D-Link DG-102SP User Manual

Manual
Building Networks for People
D-Link DG-102SP
VoIP Station Gateway
Version 1.10

2
Content s
Package Contents ................................................................................3
Introduction............................................................................................4
Features and Benefits ...........................................................................5
Getting S tarted ......................................................................................6
Configuration ......................................................................................10
Using Web-Based Management .........................................................11
Configuration Using a Console............................................................37
Using the Boot Menu ...........................................................................48
Command Line Interface .....................................................................56
T echnical S pecifications ......................................................................64
Warranty..............................................................................................67
Registration ........................................................................................70
Contacting T echnical Support ..............................................................71

3
Package Content s
System Requirements:
Contents of Package:
D-Link DG-102SP VoIP Station Gateway
Ethernet Cable (Straight-through CAT5 with RJ-45 connectors)
12V/1A A/C Power Adapter
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
Internet Explorer V ersion 6.0 or Netscape Navigator
V ersion 6.0 and Above
Computers with Windows, Macintosh, or Linux-based
operating systems with an installed Ethernet adapter

4
Introduction
The D-Link DG-102SP V oIP S tation Gateway links traditional telephony networks
to IP networks with conventional telephony devices such as analog phones or
fax machines. The DG-102SP includes two loop start Foreign Exchange
Subscriber (FXS) that interfaces with normal RJ-11 telephone connectors to
provide voice/fax communication over the IP network. The DG-102SP also
includes two 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet ports. One Ethernet port is for a DSL/
Cable Modem or other WAN devices, and the other may function as a connection
to create a home or small office LAN network. Enabling Nat on the DG-102SP
will allow multiple clients to connect to the Internet. It can be configured and
monitored via the Console, Web browser, or Telnet and also supports SNMP
management.
By routing calls over the Internet or any IP network, this gateway can reduce or
eliminate long distance or inter-office phone charges. Corporations can also
enjoy the benefits of network consolidation and the reduction of leased lines by
relying on Internet service providers to deliver toll-quality voice communications
over the IP networks.

5
Features and Benefits
Designed for versatility and performance, the DG-102SP V oIP Gateway provides
the following features:
**
One 10/100 Fast Ethernet WAN port for connecting to a call agent
One analog POTS interface for PSTN Life Line
Two analog loop-start FXS interfaces using female RJ-11 connectors
One 10/100 Fast Ethernet LAN port for connecting to a local network
IP address assignment using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol) or static configuration
Silence suppression to reduce bandwidth consumption
Comfort noise generation for a more natural feel
Adaptive jitter buffer for smooth voice reception
Lost packet recovery ability for improved voice quality
Command port for easy configuration
Remote Software download/update
IP sharing support to allow multiple users access to the Internet via
a single IP address
Built-in PPPoE function to support dial-up connection for broadband
technology
Caller ID
QoS ensure to guarantee voice quality
Life Line support
1. Automatic fall back to PSTN in case of power failure or network
breakdown
2. Intelligent dialing mode (IP/PSTN Call) alternation via configurable
hot key (“ # “ key is the default)
3. Listening of incoming calls from PSTN
6
Getting Started
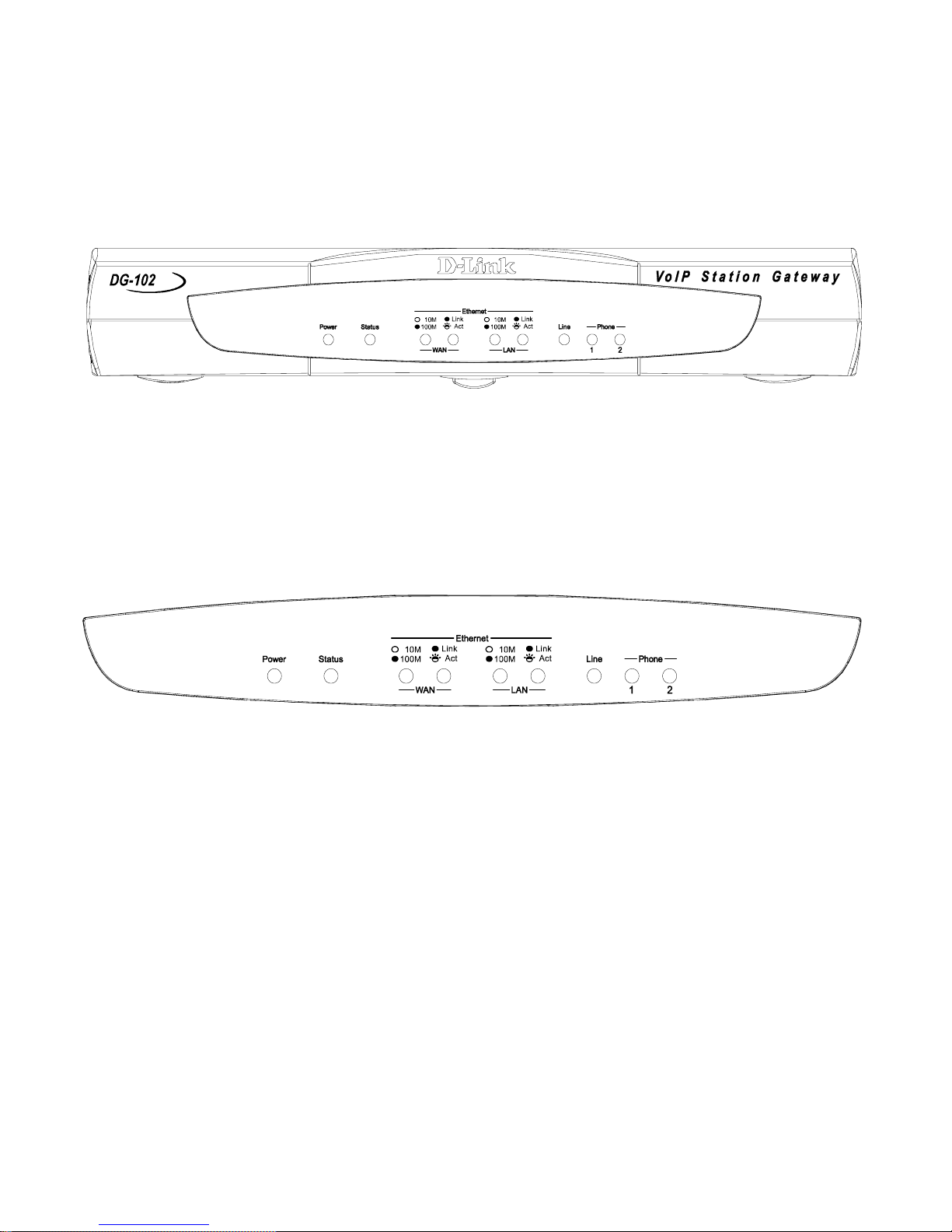
Identifying External Components
Front Panel
Understanding Indicators
Before configuring your VoIP Gateway, take a few minutes to look over this
section and familiarize yourself with the front panel LED indicators depicted
below.
Power: This LED is lit when the device is receiving power; otherwise, it
is unlit.
Status: This LED will flash quickly when the DG-102SP is either performing a self test or booting up. The LED will remain lit when the system
is ready for a connection with the call agent. It will remain dark when the
system is ready but can not receive an acknowledgement from the SIP
server.
WAN: This LED displays the connection speed, link status, and activity
on the 10/100 dual-speed Ethernet port that is used to connect to your
WAN device (usually a DSL/cable modem).

7
Getting Started
Identifying External Components
10/100M: This indicator remains unlit when there is no connection, or
the port is operating at 10Mbps through a connection to a 10BASE-T
device. It is lit when the port is operating at 100Mbps through a connection to a dual-speed or 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet device.
Link/Act: When a good link to a powered-up, but idle device is detected on a port, this indicator shines steadily. When packets are received from the device, the indicator blinks.
Rear Panel
Line: Lights when PSTN line is in use.
Phone 1 to 2: Lights when standard phone port is in use.
Note: If a powered-up device is connected to a port and the port’s Link/Act status
indicator is unlit, the most probable cause is a cabling or connection problem
(for example, wrong cable type or bad contact) or a device malfunction.
LAN: This LED displays the connection speed, link status, and activity on
the 10/100 dual-speed Ethernet port that is used to connect to your LAN.
10/100M: This indicator remains unlit when there is no connection, or
the port is operating at 10Mbps through a connection to a 10BASE-T
device. It is lit when the port is operating at 100Mbps through a connection to a dual-speed or 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet device.
Link/Act: When a good link to a powered-up, but idle device is detected on a port, this indicator shines steadily. When packets are received from the device, the indicator blinks.

8
Getting Started
Identifying External Components
Fast Ethernet LAN: A 10/100 dual-speed Ethernet port fitted with an
RJ-45 connector used to connect the VoIP gateway to a LAN device
(switch, PC, etc.). This port accepts Category 5 or higher UTP cabling
with an RJ-45 connector.
Line: RJ-1 1 phone jack for connecting to a standard telephone wall outlet through an approved (No. 26 A WG or larger) telecommunications line
cord.
Phone 1 to 2: Normal RJ-11 phone jacks used to connect analog (or
digital) telephones and fax machines. Plug your telephone(s) and/or fax
machine directly into any of these jacks.
Installation
When choosing a place to install the VoIP Gateway, please use the following
guidelines:
The power outlet should be within 1.82 meters (6 feet) of the device.
Visually inspect the power cord and see that it is secured to the AC
power connector.
AC Power Connector: For the included power adapter. Be sure to use
only the 12V1/A power adapter included with the product. Using the wrong
power adapter can damage the product and void the warranty.
Diagnostic Port: An RS-232 serial port used to configure the device.
Plug one end of a straight-through wired RS-232 cable to the device and
the other end to a serial port of a PC running a terminal emulation program (such as Microsoft HyperTerminal) or a VT-100 terminal.
Fast Ethernet WAN: A 10/100 dual-speed Ethernet port fitted with an RJ45 connector used to connect the V oIP gateway to a WAN device (usually
a router). This port accepts Category 3, 4 or 5 UTP cabling with an RJ-45
connector.

9
Getting Started
Installation
Connecting the Network Cable
Category 3, 4 or 5 UTP cable can be used to make the Ethernet connection to
your router.
Connecting the VoIP Gateway to a Hub/Switch
Connecting the VoIP Gateway to a Computer
The DG-102SP requires a straight-through cable when connecting to a
computer . make sure that your IP address on your Ethernet card is in the same
subnet as the DG-102SP otherwise it will not connect
To connect the device to either a hub or switch, you must connect the straightthrough cable to the LAN port.
When installing the unit on a desktop or shelf, the rubber feet included with the device should be attached. These cushioning feet
should be attached to the bottom corners of the device.
Do not place heavy objects on the DG-102SP at any time. Placing
the DG-102SP in a well ventilated area is very important. Not doing
so may cause damage to the unit.

10
Configuration
Configuring the VoIP Gateway
Using a web browser on a computer connected to the device via the
WAN or LAN Ethernet connections. In the discussion below , the computer
running the browser is referred to as the management station.
Using a terminal or computer running terminal emulation software
connected to the diagnostic port via an RS-232 cable. In the discussion
below, the terminal (or computer) is referred to as a console and the
connection, a console connection.
There are two ways to configure the V oIP gateway:

11
The categories listed on the left-side of the web-based management module
include:
Using Web-Based Management
The DG-102SP V oIP Gateway of fers an embedded W eb-based (hypertext) interface allowing users to manage the device from anywhere on the network
through a standard browser such as Netscape Navigator , 6.x or later , or Microsoft
Internet Explorer , 6.x or later . The Web browser act s as a universal access tool
and can communicate directly with the device using HTTP protocol. Your
browser screen may vary with the screen shots (pictures) in this guide.
Note: This Web-based Management Module does not accept Chinese language
input (or other languages requiring two bytes per character).
The first step in getting started in using Web based management for your device
is to secure a browser. A Web browser is a program that allows a person to
read hypertext, for example, Netscape Navigator , 6.x or later , or Microsoft Internet
Explorer , 6.x or later. Follow the installation instructions for the browser .
The second and last step is to configure the IP interface of the device. This can
be done manually through a console. See the Configuring the VoIP Gateway
using a Web Browser section of the “Configuration” section for specific
instructions.
Management
To begin managing your device simply run the browser you have installed on
your computer and point it to the IP address you have defined for the device.
The URL in the address bar should read similar to: http://123.123.123.123, where
the numbers 123 represent the IP address of the device.
In the page that opens, click on the following Login to the web-based
management module button:
Config IP (Config Device IP Address)
Device Information
T elephony Configuration
SIP Configuration (Server , User Agent and Peer to Peer)
DHCP Configuration (Dynamic IP Assignment and S tatic IP Assignment)
12
Using Web-Based Management
Management
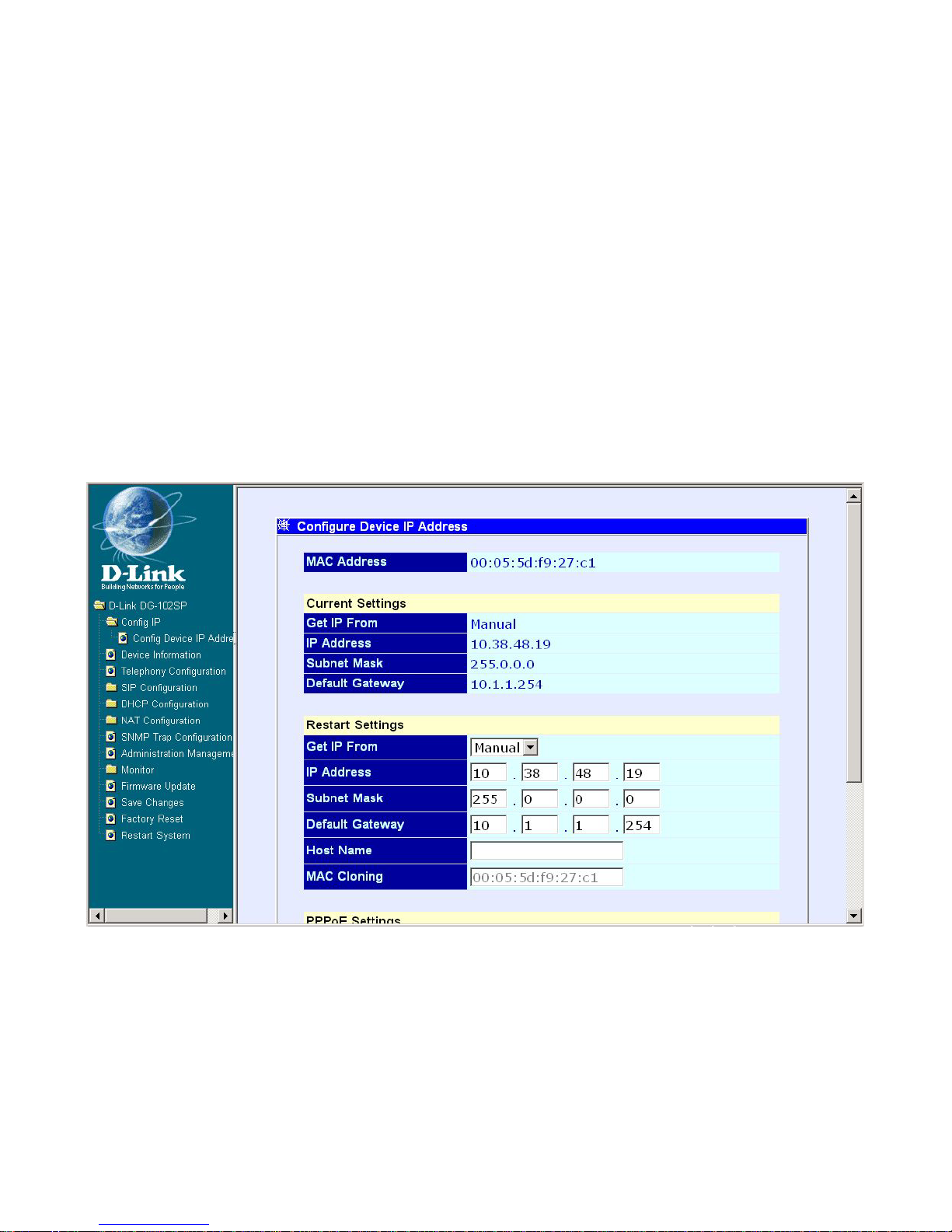
Configure Device IP Address
The items on this window are described below:
Restart Settings
Get IP From: Select the method the V oIP gateway will use to obtain it s IP
settings once it is rebooted. Choices include:
Manual: When Manual is selected, the VoIP gateway will obtain its IP
settings from the fields located just below.
Configure Device IP Address window
Restart System.
NA T Configuration (NA T Configuration and Local Server Configuration)
SNMP Trap Configuration, Administration Management
Monitor (Ethernet S tatistics, DSP Statistics, Tcid Configuration, and Cod-
ing Profile)
Firmware and Configuration Update
Save Changes
Factory Reset
13
BOOTP: When BOOTP is selected, the VoIP will attempt to obtain its
IP settings from a BOOTP server located on your LAN.
DHCP: When DHCP is selected, the VoIP will attempt to obtain its IP
settings from a DCHP server located on your LAN.
IP Address: Enter an IP address for the VoIP gateway .
Subnet Mask: Enter a subnet mask for the VoIP gateway.
Default Gateway: Enter the IP address of the WAN device (usually a
router) you are using to make the WAN connection.
Host Name: This is a user-defined host name for this V oIP Gateway.
MAC Cloning: Enter the MAC address for MAC Cloning. (This function is not
supported on this version)
PPPoE Settings (for DSL users)
State: Enables or disables the PPPoE function.
User Name: Enter the User Name for the PPPoE function.
Password: Enter the Password for the PPPoE function.
Using Web-Based Management
Management
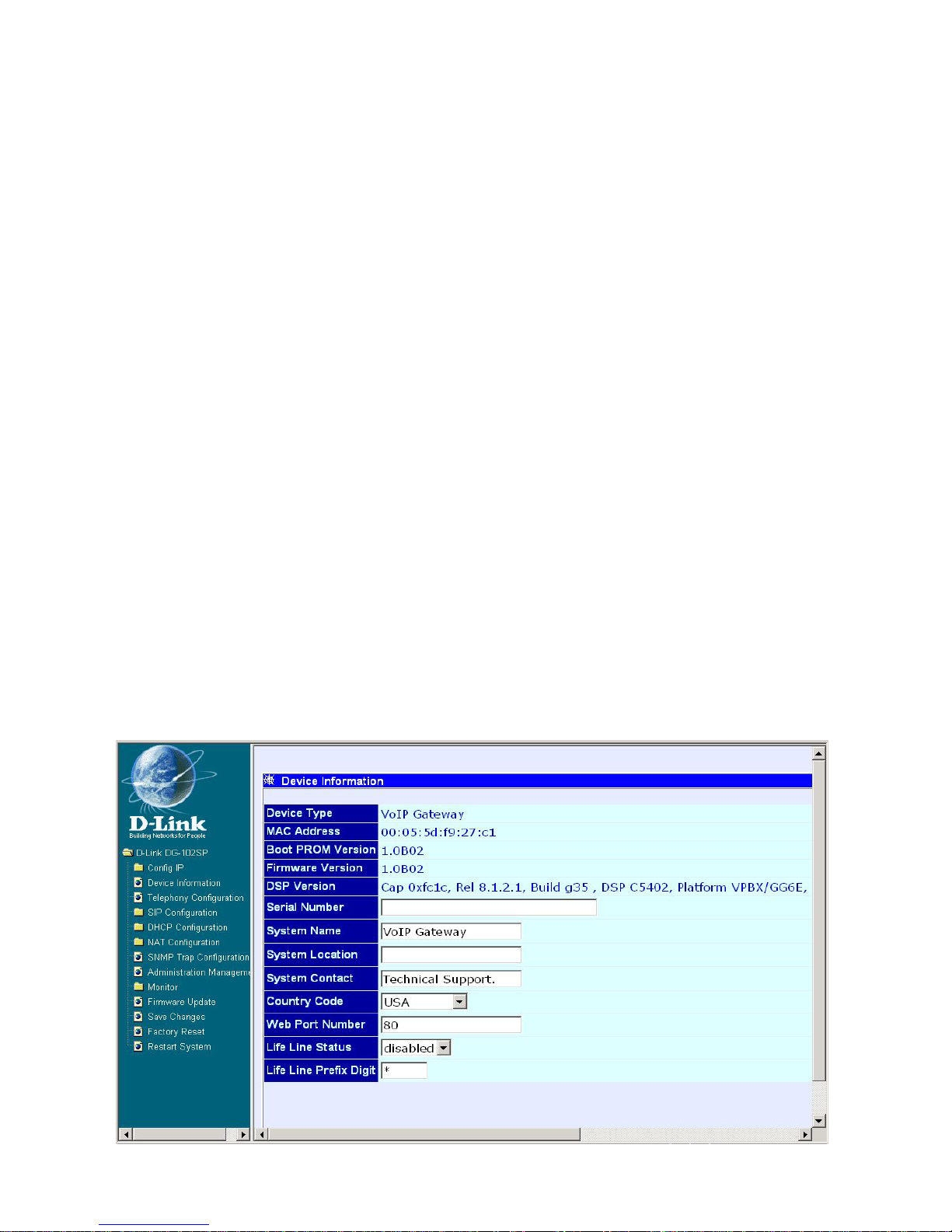
Device Information
Device Information window

14
The items on this window are described below:
Using Web-Based Management
Device Information
Device Type: This displays the model name of this device.
MAC Address: This displays the MAC address of this device.
Boot PROM Version: This displays the version number of the device’s
startup code.
Firmware Version: This displays the version number of the device’s
runtime code.
DSP Version: This displays the Digital Signal Processor version, if any.
Serial Number: This field is for a user-determined identification number .
System Name: This is a user-defined name for this device.
System Location: This is a user-defined physical location of the device.
System Contact: This is user-defined contact information for the person
or department responsible for the maintenance of this device.
Country Code: This is a user-defined country code for this device.
<0:USA (Default), 1:Japan, 2:Hong Kong, 3:Sweden, 4:China>
Web Port Number: This is a user-defined web port number.
Life Line Status: Enables or disables the Lifeline function.
Life Line Prefix Digit: This is a user-defined Lifeline prefixed key for this
device (Default is “#” key).
Click on the Save button at the bottom right of the window to save the settings.
15
Using Web-Based Management
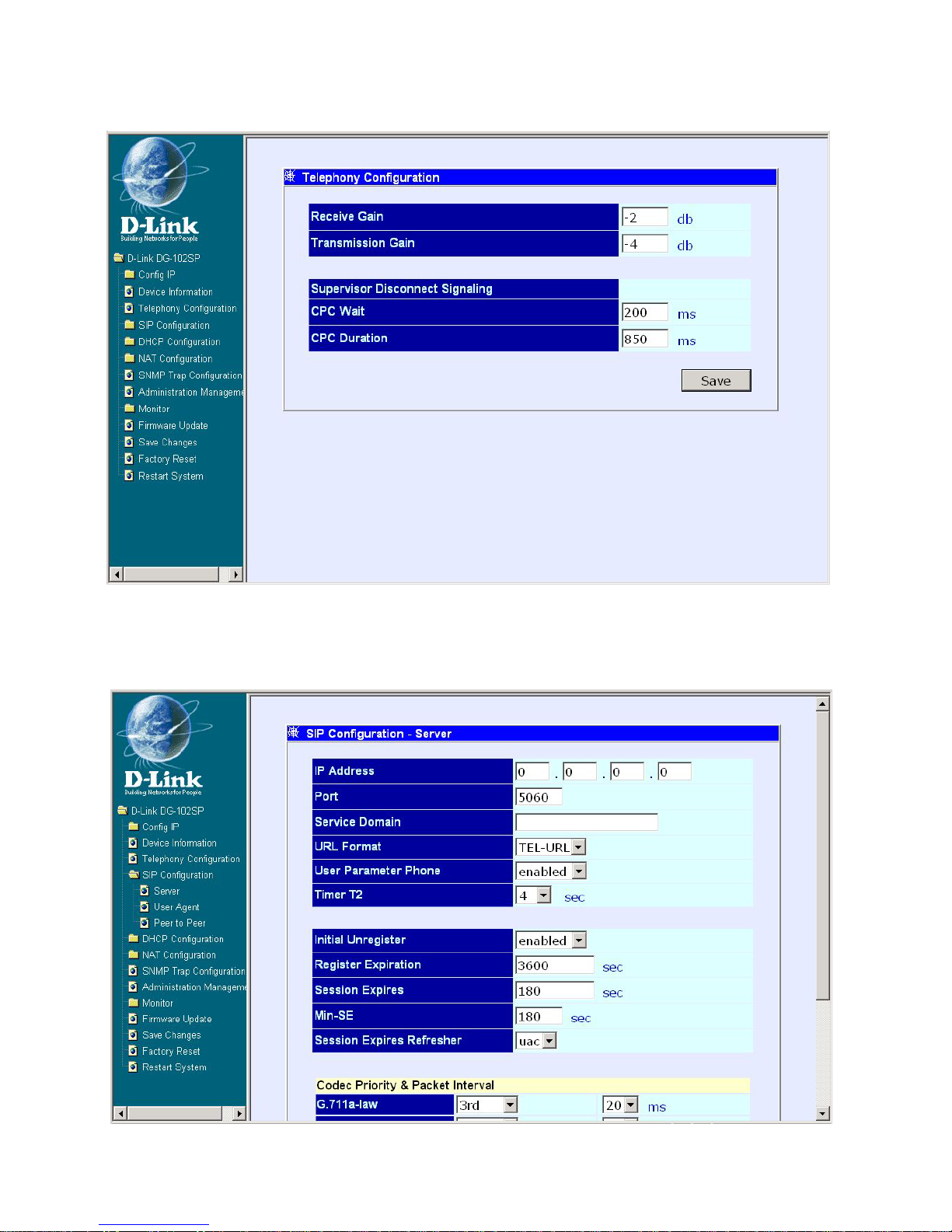
Telephony Configuration
Telephony Configuration window
Enter the desired information on the window above and then click Save.
SIP Configuration - Server
SIP Configuration window

16
Using Web-Based Management
SIP Configuration - Server
The items on this window are described below:
IP Address: Enter the IP address of SIP server.
Port: Enter the port number of SIP server (Default is 5060).
Service Domain: This is a user-defined service domain for SIP server.
URL Format: This is a user-defined URL format for SIP server.
User Parameter: This is used to enable or disable the function of attach
“user=phone” parameter in SIP-URL or not.
Timer T2: This is user-defined T2 timer of SIP protocol. (Range: 4, 8, 16,
32 sec)
Initial Unregister: Enable or disable the initial unregistered function.
Register Expiration: Enter the timer of register expiration.
Session Expires: Enter the timer of Expires.
Min-SE: Enter the timer of Min-SE.
Session Expires Refresher: Choose the session expires refresher: uac
or uas.
Click on the Save button at the bottom right of the screen to save the settings.
17
Using Web-Based Management
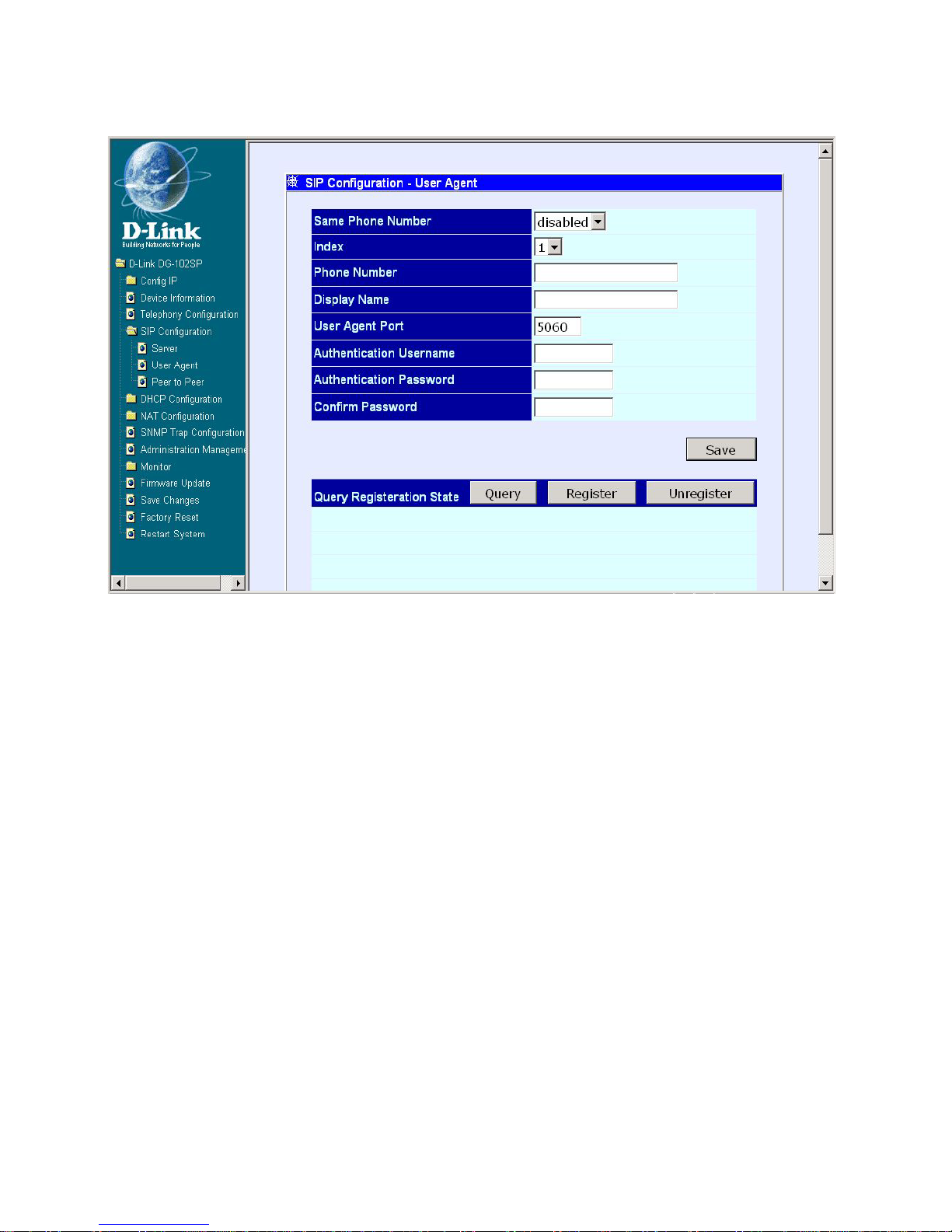
SIP Configuration - User Agent
SIP Configuration – User Agent window
The items on this window are described below:
Click on the Save button at the bottom right of the screen to save the settings.
Same Phone Number: Enable or disable the same phone number
function.
Index: Choose the Phone 1 or Phone 2.
Phone Number: This is a user-defined phone number for each phone
port.
Display Name: This is a user-defined display name for each phone port.
User Agent Port: This is a user-defined unique port number for each
phone port.
Authentication Username: Enter the Username for SIP server
authentication.
Authentication Password: Enter the Password for SIP server
authentication.
Confirm Password: Enter the Password again for confirmation.

18
Using Web-Based Management
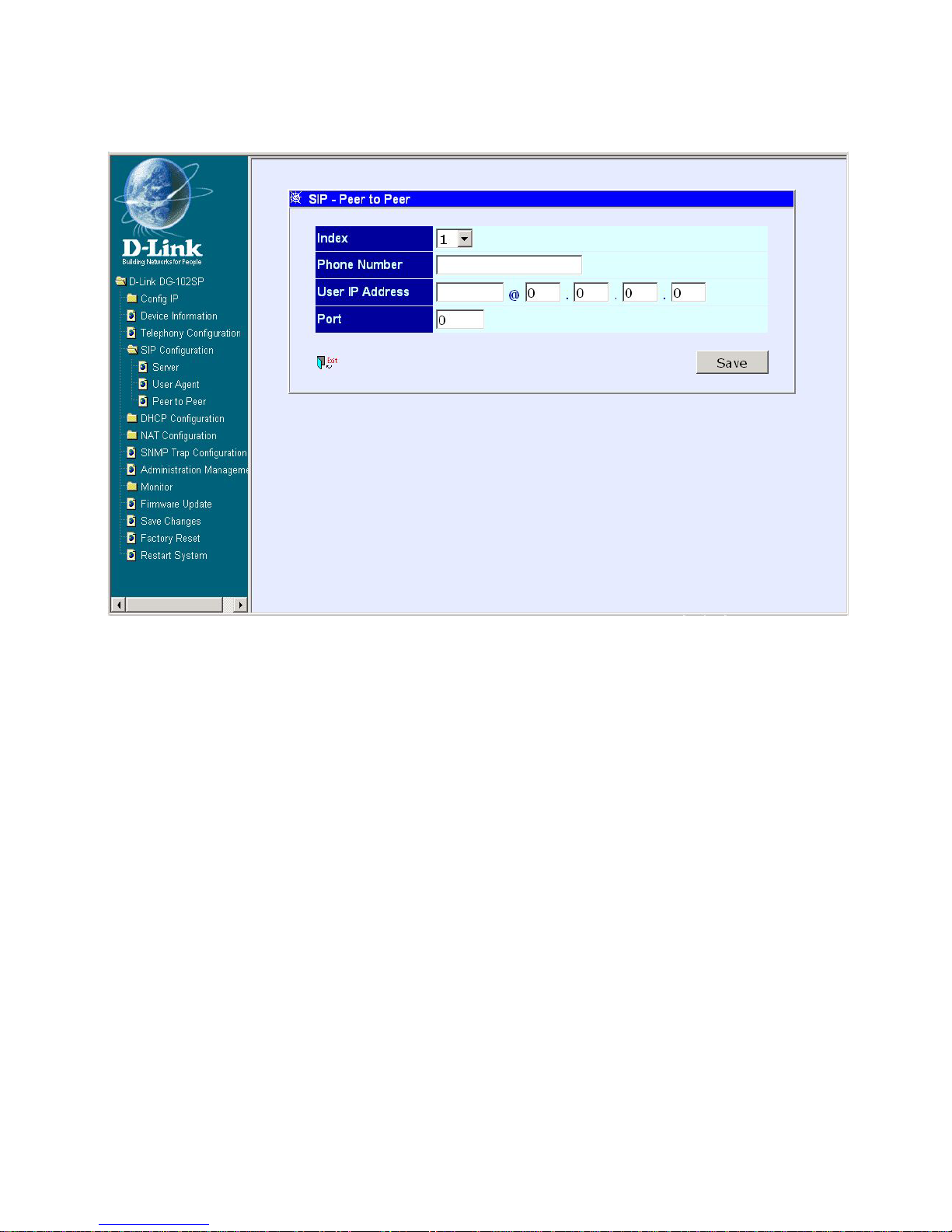
SIP Configuration - Peer to Peer
SIP Configuration – Peer to Peer window
This window displays the Peer to Peer setting for non-SIP server mode. It lists
the ten numbers, which support Peer to Peer communication.
Click one of the ten pointer icons to access and edit the second SIP
Configuration-Peer to Peer window:
19
Using Web-Based Management
The items on this window are described below:
Index: Choose the index number that you would like to edit (Form 1 to
10).
Phone Number: This is a user-defined dialing phone number of the
destination endpoint.
User IP Address: Enter the phone number and IP address of the
destination endpoint. (Format: <Destination Phone
number>@<Destination IP Address X.X.X.X>)
Port: Enter the port number of the destination endpoint.
Click on the Save button at the bottom right of the screen to save the settings.
SIP Configuration - Peer to Peer
Second SIP Configuration – Peer to Peer window
20
Using Web-Based Management
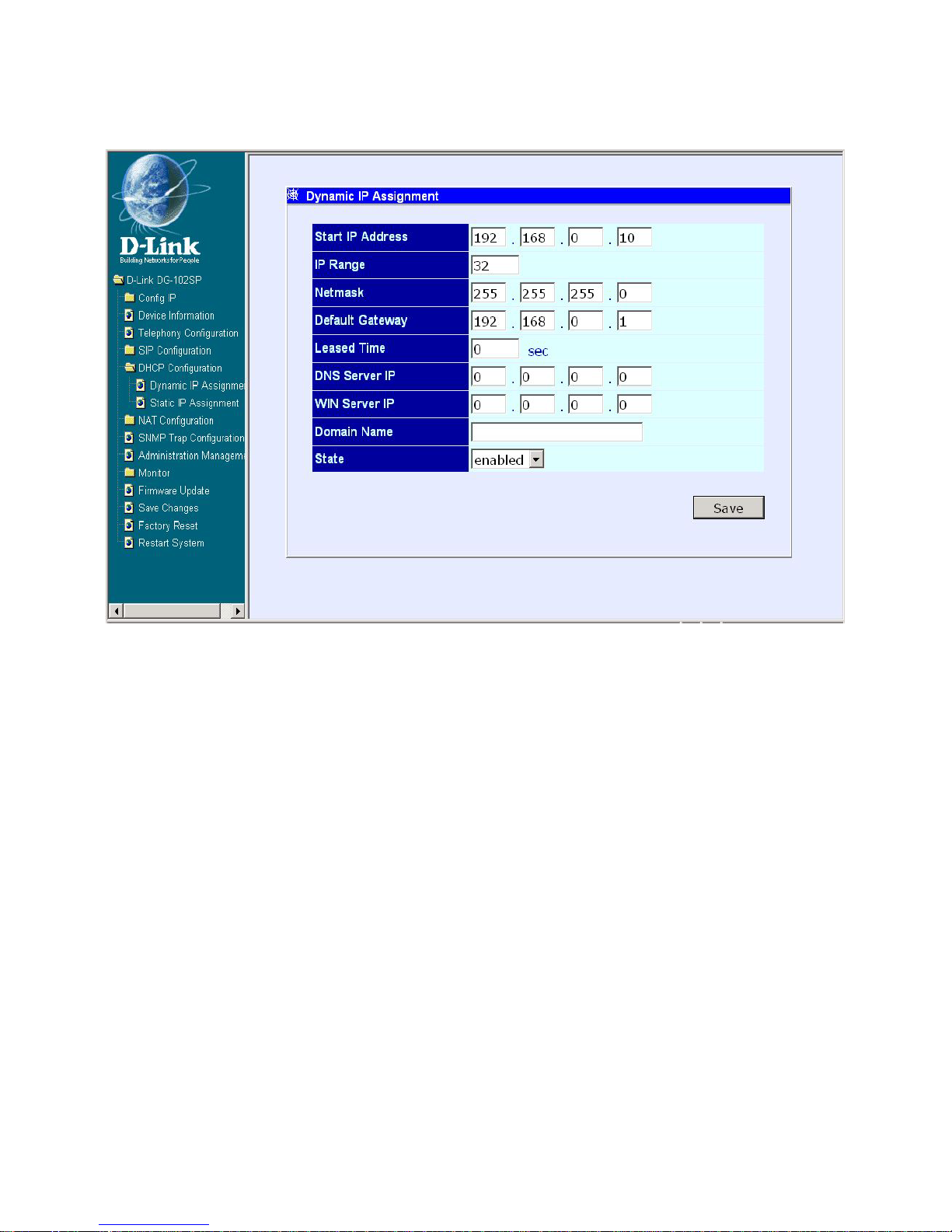
Dynamic IP Assignment
Dynamic IP Assignment window
Use the Dynamic IP Assignment to configure the device to act as a DHCP
server for the LAN.
The items on this window are described below:
Start IP Address: This is the base (starting) address for the IP pool of
unassigned IP addresses.
IP Range: This is the range of contiguous, IP addresses above the base
IP Address.
Netmask: This mask informs the client how the destination IP address is
to be divided into network, subnet, and host parts. The netmask has ones
in the bit positions in the 32-bit address which are to be used for the
network and subnet parts, and zeros for the host part.
Default Gateway: This specifies the Gateway IP Address that will be
assigned to and used by the DHCP clients.
21
Using Web-Based Management
Dynamic IP Assignment
Leased Time: This specifies the amount of time (in hours) a client can
lease an IP address from the dynamically allocated IP pool.
DNS Server IP: This specifies the Domain Name System server, used
by the DHCP clients using leased IP addresses, to translate hostnames
into IP addresses or vice-versa.
WIN Server IP: Some LANs may require using WINS servers. You may
enter the IP address of the WINS server or leave the field blank.
Domain Name: You may enter a domain name for the network group or
leave the field blank.
State: This toggles Disable and Enable for DHCP function.
Click on the Save button at the bottom right of the window to save the settings.
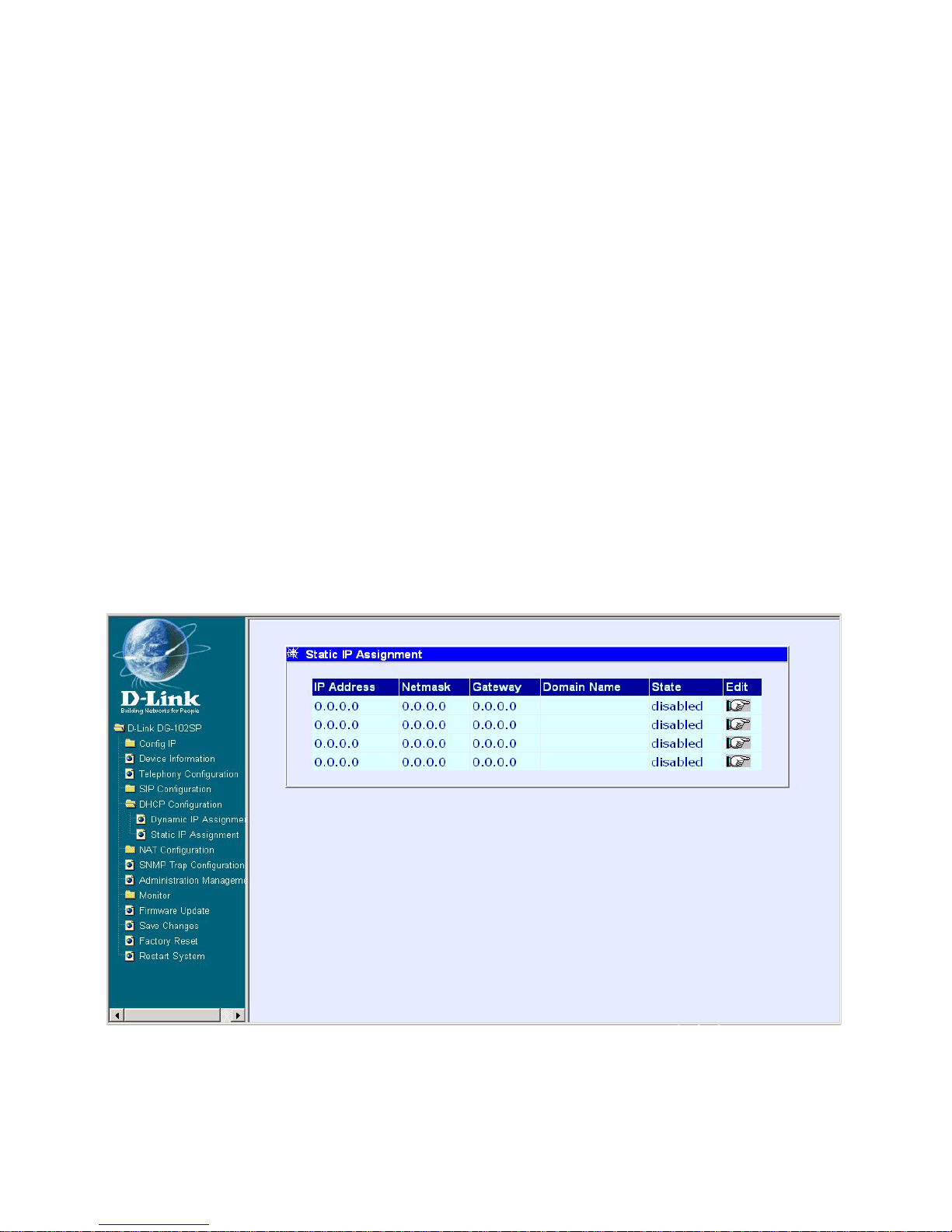
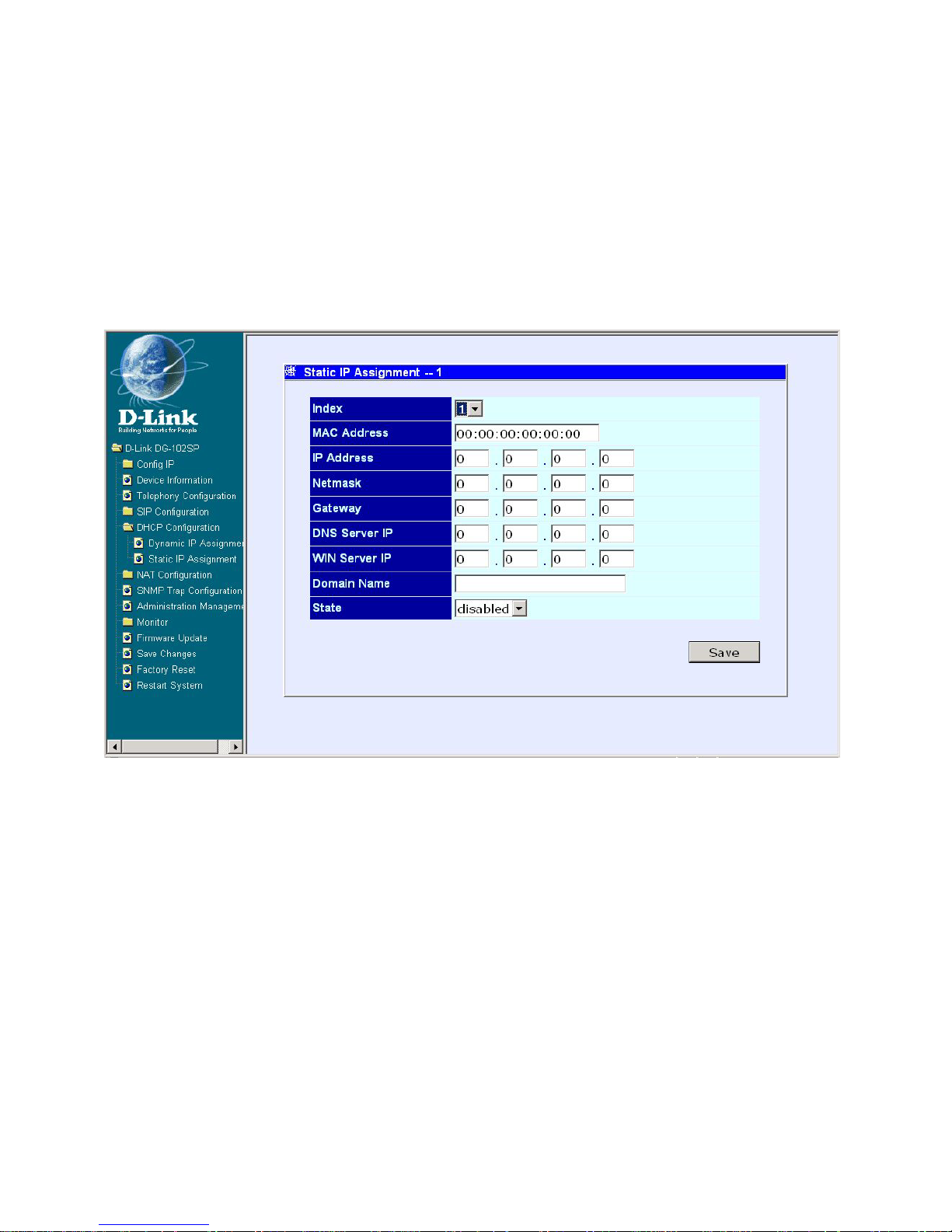
DHCP Configuration - Static IP Assignment
First Static IP Assignment window
22
Using Web Based Management
DHCP Configuration - S tatic IP Assignment
The Static IP Assignment functions in the same way as the Dynamic IP Assignment. The only difference is that a particular IP address can be assigned
to a particular host. The host is identified by the MAC Address of its NIC which
must be entered on the next screen.
Click the Edit icon on the window above to access the second Static IP As-
signment window:
Second Static IP Assignment window
The items on this window are described below:
Index: Choose the index number that you would like to edit (From 1 to 4).
MAC Address: This specifies the physical address of the particular host
that will receive the assigned IP address.
IP Address: This is the static IP address to be assigned.
All other parameters (Netmask, Gateway, DNS Server IP, WINS Server IP,
Domain Name, and S tate) are identical to those in the Dynamic IP Assignment
in the previous section.
Click on the Save button at the bottom right of the window to save the settings.
 Loading...
Loading...