D-Link DES-2218 User Manual

10/100Mbps
Ethernet/Fast Ethernet
Switch
Model DES-2218
User’s Guide
Rev. 02 (October, 1997)
6DES2218..02
Printed In Taiwan
RECYCLABLE

Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise
1. Bitte lesen Sie sich diese Hinweise sorgfältig durch.
2. Heben Sie diese Anleitung für den spätern Gebrauch auf.
3. Vor jedem Reinigen ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen. Vervenden Sie keine Flüssig- oder
Aerosolreiniger. Am besten dient ein angefeuchtetes Tuch zur Reinigung.
4. Um eine Beschädigung des Gerätes zu vermeiden sollten Sie nur Zubehörteile verwenden, die vom
Hersteller zugelassen sind.
5. Das Gerät is vor Feuchtigkeit zu schützen.
6. Bei der Aufstellung des Gerätes ist auf sichern Stand zu achten. Ein Kippen oder Fallen könnte
Verletzungen hervorrufen. Verwenden Sie nur sichere Standorte und beachten Sie die Aufstellhinweise
des Herstellers.
7. Die Belüftungsöffnungen dienen zur Luftzirkulation die das Gerät vor Überhitzung schützt. Sorgen Sie
dafür, daß diese Öffnungen nicht abgedeckt werden.
8. Beachten Sie beim Anschluß an das Stromnetz die Anschlußwerte.
9. Die Netzanschlußsteckdose muß aus Gründen der elektrischen Sicherheit einen Schutzleiterkontakt
haben.
10. Verlegen Sie die Netzanschlußleitung so, daß niemand darüber fallen kann. Es sollete auch nichts auf der
Leitung abgestellt werden.
11. Alle Hinweise und Warnungen die sich am Geräten befinden sind zu beachten.
12. Wird das Gerät über einen längeren Zeitraum nicht benutzt, sollten Sie es vom Stromnetz trennen. Somit
wird im Falle einer Überspannung eine Beschädigung vermieden.
13. Durch die Lüftungsöffnungen dürfen niemals Gegenstände oder Flüssigkeiten in das Gerät gelangen.
Dies könnte einen Brand bzw. Elektrischen Schlag auslösen.
14. Öffnen Sie niemals das Gerät. Das Gerät darf aus Gründen der elektrischen Sicherheit nur von
authorisiertem Servicepersonal geöffnet werden.
15. Wenn folgende Situationen auftreten ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen und von einer qualifizierten
Servicestelle zu überprüfen:
a – Netzkabel oder Netzstecker sint beschädigt.
b – Flüssigkeit ist in das Gerät eingedrungen.
c – Das Gerät war Feuchtigkeit ausgesetzt.
d – Wenn das Gerät nicht der Bedienungsanleitung ensprechend funktioniert oder Sie mit Hilfe dieser
Anleitung keine Verbesserung erzielen.
e – Das Gerät ist gefallen und/oder das Gehäuse ist beschädigt.
f – Wenn das Gerät deutliche Anzeichen eines Defektes aufweist.
16. Bei Reparaturen dürfen nur Orginalersatzteile bzw. den Orginalteilen entsprechende Teile verwendet
werden. Der Einsatz von ungeeigneten Ersatzteilen kann eine weitere Beschädigung hervorrufen.
17. Wenden Sie sich mit allen Fragen die Service und Repartur betreffen an Ihren Servicepartner. Somit
stellen Sie die Betriebssicherheit des Gerätes sicher.

WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE
IF THE D-LINK PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS WARRANTED ABOVE, THE CUSTOMER'S
SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE, AT D-LINK'S OPTION, REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT. THE FOREGOING
WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW,
STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. D-LINK NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER
PERSON TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE,
INSTALLATION MAINTENANCE OR USE OF D-LINK'S PRODUCTS
D-LINK SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND EXAMINATION
DISCLOSE THAT THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST OR WAS CAUSED
BY THE CUSTOMER'S OR ANY THIRD PERSON'S MISUSE, NEGLECT, IMPROPER INSTALLATION
OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE
RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
IN NO EVENT WILL D-LINK BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES, INCLUDING LOSS OF DATA, LOSS
OF PROFITS, COST OF COVER OR OTHER INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INDIRECT
DAMAGES ARISING OUT THE INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE
OR INTERRUPTION OF A D- LINK PRODUCT, HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF
LIABILITY. THIS LIMITATION WILL APPLY EVEN IF D-LINK HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
IF YOU PURCHASED A D-LINK PRODUCT IN THE UNITED STATES, SOME STATES DO NOT
ALLOW THE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION OF LIABILITY FOR INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.

Limited Warranty
Hardware:
D-Link warrants its hardware products to be free from defects in workmanship and materials, under normal use
and service, for the following lengths of time from the date of purchase from D-Link or its Authorized
Reseller:
Product Type Warranty Period
Network adapters Lifetime
Unmanaged and managed hubs (10Mbps) Lifetime *
Unmanaged and managed hubs (100Mbps) One year
Managed Switches Three years *
Unmanaged switches Lifetime *
Repeaters, MAUs , transceivers, media converters One year
Concentrators One year
Internetworking products One year
* Power supply and fans in these devices One year
Other hardware products One year
Spare parts and spare kits 90 days
If a product does not operate as warranted during the applicable warranty period, D-Link shall, at its option and
expense, (1) repair the defective product or part, (2) deliver to Customer an equivalent product or part to
replace the defective item. All products that are replaced will become the property of D-Link. Replacement
products may be new or reconditioned. Any replaced or repaired product or part has a ninety (90) day
warranty or the remainder of the initial warranty period, whichever is longer.
D-Link shall not be responsible for any software, firmware, information, or memory data of Customer
contained in, stored on, or integrated with any products returned to D-Link pursuant to any warranty.
All products with lifetime warranty have a standard five-year warranty. To qualify for lifetime warranty, the
enclosed Product Registration Card must be completed and returned to D-Link within ninety (90) days of
purchase.
Warranty service may be obtained by contacting a D-Link office within the applicable warranty period for a
Return Material Authorization (RMA) number. If a Registration Card has not been previously sent, proof of
purchase, such as a copy of the dated purchase invoice, must be provided. Once an RMA number is issued,
the defective product must be shipped back to D-Link prepaid, insured and wrapped in the original or similar
shipping package to ensure that it will not be damaged during shipment. When returning the defective product
to D-Link for service, the RMA number must be marked on the outside of the shipping package. Any product
returned without an RMA number shall be rejected and sent back to the Customer, and D-Link reserves the
right to have Customer bear the cost of sending back such products. A service charge may or may not be levied
to Customer by D-Link. To find out if a service charge is levied or not, and the charged amount, read the
RMA that is returned to Customer, or ask the D-Link office when an RMA is requested.

Software:
D-Link warrants that the software programs licensed from it will perform in substantial conformance to the
applicable published program specifications for a period of ninety (90) days from the date of purchase from DLink or its Authorized Reseller. D-Link warrants the magnetic media containing software against failure
during the warranty period. No updates are provided. D-Link's sole obligation hereunder shall be to replace
any defective software products with products which substantially conform to D-Link's applicable published
specifications. Customer assumes responsibility for the selection of the appropriate applications program and
associated reference materials. D-Link makes no warranty that its software products will work in combination
with any hardware or applications software products provided by third party, that the operation of the software
products will be uninterrupted or error free, or that all defects in the software product will be corrected. For any
third party products listed in the D-Link software product documentation or specifications as being compatible,
D-Link will make reasonable efforts to provide compatibility, except where the non-compatibility is caused by
"bug" or defect in the third party's product.
Warranty service for software products may be obtained by contacting a D-Link office within the warranty
period. Where no Product Registration Card has been sent by Customer, proof of purchase, such as a copy of
the dated purchased invoice, must be provided.
D-Link Offices to Contact for Warranty Service:
To obtain an RMA number for warranty service, contact the D-Link office nearest you. A list of contact
addresses for D-Link’s international offices is found in the back of this User’s Guide. Your Warranty
Registration Card should also be sent to your regional D-Link office.

Trademarks
Copyright 1997 D-Link Corporation.
Contents subject to change without prior notice.
D-Link is a registered trademark of D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems,
Inc.
All other trademarks belong to their respective proprietors.
Copyright Statement
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means
or used to make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or
adaptation without permission from D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems
Inc., as stipulated by the United States Copyright Act of 1976.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with this user’s guide, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user
will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may
cause radio interference in which case the user may be required to take
adequate measures.

T
ABLE OF
C
ONTENTS
BOUT THIS GUIDE
0 A
NTRODUCTION
1 I
DES-2218 Ethernet/Fast Ethernet Switch ................................................. 1
Ports ....................................................................................................................1
Switching ............................................................................................................2
Management........................................................................................................2
100Mbps Fast Ethernet Introduction.........................................................3
100BASE-TX Technology Overview.......................................................... 3
Cables and Connectors........................................................................................4
Topology.............................................................................................................4
Network...............................................................................................................5
Hubs....................................................................................................................5
Connectivity Rules..............................................................................................5
Ethernet Switching Introduction................................................................ 6
XTERNAL FEATURES
2 E
Front Panel................................................................................................ 9
LED Indicators........................................................................................11
Rear Panel............................................................................................... 12
..........................................................
.................................................................1
.......................................................9
XI
NSTALLATION
3 I
Unpacking the Switch..............................................................................13
Installing the Switch ................................................................................ 14
................................................................13
vii

Location ............................................................................................................14
Rack Mounting..................................................................................................14
Connecting Power ................................................................................... 15
Replacing the Fuse............................................................................................16
AKING NETWORK CONNECTIONS
4 M
...................................17
10BASE-T Connection.............................................................................17
100BASE-T Connection...........................................................................18
MII Connection........................................................................................ 19
SING THE CONSOLE INTERFACE
5 U
.....................................21
Connecting to the Switch.........................................................................21
Console Usage Conventions.................................................................... 22
First Time Connecting To The Switch ..................................................... 23
Steps to create a Super User or General User:...................................................24
Super and General User Privileges....................................................................24
Login On The Switch Console By Registered Users................................ 27
Changing your Password...................................................................................28
Adding and Deleting Users...............................................................................29
Setting up the Switch................................................................................31
TCP/IP Settings.................................................................................................31
Out-of-band management and console settings.................................................33
Software Updates ..............................................................................................34
SNMP Information and Console Timeout.........................................................36
SNMP Traps......................................................................................................37
SNMP Security (Community Names)...............................................................38
Switch Configuration............................................................................... 38
Controlling Individual Ports..............................................................................39
Forwarding Configuration ...................................................................... 40
Spanning Tree Protocol and Configuration............................................ 42
Introduction to Spanning Tree Protocol Parameters .........................................43
viii

Setting Spanning Tree Protocol Parameters......................................................45
Monitoring the Switch .............................................................................49
Displaying Port Statistics..................................................................................49
Resetting the Switch.................................................................................51
System Reset.....................................................................................................51
Factory Reset.....................................................................................................52
RODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
6 P
General.................................................................................................... 55
LED Indicators........................................................................................56
Environmental and Physical.................................................................... 56
ABLES AND CONNECTORS
7 C
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Connectors.......................................................57
Crossover Cable ...................................................................................... 59
MII Connector ......................................................................................... 59
RS-232 (DB9) Pin Specification.............................................................. 61
..............................................55
.............................................57
OOT CONFIGURATION FILE
8 B
NDEX
9 I
............................................................................68
............................................65
ix


0 A
This manual explains how to set up and use the D-Link DES-2218 18-port
Ethernet/Fast Ethernet switch. The contents include:
♦ Chapter 1 Introduction Introduces the features of the DES-2218.
♦ Chapter 2 External Features Introduces the external features
(including the front panel, LED indicators, and rear panel) of the
DES-2218 Ethernet switch.
♦ Chapter 3 Installation Tells how to unpack and install the switch.
♦ Chapter 4 Making Network Co nnections Tells how to connect the
switch to network stations and to other parts of your network.
♦ Chapter 5 Using the Console Interface Explains the use of the
console interface, which you can use to configure the switch with a
terminal or
♦ Appendix A Product Specifications Lists the switch’s
specifications, the standards it meets, and certifications it has passed.
BOUT THIS
telnet
connection.
G
UIDE
♦ Appendix B Cables and Connectors Gives pinout information for
the 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, MII (Media Independent Interface)
and console connectors on the switch.
♦ Appendix C Boot Configuratio n File Gives details on how to use
downloadable configuration files with the switch.
For information about how to manage your DES-2218 using a network
management system, see the appropriate Management User’s Guide.

1
1 I
This chapter introduces the D-Link DES-2218 switch, and the technologies
that it uses to give you improved network performance and reliability.
NTRODUCTION
DES-2218 Ethernet/Fast Ethernet
Switch
The DES-2218 is an Ethernet/Fast Ethernet switch for networks needing
improved performance, the ability to interconnect between 10Mbps and
100Mbps Ethernet networks, and SNMP network management capability.
Ports
The DES-2218 has eighteen ports, two NWay 10BASE-TX
Ethernet/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet ports, and sixteen 10BASE-T twistedpair Ethernet ports. Among the Fast Ethernet ports, one of the ports can also
use an industry-standard MII connector, making it possible to interface to
different types of 100BASE-X Fast Ethernet network media, such as
100BASE-FX fiber optic cable or 100BASE-T4 twisted pair.
The other 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX port can optionally serve as an uplink
port, making it possible to connect the port to an Ethernet or Fast Ethernet
hub without using a crossover cable.

All of the ports can operate in either half-duplex or full-duplex mode. Fullduplex operation, allowing the port to transmit and receive at the same time,
can double overall network bandwidth in many applications.
Switching
The DES-2218 uses store-and-forward technology to bridge packets between
ports. Forwarding and filtering occurs at full “wire speed,” 148,800 packets
per second (pps) for Fast Ethernet, and 14,880 pps for Ethernet. It has 2MB
of buffer memory for the 10Mbps ports, and 4MB for the 100Mbps ports.
The switch automatically learns Ethernet (MAC) addresses and stores them
in a forwarding table. In addition, it also supports static filtering, allowing
network administrators to define custom filters fo r network security or other
purposes.
The switch supports the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol, allowing you
to design your network with redundant bridge links.
Management
You can use any network management software supporting SNMP (the
Simple Network Management Protocol) to manage the DES-2218, including
D-Link’s Windows-based D-View management system. The DES-2218’s
internal intelligent management agent supports several standard SNMP
MIBs, along with its own proprietary management information base.
SNMP management can be done in-band, over the Ethernet or Fast Ethernet
network, or out-of-band, over the DES-2218’s RS-232 console port, using
SLIP (the Serial Line Internet Protocol).
In addition, you can manage the switch with an easy-to-use console
interface, either directly over the RS-232 console port, or over the network
using the
2
Telnet
protocol.
Introduction
DES-2218 Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
The management agent’s software is stored in Flash ROM, allowing easy
upgrade over the network.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet Introduction
Computers today have beco me increasingly powerful, with the capab ility to
accommodate very sophisticated uses such as multimedia applications,
video-conferencing, and CAD/CAM. To utilize these technologically
advanced applications more efficiently, there is also a growing demand for
faster networks that can handle heavy network traffic.
Recognizing this need for greater bandwidth and lower latency, a variety of
technologies such as FDDI, ATM, and 100Mbps Fast Ethernet have been
adopted by many vendors. 100Mbps Fast Ethernet technology stands out as
the most inexpensive and smoothest migration path for existing 10Mbps
Ethernet users.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet is a relatively new standard specified by the IEEE
802.3 networking standards committee. It is an extension of the 10Mbps
Ethernet standard with the ability to transmit and receive data at 100Mbps,
while maintaining the CSMA/CD Ethernet protocol. Since the 100Mbps
Fast Ethernet is compatible with all other 10Mbps Ethernet environments, it
provides a straightforward upgrade without wasting the company’s existing
investment in hardware, software, and trained personnel.
100BASE-TX Technology Overview
This section briefly describes a few of the technical aspects of using a
100Mbps Ethernet network.
Introduction
3

Cables and Connectors
Category 5 unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cables are supported. Cat 5 UTP
cable uses the same RJ-45 connector used with 10BASE-T, wired in exactly
the same configuration. However, the punch-down blocks in the wiring
closet must be Category 5 certified. Where these blocks do not meet the
standard, an upgrade is necessary.
Topology
A Fast Ethernet workgroup is configured in a star topology and is built
around a maximum of two repeaters. Each workgroup forms a separate
LAN (also known as a segment or collision domain), and these workgroups
can be easily interconnected through switches, bridges, or routers to form
one LAN large enough to encompass a high-rise building or campus
environment. Recent innovations in LAN hub technology such as stackable
hubs, coupled with the decreasing cost of switches, bridges, and routers,
allow the design of low-cost, efficient Fast Ethernet workgroups and
enterprise LANs.
The following factors strongly influence the architecture of Fast Ethernet
networks:
♦ The EIA/TIA 568 Wiring Standard imposes a 100 meter limit on
horizontal runs of twisted-pair cables; that is, connections from the
wiring closet to the end-station.
♦ Fast Ethernet’s increased operational speed reduces the maximum
distance between all elements of the LAN (see below).
♦ The EIA/TIA 568 Wiring Standard does not support the use of
coaxial cables for horizontal wiring.
4
Introduction

DES-2218 Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
Network
Network diameter, which is the distance between two end-stations in the
same collision domain, is the primary difference between traditiona l Ethernet
and Fast Ethernet. Due to the increased speed in Fast Ethernet and
adherence to the EIA/TIA 568 wiring rules, the network diameter of a Fast
Ethernet collision domain is limited to 205 meters; in contrast, the maximum
10BASE-T Ethernet collision domain diameter can be up to 2500 meters.
Hubs
Unlike 10BASE-T hubs, which are all functionally identical, Fast Ethernet
repeater hubs are divided into two distinct types: Class I and Class II. A
Class I hub repeats all incoming signals on one port to the other ports by first
translating them to digital signals and then retranslating them back to line
signals. These translations are necessary when connecting various network
media to the same collision domain, such as wh en combining two wire-pair
100BASE-TX media with four wire-pair 100BASE-T4 media. Only one
Class I hub can exist within the same collision domain, thus this type of hub
cannot be cascaded. A Class II repeater, on the other hand, immediately
repeats all incoming line signals on one port to the other ports; no
translations are performed. This type of hub connects identical media to the
same collision domain; for example, TX to TX. At most, two Class II hubs
can exist within the same collision do main. The cable u sed to cascad e these
hubs is called an inter-repeater link (IRL).
As mentioned earlier, stackable hubs can be used to increase the number of
available nodes in a collision domain. An entire hub stack counts as a single
repeater.
Connectivity Rules
Fast Ethernet networks should respect the following limitations:
Introduction
5
♦ The maximum length of a twisted-pair segment (that is, distance
between a port in the hub to a single-address network device such as a
PC, server, or LAN switch) is 100 meters.
♦ The maximum diameter in a collision domain is about 205 meters
using two Class II hubs and 200 meters using one Class I hub.
♦ Between any two end-stations in a collision domain, there m ay be up
to three segments and two Class II hubs or two segments and one
Class I hub.
Ethernet Switching Introduction
Another approach to pushing beyond the limits of Ethernet technology is the
development of switching technology. A switch bridges Ethernet packets at
the lowest (MAC address) level between connected Ethernet or Fast Ethernet
LAN segments.
Switching is a cost-effective way of increasing the total network capacity
available to users on a local area network. A switch increases capacity and
decreases network loading by making it possible for a local area network to
be divided into different segments (also called collision domains) which
don’t compete with each other for network transmission capacity, giving a
decreased load on each.
The switch acts as a high-speed selective bridge between the individual
segments. Traffic that needs to go from one segment to another is
automatically forwarded by the switch, without interfering with any other
segments. This allows the total network capacity to be multip lied, while still
maintaining the same network cabling and adapter cards.
For Fast Ethernet networks, a switch is an effective way of eliminating
problems of chaining hubs beyond the “two-repeater limit.” A switch can be
used to split parts of the network into different collision domain s, making it
possible to expand your Fast Ethernet network beyond the 205 meter
6
Introduction

DES-2218 Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
network diameter limit for 100BASE-TX networks. Switches supporting
both traditional 10Mbps Ethernet and 100Mbps Fast Ethernet are also ideal
for bridging between existing 10Mbps networks and new 100Mbps
networks.
Switching LAN technology is a marked improvement over the previous
generation of network bridges, which were characterized by higher latencies.
Routers have also been used to segment local area networks, but the cost of a
router and the setup and maintenance required make routers relatively
impractical. Today’s switches are an ideal solution to most kinds of local
area network congestion problems.
Introduction
7

2
2 E
This chapter explains the features visible on the front and rear panels of the
DES-2218 Ethernet switch.
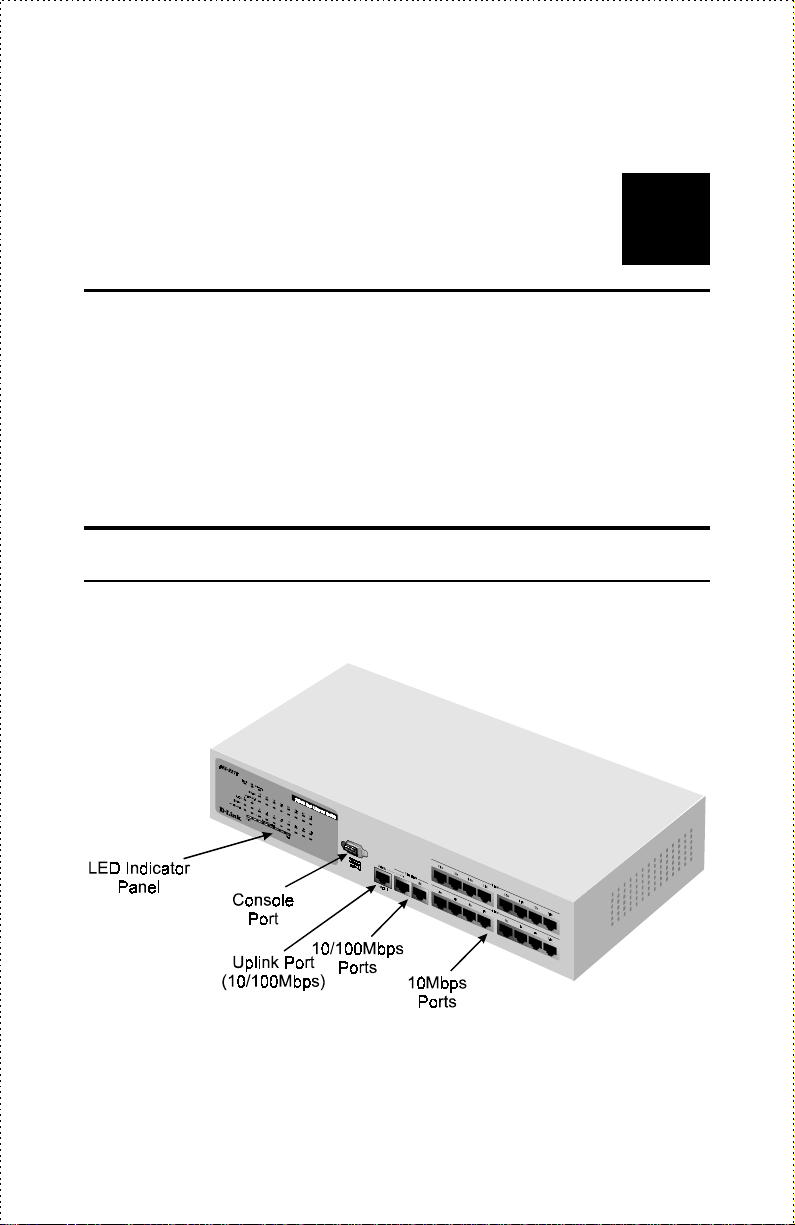
Front Panel
A front view of the DES-2218 Ethernet switch is shown below.
XTERNAL FEATURES

♦ LED Indicator Panel Gives status information about the switch
itself, as well as each of the switch ports. The LED indicator panel is
described in detail in the next section.
♦ Console Port The diagnostic console port is a standard RS-232 DB-9
connector, which can be used to connect a terminal or terminal
emulator to the switch, in order to configure or manage the switch.
The port can also be used for out-of-band network management. See
the Using the Console Interface chapter starting on page 21 for
complete information about using the console port.
♦ 100Mbps Ports The 10/100Mbps ports (ports 1 and 2) are NWay
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX MDI-X ports, suitable for connecting
directly to Ethernet or Fast Ethernet hosts or other network
equipment. The NWay feature allows the switch to automatically
detect the speed of the network connection.
♦ 10Mbps Ports The 10Mbps ports (ports 3 through 18) are 10BASE-
TX MDI-X ports, suitable for connecting directly to Ethernet hosts or
other network equipment.
♦ Uplink Port The Uplink Port is identical to Port 1, except that it is an
MDI port instead of an MDI-X port. This means that you can use it
to connect directly to a Fast Ethernet hub or switch without using a
crossover cable.
Note that the Uplink Port and Port 1 are really the same port, which
means you can’t connect devices to both Port 1 and the Uplink Port at the
same time.
10
External Features

DES-2218 Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
LED Indicators
♦ Power Lights when the DES-2218 Ethernet switch is powered on.
♦ Console Lights when the DES-2218 console interface is in use.
♦ MII Lights when the switch’s MII port is being used to connect to a
transceiver. If there is an active connection on the MII port, then the
Link/Act LED for port 2x will also light.
♦ 100M (Ports 1 and 2 ) Lights when the port is operating at 100Mbps.
Ports 1 through 4 are NWay ports that can automatically detect
whether 10BASE-T Ethernet or 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet twistedpair cable is connected.
♦ Link/Act (Ports 1 through 18) Lights green when the port is
connected to a powered-on Ethernet/Fast Ethernet station, and blinks
off briefly when information is transmitted or received on the port.
♦ FDX/Col (Ports 1 through 18) Lights green when the port is
operating in full-duplex mode. Briefly blinks amber when a collision
occurs on the Ethernet/Fast Ethernet segment.
♦ System Load Shows a bar graph giving an indication of the network
load, ranging from Low to High.
External Features
11
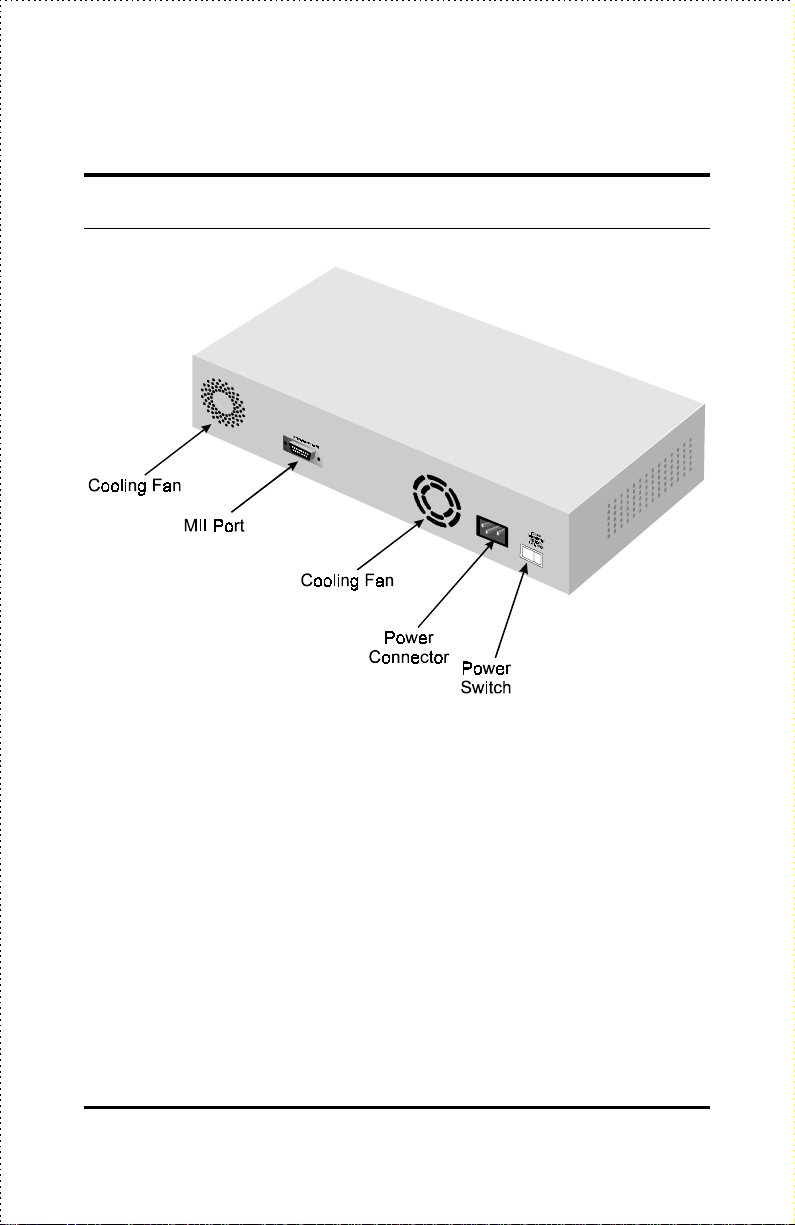
Rear Panel
♦ Cooling Fans Used to control the temperature within the switch’s
enclosure. When installing the switch, be sure not to block the fan
openings or otherwise restrict airflow.
♦ MII Port Used for connecting Fast Ethernet transceivers, which can
be used for attaching other Fast Ethernet media such as 100BASE-FX
(fiber optic) or 100BASE-T4 (4-wire twisted pair).
The MII port is shared with Port 2. If you are using the MII port, then
the 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX port labeled 2x cannot be used.
♦ Power Connector Used for connecting the power cord.
♦ Power Switch Used to turn the switch on (1 position) or off (0
position).
12
External Features
3
3 I
This chapter explains how to unpack and install your DES-2218 Ethernet
switch.
NSTALLATION
Unpacking the Switch
Open the shipping carton of your switch and carefully unpack the contents.
The carton should contain the following items:
♦ One DES-2218 Ethernet/Fast Ethernet switch
♦ One AC power cord
♦ Four rubber feet to be used for shock cushioning
♦ Eight screws and two mounting brackets
♦ This User's Guide
Inspect the switch and all accompanying items. If any item is damaged or
missing, report the problem immediately to your dealer.

Installing the Switch
Location
The site where you install the switch may greatly affect its performance.
When installing, consider the following factors:
♦ Install the switch in a cool and dry place. See Appendix A,
Specifications, for the acceptable temperature and humidity operating
ranges.
♦ Install the switch in a site free from strong electromagnetic field
generators (such as motors), vibration, dust, and direct exposure to
sunlight.
♦ Leave at least 10 cm of space at the front and rear of the switch for
ventilation.
♦ Install on a sturdy, level surface that can support at least the weight of
the switch, or in an EIA standard-size rack. For information on rack
installation, see the next section, Rack Mounting.
When installing the switch on a level surface, be sure to attach the rubber
feet at the bottom of the device. The rubber feet act as cushioning devices.
Rack Mounting
The switch can be mounted in an EIA standard 19-inch rack, which can be
placed in a wiring closet with other equipment. Attach the mounting
brackets on the switch’s front panel (one on each side), and secure them with
the provided screws. Then, use screws provided with the equipment rack to
mount the switch in the rack.
14
Installation
 Loading...
Loading...