Page 1
Dell C7765dn
Color Multifunction Printer
Security Target
Version 1.1.3
This document is a translation of the evaluated
and certified security target written in Japanese.
September 2014
Page 2

- Table of Contents -
1. ST INTRODUCTION ........................................................... 1
1.1. ST Reference ............................................................................. 1
1.2. TOE Reference ........................................................................... 1
1.3. TOE Overview ............................................................................ 1
1.3.1. TOE Type and Major Security Features ............................................... 1
1.3.2. Environment Assumptions ............................................................... 4
1.3.3. Required Non-TOE Hardware and Software ......................................... 5
1.4. TOE Description .......................................................................... 8
1.4.1. User Assumptions .......................................................................... 8
1.4.2. Logical Scope and Boundary ............................................................ 8
1.4.3. Physical Scope and Boundary ......................................................... 17
1.4.4. Guidance .................................................................................... 18
2. CONFORMANCE CLAIMS ................................................... 19
2.1. CC Conformance Claims ............................................................ 19
2.2. PP Claims, Package Claims ......................................................... 19
2.2.1. PP Claims .................................................................................... 19
2.2.2. Package Claims ............................................................................ 19
2.2.3. Conformance Rationale ................................................................. 19
3. SECURITY PROBLEM DEFINITION ...................................... 20
3.1. Threats ................................................................................... 20
3.1.1. Assets Protected by TOE ................................................................ 20
3.1.2. Threats ....................................................................................... 22
3.2. Organizational Security Policies ................................................... 23
3.3. Assumptions ............................................................................ 23
4. SECURITY OBJECTIVES .................................................... 24
4.1. Security Objectives for the TOE .................................................. 24
4.2. Security Objectives for the Environment ...................................... 25
4.3. Security Objectives Rationale ..................................................... 25
5. EXTENDED COMPONENTS DEFINITION ............................... 29
5.1. Extended Components ............................................................... 29
i
Page 3

6. SECURITY REQUIREMENTS ............................................... 30
6.1. Security Functional Requirements ............................................... 35
6.1.1. Class FAU: Security audit ............................................................. 35
6.1.2. Class FCS: Cryptographic support ................................................... 40
6.1.3. Class FDP: User data protection .................................................... 41
6.1.4. Class FIA: Identification and authentication ..................................... 46
6.1.5. Class FMT: Security management ................................................... 51
6.1.6. Class FPT: Protection of the TSF ................................................... 58
6.1.7. Class FTP: Trusted path/channels ................................................. 59
6.2. Security Assurance Requirements ............................................... 60
6.3. Security Requirement R a tionale .................................................. 61
6.3.1. Security Functional Requirements Rationale ..................................... 61
6.3.2. Dependencies of Security Functional Requirements ........................... 66
6.3.3. Security Assurance Requirements Rationale ..................................... 69
7. TOE SUMMARY SPECIFICATION ......................................... 70
7.1. Security Functions .................................................................... 70
7.1.1. Hard Disk Data Overwrite (TSF_IOW) .............................................. 71
7.1.2. Hard Disk Data Encryption (TSF_CIPHER) ........................................ 71
7.1.3. User Authentication (TSF_USER_AUTH) ........................................... 72
7.1.4. System Administrator’s Security Management (TSF_FMT) .................. 78
7.1.5. Customer Engineer Operation Restriction (TSF_CE_LIMIT) ................. 79
7.1.6. Security Audit Log (TSF_FAU) ........................................................ 80
7.1.7. Internal Network Data Protection (TSF_NET_PROT) ........................... 82
7.1.8. Fax Flow Security (TSF_FAX_FLOW) ................................................ 85
7.1.9. Self Test (TSF_S_TEST) ................................................................. 85
8. ACRONYMS AND TERMINOLOGY ........................................ 86
8.1. Acronyms ................................................................................ 86
8.2. Terminology ............................................................................. 87
9. REFERENCES .................................................................. 91
ii
Page 4

- List of Figures and Tables -
Figure 1: General Operational Environment .......................................................... 5
Figure 2: MFD Units and TOE Logical Scope .......................................................... 9
Figure 3: Authentication Flow for Private Print and Mailbox ................................... 12
Figure 4: MFD Units and TOE Physical Scope ...................................................... 17
Figure 5: Assets under and not under Protection ................................................. 21
Table 1: Function Types and Functions Provided by the TOE .................................... 2
Table 2: User Role Assumptions .......................................................................... 8
Table 3: TOE Basic Functions .............................................................................. 9
Table 4: Categories of TOE Setting Data............................................................. 21
Table 5: Threats Addressed by the TOE .............................................................. 22
Table 6: Organizational Security Policy ............................................................... 23
Table 7: Assumptions ...................................................................................... 23
Table 8: Security Objectives for the TOE ............................................................ 24
Table 9: Security Objectives for the Environment ................................................ 25
Table 10: Assumptions / Threats / Organizational Security Policies and the
Corresponding Security Objectives ............................................................... 25
Table 11: Security Objectives Rationale for Security Problem ................................ 26
Table 12: Auditable Events of TOE and Individually Defined Auditable Events .......... 35
T able 13: Oper ations between Subjects and Objects Covered by MFD Access Control SFP
.............................................................................................................. 41
Table 14: Rules for Access Control .................................................................... 42
Table 15: Rules for Explicit Access Authorization ................................................. 43
Table 16: Subjects, Information, and Operations that cause the information to flow . 44
Table 17: List of Security Functions ................................................................... 51
Table 18: Security Attributes and Authorized Roles .............................................. 52
Table 19 Initialization property ........................................................................ 53
Table 20: Operation of TSF Data ....................................................................... 54
Table 21: Security Management Functions Provided by TSF .................................. 55
Table 22: EAL3 Assurance Requirements ............................................................ 60
Table 23: Security Functional Requirements and the Corresponding Security Objectives
.............................................................................................................. 61
Table 24: Security Objectives to SFR Rationale ................................................... 62
Table 25: Dependencies of Functional Security Requirements ................................ 66
Table 26: Security Functional Requirements and the Corresponding TOE Security
Functions ................................................................................................. 70
Table 27: Management of security attributes ...................................................... 75
Table 28: Access Control .................................................................................. 76
Table 29: Details of Security Audit Log Data ....................................................... 80
iii
Page 5
Dell C7765dn Security Target
1. ST INTRODUCTION
This chapter describes Security Target (ST) Reference, TOE Reference, TOE Overview, and TOE
Description.
1.1. ST Reference
This section provides information needed to identify this ST.
ST Title: Dell C7765dn Color Multifunction Printer Security Target
ST Version: V 1.1.3
Publication Date: September 8, 2014
Author: Fuji Xerox Co., Ltd.
1.2. TOE Reference
This section provides information needed to identify this TOE.
The TOE is C7765dn Color Multifunction Printer.
The TOE is identified by the following TOE name and ROM versions.
TOE
Identification:
Version:
Manufacturer: Fuji Xerox Co., Ltd.
Dell C7765dn Color Multifunction Printer
Controller ROM Ver. 2.205.5
IOT ROM Ver. 41.1.0
ADF ROM Ver. 12.5.0
1.3. TOE Overvi ew
1.3.1. TOE Type and Major Security Features
1.3.1.1. TOE Type
This TOE, categorized as an IT product, is the Dell C7765dn Color Multifunction Printer (hereinafter
referred to as “MFD”) which has the copy, print, scan, and fax functions.
The TOE is the product which controls the whole MFD and protects the following against threats:
The document data stored on the internal HDD, the used document data, the security audit log data,
the document data exists on the internal network between the TOE and the remote, and the TOE
setting data.
1.3.1.2.
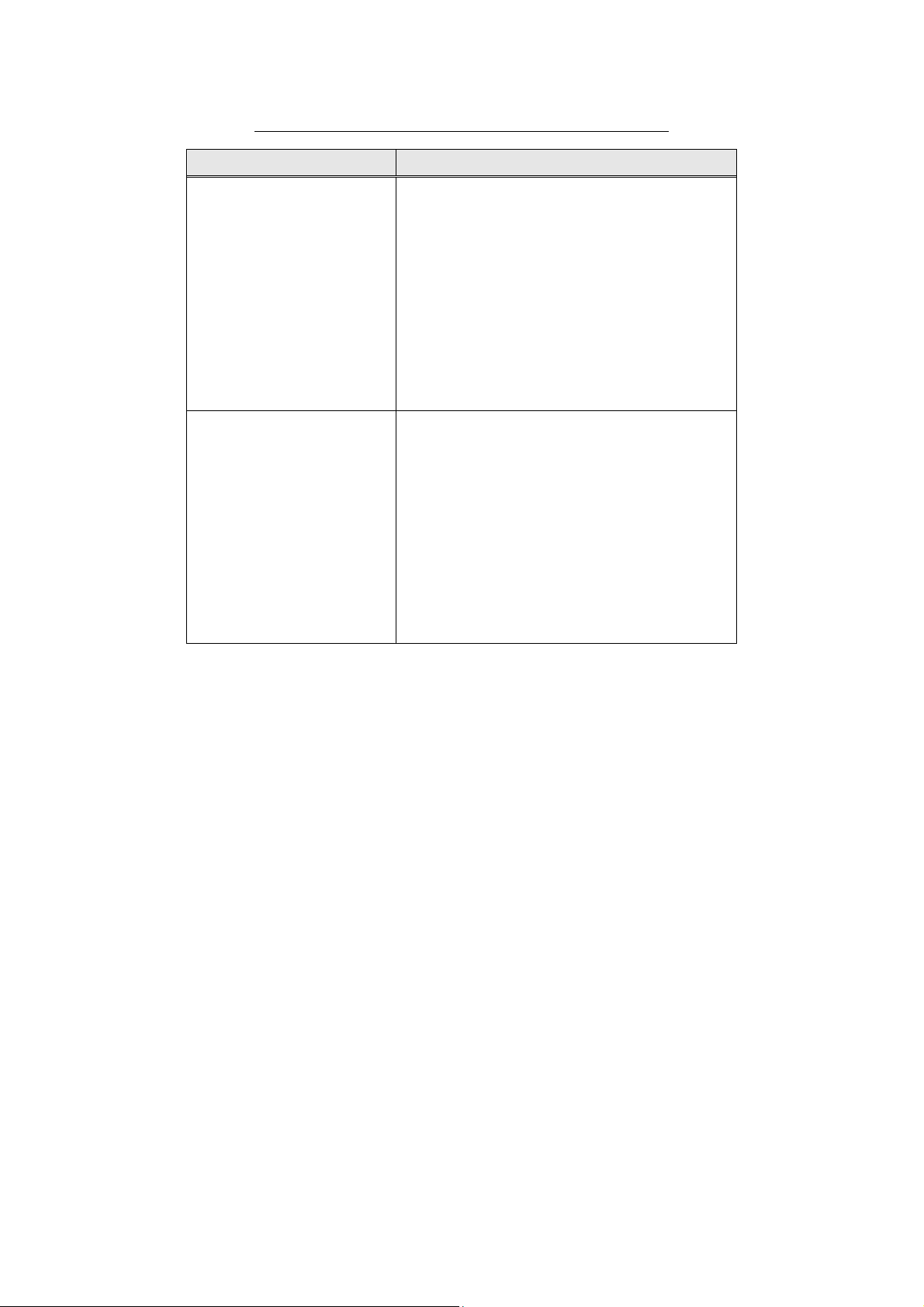
Table 1 shows the function types and functions provided by the TOE.
Function Types
- 1 -
Page 6
Dell C7765dn Security Target
Table 1: Function Types and Functions Provided by the TOE
Function types Functions provided by the TOE
- Control Panel
- Copy
- Print
- Scan
Basic Function
- Network Scan
- Fax
- Direct Fax (with local authentication only)
- Internet Fax
- Remote Configuration
- Hard Disk Data Overwrite
- Hard Disk Data Encryption
- User Authentication
- Administrator’s Security Management
Security Function
- Customer Engineer Operation Restriction
- Security Audit Log
- Internal Network Data Protection
- Fax Flow Security
- Self Test
・ Optional Fax board (out of the TOE boundary) is required to use Fax, Direct Fax, Internet Fax,
and Fax Flow Security functions.
・ To use print, scan, and Direct Fax functions, the following items shall be installed to the
external client for general user and that for system administrator: printer driver, Network Scan
Utility, and fax driver.
・ There are two types of user authentication, local authentication and remote authentication, and
the TOE behaves with either one of the authentication types depending on the setting.
In this ST, the difference of the TOE behavior is described if the TOE behaves differently
depending on the type of authentication being used. Unless specified, the behavior of the TOE
is the same for both authentication types.
There are two types of Remote Authentication: LDAP Authentication and Kerberos
Authentication. To set SA (system administrator privilege) as user role assumption in Kerberos
authentication, LDAP server is also necessary.
・ For Kerberos authentication, it is also possible to use Smart Card (CAC/PIV) instead of
authentication from the control panel with an ID and a password. User information and
certificates in Smart Card and an OCSP server are used for authentication.
In the same way as other types of authentication, LDAP server is required for setting SA. For
Smart Card authentication, an optional card reader (not included in TOE) needs to be
connected.
・
- 2 -
Page 7

Dell C7765dn Security Target
1.3.1.3. Usage and Major Security Features of TOE
The TOE is mainly used to perform the following functions:
・ Copy function and Control Panel function are to read the original data from IIT and print them
out from IOT according to the general user’s instruction from the control panel. When more
than one copy of an original data is ordered, the data read from IIT are first stored into the
MFD internal HDD. Then, the stored data are read out from the internal HDD for the required
number of times so that the required number of copies can be made.
・ Print function is to decompose and print out the print data transmitted by a general user client.
・ Configuration Web Tool is to retrieve the document data scanned by MFD from Mailbox.
It also enables a system administrator to refer to and rewrite TOE setting data via Web
browser.
・ Scan function and Control Panel function are to read the original data from IIT and store them
into Mailbox within the MFD internal HDD, according to the general user’s instruction from
the control panel.
The stored document data can be retrieved via standard Web browser by using Configuration
Web Tool or Network Scan Utility (with local authentication only).
・ Network Scan function and Control Panel function are to read the original data from IIT and
transmit the document data to FTP server, SMB server, or Mail server, according to the
information set in the MFD. This function is operated according to the general user’s
instruction from the control panel.
・ Fax function and Control Panel function are to send and receive fax data. According to the
general user’s instruction from the control panel to send a fax, the original data are read from
IIT and then sent to the destination via public telephone line. The document data are received
from the sender’s machine via public telephone line and then printed out from the recipient’s
IOT or stored in Mailbox.
・ The Internet Fax function and Control Panel function are to send and receive fax data via the
Internet, not public telephone line.
・ The Direct Fax function is to send data from a user client to the destination via public
telephone line (with local authentication only). The data are first sent to MFD as a print job
and then to the destination without being printed out.
The TOE provides the following security features:
(1) Hard Disk Data Overwrite
To completely delete the used document data in the internal HDD, the data are overwritten with
new data after any job of copy, print, scan, etc. is completed.
(2) Hard Disk Data Encryption
The document data and the security audit log data are encrypted before being stored into the
internal HDD when using any function of copy, print, scan, etc. or configuring various security
function settings.
(3) User Authentication
Access to the TOE functions is restricted to the authorized user and this function identifies and
- 3 -
Page 8

Dell C7765dn Security Target
authenticates users. A user needs to enter his/her ID and password from the fax driver, Network
Scan Utility, or Web browser of the general user client, or MFD control panel.
A user can also use Smart Card authentication (CAC/PIV) for identification and authentication.
(4) System Administrator’s Security Management
This function allows only the system administrator identified and authorized from the control
panel or system administrator client to refer to and change the TOE security function settings.
(5) Customer Engineer Operation Restriction
A system administrator can prohibit CE from referring to and changing the TOE security
function settings.
(6) Security Audit Log
The important events of TOE such as device failure, configuration change, and user operation
are traced and recorded based on when and who used what function.
(7) Internal Network Data Protection
This function protects the communication data on the internal network such as document data,
security audit log data, and TOE setting data. (The following general encryption
communication- protocols are supported: SSL/TLS, IPSec, SNMP v3, and S/MIME.)
(8) Fax Flow Security
This function prevents unauthorized access to the TOE or the internal network via Fax board
from public telephone line.
(9) Self Test
This function verifies the integrity of TSF executable code and TSF data.
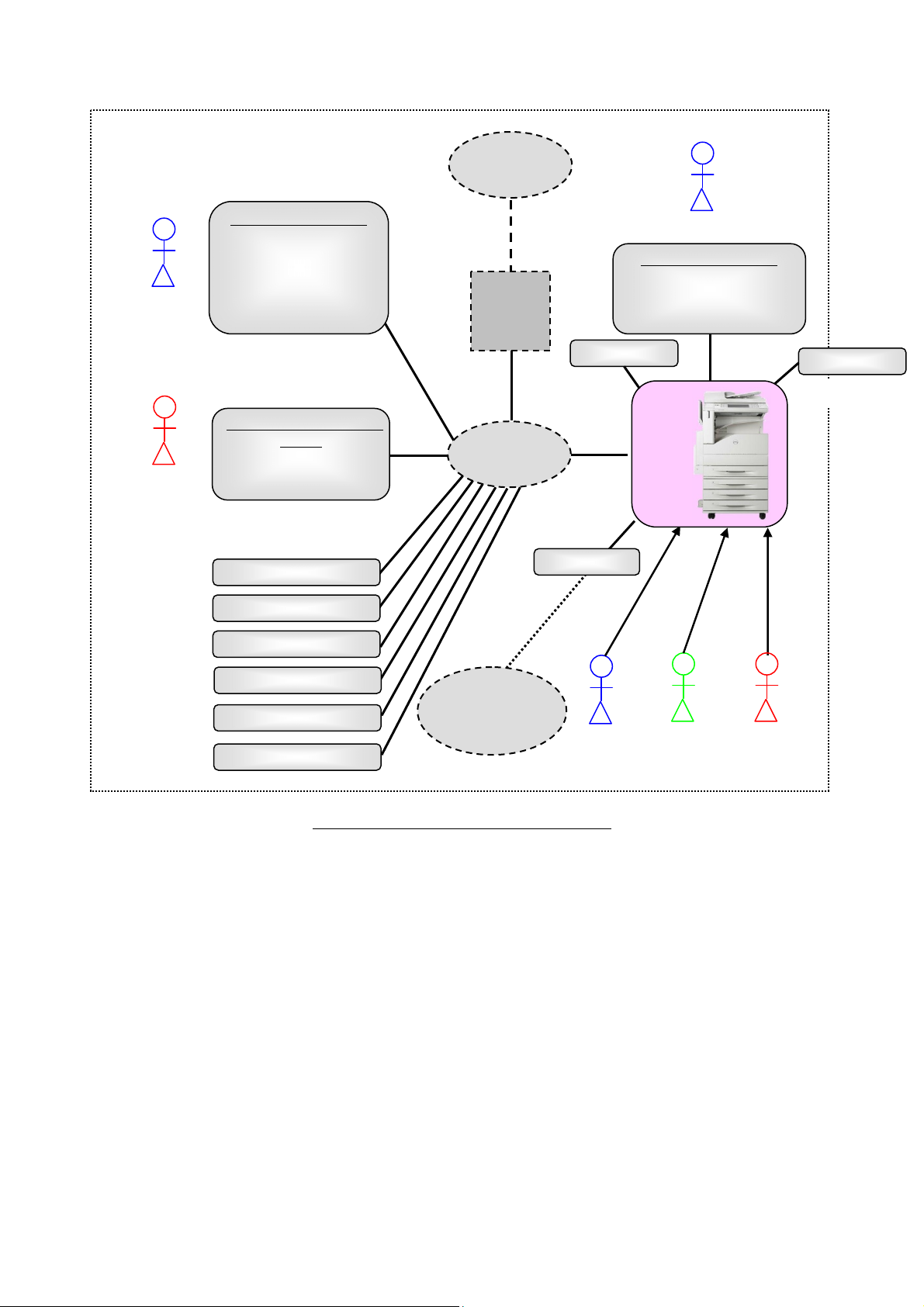
1.3.2. Environment Assumptions
This TOE is assumed to be used as an IT product at general office and to be connected to public
telephone line, user clients, and the internal network protected from threats on the external network by
firewall etc.
Figure 1 shows the general environment for TOE operation.
- 4 -
Page 9
t
Web
owser
r
General
User
System
Administrator
Dell C7765dn Security Target
General User Client
-Printer Driver
-Fax Driver
-Network Scan
Utility
Br
-
System Administrator
Client
-Web Browser
Mail Server
FTP Server
SMB Server
LDAP Server
Kerberos Server
OCSP Server
External
Network
Firewall
Internal
Network
Public
Telephone
Line
USB Media
USB
USB
Fax Board
General User
General User
General User Clien
-Printer Driver
-Fax Driver
USB
TOE
CE
System
Administrator
Card Reade
USB
Figure 1: General Operational Environment
1.3.3. Required Non-TOE Hardware and Software
In the operational environment shown in Figure 1, the TOE (MFD) and the following non-TOE
hardware/software exist.
(1) General user client:
The hardware is a general-purpose PC. When a client is connected to the MFD via the internal
network and when the printer driver, Network Scan Utility, and fax driver are installed to the
client, the general user can request the MFD to print, fax, and retrieve the document data.
The user can also request the MFD to retrieve the scanned document data via Web browser by
using scan function of the MFD. Additionally, the general user can change the settings which
he/she registered to the MFD: Mailbox name, password, access control, and automatic deletion of
- 5 -
Page 10

Dell C7765dn Security Target
document.
When the client is connected to the MFD directly via USB and printer/fax driver is installed to the
client, the user can request the MFD to print/fax the document data.
(2) System administrator client:
The hardware is a general-purpose PC. A system administrator can refer to and change TOE
setting data via Web browser.
(3) Mail server:
The hardware/OS is a general-purpose PC or server. The MFD sends/receives document data
to/from Mail server via mail protocol.
(4) FTP server:
The hardware/OS is a general-purpose PC or server. The MFD sends document data to FTP server
via FTP.
(5) SMB server:
The hardware/OS is a general-purpose PC or server. The MFD sends document data to SMB
server via SMB.
(6) LDAP server
The hardware/OS is a general-purpose PC or server. The MFD acquires identification and
authentication information from LDAP server via LDAP. In addition, it acquires SA information
of user role assumptions.
(7) Kerberos server
The hardware/OS is a general-purpose PC or server. The MFD acquires identification and
authentication information from Kerberos server via Kerberos.
(8) OCSP Server
The hardware/OS is a general-purpose PC or server.
The MFD retrieves information on revocation status of certificates other than self-signed
certificates from an OCSP server, if the certificate revocation retrieval setting is enabled.
(9) Fax board:
The Fax board is connected to external public telephone line and supports G3 protocols. The
Fax board is connected to the MFD via USB interface to enable sending and receiving of fax.
(10) Card Reader
A card reading device for supporting PKI certification that uses Smart Card (CAC/PIV).
- 6 -
Page 11

Dell C7765dn Security Target
(11) USB Media
The USB Media is used for printing data stored in the USB Media and for storing scanned data.
The OS of (1) general user client and (2) system administrator client are assumed to be Windows XP,
Windows Vista, and Windows 7.
The (6) LDAP server, (7) Kerberos server, and (8) OCSP server are assumed to be Windows Active
Directory.
The (10) Card Reader is assumed to be SCR331 or SCR3310 v2.0.
- 7 -
Page 12
Dell C7765dn Security Target
1.4. TOE Description
This section describes user assumptions and logical/physical scope of this TOE.
1.4.1. User Assumptions
Table 2 specifies the roles of TOE users assumed in this ST.
Table 2: User Role Assumptions
User Role Description
Administrator of the
organization
General user A user of TOE functions such as copy, print and fax.
System administrator
(Key operator + System
Administrator Privilege [SA])
Customer engineer (CE)
An administrator or responsible official of the organization which
owns and uses TOE.
A user who is authorized to manage the device using the system
administrator mode. A system administrator can refer to and rewrite
the TOE setting for device operation and that for security functions
via TOE control panel, and Web browser.
A user who can configure the TOE operational settings using the
interface for CE.
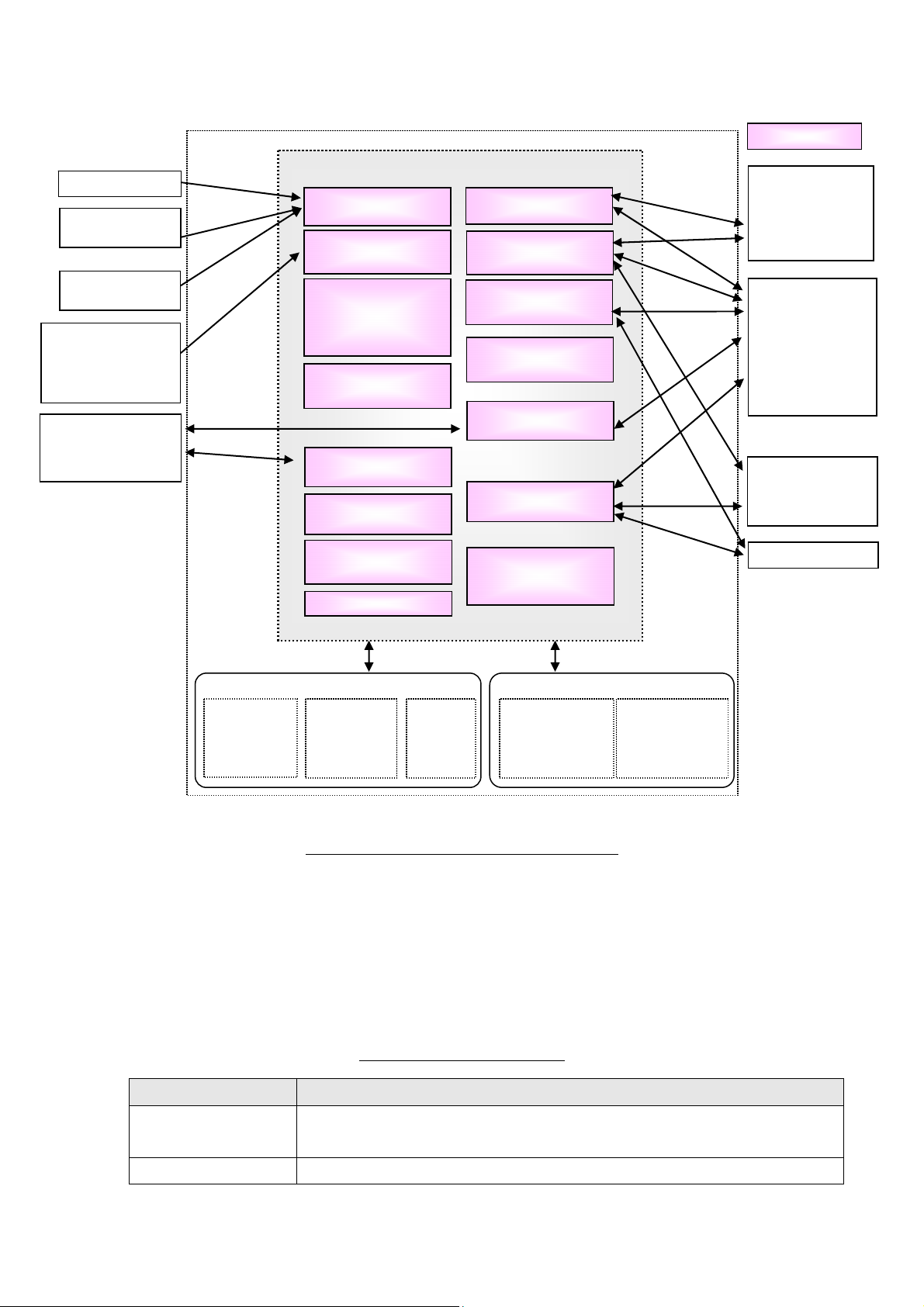
1.4.2. Logical Scope and Boundary
The logical scope of this TOE consists of each function of the programs.
Figure 2 shows the logical architecture of the MFD.
- 8 -
Page 13
Dell C7765dn Security Target
g
r
y
t
g
General User
System
Administrator
ineer
Customer
En
Card Reader
LDAP Server
Kerberos Server
OCSP Server
Fax Board
(Public Telephone
Line)
TOE
Controller ROM
Internal HDD
Used
Document
Data
Control Panel
Use
Authentication
System
Administrator’s
Security
Management
Security
Audit Log
Fax Flow
Securit
Hard Disk Data
Encryption
Hard Disk Data
Overwrite
Self T est
Document
Data
Audit
Log
Data
Remote
Confi
uration
Internal Network
Data Protection
Prin
(Decompose)
Copy
Fax / Direct Fax
/ Internet Fax
Scan / Network
Scan
Customer Engineer
Operation
Restriction
NVRAM/SEEPROM
TOE Setting
Data
Logical Scope
System
Administrator
Client
-Web Browser
General User
Client
- Printer driver
- Fax Driver
- Network Scan
Utility
- Web Browser
FTP Server
SMB Server
Mail Server
USB Media
Other Setting
Data
Figure 2: MFD Units and TOE Logical Scope
1.4.2.1.
Basic Functions
As shown in Table 3, the TOE provides the functions of control panel, copy, print, scan, network scan,
fax, Internet Fax, Direct Fax (with local authentication only), and Remote Configuration to general
user.
Table 3: TOE Basic Functions
Function Description
Control Panel
Function
Control panel function is a user interface function for general user, CE, and
system administrator to operate MFD functions.
Copy Function Copy function is to read the original data from IIT and print them out from
- 9 -
Page 14
Dell C7765dn Security Target
IOT according to the general user’s instruction from the control panel.
When more than one copy of an original is ordered, the data read from IIT
are first stored into the MFD internal HDD. Then, the stored data are read out
from the internal HDD for the required number of times so that the required
number of copies can be made.
Print Function Print function is to print out the data according to the instruction from a
general user client. The print data created via printer driver are sent to the
MFD to be analyzed, decomposed, and printed out from IOT.
The print function is of two types: the normal print in which the data are
printed out from IOT directly after decomposed and the Store Print in which
the bitmap data are temporarily stored in the internal HDD and then printed
out from IOT according to the general user’s instruction from the control
panel.
There is also the function to print data stored in an external USB Media by
designating the data from the control panel.
Scan Function,
Network Scan
Function
Scan function is to read the original data from IIT and then store them into
the internal HDD or an external USB Media according to the general user’s
instruction from the control panel.
A general user can retrieve the stored document data from a general user
client via Configuration Web Tool or Network Scan Utility (with local
authentication only).
Network scan function is to read the original data from IIT and automatically
transmit them to a general user client, FTP server, Mail server, or SMB server
according to the information set in the MFD. A general user can request this
function from the control panel.
Fax Function Fax function is to send and receive fax data. According to the general user’s
instruction from the control panel to send a fax, the original data them read
from IIT and sent to the destination via public telephone line. The document
data are received from the sender’s machine via public telephone line.
Direct Fax (with local
authentication only)
Function,
Internet Fax Function
Direct Fax function is to directly fax document data to the destination.
According to the instruction from a general user client to send a fax, the print
data created via fax driver are sent to the MFD, analyzed, and decomposed.
Then, the data are converted to the format for fax sending and sent to the
destination via public telephone line.
Internet Fax function is to send and receive fax data as in the normal Fax
function. According to the general user’s instruction from the control panel to
send a fax, the original data are read from IIT and sent to the destination via
the Internet. The document data are received from the sender’s machine via
the Internet and printed out from the recipient’s IOT.
Remote
Configuration
Remote Configuration Function enables System Administrator’s Security
Management by which a system administrator can access and rewrite TOE
- 10 -
Page 15

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Function setting data. For this, a system administrator must be authenticated by his/her
ID and password entered from Web browser of a system administrator client.
In addition remote Configuration function is to retrieve the scanned
document data and the received fax data that are stored in the internal HDD
according to the instruction from Web browser of a general user client.
1.4.2.2.
Security Functions
The security functions provided by the TOE are the following.
(1) Hard Disk Data Overwrite
To completely delete the used document data in the internal HDD, the data are overwritten with
new data after each job (copy, print, scan, Network Scan, Fax, Internet Fax, or Direct Fax) is
completed. Without this function, the used document data remain and only the management data
are deleted.
(2) Hard Disk Data Encryption
Some data such as the security audit log data and the document data in Mailbox remain in the
internal HDD even if the machine is powered off. To solve this problem, the document data and
security audit log data are encrypted before being stored into the internal HDD when operating
any function of copy, print, scan, network scan, fax, Internet Fax, and Direct Fax (with local
authentication only), or configuring various security function settings.
(3) User Authentication
Access to the TOE functions is restricted to the authorized user.
A user needs to enter his/her ID and password from the fax driver, Network Scan Utility, or Web
browser of the general user client, or MFD control panel.
A user can also use Smart Card
authentication on the control panel.
Only the identified and authenticated user can use the following functions:
a) Functions controlled by the MFD control panel:
Copy, fax (send), Internet Fax (send), scan, network scan, Mailbox, and print (This print function
requires the Accounting System preset from printer driver. A user must be authenticated from the
control panel for print job.)
b) Functions controlled by Network Scan Utility of user client(with local authentication only):
Function to retrieve document data from Mailbox
c) Functions controlled by Configuration Web Tool:
Display of device condition, display of job status and its log, function to retrieve document data
from Mailbox, and print function by file designation
Among the above functions which require user authentication, some particularly act as security
functions. The following are the security functions which prevent the unauthorized reading of
- 11 -
Page 16
Dell C7765dn Security Target
t
r
t
document data in the internal HDD by an attacker who is impersonating an authorized user:
・ The Store Print function (Private Print function) and the Mailbox function, which require user
authentication from the control panel or Smart Card.
・ The function to retrieve document data from Mailbox (Mailbox function) which requires user
authentication by using Configuration Web Tool or Network Scan Utility (with local
authentication only), and the Store Print function (Private Print function) by file designation
using Configuration Web Tool.
Figure 3 shows the authentication flow of the above functions.
User Client
Printer driver
Web Browse
Network Scan
Utility
(with local authentication
only)
TOE
Classification
Authentication
Authentication
Print Job
Private
Prin
Scanned Data,
Mailbox
Authentication from Control Panel or Smart Card
Prin
Figure 3: Authentication Flow for Private Print and Mailbox
Store Print Function (Private Print Function)
When the MFD is set to “Save as Private Charge Print,” and a user sends a print request from the
printer driver in which the Accounting System is preset, the print data are decomposed into
bitmap data, classified according to the user ID, and temporarily stored in the corresponding
Private Print area within the internal HDD.
In the same way, when a user is authenticated by entering his/her ID and password from
Configuration Web Tool for authentication, and the user sends a print request by designating the
files within a user client, the print data are temporarily stored in Private Print area according to
the user ID.
To refer to the stored print data, a user needs to enter his/her ID and password from the control
- 12 -
Page 17

Dell C7765dn Security Target
panel or to use Smart Card (CAC/PIV). When the user is authenticated, the data on the waiting
list corresponding to the user ID are displayed. The user can request printing or deletion of the
data on the list.
Mailbox Function
The scanned data and received fax data can be stored into Mailbox from IIT and Fax board which
are not shown in Figure 3.
To store the scanned data into Mailbox, a user needs to enter his/her ID and password from the
control panel or to use Smart Card (CAC/PIV). When the user is authenticated, the document data
can be scanned from IIT and stored into the internal HDD according to the user’s instruction from
the control panel.
To store the received fax data into Mailbox, user authentication is not required. Among the
received fax data transmitted over public telephone line, the following data are automatically
classified and stored into each corresponding Mailbox: the received fax data whose corresponding
Mailbox is specified by the sender, the received fax data from a particular sender (the data are
classified according to the sender’s telephone number), and the received fax data from an
unknown sender.
To retrieve, print, or delete the stored data in the Personal Mailbox corresponding to the each
registered user’s ID, user authentication is required; the MFD compares the user ID and password
preset in the device against those entered by a user from the control panel, Configuration Web
Tool, or Network Scan Utility(with local authentication only). For user authentication, Smart
Card authentication is also available on the control panel.
(4) System Administrator’s Security Management
To grant a privilege to a specific user, this TOE allows only the authenticated system
administrator to access the System Administrator mode which enables him/her to refer to and set
the following security functions from the control panel:
・ Refer to and set Hard Disk Data Overwrite;
・ Refer to and set Hard Disk Data Encryption;
・ Set the cryptographic seed key for Hard Disk Data Encryption;
・ Refer to and set the functions that use password entered from MFD control panel in user
authentication;
・ Set the ID and password of key operator (only a key operator is privileged);
・ Refer to and set the ID of SA / general user, and set the password (with local authentication
only);
・ Refer to and set the access denial when system administrator’s authentication fails;
・ Refer to and set the limit of user password length (for general user and SA) (with local
authentication only);
・ Refer to and set the SSL/TLS communication;
・ Refer to and set the IPSec communication;
・ Refer to and set the S/MIME communication;
- 13 -
Page 18

Dell C7765dn Security Target
・ Refer to and set the User Authentication;
・ Refer to and set the Store Print;
・ Refer to and set the date and time;
・ Refer to and set the Self Test;
Additionally, this TOE allows only the system administrator, who is authenticated from the
system administrator client via Web browser using Configuration Web Tool, to refer to and set the
following security functions via Configuration Web Tool:
・ Set the ID the password of key operator (only a key operator is privileged);
・ Refer to and set the ID of SA / general user, and set the password (with local authentication
only);
・ Refer to and set the access denial when system administrator’s authentication fails;
・ Refer to and set the limit of user password length (for general user and SA, with local
authentication only);
・ Refer to and set Audit Log;
・ Refer to and set the SSL/TLS communication;
・ Refer to and set the IPSec communication;
・ Refer to and set the SNMPv3 communication;
・ Refer to and set the SNMPv3 authentication password.
・ Refer to and set the S/MIME communication;
・ Create/upload/download an X.509 certificate;
・ Refer to and set the User Authentication;
(5) Customer Engineer Operation Restriction
This TOE allows only the authenticated system administrator to refer to or enable/disable the
Customer Engineer Operation Restriction setting from the control panel and Configuration Web
Tool. For this, CE cannot refer to or change the setting of each function described in (4) System
Administrator’s Security Management.
(6) Security Audit Log
The important events of TOE such as device failure, configuration change, and user operation are
traced and recorded based on when and who operated what function. Only a system administrator
can supervise or analyze the log data by downloading them in the form of tab-delimited text file
via Web browser using Configuration Web Tool. To download the log data, SSL/TLS
communication needs to be enabled.
(7) Internal Network Data Protection
The communication data on the internal network such as document data, security audit log data,
and TOE setting data are protected by the following general encryption communication-protocols:
・ SSL/TLS
・ IPSec
- 14 -
Page 19

Dell C7765dn Security Target
・ SNMP v3
・ S/MIME
(8) Fax Flow Security
A Fax board is an option and is connected to TOE controller board via USB interface. An attacker
cannot access the TOE or the internal network from public telephone line via the Fax board.
(9) Self Test
The TOE can execute the self test function to verify the integrity of TSF executable code and TSF
data.
1.4.2.3.
Settings for the Secure Operation
System administrator shall set the following to enable security functions in 1.4.2.2.
・ Hard Disk Data Overwrite
Set to [Enabled].
・ Hard Disk Data Encryption
Set to [Enabled].
・ Passcode Entry for Control Panel
Set to [Enabled].
・ Access denial when system administrator’s authentication fails
Default [5] Times.
・ User Passcode Minimum Length (for general user and SA)
Set to [9] characters
・ SSL/TLS
Set to [Enabled]
・ IPSec
Set to [Enabled]
・ S/MIME
Set to [Enabled]
・ User Authentication
Set to [Local Authentication] or [Remote Authentication]
・ Store Print
Set to [Save As Private Charge Print]
・ Audit Log
Set to [Enabled]
・ SNMPv3
Set to [Enabled]
・ Customer Engineer Operation Restriction
Set to [Enabled]
- 15 -
Page 20

・ Self Test
Set to [Enabled]
Dell C7765dn Security Target
- 16 -
Page 21
Dell C7765dn Security Target
(
)
(
)
t
(
)
(
)
r
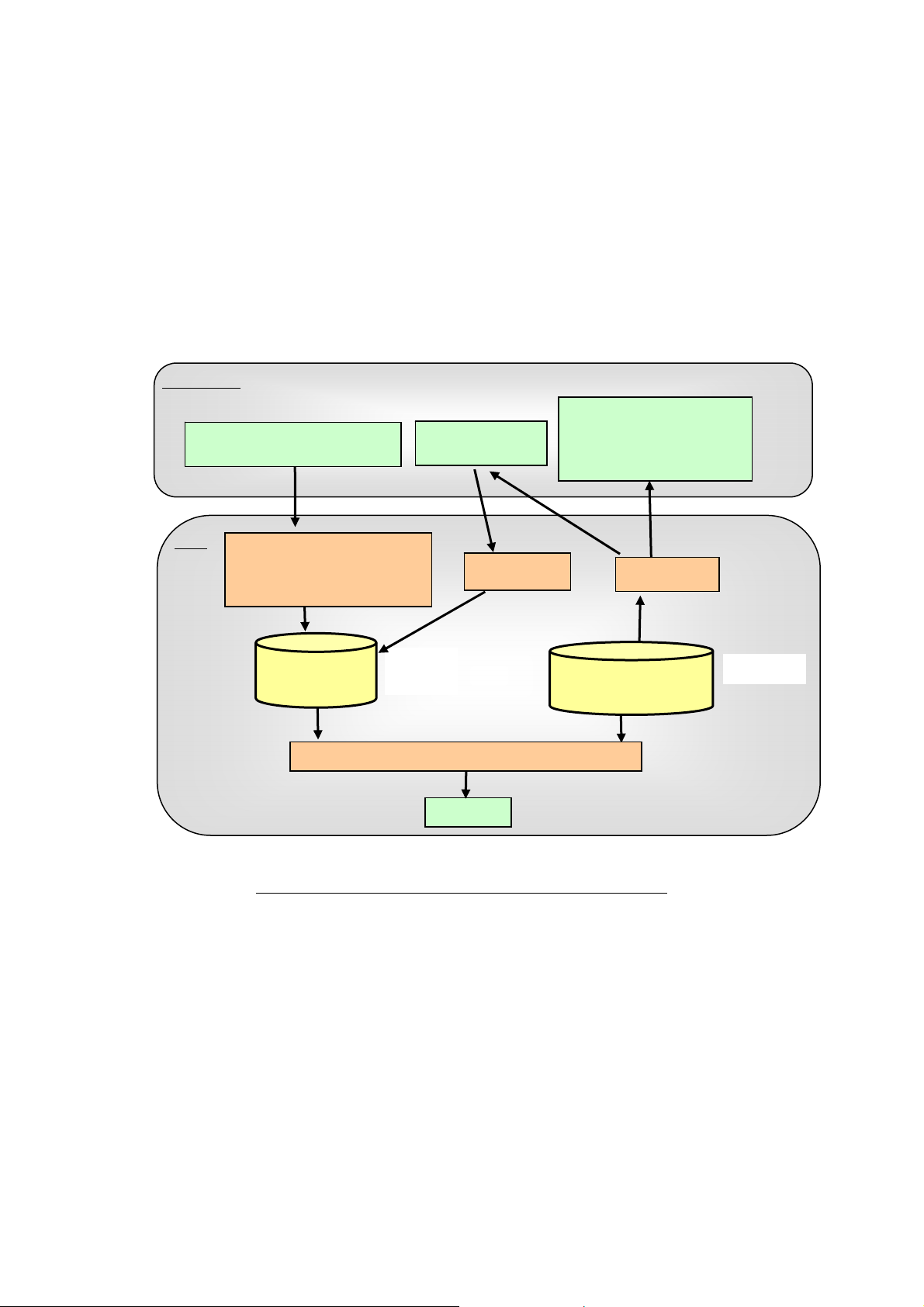
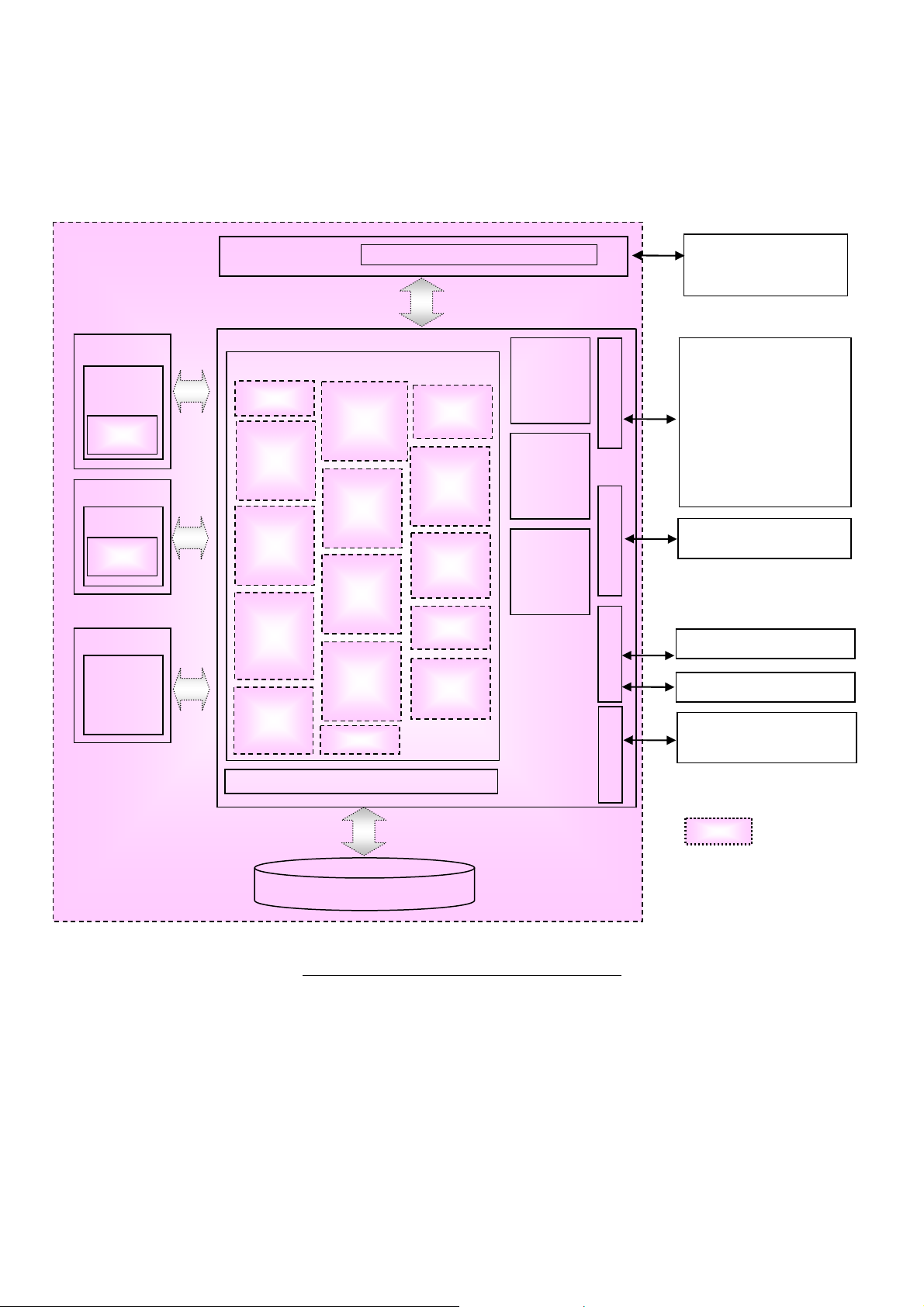
1.4.3. Physical Scope and Boundary
The physical scope of this TOE is the MFD. Figure 4 shows configuration of each unit and TOE
physical scope.
ADF
ADF
Board
ADF
ROM
IOT
IOT Board
IOT
ROM
IIT
IIT Board
Control Panel buttons, lamps, touch screen panel
Controller Board
Controller ROM
Copy
Scan /
Network
Scan
Print
(decompos
e)
Fax/ Direct
Fax
/Internet
Fax
Remote
Configura
tion
Hard Disk
Data
Overwrite
Hard Disk
Data
Encryption
Fax Flow
Security
System
Administrat
or’s Security
Management
Self T est
CPU
Internal HDD
Control
Customer
Engineer
Operation
Restriction
Security
Audit Log
User_Auth
entication
Network
Protection
Panel
Data
NVRAM
SEEPROM
DRAM
Ethernet USB
device
USB
host
USB
host
System Administrator
General User
CE
System Administrator
Client
General User Client
Mail Server
FTP Server
SMB Server
LDAP Server
Kerberos Server
OCSP Server
General User Clien
USB
Card Reade
USB Media
Fax Board
(Public T elephone Line)
: TOE
Figure 4: MFD Units and TOE Physical Scope
The MFD consists of the PWB units of controller board and control panel, IIT, and IOT,ADF.
The controller board is connected to the control panel via the internal interfaces which transmit
control data, and the controller board is connected to the Fax board, the IIT board, and IOT board via
the internal interfaces which transmit document data and control data.
The controller board is a PWB which controls MFD functions of copy, print, scan, and fax. The board
has a network interface (Ethernet) and local interfaces (USB) and is connected to the IIT board and
- 17 -
Page 22

Dell C7765dn Security Target
IOT board.
The control panel is a panel on which buttons, lamps, and a touch screen panel are mounted to use and
configure MFD functions of copy, print, scan, and fax.
The IIT (Image Input Terminal) is a device to scan an original and send its data to the controller board
for copy, scan, and fax functions.
The IOT (Image Output Terminal) is a device to output image data which was sent from the controller
board.
The ADF (Auto Document Feeder) is a device to automatically transfer original documents to IIT.
1.4.4. Guidance
The following are the guidance documents for this TOE.
・ Dell C7765dn Color Multifunction Printer User’s Guide; KB3206EN0-5
(SHA1 hash value: ffa87cc19460eeda82c42194b6dfdb1e2eefb5fb)
・ Dell C5765dn/C7765dn Security Function Supplementary Guide: KE3036EN0-1
(SHA1 hash value: 930f93de08df2629aed52f9de314e7df2adccffd)
・ Dell C7765dn Smart Card Reader Installation and Configuration Guide: KE3037EN0-3
(SHA1 hash value: 40524e2e02908e5479b981e205b7d75440c5f084)
- 18 -
Page 23

Dell C7765dn Security Target
2. CONFORMANCE CLAIMS
2.1. CC Conformance Claims
This ST and TOE conform to the following evaluation standards for information security (CC):
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation
Part 1: Introduction and general model, Version 3.1 Revision 4 Japanese Version 1.0
Part 2: Security functional components, Version 3.1 Revision 4 Japanese Version 1.0
Part 3: Security assurance components, Version 3.1 Revision 4 Japanese Version 1.0
The security functional requirements of this ST conform to CC Part 2.
The security assurance requirements of this ST conform to CC Part 3.
2.2. PP Claims, Package Claims
2.2.1. PP Claims
There is no applicable Protection Profile.
2.2.2. Package Claims
This ST conforms to EAL3.
2.2.3. Conformance Rationale
There is no applicable PP rationale since this ST does not conform to PP.
- 19 -
Page 24

Dell C7765dn Security Target
3. SECURITY PROBLEM DEFINITION
This chapter describes the threats, organizational security policies, and the assumptions for the use of
this TOE.
3.1. Threats
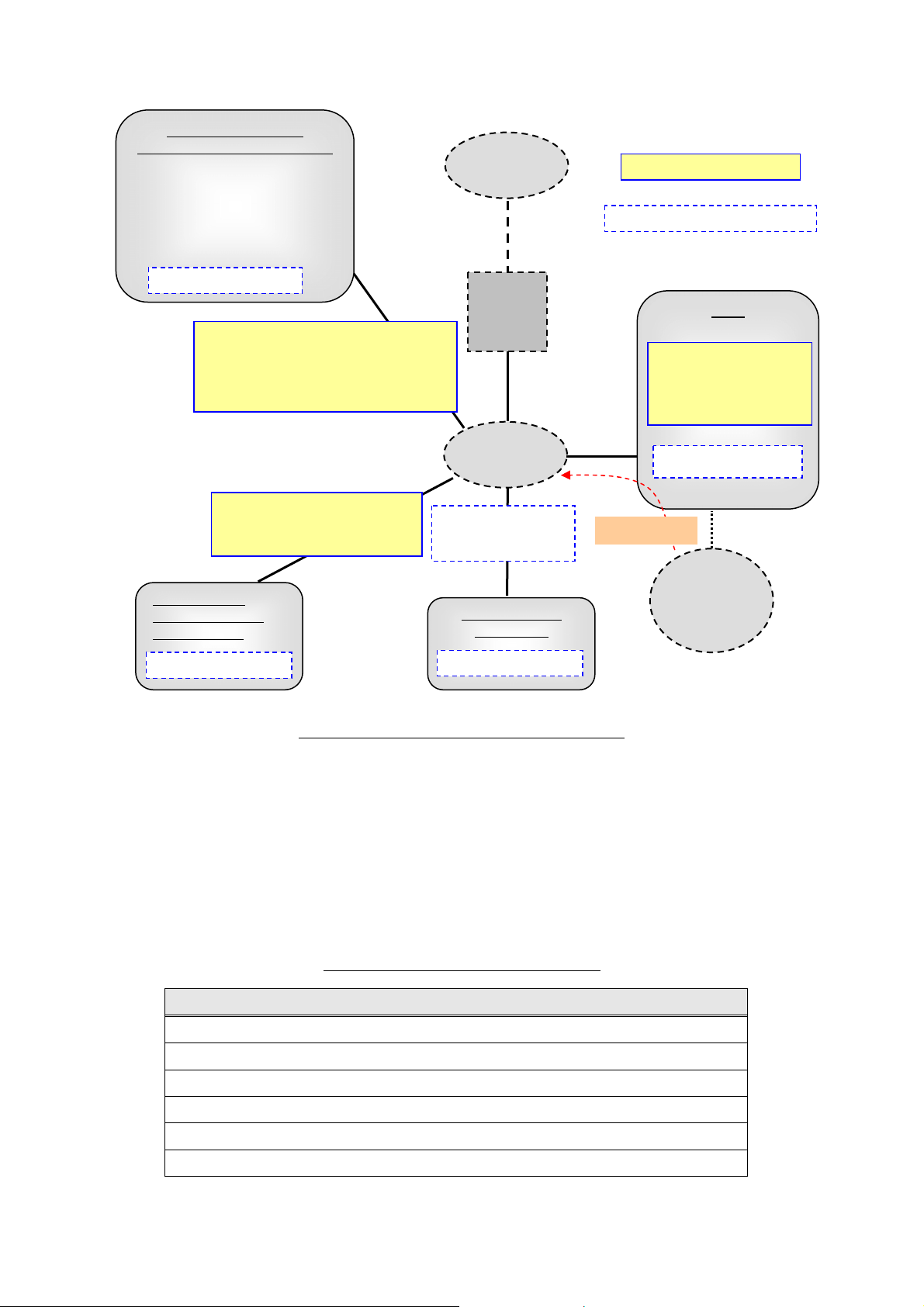
3.1.1. Assets Protected by TOE
This TOE protects the following assets (Figure 5):
(1) Right to use MFD functions
The general user’s right to use each function of the TOE is assumed as an asset to be protected.
(2) Document data stored for job processing
When a general user uses MFD functions of copy, print, fax, and scan, the document data are
temporarily stored in the internal HDD for image processing, transmission, and Store Print. The
user can retrieve the stored document data in the MFD from a general user client by
Configuration Web Tool and Network Scan Utility (with local authentication only). The stored
data include general user’s confidential information and are assumed as assets to be protected.
(3) Used document data
When a general user uses MFD functions of copy, print, fax, and scan, the document data are
temporarily stored in the internal HDD for image processing, transmission, and Store Print. When
the jobs are completed or canceled, only the management information is deleted but the data itself
remains. The residual data include general user’s confidential information and are assumed as
assets to be protected.
(4) Security audit log data
In the function of Security Audit Log, the important events such as device failure, configuration
change and user operation are recorded based on when and who operated what function. For
preventive maintenance and response to the events and detection of unauthorized access, only a
system administrator can retrieve the log data stored in MFD by Configuration Web Tool.
The log data are assumed as assets to be protected.
(5) TOE setting data
A system administrator can set TOE security functions from the MFD control panel or system
administrator client by the function of System Administrator’s Security Management. The setting
data stored in the TOE (see Table 4) can be a threat to other assets if used without authorization
and are assumed as assets to be protected.
- 20 -
Page 25
t
General User Client
System Administrator Client
- Printer Driver
- Fax Driver
- Web Browser
- Network Scan Utility
Internally Stored Data
Document data, security audit log
data, and TOE setting data
transmitted in the internal network
TOE setting data transmitted
in the internal network
- LDAP Server
- Kerberos Server
- OCSP Server
Internally Stored Data
Dell C7765dn Security Target
External
Network
Firewall
Internal
Network
General Data on the
Internal Network
General Clien
and Server
Internally Stored Data
Asset under protection
Asset not under protection
TOE
Document Data
Used Document Data
Security Audit Log Data
TOE Setting Data
Other Setting Data
Inaccessible
Public
Telephone
Line
Figure 5: Assets under and not under Protection
Note) The data stored in a general client and server within the internal network and the general data on
the internal network are not assumed as assets to be protected. This is because TOE functions prevent
the access to the internal network from public telephone line and it cannot be a threat.
Table 4 categorizes the TOE setting data recorded on NVRAM and SEEPROM of the controller
board.
Table 4: Categories of TOE Setting Data
Categories of TOE Setting Data (Note)
Data on Hard Disk Data Overwrite
Data on Hard Disk Data Encryption
Data on use of password entered from MFD control panel in user authentication
Data on minimum password length of user password
Data on ID and password of key operator
Data on ID and password of SA/General user
- 21 -
Page 26
Dell C7765dn Security Target
Categories of TOE Setting Data (Note)
Data on access denial due to authentication failures of system administrator
Data on Customer Engineer Operation Restriction
Data on Internal Network Data Protection
Data on Security Audit Log
Data on Mailbox
Data on User Authentication
Data on Store print
Data on date and time
Data on Self Test
Note: The setting data other than TOE setting data are also stored on NVRAM and SEEPROM. Those
setting data, however, are not assumed as assets to be protected because they do not engage in TOE
security functions.
* Only the time zone / summer time information is saved in NVRAM as the data on date and time.
3.1.2. Threats
Table 5 identifies the threats addressed by the TOE. An attacker is considered to have the disclosed
information on TOE operations and low-level attack capability.
Table 5: Threats Addressed by the TOE
Threat (Identifier) Description
An attacker may remove the internal HDD and connect it to commercial
tools so that he/she can read out and leak the document data, used
T.RECOVER
document data, security audit log data from the HDD without
authorization.
An attacker may access, read, or alter, from control panel or system
T.CONFDATA
administrator client, the TOE setting data which only a system
administrator is allowed to access.
An attacker may read document data and security audit log data from
T.DATA_SEC
control panel or Web browser without authorization.
An attacker may intercept or alter document data, security audit log
T.COMM_TAP
data, and TOE setting data on the internal network.
An attacker may access the TOE and use TOE functions without
T.CONSUME
authorization.
- 22 -
Page 27
Dell C7765dn Security Target
3.2. Organizational Security Policies
Table 6 below describes the organizational security policy the TOE must comply with.
Table 6: Organizational Security Policy
Organizational Policy
Description
(Identifier)
TOE shall ensure that the internal network cannot be accessed via
P.FAX_OPT
public telephone line.
P.VERIFY The TOE shall execute self-test to verify the integrity of TSF executable
code and TSF data.
The TOE shall execute HDD overwrite to delete the used document
P.OVERWRITE
data in the internal HDD.
3.3. Assumptions
Table 7 shows the assumptions for the operation and use of this TOE.
Table 7: Assumptions
Assumption
(Identifier)
Description
Personnel Confidence
A.ADMIN
A.USER
Protection Mode
A.SECMODE
A.ACCESS
A system administrator shall have the necessary knowledge of TOE
security functions to perform the given role of managing the TOE and
shall not operate the TOE with malicious intent.
TOE users shall be trained and have competence about the TOE
operation and precautions according to the policies of their
organization and the product guidance.
A system administrator shall configure and set the TOE properly
according to the security policy of organization and the product
guidance document to manage the TOE and its external environment.
The TOE is located in a restricted or monitored environment that
provides protection from unmanaged access to the physical
components and data interfaces of the TOE.
- 23 -
Page 28
Dell C7765dn Security Target
4. SECURITY OBJECTIVES
This chapter describes the security objectives for the TOE and for the environment and the rationale.
4.1. Security Objectives for the TOE
Table 8 defines the security objectives to be accomplished by the TOE.
Security
Objectives(Identifier)
O.AUDITS
O.CIPHER
O.COMM_SEC
O.FAX_SEC
O.MANAGE
Table 8: Security Objectives for the TOE
Description
The TOE must provide the Security Audit Log function and its log data
which are necessary to monitor unauthorized access.
The TOE must encrypt the document data, used document data, and
security audit log data to be stored into the HDD so that they cannot be
analyzed even if retrieved.
The TOE must provide encryption communication function to protect the
document data, security audit log data, and TOE setting data on the
internal network between TOE and the remote from interception and
alteration.
The TOE must prevent the unauthorized access to the internal network via
Fax modem from public telephone line.
The TOE must inhibit a general user from accessing the TOE setting data.
The TOE allows only the authenticated system administrator to access the
system administrator mode which enables him/her to configure the
security functions.
O.RESIDUAL
O.USER
O.RESTRICT The TOE must inhibit an unauthorized user from using the TOE functions.
O.VERIFY The TOE must provide self-test function to verify the integrity of TSF
The TOE must provide overwrite function to prevent the used document
data in the internal HDD.
The TOE must provide the function to identify TOE user and allow only
the authorized user to retrieve, and delete the document data and to change
the password.
executable code and TSF data.
- 24 -
Page 29
Dell C7765dn Security Target
4.2. Security Objectives for the Environment
Table 9 defines the security objectives for the TOE environment.
Security
Objectives(Identifier)
OE.ADMIN
OE.USER
OE.SEC
OE.PHYSICAL
Table 9: Security Objectives for the Environment
Description
A system administrator who is assigned by an organization administrator
as an appropriate and reliable person for this TOE management and who
receives necessary training to manage the TOE.
The system administrator shall ensure that users have competence by
training users about the TOE operation and precautions according to the
policies of their organization and the product guidance.
A system administrator shall configure and set the TOE properly according
to the security policy of organization and the product guidance document
to manage the TOE.
In addition, a system administrator shall manage the external IT
environment according to the security policy of organization and the
product guidance document.
The TOE shall be placed in a secure or monitored area that provides
protection from unmanaged physical access to the TOE.
4.3. Security Objectives Rationale
The security objectives are established to correspond to the assumptions specified in Security Problem
Definition, to counter the threats, or to realize the organizational security policies. Table 10 shows
assumptions / threats / organizational security policies and the corresponding security objectives.
Moreover, Table 11 shows that each defined security problem is covered by the security objectives.
Table 10: Assumptions / Threats / Organizational Security Policies and the Corresponding Security
Objectives
Security Problems
A.ADMIN
A.USER
A.SECMODE
A.ACCESS
T.RECOVER
T.CONFDATA
T.COMM_TAP
T.DATA_SEC
T.CONSUME
Security Objectives
O.AUDITS
P.FAX_OPT
P.VERIFY
P. OVERWRITE
O.CIPHER
O.COMM_SEC
- 25 -
Page 30

Security Problems
Security Objectives
Dell C7765dn Security Target
A.ADMIN
A.USER
A.SECMODE
A.ACCESS
T.RECOVER
T.CONFDATA
T.COMM_TAP
T.DATA_SEC
T.CONSUME
P.FAX_OPT
P.VERIFY
P. OVERWRITE
O.FAX_SEC
O.MANAGE
O.RESIDUAL
O.VERIFY
O.USER
O.RESTRICT
OE.ADMIN
OE.USER
OE.SEC
OE.PHYSICAL
Table 11: Security Objectives Rationale for Security Problem
Security Problem Security Objectives Rationale
By satisfying the following objective, A.ADMIN can be realized:
By OE.ADMIN, a system administrator is assigned by an organization
A.ADMIN
administrator as an appropriate and reliable person for this TOE
management, and receives necessary training to manage the TOE and
performs the TOE management according to the guidance.
A.USER
A.SECMODE
A.ACCESS
By satisfying the following objective, A.USER can be realized:
By OE.USER, a system administrator trains users about the TOE
operation and precautions according to the policies of their
organization and the product guidance, and users have competence.
By satisfying the following objectives, A.SECMODE can be realized:
By OE.SEC, a system administrator shall configure and set the TOE
properly according to the security policy of organization and the
product guidance document to manage the TOE.
In addition, a system administrator shall manage the external IT
environment according to the security policy of organization and the
product guidance document.
By satisfying the following objective, A.ACCESS can be realized:
By OE.PHYSICAL, a system administrator places the TOE in a secure
or monitored area that provides protection from unmanaged physical
access to the TOE.
- 26 -
Page 31

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Security Problem Security Objectives Rationale
By satisfying the following objective, T.RECOVER can be countered:
By OE.SEC, it is necessary to enable the TOE security functions (i.e.
Hard Disk Data Overwrite) and disable the reading-out of the
document data and security audit log data in the internal HDD as well
T.RECOVER
as the recovery of the used document data. To be specific, this threat
can be countered by the following security objectives: O.CIPHER.
By O.CIPHER, the document data and security audit log data in the
internal HDD are encrypted to disable the reference and reading-out of
the document data, used document data, and security audit log data.
By satisfying the following objective, T.CONFDATA can be
countered:
By OE.SEC, it is necessary to enable the security functions (i.e. User
Authentication with Password, System Administrator Password,
Access Denial due to System Administrator’s Authentication Failures,
Customer Engineer Operation Restriction, and Security Audit Log) and
permits only the authenticated system administrator to change the TOE
setting data. In addition, it is necessary to manage the external IT
environment according to the security policy of organization and the
T.CONFDATA
product guidance document.
To be specific, this threat can be countered by the following security
objectives, O.MANAGE, O.USER, and O.AUDITS:
By O.MANAGE, only the authenticated system administrator is
allowed to enable/disable the TOE security functions and to refer to /
update the TOE setting data.
By O.USER, only the authorized user is allowed to change the
password.
By O.AUDITS, the audit log function necessary to monitor
unauthorized access and the security audit log data are provided.
T.CONSUME
T.COMM_TAP
By satisfying the following objective, T.CONSUME can be countered.
By O.RESTRICT, the access to the TOE can be controlled.
By satisfying the following objectives, T.COMM_TAP can be
countered.
By OE.SEC, the document data, security audit log data, and TOE
setting data on the internal network can be protected from interception.
By O.COMM_SEC, the client/server authentication function of
encryption communication protocol allows only the authorized user to
send/receive the communication data. Encrypting communication data
with encryption function also disables the interception and alteration of
the internal network data (incl. document data, security audit log data,
and TOE setting data).
- 27 -
Page 32

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Security Problem Security Objectives Rationale
By satisfying the following objectives, T.DATA_SEC can be countered.
By OE.SEC, it is necessary to enable the following passwords, user
authentication function, and security audit log function: User Password,
System Administrator Password, Local Authentication or Remote
Authentication, Security Audit Log. Then, only the authenticated user
is allowed to access the security audit log data and document data. In
addition, it is necessary to manage the external IT environment
T.DATA_SEC
according to the security policy of organization and the product
guidance document.
By O.USER, only the authenticated user is allowed to read out the
document data and security audit log data stored in the internal HDD.
By O.MANAGE, only the authenticated system administrator is
allowed to configure the TOE security functions.
By O.AUDITS, the audit log function necessary to monitor
unauthorized access and the security audit log data are provided.
By satisfying the following objectives, P.FAX_OPT can be observed.
By O.FAX_SEC, the access to the internal network via public
P.FAX_OPT
telephone line is disabled. This realizes P.FAX_OPT.
Since the data received from public telephone line are not sent to the
internal network, the internal network cannot be accessed.
P. VERIFY By satisfying the following objectives, P .VERIFY can be observed.
By OE.SEC, it is necessary to enable the following security function,
and execute self-test to verify the integrity of TSF executable code and
TSF data.
-Self T est
The TOE can execute the self test function to verify the integrity of
TSF executable code and TSF data.
By satisfying the following objectives, P.OVERWRITE can be
observed.
By OE.SEC, it is necessary to enable the following security function,
and execute HDD overwrite to delete the used document data in the
P.OVERWRITE
internal HDD..
-Hard Disk Data Overwrite
The TOE can execute HDD overwrite to delete the used document data
in the internal HDD.
- 28 -
Page 33

Dell C7765dn Security Target
5. EXTENDED COMPONENTS DEFINITION
5.1. Extended Components
This ST conforms to CC Part 2 and CC Part 3, and there are no extended components which shall be
defined.
- 29 -
Page 34

Dell C7765dn Security Target
6. SECURITY REQUIREMENTS
This chapter describes the security functional requirements, security assurance requirements, and
security requirement rationale.
The terms and phrases used in this chapter are defined below.
- Subject
Term/phrase Definition
Key Operator Process Operation upon using Mailbox and Store Print when
the user authentication of key operator succeeded.
SA Process Operation upon using Mailbox and Store Print when
the user authentication of SA succeeded.
General User Process Operation upon using Mailbox and Store Print when
the user authentication of general user succeeded.
Receiving information from
public telephone line
Sending information to public
telephone line
Sending information to the
internal network
Receiving information from the
internal network.
- Object
Term/phrase Definition
Mailbox A logical box created in the MFD internal HDD.
To receive the document data from the sender’s
machine via public telephone line, as receiving fax
data.
To send the document data to the destination via public
telephone line according to the general user’s
instruction from the control panel or client PC, as
sending fax data.
To send the Network Scan data or the data received by
Internet Fax to the destination, a client PC, within the
internal network.
To receive the print data or the Direct Fax (with local
authentication only) /Internet Fax data from the sender,
a client PC, within the internal network.
Mailbox can store the scanned document data or the
document data received via fax, categorizing by users
and senders.
Personal Mailbox The Mailbox privately used by a general user. Each
user can create his/her own Personal Mailbox.
Shared Mailbox The Mailbox shared by any general user. Key operator
can create the Shared Mailbox.
Store Print A print function in which bitmap data (decomposed
print data) are temporarily stored in the MFD internal
HDD and then printed out according to the
- 30 -
Page 35

Dell C7765dn Security Target
authenticated general user’s instruction from the
control panel.
Used document data stored in the
internal HDD
The remaining data in the MFD internal HDD even
after deletion. The document data are first stored into
the internal HDD, used, and then only their files are
deleted.
Document data Document data means all the data including image data
transmitted across the MFD when any of copy, print,
scan or fax functions is operated by a general user.
Security Audit Log Data The chronologically recorded data of important events
of the TOE. The events such as device failure,
configuration change, and user operation are recorded
based on when and who caused what event and its
result.
- Operation
Term/phrase Definition
Delivery MFD receives the data from public telephone line for
fax function.
Modify of behavior To change the settings of the following information:
User Authentication (Local, Remote)
Store Print (Save or Deletion of login failure job)
Internal Network Data Protection (Certificate and
encryption type)
Hard Disk Data Overwrite (number of overwrite, data
of overwrite)
Modify Changes of TSF data and security attributes(user
- Data
Data on public telephone line
Fax data
- Security attributes
General User role Indicates the authority required for general user to use
SA role Indicates the authority required for SA to use the TOE.
Key Operator role Indicates the authority required for key operator to use
identifier).
Term/phrase Definition
The data which flow on public telephone line for fax
communication.
Term/phrase Definition
the TOE.
the TOE.
- 31 -
Page 36

Dell C7765dn Security Target
General User identifier User ID and password used to authenticate and identify
general user.
SA identifier User ID and password used to authenticate and identify
SA.
Key Operator identifier User ID and password used to authenticate and identify
key operator.
Owner identifier of Mailbox
(Personal, Shared)
Data on each Mailbox, incl. permitted user, box name,
password, conditions for deleting documents, etc.
Owner identifier of Store Print Data on Private Print, incl. user ID, password,
measures to be taken at authentication failure, etc.
- Entity outside the TOE
Term/phrase Definition
System Administrator This term covers both key operator and SA.
Key Operator An authorized user who manages MFD maintenance
and makes TOE security function settings.
System Administrator Privilege
(SA)
The user(s) who manage MFD maintenance and
configure TOE security functions. SA can be
created/registered by key operator or the other SA who
is already registered.
General User Any person who uses copy, scan, fax, and print
functions of MFD.
- Other terminology
Term/phrase Definition
The Fuji Xerox’s standard
method, FXOSENC
The Fuji Xerox’s standard algorithm to generate a
cryptographic key. This is used when MFD is booted.
AES The FIPS-standard encryption algorithm used for
encryption/decryption of Hard Disk data.
Access denial due to
authentication failure of system
administrator ID
When the number of unsuccessful authentication
attempts of system administrator ID has exceeded the
specified number of times, the control panel does not
accept any operation except power-on and power-off,
and the web browser do not accept authentication
operation until the MFD main unit is powered off/on.
Data on use of password entered
from MFD control panel in user
authentication
Data on minimum user password
length
The data on whether to enable/disable the use of
password to be entered from MFD control panel in user
authentication. Included in the TOE setting data.
Minimum user password length to set the SA/ General
User password from MFD control panel.
Included in the TOE setting data.
- 32 -
Page 37

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Data on ID of key operator ID data for key operator authentication. Included in the
TOE setting data.
Data on password of key operator Password dat a for key operator authentication.
Included in the TOE setting data.
Data on ID of SA ID data for SA authentication. Included in the TOE
setting data.
Data on password of SA Password data for SA authentication. Included in the
TOE setting data.
Data on ID of General User ID data for general user authentication. Included in the
TOE setting data.
Data on password of General User Password data for general user authentication. Included
in the TOE setting data.
Data on access denial due to
authentication failures of system
administrator
The data on whether to enable/disable access denial
due to authentication failure of system administrator
ID. They also incorporate the data on the allowable
number of the failures before access denial. Included in
the TOE setting data.
Data on Security Audit Log The data on whether to enable/disable the function to
trace/ record the important events of the TOE such as
device failure, configuration change, and user
operation, based on when and who operated what
function.
Data on User Authentication The data on whether to enable/disable the
authentication function using the data on user
authentication when copy, scan, fax, and print
functions of MFD are used. It also incorporates the
data on the setting. Included in the TOE setting data.
Data on Store Print The setting data on whether to store the received print
data to Private Print area or print it out. Included in the
TOE setting data.
Data on Internal Network Data
Protection
Data on Customer Engineer
Operation Restriction
The data on whether to enable/disable the general
encryption communication protocols to protect the
communication data on the internal network such as
document data, security audit log data, and TOE setting
data. They also incorporate the data on the setting.
Included in the TOE setting data.
The data on whether to enable/disable Customer
Engineer Operation Restriction. Included in the TOE
setting data.
- 33 -
Page 38

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Data on Hard Disk Data
Encryption
The data on whether to enable/disable the functions
related to Hard Disk Data Encryption. They also
incorporate the data on the encryption seed key.
Included in the TOE setting data.
Data on Hard Disk Data
Overwrite
The data on whether to enable/disable the functions
related to Hard Disk Data Overwrite. They also
incorporate the data on the number of pass (overwrite
procedure). Included in the TOE setting data.
Data on date and time The data on the time zone / summer time information /
present date and time.. Included in the TOE setting
data.
Data on Self Test The data on whether to enable/disable the functions
related to Self Test. Included in the TOE setting data.
Public telephone line The line/network on which the data flow for fax
communication.
System Administrator mode An operation mode that enables a system administrator
to refer to and rewrite TOE setting for device operation
and that for security functions according to the
operational environment. This mode is distinguished
from the operation mode that enables a general user to
use the MFD functions.
Certificate Defined in the X.509 which is recommended by ITU-T.
The data for user authentication (name, identification
name, organization where he/she belongs to, etc.),
public key, expiry date, serial number, signature, etc.
Printer driver Software to convert the data on a general user client
into print data written in page description language
(PDL), a readable format for MFD. Used on the user
client.
Fax Driver Software for Direct Fax (with local authentication
only) function, which enables a general user to fax data
to the destination directly from a general user client
through MFD. The user can send the fax data just as
printing. Used on the user client.
Network Scan Utility (with local
authentication only)
Software for a general user client to retrieve the
document data stored in Mailbox of MFD.
- 34 -
Page 39

Dell C7765dn Security Target
6.1. Security Functional Requirements
Security functional requirements which the TOE offers are described below. The security functional
requirements are based on the class and component which are specified by the [CC part 2].
6.1.1. Class FAU: Security audit
FAU_GEN.1 Audit data generation
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: FPT_STM.1 Reliable time stamps
FAU_GEN.1.1 The TSF shall be able to generate an audit record of the following
auditable events:
a) Start-up and shutdown of the audit functions;
b) All auditable events for the [selection, choose one of: minimum,
basic, detailed, not specified] level of audit; and
c) [assignment: other specifically defined auditable events].
[selection, choose one of: minimum, basic, detailed, not specified]
- not specified
[assignment: other specifically defined auditable events]
- the actions to be audited (defined by CC) and the corresponding
auditable events (events to be recorded as execution log) of TOE. Shown
in Table 12
Table 12: Auditable Events of TOE and Individually Defined Auditable Events
Functional
Requirements
FAU_GEN.1 None -
FAU_SAR.1 a) Basic: Reading of information from the audit
records.
FAU_SAR.2 a) Basic: Unsuccessful attempts to read information
from the audit records.
FAU_STG.1 None FAU_STG.4 a) Basic: Actions taken due to the audit storage
failure.
FCS_CKM.1 a) Minimal: Success and failure of the activity.
b) Basic: The object attribute(s), and object value(s)
excluding any sensitive information (e.g. secret or
Actions to be audited (defined by CC) Auditable events of
Basic: Successful
download of security
audit log data.
Basic: Unsuccessful
download of security
audit log data.
None
None
TOE
- 35 -
Page 40

Dell C7765dn Security Target
private keys).
FCS_COP.1 a) Minimal: Success and failure, and the type of
None
cryptographic operation.
b) Basic: Any applicable cryptographic mode(s) of
operation, subject attributes and object attributes.
FDP_ACC.1 None FDP_ACF.1 a) Minimal: Successful requests to perform an
operation on an object covered by the SFP.
b) Basic: All requests to perform an operation on an
object covered by the SFP.
c) Detailed: The specific security attributes used in
making an access check.
Basic: Creation/deletion
of Mailbox.
User name, job
information, and
success/failure
regarding access to
Mailbox and execution
of Store Print.
FDP_IFC.1 None -
FDP_IFF.1 a) Minimal: Decisions to permit requested
None
information flows.
b) Basic: All decisions on requests for information
flow.
c) Detailed: The specific security attributes used in
making an information flow enforcement decision.
d) Detailed: Some specific subsets of the
information that has flowed based upon policy
goals (e.g. auditing of downgraded material).
FDP_RIP.1 None FIA_AFL.1 a) Minimal: the reaching of the threshold for the
unsuccessful authentication attempts and the actions
(e.g. disabling of a terminal) taken and the
subsequent, if appropriate, restoration to the normal
state (e.g. re-enabling of a terminal).
FIA_ATD.1 None FIA_SOS.1 a) Minimal: Rejection by the TSF of any tested
secret;
b) Basic: Rejection or acceptance by the TSF of any
tested secret;
c) Detailed: Identification of any changes to the
defined quality metrics
- 36 -
<Minimal>
Authentication lock of
system administrator
Authentication failure
from control panel and
Configuration Web
Tool.
<Individually defined
auditable events>
Registration of user and
changes in user
registration data
(password)
Page 41

Dell C7765dn Security Target
FIA_UAU.1 a) Minimal: Unsuccessful use of the authentication
mechanism;
b) Basic: All use of the authentication mechanism.
c) Detailed: All TSF mediated actions performed
before authentication of the user.
FIA_UAU.7 None FIA_UID.1 a) Minimal: Unsuccessful use of the user
identification mechanism, including the user
identity provided;
b) Basic: All use of the user identification
mechanism, including the user identity provided.
FIA_USB.1 a) Minimal: Unsuccessful binding of user security
attributes to a subject (e.g. creation of a subject).
b) Basic: Success and failure of binding of user
security attributes to a subject (e.g. success or
failure to create a subject).
FMT_MOF.1 a) Basic: All modifications in the behavior of the
functions in the TSF.
< Basic >
Success/failure of
authentication
< Basic >
Success/failure of
authentication
< Basic >
Registration of system
administrator, and
changes in user
registration data (role)
<Basic>
Changes in security
function configuration.
FMT_MSA.1 a) Basic: All modifications of the values of security
attributes.
FMT_MSA.3 a) Basic: Modifications of the default setting of
permissive or restrictive rules.
b) Basic: All modifications of the initial values of
security attributes.
FMT_MTD.1. a) Basic: All modifications to the values of TSF
data.
<Basic>
Creation/deletion of
Mailbox.
User name, job
information, and
success/failure
regarding access to
Mailbox and execution
of Store Print.
None
<Individually defined
auditable events>
Changes in registration
data (ID, password) of
system administrator,
and in the setting of
security functions.
FMT_SMF.1 a) Minimal: Use of the management functions. < Minimal >
Access to system
- 37 -
Page 42

Dell C7765dn Security Target
administrator mode
FMT_SMR.1 a) Minimal: modifications to the group of users that
are part of a role;
b) Detailed: every use of the rights of a role.
FPT_STM.1 a) Minimal: changes to the time;
b) Detailed: providing a timestamp.
FPT_TST.1 a) Minimal: Termination of an interactive session
by the session locking mechanism.
FTP_TRP.1 a) Minimal: Failures of the trusted path functions.
b) Minimal: Identification of the user associated
with all trusted path failures, if available.
c) Basic: All attempted uses of the trusted path
functions.
d) Basic: Identification of the user associated with
all trusted path invocations, if available.
<Minimal>
Registration of system
administrator, changes
in user registration data
(role), and deletion of
system administrator
<Minimal>
Changes in time setting.
<Basic>
Execution of Self Test
and the test result
<Minimal>
Failure of the trusted
Communication within a
specified period of time,
and client host data
(host name or IP
address)
FAU_GEN.1.2 The TSF shall record within each audit record at least the following
information:
a) Date and time of the event, type of event, subject identity (if
applicable), and the outcome (success or failure) of the event; and
b) For each audit event type, based on the auditable event definitions of
the functional components included in the PP/ST, [assignment: other
audit relevant information].
[assignment: other audit relevant information].
- none
FAU_SAR.1: Audit review
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: FAU_GEN.1 Audit data generation
FAU_SAR.1.1 The TSF shall provide [assignment: authorized users] with the capability
to read [assignment: list of audit information] from the audit records.
FAU_SAR.1.2 The TSF shall provide the audit records in a manner suitable for the user
to interpret the information.
- 38 -
Page 43

Dell C7765dn Security Target
[assignment: authorized users]
- system administrator
[assignment: list of audit information]
- all log information
FAU_SAR.1.2 The TSF shall provide the audit records in a manner suitable for the user
to interpret the information.
FAU_SAR.2 Restricted audit review
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: FAU_SAR.1 Audit review
FAU_SAR.2.1 The TSF shall prohibit all users read access to the audit records, except
those users that have been granted explicit read-access.
FAU_STG.1 Protected audit trail storage
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: FAU_GEN.1 Audit data generation
FAU_STG.1.1 The TSF shall protect the stored audit records in the audit trail from
unauthorized deletion.
FAU_STG.1.2 The TSF shall be able to [selection, choose one of: prevent, detect]
unauthorized modifications to the stored audit records in the audit trail.
[selection, choose one of: prevent, detect]
- prevent
FAU_STG.4 Prevention of audit data loss
Hierarchical to: FAU_STG.3 Action in case of possible audit data loss
Dependencies: FAU_STG.1 Protected audit trail storage
FAU_STG.4.1 The TSF shall [selection, choose one of: “ignore audited events”,
“prevent audited events, except those taken by the authorized user with
special rights”, “overwrite the oldest stored audit records”] and
[assignment: other actions to be taken in case of audit storage failure] if
the audit trail is full.
[selection, choose one of: “ignore audited events”, “prevent audited
events, except those taken by the authorized user with special rights”,
“overwrite the oldest stored audit records”]
- overwrite the oldest stored audit records
- 39 -
Page 44

Dell C7765dn Security Target
[assignment: other actions to be taken in case of audit storage failure]
- no other actions to be taken
6.1.2. Class FCS: Cryptographic support
FCS_CKM.1 Cryptographic key generation
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: [FCS_CKM.2 Cryptographic key distribution, or
FCS_COP.1 Cryptographic operation]
FCS_CKM.4 Cryptographic key destruction
FCS_CKM.1.1 TSF shall generate cryptographic keys in accordance with a specified
cryptographic key generation algorithm [assignment: cryptographic key
generation algorithm] and specified cryptographic key sizes [assignment:
cryptographic key sizes] that meet the following: [assignment: list of
standards].
[assignment: list of standards]
- none
[assignment: cryptographic key generation algorithm]
- the Fuji Xerox’s standard method, FXOSENC
[assignment: cryptographic key sizes]
- 256bits
FCS_COP.1 Cryptographic operation
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: [FDP_ITC.1 Import of user data without security attributes, or
FDP_ITC.2 Import of user data with security attributes, or
FCS_CKM.1 Cryptographic key generation]
FCS_CKM.4 Cryptographic key destruction
FCS_COP.1.1 The TSF shall perform [assignment: list of cryptographic operations] in
accordance with a specified cryptographic algorithm [assignment:
cryptographic algorithm] and cryptographic key sizes [assignment:
cryptographic key sizes] that meet the following: [assignment: list of
standards].
[assignment: list of standards]
- FIPS PUB 197
[assignment: cryptographic algorithm]
- AES
[assignment: cryptographic key sizes]
- 40 -
Page 45

Dell C7765dn Security Target
- 256bits
[assignment: list of cryptographic operations]
- encryption of the document data and security audit log data to be
stored in the internal HDD and decryption of the document data and
security audit log data retrieved from the internal HDD.
6.1.3. Class FDP: User data protection
FDP_ACC.1 Subset access control
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: FDP_ACF.1 Security attribute based access control
FDP_ACC.1.1 The TSF shall enforce the [assignment: access control SFP] on
[assignment: list of subjects, objects, and operations among subjects and
objects covered by the SFP].
[assignment: access control SFP]
- MFD access control SFP
[assignment: list of subjects, objects, and operations among subjects and
objects covered by the SFP].
- subjects, objects, and operations between subjects and objects listed in
Table 13
Table 13: Operations between Subjects and Objects Covered by MFD Access Control SFP
Subject Object Operation
Key operator process Mailbox Deletion of Personal Mailbox
Creation of Shared Mailbox
Deletion of Shared Mailbox
Deletion of all document data
Retrieval of all document data
Store Print Deletion of all document data
Retrieval of all document data
SA process Mailbox Creation of Personal Mailbox
Deletion of Personal Mailbox
Deletion of all document data
Retrieval of all document data
Store Print Deletion of all document data
Retrieval of all document data
General user process Mailbox Creation of Personal Mailbox
Deletion of Personal Mailbox
Deletion of all document data
Retrieval of all document data
- 41 -
Page 46

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Store Print Deletion of document data
Retrieval of document data
FDP_ACF.1 Security attribute based access control
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: FDP_ACC.1 Subset access control
FMT_MSA.3 Static attribute initialization
FDP_ACF.1.1 The TSF shall enforce the [assignment: access control SFP] to objects
based on the following: [assignment: list of subjects and objects
controlled under the indicated SFP, and for each, the SFP-relevant
security attributes, or named groups of SFP-relevant security attributes].
[assignment: access control SFP]
- MFD access control SFP
[assignment: list of subjects and objects controlled under the indicated
SFP, and for each, the SFP-relevant security attributes, or named groups
of SFP-relevant security attributes].
- general user identifier corresponding to the general user process, SA
identifier corresponding to the SA process, Key operator identifier
corresponding to the Key operator process,
- owner identifier corresponding to each Mailbox, owner identifier
corresponding to each Store Print area
FDP_ACF.1.2 The TSF shall enforce the following rules to determine if an operation
among controlled subjects and controlled objects is allowed:
[assignment: rules governing access among controlled subjects and
controlled objects using controlled operations on controlled objects].
[assignment: rules governing access among controlled subjects and
controlled objects using controlled operations on controlled objects].
- the rules, shown in Table 14, for controlling the access among
controlled subjects using the controlled operations on the controlled
objects
Table 14: Rules for Access Control
Rules for Mailbox Operation in the General User Process and SA Process
- Creation of Personal Mailbox
In the general user process and SA process to create Personal Mailbox, the Personal
Mailbox in which general user identifier and SA identifier are set as its owner is
- 42 -
Page 47

Dell C7765dn Security Target
created.
- Deletion of Personal Mailbox
When the general user identifier and SA identifier of the general user process and SA
process match the owner identifier of Personal Mailbox, deletion of the
corresponding Personal Mailbox is allowed.
- Retrieval and deletion of document data in Personal Mailbox
When the general user identifier and SA identifier of the general user process and SA
process match the owner identifier of Mailbox, retrieval and deletion of the document
data inside are allowed.
- Retrieval and deletion of document data in Shared Mailbox
Retrieval and deletion of document data in Shared Mailbox are allowed.
Rules for Store Print Operation in the General User Process and SA Process
- Deletion and retrieval of document data
When the general user identifier and SA identifier of the general user process and SA
process match the owner identifier of Store Print, retrieval and deletion of the
document data inside are allowed. When the document data are deleted, the
corresponding Store Print area is also deleted.
Mailbox Operation in the Key Operator Process
-In the key operator process, creation and deletion of Shared Mailbox in which the
key operator identifier is set are allowed, and deletion of Personal Mailbox by all
registered users are allowed.
FDP_ACF.1.3 The TSF shall explicitly authorize access of subjects to objects based on
the following additional rules: [assignment: rules, based on security
attributes, that explicitly authorize access of subjects to objects].
[assignment: rules, based on security attributes, that explicitly authorise
access of subjects to objects].
- the rules, shown in Table 15, for explicitly authorizing access of the
subject to an object based on security attributes.
Table 15: Rules for Explicit Access Authorization
Rule for Mailbox Operation in the Key Operator Process
- In the key operator process, deletion of all Mailbox, deletion and retrieval of the
document data inside are allowed.
Rule for Store Print Operation in the Key Operator Process and SA Process
- In the key operator process and SA process, regarding all Store Print, deletion and
retrieval of the document data inside are allowed.
FDP_ACF.1.4 The TSF shall explicitly deny access of subjects to objects based on the
following additional rules [assignment: rules, based on security
- 43 -
Page 48

Dell C7765dn Security Target
attributes, that explicitly deny access of subjects to objects].
[assignment: rules, based on security attributes, that explicitly deny
access of subjects to objects].
- no rules that explicitly deny the access
FDP_IFC.1 Subset information flow control
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FDP_IFF.1 Simple security attributes
FDP_IFC.1.1 The TSF shall enforce the [assignment: information flow control SFP] on
[assignment: list of subjects, information, and operations that cause
controlled information to flow to and from controlled subjects covered
by the SFP].
[assignment: list of subjects, information, and operations that cause
controlled information to flow to and from controlled subjects covered
by the SFP]
- subjects, information, and operations that cause the information to
flow, which are listed in Table 16.
Table 16: Subjects, Information, and Operations that cause the information to flow
Subject Information Operation
Receiving information from public
telephone line
Data on public
telephone line
Delivery
Sending information to the internal
network
[assignment: information flow control SFP]
- Fax information flow control SFP
FDP_IFF.1 Simple security attributes
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FDP_IFC.1 Subset information flow control
FMT_MSA.3 Static attribute initialization
FDP_IFF.1.1 The TSF shall enforce the [assignment: information flow control SFP]
based on the following types of subject and information security
attributes: [assignment: list of subjects and information controlled under
the indicated SFP, and for each, the security attributes].
[assignment: information flow control SFP]
- 44 -
Page 49

Dell C7765dn Security Target
- Fax information flow control SFP
[assignment: list of subjects and information controlled under the
indicated SFP, and for each, the security attributes]
- none. (Sending information to public telephone line, receiving
information from the internal network, and the corresponding data on
the public telephone line are not controlled under the Fax information
flow control SFP).
FDP_IFF.1.2 The TSF shall permit an information flow between a controlled subject
and controlled information via a controlled operation if the following
rules hold: [assignment: for each operation, the security attribute-based
relationship that must hold between subject and information security
attributes].
[assignment: for each operation, the security attribute-based relationship
that must hold between subject and information security attributes]
- the data received from public telephone line must not be sent to the
internal network at any case
FDP_IFF.1.3 The TSF shall enforce the [assignment: additional information flow
control SFP rules].
[assignment: additional information flow control SFP rules]
- none.
FDP_IFF.1.4 The TSF shall explicitly authorize an information flow based on the
following rules: [assignment: rules, based on security attributes, that
explicitly authorize information flows].
[assignment: rules, based on security attributes, that explicitly authorize
information flows]
- none.
FDP_IFF.1.5 The TSF shall explicitly deny an information flow based on the
following rules: [assignment: rules, based on security attributes, that
explicitly deny information flows].
[assignment: rules, based on security attributes, that explicitly deny
information flows].
- none.
FDP_RIP.1 Subset residual information protection
- 45 -
Page 50

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: No dependencies
FDP_RIP.1.1 The TSF shall ensure that any previous information content of a resource
is made unavailable upon the [selection: allocation of the resource to,
deallocation of the resource from] the following objects: [assignment:
list of objects].
[assignment: list of objects]
- used document data stored in the internal HDD
[selection: allocation of the resource to, deallocation of the resource
from]
- deallocation of the resource from
6.1.4. Class FIA: Identification and authentication
FIA_AFL.1 (1) Authentication failure handling
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FIA_UAU.1 Timing of authentication
FIA_AFL.1.1 (1) The TSF shall detect when [selection: [assignment: positive integer
number], an administrator configurable positive integer within
[assignment: range of acceptable values]] unsuccessful authentication
attempts occur related to [assignment: list of authentication events].
[assignment: list of authentication events]
- key operator authentication
[selection: [assignment: positive integer number] , an administrator
configurable positive integer within [assignment: range of acceptable
values]
- [assignment: positive integer number]
[assignment: positive integer number]
- 5
FIA_AFL.1.2 (1) When the defined number of unsuccessful authentication attempts has
been [selection: met, surpassed], the TSF shall [assignment: list of
actions].
[selection: met, surpassed]
- met
[assignment: list of actions]
- never allow the control panel to accept any operation except power
cycle. Web browser is also inhibited from accepting authentication
- 46 -
Page 51

Dell C7765dn Security Target
operation until the main unit is cycled.
FIA_AFL.1(2) Authentication failure handling
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FIA_UAU.1 Timing of authentication
FIA_AFL.1.1 (2) The TSF shall detect when [selection: [assignment: positive integer
number], an administrator configurable positive integer within
[assignment: range of acceptable values]] unsuccessful authentication
attempts occur related to [assignment: list of authentication events].
[assignment: list of authentication events]
- SA authentication (with local authentication)
[selection: [assignment: positive integer number] , an administrator
configurable positive integer within [assignment: range of acceptable
values]
- [assignment: positive integer number]
[assignment: positive integer number]
- 5
FIA_AFL.1.2 (2) When the defined number of unsuccessful authentication attempts has
been [selection: met, surpassed], the TSF shall [assignment: list of
actions].
[selection: met, surpassed]
- met
[assignment: list of actions]
- never allow the control panel to accept any operation except power
cycle. Web browser is also inhibited from accepting authentication
operation until the main unit is cycled.
FIA_AFL.1 (3) Authentication failure handling
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FIA_UAU.1 Timing of authentication
FIA_AFL.1.1 (3) The TSF shall detect when [selection: [assignment: positive integer
number], an administrator configurable positive integer within
[assignment: range of acceptable values]] unsuccessful authentication
attempts occur related to [assignment: list of authentication events].
[assignment: list of authentication events]
- general user authentication
- 47 -
Page 52

Dell C7765dn Security Target
[selection: [assignment: positive integer number] , an administrator
configurable positive integer within [assignment: range of acceptable
values]
- [assignment: positive integer number]
[assignment: positive integer number]
- 1
FIA_AFL.1.2 (3) When the defined number of unsuccessful authentication attempts has
been [selection: met, surpassed], the TSF shall [assignment: list of
actions].
[selection: met, surpassed]
- met
[assignment: list of actions]
- have the control panel to display the message of “authentication was
failed” and to require reentry of the user information. The TSF shall also
have Web browser and Network Scan Utility (with local authentication
only) to reenter the user information
FIA_AFL.1 (4) Authentication failure handling
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FIA_UAU.1 Timing of authentication
FIA_AFL.1.1 (4) The TSF shall detect when [selection: [assignment: positive integer
number], an administrator configurable positive integer within
[assignment: range of acceptable values]] unsuccessful authentication
attempts occur related to [assignment: list of authentication events].
[assignment: list of authentication events]
- SA authentication (with remote authentication)
[selection: [assignment: positive integer number] , an administrator
configurable positive integer within [assignment: range of acceptable
values]
- [assignment: positive integer number]
[assignment: positive integer number]
- 1
FIA_AFL.1.2 (4) When the defined number of unsuccessful authentication attempts has
been [selection: met, surpassed], the TSF shall [assignment: list of
actions].
[selection: met, surpassed]
- 48 -
Page 53

Dell C7765dn Security Target
- met
[assignment: list of actions]
- have the control panel to display the message of “authentication was
failed” and to require reentry of the user information. The TSF shall also
have Web browser to reenter the user information
FIA_ATD.1 User attribute definition
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: No dependencies.
FIA_ATD.1.1 The TSF shall maintain the following list of security attributes belonging
to individual users: [assignment: list of security attributes].
[assignment: list of security attributes].
- Key Operator role
- SA role
- General User role
FIA_SOS.1.1 The TSF shall provide a mechanism to verify that secrets (SA password
and U.NORMAL password when local authentication is used) meet
[assignment: a defined quality metric].
[assignment: a defined quality metric].
- Password length is restricted to 9 or more characters
FIA_UAU.1 Timing of authentication
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FIA_UID.1 Timing of identification
FIA_UAU.1.1 The TSF shall allow [assignment: list of TSF mediated actions] on behalf
of the user to be performed before the user is authenticated.
[assignment: list of TSF mediated actions]
- data receive from public telephone line
- storing the print job delivered from user client
FIA_UAU.1.2 The TSF shall require each user to be successfully authenticated before
allowing any other TSF-mediated actions on behalf of that user.
FIA_UAU.7 Protected authentication feedback
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FIA_UAU.1 Timing of authentication
- 49 -
Page 54

Dell C7765dn Security Target
FIA_UAU.7.1 The TSF shall provide only [assignment: list of feedback] to the user
while the authentication is in progress.
[assignment: list of feedback]
- display of asterisks (“*”) to hide the entered password characters
FIA_UID.1 Timing of identification
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: No dependencies
FIA_UID.1.1 The TSF shall allow [assignment: list of TSF-mediated actions] on
behalf of the user to be performed before the user is identified.
[assignment: list of TSF-mediated actions]
- fax receive from public telephone line
- storing the print job delivered from user client
FIA_UID.1.2 The TSF shall require each user to be successfully identified before
allowing any other TSF-mediated actions on behalf of that user.
FIA_USB.1 User-subject binding Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: FIA_ATD.1 User attribute definition
FIA_USB.1.1 The TSF shall associate the following user security attributes with
subjects acting on the behalf of that user: [assignment: list of user
security attributes].
[assignment: list of user security attributes].
- Key Operator role
- SA role
- General User role
FIA_USB.1.2 The TSF shall enforce the following rules on the initial association of
user security attributes with subjects acting on the behalf of users:
[assignment: rules for the initial association of attributes].
[assignment: rules for the initial association of attributes].
- none
FIA_USB.1.3 The TSF shall enforce the following rules governing changes to the user
security attributes associated with subjects acting on the behalf of users:
- 50 -
Page 55

Dell C7765dn Security Target
[assignment: rules for the changing of attributes].
[assignment: rules for the changing of attributes].
- none
6.1.5. Class FMT: Security management
FMT_MOF.1 Management of security functions behavior
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FMT_SMR.1 Security roles
FMT_SMF.1 Specification of Management Functions
FMT_MOF.1.1 The TSF shall restrict the ability to [selection: determine the behavior of,
disable, enable, modify the behavior of] the functions [assignment: list of
functions] to [assignment: the authorized identified roles].
[selection: determine the behavior of, disable, enable, modify the
behavior of]
- enable, disable, or modify the behavior of
[assignment: list of functions]
- for security listed in Table 17
[assignment: the authorized identified roles]
- the roles listed in Table 17
Table 17: List of Security Functions
Security Functions Operations Roles
Use of password entered from MFD control
enable, disable Key operator, SA
panel in user authentication
Access denial due to authentication failure
enable, disable Key operator, SA
of system administrator ID
User Authentication enable, disable,
Key operator, SA
modify
Security Audit Log enable, disable Key operator, SA
enable, disable,
Store Print
Key operator, SA
modify
Internal Network Data Protection enable, disable,
Key operator, SA
modify
Customer Engineer Operation Restriction enable, disable Key operator, SA
Hard Disk Data Encryption enable, disable Key operator, SA
Hard Disk Data Overwrite enable, disable,
Key operator, SA
modify
- 51 -
Page 56

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Self Test enable, disable Key operator, SA
FMT_MSA.1 Management of security attributes
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: [FDP_ACC.1 Subset access control, or
FDP_IFC.1 Subset information flow control]
FMT_SMR.1 Security roles
FMT_SMF.1 Specification of Management Functions
FMT_MSA.1.1 The TSF shall enforce the [assignment: access control SFP(s),
information flow control SFP(s)] to restrict the ability to [selection:
change default, query, modify, delete, [assignment: other operations]] the
security attributes [assignment: list of security attributes] to [assignment:
the authorized identified roles].
[assignment: access control SFP(s), information flow control SFP(s)]
- MFD access control SFP
[selection: change default, query, modify, delete, [assignment: other
operations]]
- query, modify, delete,[assignment: other operations]
[assignment: other operations]
- create
[assignment: list of security attributes]
- user identifier, Mailbox owner identifier, and Store Print owner
identifier
[assignment: the authorized identified roles].
- the operations and roles listed in Table 18
Table 18: Security Attributes and Authorized Roles
Security Attribute Operations Roles
Key operator identifier modify Key operator
SA identifier (with local
authentication only)
General user identifier (with local
authentication only)
Mailbox owner identifier
query, modify delete,
Key operator, SA
create
query, modify delete,
Key operator, SA
create
query, delete, create General user , SA
(Personal Mailbox)
All Mailbox owner identifier
query, delete, create Key operator
(All of Personal Mailbox)
Mailbox owner identifier
query, delete, create Key operator
(Shared Mailbox)
- 52 -
Page 57

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Store Print owner identifier query, delete Key operator,
SA , General user
All Store Print owner identifier query, delete Key operator, SA
FMT_MSA.3 Static attribute initialization
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: FMT_MSA.1 Management of security attributes
FMT_SMR.1 Security roles
FMT_MSA.3.1 The TSF shall enforce the [assignment: access control SFP, information
flow control SFP] to provide [selection, choose one of: restrictive,
permissive, [assignment: other property]] default values for security
attributes that are used to enforce the SFP.
[assignment: access control SFP, information flow control SFP]
- MFD access control SFP
[selection, choose one of: restrictive, permissive, [assignment: other
property]]
- [assignment: other property]
- Initialization property in Table 19
Table 19 Initialization property
Object Security Attributes Default
mail box Owner identifier of mail box Creator’s user identifier and
store print Owner identifier of store
available user identifier
print
FMT_MSA.3.2 The TSF shall allow the [assignment: the authorized identified roles] to
specify alternative initial values to override the default values when an
object or information is created.
[assignment: the authorized identified roles]
- none
FMT_MTD.1 Management of TSF data
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FMT_SMR.1 Security roles
FMT_SMF.1 Specification of Management Functions
FMT_MTD.1.1 The TSF shall restrict the ability to [selection: change default, query,
- 53 -
Page 58

Dell C7765dn Security Target
modify, delete, clear, [assignment: other operations]] the [assignment:
list of TSF data] to [assignment: the authorized identified roles].
[selection: change default, query, modify, delete, clear, [assignment:
other operations]]
- query, modify, delete
[assignment: other operations]]
- create
[assignment: list of TSF data]
- TSF data listed in Table 19
[assignment: the authorized identified roles].
- the roles listed in Table 20
Table 20: Operation of TSF Data
TSF Data Operations Roles
Data on key operator ID modify Key operator
Data on key operator Password modify Key operator
Data on SA ID (with local
authentication only)
Data on SA Password (with local
query, modify , delete,
Key operator, SA
create
modify Key operator, SA
authentication only)
Data on General user ID (with local
authentication only)
Data on General user Password (with
local authentication only)
query, modify, delete,
Key operator, SA
create
modify Key operator,
SA ,General user
Data on User Authentication query, modify Key operator, SA
Data on use of password entered from
query, modify Key operator, SA
MFD control panel in user
authentication
Data on minimum password length of
query, modify Key operator, SA
user password (with local
authentication only)
Data on store print
query, modify Key operator, SA
Data on Access denial due to
query, modify Key operator, SA
authentication failure of system
administrator
Data on Security Audit Log query, modify Key operator, SA
Data on Internal Network Data
query, modify, delete Key operator, SA
Protection
- 54 -
Page 59

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Data on Customer Engineer Operation
query, modify Key operator, SA
Restriction
Data on Hard Disk Data Encryption query, modify Key operator, SA
Data on Hard Disk Data Overwrite query, modify Key operator, SA
Data on date and time query, modify Key operator, SA
Data on Self Test query, modify Key operator, SA
FMT_SMF.1 Specification of Management Functions
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: No dependencies
FMT_SMF.1.1 The TSF shall be capable of performing the following management
functions: [assignment: list of management functions to be provided by
the TSF].
[assignment: list of management functions to be provided by the TSF]
- Security Management Functions listed in Table 21
Table 21: Security Management Functions Provided by TSF
Functional
Management items defined by CC Management functions of
requirements
FAU_GEN.1
There are no management activities
foreseen.
FAU_SAR.1
a) maintenance (deletion, modification,
addition) of the group of users with read
FAU_SAR.2
FAU_STG.1
FAU_STG.4
access right to the audit records.
None
None
a) maintenance (deletion, modification,
addition) of actions to be taken in case of
audit storage failure.
FCS_CKM.1 None
FCS_COP.1 None
FDP_ACC.1 None
FDP_ACF.1
a) Managing the attributes used to make
explicit access or denial based decisions.
FDP_IFC.1 None
FDP_IFF.1 a) Managing the attributes used to make
TOE
Management of data on
Security Audit Log settings
Management of data on key
operator (ID and password)
Management of data on SA
(ID and password) (with
local authentication only)
-
None
Reason: The control
parameter of audit log is
fixed and is not managed.
Management of data on
Hard Disk Data Encryption
Management of owner
identifier of Mailbox
Management of owner
identifier of store print
Management of data on store
print
None
- 55 -
Page 60

Dell C7765dn Security Target
explicit access based decisions.
FDP_RIP.1 a) The choice of when to perform residual
information protection (i.e. upon allocation
or deallocation) could be made
configurable within the TOE.
FIA_AFL.1 a) Management of the threshold for
unsuccessful authentication attempts;
b) Management of actions to be taken in
the event of an authentication failure.
FIA_ATD.1
a) if so indicated in the assignment, the
authorized administrator might be able to
define additional security attributes for
users.
FIA_SOS.1
a) the management of the metric used to
verify the secrets.
Reason: Access is restricted
and does not need to be
managed.
Management of data on
Hard Disk Data Overwrite
Management of allowable
number of system
administrator’s
authentication failures
Management of Access
Denial
None
Reason: There are no
additional security attributes
and there are no additional
security attributes to be
managed.
- Management of data on
minimum password length of
user password
FIA_UAU.1
a) Management of the authentication data
by an administrator;
b) Management of the authentication data
by the associated user;
c) Managing the list of actions that can be
taken before the user is authenticated.
FIA_UAU.7 None
FIA_UID.1
a) The management of the user identities.
b) If an authorised administrator can
change the actions allowed before
identification, the managing of the action
lists.
FIA_USB.1
a) an authorized administrator can define
default subject security attributes.
b) an authorized administrator can change
subject security attributes.
FMT_MOF.1 a) Managing the group of roles that can
- Management of data on use
of password entered from
MFD control panel in user
authentication.
- Management of data on key
operator(ID and password)
- Management of data on SA
and general user (ID and
password) (with local
authentication only)
- Management of data on
user authentication.
-
- Management of data on key
operator(ID)
- Management of data on SA
and general user (ID) (with
local authentication only)
- Management of data on
user authentication.
None
Reason: Action and security
attributes are fixed and are
not managed.
Management of data on
- 56 -
Page 61

Dell C7765dn Security Target
interact with the functions in the TSF;
Customer Engineer
Operation Restriction
FMT_MSA.1
a) managing the group of roles that can
interact with the security attributes;
None
Reason: The role group is
fixed and is not managed.
b) management of rules by which security
attributes inherit specified values.
FMT_MSA.3
a) managing the group of roles that can
specify initial values;
b) managing the permissive or restrictive
None
Reason: The role group is
only a system administrator
and is not managed.
setting of default values for a given access
control SFP;
c) management of rules by which security
attributes inherit specified values.
FMT_MTD.1. a) Managing the group of roles that can
interact with the TSF data.
Management of data on
Customer Engineer
Operation Restriction
FMT_SMF.1 None
FMT_SMR.1 a) Managing the group of users that are
part of a role.
None
Reason: The role group is
fixed and is not managed
FPT_STM.1
a) management of the time.
Management of time and
data.
FPT_TST.1
a) management of the conditions under
which TSF self testing occurs, such as
Management of data on Self
Test.
during initial start-up, regular interval, or
under specified conditions;
b) management of the time interval if
appropriate.
FTP_TRP.1
a) Configuring the actions that require
trusted path, if supported.
Management of data on
Internal Network Data
Protection.
FMT_SMR.1 Security roles
Hierarchical to: No other components
Dependencies: FIA_UID.1 Timing of identification
FMT_SMR.1.1 The TSF shall maintain the roles [assignment: the authorized identified
roles].
[assignment: the authorized identified roles]
- system administrator, SA, general user
FMT_SMR.1.2 The TSF shall be able to associate users with roles.
- 57 -
Page 62

Dell C7765dn Security Target
6.1.6. Class FPT: Protection of the TSF
FPT_STM.1 Reliable time stamps
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: No dependencies.
FPT_STM.1.1 The TSF shall be able to provide reliable time stamps.
FPT_TST.1 TSF testing
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: No dependencies.
FPT_TST.1.1 The TSF shall run a suite of self tests [selection: during initial start-up,
periodically during normal operation, at the request of the authorised
user, at the conditions [assignment: conditions under which self test
should occur]] to demonstrate the correct operation of [selection:
[assignment: parts of TSF], the TSF].
[selection: during initial start-up, periodically during normal operation, at
the request of the authorised user, at the conditions [assignment:
conditions under which self test should occur]]
- at the conditions [assignment: conditions under which self test should
occur]
[assignment: conditions under which self test should occur]
- at initiation under which self test is set
[selection: [assignment: parts of TSF], the TSF].
- [assignment: parts of TSF]
- TSF executable code
FPT_TST.1.2 The TSF shall provide authorised users with the capability to verify the
integrity of [selection: [assignment: parts of TSF data], TSF data].
[selection: [assignment: parts of TSF data], TSF data]
- [assignment: parts of TSF data]
- TSF data (excluding audit log data and present time data)
FPT_TST.1.3 The TSF shall provide authorised users with the capability to verify the
integrity of [selection: [assignment: parts of TSF], TSF].
[selection: [assignment: parts of TSF], TSF]
- assignment: parts of TSF
- TSF executable code in program ROM
- 58 -
Page 63

Dell C7765dn Security Target
6.1.7. Class FTP: Trusted path/channels
FTP_TRP.1 Trusted path
Hierarchical to: No other components.
Dependencies: No dependencies.
FTP_TRP.1.1 The TSF shall provide a communication path between itself and
[selection: remote, local] users that is logically distinct from other
communication paths and provides assured identification of its end
points and protection of the communicated data from [selection:
modification, disclosure, [assignment: other types of integrity or
confidentiality violation]].
[selection: remote, local]
- remote
[selection: modification, disclosure, [assignment: other types of integrity
or confidentiality violation]].
- modification, disclosure
FTP_TRP.1.2 The TSF shall permit [selection: the TSF, local users, remote users] to
initiate communication via the trusted path.
[selection: the TSF, local users, remote users]
- remote users
FTP_TRP.1.3 The TSF shall require the use of the trusted path for [selection: initial
user authentication, [assignment: other services for which trusted path is
required]].
[selection: initial user authentication, [assignment: other services for
which trusted path is required]].
- [assignment: other services for which trusted path is required]
- TOE communication service via Web, communication service for
printer driver, communication service for fax driver, communication
service for network utility, communication service for other services
which require trusted path
- 59 -
Page 64

Dell C7765dn Security Target
6.2. Security Assurance Requirements
The requirements for the TOE security assurance are described in Table 22.
The evaluation assurance level of the TOE is EAL3. All the requirement components for assurance are
quoted directly from the component of EAL3 specified by [the CC part 3].
Table 22: EAL3 Assurance Requirements
Assurance
Assurance Component Name
Requirements
Class ADV: Development
ADV_ARC.1 Security architecture description
ADV_FSP.3 Functional specification with complete summary
ADV_TDS.2 Architectural design
Class AGD: Guidance documents
AGD_OPE.1 Operational user guidance
AGD_PRE.1 Preparative procedures
Class ALC: Life-cycle support
ALC_CMC.3 Authorization controls
ALC_CMS.3 Implementation representation CM coverage
ALC_DEL.1 Delivery procedures
ALC_DVS.1 Identification of security measures
ALC_LCD.1 Developer defined life-cycle model
Class ASE: Security Target evaluation
ASE_CCL.1 Conformance claims
ASE_ECD.1 Extended components definition
ASE_INT.1 ST introduction
ASE_OBJ.2 Security objectives
ASE_REQ.2 Derived security requirements
ASE_SPD.1 Security problem definition
ASE_TSS.1 TOE summary specification
Class A TE: T ests
ATE_COV.2 Analysis of coverage
ATE_DPT.1 Testing: basic design
ATE_FUN.1 Functional testing
ATE_IND.2 Independent testing - sample
Class AV A: Vulnerability assessment
AVA_VAN.2 Vulnerability analysis
- 60 -
Page 65

Dell C7765dn Security Target
6.3. Security Requirement Rationale
6.3.1. Security Functional Requirements Rationale
Table 23 lists security functional requirements and the corresponding security objectives. As shown in
Table 23, each security functional requirement corresponds to at least one security objective of the
TOE.
Table 24 shows the rationale demonstrating that each security objective is assured by TOE security
functional requirements.
Table 23: Security Functional Requirements and the Corresponding Security Objectives
Security Objectives
Security Functional
Requirements
FAU_GEN.1
FAU_SAR.1
FAU_SAR.2
FAU_STG.1
FAU_STG.4
FCS_CKM.1
FCS_COP.1
FDP_ACC.1
FDP_ACF.1
FDP_IFC.1
O.AUDITS
O.CIPHER
O.COMM_SEC
O.FAX_SEC
O.MANAGE
O.RESIDUAL
O.RESTRICT
O.USER
O.VERIFY
FDP_IFF.1
FDP_RIP.1
FIA_AFL.1 (1)
FIA_AFL.1 (2)
FIA_AFL.1 (3)
FIA_AFL.1 (4)
FIA_ATD.1
FIA_SOS.1
FIA_UAU.1
FIA_UAU.7
FIA_UID.1
FIA_USB.1
FMT_MOF.1
- 61 -
Page 66

Security Objectives
Security Functional
Requirements
Dell C7765dn Security Target
O.AUDITS
O.CIPHER
O.COMM_SEC
O.FAX_SEC
O.MANAGE
O.RESIDUAL
O.RESTRICT
O.USER
O.VERIFY
FMT_MSA.1
FMT_MSA.3
FMT_MTD.1
FMT_SMF.1
FMT_SMR.1
FPT_STM.1
FPT_TST.1
FTP_TRP.1
Table 24: Security Objectives to SFR Rationale
Security Objectives Security Functional Requirements Rationale
O. AUDITS is the objective that provides the function to record auditable
events and its log data.
By satisfying the following security requirements, O.AUDITS can be
realized.
By FAU_GEN.1, the security audit log data are generated for the
auditable events: (However, audit is unnecessary for the following
functional requirements for each reason described below.)
- FAU_STG.4: The total number of security audit log data events is
fixed. The data are stored and updated automatically.
- FCS_CKM.1: When cryptographic key generation fails, a system error
occurs at the time of booting of the MFD.
O.AUDITS
- FSC_COP.1: An encryption failure is monitored as job status.
- FDP_IFF.1: The flow is fixed. No event is to be monitored.
- FMT_MSA.3: No change is to be applied to default values and rules.
By FAU_SAR.1, the authorized system administrator can read the
security audit log data from an audit log file.
By FAU_SAR.2, only the authorized system administrator can access the
security audit log data.
By FAU_STG.1, the security audit log data stored in an audit log file is
protected from unauthorized deletion and alteration.
By FAU_STG.4, when the security audit log data is full, the oldest stored
audit record is overwritten and a new audit event is stored into the audit
- 62 -
Page 67

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Security Objectives Security Functional Requirements Rationale
log file.
By FPT_STM.1, the auditable events are recorded with time stamp in the
audit log, using highly reliable clock of the TOE.
O. CIPHER is the objective that encrypts the used document data and the
security audit log data i in the internal HDD so that they cannot be
analyzed even if retrieved.
By satisfying the following security requirements, O.CIPHER can be
realized.
O.CIPHER
By FCS_CKM.1, the cryptographic key is generated in accordance with
the specified cryptographic key size (256 bits).
By FCS_COP.1, the document data and security audit log data to be
stored into the internal HDD are encrypted and then decrypted when the
data are read, in accordance with the determined cryptographic algorithm
and cryptographic key size.
O.COMM_SEC
O.FAX_SEC
O.MANAGE
O.COMM_SEC is the objective that protects the document data, security
audit log data, and TOE setting data on the internal network from
interception and alteration.
By satisfying the following security requirements, O.COMM_SEC can
be realized:
By FTP_TRP.1, a highly reliable communication path is provided
through communication data encryption protocol so that the document
data, security audit log data, and TOE setting data on the internal
network between the TOE and the remote can be protected from threats.
O.FAX_SEC is the objective that prevents the unauthorized access to the
internal network via public telephone line.
By satisfying the following security requirements, O.FAX_SEC can be
realized:
By FDP_IFC.1 and FDP_IFF.1, the internal network to which the TOE is
connected is prevented from being accessed via public telephone line
from the communication path of TOE fax modem.
O. MANAGE is the objective that allows only an authenticated system
administrator to access the system administrator mode for security
function setting and inhibits a general user from accessing the TOE
setting data. By satisfying the following security requirements,
O.MANAGE can be realized:
By FIA_AFL.1 (1), successive attacks are prevented because the power
needs to be cycled when the number of key operator authentication
failures reaches the defined number of times.
By FIA_AFL.1 (2), successive attacks are prevented because the power
needs to be cycled when the number of SA authentication failures (at
- 63 -
Page 68

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Security Objectives Security Functional Requirements Rationale
local authentication) reaches the defined number of times.
By FIA_UAU.1 and FIA_UID.1, user authentication is performed to
identify an authorized system administrator or general user.
By FIA_UAU.7, unauthorized disclosure of the authentication
information (password) is prevented because the authentication feedback
is protected.
By FMT_MOF.1, the person who enables/disables TOE security
functions and makes functional settings is limited to system
administrator.
By FMT_MTD.1, the person who can make settings of TOE security
functions is limited to system administrator. Thus, only system
administrators can query, modify, and create TSF data.
By FMT_SMF.1, TOE security management functions are provided for
system administrator.
By FMT_SMR.1 (1), the role related to the security is limited to system
administrator by maintaining the role of system administrator as a user
who has special authority.
O.RESIDUAL
O.RESTRICT
O.RESIDUAL is the objective that disables the reproduction and
recovery of the used document data in the internal HDD.
By satisfying the following security requirements, O.RESIDUAL can be
realized:
By FDP_RIP.1, the previous information of the used document data
stored in the internal HDD is made unavailable.
O.RESTRICT is the objective that offers the function to inhibit an
unauthorized person from using the TOE.
By satisfying the following security requirements, O.RESTRICT can be
realized:
By FIA_AFL.1 (1), successive attacks are prevented because the power
needs to be cycled when the number of key operator authentication
failures reaches the defined number of times.
By FIA_AFL.1 (2), successive attacks are prevented because the power
needs to be cycled when the number of SA authentication failures (at
local authentication) reaches the defined number of times.
By FIA_AFL.1 (3), when general user authentication fails, “incorrect
password” message is displayed, requesting password re-entry.
By FIA_AFL.1 (4), when SA authentication fails (at remote
authentication), “incorrect password” message is displayed, requesting
password re-entry.
By FIA_UIA.1 and FIA_UID.1, user authentication is performed to
identify an authorized general user and system administrator.
- 64 -
Page 69

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Security Objectives Security Functional Requirements Rationale
By FIA_UAU.7, unauthorized disclosure of the authentication
information (password) is prevented because the authentication feedback
is protected.
O.USER is the objective that identifies the TOE user and allows only the
authorized user to retrieve, and delete the document data and to change
password.
By satisfying the following security requirements, O.USER can be
realized:
By FDP_ACC.1 and FDP_ACF.1, user authentication is performed. Only
authorized user is allowed to operate the objects.
By FIA_AFL.1 (1), successive attacks are prevented because the power
needs to be cycled when the number of key operator authentication
failures reaches the defined number of times.
By FIA_AFL.1 (2), successive attacks are prevented because the power
needs to be cycled when the number of SA authentication failures (at
local authentication) reaches the defined number of times.
By FIA_AFL.1 (3), when general user authentication fails, “incorrect
password” message is displayed, requesting password re-entry.
By FIA_AFL.1 (4), when SA authentication fails (at remote
authentication), “incorrect password” message is displayed, requesting
password re-entry.
O.USER
By FIA_ATD.1 and FIA_USB.1, each role of key operator, SA, and
general user is maintained and only the authorized users are associated
with the subjects.
By FIA_SOS1, the minimum length of password for SA and general user
is limited.
By FIA_UAU.1 and FIA_UID.1, user authentication is performed to
identify an authorized general user and system administrator.
By FIA_UAU.7, unauthorized disclosure of the authentication
information (password) is prevented because the authentication feedback
is protected.
By FMT_MSA.1, the query, modify, deletion, and creation of security
attributes are managed.
By FMT_MSA.3, the suitable default values are managed.
By FMT_MTD.1, the setting of password for key operator is limited to
key operator, that for SA is limited to key operator and SA, and that for
general user is limited to system administrator and the general user
(when it is his/her own).
By FMT_SMF.1, TOE security management functions are provided for
authorized users.
- 65 -
Page 70

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Security Objectives Security Functional Requirements Rationale
By FMT_SMR.1, the role of general user and system administrator is
maintained and associated with the general user and system
administrator.
O. VERIFY is the objective that provides the function to verify the
integrity of TSF executable code.
By satisfying the following security requirements, O. VERIFY can be
realized.
By FPT_TST.1 the TOE can execute the self test function to verify the
O. VERIFY
integrity of TSF executable code and TSF data upon initiation.
: (However, verification is unnecessary for the following TSF data for
each reason described below.)
- Security audit log data: Not affect TSF.
- Present data and time : Generated by the battery backed-up hardware
real-time clock, and becomes a system error at the data destruction.
6.3.2. Dependencies of Security Functional Requirements
Table 25 describes the functional requirements that security functional requirements depend on and
those that do not and the reason why it is not problematic even if dependencies are not satisfied.
Table 25: Dependencies of Functional Security Requirements
Functional Requirement Dependencies of Functional Requirements
Requirement that
Requirement that is not dependent on
Requirement and its name
is dependent on
and its rationale
FAU_GEN.1
FPT_STM.1 -
Audit data generation
FAU_SAR.1
FAU_GEN.1 -
Audit review
FAU_SAR.2
FAU_SAR.1 -
Restricted audit review
FAU_STG.1
Protected audit trail
FAU_GEN.1 storage
FAU_STG.4
Prevention of audit data
loss
FAU_STG.1 -
- 66 -
Page 71

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Functional Requirement Dependencies of Functional Requirements
Requirement and its name
FCS_CKM.1
Cryptographic key
generation
(The stored data in the
internal HDD)
FCS_COP.1
Cryptographic operation
(The stored data in the
internal HDD)
FDP_ACC.1
Subset access control
Requirement that
is dependent on
Requirement that is not dependent on
and its rationale
FCS_CKM.4:
A cryptographic key is generated when MFD is
booted, and stored on DRAM (volatile memory).
A cryptographic key does not need to be
FCS_COP.1
destructed because this key is lost when the MFD
main unit is powered off.
Therefore, the dependency on FCS_CKM.4 does
not need to be satisfied.
FCS_CKM.4:
A cryptographic key is generated when MFD is
booted, and stored on DRAM (volatile memory).
FCS_CKM.1
A cryptographic key does not need to be
destructed because this key is lost when the MFD
main unit is powered off.
FDP_ACF.1 -
FDP_ACF.1
Security attribute based
access control
FDP_IFC.1
Subset information flow
control
(Fax information flow)
FDP_IFF.1
Simple security attributes
(Fax information flow)
FDP_RIP.1
Subset residual
information protection
FIA_AFL.1(1)
Authentication failure
handling
(Key operator)
FDP_ACC.1
-
FMT_MSA.3
FDP_IFF.1 -
FMT_MSA.3:
FDP_IFC.1
A static attribute initialization is not required
because Fax Information Flow has no security
attribute.
None
FIA_UAU.1
FIA_AFL.1(2)
Authentication failure
handling
(SA, local authentication)
FIA_UAU.1
- 67 -
Page 72

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Functional Requirement Dependencies of Functional Requirements
Requirement and its name
FIA_AFL.1(3)
Authentication failure
handling
(General user)
FIA_AFL.1(4)
Authentication failure
handling
(SA, remote
authentication)
FIA_ATD.1
User attribute definition
FIA_SOS.1
Verification of secrets
FIA_UAU.1
Timing of authentication
FIA_UAU.7
Protected authentication
feedback
Requirement that
is dependent on
FIA_UAU.1
FIA_UAU.1
FIA_UID.1
FIA_UID.1
Requirement that is not dependent on
and its rationale
None
None
FIA_UID.1
Timing of identification
FIA_USB.1
User-subject binding
FMT_MOF.1
Management of security
functions behavior
FMT_MSA.1
Management of security
attributes
FMT_MSA.3
Static attribute
initialization
FMT_MTD.1
Management of TSF data
FMT_SMF.1
Specification of
management functions
None
FIA_ATD.1 -
FMT_SMF.1
-
FMT_SMR.1
FDP_ACC.1
FMT_SMF.1
-
FMT_SMR.1
FMT_MSA.1
-
FMT_SMR.1
FMT_SMF.1
-
FMT_SMR.1
None
FMT_SMR.1
Security roles
FIA_UID.1
- 68 -
Page 73

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Functional Requirement Dependencies of Functional Requirements
Requirement that
Requirement that is not dependent on
Requirement and its name
is dependent on
and its rationale
FPT_STM.1
None
Reliable time stamp
FPT_TST.1
None
TSF testing
FTP_TRP.1
None
Trusted Path
6.3.3. Security Assurance Requirements Rationale
This TOE is for a MFD, a commercial product. The following threats are assumed to be caused by a
low-level attacker: attack or interception/alteration of data on internal network via a MFD external
interface from control panel, Web browser of system administrator’s client; and reading-out of
information by removing the internal HDD and connecting it to a commercial tool.
To counter these threats, this TOE is required to provide the security functions which assure security.
The evaluation assurance level of the TOE is EAL3 which includes the following analyses:
- Analysis of the security measures of the TOE at development phase
(Performing/analyzing systematic tests and evaluating the management of the development
environment and the developed products.)
- Analysis of whether the sufficient guidance information is included so that the security functions can
be used safely.
Therefore, EAL 3 is the reasonable evaluation level for this TOE.
- 69 -
Page 74

Dell C7765dn Security Target
7. TOE SUMMARY SPECIFICATION
This chapter describes the summary specifications of the security functions provided by this TOE.
7.1. Security Functions
Table 26 shows security functional requirements and the corresponding TOE security functions.
The security functions described in this section satisfy the TOE security functional requirements that
are specified in section 6.1 of this ST.
Table 26: Security Functional Requirements and the Corresponding TOE Security Functions
Security Functions
Security Functional
TSF_IOW
TSF_CIPHER
TSF_USER_AUTH
TSF_FMT
TSF_CE_LIMIT
TSF_FAU
TSF_NET_PROT
Requirements
FAU_GEN.1
FAU_SAR.1
FAU_SAR.2
FAU_STG.1
FAU_STG.4
FCS_CKM.1
FCS_COP.1
FDP_ACC.1
FDP_ACF.1
TSF_FAX_FLOW
TSF_SELF_TEST
FDP_IFC.1
FDP_IFF.1
FDP_RIP.1
FIA_AFL.1 (1)
FIA_AFL.1 (2)
FIA_AFL.1 (3)
FIA_AFL.1 (4)
FIA_ATD.1
FIA_SOS.1
FIA_UAU.1
FIA_UAU.7
FIA_UID.1
FIA_USB.1
FMT_MOF.1
FMT_MSA.1
- 70 -
Page 75

Security Functions
Security Functional
Requirements
Dell C7765dn Security Target
TSF_IOW
TSF_CIPHER
TSF_USER_AUTH
TSF_FMT
TSF_CE_LIMIT
TSF_FAU
TSF_NET_PROT
TSF_FAX_FLOW
TSF_SELF_TEST
FMT_MSA.3
FMT_MTD.1
FMT_SMF.1
FMT_SMR.1
FPT_STM.1
FPT_TST.1
FTP_TRP.1
The summary of each TOE security function and the corresponding security functional requirements
are described below.
7.1.1. Hard Disk Data Overwrite (TSF_IOW)
According to Hard Disk Data Overwrite setting which is configured by a system administrator with
the system administrator mode, the used document data in the internal HDD are deleted by either one
or three pass overwrite procedure on the document data area when each job of copy, print, scan,
Network Scan, fax, Internet Fax, or Direct Fax is completed.
This is because whether to prioritize efficiency or security depends on the usage environment of the
MFD.
When efficiency is prioritized, one pass overwrite procedure is applied. When security is prioritized,
three pass overwrite procedure is applied. Three pass overwrite has lower processing speed than one
pass but can provide more solid overwrite function. Therefore, three pass is an appropriate number of
times to overwrite.
(1) FDP_RIP.1 Subset Residual Information Protection
To control the overwrite function conducted after each job, two options are available: one pass
(zero) overwrite procedure and three pass (random number / random number / zero) overwrite
procedure.
List of the used document data which are to be overwritten and deleted is on the internal HDD.
When the existence of the used document data are found in this list at the time of booting the
TOE, the overwrite function is performed.
7.1.2. Hard Disk Data Encryption (TSF_CIPHER)
According to Hard Disk Data Encryption setting which is configured by a system administrator with
- 71 -
Page 76

Dell C7765dn Security Target
the system administrator mode, the document data and security audit log data are encrypted before
stored into the internal HDD when operating any function of copy, print, scan, Network Scan, fax,
Internet Fax, Direct Fax, or configuring various security function settings.
(1) FCS_CKM.1 Cryptographic key generation
The TOE uses the “hard disk data encryption seed key” configured by a system administrator and
generates a 256-bit encryption key at the time of booting through FXOSENC algorithm, which is
Fuji Xerox’s standard method and a secure algorithm with sufficient complexity. (When the "hard
disk data encryption seed key" is the same, the same cryptographic key is generated.)
(2) FCS_COP.1 Cryptographic operation
Before storing the document data and security audit log data into the internal HDD, the TOE
encrypts the data using the 256-bit cryptographic key generated at the time of booting
(FCS_CKM.1) and the AES algorithm based on FIPS PUBS 197. When reading out the stored
data, the TOE decrypts the data also using the 256-bit cryptographic key generated at the time of
booting and the AES algorithm.
7.1.3. User Authentication (TSF_USER_AUTH)
Access to the TOE functions is restricted to the authorized user.
A user needs to enter his/her ID and password from the fax driver, Network Scan Utility, or Web browser
of the general user client, or MFD control panel.
control panel
After a user enters his/her ID and password, an MFD identifies and authenticates the user based on user
information stored in the MFD or an external server.
There are the following two types of authentication depending on how user information is registered.
a) Local Authentication
In local authentication, authentication is managed by using the user information registered in the
TOE.
b) Remote Authentication
Authentication is performed by remote authentication server. User information is not registered in
the TOE. In remote authentication, authentication is performed by using the user information
managed by remote authentication server (LDAP server or Kerberos server).
Only the authenticated user can use the following functions:
a) Functions controlled by the MFD control panel
Copy, fax (send), Internet Fax (send), scan, network scan, Mailbox operation, and print (This
print function requires the Accounting System preset from printer driver. A user must be
authenticated from the control panel for print job.)
b) Functions controlled by Network Scan Utility of user client (with local authentication only)
A user can also use Smart Card authentication on the
- 72 -
Page 77

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Function to retrieve document data from Mailbox.
c) Functions controlled by Configuration Web Tool
Display of device condition, display of job status and its log, function to retrieve document data
from Mailbox, and print function by file designation
In addition, access to and setting change of the TOE security functions are restricted to the authorized
system administrator. A system administrator needs to enter his/her ID and password from MFD
control panel or system administrator client.
In Smart Card authentication, an MFD identifies and authenticates users by comparing user information
and certificates stored in Smart Card (CAC/PIV) and those in Kerberos server.
Only the authenticated user can use the following functions:
Functions controlled by the MFD control panel
Copy, fax (send), Internet Fax (send), scan, network scan, Mailbox operation, and print (This
print function requires the Accounting System preset from printer driver. A user must be
authenticated from the control panel for print job.).
For users successfully identified and authenticated with Smart Card authentication (CAC/PIV),
TOE gives the authority to refer to and change the settings of TOE’s security functions from the
control panel, based on the SA authority information stored in LDAP server.
For user authentication that uses Configuration Web Tool or Network Scan Utility, Smart Card
information is not used. Instead, user information for local authentication or remote authentication
is used.
(1) FIA_AFL.1 (1) Authentication failure handling
The function of the TOE to handle the authentication failures is provided for the key operator
authentication which is performed before accessing the system administrator mode. When the
number of unsuccessful authentication attempts with system administrator ID reaches 5 times, the
control panel does not accept any operation except power cycle, and the web browser do not
accept authentication operation until the MFD main unit is powered off/on.
(2) FIA_AFL.1 (2) Authentication failure handling
The function of the TOE to handle the authentication failures is provided for the SA
authentication upon local authentication which is performed before accessing the system
administrator mode. When the number of unsuccessful authentication attempts with system
administrator ID reaches 5 times, the control panel does not accept any operation except power
cycle, and the web browser do not accept authentication operation until the MFD main unit is
powered off/on.
(3) FIA_AFL.1 (3) Authentication failure handling
The function of the TOE to handle the authentication failures is provided for the general user
- 73 -
Page 78

Dell C7765dn Security Target
authentication which is performed before using the MFD functions. When the entered password
does not match the one set by an authorized user, the message saying “authentication was failed”
is displayed on the control panel, requesting re-entry of the user information.
Re-entry of user information is also required at Web browser and Network Scan Utility (with
local authentication only).
(4) FIA_AFL.1 (4) Authentication failure handling
The function of the TOE to handle the authentication failures is provided for the SA
authentication upon remote authentication which is performed before using the MFD functions.
When the entered password does not match the one set by SA, the message saying “authentication
was failed” is displayed on the control panel, requesting re-entry of the user information.
Re-entry of user information is also required at Web browser.
(5) FIA_ATD.1 User attribute definition
The function of the TOE to define and retain the roles of key operator, SA, and general user.
(6) FIA_SOS.1 Verification of secrets
When setting a password of SA and general user, the TOE rejects settings if the password is less
than the minimum number of characters.
(7) FIA_UAU.1 Timing of authentication
FIA_UID.1 Timing of identification
The TOE requests a user to enter his/her ID and password before permitting him/her to operate
the MFD function via Web browser, Network Scanner Utility, and fax driver of a user client, or
the control panel. The entered user ID and password are verified against the data registered in
the TOE setting data.
This identification (FIA_UID.1) and the authentication (FIA_UAU.1) are simultaneously
performed, and the operation is allowed only when both of the identification and authentication
succeed.
When receiving print job from user client, the TOE receives and stores print job in Mailbox
without user identification and authentication.
When receiving fax data by the public telephone line, the TOE receives the fax data and stores
them in Mailbox without user identification and authentication.
(8) FIA_UAU.7 Protected authentication feedback
The TOE offers the function to display the same number of asterisks (`*`) as the entered-password
characters on the control panel, or Web browser, in order to hide the password at the time of user
authentication.
(9) FIA_USB.1 User-subject binding
- 74 -
Page 79

Dell C7765dn Security Target
With the authenticated ID, TOE associates the roles of key operator, SA, and general user with the
subjects.
(10) FMT_MSA.1 Management of security attributes
With the user authentication function, the TOE permits the authenticated user to handle the
identities related to each Mailbox and Store Print as shown in Table 27.
Table 27: Management of security attributes
Security Attributes Operations Roles
Key operator identifier modify Key operator
SA identifier (with local
authentication only)
General user identifier
(with local authentication
query, modify ,delete,
create
query, modify ,delete,
create
Key operator, SA
Key operator, SA
only)
Mailbox owner identifier
query, delete, create General user, SA
(Personal Mailbox)
All Mailbox owner
query, delete Key operator
identifier (All of Personal
Mailbox)
Mailbox owner identifier
query, delete, create Key operator
(Shared Mailbox)
Store Print owner identifier query, delete Key operator, SA,
General user
All Store Print owner
query, delete Key operator, SA
identifier
(11) FMT_MTD.1 Management of TSF data
FMT_SMF.1 Specification of management functions
The TOE provides the user interface for setting password only to the authenticated authorized
user.
The setting of password for key operator is limited to key operator, that for SA (with local
authentication only) is limited to key operator and SA, and that for general user (with local
authentication only) is limited to system administrator and the general user (when it is his/her
own).
(12) FMT_SMR.1 Security role
The TOE maintains the roles of system administrator and general user and associates these roles
to the authorized users.
(13) FDP_ACC.1 Subset access control
- 75 -
Page 80

Dell C7765dn Security Target
FDP_ACF.1 Security attribute based access control
With the user authentication function, the TOE permits the authenticated user to operate Mailbox
and Store Print (Private Print) as shown in Table 28.
Table 28: Access Control
Personal Mailbox Shared Mailbox Store Print
Creation of Mailbox Available for general
user, SA
Deletion of Mailbox Available for
registered general
Available for key
operator
Available for key
operator
-
-
user ,SA and key
operator
Retrieval and
Deletion of document
data
Available for
registered general
user ,SA and key
Available for general
user, SA and key
operator
Available for general
user, SA and key
operator
operator
Retrieval and
Deletion of all
Available for key
operator
Available for key
operator
Available for SA and
key operator
document data
User authentication is performed before accessing Mailbox or Store Print.
a) Private Print Function
When the MFD is set to “Save as Private Charge Print,” and a user sends a print request from the
printer driver in which the Accounting System is preset, the print data are decomposed into
bitmap data, classified according to the user ID, and temporarily stored in the corresponding
Private Print area within the internal HDD.
In the same way, when a user is authenticated by entering his/her ID and password from
Configuration Web Tool for authentication, and the user sends a print request by designating the
files within a user client, the print data are temporarily stored in Private Print area according to
the user ID.
To refer to the stored print data, a user needs to enter his/her ID and password from the control
panel or to use Smart Card (CAC/PIV). When the user is authenticated, the data on the waiting
list corresponding to the user ID are displayed. The user can request printing or deletion of the
data on the list.
b) Mailbox Function
The scanned data and received fax data can be stored into Mailbox from IIT and Fax board which
are not shown in Figure 3.
To store the scanned data into Mailbox, a user needs to enter his/her ID and password from the
MFD control panel or to use Smart Card (CAC/PIV). When the user is authenticated, the
- 76 -
Page 81

Dell C7765dn Security Target
document data can be scanned from IIT and stored into the internal HDD according to the user’s
instruction from the control panel.
To store the received fax data into Mailbox, user authentication is not required. Among the
received fax data transmitted over public telephone line, the following data are automatically
classified and stored into each corresponding Mailbox: the received fax data whose corresponding
Mailbox is specified by the sender, the received fax data from a particular sender (the data are
classified according to the sender’s telephone number), and the received fax data from an
unknown sender.
To retrieve, print, or delete the stored data in the Personal Mailbox corresponding to each
registered user ID, user authentication is required; the MFD compares the user ID and password
preset in the MFD against those entered by a general user from the control panel, Configuration
Web Tool, or Network Scan Utility (with local authentication only). For user authentication,
Smart Card authentication is also available on the control panel.
Mailbox Operation by a General User / SA
- Creation of Personal Mailbox
When a general user / SA operates to create Personal Mailbox, the Personal Mailbox in which
general user identifier / SA identifier is set as its owner is created.
- Deletion of Personal Mailbox
When the general user identifier / SA identifier matches the owner identifier of Personal
Mailbox, deletion of the corresponding Personal Mailbox is allowed.
- Retrieval and deletion of document data in Personal Mailbox
When the general user identifier / SA identifier matches the owner identifier of Personal
Mailbox, retrieval and deletion of the document data inside are allowed.
- Retrieval and deletion of document data in Shared Mailbox
Retrieval and deletion of document data in Shared Mailbox are allowed.
Store Print Operation by a General User / SA
- Deletion and retrieval of document data
When the general user identifier / SA identifier matches the owner identifier of Store Print area,
retrieval and deletion of the document data inside are allowed. When the document data are
deleted, the corresponding Store Print area is also deleted.
Mailbox Operation by the Key Operator
Creation and deletion of Shared Mailbox are allowed.
For all Mailboxes, the key operator's operations to delete Mailbox, and to retrieve, and delete
the document data inside are allowed.
Store Print Operation by the Key Operator / SA
For all the Store Print areas, the key operator's / SA's operations to retrieve and delete the
document data inside are allowed.
- 77 -
Page 82

Dell C7765dn Security Target
7.1.4. System Administrator’s Security Management (TSF_FMT)
To grant a privilege to a specific user, this function allows only the authorized system administrator to
access the system administrator mode which enables him/her to refer to and configure the settings of
the following TOE security functions from the control panel or system administrator client.
(1) FMT_MOF.1 Management of security functions behavior
FMT_MTD.1 Management of TSF data
FMT_SMF.1 Specification of management functions
The TOE provides a user interface which allows only the authenticated system administrator to
refer to / change the TOE setting data related to the following TOE security functions and to make
setting whether to enable/disable each function.
With these functions, the required security management functions are provided.
The settings of the following TOE security functions can be referred to and changed from the
control panel.
・ Refer to the setting of Hard Disk Data Overwrite, enable/disable it, and set the number of pass
(overwrite procedure);
・ Refer to the setting of Hard Disk Data Encryption and enable/disable it;
・ Set the cryptographic seed key for Hard Disk Data Encryption;
・ Refer to the setting on the use of password entered from MFD control panel in user
authentication, and enable/disable it;
・ Refer to the setting of access denial due to authentication failure of system administrator
identification, enable/disable it, and set the allowable number of the failures before access
denial;
・ Change the key operator ID and password (only a key operator is privileged);
・ Refer to the setting of access denial due to authentication failure of system administrator,
enable/disable it, and set the allowable number of failures;
・ Refer to and set the minimum password length (for general user and SA, with local
authentication only);
・ Refer to the setting of SSL/TLS communication of Internal Network Data Protection,
enable/disable it, and configure the details;
・ Refer to the setting of IPSec communication of Internal Network Data Protection,
enable/disable it, and configure the details;
・ Refer to the setting of S/MIME communication of Internal Network Data Protection,
enable/disable it, and configure the details;
・ Refer to the setting of User Authentication and select disable/Local Authentication/Remote
Authentication, and configure the details;
・ Refer to the setting of Smart Card authentication, enable/disable it, and configure the details;
・ Refer to the setting of Store Print and set store/print;
・ Refer to and set date and time;
・ Refer to the setting of Self Test and enable/disable it;
- 78 -
Page 83

Dell C7765dn Security Target
With Configuration Web Tool, the settings of the following TOE security functions can be referred to
and changed from a system administrator client via Web browser.
・ Change the key operator ID and password (only a key operator is privileged);
・ Refer to the setting of ID of SA and general user and change the ID and password (with local
authentication only);
・ Refer to the setting of access denial due to authentication failures of system administrator,
enable/disable it, and set the allowable number of the failures before access denial;
・ Refer to and set the minimum password length (for general user and SA, with local
authentication only);
・ Refer to the setting of Security Audit Log and enable/disable it,
(When Security Audit Log data are enabled, security audit log data can be downloaded in the
form of tab-delimited text to a system administrator client.);
・ Refer to the setting of SSL/TLS communication of Internal Network Data Protection,
enable/disable it, and configure the details;
・ Refer to the setting of IPSec communication of Internal Network Data Protection,
enable/disable it, and configure the details;
・ Refer to the setting of SNMP v3 communication of Internal Network Data Protection,
enable/disable it, and configure the details;
・ Set the authentication password for SNMPv3 communication;
・ Refer to the setting of S/MIME communication of Internal Network Data Protection,
enable/disable it, and configure the details;
・ Download/upload and create an X.509 certificate;
・ Refer to the setting of User Authentication and select disable/Local Authentication/Remote
Authentication, and configure the details;
・ Refer to the setting of Smart Card authentication, enable/disable it, and configure the details;
(2) FMT_MSA.1 Management of security attributes
The TOE restricts the handling of the general user identifier only to a system administrator.
(3) FMT_MSA.3 Static attribute initialization
Regarding Mailbox and Store Print, the TOE sets the user identifier created as owner identifier
and the available user identifier, and set them as default values of security attributes.
(4) FMT_SMR.1 Security roles
The system administrator's role is maintained and the role is associated with a system
administrator.
7.1.5. Customer Engineer Operation Restriction (TSF_CE_LIMIT)
A system administrator can restrict CE’s operation in the system administrator mode to inhibit CE
- 79 -
Page 84

Dell C7765dn Security Target
from referring to / changing the settings related to System Administrator’s Security Management
(TSF_FMT). This function can prevent setting change by an attacker who is impersonating CE.
(1) FMT_MOF.1 Management of security functions behavior
FMT_MTD.1 Management of TSF data
FMT_SMF.1 Specification of management functions
The TOE provides a user interface which allows only the authenticated system administrator to
refer to / change (enable/disable) the TOE settings related to Customer Engineer Operation
Restriction from the control panel and Configuration Web Tool.
With these functions, the required security management functions are provided.
(2) FMT_SMR.1 Security roles
The system administrator's role is maintained and the role is associated with a system
administrator.
7.1.6. Security Audit Log (TSF_FAU)
According to Security Audit Log setting which is configured by a system administrator using the
system administrator mode, the important events of the TOE such as device failure, configuration
change, and user operation are traced and recorded based on when and who operated what function.
All the TOE users are the targets of this audit log.
(1) FAU_GEN.1 Audit data generation
It is assured that the defined auditable event is recorded in the audit log.
Table 29 shows the details of the audit log data.
Table 29: Details of Security Audit Log Data
The auditable events are recorded with the following fixed size entries:
- Log ID: consecutive numbers as an audit log identifier (1 - 60000)
- Date: date data (yyyy/mm/dd, mm/dd/yyyy, or dd/mm/yyyy)
- Time: time data (hh:mm:ss)
- Logged Events: event name (arbitrary characters of up to 32 digits)
- User Name: user name (arbitrary characters of up to 32 digits)
- Description: description on events
(arbitrary characters of up to 32 digits, see below for details)
- Status: status or result of event processing
(arbitrary characters of up to 32 digits, see below for details)
- Optionally Logged Items: additional information recorded to audit log
(except common record items)
Logged Events Description Status
Change in Device Status
System Status
Started normally (cold boot)
-
Started normally (warm boot)
- 80 -
Page 85

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Logged Events Description Status
Shutdown requested
User operation (Local) Start/End
Self T est Successful/Failed
User Authentication
Login Successful, Failed (Invalid
UserID), Failed (Invalid
Logout
Login/Logout
Locked System Administrator
Authentication
Detected continuous Authentication Fail
Password), Failed
(Number of authentication
failures recorded)
Change in Audit Policy
Audit Policy Audit Log Enable/Disable
Job Status
Print
Copy
Scan
Job Status
Fax
Mailbox
Print Reports
Job Flow Service
Change in Device Settings
Adjust Time
Create Mailbox
Device Settings
Delete Mailbox
Switch Authentication Mode
Change Security Setting
Access to Data Stored in Device
Import Certificate
Delete Certificate
Add Address Entry
Device Data
Delete Address Entry
Completed, Completed
with Warnings, Canceled
by User, Canceled by
Shutdown, Aborted,
Unknown
Successful/Failed
Successful
(Setting items recorded)
Successful/Failed
Edit Address Entry
Export Audit Log
Communication Trusted Communication
- 81 -
Failed
(Protocol and
communication
destination stored)
Page 86

Dell C7765dn Security Target
(2) FAU_SAR.1 Audit review
It is assured that all the information recorded in the audit log can be retrieved.
Security audit log data can be downloaded in the form of tab-delimited text by pressing the button
“store as a text file.” To download security audit log data, SSL/TLS communication needs to be
enabled before using Web browser.
(3) FAU_SAR.2 Restricted audit review
The person who retrieves the security audit log data is limited to the authenticated system
administrator. A system administrator can access the security audit log data only via Web browser
and the access from the control panel is inhibited. Therefore, a system administrator needs to log
in from Web browser to access the security audit log data.
(4) FAU_STG.1 Protected audit trail storage
There is no function to delete the security audit log data, and the security audit log data are
protected from untrusted alteration and modification.
(5) FAU_STG.4 Prevention of audit data loss
When security audit log data are full, the oldest stored audit record is overwritten with the new
data so that the new data is not lost but surely recorded.
Auditable events are stored with time stamps into NVRAM. When the number of stored events
reaches 50, the 50 logs on NVRAM is stored into one file (“audit log file”) within the internal
HDD. Up to 15,000 events can be stored. When the number of recorded events exceeds 15,000,
the oldest audit log file is overwritten and a new audit event is stored.
(6) FPT_STM.1 Reliable time stamps
The time stamp of TOE’s clock function is issued when the defined auditable event is recorded in
the audit log file.
By TSF_FMT, only a system administrator is enabled to change the clock setting.
7.1.7. Internal Network Data Protection (TSF_NET_PROT)
Internal Network Data Protection is provided by the following four protocols which are configured by
a system administrator using the system administrator mode:
(1) FTP_TRP.1 Trusted Path
The document data, security audit log data, and TOE setting data are protected by the encryption
communication protocol that ensures secure data communication between the TOE and IT
products (communication service via Web, communication service for printer driver,
communication service for fax driver, communication service for network utility, communication
service for other services which require trusted path). This trusted path is logically distinct from
other communication paths and provides assured identification of its endpoints and protection of
- 82 -
Page 87

Dell C7765dn Security Target
the communication data from modification or disclosure.
a) SSL/TLS
According to the SSL/TLS communication which is configured by a system administrator using
the system administrator mode, SSL/TLS ensuring secure data transmission is supported. This
protects the security of document data, security audit log data, and TOE setting data on the
internal network.
By supporting SSL/TLS, the TOE can act as SSL/TLS server or SSL/TLS client. Moreover,
SSL/TLS can protect data transmission between the TOE and the remote from interception and
alteration. Protection from interception is realized by encrypting transmission data with the
following cryptographic keys. A cryptographic key is generated at the time of starting a session
and lost at the time of ending the session or powering off the MFD main unit.
Cryptographic key generated as SSLv3/TLSv1/TLSv1.2 upon every session
Specifically, one of the cryptographic suites below is adopted:
Cryptographic Suites of SSL/TLS Cryptographic Method and
Hash Method
Size of Secret Key
SSL_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA RC4 / 128 bits SHA-1
SSL_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA 3-Key Triple-DES / 168 bits SHA-1
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA AES / 128 bits SHA-1
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA AES / 256 bits SHA-1
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 AES / 128 bits SHA256
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 AES / 256 bits SHA256
Protection from the alteration is realized by HMAC (Hashed Message Authentication Code IETF RFC 2104) of SSL/TLS.
When SSL/TLS communication is enabled on the Web client, requests from the client must be
received via HTTPS. The SSL/TLS communication needs to be enabled before IPSec, SNMPv3,
or S/MIME is enabled or before security audit log data are downloaded by a system administrator.
b) IPSec
According to the IPSec communication which is configured by a system administrator using the
system administrator mode, IPSec ensuring secure data transmission is supported. This protects
the security of document data, security audit log data, and TOE setting data on the internal
network.
IPSec establishes the security association to determine the parameters (e.g. private key and
cryptographic algorithm) to be used in the IPSec communication between the TOE and the
remote. After the association is established, all transmission data among the specified IP
addresses are encrypted by the transport mode of IPSec until the TOE is powered off or reset. A
cryptographic key is generated at the time of starting a session and lost at the time of ending the
session or powering off the MFD main unit.
- 83 -
Page 88

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Cryptographic key generated as IPSec (ESP: Encapsulating Security Payload) at every session
Specifically, one of the following combinations between secret-key cryptographic method and
hash method is adopted:
Cryptographic Method and Size
Hash Method
of Secret Key
AES / 128 bits SHA-1
3-Key Triple-DES / 168 bits SHA-1
c) SNMPv3
According to the SNMP v3 communication which is configured by a system administrator using
the system administrator mode, SNMP v3 is supported. This is one of the security solutions for
the network management protocol, SNMP. As defined in IETF RFC3414, SNMP v3 is used for
not only data encryption but also authentication of each SNMP message.
To enable this function, both authentication password and privacy password need to be set up in
both the TOE and the remote server. Length of both passwords must be 8 characters or more.
Authentication of SNMP v3 uses SHA-1 hash function; encryption of the protocol uses
CBC-DES. A cryptographic key is generated at the time of starting a session and lost at the time
of ending the session or powering off the MFD main unit.
Cryptographic key generated as SNMP v3 at every session:
Cryptographic Method and Size
Hash Method
of Secret Key
DES / 56 bits SHA-1
d) S/MIME
According to the S/MIME communication which is configured by a system administrator using
the system administrator mode, S/MIME ensuring secure mail communication is supported. This
protects the security of document data on the internal and external networks.
By S/MIME encrypting mail function, the document data being transmitted to/from the outside by
E-mail are protected from interception. By S/MIME signature mail function, the document data
are protected from interception and alteration.
A cryptographic key is generated at the time of starting mail encryption and lost at the time of
completion of the encryption or powering off the MFD main unit.
- 84 -
Page 89

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Secret-key cryptographic method generated as S/MIME for every mail
Cryptographic Method and Size
of Secret Key
3Key Triple-DES/168 bits
AES / 128 bits
AES / 192 bits
AES / 256 bits
Hash method generated as S/MIME for every mail
hash method
SHA1
SHA256
7.1.8. Fax Flow Security (TSF_FAX_FLOW)
This function inhibits unauthorized access to the TOE via the Fax board, which is connected to the
controller board via USB interface, at any case. The data on public telephone line are not delivered to
the internal network.
(1) FDP_IFC.1 Subset information flow control
FDP_IFF.1 Simple security attributes
The data on public telephone line are not delivered to the internal network.
7.1.9. Self Test (TSF_S_TEST)
The TOE can execute a self test function to verify the integrity of TSF executable code and TSF
data.
(1) FPT_TST.1 TSF testing
TOE verifies the area of NVRAM and SEEPROM including TSF data upon initiation, and
displays an error on the control panel if an error occurs.
However, an error is not detected for the data on audit logs and time and date as these are not
included in the target. Also, when Self Test function is set to be executed upon initiation, TOE
calculates the checksum of Controller ROM to confirm if it matches the specified value, and
displays an error on the control panel if an error occurs.
- 85 -
Page 90

Dell C7765dn Security Target
8. ACRONYMS AND TERMINOLOGY
8.1. Acronyms
The following acronyms are used in this ST:
Acronym Definition
ADF Auto Document Feeder
CAC Common Access Card
CC Common Criteria
CE Customer Engineer / Customer Service Engineer
DRAM Dynamic Random Access Memory
EAL Evaluation Assurance Level
FIPS PUB Federal Information Processing Standard publication
IIT Image Input Terminal
IOT Image Output Terminal
IT Information Technology
IP Internet Protocol
MFD Multi Function Device
NVRAM Non Volatile Random Access Memory
OCSP Online Certificate Status Protocol
PDL Page Description Language
PIV Personal Identity Verification
PP Protection Profile
SAR Security Assurance Requirement
SEEPROM Serial Electronically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory
SFP Security Function Policy
SFR Security Functional Requirement
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
SOF Strength of Function
ST Security Target
TOE Target of Evaluation
TSF TOE Security Function
- 86 -
Page 91

8.2. Terminology
The following terms are used in this ST:
Term Definition
Dell C7765dn Security Target
User
System Administrator
Privilege (SA)
System Administrator
Customer Engineer
(CE)
Attacker A malicious user of TOE
Control Panel
General User Client A client for general user.
System Administrator
Client
Configuration Web
Tool
Any entity outside the TOE who interacts with the TOE: i.e. general user,
system administrator, and CE.
A user authorized by key operator to manage MFD maintenance and
configure TOE security functions.
An authorized user who manages MFD maintenance and configures TOE
security functions. This term covers both key operator and SA.
Customer service engineer, an engineer who maintains and repairs MFD.
A panel of MFD on which buttons, lamps, and a touch screen panel are
mounted to operate the MFD
A client for system administrator. An administrator can refer to and rewrite
TOE setting data of MFD via Web browser.
Configuration Web Tool is a service on a Web server in the TOE to
confirm the status of the TOE, change settings of the TOE, and request
retrieval and printing of documents toward the TOE via the Web browser
of the user client.
Configuration Web Tool can be used via the Windows standard Web
browser.
The full name of Configuration Web Tool is Dell Printer Configuration
Web T ool.
System Administrator
Mode
Fax Driver
Network Scan Utility
(with local
authentication only)
Printer driver
An operation mode that enables a system administrator to refer to and
rewrite TOE setting for device operation and that for security functions
according to the operational environment. This mode is distinguished from
the operation mode that enables a general user to use the MFD functions.
Software for Direct Fax (with local authentication only) function, which
enables a general user to fax data to the destination directly from a general
user client through MFD. The user can send the fax data just as printing.
Used on the user client.
Software for a general user client to retrieve the document data stored in
Mailbox of MFD.
Software to convert the data on a general user client into print data written
in page description language (PDL), a readable format for MFD. Used on
the user client.
- 87 -
Page 92

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Term Definition
Print Data
The data written in PDL, a readable format for MFD, which are to be
converted into bitmap data by the TOE decompose function.
The data that are transmitted by command and response interactions. This
Control Data
is one the type of the data transmitted between MFD hardware units.
The decomposed data of the data read by the copy function and the print
data transmitted from a user client to MFD by the print function. Bitmap
Bitmap Data
data are stored into the internal HDD after being compressed in the unique
process.
A function to analyze and convert the print data written in PDL into
Decompose Function
bitmap data.
To analyze and convert the data written in PDL into bitmap data by the
Decompose
decompose function.
Original Texts, images and photos to be read from IIT in the copy function.
Document data means all the data, including images, transmitted across
the MFD when any of copy, print, scan or fax functions is used by a
general user. The document data includes:
- Bitmap data read from IIT and printed out from IOT (copy function),
- Print data sent by general user client and its decomposed bitmap data
Document Data
(print function),
- Bitmap data read from IIT and then stored into the internal HDD (scan
function),
- Bitmap data read from IIT and sent to the fax destination and the bitmap
data faxed from the sender’s machine and printed out from the recipient’s
IOT (fax function).
Used Document Data
Security Audit Log
Data
Internally Stored Data
General Data
TOE Setting Data
The remaining data in the MFD internal HDD even after deletion. The
document data are first stored into the internal HDD, used, and then only
their files are deleted.
The chronologically recorded data of important events of the TOE. The
events such as device failure, configuration change, and user operation are
recorded based on when and who caused what event and its result.
The data which are stored in a general user client or in the general client
and server, but do not include data regarding TOE functions.
The data on the internal network. The general data do not include data
regarding TOE functions.
The data which are created by the TOE or for the TOE and may affect the
TOE security functions. Included in the TSF data, specifically they include
the information regarding the functions of Hard Disk Data Overwrite,
Hard Disk Data Encryption, System Administrator’s Security
Management, Customer Engineer Operation Restriction, Use of password
entered from MFD control panel in user authentication, ID and password
- 88 -
Page 93

Dell C7765dn Security Target
Term Definition
of users, access denial due to authentication failure of system
administrator, Internal Network Data Protection, Security Audit Log, User
Authentication, Report Print, Auto Clear, Data/Time, and Self Test.
General Client and
Client and server which do not directly engage in TOE operations
Server
Deletion from the internal HDD means deletion of the management
information. When deletion of document data from the internal HDD is
Deletion from the
Internal Hard Disk
Drive (HDD)
requested, only the management information corresponding to the data is
deleted. Therefore, user cannot access the document data which were
logically deleted. However, the document data themselves are not deleted
but remain as the used document data until new data is written in the same
storage area.
To write over the area of the document data stored in the internal HDD
Overwrite
when deleting the data.
The 12 alphanumeric characters to be entered by a user. When data in the
Cryptographic Seed
internal HDD are encrypted, a cryptographic key is generated based on the
Key
cryptographic seed key.
The 256-bit data which is automatically generated based on the
Cryptographic Key
cryptographic seed key. Before the data are stored into the internal HDD,
they are encrypted with the cryptographic key.
Network A general term to indicate both external and internal networks.
External Network
Internal Network
User Authentication
Local Authentication
Remote
Authentication
USB Media
Smart Card
Authentication
The network which cannot be managed by the organization that manages
the TOE. This does not include the internal network.
Channels between MFD and highly reliable remote server / client PC. The
channels are located in the network of the organization, the owner of the
TOE, and are protected from the security risks coming from the external
network.
A function to limit the accessible TOE functions by identifying the user
before he/she uses each TOE function.
There are two modes, Local Authentication and Remote Authentication,
and either mode is used for operation.
Smart Card authentication is also available on the control panel.
A mode to manage user authentication of the TOE using the user
information registered in the MFD.
A mode to manage user authentication of the TOE using the user
information registered in the remote authentication server.
A USB flash drive (USB memory) that is used for storing scanned data
and for printing stored data.
A function to identify and authenticate users by communicating with
Kerberos server and OCSP server using user information and certificates
- 89 -
Page 94

Term Definition
OCSP Server
Dell C7765dn Security Target
stored in Smart Card (CAC/PIV).
The OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol) is a protocol for obtaining
the revocation status of X. 509 digital certificates in real time. A server
that can use the OCSP is called an OCSP server (or OCSP responder).
With an OCSP server, a client does not need to obtain and verify a CRL.
- 90 -
Page 95

Dell C7765dn Security Target
9. REFERENCES
The following documentation was used to prepare this ST.
Short Name Document Title
Part 1: Introduction and general model (September 2012 Version 3.1 Revision 4)
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation - Version 3.1
[CC Part 1]
[CC Part 2]
Part 1: Introduction and general model, dated September 2012, CCMB-2012-09-001
(Japanese version 1.0, dated November 2012,
translated by Information-Technology Promotion Agency, Japan)
Part 2: Security functional components (September 2012 Version 3.1 Revision 4)
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation - Version 3.1
Part 2: Security functional components, dated September 2012, CCMB-2012-09-002
(Japanese version 1.0, dated November 2012,
translated by Information-Technology Promotion Agency, Japan)
[CC Part 3]
[CEM]
Part 3: Security assurance components (September 2012 Version 3.1 Revision 4)
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation - Version 3.1
Part 3: Security assurance components, dated September 2012, CCMB-2012-09-003
(Japanese version1.0, dated November 2012,
translated by Information-Technology Promotion Agency, Japan)
Common Methodology for Information Technology Security Evaluation - Version 3.1
Evaluation Methodology, dated September 2012, CCMB-2012-09-004
(Japanese version 1.0, dated November,
translated by Information-Technology Promotion Agency, Japan)
- 91 -
 Loading...
Loading...