y
r
t
Panel
side
t
Fig. 4-2
y
!0
Fig. 4-4
9
Page 10
TK-8180
CN1
CN403
q
w
Cushion
(G13-1994-04)
20 x 30 x 12 mm
Cushion
(G13-1992-04)
21 x 21 x 2.5 mm
VGS-1
CN4
■ Connect the KRK-10 main panel to the rear panel
with the cable
8. Insert one 14-pin connector of the cable (E30-7514-05)
into the connector (CN3) of the interface unit (A/2) of the
main panel. ( !1 )
9. Secure the cable bush on the main panel and fit the water-
proof packing (orange) ( !2 ) securely over top.
!5
!6
INSTALLATION
10. Install the molded cover ( !3 ) over the connector on the
main panel and secure it with two screws ( !4 ).
11. Insert the other 14-pin connector of the cable into the
connector (CN4) of the interface unit (B/2) of the rear
panel. ( !5 )
12. Secure the cable bush on the rear panel and fit the waterproof packing (orange) ( !6 ) securely over top.
13. Install the molded cover ( !7 ) over the connector on the
rear panel and secure it with two screws ( !8 ).
Note : A cable can be connected from the left side as shown
in the Figure 4-5 or from right side.
However, the 14-pin connector must be connected to correct
direction.
!7
!8
!8
!4
5.
Voice Guide & Storage Unit (VGS-1 : Option)
5-1. Installing the VGS-1 unit in the transceiver
1. Remove the cabinet, top packing and shielding plate of the
transceiver.
2. Attach two cushions to VGS-1 as shown in Figure 5. ( q )
Note : Be sure not to cover the connector with the bottom
cushion.
3. Insert the VGS-1 connector (CN1) into the TX-RX unit (B/3)
connector (CN403). ( w )
Note : You must setup using the KPG-89D.
!3
!4
Fig. 4-5
CN3
!1
!2
!2
(Right side)
10
Fig. 5
Page 11

INSTALLATION
6. Voice Scrambler Board Connection
1. Remove the front panel from the transceiver.
2. Solder each lead of the scrambler board to a necessary
location of each landing on the component side of the TXRX unit (B/3).
3. Wrap the scrambler board in a cushion and install it on the
front of the chassis as shown in Figure 7-2.
Note : You must setup using the KPG-89D.
TX-RX unit (B/3)
Solder land
GND (GND)
RXD1
TXD1 (PTT)
TXD2
OPT1 (CODE SELECT1)
OPT3 (CODE SELECT2)
OPT4 (ECHO PTT)
OPT5 (CODE SELECT8)
OPT2 (SCRAMBLE)
RXEO (RX OUT)
OPT6 (CODE SELECT4)
7. ANI Board Connection
1. Remove the front panel from the transceiver.
2. Solder each lead of the scrambler board to a necessary
location of each landing on the component side of the TXRX unit (B/3).
3. Wrap the scrambler board in a cushion and install it on the
front of the chassis as shown in Figure 7-2.
Note : You must setup using the KPG-89D.
OPT1 (CH BUSY)
OPT5 (EMERGENCY)
DTI (DATA OUT)
TCTL (TONE CTRL)
AUDIH (AUDIO INHIB)
OPT2 (AUX I/O)
STON (SIDE TONE)
RXD2
DTI
TCTL
TXO (TX OUT)
AUDIH
STON
TXI (TX IN)
RXEI (RX IN)
8C (+V)
Fig. 6
TX-RX unit (B/3)
Solder land
GND (A–)
RXD1
TXD1
TXD2
RXD2
OPT3 (KEY)
OPT4 (PTT)
5E (A+)
TXO
RXEO
TXI
RXEI
OPT6
8C
Fig. 7-1
5E
Voice scrambler
ANI board
TK-8180
ANI board
3M double coated cushion
No. 4008 (or No.4408)
25 x 110 mm
Voice scrambler board
Fig. 7-2
8. GPS Receiver Connection
8-1. Installing the GPS receiver
1. Remove the cabinet, top packing and shielding plate of the
transceiver.
2. Remove the front panel from the transceiver.
3. Attach two cushions to the top of the GPS receiver.
4. Attach the GPS receiver to the shield case with two cushions as shown in Figure 8-2.
5. Solder each lead of the GPS receiver to a necessary location of each landing on the component side of the TX-RX
unit (B/3).
6. Place the GPS antenna cable in the hollow at the rear of
the chassis. (Fig. 8-2 q )
Note : If the GPS receiver is installed, cut the base of the
convex tab of the top packing with a pair of nippers, or
similar tool. (Fig. 8-3 w )
If the convex tab of the top packing is cut off, the water
proofing property is no longer guaranteed.
Note : You must setup using the KPG-89D.
TX-RX unit (B/3)
Solder land
RXD1 (DATA OUT1)*
GND (GND)
RXD2 (DATA OUT1)*
*1 : Depending on the connected optional accessory, the
DATA OUT1 may connect to either RXD1 or RXD2.
TXD1
TXD2
OPT1
OPT3
OPT4
OPT5
5E (+5V)
DTI
TCTL
TXO
AUDIH
OPT2
STON
RXEO
TXI
RXEI
OPT6
8C
Fig. 8-1
1
1
GPS receiver
11
Page 12
TK-8180
TX-RX unit (B/3)
Solder land
GND (GND)
RXD1
TXD1
TXD2
RXD2 (DATA OUT1)
OPT1
OPT3
OPT4
OPT5
5E (+5V)
DTI
TCTL
TXO
AUDIH
OPT2
STON
RXEO
TXI
RXEI
OPT6
8C
GPS receiver
INSTALLATION
3M Double coated cushion
No. 4016 (or No. 4416)
30 x 25 mm
GPS receiver
3M Double coated cushion
No. 4016 (or No. 4416)
30 x 25 mm
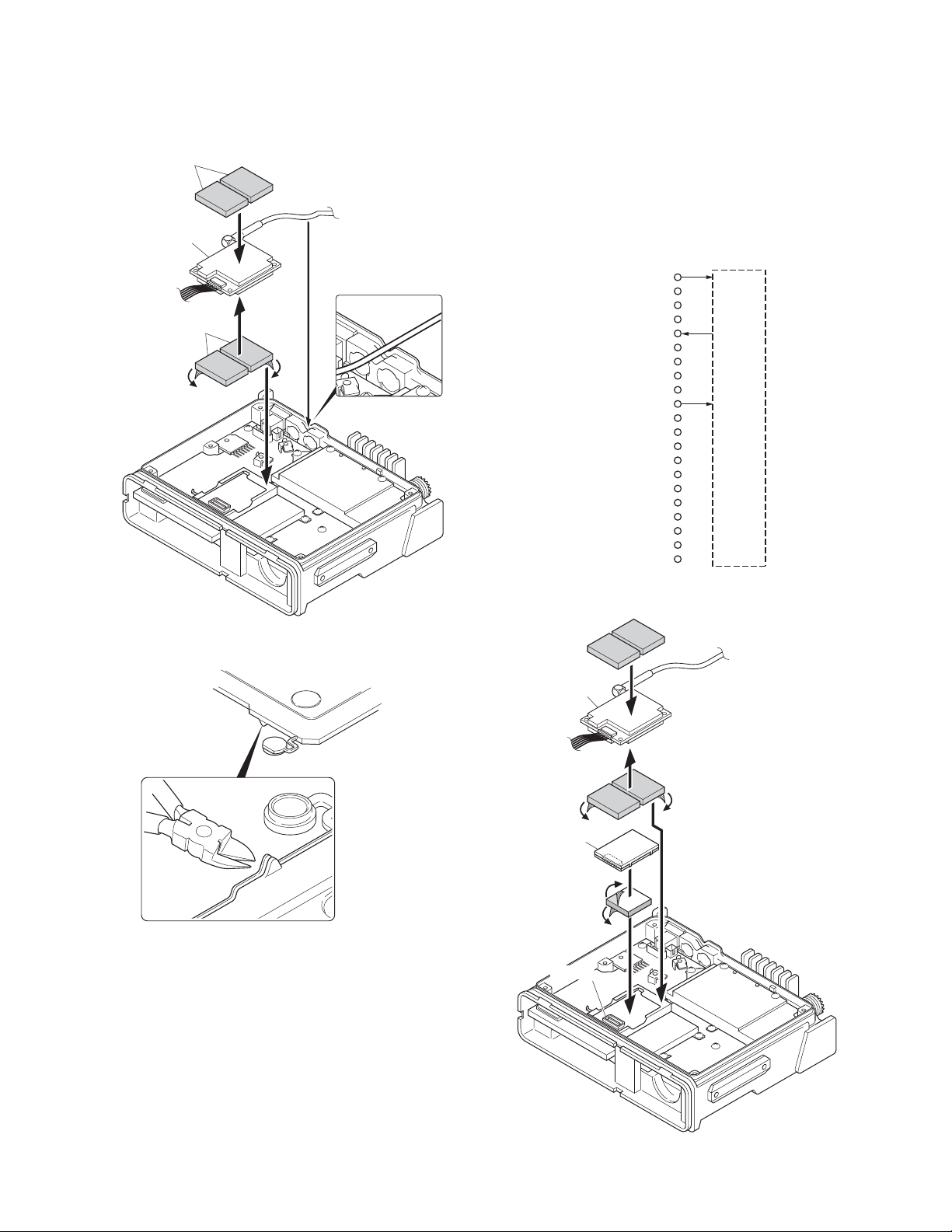
4. Insert the VGS-1 connector (CN1) into the TX-RX unit (B/3)
connector (CN403).
5. Perform step 3 to 6 of “8-1. Installing the GPS receiver”
described on page 11.
Note : You must setup using the KPG-89D.
q
Fig. 8-4
8-2.
1. Remove the cabinet, top packing and shielding plate of the
2. Remove the front panel from the transceiver.
3. Attach a cushion to the bottom of the VGS-1 as shown in
12
Fig. 8-2
w
Fig. 8-3
Installing the GPS receiver together with the VGS-1
transceiver.
Figure 8-5.
Note : Be sure not to cover the connector with the cushion.
GPS receiver
VGS-1
CN1
CN403
Fig. 8-5
Page 13
CN901
w
q
e
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
TK-8180
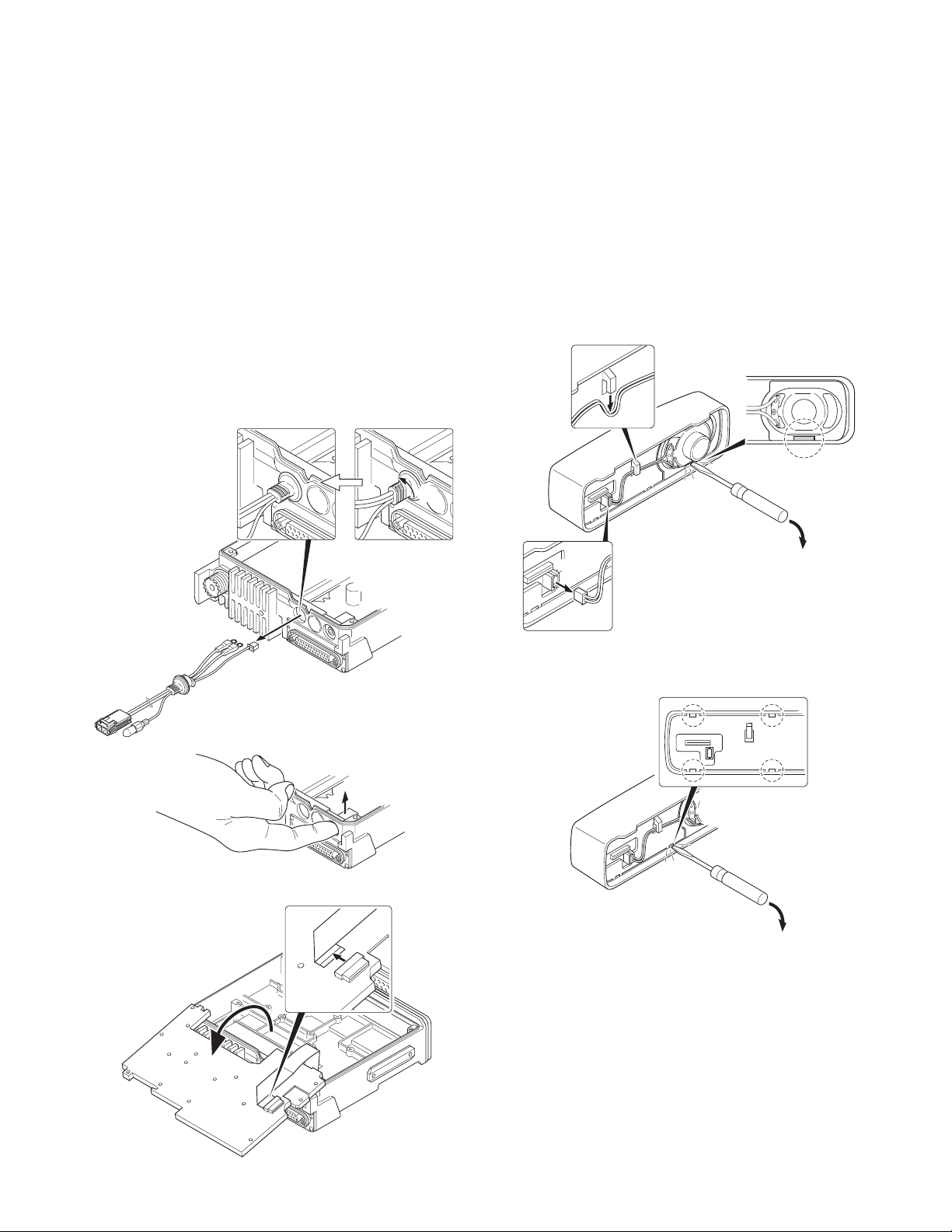
1. Precautions on Disassembly
■ TX-RX PCB (TX-RX unit B/3) Disassembly
1. Remove all screws and antenna terminals on the TX-RX
PCB.
2. Rotate the bush of the power supply cable 90 degrees
counterclockwise as viewed from the rear of the chassis
( q ) and remove the power supply cable from the chassis
( w ).
3. When the speaker phone jack is pushed up, using your
finger, from the rear of the chassis ( e ), the TX-RX PCB is
removed from the chassis.
Note : The TX-RX PCB and D-sub PCB (TX-RX unit A/3) are
connected with a flat cable. Remove them carefully.
4. Turn the TX-RX PCB over and remove the flat cable from
the connector (CN427). ( r )
5. Remove the TX-RX PCB from the chassis.
q
■ Removing the speaker hardware fixture
(J21-8481-03) and holder (J19-5468-03)
1. Remove the speaker lead from the holder hook. ( q )
2. Remove the speaker connector from the display unit con-
nector (CN901). ( w )
3. When removing the speaker hardware fixture, insert a flat-
head screwdriver at the position shown in Figure 2-1 and
tilt it in the direction shown by the arrow. ( e )
4. To remove the holder, insert a flat-head screwdriver into
tab of the holder and tilt it in the direction shown by the
arrow. ( r )
w
Fig. 1-1
Fig. 1-2
Fig. 2-1
e
r
r
Fig. 2-2
CN427
Fig. 1-3
13
Page 14
TK-8180
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
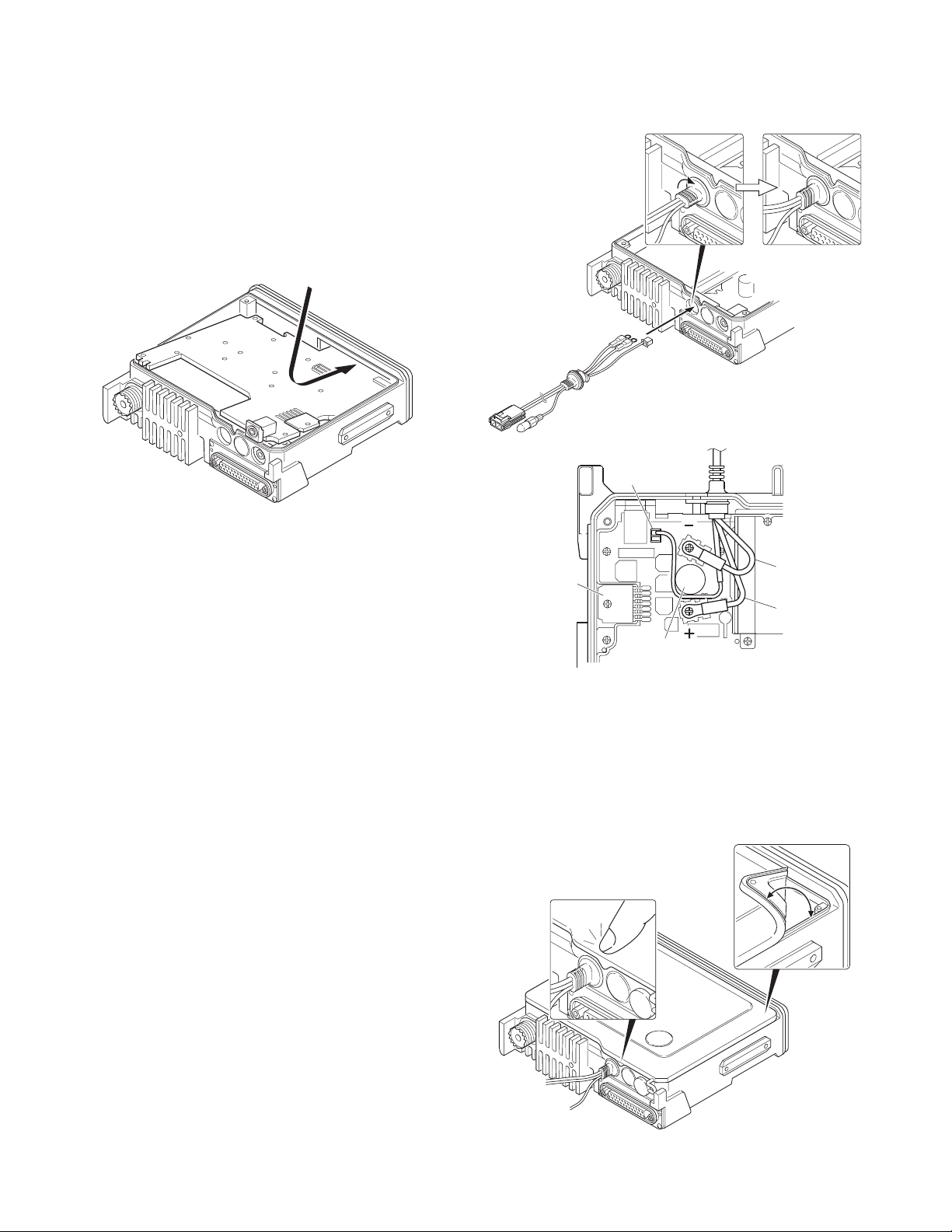
2. Precautions on Reassembly
■ TX-RX PCB (TX-RX unit B/3) Reassembly
1. With the TX-RX PCB turned over, insert the flat cable from
the D-sub PCB (TX-RX unit A/3) into the connector
(CN427) on the TX-RX PCB.
2. Place the TX-RX PCB at its original position, tilt the TX-RX
PCB and install the chassis as shown in Figure 3.
w
q
Fig. 4-1
CN804
Fig. 3
■ Securing the Audio IC (IC417) with screws
The screws for the audio IC are 8mm screws. These are
longer than the other screws, so take care not to confuse
them.
■ FINAL shield case (F10-2489-03) installation
procedure
1. Place the shield case on the final section of the TX-RX unit
(B/3).
2. The shield case is installed on the positioning boss of the
chassis by pushing down on “PUSH2” (on the shield case)
while pushing “PUSH1” (stamped on two parts on the
shield case) to the right.
■ Power supply cable installation procedure
1. Pass the power supply cable through the chassis hole
( q ) as shown in Figure 4-1 and insert the bush into the
chassis hole.
2. Rotate the bush of the power supply cable 90 degrees
clockwise as viewed from the rear of the chassis. ( w )
3. Align the ignition sense connector (yellow) of the power
supply cable around the chemical capacitor (C801) and
connect it to the TX-RX unit (B/3) connector (CN804).
4. Align the + (positive) terminal of the power supply cable
(red) as shown in Figure 4-2 and fix it to the terminal strip
with a screw.
5. Align the – (negative) terminal of the power supply cable
(black) as shown in Figure 4-2 and fix it to the terminal strip
with a screw.
IC417
Black
Red
C801
Fig. 4-2
■ Top packing installation procedure
1. Place the top packing over the shielding plate.
2. Fit the convex tab of the top packing into the hollow of the
chassis. ( q )
3. Fit the chassis into the groove of the top packing. ( w )
Verify that the top packing is in close contact with the
chassis.
w
q
14
Fig. 5
Page 15
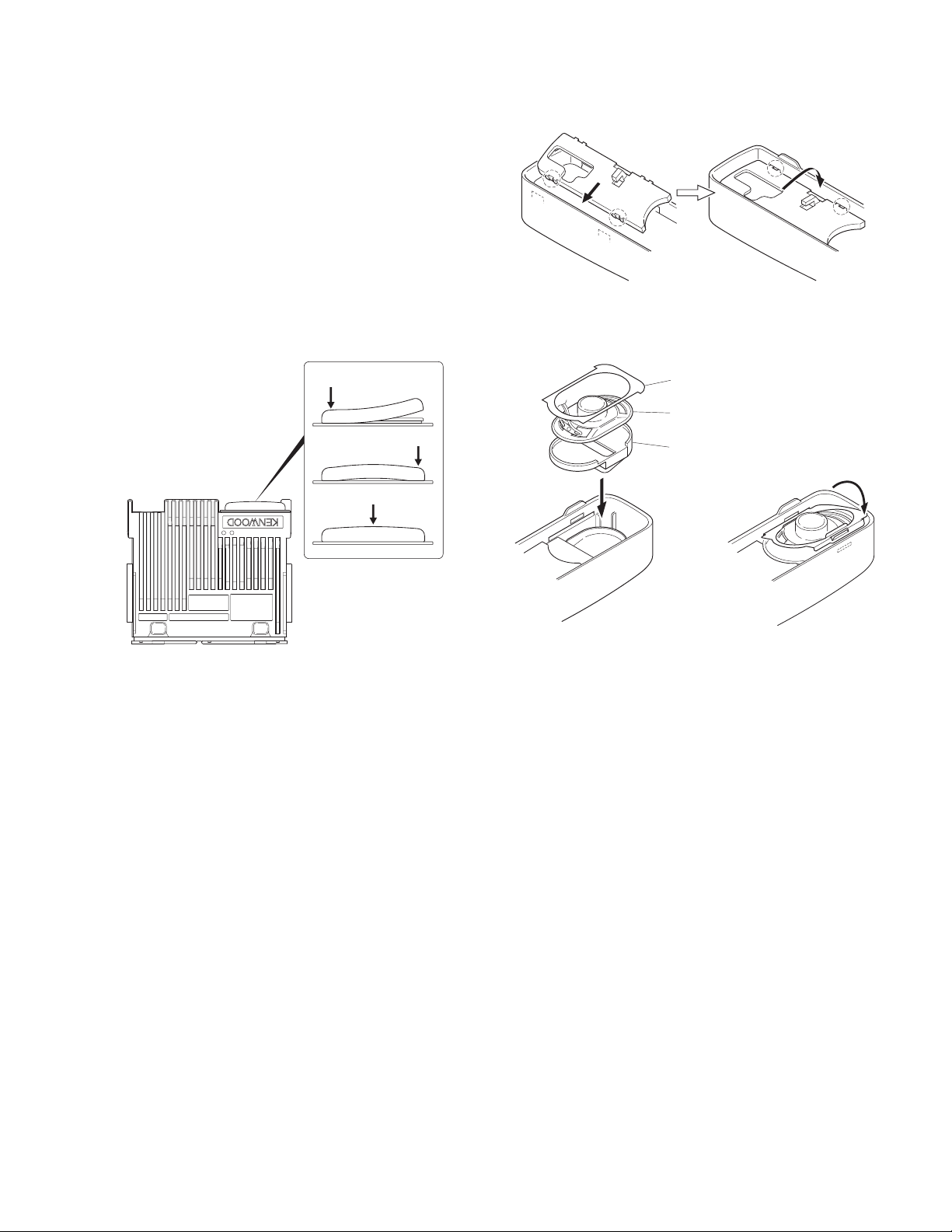
q
w
DISASSEMBLY FOR REPAIR
■ D-sub cap installation procedure
To improve water resistance, fit the D-sub cap into the Dsub terminal hardware fixture of the transceiver in the following order:
1. Fit the left side ( q ) of the D-sub cap into the hardware
fixture.
2. Fit the right side ( w ) of the D-sub cap into the hardware
fixture.
3. Fit the center ( e ) of the D-sub cap into the hardware fix-
ture.
Verify that the D-sub cap is in close contact with the hard-
ware fixture.
TK-8180
Fig. 7-1
q
w
e
Fig. 6
■ Installing the holder (J19-5468-03) and speaker
hardware fixture (J21-8481-03)
1. Insert two tabs of the holder (J19-5468-03) into the hol-
lows in the top of the panel. ( q )
2. Push the two tabs of the holder in on the opposite side of
those in step 1 above and fit them into the hollow in the
bottom of the panel. ( w )
Note : Push in the holder until it snaps in place.
3. Install the speaker holder onto the panel. ( e )
Note : To improve water resistance, fit the panel into the
groove of the holder.
4. Place the speaker into the speaker holder.
Note : The speaker must not ride on the holder rib.
5. Place the spacer on the speaker.
6. Insert the hardware fixture (J21-8481-03) into the hollow
of the panel as shown in Figure 7-3, then push two parts
of the hardware fixture and fit it into the hollow of the top
of the panel. (Fig. 7-3 r )
Note : Push in the hardware fixture until it snaps in place.
7. Insert the speaker connector into the display unit connec-
tor (CN901).
8. Place the speaker lead on the holder hook.
Spacer
Speaker
Speaker holder
e
Fig. 7-2 Fig. 7-3
r
15
Page 16
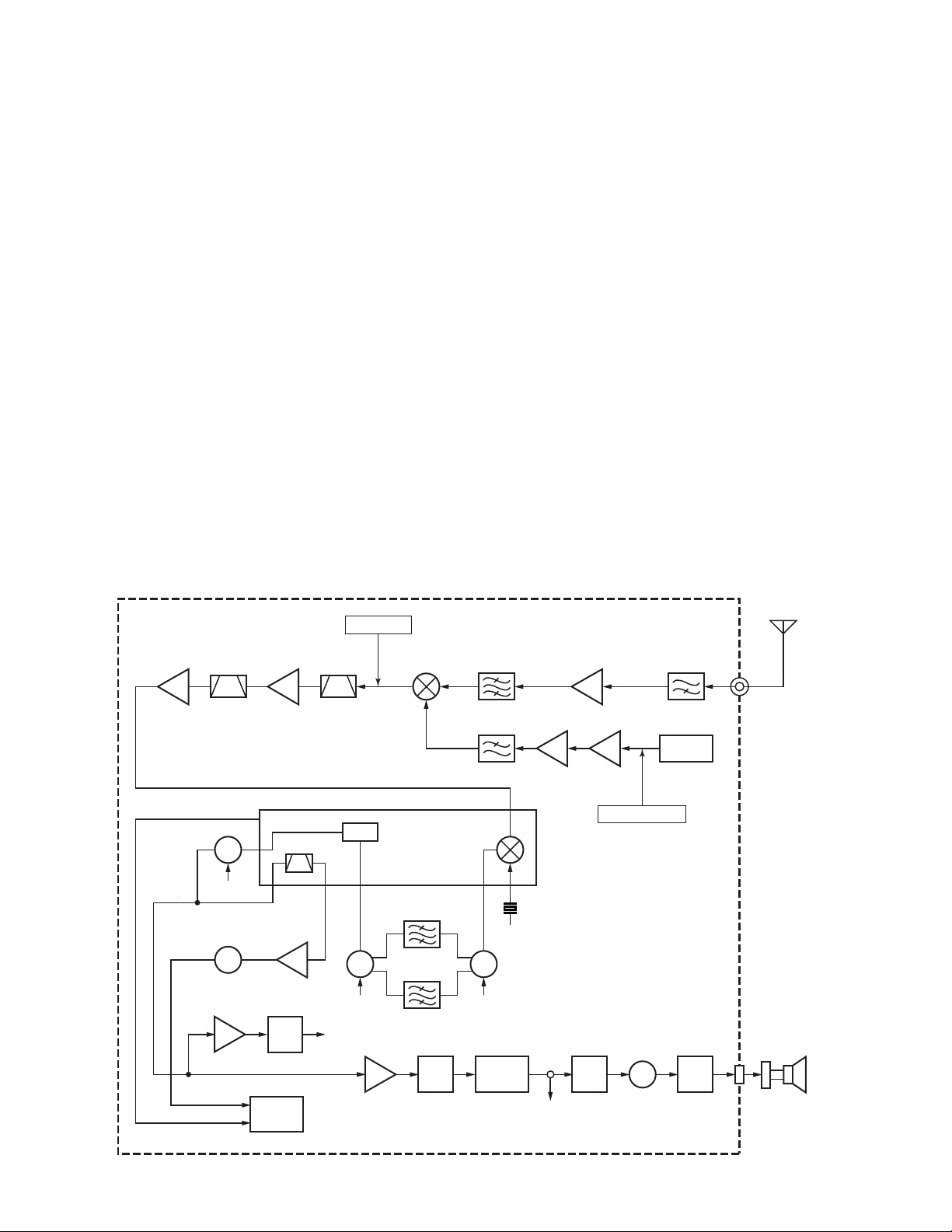
TK-8180
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
1. Outline
The TK-8180 is a UHF/FM transceiver designed to operate
in the frequency range of 450 to 520MHz. Transmission output power is 30 watts (490~520MHz : 25W). The maximum
channel capacity is 512.
The unit consists of receiver, transmitter, phase-locked
loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer, and control circuits.
2. Receiver Circuit
The receiver is double conversion superheterodyne, de-
signed to operate in the frequency range of 450MHz to
520MHz.
The receiver circuit consists of the following : 2-1 front-
end circuit, 2-2 first mixer, 2-3 IF amplifier circuit, 2-4 audio
amplifier circuit, and 2-5 squelch circuit.
2-1. Front-end Circuit
The front-end circuit consists of former HPF (D107, D108,
D109 and D110), RF amplifier Q103, and latter BPF (D103,
D104, D105 and D106). The BPF covers frequency ranges
450 to 520MHz.
The latter BPF (D103, D104, D105 and D106) attenuates
the unwanted signals, and sends only the necessary signal to
the first mixer.
TX-RX UNIT (X57-699)
44.85MHz
IF AMP
Q172
MCF MCF
IF AMP
Q171
1st MIX DBM
IC171
2-2. First Mixer
The signal from the BPF is heterodyned with the first local
oscillator signal from the PLL frequency synthesizer circuit at
the first mixer DBM (IC171) to become a 44.85MHz first intermediate frequency (IF) signal. The first IF signal is fed
through a monolithic crystal filter (XF171) to further remove
spurious signals.
2-3. IF Amplifier
The first IF signal is amplified by Q171 and Q172, and then
enters IC172 (FM system IC). The signal is heterodyned
again with a second local oscillator signal (44.395MHz) with
in IC172 to become a 455kHz second IF signal. The second
IF signal is fed through a 455kHz ceramic filters (CF172;
Wide, CF171; Narrow) to further eliminate unwanted signal,
and the quadrature detection circuit FM-detects the signal to
produce a base-band signal and output it from pin 9.
2-4. Audio Amplifier
The demodulated audio signal from IC172 goes to IC415
through the AF amplifier (IC412) and IC413. The audio signal
goes to an electronic volume (IC410) and is amplified to drive
a loudspeaker by an audio power amplifier (IC417). The audio
output can be provided to external 4Ω speaker through the
speaker jack output (J401) on the rear panel. Q419 is a mute
switch.
450~520MHz
RX ANT
BPF
D103~D106
RF AMP
Q103
HPF
D107~D110
RSSI
DET
SQL
XF171
(2/2)
Q178
SW
W/N
NOISE DET
D173
DET
IC407
ASQ
RSSI
XF171
(1/2)
FM SYSTEM IC : IC172
QUD
NOISE
AMP
Q175
SW
D172
IC410
DAC
IC404
CPU
CFSW
DEO
AMP
IC412 (B/2)
CF172
(Wide)
CF171
(Narrow)
455kHz
IC413
SW
LPF
SW
CFSW
IC415
AQUA
D171
-L
Buff AMP
Q313
X171
44.395MHz
AFO
Buff AMP
Q311
RX
–44.85MHz
f
405.15~475.15MHz
IC410
DAC
Q419
MUTE
Q306
RX VCO
IC417
AF
AMP
INT. SP
16
Fig. 1 Receiver circuit
Page 17

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-8180
2-5. Squelch Circuit
The output signal from IC172 enters FM IC again, then
passed through a band-pass filter.
The noise component output from IC172 is amplified by
Q175 and rectified by D173 to produce a DC Voltage corresponding to the noise level. The DC voltage is sent to the
analog port of the CPU (IC404).
IC172 outputs a DC voltage (RSSI) corresponding to the
input of the IF amplifier.
3. Transmitter Circuit
The transmitter circuit consists of the following circuits : 31 microphone circuit, 3-2 modulation level adjustment circuit,
3-3 driver and final power amplifier circuit, and 3-4 automatic
power control circuit.
3-1. Microphone Circuit
The audio signal from the microphone goes into TX-RX
unit (X57-699) from the display unit (X54-348) and passes
through the mute switch (Q416). The audio signal is amplified by the microphone amplifier (IC414) and is input into the
TXIN terminal of the audio processor (IC415) after passing
through the multiplexer (IC413).
The input audio signal is output from the MOD terminal of
the audio processor (IC415) and is amplified by the audio frequency amplifier (IC412) after passing through the electric
volume (IC410).
DISPLAY UNIT
(X54-348) TX-RX UNIT (X57-699)
3-2. Modulation Level Adjustment Circuit
The audio signal amplified by the audio frequency amplifier (IC412) is added to the low speed data LSD passed
through the low pass filter (IC409). The combined signals is
supplied to the VCO (voltage controlled oscillator) and the
VCXO (voltage controlled crystal oscillator) X301, respectively.
3-3. Driver and Final Power Amplifier Circuit
The transmit signal obtained from the TX VCO buffer amplifier Q311, is amplified to approximately +17dBm by the
driver amplifiers Q313, Q1 and Q2. This amplified signal is
passed to the power amplifier module (power module) IC1,
which consists of a MOS-FET amplifier and is capable of
transmission output power.
3-4. Automatic Power Control Circuit
The automatic transmission power control (APC) circuit
stabilizes the transmitter output power at a predetermined
level by detecting the power module output with a diodes
D6, D7 and D8. Diodes D6, D7 and D8 apply a voltage to DC
amplifier IC72 (A/2). IC72 (B/2) compares the APC control
voltage (PC) generated by microprocessor IC404 and DC amplifier IC71 (A/2, B/2) with the detection output voltage
from IC72 (A/2) to control the Vgg pin of IC1, and stabilizes
transmission output.
The APC circuit is configured to protect over-current of the
power module due to fluctuations of the load at the antenna
end and to stabilize transmission output at voltage and temperature variations.
J901
Mojular
jack
MIC
SW
SW
D-SUB
MI2
IC414Q416
AMP
Q417
IC413
Multi-
plexer
TXIN
D-SUB
DI
LSDO
AQUA-L
IC409
LPF
MOD
IC410 IC412IC415
DAC
AMP
IC408
DC
AMP
Fig. 2 Microphone and modultion level adjustment circuit
Q313
Drive
AMP
Q1
Drive
AMP
PC
MP
Q2
Drive
AMP
DC
AMP
IC71 IC72
IC1
Final
AMP
DC
AMP
Gate
bias
D2,D3,
D11
SW
D6 D7
DET
DET
D8
DET
MOD
MB
Q307
TX VCO
VCXO
16.8MHz
X301
Q311
Buff
AMP
Fig. 3 Drive and Final power amplifier and automatic power control circuit
MOD
(for VCO)
MB
(for VCXO)
ANT
17
Page 18
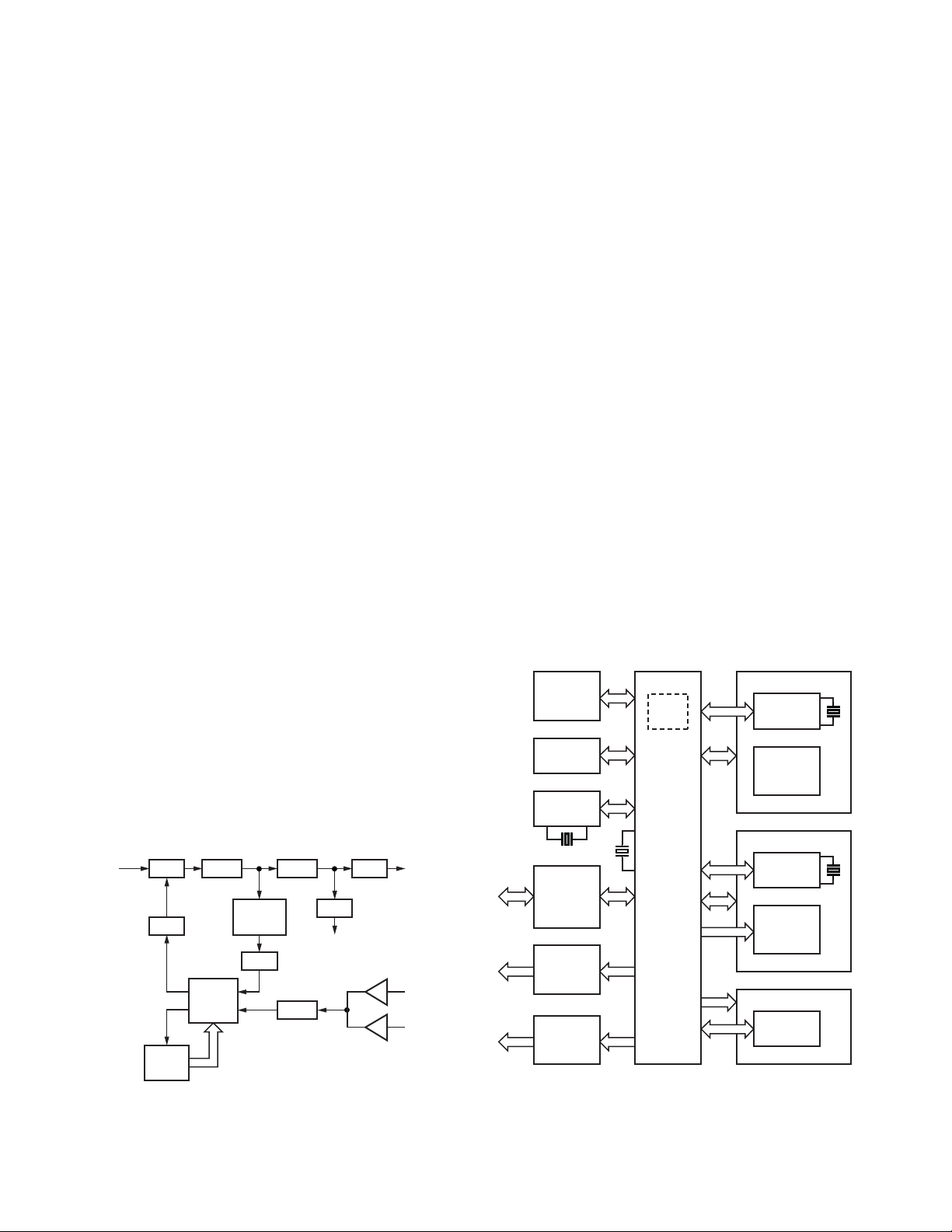
TK-8180
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4. Frequency Synthesizer Unit
4-1. Frequency Synthesizer
The frequency synthesizer consists of the TCXO (X301),
VCO, PLL IC (IC301) and buffer amplifiers.
The TCXO generates 16.8MHz. The frequency stability is
2.5ppm within the temperature range of –30 to +60°C. The
frequency tuning and modulation of the TCXO are done to
apply a voltage to pin 1 of the TCXO. The output of the TCXO
is applied to pin 8 of the PLL IC.
The VCO consists of 2VCO and covers a dual range of the
405.15~475.15MHz and the 450~520MHz. The VCO generates 405.15~475.15MHz for providing to the first local signal
in receive. The operating frequency is generated by Q307 in
transmit mode and Q306 in receive mode. The oscillator frequency is controlled by applying the VCO control voltage, obtained from the phase comparator (IC301) to the variable capacitor diodes (D308 and D311 in transmit mode and D309
and D313 in receive mode).
The T/R pin of IC404 goes “high” in receive mode causing
Q307 and Q309 to turn off, and Q306, Q308 and Q310 turn
on. The T/R pin goes “low” in transmit mode.
The outputs from Q306 and Q307 are amplified by buffer
amplifier (Q311) and doubled by Q301 and then sent to PLL
IC.
The PLL IC consists of a prescaler, reference divider,
phase comparator, charge pump (The frequency step of the
PLL circuit is 20 or 25kHz). The input signal from the pins 8
and 5 of the PLL IC is divided down to the 20 or 25kHz and
compared at phase comparator. The phase comparator output signal is fed into a low-pass filter (Q302 and Q303) before
being applied to the VCO as a frequency control voltage. This
low-pass filter’s power is supplied by the DC/DC converter
(IC251 and Q251). The DC signal is applied to the CV of the
VCO and locked to keep the VCO frequency constant.
PLL data is output from DT (pin 112), PCK (pin 82) and PLE
(pin 81) of the microprocessor (IC404). The data are input to
the PLL IC when the channel is changed or when transmission is changed to reception and vice versa. A PLL lock condition is always monitored by the pin 80 (UL) of the microprocessor. When the PLL is unlocked, the UL goes low.
T/R
(TX : Low)
Q302
Q303
T/R
LPF
UL
CPU
IC404
CV
IC301
20
PLL
15
DT,PCK,PLE
Q311
BUFF
Q301
Doubler
x2
BPF
5
8
Q313
BUFFVCO
TCXO
X301
SW
To mixer
MB
D316
SW
D315
IC408
To
drive
amp
FC
BAL
5. Control Circuit
The block diagram of the control circuit is shown in Figure
5.
The CPU (IC404) is a 16-bit microcomputer that contains a
256k-byte Mask ROM and a 20k-byte RAM. This CPU is connected with an external 512k-byte Flash ROM (IC405) and
operates in memory expansion mode.
The Firmware Program is stored in the Flash ROM and the
user data and adjustment data are stored in the EEPROM
(IC401). The CPU and Flash ROM are connected with an 8 bit
bus and the EEPROM and RTC IC (IC402) are connected with
a I2C bus (*1). The RTC IC (IC402) has a clock function and is
controlled by the CPU (IC404).
Serial communication with a PC is performed through two
paths: through the 232C Level converter IC (IC416) and
through the Display Unit Panel CPU (IC902). The 8 bit Shift
Register (IC403) is used as an 8-port Extended Output Port.
IC410 is an 8 bit-8ch D/A converter. The channels are set as
follows:
Ch1 : Modulation balance
Ch2 : Deviation Factor
Ch3 : Max Power Level
Ch4 : Reception tuning circuit
Ch5 : Deviation Factor
Ch6 : Speaker volume
Ch7 : VCXO control voltage
Ch8 : DEO output level
*1: I2C bus is a registered trademark of PHILIPS of the Netherlands.
IC405
Flash
ROM
IC401
EEPROM
IC402
RTC IC
IC416
232C
Level
converter
IC403
8bit Shift
register
IC410
D/A
converter
Mask
ROM
IC404
CPU
Fig. 5 Control circuit block diagram
Display unit
IC902
CPU
IC903
LCD
driver
Signal block
IC415
AQUA-L
IC413
Multi-
plexer
RF block
IC301
PLL IC
18
Fig. 4 PLL block diagram
Page 19
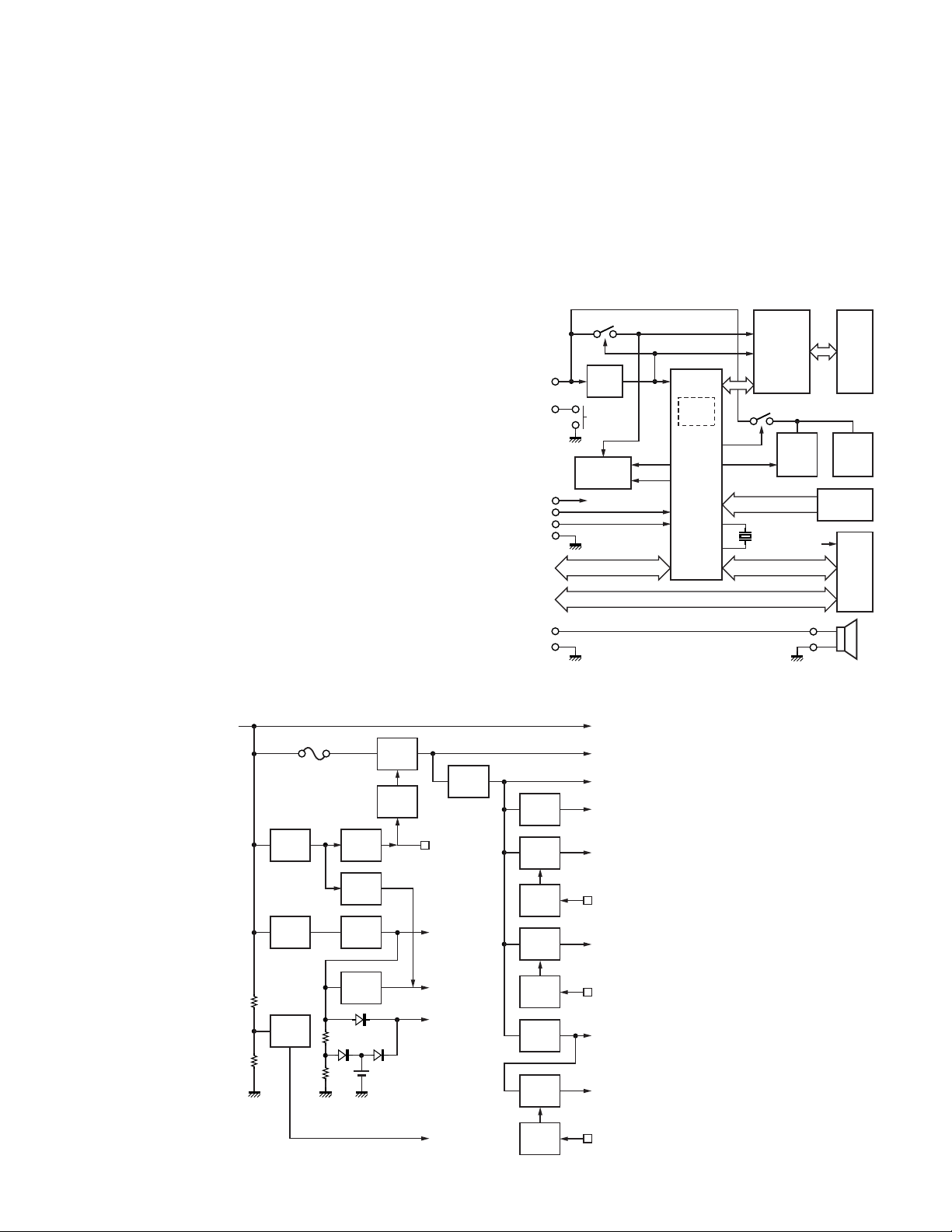
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
TK-8180
6. Power Supply Circuit
The block diagram of the power supply circuit is shown in
Figure 6.
Power is always supplied from +B to the circuit (5M, +B)
that is always started and the circuits (SB, 8C, 5E, 8T, 8R, 5C,
5R) controlled by the CPU (IC404). When +B is supplied to
the transceiver, Q801, D805 and IC805, regulate the voltage
(5M) which is supplied to the circuit around the CPU. The
CPU starts.
When the CPU detects that the +B voltage is higher than
the voltage prescribed by IC802, the transceiver power (SB)
is turned ON by controlling the SBC signal (Low: transceiver
power OFF, High: transceiver power ON).
The CPU controls the TXC signal (Low: Transmission system power OFF, High: Transmission system power ON) during transmission to supply power (8T) to the transmission circuit. The CPU controls the RXC signal (Low: Reception system power OFF, High: Reception system power ON) during
reception to supply power (8R, 5R) to the reception circuit.
When the CPU detects the PSW (Power Switch) signal,
IGN (Ignition Sense) signal or INT signal, it controls the SBC
signal and turns the transceiver power (SB) OFF.
If +B is not provided to the transceiver, power is supplied
to only the RTC IC (IC402) through the secondary battery connected with CN401 to back up the clock.
7. Display Circuit
The display unit consists of the Panel CPU (IC902), the
LCD driver (IC903), the TX/BUSY LED, the KEY detection, the
Backlight and the Microphone jack circuits.
The Panel CPU is a 16-bit microcomputer that contains a
64k-byte Mask ROM and a 2k-byte RAM.
Power supply : 10.8~15.7V
F801
5A
D804
DET
Q801,D805
REG
Q802
SW
Q812
SW
IC805
AVR
Q810
SW
Q807
SW
5M
SBC
CPU
Flash memory
EEPROM
Ext-I/O
IC803
AVR
The Panel CPU performs serial communication with the
Main CPU (IC404) on the TX-RX unit (B/3) and the Panel CPU
detects keys and sends data communication contents
through the MIC Jack to the Main CPU. The Panel CPU receives commands from the Main CPU and controls the display system.
The LCD operates with 1/9 duty under the LCD driver
(IC903) control. The LCD and KEY Backlights are controlled
by Q909. The display brightness of the LCD Backlight can be
changed.
Q910
IC903
8C
PSW
SB
RST2
SHIFT
PSENS
SPO
GND
IC901
AVR
POWER
SW
TX/Busy
LED
RXD, TXD
RED
GRN
Mask
ROM
IC902
CPU
MIC, ME
LCD
driver
Q909
BLCI
DIMM
HK, PTT, DM, BLC2
LCD
back
light
FKEY [1~10]
LCD
KEY
back
light
Function
KEY
SB
MIC
jack
SP
Fig. 7 Display circuit
+B
Final amp.
SB
Audio amp, PA connector
Panel block, D-sub block
8C
Internal option
Panel block
5E
IC807
AVR
Q803
SW
Q806
SW
Q804
SW
Internal option
TX-drive
8T
APC block
ANT SW
TXC
8R
IF block
IC802
DET
IC801
DET
CN401
CPU #17
: RST1
RTC IC
CPU #24
: INT
Fig. 6 Power supply circuit
Q808
SW
IC804
AVR
Q805
SW
Q809
SW
RXC
VCXO, VCO, PLL IC
IF detection IC
5C
DC/DC converter
D/A converter
MIC amp, AQUA
AF block
5R
IF block
RXC
19
Page 20
TK-8180
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
Microprocesser : 30625MGP-169GP (TX-RX unit IC404)
Pin No. Port Name I/O Function
1VREF-+5V
2 AVCC - +5V
3 SBC O Switched B control
4 RXC O RX control
5 TXC O TX control
6PCOTX APC adjust
7 HSDO O High speed data output
8 STSW O Side tone switch
9 RTCL/EEPCL O RTC/EEPROM clock
10 HSDIN I High speed data input
11 NC - Non-connection
12 RTDT/EEPDAT I/O RTC/EEPROM data
13 BYTE - +5V
14 CNVSS - DGND (Vss)
15 DMUTE O Det mute
16 AM2 O Audio mute 2
17 RST I Reset
18 Xout O 11.0592MHz clock output
19 DGND - DGND (Vss)
20 Xin I 11.0592MHz clock input
21 VCC1 - +5V
22 NMI - +5V
23 PSW I Power switch input
24 INT I BATT voltage INT
25 INTRA I RTC INT
26 SHIFT/MODEL I/O Beat shift/Model select
27 BEEP O Beep output
28 SPSTB O Shift register strobe
29 SOE O Shift register output enable
30 AIO5 I/O AUX I/O 5
31 AIO9 I/O AUX I/O 9
32 DSTB O D/A converter LD
33 LSDO O Low speed data output
34 RXD2 I RXD2
35 TXD2 O TXD2
36 TXD1 O TXD1/PTT (Scrambler board)
37 Vcc1 - +5V
38 RXD1 I RXD1
39 DGND - DGND (Vss)
40 MM1 O MIC mute 1
41 PSENS I Panel sense
42 TXD O TXD
43 RXD I RXD
44 AFDAT O BB TDATA and DTRCLK
45 AFDIO I/O BB DI/O
46 AFDIR O BB DIR
47 DTRLOAD O BB DTMF enable
48 AFSTD I BB STD
Pin No. Port Name I/O Function
49 LSW O BB LIM switch
50 RDY - +5V
51 NC - Non-connection
52 HOLD - +5V
53 NC - Non-connection
54~57 AIO4~AIO1 I/O AUX I/O 4~1
58 NC - Non-connection
59 RD O Read (RD)
60 NC - Non-connection
61 WR O Write (WR)
62~64 AIO8~AIO6 I/O AUX I/O 8~6
65,66 NC - Non-connection
67 RST2 O Display µ-com reset
68 CS0 O Chip select 0
69 NC - Non-connection
70~79 A18~A9 O Address bus 18~9
80 UL I PLL unlock
81 PLE O PLL enable
82 PCK O PLL clock
83 NC - Non-connection
84 OPT6 I/O Option boad I/F 6
85 VCC2 - +5V
86 A8 O Address bus 8
87 DGND - DGND (Vss)
88~95 A7~A0 O Address bus 7~0
96 IGN I Ignition sense
97 AFRTM I BB RDF/FD
98 TCLK/DTRDO I BB TCLK and DTRDO
99 MM2 O MIC mute2
100 T/R O TX/RX switch
101 AM1 O Audio mute 1
102 EMTON O EM tone switch
103 NC - Non-connection
104~111 D7~D0 I/O Data bus7~0
112 DT O Serial data
113 CK O Serial clock
114 W/N O Wide/Narrow switch
115~117 OPT 1~OPT 3 I/O Option boad I/F 1~3
118,119 OPT 4, OPT 5 O Option boad I/F 4, 5
120 H/L O High/Low power switch
121 THP I TX thermal input
122,123 NC - Non-connection
124 ASQ I RX analog SQ. input
125 RSSI I RX RSSI input
126 NC - Non-connection
127 AGND - AGND (Vss)
128 LSDIN I Low speed data input
20
Page 21

SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
Microprocesser : 30302M8-8Z7GP (Display unit IC902)
Pin No. Port Name I/O Function
1~4 NC - Non-connection
5 SHIFT O Beat shift
6BYTE-+5V
7 CNVSS - GND
8,9 NC - Non-connection
10 RST I Reset
11 Xout O 14.7456MHz clock output
12 GND - GND
13 Xin I 14.7456MHz clock input
14 VCC - +5V
15 NMI - +5V
16 BLC2 O MIC backlight control
17 BLC1 O Key & LCD backlight control
18 DIMM O Dimmer control
19 LEDG O LED green
20 LEDR O LED red
21 NC - Non-connection
22 LCDCK O LCD serial clock
23 LCDDT O LCD serial data
24 LCDCS O LCD chip select
25 LCDRST O LCD reset
26 NC - Non-connection
27 RXD2 I RXD2 (Main µ-com)
28 TXD2 O TXD2 (Main µ-com)
29 PTT/TXD I/O PTT/TXD (COM0)
30 NC - Non-connection
31 DM O MIC DM
32,33 NC - Non-connection
34 HK/RXD I HOOK/RXD (COM0)
35~44 NC - Non-connection
45 TP1 I LCD check
46~59 NC - Non-connection
60 VCC - +5V
61 NC - Non-connection
62 VSS - GND
63~70 NC - Non-connection
71~82 S22~S11 I Non-connection
Pin No. Port Name I/O Function
83 S10 I Front panel key (R down [ ])
84 S9 I Front panel key (R up [ ])
85 S8 I Front panel key ( ■ )
86 S7 I Front panel key (C)
87 S6 I Front panel key (B)
88 S5 I Front panel key (A)
89 S4 I Front panel key (S)
90 S3 I Front panel key ( )
91 S2 I Front panel key (L down [ ])
92 S1 I Front panel key (L up [ ])
93 NC - Non-connection
94 AVSS - GND
95 NC - Non-connection
96 VREF - +5V
97 AVCC - +5V
98~100 NC - Non-connection
Shift Register : BU4094BCFV (TX-RX unit IC403)
Pin No. Port Name I/O Function
1 STRB I Storage enable input
2 DATA I Serial data input
3 CLK I Serial clock input
4Q1OAUX output 1
5Q2OPublic address
6Q3OHorn alert
7Q4OScrambler switch
8 Vss -
9Qs O
10 Q’s O
11 Q8 O Ceramic filter switch
12 Q7 O Non-connection
13 Q6 O AUX output 2
14 Q5 O Gate switch
15 OE I Output enable
16 VDD -
TK-8180
21
Page 22

TK-8180
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION
Display unit (X54-3480-10)
Ref. No. Part Name Description
IC901 IC Voltage regulator/ 5V
IC902 IC Microprocessor
IC903 IC LCD driver
Q901,902 Transistor HOOK switch
Q904 Transistor TX indication LED switch
Q905 Transistor BUSY indication LED switch
Q906 Transistor Dimmer switch control
Q907 Transistor Dimmer switch
Q909 Transistor Backlight control switch
Q910 Transistor 8C switch
Q911 Transistor 8C switch control
Q913 Transistor Backlight control
D901,902 Zener diode Voltage protection
D903 Varistor Current limitter
D904~906
D907 LED TX/Busy indication
D909~920
D921~930
Diode Surge protection
LED LCD backlight
LED KEY backlight
TX-RX unit (X57-6990-10)
Ref. No. Part Name Description
IC1 IC Power module
IC71,72 IC DC amp for TX APC
IC171 IC RX 1st mixer
IC172 IC FM IF system IC
IC251 IC DC-DC converter
IC301 IC PLL system IC
IC302 IC PLL CP switch
IC401 IC EEPROM
IC402 IC RTC processor
IC403 IC Shift register
IC404 IC Microprocessor
IC405 IC Flash memory
IC406 IC HSD BPF/HSD compalator
IC407 IC DET amp/Data LPF (DB-25)
IC408 IC LSD buffer amp/VCXO bias amp
IC409 IC LSD LPF/Voltage DC-reference
IC410 IC D/A converter
Ref. No. Part Name Description
IC411 IC RF BPF tuning voltage DC amp
IC412 IC Modulation LPF/DET amp
IC413 IC AF switch IC
IC414 IC MIC amp
IC415 IC AQUA-L
IC416 IC Level converter IC (RS-232C)
IC417 IC Audio IC
IC801 IC Voltage detector (CPU Reset)
IC802 IC Voltage detector (INT)
IC803 IC Voltage regulator/ 8V
IC804,805
IC807 IC Voltage regulator/ 5V
Q1 Transistor TX pre-driver
Q2 Transistor TX driver
Q3 Transistor TX gate switch
Q70 Transistor High/Low power switch
Q72 FET High/Low power switch
Q103 Transistor Front-end LNA
Q171,172 Transistor IF amp
Q173,174 Transistor W/N CF switch control
Q175 Transistor Noise Amp
Q176 FET DET mute switch
Q177 Transistor W/N CF switch control
Q178 Transistor W/N discrete switch
Q179 Transistor W/N CF switch control
Q251 Transistor Ripple filter
Q301 Transistor PLL f-in doubler amp
Q302,303 Transistor PLL LPF
Q306,307 FET TX/RX VCO
Q308~310
Q311 Transistor VCO buffer amp
Q312 Transistor Ripple filter
Q313 Transistor VCO buffer amp
Q402 Transistor Beat shift switch
Q403 FET AF switch (Voice)
Q405 Transistor AQUA control switch
Q406 FET AF switch (LSD)
Q409 Transistor AF mute switch
Q410,411 Transistor MIC AGC
Q412 FET AF mute switch
IC Voltage regulator/ 5V
Transistor TX/RX VCO switch
22
Page 23
COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION
TK-8180
Ref. No. Part Name Description
Q413,414 FET AF Switch
Q415 FET AF Switch (Voice)
Q416,417 FET MIC mute switch
Q418 Transistor AF mute control switch
Q419 Transistor AF mute switch
Q600 Transistor MIC mute switch
Q701,702 Transistor Inverter switch
Q801 Transistor Voltage regulator/ 8.5V
Q802 Transistor SB control switch
Q803 Transistor 8T switch
Q804 Transistor 8R switch
Q805 Transistor 5R switch
Q806 Transistor 8T control switch
Q807 Transistor SB control switch
Q808 Transistor 8R control switch
Q809 Transistor 5R control switch
Q810 FET SB switch
Q811 Transistor Ignition sense control switch
Q812 Transistor CPU reset switch
D1 Zener diode Voltage protection
D2,3 Diode ANT switch
D6~8 Diode RF detector
D103~110
D111 Diode ANT switch
D171,172 Diode W/N CF switch
D173 Diode SQ noise-amp detector
D174 Diode DET mute switch control
Variable RF BPF tuning
capacitance diode
Ref. No. Part Name Description
D251 Diode Reverse voltage protection
D308,309 Variable
capacitance diode
D311 Variable Frequency control for TX/RX VCO
capacitance diode
D313 Variable Frequency control for TX/RX VCO
capacitance diode
D314 Variable Modulation control for TX VCO
capacitance diode
D315,316 Diode TX/RX band switch
D402~404
D405,406 Zener diode Voltage protection
D407 Diode DC detector
D408,409 Diode MIC-amp AGC detector
D412~414
D416 Diode AF mute control
D417,418 Diode Isolator
D421~423
D600,601 Diode MIC mute control
D701 Zener diode Voltage protection
D702,703 Diode Voltage protection
D704~708
D709,710 Zener diode Voltage protection
D711~713
D714 Zener diode Voltage protection
D801 Surge absorber Voltage protection
D802 Diode DC reverse connection protect
D804,805 Zener diode Voltage protection
Diode RTC battery control
Diode Surge protect
Diode Voltage protection
Diode Surge protect
Diode Surge protect
Frequency control for TX/RX VCO
23
Page 24
TK-8180
PARTS LIST
✽ New Parts. indicates safety critical components.
Parts without Parts No. are not supplied.
Les articles non mentionnes dans le Parts No. ne sont pas fournis.
Teile ohne Parts No. werden nicht geliefert.
TK-8180 (Y51-5030-10)
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10)
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
Ref. No.
TK-8180 DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10)
11B✽ A01-2194-11 CABINET
23A✽ A62-1094-23 PANEL ASSY
42A✽ B09-0681-03 CAP (KAP-2)
51D✽ B62-1766-10 INSTRUCTION MANUAL
72BE04-0167-05 RF COAXIAL PECEPTACLE (M)
82B✽ E30-7520-05 DC CORD (PIG TAIL)
92C✽ E30-7523-05 DC CORD ASSY (WATER-PROOF)
10 2A ✽ E37-1110-05 FLAT CABLE (30P/D-SUB)
11 1A ✽ E37-1118-05
12 2A ✽ E37-1120-05 FLAT CABLE (30P/TX-RX)
13 3B ✽ E37-1124-05
15 2B ✽ F10-2488-02 SHIELDING PLATE (CHASSIS)
16 1A ✽ F10-2489-03 SHIELDING CASE (FINAL)
17 1A ✽ F10-2490-03 SHIELDING CASE (VCO)
18 1C F52-0024-05 FUSE (BLADE) 15A/32V
20 3B ✽ G10-1342-04 FIBROUS SHEET (BIRITSUKI)
21 2A ✽ G11-4290-04 RUBBER SHEET (CHASSIS)
22 1B ✽ G11-4343-04 SHEET
23 1A G13-2018-04 CUSHION
24 2B ✽ G13-2047-04 CUSHION (DC SCREW)
25 1B ✽ G53-1613-01 PACKING (SHIELD PLATE)
26 3A ✽ G53-1614-23 PACKING (CHASSIS)
27 1A ✽ G53-1616-03 PACKING (PHONE JACK)
28 2B ✽ G53-1626-03 PACKING (D-SUB OUTER)
29 3B ✽ G53-1643-04 PACKING (DC CORD)
LEAD WIRE WITH CONNECTOR (SHORT CABLE)
LEAD WIRE WITH CONNECTOR (2P/SP)
Destination
L : Scandinavia K : USA P : Canada
Y : PX (Far East, Hawaii) T : England E : Europe
Y : AAFES (Europe) X : Australia M :Other Areas
Ref. No.
101 3B ✽ B11-1825-04 FILTER (LCD)
102 3B ✽ B38-0888-05 LCD
D907 B30-2151-05 LED (R/G)
D909-920 ✽ B30-2281-05 LED (Y)
D921-930 ✽ B30-2282-05 LED (Y)
C904 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C906 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C907,908 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C909-911 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C912,913 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C914 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C915 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C916,917 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C918 C92-0628-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 10WV
C920 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C921 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C922 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C924,925 CC73GCH1H100D CHIP C 10PF D
C926-928 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C930 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C931 C92-0784-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 10WV
C932-934 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C935 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C936 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C937 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C938 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
Address
New
parts
Parts No. Description
Destination
30 3B ✽ G53-1645-03 PACKING (D-SUB INNER)
31 2A ✽ G53-1662-04 PACKING (O RING)
32 2C ✽ H02-0624-03 INNER PACKING CASE
33 2D ✽ H12-3170-01 PACKING FIXTURE (LOWER)
34 1D ✽ H12-3171-03 PACKING FIXTURE (UPPER)
36 2D H25-2352-04 PROTECTION BAG (250/350/0.07)
37 3D ✽ H52-2069-02 ITEM CARTON CASE
39 1C J19-1584-05 HOLDER (ACCESSORY)
40 3B ✽ J19-5464-13 HOLDER (SP)
41 3B ✽ J19-5468-02 HOLDER (PANEL)
42 2B ✽ J21-8479-02 HARDWARE FIXTURE (D-SUB)
43 3B ✽ J21-8481-03 HARDWARE FIXTURE (SP)
44 2C J29-0662-03 BRACKET (ACCESSORY)
45 3B ✽ J30-1289-04 SPACER (SP)
47 3A ✽ K29-9312-21 KEY TOP
A2BN09-2409-05 HEXAGON HEAD SCREW (D-SUB)
B 1A,2A ✽ N67-3008-48
C
D1AN87-2608-46
49 2C ✽ N99-2039-05 SCREW SET (ACCESSORY)
51 3B ✽ T07-0750-05 SPEAKER
52 1C ✽ T91-0639-05 MICROPHONE (ACCESSORY)
54 2A W09-0971-05 LITHIUM CELL
1A,2A,2B
✽ N87-2606-48
PAN HEAD SEMS SCREW W (FINAL IC)
BRAZIER HEAD TAPTITE SCREW (ANT,PCB)
BRAZIER HEAD TAPTITE SCREW (AUDIO IC)
103 3B ✽ E29-1202-04 INTER CONNECTOR (LCD)
CN901 E40-5704-05 PIN ASSY
CN902 ✽ E40-6372-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR
J901 3B E08-0877-05 MODULAR JACK
104 3B ✽ G11-4342-04 SHEET
105 3B ✽ J19-5467-03 HOLDER (LCD)
106 3B ✽ J21-8470-03 HARDWARE FIXTURE (LCD)
- ✽ J31-0551-05 COLLAR
L901,902 L40-1095-85 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (1.0UH)
L903-907 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
L908,909 L92-0163-05 BEADS CORE
X901 ✽ L77-1956-05 CRYSTAL RESONATOR (14.7456MHZ)
CP901-911 RK75HA1J101J CHIP-COM 100 J 1/16W
R901 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R903 RK73GB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R904 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R905 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R907 RK73GB1J333J CHIP R 33K J 1/16W
R909-911 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R913-916 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R917 RK73FB2A471J CHIP R 470 J 1/10W
R918 RK73FB2A271J CHIP R 270 J 1/10W
R919 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R920 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R925 RK73HB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R926 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
24
Page 25
Ref. No.
R927-935 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R936 RK73HB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R939 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R940 RK73HB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R941 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
PARTS LIST
Destination
Ref. No.
C44 C93-0573-05 CHIP C 120PF J
C45 C93-0553-05 CHIP C 3.0PF C
C47 CC73GCH1H0R5B CHIP C 0.5PF B
C48 CC73GCH1H030B CHIP C 3.0PF B
C49 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
Address
New
parts
TK-8180
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10)
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)
Parts No. Description
Destination
R942 RK73EB2B470J CHIP R 47 J 1/8W
R943 RK73EB2B101J CHIP R 100 J 1/8W
R944 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R945 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R947-950 RK73FB2A101J CHIP R 100 J 1/10W
R951,952 RK73FB2A391J CHIP R 390 J 1/10W
R953,954 RK73FB2A821J CHIP R 820 J 1/10W
R955-958 RK73HB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R959 RK73HB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R962,963 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R967 RK73HB1J271J CHIP R 270 J 1/16W
R969 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R970 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R971 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
D901,902 02DZ18(X,Y) ZENER DIODE
D903 MINISMDC020 VARISTOR
D904-906 DA204U DIODE
IC901 TA78L05F MOS IC
IC902 ✽ 30302M8-8Z7GP MCU
IC903 ✽ LC75810T-8726 MOS IC
Q901,902 DTC144EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q904-906 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q907 2SC2873(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q909,910 ✽ 12A02CH TRANSISTOR
Q911 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q913 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
TH901 ✽ S1R103J440H THERMISTOR
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)
C1 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C2-5 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C6 C92-0585-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 16WV
C7,8 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C9 CC73GCH1H060D CHIP C 6.0PF D
C50 C93-0558-05 CHIP C 8.0PF D
C51 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C52 CC73GCH1H0R5B CHIP C 0.5PF B
C53 C93-0560-05 CHIP C 10PF D
C55 CC73GCH1H020B CHIP C 2.0PF B
C56 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C57 CC73GCH1H0R5B CHIP C 0.5PF B
C58 CC73GCH1H020B CHIP C 2.0PF B
C59 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C60 C93-0556-05 CHIP C 6.0PF D
C61,62 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C74 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C76,77 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C79,80 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C119 CC73GCH1H050B CHIP C 5.0PF B
C121 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C124 CC73GCH1H100D CHIP C 10PF D
C125 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C127 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C128 CC73GCH1H090B CHIP C 9.0PF B
C129 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C130 CC73GCH1H050B CHIP C 5.0PF B
C131 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C132 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C133 CC73GCH1H060B CHIP C 6.0PF B
C134 CC73GCH1H030B CHIP C 3.0PF B
C135 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C136 CC73GCH1H040B CHIP C 4.0PF B
C137 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C138 CC73GCH1H050B CHIP C 5.0PF B
C139 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C140 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C141 CC73GCH1H090B CHIP C 9.0PF B
C142 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C143 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C10 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C13-15 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C16 CC73GCH1H060D CHIP C 6.0PF D
C17 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C18 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C19 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C20 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C21 CK73FB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C22 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C24 C92-0606-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 10WV
C25 C93-0550-05 CHIP C 1.0PF C
C26 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C27 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C28 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C29-31 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C32 ✽ C92-0834-05 ELECTRO 47UF 25WV
C33-35 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C38-40 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C42 C93-0555-05 CHIP C 5.0PF C
C43 CC73FCH1H030C CHIP C 3.0PF C
C144 CC73GCH1H070B CHIP C 7.0PF B
C145 CC73GCH1H1R5B CHIP C 1.5PF B
C146 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C147 CC73GCH1H050B CHIP C 5.0PF B
C148 CC73GCH1H010B CHIP C 1.0PF B
C149 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C150 CC73GCH1H050B CHIP C 5.0PF B
C151 CC73GCH1H010B CHIP C 1.0PF B
C152 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C153 CC73GCH1H050B CHIP C 5.0PF B
C154 CC73GCH1H1R5B CHIP C 1.5PF B
C155,156 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C171 CC73GCH1H060B CHIP C 6.0PF B
C173 CC73GCH1H120J CHIP C 12PF J
C175 CC73GCH1H060B CHIP C 6.0PF B
C176-178 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C181 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C182,183 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C184 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C185 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
25
Page 26
TK-8180
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
Ref. No.
C186 CC73GCH1H330J CHIP C 33PF J
C187 CC73GCH1H390J CHIP C 39PF J
C188,189 CC73GCH1H040B CHIP C 4.0PF B
C190 CC73GCH1H390J CHIP C 39PF J
C192-194 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
PARTS LIST
Destination
Ref. No.
C318 C92-0657-05 CHIP-TAN 2.2UF 20WV
C320 C92-0657-05 CHIP-TAN 2.2UF 20WV
C322 CK73GB1E473J CHIP C 0.047UF J
C323 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C324 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
Address
New
parts
Parts No. Description
Destination
C195 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C196,197 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C198 CC73GCH1H680J CHIP C 68PF J
C199 CC73GCH1H390J CHIP C 39PF J
C200,201 CC73GCH1H040B CHIP C 4.0PF B
C202 CC73GCH1H390J CHIP C 39PF J
C204-206 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C207 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C208,209 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C210 CC73GCH1H680J CHIP C 68PF J
C211 CC73GCH1H100D CHIP C 10PF D
C212 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C213 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C214 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C215 CC73GCH1H180J CHIP C 18PF J
C216 CC73GCH1H150J CHIP C 15PF J
C217 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C218 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C219 CK73FB1C105K CHIP C 1.0UF K
C220,221 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C222 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C223 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C224,225 CC73GCH1H271J CHIP C 270PF J
C226,227 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C228 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C229 CK73GB1C333K CHIP C 0.033UF K
C230 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C231 CC73GCH1H820J CHIP C 82PF J
C232,233 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C234 CK73FB1C224K CHIP C 0.22UF K
C325 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C327 CK73FB1E224K CHIP C 0.22UF K
C331 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C333 CC73GCH1H050B CHIP C 5.0PF B
C334 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C335 CK73GB1C223K CHIP C 0.022UF K
C338 C92-0502-05 CHIP-TAN 0.33UF 35WV
C339 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C342 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C343 C92-0628-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 10WV
C346,347 CC73GCH1H220G CHIP C 22PF G
C350 CC73GCH1H080D CHIP C 8.0PF D
C351 CC73GCH1H0R5B CHIP C 0.5PF B
C352 CC73GCH1H120J CHIP C 12PF J
C353 CC73GCH1H471J CHIP C 470PF J
C354 CC73GCH1H040B CHIP C 4.0PF B
C355 CC73GCH1H050B CHIP C 5.0PF B
C356 CC73GCH1H0R5B CHIP C 0.5PF B
C357 CC73GCH1H060B CHIP C 6.0PF B
C358 CC73GCH1H050B CHIP C 5.0PF B
C359,360 CC73GCH1H070B CHIP C 7.0PF B
C361-363 CC73GCH1H471J CHIP C 470PF J
C364 CC73GCH1H0R5B CHIP C 0.5PF B
C365 CC73GCH1H0R3B CHIP C 0.3PF B
C367 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C368 CC73GCH1H471J CHIP C 470PF J
C369,370 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C371 C92-0560-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 6.3WV
C372 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C373 CC73GCH1H471J CHIP C 470PF J
C235 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C236 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C237 C92-0712-05 CHIP-TAN 22UF 6.3WV
C238 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C239,240 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C241 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C251,252 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C253 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C255 C92-0694-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 16WV
C256 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C257 C92-0519-05 CHIP-TAN 1.0UF 25WV
C258 C92-0516-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 16WV
C259 C92-0628-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 10WV
C260-262 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C299 CC73GCH1H0R5B CHIP C 0.5PF B
C302 CC73GCH1H0R5B CHIP C 0.5PF B
C306 CC73GCH1H100D CHIP C 10PF D
C307 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C308 CC73GCH1H100D CHIP C 10PF D
C309 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C311 CC73GCH1H390J CHIP C 39PF J
C312 C92-0555-05 CHIP-TAN 0.047UF 35WV
C314 CK73FB1E104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C316 CC73GCH1H080D CHIP C 8.0PF D
C317 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
26
C374 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C375 CC73GCH1H270J CHIP C 27PF J
C376-378 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C379 CC73GCH1H060D CHIP C 6.0PF D
C380,381 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C382 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C383 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C384 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C385 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C386 C92-0713-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 6.3WV
C387,388 CC73GCH1H050C CHIP C 5.0PF C
C389 CC73GCH1H060B CHIP C 6.0PF B
C390 CC73GCH1H120J CHIP C 12PF J
C391 CC73GCH1H020B CHIP C 2.0PF B
C392 CC73GCH1H120J CHIP C 12PF J
C393 CC73GCH1H060B CHIP C 6.0PF B
C394 CC73GCH1H040B CHIP C 4.0PF B
C395 CC73GCH1H020B CHIP C 2.0PF B
C396 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C397 CC73GCH1H120J CHIP C 12PF J
C398 CC73GCH1H010B CHIP C 1.0PF B
C400 CK73FB1A105K CHIP C 1.0UF K
C403 CK73HB1A104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C404 CC73HCH1H050C CHIP C 5.0PF C
C406 CC73GCH1H0R3B CHIP C 0.3PF B
Page 27

Ref. No.
C407 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C408,409 CC73HCH1H150G CHIP C 15PF G
C410-412 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C420,421 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C422 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
PARTS LIST
Destination
Ref. No.
C498 CC73HCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C499 CK73GB1H821K CHIP C 820PF K
C500 CC73HCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C501 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C502 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
Address
New
parts
TK-8180
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)
Parts No. Description
Destination
C423 CK73FF1C105Z CHIP C 1.0UF Z
C424 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C425-428 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C429 CK73GB1A105K CHIP C 1.0UF K
C430,431 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C432 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C433 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C434 CK73GB1H561K CHIP C 560PF K
C435 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C436,437 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C438 CK73GB1E103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C439 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C440 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C441 CK73FB0J106K CHIP C 10UF K
C442 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C443 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C444 CC73GCH1H390J CHIP C 39PF J
C445 CC73GCH1H150J CHIP C 15PF J
C446 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C447 CK73HB1A333K CHIP C 0.033UF K
C448 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C450 CK73FB0J106K CHIP C 10UF K
C451 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C452 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C453 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C454 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C455 C92-0589-05 CHIP-TAN 47UF 6.3WV
C457 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C459 C92-0628-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 10WV
C460-463 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C503 CC73GCH1H680J CHIP C 68PF J
C504 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C505,506 CK73GB1A105K CHIP C 1.0UF K
C507 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C511 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C512,513 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C514 CC73GCH1H820J CHIP C 82PF J
C515,516 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C517 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C518 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C519,520 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C524 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C525,526 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C528 CK73GB1H222K CHIP C 2200PF K
C529 CC73GCH1H470J CHIP C 47PF J
C530 CK73FB0J106K CHIP C 10UF K
C531 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C532 CK73GB1E123K CHIP C 0.012UF K
C533 CK73GB1E153K CHIP C 0.015UF K
C534 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C535 CK73GB1C683K CHIP C 0.068UF K
C536,537 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C538 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C539,540 C92-0628-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 10WV
C541 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C542 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C543,544 C92-0628-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 10WV
C545 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C546 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C547-549 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C464 CK73HB1A333K CHIP C 0.033UF K
C465 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C467,468 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C469 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C470 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C472 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C475 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C476 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C477 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C478 CC73HCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C479,480 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C481 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C482 CK73FB1A475K CHIP C 4.7UF K
C483 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C484 CK73FB1A475K CHIP C 4.7UF K
C485 CK73FB1A105K CHIP C 1.0UF K
C487 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C488 CC73GCH1H120J CHIP C 12PF J
C489 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C490 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C491,492 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C493 CK73FB1A475K CHIP C 4.7UF K
C495 CC73GCH1H181J CHIP C 180PF J
C496 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C497 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C550 CC73HCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C551-553 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C554 CC73HCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C555-557 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C558 CC73HCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C559 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C560,561 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C562-565 C92-0519-05 CHIP-TAN 1.0UF 25WV
C566 CK73FB1C105K CHIP C 1.0UF K
C567 CC73HCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C568 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C570 CK73FB1C105K CHIP C 1.0UF K
C572,573 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C574 C92-0672-05 ELECTRO 22UF 16WV
C575 ✽ C92-0834-05 ELECTRO 47UF 25WV
C576 ✽ C92-0836-05 ELECTRO 330UF 16WV
C577 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C578 ✽ C92-0834-05 ELECTRO 47UF 25WV
C579 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C580 ✽ C92-0834-05 ELECTRO 47UF 25WV
C581,582 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C583 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C584 CC73GCH1H220J CHIP C 22PF J
C585-587 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C588 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
27
Page 28

TK-8180
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
Ref. No.
C591 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C592,593 CC73GCH1H070D CHIP C 7.0PF D
C594 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C595 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C701 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C702-704 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C705-711 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C712 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C713 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C714,715 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C716,717 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C718-720 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C721 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C722,723 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C801 C92-0777-05 ELECTRO 1000UF 25WV
C802 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C803 CK73GB1E473J CHIP C 0.047UF J
C804 CC73GCH1H471J CHIP C 470PF J
C805 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C806 CC73GCH1H101J CHIP C 100PF J
C807 CK73GB1E473J CHIP C 0.047UF J
C808 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C809 CC73GCH1H471J CHIP C 470PF J
C810 CK73GB1E473J CHIP C 0.047UF J
C811,812 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C813,814 CC73GCH1H471J CHIP C 470PF J
C815 C92-0585-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 16WV
C816 C92-0628-05 CHIP-TAN 10UF 10WV
C817 CC73GCH1H471J CHIP C 470PF J
C818 CK73GB1H472K CHIP C 4700PF K
C819,820 CK73GB1C104K CHIP C 0.10UF K
C821 C92-0585-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 16WV
C822 CC73GCH1H471J CHIP C 470PF J
C823 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C824 CK73GB1H103K CHIP C 0.010UF K
C825 CK73HB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C826 CK73GB1H471K CHIP C 470PF K
C831,832 C92-0585-05 CHIP-TAN 4.7UF 16WV
TC301,302 C05-0396-05 CERAMIC TRIMMER CAP (8PF)
CN1-3 E23-1081-05 TERMINAL
CN13 E23-1081-05 TERMINAL
CN100-102 E23-1081-05 TERMINAL
CN202,203 E23-1081-05 TERMINAL
CN301,302 ✽ E40-6404-05 PIN ASSY
CN322,323 E23-1081-05 TERMINAL
CN326 E23-1081-05 TERMINAL
CN329 E23-1081-05 TERMINAL
CN403 ✽ E40-6361-05 PIN ASSY
CN427 ✽ E40-6371-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR
CN428 ✽ E40-6373-05 PIN ASSY
CN429 ✽ E40-6412-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR
CN701 ✽ E40-6371-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR
CN802,803 ✽ E23-1260-04 TERMINAL
CN804 E40-3246-05 PIN ASSY
CN815 E23-1081-05 TERMINAL
J401 E11-0425-05 3.5D PHONE JACK (3P)
J701 E58-0494-05 SUB SOCKET (D)
F401 ✽ F53-0352-05 FUSE (2A)
F801 F53-0278-05 FUSE (5A)
PARTS LIST
Destination
Ref. No.
CN401 J19-5386-05 HOLDER
CD171 L79-1701-05 TUNING COIL
CF171 L72-0986-05 CERAMIC FILTER
CF172 L72-0998-05 CERAMIC FILTER
L1 L40-1875-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (18NH)
L2 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
L3 L40-2275-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (22NH)
L4 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
L5,6 L92-0179-05 FERRITE CHIP
L7 L34-4638-05 AIR-CORE COIL
L8 ✽ L34-4758-05 AIR-CORE COIL
L9,10 ✽ L34-4743-05 AIR-CORE COIL
L12 ✽ L34-4743-05 AIR-CORE COIL
L13 L34-4482-05 AIR-CORE COIL
L101 L41-8268-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L108 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
L109 L41-1878-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L110-113 L34-4565-05 AIR-CORE COIL
L114-117 L41-8268-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L119 L41-3378-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L171,172 L41-1578-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L173,174 L39-1421-05 TOROIDAL COIL
L175 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
L176 L39-1421-05 TOROIDAL COIL
L177 ✽ L41-2785-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L178,179 ✽ L41-3988-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L180 L40-6875-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (68NH)
L181 L40-1001-86 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (10UH)
L182 L40-1085-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (100NH)
L183,184 ✽ L41-3988-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L185 L40-6875-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (68NH)
L186 L40-1001-86 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (10UH)
L187 L40-1085-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (100NH)
L188 L40-8281-86 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (0.82UH)
L189 L40-1091-86 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (1.0UH)
L251 ✽ L33-1468-05 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L301 L40-2295-85 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (2.2UH)
L302 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
L304-306 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
L309,310 L40-1095-85 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (1.0UH)
L311,312 L41-1098-08 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L314 L34-4607-05 AIR-CORE COIL
L315-317 L41-1098-08 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L318,319 L40-2275-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (22NH)
L320 L40-1075-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (10NH)
L321 L40-8265-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (8.2NH)
L322 ✽ L41-5668-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L323 L41-4763-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L324 ✽ L41-2263-14 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L325 L34-4605-05 AIR-CORE COIL
L326 L41-1098-08 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR
L327 L40-3375-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (33NH)
L328 L40-2275-92 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (22NH)
L401,402 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L403-407 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
L408 L92-0138-05 FERRITE CHIP
L409 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
L410,411 L92-0179-05 FERRITE CHIP
L701,702 L92-0140-05 FERRITE CHIP
Address
New
parts
Parts No. Description
Destination
28
Page 29

PARTS LIST
Ref. No.
X171 L77-1762-05 CRYSTAL RESONATOR (44.395MHZ)
X301 L77-1952-05 TCXO (16.8MHZ)
X401 L77-1802-05 CRYSTAL RESONATOR (32768HZ)
X403 L77-1965-05 CRYSTAL RESONATOR (3.6864MHZ)
X404 L77-1950-05 CRYSTAL RESONATOR (11.0592MHZ)
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
Destination
TK-8180
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)
Ref. No.
R134 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R171 RK73GB1J271J CHIP R 270 J 1/16W
R172 RK73GB1J180J CHIP R 18 J 1/16W
R173 RK73GB1J271J CHIP R 270 J 1/16W
R174 RK73GB1J680J CHIP R 68 J 1/16W
Address
New
parts
Parts No. Description
Destination
XF171 ✽ L71-0618-05 MCF (44.85M)
CP401 R90-0740-05 MULTIPLE RESISTOR
CP402-417 RK75HA1J102J CHIP-COM 1.0K J 1/16W
R1 RK73GB1J821J CHIP R 820 J 1/16W
R2 RK73GB1J5R6J CHIP R 5.6 J 1/16W
R3 RK73GB1J821J CHIP R 820 J 1/16W
R4 RK73GB1J333J CHIP R 33K J 1/16W
R5 RK73GB1J682J CHIP R 6.8K J 1/16W
R6 RK73GB1J221J CHIP R 220 J 1/16W
R7 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R8 RK73GB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R9 RK73GB1J220J CHIP R 22 J 1/16W
R10 RK73GB1J561J CHIP R 560 J 1/16W
R11 RK73GB1J272J CHIP R 2.7K J 1/16W
R12 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R13 RK73GB1J331J CHIP R 330 J 1/16W
R14 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R15 RK73FB2A221J CHIP R 220 J 1/10W
R16,17 RK73FB2A470J CHIP R 47 J 1/10W
R18 RK73FB2A221J CHIP R 220 J 1/10W
R19 RK73GB1J151J CHIP R 150 J 1/16W
R21 RK73GB1J331J CHIP R 330 J 1/16W
R22 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R23 RK73GB1J682J CHIP R 6.8K J 1/16W
R24 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R25 R92-1261-05 CHIP R 150 J 1/2W
R26 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R27 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R28 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R29 RK73GB1J823J CHIP R 82K J 1/16W
R30 R92-1061-05
R31 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R33 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R38 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R71 RK73GB1J563J CHIP R 56K J 1/16W
R72 RK73GB1J333J CHIP R 33K J 1/16W
R75 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R76-78 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R79 RK73GB1J224J CHIP R 220K J 1/16W
R81,82 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R84 RK73GB1J124J CHIP R 120K J 1/16W
R85 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R86 RK73GB1J824J CHIP R 820K J 1/16W
R87 RK73GB1J823J CHIP R 82K J 1/16W
R88,89 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R90 RK73GB1J334J CHIP R 330K J 1/16W
R108 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R109 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R115,116 RK73GB1J183J CHIP R 18K J 1/16W
R119 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R120 RK73GB1J221J CHIP R 220 J 1/16W
R121-124 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R126 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R129-133 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
JUMPER REST
0 OHM
R175 RK73GB1J222J CHIP R 2.2K J 1/16W
R176 RK73GB1J470J CHIP R 47 J 1/16W
R177 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R178 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R179 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R180 RK73GB1J821J CHIP R 820 J 1/16W
R181 RK73GB1J331J CHIP R 330 J 1/16W
R182 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R183 RK73GB1J680J CHIP R 68 J 1/16W
R184 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R185 RK73GB1J821J CHIP R 820 J 1/16W
R186 RK73GB1J331J CHIP R 330 J 1/16W
R187 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R188 RK73GB1J680J CHIP R 68 J 1/16W
R189 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R190 RK73GB1J153J CHIP R 15K J 1/16W
R191,192 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R193 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R194,195 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R196 RK73GB1J153J CHIP R 15K J 1/16W
R197,198 RK73GB1J334J CHIP R 330K J 1/16W
R199 RK73GB1J560J CHIP R 56 J 1/16W
R200 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R202 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R203 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R204 RK73GB1J222J CHIP R 2.2K J 1/16W
R205 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R206 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R207 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R208 RK73GB1J392J CHIP R 3.9K J 1/16W
R209 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R210 RK73GB1J272J CHIP R 2.7K J 1/16W
R212 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R217 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R221 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R251 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R252 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R253 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R254,255 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R256 RK73GB1J124J CHIP R 120K J 1/16W
R257 RK73GB1J153J CHIP R 15K J 1/16W
R258 RK73GB1J220J CHIP R 22 J 1/16W
R295 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R298 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R301 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R302 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R303 RK73GB1J561J CHIP R 560 J 1/16W
R305 RK73GB1J560J CHIP R 56 J 1/16W
R306 RK73GB1J183J CHIP R 18K J 1/16W
R307 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R308 RK73GB1J392J CHIP R 3.9K J 1/16W
R309,310 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R311 RK73GB1J182J CHIP R 1.8K J 1/16W
R312 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R315 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
29
Page 30

TK-8180
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
Ref. No.
R316 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R317 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R318 R92-2577-05 METAL-R 1.8K J 1/4W
R319 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R320 RK73GB1J180J CHIP R 18 J 1/16W
PARTS LIST
Destination
Ref. No.
R428 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R429,430 RK73HB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R431 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R432 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R434 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
Address
New
parts
Parts No. Description
Destination
R321 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R322 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R323 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R325 RK73GB1J154J CHIP R 150K J 1/16W
R326 RK73GB1J271J CHIP R 270 J 1/16W
R327 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R330 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R332 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R333-335 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R336 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R337 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R339 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R340 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R341,342 RK73GB1J181J CHIP R 180 J 1/16W
R343 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R344 RK73GB1J470J CHIP R 47 J 1/16W
R345,346 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R347 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R348 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R349,350 RK73GB1J333J CHIP R 33K J 1/16W
R351 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R352 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R353 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R355 RK73GB1J560J CHIP R 56 J 1/16W
R356,357 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R358 RK73GB1J822J CHIP R 8.2K J 1/16W
R359 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R360 RK73GB1J121J CHIP R 120 J 1/16W
R361 RK73GB1J221J CHIP R 220 J 1/16W
R362 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R435 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R437 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R439 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R440-444 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R445,446 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R447 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R448 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R449 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R450 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R451 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R452 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R453 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R454 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R455,456 RK73HB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R457 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R458,459 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R461 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R465 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R466 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R467 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R468 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R469 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R470 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R471,472 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R473,474 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R475 RK73GB1J101J CHIP R 100 J 1/16W
R476 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R477,478 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R481 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R482 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R365,366 RK73GB1J222J CHIP R 2.2K J 1/16W
R367 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R369 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R370 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R371 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R373 RK73GB1J100J CHIP R 10 J 1/16W
R375 RK73GB1J331J CHIP R 330 J 1/16W
R376,377 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R378 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R400 RK73HH1J105D CHIP R 1.0M D 1/16W
R401 ✽ RK73HH1J362D CHIP R 3.6K D 1/16W
R402 RK73HH1J512D CHIP R 5.1K D 1/16W
R403 RK73HH1J105D CHIP R 1.0M D 1/16W
R405,406 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R407 RK73HB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R410 RK73HB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R411,412 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R414 RK73HB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R415 RK73HB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R416 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R418,419 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R420 RK73HB1J334J CHIP R 330K J 1/16W
R421,422 RK73HB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R423 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R424-427 RK73HB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
30
R483-486 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R487 RK73GB1J185J CHIP R 1.8M J 1/16W
R488,489 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R490 RK73GB1J184J CHIP R 180K J 1/16W
R491 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R492 RK73GB1J684J CHIP R 680K J 1/16W
R493 RK73GB1J105J CHIP R 1.0M J 1/16W
R494,495 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R496 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R497 RK73GB1J332J CHIP R 3.3K J 1/16W
R498 RK73GB1J274J CHIP R 270K J 1/16W
R499 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R500 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R501 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R502 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R503 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R504 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R505 RK73GB1J683J CHIP R 68K J 1/16W
R506,507 RK73GB1J224J CHIP R 220K J 1/16W
R508 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R509 RK73GB1J333J CHIP R 33K J 1/16W
R511 RK73HB1J152J CHIP R 1.5K J 1/16W
R512 RK73GB1J153J CHIP R 15K J 1/16W
R513 RK73GB1J564J CHIP R 560K J 1/16W
R514 RK73GB1J183J CHIP R 18K J 1/16W
Page 31

Ref. No.
R515 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R517 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R519 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R520 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R521 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
PARTS LIST
Destination
Ref. No.
R592 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R594 RK73GB1J681J CHIP R 680 J 1/16W
R595 RK73GB1J274J CHIP R 270K J 1/16W
R596 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R597 RK73GB1J105J CHIP R 1.0M J 1/16W
Address
New
parts
TK-8180
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)
Parts No. Description
Destination
R522 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R523 RK73GB1J564J CHIP R 560K J 1/16W
R524 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R525 RK73HB1J152J CHIP R 1.5K J 1/16W
R526 RK73GB1J274J CHIP R 270K J 1/16W
R527 RK73GB1J392J CHIP R 3.9K J 1/16W
R528 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R529 RK73GB1J684J CHIP R 680K J 1/16W
R530 RK73GB1J334J CHIP R 330K J 1/16W
R531 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R532 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R533 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R534 RK73GB1J273J CHIP R 27K J 1/16W
R535 RK73GB1J394J CHIP R 390K J 1/16W
R536 RK73GB1J153J CHIP R 15K J 1/16W
R539 RK73GB1J393J CHIP R 39K J 1/16W
R540 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R541,542 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R545 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R546 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R548 RK73GB1J823J CHIP R 82K J 1/16W
R549 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R550 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R552 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R553 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R554 RK73GB1J563J CHIP R 56K J 1/16W
R555 RK73GB1J123J CHIP R 12K J 1/16W
R556 RK73GB1J563J CHIP R 56K J 1/16W
R557 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R558 RK73GB1J394J CHIP R 390K J 1/16W
R598 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R599 RK73GB1J184J CHIP R 180K J 1/16W
R600 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R601 RK73GB1J474J CHIP R 470K J 1/16W
R602 RK73GB1J105J CHIP R 1.0M J 1/16W
R603,604 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R606 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R607 RK73GB1J274J CHIP R 270K J 1/16W
R608 RK73GB1J184J CHIP R 180K J 1/16W
R609 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R610 RK73GB1J154J CHIP R 150K J 1/16W
R611 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R612,613 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R614 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R615,616 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R617 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R618 RK73GB1J224J CHIP R 220K J 1/16W
R619 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R620 RK73GB1J224J CHIP R 220K J 1/16W
R621,622 R92-0670-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R623,624 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R625 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R629,630 R92-0670-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R632 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R633 R92-0670-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R636 R92-0670-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R641,642 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R643 RK73GB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R644 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R645 RK73GB1J562J CHIP R 5.6K J 1/16W
R559 RK73GB1J124J CHIP R 120K J 1/16W
R560 RK73GB1J394J CHIP R 390K J 1/16W
R563 RK73GB1J394J CHIP R 390K J 1/16W
R565 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R566 RK73GB1J105J CHIP R 1.0M J 1/16W
R567 RK73GB1J394J CHIP R 390K J 1/16W
R568 RK73GB1J124J CHIP R 120K J 1/16W
R569 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R570 RK73GB1J154J CHIP R 150K J 1/16W
R571 RK73GB1J124J CHIP R 120K J 1/16W
R572 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R573 RK73GB1J682J CHIP R 6.8K J 1/16W
R574,575 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R576 RK73GB1J224J CHIP R 220K J 1/16W
R578 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R579 RK73GB1J223J CHIP R 22K J 1/16W
R580,581 RK73GB1J151J CHIP R 150 J 1/16W
R582 RK73GB1J105J CHIP R 1.0M J 1/16W
R583,584 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R585 RK73GB1J184J CHIP R 180K J 1/16W
R586 RK73GB1J102J CHIP R 1.0K J 1/16W
R587 RK73GB1J154J CHIP R 150K J 1/16W
R588 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R589,590 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R591 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R646 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R647 RK73GB1J104J CHIP R 100K J 1/16W
R648 RK73GB1J222J CHIP R 2.2K J 1/16W
R651 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R652 RK73GB1J561J CHIP R 560 J 1/16W
R653 RK73GB1J2R2J CHIP R 2.2 J 1/16W
R654 R92-0670-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R655 R92-1252-05 CHIP R 0 OHM J 1/16W
R657 RK73HB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R658 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
R659 RK73GB1J333J CHIP R 33K J 1/16W
R661 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R663,664 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R701-705 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R706-710 RK73GB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R711-713 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R714-720 RK73GB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R800 RK73HH1J105D CHIP R 1.0M D 1/16W
R801 RK73GB1J224J CHIP R 220K J 1/16W
R802 RK73GB1J334J CHIP R 330K J 1/16W
R803 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R804 RK73HH1J104D CHIP R 100K D 1/16W
R805 RK73GB1J471J CHIP R 470 J 1/16W
R806,807 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R808,809 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
31
Page 32

TK-8180
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
Ref. No.
R811,812 RK73GB1J103J CHIP R 10K J 1/16W
R813 RK73GB1J472J CHIP R 4.7K J 1/16W
R814 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
R815 RK73GB1J683J CHIP R 68K J 1/16W
R818 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
PARTS LIST
Destination
Ref. No.
IC414 TC75W51FU MOS IC
IC415 ✽ AQUA-L MOS IC
IC416 ADM202EARN MOS IC
IC417 2A ✽ TA7252AP ANALOG IC
IC801 S-80942CNNBG9C MOS IC
Address
New
parts
Parts No. Description
Destination
R900-903 R92-1368-05 CHIP R 0 OHM
D1 02DZ5.6(X,Y) ZENER DIODE
D2 XB15A709 DIODE
D3 XB15A407A2GB DIODE
D6-8 HSM88AS DIODE
D103-106 1SV286 VARIABLE CAPACITANCE DIODE
D107-110 ✽ 1SV291 VARIABLE CAPACITANCE DIODE
D111 HVC131 DIODE
D171,172 DAN235E DIODE
D173 RB706F-40 DIODE
D174 MA2S111 DIODE
D251 1SS388 DIODE
D308,309 ✽ BB664 VARIABLE CAPACITANCE DIODE
D311 ✽ BB664 VARIABLE CAPACITANCE DIODE
D313 ✽ BB664 VARIABLE CAPACITANCE DIODE
D314 1SV278 VARIABLE CAPACITANCE DIODE
D315,316 HVC131 DIODE
D402-404 1SS388 DIODE
D405 EMZ6.8N ZENER DIODE
D406 02DZ5.1(Y) ZENER DIODE
D407 RB706F-40 DIODE
D408,409 MA742 DIODE
D412-414 DA204U DIODE
D416 DAN202U DIODE
D417,418 1SS388 DIODE
D421-423 1SS388 DIODE
D600,601 1SS388 DIODE
D701 02DZ18(X,Y) ZENER DIODE
D702,703 1SS355 DIODE
D704-708 DA204U DIODE
D709,710 02DZ18(X,Y) ZENER DIODE
D711-713 DA204U DIODE
D714 02DZ18(X,Y) ZENER DIODE
D801 22ZR-10D SURGE ABSORBER
D802 DSA3A1 DIODE
D804 02DZ18(X,Y) ZENER DIODE
D805 02CZ9.1(X,Y) ZENER DIODE
IC1 2A ✽ RA30H4452M-23 MOS IC
IC71,72 TA75W01FU MOS IC
IC171 ✽ SPM5001 MOS IC
IC172 TA31136FN MOS IC
IC251 ✽ MAX5026EUT+T MOS IC
IC301 ADF4111BCP7 MOS IC
IC302 TC7S66FU MOS IC
IC401 AT24256N10SI27 ROM IC
IC402 RV5C386A MOS IC
IC403 BU4094BCFV MOS IC
IC404 30625MGP-169GP MPU
IC405 AT29C040A-90TI ROM IC
IC406-409 TC75W51FU MOS IC
IC410 M62364FP MOS IC
IC802 XC61CN5002NR MOS IC
IC803 TA7808F ANALOG IC
IC804 TA7805F MOS IC
IC805 NJM78L05UA BI-POLAR IC
IC807 ✽ XC6201P502PR MOS IC
Q1 2SC5108(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q2 2SC5192 TRANSISTOR
Q3 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q70 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q72 2SK1824 FET
Q103 2SC3357 TRANSISTOR
Q171,172 2SC5108(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q173 DTA114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q174 DTC144EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q175 2SC4617(Q) TRANSISTOR
Q176 2SK1824 FET
Q177 DTC144EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q178 DTA144EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q179 DTC144EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q251 2SC4617(S) TRANSISTOR
Q301 2SC5108(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q302,303 2SC4116(BL) TRANSISTOR
Q306,307 2SK508NV(K52) FET
Q308,309 2SC4116(GR) TRANSISTOR
Q310 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q311 2SC5108(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q312 2SC4617(S) TRANSISTOR
Q313 2SC5108(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q402 DTC114YE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q405 DTA114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q406 HN1J02FU FET
Q409 DTC363EU DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q410 2SC4116(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q411 2SA1586(Y,GR) TRANSISTOR
Q412 2SK1824 FET
Q413,414 2SJ243 FET
Q415 HN1L02FU FET
Q416,417 2SJ243 FET
Q418 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q419 DTC363EU DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q600 DTA144EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q701,702 2SD2114K(W) TRANSISTOR
Q801 2SC2873(Y) TRANSISTOR
Q802 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q803-805 ✽ 12A02CH TRANSISTOR
Q806-809 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q810 ✽ 2SJ645 FET
Q811 DTC114TE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
Q812 DTC114EE DIGITAL TRANSISTOR
TH1 S1R104J475H THERMISTOR
TH171 ✽ S1R473J475H THERMISTOR
IC411 LMC7101BIM5 MOS IC
IC412 TC75W51FU MOS IC
IC413 ✽ TC7MZ4053FK MOS IC
32
Page 33

TK-8180
EXPLODED VIEW
BA
1
A: N09-2409-05
B M3 x 8 : N67-3008-48
C M2.6 x 6 (Br-Tap) : N87-2606-48
D M2.6 x 8 (Br-Tap) : N87-2608-46
23
22
1
C
Cx2
Cx3
B
B
17
C
D
IC417
16
11
54
C
Cx3
IC1
C
27
Bx2
Cx2
25
Cx2
Cx2
12
C
705
C
4
706
47
TX-RX unit
(B/3)
TX-RX unit
2
(C/3)
701
702
21
10
TX-RX
unit (A/3)
704
26
3
703
31
29
Cx2
C
8
15
24
30
A
C
A
C
42
28
C
7
J901
103
Right Side
Front
Rear
20
20
41
Display unit
105
106
101
102
103
13
20
20
104 x2
43
45
2
51
40
Parts with the exploded numbers larger than 700 are not supplied.
33
Page 34

TK-8180
52 Microphone
(T91-0639-05)
PACKING
707 Pamphlet x 2
DC
5 Instruction manual
(B62-1766-10)
1
18 Fuse (Blade)
15A/32V
(F52-0024-05) x 2
9 DC cord assy
(Water-proof)
(E30-7523-05)
44 Bracket
(J29-0662-03)
2
39 Holder
(J19-1584-05)
49 Screw set
(N99-2039-05)
32 Inner packing case
(H02-0624-03)
34 Packing fixture (Upper)
(H12-3171-03)
36 Protection bag
(H25-2352-04)
34
33 Packing fixture (Lower)
(H12-3170-01)
3
37 Item carton case
(H52-2069-02)
Parts with the exploded numbers larger than 700 are not supplied.
Page 35

ADJUSTMENT
TK-8180
Controls
Power
switch
Modular
MIC jack
Volume
Up/Down key
Programmable
function keys
LCD
Channel
Up/Down key
Panel Test Mode
■ Test mode operation features
This transceiver has a test mode.
press [A] key and turn power on. Hold [A] key until frequency version appears on LCD.
ited by programming. To exit test mode, switch the power
on again. The following functions are available in test mode.
■ Key operation
Key “FNC” not appears
Function Display
[S]
[A] Function on “FNC” appears
[B]
[C] Test signaling CH up Signaling No.
[ ]/[ ]
[ ]/[ ] Volume up/down -
[ ] Squelch on/off
[■] Narrow/Wide 4k/Wide 5k Narrow : “n”,
Microphone key
[PTT] Transmit -
[0] to [9] Use as the DTMF keypad. -
and [A], If a key is pressed during
[B], [C], transmission, the DTMF
[D], [#], corresponding to the key
[✳] that was presses is sent.
Shifts to Panel tuning mode
MSK 1200bps and 2400bps 2400bps : icon appears
Test frequency CH up/down
To enter test mode,
Test mode can be inhib-
-
Channel No.
Wide 4k : “s”,
Wide 5k : “w”
Key “FNC” appears
Function Display
[S] High power / Low power Low : icon appears
[A] Function off -
[B] Compander on/off On : icon appears
[C] Beat shift on/off On : icon appears
[ ]/[ ] Function off -
[ ]/[ ] Function off -
[ ] Squelch level 0 On : icon appears
[■] LCD all lights LCD all point appears
Microphone key
[PTT] Transmit -
[0] to [9] and
[A], [B], [C],
[D], [#], [✳]
Function off -
Notes :
• If a [S], [A], [B], [C] key is pressed during transmission, the
DTMF corresponding to the key that was pressed is sent.
• The “Wide 4k” can not use, please skip it.
• LED indicator
Red LED Lights during transmission.
Green LED Lights when there is carrier.
• Sub LCD indicator
“FNC” Appears at function on.
• LCD display in panel test mode
n1 1
n : Narrow
s : Wide 4k
w : Wide 5k
–
Signaling No.
Channel No.
■ Frequency and Signaling
The set has been adjusted for the frequencies shown in
the following table. When required, readjust them following
the adjustment procedure to obtain the frequencies you want
in actual operation.
• Test frequency
CH RX (MHz) TX (MHz)
1 485.05000 485.10000
2 450.05000 450.10000
3 519.95000 519.90000
4 485.00000 485.00000
5 485.20000 485.20000
6 485.40000 485.40000
7~16 - -
35
Page 36

TK-8180
ADJUSTMENT
• Test signaling
No. RX TX
1 None None
2 None 100Hz Square Wave
3 LTR Data : LTR Data :
AREA=0, GOTO=12 AREA=0, GOTO=12
HOME=12 HOME=12
ID=47, FREE=25 ID=47, FREE=25
4 QT : 67.0Hz QT : 67.0Hz
5 QT : 151.4Hz QT : 151.4Hz
6 QT : 210.7Hz QT : 210.7Hz
7 QT : 254.1Hz QT : 254.1Hz
8DQT : D023N DQT : D023N
9 DQT : D754I DQT : D754I
10 DTMF : 159D DTMF : 159D
11 None DTMF Code 9
12 2-tone : 2-tone :
A : 304.7Hz A : 304.7Hz
B : 3106.0Hz B : 3106.0Hz
13 Single Tone : 979.9Hz Single Tone : 979.9Hz
14 None Single Tone : 1000Hz
15 5-tone (CCIR 12345) 5-tone (CCIR 12345)
16 None MSK
17 MSK : MSK :
Preamble : 0xAAAA Preamble : 0xAAAA
Sync : 0x23EB Sync : 0x23EB
Data : 0x230960C6AAAA Data : 0x230960C6AAAA
CRC : 0xC4D7 CRC : 0xC4D7
Note : The “5-tone signaling” can not use, please skip it.
Panel Tuning Mode
■ Preparations for tuning the transceiver
Before attempting to tune the transceiver, connect the
unit to a suitable power supply.
Whenever the transmitter is turned, the unit must be con-
nected to a suitable dummy load (i.e. power meter).
The speaker output connector must be terminated with a
4Ω dummy load and connected to an AC voltmeter and an
audio distortion meter or a SINAD measurement meter at all
times during tuning.
■ Transceiver tuning
(To place transceiver in tuning mode)
Press [S] key, now in tuning mode. Use [B] key to write
tuning data through tuning modes, and [
ing requirements (1 to 256 appeares on LCD).
Use [C] key to select the adjustment item through tuning
modes. Use [A] key to adjust 3 or 5 reference level adjustments, and use [■] key to switch between Wide 5k/Wide 4k/
Narrow.
Channel appears on LCD. Set channel according to tuning
requirements.
36
]/[ ] to adjust tun-
• LCD display in panel tuning mode
n
n : Narrow
s : Wide 4k
w : Wide 5k
B
AL 256
Adjustment item
Adjustment value (1~256)
■ Key operation
Key Function
Push Hold (1 second)
[S]
[A] To enter 3 or 5 reference -
[B]
[C]
[ ]/[ ]
[ ]/[ ] Volume level up/down Continuation up/down
[ ] Squelch on/off -
[■] Selects Narrow, -
End of panel tuning mode
level adjustments
Writes the adjustment value
Go to next adjustment item
Adjustment value up/down
Wide 4k, Wide 5k
-
-
Back to last adjustment item
Continuation up/down
■ 3 or 5 reference level adjustments frequency
Tuning point RX (MHz) TX (MHz)
Low 450.05000 450.10000
Low’ 467.55000 467.60000
Center 485.05000 485.10000
High’ 502.55000 502.60000
High 519.95000 519.90000
■ Adjustment item and Display (✳✳✳ : 1~256)
Order Adjustment item Display
1 Frequency FREQ ✳✳✳
2 Shift 1 SHFT1 ✳✳✳
3 Shift 2 SHFT2 ✳✳✳
4 Max high power M HPWR ✳✳✳
5 Max low power M LPWR ✳✳✳
6 High power HPWR ✳✳✳
7 Low power LPWR ✳✳✳
8 Balance B AL ✳✳✳
9 Max deviation DEV ✳✳✳
10 QT Q T ✳✳✳
11 DQT D QT ✳✳✳
12 LTR L T R ✳✳✳
13 DTMF DTMF ✳✳✳
14 MSK M SK ✳✳✳
15 Tone TONE ✳✳✳
16 Sensitivity 1 SENS1 ✳✳✳
17 Squelch S Q L ✳✳✳
18 Low RSSI LRSSI ✳✳✳
19 Squelch tight SQLT ✳✳✳
20 High RSSI HRSSI ✳✳✳
Page 37

■ Flow chart
Note : The “Wide 4k” can not use, please skip it.
Frequency
[C]
Shift 1
[C]
Shift 2
[C]
Max high power
[C]
Max low power
[C]
High power
[C]
Low power
[C]
Balance Narrow
[C] [C]
Max deviation Narrow
[C] [A]
QT Narrow
[C] [C]
DQT Narrow
[C] [A]
LTRNarrow
[C] [C][A]
DTMF Narrow
[C] [C] [C]
MSK Narrow
[C] [C] [C]
Tone Narrow
[C] [C] [C]
Sensitivity 1
[C]
Squelch Narrow
[C] [C][A]
Low RSSI Narrow
[C] [C] [C][A]
Squelch tight Narrow
[C] [C] [C][A]
High RSSI Narrow
[C] [C] [C][A]
[A]
[A]
[A]
[A]
[A]
[A]
[ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[A]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [ ]
Balance Wide 4k Balance Wide 5k
Max deviation Wide 4k Max deviation Wide 5k
[C] [C]
QT Wide 4k QT Wide 5k
DQT Wide 4k DQT Wide 5k
[C] [C]
DTMF Wide 4k DTMF Wide 5k
MSK Wide 4k MSK Wide 5k
Tone Wide 4k Tone Wide 5k
Squelch Wide 4k
[C] [A] [A]
Low RSSI Wide 4k
[A] [A]
Squelch tight Wide 4k Squelch tight Wide 5k
[A] [A]
High RSSI Wide 4k High RSSI Wide 5k
[A] [A]
ADJUSTMENT
[ ] [ ]
[C][A]
[C][A]
LTRWide 5k
Squelch Wide 5k
Low RSSI Wide 5k
3 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
5 reference level
adjustments
5 reference level
adjustments
5 reference level
adjustments
5 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
5 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments
TK-8180
3 reference level
adjustments
3 reference level
adjustments exit
5 reference level
adjustments
5 reference level
adjustments exit
Low
[C]
Center
[C]
High
[C]
Low
[C]
Low’
[C]
Center
[C]
High’
[C]
High
[C]
[A]
[A]
[A]
[A]
[A]
[A]
[A]
[A]
37
Page 38

TK-8180
ADJUSTMENT
Test Equipment Required for Alignment
Test Equipment Major Specifications
1. Standard Signal Generator Frequency Range 400 to 520MHz
(SSG) Modulation Frequency modulation and external modulation
Output 0.1µV to greater than 1mV
2. Power Meter Input Impedance 50Ω
Operation Frequency 400 to 520MHz or more
Measurement Capability Vicinity of 50W
3. Deviation Meter Frequency Range 400 to 520MHz
4. Digital Volt Meter Measuring Range 1 to 20V DC
(DVM) Accuracy High input impedance for minimum circuit loading
5. Oscilloscope DC through 30MHz
6. High Sensitivity Frequency Range 10Hz to 600MHz
Frequency Counter Frequency Stability 0.2ppm or less
7. Ammeter 13A or more
8. AF Volt Meter Frequency Range 50Hz to 10kHz
(AF VTVM) Voltage Range 3mV to 3V
9. Audio Generator (AG) Frequency Range 50Hz to 5kHz
Output 0 to 1V
10. Distortion Meter Capability 3% or less at 1kHz
Input Level 50mV to 10Vrms
11. Voltmeter Measuring Range 10 to 1.5V DC or less
Input Impedance 50kΩ/V or greater
12. 4Ω Dummy Load Approx. 4Ω, 20W
13. Regulated Power Supply 13.6V, approx. 20A (adjustable from 9 to 20V)
Useful if ammeter requipped
Test cable for microphone input (E30-3360-08)
GREEN
1
RED
2
BLACK
3
BLUE
4
SHIELD
5
WHITE
6
GRAY
7
YELLOW
8
PTT
MIC-E
MIC
HK
1
2
E
3
4
5
6
7
8
MIC connector (Front panel view)
1 : BLC
8
2 : +B
3 : GND
4 : PTT/TXD
(PC serial data
1
from radio)
5 : MICE
6 : MIC
7 : HOOK/RXD
(PC serial data
to radio)
8 : DM
Tuning cable (E30-3383-05)
Adapter cable (E30-3383-05) is
required for injecting an audio if
PC tuning is used.
See “PC Mode” section fot the
connection.
Lead wire +
Check Jig for the VGS-1
KENWOOD part : W05-1127-00
to transceiver
MIC
Shield wire –
to VGS-1
38
Page 39

Common Section
Item Condition
1. Setting 1) Power supply voltage
DC power supply terminal : 13.6V
2) SSG standard modulation
[Wide 5k] MOD : 1kHz, DEV : 3kHz
[Wide 4k] MOD : 1kHz, DEV : 2.4kHz
[Narrow] MOD : 1kHz, DEV : 1.5kHz
ADJUSTMENT
Measurement Adjustment
Test-
equipment
Unit Terminal PartsUnit Method
TK-8180
Specifications/Remarks
2. VCO lock [Panel test mode]
voltage 1) CH-Sig : 3-1 panel (B/3)
• RX
2) CH-Sig : 2-1 DVM TX-RX CV Check 1.5V±0.5V
• TX [Panel tuning mode] LPWR* TX-RX TC302 8.1V ±0.1V
3) CH-Sig : 3-1 (B/3)
PTT : ON
4) CH-Sig : 2-1 Check 1.5V±0.5V
PTT : ON
* TX can be continued on unlock condition in panel tuning mode.
Power meter
Rear ANT TX-RX TC301 8.1V ±0.1V
(B/3)
Transmitter Section (K market model skips adjustment of Wide 4k)
Measurement Adjustment
Item Condition
1. Frequency 1) Adj item : [FREQ] f. counter Rear ANT Front [ ],[ ] Center frequency Note : After replacing the
adjust Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel panel ± 100Hz VCXO (X301) align frequency.
PTT : ON
Test-
equipment
Unit Terminal PartsUnit Method
Specifications/Remarks
2. Frequency 1) Adj item : [SHFT1] [L SHFT1] ± 100Hz
shift 1 Adjust : [✳✳✳]
adjust 2) Adj item : [L SHFT1] → [C SHFT1]
3. Frequency 1) Adj item : [SHFT2] [L SHFT2] ± 100Hz
shift 2 Adjust : [✳✳✳]
adjust 2) Adj item : [L SHFT2] → [C SHFT2]
4. Max high 1) Adj item : [MHPWR]
power Adjust : [✳✳✳] [L’ MHPWR],
adjust 2) Adj item : [L MHPWR] → [C MHPWR]
[C SHFT1] → [H SHFT1]
Adjust : [✳✳✳] [H SHFT1]
PTT : ON
[C SHFT2] → [H SHFT2]
Adjust : [✳✳✳] [H SHFT2]
PTT : ON
Power meter
[L’ MHPWR] → [C MHPWR]→
[H’ MHPWR] → [H MHPWR]
Adjust : [✳✳✳] [H MHPWR]
PTT : ON : 28W
Low frequency+5.00kHz
Center frequency+5.00kHz
High frequency+5.00kHz
Low frequency+6.25kHz
Center frequency+6.25kHz
High frequency+6.25kHz
[L MHPWR], ±3W
: 33W
[H’ MHPWR],
39
Page 40

TK-8180
ADJUSTMENT
Measurement Adjustment
Item Condition
5. Max low 1) Adj item : [MLPWR]
power Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel panel
adjust 2) Adj item : [L MLPWR] →
[L’ MLPWR] → [C MLPWR]→
[H’ MLPWR] → [H MLPWR]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
Test-
equipment
Power meter
Unit Terminal PartsUnit Method
Rear ANT Front [ ],[ ] 15W ± 1W
Specifications/Remarks
6. High power 1) Adj item : [HPWR]
adjust Adjust : [✳✳✳] Ammeter [L’ HPWR], 9A or less
2) Adj item : [L HPWR] → [C HPWR]
[L’ HPWR] → [C HPWR] → : 30W
[H’ HPWR] → [H HPWR] [H’ HPWR],
Adjust : [✳✳✳] [H HPWR]
PTT : ON : 25W
7. High power [Panel test mode] Check 25~35W
check 1) CH-Sig : 1-1 9A or less
PTT : ON
2) CH-Sig : 2-1
PTT : ON
3) CH-Sig : 3-1 21~29W
PTT : ON 9A or less
8. Low power 1) Adj item : [LPWR] Front [ ],[ ] 5.0W ±0.5W
adjust Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel 5A or less
2) Adj item : [L LPWR] →
[L’ LPWR] → [C LPWR] →
[H’ LPWR] → [H LPWR]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
9. Low power [Panel test mode] Check 3.5~6.5W
check 1) CH-Sig : 1-1 5A or less
Set low power (Push [S])
PTT : ON
Power meter
[L HPWR], ± 1W
2) CH-Sig : 2-1
PTT : ON
3) CH-Sig : 3-1
PTT : ON
10. DQT 1) Adj item : [n BAL]
balance Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel panel lation waves into
adjust Deviation meter filter square waves.
LPF : 3kHz Deviation Front Modular
HPF : OFF meter panel MIC jack
• Narrow 2) Adj item : [nL BAL] →
[nC BAL] → [nH BAL] AG
Adjust : [✳✳✳] AF VTVM
PTT : ON
• Wide 4k 3) Adj item : [s BAL]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
• Wide 5k 4) Adj item : [w BAL]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
Power meter
Oscilloscope
Rear ANT Front [ ],[ ] Make the demodu-
40
Page 41

ADJUSTMENT
Measurement Adjustment
Item Condition
11. Max DEV 1) Adj item : [n DEV]
adjust Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel panel (According to the
AG : 1kHz/50mV at MIC terminal
Deviation meter filter Deviation Front Modular
LPF : 15kHz meter panel MIC jack
HPF : OFF
• Narrow 2) Adj item : [nL DEV] → AG
[nC DEV] → [nH DEV] AF VTVM
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
Test-
equipment
Power meter
Oscilloscope
Unit Terminal PartsUnit Method
Rear ANT Front [ ],[ ] 2.10kHz ± 0.10kHz
larger +, –)
TK-8180
Specifications/Remarks
• Wide 4k 3) Adj item : [s DEV] 3.30kHz ±0.10kHz
• Wide 5k 4) Adj item : [w DEV] 4.20kHz ± 0.10kHz
12. MIC [Panel test mode] Check 2.5~3.5kHz
sensitivity 1) CH-Sig : 1-1
check
(Wide 5k only) PTT : ON
13.
QT deviation
adjust Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel
• Narrow 2) Adj item : [nL QT] →
• Wide 4k 3) Adj item : [s QT] 0.60kHz ±0.10kHz
• Wide 5k 4) Adj item : [w QT] 0.75kHz ±0.10kHz
Adjust : [✳✳✳] (According to the
PTT : ON larger +, –)
Adjust : [✳✳✳] (According to the
PTT : ON larger +, –)
AG : 1kHz/5mV at MIC terminal
1) Adj item : [n QT] Front [ ],[ ] 0.35kHz ± 0.05kHz
Deviation meter filter
LPF : 3kHz
HPF : OFF
[nC QT] → [nH QT]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
14. DQT 1) Adj item : [n DQT] 0.35kHz ±0.05kHz
deviation Adjust : [✳✳✳]
adjust Deviation meter filter
LPF : 3kHz
HPF : OFF
• Narrow 2) Adj item : [nL DQT] →
[nC DQT] → [nH DQT]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
• Wide 4k 3) Adj item : [s DQT] 0.60kHz ± 0.10kHz
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
• Wide 5k 4) Adj item : [w DQT] 0.75kHz ±0.10kHz
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
41
Page 42

TK-8180
ADJUSTMENT
Measurement Adjustment
Item Condition
15. LTR 1) Adj item : [n LTR]
deviation Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel panel
adjust Deviation meter filter
LPF : 3kHz Deviation Front Modular
HPF : OFF meter panel MIC jack
• Narrow 2) Adj item : [nL LTR] →
[nC LTR] → [nH LTR] AG
Adjust : [✳✳✳] AF VTVM
PTT : ON
Test-
equipment
Power meter
Oscilloscope
Unit Terminal PartsUnit Method
Rear ANT Front [ ],[ ] 0.75kHz ± 0.10kHz
Specifications/Remarks
• Wide 3) Adj item : [w LTR] 1.00kHz ± 0.10kHz
16. DTMF 1) Adj item : [n DTMF] 1.5kHz ± 0.1kHz
deviation Adjust : [✳✳✳]
adjust Deviation meter filter
• Narrow LPF : 15kHz
• Wide 4k 2) Adj item : [s DTMF] 2.4kHz ± 0.1kHz
• Wide 5k 3) Adj item : [w DTMF] 3.0kHz ± 0.1kHz
17. MSK 1) Adj item : [n MSK] 1.5kHz ± 0.1kHz
deviation Adjust : [✳✳✳]
adjust Deviation meter filter
• Narrow LPF : 15kHz
• Wide 4k 2) Adj item : [s MSK] 2.4kHz ± 0.1kHz
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
• Wide 5k 3) Adj item : [w MSK] 3.0kHz ± 0.1kHz
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
18. TONE 1) Adj item : [n TONE] 1.5kHz ± 0.1kHz
deviation Adjust : [✳✳✳]
adjust Deviation meter filter
• Narrow LPF : 15kHz
• Wide 4k 2) Adj item : [s TONE] 2.4kHz ± 0.1kHz
• Wide 5k 3) Adj item : [w TONE] 3.0kHz ± 0.1kHz
HPF : OFF
PTT : ON
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
PTT : ON
42
Page 43

TK-8180
ADJUSTMENT
Receiver Section (K market model skips adjustment of Wide 4k)
Measurement Adjustment
Item Condition
1. Sensitivity 1) Adj item : [SENS1] SSG Rear ANT Front [ ],[ ] Enter the following Note : After replacing the
adjust Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel panel adjustment values EEPROM (IC401) aline
2) Adj item : [L SENS1] → AF VTVM EXT. SP to the transceiver sensitivity.
[L’ SENS1] → [C SENS1] →
[H’ SENS1] → [H SENS1] [ ] keys.
Adjust : [✳✳✳] [L SENS1] : 70
2. Sensitivity [Panel test mode] Check 12dB SINAD or more
check 1) CH-Sig : 1-1
SSG output
Wide 5k : –116dBm (0.35µV)
(MOD : 1kHz/±3kHz)
Narrow : –116dBm (0.35µV)
(MOD : 1kHz/±1.5kHz)
Test-
equipment
Oscilloscope
Unit Terminal PartsUnit Method
by pressing [ ] and
[L’ SENS1] : 90
[C SENS1] : 115
[H’ SENS1] : 138
[H SENS1] : 164
After setting the
adjustment value,
press [B] key.
The adjustment
value will be stored
in memory.
Specifications/Remarks
3. Squelch 1) Adj item : [n SQL] After input signal After adjusting SQL, check
(Preset) Adjust : [✳✳✳] from SSG, press [B] SQL open/close.
adjust SSG output :
• Narrow (MOD : 1kHz/±1.5kHz) will be stored in : Open
2) Adj item : [nL SQL] → : Close
[nC SQL] → [nH SQL] [nC SQL] MOD 1kHz/±1.5kHz
Adjust : [✳✳✳] [sC SQL] MOD 1kHz/±2.4kHz
• Wide 4k 3) Adj item : [s SQL]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
SSG output :
(MOD : 1kHz/±2.4kHz)
4) Adj item : [sL SQL] →
[sC SQL] → [sH SQL]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
• Wide 5k 5) Adj item : [w SQL]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
SSG output :
(MOD : 1kHz/±3.0kHz)
6) Adj item : [wL SQL] →
[wC SQL] → [wH SQL]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
12dB SINAD level
12dB SINAD level
12dB SINAD level
key. That numeric SSG 12dB SINAD level + 4dB
memory. SSG 12dB SINAD level – 6dB
[wC SQL] MOD 1kHz/±3.0kHz
43
Page 44

TK-8180
ADJUSTMENT
Measurement Adjustment
Item Condition
4. Low RSSI 1) Adj item : [n LRSSI] SSG Rear ANT After input signal The following erroneous
adjust Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel from SSG, press [B] performance may occur if any
• Narrow SSG output :
(MOD : 1kHz/±1.5kHz)
2) Adj item : [nL LRSSI] → when it is the ANT OPEN
[nC LRSSI] → [nH LRSSI] state, is performed.
Adjust : [✳✳✳] • The antenna bar ( ) cannot
• Wide 4k 3) Adj item : [s LRSSI] • Scan does not stop.
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
SSG output :
(MOD : 1kHz/±2.4kHz)
4) Adj item : [sL LRSSI] →
[sC LRSSI] → [sH LRSSI]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
• Wide 5k 5) Adj item : [w LRSSI]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
SSG output :
(MOD : 1kHz/±3.0kHz)
12dB SINAD level
12dB SINAD level
12dB SINAD level
Test-
equipment
AF VTVM EXT. SP key. That numeric irregular RSSI adjustment,
Oscilloscope
Unit Terminal PartsUnit Method
will be stored in such as pressing the [B] key
memory. assigned for determination
Specifications/Remarks
appear correctly.
6) Adj item : [wL LRSSI] →
[wC LRSSI] → [wH LRSSI]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
5. Squelch 1) Adj item : [n SQLT] After input signal After adjusting SQL, check
(Tight) Adjust : [✳✳✳] from SSG, press [B] SQL open/close.
adjust SSG output key. That numeric SSG 12dB SINAD level +10dB
• Narrow : 12dB SINAD+5dB level will be stored in : Open
(MOD : 1kHz/±1.5kHz) memory. SSG 12dB SINAD level
2) Adj item : [nL SQLT] →
[nC SQLT] → [nH SQLT]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
• Wide 4k 3) Adj item : [s SQLT]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
SSG output
: 12dB SINAD+5dB level
(MOD : 1kHz/±2.4kHz)
4) Adj item : [sL SQLT] →
[sC SQLT] → [sH SQLT]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
• Wide 5k 5) Adj item : [w SQLT]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
SSG output
: 12dB SINAD+5dB level
(MOD : 1kHz/± 3.0kHz)
: Close
[nC SQLT] MOD 1kHz/± 1.5kHz
[sC SQLT] MOD 1kHz/±2.4kHz
[wC SQLT] MOD 1kHz/±3.0kHz
44
6) Adj item : [wL SQLT] →
[wC SQLT] → [wH SQLT]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
Page 45

TK-8180
ADJUSTMENT
Measurement Adjustment
Item Condition
6. High RSSI 1) Adj item : [n HRSSI] SSG Rear ANT After input signal The following erroneous
adjust Adjust : [✳✳✳] panel from SSG, press [B] performance may occur if any
• Narrow SSG output : –70dBm AF VTVM EXT. SP key. That numeric irregular RSSI adjustment,
(MOD : 1kHz/±1.5kHz)
2) Adj item : [nL HRSSI] → when it is the ANT OPEN
[nC HRSSI] → [nH HRSSI] state, is performed.
Adjust : [✳✳✳] • The antenna bar ( ) cannot
• Wide 4k 3) Adj item : [s HRSSI] • Scan does not stop.
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
SSG output : –70dBm
(MOD : 1kHz/±2.4kHz)
4) Adj item : [sL HRSSI] →
[sC HRSSI] → [sH HRSSI]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
• Wide 5k 5) Adj item : [w HRSSI]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
SSG output : –70dBm
(MOD : 1kHz/±3.0kHz)
Test-
equipment
Oscilloscope
Unit Terminal PartsUnit Method
will be stored in such as pressing the [B] key
memory. assigned for determination
Specifications/Remarks
appear correctly.
6) Adj item : [wL HRSSI] →
[wC HRSSI] → [wH HRSSI]
Adjust : [✳✳✳]
Adjustment Points
TX-RX UNIT (B/3)
Component side view
CV
ANT
TC301
CV
TX-RX UNIT (B/3)
Foil side view
TC302
PSENS
PSW
RST2
TXD
RXD
45
Page 46

TK-8180
TERMINAL FUNCTION
Display unit (X54-3480-10)
Pin No.
Name Description
CN901 (to internal speaker)
1 GND Ground.
2 SPO Speaker output.
CN902 (to TX-RX unit B/3 CN429)
1 SPO Speaker input.
2 SPO Speaker input.
3 SPO Speaker input.
4 SPO Speaker input.
5 SPO Speaker input.
6 SPO Speaker input.
7 GND Ground.
88C 8V input.
9SB Power input of switched power supply.
10 SB Power input of switched power supply.
11 NC Non-connenction.
12 PSW Detection signal output of power switch.
13 GND Ground.
14 GND Ground.
15 MIC MIC signal output.
16 ME MIC ground.
17 GND Ground.
18 PSENS Detection signal output of display unit.
19 RST2 Reset signal input.
20 GND Ground.
21 GND Ground.
22 GND Ground.
23 NC Non-connenction.
24
SHIFT/MODEL
25 NC Non-connenction.
26 5C 5V output.
27 TXD Serial data signal input.
28 RXD Serial data signal output.
29 GND Ground.
30 GND Ground.
1 BLC MIC backlight control.
2SB DC 13.6V±15%, 200mA typ.
3E Ground.
Control signal input of beat-shift function.
J901 (MIC jack)
Pin No.
Name Description
4 PTT/TXD PTT : PTT input, TXD : Serial data output.
5ME MIC ground.
6 MIC MIC signal input.
7
HOOK/RXD
8DM MIC data detection.
HOOK : Hook detection, RXD : Serial data input.
TX-RX unit (X57-6990-10) (A/3)
Pin No.
Name Description
CN701 (to TX-RX unit B/3 CN427)
1 AUXIO6 AUX input/output 6.
2 AUXIO7 AUX input/output 7.
3 AUXIO1 AUX input/output 1.
4 AUXIO2 AUX input/output 2.
5 RXD2 Serial data output 2.
6 AUXIO3 AUX input/output 3.
7 TXD2 Serial data input 2.
8 AUXIO4 AUX input/output 4.
9 AUXIO8 AUX input/output 8.
10 AUXIO5 AUX input/output 5.
11 AUXIO9 AUX input/output 9.
12 AUXO1 AUX input 1.
13 TXD1 Serial data input 1.
14 AUXO2 AUX input 2.
15 RXD1 Serial data output 1.
16 GND Ground.
17 ME MIC ground.
18 MI2 External MIC output.
19 DEO Detected signal input.
20 GND Ground.
21 5C 5V.
22 DI Data signal output.
23 AFO RX filtered audio input.
24 SB Power input after power switch.
25 SB Power input after power switch.
26 SB Power input after power switch.
27 SB Power input after power switch.
28 SB Power input after power switch.
29 SB Power input after power switch.
30 NC Non-connenction.
46
Page 47

TERMINAL FUNCTION
TK-8180
Pin No.
Name Description
J701 (ACC 25-pin)
1NC Non-connenction.
2 RXD1 Serial data input 1. RS-232C level.
Input voltage range : ±30V max.
L≤0.4V, H≥2.4V, Zi≥5kΩ
3TXD1 Serial data output 1. RS-232C level.
L≤–5V, H≥5V/3kΩ load, Zo≤2kΩ
4AUXI/O9 AUX input/output 9.
Active low with 47kΩ pull-up to 5V
5DI Data signal input.
Data input level adjustable (2.0Vp-p typ.)
6 MI2 External MIC input. DC-coupled
7 GND Ground.
8AUXI/O8 AUX input/output 8. Same as AUXI/O9
9TXD2 Serial data output 2. TTL level.
L≤0.7V, H≥4.2V/25kΩ load, Zo≤1kΩ
10 RXD2 Serial data input 2. TTL level.
Input voltage range : +5/0V max.
L≤0.8V, H≥4.2V
11 GND Ground.
12 AUXI/O7 AUX input/output 7. Same as AUXI/O9
13 AUXI/O6 AUX input/output 6. Same as AUXI/O9
14 SB Power output after power switch.
DC13.6V± 15%, 2.0A max.
15 AUXO2 AUX output 2. Open collector (500mA max.)
(Default none) L≤0.3V
16 AUXO1 AUX Output 1. Same as AUXO2
17 AFO RX filtered audio output (DC-coupled).
AF low level output.
Wide : 700mVp-p typ.
Narrow : 700mVp-p typ.
18 GND Ground.
19 DEO Detected signal output (DC-coupled).
AF output level adjustable (740mVp-p typ.)
20 AUXI/O5 AUX input/output 5. Same as AUXI/O9
21 AUXI/O4 AUX input/output 4. Same as AUXI/O9
22 AUXI/O3 AUX input/output 3. Same as AUXI/O9
23 AUXI/O2 AUX input/output 2. Same as AUXI/O9
24 AUXI/O1 AUX input/output 1. Same as AUXI/O9
25 ME MIC ground.
(Standard modulation)
TX-RX unit (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
Pin No.
Name Description
CN301 (to TX-RX unit C/3)
1 REF Reference signal otput to the PLL IC.
2 Fin Complementary signal output to the PLL IC.
3 CPGND Ground.
45C 5V output.
5 GND Ground
6CP
1UL Control signal input form the PLL IC.
2 PLE Control signal output to the PLL IC.
3DT Control signal output to the PLL IC.
4 PCK Control signal output to the PLL IC.
5 GND Ground.
6 DGND Ground.
1 OPT1 VGS busy signal input. Option boad I/F 1.
2 OPT3 VGS playback signal input. Option boad I/F 3.
3 RXD1 Serial data input.
4 TXD1
5 CLK Serial clock output.
6 OPT4 VGS enable output. Option boad I/F 4.
7USEL
8 OPT5 VGS reset signal output. Option boad I/F 5.
9 DGND Ground.
10 AGND Ground.
11 AO VGS audio input. Zin≥10kΩ, 1Vp-p max,
12 AI VGS audio output. Zo≥10kΩ
13 AGND Ground.
14 5E 5V power supply output. 78mA max
15 STON Side tone input. 1kHz, 5Vp-p
Signal input from charge pump block in the PLL IC.
CN302 (to TX-RX unit C/3)
CN403 (to VGS-1)
Output : L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
Input : L≤1.0V, H≥4.0V, Input voltage : 0V~5.0V
Output : L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
Input : L≤1.0V, H≥4.0V, Input voltage : 0V~5.0V
Input : L≤1.0V, H≥4.0V, Input voltage : 0V~5.0V
Serial data output / PTT singanl output (SC20-460).
Output : L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
Output : L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
UART speed select output. L : 19200bps fixed
Output : L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
Input Voltage : 0V~5.0V
47
Page 48

TK-8180
TERMINAL FUNCTION
Pin No.
Name Description
16 DTI Data signal input.
Zin≥22kΩ, 600± 200mVp-p
17 TCTL Speaker mute signal input.
Input : L≤1.0V, H≥4.0V, Input voltage : 0V~5.0V
18 NC Non-connection.
19 AUDIH MIC mute signal input.
20 OPT2 Option boad I/F 2.
Output : L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
Input : L≤1.0V, H≥4.0V, Input voltage : 0V~5.0V
21 TXO MIC signal output (AC coupled) before pre-
emphasis. Zo>2.2kΩ, 130±50mVp-p typ.
22 RXEO Audio signal output (DC coupled) after de-
emphasis. Zo>30kΩ, 1± 0.3Vp-p typ.
23 RXEI Audio signal input (DC coupled) after de-
emphasis. Zin>15kΩ, 1± 0.3Vp-p typ.
24 TXI MIC signal input (AC coupled) before pre-
emphasis. Zin>22kΩ, 500± 50mVp-p typ.
25 OPT6 Option boad I/F 6.
Output : L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
26 8C Power input after power switch.
8.0V typ, 100mA max
CN427 (to TX-RX unit A/3 CN701)
1NC Non-connenction.
2SB Power output after power switch.
3SB Power output after power switch.
4SB Power output after power switch.
5SB Power output after power switch.
6SB Power output after power switch.
7SB Power output after power switch.
8 AFO RX filtered audio output.
9DI Data signal input.
10 5C 5V.
11 GND Ground.
12 DEO Detected signal output.
13 MI2 External MIC input.
14 ME MIC ground.
15 GND Ground.
16 RXD1 Serial data input 1.
17 AUXO2 AUX output 2.
18 TXD1 Serial data output 1.
Pin No.
Name Description
19 AUXO1 AUX output 1.
20 AUXIO9 AUX input/output 9.
21 AUXIO5 AUX input/output 5.
22 AUXIO8 AUX input/output 8.
23 AUXIO4 AUX input/output 4.
24 TXD2 Serial data output 2.
25 AUXIO3 AUX input/output 3.
26 RXD2 Serial data input 2.
27 AUXIO2 AUX input/output 2.
28 AUXIO1 AUX input/output 1.
29 AUXIO7 AUX input/output 7.
30 AUXIO6 AUX input/output 6.
CN428
1SB Power output of switched power supply.
2 SPI Speaker output.
3 SPO Speaker input.
4PA Control signal output of PA function.
5 HOR Control signal output of Horn alert function.
6 GND Ground.
CN429 (to Display unit CN902)
1 (DM) Reserve.
2 GND Ground.
3 RXD Serial data signal input.
4 TXD Serial data signal output.
5NC Non-connenction.
65C 5V output.
7
SHIFT/MODEL
8 (CLK) Reserve.
9 (LCDDO) Reserve.
10 (LCDDI) Reserve.
11 (LCDRST) Reserve.
12 RST2 Reset signal output.
13 PSENS Detection signal input of display unit.
14 GND Ground.
15 ME MIC ground.
16 MIC MIC signal input.
17 GND Ground.
18 GND Ground.
19 PSW Detection signal input of power switch.
20 NC Non-connenction.
Control signal output of beat-shift function.
48
Page 49

TERMINAL FUNCTION
TK-8180
Pin No.
Name Description
21 SB Power output of switched power supply.
22 SB Power output of switched power supply.
23 8C 8V output.
24 GND Ground.
25 SPO Speaker output.
26 SPO Speaker output.
27 SPO Speaker output.
28 SPO Speaker output.
29 SPO Speaker output.
30 SPO Speaker output.
CN804
1 IGN Ignition sense input.
2 GND Ground.
Solder Land
Name Description
to ANI board
GND (A–) Ground.
OPT1 TX sens signal output. Conv. L : TX, H : Not TX
(CH BUSY) LTR L : Link complete, H : Not link complete
L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
OPT3 TX control signal input. Active low.
(KEY) L≤1.0V, H≥ : 4.0V, Input voltage 0V~5.0V
OPT4 PTT signal output. L : TX, H : Not TX
(PTT) L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
OPT5 Emergency signal output.
(EMERGENCY)
5E (A+) 5V power supply (78mA max.).
DTI Data signal input. Zin>22kΩ, 600± 200mVp-p
(DATA OUT) (Standard modulation)
TCTL Speaker mute signal input. H : Unmute
(TONE CTRL) L≤0.8V, H≥4.2V, Input voltage : 0V~5.0V
AUDIH MIC mute signal input. L : Mute
(AUDIO INHIB)
OPT2 Emergency signal input. Active low.
(AUX I/O) L≤1.0V, H≥ : 4.0V, Input voltage 0V~5.0V
STON Side tone input. 1kHz, 5Vp-p
(SIDE TONE)
L : Emergency function is operated,
H : Emergency function is not operated
L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
Name Description
to Scrambler board
GND (GND) Ground.
TXD1 PTT signal output. L : TX, H : Not TX
(PTT) L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
(PTT signal input) Actiive low.
L≤1.0V, H≥4.0V, Inut voltage : 0V~5.0V
OPT1 (DODE Scramble code signal output 1.
SELECT1) L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
OPT3 (CODE Scramble code signal output 2.
SELECT2) L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
OPT4 Echo PTT signal output. L : TX, H : Not TX
(ECHO PTT) L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
OPT5 (CODE Scramble code signal output 4.
SELECT8) L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
TXO MIC signal output (AC coupled) before
(TX OUT) pre-enphasis. Zo>2.2kΩ, 130± 50mVp-p typ.
(Standard modulation)
OPT2 Scrambler control signal output.
(SCRAMBLE) L : ON, H : OFF. L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
RXEO Audio signal output (DC coupled) after
(RX OUT) de-enphasis. Zo>30kΩ, 1±0.3Vp-p typ.
(Standard modulation)
TXI MIC signal input (AC coupled) before
(TX IN) pre-enphasis. Zin>2.2kΩ, 130± 50mVp-p typ.
(Standard modulation)
RXEI Audio signal input (DC coupled) after
(RX IN) de-enphasis. Zin>15kΩ, 1± 0.3Vp-p typ.
(Standard modulation)
OPT6 (CODE Scramble code signal output 3.
SELECT4) L≤0.45V, H≥4.7V/25kΩ load
8C (+V) 8V AVR output. 8.0V typ, 100mA max.
to GPS receiver
GND (GND) Ground.
1
RXD1*
(DATA OUT1)
1
RXD2*
(DATA OUT1)
5E (+5V) 5V
*1 : Depending on the connected optional accessory, the DATA
OUT1 may connect to either RXD1 or RXD2.
Data output.
Data output.
49
Page 50

9
TK-8180 PC BOARD
1
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) Component side view (J72-0932-09)
2
PSW
3
D907
4
5
7
HK
ME
E
6
1
BLC
DM
MIC
PTT
SB
8
J901
2
LEFT DOWN
LEFT UP
D927
D928
COM7_2
COM6_2
COM8_1
COM9_1
D921
COM5_2
COM4_2
COM1_1
COM2_1
COM3_2
COM2_2
COM3_1
COM4_1
SEG1
D909
D915
COM5_1
JIHGFEDCBA
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
SEG26
SEG27
SEG28
ED1
CP904
D910
CP902
CP901
D916
SEG16
SEG17
SEG18
SEG19
COM6_1
COM7_1
COM8_2
COM9_2
SA
D922
SEG20
SEG21
SEG22
CP907
CP906
CP905
D923
CP908
CP903
SEG23
D911
D917
SEG24
SEG25
SEG31
SEG32
SEG33
10
11
12
13
7
8
9
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) Foil side view (J72-0932-09)
C916
ME
MIC
L901
C911
L902
I
C907
GND
GNDNCSB
C913
C914
PSW
Q911
R963
R962
SB
8C
Q910
SPO
GND
D902
Q901
Q902
SPO
SPO
SPO
1
2
2
SPO
SPO
1
R910
R909
R905
R907
R911
GND
SPO
CN901
R920
D903
C924
R914
R915
R916
R919
X901
R913
R936
C925
R931
R932
R933
R930
L909
R940
R941
R934
R935
L908
1
C936
7
BLC
ME
HK
SP2
C915
D904
+
D905
D901
5C
GND
SHIFT/MODEL
TXDNCNC
C918
IC901
O
C917
GND
GND
C910
C926
C908
CN902
PSENS
RST2
G
GND
R904
2
SB
E
PTT
MIC
DM
C912
C909
R903
R901
C904
8
C906
30
GND
GND
29
Q904 Q905
R917 R918
D906
RXD
C921
R929
25
26
R928
R944
Q909
R945
Q913
R925
C938
1
R926R927
IC902
TP1
50
R970
C928
100
51
Q907
C927
L903
E
C
B
C920
L904
C922
R939
Q906
C934
C932
CP911
76
75
R942
C933
C935
CP909
R957
R958
R959
100
R943
R956
1
CP910
R955
C
14
50
Page 51

JKLMNOPQRS
SEG26
ED1
SEG31
SEG27
SEG28
SEG32
SEG33
PC BOARD TK-8180
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) Component side view (J72-0932-09)
SEG29
SEG30
C937
SEG34
SEG35
SEG36
SEG37
SEG38
SEG39
SEG40
SEG46
SEG47
SEG48
SEG49
SEG50
SEG56
SEG57
SEG58
SEG59
SEG60
D912
D918
SEG41
SEG42
SEG43
SEG44
<
BC
D926
SEG45
SEG51
D913
D919
SEG52
SEG53
SEG54
SEG55
SEG61
D925
>
SEG62
SEG63
SEG64
SEG65
SEG66
D914
D920
SEG71
SEG67
SEG72
SEG68
SEG73
SEG69
SEG70
SEG74
SEG75
D924
RIGHT UP
D929
RIGHT DOWN
D930
J72-0932-09
Ref. No.
Address
D907 3C
D909 3G
D910 3H
D911 3I
D912 3K
D913 3L
D914 3N
D915 4G
D916 4H
D917 4I
D918 4K
D919 4L
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Ref. No.
Address
D920 4N
D921 6F
D922 6G
D923 6I
D924 6O
D925 6M
D926 6K
D927 3D
D928 5D
D929 3P
D930 5P
Component side
Foil side
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
33
R957
R958
09
R943
R956
R959
100
1
CP910
R955
C931
R953
R951
L905
L906
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) Foil side view (J72-0932-09)
R947
R948
R971
L907
R949
TH901
R954
51
50
J72-0932-09
C930
R952
IC903
25 26
7576
R969
R950
R967
Ref. No.
Address
IC901 10C
IC902 12H
IC903 12K
Q901 10D
Q902 10D
Q904 12B
Q905 12C
Q906 10I
Q907 9I
Q909 9H
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Ref. No.
Address
Q910 10D
Q911 9D
Q913 9H
D901 10C
D902 12D
D903 9F
D904 9C
D905 10C
D906 10C
Component side
Foil side
8
9
10
11
12
13
51
14
Page 52

JKLMNOPQRSIHGFEDCBA
TK-8180 PC BOARD
1
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) Component side view (J72-0932-09) DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) Component side view (J72-0932-09)
2
PSW
3
D907
4
5
7
HK
ME
E
6
1
BLC
DM
MIC
PTT
SB
8
J901
2
7
LEFT DOWN
LEFT UP
D927
D928
COM7_2
COM6_2
COM8_1
COM9_1
D921
COM5_2
COM4_2
COM1_1
COM2_1
COM3_2
COM2_2
COM3_1
COM4_1
SEG1
D909
D915
COM5_1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
SEG26
SEG27
SEG28
SEG29
SEG30
SEG36
SEG37
SEG38
SEG39
SEG40
SEG46
SEG47
SEG48
SEG49
SEG50
SEG56
SEG57
SEG58
SEG59
SEG60
SEG66
ED1
CP904
D910
CP902
CP901
D916
SEG16
SEG17
SEG18
SEG19
COM6_1
COM7_1
COM8_2
COM9_2
SA<BC
D922
SEG20
SEG21
SEG22
CP907
CP906
CP905
D923
CP908
CP903
SEG23
D911
D917
SEG24
SEG25
SEG31
SEG32
SEG33
C937
SEG34
SEG35
D912
D918
SEG41
D926
SEG42
SEG43
SEG44
SEG45
SEG51
D913
D919
SEG52
SEG53
SEG54
SEG55
D925
SEG61
>
SEG62
SEG63
SEG64
D914
D920
SEG65
SEG71
SEG67
SEG72
SEG68
SEG73
SEG69
SEG74
SEG70
SEG75
D924
PC BOARD TK-8180
Ref. No.
Address
Ref. No.
RIGHT UP
D929
RIGHT DOWN
D930
J72-0932-09
D907 3C
D909 3G
D910 3H
D911 3I
D912 3K
D913 3L
D914 3N
D915 4G
D916 4H
D917 4I
D918 4K
D919 4L
Component side
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Foil side
Address
D920 4N
D921 6F
D922 6G
D923 6I
D924 6O
D925 6M
D926 6K
D927 3D
D928 5D
D929 3P
D930 5P
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
10
11
12
13
8
9
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) Foil side view (J72-0932-09) DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10) Foil side view (J72-0932-09)
Q909
R945
R925
C938
Q913
1
IC902
50
R970
C928
100
51
Q907
L903
E
C
B
C927
C920
L904
C922
R939
Q906
C934
C932
CP911
76
75
R942
C933
C935
CP909
R957
R958
R959
100
CP910
R943
R956
1
R955
C931
R953
R951
L905
L906
C930
R952
IC903
25 26
7576
R969
R967
R950
R971
R948
L907
R949
TH901
R947
R954
51
50
J72-0932-09
1
C936
7
BLC
ME
HK
ME
GND
L901
C911
L902
I
C916
C907
GND
MIC
C913
C914
Q911
R963
R962
SB
PSW
GNDNCSB
8C
Q910
SPO
GND
D902
Q901
Q902
SPO
SPO
SPO
1
2
2
SPO
SPO
1
R910
R909
R905
R907
R911
GND
SPO
CN901
R920
D903
C924
R914
R915
R916
R919
X901
R913
R936
C925
R931
R932
R933
R930
L909
R940
R941
R934
R935
L908
R929
25
26
R928
R944
R926R927
TP1
SP2
C915
D904
+
D905
D901
5C
GND
SHIFT/MODEL
TXDNCNC
O
C917
GND
GND
C910
C926
C918
IC901
G
C908
CN902
PSENS
RST2
R904
2
SB
E
PTT
MIC
DM
8
C912
C909
R903
R901
C904
D906
C906
30
RXD
GND
GND
29
Q904 Q905
C921
R917 R918
Ref. No.
Address
IC901 10C
IC902 12H
IC903 12K
Q901 10D
Q902 10D
Q904 12B
Q905 12C
Q906 10I
Q907 9I
Q909 9H
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Ref. No.
Address
Q910 10D
Q911 9D
Q913 9H
D901 10C
D902 12D
D903 9F
D904 9C
D905 10C
D906 10C
Component side
Foil side
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
14
Page 53

JIHGFEDCBA
TK-8180
1
2
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (A/3) Component side view (J72-0931-19 A/3)
3
4
R706
R718
C716
5
6
J72-0931-19 A/3
C707
13
PC BOARD
R707
R719
25
C717
C708
C718
R708
C709
C719
C710
R709
C713
R717
C711
R710
C720
C723
D714
C722
C712
C706
C714
D710
C705
C715
D709
C721
14
1
10
11
12
13
TXD2
AUXIO3
RXD2
AUXIO2
AUXIO1
AUXIO7
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
30
AUXIO6
Component side
1
SBSBSBSBSB
NC
7
DI
5C
SB
AFO
GND
ME
MI2
DEO
CN701
GND
RXD1
AUXO2
TXD1
AUXO1
AUXIO9
AUXIO5
AUXIO8
AUXIO4
Ref. No. Address
8
D709 6G
D710 6G
D714 6F
Layer 4
9
Foil side
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (C/3)
Component side view (J72-0931-19 C/3)
CP
5C
Fin
GND
CPGND
REF
J72-0931-19 C/3
L305
R301
C309
C397
R373
1
5
L304
R320
R319
1620
15
IC301
11
610
R321
C396
C322
R323
R332
R330
R327
R325
C335
PLE
UL
PCK
DT
DGND
GND
Ref. No. Address
IC301 12E
Component side
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Foil side
14
52
Page 54

ABCDE FGH I J
PC BOARD
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (A/3) Foil side view (J72-0931-19 A/3)
J701
AUX
AUX
AUX
AUX
AUX
I/O5
AUX
GND RXD2TXD2MI2DITXD1RXD1NC
I/O8
I/O4
I/O3
D706D707D708 D711D712D713
R703R704R705 R711R712R713
I/O2
I/O1
GND
26
GND
1
14
D703
Q701
AUX
I/O9
D702
Q702
TK-8180
25
MEDEOGNDAFOSB AUXO1AUXO2
AUX
AUX
I/O7
I/O6
13
27
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
C701
C702 C703C704
L701
L702
R716
Ref. No. Address
D711 6H
D712 6H
D713 6F
R715
Ref. No. Address
Q701 6C
Q702 6D
D701 7D
D702 6D
D703 6C
D701
Ref. No. Address
D704 7G
D705 7F
D706 6G
D707 6G
D708 6E
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (C/3)
Foil side view (J72-0931-19 C/3)
R378
R308
1
5
+
C386
34
IC302
R377
J72-0931-19 C/3
R714
R720
J72-0931-19 A/3
D704D705
R701R702
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Ref. No. Address
IC302 11E
Component side
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Component side
Foil side
Foil side
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
53
14
Page 55

C
1
3
3
R
2
8
5
TK-8180 PC BOARD
1
JIHGFEDCBA
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
Component side view (J72-0931-19 B/3)
10
11
12
13
14
C801
+
CN803
GND
CN802
+B
D406
R800
Q811
R804
D801
F801
C450
24
1
C824
R546
C823
C826
C467
R549
C454
L411
L410
R802
R801
IC410
C814
C819
14
IC802
R552
32
1
C22
L4
C803
C802
R18
R16
C21
R17
C20
C19
+
C17
D1
C24
R15
D802
R545
12 13
C472
R508
C445
R499
R542
R503
D405
C446
1
8
IC407
45
C441
R475
C444
R498
R496
C18
R14
R19
Q3
+
C6
R75
L324
R76
R71
R21
R77
R72
C339
1
IC7
4
C30
L32
C398
2
J401
EXT. SP
1
2
CN804
SPO
R654
R653
C577
SPI
C579
1
SB
SB
6GND
CN428
PA
3
+
HOR
C576
4
7
5
IC417
IGN
GND
Q804
R807
R812
Q808
+
C580
Q806
R811
R806
Q803
8T
+
C578
C575
+
R623
R642
16
Q418
IC416
D412
R652
C573
C572
R648
Q419
89
1
C570
R644
R651
+
C564
C562
C563
+
C574
R645
+
C566
5C
+
+
C565
6
1
D416
C560
C561
R655
R632
R641
F401
7
R622
R621
8
R643
TTL
R630
R633
R636
PA
HOR
R625R629
RS-232C
R624
D413
D418
D414
C546
9
C592 C593
CLKC
54
32K
CHAE
CN401
BATT
R809
C813
1234
IC801
C818
R400
R591
R903
R575
1
NC
DM
TXD
RXD
GND
J72-0931-19 B/3
R900
R901
R902
5C
CLK
LCDDI
LCDDO
SHIFT/MODEL
Q812
D600
R572
R574
RST2
LCDRST
CN429
Q416
C542
GND
PSENS
G
C500
ME
Q600
D
S
R615
MIC
GND
D601
R612
R617
+
PW
GND
R616
R646
R620
C543
C498
SB
NC
C538
SB
8C
C540
+
C539
GND
SPO
Q417
R603
R604
R594
R589
SPO
SPO
S
D
G
R592
SPO
R596
8
C483
IC414
45
1
+
C544
D409
C512C513
R580
Q410
C506
C505
GND
C501
R569
C511
R586
R606
D408
C530
D422
RXD1
R573
TXD1
R597
D421
TXD2
R465
RXD2
OPT1
R618
R619
R613
+
R581
Q411
30
SPO
SPO
AD-0 AD-1
R445
R446
OPT3
OPT4
5M
OPT5
R474
C427
C421
5E
R403
C420
C428
R473
R484
C422
DTI
R483
1
OPT1
OPT3
2
R485
C424
AO
EXTLIM
R595
C425
C430
R488
R487
R489
C435
C436
C595
C586
C588
RXO RXI
CLK
RXD1
TXD1
OPT4
R486
TCTL
USEL
CN403
OPT5
5E
TXO
TXO
RXEI
TCTL
OPT6
STON
DGNDAOAGND
AUDIH
AGNDAI5E
DTINCOPT2
RXEO
TXI
8C
26 25
C437
C585
C587
R491
C431
C432
C426
C831
IC807
O
++
OPT2
AUDIH
G
STON
AI
I
RXEO
C439
C832
TXI
R590
8C
G
R600
C534
RXEI
D
S
Q413
R302
X301
R362
CN
UL
1
C260
DT
C261
5
GND
L
8C
OPT6
Page 56

JKLMNOPQRS
22
L4
20
19
17
C32
R21
C76
R77
R75
18
R76
IC71
R79
54
R71
R72
R78
8T
C392
C394
C333
C398
C302
L324
L323
C339
R302
X301
R362
UL
1
C260C261
DT
56
GND
R305
CN302
DGND
L306
L322
C395
L301
PCK
L321
C393
R303
C306
2PLE
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
Component side view (J72-0931-19 B/3)
IC1
4
L5
C390
C307
CN301
2Fin
REF
1
+
R81
R90
Q70
C391
5C
CPGND
GND
L6
C26
C27
C28
C29
R85
C77
R84
18
R87
IC72
54
R26
C316
R369
C327
D
G
Q72
Q301
L327
R318
R326
R333
R315
R86
S
R88
R376
C308
+
R307
+
+
+
C318
C320
R89
C262
C311
R310
R370
R306
C317
C324
R309
C323
C312
R311
C314
R316
R322
R317
C338
R312
Q302Q303
CV
R82
C74
L320
C389
R371
L302
C331
CP
GND
56
D103
D104
D105
D106
BPF
L110
C127
C129
R133
C132
C131
C137
C140
C139
8R
C128
C133
C135
C136
C141
L111
L112
L113
R177
R121
R122
R123
R124
R126
GND
C25
R134
C130
C134
C138
C142
R295
R298
R115
CF172
WIDE
CF171
NARROW
LO
GND
5R
PC BOARD TK-8180
Ref. No.
Address
IC1 3K
IC71 7J
IC72 7L
IC172 9P
IC407 7G
IC410 8F
IC414 11E
IC416 8D
IC417 5C
IC801 11B
IC802 2G
IC807 12H
Q3 7I
Q70 7K
Q72 7L
Q171 11P
Q175 10O
Q176 9P
Q177 9O
Q179 10O
Q301 8L
Q302 10L
Q303 11L
Q410 12D
Q411 12D
Q413 10I
Q416 12C
Q417 11D
Q418 6D
Q419 7D
Component side
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Foil side
C221
C225
C224
R206
R202
C241
C234
D173
R207
C42
C214
C227
C220
R109
R221
C45
R197
R203
C236
R198
Q175
C228
TH171
C60
C53
C223
R199
C222
Q177
R30
C50
C44
X171
1
IC172
89
+
C237
R212
Q179
D174
CD171
R200
C226
L182
C193
R181
XF171
TH1
R31
16
R182
L188
C198
C197
R183
C31
R217
C211
C229
R204
S
D
G
C235
XF171
C196
R184
C194
R180
Q171
C192
C212
C231
R205
Q176
L181
C233
C195
Ref. No.
Address
Q600 11C
Q803 2E
Q804 2D
Q806 2E
Q808 3D
Q811 2F
Q812 11C
D1 5I
D103 8M
D104 9M
D105 10M
D106 10M
D173 10O
D174 10P
D405 8G
D406 7F
D408 11E
D409 11D
D412 9D
D413 9C
D414 8C
D416 6D
D418 7D
D421 13E
D422 13E
D600 12C
D601 11C
D801 6F
D802 6G
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
55
14
Page 57

JKLMNOPQRSIHGFEDCBA
TK-8180 PC BOARD
1
6GND
C576
IC417
EXT. SP
HOR
J401
CN428
PA
7
1
SPO
R654
R653
C577
SPI
C579
SB
2
3
+
4
5
6
R642
D416
C560
C561
R655
R632
R641
F401
7
R622
R621
R629
8
R643
TTL
R630
R633
R636
PA
HOR
R625
RS-232C
R624
D413
D418
D414
C546
R623
9
CLKC
32K
CHAE
10
CN401
BATT
D601
C538
R617
GND
GND
R646
R612
+
C543
NC
PW
R616
R620
C498
SB
Q417
C540
R603
+
R604
C539
R594
R589
8C
SB
SPO
SPO
SPO
GND
11
12
13
IC801
R591
R903
R809
C813
1
DM
1234
C818
R400
RXD
GND
R575
5C
NC
TXD
Q812
R900
R572
R901
R902
R574
CLK
RST2
LCDDI
LCDDO
LCDRST
SHIFT/MODEL
G
Q416
D600
C542
C500
ME
GND
PSENS
CN429
Q600
D
S
R615
MIC
J72-0931-19 B/3
14
16
S
D
G
R592
SPO
CN804
1
2
1
SB
Q418
IC416
+
30
SPO
SPO
IGN
GND
D412
R618
R619
R613
R581
+
R652
C573
C572
R648
Q419
89
1
+
Q411
C570
R644
C544
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
Component side view (J72-0931-19 B/3)
C801
+
R465
RXD2
R800
CN803
GND
CN802
+B
D406
OPT1
Q811
R804
D801
F801
C450
24
1
AD-0 AD-1
R445
R446
OPT3
OPT4
C824
R549
C454
R546
C823
C826
C467
5M
OPT5
L411
L410
R801
IC410
R474
C814
C819
R802
14
IC802
C427
C421
5E
32
R552
R403
C420
C428
R473
R484
C422
DTI
C803
R545
12 13
C592 C593
R483
1
OPT1
OPT3
2
R485
C424
C802
D802
C472
R542
C446
R508
1
8
IC407
C445
R503
45
R499
D405
C441
AO
R488
RXD1
TXD1
R486
TCTL
EXTLIM
C425
C430
R487
R489
CLK
TCTL
USEL
STON
DGNDAOAGND
CN403
OPT4
OPT5
AGNDAI5E
DTINCOPT2
R491
C431
C432
C426
C831
IC807
++
5E
TXO
AUDIH
Q808
C580
R651
D409
C512C513
R580
Q410
Q804
R807
R812
+
C578
C575
+
+
C564
C562
+
C506
C563
C483
C505
GND
8T
C574
R645
8
1
C501
R569
C511
R586
R606
+
+
+
C565
R596
IC414
D408
RXD1
Q806
R811
R806
C566
45
R573
C530
D422
TXD1
Q803
5C
R597
D421
TXD2
R475
C435
TXO
AUDIH
RXEO
C437
O
OPT2
C436
RXEI
OPT6
TXI
8C
26 25
C585
G
STON
C444
C595
R498
C586
C587
AI
I
RXEO
R496
R595
R590
C588
RXO RXI
8C
C439
C832
TXI
G
R600
C534
RXEI
R18
R15
D
S
R16
Q413
OPT6
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
PC BOARD TK-8180
1
Component side view (J72-0931-19 B/3)
2
Ref. No.
Address
Ref. No.
Address
Q600 11C
Q803 2E
Q804 2D
Q806 2E
Q808 3D
Q811 2F
Q812 11C
D1 5I
D103 8M
D104 9M
D105 10M
D106 10M
D173 10O
D174 10P
D405 8G
D406 7F
D408 11E
D409 11D
D412 9D
D413 9C
D414 8C
D416 6D
D418 7D
D421 13E
D422 13E
D600 12C
D601 11C
D801 6F
D802 6G
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
IC1
R30
C60
IC1 3K
IC71 7J
IC72 7L
C53
IC172 9P
IC407 7G
IC410 8F
IC414 11E
1
C22
L4
C20
C19
+
C21
R17
C17
D1
C24
C32
+
C29
C28
C27
L5
L6
C26
4
C25
C42
C45
C44
C50
TH1
R31
C31
IC416 8D
IC417 5C
IC801 11B
IC802 2G
IC807 12H
Q3 7I
Q70 7K
Q72 7L
Q171 11P
Q175 10O
Q176 9P
Q177 9O
Q179 10O
Q301 8L
Q302 10L
Q303 11L
Q410 12D
Q411 12D
Q413 10I
Q416 12C
Q417 11D
Q418 6D
Q419 7D
C18
R14
R19
Q3
+
C6
R21
C76
R77
R75
18
R76
IC71
R79
54
R71
R72
R78
8T
C390
C392
C394
C333
C398
C302
L324
L323
C339
R302
X301
R362
UL
1
C260
DT
C261
56
GND
R305
CN302
DGND
L306
L322
C395
L301
PCK
R303
C306
2PLE
L321
C393
C307
CN301
2Fin
REF
1
R85
C77
R84
18
R87
IC72
R81
R90
Q70
C391
GND
54
C316
R369
C327
D
G
L327
R326
R333
R315
S
Q72
Q301
R376
C308
R307
+
+
R318
+
R86
R88
+
C312
C318
C320
C338
R89
C262
C311
R310
R370
R306
C317
C324
R309
C323
R311
C314
R316
R322
R317
R312
CV
R82
C74
L320
C389
R371
L302
C331
5C
CP
CPGND
GND
56
R26
Q302Q303
D103
D104
D105
D106
BPF
L110
C127
C129
R133
C131
C137
C139
C128
C132
C133
C135
C136
C140
C141
8R
L111
L112
L113
R126
R177
GND
R121
R122
R123
R124
R134
C130
C134
C138
C142
R295
R298
R115
IC172
+
C237
L182
C193
R181
16
R212
D174
R182
L188
C198
C197
R183
R217
C211
C229
R204
S
D
G
C235
XF171
C196
R184
C194
R180
Q171
C192
C212
C231
R205
Q176
L181
C233
C195
X171
C220
R203
R109
C236
R198
Q175
C228
R197
Q177
C223
R199
TH171
C222
Q179
R200
C226
1
89
CD171
XF171
C214
C221
C225
CF172
WIDE
CF171
NARROW
LO
GND
5R
C224
R206
R202
C241
C234
D173
R207
C227
R221
Component side
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
8C
Foil side
Page 58

R
R608
6
8
R507
C
Q414
1
5
2
3
/
TK-8180 PC BOARD
1
2
JIHGFEDCBA
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
Foil side view (J72-0931-19 B/3)
10
11
12
D7
D6
C156
L187
C205
R186
L185
C202
C200
C189
D2
L101
C144
C145
L183
C52
L10
C47
L179
L9
C146
R129
C217
R193
C218
C219
ANT
L12
L8
R38
CN100
C149
L114
R130 R131
C147
C148
D107
C216
L189
R209
R210
R208
C230
C232
+
C259
L178
C188
C187
C43
C238
CN202
R178
C30
C150
C151
D108
C215
R190
R196
Q178
R22
L115
R23
C152
L177
C186
C185
C153
C154
D109
Q174
D171
C183
CN1
CN101
C155
R132
L116
R192
L176
D3
D110
Q173
R191
C239
C182
C119
C213
C240
R195
D172
C181
L175
C35
C39
L117
R194
R176
R116
L174
IC171
16
C184
CN2
CN3
L7
C38
C34
R25
CN102
Q103
E
B
C
R120
C121
C143
C178
R179
R175
43
R174
L109
C124
L173
R119
C383
L119
L171
R171
R173
R172
L108
R366
L172
C176
C177
C382
C380
C173
C175
C80
C125
C171
CN329
D316
D315
D309
C384
TC301
C350
L312
C385
C346
R252
C252
R367
C1
R365
C381
C334
L310
C251
C387
L328
C360
D313
R251
C253
R347
S
C357
L314
R2
R1
C388
C379
R343
Q306
G
CV
R3
C377
R361
Q308
C362
D
C342
R335
C2
R359
L319
Q313
R336
Q251
+
R5
C376
C355
C255
Q1
R4
R360
C353
R344
C369
R6
C375
R342
L317
C371
+
R254
C4
C378
R345
L315
C374
R356
C370
Q312
R253
C256
C3
R7
CN326
R357
C365
R255
+
C257
CN13
C9
L1
R8
C5C7C8
R9
R352
R358
C372
D314
Q307
C361
R341
Q309
R351
R353
R334
D251
R256R257
6
1
R11
C373
L318
C594
L309
IC251
C14
R355
Q311
R375
C354
G
C359
34
4
C368
C343
D
S
L316
Q2
R10
R350
1
23
R349
R337R339
TC302
L251
C10
+
C356
C358
D308
Q310
D311
L3
R12
R346
C364
C352
C351
L311
R258
C13
R348
R340
C363
L326
L325
R33
R13
C325
+
L2
C258
C16
C15
C367
C347
C79
R28
Q409
CN322 CN323
R579
C479
R647
C519
R557
R664
C477
R553
C480
R663
R558
R521
Q415
C525
6
R609
6
1
C584
C400
34
1
R587
C591
R585
R576
R583
R571
C517
R568
R567
C499
C492
34
C537
C518
R584
R570
C507
Q406
C526
R523
R530
C535
C520
D
S
G
R588
1
IC412
45
C469
R611
R610
C531
C514
C503
C482
C4
R55
Q412
C524
C4
R661
+
C459
R601
2
R555
8
R
R598
D8
C56
C62
C58
C57
R29
D111
C61
C49
R27
C55
C59
L13
R24
C48
C51
R108
3
4
5
6
7
8
C209
C210
L186
C207
C208
R188
R189
9
Q172
R185
L184
C201
L180
C206
CN203
R187
C204
C199
C190
13
14
56
J72-0931-19 B
Page 59

JKLMNOPQRS
C492
C517
R567
R576
C584
+
C459
25
C535
R587
C520
R602
C518
C529
C591
R601
R584
25
R585
26
C514
R583
R571
R568
32
C503
C499
C482
C484
R570
7
C507
4
Q406
R556
34
C526
D
0
S
G
Q412
8
C524
R588
C460
1
8
1
IC412
R523
45
C469
R530
R611
R659
R610
C537
R661
C531
R598
5
931-19 B/3
R507
R608
1
R555
Q414
C33
C448
R509
45
R519
C533
IC415
C488
C495
R550
D407
D
G
IC409
R515
C532
C528
R563
C485
R539
S
C496
C40
1
8
C457
R607
R560
R529
R535
C536
R528
R599
R559
C465
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
Foil side view (J72-0931-19 B/3)
C455
C433
R490
C407
C429
1617
+
C812
C816
C808
C453
C434
R520
IC403
16
L408
IC405
R514
R492
R517
89
1
R513
R512
R504
R500
C452
C438
1
8
IC406
45
R501
CP416
CP414
1
CP412
R469
CP411
CP409
R481
32
R467
R808
C451
R494
R472
R471
R470
R482
Q807
IC408
17
16
10
9
R554
R548
C475
C493
C489
R541
CN815
R582
R578
O
G
IC804
I
R532
R534
C462
R522
X403
C491
R566
R524
Q405
C463
R527
R540
1
89
IC413
16
C476
R533
5
1
R526
C468
C461
R565
R536
C470
R531
C497
34
+
IC411
Q805
R813
Q809
Q802
R805
C809
R818
D804
R815
R814
1458
R497
R493
R502
C442
C443
R461
R459
CP417
CP415
CP413
C423
CP410
CP408
CP407
R468
G
Q810
C822
C
R451R452
E
C554
C550
R447
R449
R448
R450
IC404
R416
CP402
C810
C541
R443
R444
R476
D
C820
I
C821
R466
C478
C817
S
R803
Q801
C805
B
C804
C806
D805
R505 R506
C440
R495
R453R454
R455
R456
R457
R458
65
102
103 128
R478
CP403
CP404
CP406
CP405
G
R614
C582
R442
L407
O
R441
C487
+
L406
C581
IC805
R440
L405
C481
PC BOARD TK-8180
Ref. No.
Address
Ref. No.
R439
C583
+
R437
3964
38
1
L404
C815
CN427
R434R435
R423
L403
C490
C807
C811
AFO
GND
DEO
MI2
GND
RXD1
AUXO2
TXD1
AUXO1
AUXIO9
AUXIO5
AUXIO8
AUXIO4
TXD2
AUXIO3
RXD2
AUXIO2
AUXIO1
AUXIO7
AUXIO6
R477
R430
R429
R428
R511
R525
R427
R426
R405
R422
R657
R421
R419
R418
R425
R424
R658
R414
R415
R412
PSENS
C502
NC
SB
SB
SB
SB
SB
SB
DI
5C
ME
R410
R431
C412
1
30
D417
C447
C464
R411
R406
R420
R432
C408 C409
L402
C504
O
C825
C568
D423
C411
L401
C515
C516
I
C556
R407
Q402
C567
C559
C558
C557
C553
C552
C549
C555
C551
C548
C547
C545
IC803
D403
X404
C406
X401
D404
R401R402
RXDTXDRST2PSW
C404
C403
D402
C410
8
1
L409
G
10
IC402
56
1
CP401
IC401
45
IC171 11D
IC251 12H
IC401 10P
IC402 10Q
IC403 9M
IC404 11N
IC405 11M
IC406 8M
IC408 7M
IC409 8J
IC411 8L
IC412 11J
IC413 12K
IC415 9K
IC803 4P
IC804 2L
IC805 6O
Q1 7G
Q2 7H
Q103 7E
Q172 9B
Q173 9D
Q174 9D
Q178 10C
Q251 12G
Q306 9G
Q307 10H
Q308 9G
Q309 10H
Q310 9I
Q311 9H
Q312 11H
Q313 9G
Q402 11P
Q405 11K
Q406 11J
Q409 9J
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Q412 11J
Q414 12J
Q415 12J
Q801 6N
Q802 3N
Q805 2M
Q807 3M
Q809 2N
Q810 4N
D2 6B
D3 6D
D6 6B
D7 5B
D8 4B
D107 7C
D108 7C
D109 7D
D110 7D
D111 7B
D171 9D
D172 10D
D251 12H
D308 11H
D309 11F
D311 11I
D313 11F
D314 9H
D315 9F
D316 8F
D402 9P
D403 10P
D404 9P
D407 12J
D417 9P
D423 9P
D804 3N
D805 6N
Component side
Foil side
1
2
Address
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
57
14
Page 60

JKLMNOPQRSIHGFEDCBA
TK-8180 PC BOARD
1
2
D6
C156
C52
D2
L101
C144
C145
L10
L9
C47
C146
R129
ANT
L12
L8
C43
R38
CN100
C149
L114
R130 R131
C147
C148
D107
C30
C150
C151
D108
R22
L115
R23
C152
C153
C154
D109
C56
C62
C58
C57
D8
R29
C61
C49
R27
D111
C55
C59
L13
R24
D7
C48
C51
R108
3
4
5
6
7
8
C209
10
11
C210
L186
C207
C208
R189
9
C206
Q172
R185
L184
C201
CN203
L180
R188
R187
C204
C199
C190
L187
C205
R186
L185
C202
C200
L183
C189
C218
C219
L179
C217
R193
+
C216
L189
R210
C259
C187
R209
R208
C230
C232
L178
C188
R178
C215
C238
CN202
R190
R196
Q178
L177
C186
Q174
D171
C183
C185
12
13
CN101
C155
R132
L116
L176
CN1
D110
Q173
R192
R191
C239
C182
D3
C119
C213
C240
R195
D172
C181
L175
C35
C39
L117
R194
R176
R116
L174
IC171
16
C184
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
Foil side view (J72-0931-19 B/3)
CN2
CN3
L7
C33
C514
C503
C482
C484
R556
Q412
C524
C460
+
C459
R602
C529
R601
25
26
32
1
R555
8
R659
R598
R507
R608
C488
C495
Q414
C448
R509
45
R519
C533
IC415
R550
D407
D
G
IC409
R515
C532
C528
R563
C485
R539
S
C496
C40
1
8
C457
R607
R560
R529
R535
C536
R528
R599
C465
R25
CN102
Q103
E
B
C
R120
C121
C143
C178
R179
R175
43
R174
L109
C124
L173
R119
L119
L171
R172
L108
C383
R366
L172
R171
R173
C176
C177
C382
C380
C173
C175
C80
C125
C171
CN329
D316
D315
D309
C384
TC301
C350
L312
R252
C252
R367
C385
R365
C346
L310
C251
C1
C381
C334
C360
D313
C387
L328
R347
R251
C253
R2
C388
C379
R343
Q306
S
C357
L314
CV
R1
C377
R361
Q308
G
R335
R3
R359
C362
D
C342
R336
Q251
C2
C7
L319
Q313
+
R5
C376
C355
C255
Q1
R6
R4
R360
R342
L317
C353
R344
+
C369
R254
C4
C378
C375
R345
L315
C371
C370
R253
C256
C3
R7
CN326
R357
C365
C374
R356
Q312
+
R255
C257
L1
C5
R358
C372
CN13
C9
R8
R9
R352
D314
Q307
Q309
R353
R334
R256R257
C373
L318
C594
C361
R341
R351
D251
6
1
R11
C8
R355
R375
G
L309
IC251
C14
Q311
C343
C354
D
S
C359
L316
34
4
Q2
R10
C368
R350
1
23
R349
R337R339
TC302
D308
L251
C10
+
C356
C358
R12
Q310
R346
C364
D311
C79
R33
C16
R13
L2
C325
+
C258
C15
C367
C347
R28
Q409
CN323
CN322
R579
C479
R647
C519
R557
R664
C477
R553
C480
R663
R558
R521
Q415
C525
6
R609
R576
C517
R567
C492
6
1
C584
C400
34
1
R587
C518
C591
R584
R585
R583
R571
R568
C499
Q406
34
R523
R530
C537
C520
R570
C507
C526
G
R611
R610
C531
C535
D
S
R588
1
IC412
45
C469
R661
L3
C13
R348
R340
C363
L326
L325
C352
C351
L311
R258 C411
C38
C34
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
Foil side view (J72-0931-19 B/3)
C455
C433
R490
C407
C429
1617
+
C812
C816
C808
C453
C434
R520
IC403
16
L408
IC405
R514
R492
R517
89
1
R513
R512
R504
R500
C452
C438
1
8
IC406
45
R501
CP416
CP414
1
CP412
R469
CP411
CP409
R481
R467
32
R808
R494
R472
R471
R470
17
16
10
9
R554
R559
R548
C475
C493
C489
R541
R582
R578
CN815
89
G
R522
C491
R524
Q405
C463
R527
R540
IC413
C476
R532
R534
C462
X403
R566
1
16
R533
5
1
R526
R565
R536
C470
IC804
C468
R531
C461
C497
34
O
I
+
IC411
Q805
R813
Q809
Q802
R805
C809
R818
R506
R505
C440
R457
CP405
C806
R456
G
S
Q801
B
R453
R454
R455
CP404
D804
Q810
C822
C
C804
R451R452
CP403
E
C554
C550
R447
R449
R448
R450
IC404
R416
CP402
C810
C541
R443
R444
Q807
R815
C817
R814
R803
C805
D805
IC408
1458
C451
R495
R497
R493
R502
C442
C443
R461
R458
R459
65
CP417
CP415
CP413
C423
CP410
CP408
R482
CP407
102
103 128
R478
R468
CP406
R476
C582
D
C820
I
O
G
+
C821
R614
R440
R441
R442
R466
L406
L407
C487
C478
PC BOARD TK-8180
Ref. No.
Address
IC171 11D
C581
IC805
R439
L405
C481
C583
+
R437
3964
L404
C815
CN427
R434
R435
38
1
C490
C807
C811
AUXO2
AUXO1
AUXIO9
AUXIO5
AUXIO8
AUXIO4
AUXIO3
AUXIO2
AUXIO1
AUXIO7
AUXIO6
R477
R423
L403
PSENS
C502
RXD1
TXD1
TXD2
RXD2
AFO
GND
DEO
GND
R430
R429
R428
R511
R525
R427
R426
R405
R422
R657
R421
R419
R418
R415
R412
NC
SB
SB
SB
SB
SB
SB
DI
5C
MI2
ME
R410
R431
R425
R424
R658
R414
C412
1
30
D417
C447
C464
R411
R406
R420
R432
C409
C408
L402
C504
O
C825
C568
D423
L401
C515
C516
I
C556
R407
Q402
C567
C559
C558
C557
C553
C552
C549
C555
C551
C548
C547
C545
IC803
X401
D404
D403
X404
C406
R401
R402
C403
D402
C410
8
1
C404
L409
10
1
G
IC402
IC401
56
IC251 12H
IC401 10P
IC402 10Q
IC403 9M
IC404 11N
IC405 11M
IC406 8M
IC408 7M
IC409 8J
IC411 8L
IC412 11J
IC413 12K
IC415 9K
IC803 4P
IC804 2L
IC805 6O
Q103 7E
Q172 9B
Q173 9D
Q174 9D
Q178 10C
Q251 12G
Q306 9G
Q307 10H
Q308 9G
Q309 10H
Q310 9I
Q311 9H
Q312 11H
Q313 9G
Q402 11P
CP401
Q405 11K
Q406 11J
Q409 9J
45
Q1 7G
Q2 7H
Component side
Layer 1
Layer 2
Ref. No.
Address
Q412 11J
Q414 12J
Q415 12J
Q801 6N
Q802 3N
Q805 2M
Q807 3M
Q809 2N
Q810 4N
D2 6B
D3 6D
D6 6B
D7 5B
D8 4B
D107 7C
D108 7C
D109 7D
D110 7D
D111 7B
D171 9D
D172 10D
D251 12H
D308 11H
D309 11F
D311 11I
D313 11F
D314 9H
D315 9F
D316 8F
D402 9P
D403 10P
D404 9P
D407 12J
D417 9P
D423 9P
D804 3N
D805 6N
Layer 3
RXDTXDRST2PSW
J72-0931-19 B/3
Layer 4
Foil side
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
14
Page 61

A B C D E
TK-8180 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
1
2
3
4
5
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10)
FKEY[1]
FKEY[2]
FKEY[3]
FKEY[4]
4.97V
D902
1u
L901
4.61V
5.02V
J901
8
DM
7
HK
MIC
6
5
ME
7
PTT
3
E
SB
2
1
BLC
13.3V
T:0.01V
R:5.02V
C910
100p
0.01u
C906
C904 100p
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
D901
FKEY[5]
FKEY[6]
FKEY[7]
FKEY[8] FKEY[10]
POWER
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR/5V
7.84V
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
02DZ18(X,Y)
100p
C909
02DZ18(X,Y)
C936 0.1u
1000p
C912
C911
C914
100p
100p
1000p
C915
C913
1000p
1u
L902
5.03V
SP2
FKEY[9]
C916
7.84V
R905
Q901
DTC144EE
3
0.1u
4.7k
R901
R903
R904
1k
470
1k
FKEY[10]
FKEY[9]
FKEY[8]
FKEY[7]
FKEY[6]
FKEY[5]
FKEY[4]
FKEY[3]
FKEY[2]
FKEY[1]
IC901
TA78L05F
IN
COM
2
7.10V
8C SW
CONTROL
DTC114EE
OUT
8C SW
10k
R962
Q911
Q901,902
HOOK SW
CP909
100*2
CP908
100*2
CP907
100*2
CP906
100*2
CP905
100*2
CP904
100*2
CP903
100*2
CP902
100*2
CP901
100*2
1
C917
Q910
12A02CH
R963
33k
R907
0.01V
Q902
DTC144EE
5.05V
10k
CP910
100*2
S20
S19
S18
76
S17
77
S16
78
S15
79
S14
80
S13
81
S12
82
S11
83
S10
84
S9
85
S8
86
S7
87
S6
88
S5
89
S4
90
S3
91
S2
92
S1
93
NC
94
AVSS
95
NC
96
VREF
97
C918
0.1u
10u10
AVCC
98
NC
99
NC
100
7.84V
R911
47k
R909
D904
DA204U
47k
NC
NCNCNCNCSHIFT
123456789
47k
R910
D905
D906
DA204U
DA204U
D904-906
SURGE PROTECTION
S21
5.04V
S22
CP911
L903
100*2
NC
NC
NCNCNC
NCNCNC
NC
BYTE
CNVSSNCNC
RST
101112131415161718192021222324
470
1000p
C938
R925
C922
0.01u
C920
100p
L904
VSS
MICROPROCESSOR
IC902
30302M8-8Z7GP
Xout
VSS
Xin
VCC
1k
R919
C924
10p
0
C925
R920
X901
L77-1956-05
47k
R926
10p
NMI
1k
R927
VCC
BLC2
51525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475
HK/RXD
PTT/TXD
LCDDT
LCDCS
25
1k
R9321kR9331kR9341kR935
D903
MINISMDC020
CURRENT
LIMITER
NCNCNCNCNCNCNC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
TP1
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
DM
NC
TXD2
RXD2
NC
LCDRST
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
R944
34
0
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
470k
R913
L909
L908
470k
R916
470k
R914
R915
R941
1k
R940
100
10k
470k
R936
LCDRST
LCDCS
LCDCK
LCDDT
SW_8C
5C
RX
TX
RST
NC
NC
BLC1
DIMM
LEDG
LEDRNCLCDCK
1k
R928 1k
R929
R9301kR931 1k
6
7
58
X54-348 1/2
T:4.80V
R:0.01V
R917
TX
INDICATION
LED SW
Q904
DTC114EE
TX BUSY
C921
1000p
D907
B30-2151-05
TX/BUSY
INDICATION
ME
PSW
SB
BACKLIGHT CONTROL SW
7.79V
Q909
12A02CH
0.66V
0V
Q906
DTC114EE
DIMMER SW
CONTROL
1000p
R939
DIMMER SW
4.7k
Q907
2SC2873(Y)
R943
270
470
R918
BUSY
INDICATION
LED SW
Q905
DTC114EE
R:0.01V
BUSY:4.83V
C927
C926
1000p
R942
7.84V
10k
R970
7.10V
47
4.62V
100
C928
1000p
BACKLIGHT
CONTROL
10k
R945
Q913
DTC114EE
D909
D910
D911
R947
100
D912
D913
B30-2281-05
D914
100
R948
D909-920
LCD BACKLIGHT
LCD
D915
D916
B30-2281-05
D917
R949
B30-2281-05
100
D918
D919
D920
R950
B30-2281-05
100
D921
D922
D923
R951
D924
D925
B30-2282-05
D926
390
R952
D921-930
KEY BACKLIGHT
Key
B30-2282-05
390
D927
D928
R953
D929
B30-2282-05
D930
820
R954
8C
B30-2282-05
820
Page 62

JIHGF
DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10)
COM[6]
COM[7]COM[8]
92
COM6_2
COM7_2
LCD
B38-0888-05
COM8_1
COM9_1
123456789
COM[9]
R967
270
TH901
R971
-t
1k
S1R103J440H
L907
100k
C937
C932
0.01u
0.01u
LCDRST
LCDCS
LCDCK
LCDDT
SW_8C
5C
RX
TX
RST
ME
PSW
SB
8C
470p
C935
R958
4.7k
R959 10k
R957
4.7k
C934
R956
4.7k
0.01u
COM[5]
COM5_2
COM1_1
COM[1]
COM[4]
COM4_2
COM2_1
COM[2]
C933
COM[3]
COM3_2
COM3_1
COM[3]
R969
C930
0.01u
C931
4.7u10
5.05V
7.43V
R955
0.01u
4.7k
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM TK-8180
S[1]
S[2]
S[3]
S[4]
S[5]
S[6]
S[7]
S[8]
S[9]
S[10]
S[11]
S[12]
S[13]
S[14]
S[15]
S[26]
S[27]
S[28]
S[29]
S[30]
S[36]
S[37]
S[38]
S[39]
S[40]
S[46]
S[47]
S[48]
S[49]
S[50]
SEG52
S[52]
S[58]
S58
S18
S[18]
SEG48
SEG53
S[53]
S[57]
S57
S19
S[19]
SEG49
SEG54
S[54]
S[56]
S56
S20
S[20]
SEG50
SEG55
S[55]
S[55]
S55
S21
S[21]
S[56]
SEG56
SEG61
S[61]
S[54]
S54
S22
S[22]
COM[2]
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
COM2_2
COM4_1
COM5_1
COM6_1
COM7_1
COM8_2
COM9_2
SEG16
SEG17
10111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546
S[16]
COM[7]
COM[8]
COM[9]
COM[9]
COM[8]
COM[7]
COM[6]
COM[5]
COM[4]
COM[3]
COM[2]
COM[1]
S[17]
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
COM[4]
0
COM[5]
L906
COM[6]
L905
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG18
SEG19
SEG20
SEG21
SEG22
S[18]
S[19]
S[20]
S[22]
S[21]
S[75]
S[74]
S[73]
S73
S74
S75
S76
S77
S78
CoM10/S79
CoM9/S80
CoM8
CoM7
CoM6
CoM5
CoM4
CoM3
CoM2
CoM1
VDD
VLCD
VLCD0
VLCD1
VLCD2
VLCD3
VSS
oSC
RES
CE
CL
DI
S1S2S3S4S5S6S7S8S9
123456789
S[2]
S[3]
S[1]
SEG13
SEG23
S[23]
S[72]
S72
S[4]
SEG14
SEG24
S[24]
S[71]
S71
S[5]
SEG15
SEG25
S[25]
S[70]
S70
S[6]
SEG26
SEG31
S[31]
S[69]
S69
S[7]
SEG27
SEG32
S[32]
S[68]
S68
S[8]
SEG37
SEG36
SEG30
SEG29
SEG28
SEG33
SEG34
SEG35
SEG41
SEG42
S[33]
S[35]
S[34]
S[41]
S[42]
S[67]
S[66]
S[65]
S[64]
S[63]
S63
S64
S65
S66
S67
LCD DRIVER
IC903
LC75810T-8726
S10
S11
S12
S13
101112131415161718192021222324
S[9]
S[10]
S[12]
S[11]
S[13]
SEG38
SGE43
S[43]
S[62]
S62
S14
S[14]
SEG39
SEG44
S[44]
S[61]
S61
S15
S[15]
SEG40
SEG45
S[45]
S[60]
S60
S16
S[16]
SEG46
SEG51
S[51]
S[59]
S59
S17
S[17]
SEG47
S[57]
SEG57
SEG62
S[62]
S[53]
S53
S23
S[23]
S[58]
SEG58
SEG63
S[63]
S[52]
51525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475
S52
S24
25
S[24]
S[59]
SEG59
SEG64
S[64]
S[51]
S51
S50
S49
S48
S47
S46
S45
S44
S43
S42
S41
S40
S39
S38
S37
S36
S35
S34
S33
S32
S31
S30
S29
S28
S27
S26
S25
S[25]
S[60]
SEG60
SEG65
S[65]
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
S[66]
SEG66
SEG71
S[71]
S[67]
SEG67
SEG72
S[72]
1000p
C908
S[50]
S[49]
S[48]
S[47]
S[46]
S[45]
S[44]
S[43]
S[42]
S[41]
S[40]
S[39]
S[38]
S[37]
S[36]
S[35]
S[34]
S[33]
S[32]
S[31]
S[30]
S[29]
S[28]
S[27]
S[26]
S[68]
SEG68
SEG73
S[73]
1000p
C907
S[69]
SEG69
SGE74
S[74]
474849505152535455565758596061626364656667686970717273747576777879808182838485868788899091
S[70]
SEG70
SEG75
S[75]
GND
GND
RXD
TXD
5C
NC
SHIFT/MODEL
NC
GND
GND
GND
RST2
PSENS
GND
ME
MIC
GND
GND
PSW
NC
SB
SB
8C
GND
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
1
2
3
4
CN902
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
TO TX-RX UNIT (B/3) CN429
5
6
Note : The components marked with a dot (•) are parts of layer 1.
1
SP CONNECTOR
2
X54-348 2/2
CN901
7
59
Page 63

DISPLAY UNIT (X54-3480-10)
FKEY[1]
FKEY[2]
FKEY[3]
FKEY[4]
4.97V
D902
1u
L901
4.61V
5.02V
J901
8
DM
7
HK
MIC
6
5
ME
7
PTT
3
E
SB
2
1
BLC
13.3V
T:0.01V
R:5.02V
C910
100p
0.01u
D901
C906
C904 100p
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
FKEY[5]
FKEY[6]
FKEY[7]
FKEY[9]
FKEY[8] FKEY[10]
POWER
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR/5V
7.84V
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
02DZ18(X,Y)
100p
C909
02DZ18(X,Y)
C936 0.1u
1000p
C912
C911
100p
C914
100p
C915
1000p
C913
1000p
1u
L902
5.03V
SP2
T:4.80V
R:0.01V
FKEY[10]
FKEY[9]
FKEY[8]
FKEY[7]
FKEY[6]
FKEY[5]
FKEY[4]
FKEY[3]
FKEY[2]
FKEY[1]
IC901
TA78L05F
3
IN
OUT
COM
2
0.1u
C916
8C SW
R962
12A02CH
10k
7.84V
7.10V
8C SW
CONTROL
Q911
DTC114EE
R907
4.7k
R905
Q901
DTC144EE
Q901,902
HOOK SW
R901
1k
R903
470
R904
1k
R917
TX
INDICATION
LED SW
Q904
DTC114EE
TX BUSY
C921
1000p
D907
B30-2151-05
TX/BUSY
INDICATION
CP909
100*2
CP908
100*2
CP907
100*2
CP906
100*2
CP905
100*2
CP904
100*2
CP903
100*2
CP902
100*2
CP901
100*2
5.05V
1
C917
Q910
10k
R963
33k
0.01V
Q902
DTC144EE
470
R918
C918
0.1u
7.84V
R911
270
BUSY
INDICATION
LED SW
Q905
DTC114EE
R:0.01V
BUSY:4.83V
10u10
47k
R909
D904
DA204U
47k
CP910
100*2
S19
S18
76
S17
77
S16
78
S15
79
S14
80
S13
81
S12
82
S11
83
S10
84
S9
85
S8
86
S7
87
S6
88
S5
89
S4
90
S3
91
S2
92
S1
93
NC
94
AVSS
95
NC
96
VREF
97
AVCC
98
NC
99
NC
100
NC
NCNCNCNCSHIFT
123456789
47k
R910
D905
DA204U
D904-906
SURGE PROTECTION
0.66V
0V
Q906
DTC114EE
DIMMER SW
CONTROL
C927
C926
1000p
1000p
S20
D906
DA204U
R939
S22
S21
5.04V
DIMMER SW
4.7k
Q907
2SC2873(Y)
CP911
L903
100*2
NC
BYTE
CNVSSNCNC
RST
101112131415161718192021222324
470
1000p
C938
R925
C922
0.01u
C920
100p
L904
VSS
MICROPROCESSOR
IC902
30302M8-8Z7GP
Xout
VSS
Xin
VCC
1k
R919
C924
10p
0
C925
R920
X901
L77-1956-05
47k
R926
10p
NMI
1k
R927
NC
NC
NCNCNC
NCNCNC
BACKLIGHT CONTROL SW
Q909
12A02CH
7.84V
10k
R970
7.10V
R942
R943
47
4.62V
100
C928
1000p
BACKLIGHT
CONTROL
10k
R945
Q913
DTC114EE
D909
D910
D911
R947
VCC
BLC2
R928 1k
7.79V
NC
NC
BLC1
DIMM
1k
R929
D912
D913
B30-2281-05
D914
100
R948
LCD BACKLIGHT
NC
LEDG
R9301kR931 1k
B30-2281-05
100
D909-920
NC
LEDRNCLCDCK
R9321kR9331kR9341kR935
MINISMDC020
LCD
D915
D916
B30-2281-05
D917
100
R949
LCDDT
D903
CURRENT
LIMITER
D918
D919
D920
R950
51525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475
HK/RXD
PTT/TXD
TXD2
RXD2
LCDCS
25
1k
B30-2281-05
100
NCNCNCNCNC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
TP1
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
DM
NC
NC
LCDRST
D921
D922
D923
R951
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
R944
0
L909
L908
470k
470k
R916
R913
D924
D925
B30-2282-05
D926
390
R952
D921-930
KEY BACKLIGHT
470k
470k
R914
R915
Key
B30-2282-05
390
D927
D928
R953
R941
1k
R940
100
10k
R936
D929
B30-2282-05
D930
820
R954
LCDRST
LCDCS
LCDCK
LCDDT
SW_8C
PSW
B30-2282-05
820
S[1]
S[2]
S[3]
S[4]
S[5]
S[6]
S[7]
S[8]
S[9]
S[10]
S[11]
S[12]
S[13]
S[14]
S[15]
S[26]
S[27]
S[28]
S[29]
S[30]
S[36]
S[37]
S[38]
S[39]
S[40]
S[46]
S[47]
S[48]
S[49]
S[50]
S[56]
S[57]
S[58]
S[59]
S[60]
S[66]
S[67]
S[68]
S[69]
SEG71
S[71]
SEG67
SEG72
S[72]
SEG68
SEG73
S[73]
SEG69
SGE74
S[74]
S[70]
474849505152535455565758596061626364656667686970717273747576777879808182838485868788899091
SEG70
SEG75
S[75]
LCD
B38-0888-05
COM[2]
COM[3]
COM[4]
COM[5]
COM[6]
COM[7]COM[8]
92
SEG1
COM2_2
COM3_2
COM4_2
COM5_2
COM6_2
COM7_2
COM8_1
COM9_1
COM1_1
COM2_1
COM3_1
COM4_1
COM[2]
COM[3]
COM[4]
COM5_1
COM[5]
123456789
COM[9]
COM[1]
SEG2
COM6_1
COM7_1
COM8_2
COM9_2
10111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546
COM[6]
COM[7]
COM[8]
COM[9]
SEG16
S[16]
SEG17
S[17]
SEG18
S[18]
SEG19
S[19]
SEG10
SEG20
S[20]
S[75]
SEG11
SEG21
S[21]
S[74]
SEG12
SEG22
S[22]
S[73]
SEG13
SEG23
S[23]
S[72]
SEG14
SEG24
S[24]
S[71]
SEG15
SEG25
S[25]
S[70]
SEG26
SEG31
S[31]
S[69]
SEG27
SEG32
S[32]
S[68]
SEG28
SEG33
S[33]
S[67]
SEG29
SEG34
S[34]
S[66]
SEG30
SEG35
S[35]
S[65]
SEG36
SEG41
S[41]
S[64]
SEG37
SEG42
S[42]
S[63]
SEG38
SGE43
S[43]
S[62]
SEG39
SEG44
S[44]
S[61]
SEG40
SEG45
S[45]
S[60]
SEG46
SEG51
S[51]
S[59]
SEG47
SEG52
S[52]
S[58]
SEG48
SEG53
S[53]
S[57]
SEG49
SEG54
S[54]
S[56]
SEG50
SEG55
S[55]
S[55]
SEG56
SEG61
S[61]
S[54]
SEG57
SEG62
S[62]
S[53]
SEG58
SEG63
S[63]
S[52]
SEG59
SEG64
S[64]
S[51]
SEG60
SEG65
S[65]
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG66
51525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475
S51
S52
S53
S54
S55
S56
S57
S58
S59
S60
S61
S62
S63
S64
S65
S66
S67
S68
S69
S70
S71
S72
S73
S74
S75
76
S76
77
S77
78
S78
79
CoM10/S79
80
CoM9/S80
L907
C937
0.01u
TH901
S1R103J440H
100k
C932
R958
4.7k
R967
270
R971
-t
0.01u
R957
4.7k
1k
C934
0.01u
R956
4.7k
C933
R969
C930
0.01u
C931
4.7u10
R955
0.01u
0
5.05V
7.43V
4.7k
470p
C935
LCDRST
LCDCS
LCDCK
LCDDT
5C
RX
TX
RST
ME
SW_8C
5C
RX
TX
RST
ME
R959 10k
L906
L905
COM[9]
COM[8]
COM[7]
COM[6]
COM[5]
COM[4]
COM[3]
COM[2]
COM[1]
81
CoM8
82
CoM7
83
CoM6
84
CoM5
85
CoM4
86
CoM3
87
CoM2
88
CoM1
89
VDD
90
VLCD
91
VLCD0
92
VLCD1
93
VLCD2
94
VLCD3
95
VSS
96
oSC
97
RES
98
CE
99
CL
100
DI
S1S2S3S4S5S6S7S8S9
123456789
S[2]
S[3]
S[1]
LCD DRIVER
IC903
LC75810T-8726
S10
S11
S12
S13
S14
S15
S16
S17
S18
S19
S20
S21
S[18]
S[19]
S[20]
S[21]
S22
S[22]
101112131415161718192021222324
S[5]
S[4]
S[8]
S[9]
S[7]
S[6]
S[10]
S[12]
S[11]
S[14]
S[13]
S[15]
S[16]
S[17]
PSW
SB
8C
SB
8C
S23
S[23]
S24
S[24]
50
S[50]
S50
49
S[49]
S49
48
S[48]
S48
47
S[47]
S47
46
S[46]
S46
45
S[45]
S45
44
S[44]
S44
43
S[43]
S43
42
S[42]
S42
41
S[41]
S41
40
S[40]
S40
39
S[39]
S39
38
S[38]
S38
37
S[37]
S37
36
S[36]
S36
35
S[35]
S35
34
S[34]
S34
33
S[33]
S33
32
S[32]
S32
31
S[31]
S31
30
S[30]
S30
29
S[29]
S29
28
S[28]
S28
27
S27
S[27]
26
S26
S[26]
S25
25
S[25]
1000p
C908
1000p
C907
GND
GND
RXD
TXD
5C
NC
SHIFT/MODEL
NC
GND
GND
GND
RST2
PSENS
GND
ME
MIC
GND
GND
PSW
NC
SB
SB
8C
GND
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
CN902
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
1
2
TO TX-RX UNIT (B/3) CN429
CN901
SP CONNECTOR
Page 64

A B C D E
TK-8180 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
1
2
3
4
TO DISPLAY UNIT CN902
5
SHIFT/MODEL
6
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)(B/3)
C801
L411
L410
470p
C826
1000u25
T:7.91V
R:7.46V
220k
R801
330k
R802
R800
1
1M
2
S-80942CNNBG9C
1
4.99V
C478 100p
C487 1000p
C481 1000p
C490
C498
C500
C502
C504 1000p
R900
R901
R902
R400
C515 1000p
C516 1000p
R903
VSS
2
VDD
VOLTAGE
DETECTOR
(CPU RESET)
1000p
100p
100p
1000p
0
0
0
1M
0
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
GND
PSW
GND
GND
GND
PSENS
RST2
(LCDRST)
(LCDDI)
(LCDDO)
(CLK)
GND
(DM)
CN802
CN803
CN804
GND
CN429
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SB
SB
NC
MIC
ME
NC
TXD
RXD
+B
GND
IGN
8C
5C
D801
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
D802
D801
22ZR-10D
D802
DC REVERSE
CONNECTION
PROTECT
VOLTAGE
DETECTOR(INT)
2
VIN
NC
3
R804
100k
IC801
oUT
CD
R572
0
R574
0
R575
0
R591
0
C802
DSA3A1
1
VOUT
IC802
VSS
XC61CN5002NR
4
C823
1000p
4
3
C818
4700p
Q812
DTC114EE
CPU RESET SW
SPO
PSW
PSENS
RST2
LCDRST
LCDDI
LCDDO
TXD
RXD
C824
R809
C813
DM
1000p
C803
C814 470p
0.01u
47k
0.047u
C819 0.1u
470p
470p
C804
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
IGNITION SENS
CONTROL SW
DTC114TE
1
C807
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR/8V
8C
SB
CK
5C
OPT3
OPT1
RXD1INT
C806
Q811
IC803
TA7808F
IN2OUT
GND
0.047u
IC803
TXD1
IGN
4.99V8.21V
0.1u
T:0.005V
R:4.93V
R:4.98V
OPT2
100p
C595
SBC
IGN
C821
T:4.95V
R:0.003V
TXAO
100p
C585
C831
RXEMAO
4.7u16
100p
C586
+B
SB
5M
5M
8C
5E
4.7u16
8T
8R
RXEMAI
100p
C587
5C
5R
TXAI
C588 1000p
5M
5M
5M
8C
C439 1000p
4.99V
AT24256N10SI27
4
3
2
1
BEAT SHIFT SW
DTC114YE
D421,422
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
D421
1SS388
D422
1SS388
C822
470p
100p
C431
C817
T:7.83V
R:7.95V
C812
5E
Q810
2SJ645
47k
470p
R814
NJM78L05UA
3
C810
0.047u
REGULATOR/5V
R811
10k
10k
R812
0.1u
C816
5R CONTROL SW
DATAOU T
SIDETONE
SB SW
T:7.60V
R:8.09V
68k
R815
DTC114EE
SB CONTROL SW
R818
IC805
IN1OUT
COM
2
VOLTAGE
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR/5V
XC6201P502PR
3
C832
4.7u16
10u10
5R SW
Q805
12A02CH
47k
R808
4.28V
DTC114EE
TCTL
C435 1000p
Q807
47k
C820
IC807
VIN1VOUT
VSS
2
8T CONTROL SW
Q806
DTC114EE
8R CONTROL SW
Q808
DTC114EE
5V
R813
4.7k
Q809
AUDIH
100p
100p
C437
C436
F801
470
100p
R805
F53-0278-05
SB CONTROL SW
D804
3
C811
OPT4
02DZ18(X,Y)
R803
C805
7.96V
0.1u
C815
T:7.96V
R:7.97V
OPT5
DTC114EE
C809
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
/8.5V
10k
1000p
02CZ9.1(X,Y)
4.7u16
R806
R807
1
0.1u
C808
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR/5V
1.8M
C430 100p
R487
Q802
470p
Q801
2SC2873(Y)
8.83V
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
D805
8T SW
Q803
12A02CH
10k
T:7.2V
R:7.95V
8R SW
Q804
12A02CH
10k
T:7.94V
R:7.25V
IC804
TA7805F
IN2OUT
GND
3
AO
T:12.7V
R:13.5V
AI
R401
3.6k(D)
R402
5.1k(D)
D
RV5C386A
10
VDD
9
OSCIN
8
OSCOUT
7
CLKC
6
RTC PROCESSOR
EEPROM
IC401
SDA
GND
SCL
NC
A1
VCC
A0
Q402
X404
L77-1950-05
SHIFT
REGISTER
AO1
PA
HOR
AO2
D402
1SS388
D402-404
RTC BATTERY
CONTROL
D403
1SS388
IC402
32KOUT
SCL
SDA
INTRB
VSSINTRA
5
6
7
WP
8
C406
D
1
2
3
4
5
C410
0.1u
D
0.3p
C408
C409
BU4094BCFV
1
STRB
2
DATA
3
CLK
4
Q1
5
Q2
6
Q3
7
Q4
8
VSS
C407 0.01u
IC403
5E
D404
1SS388
X401
5p
L77-1802-05
0.1u
C404
C403
CN401
J19-5386-05
CP401
100
INTRA
INT
RST
4.99V
15p
D
15p
0.1u
C411
16
4.99V
VDD
15
OE
14
Q5
GSW
13
Q6
12
Q7
11
Q8
CFSW
10
Q’S
9
QS
8C
RTCL/EEPCL
RTDT/EEPDAT
XOUT
INTRA
SHIFT/MODEL
SPSTB
SPSTB
RXC
OPT6
SBC
TXC
RST
XIN
5M
INT
DT
SOE
CK
MIC
ME
7
60
X57-699 1/9
100p
C428
100p
C427
100p
C420
100p
C421
1M
R403
1000p
C422
CN403
100p
100p
1000p
0
0
0
C425
C424
C426
R483
R473
R474
OPT31OPT14TXD13RXD16OPT45CLK8OPT57USEL10AGND
2
0
R484
0
R485
0
R4880R486
DGND12AI11AO145E13AGND
9
C432
1000p
R489 0
0
R491
DTI 15STON18NC17TCTL20OPT219AUDIH
16
RXEO21TXO24TXI23RXEI
22
OPT6
25
OPT6
RXAI
RXAO
R445
10k
R446
10k
8C
RXI
RXO
OPT1
OPT3
OPT4
TXD2
TXD2
RXD2
RXD2
OPT1
OPT3
OPT4
OPT5
OPT5
TXD1
RXD1INT
8C
26
GND
TXD1
RXD1
OPT2
TCTL
TXAO
TXAI
AUDIH
RXEMAI
TCTL
RXEMAO
SIDETONE
TXI
TXO
AUDIH
OPT2
RXEI
STON
RXEO
DATAOU T
5E
DTI
Page 65

TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
IGN
JIHGF
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM TK-8180
SBC
TXC
RTCL/EEPCL
RTDT/EEPDAT
RST
XOUT
XIN
5M
INT
INTRA
SHIFT/MODEL
DT
SPSTB
SOE
SPSTB
RXC
CK
MIC
ME
OPT6
4.987V
PC
DMUTE
AM2
PSW
AIO5
AIO9
D423
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
RXD2
TXD2
TXD1
RXD1INT
RXD1EXT
L401
5M
HSDIN
HSDO
DSTB
LSDIN
DT
CK
DSTB
MM2
DT
AM1
OPT3
OPT2
OPT1
115
116
117
OPT1
OPT2
OPT3
IC404
30625MGP-169GP
RDYNCHOLDNCAI04
47k
47k
R466
R476
W/N
0
CP4021kCP403
R416
113
114
CK
W/N
1k
R448
470k
R447
470k
R449
112
R450
DT
AIO3
1k
110
111
D0
AIO2
AIO1NCRDNCWR
1k01k
1k
R452
R454
470k
470k
R453
R451
D2D0D3D1D4D5D6
1k
CP404
CP4051kCP406
107
108
109
470
470
R456
R455
R457 47k
D7
1k
D
470k
47k
103
104
105
106
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
NC
102
EMTON
101
AM1
100
T/R
99
MM2
98
TCLK/DTRDO
97
AFRTM
96
IGN
95
A0
94
A1
93
A2
92
A3
91
A4
90
A5
89
A6
88
A7
87
DGND
86
A8
85
VCC2
84
OPT6
83
NC
82
PCK
81
PLE
80
UL
79
A9
78
A10
77
A11
76
A12
75
A13
74
A14
73
A15
72
A16
71
A17
70
A18
69
NC
68
CS0
67
RST2
66
NC
65
NC
AIO8
AIO7
AIO6
R467
CP407
1k
CP408
1k
CP409
CP410
CP411
D
R465
R470
CP412
1k
CP413
1k
CP414
1k
CP415
1k
CP416
1k
CP417
1k
R471 1k
R472
R481 470k
R468
R478
TCLK/DTRDO
D
A11
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
CSO
RST2
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
AFRTM
PCK
PLE
UL
T/R
0
R482
47k
1k
1k
1k
C423
R469
1u
1k
47k
1k
1k
64
HSDIN
HSDO
470k
470k
R458
R459
R461 470k
R412
R415
R418
R419
R420
R422
R405
R406
R411
R414
R421
R657
L402
R407
5C
4.989V
5M
5M
470k
470k
47k
47k
330k
D423
1SS388
R410
10k
D417
1SS388
D418
1SS388
D417,418
ISOLATOR
10k
47k
4.7k
47k
470k
470k
C412
470k
10k
0.1u
R658
R424
R425
R432 1k
R426
R427
R428
R429
R430
R431
ASQ
THP
H/L
OPT5
L406
121
THP
AFDIR
L407
119
120
H/L
DTRLOAD
OPT4
118
OPT4
OPT5
MICROPROCESSOR
AFSTD
LSW
RSSI
L404
LSDIN
DGND
L405
122
123
124
125
126
127
NC
AGND
MM1
PSENS
NC
NC
ASQ
RSSI
TXD
RXD
AFDAT
AFDIO
L403
128
1
VREF
2
AVCC
3
SBC
4
RXC
5
TXC
6
PC
7
HSDO
8
STSW
9
RTCL/EEPCL
10
HSDIN
11
NC
12
RTDT/EEPDAT
13
BYTE
14
0
CNVSS
15
DMUTE
16
AM2
17
1k
RST
18
1k
XOUT
19
DGND
20
XIN
21
VCC1
22
NMI
23
PSW
24
INT
25
INTRA
26
SHIFT/MODEL
27
BEEP
28
SPSTB
29
SOE
1k
30
AIO5
31
1k
AIO9
32
DSTB
33
LSDO
34
0
RXD2
35
470
TXD2
36
470
TXD1
37
VCC1
0
38
RXD1
39404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263
D
470k
R477
0
R423
47k
R434
R435
0
R437
R439
1k
R440
1k
R441
1k
R442
1k1k1k
R443
R444
R525
RD
WR
AI06
AI07
AI04
AI03
AI02
TXD
RXD
PSENS
BEEP
R511
1.5k
1.5k
C464
C447
0.033u
0.033u
D D
DTRLOAD
AFDAT
AFDIO
AFDIR
AFSTD
AI01
AI08
EMTON
LSDIN
BEEP
LSDO
STSW
SCSW
OPT6
LSW
MM1
RXC
CK
MIC
ME
61
X57-699 2/9
Page 66

K L M N O
TK-8180 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
DSTB
DT
MM2
AM1
FLASH MEMORY
IC405
HSDIN
HSDO
4.99V
AT29C040A-90TI
1
A11
2
A9
3
A8
5M
L408
5C
10CL
4
A13
5
A14
6
A17
7
WR
8
9
A18
10
A16
11
A15
12
A12
C429 1u
13
A7
14
A6
15
A5
16
A4
32
oE
A11
A9
A8
A13
A14
A17
WE
VCC
A18
A16
A15
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
DI
DEO
MP
MOD
MB
TV
RD
31
A10
A10
30
CE
CSO
29
Io7
D7
28
Io6
D6
27
Io5
D5
26
Io4
D4
25
Io3
D3
24
GND
23
Io2
D2
22
Io1
D1
21
Io0
D0
20
A0
A0
19
A1
A1
18
A2
A2
17
A3
A3
D
R522
100k
1
OUTPUT
2
V+
3
INPUT+
RF BPF TUNING
VOLTAGE DC AMP
0.1u
C433
180k
560p
C434
R490
100
R475
270k
R526
0.01u
C462
IC411
LMC7101BIM5
INPUT-
1
680k
R492
2
3
4
C441
10u
D405
EMZ6.8N
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
4
567
R496
100k
2.49V
5
V-
4
HSD BPF/HSD
COMPALATOR
IC406
TC75W51FU
+
+––
VSS
C438
0.01u
VSS
VDD
R533
D406
R528
R509
02DZ5.1(Y)
C450 10u
C451
8
7
6
5
C452
C453
0.1u
47k
1
33k
2
3
4
VSS
LSD LPF/VOLTAGE
DC-REFERENCE
D/A CONVERTER
IC410
M62364FP
13
VIN5
14
VOUT5
15
VOUT6
16
VIN6
17
DO
18
VDAref
19
RESET
20
GND
21
VIN7
22
VOUT7
23
VOUT8
24
VIN8
C454
R534
15k
R512
0.01u
560k
R513
18k
R514
100p
R520
IC409
TC75W51FU
+
–
+
R527
3.9k
C463
100k
R499
R503
R508
100k
1k
C445
15p
123
DET AMP/
–
DATA LPF (DB-25)
+
C444
39p
270k
100k
8
7
6
5
VDD
8
C446
1.53V
R494
R495 4.7k
C440
IC407
TC75W51FU
0.01u
R500
0
0.87V
4.7k
0.1u
1M
R493
R497
3.3k
R504
R505
R506
R502
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
LSD BUFFER AMP/
VCXO BIAS AMP
10k
1
2
68k
3
4
220k
C443
0.01u
10k
C467 0.01u
47u6.3
C455
IC408
TC75W51FU
--+
+
VSS
4.7k
R501
C448
0.1u
R507
C442
VDD
100p
220k
2.50V
+
–
R498
27k
VDD
–
0
VIN4
VOUT4
VOUT3
VIN3
VDD
VIN2
VOUT2
VOUT1
VIN1
0.01u
R565
0
0.01u
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
DT
MM2
AM1
AF
10k
R545
C472
R539
D407
RB706F-40
0.1u
0
R542
2.49V
39k
DC DETECTOR
2.50V
V_REF
MM1
BEEP
AGND
LIMLV
47k
R540
C465
4.98V
AF SW
(LSD)
Q406
R523
C584
R530
330k
R532
560k
22p
1k
R554
C475
8
VDD
123
56k
100p
+
–
R550
R664
R529
680k
22p
2.48V
4.7k
R557
4.7k
R535
390k
567
–
+
VSS
4
C469
0.1u
2.50V
12k
R555
56k
R556
4.7k
C479
1000p
C460
4.98V
MODULATION
LPF/DEF AMP
AQUA
CONTROL
SW
4
0.01u
IC412
TC75W51FU
R521
47k
C400
1u
Q405
DTA114EE
R548
82k
123
HN1J02FU
6
5
12
R549
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
R515
R536
47k
R546
0
R517
22k
2.50V
100k
R519
470p
100k
C459
C457
10u10
C470
15k
0.01u
11
10
DI
CLK
LD
2.50V
8
7
6
5
EMTON
LSDIN
LSW
MM1
BEEP
LSDO
STSW
RXC
CK
SCSW
MIC
ME
OPT6
62
X57-699 3/9
LSDO
EMTON
LSW
C477
R553
4.7k
1000p
R663
4.7k
4.92V
MM1
BEEP
SIDETONE
R541 0
LSDIN
RXDET
DATAOUT
STSW
RXC
CK
SCSW
MIC
ME
OPT6
Page 67

TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
TSRQP
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM TK-8180
DT
MM2
AM1
AF
V_REF
MM1
BEEP
AGND
LIMLV
LSDIN
RXEMAO
RXEMAI
5C
C497
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
C480
1000p
4.98V
C483
1000p
AF SW IC
IC413
TC7MZ4053FK
1Y
0Y
YCoM
1Z
XCoM
ZCoM
0Z
INH
VEE
GND
5C
DT
AO
C541
R614
AM1
AM1
0.1u
0
AF
C530
2.50V
22p
R569
100k
MA742
1u
C505
MA742
1u
C506
D408,409
MIC-AMP
AGC DETECTOR
C485
2.81V
D408
D409
DTC363EU
4.93V
1u
C476
0.1u
R597
R573
C591
0.1u
Q409
R558
390k
MIC AMP
IC414
TC75W51FU
5
6
7
8
VDD
0.01u
16
VCC
15
14
13
1X
12
0X
11
A
10
B
9
C
4
VSS
3
+
–
2
+
–
1
C501
AM2
T/R
R:4.90V
T:0V
0.1u
C496
TXAI
TXAO
10u
1M
C511
6.8k
0.1u
C512
C513
AF MUTE SW
C519
1000p
R559
120k
1000p
1000p
R580
R581
150
150
R606
0
R586
1k
2SC4116(Y)
2SA1586(Y,GR)
R524
10k
R560
C488
4.7u
4.7u
C482
C489
C484
MIC AGC
Q410
Q411
MIC AGC
C461
390k
R563
12p
0.1u
4.7u
C493
R531
10k
0.01u
C495
180p
390k
R579
R589
0
22k
C468
0.01u
A
A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
AFSTD
DTRLOAD
C538
1000p
R603
0
R592
0
R604
0
680
R594
0
R596
R576
220k
C492
0.1u
C491
0.1u
0.1u
C507
C499
150k
R570
820p
120k
120k
R571
R568
C503
68p
RXIN
AGND
RXINO
AGNDIN
TXIN
TXINO
LIMLV
EXTLIMIN
MOD
VDD
DTRLOADN
STD
FILTERO
IC415
AQUA-L
TCLK/DTRDO11TDATA/DTRCLK12DI/O13RDF/FD14SCLK15DIR16XOUT
10
AFDAT
AFDIO
TCLK/DTRDO
R618
220k
D601
1SS388
MIC MUTE
R616
4.7k
Q417
2SJ243
2SJ243
2.49V
180k
7p
Q416
R615
C542
AF SW
R584
0
AF
MUTE
SW
Q412
2SK1824
R588
4.7k
1000p
C520
R617
1000p
4.7k
C524
LSDIN
100k
Q413
2SJ243
CONTROL
4.83V
C543
10u10
4.88V
R620
220k
MIC MUTE
CONTROL
D600
1SS388
0
R590
0.1u
C526
1000p
C529
C528
R600
4.7k
R595
270k
R587
150k
R601
470k
R602
1M
R599
180k
R598
47p
2200p
R619
AF SW
R661
4.7k
100k
C534
C525
0.1u
R607
270k
C533
C532
HN1L02FU
4.7k
4.98V
R646
4.7k
1000p
0.015u
R608
0.012u
180k
AF SW
(VOICE)
Q415
C531
Q414
2SJ243
1000p
2.49V
C536
R659
C544
10u10
MIC MUTE SW
Q600
DTA144EE
AUDIH
RXAO
RXAI
10k
R552
22k
R609
C535
0.068u
100k
R647
0.1u
0.1u
C537
33k
150k
R610
10k
R611
AI
R613
Q416,417
MIC MUTE SW
R:4.98V
T:0V
R567
390k
1M
R583
82p
C514
26272829303132
RXAF
RXAFIN
DTRAIN
AMP4O
AMP4N
AMP4P
AMP3O
AMP3N
AMP3P
VSS
XIN
0
R578
3.6864MHz
L77-1965-05
AFDIR
C592
100k
R612
100k
0
R585
C518
25
24
0.1u
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
R582
1M
X403
7p
C593
R:4.92V
T:0V
C540
10u10
C539
10u10
C517
0.01u
R566
A
EXPOUT
AFRTM
STSW
RXC
CK
SCSW
MIC
ME
OPT6
CK
RXC
OPT6
STSW
MI2
AFO
ME
63
X57-699 4/9
Page 68

U V W X Y
TK-8180 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)(C/3)
R308
3.9k
R378
R373
DT
4.99V
0.01u
C331
L302
1
3
5
CN301
REF
CPGND
GND
Fin
2
5C
4
CP
6
CP
CPGND
5C
Fin
GND
REF
0.01u
10k
10
L305
C397
12p
C396
C386
10u6.3
1
2
3
PLL CP SW
TC7S66FU
IN/OUT
OUT/IN
GND
IC302
L304
100p
C309
VCC
CONT
R301
PLL SYSTEM IC
1617181920
VP
DVDD
DVDD
MUXOUT
RFEin
DGND
DGND
9
10
A
4.99V
4.99V
15
14
LE
13
DATA
12
CLK
11
CE
5
0
R377
4
CP
Rset
1
CPGND
2
AGND
0
3
IC301
AGND
ADF4111BCP7
4
RFinB
5
RFinA
AVDD
AVDD
678
4.99V
C322
R319
10
R320
18
R321
10k
0.047u
R323
R332
R330
R327
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
5C
150k
R325
1k
10
10
10
C335
0.022u
UL
PLE
DT
PCK
GND
DGND
CN302
1
3
5
2
4
6
L306
PCKULPLE
C260
100p
C261
100p
4.75V
L114
C307 470p
56
R305
C314
100
C323
C324
R309
470p
0.1u
C317
100p
33n
L327
0.31V
C316
C389
C391
6p
8p
100
39p
C262
C148
1p
R130
R310
RF BPF
TUNING
D108
1SV291
100k
C149
100p
L115
470p
C311
C147
5p
8.2n
C393
6p
2p
L321
L320
10n
8.2n
12p
12p
C392
C390
C151
1p
RF BPF
TUNING
D109
C150
5p
1SV291
100k
R131
8.2n
C152
470p
L116
C394
C302
C395
0.5p
2p
L323
L322
5.6n
4.7n
5p
4p
C333
C154
1.5p
RF BPF
TUNING
C153
D110
5p
1SV291
100k
R132
8.2n
C155
C398
470p
L117
L324
2.2n
1p(B)
C339
470p
L108
R119
18k
R115
FRONT-END LNA
3.22V
C119
5p
18k
R116
8.2n
2SC3357
FL:2.5V
FC:4.0V
FH:5.8V
L109
Q103
470p
C121
R307
R311
1.8k
0
C312
0.047u35
8R
7.90V
0
470p
C125
18n
C124
R134
10p
0
L110
C127
D103
RF BPF
TUNING
5T
L34-4565-05
22p
R121
1SV286
100k
2.46V
220
R120
0.1u
C128
C129
R312
2.2u20
C130
5p
9p
470p
C318
1k
C320
2.2u20
Q302
2SC4116(BL)
PLL LPF
5T
L111
22p
C132
D104
1SV286
RF BPF
TUNING
R316
C133
L34-4565-05
100k
R122
C131
2SC4116(BL)
PLL LPF
100k
C134
6p
470p
3p
R318
1.8k
R317
0
Q303
RF BPF
TUNING
L112
C135
D105
C327
R322
5T
L34-4565-05
22p
R123
1SV286
10.36V
0.22u
R326
0
C136
100k
C137
11CL
R333
270
C338
C138
5p
4p
L113
C140
D106
RF BPF
TUNING
470p
0
0.33u35
5T
C141
L34-4565-05
22p
R124
1SV286
C142
470p
9p
100k
C139
CV
AM1
470p
5C
4.99V
X301
L77-1952-05
R362
VC
MB
0
GND
oUTPUT
16.8MHz
C308
R369
R371
0
0
10p
AM1
C156
R108
0
470p
ANT SW
D111
HVC131
TV
10
R302
4.99V
VCC
L301
R303
2.2u
560
10p
C306
PLL F_IN
DOUBLER AMP
10k
R306
Q301
2SC5108(Y)
R376
0
10k
R370
C145
1.5p
RF BPF
TUNING
D107
C144
7p
1SV291
L101
8.2n
100k
R129
470p
C146
R133
100k
MI2
AFO
ME
64
X57-699 5/9
MI2
AFO
ME
Page 69

TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
5C
C343
R337
10k
D314
D308,311
FREQUENCY
CONTROL FOR
TX/RX VCO
L309
D311
BB664
BB664
470p
L312
C253
C346
22p
1.0u
2SC4617(S)
0.01u
L311
C351
RIPPLE
FILTER
C347
22p
1.0u
C350
TC301
Q251
C255
1u
0
D308
R252
4.7k
C252
470p
L310
C342
1u
CV
CV
1000p
D313
BB664
D309
BB664
D309,313
FREQUENCY
CONTROL FOR
TX/RX VCO
C251
1k
1k
0
1k
11CL
CV
AM1
MOD
10u10
R334
R315
R336
R335
R251
10CL
MODULATION
CONTROL
FOR TX VCO
1SV278
C352
TC302
0.5p(B)
L314
L34-4607-05
17.5n
8p
8p
10u16
L325
L34-4605-05
12.5n
12p
8p
L315 1.0u
C357
2SK508NV(K52)
5p
C355
TX/RX VCO
R2540R255
10k
R253
0.01u
C256
0.5p
C356
2SK508NV(K52)
4p
C354
6p
Q306
1u25
C257
C358
5p(B)
TX/RX VCO
Q307
C360
0
C353
7p
L317
R342
C362
R256
R257
L326
1.0u
7p(B)
C359
3.69V
470p
1.0u
180
REVERSE
470p
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
D251
MAX5026EUT+T
1
PGND
2
GND
120k
3
FB
15k
DC-DC CONVERTER
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM TK-8180
RIPPLE FILTER
Q312
L316
R341
C361
1.0u
180
470p
IC251
3.93V
TX/RX
VCO SW
Q309
2SC4116(GR)
C365
0.3p
1SS388
LX
VCC
SHDN
C364
C363
0.5p
6
5
4
470p
4.7k
R351
TX/RX
VCO SW
Q308
2SC4116(GR)
10u
4.50V
L251
C258
4.7u16
C299
3.94V
2SC4617(S)
470p
C370
10
R258
R343
470p
C369
R352
3.86V
33k
R349
C594
R375
330
470p
VCO
BUFFER
AMP
Q311
2SC5108(Y)
33k
R350
R353
4.7k
R:0V
R348
T:2.3V
10k
TX/RX
VCO SW
R:4.88V
Q310
T:0V
DTC114EE
R347
4.7k
4.7k
C334
C325
1000p
1000p
22
T/R
R339
100k
R340
100
0.5p
R344
47
R345
0
C371
L318
C368
C367
22n
C372
0.39V
10u6.3
22p
470p
1000p
R355
R356
C374
C373
4.99V
10k
1000p
C376
470p
C375
27p
56
470p
C377
R357
R358
10k
8.2k
470p
R359
22n
L319
2SC5108(Y)
C378
100
4.3V
220
R361
VCO BUFFER
AMP
Q313
1.02V
120
470p
R360
C379
T:2.84V
R:2.13V
L328
C381
22n
6p
C388
470p
5p
5p
2.2k
R365
C387
R366
470p
C380
C382
0.01u
5R
ADACABAAZ
D316
HVC131
D315,316
TX/RX
D315
BAND SW
HVC131
T:0V
R:2.83V
T:3.55V
C384
R:0V
0.01u
C385
R367
470p
3.3k
8T
8T
AM1
2.2k
C383
1000p
5R
33n
L119
1k
R179
C175
6p
C177
R172
18
270
R171
L173
L39-1421-05
470p
R173
R174
L172
L171
15n
15n
6p
12p
C173
C171
1k
R177
C176
R126
0
470p
MI2
AFO
ME
270
0.87V
68
C178
470p
L174
L39-1421-05
R175
2.2k
IC171
SPM5001
6
G2
5
S1
4
S2
RX 1ST MIXER
C181
470p
L175
R176
4.97V
47
4.35V
L176
L39-1421-05
1
G1
2
D1
3
D2
C182
0.01u
C183
0.01u
C185
0.01u
C184
470p
33p
C186
L177
270n
R178
C190
0.84V
L180
C192
68n
0.01u
39p
R180
XF171
C187
L71-0618-05
0
39p
390n
L178
4p
C188
4p
C189
390n
L179
R182
3.3k
R181
330
2SC5108(Y)
820
0.01u
Q171
IF AMP
C193
L181
R183
C194
5R
4.96V
10u
C195
470p
68
C196
0.01u
4.41V
0.01u
L182
100n
0.07V
R184
C197
0.01u
68p
C198
10
C199
XF171
L71-0618-05
39p
390n
4p
C200
L183
L185
C202
390n
4p
C201
L184
C204
68n
39p
0.01u
MI2
AFO
ME
65
X57-699 6/9
Page 70

AE AF AG AH AI
TK-8180 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
IC1
RA30H4452M
POWER MODULE
RF_IN2VGG3VDD4RF_oUT
1
H:3.44V
L:3.03V
R16
47
C21
R17
R28
47
0
22p
47p
C17
C19
TX GATE SW
DTC114EE
470p
R77 100k
IC71
TA75W01FU
1
OUT1
2
IN1-
OUT-B
3
IN1+
45
VEE
C76
DC AMP
FOR TX APC
Q3
VCC
IN2-
IN2+
470p
R15
100p
C20
220
R18
470p
D1
C22
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
8
7
6
R78
MP
470p
220
02DZ5.6(X,Y)
R19
150
R79
220k
100k
C24
C9
6p
22
4.7u16
TX DRIVER
Q2
2SC5192
0.61V
10
R12
C10
R10 560
100p
R11
2.7k
C7
100p
C8
100p
C16
6p
L3
R13
330
22n
C13
100p
L2
C14
100p
C15
100p
0
R14
C18
56k
R75
47k
R71
R76
33k
R72
100k
PC
GSW
100p
1.12V
R8
L1
470
18n
C5
100p
R9
C6
0.84V
C1
1000p
8T
AM1 AM1
C2
R2
5.6
100p
R3
R1
820
820
R4
TX PRE-DRIVER
C3
R6
220
100p
Q1
2SC5108(Y)
R5
6.8k
0.12V
33k
R7
10
C4
T:7.81V
R:0V
4.7u10
H:13.02V
L:13.39V
100p
C34
100p
C35
XB15A407A2GB
22p
C38
22p
0
R38
C39
HIGH/LOW
POWER SW
1p
C25
L4
L6
L5
22p
C26
330
C33
R21
+B
47p
100p
L7
10T
1.6V
R25
150
1/2
100p
470p
47u25
C29
C32
C28
C27
C40
22p
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
ANT SW
D3
5p
C42
L8
2.5T
100k
R82
DC AMP
FOR TX APC
R85
TA75W01FU
1
OUT1
2
IN1-
3
IN1+
4
VEE
C77 470p
3p
C43
100k
IC72
8
VCC
7
OUT-B
6
IN2-
5
IN2+
C74
100p
R81
100k
Q70
DTC114EE
H/L
D2
ANT SW
XB15A709
R84
120k
R90
330k
C44
120p
R86
820k
2SK1824
HIGH/LOW
POWER SW
R87
82k
H:3.21V
L:1.19V
R89
100k
R88
100k
Q72
8T
0.01u
C230
C231
82p
R205
3.3k
RB706F-40
1000p
C232
D173
10
R209
CD171
R208 3.9k
C233
1000p
Q177
DTC144EE
Q177,179
W/N CF SW
CONTROL
5C
4.99V
4.94V
L79-1701-05
R210
Q176
2SK1824
C235
SQ NOISE-AMP
DETECTOR
47k
R207
-t
R221
47k
TH171
W/N DISCRETE SW
Q178
DTA144EE
2.7k
DET MUTE SW
C237
22u6.3
R212
100k
D174
0.1u
MA2S111
DET MUTE SW
CONTROL
R109
1k
Q179
DTC144EE
C234
0.22u
47k
C238
C143
C236
0.01u
0.01u
0.01u
RXDET
DMUTE
RSSI
W/N
ASQ
MI2
AFO
5R
4.96V
10u
470p
L186
C207
68
R188
0.01u
C208
R187
3.3k
C205
R186
330
IF AMP
Q172
0.84V
2SC5108(Y)
820
R185
MI2
AFO
C206
0.01u
0.01u
R189
0.07V
10
4.37V
L187
100n
C210
C209
0.01u
68p
R217
0
C211
10p
C212
L188
CFSW
470p
820n
C213
W/N CF SW
CONTROL
Q173
DTA114EE
W/N CF SW
CONTROL
Q174
DTC144EE
0.01u
5C
FM IF SYSTEM IC
4.99V
C214
R190
C240
0.1u
C239
W/N CF SW
D171
DAN235E
15k
0.1u
X171
L77-1762-05
0.1u
R191
R192
C215
18p
22k
22k
C216
C217
N:4.85V
CF171
L72-0986-05
CF172
L72-0998-05
W:4.96V
15p
1000p
L189
R193
1u
47k
R194
R195
C218
0.01u
22k
W/N CF SW
D172
DAN235E
22k
C219
IC172
TA31136FN
1
OSCIN
MIXIN
2
OSCOUT
GND
3
MIXOUT
N-REC
4
VCC
N-DET
5
IFIN
RSSI
6
DEC
IFOUT
7
1u
C220
R196
89
C221
0.1u
0.1u
R197
330k
C222
1000p
15k
NOISE AMP
2SC4617(Q)
Q175
FILOUT
FILIN
R198
330k
C224
270p
C225
270p
C223
QUAD
AFOUT
10u10
16
15
C259
14
13
12
11
10
2.2k
R204
C229
0.033u
C227
1000p
C241
1000p
4.7k
R202
R206
1k
3.3k
R203
R200
3.3k
C228
0.1u
C226
1000p
56
R199
0.1u
ME
66
X57-699 7/9
ME
Page 71

TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10) (B/3)
C31
R23
L9
1.5T
C47
0.5p(B)
C48
3p(B)
RF DETECTOR
D6
HSM88AS
C49
R26
100p
10k
3p
C45
R27
100k
C51
100p
8p
C57
C50
0.5p(B)
C58
2p(B)
RF DETECTOR RF DETECTOR
D7
HSM88AS
C59
ANAMALAKAJ
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM TK-8180
IC417
AUDIO IC
TA7 2 52AP
C80
R31
3.3k
470p
-t
TH1
C30
6.8k
L10
1.5T
C53
R29
82k
100p
C61
100p
470p
100k
470p
INPUTNFD.C
GND
OUT PUT
BOOTSTRAP
C576
R653
C577
47u25
C578
330u16
2.2
0.1u
R654
1000p
C579
0
VCC
6.76V
47u25
C580
ANT
SB
SB
13.61V
1000p
C582
R655
0
C581
1000p
C583
470p
SB
SPI
SPO
PA
HOR
GND
CN428
1
2
3
4
5
6
EXT.SP
J401
1.44V
R648
2.2k
1000p
C572
1234567
47u25
560
1000p
C575
R652
C573
0
22u16
C574
R651
L12
1.5T
0.5p(B)
2p(B)
HSM88AS
0
C79
R33
470p
R30
TCTL
HOR
0
5C
4.99V
4.7k
R642
AF MUTE
CONTROL
0.1u
C560
D416
DAN202U
R641
4.7k
47k
C561
0.1u
R632
PA
SPO
R644
Q418
DTC114EE
AF MUTE
CONTROL SW
1k
4.41V
C566
1u
AF MUTE SW
R645
C570
1u
5.6k
Q419
DTC363EU
6p
C60
L13
9.5T
D8
R24
C56
100k
100p
C62
100p
1k
R22
C52
10p
C55
8T
CN427
AUXIO6
C568
1000p
30
AUXIO7
29
AUXIO1
28
AUXIO2
27
RXD2
26
AUXIO3
25
TXD2
24
AUXIO4
23
AUXIO8
22
AUXIO5
21
AUXIO9
20
AUXO1
19
TXD1
18
AUXO2
17
RXD1
16
GND
15
ME
14
MI2
13
DEO
12
GND
11
5C
10
DI
9
AFO
8
SB
7
SB
6
SB
5
SB
4
SB
3
SB
2
NC
1
AIO6
AIO7
AIO1
AM1
MI2
AFO
ME
THP
AIO2
AIO3
AIO4
AIO8
AIO5
AO1
AO2
DEO
5C
SB
DI
AIO9
RXD2
RXD1EXT
TXD1
TXD2
5C
47k
R623
D412
DA204U
R621
C545
1000p
F401
F53-0352-05
R633
0
R636
0
0
R622
47k
R624
SURGE PROTECT
C547
0
DA204U
D412-414
D413
1000p
C548
C549
C550
1000p
1000p
100p
4.7k
R625
C551
C552
C553
C554
D414
DA204U
1000p
1000p
1000p
100p
R629
R630
C555
C556
C557
C558
C559
1000p
1000p
1000p
100p
1000p
C567
100p
470
R643
0
0
IC416
ADM202EARN
R2IN
R2OUT
10
T2OUT
T2IN
11
V-
T1IN
12
C2-
R1OUT
13
C2+
R1IN
14
C1-
T1OUT
15
V+
GND
16
C1+
VCC
LEVEL
C546
0.01u
CONVERTER
IC (RS-232C)
C825
1000p
89
7
6
1u25
5
C562
4
1u25
3
C563
2
1
1u25
C565
1u25
C564
67
X57-699 8/9
Page 72

AO AP AQ AR AS
TK-8180 SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
RX-FRONT
(E23-1081-05)
RX-IF
(E23-1081-05)
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)(A/3)
CN701
AUXIO6
1
AUXIO7
2
AUXIO1
3
AUXIO2
4
RXD2
5
AUXIO3
6
TXD2
7
AUXIO4
8
AUXIO8
9
AUXIO5
10
AUXIO9
11
AUXO1
12
TXD1
13
AUXO2
14
RXD1
15
GND
16
ME
17
MI2
18
DEO
19
GND
20
5C
21
DI
22
AFO
23
SB
24
SB
25
SB
26
SB
27
SB
28
SB
29
NC
30
E
Note : The components marked with a dot (•) are parts of layer 1.
TX-MODULE
(E23-1081-05)
D701
C701
1000p
E
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
VCO
(E23-1081-05)
CN322 CN323 CN326 CN329CN100 CN102CN101
TX-DRIVE
SURGE PROTECT
Q702
Q701
(E23-1081-05)
D704-708,711-713
R706
470
R707
470
R708
470
R709
470
R710
470
C711
E
100p
C702
C704
E
100p
C703
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
E
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
E E
CN2 CN3CN1CN203CN202 CN13 CN815
47k
R701
D704
E
DA204U
R702
47k
D705
E
DA204U
47k
R703
D706
E
DA204U
47k
R704
D707
E
DA204U
47k
R705
D708
E
DA204U
L701
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
02DZ18(X,Y)
E
L702
D702
1SS355
2SD2114K(W)
INVERTER SW
D703
1SS355
2SD2114K(W)
INVERTER SW
C707
1000p
E
C708
1000p
E
C709
1000p
E
C710
1000p
E
1000p
100p
D710
02DZ18(X,Y)
D709
02DZ18(X,Y)
AVR
(E23-1081-05)
R711
R713
D713
DA204U
E
R712
E
E
E
E
47k
R714
D711
DA204U
D712
DA204U
470
C706
E
C705
47k
47k
1000p
R715
1000p
470
R720
470
R717
470
C712
RX-IF GND
E
C714
R716
470
100p
E
C718
C719
C713
R718
R719
470
470
100p
R295
0
R298
0
L409
D
C716
1000p
E
C717
1000p
E
100p
E
100p
E
1000p
E
C720
E
100p
D714
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
C715
100p
E
02DZ18(X,Y)
C722 100p
E
C721
1000p
E
27
13
25
12
24
11
23
10
22
9
21
8
20
7
19
6
18
5
17
4
16
3
15
2
14
1
26
C723 100p
E
E
E
J701
TTL SPECIFICATION
(DEFAULT)
AUXI/O6
ME
AUXI/O7
AUXI/O1
GND
AUXI/O2
RXD2
AUXI/O3
TXD2
AUXI/O4
AUXI/O8
AUXI/O5
GND
DEO
MI2
GND
DI
AFO
AUXI/O9
AUXO1
TXD1
AUXO2
RXD1
SB
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
68
X57-699 9/9
7
Page 73

-t
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
A
D
D D
-t
A
D
A
A
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
R199
56
R210
2.7k
C384
0.01u
Q178
DTA144EE
C215
18p
C222
1000p
R197
330k
C213
0.01u
C217
1000p
X171
L77-1762-05
R203
3.3k
C216
15p
C225
270p
C218
0.01u
R205
3.3k
R200
3.3k
C232
1000p
R190
15k
C220
0.1u
R198
330k
C382
0.01u
C224
270p
R209
10
R193
47k
C185
0.01u
C234
0.22u
C238
0.01u
R202
4.7k
R212
100k
C214
0.1u
R207
47k
C231
82p
C221
0.1u
D315
HVC131
C223
0.1u
C228
0.1u
D316
HVC131
C385
470p
L189
1u
C233
1000p
R208 3.9k
R367
3.3k
C230
0.01u
C380
470p
C226
1000p
R206
1k
C186
33p
C383
1000p
C229
0.033u
R365
2.2k
D173
RB706F-40
C236
0.01u
C374
1000p
VC
GND
R2540R255
0
R253
10k
2SC4116(BL)
Q303
2SC4116(BL)
Q302
C327
0.22u
R356
10k
R352
10
R303
560
C255
10u16
R333
0
C257
1u25
C370
470p
C253
0.01u
C256
0.01u
R317
0
C381
470p
C815
4.7u16
R815
68k
C804
470p
2
COM
3
IN1OUT
C812
0.1u
C817
470p
C802
1000p
R805
470
R813
4.7k
R802
330k
R807
10k
C806
100p
C810
0.047u
Q806
DTC114EE
Q808
DTC114EE
R812
10k
R814
47k
R806
10k
R808
47k
C808
0.1u
C819 0.1u
3
GND
1
IN2OUT
C813
470p
C811
0.1u
C816
10u10
C821
4.7u16
Q802
DTC114EE
C820
0.1u
C807
0.047u
C822
470p
C809
470p
Q809
DTC114EE
R809
47k
C805
1000p
Q807
DTC114EE
R811
10k
R801
220k
D805
02CZ9.1(X,Y)
C803
0.047u
C814 470p
R803
10k
C801
1000u25
IC803
TA7808F
3
GND
1
IN2OUT
R302
10
R251
1k
R252
4.7k
D801
22ZR-10D
D802
DSA3A1
J401
R654
0
C581
1000p
C583
470p
R655
0
2SC2873(Y)
Q801
12A02CH
Q803
12A02CH
Q804
C42
5p
R17
47
L4
R16
47
L6
C27
47p
R15
220
C21
470p
R86
820k
R18
220
R77 100k
R14
0
C6
4.7u16
R21
330
C44
120p
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
C18
470p
R89
100k
C32
47u25
R75
47k
C19
47p
L7
10T
R84
120k
R79
220k
C20
100p
2SK1824
Q72
L5
Q3
DTC114EE
C28
100p
C29
470p
R71
56k
R76
100k
D1
02DZ5.6(X,Y)
R19
150
R85
100k
C33
100p
R87
82k
R88
100k
C22
470p
R72
33k
C34
100p
D6
HSM88AS
C24
4.7u10
R25
150
1/2
R82
100k
IC71
TA7 5 W01FU
1
2
3
45
6
7
8
C35
100p
R78
100k
ANT
R81
100k
C17
22p
C1
1000p
D7
HSM88AS
C26
22p
D171
DAN235E
R196
15k
R191
22k
R194
22k
R192
22k
R195
22k
Q174
DTC144EE
Q173
DTA114EE
R257
15k
C258
4.7u16
D251
1SS388
R256
120k
R258
22
R305
56
2SK1824
Q176
D174
MA2S111
C235
0.1u
TH171
47k
2SJ645
Q810
1
VSS
2
VDD
4
3
1
2
4
VSS
3
NC
IC405
AT29C040A-90TI
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
C406
0.3p
R434
47k
R451
470k
C423
1u
R418
47k
L401
R420
330k
R461 470k
R431
0
R458
470k
L406
R453
470k
R482
47k
R432 1k
R419
47k
R405
470k
C412
0.1u
5M
5M
R424
1k
R428
0
R469
1k
L402
R467
0
R447
470k
R411
470k
R427
1k
R430
470
R422
47k
R481 470k
R421
47k
R426
1k
R406
470k
R449
470k
R470
1k
R429
470
R471 1k
R425
1k
R414
10k
R465
47k
R457 47k
R410
10k
R459
470k
R415
470k
R468
47k
D403
1SS388
D402
1SS388
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
C410
0.1u
CP401
100
D404
1SS388
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
STRB
2
DATA
3
CLK
4
Q1
5
Q2
6
Q3
7
Q4
8
VSS
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
IC410
M62364FP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
C429 1u
C454
0.01u
C407 0.01u
C517
0.01u
C506
1u
R585
180k
R570
150k
C480
1000p
R553
4.7k
C518
0.1u
C463
0.01u
C528
2200p
R552
10k
C520
1000p
C489
0.1u
R540
47k
R532
1k
R599
180k
C535
0.068u
R610
150k
R586
1k
C475
100p
R597
1M
C491
0.1u
C485
1u
R576
220k
C477
1000p
R568
120k
R606
0
C538
1000p
R559
120k
C488
12p
R536
15k
C479
1000p
R581
150
C484
4.7u
R563
390k
R571
120k
R545
10k
R608
180k
C505
1u
C482
4.7u
R587
150k
C495
180p
R541 0
R566
1M
R609
22k
C531
1000p
IC415
AQUA-L
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TCLK/DTRDO11TDATA/DTRCLK12DI/O13RDF/FD14SCLK15DIR16XOUT
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
262728
293031
32
C524
1000p
R616
4.7k
C533
0.015u
2SJ243
Q413
R600
4.7k
R550
4.7k
C537
0.1u
R548
82k
R596
0
R580
150
C470
0.01u
R583
0
2SJ243
Q417
R578
0
R560
390k
R567
390k
C525
0.1u
C532
0.012u
R588
4.7k
C503
68p
R557
4.7k
C534
1000p
C472
0.1u
C499
820p
R542
0
C526
0.1u
C514
82p
C493
4.7u
R558
390k
C507
0.1u
C529
47p
R603
0
R602
1M
R607
270k
R601
470k
Q405
DTA114EE
C492
0.1u
R527
3.9k
R528
47k
R598
4.7k
C476
0.1u
C536
0.1u
R494
4.7k
R501
4.7k
C443
0.01u
C433
0.1u
R495 4.7k
C438
0.01u
R493
1M
C440
0.1u
C497
1000p
C452
100p
R500
0
R519
100k
C448
100p
R514
18k
C459
10u10
C453
0.1u
R520
0
R505
68k
R515
100k
R512
15k
R506
220k
C457
470p
R504
10k
R513
560k
C451
0.01u
R517
22k
R524
10k
1
2
3
4
VSS
5
6
7
8
VDD
1
2
3
4
VSS
5
6
7
8
VDD
IC408
TC75W51FU
1
2
3
4
VSS
5
6
7
8
VDD
R522
100k
R526
270k
R533
100k
C462
0.01u
1
OUTPUT
2
V+
3
INPUT+
4
5
IC412
TC75W51FU
123
4
VSS
567
8
VDD
R530
330k
R521
47k
R523
560k
C460
0.01u
C465
22p
C469
0.1u
D407
RB706F-40
R539
39k
R535
390k
R529
680k
1
2
3
4
VSS
5
6
7
8
VDD
R594
680
R589
0
C511
0.1u
R573
6.8k
C501
22p
R569
100k
C496
0.1u
C483
0.01u
IC407
TC75W51FU
123
4
VSS
567
8
VDD
R496
100k
R498
270k
C444
39p
D406
02DZ5.1(Y)
C446
0.01u
C445
15p
R503
100k
R499
100k
R592
0
C824
0.01u
C823
1000p
CN428
1
2
3
4
5
6
R604
0
2SJ243
Q416
R534
27k
C540
10u10
C539
10u10
C544
10u10
C543
10u10
R613
100k
R619
100k
R612
100k
R617
100k
R615
4.7k
R618
220k
R620
220k
C542
1000p
R472
1k
L407
C441
10u
C450 10u
C530
10u
R508
1k
R614
0
C541
0.1u
L301
2.2u
C371
10u6.3
C237
22u6.3
L409
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
C519
1000p
R565
0
4
6
123
5
R366
2.2k
L302
C239
0.1u
C240
0.1u
R657
4.7k
R658
0
R131
100k
C148
1p
C152
470p
C150
5p
L114
8.2n
C155
470p
L117
8.2n
C154
1.5p
C146
470p
C149
470p
C151
1p
R129
100k
C144
7p
R130
100k
L115
8.2n
L116
8.2n
R132
100k
C145
1.5p
C153
5p
C124
10p
R122
100k
C133
6p
R126
0
C176
470p
C121
470p
D103
1SV286
R116
18k
C142
470p
C134
3p
C137
470p
R120
220
D104
1SV286
R121
100k
L111
L34-4565-05
5T
C131
470p
R124
100k
C132
22p
C136
4p
R123
100k
C140
22p
C141
9p
D105
1SV286
C125
470p
L109
18n
C135
22p
R119
0
2SC3357
Q103
L110
L34-4565-05
5T
C127
22p
C139
470p
C138
5p
R115
18k
C129
470p
C119
5p
C130
5p
D106
1SV286
R172
18
C175
6p
L172
15n
R173
270
L171
15n
C181
470p
R171
270
C173
12p
R175
2.2k
C178
470p
C171
6p
1
2
3
4
S2
5
S1
6
G2
C177
470p
C182
0.01u
R174
68
L175
R176
47
C184
470p
C183
0.01u
C376
470p
R359
100
C375
27p
R358
8.2k
R360
120
C378
470p
2SC5108(Y)
Q313
R357
10k
L319
22n
C377
470p
R361
220
C379
6p
R2
5.6
R10 560
C15
100p
C7
100p
C5
100p
R7
10
R4
33k
R1
820
R13
330
L3
22n
C3
100p
R8
470
2SC5108(Y)
Q1
R3
820
R6
220
C14
100p
R5
6.8k
L2
C2
100p
C4
100p
L1
18n
R9
22
C10
100p
C9
6p
R12
10
R11
2.7k
C8
100p
C16
6p
IC1
RA30H4452M
1
RF_IN2VGG3VDD4RF_oUT
C74
100p
C38
22p
C39
22p
C40
22p
D2
XB15A709
C43
3p
C57
L10
1.5T
C48
L13
9.5T
C53
10p
C58
L9
1.5T
C60
6p
C50
8p
C45
3p
C47
L12
1.5T
R26
10k
C51
100p
R27
100k
C49
100p
C59
100p
R29
82k
C61
100p
R311
1.8k
C318
2.2u20
C320
2.2u20
R322
0
R316
100k
R326
270
C338
0.33u35
R307
0
C333
5p
R371
0
C391
2p
L327
33n
C302
0.5p
L320
10n
C393
6p
L322
5.6n
L321
8.2n
C395
2p
C389
6p
L324
2.2n
2SC5108(Y)
Q301
C390
12p
L323
4.7n
R306
10k
C392
12p
C311
39p
C339
470p
C308
10p
R309
100
C398
1p(B)
C394
4p
C317
100p
R310
100
C252
470p
C251
470p
C369
470p
C360
7p
C343
10u10
C342
1000p
C364
0.5p
C355
5p
R351
4.7k
L312
1.0u
C351
0.5p(B)
L326
1.0u
C357
6p
L311
1.0u
R344
47
R345
0
D314
1SV278
C346
22p
R337
10k
D309
BB664
R341
180
C353
470p
C350
8p
L316
1.0u
D313
BB664
L317
1.0u
C365
0.3p
C362
470p
R335
0
C352
12p
R336
1k
R342
180
R343
4.7k
TC301
8p
C363
470p
C347
22p
C361
470p
D308
BB664
D311
BB664
R347
4.7k
C356
0.5p
R340
100
R339
100k
C354
4p
TC302
8p
R334
0
C368
470p
C372
22p
R349
33k
L318
22n
R350
33k
R355
56
Q310
DTC114EE
C367
1000p
C373
470p
R353
4.7k
C312
0.047u35
C25
1p
R318
1.8k
C147
5p
C316
8p
C156
470p
C13
100p
R554
56k
R556
56k
R555
12k
R133
100k
C259
10u10
C219
1u
C76
470p
C77 470p
C467 0.01u
R134
0
C591
0.1u
C388
5p
C387
5p
L328
22n
R375
330
C594
470p
C325
1000p
C334
1000p
R511
1.5k
R525
1.5k
C464
0.033u
C447
0.033u
R188
68
R180
820
C187
39p
C196
0.01u
C206
0.01u
C210
68p
R178
0
C193
0.01u
L182
100n
C198
68p
C211
10p
L180
68n
R189
10
C201
4p
C192
0.01u
C209
0.01u
C204
0.01u
C194
0.01u
R184
10
C212
470p
L188
820n
C199
39p
L181
10u
C205
0.01u
C190
39p
R187
3.3k
L185
68n
R182
3.3k
L186
10u
R186
330
R183
68
C188
4p
C195
470p
R181
330
L187
100n
C189
4p
R217
0
R185
820
C202
39p
C200
4p
C207
470p
C197
0.01u
C208
0.01u
L178
390n
L179
390n
L183
390n
L184
390n
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2SK1824
Q412
C323
470p
C324
0.1u
L177
270n
CN802
CN803
CN804
2
1
C455
47u6.3
R179
1k
R177
1k
C52
C55
C56
100p
R24
100k
D8
HSM88AS
C62
100p
R33
0
C79
470p
TH1
100k
C30
470p
C31
470p
R23
6.8k
C80
470p
R22
1k
C331
0.01u
R332
10
R325
150k
R321
10k
R330
10
C335
0.022u
CN302
1
2
3
4
5
6
R320
18
CN301
1
2
3
4
5
6
C397
12p
C309
100p
C396
0.01u
1
2
3
4
5
678
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1617181920
R323
1k
R327
10
R373
10
R319
10
C143
0.01u
R315
1k
R546
0
C584
22p
R108
0
L305
C400
1u
R509
33k
C306
10p
R109
1k
R204
2.2k
C227
1000p
C241
1000p
R221
47k
L410
L411
R800
1M
CN322 CN323 CN326 CN329CN100 CN102CN101
CN2 CN3CN1CN203CN202 CN13 CN815
C128
9p
R818
47k
C826
470p
L304
Q811
DTC114TE
R804
100k
R549
47k
R412
470k
R477
470k
R478
470k
Q2
2SC5192
R416
0
D417
1SS388
D418
1SS388
C818
4700p
Q402
DTC114YE
C408
15p
R90
330k
Q70
DTC114EE
Q177
DTC144EE
Q179
DTC144EE
R370
10k
Q812
DTC114EE
C592
7p
C593
7p
R31
3.3k
L101
8.2n
L119
33n
R595
270k
D601
1SS388
Q600
DTA144EE
R647
100k
D111
HVC131
R38
0
C358
5p(B)
R376
0
R369
0
R28
0
R584
0
R659
33k
L310
1u
C359
7p(B)
R475
100
1
PGND
2
GND
3
FB
4
5
6
IC404
30625MGP-169GP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
39404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
L8
2.5T
L251
10u
R661
4.7k
R663
4.7k
R664
4.7k
C513
1000p
C512
1000p
C262
100p
C260
100p
C261
100p
R308
3.9k
R377
0
0
1
IN/OUT
2
OUT/IN
3
GND
4
5
R378
10k
C832
4.7u16
2
VSS
3
VIN1VOUT
C831
4.7u16
C322
0.047u
R362
0
C386
10u6.3
R301
D405
EMZ6.8N
CP4021kCP403
1k
CP404
1k
CP4051kCP406
1k
CP407
1k
CP408
1k
CP409
1k
CP410
1k
CP411
1k
CP412
1k
CP413
1k
CP414
1k
CP415
1k
CP416
1k
CP417
1k
C702
100p
R709
470
D709
02DZ18(X,Y)
D707
DA204U
C703
100p
D713
DA204U
R706
470
C720
100p
C715
100p
C707
1000p
C712
100p
D702
1SS355
C719
100p
C713
1000p
2SD2114K(W)
Q702
C711
1000p
R708
470
C721
1000p
R712
47k
C714
100p
R719
470
L701
R716
470
R717
470
D704
DA204U
CN701
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
C716
1000p
R713
47k
R707
470
R714
470
R720
470
D712
DA204U
R710
470
R718
470
R715
470
2SD2114K(W)
Q701
C701
1000p
L702
D714
02DZ18(X,Y)
D705
DA204U
R711
47k
D706
DA204U
C718
100p
C723 100p
C708
1000p
C722 100p
C709
1000p
C705
1000p
D708
DA204U
D711
DA204U
C710
1000p
C706
1000p
C704
100p
D710
02DZ18(X,Y)
D703
1SS355
C717
1000p
J701
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
10
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
+B
SB
5M
5M
8C
5E
8T
TCTL
DATAOU T
R485
0
C424
1000p
RXEMAO
SIDETONE
OPT2
C587
100p
C427
100p
C595
100p
TXAO
C436
100p
RXEMAI
C588 1000p
C431
100p
C439 1000p
OPT4
C435 1000p
R491
0
C425
100p
C430 100p
AUDIH
R403
1M
R483
0
R473
0
AI
R4880R486
0
C422
1000p
C432
1000p
C420
100p
R484
0
C421
100p
OPT3
TXD1
C428
100p
C585
100p
OPT5
RXD1INT
AO
C437
100p
R489 0
R487
1.8M
CN403
2
OPT31OPT14TXD13RXD16OPT45CLK8OPT57USEL10AGND
9
DGND12AI11AO145E13AGND
16
DTI 15STON18NC17TCTL20OPT219AUDIH
22
RXEO21TXO24TXI23RXEI
26
8C
25
OPT6
C586
100p
C426
100p
R474
0
R574
0
C502
1000p
C490
1000p
C481 1000p
C487 1000p
R572
0
R902
0
R901
0
C500
100p
C498
100p
C515 1000p
CN429
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
R575
0
R900
0
C478 100p
C516 1000p
C504 1000p
R903
0
R400
1M
LCDRST
R591
0
RXAI
AIO9
AIO5
PSW
RXD1INT
A4
A12
A15
A16
A18
A5
A6
A7
A17
A14
A13
A11
A8
A9
WR
A3
A2
A1
A0
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
RD
A10
CSO
L405
L404
L403
D2D0D3D1D4D5D6
D7
OPT5
OPT4
OPT3
OPT2
OPT1
RSSI
W/N
ASQ
THP
H/L
A2
A3
A0
A1
A5
A6
A7
A4
TCLK/DTRDO
A8
A9
A11
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
CSO
L408
R625
4.7k
R624
47k
C565
1u25
R630
0
D414
DA204U
1000p
R622
0
C546
0.01u
C559
1000p
R623
47k
R621
0
F401
F53-0352-05
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
R633
0
R629
0
R643
470
C563
1u25
D413
DA204U
1000p
D412
DA204U
C567
100p
R636
0
C564
1u25
C562
1u25
CN427
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
R590
0
Q409
DTC363EU
T/R
Q418
DTC114EE
C570
1u
C574
22u16
R642
4.7k
C560
0.1u
1234567
R648
2.2k
R653
2.2
C576
330u16
C577
0.1u
R641
4.7k
R632
47k
Q419
DTC363EU
R651
0
R645
5.6k
C561
0.1u
D416
DAN202U
C566
1u
R644
1k
MB
R30
0
OPT1
OPT3
OPT4
OPT5
OPT2
RXD1INT
TXD1
TXD2
RXD2
5E
DATAOU T
TCTL
TXAO
TXAI
RXEMAO
AUDIH
SIDETONE
RXEMAI
8C
5E
5C
5M
8R
5C
5M
5R
AM2
PSENS
LCDDO
LCDDI
RST2
5C
SB
8C
RXD
TXD
PSW
SPO
PC
T/R
PCK
PLE
UL
RST2
TXD
RXD
PSENS
AFDAT
AFDIO
AFDIR
AFSTD
DTRLOAD
AI04
AI03
AI02
AI01
AI07
AI08
RD
WR
TV
MB
10CL
5C
5M
DEO
DI
5C
5C
DM
OPT1
L108
L309
1u
D421
1SS388
D422
1SS388
R446
10k
R445
10k
TXD2
TXD1
RXD2
D423
1SS388
R407
10k
R579
22k
R295
0
R298
0
SIDETONE
DATAOU T
AM2
RXEMAI
RXEMAO
5M
AI
AO
RXAO
AUDIH
MP
RXDET
T/R
5R
5R
R348
10k
8R
MOD
10CL
5R
8T
5R
CFSW
5C
GSW
+B
PC
MP
H/L
RXDET
RSSI
ASQ
W/N
TCTL
HOR
PA
SPO
AIO6
AIO7
AIO1
AIO2
AIO3
AIO4
AIO8
AIO5
AO1
AO2
DEO
AIO9
5C
SB
DI
TXD2
TXD1
RXD2
5C
5C
TCLK/DTRDO
AFRTM
DTRLOAD
AFSTD
AFDAT
AFDIO
AFRTM
AFDIR
TV
5C
RXAI
RXAO
RXD1EXT
TXAI
AI06
MOD
THP
8C
SB
INPUTNFD.C
GND
OUT PUT
BOOTSTRAP
VCC
SB
R646
4.7k
5C
L306
PCKULPLE
5M
C307 470p
C299
0.5p
DMUTE
DMUTE
RXD1EXT
EXT.SP
LSD BUFFER AMP/
VCXO BIAS AMP
LSDO
+
+
–
–
--+
+
MODULATION
LPF/DEF AMP
–
–
+
+
SB
SPI
GND
HOR
PA
SPO
AM1
CV
5C
Fin
CP
GND
DGND
GND
PCK
DT
PLE
UL
CV
VCO
(E23-1081-05)
RX-FRONT
(E23-1081-05)
TX-MODULE
(E23-1081-05)
TX-DRIVE
(E23-1081-05)
AVR
(E23-1081-05)
CPGND
REF
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)(C/3)
RX-IF GND
TXD1
RXD2
ME
AUXI/O1
AUXO1
AUXI/O5
AUXI/ O9
TXD2
AUXI/O3
DI
AFO
MI2
RXD1
AUXI/O4
AUXI/ O6
GND
(DEFAULT)
AUXI/O8
GND
GND
AUXI/O2
DEO
AUXO2
NC
SB
AUXI/O7
SB CONTROL SW
SB CONTROL SW
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
VOLTAGE
DETECTOR(INT)
IGNITION SENS
CONTROL SW
CPU RESET SW
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
/8.5V
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
RTC PROCESSOR
BEAT SHIFT SW
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR/8V
8T CONTROL SW
8T SW
8R SW
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR/5V
5R CONTROL SW
SPSTB
CK
RXC
MIC
ME
OPT6
DET AMP/
DATA LPF (DB-25)
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
FLASH MEMORY
D/A CONVERTER
SHIFT
REGISTER
OPT6
ME
MIC
CK
SCSW
RXC
STSW
BEEP
LSW
MM1
AUXIO4
AUXIO6
RXD2
SB
AUXO1
GND
GND
SB
TXD2
AUXIO2
SB
RXD1
DEO
AUXIO9
AFO
AUXIO1
AUXIO5
SB
AUXO2
MI2
SB
AUXIO7
AUXIO3
AUXIO8
NC
TXD1
ME
5C
SB
DC DETECTOR
MM2
DT
DSTB
HSDIN
HSDO
AQUA
CONTROL
SW
LSDIN
AF SW
EMTON
AM1
V_REF
AM1
AF
AF MUTE SW
SOE
SPSTB
RST
XOUT
INT
INTRA
SHIFT/MODEL
DT
TXC
SBC
RTDT/EEPDAT
RTCL/EEPCL
XIN
LSD LPF/VOLTAGE
DC-REFERENCE
PLL SYSTEM IC
LEVEL
CONVERTER
IC (RS-232C)
RF BPF TUNING
VOLTAGE DC AMP
DC-DC CONVERTER
REVERSE
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
DC AMP
FOR TX APC
DC AMP
FOR TX APC
MICROPROCESSOR
DT
MM2
DTDT
AM1
AF MUTE
CONTROL
AF MUTE
CONTROL SW
AF MUTE SW
W/N CF SW
W/N CF SW
CONTROL
PLL F_IN
DOUBLER AMP
PLL LPF
DC REVERSE
CONNECTION
PROTECT
D801
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
D802
RF DETECTOR
ANT SW
FRONT-END LNA
RF BPF
TUNING
RF BPF
TUNING
RF BPF
TUNING
RF BPF
TUNING
PLL LPF
D315,316
VCO BUFFER
AMP
VCO
BUFFER
AMP
MODULATION
CONTROL
FOR TX VCO
TX/RX
BAND SW
TX/RX
VCO SW
D309,313
FREQUENCY
CONTROL FOR
TX/RX VCO
TX PRE-DRIVER
DET MUTE SW
CONTROL
DET MUTE SW
W/N DISCRETE SW
MIC-AMP
AGC DETECTOR
D408,409
MIC AGC
MIC AGC
SQ NOISE-AMP
DETECTOR
Q177,179
W/N CF SW
CONTROL
TX DRIVER
TX GATE SW
MIC MUTE SW
MIC MUTE SW
Q416,417
SB SW
HIGH/LOW
POWER SW
AF
MUTE
SW
ANT SW
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
INVERTER SW
ISOLATOR
D417,418
MIC MUTE
CONTROL
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
5M
LSW
BEEP
MM1
LSDO
EMTON
LSDIN
OPT6
ME
RXC
CK
SCSW
STSW
MIC
MM1
BEEP
OPT6
STSW
CK
RXC
ME
LSDIN
LIMLV
AGND
IC803
8R CONTROL SW
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
HIGH/LOW
POWER SW
W/N CF SW
CONTROL
DI
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)(B/3)
TX-RX UNIT (X57-6990-10)(A/3)
TTL SPECIFICATION
BEEP
ME ME ME
AM1
AF
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
INVERTER SW
RX-IF
(E23-1081-05)
AM1
5C5C
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
SBC
CK
IGNIGN
IGN
HSDIN
HSDO
DSTB
LSDIN
DT
CK
MI2
AFO
MI2
AFO
MI2
AFO
MI2
AFO
8T8T
AM1AM1 AM1 AM1
D423
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
CV
11CL
8T 8T
POWER MODULE
RF DETECTOR RF DETECTOR
IC413
TC7MZ4053FK
AF SW IC
SPO
GND
GND
GND
NC
(LCDDO)
8C
ME
SPO
(DM)
SB
(LCDDI)
5C
NC
MIC
SPO
SPO
(LCDRST)
RXD
SB
SHIFT/MODEL
GND
SPO
RST2
SPO
GND
TXD
(CLK)
PSW
PSENS
VOUT
VIN
D804
02DZ18(X,Y)
IC802
XC61CN5002NR
oUT
CD
F801
F53-0278-05
RTC BATTERY
CONTROL
D402-404
R402
5.1k(D)
R401
3.6k(D)
C404
5p
C403
0.1u
CN401
J19-5386-05
IC402
RV5C386A
32KOUT
SCL
SDA
INTRB
VSS
INTRA
CLKC
OSCOUT
OSCIN
VDD
INT
INTRA
RST
IC401
AT24256N10SI27
EEPROM
SDA
SCL
WP
VCC
A0
A1
NC
GND
IC804
TA7805F
12A02CH
Q805
5R SW
MIC
CK
RXC
SPSTB
ME
OPT6
SOE
RTCL/EEPCL
XIN
DT
SBC
XOUT
RTDT/EEPDAT
INT
INTRA
SPSTB
TXC
RST
SHIFT/MODEL
5M
OPT6
8C
TXD2
OPT2
RXD1
GND
AUDIH
TXD1
STON
TCTL
5E
RXEO
DTI
OPT3
TXI
RXD2
TXO
OPT4
OPT5
RXEI
OPT1
RXO
RXI
QS
Q’S
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
OE
VDD
IC403
BU4094BCFV
CFSW
GSW
HOR
AO1
AO2
PA
ME
STSW
MM1
LSDIN
OPT6
RXC
SCSW
LSW
CK
LSDO
MIC
BEEP
EMTON
HSDIN
HSDO
DSTB
DT
MM2
AM1
R452
R439
R450
R437
R456
R443
R435
R444
R455
R442
R440
R448
R454
R441
R423
R466
R476
1k01k
0
470
1k1k1k
470
1k
1k
1k
1k
1k
0
47k
47k
DGND
MM1
PSENS
TXD
RXD
AFDAT
AFDIO
AFDIR
DTRLOAD
AFSTD
LSW
RDYNCHOLDNCAI04
AIO3
AIO2
AIO1NCRDNCWR
AIO8
AIO7
AIO6
NC
NC
RST2
CS0
NC
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
UL
PLE
PCK
NC
OPT6
VCC2
A8
DGND
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
IGN
AFRTM
TCLK/DTRDO
MM2
T/R
AM1
EMTON
NC
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
DT
CK
W/N
OPT1
OPT2
OPT3
OPT4
OPT5
H/L
THP
NC
NC
ASQ
RSSI
NC
AGND
LSDIN
VREF
AVCC
SBC
RXC
TXC
PC
HSDO
STSW
RTCL/EEPCL
HSDIN
NC
RTDT/EEPDAT
BYTE
CNVSS
DMUTE
AM2
RST
XOUT
DGND
XIN
VCC1
NMI
PSW
INT
INTRA
SHIFT/MODEL
BEEP
SPSTB
SOE
AIO5
AIO9
DSTB
LSDO
RXD2
TXD2
TXD1
VCC1
RXD1
9
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
10
99
100
101
102
A11
A9
A8
A13
A14
A17
WE
VCC
A18
A16
A15
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
Io0
Io1
Io2
GND
Io3
Io4
Io5
Io6
Io7
CE
A10
oE
VIN1
VOUT1
VOUT2
VIN2
VDD
LD
CLK
DI
VIN3
VOUT3
VOUT4
VIN4
VIN5
VOUT5
VOUT6
VIN6
DO
VDAref
RESET
GND
VIN7
VOUT7
VOUT8
VIN8
DT
AM1
AF
V_REF
MM2
STSW
SCSW
CK
RXC
ME
OPT6
LSDIN
MIC
MM1
BEEP
LIMLV
AGND
IC409
TC75W51FU
IC406
TC75W51FU
INPUT-
V-
IC411
LMC7101BIM5
HSD BPF/HSD
COMPALATOR
IC414
TC75W51FU
MIC AMP
D408
MA742
D409
MA742
2SC4116(Y)
Q410
2SA1586(Y,GR)
Q411
AF SW
RXAF
RXAFIN
EXPOUT
FILTERO
RXINO
RXIN
AGND
XIN
VSS
AMP3P
AMP3N
AMP3O
AMP4P
AMP4N
AMP4O
DTRAIN
AGNDIN
TXIN
TXINO
LIMLV
EXTLIMIN
MOD
VDD
DTRLOADN
STD
C
B
A
0X
1X
XCoM
YCoM
VCC
1Y
0Y
1Z
ZCoM
0Z
INH
VEE
GND
TXAI
TXAO
X403
3.6864MHz
L77-1965-05
R582
1M
Q415
HN1L02FU
AF SW
(VOICE)
2SJ243
Q414
R611
10k
ME
MI2
AFO
D108
1SV291
RF BPF
TUNING
D107
1SV291
RF BPF
TUNING
D109
1SV291
RF BPF
TUNING
D110
1SV291
RF BPF
TUNING
ME
MI2
AFO
L113
L34-4565-05
5T
L112
L34-4565-05
5T
oUTPUT
VCC
X301
16.8MHz
L77-1952-05
AM1
CV
11CL
IC301
ADF4111BCP7
CE
CLK
DATA
LE
MUXOUT
DVDD
DVDD
VP
Rset
CP
CPGND
AGND
AGND
RFinB
RFinA
AVDD
AVDD
RFEin
DGND
DGND
PLL CP SW
IC302
TC7S66FU
CONT
VCC
FREQUENCY
CONTROL FOR
TX/RX VCO
D308,311
2SK508NV(K52)
Q307
TX/RX VCO
L325
L34-4605-05
12.5n
2SC4116(GR)
Q309
TX/RX
VCO SW
2SC4617(S)
Q312
RIPPLE FILTER
2SC4116(GR)
Q308
TX/RX
VCO SW
2SK508NV(K52)
Q306
TX/RX VCO
IC251
MAX5026EUT+T
SHDN
VCC
LX
2SC4617(S)
Q251
RIPPLE
FILTER
L173
L39-1421-05
G1
D1
D2
L176
L39-1421-05
XF171
L71-0618-05
XF171
L71-0618-05
2SC5108(Y)
Q172
IF AMP
ME
MI2
AFO
L174
L39-1421-05
L314
L34-4607-05
17.5n
L315 1.0u
2SC5108(Y)
Q311
D3
XB15A407A2GB
ANT SW
IN2+
IN2-
OUT-B
VCC
OUT1
IN1-
IN1+
VEE
IC72
TA7 5 W01FU
OUT1
IN1-
IN1+
VEE
IN2+
IN2-
OUT-B
VCC
CF172
L72-0998-05
CF171
L72-0986-05
D172
DAN235E
W/N CF SW
AFOUT
QUAD
IFOUT
RSSI
N-DET
N-REC
GND
MIXIN
OSCIN
OSCOUT
MIXOUT
VCC
IFIN
DEC
FILOUT
FILIN
IC172
TA31136FN
FM IF SYSTEM IC
CD171
L79-1701-05
2SC4617(Q)
Q175
NOISE AMP
ME
MI2
AFO
0.5p(B)
3p(B)
2p(B)
0.5p(B)
0.5p(B)
2p(B)
1000p
1000p
47u25
47u25
1000p
47u25
560
1000p
C582
C572
C575
C579
C578
R652
C580
C573
C555
1000p
C545
1000p
C551
1000p
C548
1000p
C547
1000p
C549
1000p
C552
1000p
C556
1000p
C557
1000p
C553
1000p
C558
100p
C550
100p
C554
100p
SURGE PROTECT
D412-414
C1+
V+
C1-
C2+
C2-
V-
T2OUT
R2IN
R2OUT
T2IN
T1IN
R1OUT
R1IN
T1OUT
GND
VCC
IC416
ADM202EARN
RXD1
DEO
SB
SB
AFO
DI
AUXIO4
MI2
AUXO1
NC
SB
AUXIO6
TXD1
RXD2
AUXIO8
AUXIO2
GND
AUXIO3
SB
GND
AUXIO7
AUXO2
SB
SB
AUXIO5
AUXIO9
ME
TXD2
5C
AUXIO1
R702
R701
R705
R704
R703
47k
47k
47k
47k
47k
+B
GND
GND
IGN
VOLTAGE
DETECTOR
(CPU RESET)
IC801
S-80942CNNBG9C
VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
D421,422
X404
L77-1950-05
C409
15p
C411
0.1u
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR/5V
IC807
XC6201P502PR
IC805
NJM78L05UA
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR/5V
X401
L77-1802-05
C434
560p
R492
680k
R490
180k
R497
3.3k
R507
220k
C442
0.1u
R502
10k
Q406
HN1J02FU
AF SW
(LSD)
D600
1SS388
MIC MUTE
CONTROL
C468
0.01u
C461
0.01u
R531
10k
CPGND
REF
Fin
GND
CP
5C
C314
0.1u
R312
1k
RX 1ST MIXER
IC171
SPM5001
2SC5108(Y)
Q171
IF AMP
C825
C568
SURGE PROTECT
D704-708,711-713
D701
02DZ18(X,Y)
TO DISPLAY UNIT CN902
IC417
TA7 2 52AP
AUDIO IC
–
–
+
+
–
–
+
+
–
–
+
+
1.53V
0.87V
4.99V
4.99V
4.99V
4.99V
4.99V
4.99V
0.31V
10.36V
1.6V
1.02V
T:2.84V
R:2.13V
T:0V
R:2.83V
4.3V
T:3.55V
R:0V
3.86V
3.69V
R:4.88V
T:0V
R:0V
T:2.3V
4.99V
7.90V
4.97V
4.35V
0.87V
2.46V
3.22V
FL:2.5V
FC:4.0V
FH:5.8V
4.99V8.21V
T:12.7V
R:13.5V
7.96V
T:7.83V
T:7.96V
R:7.97V
T:7.2V
R:7.95V
T:4.95V
R:0.003V
R:7.95V
T:7.94V
R:7.25V
T:0.005V
R:4.93V
5V
R:4.98V
4.28V
T:7.91V
R:7.46V
4.99V
0.84V
0.12V
1.12V
0.61V
H:3.44V
L:3.03V
H:13.02V
L:13.39V
H:3.21V
L:1.19V
N:4.85V
4.99V
4.94V
4.99V
4.96V
4.37V
0.07V
0.84V
0.07V
4.41V
4.96V
0.84V
4.99V
4.99V
4.987V
4.989V
4.99V
2.49V
2.50V
2.50V
2.50V
4.98V
2.50V
2.49V
2.50V
4.98V
2.50V
4.93V
2.49V
4.92V
4.98V
2.48V
2.81V
R:4.90V
T:0V
R:4.92V
T:0V
R:4.98V
T:0V
2.49V
4.83V
4.88V
4.98V
4.99V
1.44V
13.61V
4.41V
W:4.96V
4.99V
4.75V
3.94V
3.93V
4.50V
T:7.81V
R:0V
T:7.60V
R:8.09V
8.83V
0.39V
6.76V
Page 74

CN429
(DM)
GND
RXD
TXD
NC
5C
SHIFT/MODEL
(CLK)
(LCDDO)
(LCDDI)
(LCDRST)
RST2
PSENS
GND
ME
MIC
GND
GND
PSW
NC
SB
SB
8C
GND
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
CN701
AUXIO6
AUXIO7
AUXIO1
AUXIO2
RXD2
AUXIO3
TXD2
AUXIO4
AUXIO8
AUXIO5
AUXIO9
AUXO1
TXD1
AUXO2
RXD1
GND
ME
MI2
DEO
GND
5C
DI
AFO
SB
SB
SB
SB
SB
SB
NC
CN902
GND
GND
RXD
TXD
5C
NC
SHIFT/MODEL
NC
GND
GND
GND
RST2
PSENS
GND
ME
MIC
GND
GND
PSW
NC
SB
SB
8C
GND
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
SPO
CN427
AUXIO6
AUXIO7
AUXIO1
AUXIO2
RXD2
AUXIO3
TXD2
AUXIO4
AUXIO8
AUXIO5
AUXIO9
AUXO1
TXD1
AUXO2
RXD1
GND
ME
MI2
DEO
GND
5C
DI
AFO
SB
SB
SB
SB
SB
SB
NC
LCD
B38-0888-05
DISPLAY UNIT
(X54-3480-10)
ANT
26 PIN BOARD TO BOARD CONNECTOR
DGND
CN403
OPT6
OPT2
AO
1
TXD1
AGND
OPT3
TXI
TXO
5E
DTI
CLK
OPT4
AUDIH
RXEO
NC
USEL
26
RXD1
AI
8C
STON
RXEI
OPT5
AGND
TCTL
OPT1
INT. SP
J701
SB
SPI
SPO
HOR
GND
PA
CN301 CN302
REF
Fin
CPGND
5C
GND
CP
UL
PLE
DT
PCK
GND
DGND
1
6
1
6
DM
PTT
HK
E
MIC
SB
ME
BLC
8
1
1
30
30
1
1
30
30
1
COM
1~9
SEG
1~75
CN901
J901
CN428
R30
SPO
GND
EXT. SP
NC
SB
RXD1
AUXO2
TXD1
AUXO1
AUXI/O9
AFO
DI
GND
MI2
DEO
GND
AUXI/O5
AUXI/O8
AUXI/O4
TXD2
AUXI/O3
RXD2
AUXI/O2
GND
AUXI/O1
AUXI/O7
ME
AUXI/O6
1
2
2
IGN
1
CN804
GND
1
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
AUDIO IC
TA7252AP
IC417
1
7
1
POWER
MODULE
RA30H4452M
IC1
4
–
DC 13.6 V
+
TX-RX UNIT
(X57-6990-10) (B/3)
TX-RX UNIT
(X57-6990-10) (C/3)
TX-RX UNIT
(X57-6990-10) (A/3)
INTERCONNECTION DIAGRAM
TK-8180
69
Page 75

K
B
4
s
C
W
C
*
TK-8180 BLOCK DIAGRAM
DC
DISPLAY UNIT
(X54-348)
MIC
SEG*75
LCD
COM*9
Q906,Q907
DTC114EE, 2SC2873(Y)
DIMMER
DIMMER
SW
13.6V
IGN
SENS
AFO
BLC
SB
E
PTT
ME
MIC
HOOK
DM
PTT
DM
BLC
LCD
DRIVER
IC903
LC75810T
-8726
VDD
VLCD
TX
LED
BUSY
LED
10KEY
LCD BackLight*12
KEY BackLight*10
D802
DSA3A1
PROTECT
D801
22ZR-10D
PROTECT
D804,Q802
02DZ18(X,Y)
DTC114EE
PROTECT
IC802
XC61CN5002NR
Voltage
DETECTOR
Protect
Surge
Protect
*3
D904,D905,D906
DA204U
5V, 8C
Q904
8C
DTC114EE
SW
Q905
8C
DTC114EE
SW
Q913,Q909
DTC114EE,12A02CH
8C
SW
Q801,D805
2SC2873(Y),02CZ9.1(X,Y)
AVR
8.5V
Q810
2SJ645
S-80942CNNBG9C
SW
TA7808F
Q807
SW
DTC114EE
SBC
INT
Q811
DTC114TE
SW
Q901,Q902
DTC144EE
HK/RXD
PTT/TXD1
DM
BLC2
LDT
LCK
LRES
LCS
µ-com
IC902
30302M8-***GP
RED
GR E
S [1:10]
BLC1
IC803
AVR
IGN
8V
IC805
NJM78L05UA
AVR
5V
IC801
DETECTOR
12A02CH,DTC114EE
12A02CH,DTC114EE
XC6201P502PR
Xin
Xout
VDD
DIMM
RXD2
TXD2
RST
Voltge
IC804
TA7805F
AVR
5V
Q803,Q806
SW
TXC
Q804,Q808
SW
RXC
AVR
5V
IC807
MI2
X901
14.7456MHz
5V
DIMMER
POWER SW
INT. SP
Q417
2SJ243
Q416
2SJ243
RST1
Q805,Q809
12A02CH,DTC114EE
SW
8T
RXC
8R
MM2
MM1
IC901
TA78L05F
AVR
8C
PSW
SP
+B
5M
SB
8C
5C
5R
5E
HSDO
SW
5C
SIDE
TONE
Q406
HN1J02FU
EMTON
5C
IC414
TC75W51FU
MIC
AMP
AGC
D408,D409
MA742*2
Q410,Q411
2SC4116(Y)
2SA1586(Y,GR)
2SJ243
AO
AI
VGS-1
PSENS
BEAT
SHIFT
Q402
DTC114YE
IC251
MAX5026EUT+T
DC-DC
Converter
Scrambler Board
TXAI
TC7MZ4053
FK(3/3)
Q414
SW
Q415
HN1L02FU
SW
RXAF
RST1
IGN
INT
PSW
X404
MB
ASQ
ANI Board
RXOUT
TXAO
IC413
Q413
2SJ243
REC SRC
REC SRC
SHIFT/MODEL
Xin
11.0592MHz
Xout
TXD
RXD
RST2
Q251
2SC4617(S)
Ripple
Filter
X301
16.8MHz
VCXO
5C
D173
RB706F-40
DET
DATA
OUT
RXIN
SCSW
TC7MZ4053FK(2/3)
Q409
DTC363EU
MUTE
SW
SCSW
AM2
SW
STSW
STSW
5M
Q302,Q303
2SC4116(BL)*2
11CL
10CL
Q175
2SC4617(Q)
Noise AMP
5R
DMUTE
2SK1824
TC75W51FU(2/2)
HSDO
TC7MZ4053FK
SW
TXIN
IC413
BEEP
SW
SW
HSDO
Q176
T/R
MOD
Q309
2SC4116
(GR)
CV
Active
Loop
Filter
PLL
PCK
CF SW
MUTE
SW
IC412
IC413
(1/3)
Q406
HN1J02FU
DT
Q307: 2SK508NV(
D308,D311,D314:
TX
VCO
SW
RX
VCO
Q306: 2SK508NV(
D309,D313: BB66
SW
Q308
2SC4116(GR)
IC301
ADF4111BCP7
5CUL
PLE
D171
DAN235E
SW
FM IC
44.395MHz
RXDET
5C
5C
AMP
SW
LSDI
DTRLOAD, AFSTD,
TCLK/DTRDO,
AFDAT, AFDIO
AFRTM, CK, AFDIR
Q310
DTC114EE
IN V
T/R
CF171
CF
CF172
CF
TA3
X171
IC407
TC75W
AMP
TC75
LPF
5C
IC415
Audio proce
AQUA-L
µ-com
IC404
30625MGP-*
I
I
70
THP, UL, ASQ,
RSSI, HSDIN,
LSDIN
OPT1, OPT2,
OPT3, OPT4,
OPT5
Page 76

BLOCK DIAGRAM TK-8180
307: 2SK508NV(K52)
308,D311,D314: BB664*2,1SV278
Q310
DTC114EE
T/R
IN V
2SC5108(Y)
306: 2SK508NV(K52)
309,D313: BB664*2
T/R
R)
BPF
C
CF171
CF
CF172
D172
DAN235E
SW
CF
TA31136FN
X171
IC407
TC75W51FU(2/2)
TC75W51FU
LPF
IC172
RSSI
IC406
CD171
COMP
CD
HSDI
M IC
.395MHz
5C
AMP
I
5C 5C
:
IC415
Audio processor
AQUA-L
3.6864MHz
Flash ROM
IC405
AT29C040A-90TI
, AFSTD,
DO,
FDIO
K, AFDIR
A [0:18],
RD, WR,
CS0
µ-com
IC404
30625MGP-***GP
2,
4,
2SC4617(S)
5CL
Ripple
Q311
Q301
2SC5108(Y)
*2
5C
CF SW
2SC5108(Y)
IF AMP
Q178
DTA144EE
SW
W/N
AFO
RXAF
Xin
Xout
5M 5M
RTCL/
D [0:7]
EEPCL
Q312
Filter
5C
Q313
2SC5108(Y)
Buff AMPBuff AMP
5C
Q172
XF171 XF171
MCF
2Pole
5R
MOD
LSDO
5C
X403
TC75W51FU(1/2)
EEPROM
IC401
AT24256N10SI27
RTDT/
EEPDAT
LPF
2SC5108(Y)
IF AMP
5R
IC412
TC75W51FU(1/2)
IC409
TC75W51FU(1/2)
5C
DI
IC407
5M
RTC
IC402
RV5C386A
INTRA
SPSTB1, SOE,
CK, DT
Q171
MOD
5C
5C
TX
450~520MHz
ATT
8T
T/R
D315,D316
HVC131*2
SW
5R
RX Local
405.15~475.15MHz
MCF
2Pole
DEO
AF
DAC
IC410
M62364FP
BAL
DT,CK,DSTB
X401
32.768kHz
DT, CK,
PCK, PLE,
TXC, RXC, SBC
T/R, W/N,
DMUTE,
RECSRC/SELF,
AM, AM2
EMTON,
DSTB,
APC,
HSDO,
LSDO,
BEEP
MM1, MM2
H/L,
STSW
Shift Register
BU4094BCFV
Q1
2SC5108(Y)
8T
ATTLPF
IC171
SPM5001
Mixer
5R
5C
AUX I/O1~
AUX I/O9
IC403
2SC5192
S1R104J475H
8T
TV
D103,D104
D105,D106
1SV286*4
DEO
AF
FC
IC408
TC75W51FU
(2/2)
Q2
8T
TH1
TEMP
DET
THP
TA75W01FU(1/2)
TUNE
BPF
SIDE TONE
5C
IC411
LMC7101BIM5
10CL
MP
TXD1,RXD1
TXD2,RXD2
5C
5M
ATT
+B
GSW
TA75W01FU(1/2)
8T
DC
IC71
AMPDCAMP
8T 8T
PC
Q103
2SC3357
RF AMP
8R
IC408
TC75W51FU(1/2)
5C
TV
AUXO1~
AUXO2
AUXI/O1~
AUXI/O9
D413,D414
DA204U
Surge
Protect
RS232
DRIVER
IC416
ADM202EARN
AUXO1
PA
HOR
SCSW
CFSW
AUXO2
GSW
D3: XB15A407A2GB
IC1
RA30H4452M
POW
AMP
GATE
Q3
DTC114EE
SW
IC72
TA75W01FU(2/2)
APC
IC71
PO DET
PO REF
MP
HPF
D107,D108
D109,D110
1SV291*4
Q419
DTC363EU
MUTE
SW
INV
AM
MB
D702,D703,D709,D710
Q418
DTC114EE
1SS355,02DZ18(X,Y)
Surge
Protect
D704~D708
D711~D713,D412
DA204U
Surge
Protect
TXD1,RXD1
TXD2,RXD2
AFO
DEO
MI2
DI
ME
SB
GND
D2: XB15A709
D111: HVC131
ANT
SW
8T
TA75W01FU
1234567
POW
IC72
(2/2)
NC
TXD1 RXD1AUX I/O6 AUX I/O7 AUX I/O8 AUX I/O9GND
DI
GND MI2
8910111213
TXD2
RXD2
POW
DET
DET
D6
HSM88AS
DC
AMP
8T
HiPo: 0V/LoPo: 5V
AF AMP
IC417
TA7252AP
SB
14
15
AUXO2AUXO1
16
17181920212223
AFO
GND
DEO
ACC D-Sub 25pin
24
AUX I/O1 AUX I/O2 AUX I/O3 AUX I/O4 AUX I/O5
25
ME
LPF
POW
DET
D7
HSM88ASD8HSM88AS
GAIN
Q72
2SK1824
SW
H/L
SP
ACC 26pin
OPT3 2
TXD1 4
OPT4 6
OPT5 8
AGND 10
AI 12
5E 14
DTI 16
NC 18
OPT2 20
RXEO 22
TXI 24
8C 26
1
SB
SPI
SPO
PA
HOR
GND
6
EXT.
SP
1 OPT1
3 RXD1
5 CLK
7 USEL
9 DGND
11 AO
13 AGND
15 STON
17 TCTL
19 AUDIH
21 TXO
23 RXEI
25 OPT6
71
Page 77

TK-8180
W
e
a
Receiver Section
LEVEL DIAGRAM
Radio Frequency 44.85MHz
N
–105.5dBm
–122.0dBm –112.0dBm –117.0dBm –118.5dBm –108.0dBm
ANT
–119.5dBm
HPF BPF
Transmitter Section
W: 5.0mVrms
N: 6.3mVrms
W: 5.0mVrms
N: 6.3mVrms
Q103
L173
W: 72.5mVrms
N: 91.3mVrms
L176
IC171
W: 72.5mVrms
N: 91.3mVrms
XF171
(1/2)
W: 340mVrms
N: 180mVrms
–109.5dBm
Q171 Q172
SG input level for 12dB SINAD ar
connecting SG to each point via
TX-RX unit (B/3)
W: 140mVrms
N: 70mVrms
XF171
(2/2)
W: 96mVrms
N: 48mVrms
72
MIC
IC414
21
MIC input : 3kHz DEV. (Wide), 1.5kHz DEV. (Narrow) at 1kHz MOD.
Transmitting frequency : Center frequency
IC413
12 14
IC415
26
43
IC410
IC412
21
Q307
TX
VCO
Page 78

LEVEL DIAGRAM
455kHz Audio Frequency
TK-8180
W: –83.5dBm
N: –83.0dBm
5.5dBm
dBm
16
2
INAD are obtained Measured by
oint via a 0.01µF capacitor.
CF171/
CF172
35
IC172
W: –86.0dBm
N: –86.0dBm
200mVrms
IC412
9
AF VTVM
AF level obtained when the AF output level is adjusted for 4.00V/4Ω
with the front panel AF VOL control. Measured with AF voltmeter
connected to the external speaker jack, receiving a –53dBm SSG
signal modulated at 1kHz, DEV. WIDE 3kHz (NARROW 1.5kHz).
67
315mVrms 190mVrms 88mVrms 4.00Vrms
IC413
115
IC415
526
TX-RX unit
16 15
(B/3)Power module
IC410
IC417
15
J401
4Ω
6mVrms
8mVrms
307
TX
CO
–0.5dBm
Q313
Wattmeter by 50Ω
+2.5dBm +8dBm +17dBm
14
Q1
Q2
450~490MHz : 30W
490~520MHz : 25W
IC1
ANT
73
Page 79

TK-8180
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES: KRK-10
■ External View
(Control Head Remote Kit: 23ft/7m)
■ Parts List
✽ : New Parts
Ref. No.
1 ✽ A62-1101-01 MAIN PANEL
2 ✽ A82-0056-11 REAR PANEL
4 ✽ E30-7514-05 TRUNK CABLE
5 ✽ E37-1121-05 FLAT CABLE
7 ✽ F07-1884-03 MOLDING COVER
9 ✽ G53-1614-23 PACKING
11 ✽ H12-3163-03 PACKING FIXTURE
12 H25-0029-04 PROTECTION BAG (60/110/0.07)
13 H25-2327-04 PROTECTION BAG (100/250/0.07)
14 H25-2352-04 PROTECTION BAG (250/350/0.07)
15 ✽ H52-2042-02 ITEM CARTON CASE
17 J29-0698-03 BRACKET
A N08-0550-04 DRESSED SCREW
B ✽ N80-2608-48 PAN HEAD TAPTITE SCREW
19 ✽ N99-2040-05 SCREW SET
Address
New
Parts No. Description
parts
KRK-10
■ Components Description
Ref. No. Part Name Description
IC1,2 IC Buffer amp
D2 Varistor Current limiter
D3~6 Diode Surge protect
D9~11 Diode Surge protect
D12~20 Varistor Surge protect
INTERFACE UNIT (X46-3310-20)
C14 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
C41 CK73GB1H102K CHIP C 1000PF K
CN1 E40-6371-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR
CN2 E40-6412-05 FLAT CABLE CONNECTOR
CN3,4 E40-6377-05 PIN ASSY
L2,3 L40-1091-86 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (1.0UH)
L5,6 L40-1091-86 SMALL FIXED INDUCTOR (1.0UH)
R1 RK73GB1J473J CHIP R 47K J 1/16W
D2 MINISMDM075/24 VARISTOR
D3-6 DA204U DIODI
D9-11 DA204U DIODE
D12-20 ✽ AVRM1608080MAA VARISTOR
IC1,2 TC7WT125FU MOS IC
74
Page 80

TK-8180
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES: KRK-10
■ Exploded View and Packing
12 Protection bag (H25-0029-04)
A Dressed screw (N08-0550-04) x 2
12 Protection bag
(H25-0029-04)
7 Molding cover
(F07-1884-03)
14 Protection bag
(H25-2352-04)
4 Trunk cable
(E30-7514-05)
19 Screw set
(N99-2040-05)
13 Protection bag
(H25-2327-04)
13 Protection bag
(H25-2327-04)
11 Packing fixture
(H12-3163-03)
(Control Head Remote Kit: 23ft/7m)
13 Protection bag
(H25-2327-04)
17 Bracket
(J29-0698-03)
15 Item carton case
(H52-2042-02)
9 Packing
(G53-1614-23)
5 Flat cable
(E37-1121-05)
1 Main panel
(A62-1101-01)
4 Trunk cable
(E30-7514-05)
7 Molding cover
(F07-1884-03)
Interface unit
(X46-3310-20) (B/2)
B Pan head taptite screw
(N80-2608-48) x 4
Interface unit
(X46-3310-20) (A/2)
4 Trunk cable
(E30-7514-05)
2 Rear panel
(A82-0056-11)
B Pan head taptite screw
(N80-2608-48) x 4
7 Molding cover
(F07-1884-03)
75
Page 81

TK-8180
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES: KRK-10
■ PC Board
INTERFACE UNIT (X46-3310-20)
Component side view (J72-0934-09)
CN2
SPI
SPI
SPI
SPI
SPI
SPI
GND8CSBSBNC
PSW
GND
GND
MICMEGND
PSENS
RST2
LCDRST
LCDDI
LCDDO
CLK
SHIFTNC5C
TXD
RXD
GND
DM
PSENS
PSW
SB
8C
SPI
RST2
R1
D10
D20
D11
1
TXD RXD
8
C41
IC2
1
45
D9
5C
30
GND
SHIFT
ME
L6
L5
MIC
INTERFACE UNIT (X46-3310-20)
Foil side view (J72-0934-09)
(Control Head Remote Kit: 23ft/7m)
CN4
1
RST2
SHIFT
GND
TXD
RXD
PSENS
ME
MIC
PSW
GND
SB
8C
GND
SPI
14
J72-0934-09 B/2
J72-0934-09 A/2
76
J72-0934-09 B/2
J72-0934-09 A/2
CN3
SPI
8C
SB
L2
L3
D13
NC
PSW
GND
CN1
GND
PSENS
D16
D14
D15
ME
MIC
PSW
5C
D3
D4
D6
8
C14
IC1
45
1
D5
TXD RXD
RST2
SHIFT
D17
D18
D19
30
5C
NC
DM
CLK
TXD
RXD
GND
PSENS
RST2
LCDDI
LCDRST
LCDDO
SHIFT
GND
Component side
Layer 1
Layer 2
Foil side
MIC
ME
D2
SB
GND
D12
1
8C
SB
SPI
SPI
SPI
SPI
SPI
SPI
GND
SPI
GND
8C
SB
GND
PSW
MIC
ME
PSENS
RXD
TXD
GND
SHIFT
RST2
1
14
Component side
Layer 1
Layer 2
Foil side
Page 82

TK-8180
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES: KRK-10
■ Schematic Diagram
INTERFACE UNIT (X46-3310-20) (A/2)
CN1
1
SPI
2
SPI
3
SPI
4
SPI
5
SPI
6
SPI
7
GND
8
8C
9
SB
10
SB
11
NC
12
PSW
13
GND
14
GND
15
MIC
16
ME
17
GND
18
PSENS
19
RST2
(LCDDI)
(CLK)
SHIFT
TXD
RXD
GND
(DM)
5C
NC
E40-6371-05
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
D12
D16
D13
D17
D18
D19
D14
D15
1
2
3
4
(LCDRST)
(LCDDO)
C14 1000p
G1
A1
Y2
GND
D2
VCC
G2
IC1
Y1
A2
Radio Side
D3
D5
8
D4
7
6
5
D6
(Control Head Remote Kit: 23ft/7m)
CN3
1
SPI
2
GND
3
8C
4
SB
5
GND
6
L2 1u
L3
1u
IC1 : TC7WT125FU
D2 : MINISMDM075/24
D3~6 : DA204U
D12~19 : AVRM1608080MAA
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
E40-6377-05
PSW
MIC
ME
PSENS
RXD
TXD
GND
SHIFT
RST2
INTERFACE UNIT (X46-3310-20) (B/2)
CN4
14
SPI
13
GND
12
8C
11
SB
10
GND
9
PSW
8
MIC
7
ME
6
PSENS
5
RXD
4
TXD
3
GND
2
SHIFT
1
RST2
E40-6377-05
A
IC2 : TC7WT125FU
D9~11 : DA204U
D20 : AVRM1608080MAA
L5 1u
L6 1u
D9
Display Side
D10
A
D11
A
1
G1
2
A1
3
Y2
4
GND
D20
C41 1000p
IC2
VCC
CN2
30
SPI
29
SPI
28
SPI
27
SPI
26
SPI
25
SPI
24
GND
23
8C
22
SB
21
SB
20
NC
19
PSW
18
GND
17
GND
16
MIC
15
ME
14
GND
13
PSENS
12
RST2
11
(LCDRST)
10
(LCDDI)
9
(LCDDO)
8
(CLK)
7
SHIFT
6
NC
5
5C
4
TXD
3
RXD
2
GND
A
1
E40-6412-05
(DM)
47k
8
R1
7
G2
6
Y1
5
A2
A
77
Page 83

TK-8180
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES: KRK-10
■ Terminal Function
Pin No.
78
Name Description
CN1 (Radio side)
1 SPI Speaker input.
2 SPI Speaker input.
3 SPI Speaker input.
4 SPI Speaker input.
5 SPI Speaker input.
6 SPI Speaker input.
7 GND Ground.
88C 8V input.
9SB Power input of switched power supply.
10 SB Power input of switched power supply.
11 NC -
12 PSW Detection signal output of Power switch.
13 GND Ground.
14 GND Ground.
15 MIC MIC signal output.
16 ME MIC ground.
17 GND Ground.
18 PSENS Detection signal output of Display unit.
19 RST2 Reset signal input.
20
(LCDRST)
21 (LCDDI) Reserve.
22 (LCDDO) Reserve.
23 (CLK) Reserve.
24 SHIFT Control signal input of Beat-Shift function.
25 5C 5V input.
26 NC -
27 TXD Serial data signal input.
28 RXD Serial data signal output.
29 GND Ground.
30 (DM) Reserve.
1 (DM) Reserve.
2 GND Ground.
3 RXD Serial data signal input.
4 TXD Serial data signal output.
55C 5V input.
6NC -
7 SHIFT Control signal output of Beet-Shift function.
8 (CLK) Reserve.
9 (LCDDO) Reserve.
10 (LCDDI) Reserve.
11
(LCDRST)
12 RST2 Reset signal output.
13 PSENS Detection signal input of Display unit.
14 GND Ground.
Reserve.
CN2 (Display side)
Reserve.
(Control Head Remote Kit: 23ft/7m)
Pin No.
Name Description
15 ME MIC ground.
16 MIC MIC signal input.
17 GND Ground.
18 GND Ground.
19 PSW Detection signal input of Power switch.
20 NC -
21 SB Power output of switched power supply.
22 SB Power output of switched power supply.
23 8C 8V output.
24 GND Ground.
25 SPI Speaker output.
26 SPI Speaker output.
27 SPI Speaker output.
28 SPI Speaker output.
29 SPI Speaker output.
30 SPI Speaker output.
CN3 (Radio side)
1 SPI Speaker output.
2 GND Ground.
38C 8V output.
4SB Power output of switched power supply.
5 GND Ground.
6 PSW Detection signal input of Power switch.
7 MIC MIC signal input.
8ME MIC ground.
9 PSENS Detection signal input of Display unit.
10 RXD Serial data signal input.
11 TXD Serial data signal output.
12 GND Ground.
13 SHIFT Control signal output of Beat-Shift function.
14 RST2 Reset signal output.
CN4 (Display side)
1 RST2 Reset signal input.
2 SHIFT Control signal input of Beat-Shift function.
3 GND Ground.
4 TXD Serial data signal input.
5 RXD Serial data signal output.
6 PSENS Detection signal output of Display unit.
7ME MIC ground.
8 MIC MIC signal output.
9 PSW Detection signal output of Power switch.
10 GND Ground.
11 SB Power input of switched power supply.
12 8C 8V input.
13 GND Ground.
14 SPI Speaker input.
Page 84

OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
TK-8180
KAP-2 (Horn Alert/P.A. Relay Unit)
■ External View
KCT-40 (Radio Interface Cable)
■ External View
KMC-35 (Microphone)
■ External View
KMC-36 (Keypad Microphone)
■ External View
KCT-46 (Ignition Sense Cable)
■ External View
79
Page 85

TK-8180
GENERAL
Frequency range ....................................... 450~520MHz
Number of channels .................................. Zone : Max. 128 per radio Ch/GID : Max. 250 per zone
Channel spacing ........................................ Wide : 25kHz Narrow : 12.5kHz
Operating voltage ...................................... 13.6V DC ± 15%
Current drain
Standby.................................................. 0.4A
Receive .................................................. 1.0A
Transmit................................................. 9.0A
Duty cycle ................................................. Transmit : 20%
Operating temperature range.................... –22°F~+140°F (–30°C~+60°C)
Frequency stability .................................... ±0.00025% (–22°F~+140°F)
Antenna impedance .................................. 50Ω
Channel frequency spread ........................ 70MHz
Dimensions (W x H x D) ............................ 6-5/16 x 1-3/4 x 6-3/16 in. (160 x 45 x 157 mm)
(Projections not included)
Weight (net) .............................................. 3.31lbs. (1.5kg)
RECEIVER (Measurements made per EIA/TIA-603)
Sensitivity (12dB SINAD)........................... Wide : 0.25µVNarrow : 0.28µV
Selectivity .................................................. Wide : 80dB Narrow : 67dB
Intermodulation distortion ......................... W/N : 75dB (±50, 100kHz)
Spurious response .................................... 85dB
Audio output (4Ω impedance) ................... 4W with less than 5% distortion
SPECIFICATIONS
(Max. 512 [Conv. Ch’s + GID’s] total per radio)
TRANSMITTER (Measurements made per EIA/TIA-603)
RF power output ....................................... 30 to 1W (490~520MHz : 25 to 1W)
Spurious response .................................... 70dB
Type of emission ....................................... Wide : 16K0F3E Narrow : 11K0F3E
FM hum & noise ....................................... Wide : 50dB Narrow : 45dB
Audio distortion ......................................... W/N : 3%
Microphone impedance ............................ 600Ω
KENWOOD CORPORATION
2967-3, Ishikawa-machi, Hachioji-shi, Tokyo, 192-8525 Japan
KENWOOD U.S.A. CORPORATION
P. O. BOX 22745, 2201 East Dominguez Street, Long Beach, CA 90801-5745, U.S.A.
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS CANADA INC.
6070 Kestrel Road, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada L5T 1S8
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Rembrücker Str. 15, 63150 Heusenstamm, Germany
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS BELGIUM N.V.
Leuvensesteenweg 248 J, 1800 Vilvoorde, Belgium
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS FRANCE S.A.
13, Boulevard Ney, 75018 Paris, France
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS U.K. LIMITED
KENWOOD House, Dwight Road, Watford, Herts., WD18 9EB United Kingdom
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS EUROPE B.V.
Amsterdamseweg 37, 1422 AC Uithoorn, The Netherlands
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS ITALIA S.p.A.
Via G. Sirtori, 7/9 20129 Milano, Italy
KENWOOD IBERICA S.A.
Bolivia, 239-08020 Barcelona, Spain
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS AUSTRALIA PTY. LTD.
(A.C.N. 001 499 074)
16 Giffnock Avenue, Centrecourt Estate, North Ryde, N.S.W. 2113 Australia
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS (HONG KONG) LTD.
Unit 3712-3724, Level 37, Tower one Metroplaza, 223 Hing Fong Road, Kwai Fong, N.T., Hong Kong
KENWOOD ELECTRONICS SINGAPORE PTE LTD.
1 Genting Lane #07-00 Kenwood Building, Singapore 349544
 Loading...
Loading...