Page 1

en3700
HP Jetdirect
ew2400
620n
Administrator's
Guide
Page 2

Administrator’s Guide
HP Jetdirect Print Servers
Models: 620n
en3700
ew2400
Page 3

© 2003-2014 Copyright Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
© 2014 Copyright Hewlett-Packard Company
All rights reserved. Reproduction, adaptation, or translation without prior written
permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the copyright laws.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein
should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable
for technical or editiorial errors or omissions contained herein.
5, 11/2014
Edition
Trademark Credits
Microsoft®, MS-DOS®, Windows®, are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation. NetWare® and Novell® are registered trademarks of Novell
Corporation. IBM®, IBM Warp Server®, Operating System/2® are registered
trademarks of International Business Machines Corp. Ethernet is a registered
trademark of Xerox Corporation. PostScript is a trademark of Adobe Systems,
Incorporated. UNIX® is a registered trademark of the Open Group.
Page 4

Table of Contents
1. Introducing the HP Jetdirect Print Server
Introduction ............................................................................. 7
Supported Print Servers.......................................................... 8
Supported Network Protocols ................................................. 8
Security Protocols .................................................................. 10
Supplied Manuals.................................................................. 12
HP Support ............................................................................ 12
Product Registration.............................................................. 14
Product Accessibility ............................................................. 14
2. HP Software Solutions Summary
Introduction ........................................................................... 15
HP Jetdirect Printer Installer for UNIX .............................. 19
HP Web Jetadmin.................................................................. 20
Internet Printer Connection Software.................................. 23
HP IP/IPX Printer Gateway for NDPS................................. 26
HP WPS Assistant (Mac OS X)............................................. 27
HP LaserJet Utilities for Mac OS......................................... 28
3. TCP/IP Configuration
Introduction ........................................................................... 34
Default IP Address ................................................................ 35
Using BOOTP/TFTP.............................................................. 40
Using DHCP........................................................................... 62
Using RARP ........................................................................... 70
Using the arp and ping Commands...................................... 72
Using Telnet........................................................................... 74
Using the Embedded Web Server ......................................... 98
Using the Printer Control Panel........................................... 99
Moving to Another Network................................................ 100
4. Using the Embedded Web Server
Introduction ......................................................................... 101
Requirements....................................................................... 103
Viewing the Embedded Web Server ................................... 104
HP Jetdirect Home Tab....................................................... 107
Networking Tab ................................................................... 109
Other Links.......................................................................... 153
ENWW 4
Page 5

5. Configuring for LPD Printing
Introduction ......................................................................... 154
LPD Setup Overview ........................................................... 156
LPD on UNIX Systems........................................................ 158
LPD on Windows NT/2000/Server 2003 Systems .............. 162
LPD on Windows XP Systems............................................. 167
LPD on Mac OS Systems..................................................... 169
6. FTP Printing
Introduction ......................................................................... 172
Requirements....................................................................... 172
Print Files ............................................................................ 173
Using FTP Printing ............................................................. 173
Example of an FTP Session................................................. 178
7. Security Features
Introduction ......................................................................... 179
Using Security Features...................................................... 183
8. Troubleshooting the HP Jetdirect
Print Server
Introduction ......................................................................... 185
Resetting to Factory Defaults ............................................. 186
General Troubleshooting..................................................... 188
Troubleshooting Wireless Print Servers ........................... 196
Troubleshooting an LPD UNIX Configuration .................. 200
9. HP Jetdirect Configuration Page
Introduction ......................................................................... 202
Configuration Page Format................................................. 203
Configuration Page Messages............................................. 205
Error Messages .................................................................... 225
A. TCP/IP Overview
Introduction ......................................................................... 236
IP Address............................................................................ 237
Configuring IP Parameters................................................. 240
Subnets................................................................................. 241
Gateways.............................................................................. 242
Syslog Server ....................................................................... 242
ENWW 5
Page 6

B. The HP Jetdirect EIO Control Panel Menu
Introduction..........................................................................245
Classic Control Panel...........................................................246
Graphical Control Panel ......................................................249
C. OpenSSL Statements
Index
ENWW 6
Page 7

1
Introducing the HP Jetdirect
Print Server
Introduction
HP Jetdirect print servers allow you to connect printers and other
devices directly to a network. By attaching a device directly to a
network, you can install it in a convenient location and share it with
multiple users. In addition, a network connection allows data
transfers to or from the device at network speeds.
HP Jetdirect EIO internal print servers are installed in HP printers
that have a compatible enhanced input/output (EIO) slot.
HP Jetdirect external print servers connect printers to the network
by adapting the printer’s USB port to the network.
Note Unless otherwise specified, the term print server in
this manual refers to the HP Jetdirect print servers
and not a separate computer running print server
software.
When connected through a wireless connection to
your network, an HP Jetdirect wireless print server
provides the same printing services as Jetdirect
print servers connected by network cables.
ENWW 7
Page 8

Supported Print Servers
The features and capabilities of HP Jetdirect print servers depend
on the print server’s product model and its operating firmware
version. See Table 1.1
Table 1.1 Supported Products
.
Model Product
Number
ew2400 J7951A USB 2.0 10/100TX
en3700 J7942A USB 2.0 10/100TX Full** V.28.xx.nnnnnnnn
620n J7934A EIO slot 10/100TX Full** V.28.xx.nnnnnnnn
* Limited support includes TCP/IP, IPX Direct Mode printing, AppleTalk (EtherTalk),
LPD/Windows printing, limited upgrade capabilities.
** Full support includes TCP/IP, IPX/SPX, AppleTalk (EtherTalk), LPR/LPD, Security.
See Table 1.2
*** xx represents a release number. nnnnnnnn, if it appears, is an encoded value for
HP support use only.
Printer
Connect
.
Network
Connect
wired, or
802.11g
wireless
Network
Protocols
and Features
Limited* V.28.xx.nnnnnnnn
Firmware
Version***
The installed firmware version can be identified using various
methods, including the HP Jetdirect configuration page (see
Chapter 9
Chapter 4
updates, see “Firmware
), Telnet (see Chapter 3), embedded Web server (see
), and network management applications. For firmware
Upgrades”.
Supported Network Protocols
Note For HP Jetdirect wireless print servers, this section
assumes that a wireless connection to your network
has been established.
The supported network protocols, and popular network printing
environments that use those protocols, are listed in Table 1.2
ENWW Introducing the HP Jetdirect Print Server 8
.
Page 9
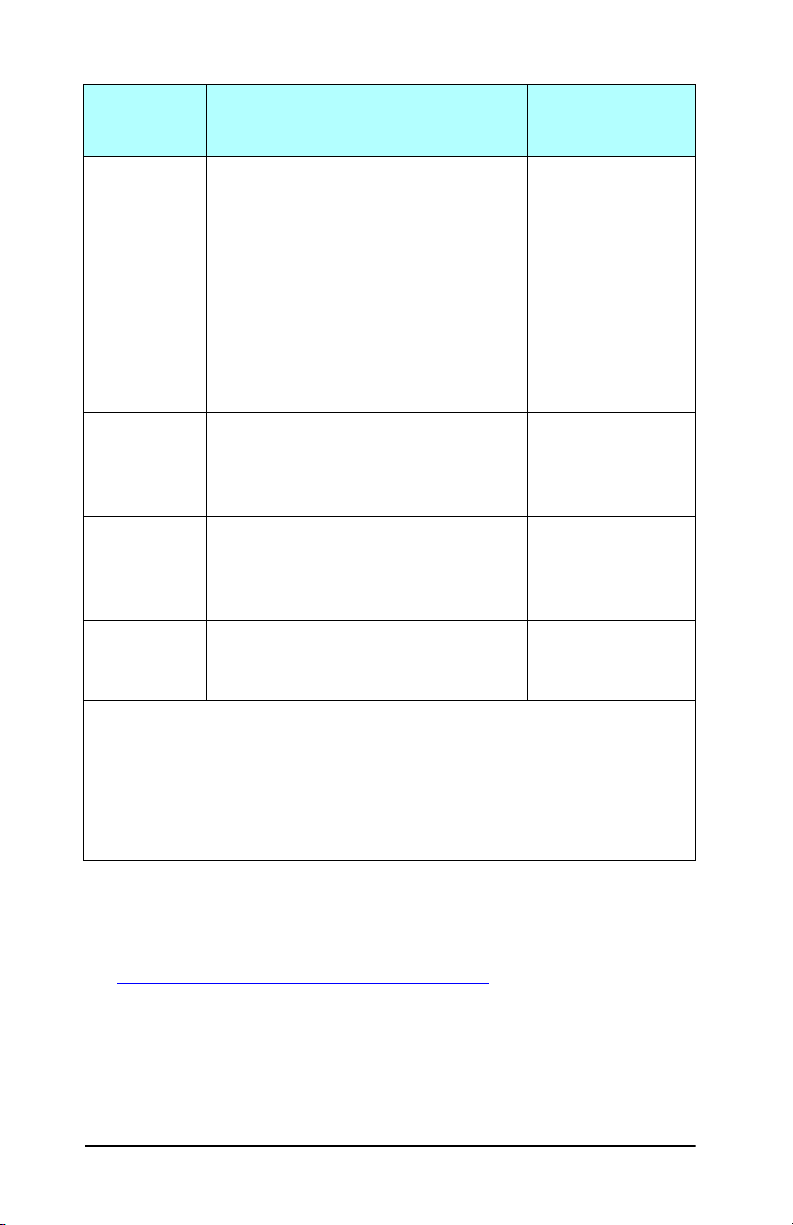
Table 1.2 Supported Network Protocols
Supported
Network
Protocols
TCP/IP Microsoft Windows 98/Me/NT4.0/2000/XP
IPX/SPX and
compatible
AppleTalk
(EtherTalk
only)
DLC/LLC Microsoft Windows NT** J7942A (en3700)
Network Printing Environments* Product Support
(32- and 64-bit), Direct Mode printing
Novell NetWare 5, 6.x using NDPS
UNIX and Linux, including:
Hewlett-Packard HP-UX, Sun
Microsystems Solaris (SPARCsystems
only), IBM AIX**, HP MPE-iX**, RedHat
Linux**, SuSE Linux**
LPR/LPD (Line Printer Daemon)**
IPP (Internet Printing Protocol)
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
Novell NetWare**
Microsoft Windows 98/Me/NT4.0/2000/XP
(32-bit only), Direct Mode printing
Apple Mac OS J7951A (ew2400)
J7951A (ew2400)***
J7942A (en3700)
J7934A (620n)
J7951A (ew2400)***
J7942A (en3700)
J7934A (620n)
J7942A (en3700)
J7934A (620n)
J7934A (620n)
* Refer to the current HP Jetdirect product data sheets for additional network systems
and versions. For operation with other network environments, consult your system
vendor or authorized HP dealer.
** For these network systems, contact your network system vendor for software,
documentation, and support.
*** Supported: Windows IP/IPX Direct Mode printing and LPD/Windows are supported.
Not Supported: NetWare, IPP, LPD/UNIX are not supported.
If not supplied with this product, HP network setup and
management software for supported systems may be obtained from
HP support at:
http://www.hp.com/support/net_printing
For software to set up network printing on other systems, contact
your system vendor.
ENWW Introducing the HP Jetdirect Print Server 9
Page 10

Security Protocols
SNMP (IP and IPX)
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is used by network
management applications for device management. HP Jetdirect
print servers support SNMP and standard MIB-II (Management
Information Base) objects on both IP and IPX networks.
HP Jetdirect ew2400 print servers support an SNMP v1/v2c agent
only.
Full-featured HP Jetdirect print servers (such as 620n and en3700)
support an SNMP v1/v2c agent, and an SNMP v3 agent for
enhanced security.
HTTPS
The following HP Jetdirect print servers support HTTPS (Secure
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) for secure, encrypted management
communications between the embedded Web server and your Web
browser.
● HP Jetdirect 620n internal print server (EIO)
● HP Jetdirect en3700 external print server
● HP Jetdirect ew2400 external wired/wireless print server
Authentication
EAP/802.1X Server-Based Authentication
As a network client, HP Jetdirect full-featured print servers (such
as 620n, en3700) support network access using the Extensible
Authentication Protocol (EAP) on an IEEE 802.1X network. The
IEEE 802.1X standard provides a port-based authentication
protocol where a port can allow or block access depending on client
authentication results.
When using an 802.1X connection, the print server supports
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) with an authentication
server, such as a RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User
Service, RFC 2138) server.
ENWW Introducing the HP Jetdirect Print Server 10
Page 11

Full-featured print servers support the following EAP/802.1X
method:
● PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol). PEAP is
a mutual authentication protocol that uses digital certificates
for network server authentication and passwords for client
authentication. For additional security, the authentication
exchanges are encapsulated within TLS (Transport Layer
Security). Dynamic encryption keys are used for secure
communications.
The network infrastructure device that connects the print server to
the network (such as an HP Procurve switch) must also support the
EAP/802.1X method used. In conjunction with the authentication
server, the infrastructure device can control the degree of network
access and services available to the print server client.
To configure the print server for EAP/802.1X authentication, you
must access the embedded Web server through your Web browser.
For more information, see Chapter 4
.
Wireless Print Server Authentication
HP Jetdirect ew2400 wired/wireless external print servers do not
support server-based authentication. They are intended for
small-office networks where authentication servers are not
typically used.
However, for security on wireless networks, some form of client
authentication is highly desired. The HP Jetdirect ew2400 supports
the following wireless authentication methods:
● Shared Key. Authentication is based on a secret, common Wired
Equivalent Privacy (WEP) key that must be configured on each
wireless device. A device that does not have the proper WEP key
cannot access the network. Static WEP encyrption protocols are
used for network communications.
● WPA-PSK. Authentication is based on Wi-Fi Protected Access
(WPA) standards through a Pre-Shared Key (PSK). When
selecting WPA-PSK authentication, a user-specified pass-phrase
must be entered to generate the pre-shared key. With WPA-PSK
authentication, dynamic WPA encryption protocols are used for
network communications to provide enhanced security.
ENWW Introducing the HP Jetdirect Print Server 11
Page 12
Supplied Manuals
The manuals listed below are supplied with your print server or
with printers that have factory-installed print servers.
● Start or Use guides, or equivalent printer documentation
(shipped with printers that have factory-installed HP Jetdirect
print servers).
● This manual, the HP Jetdirect Print Server Administrator’s
Guide for the applicable Jetdirect product models.
HP Support
HP Online Support
Click your way to a quick solution! The HP Web site:
http://www.hp.com/support/net_printing
is a great place to start for answers to questions about your
HP Jetdirect print server — 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
Firmware Upgrades
Hewlett-Packard offers downloadable firmware upgrades for
HP Jetdirect print servers that contain upgradeable memory.
The upgrades are available from the World Wide Web at:
http://www.hp.com/go/webjetadmin_firmware
Firmware Installation Tools
Note HP Jetdirect ew2400 print servers will have limited
upgrade capabilities. A network cable must be used.
A firmware upgrade through a wireless connection
is not supported.
ENWW Introducing the HP Jetdirect Print Server 12
Page 13

Firmware upgrades for supported HP Jetdirect print servers may
be installed over a network using one of the following firmware
installation tools:
● HP Jetdirect Download Manager (Windows). HP Jetdirect
Download Manager can be downloaded from HP online support
at:
http://www.hp.com/go/dlm_sw
● HP Web Jetadmin may be used on supported systems. For more
information on HP Web Jetadmin, visit:
http://www.hp.com/go/webjetadmin/
● The embedded Web server resident on the print server provides
a firmware upgrade feature using your Web browser. For more
information see Chapter 4
● FTP (File Transfer Protocol) may be used to transfer a firmware
.
upgrade image file to the print server. To start an FTP session,
use the device IP address or host name. If a password is set, it
must be entered to log into the device. After user login, typical
FTP commands to upgrade the device are illustrated below:
ftp> bin
ftp> hash
ftp> cd /download
ftp> put <firmware image filename; specify full pathname>
ftp>######### <Wait for FTP to complete the download>
ftp> bye
ENWW Introducing the HP Jetdirect Print Server 13
Page 14
HP Support By Phone
Highly trained technicians are ready to take your call. For the most
recent HP support telephone numbers and available services
worldwide, visit:
http://www.hp.com/support/support_assistance
Note For toll-free support in the USA and Canada, call
1-800-HPINVENT or 1-800-474-6836.
Note Telephone fees are the responsibility of the caller.
Rates may vary. Contact your local telephone
company for current rates.
Product Registration
To register your HP Jetdirect print server, use the following
HP Web page:
http://www.hp.com/go/jetdirect_register
Product Accessibility
Product Accessibility
For information on HP’s commitment to accessibility of HP Jetdirect
print server products:
■ Visit the HP Web site at: http://www.hp.com/accessibility
■ Send email to: accessibility@hp.com
ENWW Introducing the HP Jetdirect Print Server 14
Page 15
2
HP Software Solutions Summary
Introduction
HP provides a variety of software solutions to set up or manage your
HP Jetdirect-connected network devices. See Table 2.1
determine which software is best for you.
Note For more information on these and other solutions,
visit HP online support at:
to help you
http://www.hp.com/support/net_printing
ENWW 15
Page 16
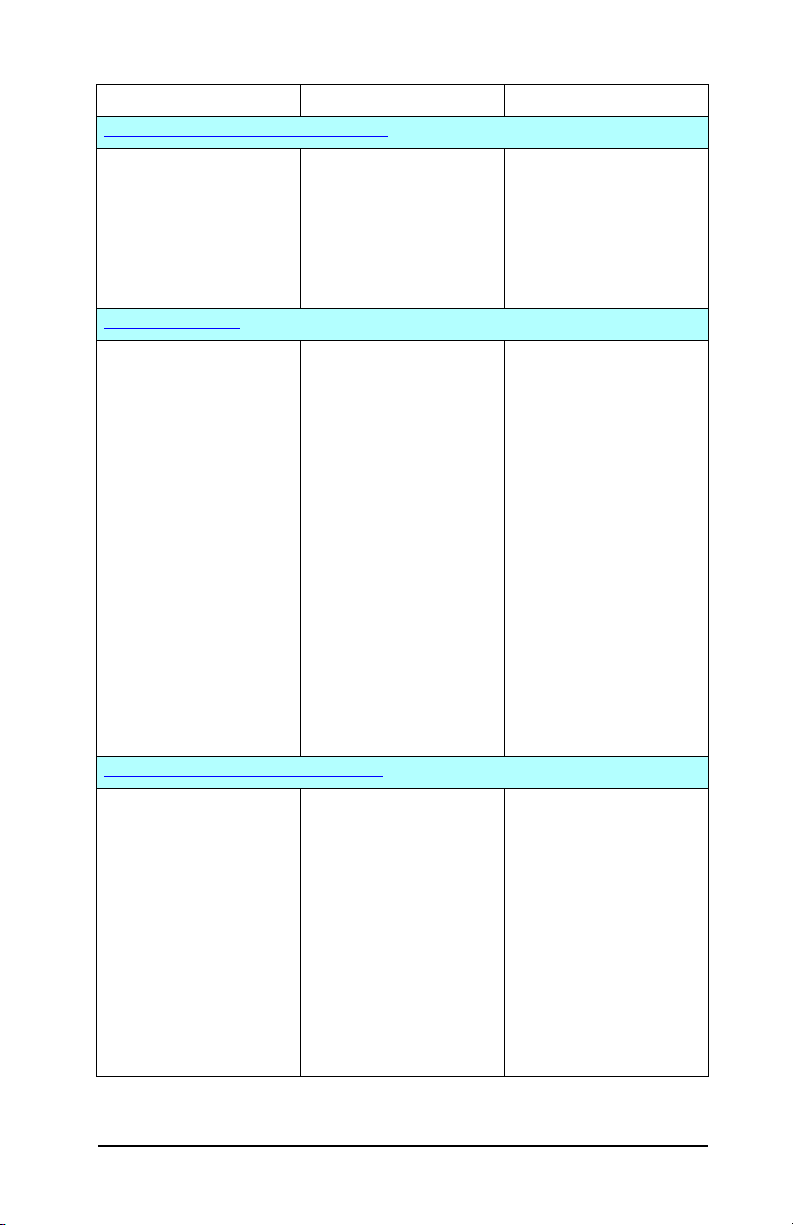
Table 2.1 Software Solutions
Operating Environment Function Remarks
HP Jetdirect Printer Installer for UNIX
HP-UX 10.x-10.20, 11.x
Solaris 2.6, 7, 8
(SPARCsystems only)
TCP/IP
HP Web Jetadmin
(See the HP Website for
supported system
updates.)
Windows 2000, XP
Professional, Server 2003
HP-UX*
Solaris*
Linux*
NetWare*
TCP/IP, IPX/SPX
*Supports queue creation
and peripheral
management from
HP Web Jetadmin hosted
on a supported system.
Internet Printer Connection Software
Windows NT 4.0, 2000
(Intel)
TCP/IP only
Note: Microsoft Internet
Printing software is also
integrated with
Windows 2000, XP, Server
2003.
Fast and easy installation
of HP Jetdirect-connected
printers.
Remote installation,
configuration, and
management of
HP Jetdirect-connected
print servers, non-HP
printers that support the
standard MIBs, and
printers with embedded
Web servers.
Alerts and consumables
management.
Remote firmware
upgrades for HP Jetdirect
print servers.
Asset tracking and
utilization analysis.
Printing through the
Internet to Internet Printing
Protocol (IPP)-enabled
HP Jetdirect-connected
printers.
● Not supported on
value-based products,
such as ew2400
● HP’s preferred solution
for ongoing
management and
installation of multiple
printers anywhere on
your intranet
● Browser-based
management
● Allows economical
distribution of
high-quality hardcopy
documents over the
Internet, replacing fax,
mail, and overnight
services
● Requires HP Jetdirect
print server (firmware
version x.20.00 or later)
● IPP is not supported on
value-based products,
such as ew2400
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 16
Page 17
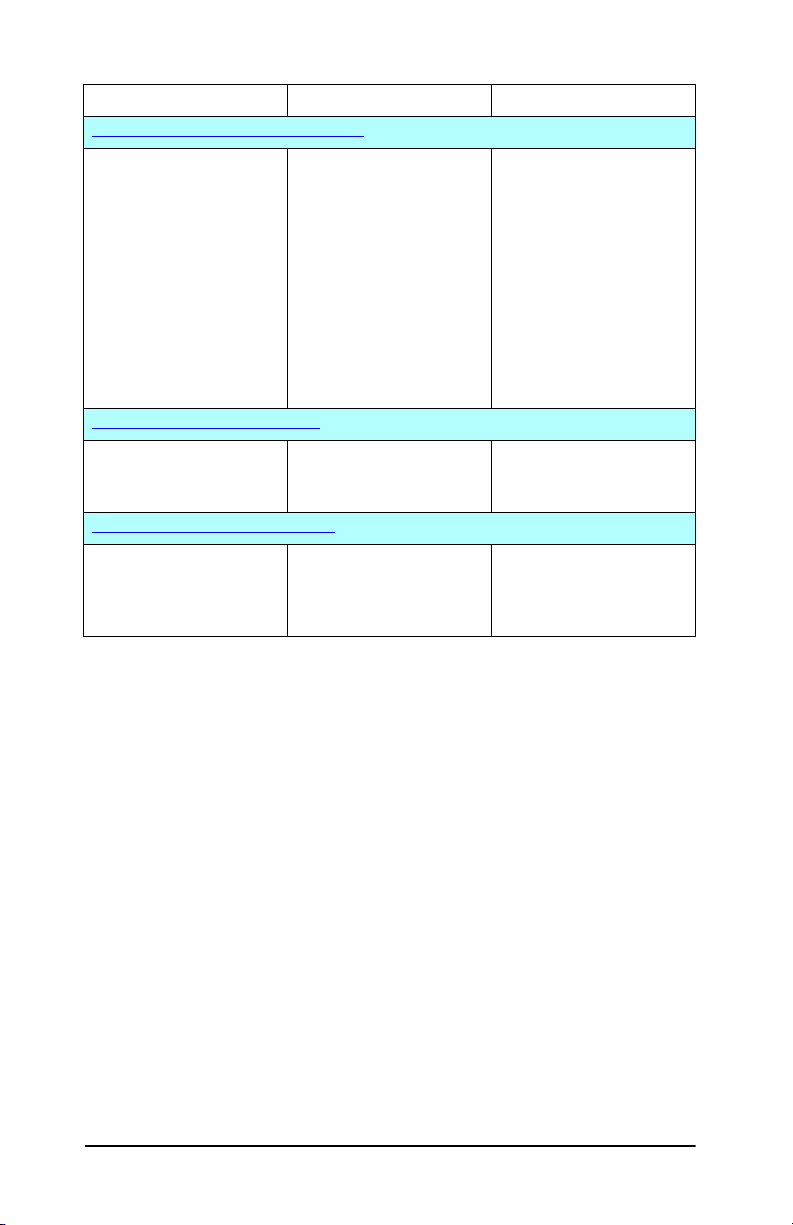
Table 2.1 Software Solutions (3 of 3)
Operating Environment Function Remarks
HP IP/IPX Printer Gateway for NDPS
NetWare 5.x, 6.x Simplified installation,
printing, and bidirectional
management of
HP Jetdirect-connected
printers under Novell
Distributed Print Services
(NDPS).
Allows automatic
discovery and installation
of HP Jetdirect-connected
printers into NDPS.
HP WPS Assistant (Mac OS X)
Mac OS X 10.1.5 or later
Configuration of HP
Jetdirect wireless print
servers.
HP LaserJet Utilities for Mac OS
Mac OS 9.x, X 10.x(Classic
Mode)
Configuration and
management of
HP Jetdirect-connected
printers.
● Frees up user licenses
● Allows disabling of
SAPs to reduce
network traffic
● Not supported on
value-based products,
such as ew2400
●
May be downloaded
from HP’s Website.
● May be downloaded
from HP’s Website.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 17
Page 18

ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 18
Page 19

HP Jetdirect Printer Installer for UNIX
The HP Jetdirect Printer Installer for UNIX contains support for
HP-UX and Solaris systems. The software installs, configures and
provides diagnostics capabilities for HP printers connected to
TCP/IP networks using full-featured HP Jetdirect print servers.
Value-based print servers, such as HP Jetdirect ew2400 print
servers, are not supported.
The software is distributed through the following methods:
● HP online support at:
http://www.hp.com/support/net_printing
For system requirements and installation information, see the
documentation provided with the software.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 19
Page 20
HP Web Jetadmin
HP Web Jetadmin is an enterprise management tool that allows
you to remotely install, configure and manage a wide variety of HP
and non-HP network printing devices simply through a standard
Web browser. HP Web Jetadmin can be used to proactively manage
both individual or groups of devices.
While HP Web Jetadmin supports devices that contain Standard
Printer MIB (Management Information Base) objects for common
management, it is well-integrated with HP Jetdirect print servers
and HP printers to provide enhanced management features.
To use HP Web Jetadmin, see the online help and documentation
supplied with the software.
System Requirements
HP Web Jetadmin software runs on Microsoft Windows
2000, Windows XP Professional, and Windows Server 2003 systems.
For information on supported operating systems, clients, and
compatible browser versions, visit HP online support at
http://www.hp.com/go/webjetadmin
Note When installed on a supported host server,
HP Web Jetadmin can be accessed from any client
through a compatible Web browser by browsing to
the HP Web Jetadmin host. This allows printer
installation and management on Novell NetWare
and other networks.
.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 20
Page 21

Installing HP Web Jetadmin
Before installing the HP Web Jetadmin software, you must have
administrator or root privileges on the local system:
1. Download the installation files from HP online support at
http://www.hp.com/go/webjetadmin
2. Follow the instructions on the screen to install the HP Web
Jetadmin software.
Note Installation instructions are also contained in the
HP Web Jetadmin install file.
Verifying Installation and Providing Access
● Verify that the HP Web Jetadmin software is correctly installed
by navigating to it with your browser as shown in the following
example:
http://systemname.domain:port/
where systemname.domain is the host name of your Web server
and port is the port number assigned during installation. By
default, the port number is 8000.
.
● Provide users access to HP Web Jetadmin software by adding a
link to your Web server’s home page that is addressed to HP Web
Jetadmin’s URL. For example:
http://systemname.domain:port/
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 21
Page 22

Configuring and Modifying a Device
Using your browser, navigate to HP Web Jetadmin’s URL.
For example:
http://systemname.domain:port/
Note In place of systemname.domain, the IP address of
the host computer on which HP Web Jetadmin is
installed can be used.
Follow the instructions on the appropriate home page to find and
manage your printer.
Removing HP Web Jetadmin Software
To remove HP Web Jetadmin software from your Web server, use
the uninstall program provided with the software package.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 22
Page 23

Internet Printer Connection Software
Full-featured HP Jetdirect print servers (such as 620n or en3700)
support the Internet Printing Protocol (IPP). Value-based print
servers (such as ew2400) are not supported.
Using the appropriate software on your system, you can create an
IPP print path from your system to a supported
HP Jetdirect-connected printer over the Internet.
Note For incoming print path requests, the network
administrator must configure the firewall to accept
incoming IPP requests. Security features available
in the software are currently limited.
Features and benefits provided by Internet printing include:
● High-quality, time-sensitive documents can be printed remotely,
in full-color or black-and-white
● Documents can be printed remotely at a fraction of the cost of
current methods (such as fax, mail, or overnight delivery
services)
● The traditional LAN printing model can be extended to that of
an Internet Printing Model
● IPP requests for sending print jobs can be transmitted outbound
through firewalls
HP-Supplied Software
HP Internet Printer Connection software allows you to set up
Internet printing from Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 clients.
1. To obtain the software:
Download the HP Internet Printer Connection software from
HP online support at:
http://www.hp.com/go/inpw_sw
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 23
Page 24
2. To install the software and set up the print path to the printer,
follow the instructions provided with the software. Contact your
network administrator to get the IP address or URL of the
printer to complete the setup.
HP Software System Requirements
● Computer running Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 (Intel-based) or
Windows 2000
● IPP-enabled HP Jetdirect print server (such as HP Jetdirect
620n or en3700)
HP Software Supported Proxies
Web proxy with support for HTTP v1.1 or greater (may not be
needed if printing over an intranet).
Microsoft Supplied Software
Note Contact Microsoft for support of Windows IPP
software.
Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003 Integrated Software
On Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003 systems, an alternative to using
the HP supplied software is to use the IPP-client software
integrated with the Windows system. The IPP implementation on
the HP Jetdirect print server is compatible with the Windows
system IPP-client software.
To set up a print path to an HP Jetdirect-connected Internet printer
using the Windows 2000/XP IPP-client software, proceed as follows:
1. Open the Printers folder (click Start, select Settings, and
select Printers).
2. Run the Add Printer wizard (double-click Add Printer), then
click Next.
3. Select the option for a network printer and click Next.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 24
Page 25
4. Select Connect to a printer on the Internet and enter the
print server’s URL:
http://IP_address[/ipp/port#]
where IP_address is the IP address configured on the
HP Jetdirect print server. [/ipp/port#] identifies the port
number, which is port 1 for single-port 620n and en3700 print
servers (default is /ipp/port1).
Example:
http://192.160.45.40 An IPP connection to HP Jetdirect
620n/en3700 print server with IP
address 192.160.45.40. (“/ipp/port1” is
assumed and not required.)
Then click Next.
5. You will be prompted for a printer driver (the HP Jetdirect
print server does not contain printer drivers, so your system
cannot automatically obtain the driver). Click OK to install the
printer driver onto your system and follow the instructions on
the screen. (You may need your printer CD-ROM to install
the driver.)
6. To complete the print path setup, follow the instructions on
the screen.
Windows Me IPP Client
The IPP implementation on the HP Jetdirect print server is
compatible with Windows Me IPP-client software. The IPP client
is installed from the Add-Ons folder on the Windows Me CD-ROM.
For installation and setup of a Windows Me IPP client, see the
instructions provided with the Windows Me CD-ROM.
Novell Supplied Software
The HP Jetdirect print server is compatible with IPP running on
NetWare 5.1 with SP1 or later. For NetWare client support, refer
to your NetWare technical documentation or contact Novell.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 25
Page 26

HP IP/IPX Printer Gateway for NDPS
NDPS (Novell Distributed Print Services) is a printing architecture
developed by Novell in partnership with Hewlett-Packard. NDPS
simplifies and streamlines the administration of network printing.
It eliminates the need to set up and link print queues, printer
objects, and print servers. Administrators can use NDPS to manage
networked printers within supported NetWare environments.
The HP IP/IPX Printer Gateway is a NetWare Loadable Module
(NLM) developed by HP to provide functionality and compatibility
with Novell's NDPS for full-featured HP Jetdirect print servers.
Value-based print servers, such as ew2400, are not supported.
The HP Gateway seamlessly integrates HP Jetdirect-attached
printers into the NDPS environment. Using the HP Gateway, an
administrator can view statistics, configure gateway settings, and
configure printing for HP Jetdirect-connected printers.
Features
Features and benefits provided by the HP Gateway and NDPS
include:
● Smart detection of printers in NetWare 5.x, 6.x environments
● Automatic installation of printers using IP/IPX
● Tight integration with Novell's NDS and NWAdmin
● Status updates from printers
● Simplified Automatic Driver Download
● Reduced SAP Traffic
● Reduced number of required NetWare User Licenses
● Native TCP/IP printing with NetWare 5.x, 6.x
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 26
Page 27
To Get the Software
The HP IP/IPX Printer Gateway is included with all current
versions of NDPS. Novell NetWare 5.x and 6.x includes NDPS.
To obtain the most recent software version, or to obtain the related
documentation:
■ Visit http://www.hp.com/go/hpgate_sw
■ Select and follow the instructions for downloading drivers and
software.
System requirements and Novell Client support are included in the
documentation supplied with the software.
Configure Mac OS X
To configure a network connection for Mac OS 9.x or X systems, use the
Embedded Web server.
Note
The HP Jetdirect wireless print server must be in a
factory default state with the wireless port enabled.
Once a wireless connection has been created, you will need to use
other utilities (such as the HP LaserJet Utility for Mac OS) to
configure and manage your printer for printing.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 27
Page 28

HP LaserJet Utilities for Mac OS
Note The HP LaserJet Utilities for Mac OS allow you to
configure and manage your HP Jetdirect-connected
printers on networks that use the AppleTalk
(EtherTalk) protocol.
On TCP/IP networks, you can use Mac OS system
utilities to discover and install your printer:
● On Mac OS 9.x systems, use the Apple Desktop
Printer Utility to set up LPR/LPD printing.
● On Mac OS X 10.x systems, use the Print Center
to select IP Printing or Rendezvous to install your
printer.
TCP/IP printer configuration is also supported
through other tools, such as the embedded Web
server.
Installing the Printer Software
To install the printer software for Mac OS systems, follow the
instructions in the documentation supplied with your printer.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 28
Page 29

Note Automatic virus detection programs might interfere
with the installation of this software. Turn off any
such programs that are active on your Mac OS
computer before proceeding with the installation
process.
For more information about configuring your printer driver, see
the online documentation provided on the CD-ROM that came with
the printer.
Configuring the Printer
The HP LaserJet Utility allows printer settings such as printer
name and preferred zone to be configured from your Mac OS system.
Hewlett-Packard recommends that only network administrators
use the printer configuration capabilities of this utility.
If this printer is to be serviced by a print spooler, set up the printer's
name and zone before configuring the spooler to capture the printer.
Running the HP LaserJet Utility
1. With the printer turned on and online, and the print server
connected to the printer and to the network, double-click the
HP LaserJet Utility icon.
2. If the printer’s name is not listed as the target printer, click
Select Printer. The Select a Target Printer window appears.
■ Select the zone, if necessary, from the AppleTalk Zones list in
which the printer resides. The zone the printer is in is shown
on the configuration page. See the hardware installation guide
for your print server or your printer's Getting Started guide
for instructions on printing a configuration page.
■ Select the printer from the Available Printers list and
click OK.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 29
Page 30
Verifying Network Configuration
To verify your current network configuration, print a Jetdirect
configuration page. If you have not printed a configuration page
from your printer, see your printer documentation for instructions
(see Chapter 9
panel, make sure a
for more information). If your printer has a control
READY message appears on the control panel for
at least 1 minute, then print the page. The current configuration is
listed under “AppleTalk” on the configuration page.
Note If you have multiple printers on your network, you
need to print a configuration page to identify the
printer’s name and zone.
Renaming the Printer
The factory supplies a default name for your printer.
Hewlett-Packard highly recommends that you rename your
printer to avoid having multiple printers with similar
names on your network.
CAUTION After you have renamed the printer and have set up
print queues to that printer, use caution when
changing the printer name again. If you rename the
printer again, the queues for that printer will no
longer function.
Note The name may be up to 32 characters in length.
A warning beep indicates that an illegal character
was typed. For illegal characters, see the Help
system integrated with the software.
You can name your printer anything you like—for example,
“Michael’s LaserJet 4000.” The HP LaserJet Utility has the ability
to rename devices located in different zones, as well as the local zone
(no zones need to be present in order to use the HP LaserJet Utility).
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 30
Page 31

1. Select the Settings icon from the scrolling icon list. The
Please select a setting: dialog appears.
2. Select Printer Name in the list.
3. Click Edit. The Set Printer Name dialog box appears.
4. Type the new name.
5. Click OK.
Note If you try to name your printer the same name
as another printer, an alert dialog box appears
directing you to select another name. To select
another name, repeat steps 4 and 5.
6. If your printer is on an EtherTalk network, continue with the
next section, “Selecting a Zone
.”
7. To exit, select Quit from the File menu.
Notify everyone on your network of the new name for your printer
so they can select the printer in the Chooser.
Selecting a Zone
The HP LaserJet Utility allows you to select a preferred zone for
your printer on a Phase 2 EtherTalk network. Instead of your
printer remaining on the default zone, which is set by the router,
this utility lets you select the zone on which your printer appears.
The zones on which your printer can reside are limited by your
network configuration. The HP LaserJet Utility only enables
you to select a zone that is already configured for your
network.
Zones are groups of computers, printers, and other AppleTalk
devices. They can be grouped by physical location (for example,
Zone A may contain all the printers on the network in building A).
They may also be grouped logically (for example, all printers used
in the finance department).
1. Select the Settings icon from the scrolling icon list. The Please
Select a Setting: dialog box appears.
2. Select Printer Zone in the list and click Edit. The Select a
Zone dialog box appears.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 31
Page 32

3. Select your preferred network zone from the Select a Zone: list
and click Set Zone.
4. To exit, select Quit from the File menu.
Notify everyone on your network of the new zone for your printer
so they can select the printer in the Chooser.
Selecting Your Printer
1. Select the Chooser from the Apple menu.
2. Select the printer icon for use with your printer. If the
appropriate printer icon does not appear in the Chooser, or you
are not sure which icon to select for your printer, see “Installing
the Printer Software” in this chapter.
3. If AppleTalk is not active, an alert dialog box appears on your
screen. Select OK. The Active button turns on.
If your network is linked to other networks, the AppleTalk
Zones list dialog box appears in the Chooser.
4. If applicable, select the zone in the AppleTalk Zones scrolling
list where your printer is located.
5. Select the printer name you want to use from the list of printer
names in the upper-right area of the Chooser. If the printer's
name does not appear in the list, make sure the following tasks
have been performed:
■ the printer is turned on and is online.
■ the print server is connected to the printer and to the network.
■ the printer cable connections are secure.
READY message should appear if the printer has a control panel
A
display. See Chapter 8
for more information.
Note If your printer is the only name listed in the
dialog box, you must still select it. Your printer
remains selected until you select a different printer
with the Chooser.
6. Click Setup or Create in the Chooser; then, if prompted, select
the appropriate PostScript Printer Description file (PPD) for the
printer. For more information, see the online documentation.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 32
Page 33

7. Set Background Printing to ON or OFF.
If background printing is turned OFF when you send a print job
to the printer, status messages appear on your screen and you
have to wait until the messages clear before continuing your
work. If background printing is turned ON, the messages are
redirected to the PrintMonitor and you can continue working
while the printer is printing your job.
8. Exit the Chooser.
To display your user name on the network when you are printing
documents, go into the Control Panel on your Mac OS computer,
select Sharing Setup, then type your owner name.
Testing the Configuration
1. Select Print Window from the File menu, or if no window is
open, select Print Desktop.
The Print dialog box appears.
2. Click Print.
If the printer prints the job, you have connected your printer to
your network correctly. If your printer does not print, see
Chapter 8
.
ENWW HP Software Solutions Summary 33
Page 34

3
TCP/IP Configuration
Introduction
To operate properly on a TCP/IP network, the HP Jetdirect print
server must be configured with valid TCP/IP network configuration
parameters, such as an IP address that is valid for your network.
For general information on TCP/IP networks, see Appendix A
Server-Based and Manual TCP/IP Configuration
When in a factory-default state and powered on, the HP Jetdirect
print server will try to obtain its TCP/IP configuration using a
server-based method, such as BOOTP/TFTP, DHCP/TFTP, or
RARP. These server-based methods are described later in this
chapter. Depending on the print server model, up to two minutes
may be used for these methods. If configuration is not successful, a
default IP address will be assigned.
.
The print server may also be configured manually. Manual-based
tools include Telnet, a Web browser, the printer control panel, arp
and ping commands (when the default IP address is 192.0.0.192),
or SNMP-based management software. TCP/IP configuration
values assigned manually will be retained when powered off/on.
The print server can be reconfigured to use either server-based or
manual configuration of TCP/IP settings at any time.
To identify the IP address that is configured on the print server at
any time, see the HP Jetdirect configuration page.
ENWW 34
Page 35

Default IP Address
When in a factory-default state (for example, when shipped from
the factory or after a cold-reset), the HP Jetdirect print server has
no IP address. A default IP address may or may not be assigned
depending on the network environment.
Default IP Address Will Not Be Assigned
A default IP address will not be assigned if a server-based method
(such as BOOTP or DHCP) is successful. And if the print server is
powered off/on, the same method will again be used to retrieve IP
configuration settings. If this method now fails to retrieve the IP
configuration settings (for example, the BOOTP or DHCP server is
no longer available), a default IP address will not be assigned.
Instead, the print server will continue to send IP configuration
requests indefinitely. You must cold-reset the print server to change
this behavior.
In addition, a default IP address will not be assigned if a network
cable is not attached to a wired print server.
Default IP Address Will Be Assigned
A default IP address will be assigned if the factory-default methods
fail, or if the print server has just been reconfigured by an
administrator to use a server-based method (such as BOOTP or
DHCP) that fails.
If a default IP address is assigned, the address will depend on the
network to which the print server is connected. The print server
senses broadcast packets on the network to determine the
appropriate default IP settings:
● On small private networks that adhere to automated,
standards-based IP address assignments, the print server uses
a link-local addressing technique to assign a unique IP address.
Link-local addressing is limited to a local IP subnet (not routed)
and may be referenced as Auto IP. The IP address assigned will
be in the range of 169.254.1.0 to 169.254.254.255 (commonly
referenced as 169.254/16). However, it can be further modified
for your network using supported TCP/IP configuration tools if
necessary.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 35
Page 36

With link-local addresses, subnetting is not used. The subnet
mask will be 255.255.0.0, and cannot be changed.
Link-local addresses will not route off the local link, and access
to or from the Internet will not be available. The default gateway
address will be the same as the link-local address.
If a duplicate address is sensed, the HP Jetdirect print server
will automatically reassign its address, if necessary, in
accordance with standard link-local addressing methods.
● On large or enterprise IP networks, a temporary address of
192.0.0.192 will be assigned until it is reconfigured with a valid
address through supported TCP/IP configuration tools. We refer
to this address as Legacy Default IP.
● On mixed-environment networks, the self-assigned default IP
address may be either 169.254/16 or 192.0.0.192. In this case,
you should verify on the Jetdirect configuration page that the
assigned default IP address is as expected.
The IP address configured on your print server may be determined
by inspecting the Jetdirect configuration page for the print server.
See Chapter 9
.
Default IP Address Configuration Options
Default IP Parameter
A Default IP configuration parameter on the print server controls
how the default IP address is assigned. Whenever the print server
is unable to obtain an IP address during a forced TCP/IP
reconfiguration (for example, when manually configured to use
BOOTP or DHCP), this parameter will determine the default IP
address to use.
When the print server is in a factory-default state, this parameter
is undefined.
If the print server is initially configured with a default IP address
(either a link-local IP address or the legacy default 192.0.0.192 IP
address), the Default IP parameter will be set to either Auto IP or
Legacy Default IP to match.
The Default IP parameter can be changed through a supported
configuration tool, such as Telnet, a Web browser, a printer control
panel, and SNMP management applications.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 36
Page 37

DHCP Requests Enable/Disable
When a default IP address is assigned, you can configure the print
server to send, or not send, periodic DHCP requests. DHCP requests
are used to retrieve IP configuration settings from a DHCP server
on the network. By default, this parameter is enabled, allowing
DHCP requests to be transmitted. However, this parameter may be
disabled through supported configuration tools such as Telnet, a
Web browser, and SNMP management applications.
HP Jetdirect Wireless Print Server. When initially powered
on, a factory-default wired/wireless print server that has no
connection to a network will likely self-assign a link-local IP
address. If a network connection to a DHCP server-based network
is made, the IP address will likely be reconfigured because DHCP
requests on the print server are enabled by default.
Default IP on Wireless and Wired Print Servers
Wired and wireless print servers may have different default IP
configuration results:
● When powered on, a factory-default print server connected to a
network through a cable (wired) will systematically use BOOTP,
DHCP, and RARP to retrieve its IP settings. Up to two minutes
are used. If configuration is not successful, a default IP address
will be assigned as described previously.
● For a factory-default wired/wireless print server that is not
connected through a cable, only a wireless Ad Hoc connection is
initially available. In this case, retrieval of IP settings from a
network is limited to about four seconds. During this time, a
single BOOTP request is transmitted, and broadcast packets
are sensed. Because a response from a BOOTP server on an Ad
Hoc network is unlikely, and the number of broadcast packets
sensed will be minimal, a default IP configuration using
link-local addressing is likely.
However, the IP configuration may change once the wireless
print server is connected a DHCP network because the sending
of DHCP requests will be enabled by default.
Configuration tools that require a specific default IP address on the
print server for initial communication may not work without
modification. For the default IP address settings actually
configured on the print server, see the Jetdirect configuration page.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 37
Page 38

TCP/IP Configuration Tools
When a network connection has been established, an HP Jetdirect
print server can be configured with valid TCP/IP parameters for
your network in the following ways:
● Using Software. You can use installation, setup, and
management software running on supported systems. For more
information see Chapter 2
● BOOTP/TFTP. You can download the data from a
network-based server using BOOTP (Bootstrap Protocol) and
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) each time the printer is
turned on. For more information, see “Using BOOTP/TFTP
The BOOTP daemon, bootpd, must be running on a BOOTP
server that is accessible by the printer.
● DHCP/TFTP. You can use Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) and TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) each
time the printer is turned on. These protocols are supported on
HP-UX, Solaris, Red Hat Linux, SuSE Linux, Windows
NT/2000/Server 2003, NetWare and Mac OS systems. (Refer to
your network operating system manuals to verify that your
server operating system supports DHCP.) For more
information, see “Using DHCP
, “HP Software Solutions Summary”.
”.
”.
Note Linux and UNIX systems: For more information,
see the bootpd “man” page.
On HP-UX systems, a sample DHCP configuration
file (dhcptab) may be located in the /etc directory.
Since HP-UX presently does not provide Dynamic
Domain Name Services (DDNS) for its DHCP
implementations, HP recommends that you set all
print server lease durations to infinite. This ensures
that print server IP addresses remain static until
such time as Dynamic Domain Name Services
are provided.
● RARP. A network-based server can use RARP (Reverse Address
Resolution Protocol) to answer the print server's RARP request
and supplying the print server with the IP address. The RARP
method only allows you to configure the IP address. For more
information, see “Using RARP
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 38
”.
Page 39

● arp and ping commands. (For print servers configure with
Legacy default IP address 192.0.0.192 only) You can use the arp
and ping commands from your system. For more information,
see “Using the arp and ping Commands
● Telnet. You can set configuration parameters using Telnet. In
”.
order to set configuration parameters, set up a Telnet
connection from your system to the HP Jetdirect print server
using the default IP address. Once configured, the print server
saves the configuration when powered off/on. For more
information, see “Using Telnet
● Embedded Web server. You can browse to the embedded Web
”.
server on the HP Jetdirect print server to set configuration
parameters. For more information, see Chapter 4
● Printer Control Panel. (HP Jetdirect 620n print servers only)
.
You can manually enter the configuration data using the printer
control panel keys. The control panel method allows you to
configure only a limited subset of configuration parameters.
Therefore, control panel configuration is recommended only
during troubleshooting or for simple installations. If control
panel configuration is used, the print server saves the
configuration when powered off/on. For more information, see
“Using the Printer Control Panel
”.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 39
Page 40

Using BOOTP/TFTP
Note For HP Jetdirect wireless print servers, this section
assumes that a wireless connection to your network
has been established.
BOOTP (Bootstrap Protocol) and TFTP (Trivial File Transfer
Protocol) provide a convenient way to automatically configure the
HP Jetdirect print server for TCP/IP network operation. When
powered on, the Jetdirect print server sends a BOOTP request
message onto the network. A properly configured BOOTP server
on the network will respond with a message that contains basic
network configuration data for the Jetdirect print server. The
BOOTP server’s response may also identify a file that contains
extended configuration data for the print server. The Jetdirect print
server downloads this file using TFTP. This TFTP configuration file
may be located on the BOOTP server, or a separate TFTP server.
BOOTP/TFTP servers are typically UNIX or Linux systems.
Windows NT/2000/Server 2003 and NetWare servers can respond
to BOOTP requests. Windows NT/2000/Server 2003 servers are
configured through Microsoft DHCP services (see Using DHCP
However, Windows NT/2000/Server 2003 systems may require
third-party software for TFTP support. For setup of NetWare
BOOTP servers, refer to your NetWare documentation.
).
Note If the Jetdirect print server and BOOTP/DHCP
server are located on different subnets, IP
configuration may fail unless the routing device
supports “BOOTP Relay” (allows the transfer of
BOOTP requests between subnets).
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 40
Page 41

Why Use BOOTP/TFTP?
Using BOOTP/TFTP to download configuration data has the
following benefits:
● Enhanced configuration control of the HP Jetdirect print server.
Configuration by other methods, such as a printer control panel,
are limited to select parameters.
● Ease of configuration management. Network configuration
parameters for the entire network can be in one location.
● Ease of HP Jetdirect print server configuration. Complete
network configuration can be automatically downloaded each
time the print server is powered on.
Note BOOTP operation is similar to DHCP, but the
resulting IP parameters will be the same when
powered off/on. In DHCP, IP configuration
parameters are leased and may change over time.
When in its factory-default state and powered on, the HP Jetdirect
print server will attempt to automatically configure itself using
several dynamic methods, one of which is BOOTP.
BOOTP/TFTP on UNIX
This section describes how to configure the print server using
BOOTP (Bootstrap Protocol) and TFTP (Trivial File Transfer
Protocol) services on UNIX servers. BOOTP and TFTP are used
to download network configuration data from a server to the
HP Jetdirect print server over the network.
Systems That Use Network Information Service (NIS)
If your system uses NIS, you may need to rebuild the NIS map with
the BOOTP service before performing the BOOTP configuration
steps. Refer to your system documentation.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 41
Page 42

Configuring the BOOTP Server
For the HP Jetdirect print server to obtain its configuration data
over the network, the BOOTP/TFTP servers must be set up with
the appropriate configuration files. BOOTP is used by the print
server to obtain entries in the /etc/bootptab file on a BOOTP
server, while TFTP is used to obtain additional configuration
information from a configuration file on a TFTP server.
When the HP Jetdirect print server is powered on, it broadcasts a
BOOTP request that contains its MAC (hardware) address. A
BOOTP server daemon searches the /etc/bootptab file for a
matching MAC address, and if successful, sends the corresponding
configuration data to the Jetdirect print server as a BOOTP reply.
The configuration data in the /etc/bootptab file must be properly
entered. For a description of entries, see “Bootptab File Entries
”.
The BOOTP reply may contain the name of a configuration file
containing enhanced configuration parameters. If the HP Jetdirect
print server finds such a file, it will use TFTP to download the file
and configure itself with these parameters. For a description of
entries, see “TFTP Configuration File Entries
“. Configuration
parameters retrieved through TFTP are optional.
Note HP recommends that the BOOTP server be located
on the same subnet as the printers it serves.
BOOTP broadcast packets may not be
forwarded by routers unless the routers are
properly configured.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 42
Page 43

Bootptab File Entries
An example of a /etc/bootptab file entry for an HP Jetdirect
print server is provided below:
picasso:\
:hn:\
:ht=ether:\
:vm=rfc1048:\
:ha=0001E6123456:\
:ip=192.168.40.39:\
:sm=255.255.255.0:\
:gw=192.168.40.1:\
:lg=192.168.40.3:\
:T144=“hpnp/picasso.cfg”:
Note that the configuration data contains “tags” to identify the
various HP Jetdirect parameters and their settings. Entries and
tags supported by the HP Jetdirect print server are listed in Table
3.1.
Table 3.1 Tags Supported in a BOOTP/DHCP Boot file (1 of 4)
Item RFC
2132
Option
Description
nodename -- The name of the peripheral. This name identifies an entry
ht -- The hardware type tag. For the HP Jetdirect print server,
vm -- The BOOTP report format tag (required). Set this
ha -- The hardware address tag. The hardware (MAC) address
ip -- The IP address tag (required). This address will be the
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 43
point to a list of parameters for a specific peripheral.
nodename must be the first field in an entry. (In the
example above, nodename is “picasso”.)
set this to ether (for Ethernet). This tag must precede the
ha tag.
parameter to rfc1048.
is the link-level, or station address of the HP Jetdirect print
server. It can be found on the HP Jetdirect configuration
page as the HARDWARE ADDRESS. On HP Jetdirect
external print servers, it is printed on a label attached to
the print server.
HP Jetdirect print server’s IP address.
Page 44

Table 3.1 Tags Supported in a BOOTP/DHCP Boot file (2 of 4)
Item RFC
2132
Option
Description
sm 1 The subnet mask tag. The subnet mask will be used by
the HP Jetdirect print server to identify the portions of an
IP address that specify the network/subnetwork number
and the host address.
gw 3 The gateway IP address tag. This address identifies the
IP address of the default gateway (router) that the
HP Jetdirect print server will use for communications
with other subnets.
ds 6 DNS (Domain Name System) server’s IP address tag.
Only a single name server can be specified.
lg 7 The syslog server’s IP address tag. It specifies the server
that the HP Jetdirect print server sends syslog messages
to. For more information, see Appendix A
.
hn 12 The host name tag. This tag does not take a value but
causes the BOOTP daemon to download the host name
to the HP Jetdirect print server. The host name will be
printed on the Jetdirect configuration page, or returned on
an SNMP sysName request by a network application.
dn 15 Domain name tag. Specifies the domain name for the
HP Jetdirect print server (for example, support.hp.com). It
does not include the host name; it is not the Fully Qualified
Domain Name (such as printer1.support.hp.com).
ef 18 Extensions file tag that specifies the relative path name of
the TFTP configuration file.
Note: This tag is similar to the vendor-specific tag T144,
described below.
na 44 Tag for IP addresses of the NetBIOS-over-TCP/IP Name
Server (NBNS). A primary and secondary server may be
specified in order of preference.
lease-time 51 DHCP IP address lease duration time (seconds).
tr 58 DHCP T1 timeout, specifying the DHCP lease renewal
time (seconds).
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 44
Page 45

Table 3.1 Tags Supported in a BOOTP/DHCP Boot file (3 of 4)
Item RFC
2132
Option
Description
tv 59 DHCP T2 timeout, specifying the DHCP lease rebind time
(seconds).
T69 69 The IP address (in hexadecimal) of the preferred outgoing
e-mail SMTP (Simple Mail Transport Protocol) server, for
use with supported Scan devices.
T144 -- An HP-proprietary tag that specifies the relative path name
of the TFTP configuration file. Long path names may be
truncated. The path name must be in double quotes (for
example, “pathname”). For file format information, refer to
“TFTP Configuration File Entries
“.
Note: Standard BOOTP option 18 (extensions file path)
also allows a standard tag (ef) to specify the relative path
name of the TFTP configuration file.
T145 -- Idle Timeout option. An HP-proprietary tag to set the idle
timeout (seconds), which is the amount of time that a print
data connection may remain idle before being closed. The
range is 1 - 3600 seconds.
T146 -- Buffer Packing option. An HP-proprietary tag to set buffer
packing for TCP/IP packets.
0 (default): Normal data buffers are packed before sending
to the printer.
1: Disable buffer packing. Data is sent to the printer
when received.
T147 -- Write Mode option. An HP-proprietary tag that controls the
TCP PSH flag setting for device-to-client data transfers.
0 (default): disables this option, flag not set.
1: all-push option. The push bit is set in all data packets.
T148 -- IP Gateway Disable option. An HP-proprietary tag to
prevent configuration of a Gateway IP address.
0 (default): allows an IP address.
1: prevents a Gateway IP address to be configured.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 45
Page 46

Table 3.1 Tags Supported in a BOOTP/DHCP Boot file (4 of 4)
Item RFC
2132
Option
Description
T149 -- Interlock Mode option. An HP-proprietary tag that specifies
T150 -- TFTP server’s IP address option. An HP-proprietary tag to
T151 -- Network Configuration option. An HP-proprietary tag to
whether an acknowledgement (ACK) on all TCP packets
is required before the printer is allowed to close a Port 9100
print connection. A Port Number and Option value are
specified, in the form:
<Port Number><Option>
<Port Number>: For supported HP Jetdirect print servers,
the Port Number is 1 (default).
<Option>: Option value 0 (default) disables interlock, 1
enables.
Example: 1 1 specifies <Port 1>, <interlock enabled>
specify the TFTP server’s IP address where the TFTP
configuration file is located.
specify either “BOOTP-ONLY” or “DHCP-ONLY” requests
be sent.
A colon (:) indicates the end of a field, and a backslash (\) indicates
that the entry is continued on the next line. Spaces are not allowed
between the characters on a line. Names, such as host names, must
begin with a letter and can contain only letters, numbers, periods
(for domain names only), or hyphens. The underline character (_)
is not allowed. Refer to your system documentation or online help
for more information.
TFTP Configuration File Entries
To provide additional configuration parameters for your
HP Jetdirect print server, such as SNMP (Simple Network
Management Protocol) or non-default settings, an additional
configuration file can be downloaded using TFTP. This TFTP
configuration file’s relative path name is specified in the BOOTP
reply using the /etc/bootptab file’s T144 vendor-specific tag
(or the “ef” standard BOOTP tag) entry. An example of a TFTP
configuration file is provided below (the symbol ‘#’ denotes a
remark and is not included in the file).
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 46
Page 47

#
# Example of an HP Jetdirect TFTP Configuration File
#
# Allow only Subnet 192.168.10 access to peripheral.
# Up to 10 ‘allow’ entries can be written through TFTP.
# Up to 10 ‘allow’ entries can be written through Telnet
# or embedded Web server.
# ‘allow’ may include single IP addresses.
#
allow: 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0
#
#
# Disable Telnet
#
telnet-config: 0
#
# Enable the embedded Web server
#
ews-config: 1
#
# Detect SNMP unauthorized usage
#
auth-trap: on
#
# Send Traps to 192.168.10.1
#
trap-dest: 192.168.10.1
#
# Specify the Set Community Name
#
set-cmnty-name: 1homer2
#
# End of file
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 47
Page 48

Table 3.2 lists supported TFTP commands (HP Jetdirect firmware
version V.28.xx or later).
Table 3.3
describes the TFTP parameters.
Table 3.2 List of Supported TFTP Commands (1 of 2)
General
● passwd:
● sys-location:
● sys-contact:
TCP/IP Main
● host-name:
● parm-file:
● domain-name:
● pri-dns-svr:
TCP/IP Print Options
● 9100-printing:
● ftp-printing:
● ipp-printing:
● lpd-printing:
● banner:
TCP/IP Raw Print Ports
● raw-port:
TCP/IP Access Control
● allow: netnum [mask]
TCP/IP Other Settings
● syslog-config:
● syslog-svr:
● syslog-max:
● syslog-priority:
● syslog-facility:
● slp-config:
● slp-keep-alive:
● ttl-slp:
● mdns-config:
● mdns-service-name:
● mdns-pri-svc:
● ssl-state:
● security-reset:
● tftp-parameter-attribute:
● sec-dns-svr:
● pri-wins-svr:
● sec-wins-svr:
● smtp-svr:
● interlock:
● buffer-packing:
● write-mode:
● mult-tcp-conn:
● ipv4-multicast:
● idle-timeout:
● user-timeout:
● ews-config:
● tcp-mss:
● tcp-msl:
● telnet-config:
● default-ip:
● default-ip-dhcp:
● dhcp-arbitration:
● phone-home-config:
● web-refresh:
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 48
Page 49

Table 3.2 List of Supported TFTP Commands (2 of 2)
SNMP
● snmp-config:
● get-cmnty-name:
● set-cmnty-name:
IPX/SPX
● ipx-config:
● ipx-unit-name:
● ipx-frametype:
● ipx-sapinterval:
● ipx-nds-tree:
AppleTalk
● appletalk:
● name-override:
DLC/LLC
● dlc/llc-config:
Other Settings
● link-type:
● upgrade:
● webscan-config:
● scan-idle-timeout:
● scan-email-config:
Support
● support-name:
● support-number:
● auth-trap:
● trap-dest:
● ipx-nds-context:
● ipx-job-poll:
● pjl-banner:
● pjl-eoj:
● pjl-toner-low:
● MFP-config:
● usb-mode:
● status-page-lang:
● network-select:
● support-url:
● tech-support-url:
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 49
Page 50

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (1 of 12)
General
passwd:
(passwd-admin:)
A password (up to 16 alphanumeric characters) that allows administrators to
control changes of HP Jetdirect print server configuration parameters through
Telnet, HP Web Jetadmin, or embedded Web server. The password may be
cleared by a cold reset.
sys-location:
(host-location:, location:)
Identifies the physical location of the printer (SNMP sysLocation object). Only
printable ASCII characters are allowed. The maximum length is 64 characters. The
default location is undefined. (Example: 1st floor, south wall)
sys-contact:
(host-contact:, contact:)
ASCII character string (up to 64 characters) that identifies the person who
administers or services the printer (SNMP sysContact object). This may include
how to contact this person. The default contact is undefined.
ssl-state:
Sets the print server’s security level for Web communications:
1 (default): Forced redirection to the HTTPS port. Only HTTPS (secure HTTP)
communications can be used.
2: Disable forced redirection to HTTPS. Both HTTP and HTTPS communications
can be used.
security-reset:
Reset security settings on the print server to factory default values. 0 (default) does
not reset, 1 resets the security settings.
tftp-parameter-attribute:
Specifies whether TFTP parameters can be manually overwritten on the print
server (for example, through Telnet) after it has been configured by TFTP.
tftp-ro (default): Do not allow TFTP parameters to be manually changed, and
always overwrite manual configurations.
tftp-rw: Allow TFTP parameters to be manually changed, and always overwrite
manual configurations.
manual-ro: Do not allow TFTP parameters to overwrite manually configured
parameters.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 50
Page 51

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (2 of 12)
TCP/IP Main
host-name:
(sys-name:, name:)
Specifies the node name that will appear on the Jetdirect configuration page.
Default is NPIxxxxxx, where xxxxxx is the last six digits of the LAN hardware
address.
parm-file:
Specifies the path and file name whose contents are sent to the printer for printing
each time the print server is powered on. The path and filename entry is limited to
64 alphanumeric characters.
domain-name:
The domain name for the device (for example, support.hp.com). It does not
include the host name; it is not the Fully Qualified Domain Name (such as
printer1.support.hp.com).
pri-dns-svr:
(dns-srv)
The IP address of the DNS (Domain Name System) server.
sec-dns-svr:
The IP address of a secondary DNS server to use if the primary DNS server is
unavailable.
pri-wins-svr:
(pri-wins-srv:)
The IP address of the primary Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) server.
sec-wins-svr:
(sec-wins-srv:)
The IP address of the secondary Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) server.
smtp-svr:
The IP address of the outgoing e-mail Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP)
server, for use with supported Scan devices.
TCP/IP Print Options
9100-printing:
(9100-config:)
Enables or disables printing to TCP port 9100 on the print server. 0 disables,
1 (default) enables.
ftp-printing:
(ftp-config:, ftp:)
Enables or disables the ability to print through FTP: 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 51
Page 52

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (3 of 12)
ipp-printing:
(ipp-config:, ipp:)
Enables or disables the ability to print through IPP: 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
lpd-printing:
(lpd-config:, lpd:)
Enables or disables LPD (Line Printer Daemon) printing services on the Jetdirect
print server. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
banner:
A port-specific parameter that specifies printing an LPD banner page. 0 disables
banner pages. 1 (default) enables banner pages.
interlock:
(interlock-mode:)
Specifies whether an acknowledgement (ACK) on all TCP packets is required
before the printer is allowed to close a Port 9100 print connection. A Port Number
and Option value are specified. For current HP Jetdirect print servers, the Port
Number is 1. Option value 0 (default) disables interlock, 1 enables. For example,
“interlock 1 1” specifies Port 1, interlock enabled.
buffer-packing:
(packing:)
Enables or disables buffer packing for TCP/IP packets.
0 (default): is normal, the data buffer is packed before sending to the printer.
1: disables buffer packing, data is sent to the printer as it is received.
write-mode:
Controls the setting of the TCP PSH flag for device-to-client data transfers.
0 (default): disables this option, flag is not set.
1: all-push option. The push bit is set in all data packets.
mult-tcp-conn:
Enables or disables multiple TCP connections.
0 (default): allows multiple connections.
1: disables multiple connections.
TCP/IP Raw Print Ports
raw-port:
(addrawport:)
Specifies additional ports for printing to TCP port 9100. Valid ports are 3000 to
9000, which are application-dependent.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 52
Page 53

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (4 of 12)
TCP/IP Access Control
allow: netnum [mask]
Makes an entry into the host access list stored on the HP Jetdirect print server.
Each entry specifies a host or network of hosts that are allowed to connect to the
printer. The format is “allow: netnum [mask]” where netnum is a network number
or host IP address, and mask is an address mask of bits applied to the network
number and host address to verify access. Up to 10 access list entries are allowed.
If there are no entries, all hosts are permitted access. For example,
allow: 192.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 allows hosts on network 192.
allow: 192.168.1.2 allows a single host. In this case, the default mask
255.255.255.255 is assumed and is not required.
allow: 0 This entry clears the host access list.
For additional information, see Chapter 7
TCP/IP Other Settings
syslog-config:
Enables or disables syslog server operation on the print server: 0 disables,
1 (default) enables.
syslog-svr:
(syslog-srv:)
The syslog server’s IP address. It specifies the server that the HP Jetdirect print
server sends syslog messages to. For more information, see Appendix A
syslog-max:
Specifies the maximum number of syslog messages that can be sent by the
HP Jetdirect print server on a per-minute basis. This setting allows administrators
to control the log file size. The default is 10 per minute. If it’s set to zero, the number
of syslog messages is not restricted.
syslog-priority:
Controls the filtering of syslog messages sent to the syslog server. The filter
range is 0 to 8, with 0 being the most specific and 8 the most general. Only
messages that are lower than the filter level specified (or higher in priority) are
reported. The default is 8, messages of all priorities are sent. If 0, all syslog
messages are disabled.
syslog-facility:
A code used to identify the source facility of a message (for example, to identify
the source of selected messages during troubleshooting). By default, the
HP Jetdirect print server uses LPR as the source facility code, but local user values
of local0 through local7 can be used to isolate individual or groups of print servers.
slp-config:
Enables or disables the Service Location Protocol (SLP) operation on the print
server: 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
.
.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 53
Page 54

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (5 of 12)
slp-keep-alive:
Specifies a time period for the print server to send multicast packets on the network
to prevent being deleted from network device tables. Some infrastructure devices,
such as switches, may delete active devices from their device tables due to
inactivity on the network. To enable this feature, set a value from 1 to 1440 minutes.
Set 0 to disable this feature.
ttl-slp:
Specifies the IP multicast “Time To Live” (TTL) setting for Service Location Protocol
(SLP) packets. The default value is 4 hops (the number of routers from the local
network). The range is 1-15. When set to a -1, multicast capability is disabled.
mdns-config:
Enables or disables Multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) services. 0 disables,
1 (default) enables. mDNS is typically used on small networks for IP address and
name resolution (through UDP port 5353) where a conventional DNS server is
neither used or available.
mdns-service-name:
Specifies an alphanumeric string of up to 64 ASCII characters assigned to this
device or service. This name is persistent and is used to resolve a particular device
or service if socket information (such as the IP address) changes from session to
session. Apple Rendezvous will display this service. The default service name is
the printer model and the LAN Hardware (MAC) address.
mdns-pri-svc:
Specifies the mDNS highest priority service to use for printing.To set this
parameter, choose one of the following printing option numbers:
1: Port 9100 printing
2: IPP port printing
3: The default LPD raw queue
4: The default LPD text queue
5: The default LPD auto queue
6: The default LPD binps (binary postscript) queue
7 through 12: If user-specified LPD queues are defined, corresponds to
user-specified LPD queues 5 through 10.
The default selection will depend on the printer, typically port 9100 printing or LPD
binps.
ipv4-multicast:
Enables or disables the receipt and transmission of IP version 4 multicast packets
by the print server. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 54
Page 55

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (6 of 12)
idle-timeout:
The number of seconds that an idle print data connection is allowed to remain
open. Since the card supports only a single TCP connection, the idle timeout
balances the opportunity of a host to recover or complete a print job against the
ability of other hosts to access the printer. The acceptable values range from 0 to
3600 (1 hour). If “0” is typed, the timeout mechanism is disabled. The default is
270 seconds.
user-timeout:
(telnet-timeout:)
An integer (1..3600) that specifies the number of seconds that your Telnet or FTP
session can be idle before it will be automatically disconnected. The default is 900
seconds. 0 disables the timeout.
CAUTION: Small values, such as 1-5, may effectively disable the use of Telnet.
A Telnet session may terminate before any changes can be made.
ews-config:
(web:)
Enables or disables the print server’s embedded Web server to change
configuration values: 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
tcp-mss:
(subnets-local:)
Specifies the maximum segment size (MSS) that the HP Jetdirect print server will
advertise for use when communicating with local subnets (Ethernet MSS=1460
bytes or more) or remote subnets (MSS=536 bytes):
0 (default): All networks are assumed to be local (Ethernet MSS=1460 bytes or
more).
1: Use MSS=1460 bytes (or more) for subnets, and MSS=536 bytes for remote
networks.
2: All networks are assumed to be remote (MSS=536 bytes), except the local
subnet.
MSS affects performance by helping to prevent IP fragmentation that may result
in data retransmission.
tcp-msl:
Specifies the maximum segment life (MSL) in seconds. The range is 5 - 120
seconds. The default is 15 seconds.
telnet-config:
(telnet:)
If set to 0, this parameter instructs the print server not to allow incoming Telnet
connections. To regain access, change the setting in the TFTP configuration file
and power cycle the print server, or cold reset the print server to factory default
values. If this parameter is set to 1, incoming Telnet connections are allowed.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 55
Page 56

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (7 of 12)
default-ip:
Specifies the IP address to use when the print server is unable to obtain an IP
address from the network during a forced TCP/IP reconfiguration (for example,
when powered off/on or manually configured to use BOOTP/DHCP).
DEFAULT_IP: sets the legacy default IP address 192.0.0.192.
AUTO_IP: sets a link-local IP address 169.254.x.x.
The initial setting is determined by the IP address obtained when first powered on.
default-ip-dhcp:
Specifies whether DHCP requests will be periodically transmitted when a legacy
default IP address 192.0.0.192 or link-local IP address 169.254.x.x has been
automatically assigned.
0: Disables DHCP requests.
1 (default): Enables DHCP requests.
dhcp-arbitration:
Specifies the amount of time, in seconds, that the print server will wait for DHCP
configuration offers. A value from 1 to 10 may be set. The default is 5 seconds.
phone-home-config:
Specifies privacy settings on the print server during embedded Web server access.
This command controls whether statistical data on product use may be sent to HP.
For HP to collect data, Internet access is required.
2: Prompt the user to allow sending data on initial access to the Networking tab of
the embedded Web server. This is the factory-default and cold-reset value. Once
changed, this value cannot be re-selected.
1: Allows the sending of data to HP without prompting the user.
0: Disables sending data to HP without prompting the user.
web-refresh:
Specifies the time interval (1 -99999 seconds) for embedded Web server
diagnostic page updates. If set to 0, the refresh rate is disabled.
SNMP
snmp-config:
Enables or disables SNMP operation on the print server. 0 disables, 1 (default)
enables SNMP.
CAUTION: Disabling SNMP will disable all SNMP agents (SNMP v1, v2, v3) as
well as communications with HP Web Jetadmin. In addition, firmware upgrades
through current HP downloading utilities will be disabled.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 56
Page 57

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (8 of 12)
get-cmnty-name:
(get-community-name:)
Specifies a password that determines which SNMP GetRequests the HP Jetdirect
print server will respond to. This is optional. If a user-specified get community name
is set, the print server will respond to either a user-specified community name or
the factory-default. The community name must be ASCII characters. The
maximum length is 255 characters.
set-cmnty-name:
(set-community-name:)
Specifies a password that determines which SNMP SetRequests (control
functions) the HP Jetdirect print server will respond to. The community name of
an incoming SNMP SetRequest must match the print server’s “set community
name” for the print server to respond. (For additional security, you may limit
configuration access through the print server’s host access list). Community
names must be ASCII characters. The maximum length is 255 characters.
auth-trap:
(authentication-trap:)
Configures the print server to send (on) or not send (off) SNMP authentication
traps. Authentication traps indicate that an SNMP request was received, but the
community name check failed. The default is “on.”
trap-dest:
(trap-destination:)
Enters a host’s IP address into the HP Jetdirect print server’s SNMP trap
destination list. The command format is:
trap-dest: ip-address [community name] [port number]
The default community name is ”public”; the default SNMP port number is ”162”.
The port number cannot be specified without a community name.
If a ”trap-community-name” command is followed by ”trap-dest” commands, the
trap community name will be assigned to those entries unless a different
community name is specified in each ”trap-dest” command.
To delete the table, use ”trap-dest: 0”.
If the list is empty, the print server does not send SNMP traps. The list may contain
up to three entries. The default SNMP Trap Destination List is empty. To receive
SNMP traps, the systems listed on the SNMP trap destination list must have a trap
daemon to listen to those traps.
IPX/SPX
ipx-config:
(ipx/spx:)
Enables or disables IPX/SPX protocol operation on the print server: 0 disables,
1 (default) enables.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 57
Page 58

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (9 of 12)
ipx-unit-name:
A user-assigned alphanumeric name assigned to the print server (31 characters
maximum). By default, the name will be NPIxxxxxx, where xxxxxx are the last six
digits of the LAN hardware address.
ipx-frametype:
Specify the IPX frame type setting available for your print server model: AUTO
(default), EN_SNAP, EN_8022, EN_8023, EN_II.
ipx-sapinterval:
Specifies the time interval (1 to 3600 seconds) that the HP Jetdirect print server
waits between Service Advertising Protocol (SAP) broadcasts on the network. The
default is 60 seconds. 0 disables SAP broadcasts.
ipx-nds-tree:
Identifies the name of the Novell Directory Services (NDS) tree for this printer.
ipx-nds-context:
An alphanumeric string, up to 256 characters, that specifies the NDS context for
the HP Jetdirect print server.
ipx-job-poll:
Specifies the time interval (seconds) that the HP Jetdirect print server will wait to
check for print jobs in a print queue.
pjl-banner:
(ipx-banner:)
Enables or disables printing an IPX banner page. 0 disables banner pages.
1 (default) enables banner pages.
pjl-eoj:
(ipx-eoj:)
Enables or disables IPX end-of-job notification. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
pjl-toner-low:
(ipx-toner-low:)
Enables or disables IPX toner-low notification. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
AppleTalk
appletalk:
(at-config:, ethertalk:)
Enables or disables AppleTalk (EtherTalk) protocol operation on the print server:
0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
name-override:
(External print servers only) Specifies the name of the AppleTalk network. Up to
32 characters may be used.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 58
Page 59

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (10 of 12)
DLC/LLC
dlc/llc-config:
(dlc/llc:)
Enables or disables DLC/LLC protocol operation on the print server: 0 disables,
1 (default) enables.
Other Settings
link-type:
(10/100 Fast Ethernet) Sets the print server’s link speed (10 or 100 Mbps) and
communication mode (Full- or Half-Duplex). Selections are AUTO, 100FULL,
100HALF, 10FULL, 10HALF.
For AUTO (default), the print server uses autonegotiation to determine the link
speed and mode. If autonegotiation fails, then 100HALF is set.
upgrade:
To configure one or more Jetdirect print servers with the name and location of a
firmware upgrade file.
CAUTION: Ensure that command parameters are properly entered and that the
upgrade file is a higher version than the currently installed version. The print server
will attempt to upgrade when the upgrade file contains a higher version than the
installed version.
The command format is:
upgrade: <TFTP server IP> <Version> <Product Number> <Filename>
where,
TFTP Server IP is the IP address of the TFTP server,
Version specifies the firmware version of the upgrade file,
Product Number specifies and must match the product number of the print server,
Filename is the path and filename of the firmware upgrade file.
webscan-config:
Enables or disables the Web Scan feature on the print server when connected to
a supported device. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
scan-idle-timeout:
Specifies the number of seconds (1 - 3600) that an idle scan connection is allowed
to remain open. 0 disables the timeout. The default is 300 seconds.
scan-email-config:
Enable or disable the scan-to-email feature in the Web Scan server. 0 disables,
1 (default) enables.
MFP-config:
Enable or disable print server support of the client software provided with your
multifunction or all-in-one peripheral.
0 (default): disables client software support (allows printing only).
1: enables client software support (allows printing and scanning).
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 59
Page 60

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (11 of 12)
usb-mode:
Specifies the communication mode over the USB port on the HP Jetdirect print
server.
● Auto (default): Automatically negotiates and sets the highest
communication mode possible for the attached printer or device.
● MLC: (Multiple Logical Channels) An HP-proprietary communication mode that
allows multiple channels of simultaneous print, scan and status
communications.
● BIDIR: A standard connection that supports bi-directional communications
between the printer and print server. The print server sends print data and
receives status from the printer.
● UNIDIR: A standard connection in which data is transferred in one direction
only (to the printer).
status-page-lang:
Specifies the page description language (PDL) that the print server will use to send
the Jetdirect configuration/status page to the printer.
● Auto (default): The PDL is auto-detected when the print server is powered on
or after a cold-reset.
● PCL: Hewlett-Packard Printer Control Language
● ASCII: Standard ascii characters
● HPGL2: Hewlett-Packard Graphics Language (v2)
● PS: Postscript language
network-select:
(For HP Jetdirect products with a dual wired/wireless port, such as model ew2400)
Specifies the active behavior of the print server.
● Auto (default): Automatically detects whether a network cable is attached. If a
network cable is not attached, only the IEEE 802.11g wireless port will be
active. However, if a network cable is attached, then only the IEEE 802.3 wired
port will be active. Use caution when plugging in a network cable on an
active wireless network. Wireless access to the device will be terminated.
● Wired: Only the 802.3 wired port will be active.
● Wireless: Only the 802.11g wireless port will be active.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 60
Page 61

Table 3.3 TFTP Configuration File Parameters (12 of 12)
Support
support-name:
(support-contact:)
Typically used to identify the name of a person to contact for support of this device.
support-number:
Typically used to specify a phone number or extension to call for support of this
device.
support-url:
A Web URL for product information on this device over the Internet or an intranet.
tech-support-url:
A Web URL for technical support over the Internet or an intranet.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 61
Page 62

Using DHCP
Note For HP Jetdirect wireless print servers, this section
assumes that a wireless connection to your network
has been established.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP, RFC 2131/2132) is
one of several auto configuration mechanisms that the HP Jetdirect
print server uses. If you have a DHCP server on your network, the
HP Jetdirect print server automatically obtains its IP address
from that server and registers its name with any RFC 1001
and 1002-compliant dynamic name services as long as a WINS
(Windows Internet Naming Service) server IP address has been
specified.
A TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) configuration file may also
be used with DHCP to configure extended parameters. For more
information on TFTP parameters, see “Using BOOTP/TFTP
Note DHCP services must be available on the server.
Refer to your system documentation or online help
to install or enable DHCP services.
”.
Note If the Jetdirect print server and BOOTP/DHCP
server are located on different subnets, IP
configuration may fail unless the routing device
allows the transfer of DHCP requests between
subnets.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 62
Page 63

UNIX Systems
For more information on setting up DHCP on UNIX systems, see
the bootpd man page.
On HP-UX systems, a sample DHCP configuration file (dhcptab)
may be located in the /etc directory.
Since HP-UX presently does not provide Dynamic Domain Name
Services (DDNS) for its DHCP implementations, HP recommends
that you set all print server lease durations to “infinite”. This
ensures that print server IP addresses remain static until dynamic
domain name services are provided.
Windows Systems
HP Jetdirect print servers support IP configuration from a
supported Windows DHCP server. This section describes how to set
up a pool, or “scope,” of IP addresses that the Windows server can
assign or lease to any requester. When configured for BOOTP or
DHCP operation and powered on, the HP Jetdirect print
server automatically sends a BOOTP or DHCP request for its IP
configuration. If properly set up, a Windows DHCP server will
respond with the print server’s IP configuration data.
Note This information is provided as an overview. For
specific information or for additional support, see
the information supplied with your DHCP server
software.
Note To avoid problems resulting from IP addresses
that change, HP recommends that all printers
be assigned IP addresses with infinite leases or
reserved IP addresses.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 63
Page 64

Windows NT 4.0 Server
To set up a DHCP scope on a Windows NT 4.0 server, perform the
following steps:
1. At the Windows NT server, open the Program Manager window
and double-click the Network Administrator icon.
2. Double-click the DHCP Manager icon to open this window.
3. Select Server and select Server Add.
4. Type the server IP address, then click OK to return to the
DHCP Manager window.
5. In the list of DHCP servers, click on the server you have just
added, then select Scope and select Create.
6. Select Set up the IP Address Pool. In the IP Address Pool
section, set up the IP address range by typing the beginning IP
address in the Start Address box and the ending IP address in
the End Address box. Also type the subnet mask for the subnet
to which the IP address pool applies.
The starting and ending IP addresses define the end points of
the address pool assigned to this scope.
Note If desired, you can exclude ranges of IP addresses
within a scope.
7. In the Lease Duration section, select Unlimited, then
select OK.
HP recommends that all printers be assigned infinite leases to
avoid problems resulting from IP addresses that change. Be
aware, however, that selecting an unlimited lease duration for
the scope causes all clients in that scope to have infinite leases.
If you want clients on your network to have finite leases, you
can set the duration to a finite time, but you should configure
all printers as reserved clients for the scope.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 64
Page 65

8. Skip this step if you have assigned unlimited leases in the
previous step. Otherwise, select Scope and select Add
Reservations to set up your printers as reserved clients. For
each printer, perform the following steps in the Add Reserved
Clients window to set up a reservation for that printer:
a. Type the selected IP address.
b. Obtain the MAC address or hardware address from the
configuration page, and type this address in the Unique
Identifier box.
c. Type the client name (any name is acceptable).
d. Select Add to add the reserved client. To delete a
reservation, in the DHCP Manager window, select Scope
and select Active Leases. In the Active Leases window,
click on the reservation you want to delete and
select Delete.
9. Select Close to return to the DHCP Manager window.
10. Skip this step if you are not planning to use WINS (Windows
Internet Naming Service). Otherwise perform the following
steps when configuring your DHCP server:
a. From the DHCP Manager window, select DHCP Options
and select one of the following:
Scope — if you want Name Services only for the
selected scope.
Global — if you want Name Services for all scopes.
b. Add the server to the Active Options list. From the DHCP
Options window, select WINS/NBNS Servers (044) from
the Unused Options list. Select Add, then select OK.
A warning may appear requesting that you set the node
type. You do this in step 10d.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 65
Page 66

c. You must now provide the IP address of the WINS server
by doing the following:
● Select Value, then Edit Array.
● From the IP Address Array Editor, select Remove to
delete any undesired addresses previously set. Then
type in the IP address of the WINS server and select
Add.
● Once the address appears in the list of IP addresses,
select OK. This returns you to the DHCP Options
window. If the address you have just added appears in
the list of IP addresses (near the bottom of the window)
return to step 10d. Otherwise, repeat step 10c.
d. In the DHCP Options window, select WINS/NBT Node
Type (046) from the Unused Options list. Select Add to
add the node type to the Active Options list. In the Byte
box, type 0x4 to indicate a mixed node, and select OK.
11. Click Close to exit to Program Manager.
Windows 2000 Server/Server 2003
To set up a DHCP scope on a Windows 2000 server or Server 2003
system, perform the following steps:
1. Run the Windows DHCP manager utility.
■ Windows 2000: Click Start, then select Settings and
Control Panel. Open the Administrative Tools folder and
run the DHCP utility.
■ Server 2003: Click Start, then select Control Panel. Open
the Administrative Tools folder and run the DHCP utility.
2. In the DHCP window, locate and select your Windows server in
the DHCP tree.
If your server is not listed in the tree, select DHCP and click
the Action menu to add the server.
3. After selecting your server in the DHCP tree, click the Action
menu and select New Scope. This runs the Add New Scope
Wizard.
4. In the Add New Scope Wizard, click Next.
5. Enter a Name and Description for this scope, then click Next.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 66
Page 67

6. Enter the range of IP addresses for this scope (beginning IP
address and ending IP address). Also, enter the subnet mask.
then click Next.
Note If subnetting is used, the subnet mask defines
which portion of an IP address specifies the subnet
and which portion specifies the client device. For
more information, see Appendix A
.
7. If applicable, enter the range of IP addresses within the scope
to be excluded by the server. Then click Next.
8. Set the IP address lease duration for your DHCP clients. Then
click Next.
HP recommends that all printers be assigned reserved IP
addresses. This can be accomplished after you set up the scope
(see step 11
).
9. Select No to configure DHCP options for this scope later. Then
click Next.
To configure DHCP options now, select Yes and click Next.
a. If desired, specify the IP address of the router (or default
gateway) to be used by clients. Then click Next.
b. If desired, specify the Domain Name and DNS (Domain
Name System) servers for clients. Click Next.
c. If desired, specify WINS server names and IP addresses.
Click Next.
d. Select Yes to activate the DHCP options now, and click
Next.
10. You have successfully set up the DHCP scope on this server.
Click Finish to close the wizard.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 67
Page 68

11. Configure your printer with a reserved IP address within the
DHCP scope:
a. In the DHCP tree, open the folder for your scope and select
Reservations.
b. Click the Action menu and select New Reservation.
c. Enter the appropriate information in each field, including
the reserved IP address for your printer. (Note: the MAC
address for your HP Jetdirect-connected printer is
available on the HP Jetdirect configuration page.)
d. Under “Supported types”, select DHCP only, then click
Add. (Note: Selecting Both or BOOTP only will result in
a configuration through BOOTP due to the sequence in
which HP Jetdirect print servers initiate configuration
protocol requests.)
e. Specify another reserved client, or click Close. The
reserved clients added will be displayed in the
Reservations folder for this scope.
12. Close the DHCP manager utility.
NetWare Systems
NetWare 5.x servers provide DHCP configuration services for
network clients, including the HP Jetdirect print server. To set up
DHCP services on a NetWare server, refer to Novell documentation
and support.
To Discontinue DHCP Configuration
CAUTION Changes to an IP address on your HP Jetdirect
print server may require updates to printer or
system printing configurations for clients or
servers.
If you do not want your HP Jetdirect print server configured
through DHCP, you must reconfigure the print server to use a
different configuration method.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 68
Page 69

1. (For internal print servers) If you use the printer control panel
to set Manual or BOOTP configuration, then DHCP will not be
used.
2. You can use Telnet to set Manual (status indicates “User
Specified”) or BOOTP configuration, then DHCP will not
be used.
3. You can manually modify the TCP/IP parameters through a
supported Web browser using the Jetdirect embedded Web
server or HP Web Jetadmin.
If you change to BOOTP configuration, the DHCP-configured
parameters are released and the TCP/IP protocol is initialized.
If you change to Manual configuration, the DHCP-configured IP
address is released and the user-specified IP parameters are used.
Therefore, if you manually provide the IP address, you
should also manually set all of the configuration
parameters, such as subnet mask, default gateway, and
idle timeout.
Note If you choose to re-enable a DHCP configuration,
the print server will acquire its configuration
information from a DHCP server. This means that
when you choose DHCP and complete your
configuration session (using Telnet, for example),
the TCP/IP protocol for the print server is
re-initialized and all current configuration
information is deleted. The print server then
attempts to acquire new configuration information
by sending DHCP requests on the network to a
DHCP server.
For DHCP configuration through Telnet, refer to “Using Telnet” in
this chapter.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 69
Page 70

Using RARP
Note For HP Jetdirect wireless print servers, this section
assumes that a wireless connection to your network
has been established.
This section describes how to configure the print server using the
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) on UNIX and Linux
systems.
This setup procedure enables the RARP daemon running on your
system to respond to a RARP request from the HP Jetdirect print
server and to supply the IP address to the print server.
1. Turn the printer off.
2. Log onto your UNIX or Linux system as a superuser.
3. Make sure the RARP daemon is running on your system by
typing the following command at the system prompt:
ps -ef | grep rarpd (Unix)
ps ax | grep rarpd (BSD or Linux)
4. The system response should be similar to the following:
861 0.00.2 24 72 5 14:03 0:00 rarpd -a
860 0.00.5 36 140 5 14:03 0:00 rarpd -a
5. If the system does not display a process number for the RARP
daemon, see the rarpd man page for instructions on starting the
RARP daemon.
6. Edit the /etc/hosts file to add your designated IP address and
node name for the HP Jetdirect print server. For example:
192.168.45.39 laserjet1
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 70
Page 71

7. Edit the /etc/ethers file (/etc/rarpd.conf file in
HP-UX 10.20) to add the LAN hardware address/station
address (from the configuration page) and the node name
for the HP Jetdirect print server. For example:
00:01:E6:a8:b0:00 laserjet1
Note If your system uses Network Information Service
(NIS), you need to incorporate changes to the NIS
host and ethers databases.
8. Turn the printer on.
9. To verify that the card is configured with the correct IP address,
use the ping utility. At the prompt, type:
ping <IP address>
where <IP address> is the assigned address from RARP.
10. If ping does not respond, see Chapter 8
.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 71
Page 72

Using the arp and ping Commands
Note For HP Jetdirect wireless print servers, this section
assumes that a wireless connection to your network
has been established.
You can configure an HP Jetdirect print server with an IP address
using an ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) command from a
supported system. The protocol is not routable, that is, the
workstation from which the configuration is made must be located
on the same network segment as the HP Jetdirect print server.
Using the arp and ping commands with HP Jetdirect print servers
requires the following:
● Windows NT/2000/XP/Server 2003 or UNIX system configured
for TCP/IP operation
● A legacy default IP address 192.0.0.192 has been set on the print
server
● The LAN hardware (MAC) address of the HP Jetdirect print
server (specified on an HP Jetdirect configuration page, or on
a label attached to HP Jetdirect external print servers)
Note On some systems, superuser rights may be required
for the arp command.
After an IP address is assigned through arp and ping commands,
use other tools (such as Telnet, embedded Web server, or HP Web
Jetadmin software) to configure other IP parameters.
To configure a Jetdirect print server, use the following commands:
arp -s <IP address> <LAN hardware address>
ping <IP address>
where <IP address> is the desired IP address to be assigned to
the print server. The arp command writes the entries to the arp
cache on the workstation, and the ping command configures the
IP address on the print server.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 72
Page 73

Depending on the system, the LAN hardware address may require
a specific format.
For example:
● For Windows NT 4.0, 2000, XP, Server 2003
arp -s 192.168.45.39 00-01-E6-a2-31-98
ping 192.168.45.39
● For UNIX
arp -s 192.168.45.39 00:01:E6:a2:31:98
ping 192.168.45.39
Note Once the IP address has been set on the print server,
additional arp and ping commands will be ignored.
Once the IP address is configured, arp and ping
cannot be used unless the print server is reset to
factory values (see Chapter 8
).
On UNIX systems, the arp -s command may vary
between different systems.
Some BSD-based systems expect the IP address (or
host name) in reverse order. Other systems may
require additional parameters. See your system
documentation for specific command formats.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 73
Page 74

Using Telnet
Note For HP Jetdirect wireless print servers, this section
assumes that a wireless connection to your network
has been established.
This section describes how to configure the print server
using Telnet.
Although a Telnet connection may be protected by an administrator
password, Telnet connections are not secure. For networks with
high security levels, Telnet connections can be disabled on the print
server using other tools (for example, TFTP, embedded Web server,
or HP Web Jetadmin software).
Creating a Telnet Connection
To use Telnet commands with the HP Jetdirect print server, a route
must be available from your workstation to the print server. If the
print server and your computer must have a similar IP address,
that is, the network portion of their IP addresses match, chances
are that a route will exist. For information on IP address structure,
see Appendix A
.
If their IP addresses do not match, then you can either change your
workstation’s IP address to match, or you can try an operating
system command to create a route to the print server. (For example,
if the print server is configured with a legacy default IP address
192.0.0.192, a route will not likely exist.)
On Windows systems, you can use the “route” command at a
Windows command (DOS) prompt to create a route to the print
server.
For information on system command prompts, see your Windows
online help. On Windows NT systems, the command prompt utility
is in the Programs folder (click Start, Programs, Command
Prompt). On Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003 systems, it is in the
Accessories folder in the Programs or All Programs folder.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 74
Page 75

To use the route command, you will also need the IP address of your
workstation. To view it, you can enter the appropriate command at
the command prompt:
C:\> ipconfig (on Windows NT/2000/XP/Server 2003)
C:\> winipconfig (on Windows 98)
To create a route from the system command prompt, enter the
following command:
route add <Jetdirect IP Address> <system IP Address>
where <Jetdirect IP address> is the IP address configured on
the HP Jetdirect print server, and <system IP address> is the
IP address of the workstation's network card that is attached to the
same physical LAN as the print server.
For example, to create a route from your workstation with IP
address 169.254.2.1 to a print server with a default IP address of
192.0.0.192, try this command:
route add 192.0.0.192 169.254.2.1
CAUTION Using Telnet to manually set an IP address will
override dynamic IP configuration (such as
BOOTP, DHCP, or RARP), resulting in a static
configuration. In a static configuration, the IP
values are fixed and the operation of BOOTP,
DHCP, RARP and other dynamic configuration
methods may no longer function.
Whenever you are manually changing an IP
address, you should also reconfigure the subnet
mask and default gateway at the same time.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 75
Page 76

A Typical Telnet Session
Initiating a typical Telnet session is illustrated below.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 76
Page 77

To set configuration parameters, you must set up a Telnet session
from your system to the HP Jetdirect print server.
1. Type the following at the system prompt:
telnet <IP address>
where <IP address> is the IP address listed on the Jetdirect
configuration page. See Chapter 9
.
2. A connection to the HP Jetdirect print server will be displayed.
If the server responds with “connected to IP address”, press
Enter twice to make sure that the Telnet connection is
initialized.
3. If prompted for a user name and password, enter the correct
values.
By default, the Telnet interface does not require a user name or
password. If an administrator password has been set, you will
be prompted for a user name and this password before you can
enter and save Telnet command settings.
4. By default, a Command Line interface is provided. To configure
parameters using a Menu interface, enter Menu. For more
information, see “User Interface Options
”.
For a list of supported commands and parameters, see “Telnet
Commands and Parameters”.
User Interface Options
The HP Jetdirect print server provides two interface options to
enter Telnet commands: a Command Line Interface (Default)
a Menu Interface
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 77
.
and
Page 78

Command Line Interface (Default)
Using the Telnet command line interface, you can set configuration
parameters using the following procedures:
Note During a Telnet session, enter ? to view available
configuration parameters, the correct command
format, and a list of commands.
To list additional (or advanced) commands, enter
the command advanced before entering ?.
To display current configuration information,
enter /.
1. At the Telnet prompt “>” type:
<parameter>: <value>
then press Enter, where <parameter> refers to the
configuration parameter you are defining, and <value> refers
to the definitions you are assigning to that parameter. Each
parameter entry is followed by a carriage return.
See Table 3.4
for configuration parameters.
2. Repeat the previous step to set any additional configuration
parameters.
3. When you have finished typing the configuration parameters,
type exit or quit (depending on your system).
When prompted whether to save settings that you have
changed, enter Y (default) for Yes, or N for No.
If you enter save instead of exit or quit, you will not be
prompted to save settings.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 78
Page 79

Telnet Commands and Parameters. Table 3.4 lists the
available Telnet commands and parameters.
Note If a parameter is supplied dynamically (for example,
from a BOOTP or DHCP server), its value cannot
be changed using Telnet without first setting
Manual configuration. To set Manual configuration,
see the ip-config command.
Whenever you are manually changing an IP
address, you should also reconfigure the subnet
mask and default gateway at the same time.
Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (1 of 18)
User Control Commands
Command Description
? Displays the Help and Telnet commands.
/ Displays current values.
menu Displays the Menu Interface
parameters.
advanced Enables the Advanced commands. Help (?) will include the
Advanced commands in the list.
general Disables the Advanced commands. Help (?) will not include
Advanced commands (default).
save Save the configuration values and exit the session.
exit Exit the session.
export Export the settings to a file for editing, and importing through
Telnet or TFTP (this command is only supported by systems,
such as UNIX, that support input/output redirection).
General
Command Description
passwd Set the administrator password (shared with the embedded
Web server and HP Web Jetadmin). For example,
“passwd jd1234 jd1234” sets the password to jd1234.
Note that “jd1234” is entered twice for confirmation.
Up to 16 alphanumeric characters may be used. When
initiating the next Telnet session, you will be prompted for a
user name and this password.
To clear the password, enter the command without
password and confirmation entries.
Passwords may be cleared by a cold reset.
for access to configuration
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 79
Page 80

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (2 of 18)
sys-location Alpha-numeric string (up to 255 characters), typically used
to identify a location.
sys-contact Alpha-numeric string (up to 255 characters), typically used
to identify the name of a network or device administrator.
ssl-state Sets the print server’s security level for Web
communications:
1 (default): Forced redirection to the HTTPS port. Only
HTTPS (secure HTTP) communications can be used.
2: Disable forced redirection to HTTPS. Both HTTP and
HTTPS communications can be used.
security-reset Reset security settings on the print server to factory default
values. 0 (default) does not reset, 1 resets the security
settings.
Wireless 802.11 Main
Command Description
network-type Specify the 802.11g wireless network topology:
Infrastructure: The print server will communicate on the
network with other wired or wireless devices through an
Access Point.
Ad Hoc: (default) The print server will communicate with
other wireless devices directly, without using an Access
Point.
desired-ssid Specify the desired Service Set Identifier (SSID), or Network
encryption Specify the use of encryption. 0 (default) disables, 1
wep-key-method Specify the format for WEP key entry. WEP key entries must
Name, for the print server. Up to 32 alphanumeric characters
may be used.
The factory-default SSID is hpsetup in Ad Hoc mode. An
Infrastructure network SSID of hpsetup should not be
used.
If the ssid command is issued without an entry (a blank
SSID), the desired SSID will be assigned <AUTO>, where
it will associate with the first network that matches its
authentication settings.
enables.
be of the proper length.
ASCII: (default) Use alphanumeric ASCII characters (0 - 9,
a - z, A - Z). For 40/64-bit encryption, enter 5 characters. For
104/128-bit encryption, enter 13 characters. ASCII entries
are case-sensitive.
HEX: Use hexadecimal digits (0 - 9, a - f, A - F). For 40/64-bit
encryption, enter10 hexadecimal digits. For 104/128-bit
encryption, enter 26 hexadecimal digits. HEX entries are not
case-sensitive.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 80
Page 81

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (3 of 18)
wep-key Specify a static WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption
key. The print server can store up to four WEP keys using
four key positions (Key 1, 2, 3, 4). To enter a WEP key,
specify the key position followed by the encryption key value.
For example,
wep-key 1 0123456789net
assigns Key 1 with a 128-bit WEP key specified by the value
0123456789net.
You can use the wep-key-method command to specify the
format of the key value (hexadecimal digits, or alphanumeric
ASCII characters). Alternatively, you can insert an optional
parameter (ASCII or HEX) after the key position. For
example,
wep-key 1 ASCII 0123456789net
assigns Key 1 with a 128-bit WEP key specified by the
alphanumeric ASCII characters 0123456789net.
When assigning static WEP keys, ensure that key positions
and key values match other wireless devices on the network.
Ensure that all key values entered are of the same length,
and that WEP key lengths use the proper number of
characters or digits.
transmit-key Specify the WEP key position (1, 2, 3, 4) that the print server
desired-channel (Ad Hoc) Specify a desired channel that the print server will
auth-type Specify a link-based authentication method for the print
will use for encrypted communications. For example,
transmit-key 2
specifies that Key 2 will be used for encrypted
communications, matching other devices on the network.
use for Ad Hoc network association requests. For ew2400,
the default is channel 11.
10: Use channel 10 (2457 MHz).
11: Use Channel 11 (2462 MHz).
The print server will use this channel to broadcast its
availability if it fails to detect and associate with the specified
Ad Hoc network on any channel.
server before network access is allowed.
Open: (default) Use Open System authentication if your
wireless network does not require authentication for network
access. However, your network may still use WEP
encryption keys for data security.
Shared_Key: Use Shared Key authentication if your
network requires that each device be configured with the
same secret WEP key for network access.
Selecting Shared_Key is not valid with the
wpa-auth-type command when setting WPA-PSK
authentication.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 81
Page 82

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (4 of 18)
wpa-auth-type This command is not compatible with the Shared Key
authentication option in the auth-type command. Use this
command to specify WPA-PSK authentication.
PSK: WPA-PSK provides enhanced authentication where
an authentication server is not used. Instead, a Pre-shared
key provides device authentication. A Pre-shared key is
generated when you specify a network pass-phrase using
the psk-passphrase command. The dynamic-encrypt
command should be set to the Robust option.
psk-passphrase Specify a pass-phrase that is used to generate a network
dynamic-encrypt For WPA-PSK authentication, use this command to set the
802.11 Wireless Diagnostics
Command Description
Current SSID (Read-only parameter) The network name (SSID) to which
Current Channel (Read-only parameter) The channel that the wireless print
Signal Strength (Read-only parameter) The strength of the radio signal
Access Point Mac (Read-only parameter) The Media Access Control (MAC)
Pre-shared key. A pass-phrase must be from 8 to 63 ASCII
characters in the hexadecimal range 21 through 7E
(characters 0-9, a-z, A-Z and numerous special characters
including !, @, #, $, %, ^, &, (, ), _, +, =, -, {, }, [, ], \, /, “, <,
>, ?, “, ‘, ~).
print server for dynamic Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
encryption. Specify Robust as the command option.
the wireless print server connected.
server is currently using.
received by the print server.
<blank>: No radio signal detected while the print server is
scanning.
No Signal: No radio signal detected on any channel.
Poor/Marginal/Good/Excellent: Indicates the detected
signal strength level.
address of the Access Point used for Infrastructure mode
communications. For example,
00:a0:f8:38:7a:f7
specifies that the Access Point with MAC address
00a0f8387af7 was used for communicating on the network.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 82
Page 83

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (5 of 18)
TCP/IP Main
Command Description
host-name Alphanumeric string (up to 32 characters), to assign or
ip-config Specify the configuration method:
ip IP address for the print server, in dotted notation. For
subnet-mask A value (in dotted notation) that identifies the network and
default-gw The IP address of a default gateway, in dotted notation.
change the name of the network device. For example,
“host-name printer1” assigns the name “printer1” to the
device. The default host name is NPIxxxxxx, where xxxxxx
are the last six digits of the LAN hardware (MAC) address.
manual: The print server will wait for IP parameters using
manual tools (such as Telnet, embedded Web server,
control panel, installation/management software). Status
will be User Specified.
bootp: The print server will send BOOTP requests on the
network for dynamic IP configuration.
dhcp: The print server will send DHCP requests on the
network for dynamic IP configuration.
auto_ip: The print server will be automatically configured
with a unique link-local address 169.254.x.x.
example:
ip-config manual
ip 192.168.45.39
where ip-config specifies manual configuration and ip
manually sets the IP address 192.168.45.39 on the print
server.
Specifying 0.0.0.0 clears the IP address.
If you exit and save a new IP address, it must be specified
on the next Telnet connection.
host portions of an IP address in received messages. For
example,
subnet-mask 255.255.255.0
stores the subnet mask value 255.255.255.0 on the print
server. The value 0.0.0.0 disables the subnet mask. For
more information see Appendix A
.
For example,
default-gw 192.168.40.1
assigns 192.168.40.1 as the IP address of the default
gateway for the print server.
Note: If the HP Jetdirect print server is configured by DHCP
and you manually change the subnet mask or the default
gateway address, you should manually change the print
server’s IP address. This will release the DHCP-assigned
address back to the DHCP IP address pool.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 83
Page 84

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (6 of 18)
Config Server (Read-only parameter) The IP address of the server (such
as a BOOTP or DHCP server) that last configured the IP
address on the HP Jetdirect print server.
TFTP Server (Read-only parameter) The IP address of the TFTP server
TFTP Filename (Read-only parameter) The path and TFTP filename on the
domain-name The domain name for the device. For example,
pri-dns-svr IP address of the primary DNS (Domain Name System)
sec-dns-svr IP address of a secondary DNS server to use if the primary
pri-wins-svr The IP address of the primary Windows Internet Naming
sec-wins-svr The IP address of the secondary Windows Internet Naming
smtp-svr (SMTP Mail Server) The IP address of the outgoing e-mail
TCP/IP Print Options
Command Description
9100-printing Enables or disables printing to TCP port 9100 on the print
ftp-printing Enables or disables the ability to print through FTP. 0
ipp-printing Enables or disables the ability to print using IPP. 0 disables,
lpd-printing Enables or disables the ability to print using LPD. 0 disables,
banner Enables or disables printing an LPD banner page. 0 disables
that provided TFTP parameters to the HP Jetdirect print
server.
TFTP server. For example,
hpnp/printer1.cfg
domain-name support.hp.com
assigns support.hp.com as the domain name.
The domain name does not include the host name; it is not
the Fully Qualified Domain Name (such as
printer1.support.hp.com).
server.
DNS server is unavailable.
Service (WINS) server, in dotted notation.
Service (WINS) server, in dotted notation.
Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP) server, for use with
supported Scan devices.
server. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
disables, 1 (default) enables. (TCP ports 20, 21)
1 (default) enables. (TCP port 631)
1 (default) enables.(TCP port 515)
banner pages. 1 (default) enables banner pages.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 84
Page 85

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (7 of 18)
interlock Specifies whether an acknowledgement (ACK) on all TCP
packets is required before the printer is allowed to close a
Port 9100 print connection. A Port Number and Option value
are specified. For HP embedded print servers, the default
Port Number is 1. Option value 0 (default) disables interlock,
1 enables. For example,
“interlock 1 1” specifies port 1, interlock enabled.
mult-tcp-conn (Restrict Multiple Ports) Enables or disables multiple TCP
buffer-packing Enables or disables buffer packing for TCP/IP packets.
write-mode Controls the setting of the TCP PSH flag for device-to-client
TCP/IP LPD Queues
Command Description
addq Adds a user-defined queue. The queue name (up to 32
deleteq Delete a user-specified queue. The queue name must be
defaultq Name of the queue to be used if the queue specified for a
addstring Adds a user-defined character string that may be prepended
deletestring Deletes a user-defined string. The string name is specified
TCP/IP Raw Print Ports
Command Description
raw-port Specifies additional ports for printing to TCP port 9100. Valid
connections. Allows you to restrict the use of multiple ports.
1 (default): allows multiple connections.
0: disables multiple connections.
1 (default): is normal, the data buffer is packed before
sending to the printer.
0: disables buffer packing, data is sent to the printer as it is
received.
data transfers.
0 (default): disables this option, flag is not set.
1: all-push option. The push bit is set in all data packets.
displayable ASCII characters), prepend string name,
append string name, and processing queue (typically, RAW)
must be specified in the command line. Up to six
user-defined queues may be added.
specified in the deleteq command line.
print job is unknown. By default, the default queue is AUTO.
or appended to print data. Up to eight character strings may
be specified. A string name and the character string contents
are specified in the addstring command line.
in the deletestring command line.
ports are 3000 to 9000, which are application-dependent.
Up to two ports can be specified.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 85
Page 86

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (8 of 18)
TCP/IP Access Control
Command Description
allow Makes an entry into the host access list stored on the
TCP/IP Other
Command Description
syslog-config Enables or disables syslog server operation on the print
syslog-svr The syslog server’s IP address in dotted notation. It specifies
syslog-max Specifies the maximum number of syslog messages that
syslog-priority Controls the filtering of syslog messages sent to the syslog
syslog-facility A code used to identify the source facility of a message (for
HP Jetdirect print server. Each entry specifies a host or
network of hosts that are allowed to connect to the printer.
The format is “allow netnum [mask]” where netnum is a
network number or host IP address, and mask is an address
mask of bits applied to the network number and host address
to verify access. Up to 10 access list entries are allowed. If
there are no entries, all hosts are permitted access. For
example,
allow 192.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
allows hosts on network 192.
allow 192.168.1.2
allows a single host. In this case, the default mask
255.255.255.255 is assumed and is not required.
allow 0 clears the host access list.
For additional information, see Chapter 7
.
server: 0 disables, 1 (default) enables. (UDP port 514)
the server that the HP Jetdirect print server sends syslog
messages to. For example,
syslog-svr: 192.168.40.1
assigns 192.168.40.1 as the IP address of that server.
For more information, see Appendix A
.
can be sent by the HP Jetdirect print server on a per-minute
basis. This setting allows administrators to control the log
file size. The default is 10 per minute. If it’s set to zero, the
number of syslog messages is not restricted.
server. The filter range is 0 to 8, with 0 being the most
specific and 8 the most general. Only messages that are
lower than the filter level specified (or higher in priority) are
reported. The default setting is 8, where messages of all
priorities are sent.
If 0, all syslog messages are disabled.
example, to identify the source of selected messages during
troubleshooting). By default, the HP Jetdirect print server
uses LPR as the source facility code, but local user values
of local0 through local7 can be used to isolate individual or
groups of print servers.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 86
Page 87

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (9 of 18)
slp-config Enables or disables the Service Location Protocol (SLP)
operation on the print server: 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
SLP is used by selected HP software applications (through
UDP port 427) to automate device discovery.
slp-keep-alive Specifies a time period for the print server to send multicast
mdns-config Enables or disables Multicast Domain Name System
mdns-service-name Specifies an alphanumeric string of up to 64 ASCII
mDNS Domain
Name
mdns-pri-svc Specifies the mDNS highest priority service to use for
ttl-slp Specifies the IP multicast “Time To Live” (TTL) setting for
packets on the network to prevent being deleted from
network device tables. Some infrastructure devices, such as
switches, may delete active devices from their device tables
due to inactivity on the network. To enable this feature, set
a value from 1 to 1440 minutes. Set 0 to disable this feature.
(mDNS) services. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables. mDNS is
typically used on small networks for IP address and name
resolution (through UDP port 5353) where a conventional
DNS server is not available.
characters assigned to this device or service. This name is
persistent and is used to resolve a particular device or
service if socket information (such as the IP address)
changes from session to session. Apple Rendezvous will
display this service. The default service name is the printer
model and the LAN Hardware (MAC) address.
(Read-only parameter) Specifies the mDNS domain name
assigned to the device, in the form <host name>.local. If a
user-specified host name has not been assigned, the default
host name NPIxxxxxx is used, where xxxxxx are the last 6
digits of the LAN hardware (MAC) address.
printing.To set this parameter, choose one of the following
printing option numbers:
1: Port 9100 printing
2: IPP port printing
3: The default LPD raw queue
4: The default LPD text queue
5: The default LPD auto queue
6: The default LPD binps (binary postscript) queue
7 through 12: If user-specified LPD queues are defined,
corresponds to user-specified LPD queues 5 through 10.
The default selection will depend on the printer, typically port
9100 printing or LPD binps.
Service Location Protocol (SLP) packets. The default value
is 4 hops (the number of routers from the local network).
The range is 1-15. When set to a -1, multicast capability
is disabled.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 87
Page 88

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (10 of 18)
ipv4-multicast Enables or disables the receipt and transmission of IP
version 4 multicast packets by the print server. 0 disables,
1 (default) enables.
idle-timeout An integer (1to 3600) that specifies the number of seconds
user-timeout An integer (1to 3600) that specifies the number of seconds
cold-reset Sets TCP/IP factory default settings. After a cold reset,
ews-config Enables or disables the print server’s embedded Web
web-refresh Specifies the time interval (1 -99999 seconds) for embedded
tcp-mss Specifies the maximum segment size (MSS) that the
tcp-msl Specifies the maximum segment life (MSL) in seconds. The
an idle print data connection is allowed to remain open. For
example,
idle-timeout 120
assigns 120 seconds as the desired idle timeout value.
The default is 270 seconds. If set to 0, the connection will
not terminate and other hosts will not be able to make a
connection.
that your Telnet or FTP session can be idle before it will be
automatically disconnected. The default is 900 seconds.
0 disables the timeout.
CAUTION: Small values, such as 1-5, may effectively
disable the use of Telnet. A Telnet session may terminate
before any changes can be made.
power cycle the print server. Parameters for other
subsystems, such as IPX/SPX or AppleTalk, are not
affected.
server. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
For more information, see Chapter 4
.
Web server diagnostic page updates. If set to 0, the refresh
rate is disabled.
HP Jetdirect print server will advertise for use when
communicating with local subnets (Ethernet MSS=1460
bytes or more) or remote subnets (MSS=536 bytes):
0: (default) All networks are assumed to be local (Ethernet
MSS=1460 bytes or more).
1: Use MSS=1460 bytes (or more) for subnets, and
MSS=536 bytes for remote networks.
2: All networks are assumed to be remote (MSS=536 bytes),
except the local subnet.
MSS affects performance by helping to prevent IP
Fragmentation that may result in data retransmission.
range is 5 - 120 seconds. The default is 15 seconds.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 88
Page 89

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (11 of 18)
gw-disable Specifies whether or not to automatically assign the device
IP address as the gateway when a network gateway is not
configured.
0: A gateway using the device IP address will be assigned.
1: A gateway is not assigned. The gateway address 0.0.0.0
will be configured.
default-ip Specifies the IP address to use when the print server is
unable to obtain an IP address from the network during a
forced TCP/IP reconfiguration (for example, when powered
off/on or manually configured to use BOOTP/DHCP).
DEFAULT_IP: sets the legacy default IP address
192.0.0.192.
AUTO_IP: sets a link-local IP address 169.254.x.x.
The initial setting is determined by the IP address obtained
when first powered on.
default-ip-dhcp Specifies whether DHCP requests will be periodically
dhcp-fqdn-config
dhcp-fqdn-behavior
dhcp-arbitration Specifies the amount of time, in seconds, that the print
transmitted when a legacy default IP address 192.0.0.192
or link-local IP address 169.254.x.x has been automatically
assigned.
0: Disables DHCP requests.
1 (default): Enables DHCP requests.
Specifies configuration control of the Fully Qualified Domain
Name (FQDN), using either DHCP, manual configuration,
or both. The fully qualified domain name consists of the
device’s host name and domain name. Select one of the
following command values:
0 (default): DHCP may be used to supply the host name and
domain name. The host name may be changed using a
manual configuration method (such as the embedded Web
server, printer control panel, or Telnet). However, the
domain name cannot be manually changed if it was
configured through DHCP.
1: Keep DHCP settings only. Once the Fully Qualified
Domain Name is configured through DHCP, manual
changes cannot be made.
2: Keep manual settings. The settings can be manually
configured. DHCP may be used only if the settings are
factory-default values.
3: Keep manual settings only. While manual configuration
methods may be used, configuration through DHCP is not
allowed.
server will wait for DHCP configuration offers. A value from
1 to 10 may be set. The default is 5 seconds.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 89
Page 90

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (12 of 18)
phone-home-config Specifies privacy settings on the print server during
embedded Web server access. This command controls
whether statistical data on product use may be sent to HP.
For HP to collect data, Internet access is required.
2: Prompt the user to allow sending data on initial access to
the Networking tab of the embedded Web server. This is the
factory-default and cold-reset value. Once changed, this
value cannot be re-selected.
1: Allows the sending of data to HP without prompting the
user.
0: Disables sending data to HP without prompting the user.
TCP/IP Diagnostics
Command Description
Last Config IP (Read-only parameter) The IP address of the system from
TCP Conns Refused (Read-only parameter) The number of client TCP
TCP Access Denied (Read-only parameter) The number of times that client
DHCP Lease Time (Read-only parameter) DHCP IP address lease duration
DHCP Renew Time (Read-only parameter) DHCP T1 timeout, specifying the
DHCP Rebind Time (Read-only parameter) DHCP T2 timeout, specifying the
SNMP
Command Description
snmp-config Enables or disables SNMP operation on the print server.
get-cmnty-name Specifies a password that determines which SNMP
which the HP Jetdirect print server’s IP address was
configured.
connections that are refused by the print server.
systems were denied access to the print server because
there was no allowable entry in the print server’s host access
list.
time (seconds).
DHCP lease renewal time (seconds).
DHCP lease rebind time (seconds).
0 disables, 1 (default) enables SNMP.
CAUTION: Disabling SNMP will disable all SNMP agents
(SNMP v1, v2, v3) as well as communications with
management applications, such as HP Web Jetadmin. In
addition, firmware upgrades through current HP
downloading utilities will be disabled.
GetRequests the HP Jetdirect print server will respond to.
This is optional. If a user-specified get community name is
set, the print server will respond to either a user-specified
community name or the factory-default. The community
name must be ASCII characters. The maximum length is
255 characters.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 90
Page 91

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (13 of 18)
set-cmnty-name Specifies a password that determines which SNMP
SetRequests (control functions) the HP Jetdirect print server
will respond to. The community name of an incoming SNMP
SetRequest must match the print server’s “set community
name” for the print server to respond. (For additional
security, you may limit configuration access through the print
server’s host access list.) Community names must be ASCII
characters. The maximum length is 255 characters.
default-get-cmnty Enables or disables the default Get community name.
0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
Disabling this parameter may prohibit communications with
SNMP management applications.
SNMP Traps
Command Description
auth-trap Configures the print server to send (on) or not send (off)
trap-dest Enters a host IP address into the HP Jetdirect print server’s
IPX/SPX
Command Description
ipx-config Enables or disables IPX/SPX protocol operation on the print
ipx-unitname (Print Server Name) A user-assigned alphanumeric name
Address (Read-only parameter) Identifies the IPX network and node
SNMP authentication traps. Authentication traps indicate
that an SNMP request was received, but the community
name check failed. 0 is off, 1 (default) is on.
SNMP trap destination list. The command format is:
trap-dest: ip-address [community name] [port number]
The default community name is ‘public’; the default SNMP
port number is ‘162’. The port number cannot be specified
without a community name.
To delete the table, use ‘trap-dest: 0’.
If the list is empty, the print server does not send SNMP
traps. The list may contain up to three entries. The default
SNMP Trap Destination List is empty. To receive SNMP
traps, the systems listed on the SNMP trap destination list
must have a trap daemon to listen to those traps.
server. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables. For example,
ipx-config 0 will disable IPX/SPX operation.
assigned to the print server (31 characters maximum). By
default, the name will be NPIxxxxxx, where xxxxxx are the
last six digits of the LAN hardware address.
numbers detected on the network, in the form
NNNNNNNN:hhhhhhhh (hexadecimal), where
NNNNNNNN is the network number and hhhhhhhh is the
LAN hardware address of the print server.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 91
Page 92

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (14 of 18)
ipx-frametype Specifies the IPX frame type settings available for your print
server model: AUTO (default), EN_SNAP, EN_8022,
EN_8023, EN_II. For more information, see Chapter 9
ipx-sapinterval Specifies the time interval (1 to 3600 seconds) that the
ipx-mode (Read-only parameter) Specifies the NetWare mode
ipx-nds-tree An alphanumeric string, up to 31 characters, that specifies
ipx-nds-context An alphanumeric string, up to 256 characters, that specifies
ipx-job-poll Specifies the time interval (1 to 255 seconds) that the
pjl-banner
ipx-banner
pjl-eoj
ipx-eoj
pjl-toner-low
ipx-toner-low
AppleTalk
Command Description
appletalk Enables or disables AppleTalk (EtherTalk) protocol
name-override (External print servers only) Specifies the name of the
Name (Read-only parameter) The name of the printer on the
Print Type (Read-only parameter) Specifies the AppleTalk network
Zone (Read-only parameter) The name of the AppleTalk network
Phase (Read-only parameter) AppleTalk phase 2 (P2) is
HP Jetdirect print server waits between Service Advertising
Protocol (SAP) broadcasts on the network. The default is
60 seconds. 0 disables SAP broadcasts.
configured on the print server, either RPRINTER or
QSERVER mode.
the NDS tree name for the print server.
the NDS context for the HP Jetdirect print server.
HP Jetdirect print server will wait to check for print jobs in
a print queue. The default is 2 seconds.
Enables or disables printing an IPX banner page through
Printer Job Language (PJL). 0 disables banner pages. 1
(default) enables banner pages.
Enables or disables IPX end-of-job notification through PJL.
0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
Enables or disables IPX toner-low notification through PJL.
0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
operation on the print server. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
For example,
appletalk 0 will disable AppleTalk operation
AppleTalk network. Up to 32 characters may be used.
AppleTalk network. A number after the name indicates that
there are multiple devices with this name, and this is the Nth
instance of the name.
printer type reported by the Jetdirect print server. Up to three
print types may be reported.
zone on which the printer is located.
preconfigured on the HP Jetdirect print server.
.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 92
Page 93

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (15 of 18)
Status (Read-only parameter) Indicates the current AppleTalk
configuration status.
READY: Indicates the HP Jetdirect print server is awaiting
data.
DISABLED: Indicates that AppleTalk was manually
disabled.
INITIALIZING: Indicates that the print server is registering
the node address or name. An additional status message
may also be displayed.
DLC/LLC
Command Description
dlc/llc-config Enables or disables DLC/LLC protocol operation on the print
server. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables. For example,
dlc/llc-config 0 will disable DLC/LLC operation.
strict-8022 Controls DLC/LLC protocol interpretation:
0 (default): disables, that is, provides loose interpretation.
1: enables, that is, provides strict interpretation).
Other
Command Description
upgrade To configure one or more Jetdirect print servers with the
name and location of a firmware upgrade file.
CAUTION: Ensure that command parameters are properly
entered and that the upgrade file is a higher version than the
currently installed version. The print server will attempt to
upgrade when the upgrade file contains a higher version
than the installed version.
The command format is:
upgrade: <TFTP server IP> <Version> <Product Number>
<Filename>
where,
<TFTP Server IP> is the IP address of the TFTP server,
<Version> specifies the firmware version of the upgrade file,
<Product Number> specifies and must match the product
number of the print server,
<Filename> is the path and filename of the firmware
upgrade file.
laa Specifies a locally administered address (LAA) that replaces
the factory-assigned LAN Hardware (MAC) address. If LAA
is used, a user-specified string of exactly 12 hexadecimal
digits must be entered.
For Ethernet print servers, the LAA address must start with
hexadecimal X2, X6, XA, or XE, where X is any hexadecimal
digit 0 through F.
The default address is the factory-assigned address.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 93
Page 94

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (16 of 18)
webscan-config (Web Scan Config) Enables or disables the Web Scan
feature on the print server when connected to a supported
device. 0 disables, 1 (default) enables.
scan-idle-timeout Specifies the number of seconds (1 - 3600) that an idle scan
scan-email-config (Email Scan Config) Enable or disable the scan-to-email
MFP-config (MFP config) Enable or disable print server support of the
usb-mode Specifies the communication mode over the USB port on the
usb-speed (Read-only parameter, USB 2.0 products only) Specifies the
connection is allowed to remain open. 0 disables the
timeout. The default is 300 seconds.
feature in the Web Scan server. 0 disables, 1 (default)
enables.
client software provided with your multifunction or all-in-one
peripheral.
0 (default): disables client software support (allows printing
only).
1: enables client software support (allows printing and
scanning).
HP Jetdirect print server.
● Auto (default): Automatically negotiates and sets the
highest communication mode possible for the attached
printer or device.
● MLC: (Multiple Logical Channels) An HP-proprietary
communication mode that allows multiple channels of
simultaneous print, scan and status communications.
● BIDIR: A standard connection that supports
bi-directional communications between the printer and
print server. The print server sends print data and
receives status from the printer.
● UNIDIR: A standard connection in which data is
transferred in one direction only (to the printer).
autonegotiated communication speed over the USB
connection between the HP Jetdirect print server and the
device.
● Full Speed: 12 Mbits/sec as specified in the USB v2.0
specifications, compatible with USB v1.1 specifications.
● Hi-Speed: 480 Mbits/sec for USB v2.0 devices only.
● Disconnected: The USB port is not connected.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 94
Page 95

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (17 of 18)
status-page-lang Specifies the printer job language (PJL) that the print server
will use to send the Jetdirect configuration/status page to the
printer.
● Auto (default): The PDL is auto-detected when the print
server is powered on or after a cold-reset.
● PCL: Hewlett-Packard Printer Control Language
● ASCII: Standard ascii characters
● HPGL2: Hewlett-Packard Graphics Language (v2)
● PS: Postscript language
link-type (10/100 Fast Ethernet) Sets the print server’s link speed (10
network-select (For HP Jetdirect products with a dual wired/wireless port,
job-timeout (External print servers only) Specifies the time period after
Support
Command Description
Web JetAdmin URL (Read-only parameter) If HP Web Jetadmin discovers this
Web JetAdmin
Name
support-name Typically used to identify the name of a person to contact for
or 100 Mbps) and communication mode (Full- or
Half-Duplex). Selections are AUTO, 100FULL, 100HALF,
10FULL, 10HALF.
For AUTO (default), the print server uses autonegotiation to
determine the link speed and mode. If autonegotiation fails,
then 100HALF is set.
such as model ew2400) Specifies the active behavior of the
print server.
● Auto (default): Automatically detects whether a network
cable is attached. If a network cable is not attached, only
the IEEE 802.11g wireless port will be active. However,
if a network cable is attached, then only the IEEE 802.3
wired port will be active. Use caution when plugging
in a network cable on an active wireless network.
Wireless access to the device will be terminated.
● Wired: Only the 802.3 wired port will be active.
● Wireless: Only the 802.11g wireless port will be active.
which an idle connection to the printer (for example, through
the USB port) will be closed.
An integer from 30 to 4294967295 seconds may be
specified. If 0 is specified, the default value of 270 seconds
is used.
device, the URL to access HP Web Jetadmin will be
specified.
(Read-only parameter) If HP Web Jetadmin discovers this
device, the name of the HP Web Jetadmin host will be
specified (if known).
support of this device.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 95
Page 96

Table 3.4 Telnet Commands and Parameters (18 of 18)
support-number Typically used to specify a phone or extension number to
call for support of this device.
support-url A Web URL address for product information on this device
over the Internet or an intranet.
tech-support-url A Web URL address for technical support over the Internet
or an intranet.
Menu Interface
An optional Menu interface is displayed when you type menu at the
Telnet command prompt. The Menu interface eliminates the need
to memorize commands, and provides structured menu lists for easy
access to configuration parameters.
Figure 3.1
illustrates the Menu interface, using the TCP/IP menus
as an example.
● From the Main Menu screen, select and enter a menu number.
If there are submenus, select and enter a submenu number.
● If you want to change a parameter setting, enter “Y” (for “Yes”)
when prompted.
Changes to parameters are made by editing the setting through
the use of the Backspace key. If an unrecognized value is
entered, the correct entry options will be displayed.
Note Changes are not saved on the Jetdirect print server
until you exit a menu and, when prompted, choose
to save your changes.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 96
Page 97

Figure 3.1 Example: Using the Menu Interface
Main Menu
-------------------------------
1. General Menu
2. TCP/IP Menu...
3. SNMP Menu...
4. IPX/SPX Menu
5. AppleTalk Menu
6. DLC/LLC Menu
7. Other Settings
8. Support Settings
9. Wireless Settings
?. Help
e. Exit Menu
0. Exit Telnet
Enter Selection => 2
For the TCP/IP Menu, select 2.
-------------------------------
1. TCP/IP - Main Settings
2. TCP/IP - Print Options
3. TCP/IP - Raw Print Ports
4. TCP/IP - Access Control
5. TCP/IP - Other Settings
6. TCP/IP - Diagnostics
0. Return to Main Menu
TCP/IP Menu
For parameters listed in
TCP/IP Main Settings,
Enter Selection => 1
TCP/IP - Main Settings
-------------------------------
Host Name : printer1
IP Config Method : USER SPECIFIED
IP Address : 192.168.45.39
Subnet Mask : 255.255.0.0
Default Gateway : 192.168.40.1
Config Server : 192.168.2.21
TFTP Server : 192.168.2.21
TFTP File Name : hpnp/print.cfg
Domain Name : Not Specified
DNS Server : Not Specified
Pri WINS Server : Not Specified
Sec WINS Server : Not Specified
SMTP Mail Server : Not Specified
Would you like to change any of the settings? (Y/[N]):Y
select 1.
To edit these parameters, enter Y. Use the Backspace key to edit the
parameters.
Changes are not saved until you save them when you exit the session.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 97
Page 98

Using Telnet to Erase the Existing IP Settings
To erase the IP address during a Telnet session, use the following
command line entries:
1. Type cold-reset, then press Enter.
2. Type quit, then press Enter to exit Telnet.
3. Power the print server off/on.
Note This procedure resets all TCP/IP parameters, but
only affects the TCP/IP subsystem. Parameters for
other subsystems such as IPX/SPX or AppleTalk are
not affected.
To reset all parameters to factory default values,
refer to Chapter 8
.
Using the Embedded Web Server
You can set IP parameters on HP Jetdirect print servers that
support the embedded Web server. For more information, refer to
Chapter 4
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 98
.
Page 99

Using the Printer Control Panel
When supported by the printer, HP Jetdirect internal print servers
provide a configuration menu that can be accessed from the printer’s
control panel. Using this menu, you can enable or disable network
protocols and set basic network parameters.
Note For instructions on using the control panel for your
printer, refer to your printer documentation.
When accessing the HP Jetdirect menu from the printer’s control
panel, you can set the following TCP/IP network configuration
parameters:
● IP host name
● DHCP lease behavior (release or renew)
● IP address of the print server
● Subnet mask
● Default gateway address
● Syslog server address
● Idle timeout period
If you need to configure more TCP/IP parameters than allowed by
control panel configuration, use an alternate configuration tool
(such as Telnet or the embedded Web server) as described in this
chapter.
If the HP Jetdirect print server is configured with TCP/IP
parameters from the printer control panel, the configuration is
saved on the print server when powered off/on.
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 99
Page 100

Moving to Another Network
Note For HP Jetdirect wireless print servers, this section
assumes that a wireless connection to your network
has been established.
Moving an HP Jetdirect wireless print server to
another network will require a new wireless
connection to that network.
When moving an HP Jetdirect print server that is configured with
an IP address to a new network, make sure that the IP address does
not conflict with addresses on the new network. You may change
the IP address of the print server to one that can be used on the new
network, or erase the current IP address and configure another
address after it is installed on the new network. See Chapter 8
“Troubleshooting the HP Jetdirect Print Server
reset the print server to factory default settings.
If the current BOOTP server is not reachable, you may need to
locate a different BOOTP server and configure the printer to this
server.
If the print server was configured using BOOTP, DHCP or RARP,
edit the appropriate system files with updated settings. If the IP
address was manually set (for example, from the printer control
panel or Telnet), reconfigure IP parameters as described in this
chapter.
,” for instructions to
,
ENWW TCP/IP Configuration 100
 Loading...
Loading...