HIT HA12187FP Datasheet

HA12187FP
Bus Interface Driver/Receiver IC
ADE-207-174A (Z)
2nd Edition
Jun. 1999
Description
The HA12187FP was developed to be used as a bus interface driver/receiver IC in automotive audio
equipment controllers. It implements a two-wire serial bus.
Functions
• Two-input OR circuit
• Input comparator circuit
• Current output driver circuit
• Receiver input comparator circuit
• Receiver output circuit
• Standby circuit
Features
• Supports two data inputs (Pins 1 and 3 are the input pins)
• Comparators with hysteresis characteristics were adopted for the inputs
• Current drive output drivers adopted (Output current: 3.8 mA typical)
• Comparators with hysteresis characteristics were adopted for the receivers
• Wide receiver common-mode input operating range (Common-mode input operating range: 0 to 5 V
typical)
• The driver output and the receiver input can withstand high voltages (Maximum rating: 18 V)
• Standby function (The IC enters standby mode when pin 8 goes low)
• Operating power-supply voltage range: 5 V ±0.5 V
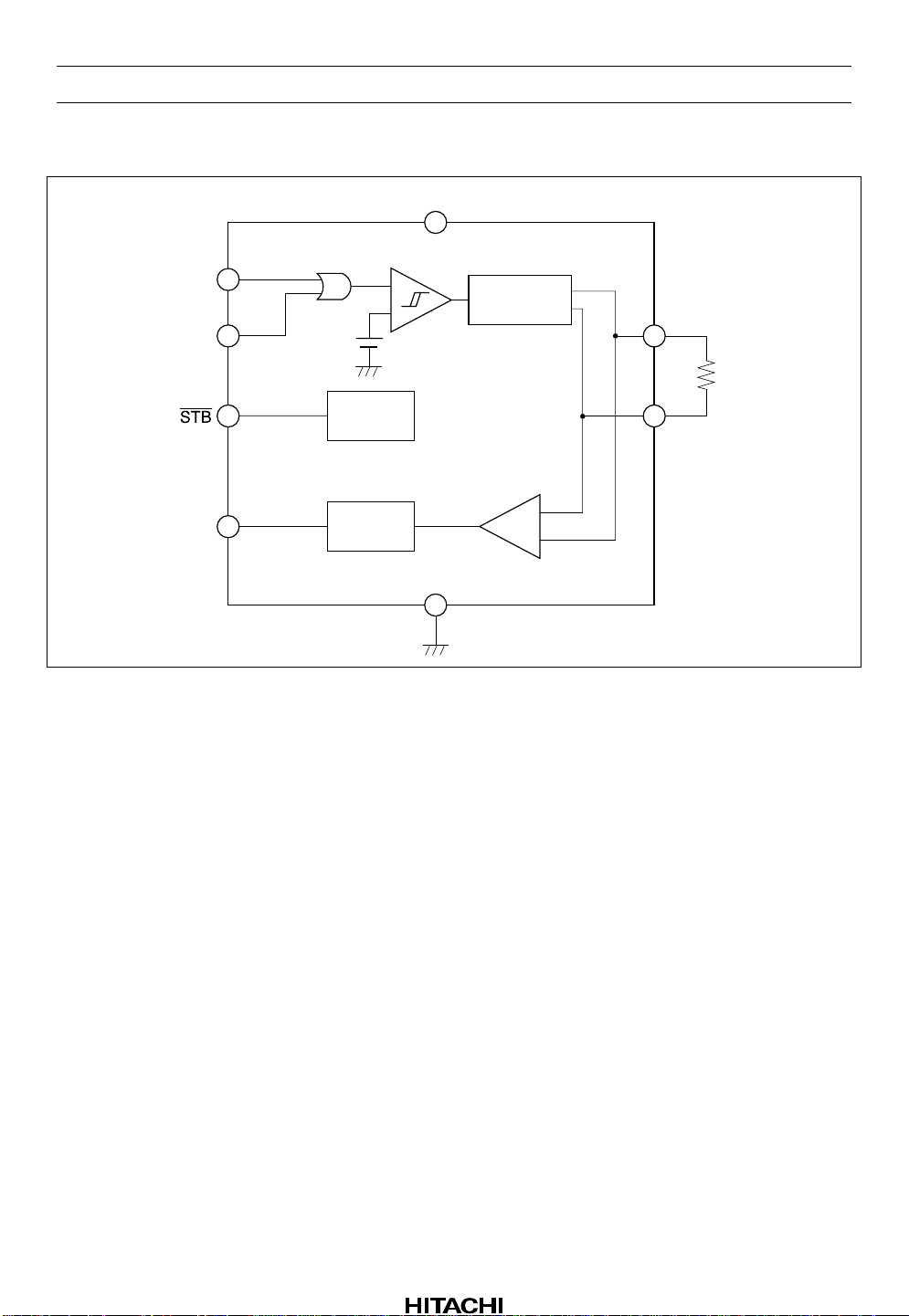
HA12187FP
Block Diagram
S1
V
CC
7
1
3S2
+
–
Driver output
(current)
BUS (+)
6
8
2R
BIAS
Receiver
output
COM
5
BUS (–)
–
+
4
Rev.2, Jun. 1999, page 2 of 23
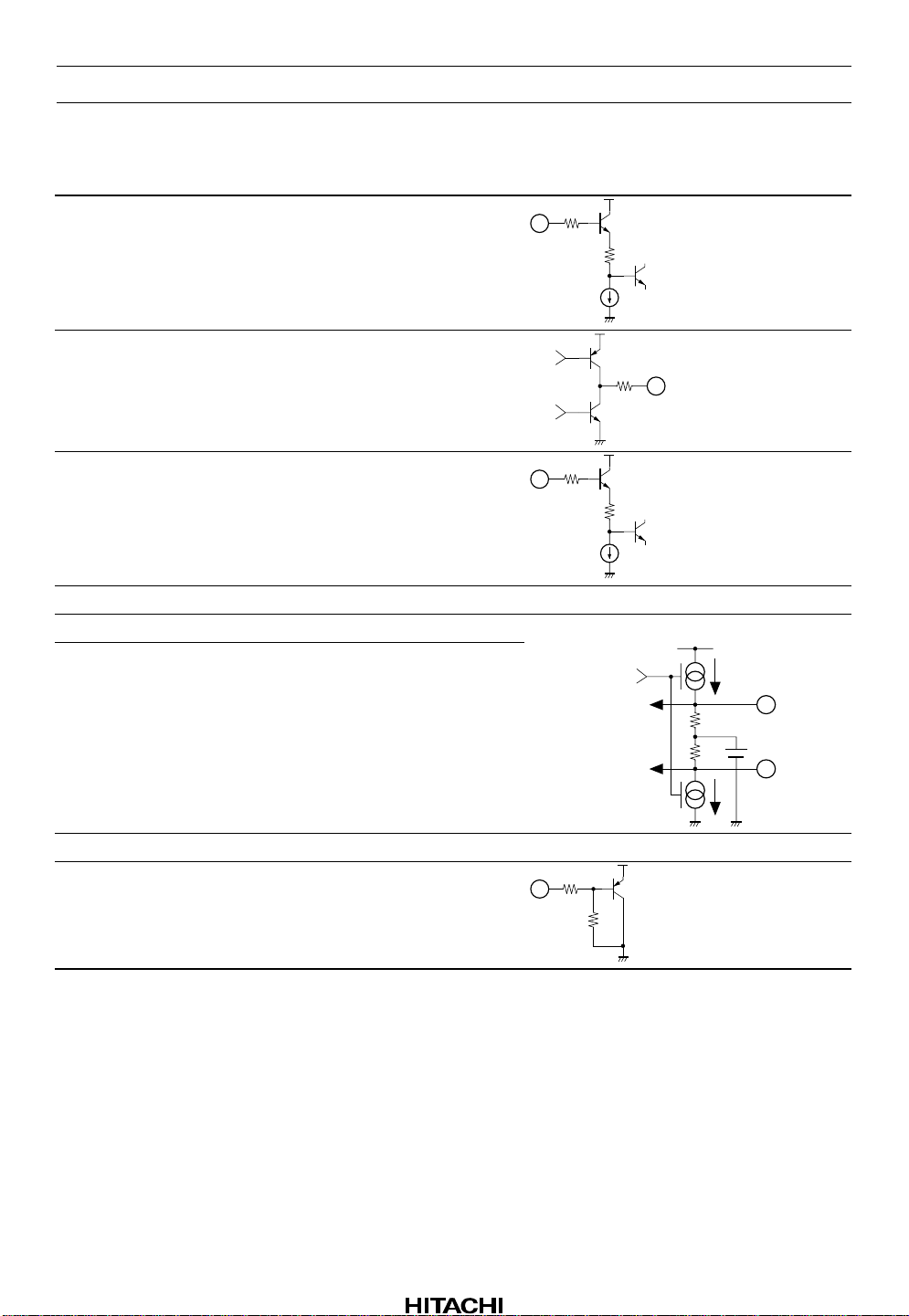
Pin Functions
Pin No. Symbol Function Equivalent Circuit
1 S1 Data input
1
20 k
HA12187FP
2 R out Receiver output
3 S2 Data input
4GNDGND
5 BUS (–) Bus output (–) Receiver input (–)
6 BUS (+) Bus output (+) Receiver input (+)
7VCCPower supply
8 STB Standby control input
SW
SW
3
Receiver input (+)
Receiver input (–)
8
20 k
100 k
100
20k
SW
2
I
6
V
REF
5
I
Rev.2, Jun. 1999, page 3 of 23

HA12187FP
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Ta = 25°C)
Item Symbol Ratings Unit Notes
Power-supply voltage V
Allowable power dissipation Pd 400 mW Ta ≤ 85°C
Operating temperature Topr –40 to 85 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –55 to 125 °C
Input voltage Vin –1.0 to 6.7 V
Bus input voltage Bus 18 V
Note: Recommended operating power supply voltage range: 5 V ±0.5 V
CC
7V
Rev.2, Jun. 1999, page 4 of 23

HA12187FP
Electrical Characteristics (VCC = 5.0 V, Ta = 25°C)
Test
Test
Item Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
S1 High-level input
voltage
V
IHS1
3.5 — — V V1 = 0 V → 5 V, V3 = 0 V
With the potential
difference between pin 5
and pin 6 120 mV or more
Low-level input
voltage
V
ILS1
— — 1.5 V V1 = 5 V → 0 V, V3 = 0 V
With the potential
difference between pin5
and pin 6 20 mV or less
High-level input
I
IHS1
— — 1 µA V1 = 5 V, V3 = 0 V 1
current
Low-level input
I
ILS1
— — 1 µA V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0 V 1
current
S2 High-level input
voltage
V
IHS2
3.5 — — V V3 = 0 V → 5 V, V1 = 0 V
With the potential
difference between pin 5
and pin 6 120 mV or more
Low-level input
voltage
V
ILS2
— — 1.5 V V3 = 5 V → 0 V, V1 = 0 V
With the potential
difference between 5 and
pin 6 20 mV or less
High-level input
I
IHS2
— — 1 µA V1 = 0 V, V3 = 5 V 3
current
Low-level input
I
ILS2
— — 1 µA V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0 V 3
current
Driver High-level
I
OH
3.0 3.8 4.8 mA IOH = | V
OHD+
– V
| / 62 Ω 5, 6 Figure 1
OHD–
output current
Low-level output
leakage current
Reference
I
OL
V
OP+
— — 1 µA Pin 5 voltage = V
IOL = | V
OP+
– V
OP–
OP–
| / RI
2.3 2.5 2.7 V V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0 V 6
operating
voltage (+)
Reference
V
OP–
2.3 2.5 2.7 V V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0 V 5
operating
voltage (–)
Current drain 1 ICCH 5.5 7.3 9.5 mA V1 = 5 V, V3 = 0 V 7 Figure 1
Current drain 2 ICCL 1.7 2.2 2.7 mA V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0 V 7 Figure 1
Pin
Circuit
1 Figure 1
1
3 Figure 1
3
5, 6
Rev.2, Jun. 1999, page 5 of 23

HA12187FP
Electrical Characteristics (VCC = 5.0 V, Ta = 25°C) (cont)
Item Symbol Min Typ Max Unit Test Condition
Recei
ver
Power supply off output
leakage current
STB on voltage VSTBon — — 1.5 V V8 = 5 → 0 V, V1 = 5 V, V8
STB off voltage VSTBoff 3.5 — — V V8 = 0 → 5 V, V1 = 5 V, V8
Standby mode current
drain
Standby mode leakage
current
Delay time (L → H) DLY1 — 600 800 nS See the operating
Delay time (H → L) DLY2 — 450 800 nS See the operating
Note: 1. I1 is the measured current when V6 = (V
High-level input
voltage (1)
Low-level input
voltage (1)
Input hysteresis
voltage (1)
High-level
common-mode
input voltage
Low-level
common-mode
input voltage
Receiver input
resistance*
1
High-level
output voltage
Low-level output
voltage
) – 0.3 V.
(V
OP+
V
IH1
— 80 120 mV V6 = 0 → 5 V, pin 2 = 4 V
or more, V1 = 0V, V3 = 0V,
V5 = V
V
IL1
20 45 — mV V6 = 5 → 0 V, pin 2 = 1 V
OP–
, V
IH1
= V6 – V5
or less, V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0 V,
V
V
IHYS1
IHCOM
V5 = V
10 35 60 mV V
IHYS1
= V
4.5 — — V V5 = 0 → 5 V, pin 2 = 4 V
OP–,VIL1
IH1
= V6 – V5
– V
IL1
or more, V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0
V, V6 – V5 = 120 mV
V
ILCOM
5 ——V V5 = 0 → 5 V, pin 2 = 1 V
or less, V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0 V,
V6 – V5 = 20 mV
RI 25 35 45
V
V
I
OLEAK
OH
OL
4.5 — — V V1 = 5 V, V3 = 0 V 2 Figure 1
— — 1.0 V V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0 V 2 Figure 1
——1 µAVCC off, V8 = 0 V, V6 = 5 V,
kΩ
V1 = 0 V,
0.6V
=
RI
I1−I2
V1 = 0 V, V3 = 0 V, SW1
on
≤ 20 µA
CC
≥ 4.5 mA
CC
I
CCstb
when I
when I
— 10 20 µA V1 = 5 V, V3 = 0 V, V8 = 0V7 Figure 4
Istb-Leak — — 1 µA V1 = 5 V, V3 = 0 V, V8 = 0
V, V6 = 5 V, SW1 on
waveform figure
waveform figure
) + 0.3 V, and I2 is the measured current when V6 =
OP+
Test
Test
Pin
Circuit
2 Figure 2
2 Figure 2
5 Figure 2
5 Figure 2
5, 6 Figure 3
5, 6 Figure 4
7 Figure 4
7 Figure 4
5, 6 Figure 4
2 Figure 5
2 Figure 5
Rev.2, Jun. 1999, page 6 of 23
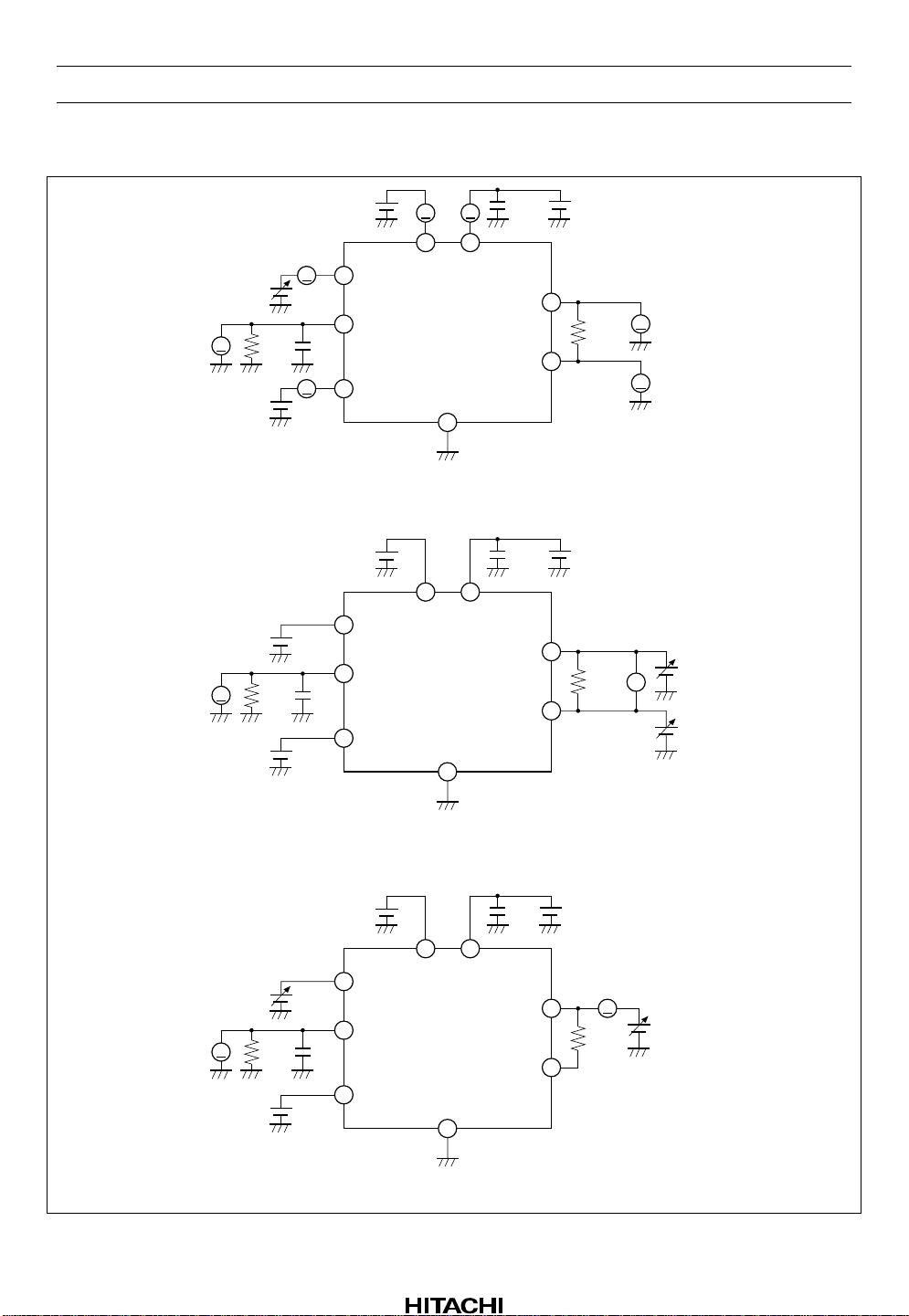
Test Circuits
HA12187FP
V8
5 V
A
A
1
2
20 p
3
V1
V
47 k
V3
0 V
A
8
HA12187FP
4
0.1 µ
A
7
V
CC
5 V
6
V
62 Ω
5
V
Test Circuit 1
V8
5 V
8
20 p
1
2
3
HA12187FP
4
V1
0 V
V
47 k
V3
0 V
0.1 µ
7
V
CC
5 V
6
62 Ω
5
V6
V
V5
Test Circuit 2
V8
5 V
8
20 p
1
2
3
HA12187FP
4
V1
V
47 k
V3
0 V
0.1 µ
7
V
CC
5 V
6
5
A
62 Ω
V6
Test Circuit 3
Rev.2, Jun. 1999, page 7 of 23
 Loading...
Loading...