Gateway 7001 User Manual

User Guide
Gateway 7001 Series Access Point

Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Overview of the Gateway 7001 Series of self-managed APs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Features and benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Default settings and supported administrator/client platforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Administrator’s computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Wireless client computers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Understanding dynamic and static IP addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
How does the access point obtain an IP address at startup? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Dynamic IP addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Static IP addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Recovering an IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2 Quick Setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Setting up the access point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Unpacking the access point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Connecting the access point to network and power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Setting up connections for a guest network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Turning on the access point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Running KickStart to find access points and assign IP addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Logging on to the administration Web pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Configuring basic settings and starting the wireless network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
What’s next? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
3 Configuring Basic Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Navigating to basic settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Reviewing and describing the access point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Providing administrator password and wireless network name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Setting configuration policy for new access points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Updating basic settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Understanding basic settings for a standalone access point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Understanding indicator icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4 Managing Access Points and Clusters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Navigating to access points management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Understanding clustering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
What is a cluster? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
How many APs can a cluster support? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
What kinds of APs can cluster together? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Which settings are shared in the cluster configuration and which are not? . . . . . . . . 43
www.gateway.com
i

Cluster mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Standalone mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Cluster formation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Cluster size and membership . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Intra-cluster security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Auto-Synch of Cluster Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Cluster recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Understanding access point settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Working with access points in a cluster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Modifying the location description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Removing an access point from the cluster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Adding an access point to a cluster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Navigating to information for a specific AP and managing standalone APs . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Navigating to an AP by using its IP address in a URL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
5 Managing User Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Navigating to user management for clustered access points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Viewing and changing user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Viewing user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Adding a user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Editing a user account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
6 Session Monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Navigating to session monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Understanding session monitoring information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Viewing session information for access points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Sorting session information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Refreshing session information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
7 Advanced Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Configuring an Ethernet (wired) interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Navigating to Ethernet (wired) settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Setting the DNS name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Enabling or Disabling Guest Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Specifying a physical or virtual Guest network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Configuring Internal interface Ethernet settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Configuring Guest interface Ethernet settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Configuring a wireless interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Navigating to wireless settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configuring the radio interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configuring internal LAN wireless settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Configuring guest network wireless settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Enabling a network time protocol server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Navigating to time protocol settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
ii
www.gateway.com

Enabling or disabling a network time protocol (NTP) server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Configuring network security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Understanding security issues on wireless networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
How do I know which security mode to use? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Navigating to security settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Configuring security settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Setting up Guest Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Understanding the guest interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Configuring the guest interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Using the guest network as a client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Deployment example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Configuring radio settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Understanding radio settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Navigating to radio settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Configuring radio settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Controlling access by MAC address filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Navigating to MAC filtering settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Using MAC address filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Configuring a Wireless Distribution System (WDS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Understanding the WDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Navigating to WDS settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Configuring WDS settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Configuring security settings on wireless clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Network infrastructure and choosing between built-in or external authentication server 122
Setting the administrator password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Navigating to administrator password setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Setting the administrator password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
8 Maintenance and Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Ethernet (Wired) settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Wireless settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Event log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Transmit/receive statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Associated wireless clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Rebooting the access point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Resetting the configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Upgrading the firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
9 Troubleshooting and Getting Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Known problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Telephone numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
www.gateway.com
iii

A Glossary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
B Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
C Safety, Regulatory, and Legal Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
iv
www.gateway.com

Chapter 1
■ Features and benefits
Introduction
■ Networking
■ Maintainability
■ Default settings and supported
administrator/client platforms
1

Overview of the Gateway 7001 Series of self-managed APs
The Gateway 7001 Series of self-managed APs (access points) provide continuous,
high-speed access between your wireless and Ethernet devices. They are advanced, turnkey
solutions for wireless networking in small and medium-sized businesses. The Gateway 7001
Series enables zero-administration wireless local area network (WLAN) deployment while
providing state-of-the-art wireless networking features.
The Gateway 7001 AP is available as a single band access point (Gateway 7001 802.11 G
Wireless Access Point) and a dual band access point (Gateway 7001 802.11 A+G Wireless
Access Point).
The single band access point can broadcast in either IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g mode.
The dual band access point is capable of broadcasting in two different IEEE 802.11 modes
simultaneously.
■ Radio One can broadcast in IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g modes.
■ Radio Two can broadcast in IEEE 802.11a or IEEE 802.11a Turbo modes.
The Gateway 7001 AP software solution emphasizes security, ease-of-administration and
industry standards—providing a standalone and fully secured wireless network without
the need for additional management applications such as legacy authentication server
software.
The following sections list features and benefits of the Gateway 7001 Series self-managed
APs, and tell you what’s next when you’re ready to get started.
2
www.gateway.com

Features and benefits
IEEE standards support and Wi-Fi compliance
■ Support for IEEE 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g wireless networking standards
(depending on model)
■ Provides bandwidth of up to 54 Mbps for 802.11a or 802.11g (11 Mbps for 802.11b,
108 Mbps for 802.11a Turbo)
■ Wi-Fi certified
Wireless features
■ Auto channel selection at startup
■ Transmit power adjustment
■ Wireless Distribution System (WDS) for connecting multiple access points wirelessly.
Extends your network with less cabling and provides a seamless experience for roaming
clients.
■ Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) support
■ Under-the-hood support for multiple SSIDs (network names) and multiple BSSIDs (basic
service set IDs) on the same access point
Security features
■ Inhibit SSID Broadcast
■ Ignore SSID Broadcast
■ Link integrity monitoring
■ Link integrity checking
■ Weak IV avoidance
■ Wireless Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
■ Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
■ Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
■ User-based access control with local authentication server
■ Local user database and user lifecycle management
■ MAC address filtering
www.gateway.com
3

Out-of-the-Box guest interface
■ Unique network name (SSID) for the Guest interface
■ Captive portal to guide guests to customized, guest-only Web page
■ VLAN and dual Ethernet options
Clustering and auto-management
■ Automatic setup with Kickstart.
■ Provisioning and plug-and-play through automatic clustering and cluster rendezvous.
The administrator can specify how new access points should be configured before they
are added to the network. When new access points are added, they can automatically
rendezvous with the cluster, and securely download the correct configuration. The
process does not require manual intervention, but is under the control of the
administrator.
■ Single universal view of clustered access points and cluster configuration settings.
Configuration for all access points in a cluster can be managed from a single interface.
Changes to common parameters are automatically reflected in all members of the
cluster.
■ Self-managed access points with automatic configuration synchronization.
The access points in a cluster periodically check that the cluster configuration is
consistent, and check for the presence and availability of the other members of the
cluster. The administrator can monitor this information through the user interface.
■ Enhanced local authentication using 802.1x without additional IT setup.
A cluster can maintain a user authentication server and database stored on the access
points. This eliminates the need to install, configure, and maintain a RADIUS
infrastructure, and simplifies the administrative task of deploying a secure wireless
network.
■ Hardware watchdog.
Networking
■ Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) support for dynamically assigning
network configuration information to systems on the LAN
Maintainability
■ Status, monitoring, and tracking views of the network including session monitoring,
client associations, transmit/receive statistics, and event log
■ Reset configuration option
■ Firmware upgrade
4
www.gateway.com

Default settings and supported administrator/client platforms
Before you plug in and boot a new access point, review the following sections for a quick
check of required hardware components, software, client configurations, and compatibility
issues. Make sure you have everything you need ready to go for a successful launch and
test of your new (or extended) wireless network.
■ Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP
■ Administrator’s computer
■ Wireless client computers
■ Understanding of DHCP IP addressing for access points and wireless clients
Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP
The Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP is a wireless communications hub for devices
on your network. It provides continuous, high-speed access between your wireless and
Ethernet devices in IEEE 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11a Turbo modes (depending
on the model).
The Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP offers an out-of-the-box Guest Interface feature
that lets you configure access points for controlled guest access of the wireless network.
This can be accomplished either by using Virtual LANs or by creating physically separate
network connections on the same access point. To support physically separate network
connections, the Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP ships with an extra network port
to be used for a dedicated guest network. (For more information on the guest interface,
see “Advanced Configuration” on page 67, and “Setting up connections for a guest
network” on page 19.)
Default settings for the Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP
Option Default Settings Related Information
System Name Gateway-AP “Setting the DNS name”
on page 69
User Name admin
The user name is read-only. It cannot be
modified.
www.gateway.com
5
Option Default Settings Related Information
Password admin “Providing administrator
password and wireless
network name” on
page 32
“Configuring security
settings on wireless
clients” on page 121
Network Name (SSID) “Gateway 7001 AP Network” for the
Internal interface
“Gateway 7001 AP Guest Network” for the
Guest interface
Network Time Protocol
(NTP)
IP Address 192.168.1.1
Connection Type Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
None “Enabling a network
The default IP address is used if you do not
use a Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) server. You can assign a
new static IP address through the
Administration Web pages.
If you have a DHCP server on the network,
then an IP address will be dynamically
assigned by the server at AP startup.
(DHCP)
If you do not have a DHCP server on the
Internal network and do not plan to use
one, the first thing you must do after
bringing up the access point is to change
the Connection Type from “DHCP” to
“Static IP”.
The Guest network must have a DHCP
server.
“Reviewing and
describing the access
point” on page 31
“Configuring internal
LAN wireless settings”
on page 76
“Configuring guest
network wireless
settings” on page 76
time protocol server” on
page 78
“Understanding
dynamic and static IP
addressing” on page 12
“Understanding
dynamic and static IP
addressing” on page 12
For information on how
to re-configure the
Connection Type, see
“Configuring Internal
interface Ethernet
settings” on page 71.
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Radio On “Configuring radio
settings” on page 104
6
www.gateway.com

Option Default Settings Related Information
IEEE 802.11 Mode 802.11g pr 802.11a+g “Configuring radio
settings” on page 104
802.11g Channel Auto “Configuring radio
settings” on page 104
Beacon Interval 100 “Configuring radio
settings” on page 104
DTIM Period 2 “Configuring radio
settings” on page 104
Fragmentation
Threshold
ATS Threshold 2347 “Configuring radio
MAX Stations 2007 “Configuring radio
Transmit Power 100 Percent (of certified level) “Configuring radio
Rate Sets Supported
(Mbps)
Rate Sets
(Basic/Advertised)
Broadcast SSID Allow “Broadcast SSID and
2346 “Configuring radio
settings” on page 104
settings” on page 104
settings” on page 104
settings” on page 104
IEEE 802.11a: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, 6
IEEE 802.11g: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, 6,
5.5, 2, 1
IEEE 802.11b: 11, 5.5, 2, 1
Atheros Turbo 5 GHz: 108, 96, 72, 48, 36,
24, 18, 12
IEEE 802.11a: 24, 12, 6
IEEE 802.11g: 11, 5.5, 2, 1
IEEE 802.11b: 2, 1
Atheros Turbo 5 GHz: 48, 24, 12
“Configuring radio
settings” on page 104
“Configuring radio
settings” on page 104
Security Mode” on
page 88
Security Mode None (plain text) “Broadcast SSID and
Security Mode” on
page 88
Authentication Type None
www.gateway.com
7

Option Default Settings Related Information
MAC Filtering Allow any station unless in list “Controlling access by
MAC address filtering”
on page 110
Guest Login Disabled “Advanced
Configuration” on
page 67
Guest Welcome Screen
Tex t
WDS Settings None “Configuring a Wireless
Thank you for using wireless Guest Access
as provided by this Gateway 7001 Series
wireless access point. When clicking
“Accept” below, you will gain access to a
wireless network which will allow you
complete access to the Internet but is
external to the corporate network. This
network is not configured to provide any
level of wireless security.
“Advanced
Configuration” on
page 67
Distribution System
(WDS)” on page 112
What the access point does not provide
The Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP is not designed to function as a gateway to the
Internet. To connect your LAN to other LANs or the Internet, you need a gateway device,
such as a router or a switch.
8
www.gateway.com

Administrator’s computer
Configuration and administration of the Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP is
accomplished with the KickStart utility (which you run from the CD) and through a
Web-based user interface (UI). The following table describes the minimum requirements
for the administrator’s computer.
Required Software or
Component
Ethernet Connection to the
First Access Point
Wireless Connection to the
Network
Web Browser / Operating
System
Description
The computer used to configure the first access point with
KickStart must have an Ethernet network connection to the
access point.
After initial configuration and launch of the first access points on
your new wireless network, you can make subsequent
configuration changes through the Administration Web pages
using a wireless connection to the “Internal” network. For wireless
connection to the access point, your administration device will
need Wi-Fi capability similar to that of any wireless client:
• Portable or built-in Wi-Fi client adapter that supports one or more
of the IEEE 802.11 modes in which you plan to run the access
point. (IEEE 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11a Turbo
modes are supported, depending on model.)
• Wireless client software such as Microsoft Windows XP or Funk
Odyssey wireless client configured to associate with the Gateway
7001 Series access point.
For more details on Wi-Fi client setup, see “Wireless client
computers” on page 11
Configuration and administration of the Gateway 7001 Series
self-managed AP is provided through a Web-based user interface
hosted on the access point. We recommend using one of the
following supported Web browsers to access the access point
Administration Web pages:
• Microsoft Internet Explorer version 5.5 or 6.x (with up-to-date
patch level for either major version) on Microsoft Windows XP or
Microsoft Windows 2000
• Netscape Mozilla on Redhat Linux version 2.4
The administration Web browser must have JavaScript enabled
to support the interactive features of the administration interface.
It must also support HTTP uploads to use the firmware upgrade
feature.
www.gateway.com
9

Required Software or
Component
Description
KickStart Wizard on
CD
CD Drive The administrator’s computer must have a CD drive to run the
Security Settings Make sure that security is disabled on the wireless client used to
You can run the KickStart CD on any laptop or computer that is
connected to the access point (through Wired or Wireless
connection). It detects Gateway 7001 Series self-managed APs
on the network. The wizard steps you through initial configuration
of new access points, and provides a link to the Administration
Web pages where you finish up the basic setup process in a
step-by-step mode and launch the network.
For more about using KickStart, see “Running KickStart to find
access points and assign IP addresses” on page 20
KickStart CD.
initially configure the access point.
10
www.gateway.com
Wireless client computers
The Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP provides wireless access to any client with a
correctly configured Wi-Fi client adapter for the 802.11 mode in which the access point
is running.
Multiple client operating systems are supported. Clients can be laptops or desktops,
personal digital assistants (PDAs), or any other hand-held, portable or stationary device
equipped with a Wi-Fi adapter and supporting drivers.
In order to connect to the access point, wireless clients need the following software and
hardware.
Required Component Description
Wi-Fi Client Adapter Portable or built-in Wi-Fi client adapter that supports one or more
of the IEEE 802.11 modes in which you plan to run the access
point. (IEEE 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11a Turbo
modes are supported, depending on model.)
Wi-Fi client adapters vary considerably. The adapter can be a PC
card built in to the client device, a portable PCMCIA or PCI card
(types of
adapter that you connect to the client by means of a cable.
The access point supports 802.11a/b/g modes (depending on
model), but you will probably make a decision during network
design phase as to which mode to use. The fundamental
requirement for clients is that they all have configured adapters
that match the 802.11 mode for which your access point(s) is
configured.
NICs), or an external device such as a USB or Ethernet
Wireless Client Software Client software such as Microsoft Windows XP or Funk Odyssey
wireless client configured to associate with the Gateway 7001
Series access point.
Client Security Settings Security should be disabled on the client used to do initial
configuration of the access point.
If the Security mode on the access point is set to anything other
than plain text, wireless clients will need to set a profile to the
authentication mode used by the access point and provide a valid
user name and password, certificate, or similar user identity proof.
Security modes are Static WEP, IEEE 802.1x, WPA with RADIUS
server, and WPA-PSK.
For information on configuring security on the access point, see
“Configuring network security” on page 80.
www.gateway.com
11

Understanding dynamic and static IP addressing
Gateway 7001 Series self-managed APs are built to auto-configure, with very little setup
required for the first access point and no configuration required for additional access points
subsequently joining a preconfigured cluster.
How does the access point obtain an IP address at startup?
When you deploy the access point, it looks for a network DHCP server and, if it finds
one, obtains an IP Address from the DHCP server. If no DHCP server is found on the
network, the AP will continue to use its default Static IP Address (192.168.1.1) until you
re-assign it a new static IP address (and specify a static IP addressing policy) or until a DHCP
server is brought online.
Important If you configure both an Internal and Guest network and
plan to use a dynamic addressing policy for both, separate
DHCP servers must be running on each network.
A DHCP server is a requirement for the Guest network.
When you run KickStart, it discovers the Gateway 7001 Series self-managed APs on the
network and lists their IP addresses and MAC addresses. KickStart also provides a link to
the administration Web pages of each access point using the IP address in the URL. (For
more information about the KickStart utility, see “Running KickStart to find access points
and assign IP addresses” on page 20.)
Dynamic IP addressing
The Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP generally expects that a DHCP server is running
on the network where the AP is deployed. Most home and small business networks already
have DHCP service provided either through a gateway device or a centralized server.
However, if no DHCP server is present on the Internal network, the AP will use the default
Static IP Address for first time startup.
Similarly, wireless clients and other network devices (such as printers) will receive their
IP addresses from the DHCP server, if there is one. If no DHCP server is present on the
network, you must manually assign static IP addresses to your wireless clients and other
network devices.
The Guest network must have a DHCP server.
12
www.gateway.com

Static IP addressing
The Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP ships with a default Static IP Address of
192.168.1.1. (See the default settings for the AP in “Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP”
on page 5.) If no DHCP server is found on the network, the AP retains this static IP address
at first-time startup.
After AP startup, you have the option of specifying a static IP addressing policy on Gateway
7001 Series self-managed APs and assigning static IP addresses to APs on the internal
network through the access point Administration Web pages. (See information about the
Connection Type box and related boxes in “Configuring Internal interface Ethernet
settings” on page 71.)
Important If you do not have a DHCP server on the Internal network
and do not plan to use one, the first thing you must do after
adding the access point is change the Connection Type
from DHCP to Static IP. You can either assign a new Static
IP address to the AP or continue using the default address.
We recommend assigning a new Static IP address so that
if later you add another Gateway 7001 Series
self-managed AP on the same network, the IP address for
each AP will be unique.
Recovering an IP Address
If you experience trouble communicating with the access point, you can recover a static
IP address by resetting the AP configuration to the factory defaults (see “Resetting the
configuration” on page 166), or you can get a dynamically assigned address by connecting
the AP to a network that has DHCP.
www.gateway.com
13

14
www.gateway.com

Chapter 2
Quick Setup
■ Unpacking the access point
■ Connecting the access point to network
and power
■ Turning on the access point
■ Running KickStart to find access points
and assign IP addresses
■ Configuring basic settings and starting
the wireless network
15

Setting up the access point
Setting up and deploying one or more Gateway 7001 Series self-managed APs is in effect
creating and launching a wireless network. The KickStart Wizard and corresponding Basic
Settings Administration Web page simplify this process. Here is a step-by-step guide to
setting up your Gateway 7001 Series self-managed APs and the resulting wireless network.
Have the KickStart CD handy, and familiarize yourself with the “Default settings and
supported administrator/client platforms” on page 5 if you have not already.
Unpacking the access point
Unpack the Access Point (AP) and familiarize yourself with its hardware ports, associated
cables, and accessories.
Access point hardware and ports
The access point includes:
■ Ethernet ports for connection to the Local Area Network (LAN) through Ethernet
network cable
■ Power over Ethernet (POE) and power adapter
16
www.gateway.com

What’s inside the access point?
An access point is a single-purpose computer designed to function as a wireless hub. Inside
the access point is a Wi-Fi radio system, a microprocessor, and sometimes a mini-PC card.
The access point boots from FlashROM that contains firmware with the configurable,
runtime features summarized in “Overview of the Gateway 7001 Series of self-managed
APs” on page 2.
As new features and enhancements become available, you can upgrade the firmware to
add new functionality and performance improvements to the access points that make up
your wireless network. (See “Upgrading the firmware” on page 168.)
www.gateway.com
17
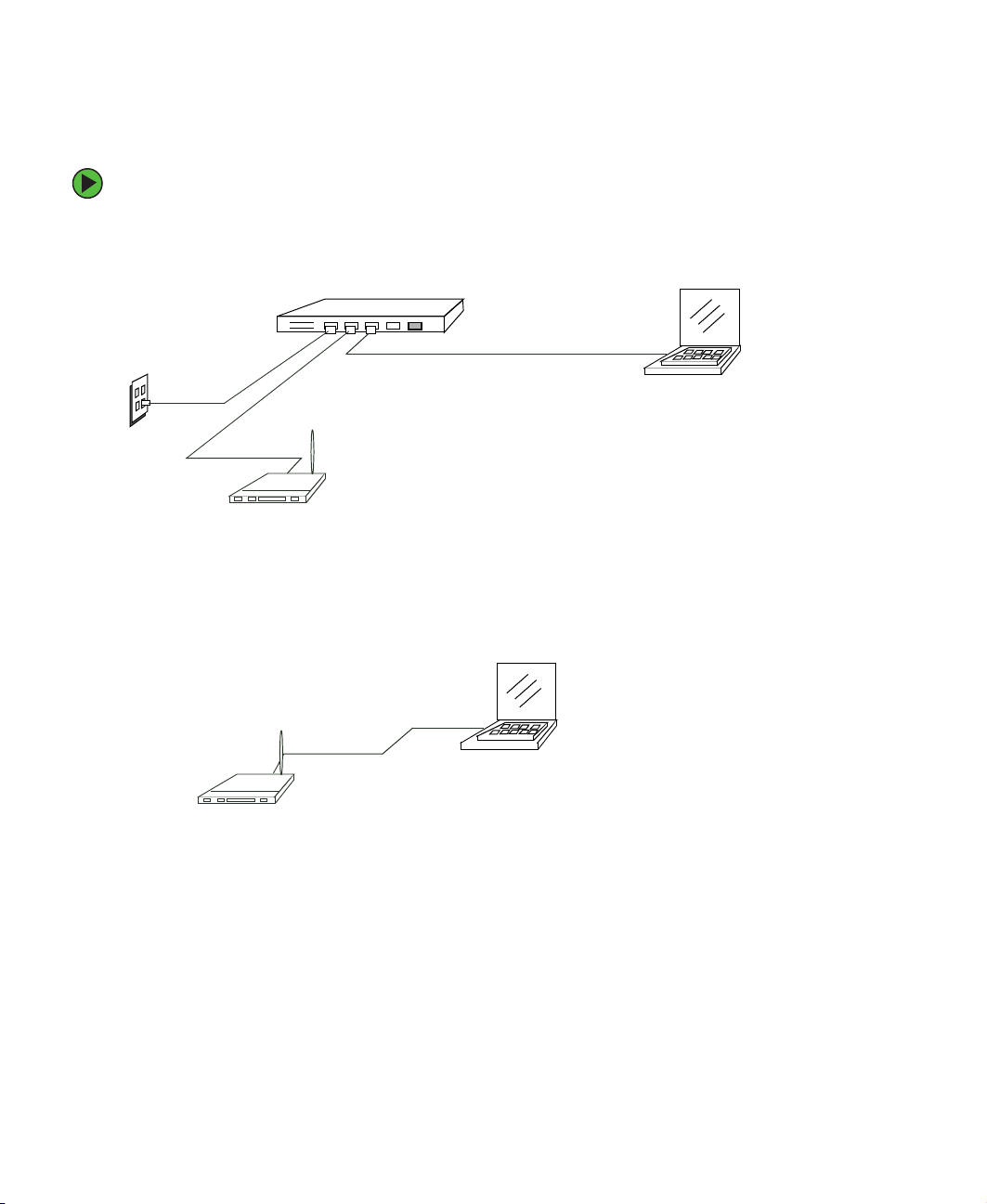
Connecting the access point to network and power
The next step is to set up the network and power connections.
To set up the network and power connections:
1 Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the network port on the access point and
the other end to the same hub where your computer is connected.
Hub
Hub to LAN
AP to hub
LAN
Access point
OR -
Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the network port on the access point and
the other end of the cable to the Ethernet port on your computer.
Access point
Admin computer to hub
Administrator computer
Administrator computer
(This computer must have an IP address on
the same subnet as the access point.)
18
www.gateway.com
Important If you use a hub, the device you use must permit broadcast
signals from the access point to reach all other devices on
the network. A standard hub should work fine. Some
switches, however, do not allow directed or subnet
broadcasts through. You may have to configure the switch
to allow directed broadcasts.
If for initial configuration use a direct wired connection
(using an Ethernet cable) between the access point and
your computer, you will need to reconfigure the cabling for
subsequent startup and deployment of the access point so
that the access point is no longer connected directly to your
computer but instead is connected to the LAN (either using
a Hub or directly).
It is possible to detect access points on the network (using
Kickstart) with a wireless connection. However, we strongly
advise against using this method. In most environments
you may have no way of knowing whether you are actually
connecting to the intended AP and also because many of
the initial configuration changes required will cause you to
lose connectivity with the AP over a wireless connection.
2 Connect the power adapter to the power port on the back of the access point, then
plug the other end of the power cord into a power outlet (preferably, using a surge
protector).
Setting up connections for a guest network
The Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP offers an out-of-the-box Guest Interface that
lets you configure an access point for controlled guest access to the network. The same
access point can function as a bridge for two different wireless networks: A secure Internal
LAN and a public Guest network. This can be done in one of two ways:
■ Physically, by connecting the two LAN ports on the access point to different networks
with two different cables, one to the internal LAN and the other to the public Guest
network.
■ Virtually, by defining two different Virtual LANs through the Administration UI.
Hardware connections for a guest VLAN
If you plan to configure a guest network using VLANs, do the following:
■ Connect eth0 to a VLAN-capable switch
■ Define VLANs on that switch
www.gateway.com
19

Hardware connections for a physically separate guest network
If you plan to configure a physically separate guest network, you need to set up your
network connections differently at this point. The Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP
ships with an extra network port to support configuration of a physically separate guest
network. Use both network ports on the access point to create two physical connections
to different networks:
■ Create a wired (Ethernet) connection from one of the network ports on the access point
to your internal LAN.
■ Create a second wired (Ethernet) connection from the other network port on the access
point to a separate network.
After you have the required physical connections set up, the rest of the configuration
process is accomplished through the Administration UI. For information on configuring
guest interface settings on the Administration UI, see “Advanced Configuration” on
page 67.
Turning on the access point
Plug in the AC power adapter and plug the power adapter into the Gateway 7001 Series
self-managed AP, then wait for its initialization process to complete.
Running KickStart to find access points and assign IP addresses
KickStart is an easy-to-use utility for discovering and identifying new Gateway access
points. KickStart scans the network looking for Gateway access points, and displays ID
details on those it finds.
20
www.gateway.com
Important Keep in mind that KickStart (and the other Gateway
administration tools) recognizes and configures only
Gateway 7001 Series self-managed APs. KickStart will not
find or configure other kinds of access points or other
devices.
Run Kickstart only in the subnet of the “Internal” network
(SSID). Do not run Kickstart on the guest subnetwork.
Kickstart will find only those access points that have IP
addresses. IP addresses are dynamically assigned to APs
if you have a DHCP server running on the network. Keep
in mind that if you deploy the AP on a network with no
DHCP server, the default static IP address (192.168.1.1)
will be used.
Use caution with non-DHCP enabled networks: Do not
deploy more than one new AP on a non-DHCP network
unless you change the IP address list in the first DHCP
server, because they will use the same default static IP
addresses and conflict with each other. (For more
information, see “Understanding dynamic and static IP
addressing” on page 12 and “How does the access point
obtain an IP address at startup?” on page 12.)
Run the KickStart CD on a laptop or computer that is connected to the same network as
your access points and use it to step through the discovery process.
www.gateway.com
21
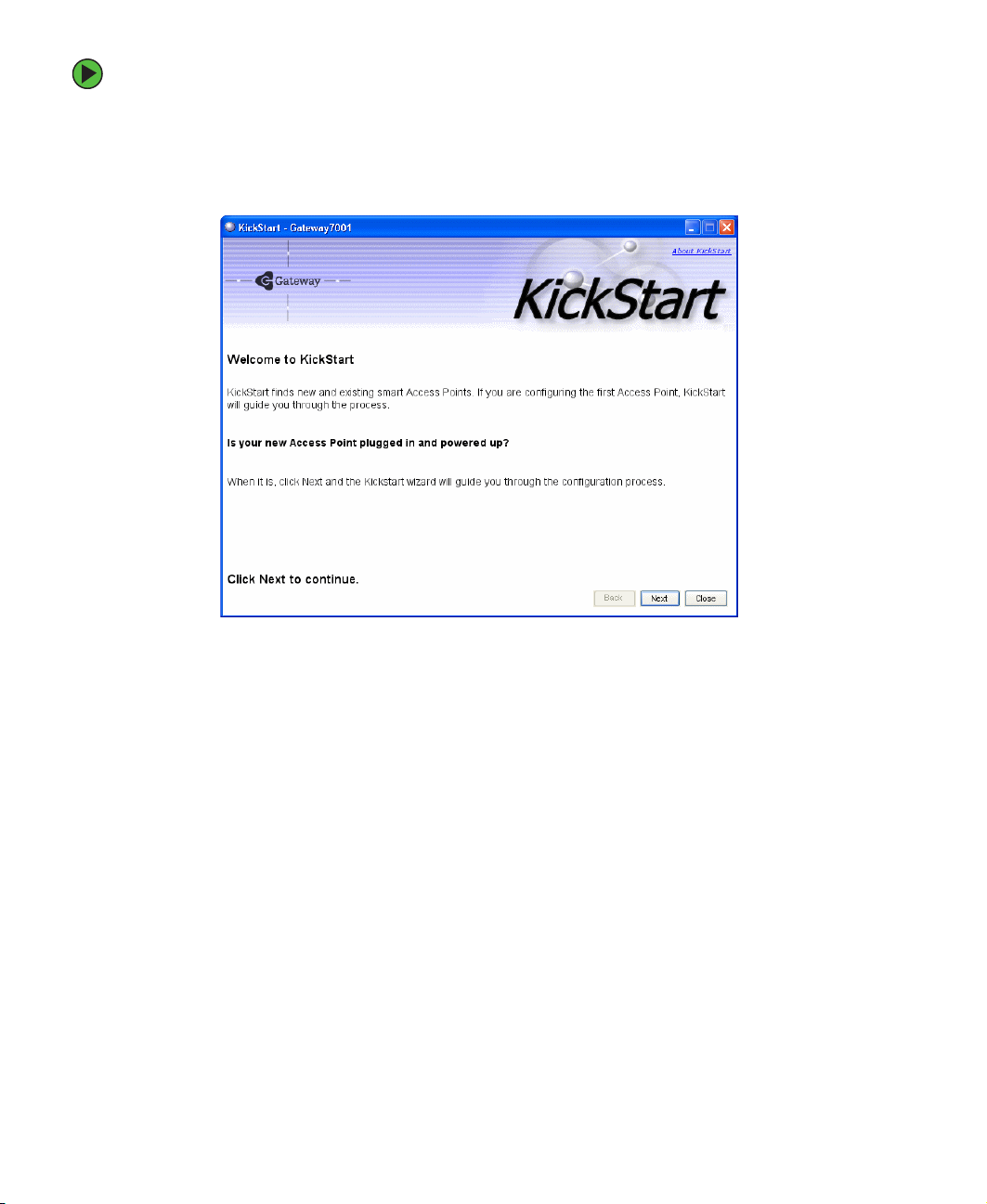
To run KickStart:
1 Insert the KickStart Wizard CD into the CD drive on your computer. If the KickStart
window is not displayed automatically, navigate to the CD drive and double-click the
Kickstart executable file to activate the KickStart utility on the CD. The KickStart
Welcom e screen is displayed.
22
www.gateway.com
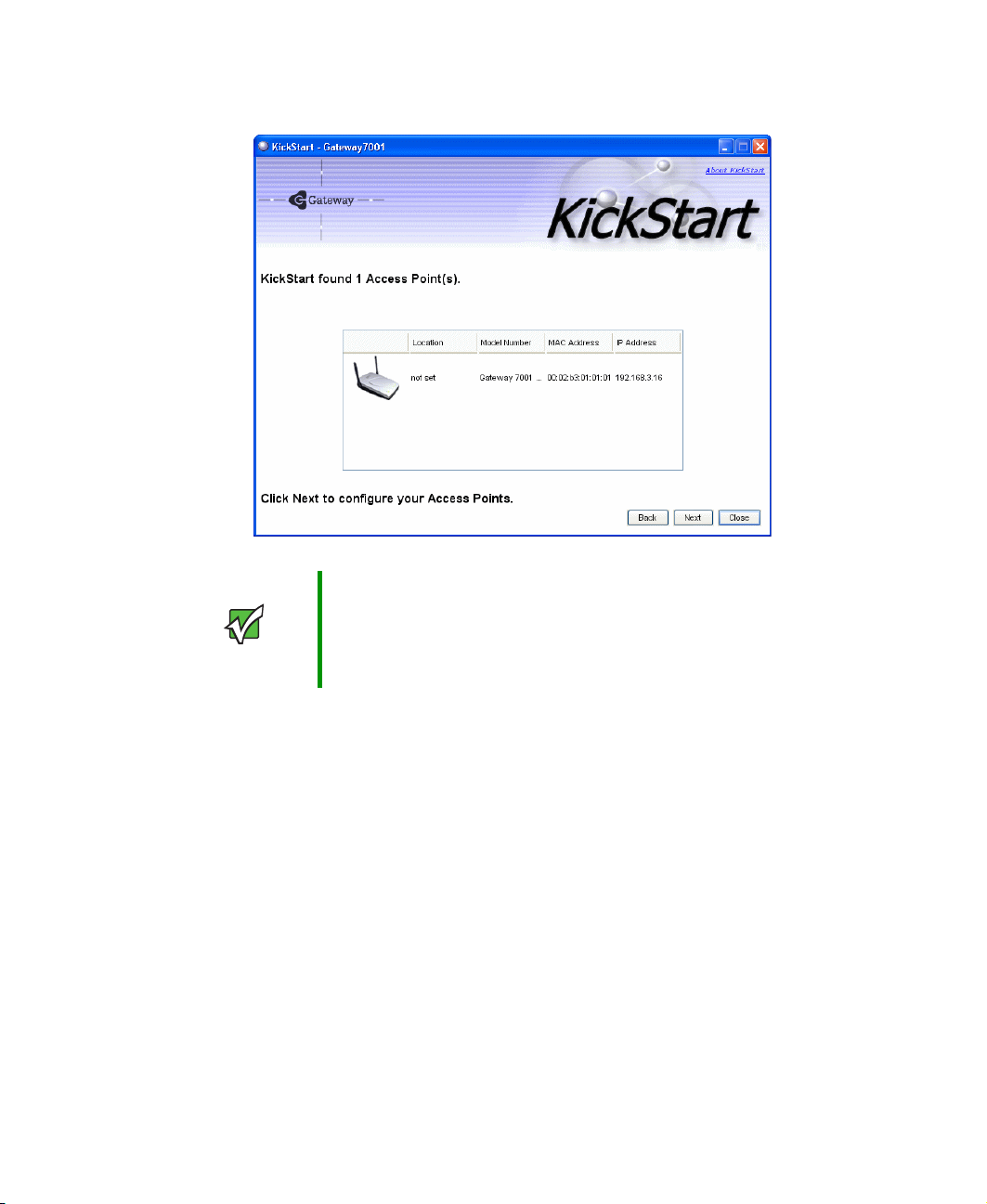
2 Click Next to search for access points. Wait for the search to complete, or until KickStart
has found your new access points.
Important If no access points are found, Kickstart indicates this and presents
some troubleshooting information about your LAN and power
connections. After you have checked hardware power and Ethernet
connections, you can click the Kickstart Back button to search again
for access points.
3 Review the list of access points found.
KickStart will detect the IP addresses of Gateway 7001 Series self-managed APs. Access
points are listed with their locations, Media Access Control (MAC) addresses, and IP
Addresses. If you are installing the first access point on a single-access-point network,
only one entry will be displayed on this screen.
Verify the MAC addresses shown here against the hardware labels for each access point.
This will be especially helpful later in providing or modifying the descriptive location
name for each access point. Click
Next to continue.
4 Go to the Access Point Administration Web pages by clicking the link provided on
the KickStart page (see “Logging on to the administration Web pages” on page 24).
www.gateway.com
23
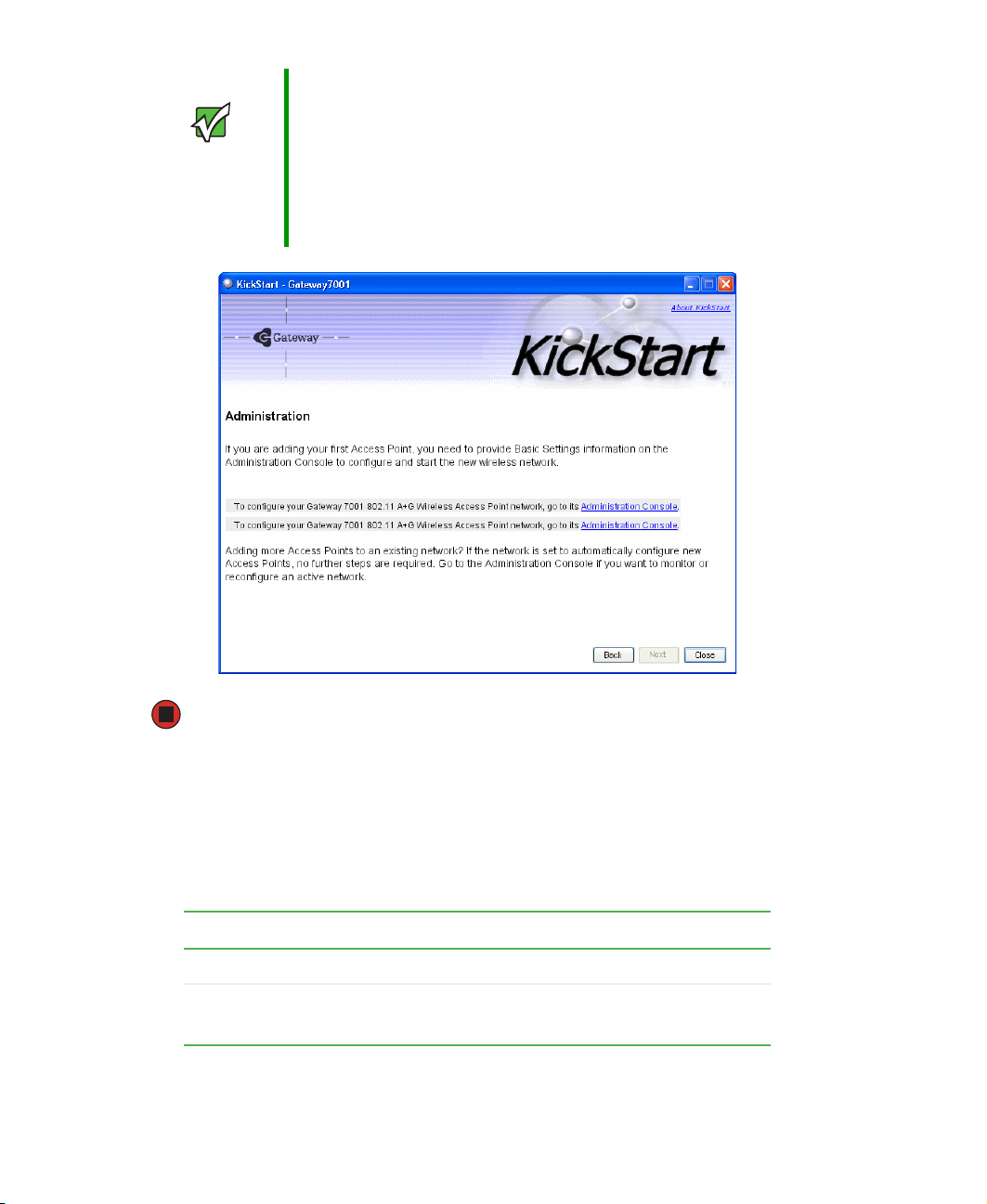
Important KickStart provides a link to the Administration Web pages
through the IP address of the first access point. The
Administration Web pages are a centralized management
tool that you can access through the IP address for any
access point in a cluster. After your other access points
are configured, you can also link to the Administration Web
pages by using the IP address for any of the other Gateway
access points in a URL (http://IPAddressOfAccessPoint).
Logging on to the administration Web pages
When you follow the link from KickStart to the Gateway 7001 Series self-managed AP
administration Web pages, you are prompted for a user name and password.
The defaults for user name and password are as follows.
Field Default Setting
User name admin
Password admin
The user name is read-only. It cannot be modified.
24
www.gateway.com
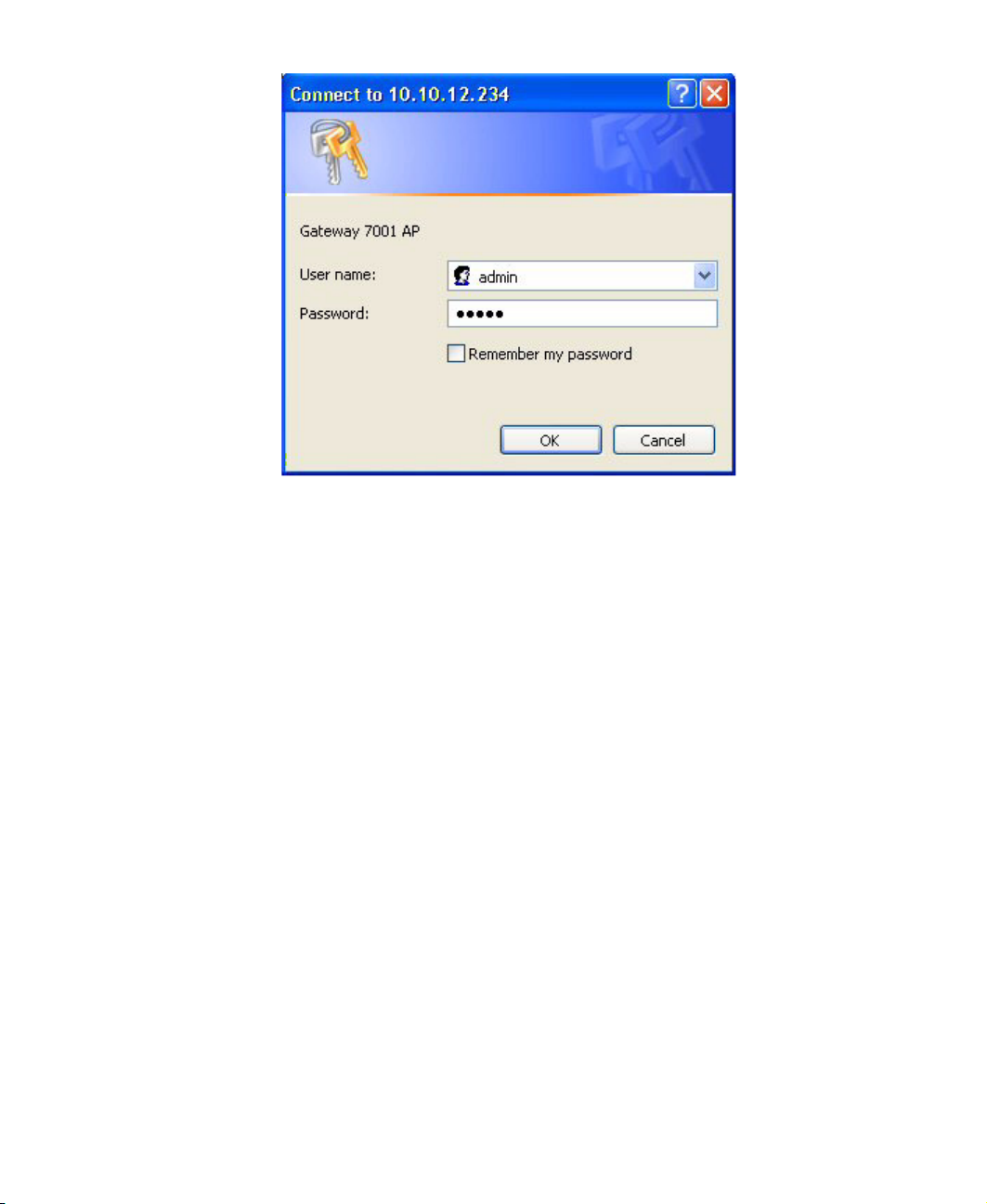
Type the user name and password and click OK.
www.gateway.com
25
 Loading...
Loading...